| Revision as of 06:38, 14 June 2021 edit78.18.227.79 (talk)No edit summaryTag: Reverted← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:47, 2 January 2025 edit undoDawnseeker2000 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, File movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers485,903 editsm date format audit, link maintenance, minor formattingTag: AWB | ||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|County in Ireland}} | {{Short description|County in Ireland}} | ||
| {{about|the county|the southern part of Dublin|Southside, Dublin}} | {{about|the county|the southern part of Dublin|Southside, Dublin|the former constituency|Dublin South (Dáil constituency)}} | ||
| {{Use |
{{Use Hiberno-English|date=July 2015}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date= |
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2025}} | ||
| {{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
| | settlement_type |
| settlement_type = County | ||
| | name |
| name = South Dublin | ||
| | native_name |
| native_name = {{Native name|ga|Átha Cliath Theas|paren=omit}} | ||
| | |
| image_shield = South Dublin Coat of Arms.png | ||
| | |
| motto = {{ubl|This We Hold in Trust|{{langx|ga|Ag Seo Ár gCúram}}}} | ||
| | |
| image_map = Island of Ireland location map South Dublin.svg | ||
| ⚫ | | map_caption = Inset showing South Dublin (darkest green in inset) within Dublin Region (lighter green) | ||
| | image_map = Island of Ireland location map South Dublin.svg | |||
| | area_total_km2 = 222.74 | |||
| ⚫ | | map_caption |
||
| | |
| seat_type = ] | ||
| | |
| seat = ] | ||
| ⚫ | | blank_name_sec1 = ] | ||
| | seat = ] | |||
| | blank_info_sec1 = D | |||
| ⚫ | | blank_name_sec1 |
||
| | |
| population_total = 301075 | ||
| | |
| population_as_of = ] | ||
| | population_footnotes = <ref name="cso2022">{{cite web | url = https://visual.cso.ie/?body=entity/ima/cop/2022&boundary=C03789V04537&guid=2ae19629-14a1-13a3-e055-000000000001 | title = Local Authorities (County Councils): South Dublin County Council | work = Census 2022 | publisher = ]| access-date = 20 November 2023}}</ref> | |||
| | population_as_of = 2016 | |||
| | population_density_km2 |
| population_density_km2 = auto | ||
| | |
| subdivision_type = ] | ||
| | |
| subdivision_name = ] | ||
| | subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| subdivision_name1 = ] | ||
| | |
| subdivision_type2 = ] | ||
| | |
| subdivision_name2 = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_title = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_name = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_title2 = ] | ||
| ⚫ | | leader_name2 = {{ubl|]|]|]}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | leader_title3 = ] | |||
| | timezone = ] | |||
| | |
| leader_name3 = ] | ||
| | |
| website = {{official website}} | ||
| | |
| timezone = ] | ||
| | |
| utc_offset = ±0 | ||
| | |
| timezone_DST = ] | ||
| | |
| utc_offset_DST = +1 | ||
| | |
| established_title = Established | ||
| | |
| established_date = 1994 | ||
| | elevation_max_m = 757 | |||
| | elevation_max_point = ] | |||
| | official_name = | |||
| ⚫ | | module = {{infobox mapframe|zoom=9}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''South Dublin''' ({{ |
'''South Dublin''' ({{langx|ga|Átha Cliath Theas}})<ref name="logainm">{{cite web |url=https://www.logainm.ie/1165433.aspx |website=Placenames Database of Ireland |title=Baile Átha Cliath Theas/South Dublin |access-date=20 November 2023}}</ref> is a ] in ], within the ] of ] and the ]. It is one of three successor counties to ], which was disestablished for administrative purposes in 1994. ] is the ] for the county. The county contains both dense suburbs of ] and stretches of unpopulated mountains. In 2022 it had a population of 301,705, making it the ] county in the state.<ref name="cso2022"/> | ||
| ==Geography and population== | ==Geography and population== | ||
| South Dublin has an area of {{convert|222.74|sqkm|0}}, making it the second |
South Dublin has an area of {{convert|222.74|sqkm|0}}, making it the second-largest of the four local government areas in Dublin. It is bounded by Dublin City ({{cvt|15|km|disp=comma}} to the northeast), the ] (separating it from ] to the north), ] (to the east), ] (to the west) and its hills adjoin the mountains of ] to the south. | ||
| The ] is ]. Other important centres of population are ] and ]. Much of the county is heavily urbanised but small rural settlements exist in the southern and western parts. South Dublin |
The ] is ]. Other important centres of population are ] and ]. Much of the county is heavily urbanised but small rural settlements exist in the southern and western parts. South Dublin's population increased from 278,767 in 2016 to 301,075 in 2022, according to the ].<ref name="cso2022"/> | ||
| ===Towns and villages=== | ===Towns and villages=== | ||
| Several urban areas in South Dublin County are also traditionally suburbs of Dublin city. |
Several urban areas in South Dublin County are also traditionally suburbs of Dublin city. For the purposes of planning and management, the County Council designates the status of towns, villages and suburbs in three tiers – '''town''', '''district centre''' and '''local centre'''. In the 2022 development plan,<ref>{{cite book |chapter-url=https://www.sdcc.ie/en/devplan2022/adopted-plan/chapter-2-core-strategy-and-settlement-strategy/chapter-2-core-strategy-and-settlement-strategy.pdf |title=South Dublin County Development Plan 2022-2028 |chapter=Chapter 2: Core Strategy and Settlement Strategy |date=22 June 2022 |publisher=South Dublin County Council |access-date=20 November 2023 |archive-date=2 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230702000502/http://www.sdcc.ie/en/devplan2022/adopted-plan/chapter-2-core-strategy-and-settlement-strategy/chapter-2-core-strategy-and-settlement-strategy.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> the towns and district centres are listed as: | ||
| * ], the county seat and the location of ] which was opened in October 1990 | * ], the county seat and the location of ] which was opened in October 1990 | ||
| * ] ("to be facilitated and developed as a Town Centre... including northward development") | * ] ("to be facilitated and developed as a Town Centre ... including northward development") | ||
| * ] (with notes on the Liffey Valley Centre, and the developing Adamstown area |
* ] (with notes on the Liffey Valley Centre, and the developing Adamstown area – a future "district centre" – and a stated aim to avoid Lucan merging with ]) | ||
| * and with a proposal to develop a Town Centre around the Liffey Valley Centre at Quarryvale | * and with a proposal to develop a Town Centre around the Liffey Valley Centre at Quarryvale | ||
| while the more local centres are noted in three groups: | while the more local centres are noted in three groups: | ||
| * '''city suburbs''' including at least ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] | * '''city suburbs''' including at least ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] | ||
| * '''villages''' such as ], ](-Lyons), and ] | * '''villages''' such as ], ](-Lyons), and ] | ||
| * '''new neighbourhoods''', some within bigger, older areas |
* '''new neighbourhoods''', some within bigger, older areas – including such as ], Ballyowen, Finnstown, and, in development, ] (mentioned in the county plan as an extension of Lucan).<ref>{{dead link|date=May 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}, South Dublin County Development Plan 2004–2010, Chapter 5 </ref> | ||
| ===Residential areas=== | ===Residential areas=== | ||
| Line 63: | Line 67: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 73: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 79: | Line 86: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *]{{div col end}} | *], southernmost part{{div col end}} | ||
| ==Terminology== | |||
| ==Legal status and terminology== | |||
| ] | |||
| In Ireland, the usage of the word ''county'' nearly always comes before rather than after the county name; thus "]" in Ireland as opposed to "]" in ], ]. In the case of those counties created after 1994, they often drop the word ''county'' entirely, or use it after the name; thus for example internet search engines show many more uses (on Irish sites) of "South Dublin" than of either "County South Dublin" or "South Dublin County". |
In Ireland, the usage of the word ''county'' nearly always comes before rather than after the county name; thus "]" in Ireland as opposed to "]" in ], ]. In the case of those counties created after 1994, they often drop the word ''county'' entirely, or use it after the name; thus for example internet search engines show many more uses (on Irish sites) of "South Dublin" than of either "County South Dublin" or "South Dublin County". The 2003 placenames order lists South Dublin without any modification.<ref>{{cite ISB|type=si|year=2003|number=519|lang=ga|name=Placenames (Provinces and Counties) Order 2003 |date=30 October 2003|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> | ||
| ==History== | |||
| In 2015, South Dublin became part of the Eastern and Midland Region.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://emra.ie/|title=Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly|website=Eastern & Midland Regional Assembly|access-date=2016-09-30}}</ref> | |||
| In 1985, ] was divided into three electoral counties: Dublin–Fingal, Dublin–Belgard, and Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown.<ref>{{cite ISB|year=1985|number=7|section=12|stitle=Establishment of Dublin Electoral Counties|name=Local Government (Reorganisation) Act 1985 |date=3 April 1985|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> At the ], the area of Dublin–Belgard was renamed as South Dublin.<ref>{{cite ISB|year=1991|number=11|section=26|stitle=Amendment of Local Government (Reorganisation) Act 1985|name=Local Government Act 1991 |date=18 May 1991|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> The name Belgard did have a historical association with the area, being the designation of one of the border fortresses of ] that existed in that area. It was altered due to a view that the name Belgard might create associations with areas of modern development in ] that now also uses that name.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} | |||
| On 1 January 1994, under the provisions of the ], County Dublin ceased to exist, and was succeeded by the counties of Fingal, Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown and South Dublin in the areas of the electoral counties.<ref>{{cite ISB|type=si|year=1993|number=400|name=Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993 Commencement Order 1993 |date=22 December 1993|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite ISB|year=1993|number=31|section=9|stitle=Establishment and boundaries of administrative counties|name=] |date=21 December 1993|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> The boundaries of South Dublin were finalised in 1993, to accommodate the ].<ref>{{cite ISB|year=1993|number=31|section=8|stitle=Alteration of certain boundaries existing before establishment day|name=Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993 |date=21 December 1993|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> | |||
| Local government in the region is further regulated by the Local Government Act 1994. This provided for the legal establishment of the following local government administrative areas: | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * South Dublin | |||
| and also recognised the extant '''Dublin Corporation''' area, vesting its powers in a renamed entity - ]. | |||
| The ] giving effect to the Act came into force on 1 January 1994.<ref>:<br /> | |||
| Section 2: ''"the county", in relation to any time before the establishment day, means the administrative county of Dublin''<br />Section 9(1) ''On the establishment day— ... (a) the county shall cease to exist.''</ref> The instrument also provided for the abolition of ] - the entity that had previously had responsibility for Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Fingal and South Dublin. The four entities collectively comprise the former entity known as ]. This entity, which had been created during the ], was abolished under the Acts. | |||
| Various organs of state use alternative subdivisions of Dublin for administrative reasons, for example, the ]. | |||
| South Dublin was based on an existing electoral division, Belgard {{lang-ga|An Bealach Ard}}, whose boundaries were only finalised in 1993, to accommodate the ], and then used when it was made an Administrative County in 1994 (Fingal and Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown's boundaries and names were both set in 1985). The name of Belgard did have a historical association with the area, being the designation of ''one'' of the border fortresses of ] that existed in that area. It was altered, however, due to a view that the name Belgard might create associations with areas of modern development in ] that now also use that name.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} Various organs of state use alternative subdivisions of the Dublin region for administrative reasons, for example the ].] | |||
| ==Local government and politics== | ==Local government and politics== | ||
| ] is the ] for the county. It was established on 1 January 1994 with the establishment of the county.<ref>{{cite ISB|year=1993|number=31|section=11|stitle=Establishment of councils of administrative counties|name=] |date=21 December 1993|access-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> It is one of local authorities in ]. The county is divided into seven ]s:<ref>{{cite ISB|year=2018|type=si|number=633|name=County of South Dublin Local Electoral Areas Order 2018 |date=19 December 2018|access-date=11 September 2020|archive-date=2 February 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190202212347/http://www.irishstatutebook.ie/eli/2018/si/633/made/en/print|url-status=live}}</ref> Clondalkin (7 councillors), Firhouse–Bohernabreena (5 councillors), ] (5 councillors), ]–] (7 councillors), Tallaght Central (6 councillors), and Tallaght South (5 councillors). | |||
| {{main|South Dublin County Council}} | |||
| '''South Dublin County Council''' is the ] for the county. It was established at ] at the same time that ] and the ] were abolished<ref><br> | |||
| :"On the establishment day— | |||
| ::(a) the county shall cease to exist, | |||
| ::(b) the borough shall cease to exist, | |||
| ::(c) the electoral counties shall cease to exist, and | |||
| ::(d) the united district of the burial board shall cease to exist."</ref> in 1994, by an ], the ]. It is one of four councils in the ]. The county is divided into five ] for the purpose of elections:<ref name="ElectionsIreland">{{cite web|url=http://electionsireland.org/results/local/council.cfm?election=2009L&area=269 |year=2009|title=Local Elections – Electoral Area Details|work=ElectionsIreland.org|access-date=15 February 2010}}</ref> Clondalkin (6 councillors), ] (5 councillors), ] (4 councillors), Tallaght Central (6 councillors), and Tallaght South (5 councillors). | |||
| The ] of ] (4 seats) and ] (5 seats) are wholly within South Dublin, and the constituency of ] is partially within South Dublin.<ref>{{cite ISB|year=2017|number=39|schedule=y|name=] |date=23 December 2017|access-date=8 August 2021}}</ref> | |||
| In 2015, South Dublin became part of the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://emra.ie/|title=Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly|website=Eastern & Midland Regional Assembly|access-date=2016-09-30|archive-date=29 September 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160929142528/http://emra.ie/|url-status=live}}</ref> South Dublin County Council sends three members to the Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly.<ref>{{cite ISB|year=2014|type=si|number=573|name=Local Government Act 1991 (Regional Assemblies) (Establishment) Order 2014|date=16 December 2014|access-date=29 January 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==Demographics== | ||
| ⚫ | ==Demographics== | ||
| {| class="infobox" style="float:right;" | |||
| {| class=wikitable | |||
| | |
|+ Main immigrant groups, 2016<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cso.ie/px/pxeirestat/Statire/SelectVarVal/define.asp?MainTable=E7050&ProductID=DB_E7&PLanguage=0&Tabstrip=&PXSId=0&SessID=7827795&FF=1&tfrequency=1|title=Central Statistics Office|access-date=12 May 2019|archive-date=10 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180310010253/http://www.cso.ie/px/pxeirestat/Statire/SelectVarVal/define.asp?MainTable=E7050&ProductID=DB_E7&PLanguage=0&Tabstrip=&PXSId=0&SessID=7827795&FF=1&tfrequency=1|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| |- |
|- | ||
| ! Nationality || Population | ! Nationality || Population | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 134: | Line 132: | ||
| |{{flag|Latvia}} || 971 | |{{flag|Latvia}} || 971 | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==Symbols== | ==Symbols== | ||
| The heraldic crest for South Dublin has the inscription "This We Hold |
The heraldic crest for South Dublin has the inscription "This We Hold in Trust" in both ] and ], while incorporating elements relating to the history, geography and present day infrastructure of the area.{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} | ||
| ==Sport== | ==Sport== | ||
| The ] club ] plays at ]. The stadium hosted the ] and the ] final in 2010 & 2011. | The ] club ] plays at ]. The stadium hosted the ] and the ] final in 2010 & 2011. | ||
| The ] in Tallaght is the home venue for both the ] and ]. The arena also hosts various National Cup & League matches. | The ] in Tallaght is the home venue for both the ] and ]. The arena also hosts various National Cup & League matches. | ||
| == |
==Twinning== | ||
| South Dublin is twinned with the ], United Kingdom.{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} | South Dublin is twinned with the ], United Kingdom.{{citation needed|date=May 2020}} | ||
| Line 164: | Line 163: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:47, 2 January 2025
County in Ireland This article is about the county. For the southern part of Dublin, see Southside, Dublin. For the former constituency, see Dublin South (Dáil constituency).County in Leinster, Ireland
| South Dublin Átha Cliath Theas | |
|---|---|
| County | |
 Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
Mottoes:
| |
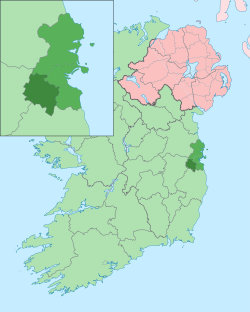 Inset showing South Dublin (darkest green in inset) within Dublin Region (lighter green) Inset showing South Dublin (darkest green in inset) within Dublin Region (lighter green) | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Province | Leinster |
| Region | Eastern and Midland |
| Established | 1994 |
| County town | Tallaght |
| Government | |
| • Local authority | South Dublin County Council |
| • Dáil constituencies | |
| • EU Parliament | Dublin |
| Area | |
| • Total | 222.74 km (86.00 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 757 m (2,484 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 301,075 |
| • Density | 1,400/km (3,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC±0 (WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (IST) |
| Vehicle index mark code | D |
| Website | Official website |
South Dublin (Irish: Átha Cliath Theas) is a county in Ireland, within the province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished for administrative purposes in 1994. South Dublin County Council is the local authority for the county. The county contains both dense suburbs of Dublin and stretches of unpopulated mountains. In 2022 it had a population of 301,705, making it the fourth most populous county in the state.
Geography and population
South Dublin has an area of 222.74 square kilometres (86 sq mi), making it the second-largest of the four local government areas in Dublin. It is bounded by Dublin City (15 km, 9.3 mi to the northeast), the River Liffey (separating it from Fingal to the north), Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown (to the east), County Kildare (to the west) and its hills adjoin the mountains of County Wicklow to the south.
The county town is Tallaght. Other important centres of population are Lucan and Clondalkin. Much of the county is heavily urbanised but small rural settlements exist in the southern and western parts. South Dublin's population increased from 278,767 in 2016 to 301,075 in 2022, according to the latest census.
Towns and villages
Several urban areas in South Dublin County are also traditionally suburbs of Dublin city. For the purposes of planning and management, the County Council designates the status of towns, villages and suburbs in three tiers – town, district centre and local centre. In the 2022 development plan, the towns and district centres are listed as:
- Tallaght, the county seat and the location of The Square Shopping Centre which was opened in October 1990
- Clondalkin ("to be facilitated and developed as a Town Centre ... including northward development")
- Lucan (with notes on the Liffey Valley Centre, and the developing Adamstown area – a future "district centre" – and a stated aim to avoid Lucan merging with Leixlip)
- and with a proposal to develop a Town Centre around the Liffey Valley Centre at Quarryvale
while the more local centres are noted in three groups:
- city suburbs including at least Rathfarnham, Ballyroan, Palmerstown, Terenure, Templeogue, Knocklyon, Firhouse, Ballycullen and Greenhills
- villages such as Rathcoole, Newcastle(-Lyons), and Saggart
- new neighbourhoods, some within bigger, older areas – including such as Kilnamanagh, Ballyowen, Finnstown, and, in development, Adamstown (mentioned in the county plan as an extension of Lucan).
Residential areas
- Adamstown
- Ballyboden
- Ballyroan
- Belgard
- Clondalkin
- Edmondstown
- Firhouse
- Greenhills
- Jobstown
- Kingswood
- Kilnamanagh
- Knocklyon
- Lucan
- Newcastle
- Palmerstown
- Rathcoole
- Rathfarnham
- Rockbrook
- Ronanstown
- Saggart
- Tallaght
- Templeogue
- Walkinstown, southernmost part
Terminology

In Ireland, the usage of the word county nearly always comes before rather than after the county name; thus "County Clare" in Ireland as opposed to "Clare County" in Michigan, USA. In the case of those counties created after 1994, they often drop the word county entirely, or use it after the name; thus for example internet search engines show many more uses (on Irish sites) of "South Dublin" than of either "County South Dublin" or "South Dublin County". The 2003 placenames order lists South Dublin without any modification.
History
In 1985, County Dublin was divided into three electoral counties: Dublin–Fingal, Dublin–Belgard, and Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown. At the 1991 local election, the area of Dublin–Belgard was renamed as South Dublin. The name Belgard did have a historical association with the area, being the designation of one of the border fortresses of the Pale that existed in that area. It was altered due to a view that the name Belgard might create associations with areas of modern development in Tallaght that now also uses that name.
On 1 January 1994, under the provisions of the Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993, County Dublin ceased to exist, and was succeeded by the counties of Fingal, Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown and South Dublin in the areas of the electoral counties. The boundaries of South Dublin were finalised in 1993, to accommodate the M50 motorway.
Various organs of state use alternative subdivisions of Dublin for administrative reasons, for example, the Dublin postal codes.
Local government and politics
South Dublin County Council is the local authority for the county. It was established on 1 January 1994 with the establishment of the county. It is one of local authorities in County Dublin. The county is divided into seven local electoral areas: Clondalkin (7 councillors), Firhouse–Bohernabreena (5 councillors), Lucan (5 councillors), Rathfarnham–Templeogue (7 councillors), Tallaght Central (6 councillors), and Tallaght South (5 councillors).
The Dáil constituencies of Dublin Mid-West (4 seats) and Dublin South-West (5 seats) are wholly within South Dublin, and the constituency of Dublin South-Central is partially within South Dublin.
In 2015, South Dublin became part of the Eastern and Midland Region. South Dublin County Council sends three members to the Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly.
Demographics
| Nationality | Population |
|---|---|
| 9,159 | |
| 7,988 | |
| 3,235 | |
| 2,726 | |
| 2,644 | |
| 2,620 | |
| 1,499 | |
| 1,434 | |
| 999 | |
| 971 |
Symbols
The heraldic crest for South Dublin has the inscription "This We Hold in Trust" in both English and Irish, while incorporating elements relating to the history, geography and present day infrastructure of the area.
Sport
The League of Ireland club Shamrock Rovers plays at Tallaght Stadium. The stadium hosted the 2009 FAI Cup final and the Setanta Sports Cup final in 2010 & 2011.
The National Basketball Arena in Tallaght is the home venue for both the Ireland national basketball team and Ireland women's national basketball team. The arena also hosts various National Cup & League matches.
Twinning
South Dublin is twinned with the London Borough of Brent, United Kingdom.
References
- ^ "Local Authorities (County Councils): South Dublin County Council". Census 2022. Central Statistics Office. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- "Baile Átha Cliath Theas/South Dublin". Placenames Database of Ireland. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- "Chapter 2: Core Strategy and Settlement Strategy" (PDF). South Dublin County Development Plan 2022-2028. South Dublin County Council. 22 June 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 July 2023. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- Tallaght, Dublin, Ireland, South Dublin County Development Plan 2004–2010, Chapter 5
- Placenames (Provinces and Counties) Order 2003 (S.I. No. 519 of 2003). Signed on 30 October 2003. Statutory Instrument of the Government of Ireland. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government (Reorganisation) Act 1985, s. 12: Establishment of Dublin Electoral Counties (No. 7 of 1985, s. 12). Enacted on 3 April 1985. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government Act 1991, s. 26: Amendment of Local Government (Reorganisation) Act 1985 (No. 11 of 1991, s. 26). Enacted on 18 May 1991. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993 Commencement Order 1993 (S.I. No. 400 of 1993). Signed on 22 December 1993. Statutory Instrument of the Government of Ireland. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993, s. 9: Establishment and boundaries of administrative counties (No. 31 of 1993, s. 9). Enacted on 21 December 1993. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993, s. 8: Alteration of certain boundaries existing before establishment day (No. 31 of 1993, s. 8). Enacted on 21 December 1993. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- Local Government (Dublin) Act 1993, s. 11: Establishment of councils of administrative counties (No. 31 of 1993, s. 11). Enacted on 21 December 1993. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 9 December 2021.
- County of South Dublin Local Electoral Areas Order 2018 (S.I. No. 633 of 2018). Signed on 19 December 2018. Statutory Instrument of the Government of Ireland. Archived from the original on 2 February 2019. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 11 September 2020.
- Electoral (Amendment) (Dáil Constituencies) Act 2017, Schedule (No. 39 of 2017, Schedule). Enacted on 23 December 2017. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 8 August 2021.
- "Eastern and Midland Regional Assembly". Eastern & Midland Regional Assembly. Archived from the original on 29 September 2016. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- Local Government Act 1991 (Regional Assemblies) (Establishment) Order 2014 (S.I. No. 573 of 2014). Signed on 16 December 2014. Statutory Instrument of the Government of Ireland. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 29 January 2022.
- "Central Statistics Office". Archived from the original on 10 March 2018. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
External links
| Places in South Dublin | ||
|---|---|---|
| County town: Tallaght | ||
| Villages and suburbs |  | |
| Regions of County Dublin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cities |  | |
| Towns and villages | ||
| Counties | ||
| Other regions | ||
| Civil sub-divisions | ||
| Baronies of Dublin | ||
| Counties of Ireland | ||
|---|---|---|
| The counties are listed per province | ||
 | ||
| ||
53°18′28″N 6°24′47″W / 53.30778°N 6.41306°W / 53.30778; -6.41306
Categories: