| Revision as of 20:59, 13 December 2019 editArminden (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users56,019 edits Correct edit back in← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:23, 13 December 2019 edit undoJerm (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers32,667 edits Undid revision 930634481 by Arminden (talk) Per WP:BRD, discuss in the articles talk page, not in the edit summary. I don't have an issue with the new heading for the section.Tag: UndoNext edit → | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| Jannaeus had brought the surviving rebels back to Jerusalem where he had eight hundred Jews, primarily Pharisees, crucified. Before their deaths, Alexander had the rebels' wives and children executed before their eyes as Jannaeus ate with his concubines. Alexander later returned the land he had seized from the Nabateans in order to have them end their support for the Jewish rebels. The remaining rebels, who numbered eight thousand, fled by night in fear of Alexander. Afterward, all rebel hostility ceased and Alexander's reign continued undisturbed.{{sfn|Eshel|2008|p=119}} | Jannaeus had brought the surviving rebels back to Jerusalem where he had eight hundred Jews, primarily Pharisees, crucified. Before their deaths, Alexander had the rebels' wives and children executed before their eyes as Jannaeus ate with his concubines. Alexander later returned the land he had seized from the Nabateans in order to have them end their support for the Jewish rebels. The remaining rebels, who numbered eight thousand, fled by night in fear of Alexander. Afterward, all rebel hostility ceased and Alexander's reign continued undisturbed.{{sfn|Eshel|2008|p=119}} | ||
| == |
== Death == | ||
| The remainder of Alexander's life continued in his final campaigns. The Nabatean king ] had defeated Alexander in battle, however, Alexander continued his Hasmonean expansion in the Transjordan region. In Gaulantis, he captured the cities of ] and Selecuia. In Gaulana and Galaaditis, the cities of Duim, ], and Pella;{{sfn|Schäfer|2003|p=75}} Pella was destroyed by Alexander's soldiers for refusing to accept their ].{{sfn|Borgen|1998|p=48}} He had taken ];{{sfn|Fitzgerald|Obbink|Holland|2004|p=362}} Alexander captured all these cities in a period of three years (83-80 BCE). Three years later, Alexander had succumbed to an illness during the siege of Ragaba.{{sfn|Schäfer|2003|p=75}} | |||
| == Citations == | == Citations == | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
| * {{cite book|last1=Kaiser|first1=Walter C.|title=History of Israel|date=1998|publisher=B&H Publishing Group|isbn=9780805431223|url=https://books.google.com/?id=acq2F4oW3DYC&pg=PA482&dq=Alexander+Jannaeus#v=onepage&q=Alexander%20Jannaeus&f=false|ref=harv}} | * {{cite book|last1=Kaiser|first1=Walter C.|title=History of Israel|date=1998|publisher=B&H Publishing Group|isbn=9780805431223|url=https://books.google.com/?id=acq2F4oW3DYC&pg=PA482&dq=Alexander+Jannaeus#v=onepage&q=Alexander%20Jannaeus&f=false|ref=harv}} | ||
| * {{cite book|last1=Saldarini|first1=Anthony J.|title=Pharisees, Scribes and Sadducees in Palestinian Society: A Sociological Approach|date=2001|publisher=Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing|isbn=9780802843586|url=https://books.google.com/?id=Bre6P-OPfEEC&pg=PA89&dq=Alexander+Jannaeus#v=onepage&q=Alexander%20Jannaeus&f=false|ref=harv}} | * {{cite book|last1=Saldarini|first1=Anthony J.|title=Pharisees, Scribes and Sadducees in Palestinian Society: A Sociological Approach|date=2001|publisher=Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing|isbn=9780802843586|url=https://books.google.com/?id=Bre6P-OPfEEC&pg=PA89&dq=Alexander+Jannaeus#v=onepage&q=Alexander%20Jannaeus&f=false|ref=harv}} | ||
| * {{cite book |
* {{cite book|last1=Schäfer|first1=Peter|title=The History of the Jews in the Greco-Roman World: The Jews of Palestine from Alexander the Great to the Arab Conquest|date=2003|publisher=Routledge|isbn=9781134403165|edition=2nd Revised|url=https://books.google.com/?id=-0aBAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA74&dq=Alexander+Jannaeus+Gadara#v=onepage&q=Alexander%20Jannaeus%20Gadara&f=false|ref=harv}} | ||
| {{sfn|Schäfer|2003|p=75}} | |||
| {{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 13 December 2019
- For other people with this name, see Alexander
| Alexander Jannaeus | |
|---|---|
 Alexander Jannaeus, woodcut designed by Guillaume Rouillé. From Promptuarii Iconum Insigniorum. Alexander Jannaeus, woodcut designed by Guillaume Rouillé. From Promptuarii Iconum Insigniorum. | |
| King of Judaea | |
| Reign | c. 103 – 76 BCE |
| Predecessor | Aristobulus I |
| Successor | Salome Alexandra |
| High Priest of Judaea | |
| Predecessor | Aristobulus I |
| Successor | Hyrcanus II |
| Born | C. 127 BCE |
| Died | C. 76 BCE |
| Spouse | Salome Alexandra |
| Dynasty | Hasmonean |
| Father | John Hyrcanus |
| Religion | Hellenistic Judaism |
Alexander Jannaeus (also known as Alexander Jannai/Yannai; Template:Lang-he-n, born Jonathan Alexander) was the second Hasmonean King of Judaea from 103 to 76 BCE. A son of John Hyrcanus, he inherited the throne from his brother Aristobulus I, and married his brother's widow, Queen Salome Alexandra. From his conquests to expand the kingdom to a bloody civil war, Alexander's reign has been generalized as cruel and oppressive with never ending conflict.
Family
Alexander Jannaeus was the third son of John Hyrcanus, by his second wife. When Aristobulus I, Hyrcanus' son by his first wife, became king, he deemed it necessary for his own security to imprison his half-brother. Aristobulus died after a reign of one year. Upon his death, his widow, Salome Alexandra had Alexander and his brothers released from prison. One of these brothers is said to have unsuccessfully sought the throne.
Alexander, as the oldest living brother, had the right not only to the throne but also to Salome, the widow of his deceased brother, who had died childless; and, although she was thirteen years older than him, he married her in accordance with Jewish law. By her, he had two sons, the eldest, Hyrcanus II became high-priest in 62 BCE and Aristobulus II who was high-priest from 66 - 62 BCE and started a bloody civil war with his brother, ending in his capture by Pompey the Great. Like his brother he was an avid supporter of the aristocratic priestly faction known as the Sadducees, his wife Salome on the other hand came from a pharisaic family (her brother was Simeon ben Shetach a famous Pharisee leader), and was more sympathetic to their cause and protected them throughout his turbulent reign. Like his father, Alexander also served as the high priest. This raised the ire of the Rabbis who insisted that these two offices should not be combined. According to the Talmud, Yannai was a questionable desecrated priest (rumor had it that his mother was captured in Modiin and violated) and was not allowed to serve in the temple according to the rabbis, this infuriated the king and sided with the Sadducees who defended him. This incident led the king to turn against the Pharisees and persecute them until his death.
War with Ptolemy Lathyrus
Alexander's first expedition was against the city of Ptolemais. While Alexander went forward to siege the city, Zoilus of Dora took the opportunity to see if he could liberate Ptolemais in hopes of establishing his rule over coastal territories. Alexander's Hasmonean army quickly defeated Zoilus's forces. Ptolemais then requested aid from Ptolemy IX Lathyros, who had been banished by his mother Cleopatra III; Ptolemy founded a kingdom in Cyprus after being cast out by his mother. The situation at Ptolemais was seized as an opportunity by Ptolemy to possibly gain a stronghold and control the Judean coast in order to invade Egypt by sea. However, an individual named Demaenetus convinced the inhabitants of their imprudent request for assistance. Realizing they had allied themselves with Ptolemy, they had unintentionally declared war on Cleopatra. When Ptolemy arrived at the city, the inhabitants denied him access.
Alexander too didn't want to be involved in a war between Cleopatra and Ptolemy, so he abandoned his campaign against Ptolemais and returned to Jeruselum. After he offered Ptolemy four hundred talents and a peace treaty in return for Zoilus's death, Alexander met him with treachery by negotiating an alliance with Cleopatra. When Alexander formed an alliance with Ptolemy, Alexader's conquest continued by capturing the coastal cities of Dora and Straton's Tower. As soon as Ptolemy learned of Alexander's scheme, he was determined to kill him. Ptolemy began to attack Ptolemais, but left his generals to besiege the city while he continued to pursue Alexander. Ptolemy's pursuit had caused much destruction in the Galilee region and captured Asochis on the Sabbath, taking ten thousand people as prisoners. Ptolemy also initiated an attack upon Sepphoris but was unsuccessful.
Battle of Asophon
Ptolemy and Alexander engaged in battle at Asophon near the Jordan River. Estimated to have fifty thousand to eighty thousand soldiers, Alexander's army consisted of both Jews and pagans. At the head of his armed forces were his elite pagan mercenaries; They specialized in Greek style phalanx. One of Ptolemy's commanders, Philostephanus, commenced the first attack by crossing the river that divides both forces. The Hasmoneans had the advantage, however, Philostephanus held back a certain amount of his forces whom he sent to recover lost ground. Perceiving as vast reinforcements, Alexander's army fled. Some of his retreating forces tried to push back but quickly dispersed as Ptolemy's forces pursued Alexander's fleeing army; Thirty thousand to fifty thousand Hasmonean soldiers died.
Ptolemy's forces at Ptolemais also succeeded in capturing the city. He then continued to conquer much of the Hasmonean Kingdom, occupying the entirety of northern Judea, the coast, and territories east of the Jordan River. While doing so, he pillaged villages and ordered his soldiers to cannibalize women and children to create psychological fear towards his enemies. At the time, Salome Alexandra was notified of Cleopatra's approachment to Judea.
Intervention of Cleopatra III
Realizing that her son amassed a formidable force in Judea, Cleopatra appointed Jewish generals Ananias and Chelkias to command her forces. She too also went with a fleet towards Judea. When Cleopatra arrived at Ptolemais, the people refused her entry so she besieged the city. Ptolemy, believing Syria was defenseless, withdrew to Cyprus after his miscalculation. While in pursuit of Ptolemy, Chelkias died at Coele-Syria.
After Ptolemy was defeated, Alexander had approached Cleopatra. Bowing before her, he requested to retain his rule. Cleopatra was urged by her subordinates to annex Judea. However, Ananias demanded she consider the residential Egyptian Jews who were the main support of her throne. This induced Cleopatra to modify her longings for Judea. Alexander and Cleopatra then met at Scythopolis to begin negotiations. He met her demands and suspended his campaigns. Cleopatra died five years after. Confident, after her death, Alexander found himself free to continue with new campaigns.
Transjordan and coastal conquest
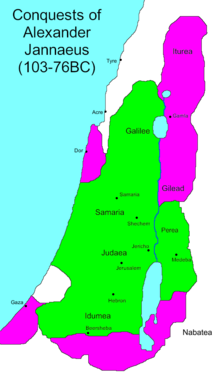
situation in 103 BCE area conquered
Alexander captured Gadara and fought to capture the strong fortress of Amathus in the Transjordan region but was defeated. Alexander was more successful in his expedition against the coastal cities, capturing Raphia and Anthedon. In 96 BCE, Jannaeus defeated the inhabitants of Gaza. This victory gained Judean control over the Mediterranean outlet of the Nabatean trade routes. Alexander initially returned his focus back to the Transjordan region, avenging his previous defeat, he destroyed Amathus.
Battle of Gaza
Determined to proceed with future campaigns despite his defeat at Amathus, Alexander set his focus on Gaza. His campaign against the city wasn't so easily achieved. Gaza's general Apollodotus strategically employed a night attack against the Hasmonean army. With a force of two thousand less-skilled soldiers and ten thousand slaves, Gaza's military was able to deceive the Hasmonean army into believing they were being attacked by Ptolemy. The Gazans killed many, and the Hasmonean army fled the battle. When morning exposed the delusive tactic, Alexader continued his assault but lost a thousand additional soldiers.
The Gazans still remained defiant in hopes that the Nabatean Kingdom would come to their aid. The city, however, would eventually suffer defeat from its leadership. Gaza at the time was governed by two brothers, Lysimachus and Apollodotus. Lysimachus had finally convinced the people to surrender, and Alexander peacefully entered the city. Though what seemed like an unaggressive Alexander, he suddenly ravaged the inhabitants. Now some men out of desperation killed their wives and children to ensure they wouldn't be captured and enslaved. Others burned down their homes to prevent the soldiers from plundering. The town council and five hundred civilians took refuge at the Temple of Apollo. There, Alexander massacred them.
Judean Civil War
War with Obodas I

The Judean Civil War initially began after the conquest of Gaza around 99 BCE. Due to Jannaeus's victory at Gaza, the Nabatean kingdom no longer had access to the Mediterranean Sea. Alexander soon captured Gadara, which caused the Nabateans to lose their main trade routes leading to Rome and Damascus. After losing Gadara, the Nabatean king Obodas I launched an attack against Alexander in a steep valley in Gadara where Alexander barely managed to escape. After Jannaeus was defeated in the Battle of Gadara against the Nabataeans, he returned to Jerusalem only to be met with fierce Jewish opposition.
Feast of Tabernacles
During the Jewish holiday Feast of Tabernacles, Alexander Jannaeus, while officiating as the High Priest at the Temple in Jerusalem, demonstrated his displeasure against the Pharisees by refusing to perform the water libation ceremony properly: instead of pouring it on the altar, he poured it on his feet. The crowd responded with shock at his mockery and showed their displeasure by pelting him with etrogim (citrons). Outraged, he ordered soldiers to kill those who insulted him, which lead to the massacre of six thousand people in the Temple courtyard. With further frustration, Alexander had wooden barriers built around the altars preventing people from sacrificing and denied daily offerings except for the priests. This incident during the Feast of Tabernacles was a major factor leading up to the Judean Civil War by igniting popular opposition against Jannaeus.
War with Demetrius III and the conclusion of the Judean Civil War
After Jannaeus succeeded early in the war, the rebels asked for Seleucid assistance. Judean insurgents joined forces with Demetrius III Eucaerus to fight against Jannaeus. Alexander had gathered six thousand, two hundred mercenaries and twenty thousand Jews for battle as Demetrius had forty thousand soldiers and three thousand horses. There were attempts from both sides to persuade each other to abandon positions but were unsuccessful. The Seleucid forces defeated Jannaeus at Shechem, and all of Alexander's mercenaries were killed in battle. This defeat forced Alexander to take refuge in the mountains. In sympathy towards Jannaeus, six thousand Judean rebels ultimately returned to him. In fear of this news, Demetrius withdrew. Nevertheless, war between Jannaeus and the rebels who returned to him continued. They fought until Alexander achieved victory. Most of the rebels died in battle, while the remaining rebels fled to the city of Bethoma until they were defeated.
Jannaeus had brought the surviving rebels back to Jerusalem where he had eight hundred Jews, primarily Pharisees, crucified. Before their deaths, Alexander had the rebels' wives and children executed before their eyes as Jannaeus ate with his concubines. Alexander later returned the land he had seized from the Nabateans in order to have them end their support for the Jewish rebels. The remaining rebels, who numbered eight thousand, fled by night in fear of Alexander. Afterward, all rebel hostility ceased and Alexander's reign continued undisturbed.
Death
The remainder of Alexander's life continued in his final campaigns. The Nabatean king Aretas III had defeated Alexander in battle, however, Alexander continued his Hasmonean expansion in the Transjordan region. In Gaulantis, he captured the cities of Gamala and Selecuia. In Gaulana and Galaaditis, the cities of Duim, Gerasa, and Pella; Pella was destroyed by Alexander's soldiers for refusing to accept their ancestral religion. He had taken Hippos; Alexander captured all these cities in a period of three years (83-80 BCE). Three years later, Alexander had succumbed to an illness during the siege of Ragaba.
Citations
- Saldarini 2001, p. 89.
- Atkinson 2012, pp. 130 & 131.
- Atkinson 2012, pp. 131 & 132.
- Atkinson 2012, pp. 132 & 133.
- Atkinson 2012, pp. 133 & 134.
- Atkinson 2012, p. 134.
- Atkinson 2012, p. 135.
- Fitzgerald, Obbink & Holland 2004, pp. 361 & 362.
- Schäfer 2003, pp. 74 & 75.
- ^ Fitzgerald, Obbink & Holland 2004, p. 362.
- ^ Atkinson 2012, p. 136.
- Eshel 2008, pp. 117 & 118.
- Kaiser 1998, p. 482.
- Eshel 2008, pp. 118 & 119.
- Eshel 2008, p. 119.
- ^ Schäfer 2003, p. 75.
- Borgen 1998, p. 48.
Bibliography
- Atkinson, Kenneth (2012). Queen Salome: Jerusalem's Warrior Monarch of the First Century B.C.E. McFarland. ISBN 9780786490738.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Borgen, Peter (1998). Early Christianity and Hellenistic Judaism. A&C Black. ISBN 9780567086266.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Eshel, Hanan (2008). The Dead Sea Scrolls and the Hasmonean State. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. ISBN 9780802862853.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fitzgerald, John Thomas; Obbink, Dirk D.; Holland, Glenn Stanfield (2004). Philodemus and the New Testament World. BRILL. ISBN 9789004114609.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kaiser, Walter C. (1998). History of Israel. B&H Publishing Group. ISBN 9780805431223.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Saldarini, Anthony J. (2001). Pharisees, Scribes and Sadducees in Palestinian Society: A Sociological Approach. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. ISBN 9780802843586.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Schäfer, Peter (2003). The History of the Jews in the Greco-Roman World: The Jews of Palestine from Alexander the Great to the Arab Conquest (2nd Revised ed.). Routledge. ISBN 9781134403165.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
| Alexander Jannaeus of JudaeaHasmonean Dynasty Died: 76 BCE | ||
| Jewish titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byAristobulus I | King of Judaea 103 BCE – 76 BCE |
Succeeded bySalome Alexandra |
| High Priest of Judaea 103 BCE – 76 BCE |
Succeeded byHyrcanus II | |
| Rulers of Israel and Judah | |
|---|---|
| Israel (united monarchy) | |
| Israel (northern kingdom) | |
| Judah (southern kingdom) | |
| Judea (Hasmonean dynasty) | |
| See also | |
- 2nd-century BC Hasmonean monarchs
- 1st-century BC Hasmonean monarchs
- 2nd-century BC High Priests of Israel
- 1st-century BC High Priests of Israel
- 1st-century BC monarchs in the Middle East
- 1st-century BCE Jews
- 2nd-century BC monarchs in the Middle East
- 2nd-century BC clergy
- 2nd-century BCE Jews
- 1st-century BC clergy
- 2nd-century BC births
- 76 BC deaths
- Hasmonean dynasty