| Revision as of 16:39, 2 August 2021 view sourceWikiman2021language (talk | contribs)105 editsNo edit summaryTag: Reverted← Previous edit |
Latest revision as of 06:42, 25 December 2024 view source Arctic Circle System (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users11,438 edits Added Korouni dialect |
| (248 intermediate revisions by 83 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
|
|
{{pp-semi-indef}} |
|
{{Short description|Dialect of the Kurdish language}} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
{{Redirect|Kalhori|the Kalhori people|Kalhor (tribe)}}{{distinguish|Sorani}} |
|
|
{{Short description|One of the Kurdish languages}} |
|
{{Infobox language |
|
{{Infobox language |
|
| name = Southern Kurdish (Pehlewani) |
|
| name = Southern Kurdish |
|
| nativename = {{lang-ku| کوردیی باشووری ,کوردی خوارگ}} |
|
| nativename = کوردی باشووری |
|
| altname = |
|
| states = ], ] |
|
| states = Eastern ], Western ] |
|
|
| region = ] |
|
| region = ] |
|
|
| ethnicity = ] |
|
| speakers = 3,000,000 in Iran, 350,000 in Turkey, Iraq |
|
|
| ref = e18 |
|
| speakers = {{sigfig|4.250000|3}} million in Iran |
|
|
| date = 2021 |
|
|
| ref = e27 |
|
|
| speakers2 = unknown number in Iraq |
|
| familycolor = Indo-European |
|
| familycolor = Indo-European |
|
| fam2 = ] |
|
| fam2 = ] |
| Line 14: |
Line 19: |
|
| fam5 = ] |
|
| fam5 = ] |
|
| fam6 = ] |
|
| fam6 = ] |
|
| dia1 = Bayray |
|
|
| dia2 = Feyli |
|
|
| dia3 = Garrusi (Bijari) |
|
|
| dia5 = Kermanshahi |
|
|
| dia6 = Kolyai |
|
|
| dia7 = Kordali |
|
|
| dia9 = Malekshahi |
|
|
| dia10 = Sanjabi |
|
|
| dia14 = ] |
|
|
| dia11 = Laki |
|
|
| dia12 = Kalhori |
|
|
| dia13 = Zangana |
|
|
| iso3 = sdh |
|
| iso3 = sdh |
|
| glotto = sout2640 |
|
| glotto = sout2640 |
|
| glottorefname = Southern Kurdish |
|
| glottorefname = Southern Kurdish |
|
| lingua = 58-AAA-c |
|
| lingua = 58-AAA-c |
|
| script = ] (]) |
|
| script = ] (]) |
|
| map = SOUTHERN KURDISH.JPG |
|
| map = SOUTHERN KURDISH.JPG |
|
| mapcaption = |
|
| mapcaption = |
|
| map2 = Kurdish languages map.svg |
|
| map2 = Kurdish languages map.svg |
|
| mapcaption2 = Geographic distribution of Kurdish and other Iranian languages spoken by Kurds |
|
| mapcaption2 = Geographic distribution of Kurdish dialects and other Iranian languages spoken by Kurds |
|
|
{{legend|#ef6662|] (Northern Kurdish)}} |
|
{{col-begin}} |
|
|
|
{{legend|#c63143|] (Central Kurdish)}} |
|
{{col-break}} |
|
|
{{legend|#156a33|]}} |
|
{{legend|#a56c24|]|Zaza}} |
|
{{legend|#00a239|]}} |
|
{{legend|#c8a65d|] (] is included)}} |
|
{{legend|#00e450|Southern}} |
|
{{legend|#b3d423|mixed dialect areas}} |
|
|
| dia1 = ] |
|
{{col-break}} |
|
|
|
| dia2 = ] |
|
{{legend|#ffd700|]}} |
|
|
{{legend|#ff8a00|]}} |
|
| dia3 = ] |
|
|
| dia4 = ] |
|
{{legend|#ce9bd8|mixed areas}} |
|
|
|
| dia5 = ] (]) |
|
{{col-end}} |
|
|
|
| dia6 = ] |
|
|
| dia7 = ] |
|
|
| dia8 = ] |
|
|
| dia9 = ] |
|
|
| dia10 = Bayray |
|
|
| dia11 = ] |
|
|
| dia12 = ] |
|
}} |
|
}} |
|
|
|
|
|
'''Southern Kurdish''' ({{lang-ku|زۆڤان کوردیی باشووری ,کوردی خوارگ|Zûwane Kurdîy başûrî, Kurdiy xwarig}}),<ref>{{Cite web|title=Kurdish, Southern|url=https://www.ethnologue.com/language/SDH|access-date=21 August 2020|website=Ethnologue}}</ref> or "Pehlewani", also known as '''Kurdiy xwarîn''' is a ] dialect predominantly spoken in Eastern ] and Western ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Kurdish language i. History of the Kurdish language |url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/kurdish-language-i |publisher=] |access-date=25 June 2019}}</ref> In Iran, it is spoken in the provinces of ] and ]. In Iraq, it is spoken in the region of ], all the way to ]. It is also the dialect of the populous ] ''Kakayî tribes'' near ] and most ] Kurds in Kermanshah Province. There are also populous diasporas of Southern Kurdish-speakers found in the ] mountains. |
|
'''Southern Kurdish''' ({{langx|ku|کوردی باشووری|Kurdî Başûrî}})<ref>{{Cite web |title=Southern Kurdish |url=https://www.ethnologue.com/language/sdh/ |access-date=8 April 2023 |website=]}}</ref> is one of the dialects of the ], spoken predominantly in northeastern ] and western ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Kurdish language i. History of the Kurdish language |url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/kurdish-language-i |publisher=] |access-date=25 June 2019}}</ref> The Southern Kurdish-speaking region spans from ] in Iraq to ] southward and ] eastward in Iran.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|pp=VII}} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
== Name == |
|
Native speakers use various different alphabets to write Southern Kurdish, the most common ones are extensions of the standard ]. |
|
|
|
'Southern Kurdish' is a linguistic term for a group of related dialects in Western Iran. Speakers are not familiar with the term and do not refer to the language as such. They generally identify the kind of Kurdish they speak as a local dialect (the Kurdish of a given village), or as a regional variety such as "Garūsi".<ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Anonby |first=Erik |title=Current issues in Kurdish linguistics |last2=Mohammadirad |first2=Masour |last3=Sheyholislami |first3=Jaffer |publisher=University of Bamberg Press |year=299 |pages=26 |chapter=Kordestan Province in the Atlas of the Languages of Iran: Research process, language distribution, and language classification}}</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
==Dialects== |
|
==Variants== |
|
|
Southern Kurdish has many variants, linguist Fattah divides them into 35 varieties. These include: |
|
The subdialects of Southern Kurdish are:<ref>{{Cite web|title=OLAC resources in and about the Southern Kurdish language|url=http://olac.ldc.upenn.edu/language/sdh|access-date=21 August 2020|website=]}}</ref> |
|
|
*''Kermanshahi'' is spoken mostly in Western Iran, in and around the city of ]. |
|
|
*''Feyli:'' referring to the ]; also known as ''Ilami'', after ]. It is spoken in Eastern ] in the ] region of ] near the Iranian border and in Western Iran in Ilam province and parts of ], by the ]. ] is a sub-dialect. It is spoken by the tribe of Ali Sherwan (Beyrey) in Ilam and by almost all Feyli Kurds in ], Mandali, Badrah and Zorbatiah in Iraq. It shares many features with ].<ref>Vahid-e-Ranjbar, Dastur-e Zaban-e Kurdi-ye Kermanshahi. Kermanshah: Taq-Bostan. 1388</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
*''Garrusi'' |
|
* '''Bîcarî''' |
|
|
** The most ] variety of Southern Kurdish spoken in and around ] in Iran. Bîcarî is the only Southern Kurdish variety detached from the greater Southern Kurdish-speaking region.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|pp=16-17}} |
|
*''Malekshahi'' |
|
|
|
* '''Qurweyî (Chahar Dawli Xarbi)''' |
|
*''Sanjâbi:'' referring to the language of the ] tribe. |
|
|
|
** The Quwreyî variety is spoken around ] in Iran and is related to the variety spoken in Asadabad and other Kurdish-speaking areas in ].{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|pp=18-19}} |
|
*'']'' |
|
|
|
* '''Kulyayî''' |
|
*''Kalhori'' referring to the ] tribe. |
|
|
|
** The Kulyayî variety is spoken northeast of Kermanshah, principally in ] and surrounding counties. The variety also spans into the ] in Hamadan Province.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|p=19}} |
|
|
* '''Bîlewerî''' |
|
|
** The principal Southern Kurdish variety in ] in Kermanshah.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|p=20}} |
|
|
* '''Dînewerî''' |
|
|
** About 83 villages in ] speak the Dînewer variety. The differences between the Dînewerî and the Kulyayî varieties are anodine.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|p=21}} |
|
|
* '''Sehne / Lekî-Kirmaşanî''' |
|
|
** The Sehne variety, or Lekî-Kirmaşanî has many similar characteristics with ] and is spoken in ] and in ]. What distinguishes it most from Lekî is the lack of the ].{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|p=21}} |
|
|
* ''']''' {{aka}} Pahlavi is quite distant, and may be a distinct language.<ref>Erik Anonby, Mortaza Taheri-Ardali & Amos Hayes (2019) ''The Atlas of the Languages of Iran (ALI)''. Iranian Studies 52. </ref> |
|
|
Other variants include: Bîstûnî, Çihrî, Hersîn, Payrawend, Kirmaşanî, Sencabî, Xalesa, Çemçemal, Qesri Şîrînî, Serpuli Zehawî, Harasam, Kelhurrî, Îwan, Erkewazî, Şêrwanî, Îlamî, Salihabadî, Rîka, Bedreyî, Melikşahî, Mêxasî, Mihran, Xaneqînî, Mendilî, Duşêxî, Kaprat, Warmizyar, Zurbatiya and Feylî.{{Sfnp|Fattah|2000|pp=22–40}} |
|
|
|
|
|
== Alphabet == |
|
|
The Southern Kurdish alphabet is very similar to the ], which is a derivation of the ]. |
|
|
Southern Kurdish has one additional letter "ۊ"; the Arabic letter waw with two dots above. |
|
|
{|class="wikitable" style="border-collapse:collapse; text-align: center; font-size: 120%; width: 100%;" |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ع}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ش}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|س}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ژ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ز}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ڕ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ر}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|د}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|خ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ح}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|چ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ج}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ت}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|پ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ب}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ا}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ئـ}}}}</span> |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 17 || 16 || 15 || 14 || 13 || 12 || 11 || 10 || 9 || 8 || 7 || 6 || 5 || 4 || 3 || 2 || 1 |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ێ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ی}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ۊ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ۆ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|و}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ە}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ھ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ن}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|م}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ڵ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ل}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|گ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ک}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ق}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ڤ}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|ف}}}}</span> |
|
|
| <span style="font-size:170%;">{{Script/Arabic|{{lang|ku-Arab|غ}}}}</span> |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 34 || 33 || 32 || 31 || 30 || 29 || 28 || 27 || 26 || 25 || 24 || 23 || 22 || 21 || 20 || 19 || 18 |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
==See also== |
|
==See also== |
|
|
*] |
|
*] |
|
*] |
|
|
*] |
|
|
|
|
|
*] |
|
==Sources== |
|
|
* Kamandar Fattah, ''Les Dialectes kurdes méridionaux: étude linguistique et dialectologique''. Louvain, Peeters, 2000, p. 55-62. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
==References== |
|
==References== |
|
{{Reflist}} |
|
{{Reflist}} |
|
|
|
|
|
==Bibliography== |
|
|
* {{citation|last=Fattah|first=Ismaïl Kamandâr|title=Les dialectes Kurdes méridionaux|date=2000|publisher=Acta Iranica|isbn=9042909188}} |
|
|
|
|
|
== Further reading == |
|
|
* {{cite journal |last=Borjian |first=Habib |date=2024 |title=Kermāšāni: The Kurdish Dialect of Kermanshah |journal=WORD |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=199–240 |doi=10.1080/00437956.2024.2381338}} |
|
|
|
|
|
==External links== |
|
==External links== |
|
{{Incubator|code=sdh|language=Southern Kurdish}} |
|
{{Incubator|code=sdh|language=Southern Kurdish}} |
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
* |
|
*Audio recordings of ] and ] in Southern Kurdish, archived with Kaipuleohone |
|
*Audio recordings of ] and ] in Southern Kurdish, archived with Kaipuleohone |
'Southern Kurdish' is a linguistic term for a group of related dialects in Western Iran. Speakers are not familiar with the term and do not refer to the language as such. They generally identify the kind of Kurdish they speak as a local dialect (the Kurdish of a given village), or as a regional variety such as "Garūsi".
Southern Kurdish has many variants, linguist Fattah divides them into 35 varieties. These include:
Other variants include: Bîstûnî, Çihrî, Hersîn, Payrawend, Kirmaşanî, Sencabî, Xalesa, Çemçemal, Qesri Şîrînî, Serpuli Zehawî, Harasam, Kelhurrî, Îwan, Erkewazî, Şêrwanî, Îlamî, Salihabadî, Rîka, Bedreyî, Melikşahî, Mêxasî, Mihran, Xaneqînî, Mendilî, Duşêxî, Kaprat, Warmizyar, Zurbatiya and Feylî.
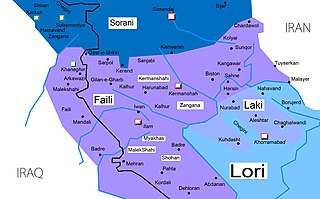
 Geographic distribution of Kurdish dialects and other Iranian languages spoken by Kurds
Kurmanji (Northern Kurdish)
Sorani (Central Kurdish)
Zaza language
Southern Kurdish (Gorani is included)
mixed dialect areas
Geographic distribution of Kurdish dialects and other Iranian languages spoken by Kurds
Kurmanji (Northern Kurdish)
Sorani (Central Kurdish)
Zaza language
Southern Kurdish (Gorani is included)
mixed dialect areas