| Revision as of 19:44, 18 February 2007 view sourceTiamut (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers31,614 edits →October 2000: changing link to direct to newly entitled page← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:27, 11 January 2025 view source Evaporation123 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,431 editsNo edit summaryTag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|2000–2005 Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation}} | |||
| {{sprotect}} | |||
| {{pp-30-500|small=yes}} | |||
| {{lowercase}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=June 2020}} | |||
| {{TotallyDisputed}} | |||
| {{Infobox military conflict | |||
| <!-- This is a controversial topic. Please read this talk page discussion before making substantial changes.--> | |||
| | conflict = Second Intifada | |||
| {{other uses|al-Aqsa (disambiguation)}} | |||
| | partof = the ] | |||
| {{Infobox Military Conflict | |||
| | image = {{align|center|{{Multiple image | |||
| |conflict=al-Aqsa Intifada | |||
| | perrow = 2 | |||
| |partof=the ] | |||
| | total_width = 350 | |||
| |image= | |||
| | border = infobox | |||
| |date=September ] - Ongoing | |||
| | image1= Faris odeh03a.jpg | |||
| |place=], ], ] | |||
| | image2= Flickr - Israel Defense Forces - Standing Guard in Nablus.jpg | |||
| |casus= | |||
| | image3= אוקטובר 2000 2.jpg | |||
| |result= | |||
| | image4= הפיגוע בצומת יגור 1.jpg | |||
| |combatant1={{flagcountry|Israel}} | |||
| | footer = '''Clockwise from top-left:'''<br />{{hlist|Palestinian child ] throws a stone at an Israeli tank in the ]|Israeli soldiers in ] during ]|Aftermath of a ] on a public transit bus near ]|Palestinian protesters confront Israeli security forces near ]}} | |||
| |combatant2={{flagcountry|Palestinian Authority}} | |||
| | footer_align = center}}}} | |||
| |Hammas | |||
| | date = 28 September 2000 – 8 February 2005<br />({{Age in years, months, weeks and days|month1=9|day1=28|year1=2000|month2=2|day2=8|year2=2005}}) | |||
| |Islamic Jihad | |||
| | place = {{hlist|Israel|] ]}} | |||
| |Hizbollah | |||
| | casus = | |||
| |commander1=]<br>]<br>] | |||
| | result = Uprising suppressed<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.haaretz.com/weekend/week-s-end/years-of-rage-1.316603 |title=Years of Rage |author=Amos Harel |author2=Avi Issacharoff |newspaper=] |date=1 October 2010 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=2 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140702094014/http://www.haaretz.com/weekend/week-s-end/years-of-rage-1.316603 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2004-sep-28-fg-intifada28-story.html |title=Losing faith in the intifada |author=Laura King |newspaper=] |date=28 September 2004 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=21 September 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120921132644/http://articles.latimes.com/2004/sep/28/world/fg-intifada28 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A52801-2004Sep26.html |title=From Jenin to Falluja |author=Jackson Diehl |newspaper=] |date=27 September 2004 |access-date=28 September 2014 |author-link=Jackson Diehl |archive-date=3 February 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140203212546/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A52801-2004Sep26.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.jewishworldreview.com/0704/chafets_2004_07_22.php3 |title=The Intifadeh is over – just listen |author=Zeev Chafetz |author-link=Ze'ev Chafets |newspaper=World Jewish Review |date=22 July 2004 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140804174542/http://www.jewishworldreview.com/0704/chafets_2004_07_22.php3 |archive-date=4 August 2014 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://jcpa.org/article/winning-counterinsurgency-war-the-israeli-experience/ |title=Winning the counterinsurgency war: The Israeli experience |author=Major-General (res) ] |website=] |date=23 August 2010 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=1 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140701102758/http://jcpa.org/article/winning-counterinsurgency-war-the-israeli-experience/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.biu.ac.il/SOC/besa/docs/perspectives57Eng.pdf |title=The need for a decisive Israeli victory over Hamas |author=Hillel Frisch |publisher=] |date=12 January 2009 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=23 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923205750/http://www.biu.ac.il/SOC/besa/docs/perspectives57Eng.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref>{{bulletedlist | |||
| |commander2=]†<br>]<br>] | |||
| | Israel constructs the ] | |||
| |strength1= | |||
| | Israel initiates the ]}} | |||
| |strength2= | |||
| | combatant1 = {{flag|Israel}} | |||
| |casualties1=1,017 Israeli dead<ref name=casualties /> | |||
| | combatant2 = {{flag|Palestinian Authority}} | |||
| |casualties2=4,046 Palestinian dead.<ref name=casualties /><br>223 more killed by Palestinians<ref name=casualties /> | |||
| * ] | |||
| <!-- WHEN EDITING THIS SECTION, PLEASE NOTE: | |||
| ** {{flag|Fatah}} | |||
| The current casualty statistics are provided by B'Tselem's newest report http://www.btselem.org/English/Statistics/Casualties.asp and need to be added up from several columns and rows. Please also update the date and total deaths in the casualties section farther down in the article. | |||
| ** {{flag|Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine}} | |||
| --> | |||
| ** {{flag|Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine}} | |||
| * {{flag|Hamas}} | |||
| * {{flag|Palestinian Islamic Jihad}} | |||
| * {{flag|Popular Resistance Committees}} | |||
| | commander1 = {{unbulletedlist | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | | |||
| }} | |||
| | commander2 = {{unbulletedlist | |||
| | {{flagicon image|Flag of Palestine - short triangle.svg}} '''PLO:''' | |||
| | ] ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ]{{POW}} | |||
| | ]{{KIA}} | |||
| | ]{{POW}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{flagicon image|Flag of al-Qassam Brigades.svg}} '''Hamas:''' | |||
| | ]{{KIA}} | |||
| | ]{{KIA}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{flagicon image|Flag of Palestine.svg}} '''Others:''' | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ]{{KIA}} | |||
| }} | |||
| | strength1 = | |||
| | strength2 = | |||
| | casualties1 = '''29 September 2000 – 1 January 2005:''' | |||
| ~1,010<ref name="casualties2">{{cite web |url=http://www.btselem.org/english/statistics/casualties.asp?sD=29&sM=09&sY=2000&eD=26&eM=12&eY=2008&filterby=event&oferet_stat=before |title=B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100701064428/http://www.btselem.org/english/statistics/Casualties.asp?sD=29&sM=09&sY=2000&eD=26&eM=12&eY=2008&filterby=event&oferet_stat=before |archive-date=1 July 2010}}</ref>{{failed verification|date=September 2014}}<!-- Oldest archive available; years grouped differently; perhaps an older version would have presented the number 945; the current corresponding page is http://www.btselem.org/statistics/fatalities/before-cast-lead/by-date-of-event --><ref name="statspage"/> Israelis total:<br />• 644–773 Israeli civilians killed by Palestinians;<br />• 215–301 Israeli troops killed by Palestinians | |||
| | casualties2 = '''29 September 2000 – 1 January 2005:''' | |||
| 3,179<ref name="statspage"/><ref name=BBCstats>{{cite news|title=Intifada toll 2000–2005|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/3694350.stm|access-date=10 November 2012|work=BBC News|date=8 February 2005|archive-date=17 January 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150117121043/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/3694350.stm|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=un2009jan9>{{cite web |url=http://www.ochaopt.org/documents/ocha_opt_gaza_humanitarian_situation_report_2009_01_09_english.pdf |title=Field Update on Gaza from the Humanitarian Coordinator |date=9 January 2009 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924055012/http://www.ochaopt.org/documents/ocha_opt_gaza_humanitarian_situation_report_2009_01_09_english.pdf |archive-date=24 September 2015}}</ref>–3,354<ref name="casualties2"/> Palestinians total:<br />• 2,739–3,168 Palestinians killed by Israeli troops;<span style="font-size:140%;">'''*'''</span><br />• 152–406 Palestinians killed by Palestinians;<br />• 34 Palestinians killed by Israeli civilians | |||
| | casualties3 = 55 foreign nationals/citizens total:<br />• 45 foreigners killed by Palestinians;<br />• 10 foreigners killed by Israeli troops<ref name=casualties2 /> | |||
| | notes = <span style="font-size:140%;">'''*'''</span>For the controversial issue of distinguishing Palestinian civilian/combatant casualties, see ]. | |||
| | units1 = {{flagicon image|Flag of the Israel Defense Forces.svg}} ]<br />{{flagicon image|Flag of the Israel Police.svg}} ]{{bulletedlist | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ]}}{{flagdeco|Israel}} ]<br />{{flagdeco|Israel}} ] | |||
| | units2 = ] ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{flagicon|Fatah}} ]<br> | |||
| {{armed forces|Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine}}<br> | |||
| {{armed forces|Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine}}<br> | |||
| {{armed forces|Hamas}}<br> | |||
| {{armed forces|Palestinian Islamic Jihad}}<br> | |||
| {{armed forces|Popular Resistance Committees}} | |||
| | territory = Israel withdraws from the ] | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ] ]. The blast killed 20 people.]] | |||
| ] in 2000 figured prominently in the Arab and world media. See also: ].]] | |||
| {{Campaignbox Al aqsa}} | |||
| The '''al-Aqsa Intifada''' ({{lang-ar|انتفاضة الأقصى}}, ''Intifā{{arabDIN|ḍ}}at El Aq{{arabDIN|ṣ}}a'' or ''Intifā{{arabDIN|ḍ}}at Al Aq{{arabDIN|ṣ}}a''; {{lang-he|אינתיפאדת אל אקצה}} (or hyphenated אינתיפאדת אל-אקצה), ''Intifādat El-Aqtzah'') is the wave of violence that began in September ] between ]s and ]is; it is also called the '''Second Intifada''' (see also ]). "]" is an Arabic word for "uprising" (literally translated as "shaking off"). "]" refers to a prominent ] on the ]. Many Palestinians consider the Intifada to be a war of national liberation against foreign occupation, whereas many Israelis consider it to be a ] campaign. | |||
| <!--End of Infobox--> | |||
| The ] (IDF) codenamed the events (prior to their outbreak) '''אירועי גאות ושפל''' ("Ebb and Tide events"). This name remained internal code in the ], but the Intifada is mostly called ''Al-Aqsa Intifada'' in Israel. | |||
| {{Campaignbox Second Intifada}} | |||
| <!--WHEN EDITING THIS SECTION, PLEASE NOTE: | |||
| The current casualty statistics are provided by B'Tselem's newest report http://www.btselem.org/English/Statistics/Casualties.asp and need to be added up from several columns and rows. Please also update the date and total deaths in the casualties section farther down in the article.--> | |||
| The '''Second Intifada''' ({{langx|ar|الانتفاضة الثانية|translit=al-Intifāḍa aṯ-Ṯāniya|lit=The Second Uprising}}; {{langx|he|האינתיפאדה השנייה|ha-Intifada ha-Shniya}}), also known as the '''Al-Aqsa Intifada''',{{sfn|BBC|2004}} was a major uprising by ] against Israel and its ] from 2000. The period of heightened violence in the ] and Israel continued until the ], which ended hostilities.{{sfn|BBC|2004}}<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Araj |first1=Bader |last2=Brym |first2=Robert J. |date=2010 |title=Opportunity, Culture and Agency: Influences on Fatah and Hamas Strategic Action during the Second Intifada |url=http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0268580909351327 |url-status=live |journal=International Sociology |language=en |volume=25 |issue=6 |pages=842–868 |doi=10.1177/0268580909351327 |issn=0268-5809 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240518055641/https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0268580909351327 |archive-date=18 May 2024 |access-date=18 May 2024 |quote=Strategic action by the two main Palestinian militant organizations, Fatah and Hamas, during the second intifada or uprising against the Israeli state and people (2000—5). ... during the second intifada, or uprising, of Palestinians against Israel between 2000 and 2005}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Smith |first=Robert B. |date=2008-04-01 |title=A Globalized Conflict: European Anti-Jewish Violence during the Second Intifada |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-006-9045-3 |journal=Quality & Quantity |language=en |volume=42 |issue=2 |pages=135–180 |doi=10.1007/s11135-006-9045-3 |issn=1573-7845 |quote=The globalization of the Arab–Israeli conflict during the period of the second intifada against Israel (from the autumn 2000 through at least the spring of 2005) has fostered anti-Jewish violence in Europe and throughout the world.}}</ref> | |||
| It is also called the '''Oslo War''' (''מלחמת אוסלו'') by those{{who}} who consider it a result of concessions made by Israel following the ], and '''Arafat's War''', after the ] whom many blame for starting it. Both groups have blamed the other for the fall of the Oslo peace process. | |||
| The general triggers for the unrest are speculated to have been centered on the failure of the ], which was expected to reach a final agreement on the ] in July 2000.{{sfn|Pressman|2006|p=114}} An uptick in violent incidents started in September 2000, after Israeli politician ] made a provocative visit to the ];{{sfn|''NPR''|2014}}{{sfn|Pressman|2006|p=114}} the visit itself was peaceful, but, as anticipated, sparked protests and riots that Israeli police put down with rubber bullets, live ammunition, and tear gas.{{sfn|Byman|2011|p=114}} Within the first few days of the uprising, the ] had fired one million rounds of ammunition.<ref name="Finkelstein, 20082">{{cite book |last=Finkelstein |first=Norman G. |author-link=Norman Finkelstein |title=Beyond Chutzpah: On the misuse of anti-Semitism and the abuse of history |date=2008 |edition=expanded paperback |location=Berkeley |chapter=4}}</ref> | |||
| The Intifada never ended officially. However, the relative success of the ], the truce agreed on by President ] and the Palestinian militant organizations, and the relatively low levels of violence during 2005, were considered by many to mark its effective end, commonly attributed to the change in Palestinian government following the death of ] and the ] from the ] and Northern ] (]). | |||
| During the first few weeks of the uprising, the ratio of Palestinians to Israelis killed was around 20 to 1.<ref name="Finkelstein, 2008">{{cite book |first=Norman G. |last=Finkelstein |author-link=Norman Finkelstein |title=Beyond Chutzpah: On the misuse of anti-Semitism and the abuse of history |edition=expanded paperback |location=Berkeley |date=2008 |chapter=4}}</ref> Israeli security forces engaged in gunfights, ], tank attacks, and airstrikes; Palestinians engaged in gunfights, ], and ].<ref name=":1">{{cite book |last=Cohen |first=Samy |chapter=Botched Engagement in the Intifada |date=2010 |title=Israel's Asymmetric Wars |pages=73–91 |location=New York |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan US |doi=10.1057/9780230112971_6 |isbn=978-1-349-28896-0}}"The al-Aqsa Intifada ushered in an era with a new brand of violence. It began with a popular uprising following Ariel Sharon's visit to Temple Mount on September 28, 2000. But unlike the first Intifada, which was basically a civil uprising against the symbols of an occupation that has lasted since June 1967, the second Intifada very quickly lapsed into an armed struggle between Palestinian activists and the Israeli armed forces. Almost from the very start, armed men took to hiding among crowds of Palestinians, using them as cover to shoot from. The IDF retaliated forcefully, each time causing several casualties."</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Kober |first=Avi |date=2007 |title=Targeted Killing during the Second Intifada:: The Quest for Effectiveness |url=https://www.erudit.org/en/journals/jcs/2009-v29-jcs_27_1/jcs27_1_1art06/ |journal=] |language=en |volume=27 |issue=1 |pages=94–114 |issn=1198-8614 |quote=Based on the assumption that there was no longer one front or one line of contact, Israel was carrying out dozens of simultaneous operations on the ground and in the air on a daily basis, including TKs, which were supposed to have multi-dimensional effects. According to Byman, TKs were mostly attractive to Israelis as they satisfied domestic demands for a forceful response to Palestinian terrorism. Byman also believes that by bolstering public morale, the TKs helped counter one of the terrorists' primary objectives – to reduce the faith of Israelis in their own government. |access-date=5 April 2022 |archive-date=5 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220405160428/https://www.erudit.org/en/journals/jcs/2009-v29-jcs_27_1/jcs27_1_1art06/ |url-status=live}}</ref> The approximate 138 ] carried out by ] after March 2001 became one of the prominent features of the Intifada and mainly targeted Israeli civilians.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last1=Matta |first1=Nada |last2=Rojas |first2=René |date=2016 |title=The Second Intifada: A Dual Strategy Arena |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/european-journal-of-sociology-archives-europeennes-de-sociologie/article/abs/second-intifada/CEF937E5D28EFA4F4F684E6D946942BF |url-status=live |journal=European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie |language=en |volume=57 |issue=1 |page=66 |doi=10.1017/S0003975616000035 |issn=0003-9756 |s2cid=146939293 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220405161756/https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/european-journal-of-sociology-archives-europeennes-de-sociologie/article/abs/second-intifada/CEF937E5D28EFA4F4F684E6D946942BF |archive-date=5 April 2022 |access-date=5 April 2022 |quote=Suicide terror, lethal attacks indiscriminately carried out against civilians via self-immolation, attained prominence in the Palestinian repertoire beginning in March 2001. From that point until the end of 2005, at which point they virtually ceased, 57 suicide bombings were carried out, causing 491 civilian deaths, 73% of the total civilians killed by Palestinian resistance organizations and 50% of all Israeli fatalities during this period. While not the modal coercive tactic, suicide terror was the most efficient in terms of lethality, our basic measure of its efficacy.}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Brym |first1=R. J. |last2=Araj |first2=B. |date=2006-06-01 |title=Suicide Bombing as Strategy and Interaction: The Case of the Second Intifada |journal=] |volume=84 |issue=4 |page=1969 |doi=10.1353/sof.2006.0081 |issn=0037-7732 |s2cid=146180585 |quote=In the early years of the 21st century, Israel, the West Bank and Gaza became the region of the world with the highest frequency of - and the highest per capita death toll due to - suicide bombing.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Schweitzer |first=Y. |date=2010 |title=The rise and fall of suicide bombings in the second Intifada |journal=Strategic Assessment |volume=13 |pages=39–48 |quote=As part of the violence perpetrated by the Palestinians during the second intifada, suicide bombings played a particularly prominent role and served as the primary effective weapon in the hands of the planners. |number=3}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Schachter |first=J. |date=2010 |title=The End of the Second Intifada? |url=https://strategicassessment.inss.org.il/wp-content/uploads/antq/fe-3427267573.pdf |journal=Strategic Assessment |volume=13 |pages=63–70 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210930061049/https://strategicassessment.inss.org.il/wp-content/uploads/antq/fe-3427267573.pdf |archive-date=30 September 2021 |quote=This article attempts to identify the end of the second intifada by focusing on the incidence of suicide bombings, arguably the most important element of second intifada-related violence. |number=3}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Sela-Shayovitz |first=R. |date=2007 |title=Suicide bombers in Israel: Their motivations, characteristics, and prior activity in terrorist organizations |journal=] |volume=1 |page=163 |quote=The period of the second Intifada significantly differs from other historical periods in Israeli history, because it has been characterized by intensive and numerous suicide attacks that have made civilian life into a battlefront. |number=2}}</ref> With a combined casualty figure for combatants and civilians, the violence is estimated to have resulted in the deaths of approximately 3,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis, as well as 64 foreign nationals.<ref name=casualties2005>{{cite web |url=http://old.btselem.org/statistics/english/Casualties.asp?sD=29&sM=09&sY=2000&eD=15&eM=1&eY=2005&filterby=event&oferet_stat=before |title=B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities 29.9.2000–15.1.2005 |website=] |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130414103627/http://old.btselem.org/statistics/english/Casualties.asp?sD=29&sM=09&sY=2000&eD=15&eM=1&eY=2005&filterby=event&oferet_stat=before |archive-date=14 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| The death toll, both military and civilian, of the entire conflict in 2000-2006 is estimated to be over 4000 Palestinians and over 1,000 Israelis,<ref name=casualties> . Intifada deaths since September 29, 2000.</ref> although this number is criticized by some sources for not differentiating between combatants and civilians. Between September 2000 and January 2005, 69 percent of Israeli fatalities were male, while over 95 percent of the Palestinian fatalities were male.<ref name=statspage /><ref name=articleid439 /> To date 63 foreign citizens have been killed (53 by Palestinians, and 10 by Israeli security forces).<ref name=casualties /> | |||
| The Second Intifada had ended with the ],{{sfn|Tucker|2019|p=958|ps=p: he and Israeli prime minister Sharon agreed in an early 2005 summit to suspend hostilities. This agreement effectively ended the Second Intifada}} as Palestinian president ] and Israeli prime minister Ariel Sharon agreed to take definitive steps to de-escalate the hostilities.{{sfn|Abbas|2005}}{{sfn|Sharon|2005}} They also reaffirmed their commitment to the "]" that had been proposed by the ] in 2003. Additionally, Sharon agreed to release 900 ]{{sfn|Reinhart|2006|p=77}} and further stated that Israeli troops would withdraw from those parts of the ] that they had re-occupied while fighting Palestinian militants during the uprising. | |||
| ==Prior events== | |||
| By signing the ], the ] committed to curbing violence in exchange for phased withdrawal of Israeli forces from parts of the ] and the ], and Palestinian self-government within those areas through the creation of the ]. However, both sides ended up deeply disappointed in the results of the Oslo Accords. | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| In the immediate five years following the Oslo signing, 405 Palestinians were killed<!--(source: B'Tselem)-->; 256 Israelis were killed, more than the number slain in the previous fifteen years (216, 172 of which were slain during the ]). | |||
| '''Second Intifada''' refers to a second Palestinian uprising, following the ], which occurred between December 1987 and 1993. ] ({{lang|ar|انتفاضة}}) translates into English as "uprising". Its root is an Arabic word meaning "the shaking off". It has been used in the meaning of "insurrection" in various Arab countries; the ], for example, were called the "bread intifada".<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://libcom.org/history/1977-egypts-bread-intifada |title=1977: Egypt's bread intifada |access-date=2 October 2016 |archive-date=2 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161002194415/https://libcom.org/history/1977-egypts-bread-intifada |url-status=live}}</ref> The term refers to a revolt against the Israeli occupation of the ]. | |||
| '''Al-Aqsa Intifada''' refers to ], the main name for the mosque compound constructed in the 8th century CE atop the ] in the ], and also known to ] as the ]. | |||
| In 1995, ] took the place of ], ] by ], a Jewish extremist opposed to the Oslo peace agreement. In the 1996 elections, Israelis elected the ] candidate, ], who promised to restore safety for Israelis by conditioning every step in the ] on Israel's assessment of the Palestinian Authority's fulfillment of its obligations in curbing violence as outlined in the Oslo agreement. Netanyahu continued the policy of construction within and expansion of existing ]s, in the ] and the ]. Though construction within the settlements was not explicitly prohibited in the Oslo agreement, many Palestinians believed that the continuing construction was contrary to the spirit of the Oslo agreement. | |||
| The Intifada is sometimes called the '''Oslo War''' (מלחמת אוסלו) by some Israelis who consider it to be the result of concessions made by Israel following the ],<ref>{{cite book |first=Itamar |last=Rabinovich |year=2004 |title=Waging Peace: Israel and the Arabs, 1948–2003 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-691-11982-3 |page= |author-link=Itamar Rabinovich |url=https://archive.org/details/wagingpeaceisrae00rabi_0/page/306 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Devin Sper |year=2004 |title=The Future of Israel |publisher=Sy Publishing |isbn=978-0-9761613-0-1 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/futureofisrael0000sper/page/335}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Binyamin Elon |year=2005 |title=God's Covenant With Israel: Establishing Biblical Boundaries in Today's World |publisher=Balfour Books |isbn=978-0-89221-627-7 |page=45|author-link=Binyamin Elon}}</ref> and '''Arafat's War''', after the ] whom some blamed for starting it. Others have named what they consider disproportionate response to what was initially a popular uprising by unarmed demonstrators as the reason for the escalation of the Intifada into an all-out war.<ref name="SBA2006">{{cite book |title=Scars of War, Wounds of Peace |last=Ben-Ami |first=Shlomo |author-link=Shlomo Ben-Ami |year=2006 |publisher=] |location=London |isbn=978-0-19-518158-6 |page= |quote=Israel's disproportionate response to what had started as a popular uprising with young, unarmed men confronting Israeli soldiers armed with lethal weapons fueled the Intifada beyond control and turned it into an all-out war. |url=https://archive.org/details/scarsofwarwounds00bena/page/267 }}</ref> | |||
| Some have claimed that ] and the ] (PA) had pre-planned the Intifada.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2006-03-29|url=http://www.mafhoum.com/press3/111P55.htm|title=How the war began|author=Khaled Abu Toameh}}</ref> They often quote a speech made in December 2000 by Imad Falouji, the PA Communications Minister at the time, where he explains that the violence had been planned since Arafat's return from the ] in July, far in advance of Sharon's visit (view of the speech). He stated that the Intifada "was carefully planned since the return of (Palestinian President) Yasser Arafat from Camp David negotiations rejecting the U.S. conditions."<ref>{{cite news|url=http://jewishweek.org/news/newscontent.php3?artid=3846|date=]|title=PA: Intifada Was Planned|publisher=]|}}</ref> ] quotes Mamduh Nofal, former military commander of the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine, who supplies more evidence of pre-] military preparations. Nofal recounts that ] "told us, Now we are going to the fight, so we must be ready".<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.theatlantic.com/doc/prem/200509/samuels|date=September ]|publisher=]|title=In a Ruined Country}}</ref> According to ], | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| Clinton's proposal... included explicit guarantees that Jews would have the right to visit and pray in and around the ]... Once Sharon was convinced that Jews had free access to the Temple Mount, there would be little the Israeli religious and nationalist Right could do to stall the peace process. When Sharon expressed interest in visiting the Temple Mount, Barak ordered GSS chief ] to approach ] with a special request to facilitate a smooth and friendly visit... Rajoub promised it would be smooth as long as Sharon would refrain from entering any of the mosques or praying publicly... Just to be on the safe side, ] personally approached ] and once again got assurances that Sharon's visit would be smooth as long as he did not attempt to enter the Holy Mosques... | |||
| A group of Palestinian dignitaries came to protest the visit, as did three Arab ] Members. With the dignitaries watching from a safe distance, the Shahab (youth mob) threw stones and attempted to get past the Israeli security personnel and reach Sharon and his entourage... Still, Sharon's deportment was quiet and dignified. He did not pray, did not make any statement, or do anything else that might be interpreted as offensive to the sensitivities of Muslims. Even after he came back near the ] under the hail of stones, he remained calm. "I came here as one who believes in coexistence between Jews and Arabs," Sharon told the waiting reporters. "I believe that we can build and develop together. This was a peaceful visit. Is it an instigation for Israeli Jews to come to the Jewish people's holiest site?"<ref>], ''The High Cost of Peace'' (Prima Publishing, 2002) ISBN 0-7615-3579-9 pp.353-354</ref> | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| ==Background== | |||
| Following Israel's pullout from ] in May 2000, the PLO official ] told reporters: "We are optimistic. Hezbollah's resistance can be used as an example for other ] seeking to regain their rights."<ref>HUSSEIN DAKROUB, Associated Press Writer. Associated Press. New York: ] ]. pg. 1</ref> | |||
| {{See also|Palestinian political violence|Israeli-occupied territories}} | |||
| ===Oslo Accords=== | |||
| Starting as early as ], ], members of Palestinian leader ]'s ] movement carried out a number of attacks on Israeli military and civilian targets, in violation of ]. In addition, the Israeli agency ''Palestinian Media Watch'' alleged that the Palestinian official TV broadcasts became increasingly militant during the summer of 2000, as Camp David negotiations faltered.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pmw.org.il/specrep-30.html|org=Palestinian Media Watch|title=Rape, Murder, Violence and War for Allah Against the Jews: Summer 2000 on Palestinian Television|accessdate=2000-03-29}}</ref> | |||
| Under the ], signed in 1993 and 1995, Israel committed to the phased withdrawal of its forces from parts of the ] and ], and affirmed the Palestinian right to ] within those areas through the creation of a ]. For their part, the ] formally recognised Israel and committed to adopting responsibility for internal security in population centres in the areas evacuated. Palestinian self-rule was to last for a five-year interim period during which a permanent agreement would be negotiated. However, the realities on the ground left both sides deeply disappointed with the Oslo process. Palestinian freedom of movement reportedly worsened from 1993 to 2000.<ref name=causes>{{cite journal|author=Jeremy Pressman|title=The Second Intifada: Background and Causes of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict|url=https://journals.lib.unb.ca/index.php/jcs/article/view/220/378|journal=]|date=11 November 2023|volume=23|issue=2|access-date=23 October 2019|archive-date=4 October 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191004233916/https://journals.lib.unb.ca/index.php/jcs/article/view/220/378|url-status=live}}</ref> Israelis and Palestinians have blamed each other for the failure of the Oslo peace process. In the five years immediately following the signing of the Oslo accords, 405 Palestinians <!-- (source: B'Tselem) --> and 256 Israelis were killed. | |||
| From 1996 Israel made extensive contingency plans and preparations, collectively code-named "Musical Charm", in the eventuality that peace talks might fail. In 1998, after concluding that the 5-year plan stipulated in the Oslo Talks would not be completed, the IDF implemented an Operation Field of Thorns plan to conquer towns in Area C, and some areas of Gaza, and military exercises at regimental level were carried out in April 2000 to that end. Palestinian preparations were defensive, and small-scale, more to reassure the local population than to cope with an eventual attack from Israel. The intensity of these operations led one Brigadier General, Zvi Fogel to wonder whether Israel's military preparations would not turn out to be a self-fulfilling prophecy.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Frisch |first=Hillel |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SLdwp_4BZhMC&pg=PA102 |title=The Palestinian Military: Between Militias and Armies |publisher=Routledge |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-134-15789-1 |page=102 |orig-date=2008 |access-date=3 October 2016 |archive-date=23 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161223214619/https://books.google.com/books?id=SLdwp_4BZhMC&pg=PA102 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| According to the ],<ref name=mitchell /> (the investigatory committee set up to look into the cause of the violence and named after the chairman of the committee, former U.S. Senator George Mitchell), the government of Israel asserted that | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| the immediate catalyst for the violence was the breakdown of the ] on ] ] and the "widespread appreciation in the international community of Palestinian responsibility for the impasse." In this view, Palestinian violence was planned by the PA leadership, and was aimed at "provoking and incurring Palestinian casualties as a means of regaining the diplomatic initiative." | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| In 1995, ] took the place of ], who had been ] by ], a Jewish extremist opposed to the Oslo peace agreement. In the 1996 elections, Israelis elected a right-wing<ref name="Schmemann" /> coalition led by the ] candidate, ] who was followed in 1999 by the ] leader ]. | |||
| The Palestine Liberation Organization, according to the same report, denied that the Intifada was planned, and asserted that "Camp David represented nothing less than an attempt by Israel to extend the force it exercises on the ground to negotiations."<ref name=mitchell>. The ] (et al) report. April 30, 2001.</ref> | |||
| The report also stated: | |||
| ===Camp David Summit=== | |||
| <blockquote>From the perspective of the PLO, Israel responded to the disturbances with excessive and illegal use of deadly force against demonstrators; behavior which, in the PLO’s view, reflected Israel’s contempt for the lives and safety of Palestinians. For Palestinians, the widely seen images of ] in Gaza on ], shot as he huddled behind his father, reinforced that perception.</blockquote> | |||
| From 11 to 25 July 2000, the ] was held between the United States ] ], Israeli Prime Minister ], and ] Chairman ]. The talks ultimately failed with each side blaming the other. There were five principal obstacles to agreement: borders and territorial contiguity, ] and the ], Palestinian refugees and their ], Israeli security concerns and Israeli settlements. Disappointment at the situation over the summer led to a significant fracturing of the PLO as many Fatah factions abandoned it to join Hamas and Islamic Jihad.<ref name="Rosen" /> | |||
| On 13 September 2000, Yasser Arafat and the ] postponed the planned unilateral declaration of an independent Palestinian state.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://transcripts.cnn.com/TRANSCRIPTS/0009/10/sm.07.html |title=Palestinian Parliament Expected to Not Declare an Independent Palestinian State |date=10 September 2000 |publisher=CNN |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=3 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303191541/http://transcripts.cnn.com/TRANSCRIPTS/0009/10/sm.07.html }}</ref> | |||
| ===Israeli settlements=== | |||
| While Peres had limited settlement construction at the request of US Secretary of State, ],<ref name="Schmemann">{{cite news |author=Schmemann |first=Serge |author-link=Serge Schmemann |date=5 December 1997 |title=In West Bank, 'Time' for Settlements Is Clearly Not 'Out' |work=] |url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C02E3D9133DF936A35751C1A961958260&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=print |url-status=live |access-date=18 December 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220326135407/https://www.nytimes.com/1997/12/05/world/in-west-bank-time-for-settlements-is-clearly-not-out.html?sec=&spon=&pagewanted=print |archive-date=26 March 2022}}</ref> Netanyahu continued construction within existing Israeli settlements<ref name=FMEP>{{Cite journal|title=Extraordinary Increase in Settlement Construction as Diplomacy Falters |journal=Settlement Report |publisher=Foundation for Middle East Peace |volume=8 |issue=2 |date=March–April 1998 |url=http://www.fmep.org/reports/archive/vol.-8/no.-2/extraordinary-increase-in-settlement-construction-as-diplomacy-falters |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130414194355/http://www.fmep.org/reports/archive/vol.-8/no.-2/extraordinary-increase-in-settlement-construction-as-diplomacy-falters |archive-date=2013-04-14 }}</ref> and put forward plans for the construction of a new neighbourhood, ], in ]. However, he fell far short of the Shamir government's 1991–92 level and refrained from building new settlements, although the Oslo agreements stipulated no such ban.<ref name=Schmemann/> Construction of housing units before Oslo, 1991–92: 13,960; after Oslo, 1994–95: 3,840; 1996–1997: 3,570.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fmep.org/settlement_info/settlement-info-and-tables/stats-data/housing-starts-in-israel-the-west-bank-and-gaza-strip-settlements-1990-2003 |title=Housing Starts in Israel, the West Bank and Gaza Strip Settlements*, 1990–2003 |publisher=Foundation for Middle East Peace |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081118071542/http://fmep.org/settlement_info/settlement-info-and-tables/stats-data/housing-starts-in-israel-the-west-bank-and-gaza-strip-settlements-1990-2003 |archive-date=18 November 2008}}</ref> | |||
| With the aim of marginalising the settlers' more militant wing, Barak courted moderate settler opinion, securing agreement for the dismantlement of 12 new outposts that had been constructed since the ] of November 1998,<ref name=Youngs>{{cite web |title=The Middle East Crisis: Camp David, the 'Al-Aqsa Intifada' and the Prospects for the Peace Process|author=Tim Youngs, International Affairs and Defence Section |publisher=] |date=24 January 2001|access-date=18 December 2007 |url=http://www.parliament.uk/commons/lib/research/rp2001/rp01-009.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080227143042/http://www.parliament.uk/commons/lib/research/rp2001/rp01-009.pdf |archive-date=27 February 2008}}</ref> but the continued expansion of existing settlements with plans for 3,000 new houses in the ] drew strong condemnation from the Palestinian leadership. Though construction within existing settlements was permitted under the Oslo agreements, Palestinian supporters contend that any continued construction was contrary to its spirit,<ref name="Schmemann" /> prejudiced the outcome of final status negotiations, and undermined Palestinian confidence in Barak's desire for peace.<ref name=Youngs /> | |||
| ==Timeline== | ==Timeline== | ||
| {{Timeline of Intifadas}} |
{{Timeline of Palestinian Intifadas}} | ||
| ===2000=== | ===2000=== | ||
| ] ] map of areas governed by the Palestinian Authority, July 2008.]] | |||
| On ], Sgt. David Biri was killed;<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/Terrorism-+Obstacle+to+Peace/Memorial/2000/Sgt+David+Biri.htm|date=]|publisher=Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs|title=Sgt. David Biri}}</ref> some Israeli sources view this as the start of the Intifada.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/myths/mf19a.html#a1|date=]|publisher=Myths and Facts|title=Myths & Facts Online: The “al-Aksa Intifada”}}</ref> Others, however, view Sharon's visit to the Temple Mount/Al-Haram Al-Sharif mosque on ] as the initiating event.<ref>{{cite news|publisher=BBC News|date=]|title=2000: 'Provocative' mosque visit sparks riots|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/september/28/newsid_3687000/3687762.stm}}</ref> While others believe it started a day later, due to the introduction of police and military presence the day following Sharon's visit, the day of prayers.<ref> - ]</ref><ref> - ]</ref> | |||
| The ], from 11 to 25 July 2000, took place between the United States ] ], Israeli Prime Minister ], and ] Chairman ]. It failed with the latter two blaming each other for the failure of the talks.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Israel/The-second-intifada |title=The second intifada |access-date=3 December 2023 |archive-date=12 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220512210653/https://www.britannica.com/place/Israel/The-second-intifada |url-status=live }}</ref> There were four principal obstacles to agreement: territory, ] and the ], Palestinian refugees and the ], and Israeli security concerns.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.vox.com/2018/11/20/18080066/israel-palestine-intifadas-first-second |title=What were the intifadas? |date=20 November 2018 |access-date=3 December 2023 |archive-date=10 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240110215245/https://www.vox.com/2018/11/20/18080066/israel-palestine-intifadas-first-second |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Ariel Sharon visits the Temple Mount==== | |||
| On 28 September, Israeli opposition leader ] and a ] party delegation guarded by hundreds of Israeli riot police visited the ], which is widely considered the ].<ref name="nytimes_outbreak">{{cite news |title=Palestinians And Israelis in a Clash at Holy Site|url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9502E4DA1E3AF93BA1575AC0A9669C8B63 |work=] |date=28 September 2000}}</ref> Israel has claimed sovereignty over the Mount and the rest of East Jerusalem ], and the compound is the ]. | |||
| The Israeli Interior Minister ], who permitted Sharon's visit, later claimed that he had telephoned the Palestinian Authority's security chief ] before the visit and gotten his reassurances that as long as Sharon didn't enter the mosques his visit wouldn't cause any problems. Rajoub vociferously denied having given any such reassurances.{{sfn|Bregman|2005|p=160}} | |||
| Shortly after Sharon left the site, angry demonstrations by Palestinian Jerusalemites outside erupted into rioting. The person in charge of the ] at the time, Abu Qteish, was later indicted by Israel for using a loud-speaker to call on Palestinians to defend Al-Aqsa, which action Israeli authorities claimed was responsible for the subsequent stone-throwing in the direction of the Wailing Wall.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Cohen |first=Hillel |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KRKsAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA73 |title=The Rise and Fall of Arab Jerusalem: Palestinian Politics and the City Since 1967 |date= March 2013|publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-136-85266-4 |language=en}}</ref> Israeli police responded with tear gas and rubber bullets, while protesters ] and other projectiles, injuring 25 policemen, of whom one was seriously injured and had to be taken to hospital. At least three Palestinians were wounded by rubber bullets.<ref name=bbc2000sept28>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/september/28/newsid_3687000/3687762.stm |work=BBC News |title=On This Day: 'Provocative' mosque visit sparks riots |date=28 September 2000 |access-date=2014-09-01 |quote=Palestinians and Israeli police have clashed in the worst violence for several years at Jerusalem's holiest site, the compound around Al-Aqsa mosque. The violence began after a highly controversial tour of the mosque compound early this morning by hardline Israeli opposition leader Ariel Sharon. ... Soon after Mr Sharon left the site, the angry demonstrations outside erupted into violence. Israeli police fired tear gas and rubber-coated metal bullets, while protesters hurled stones and other missiles. Police said 25 of their men were hurt by missiles thrown by Palestinians, but only one was taken to hospital. Israel Radio reported at least three Palestinians were wounded by rubber bullets. ... Following Friday prayers the next day, violence again broke out throughout Jerusalem and the West Bank. |archive-date=29 January 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190129133239/http://news.bbc.co.uk/onthisday/hi/dates/stories/september/28/newsid_3687000/3687762.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The stated purpose for Sharon's visit of the compound was to assert the right of all Israelis to visit the Temple Mount;<ref>{{cite news |url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9803E4DB1F3DF936A35753C1A9669C8B63&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=all|title=Unapologetic, Sharon Rejects Blame for Igniting Violence |work=] |date=5 October 2000|first=Joel|last=Greenberg|access-date=23 May 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Israeli's Tour of Holy Site Ignites Riot; Palestinians Angered By Test of Sovereignty in Jerusalem's Old City |newspaper=] |author=Lee Hockstader |date=29 September 2000 |page=A22 |url=http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P2-534994.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904080029/http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P2-534994.html |archive-date=4 September 2015 |access-date=28 September 2014}}</ref> however, according to Likud spokesman ], the actual purpose was to "show that under a Likud government will remain under Israeli sovereignty."<ref>{{cite news |title=Palestinians say opposition tour of holy site could cause bloodshed |url=http://archives.cnn.com/2000/WORLD/meast/09/27/israel.palestinians.ap/index.html |publisher=CNN |agency=] |date=27 September 2000 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041210211004/http://archives.cnn.com/2000/WORLD/meast/09/27/israel.palestinians.ap/index.html |archive-date=10 December 2004}}</ref> Ehud Barak in the Camp David negotiations had insisted that East Jerusalem, where the Haram was located, would remain under complete Israeli sovereignty.<ref name="Singh">Rashmi Singh, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200818222348/https://books.google.com/books?id=AQ_TOiLtdtAC&pg=PA38 |date=18 August 2020 }} Routledge, 2013 p.38</ref> In response to accusations by Ariel Sharon of government readiness to concede the site to the Palestinians, the Israeli government gave Sharon permission to visit the area. When alerted of his intentions, senior Palestinian figures, such as ], ], and ], all asked Sharon to call off his visit.<ref name="klein_jerusalemproblem_p98">{{cite book |author=Menachem Klein |title=The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-8130-2673-2 |page=98}}</ref> | |||
| Ten days earlier the Palestinians had observed their annual memorial day for the ], where thousands of ] and ] were massacred by ] supported by the Israeli military.<ref name="klein_jerusalemproblem_p98" /> The Israeli ] had concluded that ], who was the Israeli Defense Minister during the Sabra and Shatila massacre, was found to bear personal responsibility<ref>{{cite book|last=Schiff|first=Ze'ev|author-link=Ze'ev Schiff|author2=Ehud Ya'ari|title=Israel's Lebanon War|publisher=]|year=1984|page=|isbn=978-0-671-47991-6|url=https://archive.org/details/israelslebanonwa0000schi/page/284}}</ref> "for ignoring the danger of bloodshed and revenge" and "not taking appropriate measures to prevent bloodshed." Sharon's negligence in protecting the civilian population of Beirut, which had come under Israeli control, amounted to a ''non-fulfillment of a duty with which the Defence Minister was charged'', and it was recommended that Sharon be dismissed as Defence Minister. Sharon initially refused to resign, but after the death of an Israeli after a peace march, Sharon did resign as Defense minister, but remained in the Israeli cabinet. | |||
| The Palestinians condemned Sharon's visit to the Temple Mount as a provocation and an incursion, as were his armed bodyguards that arrived on the scene with him. Critics claim that Sharon knew that the visit could trigger violence, and that the purpose of his visit was political. According to one observer, Sharon, in walking on the Temple Mount, was "skating on the thinnest ice in the Arab-Israeli conflict."{{sfn|Shindler|2013|p=283}} | |||
| According to ''The New York Times'', many in the Arab world, including Egyptians, Palestinians, Lebanese and Jordanians, point to Sharon's visit as the beginning of the Second Intifada and derailment of the peace process.<ref>{{cite news |last=MacFarquhar |first=Neil |author-link=Neil MacFarquhar |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2006/01/05/international/middleeast/05cnd-arab.html |title=Few Kind Words for Sharon in the Arab World |date=5 January 2006 |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=16 December 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141216143022/http://www.nytimes.com/2006/01/05/international/middleeast/05cnd-arab.html |url-status=live }}</ref> According to Juliana Ochs, Sharon's visit 'symbolically instigated' the second intifada.<ref>{{cite book |author=Juliana Ochs |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mBSe-JgwPqoC&pg=PA6 |title=Security and Suspicion: An Ethnography of Everyday Life in Israel |publisher=] |year=2011 |series=The Ethnography of Political Violence |isbn=978-0-8122-4291-1 |page=6 |access-date=12 December 2015 |archive-date=2 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102113652/https://books.google.com/books?id=mBSe-JgwPqoC&pg=PA6 |url-status=live}}</ref> ] said that although Sharon's provocative actions were a rallying point for Palestinians, the Second Intifada would have erupted even had he not visited the Temple Mount.<ref>{{cite book |last=Goldberg |first=Jeffrey |title=Prisoners: A Story of Friendship and Terror |location=New York |publisher=] |date=2008 |page=258}}</ref> | |||
| ==== |
====Post-visit Palestinian riots==== | ||
| On 29 September 2000, the day after Sharon's visit, following Friday prayers, large riots broke out around the ]. Israeli police fired at Palestinians at the Temple Mount throwing stones over the ] at Jewish worshippers. After the chief of Jerusalem's police force was knocked unconscious by a stone, they switched to live ammunition and killed four Palestinian youths.{{sfn|Shindler|2013|p=283}}<ref>{{cite news |last1=Sontag |first1=Deborah |title=Battle at Jerusalem Holy Site Leaves 4 Dead and 200 Hurt |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2000/09/30/world/battle-at-jerusalem-holy-site-leaves-4-dead-and-200-hurt.html |access-date=14 November 2014 |work=] |date=30 September 2000 |archive-date=29 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141129070952/http://www.nytimes.com/2000/09/30/world/battle-at-jerusalem-holy-site-leaves-4-dead-and-200-hurt.html |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Dellios |first1=Hugh |title=4 Dead, Scores Wounded in Jerusalem Clashes |url=https://www.chicagotribune.com/2000/09/30/4-dead-scores-wounded-in-jerusalem-clashes/ |access-date=14 November 2014 |work=] |date=30 September 2000 |location=Jerusalem |quote=police clashed with stone-throwing Palestinians, killing four and wounding scores |archive-date=28 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141128195316/http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2000-09-30/news/0009300071_1_palestinian-police-officer-jerusalem-clashes-temple-mount |url-status=live}}</ref> Up to 200 Palestinians and police were injured.<ref name=cnn20000929>{{cite news |title=CNN's Jerrold Kessel on continuing violence in the Mideast |url=http://edition.cnn.com/chat/transcripts/2000/9/29/kessel/ |publisher=] |date=29 September 2000 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=19 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130919100942/http://edition.cnn.com/chat/transcripts/2000/9/29/kessel/ |url-status=live}}</ref> Another three Palestinians were killed in the Old City and on the ].<ref>{{cite book |author=Menachem Klein |title=The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-8130-2673-2 |pages=97–98}}</ref> By the end of the day, seven Palestinians had been killed and 300 had been wounded;<ref name="autogenerated2">{{cite book |author=Menachem Klein |title=The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-8130-2673-2 |page=97}}</ref> 70 Israeli policemen were also injured in the clashes.<ref name="klein_jerusalemproblem_p98" /><ref>{{cite web |date=19 October 2000 |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/041/2000/en/ |title=Israel and the Occupied Territories: Excessive use of lethal force |publisher=] |access-date=19 November 2018 |archive-date=22 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181122054850/https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/041/2000/en/ |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| On ], the Israeli opposition leader ], with a Likud party delegation, and surrounded by hundreds of Israeli riot police, visited the mosque compound of the ] in the Old City of ]. The compound is the holiest site in Judaism, and the third holiest site in ] for the majority of ]. The stated purpose for Sharon's visit of the mosque compound was to check complaints by Israeli archeologists that Muslim religious authorities had ] beneath the surface of the mount during the conversion of the ] area into a mosque. | |||
| In the days that followed, demonstrations erupted all over the ] and ]. Israeli police responded with live fire and rubber-coated bullets. In the first five days, at least 47 Palestinians were killed, and 1,885 were wounded.<ref name="autogenerated2" /> In Paris, as ] attempted to mediate between the parties, he protested to Barak that the ratio of Palestinians and Israelis killed and wounded on one day were such that he could not convince anyone the Palestinians were the aggressors. He also told Barak that "continu(ing) to fire from helicopters on people throwing rocks" and refusing an international inquiry was tantamount to rejecting Arafat's offer to participate in trilateral negotiations.<ref>{{cite book |author=Gilead Sher |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EdgAWFiDryMC&pg=PA162 |title=The Israeli–Palestinian Peace Negotiations, 1999–2001: Within Reach |publisher=] |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-7146-8542-7 |pages=161–162 |author-link=Gilead Sher |access-date=12 December 2015 |archive-date=2 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102113652/https://books.google.com/books?id=EdgAWFiDryMC&pg=PA162 |url-status=live }}: "Your account of events does not match the impression of any country in the world," he said. "At Camp David, Israel did in fact make a significant step towards peace, but Sharon's visit was the detonator, and everything has exploded. This morning, sixty-four Palestinians are dead, nine Israeli-Arabs were also killed, and you're pressing on. You cannot, Mr Prime Minister, explain this ratio in the number of wounded. You cannot make anyone believe that the Palestinians are the aggressors....When I was a company commander in Algeria, I also thought I was right. I fought the guerillas. Later I realized I was wrong. It is the honour of the strong, to reach out and not to shoot. Today you must reach out your hand. If you continue to fire from helicopters on people throwing rocks, and you continue to refuse an international inquiry, you are turning down a gesture from Arafat. You have no idea how hard I pushed Arafat to agree to a trilateral meeting. ...'</ref> During the first few days of riots, the IDF fired approximately 1.3 million bullets.<ref>Earlier estimates gave a million bullets and projectiles shot by Israeli forces in the first few days, 700,000 in the West Bank and 300,000 in the Gaza Strip. See Ben Kaspit, "Jewish New Year 2002—the Second Anniversary of the Intifada," '']'' 6 September 2002 (Heb), in Cheryl Rubenberg, ''The Palestinians: In Search of a Just Peace'', ], 2003 p. 324, p. 361 n. 5. The figure was revealed by ], then-director of Military Intelligence. ], who later became the Israeli Chief of Staff, denied the 1.3 million figure, claiming that the number reflected the demand of the command units for supplemental ammunition. {{cite news |last=Pedatzur |first=Reuven |date=4 December 2008 |title=Deflater of defeatist discourse |url=http://www.haaretz.com/deflater-of-defeatist-discourse-1.258857 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141219170311/http://www.haaretz.com/deflater-of-defeatist-discourse-1.258857 |archive-date=19 December 2014 |access-date=28 September 2014 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| Sharon's impending visit was officially announced and approved in advance with many Palestinian officials including Arafat himself, though prior to it some people on both sides protested, because of his controversial political stance. His visit was condemned by the Palestinians as a provocation and an incursion, as were his armed bodyguards that arrived on the scene with him. Critics claim that Sharon knew that the visit could trigger violence, and that the purpose of his visit was political; Sharon won the February 2001 elections in a landslide. | |||
| According to ] the early Palestinian casualties were those taking part in demonstrations or bystanders. Amnesty further states that approximately 80% of the Palestinians killed during the first month were in demonstrations where Israeli security services lives were not in danger.<ref name="Amnesty International">{{cite web|url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/library/info/MDE15/083/2001/en |title=Israel and the Occupied Territories: Broken Lives – A Year of Intifada |date=13 November 2001 |publisher=] |access-date=4 November 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140329030342/http://www.amnesty.org/en/library/info/MDE15/083/2001/en |archive-date=29 March 2014}}</ref> | |||
| On ], ], the day after Sharon's visit, following Friday prayers, large riots broke out around ] during which several Palestinians were shot dead. Already in the same day, the ], ], demonstrations and riots broke out in the ]. In the days that followed, demonstrations erupted all over the West Bank and Gaza. The same day, in the West Bank city of ], a Palestinian police officer working with Israeli police on a joint patrol opened fire and killed his Israeli counterpart Supt. Yosef Tabeja,<ref>{{cite news|date=]|title=Border Police Supt. Yosef Tabeja|publisher=Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs|url=http://www.israel-mfa.gov.il/MFA/Terrorism-+Obstacle+to+Peace/Memorial/2000/Border+Police+Supt+Yosef+Tabeja.htm}}</ref> an ] officer. | |||
| On 30 September 2000, the death of ], a Palestinian boy shot dead while sheltering behind his father in an alley in the Gaza Strip, was caught on video. Initially the boy's death and his father's wounding was attributed to Israeli soldiers. The scene assumed iconic status, as it was shown around the world and repeatedly broadcast on Arab television. The Israeli army initially assumed responsibility for the killing and apologised, and only retracted 2 months later, when an internal investigation cast doubt on the original version, and controversy subsequently raged as to whether indeed the IDF had fired the shots or Palestinian factions were responsible for the fatal gunshots.<ref>Nitzan Ben-Shaul, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200819201558/https://books.google.com/books?id=QFBiclfUJ04C&pg=PA118 |date=19 August 2020 }} ], 6 March 2007 pp.118–120.</ref> | |||
| ====October 2000 ==== | |||
| {{main|October 2000 (Israel)}} | |||
| 'October 2000' is the accepted, neutral short-hand used to describe the killings of 13 Arab demonstrators by Israeli police during several days of disturbances inside Israel following Ariel Sharon's visit to the ] or ]. Some Jews refer to as the '''Rosh Hashanah Arab Assault'''<ref></ref> because it started just before ], 5761. ] refer to it as حبة أكتوبر or "The October Ignition." | |||
| ====October 2000 events==== | |||
| The riots started when ]s, blocked main roads (such as Wadi Ara road), set banks and stores on fire and assaulted Jewish citizens. {{cn}} An Israeli civilian from ], ] was killed when an Arab youth threw a stone at his car which crashed near ]. {{cn}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|October 2000 events}} | |||
| The "October 2000 events" refers to several days of disturbances and clashes within Israel, mostly between ] and the ], as well as large-scale rioting by both Arabs and Jews. Twelve Arab citizens of Israel and a Palestinian from the Gaza Strip were killed by Israeli police, while an Israeli Jew was killed when his car was hit by a rock on the ].<!-- both sentences supported by Catigani --> During the first month of the Intifada, 141 Palestinians were killed and 5,984 were wounded, while 12 Israelis were killed and 65 wounded.<ref name="Catignani">{{cite book |last1=Catignani |first1=Sergio |year=2008 |chapter=The Al-Aqsa Intifada |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mfNBodDl0hgC&pg=PA105 |title=Israeli Counter-Insurgency and the Intifadas: Dilemmas of a Conventional Army |publisher=] |pages=104–106 |isbn=978-1-134-07997-1 |access-date=3 October 2016 |archive-date=23 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161223214612/https://books.google.com/books?id=mfNBodDl0hgC&pg=PA105 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| A general strike and demonstrations across northern Israel began on 1 October and continued for several days. In some cases, the demonstrations escalated into clashes with the ] involving ], ], and live-fire. Policemen used tear-gas and opened fire with ] and later live ammunition in some instances, many times in contravention of police protocol governing riot-dispersion. This use of live ammunition was directly linked with many of the deaths by the ]. | |||
| On 8 October, thousands of Jewish Israelis participated in violent acts in Tel Aviv and elsewhere, some throwing stones at Arabs, destroying Arab property and chanting "Death to the Arabs."<ref>{{cite news |date=19 November 2001 |url=http://www.haaretz.com/the-or-inquiry-summary-of-events-1.291940 |title=The Or Inquiry – Summary of Events |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=19 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150419015517/http://www.haaretz.com/the-or-inquiry-summary-of-events-1.291940 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Following the riots, |
Following the riots, a high degree of tension between Jewish and Arab citizens and distrust between the Arab citizens and police were widespread. An investigation committee, headed by Supreme Court Justice ], reviewed the violent riots and found that the police were poorly prepared to handle such riots and charged major officers with bad conduct. The ] reprimanded Prime Minister ] and recommended ], then the Internal Security Minister, not serve again as Minister of Public Security. The committee also blamed Arab leaders and Knesset members for contributing to inflaming the atmosphere and making the violence more severe. | ||
| ]]] | |||
| ====Ramallah |
====Ramallah lynching and Israeli response==== | ||
| {{ |
{{Main|2000 Ramallah lynching}} | ||
| On 12 October, PA police arrested two Israeli reservists who had accidentally entered ], where in the preceding weeks a hundred Palestinians had been killed, nearly two dozen of them minors.<ref>Eve Spangler, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820002151/https://books.google.com/books?id=v2AICgAAQBAJ&pg=PA183 |date=20 August 2020 }} Springer, 2015 p.183</ref> Rumours quickly spread that Israeli undercover agents were in the building, and an angry crowd of more than 1,000 Palestinians gathered in front of the station calling for their death. Both soldiers were beaten, stabbed, and disembowelled, and one body was set on fire. An Italian television crew captured the killings on video and then broadcast the tape internationally.<ref name="BBClynch">{{cite news |last=Asser |first=Martin |date=13 October 2000 |title=Lynch mob's brutal attack |work=] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/969778.stm |url-status=live |access-date=3 September 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080129215716/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/969778.stm |archive-date=29 January 2008}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Levy |first=Gideon |author-link=Gideon Levy |date=20 October 2000 |title=A conversation with Colonel Kamel al-Sheikh, Ramallah's chief of police, amid the ruins of his police station, where two Israeli soldiers were lynched by an angry mob last week |newspaper=] |url=http://home.mindspring.com/~fontenelles/Levy2.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010804004210/http://home.mindspring.com/~fontenelles/Levy2.htm |archive-date=4 August 2001}}</ref> A British journalist had his camera destroyed by rioters as he attempted to take a picture. The brutality of the killings shocked the Israeli public, who saw it as proof of a deep-seated Palestinian hatred of Israel and Jews.<ref>{{cite web |last=Feldman |first=Shai |url=http://www.tau.ac.il/jcss/sa/v3n3p7.html |title=The October Violence: An Interim Assessment |publisher=Jaffes Center for Strategic Studies |work=Strategic Assessment |volume=3 |number=3 |date=November 2000 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010629075844/http://www.tau.ac.il/jcss/sa/v3n3p7.html |archive-date=29 June 2001 }}</ref> In response, Israel launched a series of retaliatory air-strikes against Palestinian Authority targets in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The police station where the lynching had taken place was evacuated and destroyed in these operations.<ref name="revenge">{{cite news |title=A day of rage, revenge and bloodshed |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1370229/A-day-of-rage%2C-revenge-and-bloodshed.html |archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20171014065726/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1370229/A-day-of-rage-revenge-and-bloodshed.html |archive-date=14 October 2017 |date=13 October 2000 |work=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |first=Alan |last=Philps}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Israeli copters retaliate for soldiers' deaths |url=https://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast.htm#readmore |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20011123225843/http://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast.htm |archive-date=23 November 2001 |date=8 November 2000 |work=] |access-date=2009-07-03 }}</ref> Israel later tracked down and arrested those responsible for killing the soldiers. | |||
| On ], two Israeli reservists who entered ] were arrested by the PA police. An agitated Palestinian mob stormed the police station, beat the soldiers to death, and threw their mutilated bodies into the street. The killings were captured on video by an ] TV crew and broadcast on TV; .<ref name=BBClynch>{{cite news | first = Martin| last = Asser| title = Lynch mob's brutal attack| url = http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/969778.stm | publisher = ]|date = ], ]| accessdate = 2006-09-03}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://home.mindspring.com/~fontenelles/Levy2.htm|title=Interview with Ramallah's chief of police|publisher=]|date=]}}</ref> The brutality of the killings shocked the Israeli public<ref>Feldman, Shai. , Jaffes Center for Strategic Studies, ''Strategic Assessment'', Vol. 3 No. 3, November 2000.</ref> and were condemned by Palestinian leaders. | |||
| ====November–December 2000==== | |||
| In response, Israel launched a series of retaliatory air strikes against the Palestinian Authority. The violence quickly escalated and in the first six days of the Intifada, 61 Palestinians were killed and 2,657 were injured by the Israeli army and police. | |||
| Clashes between Israeli forces and Palestinians increased sharply on 1 November, when three Israeli soldiers and six Palestinians were killed, and four IDF soldiers and 140 Palestinians were wounded. In subsequent days, casualties increased as the IDF attempted to restore order, with clashes occurring every day in November. A total of 122 Palestinians and 22 Israelis were killed. On 27 November, the first day of ], Israel eased restrictions on the passage of goods and fuel through the ]. That same day, the Jerusalem settlement of ] came under Palestinian heavy machine gun fire from ]. Israel tightened restrictions a week later, and Palestinians continued to clash with the IDF and Israeli settlers, with a total of 51 Palestinians and 8 Israelis killed in December.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mideastweb.org/second_intifada_timeline.htm |title=Time Line of Second (Al-Aqsa) Intifada |publisher=MidEastWeb |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081217164830/http://mideastweb.org/second_intifada_timeline.htm |archive-date=17 December 2008}}</ref> In a last attempt by the Clinton administration to achieve a peace deal between Israelis and Palestinians, a summit was planned in Sharm el-Sheikh in December. However, Israeli Prime Minister Barak decided not to attend after the Palestinians delayed their acceptance of the ].<ref>CNN, 27 December 2000, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095434/https://edition.cnn.com/2000/WORLD/meast/12/27/mideast.06/ |date=18 November 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| ===2001=== | ===2001=== | ||
| The ] between Israel and the ] was held from 21 to 27 January 2001, at ] in the ]. Israeli prime minister ] and Palestinian President ] came closer to reaching a final settlement than any previous or subsequent peace talks yet ultimately failed to achieve their goals. | |||
| ], at the time from the ] party, ran against ] from the ]. Sharon was elected Israeli Prime Minister in February in the ]. | |||
| On 17 January 2001, Israeli teenager ] was murdered after being lured into ] by a 24-year-old Palestinian, Mona Jaud Awana, a member of Fatah's ]. She had contacted Ofir on the internet and engaged in an online romance with him for several months. She eventually convinced him to drive to Ramallah to meet her, where he was instead ambushed by three Palestinian gunmen and shot over fifteen times.<ref name="Wired">{{cite news |url=https://www.wired.com/politics/law/news/2001/01/41300 |title=Israel's 'First Internet Murder' |work=] |date=19 January 2001 |last=Hershman |first=Tania |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071019223411/http://www.wired.com/politics/law/news/2001/01/41300 |archive-date=19 October 2007 }}</ref> Awana was later arrested in a massive military and police operation, and imprisoned for life. Five other Israelis were killed in January, along with eighteen Palestinians. | |||
| On ], ], the IDF ] captured the vessel '']'', which sailed in international waters towards Palestinian Authority-controlled Gaza. The ship was laden with weaponry. The Israeli investigation that followed alleged that the shipment had been purchased by ]'s ] (PFLP-GC). The ship's value and that of its cargo was estimated at $10 million. The crew was reportedly planning to unload the cargo of weapons filled barrels — carefully sealed and waterproofed along with their contents — at a prearranged location off the Gaza coast, where the Palestinian Authority would recover them. | |||
| ], at the time from the ] party, ran against ] from the ]. Sharon was elected Israeli Prime Minister 6 February 2001 in the ]. Sharon refused to meet in person with Yasser Arafat. | |||
| On ], ], a ] ] detonated himself in the ] coastline ] dancing club. Twenty-one Israelis, most of them high school students, were killed. The attack significantly hampered American attempts to negotiate cease-fire. | |||
| Violence in March resulted in the deaths of 8 Israelis, mostly civilians, and 26 Palestinians. In ], a Palestinian sniper killed ten-month-old Israeli baby ].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9FTxoncXDwwC&q=Shalhevet+Pass&pg=PA443 |title=Protection of children during armed political conflict: a multidisciplinary perspective |editor=Charles W. Greenbaum |editor2=Philip E. Veerman |editor3=Naomi Bacon-Shnoor |publisher=Intersentia |year=2006 |isbn=978-90-5095-341-2 |access-date=8 November 2020 |archive-date=17 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210417205259/https://books.google.com/books?id=9FTxoncXDwwC&q=Shalhevet+Pass&pg=PA443 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Gordis |first=Daniel |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y7glZcS7mMgC&q=Shalhevet+Pass&pg=PA190 |title=Home to Stay: One American Family's Chronicle of Miracles and Struggles in Contemporary Israel |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-307-53090-5 |author-link=Daniel Gordis |access-date=21 June 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210417205301/https://books.google.com/books?id=y7glZcS7mMgC&q=Shalhevet%2BPass&pg=PA190 |archive-date=17 April 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> The murder shocked the Israeli public. According to the Israel police investigation the sniper aimed deliberately at the baby.<ref name=education>{{cite web|url=http://www.education.gov.il/children/page_23.htm |title=Target: Israeli Children |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131023202452/http://www.education.gov.il/children/page_23.htm |archive-date=23 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| On 30 April 2001, seven Palestinian militants were killed in an explosion, one of them a participant in Ofir Rahum's murder. The IDF refused to confirm or deny Palestinian accusations that it was responsible. | |||
| On 7 May 2001, IDF ] captured the vessel '']'', which was sailing in international waters towards Palestinian Authority-controlled Gaza. The ship was laden with weaponry. The Israeli investigation that followed said that the shipment had been purchased by ]'s ] (PFLP-GC). The ship's value and that of its cargo was estimated at $10 million. The crew was reportedly planning to unload the cargo of weapons-filled barrels—carefully sealed and waterproofed along with their contents—at a prearranged location off the Gaza coast, where the Palestinian Authority would recover it. | |||
| On 8 May 2001, two Israeli teenagers, Yaakov "Koby" Mandell (13) and Yosef Ishran (14), were kidnapped while hiking near their village. Their bodies were discovered the next morning in a cave near where they lived.<ref name=Guardian>{{cite news |title=Two Israeli boys found bludgeoned to death |date=9 May 2001 |work=] |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2001/may/09/israel1 |access-date=18 June 2012 |archive-date=25 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130825024550/http://www.theguardian.com/world/2001/may/09/israel1 |url-status=live }}</ref> ''USA Today'' reported that, according to the police, both boys had "been bound, stabbed and beaten to death with rocks." The newspaper continued, "The walls of the cave in the Judean Desert were covered with the boys' blood, reportedly smeared there by the killers."<ref name=USA>{{cite news |title=Two Israeli teenagers stoned to death |date=20 June 2001 |work=] |author=Matthew Kalman |url=https://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast/2001-05-09-slainteens.htm |access-date=18 June 2012 |author-link=Matthew Kalman |archive-date=20 April 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110420150223/http://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast/2001-05-09-slainteens.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| After a ] ] on 18 May 2001, Israel for the first time since 1967 used warplanes to attack Palestinian Authority targets in the West Bank and Gaza, killing 12 Palestinians. In the past, airstrikes had been carried out with helicopter gunships.<ref>{{cite news |date=20 May 2001 |title=Arabs seek to isolate Israel |work=] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/1340003.stm |url-status=live |access-date=1 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012112751/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/1340003.stm |archive-date=12 October 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| On 1 June 2001, an ] suicide bomber ] dancing club. Twenty-one Israeli civilians, most of them high school students, were killed and 132 injured.<ref>{{cite web |author=Karmon |first=Ely |author-link=Ely Karmon |date=11 June 2001 |title=The Palestinian Authority-Hamas Collusion – From Operational Cooperation to Propaganda Hoax |url=http://www.ict.org.il/Article.aspx?ID=806 |website=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904080030/http://www.ict.org.il/Article.aspx?ID=806 |archive-date=4 September 2015 |access-date=28 September 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-48416289.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121023030542/http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-48416289.html|archive-date=23 October 2012|title=No. 1 Hamas terrorist killed. Followers threaten revenge in Tel Aviv. |last=O'Sullivan|first=Arieh |author-link=Arieh O'Sullivan |date=25 November 2001 |newspaper=] |access-date=30 January 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2006/01/29/international/middleeast/29israel.html |title=In Hamas's Overt Hatred, Many Israelis See Hope |last=Fisher |first=Ian |author-link=Ian Fisher (journalist) |date=29 January 2006 |work=] |access-date=30 January 2009 |archive-date=11 November 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121111022312/http://www.nytimes.com/2006/01/29/international/middleeast/29israel.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.ynet.co.il/home/0,7340,L-1258,00.html |work=] |script-title=he:21 צעירות וצעירים נהרגו בפיגוע התופת בטיילת בתל אביב, לא הרחק מהדולפינריום. אלה תמונות ההרוגים בפיגוע הקשה ביותר בישראל מזה חמש שנים. ynet מביא את חלק מסיפוריהם. |language=he |trans-title=21 young people were killed in bomb attack in Tel Aviv promenade, near the Dolphinarium. These pictures of the dead worst attack in Israel for five years. Ynet brings some of their stories. |date=2 June 2001 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=24 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170724182358/http://www.ynet.co.il/home/0,7340,L-1258,00.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The attack significantly hampered American attempts to negotiate a cease-fire. | |||
| The 12 June ] by Palestinian snipers was later tied to ].<ref name="EnevBarghouti">{{cite news|last1=Enev|first1=Peter Enev|title=Barghouti gets five life terms for attacks|newspaper=Toronto Star|date=7 June 2004|id={{ProQuest|438710369}}}}</ref> | |||
| A total of 469 Palestinians and 199 Israelis were killed in 2001. Amnesty International's report on the first year of the Intifada states: | |||
| <blockquote>The overwhelming majority of cases of unlawful killings and injuries in Israel and the Occupied Territories have been committed by the IDF using excessive force. In particular, the IDF have used US-supplied helicopters in punitive rocket attacks where there was no imminent danger to life. Israel has also used helicopter gunships to carry out extrajudicial executions and to fire at targets that resulted in the killing of civilians, including children. ... Hamas and Islamic Jihad have frequently placed bombs in public places, usually within Israel, in order to kill and maim large numbers of Israeli civilians in a random manner. Both organizations have fostered a cult of martyrdom and frequently use suicide bombers.<ref name="Amnesty International"/></blockquote> | |||
| Palestinian terrorists committed a number of suicide attacks later in 2001, among them the ], with 15 civilian casualties (including 7 children);<ref>{{cite news |author=Stanage |first=Niall |date=3 February 2002 |title=Death of innocents |newspaper=] |url=https://www.kerenmalki.org/Press/IrishSBP_Death_of_Innocents.htm |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006080000/http://www.kerenmalki.org/Press/IrishSBP_Death_of_Innocents.htm |archive-date=6 October 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Ben-Zur |first=Raanan |date=27 March 2006 |title=Sbarro terrorist 'not sorry' |work=] |url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3232591,00.html |url-status=live |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006220711/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3232591,00.html |archive-date=6 October 2014}}</ref> the ] and the ], both with 3 civilian casualties;<ref>{{cite news |author=Dudkevitch |first1=Margot |last2=O'Sullivan |first2=Arieh |author2-link=Arieh O'Sullivan |date=10 September 2001 |title=Five killed as terror hits nationwide. First Israeli Arab suicide bomber strikes at Nahariya train station |url=http://info.jpost.com/C002/Supplements/CasualtiesOfWar/2001_09_09.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20021220085140/http://info.jpost.com/C002/Supplements/CasualtiesOfWar/2001_09_09.html |archive-date=20 December 2002 |newspaper=]}}</ref><ref name="Haaretz">{{cite news |author=Amos Harel |author2=Haim Shadmi |author3=David Ratner |author4=Yam Yehoshua |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/islamic-jihad-fatah-take-responsibility-for-bus-bombing-1.75877 |title=Islamic Jihad, Fatah take responsibility for bus bombing |work=] |date=28 November 2001 |access-date=18 June 2012 |archive-date=2 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102113653/http://www.haaretz.com/news/islamic-jihad-fatah-take-responsibility-for-bus-bombing-1.75877 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Blade">{{cite news |title=Suicide Bomber kills 3 Israelis ahead of Bush-Sharon meeting |url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?id=75JKAAAAIBAJ&pg=6563,4859776 |location=Toledo |newspaper=] |agency=], ] |date=30 November 2011 |page=A2 |access-date=18 June 2012 |archive-date=18 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095434/https://news.google.com/newspapers?id=75JKAAAAIBAJ&pg=6563,4859776 |url-status=live }}</ref> the Ben Yehuda Street bombing with 11 civilian deaths, many of them children;<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/MFAArchive/2000_2009/2001/12/Suicide%20bombing%20at%20the%20Ben-Yehuda%20pedestrian%20mall |title=Suicide bombing at the Ben-Yehuda pedestrian mall in Jerusalem |date=1 December 2001 |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040618133459/http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/MFAArchive/2000_2009/2001/12/Suicide%20bombing%20at%20the%20Ben-Yehuda%20pedestrian%20mall |archive-date=18 June 2004}}</ref> and the ], with 15 civilian casualties.<ref name="B'Tselem"> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120729121304/http://old.btselem.org/statistics/english/casualties.asp?sD=29&sM=09&sY=2000&eD=26&eM=12&eY=2008&filterby=event&oferet_stat=before |date=29 July 2012 }}</ref> | |||
| ===2002=== | ===2002=== | ||
| ]]] | |||
| In January, 2002, the ] ] naval commando captured the '']'', a large boat carrying weapons from ] presumably intended to be used by Palestine militants against Israel. It was discovered that top officials in the ] were involved in the smuggling. Israel claims that ] also was involved, a claim accepted by the ] Administration. | |||
| In January 2002, the ] ] naval commandos captured the '']'', a freighter carrying weapons from ] towards Israel, believed to be intended for Palestinian militant use against Israel. It was discovered that top officials in the ] were involved in the smuggling, with the Israelis pointing the finger towards ] as also being involved. | |||
| A spate of suicide bombings launched against Israel elicited a military response. A suicide bombing dubbed the ] (30 Israeli civilians were killed at Park hotel, ]) climaxed a bloody month of April 2002 (more than 130 Israelis, mostly civilians, killed in attacks). Israel launched ]. The operation led to the apprehension of many members of militant groups, as well as their weaponry and equipment. | |||
| Palestinians launched a spate of suicide bombings and attacks against Israel, aimed mostly at civilians. On 3 March, a Palestinian sniper killed 10 Israeli soldiers and settlers and wounded 4 at a checkpoint near ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://mfa.gov.il/MFA/ForeignPolicy/Terrorism/Victims/Pages/Sgt-Maj-res-%20Yochai%20Porat.aspx |title=Sgt.-Maj.(res.) Yochai Porat |date=3 March 2002 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=30 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140830185356/http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/ForeignPolicy/Terrorism/Victims/Pages/Sgt-Maj-res-%20Yochai%20Porat.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> using an ]. He was later arrested and sentenced to life imprisonment. The rate of the attacks increased, and was at its highest in March 2002.<ref name=Fal09/> | |||
| The UN estimated that 497 Palestinians were killed and 1,447 wounded during the IDF reoccupation of Palestinian areas between ] through ] and in the immediate aftermath. An estimated 70-80 Palestinians, including approximately 50 civilians, were killed in ]. Four IDF soldiers were killed there.<ref>{{cite news|date=]|title=Report of Secretary-General on recent events in Jenin, other Palestinian cities|publisher=UN|url=http://www.un.org/News/Press/docs/2002/SG2077.doc.htm}}</ref> | |||
| In addition to numerous shooting and grenade attacks, the month saw 15 suicide bombings carried out in Israel — an average of one bombing every two days. The high rate of attacks caused widespread fear throughout Israel and serious disruption of daily life throughout the country. March 2002 became known in Israel as "Black March".<ref name=Fal09>{{cite book |editor=Ophir Falk |editor2=Henry Morgenstein |title=Suicide terror: understanding and confronting the threat |publisher=Wiley |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-470-08729-9}}</ref> On 12 March ] was passed, which reaffirmed a ] and laid the groundwork for a ].<ref name=Rub03/> | |||
| Especially fierce battles took place at ]: 32 Palestinian militants, 22 Palestinian civilians, and 23 Israeli soldiers were killed in the fighting. The battle remains a flashpoint for both sides, due to false allegations of a massacre of thousands of Palestinians that surfaced during the IDF's operations in the camp. These allegations were disproved by international agencies that placed the actual death toll at below 55.<ref>{{cite web|title=Report of the Secretary-General prepared pursuant to General Assembly resolution ES-10/10|accessdate=2006-03-29|publisher=]|url=http://www.un.org/peace/jenin/}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=]|accessdate=2006-03-29|url=http://hrw.org/reports/2002/israel3/israel0502.pdf|title=Jenin: IDF Military Operation}} {{PDFlink}}</ref> | |||
| On 27 March, the wave of violence culminated with a suicide bombing during a ] celebration at the Park Hotel in ] in which 30 people were killed. The attack became known as the ].<ref name="Bts ODS">{{cite web |url=http://www.btselem.org/download/200207_defensive_shield_eng.pdf |title=Operation Defensive Shield: Palestinian Testimonies, Soldiers' Testimonies |date=July 2007 |publisher=] |access-date=7 April 2012 |archive-date=4 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304064004/http://www.btselem.org/download/200207_defensive_shield_eng.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> In total, around 130 Israelis, mostly civilians, were killed in Palestinian attacks during March 2002.<ref name=Rub03/> On 28 March, Arab leaders, whose constituencies were exposed to detailed television coverage of the violence in the conflict, set out a comprehensive ] that was endorsed by Arafat, but virtually ignored by Israel.<ref name=Rub03>],Judith Colp Rubin, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200819140014/https://books.google.com/books?id=KRjiBwAAQBAJ&pg=PT427 |date=19 August 2020 }} Oxford University Press, 2003 p.427 n.14</ref>{{sfn|Mattar|2005|p=40}}<ref>Neil Caplan, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200819133731/https://books.google.com/books?id=JyAgn_dD43cC&pg=PT167 |date=19 August 2020 }} John Wiley & Sons, 2011 p.167</ref><ref>Galia Golan, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820043011/https://books.google.com/books?id=-zqDBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA170 |date=20 August 2020 }} Routledge, 2014 p.170.</ref> | |||
| ::''See main article: ] for more information about this topic''. | |||
| On 29 March, Israel launched ], which lasted until 3 May. The IDF made sweeping incursions throughout the West Bank, and into numerous Palestinian cities. Arafat was put under siege in his ].<ref> . CBS, 29 April 2002</ref> The UN estimated that 497 Palestinians were killed and 1,447 wounded by the Israeli incursion from 1 March to 7 May.<ref name="UNPressRelease"/> A UN report cleared Israel of allegations of massacre, but criticized it for using excessive force on the civilian population. Israeli forces also arrested 4,258 Palestinians during the operation.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3685678,00.html |title=Operation Defensive Shield (2002) |work=] |date=12 March 2009 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=25 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140825062508/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3685678,00.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Israeli casualties during the operation totaled 30 dead and 127 wounded. The operation culminated with the recapturing of Palestinian Authority controlled areas.<ref name="UNPressRelease">{{cite press release |date=1 August 2002 |title=Report of Secretary-General on recent events in Jenin, other Palestinian cities |publisher=] |url=https://www.un.org/press/en/2002/SG2077.doc.htm |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=2 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402093858/http://www.un.org/press/en/2002/SG2077.doc.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In late ] to ], a stand-off developed between armed ] militants and the IDF at the Church of the Nativity in ]. Despite the code of conduct demanding respect for holy sites and a great deal of care taken to exercise the code the stand-off could not be resolved and after much delay, IDF snipers killed 7 people inside the church and wounded more than 40 people. The stand-off was resolved by the deportation of 13 Palestinian militants which the IDF has identified as terrorists to ] and the IDF ended its 38 day stand-off with the Moslems inside the church. | |||
| === |
====Battle of Jenin==== | ||
| {{Main|Battle of Jenin (2002)}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Between 2 and 11 April, a siege and fierce fighting took place in the Palestinian refugee camp of the city of ]. The camp was targeted during Operation Defensive Shield after Israel determined that it had "served as a launch site for numerous terrorist attacks against both Israeli civilians and Israeli towns and villages in the area."<ref name="mfa1">{{cite web |title=Jenin's Terrorist Infrastructure |publisher=] |access-date=22 September 2008 |date=4 April 2002 |url=http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/MFAArchive/2000_2009/2002/4/Jenin-s%20Terrorist%20Infrastructure%20-%204-Apr-2002 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090218182029/http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/MFAArchive/2000_2009/2002/4/Jenin-s%20Terrorist%20Infrastructure%20-%204-Apr-2002 |archive-date=18 February 2009 }}</ref> The Jenin battle became a flashpoint for both sides, and saw fierce urban combat as Israeli infantry supported by armor and attack helicopters fought to clear the camp of Palestinian militants. The battle was eventually won by the IDF, after it employed a dozen ] ]s to clear Palestinian ]s, detonate explosive charges, and raze buildings and gun-posts; the bulldozers proved impervious to attacks by Palestinian militants.<ref>{{cite magazine |author=Matt Rees |url=http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1002406,00.html |title=Untangling Jenin's Tale |magazine=] |date=13 May 2002 |access-date=28 September 2014 |author-link=Matt Rees |archive-date=26 October 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141026160651/http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1002406,00.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Following an Israeli intelligence report stating that Yasir Arafat paid $20,000 to ], the United States demanded democratic reforms in the ], as well the appointment of a prime minister independent of Arafat. On ] ], following U.S. pressure, Arafat appointed the moderate ] as Palestinian prime minister. | |||
| During Israeli military operations in the camp, Palestinian sources alleged that a massacre of hundreds of people had taken place. A senior Palestinian Authority official said in mid-April that some 500 had been killed.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/2165272.stm |title=UN says no massacre in Jenin |date=1 August 2002 |work=BBC News |access-date=19 May 2012 |archive-date=5 December 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061205040128/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/2165272.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> During the fighting in Jenin, Israeli officials had also initially estimated hundreds of Palestinian deaths, but later said they expected the Palestinian toll to reach "45 to 55."<ref name="NYT UN">{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2002/08/02/world/death-on-the-campus-jenin-un-report-rejects-claims-of-a-massacre-of-refugees.html |last=Bennet |first=James |author-link=James Bennet (journalist) |date=2 August 2002 |title=Death on the Campus: Jenin; U.N. Report Rejects Claims of a Massacre of Refugees |work=] |access-date=19 May 2012 |archive-date=11 December 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191211044050/https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9D04E6DD1E3BF931A3575BC0A9649C8B63 |url-status=live }}</ref> In the ensuing controversy, Israel blocked the United Nations from conducting the first-hand inquiry unanimously sought by the Security Council, but the UN nonetheless felt able to dismiss claims of a massacre in its report, which said there had been approximately 52 deaths, criticising both sides for placing Palestinian civilians at risk.<ref name="NYT UN"/><ref>{{cite news |title=U.N. report: No massacre in Jenin |url=http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/2002-08-01-unreport-jenin_x.htm |agency=] |work=] |date=1 August 2002 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=23 June 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150623064530/http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/2002-08-01-unreport-jenin_x.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Based on their own investigations, ]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/149/2002/en/ |title=Shielded from Scrutiny: IDF violations in Jenin and Nablus |date=November 2002 |publisher=] |page=2 |access-date=19 May 2012 |quote=Amnesty International's extensive research ... led it to conclude that ... some of the actions amounted to ... war crimes. |archive-date=22 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181122054904/https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/149/2002/en/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and ]<ref name="HRW May">{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/reports/2002/israel3/israel0502.pdf |title=Jenin: IDF Military Operations |date=May 2002 |publisher=] |access-date=19 May 2012 |page=3 |quote=Human Rights Watch's research demonstrates that, during their incursion into the Jenin refugee camp, Israeli forces committed serious violations of international humanitarian law, some amounting ''prima facie'' to war crimes. |archive-date=11 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121011222710/http://www.hrw.org/reports/2002/israel3/israel0502.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> charged that some IDF personnel in Jenin had committed ] but also confirmed that no massacre had been committed by the IDF. Both human rights organizations called for official inquiries; the IDF disputed the charges. | |||
| Following the appointment of Abbas, the U.S. administration promoted the ] — the ]'s plan to end the ] by disbanding militant organizations, halting settlement activity and establishing a democratic and peaceful Palestinian state. The first phase of the plan demanded that the PA suppress guerrilla and terrorist attacks and confiscate illegal weapons. Unable or unwilling to confront militant organizations and risk civil war, Abbas tried to reach a temporary cease-fire agreement with the militant factions and asked them to halt attacks on Israeli civilians. | |||
| After the battle, most sources, including the IDF and ], placed the Palestinian death toll at 52–56;<ref name=martinWT>{{cite news |url=http://www.washingtontimes.com/world/20020501-5587072.htm |title=Jenin 'massacre' reduced to death toll of 56 |author=Paul Martin |newspaper=] |date=1 May 2002 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030415055238/http://www.washingtontimes.com/world/20020501-5587072.htm |archive-date=15 April 2003}}</ref> ] documented 52 Palestinian deaths and claimed that it included at least 27 militants and 22 civilians, and an additional 3 Palestinians whose status as militants or civilians could not be ascertained,<ref name="hrwreport">{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/node/79081/section/3 |title=Jenin |website=] |date=2 May 2002 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=26 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140926080324/http://www.hrw.org/node/79081/section/3 |url-status=live }}</ref> while the IDF said that 48 militants and 5 civilians had been killed.<ref name="harel257-258">{{cite book |last1=Harel |first1=Amos |last2=Issacharoff |first2=Avi |date=2004 |script-title=he:המלחמה השביעית : איך ניצחנו ולמה הפסדנו במלחמה עם הפלסטינים |trans-title=The Seventh War: How We Won and Why We Lost in the War with the Palestinians |title=Ha-Milḥamah ha-shevi'it: ekh nitsaḥnu ṿe-lamah hifsadnu ba-milḥamah 'im ha-Palesṭinim |publisher=Yediot Aharonot |location=Tel-Aviv |isbn=978-965-511-767-7 |language=he |pages=257–258}}</ref> According to Human Rights Watch, 140 buildings had been destroyed.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Audeh |first=Ida |year=2002 |title=Narratives of Siege: Eye-Witness Testimonies from Jenin, Bethlehem, and Nablus |url=http://www.palestine-studies.org/journals.aspx?id=4341&jid=1&href=abstract |journal=] |volume=31 |issue=4 |page=13 |access-date=7 April 2012 |doi=10.1525/jps.2002.31.4.13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101228205343/http://palestine-studies.org/journals.aspx?id=4341&jid=1&href=abstract |archive-date=28 December 2010 |issn=0377-919X }}</ref> The IDF reported that 23 Israeli soldiers had been killed and 75 wounded during the battle.<ref name="HRW May"/><ref>{{cite web |title=Report of the Secretary-General prepared pursuant to General Assembly resolution ES-10/10 |access-date=29 March 2006 |publisher=] |url=https://www.un.org/peace/jenin/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20020806175121/http://www.un.org/peace/jenin/ |archive-date=6 August 2002}}</ref> | |||
| On ], Israeli naval commandos intercepted another vessel, the ''Abu Hassan'', on course to the ] from ]. It was loaded with rockets, weapons, and ammunition. Eight crew members on board were arrested including a senior ] member. | |||
| ====Siege in Bethlehem==== | |||
| In June 2003, a so-called '']'' (truce) was unilaterally declared by ] and ], which declared a ceasefire and halt to all attacks against Israel for a period of 45 days. Although violence decreased in the following month, there were several suicide bombings against Israeli civilians as well as Israeli operations against militants. | |||
| {{Main|Siege of the Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem}} | |||
| From 2 April to 10 May, a stand-off developed at the ] in ]. IDF soldiers surrounded the church while Palestinian civilians, militants, and priests were inside. During the siege, IDF snipers killed 8 militants inside the church and wounded more than 40 people. The stand-off was resolved by the deportation to Europe of 13 Palestinian militants whom the IDF had identified as terrorists, and the IDF ended its 38-day stand-off with the militants inside the church. | |||
| ===2003=== | |||
| One of the more provocative raids occurred when tanks and ]s (APCs) invaded a refugee camp outside Nablus, killing four people, two of whom were militants. Nearby Palestinians claimed a squad of Israeli police disguised as Palestinian labourers opened fire on ] as he left a Hebron mosque.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2003/06/23/wmid23.xml|date=]|title=Israel defends Hamas death|publisher=The Telegraph}}</ref> ], the Israeli counter-terrorism police unit which performed the operation stated that Qawasemah opened fire on them as they attempted to arrest him. | |||
| ] | |||
| Following an Israeli intelligence report stating that ] had paid $20,000 to ], the United States demanded democratic reforms in the ], as well the appointment of a prime minister independent of Arafat. On 13 March 2003, following U.S. pressure, Arafat appointed ] as Palestinian prime minister. | |||
| Following the appointment of Abbas, the U.S. administration promoted the ]—the ]'s plan to end the ] by disbanding militant organizations, halting settlement activity and establishing a democratic and peaceful Palestinian state. The first phase of the plan demanded that the Palestinian Authority suppress guerrilla and terrorist attacks and confiscate illegal weapons. Unable or unwilling to confront militant organizations and risk civil war, Abbas tried to reach a temporary cease-fire agreement with the militant factions and asked them to halt attacks on Israeli civilians. | |||
| On 20 May, Israeli naval commandos intercepted another vessel, the '']'', on course to the ] from ]. It was loaded with rockets, weapons, and ammunition. Eight crew members on board were arrested including a senior ] member. | |||
| On 29 June 2003, a ] was unilaterally declared by ], ] and ], which declared a ceasefire and halt to all attacks against Israel for a period of three months.<ref>{{cite news |work=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3030480.stm |title=Texts: Palestinian truces |date=29 June 2003 |access-date=28 September 2004 |archive-date=5 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140105052121/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3030480.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> Violence decreased somewhat in the following month, but suicide bombings against Israeli civilians continued as well as Israeli operations against militants. | |||
| Four Palestinians, three of them militants, were killed in gun battles during an IDF raid of ] near ] involving tanks and ]s (APCs); an Israeli soldier was killed by one of the militants. Nearby Palestinians claimed a squad of Israeli police disguised as Palestinian labourers opened fire on ] as he left a Hebron mosque.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2003/06/23/wmid23.xml |date=23 June 2003 |title=Israel defends Hamas death |newspaper=] |author=Alan Philps |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040604160641/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=%2Fnews%2F2003%2F06%2F23%2Fwmid23.xml |archive-date= 4 June 2004 }}</ref> ], the Israeli counter-terrorism police unit that performed the operation, said Qawasemah opened fire on them as they attempted to arrest him. | |||
| On ], Hamas coordinated a ] on a ] in ] killing 23 Israeli civilians, including 7 children. Hamas claimed it was a retaliation for the killing of five Palestinians (including Hamas leader ]) earlier in the week. U.S. and Israeli media outlets frequently referred to the bus bombing as shattering the quiet and bringing an end to the ceasefire. | |||
| On 19 August, Hamas coordinated a ] on a ] in ] killing 23 Israeli civilians, including 7 children. Hamas claimed it was a retaliation for the killing of five Palestinians (including Hamas leader ]) earlier in the week. U.S. and Israeli media outlets frequently referred to the bus bombing as shattering the quiet and bringing an end to the ceasefire. | |||
| Following the Hamas bus attack, ] were ordered to kill or capture all Hamas leaders in ] and the ]. The plotters of the bus suicide bombing were all captured or killed and ] was badly damaged by the IDF. Strict curfews were enforced in Nablus, Jenin, and Tulkarem; the Nablus lockdown lasted for over 100 days. In Nazlet 'Issa, over 60 shops were destroyed by Israeli civil administration ]s. The Israeli civil administration explained that the shops were demolished because they were built without a permit. Palestinians consider Israeli military curfews and property destruction to constitute collective punishment against innocent Palestinians.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/2680777.stm|publisher=BBC News|title=Israelis flatten West Bank shops|date=]}}</ref> | |||
| Following the Hamas bus attack, ] were ordered to kill or capture all Hamas leaders in ] and the ]. The plotters of the bus suicide bombing were all captured or killed and ] was badly damaged by the IDF. Strict curfews were enforced in Nablus, Jenin, and Tulkarem; the Nablus lockdown lasted for over 100 days. In ], over 60 shops were destroyed by Israeli civil administration ]s. The Israeli civil administration explained that the shops were ] because they were built without a permit. Palestinians consider Israeli military curfews and property destruction to constitute ] against innocent Palestinians.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/2680777.stm|work=BBC News|title=Israelis flatten West Bank shops|date=21 January 2003|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=19 December 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061219020234/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/2680777.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Unable to rule effectively under Arafat, Abbas resigned in September 2003. ] (Abu Ala) was appointed to replace him. The Israeli government gave up hope for negotiated settlement to the conflict and pursued a unilateral policy of physically separating Israel from Palestinian communities by beginning construction on the ]. Israel claims the barrier is necessary to prevent Palestinian attackers from entering Israeli cities. Palestinians claim the barrier separates Palestinian communities from each other and that the construction plan is a de facto annexation of Palestinian territory. | Unable to rule effectively under Arafat, Abbas resigned in September 2003. ] (Abu Ala) was appointed to replace him. The Israeli government gave up hope for negotiated settlement to the conflict and pursued a unilateral policy of physically separating Israel from Palestinian communities by beginning construction on the ]. Israel claims the barrier is necessary to prevent Palestinian attackers from entering Israeli cities. Palestinians claim the barrier separates Palestinian communities from each other and that the construction plan is a de facto annexation of Palestinian territory. | ||
| Following |
Following a 4 October ], ], which claimed the lives of 21 Israelis, Israel claimed that Syria and ] sponsored the ] and ], and were responsible for the terrorist attack. The day after the Maxim massacre, ] warplanes ] at Ain Saheb, ], which had been mostly abandoned since the 1980s. Munitions being stored on the site were destroyed, and a civilian guard was injured. | ||
| ===2004=== | ===2004=== | ||
| In response to |
In response to repeated shelling of Israeli communities with ]s and mortar shells from Gaza, the ] operated mainly in ] – to search and destroy ]s used by militants to obtain ]s, ], fugitives, cigarettes, car parts, electrical goods, foreign currency, gold, ], and cloth from ]. Between September 2000 and May 2004, ninety tunnels connecting Egypt and the Gaza Strip were found and destroyed. Raids in Rafah left many families homeless. Israel's official stance is that their houses were captured by militants and were destroyed during battles with IDF forces. Many of these houses are abandoned due to Israeli incursions and later destroyed. According to Human Rights Watch, over 1,500 houses were destroyed to create a large buffer zone in the city, many "in the absence of military necessity", displacing around sixteen thousand people.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/campaigns/gaza/|access-date=29 March 2006|title=Razing Rafah: Mass Home Demolitions in the Gaza Strip |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060324012233/http://www.hrw.org/campaigns/gaza/ |archive-date=24 March 2006}}</ref> | ||
| On |
On 2 February 2004, Israeli Prime Minister ] announced his plan to transfer all the ] from the ]. The Israeli opposition dismissed his announcement as "media spin", but the ] said it would support such a move. Sharon's right-wing coalition partners ] and ] rejected the plan and vowed to quit the government if it were implemented. ], peace advocate and architect of the ] and the ], also rejected the proposed withdrawal plan. He claimed that withdrawing from the Gaza Strip without a peace agreement would reward ]. | ||
| Following the declaration of the |
Following the declaration of the ] by Ariel Sharon and as a response to suicide attacks on ] and ] seaport (10 people were killed), the IDF launched a series of armored raids on the Gaza Strip (mainly Rafah and refugee camps around Gaza), killing about 70 ] militants. On 22 March 2004, an Israeli helicopter gunship ] Hamas leader Sheikh ], along with his two bodyguards and nine bystanders. On 17 April, after several failed attempts by Hamas to commit suicide bombings and a successful one that killed an Israeli policeman, Yassin's successor, ], was killed in an almost identical way, along with a bodyguard and his son Mohammed. | ||
| The fighting in |
The fighting in Gaza Strip escalated severely in May 2004 after several failed attempts to attack ] such as ] and ]. On 2 May, Palestinian militants attacked and ].<ref name=bbc>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3679395.stm|title=Gunmen kill Jewish settler family|work=BBC News|access-date=28 September 2012|date=3 May 2004|archive-date=2 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190402201703/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3679395.stm|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=smh20040503>{{cite news |title=Pregnant mum and four children gunned down |url=http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/05/03/1083436518982.html |newspaper=] |date=3 May 2004 |access-date=2014-09-01 |archive-date=12 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012063112/http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/05/03/1083436518982.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=ii20040503>{{cite news |last=Silverin |first=Eric |title=Pregnant mum and her four children killed in terror attack |url=http://www.independent.ie/world-news/pregnant-mum-and-her-four-children-killed-in-terror-attack-169946.html |newspaper=] |date=3 May 2004 |access-date=2014-09-01 |archive-date=15 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200315191304/https://www.independent.ie/world-news/pregnant-mum-and-her-four-children-killed-in-terror-attack-25912634.html |url-status=live }}</ref> ] classified it as a ] and said it "reiterates its call on all Palestinian armed groups to put an immediate end to the deliberate targeting of Israeli civilians, in Israel and in the Occupied Territories".<ref name=ai-p>{{cite web |title=Israel/Occupied Territories: AI condemns murder of woman and her four daughters by Palestinian gunmen |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/049/2004/en/ |publisher=] |date=4 May 2004 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=22 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181122054920/https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde15/049/2004/en/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Additionally, on 11 and 12 May, Palestinian militants destroyed two IDF ] ], killing 13 soldiers and mutilating their bodies. The IDF launched two raids to recover the bodies, killing 20–40 Palestinians and greatly damaging structures in the Zaitoun neighbourhood in Gaza and in south-west Rafah. | ||
| ] | |||
| Subsequently, on 18 May the IDF launched ] with a stated aim of striking the militant infrastructure of Rafah, destroying smuggling tunnels, and stopping a shipment of ] missiles and improved ] weapons. A total of 41 Palestinian militants and 12 civilians were killed in the operation, and about 45–56 Palestinian structures were demolished. Israeli tanks shelled hundreds of Palestinian protesters approaching their positions, killing 10. The protesters had disregarded Israeli warnings to turn back. This incident led to a worldwide outcry against the operation. | |||
| On 29 September, after a ] hit the Israeli town of ] and killed two Israeli children, the IDF launched ] in the north of the Gaza Strip. The operation's stated aim was to remove the threat of Qassam rockets from Sderot and kill the Hamas militants launching them. The operation ended on 16 October, after having caused widespread destruction and the deaths of over 100 Palestinians, at least 20 of whom were under the age of sixteen.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/israel/Story/0,2763,1328916,00.html |title=Army pulls back from Gaza leaving 100 Palestinians dead |work=] |date=16 October 2004 |first=Chris |last=McGreal |author-link=Chris McGreal |access-date=23 May 2010 |archive-date=26 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220326135412/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2004/oct/16/israel1 |url-status=live }}</ref> The IDF killed thirteen-year-old ] as she strayed into a closed military area; the commander was accused of allegedly firing his automatic weapon at her dead body deliberately to verify the death. The act was investigated by the IDF, but the commander was cleared of all wrongdoing,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.thejewishweek.com/news/newscontent.php3?artid=10201|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041204171132/http://www.thejewishweek.com/news/newscontent.php3?artid=10201|archive-date=4 December 2004|date=3 December 2004 |newspaper=] |title=Moral Quagmire}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Ben Lynfield |url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2004/1126/p07s01-wome.html |date=26 November 2004 |work=] |title=Israeli army under fire after killing girl |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=13 May 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070513000508/http://www.csmonitor.com/2004/1126/p07s01-wome.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and more recently, was fully vindicated when a Jerusalem district court found the claim to be libellous, ruled that NIS 300,000 be paid by the journalist and TV company responsible for the report, an additional NIS 80,000 to be paid in legal fees and required the journalist and television company to air a correction.<ref>{{cite news |author=Hila Raz |url=http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/business/does-it-pay-to-sue-for-libel-in-israel-1.261754 |date=20 January 2010 |newspaper=] |title=Does it pay to sue for libel in Israel? |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=9 March 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140309072837/http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/business/does-it-pay-to-sue-for-libel-in-israel-1.261754 |url-status=live }}</ref> According to Palestinian medics, Israeli forces killed at least 62 militants and 42 other Palestinians believed to be civilians.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/newsArticle.jhtml?type=topNews&storyID=6520016 |work=Reuters |title=Palestinians sift rubble after Israel's Gaza assault |date=16 October 2004 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050628015144/http://www.reuters.com/newsArticle.jhtml?type=topNews |archive-date=28 June 2005 }}</ref> According to a count performed by '']'', 87 militants and 42 civilians were killed. Palestinian refugee camps were heavily damaged by the Israeli assault. The IDF announced that at least 12 Qassam launchings had been thwarted and many militants hit during the operation. | |||
| Subsequently, on ] the IDF launched ] with a stated aim of striking the terror infrastructure of Rafah, destroying ]s, and stopping a shipment of ] missiles and improved ] weapons. The operation ended after the IDF killed 40 Palestinian militants and 12 civilians and demolished about 45-56 structures. The great destruction and killing of 10 protestors led to a worldwide outcry against the operation. | |||
| On 21 October, the ] killed ], a senior Hamas bomb maker and the inventor of the ]. | |||
| On ], after a ] hit the Israeli town of ] and killed two Israeli children, the IDF launched ] in the north of the ]. The operation's stated aim was to remove the threat of Qassam rockets from Sderot and kill the Hamas militants launching them. The operation ended on ], leaving widespread destruction and more than 100 Palestinians dead, at least 20 of whom were under the age of 16.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/israel/Story/0,2763,1328916,00.html|title=Army pulls back from Gaza leaving 100 Palestinians dead|publisher=]|date=]}}</ref> Thirteen-year-old ] was killed by the IDF; some reports claimed a commander had deliberately fired his automatic weapon at her dead body, but the soldier was cleared of all charges.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.thejewishweek.com/news/newscontent.php3?artid=10201|date=]|publisher=]|title=Moral Quagmire}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2004/1126/p07s01-wome.html|date=]|publisher=]|title=Israeli army under fire after killing girl}}</ref> According to Palestinian medics, Israeli forces killed at least 62 militants and 42 other Palestinians believed to be civilians.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L16687192.htm|publisher=Reuters|title=Palestinians sift rubble after Israel's Gaza assault|date=]}}</ref> According to a count performed by ], 87 combatants and 42 non-combatants were killed. Palestinian refugee camps were heavily damaged by the Israeli assault. The IDF announced that at least 12 Qassam launchings had been thwarted and many terrorists hit during the operation. Three Israelis also were killed, including one civilian. | |||
| On 11 November, Yasser Arafat died in Paris. | |||
| On ], the ] killed ], a senior ] bomb maker and the inventor of the ]. | |||
| Escalation in Gaza began amid the visit of ] to ] in order to achieve a ] between Palestinian factions and convince Hamas leadership to halt attacks against Israelis. Hamas vowed to continue the armed struggle, sending numerous ]s into open fields near ], and hitting a ] in ] with an anti-tank missile. | |||
| On ], ] died in ]. | |||
| On 9 December five Palestinians weapon smugglers were killed and two were arrested in the border between Rafah and ]. Later that day, ] and two of his bodyguards were injured by a missile strike. In the first Israeli airstrike against militants in weeks, an unmanned Israeli drone plane launched one missile at Abu Samahdna's car as it travelled between Rafah and Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip. It was the fourth attempt on Samhadana's life by Israel. Samhadana is one of two leaders of the ] and one of the main forces behind the smuggling tunnels. Samhadana is believed to be responsible for the ] against an American diplomatic convoy in Gaza that killed three Americans. | |||
| Escalation in Gaza began amid the visit of ] to ] in order to achieve a ] between Palestinian factions and convince Hamas leadership to halt attacks against Israelis. Hamas vowed to continue the armed struggle, while numerous ]s hit open fields near ''Nahal Oz'' and an anti-tank missile hit a ] in ]. | |||
| On 10 December, in response to Hamas firing mortar rounds into the Neveh Dekalim settlement in the Gaza Strip and wounding four Israelis (including an 8-year-old boy), Israeli soldiers fired at the Khan Younis refugee camp (the origin of the mortars) killing a seven-year-old girl. An IDF source confirmed troops opened fire at Khan Younis, but said they aimed at Hamas mortar crews.{{citation needed|date=October 2020}} | |||
| On ] five weapon smugglers were killed and two were arrested in the border between ] and ]. Later that day, Jamal Abu Samhadana and two of his bodyguards were injured by a missile strike. In the first Israeli airstrike against militants in weeks, an unmanned Israeli drone plane launched one missile at Abu Samahdna's car as it traveled between Rafah and Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip. It was the fourth attempt on Samhadana's life by Israel. Samhadana is one of two leaders of the ] and one of the main forces behind the ]s. Samhadana is believed to be responsible for the ] against an American diplomatic convoy in ] that killed three Americans. | |||
| The largest attack since the death of Yasser Arafat claimed the lives of five Israeli soldiers on 12 December, wounding ten others. Approximately 1.5 tons of explosives were detonated in a tunnel under an Israeli military-controlled border crossing on the Egyptian border with Gaza near Rafah, collapsing several structures and damaging others. The explosion destroyed part of the outpost and killed three soldiers. Two Palestinian militants then penetrated the outpost and killed two other Israeli soldiers with gunfire. It is believed that Hamas and a new Fatah faction, the "Fatah Hawks", conducted the highly organised and coordinated attack. A spokesman, "Abu Majad", claimed responsibility for the attack in the name of the ] claiming it was in retaliation for "the assassination" of Yasser Arafat, charging he was poisoned by Israel. | |||
| On ], in response to ] firing mortar rounds into the Neveh Dekalim settlement in the ] and wounding four Israelis (including an 8 year old boy), Israeli soldiers fired at the Khan Younis refugee camp (the origin of the mortars) killing a 7-year-old girl. An ] source confirmed troops opened fire at Khan Younis, but said they aimed at Hamas mortar crews. The IDF insisted that it does its utmost to avoid civilian casualties. | |||
| The largest attack since the death of ] claimed the lives of five Israeli soldiers on ], wounding ten others. Approximately 1.5 tons of explosives were detonated in a tunnel under an Israeli military-controlled border crossing on the Egyptian border with Gaza near ], collapsing several structures and damaging others. The explosion destroyed part of the outpost and killed three soldiers. Two Palestinian militants then penetrated the outpost and killed two other Israeli soldiers with gunfire. It is believed that Hamas and a new Fatah faction, the "Fatah Hawks," conducted the highly organized and coordinated attack. A spokesman, "Abu Majad," claimed responsibility for the attack in the name of the ] claiming it was in retaliation for "the assassination" of Yasser Arafat, charging he was poisoned by Israel. | |||
| ===2005=== | ===2005=== | ||
| ] were held on |
] were held on 9 January, and ] (Abu Mazen) was elected as the president of the PA. His platform was of a peaceful negotiation with Israel and non-violence to achieve Palestinian objectives. Although Abbas called on militants to halt attacks against Israel, he promised them protection from Israeli incursions and did not advocate disarmament by force. | ||
| Violence continued in the Gaza Strip, and ] froze all diplomatic and security contacts with the ]. Spokesman Assaf Shariv declared that "Israel informed international leaders today that there will be no meetings with Abbas until he makes a real effort to stop the terror |
Violence continued in the Gaza Strip, and ] froze all diplomatic and security contacts with the ]. Spokesman Assaf Shariv declared that "Israel informed international leaders today that there will be no meetings with Abbas until he makes a real effort to stop the terror." The freezing of contacts came less than one week after Mahmoud Abbas was elected, and the day before his inauguration. Palestinian negotiator ], confirming the news, declared "You cannot hold Mahmoud Abbas accountable when he hasn't even been inaugurated yet."<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.cnn.com/2005/WORLD/meast/01/14/gaza.bombing/ |date=14 January 2005 |title=Sharon suspends contacts with Palestinian Authority |publisher=CNN |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=5 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181005004326/http://www.cnn.com/2005/WORLD/meast/01/14/gaza.bombing/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/4176141.stm|date=14 January 2005|title=Israel cuts Palestinian contacts|work=BBC News|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=16 March 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060316084259/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/4176141.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| ] | |||
| Following international pressure and Israeli threat of wide military operation in the ], Abbas ordered ] to deploy in the Northern Gaza to prevent Qassam and mortar shelling over Israeli settlement. Although attacks on Israeli did not stop completely, they decreased sharply. On ], ], at the ], Sharon and Abbas declared a mutual ] between ] and the ]. They shook hands at a four-way summit which also included ] and ] at ]. However, ] and ] said the truce is not binding for their members. Israel has not withdrawn its demand to dismantle terrorist infrastructure before moving ahead in the ].<ref>{{cite news|date=]|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4245353.stm|title=Mid-East leaders announce truce|publisher=BBC News}}</ref> | |||
| Following international pressure and Israeli threat of wide military operation in the ], Abbas ordered ] to deploy in the northern Gaza Strip to prevent ] and mortar shelling over Israeli settlement. Although attacks on Israelis did not stop completely, they decreased sharply. On 8 February 2005, at the ], Sharon and Abbas declared a mutual ] between Israel and the ]. They shook hands at a four-way summit that also included ] and ] at ]. However, Hamas and ] said the truce is not binding for their members. Israel has not withdrawn its demand to dismantle terrorist infrastructure before moving ahead in the ].<ref>{{cite news|date=8 February 2005|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4245353.stm|title=Mid-East leaders announce truce|work=BBC News|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=14 June 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060614175342/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4245353.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Many warned that truce is fragile, and progress must be done slowly while observing that the truce and quiet are kept. On |
Many warned that truce is fragile, and progress must be done slowly while observing that the truce and quiet are kept. On 9–10 February night, a barrage of 25–50 ]s and ] hit ] settlement, and another barrage hit at noon. Hamas said it was in retaliation for an attack in which one Palestinian was killed near an Israeli settlement.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4252445.stm|date=10 February 2005|title=Abbas orders security crackdown|work=BBC News|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=3 October 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181003014501/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4252445.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> As a response to the mortar attack, Abbas ordered the Palestinian security forces to stop such attacks in the future. He also fired senior commanders in the Palestinian security apparatus. On 10 February, ] arrested Maharan Omar Shucat Abu Hamis, a Palestinian resident of ], who was about to launch a bus ] in the ] in ]. | ||
| On |
On 13 February 2005, Abbas entered into talks with the leaders of the Islamic Jihad and the Hamas, for them to rally behind him and respect the truce. Ismail Haniyah, a senior leader of the group Hamas said that "its position regarding calm will continue unchanged and Israel will bear responsibility for any new violation or aggression." | ||
| In the middle of June, Palestinian factions intensified bombardment over the city of ] with improvised ]s. |
In the middle of June, Palestinian factions intensified bombardment over the city of ] with improvised ]s. Palestinian attacks resulted in 2 Palestinians and 1 Chinese civilian killed by a Qassam, and 2 Israelis were killed. The wave of attacks lessened support for the ] among the Israeli public. Attacks on Israel by the ] and the ] increased in July, and on 12 July, a ] hit the coastal city of ], killing 5 civilians. On 14 July, Hamas started to shell Israeli settlements inside and outside the ] with dozens of Qassam rockets, killing an Israeli woman. On 15 July, Israel resumed its "targeted killing" policy, killing 7 Hamas militants and bombing about 4 Hamas facilities. The continuation of shelling rockets over Israeli settlements, and street battles between Hamas militants and Palestinian policemen, threatened to shatter the truce agreed in the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005. The Israeli Defence Force also started to build up armored forces around the Gaza Strip in response to the shelling. | ||
| ===End of the Second Intifada=== | |||
| ===2006=== | |||
| The ending date of the Second Intifada is disputed, as there was no definite event that brought it to an end.<ref name=Schachter>{{cite journal |last=Schachter |first=Jonathan |year=2010 |title=The End of the Second Intifada? |journal=Strategic Assessment |volume=13 |issue=3 |pages=63–69 |url=http://www.inss.org.il/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/systemfiles/(FILE)1289897140.pdf |access-date=10 August 2017 |archive-date=8 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190408094351/https://www.inss.org.il/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/systemfiles/(FILE)1289897140.pdf |url-status=live}}</ref> The general view is that it ended in 2005, while some sources include events and statistics extending as late as 2007.<ref name="Plaw2016" >Avery Plaw, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190331022531/https://books.google.com/books?id=pIDeCwAAQBAJ&pg=PT112 |date=31 March 2019 }}, ], 2016 {{ISBN|978-1-317-04671-4}} pp.63ff.</ref> | |||
| * Some commentators, such as Sever Plocker,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3558676,00.html |title=2nd Intifada Forgotten |author=Sever Plocker |work=] |date=22 June 2008 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140819220413/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3558676,00.html |archive-date=19 August 2014}}</ref> consider the intifada to have ended in late 2004. With the sickness and then death of Yasser Arafat in November 2004, the Palestinians lost their internationally recognised leader of the previous three decades, after which the intifada lost momentum and led to internal fighting between Palestinian factions (most notably the ]), as well as conflict within Fatah itself. | |||
| On ] ], the Palestinians held ] for the ]. The Islamist group ] won with an unexpected majority of 74 seats, compared to 45 seats for ] and 13 for other parties and independents. Hamas is officially declared as a ] by the ] and the ] and its gaining control over the Palestinian Authority (such as by forming the government) would jeopardize international funds to the PA, by laws which forbid sponsoring of terrorist group. | |||
| * Israel's unilateral disengagement from the Gaza Strip, announced in June 2004 and completed in August 2005, is also cited as signalling the end of the intifada, for instance by Ramzy Baroud.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Ruth Tenne |url=http://www.isj.org.uk/index.php4?id=384&issue=116 |journal=] |title=Rising of the oppressed: the second Intifada |date=Autumn 2007 |issue=116 |access-date=22 May 2009 |archive-date=8 January 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150108151127/http://www.isj.org.uk/index.php4?id=384&issue=116 |url-status=live}} Review of {{cite book |author=Ramzy Baroud |author2=Kathleen Christison |author3=Bill Christison |author4=Jennifer Loewenstein |title=The Second Palestinian Intifada: A Chronicle of a People's Struggle |publisher=] |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-7453-2547-7}}</ref> | |||
| * Some consider 8 February 2005 to be the official end of the Second Intifada, although sporadic violence still continued outside PA control or condonation.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.zionism-israel.com/his/Israel_timeline_1993_present.htm |title=Timeline (Chronology) of Israel and Zionism 1993–present day |publisher=ZioNation |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-date=3 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303181608/http://www.zionism-israel.com/his/Israel_timeline_1993_present.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Brad A. Greenberg |date=3 December 2008 |url=https://jewishjournal.com/community/67396/ |title=UC to Reopen Study in Israel |newspaper=] |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-date=24 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220324173006/https://jewishjournal.com/community/67396/ |url-status=live}}</ref> On that day, Abbas and Sharon met at the ], where they vowed to end attacks on each other.<ref name=2005ceasefire>{{cite news |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2005/WORLD/meast/02/08/mideast/ |title=Palestinian, Israeli leaders announce cease-fire |last1=Wedeman |first1=Ben |last2=Raz |first2=Guy |last3=Koppel |first3=Andrea |publisher=] |year=2005 |access-date=10 August 2017 |archive-date=12 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012113523/http://edition.cnn.com/2005/WORLD/meast/02/08/mideast/ |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1482803/Palestinian-ceasefire-ends-four-year-intifada.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1482803/Palestinian-ceasefire-ends-four-year-intifada.html |archive-date=12 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |work=] |title=Palestinian ceasefire ends four-year intifada |first=Inigo |last=Gilmore |date=4 February 2005 |access-date=23 May 2010}}{{cbignore}}</ref> In addition, Sharon agreed to release 900 ] and withdraw from West Bank towns. Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ) refused to be parties to the agreement, arguing the cease-fire was the position of the PA only.<ref name=2005ceasefire /><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/view/sustaining-an-israeli-palestinian-ceasefire |title=Sustaining an Israeli-Palestinian Ceasefire|last=Levitt |first=Matthew |publisher=] |year=2005 |access-date=10 August 2017 |archive-date=10 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810131341/http://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/view/sustaining-an-israeli-palestinian-ceasefire |url-status=live}}</ref> Five days later Abbas reached agreement with the two dissenting organizations to commit to the truce with the proviso that Israeli violation would be met with retaliation.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.imra.org.il/story.php3?id=24111 |title=Hamas, Jihad Commit to Truce Provided Israel Reciprocates |publisher=Palestine Media Center – PMC |date=13 February 2005 |access-date=10 August 2017 |archive-date=10 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810132311/http://www.imra.org.il/story.php3?id=24111 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Schachter addressed the difficulties in deciding when the Second Intifada ended. He reasoned that suicide bombing was the best criterion, being arguably the most important element of the violence involved, and that according to this criterion the intifada ended during 2005.<ref name=Schachter /> | |||
| On ] Israel launched a series of attacks against ] and ] Qassam-launchers squads, killing 9 Palestinians. The air strikes came after ]s hit southern ] and ] ], seriously wounding a 7-month-old baby. | |||
| ==Trigger for the uprising== | |||
| On ] a ] struck in ] killing 11 people and injuring 60. | |||
| The Second Intifada started on 28 September 2000, after ], a Likud party candidate for Israeli Prime Minister, made a visit to the ], also known as ], an area sacred to both Jews and Muslims, accompanied by over 1,000 security guards. He stated on that day, "the Temple Mount is in our hands and will remain in our hands. It is the holiest site in Judaism and it is the right of every Jew to visit the Temple Mount."<ref>{{cite news |first=Suzanne |last=Goldenberg |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2000/sep/29/israel |title=Rioting as Sharon visits Islam holy site |newspaper=] |date=29 September 2000 |access-date=28 September 2014 |author-link=Suzanne Goldenberg |archive-date=11 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141111222135/http://www.theguardian.com/world/2000/sep/29/israel |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| This visit was seen by Palestinians as highly provocative; and Palestinian demonstrators, throwing stones at police, were dispersed by the Israeli Army, using tear gas and rubber bullets.<ref name=Mitchell_cause>{{cite web |first=George J. |last=Mitchell |url=https://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |title=Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee |date=30 April 2001 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |page=4 |display-authors=etal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140823071635/http://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |archive-date=23 August 2014 |author-link=George J. Mitchell}} See under "What Happened?"</ref><ref>{{cite book |first=James L. |last=Gelvin |title=The Israel-Palestine conflict: one hundred years of war |publisher=] |edition=2nd |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-521-71652-9 |page=243 |author-link=James L. Gelvin}}</ref><ref name="bbctimeline">{{cite news |date=29 September 2004 |title=Al-Aqsa Intifada timeline |work=] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3677206.stm |url-status=live |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160702011849/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3677206.stm |archive-date=2 July 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Dark Times, Dire Decisions: Jews and Communism |editor-first=Jonathan |editor-last=Frankel |year=2005 |series=Studies in Contemporary Jewry |volume=XX |publisher=] |page=311 |isbn=978-0-19-518224-8}}</ref> A riot broke out among Palestinians at the site, resulting in clashes between Israeli forces and the protesting crowd. | |||
| On ], ], the leader of the ] was assassinated along with three other PRC members in an Israeli air strike. | |||
| On ], seven members of the Ghalia family ] on a ] beach. The cause of the explosion ]. Nevertheless, in response, ] declared an end to its commitment to a ceasefire declared in 2005 and announced the resumption of attacks on Israelis. Palestinians blame an Israeli artillery shelling of nearby locations in the northern Gaza Strip for the deaths, while an Israeli military inquiry cleared itself from the charges. | |||
| Some believe the Intifada started the next day, on Friday, 29 September, a day of prayers, when an Israeli police and military presence was introduced and there were major clashes and deaths.<ref name=Mitchell>{{cite web|author=George J. Mitchell |url=https://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |title=Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee |date=30 April 2001 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |quote=Mr. Sharon made the visit on September 28 accompanied by over 1,000 Israeli police officers. Although Israelis viewed the visit in an internal political context, Palestinians saw it as a provocation to start a fair intifadah. On the following day, in the same place, a large number of unarmed Palestinian demonstrators and a large Israeli police contingent confronted each other. |display-authors=etal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140823071635/http://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |archive-date=23 August 2014 |author-link=George J. Mitchell }}</ref><ref name=Cypel>{{cite book |quote=The following day, the 29th, a Friday and hence the Muslim day of prayer, the young Palestinians flared up.... |author-link=Sylvain Cypel |last=Cypel |first=Sylvain |title=Walled: Israeli Society at an Impasse |publisher=Other Press |year=2006 |page= |isbn=978-1-59051-210-4 |url=https://archive.org/details/walledisraelisoc00cype/page/6 }}</ref><ref name=Mittleman>{{cite book |quote=Then in late September Ariel Sharon visited the Temple Mount The next day, massive violence erupted in Jerusalem and Palestinian-controlled areas in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. |author=Alan Mittleman |author2=Robert A. Licht |author3-link=Jonathan Sarna |author3=Jonathan D. Sarna |title=Jewish Polity and American Civil Society: Communal Agencies and Religious Movements in the American Public Sphere |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2002 |page=161 |isbn=978-0-7425-2122-3|author-link=Alan Mittleman }}</ref> | |||
| On ] a military outpost was attacked by Palestinian militants and a gunbattle followed that left 2 Israeli soldiers and 3 Palestinian militants dead. Corporal ], an Israeli soldier, was captured and Israel warned of an imminent ] if the soldier was not returned unharmed. In the early hours of ] Israeli tanks, APCs and troops entered the Gaza strip just hours after the air force had taken out two main bridges and the only powerstation in the strip, effectively shutting down electricity and water. | |||
| ===The Mitchell Report=== | |||
| On ] The ] ] authorised "severe and harsh" ] on ] due to the ] kidnapping of two Israeli soldiers, and the killing of three others. | |||
| The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee (an investigatory committee set up to look into the causes behind the breakdown in the peace process, chaired by ]) published its report in May 2001.<ref name=mitchell>{{cite web |author=George J. Mitchell |url=https://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |title=Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee |date=30 April 2001 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |display-authors=etal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140823071635/http://unispal.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/0/6E61D52EAACB860285256D2800734E9A |archive-date=23 August 2014 |author-link=George J. Mitchell }} {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170201163408/https://eeas.europa.eu/mepp/docs/mitchell_report_2001_en.pdf |date=1 February 2017 }}</ref> In the ], the government of Israel asserted that: | |||
| <blockquote>The immediate catalyst for the violence was the breakdown of the Camp David negotiations on July 25, 2000, and the "widespread appreciation in the international community of Palestinian responsibility for the impasse". In this view, Palestinian violence was planned by the PA leadership, and was aimed at "provoking and incurring Palestinian casualties as a means of regaining the diplomatic initiative".</blockquote> | |||
| On ], ] a truce was implemented between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. A January 10, 2007 Reuters article reports: "Hamas has largely abided by a November 26 truce which has calmed Israeli-Palestinian violence in Gaza." <ref> . By Sean Maguire and Khaled Oweis. ]. Jan. 10, 2007.</ref> | |||
| The Palestine Liberation Organization, according to the same report, denied that the Intifada was planned, and asserted that "Camp David represented nothing less than an attempt by Israel to extend the force it exercises on the ground to negotiations." The report also stated: | |||
| ==Tactics== | |||
| The tactics of the two sides in the conflict are largely based upon their resources and goals. | |||
| <blockquote>From the perspective of the PLO, Israel responded to the disturbances with excessive and illegal use of deadly force against demonstrators; behavior which, in the PLO's view, reflected Israel's contempt for the lives and safety of Palestinians. For Palestinians, the widely seen images of Muhammad al-Durrah in Gaza on September 30, shot as he huddled behind his father, reinforced that perception.</blockquote> | |||
| ===Palestinians=== | |||
| On the Palestinian side, a variety of groups are involved in violence such as ], ] and the ]. They have waged a high-intensity campaign of ] and ]s against Israel. Military equipment is mostly imported light arms and homemade weapons, such as hand grenades and ]s, ]s, and the ]s. They also have increased use of remote-controlled ], a tactic which has become increasingly popular among the poorly armed groups. ]s were often used against "lightly hardened" targets such as Israeli armored jeeps and checkpoints. | |||
| The Mitchell report concluded: | |||
| Palestinians also adopted the tactic of ]. Conducted as a single or double bombing, suicide bombings are generally conducted against "soft" targets (civilians) or "lightly hardened" targets (such as checkpoints) to try to raise the cost of the war to Israelis and demoralize the Israeli society. Most suicide bombing attacks (although not all) are targeted against civilians, and conducted on crowded places in Israeli cities, such as ]ation (buses), ]s and ]s. | |||
| <blockquote>The Sharon visit did not cause the "Al-Aqsa Intifada". But it was poorly timed and the provocative effect should have been foreseen; indeed it was foreseen by those who urged that the visit be prohibited.</blockquote> | |||
| One recent development is the use of ]. Unlike most suicide bombings, the use of these not only earned condemnation from the United States and from human rights groups such as ], but also from many Palestinians and much of the Middle East press. The youngest Palestinian ] was 16-year-old Issa Bdeir, a high school student from the village of Al Doha, who shocked his friends and family when he blew himself up in a park in ], killing a teenage boy and an elderly man. The youngest attempted suicide bombing was by a 14 year old captured by soldiers at the ] before managing to do any harm. | |||
| and also: | |||
| On ], ], Israel seized an ] from a Red Crescent ambulance. The vest was detonated in front of TV cameras by an ] robot. | |||
| <blockquote>We have no basis on which to conclude that there was a deliberate plan by the PA to initiate a campaign of violence at the first opportunity; or to conclude that there was a deliberate plan by the to respond with lethal force.</blockquote> | |||
| In May ], Israel Defence minister ] claimed that ]'s ambulances were used to take the bodies of dead Israeli soldiers in order to prevent the ] from recovering their dead.<ref>{{cite news|date=2004-05|publisher=Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center at the Center for Special Studies (C.S.S)|title=Terrorist organizations exploit UNRWA vehicles: during the Israeli army operation in the Zeitun quarter of Gaza, UNWRA vehicles were used to smuggle armed terrorists out of the area and in all probability remains of Israeli soldiers as well|url=http://www.intelligence.org.il/eng/sib/5_04/unrwa.htm}}</ref> Reuters has provided video of healthy armed men entering ambulance with UN markings for transport. ] initially denied that its ambulances carry militants but later reported that the driver was forced to comply with threats from armed men. UNRWA still denies that their ambulances carried body parts of dead Israeli soldiers. | |||
| === Contributing factors === | |||
| In August 2004, Israel said that an advanced explosives-detection device employed by the IDF at the Hawara checkpoint near Nablus discovered a Palestinian ambulance had transported explosive material. | |||
| Palestinians have claimed that Sharon's visit was the beginning of the Second Intifada,<ref name=bbctimeline/> while others have claimed that Yasser Arafat had pre-planned the uprising.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Suha-Arafat-admits-husband-premeditated-Intifada|title=Suha Arafat admits husband premeditated Intifada|work=The Jerusalem Post|date=29 December 2012|access-date=28 September 2014|archive-date=14 November 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141114101835/http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Suha-Arafat-admits-husband-premeditated-Intifada|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Some, like ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Clinton |first=Bill |author-link=Bill Clinton |title=My Life |publisher=] |year=2004 |isbn=978-1-4000-3003-3}}</ref> say that tensions were high due to failed negotiations at the ] in July 2000. They note that there were Israeli casualties as early as 27 September; this is the Israeli "conventional wisdom", according to Jeremy Pressman, and the view expressed by the ].<ref name="pressman_backgroundsandcauses"/><ref name=jpost2000sep29>{{cite news |agency=] |url=http://info.jpost.com/C002/Supplements/CasualtiesOfWar/2000_09_27.html |title=Fallen soldier's father: I never thought this would happen |date=29 September 2000 |newspaper=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030219211334/http://info.jpost.com/C002/Supplements/CasualtiesOfWar/2000_09_27.html |archive-date=19 February 2003}}</ref> Most mainstream media outlets have taken the view that the Sharon visit was the spark that triggered the rioting at the start of the Second Intifada.<ref name=bbc2000sept28/><ref name=nytimes2008sept30>{{cite news |title=Battle at Jerusalem Holy Site Leaves 4 Dead and 200 Hurt |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2000/09/30/world/battle-at-jerusalem-holy-site-leaves-4-dead-and-200-hurt.html |work=] |date=30 September 2000 |first=Deborah |last=Sontag |access-date=28 September 2014 |quote=This morning, both sides started out tense, after clashes on Thursday provoked by Mr. Sharon's visit. |archive-date=29 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141129070952/http://www.nytimes.com/2000/09/30/world/battle-at-jerusalem-holy-site-leaves-4-dead-and-200-hurt.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=cnn2008sept28>{{cite news |title=Israeli troops, Palestinians clash after Sharon visits Jerusalem sacred site |url=http://archives.cnn.com/2000/WORLD/meast/09/28/jerusalem.violence.02/ |publisher=CNN |date=28 September 2000 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051108060716/http://archives.cnn.com/2000/WORLD/meast/09/28/jerusalem.violence.02/ |archive-date=8 November 2005 |quote=A visit by Likud Party leader Ariel Sharon to the site known as the Temple Mount by Jews sparked a clash on Thursday between stone-throwing Palestinians and Israeli troops, who fired tear gas and rubber bullets into the crowd.... Also Thursday , an Israeli soldier critically injured in a bomb attack on an army convoy in the Gaza Strip died of his wounds.}}</ref><ref name=telegraph>{{Cite news |title=Riot police clash with protesters at holy shrine |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1357329/Riot-police-clash-with-protesters-at-holy-shrine.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1357329/Riot-police-clash-with-protesters-at-holy-shrine.html |archive-date=12 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |work=] |date=29 September 2000 |first=Ohad |last=Gozani |access-date=23 May 2010}}{{cbignore}}</ref> In the first five days of rioting and clashes after the visit, Israeli police and security forces killed 47 Palestinians and wounded 1885,<ref name="autogenerated2"/> while Palestinians killed 5 Israelis.<ref name=btselem-idf-OT>{{cite web|url=http://www.btselem.org/English/Statistics/Casualties_Data.asp?Category=7®ion=TER |title=B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities – Israeli security force personnel killed by Palestinians in the Occupied Territories |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110605010429/http://www.btselem.org/english/Statistics/Casualties_Data.asp?Category=7®ion=TER |archive-date=5 June 2011 }}</ref><ref name=btselem-civ-OT>{{cite web|url=http://www.btselem.org/English/Statistics/Casualties_Data.asp?Category=5®ion=TER |title=B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities – Israeli civilians killed by Palestinians in the Occupied Territories |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110605010359/http://www.btselem.org/english/Statistics/Casualties_Data.asp?Category=5®ion=TER |archive-date=5 June 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ===Israel=== | |||
| The IDF adopted tactics appropriate to the enclosed, ] in which the IDF is frequently fighting. The Israeli Defense Forces stress the safety of their troops, using such heavily armored equipment as the ] tank and various military aircraft including ], ] and ] that can often lead to civilian casualties when used in urban areas. Sniper towers were used extensively in the Gaza Strip before the Israeli ] and are being increasingly employed in the West Bank. Heavily armored ] bulldozers were routinely employed to detonate ]s and ], and clear houses along the border with Egypt used to fire at Israeli troops, in "buffer zones", and during military operations in the West Bank. Until February 2005, Israel had in place a policy to demolish the family homes of suicide bombers. Due to the considerable number of Palestinians living in single homes, the large quantity of homes destroyed, and collateral damage from home demolitions, it become an increasingly controversial tactic. Families have provided timely information to Israeli forces regarding suicide bombing activities in order to prevent the demolition of their houses, although families doing so risk being executed or otherwise punished for ], either by the ] or extra-judicially by Palestinian militants. The IDF committee studying the issue recommended ending the practice because the policy was not effective enough to justify its costs to Israel's image internationally and the backlash it created among Palestinians. | |||
| Palestinians view the Second Intifada as part of their ongoing struggle for national liberation and an end to Israeli occupation,<ref name=Schulz>Schulz and Hammer, 2003, pp. 134–136.</ref> whereas many ] consider it to be a wave of Palestinian terrorism instigated and pre-planned by then Palestinian leader ].<ref name="pressman_backgroundsandcauses">{{cite journal |url=http://www.lib.unb.ca/Texts/JCS/Fall03/pressman.pdf |title=The Second Intifada: Backgrounds and Causes of the Israeli–Palestinian Conflict |author=Jeremy Pressman |journal=Journal of Conflict Studies |date=Fall 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090318174326/http://www.lib.unb.ca/Texts/JCS/Fall03/pressman.pdf |archive-date=18 March 2009|author-link=Jeremy Pressman }}</ref> | |||
| With complete ground and air superiority, mass detentions are regularly conducted; at any given time, there are about 6,000 Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails, about half of them held temporarily without a final indictment, in accordance with Israeli law. Security ] divide most Palestinian cities and interconnections between cities. The Israeli position is that those checkpoints are necessary to stop militants and limit the ability to move weapons around, while Palestinians and Israeli and International observers and organizations perceive those checkpoints as excessive, humiliating, and a major cause of the severe humanitarian situation in the Occupied Territories. Transit across checkpoints can take several hours, depending on the current security situation in Israel. Palestinian metalworking shops and other business facilities suspected by Israel of being used to manufacture weapons are regularly destroyed by airstrikes. The tactic of military "]" - long-term lockdown of civilian areas - has been used routinely. ] was kept under curfew for over 100 consecutive days, with generally under two hours per day allowed for people to get food or conduct other business. | |||
| Support for the idea that Arafat planned the uprising comes from ] leader ], who said in September 2010 that when Arafat realized that the ] in July 2000 would not result in the meeting of all of his demands, he ordered Hamas as well as Fatah and the Aqsa Martyrs Brigades, to launch "military operations" against Israel.<ref name=Abutoameh>{{cite news |url=http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Arafat-ordered-Hamas-attacks-against-Israel-in-2000 |title=Arafat ordered Hamas attacks against Israel in 2000 |author=Khaled Abu Toameh |date=29 September 2010 |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |author-link=Khaled Abu Toameh |archive-date=25 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140825095009/http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Arafat-ordered-Hamas-attacks-against-Israel-in-2000 |url-status=live }}</ref> Al-Zahar is corroborated by ], son of the Hamas founder and leader, ] ], who claims that the Second Intifada was a political maneuver premeditated by Arafat. Yousef claims that "Arafat had grown extraordinarily wealthy as the international symbol of victimhood. He wasn't about to surrender that status and take on the responsibility of actually building a functioning society."<ref>{{cite book |author=Mosab Hassan Yousef |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6qqwLB05IocC |title=Son of Hamas |publisher=] |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-85078-985-7 |pages=125–134 |author-link=Mosab Hassan Yousef |access-date=8 November 2020 |archive-date=18 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095443/https://books.google.com/books?id=6qqwLB05IocC |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Although these tactics also have been condemned internationally, Israel insists they are vital for security reasons in order to thwart terrorist attacks. Some cite figures, such as those published in ] newspaper, to prove the effectiveness of these methods ( - ). The Israeli secret services ] enable the ] (IDF, Magav, police ] and Mistaravim SF units) to thwart suicide bombings by providing real-time warnings and reliable intelligence reports. | |||
| ] quoted Mamduh Nofal, former military commander of the ], who supplied more evidence of pre-28 September military preparations. Nofal recounts that Arafat "told us, Now we are going to the fight, so we must be ready".<ref name=atlantic>{{Cite news |author=David Samuels |author-link=David Samuels (writer) |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/doc/prem/200509/samuels |date=September 2005 |work=] |title=In a Ruined Country: How Yasir Arafat destroyed Palestine |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=30 August 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080830024459/http://www.theatlantic.com/doc/prem/200509/samuels |url-status=live }}</ref> Barak as early as May had drawn up contingency plans to halt any intifada in its tracks by the extensive use of IDF snipers, a tactic that resulted in the high number of casualties among Palestinians during the first days of rioting.<ref>{{cite book |author=David Pratt |url=https://archive.org/details/intifadalongdayo0000prat |url-access=registration |title=Intifada: The Long Day of Rage |publisher=] |year=2007 |isbn=978-1-932-03363-2 |page= |quote=As far back as May 2000 Ehud Barak and his advisors had themselves drafted operational and tactical contingency plans of their own to halt the intifada in its tracks. These included the massive use of IDF snipers, which resulted in the high numbers of Palestinian dead and wounded in the first few days of the uprising. It was these tactics as much as any advanced planning that many believed transformed a series of violent clashes into a full-blown intifada.}}</ref> | |||
| Israel also pursues a policy of "targeted killings", a euphemism for the assassination of militants and especially prominent leaders. Such killings are used to single out as a target those involved in perpetrating attacks against Israelis, and to intimidate others from following suit. This tactic has been condemned as unlawful summary execution by some international human rights organizations and the ], while others (such as the ]) see it as a legitimate measure of ] against terrorism.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} Many criticize the targeted killings for placing civilians at risk, though its supporters believe it reduces civilian casualties on both sides. Israel has been criticized for the use of ] ]s in urban assassinations which often results in ] casualties. Israel in turn has criticized what it describes as a practice of militant leaders hiding among civilians in densely populated areas, thus turning them into unwitting ]s. Regardless of the would be ethical problems, targeted assassinations have been extensively employed by the ], the ], ] and some other armies in ], ] and ] since Israel has begun using this technique. {{Fact|date=February 2007}} | |||
| ====Accusations of war crimes==== | |||
| {{Expand|date=February 2007}} | |||
| In regards to the ] in 2002, ], "Israeli forces committed serious violations of ], some amounting ] to war crimes,"<ref>http://hrw.org/reports/2002/israel3/israel0502-01.htm#P49_1774</ref> while ] similarly alleged evidence that Israel had committed war crimes. The ] questioned how HRW and AI could both acknowledge the lack of a supposed Israeli massacre and the endangerment of Palestinian civilians by Palestinian gunmen and still maintain its accusation of Israel, and they and ] ] the report prejudiced<ref>,''Anti-Defamation League''</ref> | |||
| Arafat's widow Suha Arafat reportedly said on Dubai television in December 2012 that her husband had planned the uprising: "Immediately after the failure of the Camp David , I met him in Paris upon his return.... Camp David had failed, and he said to me, 'You should remain in Paris.' I asked him why, and he said, 'Because I am going to start an intifada. They want me to betray the Palestinian cause. They want me to give up on our principles, and I will not do so,'" the research institute translated Suha as saying.<ref>{{cite news |date=29 December 2012 |url=http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Suha-Arafat-admits-husband-premeditated-Intifada |title=Suha Arafat admits husband premeditated Intifada |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=14 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141114101835/http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Suha-Arafat-admits-husband-premeditated-Intifada |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Israel's ] in the summer of 2000 was, according to Philip Mattar, interpreted by the Arabs as an Israeli defeat and had a profound influence on tactics adopted in the Al Aqsa Intifada.{{sfn|Mattar|2005|p=40}} PLO official ] told reporters: "We are optimistic. Hezbollah's resistance can be used as an example for other ] seeking to regain their rights."<ref>{{cite news |author=Hussein Dakroub |work=Associated Press News |date=26 March 2002 |title=Arafat Aide, Hezbollah Leader Meet |url=https://apnews.com/d8a85d89c749693d000083673318b365 <!--http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-51643361.html--> |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=20 July 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150720195913/http://www.apnewsarchive.com/2002/Arafat-Aide-Hezbollah-Leader-Meet/id-d8a85d89c749693d000083673318b365 |url-status=live }}</ref> Many Palestinian officials have gone on record as saying that the intifada had been planned long in advance to put pressure on Israel. It is disputed however whether Arafat himself gave direct orders for the outbreak, though he did not intervene to put a brake on it<ref name="Rosen">{{Cite book |last=David M. |first=Rosen |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zQYQ0tho6mAC&pg=PA119 |title=Armies of the Young: Child Soldiers in War and Terrorism |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2005 |page=119 |isbn=978-0-8135-3568-5 |access-date=3 October 2016 |archive-date=20 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820043059/https://books.google.com/books?id=zQYQ0tho6mAC&pg=PA119 |url-status=live }}</ref> A personal advisor to Arafat, Manduh Nufal, claimed in early 2001 that the Palestinian Authority had played a crucial role in the outbreak of the Intifada.<ref name="Catignani" /> Israeli's military response demolished a large part of the infrastructure built by the PA during the years following the Oslo Accords in preparation for a Palestinian state.<ref name="Abufarha" >Nasser Abufarha, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200820013747/https://books.google.com/books?id=WpMi4fsKu0AC&pg=PA77 |date=20 August 2020 }} ], 2009 p.77.</ref> This infrastructure included the legitimate arming of Palestinian forces for the first time: some 90 paramilitary camps had been set up to train Palestinian youths in armed conflict.<ref name="Rosen" /> Some 40,000 armed and trained Palestinians existed in the occupied territories.<ref name="Singh" /> | |||
| On 29 September 2001 ], the leader of the Fatah ] in an interview to '']'', described his role in the lead up to the intifada.<ref>{{cite book |first1=Barry M. |last1=Rubin |first2=Judith Colp |last2=Rubin |title=Yasir Arafat: A Political Biography |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-19-516689-7 |page= |author1-link=Barry M. Rubin |url=https://archive.org/details/yasirarafatpolit00rubi/page/204}}</ref> | |||
| ==International Involvement== | |||
| The international community has long taken an involvement in the ], and this involvement has only increased during the Al-Aqsa Intifada. Israel annually receives $1.2 billion in economic aid and $1.8 billion in military aid from the United States, excluding loan guarantees. To put this figure in a regional context, the U.S. gives Egypt about 2 billion dollars in foreign aid, each year, much of which is military aid. Much of this is as a result of the ] and the associated peace treaty between Egypt and Israel. The Palestinian Authority generally receives about $100 million in economic aid from the United States, and the Palestinian territories are major humanitarian aid recipients. {{Fact|date=February 2007}} | |||
| <blockquote>I knew that the end of September was the last period (of time) before the explosion, but when Sharon reached the al-Aqsa Mosque, this was the most appropriate moment for the outbreak of the intifada.... The night prior to Sharon's visit, I participated in a panel on a local television station and I seized the opportunity to call on the public to go to the al-Aqsa Mosque in the morning, for it was not possible that Sharon would reach al-Haram al-Sharif just so, and walk away peacefully. I finished and went to al-Aqsa in the morning.... We tried to create clashes without success because of the differences of opinion that emerged with others in the al-Aqsa compound at the time.... After Sharon left, I remained for two hours in the presence of other people, we discussed the manner of response and how it was possible to react in all the cities (bilad) and not just in Jerusalem. We contacted all (the Palestinian) factions.</blockquote> | |||
| Additionally, private groups have become increasingly involved in the conflict, such as the ] on the side of the Palestinians, and the ] on the side of the Israelis. | |||
| Barghouti also went on record as stating that the example of Hezbollah and Israel's withdrawal from Lebanon was a factor which contributed to the Intifada.<ref name="Catignani" /> | |||
| ==Effects on Oslo Accords== | |||
| Since the start of the Al-Aqsa Intifada and its emphasis on ]s deliberately targeting ]s riding public transportation (]es), the Oslo Accords are viewed with increasing disfavor by the Israeli public. | |||
| According to ], from ]'s inside accounts of negotiations between 2001 and 2005, it would appear to be an inescapable conclusion that violence played an effective role in shaking Israeli complacency and furthering Palestinian goals: the U.S. endorsed the idea of a Palestinian State, Ariel Sharon became the first Israeli Prime Minister to affirm the same idea, and even spoke of Israel's "occupation", and the bloodshed was such that Sharon also decided to withdraw from Gaza, an area he long imagined Israel keeping.<ref name="Thrall" >], {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151121042418/http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2013/aug/15/what-future-israel/ |date=21 November 2015 }} '']'' 15 August 2013 pp.64–67.</ref> However, ], former leader of the ], considers the Intifada to be a total failure that achieved nothing for the Palestinians.<ref>{{cite news |first=Matthew |last=Gutman |title=Aqsa Brigades Leader: Intifada in Its Death Throes |work=] |date=4 August 2004}}</ref> | |||
| In May ], seven years after the Oslo Accords and five months before the start of the Al-Aqsa Intifada, a survey<ref></ref> by the Tami Steinmetz Center for Peace Research at the ] found that: 39% of all Israelis support the Accords and that 32% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years. By contrast, the May ] survey found that 26% of all Israelis support the Accords and 18% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years; decreases of 13% and 16% respectively. Furthermore, later survey found that 80% of all Israelis believe the ] have succeeded in dealing with the Al-Aqsa Intifada militarily.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} | |||
| ==Casualties== | ==Casualties== | ||
| {{See also|Category:Second Intifada casualties|Children in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict|Israeli casualties of war|Palestinian casualties of war}} | |||
| About 1,000 Israelis were killed (up to September 2004) and 6,700 were wounded in Palestinian attacks. {{Fact|date=February 2007}} | |||
| The casualty data for the Second Intifada has been reported by a variety of sources and though there is general agreement regarding the overall number of dead, the statistical picture is blurred by disparities in how different types of casualties are counted and categorized. | |||
| The sources do not vary widely over the data on Israeli casualties. ] reports that 1,053 Israelis were killed by Palestinian attacks through 30 April 2008.<ref name=casualties> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100105120054/http://www.btselem.org/English/Statistics/Casualties.asp |date=5 January 2010 }}, ].</ref>{{failed verification|date=September 2014}} <!-- link updates to http://www.btselem.org/statistics/fatalities/before-cast-lead/by-date-of-event and says Pals killed 239 Israelis in the territories + 471 in Israel proper, for a total of 710, nowhere near 1053 --> Israeli journalist ] reported similar numbers citing the ] as his source<ref name="haaretz468469">{{cite news |author=Schiff |first=Ze'ev |author-link=Ze'ev Schiff |date=24 August 2004 |title=Israeli death toll in Intifada higher than last two wars |newspaper=] |url=http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/news/israeli-death-toll-in-intifada-higher-than-last-two-wars-1.132555 |url-status=live |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150109191003/http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/news/israeli-death-toll-in-intifada-higher-than-last-two-wars-1.132555 |archive-date=9 January 2015}}</ref> in an August 2004 ''Haaretz'' article where he noted: | |||
| The ]'s statistics show 4,398 Palestinians were killed and 31,168 were wounded or injured from ] ] to ] ].<ref> . Intifada casualties chart. ].</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>The number of Israeli fatalities in the current conflict with the Palestinians exceeded 1,000 last week. Only two of the country's wars – the War of Independence and the Yom Kippur War – have claimed more Israeli lives than this intifada, which began on September 29, 2000. In the Six-Day War, 803 Israelis lost their lives, while the War of Attrition claimed 738 Israeli lives along the borders with Egypt, Syria and Lebanon.<ref name=haaretz468469/></blockquote> | |||
| A "Statistical Report Summary" <ref name=statspage> . Breakdown of Fatalities: 27 September 2000 through 1 January 2005. ].</ref> for September 27, 2000 through January 1, 2005 by the ] indicates that 56% (1542) of the 2773 Palestinians killed by Israelis were combatants. According to their data, an additional 406 Palestinians were killed by actions of their own side. 22% (215) of the 988 Israelis killed by Palestinians were combatants. An additional 22 Israelis were killed by actions of their own side. There is detailed info through September 2002 found here: <ref name=articleid439> . Statistical Analysis of Casualties in the Palestinian - Israeli Conflict, September 2000 - September 2002. ]. Article is also.</ref> | |||
| There is little dispute as to the total number of Palestinians killed by Israelis. B'Tselem reports that through 30 April 2008, there were 4,745 Palestinians killed by Israeli security forces, and 44 Palestinians killed by Israeli civilians.<ref name=casualties/> B'Tselem also reports 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians through 30 April 2008.<ref name=casualties/> | |||
| Between September 2000 and January 2005, 69 percent of Israeli fatalities were male, while over 95 percent of the Palestinian fatalities were male.<ref name=statspage>{{cite web |url=http://212.150.54.123/casualties_project/stats_page.cfm |title=Breakdown of Fatalities: 27 September 2000 through 1 January 2005 |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070703195937/http://212.150.54.123/casualties_project/stats_page.cfm |archive-date=3 July 2007 }} Full report: {{cite web |author=Don Radlauer |date=29 September 2002 |url=http://212.150.54.123/articles/articledet.cfm?articleid=439 |title=An Engineered Tragedy: Statistical Analysis of Casualties in the Palestinian – Israeli Conflict, September 2000 – September 2002 |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070928191559/http://212.150.54.123/articles/articledet.cfm?articleid=439 |archive-date=28 September 2007 }}. Also at {{cite web |author=Don Radlauer |url=http://www.eretzyisroel.org/~jkatz/mostly.html |title=An Engineered Tragedy: Statistical Analysis of Casualties in the Palestinian – Israeli Conflict, September 2000 – September 2002 |publisher=EretzYisroel.Org |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150305182911/http://www.eretzyisroel.org/~jkatz/mostly.html |archive-date=5 March 2015 }}</ref> "Remember These Children" reports that as of 1 February 2008, 119 Israeli children, age 17 and under, had been killed by Palestinians. Over the same time period, 982 Palestinian children, age 17 and under, were killed by Israelis.<ref name=child_casualties>{{cite web |url=http://www.rememberthesechildren.org/remember2000.html |title=Remember these Children |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=9 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140109063049/http://www.rememberthesechildren.org/remember2000.html |url-status=live }} Comprehensive list of all Israeli and Palestinian child casualties, age 17 and under, listed since September 2000 along with the circumstances of their deaths.</ref> | |||
| Concerning the killing of Palestinians by other Palestinians a January 2003 ''Humanist'' magazine article<ref> . By Erika Waak. ''Humanist.'' Jan-Feb 2003.</ref> reports: | |||
| :According to Freedom House's annual survey of political rights and civil liberties, ''Freedom in the World 2001-2002'', the chaotic nature of the Intifada along with strong Israeli reprisals has resulted in a deterioration of living conditions for Palestinians in Israeli-administered areas. The survey states: | |||
| ::Civil liberties declined due to: shooting deaths of Palestinian civilians by Palestinian security personnel; the summary trial and executions of alleged collaborators by the Palestinian Authority (PA); extra-judicial killings of suspected collaborators by militias; and the apparent official encouragement of Palestinian youth to confront Israeli soldiers, thus placing them directly in harm's way. | |||
| ===Combatant versus non-combatant deaths=== | |||
| The ''Humanist'' article also reports: "For over a decade the PA has violated Palestinian human rights and civil liberties by routinely killing civilians—including collaborators, demonstrators, journalists, and others—without charge or fair trial. Of the total number of Palestinian civilians killed during this period by both Israeli and Palestinian security forces, 16 percent were the victims of Palestinian security forces." | |||
| {{See also|Civilian casualties in the Second Intifada}} | |||
| Regarding the numbers of Israeli civilian versus combatant deaths, ] reports that through 30 April 2008 there were 719 Israeli civilians killed and 334 Israeli security force personnel killed.<ref name=casualties/> | |||
| [[File:Intifada deaths.svg|thumb|400px| | |||
| Internal Palestinian violence has been called an ''‘Intra’fada'' during this Intifada and the previous one.<ref> . By Leonie Schultens. April 2004. ''The Palestinian Human Rights Monitor.'' A bi-monthly publication of the ].</ref> | |||
| {| | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{legend|#093|Israeli total}} | |||
| |{{legend|#f90|Palestinian total}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{legend|#90c|Israeli breakdown}} | |||
| |{{legend|#933|Palestinian breakdown}} | |||
| |} | |||
| <br /> | |||
| The chart is based on '''B'Tselem''' casualty numbers.<ref name=casualties/> It does not include the 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians.]] | |||
| B'Tselem reports<ref name=casualties/> that through 30 April 2008, out of 4,745 Palestinians killed by Israeli security forces, there were 1,671 "Palestinians who took part in the hostilities and were killed by Israeli security forces", or 35.2%. According to their statistics, 2,204 of those killed by Israeli security forces "did not take part in the hostilities", or 46.4%. There were 870 (18.5%) who B'Tselem defines as "Palestinians who were killed by Israeli security forces and it is not known if they were taking part in the hostilities". | |||
| The B'Tselem casualties breakdown's reliability was questioned and its methodology has been heavily criticized by a variety of institutions and several groups and researchers, most notably ]'s senior researcher, retired IDF lieutenant colonel ], who claimed that B'Tselem repeatedly classifies terror operatives and armed combatants as "uninvolved civilians", but also criticized the Israeli government for not collecting and publishing casualty data.<ref>{{cite web |author=Tamar Sternthal |date=2 November 2008 |url=http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_context=9999&x_article=1533 |title=Updated: In 2007, B'Tselem Casualty Count Doesn't Add Up |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=5 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140105045255/http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_context=9999&x_article=1533 |url-status=live }} Includes translation of article in Hebrew in ''Haaretz'' presenting Dahoah-Halevi's report.<br />Original Haaretz report in Hebrew: {{cite news |author=Amos Harel |url=http://www.haaretz.co.il/news/politics/1.1356183 |title=מחקר: "בצלם" מפרסם מידע שגוי ומשמיט פרטים חיוניים |trans-title=Study: "B'Tselem" publishes false information and omits vital details |newspaper=] |date=25 October 2008 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=26 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150526211854/http://www.haaretz.co.il/news/politics/1.1356183 |url-status=live }}</ref> ], deputy managing editor of '']'' and former advisor to ], pointed to several instances where, she claimed, B'Tselem had misrepresented Palestinian rioters or terrorists as innocent victims, or where B'Tselem failed to report when an Arab allegedly changed his testimony about an attack by settlers.<ref name="Glick">{{cite news|url=http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?cid=1178708574884&pagename=JPost%2FJPArticle%2FPrinter|title=Column one: What is Israel's problem?|date=10 May 2007|newspaper=The Jerusalem Post}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}, <!-- --></ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Caroline B. Glick |date=7 January 2011 |title=Column One: Agents of influence |url=http://www.jpost.com/Opinion/Columnists/Column-One-Agents-of-influence |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |author-link=Caroline B. Glick |archive-date=27 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150527230141/http://www.jpost.com/Opinion/Columnists/Column-One-Agents-of-influence |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] (CAMERA), which said that B'Tselem repeatedly classified Arab combatants and terrorists as civilian casualties.<ref>{{cite web |author=Tamar Sternthal |url=http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_article=493&x_context=2 |title=B'Tselem, ''Los Angeles Times'' Redefine "Civilian" |publisher=] |date=7 July 2003 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140909062215/http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_article=493&x_context=2 |archive-date=9 September 2014 }}</ref><ref name="sternthal">{{cite news|last=Sternthal|first=Tamar|title=Bending the truth|work=]|access-date=26 September 2008|date=24 September 2008|url=http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3601691,00.html|archive-date=25 September 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080925181327/http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0%2C7340%2CL-3601691%2C00.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/News.aspx/128086 |title=Researcher Slams B'Tselem as Inflating Arab Civilian Casualties |author=Gil Ronen |date=26 October 2008 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=31 March 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140331035548/http://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/News.aspx/128086 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Tamar Sternthal |url=http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_context=3&x_outlet=12&x_article=1265 |title=B'Tselem's Annual Casualty Figures Questioned |publisher=] |date=3 January 2007 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=28 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150228184647/http://www.camera.org/index.asp?x_context=3&x_outlet=12&x_article=1265 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| On ], ], ] reporter Zeev Schiff published casualty figures based on ] data.<ref> {{cite news|url=http://www.haaretz.com/hasen/pages/ShArt.jhtml?itemNo=468469|title=Israeli death toll in Intifada higher than last two wars|date=]]|publisher=]}}</ref> Here is a summary of the figures presented in the article: | |||
| The Israeli ] (IPICT), on the other hand, in a "Statistical Report Summary" for 27 September 2000, through 1 January 2005, indicates that 56% (1,542) of the 2,773 Palestinians killed by Israelis were combatants. According to their data, an additional 406 Palestinians were killed by actions of their own side. 22% (215) of the 988 Israelis killed by Palestinians were combatants. An additional 22 Israelis were killed by actions of their own side.<ref name="statspage"/> | |||
| IPICT counts "probable combatants" in its total of combatants. From their full report in September 2002: | |||
| <blockquote>A 'probable combatant' is someone killed at a location and at a time during which an armed confrontation was going on, who appears most likely – but not certain – to have been an active participant in the fighting. For example, in many cases where an incident has resulted in a large number of Palestinian casualties, the only information available is that an individual was killed when Israeli soldiers returned fire in response to shots fired from a particular location. While it is possible that the person killed had not been active in the fighting and just happened to be in the vicinity of people who were, it is reasonable to assume that the number of such coincidental deaths is not particularly high. Where the accounts of an incident appear to support such a coincidence, the individual casualty has been given the benefit of the doubt, and assigned a non-combatant status.<ref name=statspage/></blockquote> | |||
| In the same 2002 IPICT full report there is a pie chart (Graph 2.9) that lists the IPICT combatant breakdown for Palestinian deaths through September 2002. Here follow the statistics in that pie chart used to come up with the total combatant percentage through September 2002: | |||
| {|class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Combatants | |||
| ! Percent of all Palestinian deaths | |||
| |- | |||
| |Full Combatants | |||
| |44.8% | |||
| |- | |||
| |Probable Combatants | |||
| |8.3% | |||
| |- | |||
| |Violent Protesters | |||
| |1.6% | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''Total Combatants''' | |||
| |'''54.7%''' | |||
| |} | |||
| On 24 August 2004, ''Haaretz'' reporter Ze'ev Schiff published casualty figures based on ] data.<ref name=haaretz468469/> The ''Haaretz'' article reported: "There is a discrepancy of two or three casualties with the figures tabulated by the Israel Defense Forces." | |||
| Here is a summary of the figures presented in the article: | |||
| * Over 1,000 Israelis were killed by Palestinian attacks in the al-Aqsa Intifada. | * Over 1,000 Israelis were killed by Palestinian attacks in the al-Aqsa Intifada. | ||
| * Palestinians sources claim 2,736 Palestinians killed in the Intifada. | * Palestinians sources claim 2,736 Palestinians killed in the Intifada. | ||
| * The ] has the names of 2,124 Palestinian dead. | * The ] has the names of 2,124 Palestinian dead. | ||
| * Out of the figure of 2,124 dead, Shin Bet assigned them to these organizations: | * Out of the figure of 2,124 dead, Shin Bet assigned them to these organizations: | ||
| ** 466 ] members | ** 466 ] members | ||
| ** 408 ]'s ] and ] | ** 408 ]'s ] and ] | ||
| ** 205 ] | ** 205 ] | ||
| ** 334 of "Palestinian security forces |
** 334 of "Palestinian security forces – for example, ], the Palestinian police, General Intelligence, and the counter security apparatus" | ||
| The article does not say whether those killed were combatants or not. Here is a quote: | |||
| As a response to IDF statistics about Palestinian casualties in the West Bank, the Israeli ] organization ] released press release stating that two thirds of the Palestinians killed in 2004 did not participate in the fighting.<ref>{{cite news|date=]|title=Two-thirds of Palestinians Killed in the West Bank This Year Did not Participate in the Fighting|url=http://www.btselem.org/English/Press_Releases/20041208.asp|publisher=B'Tselem}}</ref> B'Tselem's statistics have in turn been criticised for not differentiating between combatants and non-combatants and for defining as "civilian" Palestinians killed while engaged in attacks on Israelis.<ref>{{cite news|title=Has Israel Used Indiscriminate Force?|publisher=The Middle East Quarterly|author=Alexander A. Weinreb and Avi Weinreb|url=http://www.meforum.org/article/175}}</ref><ref>http://frontpagemag.com/Articles/Printable.asp?ID=8792</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>The Palestinian security forces – for example, Force 17, the Palestinian police, General Intelligence, and the counter security apparatus – have lost 334 of its members during the current conflict, the Shin Bet figures show.<ref name=haaretz468469/></blockquote> | |||
| Others<!--Freedom House cited above--> argue that the ] throughout the Intifada has sought to place unarmed men, women, children and the elderly in the line of fire between Israeli forces and armed Palestinians, and that television, radio, sermons, and calls from ] loudspeaker systems are used for this purpose.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.imra.org.il/story.php3?id=21044|date=]|publisher=Jerusalem Post|title=Engineering civilian casualties}}</ref> | |||
| In response to IDF statistics about Palestinian casualties in the West Bank, the Israeli human rights organization B'Tselem reported that two-thirds of the Palestinians killed in 2004 did not participate in the fighting.<ref name="autogenerated3">{{cite web |date=8 December 2004 |title=Two-thirds of Palestinians Killed in the West Bank This Year Did not Participate in the Fighting |url=http://www.btselem.org/press_releases/20041208 |publisher=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=5 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140105080659/http://www.btselem.org/press_releases/20041208 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The wave of violence continued on both sides throughout 2006. On December 27 the Israeli Human Rights Organization ] released its annual report on the Intifada. According to which, 660 Palestinians, a figure more than three times the number of Palestinians killed in 2005, and 23 Israelis, have been killed in 2006. From a December 28 '']'' article:<ref> . ''].'' Dec. 28, 2006.</ref> "According to the report, about half of the Palestinians killed, 322, did not take part in the hostilities at the time they were killed. 22 of those killed were targets of assassinations, and 141 were minors." 405 of 660 Palestinians were killed in the ], which lasted from ] till ]. | |||
| In 2009, historian ] stated in his retrospective book ''One State, Two States'' that about one third of the Palestinian deaths up to 2004 had been civilians.<ref>{{cite book |author=Benny Morris |title=One State, Two States: Resolving the Israel/Palestine Conflict |year=2009 |pages=151–152 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-300-12281-7|author-link=Benny Morris }}</ref> | |||
| ==Economic costs== | |||
| The Israeli commerce has experienced much hardship, in particular because of the sharp drop in tourism. A representative of Israel's Chamber of Commerce has estimated the cumulative economic damage caused by the crisis at 150 to 200 billion Shekels, or 35 to 45 billion US $ - against an annual GDP of 122 billion dollars in 2002. | |||
| ===Palestinians killed by Palestinians=== | |||
| Sixteen square kilometers of land in the ], most of it agricultural, was razed by Israeli military forces and more than 601 houses were completely destroyed. The Office of the United Nations Special Coordinator in the Occupied Territories (UNSCO) estimates the damage done to the Palestinian economy at over 1.1 billion dollars in the first quarter of 2002, compared to an annual GDP of 4.5 billion dollars. There are 42% of Gazans dependent on food aid, and 18% of Gaza children exhibit chronic malnutrition. Additionally, 85% of Gazans and 58% of Palestinians in the west bank lived below the poverty line.{{Fact|date=February 2007}}<!--source as well as demonstration of connection needed--> | |||
| ] reports that through 30 April 2008, there were 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians. Of those, 120 were "Palestinians killed by Palestinians for suspected collaboration with Israel".<ref name=casualties/> B'Tselem maintains a list of deaths of Palestinians killed by Palestinians with details about the circumstances of the deaths. Some of the many causes of death are crossfire, factional fighting, kidnappings, collaboration, etc.<ref name=btselemlist>. Detailed ] list. {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110603050621/http://www.btselem.org/english/statistics/Casualties_Data.asp?Category=23®ion=TER |date=3 June 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Concerning the killing of Palestinians by other Palestinians, a January 2003 ''The Humanist'' magazine article reports:<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thehumanist.org/humanist/articles/waakjf03.htm |title=Violence among the Palestinians |author=Erika Waak |work=The Humanist |publisher=] |date=January–February 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030211052937/http://www.thehumanist.org/humanist/articles/waakjf03.htm |archive-date=11 February 2003}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| {{quote|For over a decade the PA has violated Palestinian human rights and civil liberties by routinely killing civilians—including collaborators, demonstrators, journalists, and others—without charge or fair trial. Of the total number of Palestinian civilians killed during this period by both Israeli and Palestinian security forces, 16 percent were the victims of Palestinian security forces. | |||
| ... According to ]'s annual survey of political rights and civil liberties, ''Freedom in the World 2001–2002'', the chaotic nature of the Intifada along with strong Israeli reprisals has resulted in a deterioration of living conditions for Palestinians in Israeli-administered areas. The survey states: | |||
| Civil liberties declined due to: shooting deaths of Palestinian civilians by Palestinian security personnel; the summary trial and executions of alleged collaborators by the Palestinian Authority (PA); extra-judicial killings of suspected collaborators by militias; and the apparent official encouragement of Palestinian youth to confront Israeli soldiers, thus placing them directly in harm's way.}} | |||
| Internal Palestinian violence has been called an ''{{'}}Intra'fada'' during this Intifada and the previous one.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.phrmg.org/intrafada.htm |title=The {{'}}Intra'fada or 'the chaos of the weapons': An Analysis of Internal Palestinian Violence |author=Leonie Schultens |date=April 2004 |work=The Palestinian Human Rights Monitor |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040606055755/http://www.phrmg.org/intrafada.htm |archive-date=6 June 2004}}</ref> | |||
| ==Aftermath== | |||
| On 25 January 2006, the Palestinians held ] for the ]. The Islamist group Hamas won with an unexpected majority of 74 seats, compared to 45 seats for ] and 13 for other parties and independents. Hamas is officially declared as a ] by the United States and the European Union and its gaining control over the Palestinian Authority (such as by forming the government) would jeopardize international funds to the PA, by laws forbidding sponsoring of terrorist group. | |||
| On 9 June, seven members of the Ghalia family ] on a Gaza beach. The cause of the explosion remains uncertain. Nevertheless, in response, Hamas declared an end to its commitment to a ceasefire declared in 2005 and announced the resumption of attacks on Israelis. Palestinians blame an Israeli artillery shelling of nearby locations in the northern Gaza Strip for the deaths, while an Israeli military inquiry cleared itself from the charges. | |||
| On 25 June, a military outpost was attacked by Palestinian militants and a gunbattle followed that left 2 Israeli soldiers and 3 Palestinian militants dead. Corporal ], an Israeli soldier, was captured and Israel warned of an imminent ] if the soldier was not returned unharmed. In the early hours of 28 June Israeli tanks, APCs and troops entered the Gaza Strip just hours after the air force had taken out two main bridges and the only powerstation in the strip, effectively shutting down electricity and water. ] commenced, the first major phase of the ], which continues to run independently of the intifada. | |||
| On 26 November 2006, a truce was implemented between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. A 10 January 2007, Reuters article reports: "Hamas has largely abided by a November 26 truce which has calmed Israeli–Palestinian violence in Gaza."<ref>{{cite news |url=http://today.reuters.com/news/articlebusiness.aspx?type=tnBusinessNews&storyID=nL10415075 |title=Exclusive-Hamas leader says Israel's existence is a reality |author=Sean Maguire |author2=Khaled Oweis |work=Reuters |date=10 January 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071018170208/http://today.reuters.com/news/articlebusiness.aspx?type=tnBusinessNews&storyID=nL10415075 |archive-date=18 October 2007}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| === 2008–2009 Gaza–Israel War === | |||
| An intensification of the Gaza–Israel conflict, the ], occurred on 27 December 2008 (11:30 a.m. local time; 09:30 ])<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/analysis-iaf-strike-on-gaza-is-israel-s-version-of-shock-and-awe-1.260341 |title=Analysis / IAF strike on Gaza is Israel's version of 'shock and awe' |last=Harel |first=Amos |date=27 December 2008 |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=13 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150513023952/http://www.haaretz.com/news/analysis-iaf-strike-on-gaza-is-israel-s-version-of-shock-and-awe-1.260341 |url-status=live }}</ref> when Israel launched a ] codenamed ''Operation Cast Lead'' ({{langx|he|מבצע עופרת יצוקה}}) targeting the members and infrastructure of Hamas in response to the ] from the Gaza Strip.<ref name="bbc_400">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7807564.stm|title=Israel braced for Hamas response|date=2 January 2009|work=BBC News|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=25 December 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181225084007/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7807564.stm|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="BBC 7804051">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/7804051.stm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081230121114/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/7804051.stm|archive-date=30 December 2008|title=Israel pounds Gaza for fourth day|date=30 December 2008|access-date=14 January 2009|work=BBC News}}</ref><ref name="bbc_numbers_dec_30th">{{cite news|title=Israel vows war on Hamas in Gaza |date=30 December 2008 |work=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7803711.stm |access-date=30 December 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081230031820/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7803711.stm |archive-date=30 December 2008 |url-status=live}}</ref> The operation has been termed the ''Gaza massacre'' ({{langx|ar|مجزرة غزة}}) by Hamas leaders and much of the media in the ].<ref name="gaza_massacre0">{{cite news|title=Israeli Gaza 'massacre' must stop, Syria's Assad tells US senator |url=https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5hI7x-bpyN4wqfAneMcCnl-LVx-pg |agency=] |date=30 December 2008 |access-date=11 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090122180254/http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5hI7x-bpyN4wqfAneMcCnl-LVx-pg |archive-date=22 January 2009 |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="gaza_massacre8">{{cite news|title=Factions refuse Abbas' call for unity meeting amid Gaza massacre |url=http://www.turkishweekly.net/news/62543/factions-refuse-abbas-39-call-for-unity-meeting-amid-gaza-massacre.html |agency=] |work=] |date=30 December 2008 |access-date=11 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090124060300/http://www.turkishweekly.net/news/62543/factions-refuse-abbas-39-call-for-unity-meeting-amid-gaza-massacre.html |archive-date=24 January 2009 }}</ref><ref name="gaza_massacre6">{{Cite news |author=Adas |first=Basil |date=28 December 2008 |title=Iraqi leaders discuss Gaza massacre |newspaper=] |url=http://gulfnews.com/news/region/iraq/iraqi-leaders-discuss-gaza-massacre-1.150793 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090202125030/http://www.gulfnews.com/region/Iraq/10270761.html |archive-date=2 February 2009}}</ref><ref name="gaza_massacre10">"Hamas slammed the silent and still Arab position on Gaza massacre" – {{cite news|title=Israel airstrikes on Gaza kill at least 205 |url=http://www.khaleejtimes.com/DisplayArticle08.asp?xfile=data/middleeast/2008/December/middleeast_December507.xml§ion=middleeast |agency=] |newspaper=] |date=27 December 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090123164136/http://www.khaleejtimes.com/DisplayArticle08.asp?xfile=data%2Fmiddleeast%2F2008%2FDecember%2Fmiddleeast_December507.xml§ion=middleeast |archive-date=23 January 2009 }}</ref><ref name="gaza_massacre7">"it's impossible to contain the Arab and Islamic world after the Gaza massacre" – {{cite news|title=Hamas denies firing rockets from Lebanon |url=http://www.sbs.com.au/news/article/1004526/Hamas-denies-firing-rockets-from-Lebanon |agency=] |publisher=] |date=8 January 2009 |access-date=11 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090119054136/http://www.sbs.com.au/news/article/1004526/Hamas-denies-firing-rockets-from-Lebanon |archive-date=19 January 2009 }}</ref><ref name="gazza_massacre1">{{cite news |title=Arab Leaders Call for Palestinian Unity During "Terrible Massacre" |url=https://www.foxnews.com/story/arab-leaders-call-for-palestinian-unity-during-terrible-massacre |agency=] |publisher=] |date=31 December 2008 |access-date=7 January 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090122211525/http://www.foxnews.com/story/0,2933,474461,00.html |archive-date=22 January 2009 }}</ref><ref name="gazza_massacre2">{{cite news|title=Gulf leaders tell Israel to stop Gaza 'massacres' |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSLU230729 |work=] |date=30 December 2008 |access-date=7 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090118212337/http://www.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUSLU230729 |archive-date= 18 January 2009 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="gazza_massacre3">{{cite news|title=OIC, GCC denounce massacre in Gaza |url=http://www.arabnews.com/?page=1§ion=0&article=117588&d=28&m=12&y=2008 |date=28 December 2008 |agency=] |access-date=7 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090118062806/http://www.arabnews.com/?page=1§ion=0&article=117588&d=28&m=12&y=2008 |archive-date= 18 January 2009 }}</ref><ref name="gaza_massacre4">{{cite news|script-title=ar:سباق دبلوماسي لوقف مذبحة غزة |language=ar |trans-title=Diplomatic race to stop the Gaza massacre |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/arabic/middle_east_news/newsid_7810000/7810968.stm |date=5 January 2009 |access-date=11 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090106191319/http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/arabic/middle_east_news/newsid_7810000/7810968.stm |archive-date=6 January 2009 |work=BBC News |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="UN_council_6060">{{cite news|title=United Nations Security Council 6060th meeting (Click on the page S/PV.6060 record for transcript) |url=https://www.un.org/Depts/dhl/resguide/scact2008.htm |date=31 December 2008 |access-date=7 January 2009 |agency=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081217092241/http://www.un.org/Depts/dhl/resguide/scact2008.htm |archive-date=17 December 2008 }}</ref> | |||
| On Saturday, 17 January 2009, Israel announced a unilateral ceasefire, conditional on elimination of further rocket and mortar attacks from Gaza, and began withdrawing over the next several days.<ref name=ravid>{{Cite news|last=Ravid|first=Barak|title=IDF begins Gaza troop withdrawal, hours after ending 3-week offensive|work=]|access-date=28 September 2014|date=18 January 2009|url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/idf-begins-gaza-troop-withdrawal-hours-after-ending-3-week-offensive-1.268326|archive-date=17 August 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140817072019/http://www.haaretz.com/news/idf-begins-gaza-troop-withdrawal-hours-after-ending-3-week-offensive-1.268326|url-status=live}}</ref> Hamas later announced its own ceasefire, with its own conditions of complete withdrawal and opening of border crossings. A reduced level of mortar fire originating in Gaza continues, though Israel has so far not taken this as a breach of the ceasefire. The frequency of the attacks can be observed in the thumbnailed graph. The data corresponds to the article "]", using mainly ''Haaretz'' news reports from 1 February<ref>{{cite news |agency=] |author=Yuval Azoulay |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/two-idf-soldiers-civilian-lightly-hurt-as-gaza-mortars-hit-negev-1.266841 |title=Two IDF soldiers, civilian lightly hurt as Gaza mortars hit Negev |work=] |date=2 January 2009 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=2 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140702082345/http://www.haaretz.com/news/two-idf-soldiers-civilian-lightly-hurt-as-gaza-mortars-hit-negev-1.266841 |url-status=live }}</ref> up to 28 February.<ref>{{cite news |last=Yagna |first=Yanir |url=http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/news/ten-rockets-hit-southern-israel-one-damages-ashkelon-school-1.271119 |title=Ten rockets hit southern Israel, one damages Ashkelon school |work=] |date=2 April 2008 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=20 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130920154814/http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/news/ten-rockets-hit-southern-israel-one-damages-ashkelon-school-1.271119 |url-status=live }}</ref> The usual IDF responses are airstrikes on weapon smuggling tunnels.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.middleeastmonitor.com/20181227-remembering-israels-2008-war-on-gaza/ |title=Remembering Israel's 2008 War on Gaza |date=27 December 2018 |access-date=3 February 2024 |archive-date=19 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240119072814/https://www.middleeastmonitor.com/20181227-remembering-israels-2008-war-on-gaza/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The violence continued on both sides throughout 2006. On 27 December the Israeli Human Rights Organization B'Tselem released its annual report on the Intifada. According to which, 660 Palestinians, a figure more than three times the number of Palestinian fatalities in 2005, and 23 Israelis, were killed in 2006. From a 28 December ''Haaretz'' article:<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/b-tselem-israeli-security-forces-killed-660-palestinians-during-2006-1.208517 |title=B'Tselem: Israeli security forces killed 660 Palestinians during 2006 |newspaper=] |date=28 December 2006 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=13 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150513024645/http://www.haaretz.com/news/b-tselem-israeli-security-forces-killed-660-palestinians-during-2006-1.208517 |url-status=live }}</ref> "According to the report, about half of the Palestinians killed, 322, did not take part in the hostilities at the time they were killed. 22 of those killed were targets of assassinations, and 141 were minors." 405 of 660 Palestinians were killed in the ], which lasted from 28 June till 26 November. | |||
| ==Tactics== | |||
| Unlike the ], a ] civil uprising mainly focused on ] and ], the Second Intifada rapidly turned into an armed conflict between Palestinian militant groups and the Israel Defense Forces.<ref name=":1">{{cite book |last=Cohen |first=Samy |title=Israel's Asymmetric Wars |date=2010 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan US |isbn=978-1-349-28896-0 |location=New York |pages=73–91 |chapter=Botched Engagement in the Intifada |doi=10.1057/9780230112971_6}}"The al-Aqsa Intifada ushered in an era with a new brand of violence. It began with a popular uprising following Ariel Sharon's visit to Temple Mount on September 28, 2000. But unlike the first Intifada, which was basically a civil uprising against the symbols of an occupation that has lasted since June 1967, the second Intifada very quickly lapsed into an armed struggle between Palestinian activists and the Israeli armed forces. Almost from the very start, armed men took to hiding among crowds of Palestinians, using them as cover to shoot from. The IDF retaliated forcefully, each time causing several casualties."</ref> Palestinian tactics focused on Israeli civilians, soldiers, police and other security forces, and methods of attack included ],<ref>{{cite journal |author=Efraim Benmelech |author2=Claude Berrebi |url=http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/benmelech/files/JEP_0807.pdf |title=Human Capital and the Productivity of Suicide Bombers |journal=] |volume=21 |number=3 |date=Summer 2007 |pages=223–238 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100707185129/http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/benmelech/files/JEP_0807.pdf |archive-date=7 July 2010 |doi=10.1257/jep.21.3.223}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last1=Matta |first1=Nada |last2=Rojas |first2=René |date=2016 |title=The Second Intifada: A Dual Strategy Arena |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/european-journal-of-sociology-archives-europeennes-de-sociologie/article/abs/second-intifada/CEF937E5D28EFA4F4F684E6D946942BF |url-status=live |journal=European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie |language=en |volume=57 |issue=1 |page=66 |doi=10.1017/S0003975616000035 |issn=0003-9756 |s2cid=146939293 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220405161756/https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/european-journal-of-sociology-archives-europeennes-de-sociologie/article/abs/second-intifada/CEF937E5D28EFA4F4F684E6D946942BF |archive-date=5 April 2022 |access-date=5 April 2022 |quote=Suicide terror, lethal attacks indiscriminately carried out against civilians via self-immolation, attained prominence in the Palestinian repertoire beginning in March 2001. From that point until the end of 2005, at which point they virtually ceased, 57 suicide bombings were carried out, causing 491 civilian deaths, 73% of the total civilians killed by Palestinian resistance organizations and 50% of all Israeli fatalities during this period. While not the modal coercive tactic, suicide terror was the most efficient in terms of lethality, our basic measure of its efficacy.}}</ref> launching ] into ],<ref name=BBC_Q&A>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7818022.stm |title=Q&A: Gaza conflict |work=BBC News |date=18 January 2009 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=5 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140705061215/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/7818022.stm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3702088.stm |title=Gaza's rocket threat to Israel |work=BBC News |date=21 January 2008 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=23 September 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110923035807/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3702088.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> kidnapping of both soldiers<ref name="usatoday">{{cite news |url=http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/2007-06-25-israeli-palestinian_N.htm |work=] |title=Hamas releases audio of captured Israeli |date=25 June 2007 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=29 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140729121256/http://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/2007-06-25-israeli-palestinian_N.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.haaretz.com/news/diplomacy-defense/timeline-1-940-days-from-gilad-shalit-s-abduction-to-his-release-1.389452 |title=Timeline / 1,940 days from Gilad Shalit's abduction to his release |newspaper=] |date=11 October 2011 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=16 September 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120916203611/http://www.haaretz.com/news/diplomacy-defense/timeline-1-940-days-from-gilad-shalit-s-abduction-to-his-release-1.389452 |url-status=live }}</ref> and civilians, including children,<ref name=USA/><ref name="Globe_and_Mail_10_May_2001">{{cite news |title=Mr. Day Speaks the Truth |date=10 May 2001 |page=A.19 |work=] |location=Toronto |author=Marcus Gee |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/search/?q=%22When+two+teenaged+boys+were+found+dead+near+their+homes+in+the+West+Bank%2C+their+bodies+bound%2C+mutilated+and+pummelled+with+stones%2C+Mr.+Arafat+refused+to+express+regret%2C+saying+only+that+Palestinian+children+were+victims+too%22 |access-date=20 June 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121024164549/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/search/?q=%22When+two+teenaged+boys+were+found+dead+near+their+homes+in+the+West+Bank%2C+their+bodies+bound%2C+mutilated+and+pummelled+with+stones%2C+Mr.+Arafat+refused+to+express+regret%2C+saying+only+that+Palestinian+children+were+victims+too%22 |archive-date=24 October 2012 |author-link=Marcus Gee }}</ref> shootings,<ref>{{multiref2|{{cite web|url=https://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast/2001-05-09-slainteens.htm|title=Two Israeli teenagers stoned to death 1|website=usatoday.com|last=Kalman|first=Mathew|access-date=20 June 2012|publisher=].|archive-date=20 April 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110420150223/http://www.usatoday.com/news/world/mideast/2001-05-09-slainteens.htm|url-status=live}}|{{cite web|url=http://www.theglobeandmail.com/search/?q=%22When+two+teenaged+boys+were+found+dead+near+their+homes+in+the+West+Bank%2C+their+bodies+bound%2C+mutilated+and+pummelled+with+stones%2C+Mr.+Arafat+refused+to+express+regret%2C+saying+only+that+Palestinian+children+were+victims+too%22|title=Mr. Day Speaks the Truth 2|website=The Globe and Mail|last=Glee|first=Marcus|access-date=20 June 2012|publisher=]|archive-date=24 October 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121024164549/http://www.theglobeandmail.com/search/?q=%22When+two+teenaged+boys+were+found+dead+near+their+homes+in+the+West+Bank%2C+their+bodies+bound%2C+mutilated+and+pummelled+with+stones%2C+Mr.+Arafat+refused+to+express+regret%2C+saying+only+that+Palestinian+children+were+victims+too%22|url-status=bot: unknown}}|{{cite news|url=http://www.jpost.com/Israel/IDF-nabs-Zeev-Kahanes-murderer|title=IDF nabs Ze'ev Kahane's murderer|newspaper=The Jerusalem Post | Jpost.com|last=Katz|first=Yakoov|access-date=28 September 2014|publisher=]|archive-date=6 October 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006072054/http://www.jpost.com/Israel/IDF-nabs-Zeev-Kahanes-murderer|url-status=live}}|{{cite magazine|url=http://www.wired.com/politics/law/news/2001/01/41300|title=Israel's 'First Internet Murder|magazine=Wired|last=Hershman|first=Tania|access-date=15 January 2001|publisher=]|archive-date=19 October 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071019223411/http://www.wired.com/politics/law/news/2001/01/41300|url-status=bot: unknown}}|{{cite web|url=http://www.gov.il/FirstGov/TopNavEng/EngSubjects/SafeSurfingEng/TeenagersEng/SSETSurfSafetly/SSETSTOphirRachum/|title=The Murder of Ofir Rahum|access-date=22 October 2007|publisher=Israel Government Portal., Inc.|archive-date=22 October 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071022111226/http://www.gov.il/FirstGov/TopNavEng/EngSubjects/SafeSurfingEng/TeenagersEng/SSETSurfSafetly/SSETSTOphirRachum/|url-status=bot: unknown}}|||{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/7282269.stm|title="Eight killed at Jerusalem school"|last=Katz|first=Yaakov|date=7 March 2008|access-date=28 September 2014|publisher=BBC News.|archive-date=9 March 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080309202319/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/7282269.stm|url-status=live}}|{{cite web|url=http://www.nationalterroralert.com/updates/2008/03/06/terror-attack-at-jerusalem-seminary-merkaz-harav-yeshiva-8-dead/|title="Terror Attack At Jerusalem Seminary – Merkaz HaRav Yeshiva – 8 Dead"|access-date=28 September 2014|publisher=National Terror Alert Response Center.|archive-date=27 September 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927101745/http://www.nationalterroralert.com/updates/2008/03/06/terror-attack-at-jerusalem-seminary-merkaz-harav-yeshiva-8-dead/}}|{{cite web|url=http://www.upi.com/NewsTrack/Top_News/2008/03/06/jerusalem_seminary_attacked/8267/|title="Jerusalem seminary attacked"|access-date=8 March 2008|publisher=United Press International|archive-date=8 March 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080308201142/http://www.upi.com/NewsTrack/Top_News/2008/03/06/jerusalem_seminary_attacked/8267/|url-status=bot: unknown}} | |||
| }}</ref> assassination,<ref>{{cite news |author=Assaf Zohar |date=17 October 2001 |url=http://www.globes.co.il/en/article-528286 |title=Minister of Tourism Rehavam Zeevi assassinated at point-blank range in Jerusalem Hyatt |newspaper=] |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=6 October 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141006072405/http://www.globes.co.il/en/article-528286 |url-status=live }}</ref> stabbings,<ref name=USA/><ref name=IE>{{cite news |title='Get tough' call to Sharon as Jewish boys stoned to death |newspaper=] |author=Phil Reeves |url=http://www.independent.ie/world-news/get-tough-call-to-sharon--as-jewish-boys-stoned-to--death-344813.html |access-date=11 March 2011 |archive-date=26 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220326135447/https://www.independent.ie/world-news/get-tough-call-to-sharon-as-jewish-boys-stoned-to-death-26086317.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and lynchings.<ref>{{multiref2|{{cite news|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1370229/A-day-of-rage-revenge-and-bloodshed.html|title=A day of rage, revenge and bloodshed|last=Alan|first=Philips|date=13 October 2020|access-date=20 June 2012|publisher=].|archive-date=14 October 2017|archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20171014065726/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/israel/1370229/A-day-of-rage-revenge-and-bloodshed.html|url-status=bot: unknown}}|{{cite web|url=http://www.independent.ie/world-news/get-tough-call-to-sharon--as-jewish-boys-stoned-to--death-344813.html|title=Get tough' call to Sharon as Jewish boys stoned to death|access-date=11 March 2011|publisher=].|archive-date=26 March 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220326135447/https://www.independent.ie/world-news/get-tough-call-to-sharon-as-jewish-boys-stoned-to-death-26086317.html|url-status=live}}|{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/969778.stm|title=Lynch mob's brutal attack|last=Smith|first=John|date=13 October 2000|work=BBC News|access-date=16 June 2004|archive-date=29 January 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080129215716/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/969778.stm|url-status=live}}|{{cite news|url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/a-strange-voice-said-i-just-killed-your-husband-635341.html|title=A strange voice said: I just killed your husband|last=Raymond|first=Whitaker|date=14 October 2000|newspaper=] London.|access-date=9 August 2021|archive-date=15 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200615172002/https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/a-strange-voice-said-i-just-killed-your-husband-635341.html|url-status=bot: unknown}}|||| | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| Israeli tactics included curbing Palestinians' movements through the setting up of ] and the enforcement of strict ] in certain areas. Infrastructural attacks against ] targets such as police and prisons was another method to force the Palestinian Authority to repress the anti-Israeli protests and attacks on Israeli targets.{{Citation needed|date=July 2009}} | |||
| ===Palestinians=== | |||
| Militant groups involved in violence include ], ], ] (PFLP) and the ]. The most lethal Palestinian tactic was the ] (''see ]''). Conducted as a single or double bombing, suicide bombings were generally conducted against "soft" targets, or "lightly hardened" targets (such as checkpoints) to try to raise the cost of the war to Israelis and demoralize the Israeli society. Most suicide bombing attacks (although not all) targeted civilians, and were conducted in crowded places in Israeli cities, such as public transport, restaurants, shopping malls and markets. | |||
| One major development was the use of ]. Unlike most suicide bombings, the use of these not only earned condemnation from the United States and from human rights groups such as ], but also from many Palestinians and much of the Middle East press. The youngest Palestinian ] was 16-year-old Issa Bdeir, a high school student from the village of Al Doha, who shocked his friends and family when he blew himself up in a park in ], killing a teenage boy and an elderly man. The youngest attempted suicide bombing was by a 14-year-old captured by soldiers at the ] before managing to do any harm. | |||
| Militant groups also waged a high-intensity campaign of ] against Israeli military and civilian targets inside Israel and in the Palestinian Territories, utilizing tactics such as ]es, ], and ]s. Military equipment was mostly imported, while some light arms, hand grenades and ]s, ]s, and ]s were indigenously produced. They also increased use of remote-controlled ] against Israeli armor, a tactic that was highly popular among the poorly armed groups. ]s were often used against "lightly hardened" targets such as Israeli armored jeeps and checkpoints. Also, more than 1,500 Palestinian ]s killed 75 people in only the first year of the Intifada.<ref name="Luft">{{cite journal |author=Luft |first=Gal |date=July–August 2002 |title=The Palestinian H-Bomb: Terror's Winning Strategy |url=http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/58028/gal-luft/the-palestinian-h-bomb-terrors-winning-strategy |url-status=live |journal=Foreign Affairs |volume=81 |pages=2–7 |doi=10.2307/20033234 |jstor=20033234 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141028183847/http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/58028/gal-luft/the-palestinian-h-bomb-terrors-winning-strategy |archive-date=28 October 2014 |access-date=28 September 2014 |number=4}}</ref> | |||
| In May 2004, Israel Defense minister ] claimed that ]'s ambulances were used to take the bodies of dead Israeli soldiers in order to prevent the ] from recovering their dead.<ref>{{cite web |date=May 2004 |publisher=] at the Center for Special Studies (C.S.S) |title=Terrorist organizations exploit UNRWA vehicles: during the Israeli army operation in the Zeitun quarter of Gaza, UNWRA vehicles were used to smuggle armed terrorists out of the area and in all probability remains of Israeli soldiers as well |url=http://www.intelligence.org.il/eng/sib/5_04/unrwa.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040603110926/http://www.intelligence.org.il/eng/sib/5_04/unrwa.htm |archive-date=3 June 2004}}</ref> Reuters has provided video of healthy armed men entering ambulance with UN markings for transport. ] initially denied that its ambulances carry militants but later reported that the driver was forced to comply with threats from armed men. UNRWA still denies that their ambulances carried body parts of dead Israeli soldiers. | |||
| In August 2004, Israel said that an advanced explosives-detection device employed by the IDF at the Hawara checkpoint near Nablus discovered a Palestinian ambulance had transported explosive material. | |||
| Some of the Palestinian reaction to Israeli policy in the ] and ] has consisted of non-violent protest,<ref>{{cite news |author=Snitz |first=Kobi |date=15 December 2004 |title=We are all Ahmed Awwad: Lessons in Popular Resistance |publisher=] |url=http://www.zmag.org/content/showarticle.cfm?ItemID=6874 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20050418102307/http://www.zmag.org/content/showarticle.cfm?ItemID=6874 |archive-date=18 April 2005}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Palestinian Nonviolent Resistance to Occupation Since 1967 |work=Faces of Hope |date=Fall 2005 |publisher=American Friends Service Committee |url=http://www.afsc.org/israel-palestine/documents/PalestinianNonviolentResistancetooccupaltion.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051107200955/http://www.afsc.org/israel-palestine/documents/PalestinianNonviolentResistancetooccupaltion.pdf |archive-date=7 November 2005}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://qumsiyeh.org/palestiniannonviolentresistance/ |title=Palestinian non-violent resistance |publisher=Mazin Qumsiyeh |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040827021730/http://qumsiyeh.org/palestiniannonviolentresistance/ |archive-date=27 August 2004}}</ref> primarily in and near the village of ]. Groups such as the Palestinian Centre for Rapprochement, which works out of Beit Sahour, formally encourage and organize non-violent resistance.<ref>{{cite news |last=Kaufman |first=Maxine |url=http://www.peacemagazine.org/archive/v20n4p22.htm |title=Peace Magazine v20n4p22: A Glimpse of Palestinian Nonviolence |work=] |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-date=7 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111207034922/http://www.peacemagazine.org/archive/v20n4p22.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Other groups, such as the ] openly advocate non-violent resistance. Some of these activities are done in cooperation with internationals and Israelis, such as the weekly protests against the ] carried out in villages like Bi'lin,<ref>{{cite news |last=Elmer |first=Jon |url=http://newstandardnews.net/content/index.cfm/items/2248 |title=Protest, Grief as Barrier Segregates Palestinian Village from Farms |publisher=] |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110805030532/http://newstandardnews.net/content/index.cfm/items/2248 |archive-date=5 August 2011 }}</ref> Biddu<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ramallahonline.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=1902 |title=News From Within-> Home Numbers |date=13 June 2001 |access-date=14 September 2014 |archive-date=30 September 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180930202206/http://www.ramallahonline.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=1902 |url-status=live }}</ref> and Budrus.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.zmag.org/content/showarticle.cfm?ItemID=7463 |publisher=] |title=Budrus has a hammer |date=17 March 2005 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20050418120156/http://www.zmag.org/content/showarticle.cfm?ItemID=7463 |archive-date=18 April 2005}}</ref> This model of resistance has spread to other villages like Beit Sira,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.palestinemonitor.org/nueva_web/updates_news/updates/beit_sira_experience.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060527050519/http://www.palestinemonitor.org/nueva_web/updates_news/updates/beit_sira_experience.htm|archive-date=27 May 2006 |title=Palestinian non-violent resistance continues: the experience of Beit Sira |publisher=] |date=21 February 2006}}</ref> Hebron, Saffa, and Ni'lein.<ref>{{cite news |author=Jumá |first=Jamal |author-link=Jamal Jumá |date=26 March 2005 |title=The great divide |newspaper=] |url=http://www.hinduonnet.com/2005/03/26/stories/2005032602051000.htm |url-status=usurped |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606202955/http://www.hinduonnet.com/2005/03/26/stories/2005032602051000.htm |archive-date=6 June 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=Jamal Jumá |date=7–13 April 2005 |url=http://weekly.ahram.org.eg/2005/737/re2.htm |newspaper=] |title=Palestine is not for sale! |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120125223406/http://weekly.ahram.org.eg/2005/737/re2.htm |archive-date=25 January 2012 |author-link=Jamal Jumá }}</ref> During the Israeli re-invasion of Jenin and Nablus, "A Call for a Non-violent Resistance Strategy in Palestine" was issued by two Palestinian Christians in May 2002.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ncccusa.org/news/02news49.html |title=Palestinian Christians Call for Non-Violent Resistance |publisher=] |date=10 May 2002 |access-date=13 November 2011 |archive-date=26 September 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110926225228/http://www.ncccusa.org/news/02news49.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Non-violent tactics have sometimes been met with Israeli military force. For example, Amnesty International notes that "10-year-old Naji Abu Qamer, 11-year-old Mubarak Salim al-Hashash and 13-year-old Mahmoud Tariq Mansour were among eight unarmed demonstrators killed in the early afternoon of May 19, 2004 in Rafah, in the Gaza Strip, when the Israeli army open fire on a non-violent demonstration with tank shells and a missile launched from a helicopter gunship. Dozens of other unarmed demonstrators were wounded in the attack." According to Israeli army and government officials, the tanks shelled a nearby empty building and a helicopter fired a missile in a nearby open space in order to deter the demonstrators from proceeding towards Israeli army positions.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde02/002/2004/en/ |title=Israel and the Occupied Territories and the Palestinian Authority: Act Now to Stop the Killing of Children! |publisher=Amnesty International |date=20 November 2004 |access-date=19 November 2018 |archive-date=22 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181122054932/https://www.amnesty.org/en/documents/mde02/002/2004/en/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Israel=== | |||
| ] ]. Military experts cited the D9 as a key factor in keeping IDF casualties low.]] | |||
| ] (IAF) ] were used as platform for shooting ]s at Palestinian targets and employed at the ]s policy against senior militants and terrorists leaders.]] | |||
| The ] (IDF) countered Palestinian attacks with incursions against militant targets into the West Bank and Gaza Strip, adopting highly effective ] tactics. The IDF stressed the safety of their troops, using such heavily armored equipment as the ] heavy tank and armored personnel carriers, and carried out airstrikes with various military aircraft including ], ] and ] to strike militant targets. Much of the ground fighting was conducted house-to-house by well-armed and well-trained infantry. Due to its superior training, equipment, and numbers, the IDF had the upper hand during street fighting. Palestinian armed groups suffered heavy losses during combat, but the operations were often criticized internationally due to the civilian casualties often caused. Palestinian metalworking shops and other business facilities suspected by Israel of being used to manufacture weapons were regularly targeted by airstrikes, as well as Gaza Strip smuggling tunnels. | |||
| Israeli ] ]s were routinely employed to detonate ]s and ], to demolish houses along the border with Egypt that were used for shooting at Israeli troops, to create "buffer zones", and to support military operations in the West Bank. Until February 2005, Israel had in place a policy to demolish the family homes of suicide bombers after giving them a notice to evacuate. Due to the considerable number of Palestinians living in single homes, the large quantity of homes destroyed, and collateral damage from home demolitions, it became an increasingly controversial tactic. Families began providing timely information to Israeli forces regarding suicide bombing activities in order to prevent the demolition of their homes, although families doing so risked being executed or otherwise punished for ], either by the ] or extrajudicially by Palestinian militants. The IDF committee studying the issue recommended ending the practice because the policy was not effective enough to justify its costs to Israel's image internationally and the backlash it created among Palestinians.<ref>], {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160820032626/http://www.inss.org.il/uploadimages/Import/(FILE)1298360394.pdf |date=20 August 2016 }}, "''']'''", Volume 2, No. 2, October 2010.</ref> | |||
| With complete ground and air superiority, mass arrests were regularly conducted by Israeli military and police forces; at any given time, there were about 6,000 Palestinian prisoners detained in Israeli prisons, about half of them held temporarily without a final indictment, in accordance with Israeli law. | |||
| The tactic of military "]" – long-term lockdown of civilian areas – was used extensively by Israel throughout the Intifada. The longest curfew was in ], which was kept under curfew for over 100 consecutive days, with generally under two hours per day allowed for people to get food or conduct other business. | |||
| Security ] and roadblocks were erected inside and between Palestinian cities, subjecting all people and vehicles to security inspection for free passage. Israel defended those checkpoints as being necessary to stop militants and limit the ability to move weapons around. However some Palestinian, Israeli and International observers and organizations have criticized the checkpoints as excessive, humiliating, and a major cause of the humanitarian situation in the Occupied Territories. Transit could be delayed by several hours, depending on the security situation in Israel. Sniper towers were used extensively in the Gaza Strip before the Israeli ]. | |||
| The Israeli intelligence services ] and ] penetrated Palestinian militant organizations by relying on moles and sources within armed groups, tapping communication lines, and aerial reconnaissance.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.polis.leeds.ac.uk/assets/files/research/working-papers/wp16jones.pdf |publisher=School of Politics and International Studies |title=School of Politics and International Studies – Site Homepage }}{{dead link|date=June 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> The intelligence gathered allowed the IDF, ], and ], including ] and ] special forces units, to thwart hundreds of planned suicide bombings. The intelligence gathered also helped create a list of Palestinians marked for targeted killings. | |||
| Israel extensively used ], the assassinations of Palestinians involved in organizing attacks against Israelis, to eliminate imminent threats and to deter others from following suit, relying primarily on airstrikes and covert operations to carry them out. The strategy of targeted killings had been proposed by Shin Bet, which determined that while it was impossible to stop every single suicide bomber, suicide bombings could be stopped by directly attacking the conspiratorial infrastructure behind them by killing operational commanders, recruiters, couriers, weapons procurers, maintainers of safehouses, and smugglers of money which financed the bombings.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Bergman |first=Ronen |date=3 February 2018 |title=How Israel Won a War but Paid a High Moral Price |work=] |url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2018/02/03/how-israel-won-the-war-against-suicide-bombers-but-lost-its-moral-compass-ronen-bergman/ |access-date=29 September 2020 |archive-date=29 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200929192845/https://foreignpolicy.com/2018/02/03/how-israel-won-the-war-against-suicide-bombers-but-lost-its-moral-compass-ronen-bergman/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Israel was criticized for the use of ] in urban assassinations, which often resulted in civilian casualties. Israel criticized what it described as a practice of militant leaders hiding among civilians in densely populated areas, thus turning them into unwitting ]s. Throughout the Intifada, the Palestinian leadership suffered heavy losses through targeted killings. | |||
| The practice has been widely condemned as extrajudicial executions by the international community,<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Milanovic|first1=Marko|title=Lessons for human rights and humanitarian law in the war on terror: comparing Hamdan and the Israeli Targeted Killings case|journal=International Review of the Red Cross|date=June 2007|volume=89|issue=866|page=375|doi=10.1017/S181638310700104X|s2cid=146130526|url=https://www.icrc.org/eng/assets/files/other/irrc_866_milanovic.pdf|access-date=9 July 2015|archive-date=10 July 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150710155808/https://www.icrc.org/eng/assets/files/other/irrc_866_milanovic.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=8060&Cr=middle&Cr1=east |title=UN envoy condemns Israel's extra-judicial assassinations |date=25 August 2003 |publisher=UN News Centre |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=12 July 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150712161928/http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=8060&Cr=middle&Cr1=east |url-status=live }}</ref> while the Israeli High Court ruled that it is a legitimate measure of ] against terrorism.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Wilson |first=Scott |date=15 December 2006 |title=Israeli High Court Backs Military On Its Policy of 'Targeted Killings' |newspaper=] |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/12/14/AR2006121400430.html |access-date=11 September 2017 |archive-date=20 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171020081147/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/12/14/AR2006121400430.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Many{{Who|date=May 2010}} criticize the targeted killings for placing civilians at risk, though its supporters believe it reduces civilian casualties on both sides. | |||
| In response to repeated rocket attacks from the Gaza Strip, the ] imposed a ] on the area. Israel also sealed the border and closed Gaza's airspace in coordination with ], and subjected all humanitarian supplies entering the Strip to security inspection before transferring them through land crossings. Construction materials were declared banned due to their possible use to build bunkers.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/26/world/middleeast/26mideast.html |work=] |first=Sabrina |last=Tavernise |author-link=Sabrina Tavernise |title=In Gaza, the Wait to Rebuild Lingers |date=26 January 2009 |page=A6 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=16 December 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141216143032/http://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/26/world/middleeast/26mideast.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The blockade has been internationally criticized as a form of "]" against Gaza's civilian population.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://in.reuters.com/article/idINIndia-30214320071029 |work=Reuters |title=EU warns against 'collective punishment' in Gaza |date=29 October 2007 |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=2 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102113653/http://in.reuters.com/article/idINIndia-30214320071029 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==International involvement== | |||
| {{See also|Israel and the United Nations|Palestine and the United Nations|Israel-United States relations|International Solidarity Movement|International aid to Palestinians}} | |||
| The international community has long taken an involvement in the ], and this involvement has only increased during the al-Aqsa Intifada. Israel currently receives $3 billion in annual ], excluding loan guarantees.<ref>{{cite news |last=Ruebner |first=Josh |author-link=Josh Ruebner |date=26 February 2010 |title=U.S. Can't Afford Military Aid to Israel |work=] |url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/josh-ruebner/us-cant-afford-military-a_b_478104.html |access-date=16 November 2010 |archive-date=18 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110618150545/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/josh-ruebner/us-cant-afford-military-a_b_478104.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Even though Israel is a developed industrial country, it has remained as the largest annual recipient of US foreign assistance since 1976.<ref name="Mearsheimer 2007">{{cite book |last1=Mearsheimer |first1=John |author-link=John Mearsheimer |last2=Walt |first2=Stephen |author2-link=Stephen Walt |title=The Israel Lobby and U.S. Foreign Policy |year=2008 |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-0-374-53150-8}}</ref> It is also the only recipient of US economic aid that does not have to account for how it is spent.<ref name="Mearsheimer 2007"/> The Palestinian Authority receives $100 million annually in military aid from the United States and $2 billion in global financial aid, including "$526 million from ], $651 million from the ], $300 million from the US and about $238 million from the ]".<ref>{{cite news |author=O'Sullivan |first1=Arieh |author-link=Arieh O'Sullivan |last2=Friedson |first2=Felice |date=3 March 2010 |title=Jewish-Agency-style 'Palestine Network; launched in Bethleh |work=] |url=http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Jewish-Agency-style-Palestine-Network-launched-in-Bethleh |access-date=28 September 2014 |archive-date=8 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208030132/http://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Jewish-Agency-style-Palestine-Network-launched-in-Bethleh |url-status=live }}</ref> According to the United Nations, the Palestinian territories are among the leading humanitarian aid recipients.<ref>{{cite news |author=Concepcion |first=Juan Carlos |date=9 September 2013 |title=Top 10 recipients of EU aid |url=https://www.devex.com/news/top-10-recipients-of-eu-aid-81760 |newspaper=Devex |access-date=9 July 2015 |archive-date=10 July 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150710204746/https://www.devex.com/news/top-10-recipients-of-eu-aid-81760 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Zanotti |first=Jim |date=3 July 2014 |title=U.S. Foreign Aid to the Palestinians |url=https://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/mideast/RS22967.pdf |publisher=Federation of American Scientists |access-date=9 July 2015 |archive-date=10 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210810185050/https://fas.org/sgp/crs/mideast/RS22967.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Additionally, private groups have become increasingly involved in the conflict, such as the ] on the side of the Palestinians, and the ] on the side of the Israelis. | |||
| In the 2001 and 2002 ]s, the Arab states pledged support for the Second Intifada just as they had pledged support for the ] in two consecutive summits in the late 1980s.<ref>]. "Arab Summit Conferences". ''The Continuum Political Encyclopedia of the Middle East''. Ed. Sela. New York: Continuum, 2002. pp. 158–160</ref> | |||
| ==Impact on the Oslo Accords== | |||
| Since the start of the Second Intifada and its emphasis on ] deliberately targeting civilians riding public transportation (]es), the ] began to be viewed with increasing disfavor by the Israeli public. In May 2000, seven years after the Oslo Accords and five months before the start of the Second Intifada, a survey<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://social-sciences.tau.ac.il/bicohen|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060602123619/http://www.bicohen.tau.ac.il/templ001/manage.asp?siteID=5&lang=2&pageID=199|script-title=he:מכון ב.י. ולוסיל כהן למחקרי דעת קהל|archive-date=2 June 2006|website=social-sciences.tau.ac.il}}</ref> by the Tami Steinmetz Center for Peace Research at the ] found that 39% of all Israelis support the Accords and that 32% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years. In contrast, a survey in May 2004 found that 26% of all Israelis support the Accords and 18% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years; decreases of 13% and 16% respectively. Furthermore, a later survey found that 80% of all Israelis believe the ] have succeeded in dealing with the Second Intifada militarily.<ref>{{cite web|date=May 2004 |url=http://spirit.tau.ac.il/socant/peace/peaceindex/2004/data/may2004d.pdf |script-title=he:מדד השלום |publisher=The Tami Steinmetz Center for Peace Research |language=he |url-status=bot: unknown |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061108082619/http://spirit.tau.ac.il/socant/peace/peaceindex/2004/data/may2004d.pdf |archive-date=8 November 2006 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Economic effects== | |||
| ===Israel=== | |||
| The Israeli commerce experienced a significant negative effect, particularly due to a sharp drop in tourism. A representative of Israel's Chamber of Commerce estimated the cumulative economic damage caused by the crisis at 150 to 200 billion ] (US$35–45 billion) – against an annual GDP of $122 billion in 2002.<ref name=Tabarani>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AMqLgW_B_BAC&pg=PA242 |last=Tabarani |first=Gabriel G. |title=Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: From Balfour Promise to Bush Declaration: THE COMPLICATIONS AND THE ROAD FOR A LASTING PEACE |publisher=AuthorHouse |year=2008 |pages=242–243 |isbn=978-1-4343-7237-6 |access-date=20 May 2016 |archive-date=18 August 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200818220355/https://books.google.com/books?id=AMqLgW_B_BAC&pg=PA242 |url-status=live }}</ref> The Israeli economy recovered after 2005 with the sharply decrease in suicide bombings, following ]'s and ]'s efforts. | |||
| ===Palestinian Authority=== | |||
| The Office of the ] (UNSCO) estimated the damage to the Palestinian economy at over $1.1 billion in the first quarter of 2002, compared to an annual GDP of $4.5 billion.<ref name="Tabarani"/> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{div col|colwidth=40em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (1987–1993) | |||
| * ]: ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] | |||
| * ] (2001) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (2005) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] – started in 2002 | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (steadfastness) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] (2014) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ;Directly connected to the Second Intifada and its aftermath: | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| == |
==References== | ||
| === |
===Citations=== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| * | |||
| * The Telegraph | |||
| * and - ''Thinking-East'' analyses | |||
| * {{he icon}} | |||
| * | |||
| * BBC News: | |||
| * BBC News: | |||
| * - Includes weekly reports of injuries, deaths, military detention of ambulances, and many other statistics. | |||
| * | |||
| === |
===Sources=== | ||
| ==== Books ==== | |||
| * | |||
| {{refbegin|2}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| * | |||
| | first=Ahron | |||
| * | |||
| | last=Bregman | |||
| * | |||
| | title=Elusive Peace: How the Holy Land Defeated America | |||
| * | |||
| | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pxNsI4UaU-sC&pg=PT160 | |||
| * | |||
| | date=29 September 2005 | |||
| * | |||
| | publisher=Penguin Books Limited | |||
| * | |||
| | isbn=978-0-14-190613-3 | |||
| * | |||
| | pages=160– | |||
| | access-date=29 October 2020 | |||
| | archive-date=18 November 2021 | |||
| | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095446/https://books.google.com/books?id=pxNsI4UaU-sC&pg=PT160 | |||
| | url-status=live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| |first = Daniel | |||
| |last = Byman | |||
| |title = A High Price: The Triumphs and Failures of Israeli Counterterrorism | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=mYppAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA114 | |||
| |date = 15 June 2011 | |||
| |publisher = Oxford University Press | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-19-983045-9 | |||
| |pages = 114– | |||
| |access-date = 29 October 2020 | |||
| |archive-date = 18 November 2021 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095443/https://books.google.com/books?id=mYppAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA114 | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| |last=Catignani |first=Sergio | |||
| |title=Israeli Counter-Insurgency and the Intifadas: Dilemmas of a Conventional Army | |||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2C3NcBIl_60C | |||
| |date=2008 | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |isbn=978-0-203-93069-4 | |||
| |access-date=12 December 2015 | |||
| |archive-date=2 January 2016 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102113652/https://books.google.com/books?id=2C3NcBIl_60C | |||
| |url-status=live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| |first = Philip | |||
| |last = Mattar | |||
| |title = Encyclopedia of the Palestinians | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=GkbzYoZtaJMC&pg=PA40 | |||
| |year = 2005 | |||
| |publisher = Infobase Publishing | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-8160-6986-6 | |||
| |pages = 40– | |||
| |access-date = 3 October 2016 | |||
| |archive-date = 19 August 2020 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200819111423/https://books.google.com/books?id=GkbzYoZtaJMC&pg=PA40 | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | title=The Road Map to Nowhere: Israel/Palestine Since 2003 | |||
| | first=Tanya | |||
| | last=Reinhart | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| | year=2006 | |||
| | isbn= 978-1-84467-076-5 | |||
| | author-link=Tanya Reinhart | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | title=The Palestinian Diaspora: Formation of Identities and Politics of Homeland | |||
| | first1=Helena Lindholm | last1=Schulz | |||
| | first2=Juliane | last2=Hammer | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| | year=2003 | |||
| | isbn=978-0-415-26820-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| |first = Colin | |||
| |last = Shindler | |||
| |title = A History of Modern Israel | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=oSQgAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA283 | |||
| |date = 25 March 2013 | |||
| |publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| |isbn = 978-1-107-31121-3 | |||
| |pages = 283– | |||
| |access-date = 3 October 2016 | |||
| |archive-date = 23 December 2016 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20161223214233/https://books.google.com/books?id=oSQgAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA283 | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | first=Spencer C. | |||
| | last=Tucker | |||
| | title=Middle East Conflicts from Ancient Egypt to the 21st Century: An Encyclopedia and Document Collection [4 volumes] | |||
| | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Dm6pDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA958 | |||
| | date=31 August 2019 | |||
| | publisher=ABC-CLIO | |||
| | isbn=978-1-4408-5353-1 | |||
| | pages=958– | |||
| | access-date=29 October 2020 | |||
| | archive-date=18 November 2021 | |||
| | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095441/https://books.google.com/books?id=Dm6pDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA958 | |||
| | url-status=live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| |last=Yousef | |||
| |first=Mosab Hassan | |||
| |title=Son of Hamas: A Gripping Account of Terror, Betrayal, Political Intrigue, and Unthinkable Choices | |||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6qqwLB05IocC | |||
| |year=2011 | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |isbn=978-1-85078-985-7 | |||
| |access-date=8 November 2020 | |||
| |archive-date=18 November 2021 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211118095443/https://books.google.com/books?id=6qqwLB05IocC | |||
| |url-status=live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |last=Cohen |first=Hillel | |||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KRKsAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA73 | |||
| |title=The Rise and Fall of Arab Jerusalem: Palestinian Politics and the City Since 1967 | |||
| |date=2013 | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |isbn=978-1-136-85266-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| === |
==== Journal articles ==== | ||
| {{refbegin|2}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite journal | last=Pressman | first=Jeremy | title=The Second Intifada: Background and Causes of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict | journal=Journal of Conflict Studies | volume=23 | issue=2 | date=February 21, 2006 | issn=1715-5673 | url=https://journals.lib.unb.ca/index.php/JCS/article/view/220 | access-date=October 29, 2020 | archive-date=1 November 2020 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201101133442/https://journals.lib.unb.ca/index.php/JCS/article/view/220 | url-status=live }} | |||
| * | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * - Ynetnews English version of ] | |||
| ==== Articles ==== | |||
| {{Arab-Israeli Conflict}} | |||
| {{refbegin|2}} | |||
| * {{cite web |title=Al-Aqsa Intifada timeline |website=] |date=September 29, 2004 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3677206.stm |ref={{sfnref | BBC | 2004}} |access-date=October 29, 2020 |archive-date=2 July 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160702011849/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/3677206.stm |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite web |title=Full text of Abbas declaration |website=] |date=February 8, 2005 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4247327.stm |ref={{sfnref | Abbas | 2005}} |access-date=October 29, 2020 |archive-date=8 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200308184426/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/4247327.stm |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite web |title=Full text of Sharon declaration |website=] |date=February 8, 2005 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4247233.stm |ref={{sfnref | Sharon | 2005}} |access-date=October 29, 2020 |archive-date=3 December 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131203032406/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/4247233.stm |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite web | title=A Feud That Lasted A Lifetime: Ariel Sharon Vs. Yasser Arafat | website=NPR.org | date=2014-01-11 | url=https://www.npr.org/sections/parallels/2014/01/11/261390545/a-feud-that-lasted-a-lifetime-ariel-sharon-vs-yasser-arafat | ref={{sfnref | NPR | 2014}} | access-date=2022-04-05 | archive-date=5 April 2022 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220405155002/https://www.npr.org/sections/parallels/2014/01/11/261390545/a-feud-that-lasted-a-lifetime-ariel-sharon-vs-yasser-arafat | url-status=live }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| *{{commons cat inline}} | |||
| {{Israeli-Palestinian conflict|Timeline}} | |||
| {{Arab-Israeli conflict}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Post-Cold War Asian conflicts}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Israeli wars}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:27, 11 January 2025
2000–2005 Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupationThis page is subject to the extended confirmed restriction related to the Arab-Israeli conflict.
| Second Intifada | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict | |||||||||
    Clockwise from top-left: Clockwise from top-left:
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
29 September 2000 – 1 January 2005: ~1,010 Israelis total:• 644–773 Israeli civilians killed by Palestinians; • 215–301 Israeli troops killed by Palestinians |
29 September 2000 – 1 January 2005: 3,179–3,354 Palestinians total:• 2,739–3,168 Palestinians killed by Israeli troops;* • 152–406 Palestinians killed by Palestinians; • 34 Palestinians killed by Israeli civilians | ||||||||
|
55 foreign nationals/citizens total: • 45 foreigners killed by Palestinians; • 10 foreigners killed by Israeli troops | |||||||||
| *For the controversial issue of distinguishing Palestinian civilian/combatant casualties, see § Casualties. | |||||||||
| Second Intifada | |
|---|---|
Lists |
The Second Intifada (Arabic: الانتفاضة الثانية, romanized: al-Intifāḍa aṯ-Ṯāniya, lit. 'The Second Uprising'; Hebrew: האינתיפאדה השנייה, romanized: ha-Intifada ha-Shniya), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada, was a major uprising by Palestinians against Israel and its occupation from 2000. The period of heightened violence in the Palestinian territories and Israel continued until the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005, which ended hostilities.
The general triggers for the unrest are speculated to have been centered on the failure of the 2000 Camp David Summit, which was expected to reach a final agreement on the Israeli–Palestinian peace process in July 2000. An uptick in violent incidents started in September 2000, after Israeli politician Ariel Sharon made a provocative visit to the Temple Mount; the visit itself was peaceful, but, as anticipated, sparked protests and riots that Israeli police put down with rubber bullets, live ammunition, and tear gas. Within the first few days of the uprising, the IDF had fired one million rounds of ammunition.
During the first few weeks of the uprising, the ratio of Palestinians to Israelis killed was around 20 to 1. Israeli security forces engaged in gunfights, targeted killings, tank attacks, and airstrikes; Palestinians engaged in gunfights, stone-throwing, and rocket attacks. The approximate 138 suicide bombings carried out by Palestinian militant factions after March 2001 became one of the prominent features of the Intifada and mainly targeted Israeli civilians. With a combined casualty figure for combatants and civilians, the violence is estimated to have resulted in the deaths of approximately 3,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis, as well as 64 foreign nationals.
The Second Intifada had ended with the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005, as Palestinian president Mahmoud Abbas and Israeli prime minister Ariel Sharon agreed to take definitive steps to de-escalate the hostilities. They also reaffirmed their commitment to the "roadmap for peace" that had been proposed by the Quartet on the Middle East in 2003. Additionally, Sharon agreed to release 900 Palestinian prisoners and further stated that Israeli troops would withdraw from those parts of the West Bank that they had re-occupied while fighting Palestinian militants during the uprising.
Etymology
Second Intifada refers to a second Palestinian uprising, following the first Palestinian uprising, which occurred between December 1987 and 1993. "Intifada" (انتفاضة) translates into English as "uprising". Its root is an Arabic word meaning "the shaking off". It has been used in the meaning of "insurrection" in various Arab countries; the Egyptian riots of 1977, for example, were called the "bread intifada". The term refers to a revolt against the Israeli occupation of the Palestinian territories.
Al-Aqsa Intifada refers to Al-Aqsa, the main name for the mosque compound constructed in the 8th century CE atop the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, and also known to Muslims as the Haram al-Sharif.
The Intifada is sometimes called the Oslo War (מלחמת אוסלו) by some Israelis who consider it to be the result of concessions made by Israel following the Oslo Accords, and Arafat's War, after the late Palestinian leader whom some blamed for starting it. Others have named what they consider disproportionate response to what was initially a popular uprising by unarmed demonstrators as the reason for the escalation of the Intifada into an all-out war.
Background
See also: Palestinian political violence and Israeli-occupied territoriesOslo Accords
Under the Oslo Accords, signed in 1993 and 1995, Israel committed to the phased withdrawal of its forces from parts of the Gaza Strip and West Bank, and affirmed the Palestinian right to self-government within those areas through the creation of a Palestinian Authority. For their part, the Palestine Liberation Organization formally recognised Israel and committed to adopting responsibility for internal security in population centres in the areas evacuated. Palestinian self-rule was to last for a five-year interim period during which a permanent agreement would be negotiated. However, the realities on the ground left both sides deeply disappointed with the Oslo process. Palestinian freedom of movement reportedly worsened from 1993 to 2000. Israelis and Palestinians have blamed each other for the failure of the Oslo peace process. In the five years immediately following the signing of the Oslo accords, 405 Palestinians and 256 Israelis were killed.
From 1996 Israel made extensive contingency plans and preparations, collectively code-named "Musical Charm", in the eventuality that peace talks might fail. In 1998, after concluding that the 5-year plan stipulated in the Oslo Talks would not be completed, the IDF implemented an Operation Field of Thorns plan to conquer towns in Area C, and some areas of Gaza, and military exercises at regimental level were carried out in April 2000 to that end. Palestinian preparations were defensive, and small-scale, more to reassure the local population than to cope with an eventual attack from Israel. The intensity of these operations led one Brigadier General, Zvi Fogel to wonder whether Israel's military preparations would not turn out to be a self-fulfilling prophecy.
In 1995, Shimon Peres took the place of Yitzhak Rabin, who had been assassinated by Yigal Amir, a Jewish extremist opposed to the Oslo peace agreement. In the 1996 elections, Israelis elected a right-wing coalition led by the Likud candidate, Benjamin Netanyahu who was followed in 1999 by the Labor Party leader Ehud Barak.
Camp David Summit
From 11 to 25 July 2000, the Middle East Peace Summit at Camp David was held between the United States President Bill Clinton, Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak, and Palestinian Authority Chairman Yasser Arafat. The talks ultimately failed with each side blaming the other. There were five principal obstacles to agreement: borders and territorial contiguity, Jerusalem and the Temple Mount, Palestinian refugees and their right of return, Israeli security concerns and Israeli settlements. Disappointment at the situation over the summer led to a significant fracturing of the PLO as many Fatah factions abandoned it to join Hamas and Islamic Jihad.
On 13 September 2000, Yasser Arafat and the Palestinian Legislative Council postponed the planned unilateral declaration of an independent Palestinian state.
Israeli settlements
While Peres had limited settlement construction at the request of US Secretary of State, Madeleine Albright, Netanyahu continued construction within existing Israeli settlements and put forward plans for the construction of a new neighbourhood, Har Homa, in East Jerusalem. However, he fell far short of the Shamir government's 1991–92 level and refrained from building new settlements, although the Oslo agreements stipulated no such ban. Construction of housing units before Oslo, 1991–92: 13,960; after Oslo, 1994–95: 3,840; 1996–1997: 3,570.
With the aim of marginalising the settlers' more militant wing, Barak courted moderate settler opinion, securing agreement for the dismantlement of 12 new outposts that had been constructed since the Wye River Agreement of November 1998, but the continued expansion of existing settlements with plans for 3,000 new houses in the West Bank drew strong condemnation from the Palestinian leadership. Though construction within existing settlements was permitted under the Oslo agreements, Palestinian supporters contend that any continued construction was contrary to its spirit, prejudiced the outcome of final status negotiations, and undermined Palestinian confidence in Barak's desire for peace.
Timeline
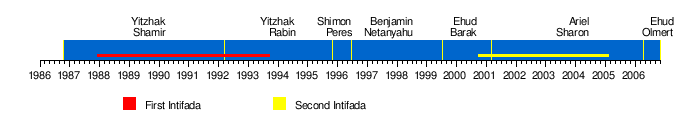
2000

The Middle East Peace Summit at Camp David, from 11 to 25 July 2000, took place between the United States President Bill Clinton, Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak, and Palestinian Authority Chairman Yasser Arafat. It failed with the latter two blaming each other for the failure of the talks. There were four principal obstacles to agreement: territory, Jerusalem and the Temple Mount, Palestinian refugees and the right of return, and Israeli security concerns.
Ariel Sharon visits the Temple Mount
On 28 September, Israeli opposition leader Ariel Sharon and a Likud party delegation guarded by hundreds of Israeli riot police visited the Temple Mount, which is widely considered the third holiest site in Islam. Israel has claimed sovereignty over the Mount and the rest of East Jerusalem since 1980, and the compound is the holiest site in Judaism.
The Israeli Interior Minister Shlomo Ben-Ami, who permitted Sharon's visit, later claimed that he had telephoned the Palestinian Authority's security chief Jibril Rajoub before the visit and gotten his reassurances that as long as Sharon didn't enter the mosques his visit wouldn't cause any problems. Rajoub vociferously denied having given any such reassurances.
Shortly after Sharon left the site, angry demonstrations by Palestinian Jerusalemites outside erupted into rioting. The person in charge of the waqf at the time, Abu Qteish, was later indicted by Israel for using a loud-speaker to call on Palestinians to defend Al-Aqsa, which action Israeli authorities claimed was responsible for the subsequent stone-throwing in the direction of the Wailing Wall. Israeli police responded with tear gas and rubber bullets, while protesters hurled stones and other projectiles, injuring 25 policemen, of whom one was seriously injured and had to be taken to hospital. At least three Palestinians were wounded by rubber bullets.
The stated purpose for Sharon's visit of the compound was to assert the right of all Israelis to visit the Temple Mount; however, according to Likud spokesman Ofir Akunis, the actual purpose was to "show that under a Likud government will remain under Israeli sovereignty." Ehud Barak in the Camp David negotiations had insisted that East Jerusalem, where the Haram was located, would remain under complete Israeli sovereignty. In response to accusations by Ariel Sharon of government readiness to concede the site to the Palestinians, the Israeli government gave Sharon permission to visit the area. When alerted of his intentions, senior Palestinian figures, such as Yasser Arafat, Saeb Erekat, and Faisal Husseini, all asked Sharon to call off his visit.
Ten days earlier the Palestinians had observed their annual memorial day for the Sabra and Shatila massacre, where thousands of Lebanese and Palestinian Muslims were massacred by Lebanese Forces supported by the Israeli military. The Israeli Kahan Commission had concluded that Ariel Sharon, who was the Israeli Defense Minister during the Sabra and Shatila massacre, was found to bear personal responsibility "for ignoring the danger of bloodshed and revenge" and "not taking appropriate measures to prevent bloodshed." Sharon's negligence in protecting the civilian population of Beirut, which had come under Israeli control, amounted to a non-fulfillment of a duty with which the Defence Minister was charged, and it was recommended that Sharon be dismissed as Defence Minister. Sharon initially refused to resign, but after the death of an Israeli after a peace march, Sharon did resign as Defense minister, but remained in the Israeli cabinet.
The Palestinians condemned Sharon's visit to the Temple Mount as a provocation and an incursion, as were his armed bodyguards that arrived on the scene with him. Critics claim that Sharon knew that the visit could trigger violence, and that the purpose of his visit was political. According to one observer, Sharon, in walking on the Temple Mount, was "skating on the thinnest ice in the Arab-Israeli conflict."
According to The New York Times, many in the Arab world, including Egyptians, Palestinians, Lebanese and Jordanians, point to Sharon's visit as the beginning of the Second Intifada and derailment of the peace process. According to Juliana Ochs, Sharon's visit 'symbolically instigated' the second intifada. Marwan Barghouti said that although Sharon's provocative actions were a rallying point for Palestinians, the Second Intifada would have erupted even had he not visited the Temple Mount.
Post-visit Palestinian riots
On 29 September 2000, the day after Sharon's visit, following Friday prayers, large riots broke out around the Old City of Jerusalem. Israeli police fired at Palestinians at the Temple Mount throwing stones over the Western Wall at Jewish worshippers. After the chief of Jerusalem's police force was knocked unconscious by a stone, they switched to live ammunition and killed four Palestinian youths. Up to 200 Palestinians and police were injured. Another three Palestinians were killed in the Old City and on the Mount of Olives. By the end of the day, seven Palestinians had been killed and 300 had been wounded; 70 Israeli policemen were also injured in the clashes.
In the days that followed, demonstrations erupted all over the West Bank and Gaza. Israeli police responded with live fire and rubber-coated bullets. In the first five days, at least 47 Palestinians were killed, and 1,885 were wounded. In Paris, as Jacques Chirac attempted to mediate between the parties, he protested to Barak that the ratio of Palestinians and Israelis killed and wounded on one day were such that he could not convince anyone the Palestinians were the aggressors. He also told Barak that "continu(ing) to fire from helicopters on people throwing rocks" and refusing an international inquiry was tantamount to rejecting Arafat's offer to participate in trilateral negotiations. During the first few days of riots, the IDF fired approximately 1.3 million bullets.
According to Amnesty International the early Palestinian casualties were those taking part in demonstrations or bystanders. Amnesty further states that approximately 80% of the Palestinians killed during the first month were in demonstrations where Israeli security services lives were not in danger.
On 30 September 2000, the death of Muhammad al-Durrah, a Palestinian boy shot dead while sheltering behind his father in an alley in the Gaza Strip, was caught on video. Initially the boy's death and his father's wounding was attributed to Israeli soldiers. The scene assumed iconic status, as it was shown around the world and repeatedly broadcast on Arab television. The Israeli army initially assumed responsibility for the killing and apologised, and only retracted 2 months later, when an internal investigation cast doubt on the original version, and controversy subsequently raged as to whether indeed the IDF had fired the shots or Palestinian factions were responsible for the fatal gunshots.
October 2000 events

The "October 2000 events" refers to several days of disturbances and clashes within Israel, mostly between Arab citizens and the Israel police, as well as large-scale rioting by both Arabs and Jews. Twelve Arab citizens of Israel and a Palestinian from the Gaza Strip were killed by Israeli police, while an Israeli Jew was killed when his car was hit by a rock on the Tel-Aviv-Haifa freeway. During the first month of the Intifada, 141 Palestinians were killed and 5,984 were wounded, while 12 Israelis were killed and 65 wounded.
A general strike and demonstrations across northern Israel began on 1 October and continued for several days. In some cases, the demonstrations escalated into clashes with the Israeli police involving rock-throwing, firebombing, and live-fire. Policemen used tear-gas and opened fire with rubber-coated bullets and later live ammunition in some instances, many times in contravention of police protocol governing riot-dispersion. This use of live ammunition was directly linked with many of the deaths by the Or Commission.
On 8 October, thousands of Jewish Israelis participated in violent acts in Tel Aviv and elsewhere, some throwing stones at Arabs, destroying Arab property and chanting "Death to the Arabs."
Following the riots, a high degree of tension between Jewish and Arab citizens and distrust between the Arab citizens and police were widespread. An investigation committee, headed by Supreme Court Justice Theodor Or, reviewed the violent riots and found that the police were poorly prepared to handle such riots and charged major officers with bad conduct. The Or Commission reprimanded Prime Minister Ehud Barak and recommended Shlomo Ben-Ami, then the Internal Security Minister, not serve again as Minister of Public Security. The committee also blamed Arab leaders and Knesset members for contributing to inflaming the atmosphere and making the violence more severe.
Ramallah lynching and Israeli response
Main article: 2000 Ramallah lynchingOn 12 October, PA police arrested two Israeli reservists who had accidentally entered Ramallah, where in the preceding weeks a hundred Palestinians had been killed, nearly two dozen of them minors. Rumours quickly spread that Israeli undercover agents were in the building, and an angry crowd of more than 1,000 Palestinians gathered in front of the station calling for their death. Both soldiers were beaten, stabbed, and disembowelled, and one body was set on fire. An Italian television crew captured the killings on video and then broadcast the tape internationally. A British journalist had his camera destroyed by rioters as he attempted to take a picture. The brutality of the killings shocked the Israeli public, who saw it as proof of a deep-seated Palestinian hatred of Israel and Jews. In response, Israel launched a series of retaliatory air-strikes against Palestinian Authority targets in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The police station where the lynching had taken place was evacuated and destroyed in these operations. Israel later tracked down and arrested those responsible for killing the soldiers.
November–December 2000
Clashes between Israeli forces and Palestinians increased sharply on 1 November, when three Israeli soldiers and six Palestinians were killed, and four IDF soldiers and 140 Palestinians were wounded. In subsequent days, casualties increased as the IDF attempted to restore order, with clashes occurring every day in November. A total of 122 Palestinians and 22 Israelis were killed. On 27 November, the first day of Ramadan, Israel eased restrictions on the passage of goods and fuel through the Karni crossing. That same day, the Jerusalem settlement of Gilo came under Palestinian heavy machine gun fire from Beit Jala. Israel tightened restrictions a week later, and Palestinians continued to clash with the IDF and Israeli settlers, with a total of 51 Palestinians and 8 Israelis killed in December. In a last attempt by the Clinton administration to achieve a peace deal between Israelis and Palestinians, a summit was planned in Sharm el-Sheikh in December. However, Israeli Prime Minister Barak decided not to attend after the Palestinians delayed their acceptance of the Clinton Parameters.
2001
The Taba Summit between Israel and the Palestinian Authority was held from 21 to 27 January 2001, at Taba in the Sinai peninsula. Israeli prime minister Ehud Barak and Palestinian President Yasser Arafat came closer to reaching a final settlement than any previous or subsequent peace talks yet ultimately failed to achieve their goals.
On 17 January 2001, Israeli teenager Ofir Rahum was murdered after being lured into Ramallah by a 24-year-old Palestinian, Mona Jaud Awana, a member of Fatah's Tanzim. She had contacted Ofir on the internet and engaged in an online romance with him for several months. She eventually convinced him to drive to Ramallah to meet her, where he was instead ambushed by three Palestinian gunmen and shot over fifteen times. Awana was later arrested in a massive military and police operation, and imprisoned for life. Five other Israelis were killed in January, along with eighteen Palestinians.
Ariel Sharon, at the time from the Likud party, ran against Ehud Barak from the Labor party. Sharon was elected Israeli Prime Minister 6 February 2001 in the 2001 special election to the Prime Ministership. Sharon refused to meet in person with Yasser Arafat.
Violence in March resulted in the deaths of 8 Israelis, mostly civilians, and 26 Palestinians. In Hebron, a Palestinian sniper killed ten-month-old Israeli baby Shalhevet Pass. The murder shocked the Israeli public. According to the Israel police investigation the sniper aimed deliberately at the baby.
On 30 April 2001, seven Palestinian militants were killed in an explosion, one of them a participant in Ofir Rahum's murder. The IDF refused to confirm or deny Palestinian accusations that it was responsible.
On 7 May 2001, IDF naval commandos captured the vessel Santorini, which was sailing in international waters towards Palestinian Authority-controlled Gaza. The ship was laden with weaponry. The Israeli investigation that followed said that the shipment had been purchased by Ahmed Jibril's Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine - General Command (PFLP-GC). The ship's value and that of its cargo was estimated at $10 million. The crew was reportedly planning to unload the cargo of weapons-filled barrels—carefully sealed and waterproofed along with their contents—at a prearranged location off the Gaza coast, where the Palestinian Authority would recover it.
On 8 May 2001, two Israeli teenagers, Yaakov "Koby" Mandell (13) and Yosef Ishran (14), were kidnapped while hiking near their village. Their bodies were discovered the next morning in a cave near where they lived. USA Today reported that, according to the police, both boys had "been bound, stabbed and beaten to death with rocks." The newspaper continued, "The walls of the cave in the Judean Desert were covered with the boys' blood, reportedly smeared there by the killers."
After a suicide bombing struck Netanya on 18 May 2001, Israel for the first time since 1967 used warplanes to attack Palestinian Authority targets in the West Bank and Gaza, killing 12 Palestinians. In the past, airstrikes had been carried out with helicopter gunships.

On 1 June 2001, an Islamic Jihad suicide bomber detonated himself in the Tel Aviv coastline Dolphinarium dancing club. Twenty-one Israeli civilians, most of them high school students, were killed and 132 injured. The attack significantly hampered American attempts to negotiate a cease-fire.
The 12 June Murder of Georgios Tsibouktzakis by Palestinian snipers was later tied to Marwan Barghouti.
A total of 469 Palestinians and 199 Israelis were killed in 2001. Amnesty International's report on the first year of the Intifada states:
The overwhelming majority of cases of unlawful killings and injuries in Israel and the Occupied Territories have been committed by the IDF using excessive force. In particular, the IDF have used US-supplied helicopters in punitive rocket attacks where there was no imminent danger to life. Israel has also used helicopter gunships to carry out extrajudicial executions and to fire at targets that resulted in the killing of civilians, including children. ... Hamas and Islamic Jihad have frequently placed bombs in public places, usually within Israel, in order to kill and maim large numbers of Israeli civilians in a random manner. Both organizations have fostered a cult of martyrdom and frequently use suicide bombers.
Palestinian terrorists committed a number of suicide attacks later in 2001, among them the Sbarro restaurant massacre, with 15 civilian casualties (including 7 children); the Nahariya train station suicide bombing and the Pardes Hanna bus bombing, both with 3 civilian casualties; the Ben Yehuda Street bombing with 11 civilian deaths, many of them children; and the Haifa bus 16 suicide bombing, with 15 civilian casualties.
2002

In January 2002, the IDF Shayetet 13 naval commandos captured the Karine A, a freighter carrying weapons from Iran towards Israel, believed to be intended for Palestinian militant use against Israel. It was discovered that top officials in the Palestinian Authority were involved in the smuggling, with the Israelis pointing the finger towards Yasser Arafat as also being involved.
Palestinians launched a spate of suicide bombings and attacks against Israel, aimed mostly at civilians. On 3 March, a Palestinian sniper killed 10 Israeli soldiers and settlers and wounded 4 at a checkpoint near Ofra, using an M1 Carbine. He was later arrested and sentenced to life imprisonment. The rate of the attacks increased, and was at its highest in March 2002.
In addition to numerous shooting and grenade attacks, the month saw 15 suicide bombings carried out in Israel — an average of one bombing every two days. The high rate of attacks caused widespread fear throughout Israel and serious disruption of daily life throughout the country. March 2002 became known in Israel as "Black March". On 12 March United Nations Security Council Resolution 1397 was passed, which reaffirmed a Two-state solution and laid the groundwork for a Road map for peace.
On 27 March, the wave of violence culminated with a suicide bombing during a Passover celebration at the Park Hotel in Netanya in which 30 people were killed. The attack became known as the Passover massacre. In total, around 130 Israelis, mostly civilians, were killed in Palestinian attacks during March 2002. On 28 March, Arab leaders, whose constituencies were exposed to detailed television coverage of the violence in the conflict, set out a comprehensive Arab Peace Initiative that was endorsed by Arafat, but virtually ignored by Israel.
On 29 March, Israel launched Operation Defensive Shield, which lasted until 3 May. The IDF made sweeping incursions throughout the West Bank, and into numerous Palestinian cities. Arafat was put under siege in his Ramallah compound. The UN estimated that 497 Palestinians were killed and 1,447 wounded by the Israeli incursion from 1 March to 7 May. A UN report cleared Israel of allegations of massacre, but criticized it for using excessive force on the civilian population. Israeli forces also arrested 4,258 Palestinians during the operation. Israeli casualties during the operation totaled 30 dead and 127 wounded. The operation culminated with the recapturing of Palestinian Authority controlled areas.
Battle of Jenin
Main article: Battle of Jenin (2002)
Between 2 and 11 April, a siege and fierce fighting took place in the Palestinian refugee camp of the city of Jenin. The camp was targeted during Operation Defensive Shield after Israel determined that it had "served as a launch site for numerous terrorist attacks against both Israeli civilians and Israeli towns and villages in the area." The Jenin battle became a flashpoint for both sides, and saw fierce urban combat as Israeli infantry supported by armor and attack helicopters fought to clear the camp of Palestinian militants. The battle was eventually won by the IDF, after it employed a dozen Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozers to clear Palestinian booby traps, detonate explosive charges, and raze buildings and gun-posts; the bulldozers proved impervious to attacks by Palestinian militants.
During Israeli military operations in the camp, Palestinian sources alleged that a massacre of hundreds of people had taken place. A senior Palestinian Authority official said in mid-April that some 500 had been killed. During the fighting in Jenin, Israeli officials had also initially estimated hundreds of Palestinian deaths, but later said they expected the Palestinian toll to reach "45 to 55." In the ensuing controversy, Israel blocked the United Nations from conducting the first-hand inquiry unanimously sought by the Security Council, but the UN nonetheless felt able to dismiss claims of a massacre in its report, which said there had been approximately 52 deaths, criticising both sides for placing Palestinian civilians at risk. Based on their own investigations, Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch charged that some IDF personnel in Jenin had committed war crimes but also confirmed that no massacre had been committed by the IDF. Both human rights organizations called for official inquiries; the IDF disputed the charges.
After the battle, most sources, including the IDF and Palestinian Authority, placed the Palestinian death toll at 52–56; Human Rights Watch documented 52 Palestinian deaths and claimed that it included at least 27 militants and 22 civilians, and an additional 3 Palestinians whose status as militants or civilians could not be ascertained, while the IDF said that 48 militants and 5 civilians had been killed. According to Human Rights Watch, 140 buildings had been destroyed. The IDF reported that 23 Israeli soldiers had been killed and 75 wounded during the battle.
Siege in Bethlehem
Main article: Siege of the Church of the Nativity in BethlehemFrom 2 April to 10 May, a stand-off developed at the Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem. IDF soldiers surrounded the church while Palestinian civilians, militants, and priests were inside. During the siege, IDF snipers killed 8 militants inside the church and wounded more than 40 people. The stand-off was resolved by the deportation to Europe of 13 Palestinian militants whom the IDF had identified as terrorists, and the IDF ended its 38-day stand-off with the militants inside the church.
2003

Following an Israeli intelligence report stating that Yasir Arafat had paid $20,000 to al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades, the United States demanded democratic reforms in the Palestinian Authority, as well the appointment of a prime minister independent of Arafat. On 13 March 2003, following U.S. pressure, Arafat appointed Mahmoud Abbas as Palestinian prime minister.
Following the appointment of Abbas, the U.S. administration promoted the Road map for peace—the Quartet's plan to end the Israeli–Palestinian conflict by disbanding militant organizations, halting settlement activity and establishing a democratic and peaceful Palestinian state. The first phase of the plan demanded that the Palestinian Authority suppress guerrilla and terrorist attacks and confiscate illegal weapons. Unable or unwilling to confront militant organizations and risk civil war, Abbas tried to reach a temporary cease-fire agreement with the militant factions and asked them to halt attacks on Israeli civilians.
On 20 May, Israeli naval commandos intercepted another vessel, the Abu Hassan, on course to the Gaza Strip from Lebanon. It was loaded with rockets, weapons, and ammunition. Eight crew members on board were arrested including a senior Hezbollah member.
On 29 June 2003, a temporary armistice was unilaterally declared by Fatah, Hamas and Islamic Jihad, which declared a ceasefire and halt to all attacks against Israel for a period of three months. Violence decreased somewhat in the following month, but suicide bombings against Israeli civilians continued as well as Israeli operations against militants.
Four Palestinians, three of them militants, were killed in gun battles during an IDF raid of Askar near Nablus involving tanks and armoured personnel carriers (APCs); an Israeli soldier was killed by one of the militants. Nearby Palestinians claimed a squad of Israeli police disguised as Palestinian labourers opened fire on Abbedullah Qawasameh as he left a Hebron mosque. YAMAM, the Israeli counter-terrorism police unit that performed the operation, said Qawasemah opened fire on them as they attempted to arrest him.
On 19 August, Hamas coordinated a suicide attack on a crowded bus in Jerusalem killing 23 Israeli civilians, including 7 children. Hamas claimed it was a retaliation for the killing of five Palestinians (including Hamas leader Abbedullah Qawasameh) earlier in the week. U.S. and Israeli media outlets frequently referred to the bus bombing as shattering the quiet and bringing an end to the ceasefire.
Following the Hamas bus attack, Israeli Defence Forces were ordered to kill or capture all Hamas leaders in Hebron and the Gaza Strip. The plotters of the bus suicide bombing were all captured or killed and Hamas leadership in Hebron was badly damaged by the IDF. Strict curfews were enforced in Nablus, Jenin, and Tulkarem; the Nablus lockdown lasted for over 100 days. In Nazlet 'Issa, over 60 shops were destroyed by Israeli civil administration bulldozers. The Israeli civil administration explained that the shops were demolished because they were built without a permit. Palestinians consider Israeli military curfews and property destruction to constitute collective punishment against innocent Palestinians.

Unable to rule effectively under Arafat, Abbas resigned in September 2003. Ahmed Qurei (Abu Ala) was appointed to replace him. The Israeli government gave up hope for negotiated settlement to the conflict and pursued a unilateral policy of physically separating Israel from Palestinian communities by beginning construction on the Israeli West Bank barrier. Israel claims the barrier is necessary to prevent Palestinian attackers from entering Israeli cities. Palestinians claim the barrier separates Palestinian communities from each other and that the construction plan is a de facto annexation of Palestinian territory.
Following a 4 October suicide bombing in Maxim restaurant, Haifa, which claimed the lives of 21 Israelis, Israel claimed that Syria and Iran sponsored the Islamic Jihad and Hezbollah, and were responsible for the terrorist attack. The day after the Maxim massacre, IAF warplanes bombed an alleged former Palestinian training base at Ain Saheb, Syria, which had been mostly abandoned since the 1980s. Munitions being stored on the site were destroyed, and a civilian guard was injured.
2004
In response to repeated shelling of Israeli communities with Qassam rockets and mortar shells from Gaza, the IDF operated mainly in Rafah – to search and destroy smuggling tunnels used by militants to obtain weapons, ammunition, fugitives, cigarettes, car parts, electrical goods, foreign currency, gold, drugs, and cloth from Egypt. Between September 2000 and May 2004, ninety tunnels connecting Egypt and the Gaza Strip were found and destroyed. Raids in Rafah left many families homeless. Israel's official stance is that their houses were captured by militants and were destroyed during battles with IDF forces. Many of these houses are abandoned due to Israeli incursions and later destroyed. According to Human Rights Watch, over 1,500 houses were destroyed to create a large buffer zone in the city, many "in the absence of military necessity", displacing around sixteen thousand people.
On 2 February 2004, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon announced his plan to transfer all the Jewish settlers from the Gaza Strip. The Israeli opposition dismissed his announcement as "media spin", but the Israeli Labour Party said it would support such a move. Sharon's right-wing coalition partners National Religious Party and National Union rejected the plan and vowed to quit the government if it were implemented. Yossi Beilin, peace advocate and architect of the Oslo Accords and the Geneva Accord, also rejected the proposed withdrawal plan. He claimed that withdrawing from the Gaza Strip without a peace agreement would reward terror.
Following the declaration of the disengagement plan by Ariel Sharon and as a response to suicide attacks on Erez crossing and Ashdod seaport (10 people were killed), the IDF launched a series of armored raids on the Gaza Strip (mainly Rafah and refugee camps around Gaza), killing about 70 Hamas militants. On 22 March 2004, an Israeli helicopter gunship killed Hamas leader Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, along with his two bodyguards and nine bystanders. On 17 April, after several failed attempts by Hamas to commit suicide bombings and a successful one that killed an Israeli policeman, Yassin's successor, Abdel Aziz al-Rantissi, was killed in an almost identical way, along with a bodyguard and his son Mohammed.
The fighting in Gaza Strip escalated severely in May 2004 after several failed attempts to attack Israeli checkpoints such as Erez crossing and Karni crossing. On 2 May, Palestinian militants attacked and shot dead a pregnant woman and her four young daughters. Amnesty International classified it as a crime against humanity and said it "reiterates its call on all Palestinian armed groups to put an immediate end to the deliberate targeting of Israeli civilians, in Israel and in the Occupied Territories". Additionally, on 11 and 12 May, Palestinian militants destroyed two IDF M-113 APCs, killing 13 soldiers and mutilating their bodies. The IDF launched two raids to recover the bodies, killing 20–40 Palestinians and greatly damaging structures in the Zaitoun neighbourhood in Gaza and in south-west Rafah.

Subsequently, on 18 May the IDF launched Operation Rainbow with a stated aim of striking the militant infrastructure of Rafah, destroying smuggling tunnels, and stopping a shipment of SA-7 missiles and improved anti-tank weapons. A total of 41 Palestinian militants and 12 civilians were killed in the operation, and about 45–56 Palestinian structures were demolished. Israeli tanks shelled hundreds of Palestinian protesters approaching their positions, killing 10. The protesters had disregarded Israeli warnings to turn back. This incident led to a worldwide outcry against the operation.
On 29 September, after a Qassam rocket hit the Israeli town of Sderot and killed two Israeli children, the IDF launched Operation Days of Penitence in the north of the Gaza Strip. The operation's stated aim was to remove the threat of Qassam rockets from Sderot and kill the Hamas militants launching them. The operation ended on 16 October, after having caused widespread destruction and the deaths of over 100 Palestinians, at least 20 of whom were under the age of sixteen. The IDF killed thirteen-year-old Iman Darweesh Al Hams as she strayed into a closed military area; the commander was accused of allegedly firing his automatic weapon at her dead body deliberately to verify the death. The act was investigated by the IDF, but the commander was cleared of all wrongdoing, and more recently, was fully vindicated when a Jerusalem district court found the claim to be libellous, ruled that NIS 300,000 be paid by the journalist and TV company responsible for the report, an additional NIS 80,000 to be paid in legal fees and required the journalist and television company to air a correction. According to Palestinian medics, Israeli forces killed at least 62 militants and 42 other Palestinians believed to be civilians. According to a count performed by Haaretz, 87 militants and 42 civilians were killed. Palestinian refugee camps were heavily damaged by the Israeli assault. The IDF announced that at least 12 Qassam launchings had been thwarted and many militants hit during the operation.
On 21 October, the Israeli Air Force killed Adnan al-Ghoul, a senior Hamas bomb maker and the inventor of the Qassam rocket.
On 11 November, Yasser Arafat died in Paris.
Escalation in Gaza began amid the visit of Mahmoud Abbas to Syria in order to achieve a Hudna between Palestinian factions and convince Hamas leadership to halt attacks against Israelis. Hamas vowed to continue the armed struggle, sending numerous Qassam rockets into open fields near Nahal Oz, and hitting a kindergarten in Kfar Darom with an anti-tank missile.
On 9 December five Palestinians weapon smugglers were killed and two were arrested in the border between Rafah and Egypt. Later that day, Jamal Abu Samhadana and two of his bodyguards were injured by a missile strike. In the first Israeli airstrike against militants in weeks, an unmanned Israeli drone plane launched one missile at Abu Samahdna's car as it travelled between Rafah and Khan Younis in the southern Gaza Strip. It was the fourth attempt on Samhadana's life by Israel. Samhadana is one of two leaders of the Popular Resistance Committees and one of the main forces behind the smuggling tunnels. Samhadana is believed to be responsible for the blast against an American diplomatic convoy in Gaza that killed three Americans.
On 10 December, in response to Hamas firing mortar rounds into the Neveh Dekalim settlement in the Gaza Strip and wounding four Israelis (including an 8-year-old boy), Israeli soldiers fired at the Khan Younis refugee camp (the origin of the mortars) killing a seven-year-old girl. An IDF source confirmed troops opened fire at Khan Younis, but said they aimed at Hamas mortar crews.
The largest attack since the death of Yasser Arafat claimed the lives of five Israeli soldiers on 12 December, wounding ten others. Approximately 1.5 tons of explosives were detonated in a tunnel under an Israeli military-controlled border crossing on the Egyptian border with Gaza near Rafah, collapsing several structures and damaging others. The explosion destroyed part of the outpost and killed three soldiers. Two Palestinian militants then penetrated the outpost and killed two other Israeli soldiers with gunfire. It is believed that Hamas and a new Fatah faction, the "Fatah Hawks", conducted the highly organised and coordinated attack. A spokesman, "Abu Majad", claimed responsibility for the attack in the name of the Fatah Hawks claiming it was in retaliation for "the assassination" of Yasser Arafat, charging he was poisoned by Israel.
2005
Palestinian presidential elections were held on 9 January, and Mahmoud Abbas (Abu Mazen) was elected as the president of the PA. His platform was of a peaceful negotiation with Israel and non-violence to achieve Palestinian objectives. Although Abbas called on militants to halt attacks against Israel, he promised them protection from Israeli incursions and did not advocate disarmament by force.
Violence continued in the Gaza Strip, and Ariel Sharon froze all diplomatic and security contacts with the Palestinian National Authority. Spokesman Assaf Shariv declared that "Israel informed international leaders today that there will be no meetings with Abbas until he makes a real effort to stop the terror." The freezing of contacts came less than one week after Mahmoud Abbas was elected, and the day before his inauguration. Palestinian negotiator Saeb Erekat, confirming the news, declared "You cannot hold Mahmoud Abbas accountable when he hasn't even been inaugurated yet."

Following international pressure and Israeli threat of wide military operation in the Gaza Strip, Abbas ordered Palestinian police to deploy in the northern Gaza Strip to prevent Qassam rocket and mortar shelling over Israeli settlement. Although attacks on Israelis did not stop completely, they decreased sharply. On 8 February 2005, at the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005, Sharon and Abbas declared a mutual truce between Israel and the Palestinian National Authority. They shook hands at a four-way summit that also included Jordan and Egypt at Sharm al-Sheikh. However, Hamas and Islamic Jihad said the truce is not binding for their members. Israel has not withdrawn its demand to dismantle terrorist infrastructure before moving ahead in the Road map for peace.
Many warned that truce is fragile, and progress must be done slowly while observing that the truce and quiet are kept. On 9–10 February night, a barrage of 25–50 Qassam rockets and mortar shells hit Neve Dekalim settlement, and another barrage hit at noon. Hamas said it was in retaliation for an attack in which one Palestinian was killed near an Israeli settlement. As a response to the mortar attack, Abbas ordered the Palestinian security forces to stop such attacks in the future. He also fired senior commanders in the Palestinian security apparatus. On 10 February, Israeli security forces arrested Maharan Omar Shucat Abu Hamis, a Palestinian resident of Nablus, who was about to launch a bus suicide attack in the French Hill in Jerusalem.
On 13 February 2005, Abbas entered into talks with the leaders of the Islamic Jihad and the Hamas, for them to rally behind him and respect the truce. Ismail Haniyah, a senior leader of the group Hamas said that "its position regarding calm will continue unchanged and Israel will bear responsibility for any new violation or aggression."
In the middle of June, Palestinian factions intensified bombardment over the city of Sderot with improvised Qassam rockets. Palestinian attacks resulted in 2 Palestinians and 1 Chinese civilian killed by a Qassam, and 2 Israelis were killed. The wave of attacks lessened support for the disengagement plan among the Israeli public. Attacks on Israel by the Islamic Jihad and the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades increased in July, and on 12 July, a suicide bombing hit the coastal city of Netanya, killing 5 civilians. On 14 July, Hamas started to shell Israeli settlements inside and outside the Gaza Strip with dozens of Qassam rockets, killing an Israeli woman. On 15 July, Israel resumed its "targeted killing" policy, killing 7 Hamas militants and bombing about 4 Hamas facilities. The continuation of shelling rockets over Israeli settlements, and street battles between Hamas militants and Palestinian policemen, threatened to shatter the truce agreed in the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005. The Israeli Defence Force also started to build up armored forces around the Gaza Strip in response to the shelling.
End of the Second Intifada
The ending date of the Second Intifada is disputed, as there was no definite event that brought it to an end. The general view is that it ended in 2005, while some sources include events and statistics extending as late as 2007.
- Some commentators, such as Sever Plocker, consider the intifada to have ended in late 2004. With the sickness and then death of Yasser Arafat in November 2004, the Palestinians lost their internationally recognised leader of the previous three decades, after which the intifada lost momentum and led to internal fighting between Palestinian factions (most notably the Fatah–Hamas conflict), as well as conflict within Fatah itself.
- Israel's unilateral disengagement from the Gaza Strip, announced in June 2004 and completed in August 2005, is also cited as signalling the end of the intifada, for instance by Ramzy Baroud.
- Some consider 8 February 2005 to be the official end of the Second Intifada, although sporadic violence still continued outside PA control or condonation. On that day, Abbas and Sharon met at the Sharm el-Sheikh Summit, where they vowed to end attacks on each other. In addition, Sharon agreed to release 900 Palestinian prisoners and withdraw from West Bank towns. Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ) refused to be parties to the agreement, arguing the cease-fire was the position of the PA only. Five days later Abbas reached agreement with the two dissenting organizations to commit to the truce with the proviso that Israeli violation would be met with retaliation.
Schachter addressed the difficulties in deciding when the Second Intifada ended. He reasoned that suicide bombing was the best criterion, being arguably the most important element of the violence involved, and that according to this criterion the intifada ended during 2005.
Trigger for the uprising
The Second Intifada started on 28 September 2000, after Ariel Sharon, a Likud party candidate for Israeli Prime Minister, made a visit to the Temple Mount, also known as Al-Haram Al-Sharif, an area sacred to both Jews and Muslims, accompanied by over 1,000 security guards. He stated on that day, "the Temple Mount is in our hands and will remain in our hands. It is the holiest site in Judaism and it is the right of every Jew to visit the Temple Mount."
This visit was seen by Palestinians as highly provocative; and Palestinian demonstrators, throwing stones at police, were dispersed by the Israeli Army, using tear gas and rubber bullets. A riot broke out among Palestinians at the site, resulting in clashes between Israeli forces and the protesting crowd.
Some believe the Intifada started the next day, on Friday, 29 September, a day of prayers, when an Israeli police and military presence was introduced and there were major clashes and deaths.
The Mitchell Report
The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee (an investigatory committee set up to look into the causes behind the breakdown in the peace process, chaired by George J. Mitchell) published its report in May 2001. In the Mitchell Report, the government of Israel asserted that:
The immediate catalyst for the violence was the breakdown of the Camp David negotiations on July 25, 2000, and the "widespread appreciation in the international community of Palestinian responsibility for the impasse". In this view, Palestinian violence was planned by the PA leadership, and was aimed at "provoking and incurring Palestinian casualties as a means of regaining the diplomatic initiative".
The Palestine Liberation Organization, according to the same report, denied that the Intifada was planned, and asserted that "Camp David represented nothing less than an attempt by Israel to extend the force it exercises on the ground to negotiations." The report also stated:
From the perspective of the PLO, Israel responded to the disturbances with excessive and illegal use of deadly force against demonstrators; behavior which, in the PLO's view, reflected Israel's contempt for the lives and safety of Palestinians. For Palestinians, the widely seen images of Muhammad al-Durrah in Gaza on September 30, shot as he huddled behind his father, reinforced that perception.
The Mitchell report concluded:
The Sharon visit did not cause the "Al-Aqsa Intifada". But it was poorly timed and the provocative effect should have been foreseen; indeed it was foreseen by those who urged that the visit be prohibited.
and also:
We have no basis on which to conclude that there was a deliberate plan by the PA to initiate a campaign of violence at the first opportunity; or to conclude that there was a deliberate plan by the to respond with lethal force.
Contributing factors
Palestinians have claimed that Sharon's visit was the beginning of the Second Intifada, while others have claimed that Yasser Arafat had pre-planned the uprising.
Some, like Bill Clinton, say that tensions were high due to failed negotiations at the Camp David Summit in July 2000. They note that there were Israeli casualties as early as 27 September; this is the Israeli "conventional wisdom", according to Jeremy Pressman, and the view expressed by the Israeli Foreign Ministry. Most mainstream media outlets have taken the view that the Sharon visit was the spark that triggered the rioting at the start of the Second Intifada. In the first five days of rioting and clashes after the visit, Israeli police and security forces killed 47 Palestinians and wounded 1885, while Palestinians killed 5 Israelis.
Palestinians view the Second Intifada as part of their ongoing struggle for national liberation and an end to Israeli occupation, whereas many Israelis consider it to be a wave of Palestinian terrorism instigated and pre-planned by then Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat.
Support for the idea that Arafat planned the uprising comes from Hamas leader Mahmoud al-Zahar, who said in September 2010 that when Arafat realized that the Camp David Summit in July 2000 would not result in the meeting of all of his demands, he ordered Hamas as well as Fatah and the Aqsa Martyrs Brigades, to launch "military operations" against Israel. Al-Zahar is corroborated by Mosab Hassan Yousef, son of the Hamas founder and leader, Sheikh Hassan Yousef, who claims that the Second Intifada was a political maneuver premeditated by Arafat. Yousef claims that "Arafat had grown extraordinarily wealthy as the international symbol of victimhood. He wasn't about to surrender that status and take on the responsibility of actually building a functioning society."
David Samuels quoted Mamduh Nofal, former military commander of the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine, who supplied more evidence of pre-28 September military preparations. Nofal recounts that Arafat "told us, Now we are going to the fight, so we must be ready". Barak as early as May had drawn up contingency plans to halt any intifada in its tracks by the extensive use of IDF snipers, a tactic that resulted in the high number of casualties among Palestinians during the first days of rioting.
Arafat's widow Suha Arafat reportedly said on Dubai television in December 2012 that her husband had planned the uprising: "Immediately after the failure of the Camp David , I met him in Paris upon his return.... Camp David had failed, and he said to me, 'You should remain in Paris.' I asked him why, and he said, 'Because I am going to start an intifada. They want me to betray the Palestinian cause. They want me to give up on our principles, and I will not do so,'" the research institute translated Suha as saying.
Israel's unilateral pullout from Lebanon in the summer of 2000 was, according to Philip Mattar, interpreted by the Arabs as an Israeli defeat and had a profound influence on tactics adopted in the Al Aqsa Intifada. PLO official Farouk Kaddoumi told reporters: "We are optimistic. Hezbollah's resistance can be used as an example for other Arabs seeking to regain their rights." Many Palestinian officials have gone on record as saying that the intifada had been planned long in advance to put pressure on Israel. It is disputed however whether Arafat himself gave direct orders for the outbreak, though he did not intervene to put a brake on it A personal advisor to Arafat, Manduh Nufal, claimed in early 2001 that the Palestinian Authority had played a crucial role in the outbreak of the Intifada. Israeli's military response demolished a large part of the infrastructure built by the PA during the years following the Oslo Accords in preparation for a Palestinian state. This infrastructure included the legitimate arming of Palestinian forces for the first time: some 90 paramilitary camps had been set up to train Palestinian youths in armed conflict. Some 40,000 armed and trained Palestinians existed in the occupied territories.
On 29 September 2001 Marwan Barghouti, the leader of the Fatah Tanzim in an interview to Al-Hayat, described his role in the lead up to the intifada.
I knew that the end of September was the last period (of time) before the explosion, but when Sharon reached the al-Aqsa Mosque, this was the most appropriate moment for the outbreak of the intifada.... The night prior to Sharon's visit, I participated in a panel on a local television station and I seized the opportunity to call on the public to go to the al-Aqsa Mosque in the morning, for it was not possible that Sharon would reach al-Haram al-Sharif just so, and walk away peacefully. I finished and went to al-Aqsa in the morning.... We tried to create clashes without success because of the differences of opinion that emerged with others in the al-Aqsa compound at the time.... After Sharon left, I remained for two hours in the presence of other people, we discussed the manner of response and how it was possible to react in all the cities (bilad) and not just in Jerusalem. We contacted all (the Palestinian) factions.
Barghouti also went on record as stating that the example of Hezbollah and Israel's withdrawal from Lebanon was a factor which contributed to the Intifada.
According to Nathan Thrall, from Elliott Abrams's inside accounts of negotiations between 2001 and 2005, it would appear to be an inescapable conclusion that violence played an effective role in shaking Israeli complacency and furthering Palestinian goals: the U.S. endorsed the idea of a Palestinian State, Ariel Sharon became the first Israeli Prime Minister to affirm the same idea, and even spoke of Israel's "occupation", and the bloodshed was such that Sharon also decided to withdraw from Gaza, an area he long imagined Israel keeping. However, Zakaria Zubeidi, former leader of the Al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades, considers the Intifada to be a total failure that achieved nothing for the Palestinians.
Casualties
See also: Category:Second Intifada casualties, Children in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, Israeli casualties of war, and Palestinian casualties of warThe casualty data for the Second Intifada has been reported by a variety of sources and though there is general agreement regarding the overall number of dead, the statistical picture is blurred by disparities in how different types of casualties are counted and categorized.
The sources do not vary widely over the data on Israeli casualties. B'Tselem reports that 1,053 Israelis were killed by Palestinian attacks through 30 April 2008. Israeli journalist Ze'ev Schiff reported similar numbers citing the Shin Bet as his source in an August 2004 Haaretz article where he noted:
The number of Israeli fatalities in the current conflict with the Palestinians exceeded 1,000 last week. Only two of the country's wars – the War of Independence and the Yom Kippur War – have claimed more Israeli lives than this intifada, which began on September 29, 2000. In the Six-Day War, 803 Israelis lost their lives, while the War of Attrition claimed 738 Israeli lives along the borders with Egypt, Syria and Lebanon.
There is little dispute as to the total number of Palestinians killed by Israelis. B'Tselem reports that through 30 April 2008, there were 4,745 Palestinians killed by Israeli security forces, and 44 Palestinians killed by Israeli civilians. B'Tselem also reports 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians through 30 April 2008.
Between September 2000 and January 2005, 69 percent of Israeli fatalities were male, while over 95 percent of the Palestinian fatalities were male. "Remember These Children" reports that as of 1 February 2008, 119 Israeli children, age 17 and under, had been killed by Palestinians. Over the same time period, 982 Palestinian children, age 17 and under, were killed by Israelis.
Combatant versus non-combatant deaths
See also: Civilian casualties in the Second IntifadaRegarding the numbers of Israeli civilian versus combatant deaths, B'Tselem reports that through 30 April 2008 there were 719 Israeli civilians killed and 334 Israeli security force personnel killed.

| Israeli total | Palestinian total |
| Israeli breakdown | Palestinian breakdown |
The chart is based on B'Tselem casualty numbers. It does not include the 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians.
B'Tselem reports that through 30 April 2008, out of 4,745 Palestinians killed by Israeli security forces, there were 1,671 "Palestinians who took part in the hostilities and were killed by Israeli security forces", or 35.2%. According to their statistics, 2,204 of those killed by Israeli security forces "did not take part in the hostilities", or 46.4%. There were 870 (18.5%) who B'Tselem defines as "Palestinians who were killed by Israeli security forces and it is not known if they were taking part in the hostilities".
The B'Tselem casualties breakdown's reliability was questioned and its methodology has been heavily criticized by a variety of institutions and several groups and researchers, most notably Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs's senior researcher, retired IDF lieutenant colonel Jonathan Dahoah-Halevi, who claimed that B'Tselem repeatedly classifies terror operatives and armed combatants as "uninvolved civilians", but also criticized the Israeli government for not collecting and publishing casualty data. Caroline B. Glick, deputy managing editor of The Jerusalem Post and former advisor to Benjamin Netanyahu, pointed to several instances where, she claimed, B'Tselem had misrepresented Palestinian rioters or terrorists as innocent victims, or where B'Tselem failed to report when an Arab allegedly changed his testimony about an attack by settlers. The Committee for Accuracy in Middle East Reporting in America (CAMERA), which said that B'Tselem repeatedly classified Arab combatants and terrorists as civilian casualties.
The Israeli International Policy Institute for Counter-Terrorism (IPICT), on the other hand, in a "Statistical Report Summary" for 27 September 2000, through 1 January 2005, indicates that 56% (1,542) of the 2,773 Palestinians killed by Israelis were combatants. According to their data, an additional 406 Palestinians were killed by actions of their own side. 22% (215) of the 988 Israelis killed by Palestinians were combatants. An additional 22 Israelis were killed by actions of their own side.
IPICT counts "probable combatants" in its total of combatants. From their full report in September 2002:
A 'probable combatant' is someone killed at a location and at a time during which an armed confrontation was going on, who appears most likely – but not certain – to have been an active participant in the fighting. For example, in many cases where an incident has resulted in a large number of Palestinian casualties, the only information available is that an individual was killed when Israeli soldiers returned fire in response to shots fired from a particular location. While it is possible that the person killed had not been active in the fighting and just happened to be in the vicinity of people who were, it is reasonable to assume that the number of such coincidental deaths is not particularly high. Where the accounts of an incident appear to support such a coincidence, the individual casualty has been given the benefit of the doubt, and assigned a non-combatant status.
In the same 2002 IPICT full report there is a pie chart (Graph 2.9) that lists the IPICT combatant breakdown for Palestinian deaths through September 2002. Here follow the statistics in that pie chart used to come up with the total combatant percentage through September 2002:
| Combatants | Percent of all Palestinian deaths |
|---|---|
| Full Combatants | 44.8% |
| Probable Combatants | 8.3% |
| Violent Protesters | 1.6% |
| Total Combatants | 54.7% |
On 24 August 2004, Haaretz reporter Ze'ev Schiff published casualty figures based on Shin Bet data. The Haaretz article reported: "There is a discrepancy of two or three casualties with the figures tabulated by the Israel Defense Forces."
Here is a summary of the figures presented in the article:
- Over 1,000 Israelis were killed by Palestinian attacks in the al-Aqsa Intifada.
- Palestinians sources claim 2,736 Palestinians killed in the Intifada.
- The Shin Bet has the names of 2,124 Palestinian dead.
- Out of the figure of 2,124 dead, Shin Bet assigned them to these organizations:
- 466 Hamas members
- 408 Fatah's Tanzim and al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades
- 205 Palestinian Islamic Jihad
- 334 of "Palestinian security forces – for example, Force 17, the Palestinian police, General Intelligence, and the counter security apparatus"
The article does not say whether those killed were combatants or not. Here is a quote:
The Palestinian security forces – for example, Force 17, the Palestinian police, General Intelligence, and the counter security apparatus – have lost 334 of its members during the current conflict, the Shin Bet figures show.
In response to IDF statistics about Palestinian casualties in the West Bank, the Israeli human rights organization B'Tselem reported that two-thirds of the Palestinians killed in 2004 did not participate in the fighting.
In 2009, historian Benny Morris stated in his retrospective book One State, Two States that about one third of the Palestinian deaths up to 2004 had been civilians.
Palestinians killed by Palestinians
B'Tselem reports that through 30 April 2008, there were 577 Palestinians killed by Palestinians. Of those, 120 were "Palestinians killed by Palestinians for suspected collaboration with Israel". B'Tselem maintains a list of deaths of Palestinians killed by Palestinians with details about the circumstances of the deaths. Some of the many causes of death are crossfire, factional fighting, kidnappings, collaboration, etc.
Concerning the killing of Palestinians by other Palestinians, a January 2003 The Humanist magazine article reports:
For over a decade the PA has violated Palestinian human rights and civil liberties by routinely killing civilians—including collaborators, demonstrators, journalists, and others—without charge or fair trial. Of the total number of Palestinian civilians killed during this period by both Israeli and Palestinian security forces, 16 percent were the victims of Palestinian security forces.
... According to Freedom House's annual survey of political rights and civil liberties, Freedom in the World 2001–2002, the chaotic nature of the Intifada along with strong Israeli reprisals has resulted in a deterioration of living conditions for Palestinians in Israeli-administered areas. The survey states:
Civil liberties declined due to: shooting deaths of Palestinian civilians by Palestinian security personnel; the summary trial and executions of alleged collaborators by the Palestinian Authority (PA); extra-judicial killings of suspected collaborators by militias; and the apparent official encouragement of Palestinian youth to confront Israeli soldiers, thus placing them directly in harm's way.
Internal Palestinian violence has been called an 'Intra'fada during this Intifada and the previous one.
Aftermath
On 25 January 2006, the Palestinians held general elections for the Palestinian Legislative Council. The Islamist group Hamas won with an unexpected majority of 74 seats, compared to 45 seats for Fatah and 13 for other parties and independents. Hamas is officially declared as a terrorist organization by the United States and the European Union and its gaining control over the Palestinian Authority (such as by forming the government) would jeopardize international funds to the PA, by laws forbidding sponsoring of terrorist group.
On 9 June, seven members of the Ghalia family were killed on a Gaza beach. The cause of the explosion remains uncertain. Nevertheless, in response, Hamas declared an end to its commitment to a ceasefire declared in 2005 and announced the resumption of attacks on Israelis. Palestinians blame an Israeli artillery shelling of nearby locations in the northern Gaza Strip for the deaths, while an Israeli military inquiry cleared itself from the charges.
On 25 June, a military outpost was attacked by Palestinian militants and a gunbattle followed that left 2 Israeli soldiers and 3 Palestinian militants dead. Corporal Gilad Shalit, an Israeli soldier, was captured and Israel warned of an imminent military response if the soldier was not returned unharmed. In the early hours of 28 June Israeli tanks, APCs and troops entered the Gaza Strip just hours after the air force had taken out two main bridges and the only powerstation in the strip, effectively shutting down electricity and water. Operation Summer Rains commenced, the first major phase of the Gaza–Israel conflict, which continues to run independently of the intifada.
On 26 November 2006, a truce was implemented between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. A 10 January 2007, Reuters article reports: "Hamas has largely abided by a November 26 truce which has calmed Israeli–Palestinian violence in Gaza."

2008–2009 Gaza–Israel War
An intensification of the Gaza–Israel conflict, the Gaza war, occurred on 27 December 2008 (11:30 a.m. local time; 09:30 UTC) when Israel launched a military campaign codenamed Operation Cast Lead (Hebrew: מבצע עופרת יצוקה) targeting the members and infrastructure of Hamas in response to the numerous rocket attacks upon Israel from the Gaza Strip. The operation has been termed the Gaza massacre (Arabic: مجزرة غزة) by Hamas leaders and much of the media in the Arab World.
On Saturday, 17 January 2009, Israel announced a unilateral ceasefire, conditional on elimination of further rocket and mortar attacks from Gaza, and began withdrawing over the next several days. Hamas later announced its own ceasefire, with its own conditions of complete withdrawal and opening of border crossings. A reduced level of mortar fire originating in Gaza continues, though Israel has so far not taken this as a breach of the ceasefire. The frequency of the attacks can be observed in the thumbnailed graph. The data corresponds to the article "Timeline of the 2008–2009 Israel–Gaza conflict", using mainly Haaretz news reports from 1 February up to 28 February. The usual IDF responses are airstrikes on weapon smuggling tunnels.
The violence continued on both sides throughout 2006. On 27 December the Israeli Human Rights Organization B'Tselem released its annual report on the Intifada. According to which, 660 Palestinians, a figure more than three times the number of Palestinian fatalities in 2005, and 23 Israelis, were killed in 2006. From a 28 December Haaretz article: "According to the report, about half of the Palestinians killed, 322, did not take part in the hostilities at the time they were killed. 22 of those killed were targets of assassinations, and 141 were minors." 405 of 660 Palestinians were killed in the 2006 Israel-Gaza conflict, which lasted from 28 June till 26 November.
Tactics
Unlike the First Intifada, a Palestinian civil uprising mainly focused on mass protests and general strikes, the Second Intifada rapidly turned into an armed conflict between Palestinian militant groups and the Israel Defense Forces. Palestinian tactics focused on Israeli civilians, soldiers, police and other security forces, and methods of attack included suicide bombings, launching rockets and mortars into Israel, kidnapping of both soldiers and civilians, including children, shootings, assassination, stabbings, and lynchings.
Israeli tactics included curbing Palestinians' movements through the setting up of checkpoints and the enforcement of strict curfews in certain areas. Infrastructural attacks against Palestinian Authority targets such as police and prisons was another method to force the Palestinian Authority to repress the anti-Israeli protests and attacks on Israeli targets.
Palestinians
Militant groups involved in violence include Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) and the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades. The most lethal Palestinian tactic was the suicide bombing (see List). Conducted as a single or double bombing, suicide bombings were generally conducted against "soft" targets, or "lightly hardened" targets (such as checkpoints) to try to raise the cost of the war to Israelis and demoralize the Israeli society. Most suicide bombing attacks (although not all) targeted civilians, and were conducted in crowded places in Israeli cities, such as public transport, restaurants, shopping malls and markets.
One major development was the use of suicide bombs carried by children. Unlike most suicide bombings, the use of these not only earned condemnation from the United States and from human rights groups such as Amnesty International, but also from many Palestinians and much of the Middle East press. The youngest Palestinian suicide bomber was 16-year-old Issa Bdeir, a high school student from the village of Al Doha, who shocked his friends and family when he blew himself up in a park in Rishon LeZion, killing a teenage boy and an elderly man. The youngest attempted suicide bombing was by a 14-year-old captured by soldiers at the Huwwara checkpoint before managing to do any harm.
Militant groups also waged a high-intensity campaign of guerrilla warfare against Israeli military and civilian targets inside Israel and in the Palestinian Territories, utilizing tactics such as ambushes, sniper attacks, and suicide bombings. Military equipment was mostly imported, while some light arms, hand grenades and explosive belts, assault rifles, and Qassam rockets were indigenously produced. They also increased use of remote-controlled landmines against Israeli armor, a tactic that was highly popular among the poorly armed groups. Car bombs were often used against "lightly hardened" targets such as Israeli armored jeeps and checkpoints. Also, more than 1,500 Palestinian drive-by shootings killed 75 people in only the first year of the Intifada.
In May 2004, Israel Defense minister Shaul Mofaz claimed that United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East's ambulances were used to take the bodies of dead Israeli soldiers in order to prevent the Israel Defense Forces from recovering their dead. Reuters has provided video of healthy armed men entering ambulance with UN markings for transport. UNRWA initially denied that its ambulances carry militants but later reported that the driver was forced to comply with threats from armed men. UNRWA still denies that their ambulances carried body parts of dead Israeli soldiers.
In August 2004, Israel said that an advanced explosives-detection device employed by the IDF at the Hawara checkpoint near Nablus discovered a Palestinian ambulance had transported explosive material.
Some of the Palestinian reaction to Israeli policy in the West Bank and Gaza Strip has consisted of non-violent protest, primarily in and near the village of Bil'in. Groups such as the Palestinian Centre for Rapprochement, which works out of Beit Sahour, formally encourage and organize non-violent resistance. Other groups, such as the International Solidarity Movement openly advocate non-violent resistance. Some of these activities are done in cooperation with internationals and Israelis, such as the weekly protests against the Israeli West Bank Barrier carried out in villages like Bi'lin, Biddu and Budrus. This model of resistance has spread to other villages like Beit Sira, Hebron, Saffa, and Ni'lein. During the Israeli re-invasion of Jenin and Nablus, "A Call for a Non-violent Resistance Strategy in Palestine" was issued by two Palestinian Christians in May 2002.
Non-violent tactics have sometimes been met with Israeli military force. For example, Amnesty International notes that "10-year-old Naji Abu Qamer, 11-year-old Mubarak Salim al-Hashash and 13-year-old Mahmoud Tariq Mansour were among eight unarmed demonstrators killed in the early afternoon of May 19, 2004 in Rafah, in the Gaza Strip, when the Israeli army open fire on a non-violent demonstration with tank shells and a missile launched from a helicopter gunship. Dozens of other unarmed demonstrators were wounded in the attack." According to Israeli army and government officials, the tanks shelled a nearby empty building and a helicopter fired a missile in a nearby open space in order to deter the demonstrators from proceeding towards Israeli army positions.
Israel


The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) countered Palestinian attacks with incursions against militant targets into the West Bank and Gaza Strip, adopting highly effective urban combat tactics. The IDF stressed the safety of their troops, using such heavily armored equipment as the Merkava heavy tank and armored personnel carriers, and carried out airstrikes with various military aircraft including F-16s, drone aircraft and helicopter gunships to strike militant targets. Much of the ground fighting was conducted house-to-house by well-armed and well-trained infantry. Due to its superior training, equipment, and numbers, the IDF had the upper hand during street fighting. Palestinian armed groups suffered heavy losses during combat, but the operations were often criticized internationally due to the civilian casualties often caused. Palestinian metalworking shops and other business facilities suspected by Israel of being used to manufacture weapons were regularly targeted by airstrikes, as well as Gaza Strip smuggling tunnels.
Israeli Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozers were routinely employed to detonate booby traps and IEDs, to demolish houses along the border with Egypt that were used for shooting at Israeli troops, to create "buffer zones", and to support military operations in the West Bank. Until February 2005, Israel had in place a policy to demolish the family homes of suicide bombers after giving them a notice to evacuate. Due to the considerable number of Palestinians living in single homes, the large quantity of homes destroyed, and collateral damage from home demolitions, it became an increasingly controversial tactic. Families began providing timely information to Israeli forces regarding suicide bombing activities in order to prevent the demolition of their homes, although families doing so risked being executed or otherwise punished for collaboration, either by the Palestinian Authority or extrajudicially by Palestinian militants. The IDF committee studying the issue recommended ending the practice because the policy was not effective enough to justify its costs to Israel's image internationally and the backlash it created among Palestinians.
With complete ground and air superiority, mass arrests were regularly conducted by Israeli military and police forces; at any given time, there were about 6,000 Palestinian prisoners detained in Israeli prisons, about half of them held temporarily without a final indictment, in accordance with Israeli law.
The tactic of military "curfew" – long-term lockdown of civilian areas – was used extensively by Israel throughout the Intifada. The longest curfew was in Nablus, which was kept under curfew for over 100 consecutive days, with generally under two hours per day allowed for people to get food or conduct other business.
Security checkpoints and roadblocks were erected inside and between Palestinian cities, subjecting all people and vehicles to security inspection for free passage. Israel defended those checkpoints as being necessary to stop militants and limit the ability to move weapons around. However some Palestinian, Israeli and International observers and organizations have criticized the checkpoints as excessive, humiliating, and a major cause of the humanitarian situation in the Occupied Territories. Transit could be delayed by several hours, depending on the security situation in Israel. Sniper towers were used extensively in the Gaza Strip before the Israeli pullout.
The Israeli intelligence services Shin Bet and Mossad penetrated Palestinian militant organizations by relying on moles and sources within armed groups, tapping communication lines, and aerial reconnaissance. The intelligence gathered allowed the IDF, Israel Border Police, and Israel Police, including Yamam and Mistaravim special forces units, to thwart hundreds of planned suicide bombings. The intelligence gathered also helped create a list of Palestinians marked for targeted killings.
Israel extensively used targeted killings, the assassinations of Palestinians involved in organizing attacks against Israelis, to eliminate imminent threats and to deter others from following suit, relying primarily on airstrikes and covert operations to carry them out. The strategy of targeted killings had been proposed by Shin Bet, which determined that while it was impossible to stop every single suicide bomber, suicide bombings could be stopped by directly attacking the conspiratorial infrastructure behind them by killing operational commanders, recruiters, couriers, weapons procurers, maintainers of safehouses, and smugglers of money which financed the bombings. Israel was criticized for the use of helicopter gunships in urban assassinations, which often resulted in civilian casualties. Israel criticized what it described as a practice of militant leaders hiding among civilians in densely populated areas, thus turning them into unwitting human shields. Throughout the Intifada, the Palestinian leadership suffered heavy losses through targeted killings.
The practice has been widely condemned as extrajudicial executions by the international community, while the Israeli High Court ruled that it is a legitimate measure of self-defense against terrorism. Many criticize the targeted killings for placing civilians at risk, though its supporters believe it reduces civilian casualties on both sides.
In response to repeated rocket attacks from the Gaza Strip, the Israeli Navy imposed a maritime blockade on the area. Israel also sealed the border and closed Gaza's airspace in coordination with Egypt, and subjected all humanitarian supplies entering the Strip to security inspection before transferring them through land crossings. Construction materials were declared banned due to their possible use to build bunkers. The blockade has been internationally criticized as a form of "collective punishment" against Gaza's civilian population.
International involvement
See also: Israel and the United Nations, Palestine and the United Nations, Israel-United States relations, International Solidarity Movement, and International aid to PalestiniansThe international community has long taken an involvement in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, and this involvement has only increased during the al-Aqsa Intifada. Israel currently receives $3 billion in annual military aid from the United States, excluding loan guarantees. Even though Israel is a developed industrial country, it has remained as the largest annual recipient of US foreign assistance since 1976. It is also the only recipient of US economic aid that does not have to account for how it is spent. The Palestinian Authority receives $100 million annually in military aid from the United States and $2 billion in global financial aid, including "$526 million from Arab League, $651 million from the European Union, $300 million from the US and about $238 million from the World Bank". According to the United Nations, the Palestinian territories are among the leading humanitarian aid recipients.
Additionally, private groups have become increasingly involved in the conflict, such as the International Solidarity Movement on the side of the Palestinians, and the American Israel Public Affairs Committee on the side of the Israelis.
In the 2001 and 2002 Arab League Summits, the Arab states pledged support for the Second Intifada just as they had pledged support for the First Intifada in two consecutive summits in the late 1980s.
Impact on the Oslo Accords
Since the start of the Second Intifada and its emphasis on suicide bombers deliberately targeting civilians riding public transportation (buses), the Oslo Accords began to be viewed with increasing disfavor by the Israeli public. In May 2000, seven years after the Oslo Accords and five months before the start of the Second Intifada, a survey by the Tami Steinmetz Center for Peace Research at the Tel Aviv University found that 39% of all Israelis support the Accords and that 32% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years. In contrast, a survey in May 2004 found that 26% of all Israelis support the Accords and 18% believe that the Accords will result in peace in the next few years; decreases of 13% and 16% respectively. Furthermore, a later survey found that 80% of all Israelis believe the Israel Defense Forces have succeeded in dealing with the Second Intifada militarily.
Economic effects
Israel
The Israeli commerce experienced a significant negative effect, particularly due to a sharp drop in tourism. A representative of Israel's Chamber of Commerce estimated the cumulative economic damage caused by the crisis at 150 to 200 billion shekels (US$35–45 billion) – against an annual GDP of $122 billion in 2002. The Israeli economy recovered after 2005 with the sharply decrease in suicide bombings, following IDF's and Shin-Bet's efforts.
Palestinian Authority
The Office of the United Nations Special Coordinator for the Middle East Peace Process (UNSCO) estimated the damage to the Palestinian economy at over $1.1 billion in the first quarter of 2002, compared to an annual GDP of $4.5 billion.
See also
- First Intifada (1987–1993)
- Taba Summit (2001)
- Sharm el-Sheikh Summit of 2005
- Israeli disengagement from Gaza (2005)
- Israeli West Bank barrier – started in 2002
- House demolition in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
- Sumud (steadfastness)
- 1990 Temple Mount riots
- Silent Intifada (2014)
- Israeli–Palestinian conflict (2015)
- Palestinian political violence
- Palestinian nationalism
- Palestinian territories
- List of modern conflicts in the Middle East
- Directly connected to the Second Intifada and its aftermath
- List of Palestinian suicide attacks
- List of Israeli civilian casualties in the Second Intifada
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2000
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2001
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2002
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2003
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2004
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2005
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2006
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2007
- Violence in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict 2008
References
Citations
- Amos Harel; Avi Issacharoff (1 October 2010). "Years of Rage". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Laura King (28 September 2004). "Losing faith in the intifada". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Jackson Diehl (27 September 2004). "From Jenin to Falluja". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Zeev Chafetz (22 July 2004). "The Intifadeh is over – just listen". World Jewish Review. Archived from the original on 4 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Major-General (res) Yaakov Amidror (23 August 2010). "Winning the counterinsurgency war: The Israeli experience". Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. Archived from the original on 1 July 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Hillel Frisch (12 January 2009). "The need for a decisive Israeli victory over Hamas" (PDF). Begin–Sadat Center for Strategic Studies. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities". B'Tselem. Archived from the original on 1 July 2010.
- ^ "Breakdown of Fatalities: 27 September 2000 through 1 January 2005". International Institute for Counter-Terrorism. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Full report: Don Radlauer (29 September 2002). "An Engineered Tragedy: Statistical Analysis of Casualties in the Palestinian – Israeli Conflict, September 2000 – September 2002". International Institute for Counter-Terrorism. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007.. Also at Don Radlauer. "An Engineered Tragedy: Statistical Analysis of Casualties in the Palestinian – Israeli Conflict, September 2000 – September 2002". EretzYisroel.Org. Archived from the original on 5 March 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Intifada toll 2000–2005". BBC News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 17 January 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- "Field Update on Gaza from the Humanitarian Coordinator" (PDF). United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. 9 January 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ BBC 2004.
- Araj, Bader; Brym, Robert J. (2010). "Opportunity, Culture and Agency: Influences on Fatah and Hamas Strategic Action during the Second Intifada". International Sociology. 25 (6): 842–868. doi:10.1177/0268580909351327. ISSN 0268-5809. Archived from the original on 18 May 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
Strategic action by the two main Palestinian militant organizations, Fatah and Hamas, during the second intifada or uprising against the Israeli state and people (2000—5). ... during the second intifada, or uprising, of Palestinians against Israel between 2000 and 2005
- Smith, Robert B. (1 April 2008). "A Globalized Conflict: European Anti-Jewish Violence during the Second Intifada". Quality & Quantity. 42 (2): 135–180. doi:10.1007/s11135-006-9045-3. ISSN 1573-7845.
The globalization of the Arab–Israeli conflict during the period of the second intifada against Israel (from the autumn 2000 through at least the spring of 2005) has fostered anti-Jewish violence in Europe and throughout the world.
- ^ Pressman 2006, p. 114.
- NPR 2014.
- Byman 2011, p. 114.
- Finkelstein, Norman G. (2008). "4". Beyond Chutzpah: On the misuse of anti-Semitism and the abuse of history (expanded paperback ed.). Berkeley.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Finkelstein, Norman G. (2008). "4". Beyond Chutzpah: On the misuse of anti-Semitism and the abuse of history (expanded paperback ed.). Berkeley.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Cohen, Samy (2010). "Botched Engagement in the Intifada". Israel's Asymmetric Wars. New York: Palgrave Macmillan US. pp. 73–91. doi:10.1057/9780230112971_6. ISBN 978-1-349-28896-0."The al-Aqsa Intifada ushered in an era with a new brand of violence. It began with a popular uprising following Ariel Sharon's visit to Temple Mount on September 28, 2000. But unlike the first Intifada, which was basically a civil uprising against the symbols of an occupation that has lasted since June 1967, the second Intifada very quickly lapsed into an armed struggle between Palestinian activists and the Israeli armed forces. Almost from the very start, armed men took to hiding among crowds of Palestinians, using them as cover to shoot from. The IDF retaliated forcefully, each time causing several casualties." Cite error: The named reference ":1" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Kober, Avi (2007). "Targeted Killing during the Second Intifada:: The Quest for Effectiveness". Journal of Conflict Studies. 27 (1): 94–114. ISSN 1198-8614. Archived from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
Based on the assumption that there was no longer one front or one line of contact, Israel was carrying out dozens of simultaneous operations on the ground and in the air on a daily basis, including TKs, which were supposed to have multi-dimensional effects. According to Byman, TKs were mostly attractive to Israelis as they satisfied domestic demands for a forceful response to Palestinian terrorism. Byman also believes that by bolstering public morale, the TKs helped counter one of the terrorists' primary objectives – to reduce the faith of Israelis in their own government.
- ^ Matta, Nada; Rojas, René (2016). "The Second Intifada: A Dual Strategy Arena". European Journal of Sociology / Archives Européennes de Sociologie. 57 (1): 66. doi:10.1017/S0003975616000035. ISSN 0003-9756. S2CID 146939293. Archived from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
Suicide terror, lethal attacks indiscriminately carried out against civilians via self-immolation, attained prominence in the Palestinian repertoire beginning in March 2001. From that point until the end of 2005, at which point they virtually ceased, 57 suicide bombings were carried out, causing 491 civilian deaths, 73% of the total civilians killed by Palestinian resistance organizations and 50% of all Israeli fatalities during this period. While not the modal coercive tactic, suicide terror was the most efficient in terms of lethality, our basic measure of its efficacy.
- Brym, R. J.; Araj, B. (1 June 2006). "Suicide Bombing as Strategy and Interaction: The Case of the Second Intifada". Social Forces. 84 (4): 1969. doi:10.1353/sof.2006.0081. ISSN 0037-7732. S2CID 146180585.
In the early years of the 21st century, Israel, the West Bank and Gaza became the region of the world with the highest frequency of - and the highest per capita death toll due to - suicide bombing.
- Schweitzer, Y. (2010). "The rise and fall of suicide bombings in the second Intifada". Strategic Assessment. 13 (3): 39–48.
As part of the violence perpetrated by the Palestinians during the second intifada, suicide bombings played a particularly prominent role and served as the primary effective weapon in the hands of the planners.
- Schachter, J. (2010). "The End of the Second Intifada?" (PDF). Strategic Assessment. 13 (3): 63–70. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2021.
This article attempts to identify the end of the second intifada by focusing on the incidence of suicide bombings, arguably the most important element of second intifada-related violence.
- Sela-Shayovitz, R. (2007). "Suicide bombers in Israel: Their motivations, characteristics, and prior activity in terrorist organizations". International Journal of Conflict and Violence. 1 (2): 163.
The period of the second Intifada significantly differs from other historical periods in Israeli history, because it has been characterized by intensive and numerous suicide attacks that have made civilian life into a battlefront.
- "B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities 29.9.2000–15.1.2005". B'Tselem. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013.
- Tucker 2019, p. 958p: he and Israeli prime minister Sharon agreed in an early 2005 summit to suspend hostilities. This agreement effectively ended the Second Intifada
- Abbas 2005.
- Sharon 2005.
- Reinhart 2006, p. 77.
- "1977: Egypt's bread intifada". Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- Rabinovich, Itamar (2004). Waging Peace: Israel and the Arabs, 1948–2003. Princeton University Press. p. 306. ISBN 978-0-691-11982-3.
- Devin Sper (2004). The Future of Israel. Sy Publishing. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-9761613-0-1.
- Binyamin Elon (2005). God's Covenant With Israel: Establishing Biblical Boundaries in Today's World. Balfour Books. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-89221-627-7.
- Ben-Ami, Shlomo (2006). Scars of War, Wounds of Peace. London: Oxford University Press. p. 267. ISBN 978-0-19-518158-6.
Israel's disproportionate response to what had started as a popular uprising with young, unarmed men confronting Israeli soldiers armed with lethal weapons fueled the Intifada beyond control and turned it into an all-out war.
- Jeremy Pressman (11 November 2023). "The Second Intifada: Background and Causes of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict". Journal of Conflict Studies. 23 (2). Archived from the original on 4 October 2019. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- Frisch, Hillel (2010) . The Palestinian Military: Between Militias and Armies. Routledge. p. 102. ISBN 978-1-134-15789-1. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- ^ Schmemann, Serge (5 December 1997). "In West Bank, 'Time' for Settlements Is Clearly Not 'Out'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 18 December 2007.
- ^ David M., Rosen (2005). Armies of the Young: Child Soldiers in War and Terrorism. Rutgers University Press. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-8135-3568-5. Archived from the original on 20 August 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- "Palestinian Parliament Expected to Not Declare an Independent Palestinian State". CNN. 10 September 2000. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Extraordinary Increase in Settlement Construction as Diplomacy Falters". Settlement Report. 8 (2). Foundation for Middle East Peace. March–April 1998. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013.
- "Housing Starts in Israel, the West Bank and Gaza Strip Settlements*, 1990–2003". Foundation for Middle East Peace. Archived from the original on 18 November 2008. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ^ Tim Youngs, International Affairs and Defence Section (24 January 2001). "The Middle East Crisis: Camp David, the 'Al-Aqsa Intifada' and the Prospects for the Peace Process" (PDF). House of Commons Library. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 February 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2007.
- "The second intifada". Archived from the original on 12 May 2022. Retrieved 3 December 2023.
- "What were the intifadas?". 20 November 2018. Archived from the original on 10 January 2024. Retrieved 3 December 2023.
- "Palestinians And Israelis in a Clash at Holy Site". The New York Times. 28 September 2000.
- Bregman 2005, p. 160.
- Cohen, Hillel (March 2013). The Rise and Fall of Arab Jerusalem: Palestinian Politics and the City Since 1967. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-85266-4.
- ^ "On This Day: 'Provocative' mosque visit sparks riots". BBC News. 28 September 2000. Archived from the original on 29 January 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
Palestinians and Israeli police have clashed in the worst violence for several years at Jerusalem's holiest site, the compound around Al-Aqsa mosque. The violence began after a highly controversial tour of the mosque compound early this morning by hardline Israeli opposition leader Ariel Sharon. ... Soon after Mr Sharon left the site, the angry demonstrations outside erupted into violence. Israeli police fired tear gas and rubber-coated metal bullets, while protesters hurled stones and other missiles. Police said 25 of their men were hurt by missiles thrown by Palestinians, but only one was taken to hospital. Israel Radio reported at least three Palestinians were wounded by rubber bullets. ... Following Friday prayers the next day, violence again broke out throughout Jerusalem and the West Bank.
- Greenberg, Joel (5 October 2000). "Unapologetic, Sharon Rejects Blame for Igniting Violence". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- Lee Hockstader (29 September 2000). "Israeli's Tour of Holy Site Ignites Riot; Palestinians Angered By Test of Sovereignty in Jerusalem's Old City". The Washington Post. p. A22. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Palestinians say opposition tour of holy site could cause bloodshed". CNN. Associated Press. 27 September 2000. Archived from the original on 10 December 2004.
- ^ Rashmi Singh, Hamas and Suicide Terrorism: Multi-causal and Multi-level Approaches Archived 18 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Routledge, 2013 p.38
- ^ Menachem Klein (2003). The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status. University Press of Florida. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-8130-2673-2.
- Schiff, Ze'ev; Ehud Ya'ari (1984). Israel's Lebanon War. Simon & Schuster. p. 284. ISBN 978-0-671-47991-6.
- ^ Shindler 2013, p. 283.
- MacFarquhar, Neil (5 January 2006). "Few Kind Words for Sharon in the Arab World". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Juliana Ochs (2011). Security and Suspicion: An Ethnography of Everyday Life in Israel. The Ethnography of Political Violence. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-8122-4291-1. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- Goldberg, Jeffrey (2008). Prisoners: A Story of Friendship and Terror. New York: Vintage Books. p. 258.
- Sontag, Deborah (30 September 2000). "Battle at Jerusalem Holy Site Leaves 4 Dead and 200 Hurt". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- Dellios, Hugh (30 September 2000). "4 Dead, Scores Wounded in Jerusalem Clashes". Chicago Tribune. Jerusalem. Archived from the original on 28 November 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
police clashed with stone-throwing Palestinians, killing four and wounding scores
- "CNN's Jerrold Kessel on continuing violence in the Mideast". CNN. 29 September 2000. Archived from the original on 19 September 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Menachem Klein (2003). The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status. University Press of Florida. pp. 97–98. ISBN 978-0-8130-2673-2.
- ^ Menachem Klein (2003). The Jerusalem Problem: The Struggle for Permanent Status. University Press of Florida. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-8130-2673-2.
- "Israel and the Occupied Territories: Excessive use of lethal force". Amnesty International. 19 October 2000. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- Gilead Sher (2006). The Israeli–Palestinian Peace Negotiations, 1999–2001: Within Reach. Routledge. pp. 161–162. ISBN 978-0-7146-8542-7. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2015.: "Your account of events does not match the impression of any country in the world," he said. "At Camp David, Israel did in fact make a significant step towards peace, but Sharon's visit was the detonator, and everything has exploded. This morning, sixty-four Palestinians are dead, nine Israeli-Arabs were also killed, and you're pressing on. You cannot, Mr Prime Minister, explain this ratio in the number of wounded. You cannot make anyone believe that the Palestinians are the aggressors....When I was a company commander in Algeria, I also thought I was right. I fought the guerillas. Later I realized I was wrong. It is the honour of the strong, to reach out and not to shoot. Today you must reach out your hand. If you continue to fire from helicopters on people throwing rocks, and you continue to refuse an international inquiry, you are turning down a gesture from Arafat. You have no idea how hard I pushed Arafat to agree to a trilateral meeting. ...'
- Earlier estimates gave a million bullets and projectiles shot by Israeli forces in the first few days, 700,000 in the West Bank and 300,000 in the Gaza Strip. See Ben Kaspit, "Jewish New Year 2002—the Second Anniversary of the Intifada," Maariv 6 September 2002 (Heb), in Cheryl Rubenberg, The Palestinians: In Search of a Just Peace, Lynne Rienner Publishers, 2003 p. 324, p. 361 n. 5. The figure was revealed by Amos Malka, then-director of Military Intelligence. Moshe Ya'alon, who later became the Israeli Chief of Staff, denied the 1.3 million figure, claiming that the number reflected the demand of the command units for supplemental ammunition. Pedatzur, Reuven (4 December 2008). "Deflater of defeatist discourse". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 19 December 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ "Israel and the Occupied Territories: Broken Lives – A Year of Intifada". Amnesty International. 13 November 2001. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014. Retrieved 4 November 2012.
- Nitzan Ben-Shaul, A Violent World: TV News Images of Middle Eastern Terror and War Archived 19 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Rowman & Littlefield, 6 March 2007 pp.118–120.
- ^ Catignani, Sergio (2008). "The Al-Aqsa Intifada". Israeli Counter-Insurgency and the Intifadas: Dilemmas of a Conventional Army. Routledge. pp. 104–106. ISBN 978-1-134-07997-1. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- "The Or Inquiry – Summary of Events". Haaretz. 19 November 2001. Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Eve Spangler, Understanding Israel/Palestine: Race, Nation, and Human Rights in the Conflict Archived 20 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Springer, 2015 p.183
- Asser, Martin (13 October 2000). "Lynch mob's brutal attack". BBC News. Archived from the original on 29 January 2008. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- Levy, Gideon (20 October 2000). "A conversation with Colonel Kamel al-Sheikh, Ramallah's chief of police, amid the ruins of his police station, where two Israeli soldiers were lynched by an angry mob last week". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 4 August 2001.
- Feldman, Shai (November 2000). "The October Violence: An Interim Assessment". Strategic Assessment. Jaffes Center for Strategic Studies. Archived from the original on 29 June 2001.
- Philps, Alan (13 October 2000). "A day of rage, revenge and bloodshed". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Israeli copters retaliate for soldiers' deaths". USA Today. 8 November 2000. Archived from the original on 23 November 2001. Retrieved 3 July 2009.
- "Time Line of Second (Al-Aqsa) Intifada". MidEastWeb. Archived from the original on 17 December 2008.
- CNN, 27 December 2000, "Mideast summit in Egypt called off" Archived 18 November 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- Hershman, Tania (19 January 2001). "Israel's 'First Internet Murder'". Wired. Archived from the original on 19 October 2007.
- Charles W. Greenbaum; Philip E. Veerman; Naomi Bacon-Shnoor, eds. (2006). Protection of children during armed political conflict: a multidisciplinary perspective. Intersentia. ISBN 978-90-5095-341-2. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- Gordis, Daniel (2003). Home to Stay: One American Family's Chronicle of Miracles and Struggles in Contemporary Israel. Random House. ISBN 978-0-307-53090-5. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- "Target: Israeli Children". Israel Ministry of Education. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013.
- "Two Israeli boys found bludgeoned to death". The Guardian. 9 May 2001. Archived from the original on 25 August 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ Matthew Kalman (20 June 2001). "Two Israeli teenagers stoned to death". USA Today. Archived from the original on 20 April 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Arabs seek to isolate Israel". BBC News. 20 May 2001. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 1 February 2017.
- Karmon, Ely (11 June 2001). "The Palestinian Authority-Hamas Collusion – From Operational Cooperation to Propaganda Hoax". International Institute for Counter-Terrorism. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- O'Sullivan, Arieh (25 November 2001). "No. 1 Hamas terrorist killed. Followers threaten revenge in Tel Aviv". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 23 October 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Fisher, Ian (29 January 2006). "In Hamas's Overt Hatred, Many Israelis See Hope". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 November 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- 21 צעירות וצעירים נהרגו בפיגוע התופת בטיילת בתל אביב, לא הרחק מהדולפינריום. אלה תמונות ההרוגים בפיגוע הקשה ביותר בישראל מזה חמש שנים. ynet מביא את חלק מסיפוריהם. [21 young people were killed in bomb attack in Tel Aviv promenade, near the Dolphinarium. These pictures of the dead worst attack in Israel for five years. Ynet brings some of their stories.]. Ynet (in Hebrew). 2 June 2001. Archived from the original on 24 July 2017. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Enev, Peter Enev (7 June 2004). "Barghouti gets five life terms for attacks". Toronto Star. ProQuest 438710369.
- Stanage, Niall (3 February 2002). "Death of innocents". The Sunday Business Post. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Ben-Zur, Raanan (27 March 2006). "Sbarro terrorist 'not sorry'". Ynetnews. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Dudkevitch, Margot; O'Sullivan, Arieh (10 September 2001). "Five killed as terror hits nationwide. First Israeli Arab suicide bomber strikes at Nahariya train station". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 20 December 2002.
- Amos Harel; Haim Shadmi; David Ratner; Yam Yehoshua (28 November 2001). "Islamic Jihad, Fatah take responsibility for bus bombing". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Suicide Bomber kills 3 Israelis ahead of Bush-Sharon meeting". The Blade. Toledo. Knight Ridder, Associated Press. 30 November 2011. p. A2. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- "Suicide bombing at the Ben-Yehuda pedestrian mall in Jerusalem". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 1 December 2001. Archived from the original on 18 June 2004.
- Statistics | B'Tselem Archived 29 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sgt.-Maj.(res.) Yochai Porat". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 3 March 2002. Archived from the original on 30 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ Ophir Falk; Henry Morgenstein, eds. (2009). Suicide terror: understanding and confronting the threat. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-08729-9.
- ^ Barry Rubin,Judith Colp Rubin, Yasir Arafat: A Political Biography Archived 19 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Oxford University Press, 2003 p.427 n.14
- "Operation Defensive Shield: Palestinian Testimonies, Soldiers' Testimonies" (PDF). B'Tselem. July 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- ^ Mattar 2005, p. 40.
- Neil Caplan, The Israel–Palestine Conflict: Contested Histories, Archived 19 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine John Wiley & Sons, 2011 p.167
- Galia Golan, Israeli Peacemaking Since 1967: Factors Behind the Breakthroughs and Failures Archived 20 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Routledge, 2014 p.170.
- Arafat Siege Could End Soon . CBS, 29 April 2002
- ^ "Report of Secretary-General on recent events in Jenin, other Palestinian cities" (Press release). United Nations. 1 August 2002. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Operation Defensive Shield (2002)". Ynetnews. 12 March 2009. Archived from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Jenin's Terrorist Infrastructure". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 4 April 2002. Archived from the original on 18 February 2009. Retrieved 22 September 2008.
- Matt Rees (13 May 2002). "Untangling Jenin's Tale". Time. Archived from the original on 26 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "UN says no massacre in Jenin". BBC News. 1 August 2002. Archived from the original on 5 December 2006. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ^ Bennet, James (2 August 2002). "Death on the Campus: Jenin; U.N. Report Rejects Claims of a Massacre of Refugees". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- "U.N. report: No massacre in Jenin". USA Today. Associated Press. 1 August 2002. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Shielded from Scrutiny: IDF violations in Jenin and Nablus". Amnesty International. November 2002. p. 2. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
Amnesty International's extensive research ... led it to conclude that ... some of the actions amounted to ... war crimes.
- ^ "Jenin: IDF Military Operations" (PDF). Human Rights Watch. May 2002. p. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
Human Rights Watch's research demonstrates that, during their incursion into the Jenin refugee camp, Israeli forces committed serious violations of international humanitarian law, some amounting prima facie to war crimes.
- Paul Martin (1 May 2002). "Jenin 'massacre' reduced to death toll of 56". The Washington Times. Archived from the original on 15 April 2003.
- "Jenin". Human Rights Watch. 2 May 2002. Archived from the original on 26 September 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Harel, Amos; Issacharoff, Avi (2004). Ha-Milḥamah ha-shevi'it: ekh nitsaḥnu ṿe-lamah hifsadnu ba-milḥamah 'im ha-Palesṭinim המלחמה השביעית : איך ניצחנו ולמה הפסדנו במלחמה עם הפלסטינים [The Seventh War: How We Won and Why We Lost in the War with the Palestinians] (in Hebrew). Tel-Aviv: Yediot Aharonot. pp. 257–258. ISBN 978-965-511-767-7.
- Audeh, Ida (2002). "Narratives of Siege: Eye-Witness Testimonies from Jenin, Bethlehem, and Nablus". Journal of Palestine Studies. 31 (4): 13. doi:10.1525/jps.2002.31.4.13. ISSN 0377-919X. Archived from the original on 28 December 2010. Retrieved 7 April 2012.
- "Report of the Secretary-General prepared pursuant to General Assembly resolution ES-10/10". United Nations. Archived from the original on 6 August 2002. Retrieved 29 March 2006.
- "Texts: Palestinian truces". BBC News. 29 June 2003. Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2004.
- Alan Philps (23 June 2003). "Israel defends Hamas death". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 4 June 2004.
- "Israelis flatten West Bank shops". BBC News. 21 January 2003. Archived from the original on 19 December 2006. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "Razing Rafah: Mass Home Demolitions in the Gaza Strip". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 24 March 2006. Retrieved 29 March 2006.
- "Gunmen kill Jewish settler family". BBC News. 3 May 2004. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 28 September 2012.
- "Pregnant mum and four children gunned down". The Sydney Morning Herald. 3 May 2004. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- Silverin, Eric (3 May 2004). "Pregnant mum and her four children killed in terror attack". Irish Independent. Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
- "Israel/Occupied Territories: AI condemns murder of woman and her four daughters by Palestinian gunmen". Amnesty International. 4 May 2004. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- McGreal, Chris (16 October 2004). "Army pulls back from Gaza leaving 100 Palestinians dead". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- "Moral Quagmire". The Jewish Week. 3 December 2004. Archived from the original on 4 December 2004.
- Ben Lynfield (26 November 2004). "Israeli army under fire after killing girl". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 13 May 2007. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Hila Raz (20 January 2010). "Does it pay to sue for libel in Israel?". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 9 March 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Palestinians sift rubble after Israel's Gaza assault". Reuters. 16 October 2004. Archived from the original on 28 June 2005.
- "Sharon suspends contacts with Palestinian Authority". CNN. 14 January 2005. Archived from the original on 5 October 2018. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Israel cuts Palestinian contacts". BBC News. 14 January 2005. Archived from the original on 16 March 2006. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "Mid-East leaders announce truce". BBC News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 14 June 2006. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "Abbas orders security crackdown". BBC News. 10 February 2005. Archived from the original on 3 October 2018. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- ^ Schachter, Jonathan (2010). "The End of the Second Intifada?" (PDF). Strategic Assessment. 13 (3): 63–69. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 April 2019. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- Avery Plaw,Targeting Terrorists: A License to Kill? Archived 31 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine, Routledge, 2016 ISBN 978-1-317-04671-4 pp.63ff.
- Sever Plocker (22 June 2008). "2nd Intifada Forgotten". Ynetnews. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Ruth Tenne (Autumn 2007). "Rising of the oppressed: the second Intifada". International Socialism (116). Archived from the original on 8 January 2015. Retrieved 22 May 2009. Review of Ramzy Baroud; Kathleen Christison; Bill Christison; Jennifer Loewenstein (2006). The Second Palestinian Intifada: A Chronicle of a People's Struggle. Pluto Press. ISBN 978-0-7453-2547-7.
- "Timeline (Chronology) of Israel and Zionism 1993–present day". ZioNation. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- Brad A. Greenberg (3 December 2008). "UC to Reopen Study in Israel". The Jewish Journal of Greater Los Angeles. Archived from the original on 24 March 2022. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ^ Wedeman, Ben; Raz, Guy; Koppel, Andrea (2005). "Palestinian, Israeli leaders announce cease-fire". CNN. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- Gilmore, Inigo (4 February 2005). "Palestinian ceasefire ends four-year intifada". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- Levitt, Matthew (2005). "Sustaining an Israeli-Palestinian Ceasefire". The Washington Institute. Archived from the original on 10 August 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- "Hamas, Jihad Commit to Truce Provided Israel Reciprocates [Mechanism to attack Israel if Israel acts]". Palestine Media Center – PMC . 13 February 2005. Archived from the original on 10 August 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- Goldenberg, Suzanne (29 September 2000). "Rioting as Sharon visits Islam holy site". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 11 November 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Mitchell, George J.; et al. (30 April 2001). "Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee". UNISPAL. p. 4. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014. See under "What Happened?"
- Gelvin, James L. (2007). The Israel-Palestine conflict: one hundred years of war (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 243. ISBN 978-0-521-71652-9.
- ^ "Al-Aqsa Intifada timeline". BBC News. 29 September 2004. Archived from the original on 2 July 2016. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- Frankel, Jonathan, ed. (2005). Dark Times, Dire Decisions: Jews and Communism. Studies in Contemporary Jewry. Vol. XX. Oxford University Press. p. 311. ISBN 978-0-19-518224-8.
- George J. Mitchell; et al. (30 April 2001). "Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee". UNISPAL. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
Mr. Sharon made the visit on September 28 accompanied by over 1,000 Israeli police officers. Although Israelis viewed the visit in an internal political context, Palestinians saw it as a provocation to start a fair intifadah. On the following day, in the same place, a large number of unarmed Palestinian demonstrators and a large Israeli police contingent confronted each other.
- Cypel, Sylvain (2006). Walled: Israeli Society at an Impasse. Other Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-1-59051-210-4.
The following day, the 29th, a Friday and hence the Muslim day of prayer, the young Palestinians flared up....
- Alan Mittleman; Robert A. Licht; Jonathan D. Sarna (2002). Jewish Polity and American Civil Society: Communal Agencies and Religious Movements in the American Public Sphere. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 161. ISBN 978-0-7425-2122-3.
Then in late September Ariel Sharon visited the Temple Mount The next day, massive violence erupted in Jerusalem and Palestinian-controlled areas in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- George J. Mitchell; et al. (30 April 2001). "Report of The Sharm el-Sheikh Fact-Finding Committee". UNISPAL. Archived from the original on 23 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014. PDF Archived 1 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- "Suha Arafat admits husband premeditated Intifada". The Jerusalem Post. 29 December 2012. Archived from the original on 14 November 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Clinton, Bill (2004). My Life. Random House. ISBN 978-1-4000-3003-3.
- ^ Jeremy Pressman (Fall 2003). "The Second Intifada: Backgrounds and Causes of the Israeli–Palestinian Conflict" (PDF). Journal of Conflict Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 March 2009.
- "Fallen soldier's father: I never thought this would happen". The Jerusalem Post. ITIM. 29 September 2000. Archived from the original on 19 February 2003.
- Sontag, Deborah (30 September 2000). "Battle at Jerusalem Holy Site Leaves 4 Dead and 200 Hurt". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
This morning, both sides started out tense, after clashes on Thursday provoked by Mr. Sharon's visit.
- "Israeli troops, Palestinians clash after Sharon visits Jerusalem sacred site". CNN. 28 September 2000. Archived from the original on 8 November 2005.
A visit by Likud Party leader Ariel Sharon to the site known as the Temple Mount by Jews sparked a clash on Thursday between stone-throwing Palestinians and Israeli troops, who fired tear gas and rubber bullets into the crowd.... Also Thursday , an Israeli soldier critically injured in a bomb attack on an army convoy in the Gaza Strip died of his wounds.
- Gozani, Ohad (29 September 2000). "Riot police clash with protesters at holy shrine". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- "B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities – Israeli security force personnel killed by Palestinians in the Occupied Territories". B'Tselem. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- "B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities – Israeli civilians killed by Palestinians in the Occupied Territories". B'Tselem. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- Schulz and Hammer, 2003, pp. 134–136.
- Khaled Abu Toameh (29 September 2010). "Arafat ordered Hamas attacks against Israel in 2000". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Mosab Hassan Yousef (2011). Son of Hamas. Tyndale House. pp. 125–134. ISBN 978-1-85078-985-7. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- David Samuels (September 2005). "In a Ruined Country: How Yasir Arafat destroyed Palestine". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 30 August 2008. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- David Pratt (2007). Intifada: The Long Day of Rage. Casemate Publishers. p. 113. ISBN 978-1-932-03363-2.
As far back as May 2000 Ehud Barak and his advisors had themselves drafted operational and tactical contingency plans of their own to halt the intifada in its tracks. These included the massive use of IDF snipers, which resulted in the high numbers of Palestinian dead and wounded in the first few days of the uprising. It was these tactics as much as any advanced planning that many believed transformed a series of violent clashes into a full-blown intifada.
- "Suha Arafat admits husband premeditated Intifada". The Jerusalem Post. 29 December 2012. Archived from the original on 14 November 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Hussein Dakroub (26 March 2002). "Arafat Aide, Hezbollah Leader Meet". Associated Press News. Archived from the original on 20 July 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Nasser Abufarha, The Making of a Human Bomb: An Ethnography of Palestinian Resistance Archived 20 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine Duke University Press, 2009 p.77.
- Rubin, Barry M.; Rubin, Judith Colp (2003). Yasir Arafat: A Political Biography. Oxford University Press. p. 204. ISBN 978-0-19-516689-7.
- Nathan Thrall, 'What Future for Israel?,' Archived 21 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine New York Review of Books 15 August 2013 pp.64–67.
- Gutman, Matthew (4 August 2004). "Aqsa Brigades Leader: Intifada in Its Death Throes". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities Archived 5 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine, B'Tselem.
- ^ Schiff, Ze'ev (24 August 2004). "Israeli death toll in Intifada higher than last two wars". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Remember these Children". Archived from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014. Comprehensive list of all Israeli and Palestinian child casualties, age 17 and under, listed since September 2000 along with the circumstances of their deaths.
- Tamar Sternthal (2 November 2008). "Updated: In 2007, B'Tselem Casualty Count Doesn't Add Up". CAMERA. Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014. Includes translation of article in Hebrew in Haaretz presenting Dahoah-Halevi's report.
Original Haaretz report in Hebrew: Amos Harel (25 October 2008). "מחקר: "בצלם" מפרסם מידע שגוי ומשמיט פרטים חיוניים" [Study: "B'Tselem" publishes false information and omits vital details]. Haaretz. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014. - "Column one: What is Israel's problem?". The Jerusalem Post. 10 May 2007.,
- Caroline B. Glick (7 January 2011). "Column One: Agents of influence". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 27 May 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Tamar Sternthal (7 July 2003). "B'Tselem, Los Angeles Times Redefine "Civilian"". CAMERA. Archived from the original on 9 September 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Sternthal, Tamar (24 September 2008). "Bending the truth". Ynetnews. Archived from the original on 25 September 2008. Retrieved 26 September 2008.
- Gil Ronen (26 October 2008). "Researcher Slams B'Tselem as Inflating Arab Civilian Casualties". Arutz Sheva. Archived from the original on 31 March 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Tamar Sternthal (3 January 2007). "B'Tselem's Annual Casualty Figures Questioned". CAMERA. Archived from the original on 28 February 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Two-thirds of Palestinians Killed in the West Bank This Year Did not Participate in the Fighting". B'Tselem. 8 December 2004. Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Benny Morris (2009). One State, Two States: Resolving the Israel/Palestine Conflict. Yale University Press. pp. 151–152. ISBN 978-0-300-12281-7.
- "B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities. Palestinians killed by Palestinians in the Occupied Territories". Detailed B'Tselem list. Archived 3 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Erika Waak (January–February 2003). "Violence among the Palestinians". The Humanist. American Humanist Association. Archived from the original on 11 February 2003.
- Leonie Schultens (April 2004). "The 'Intra'fada or 'the chaos of the weapons': An Analysis of Internal Palestinian Violence". The Palestinian Human Rights Monitor. Palestinian Human Rights Monitoring Group. Archived from the original on 6 June 2004.
- Sean Maguire; Khaled Oweis (10 January 2007). "Exclusive-Hamas leader says Israel's existence is a reality". Reuters. Archived from the original on 18 October 2007.
- Harel, Amos (27 December 2008). "Analysis / IAF strike on Gaza is Israel's version of 'shock and awe'". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 13 May 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Israel braced for Hamas response". BBC News. 2 January 2009. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "Israel pounds Gaza for fourth day". BBC News. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2009.
- "Israel vows war on Hamas in Gaza". BBC News. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 30 December 2008.
- "Israeli Gaza 'massacre' must stop, Syria's Assad tells US senator". Agence France-Presse. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 22 January 2009. Retrieved 11 January 2009.
- "Factions refuse Abbas' call for unity meeting amid Gaza massacre". Journal of Turkish Weekly. Ma'an News Agency. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 24 January 2009. Retrieved 11 January 2009.
- Adas, Basil (28 December 2008). "Iraqi leaders discuss Gaza massacre". Gulf News. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Hamas slammed the silent and still Arab position on Gaza massacre" – "Israel airstrikes on Gaza kill at least 205". Khaleej Times. Deutsche Presse-Agentur (DPA). 27 December 2008. Archived from the original on 23 January 2009.
- "it's impossible to contain the Arab and Islamic world after the Gaza massacre" – "Hamas denies firing rockets from Lebanon". Special Broadcasting Service. Agence France-Presse. 8 January 2009. Archived from the original on 19 January 2009. Retrieved 11 January 2009.
- "Arab Leaders Call for Palestinian Unity During "Terrible Massacre"". Fox News. Associated Press. 31 December 2008. Archived from the original on 22 January 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- "Gulf leaders tell Israel to stop Gaza 'massacres'". Reuters. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 18 January 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- "OIC, GCC denounce massacre in Gaza". Arab News. 28 December 2008. Archived from the original on 18 January 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- سباق دبلوماسي لوقف مذبحة غزة [Diplomatic race to stop the Gaza massacre]. BBC News (in Arabic). 5 January 2009. Archived from the original on 6 January 2009. Retrieved 11 January 2009.
- "United Nations Security Council 6060th meeting (Click on the page S/PV.6060 record for transcript)". United Nations Security Council. 31 December 2008. Archived from the original on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 7 January 2009.
- Ravid, Barak (18 January 2009). "IDF begins Gaza troop withdrawal, hours after ending 3-week offensive". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 17 August 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Yuval Azoulay (2 January 2009). "Two IDF soldiers, civilian lightly hurt as Gaza mortars hit Negev". Haaretz. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Yagna, Yanir (2 April 2008). "Ten rockets hit southern Israel, one damages Ashkelon school". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 20 September 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Remembering Israel's 2008 War on Gaza". 27 December 2018. Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 3 February 2024.
- "B'Tselem: Israeli security forces killed 660 Palestinians during 2006". Haaretz. 28 December 2006. Archived from the original on 13 May 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Efraim Benmelech; Claude Berrebi (Summer 2007). "Human Capital and the Productivity of Suicide Bombers" (PDF). Journal of Economic Perspectives. 21 (3): 223–238. doi:10.1257/jep.21.3.223. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 July 2010.
- "Q&A: Gaza conflict". BBC News. 18 January 2009. Archived from the original on 5 July 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Gaza's rocket threat to Israel". BBC News. 21 January 2008. Archived from the original on 23 September 2011. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Hamas releases audio of captured Israeli". USA Today. 25 June 2007. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Timeline / 1,940 days from Gilad Shalit's abduction to his release". Haaretz. 11 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Marcus Gee (10 May 2001). "Mr. Day Speaks the Truth". The Globe and Mail. Toronto. p. A.19. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
-
- Kalman, Mathew. "Two Israeli teenagers stoned to death 1". usatoday.com. USA TODAY. Archived from the original on 20 April 2011. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- Glee, Marcus. "Mr. Day Speaks the Truth 2". The Globe and Mail. The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Katz, Yakoov. "IDF nabs Ze'ev Kahane's murderer". The Jerusalem Post | Jpost.com. The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Hershman, Tania. "Israel's 'First Internet Murder". Wired. Wired. Archived from the original on 19 October 2007. Retrieved 15 January 2001.
{{cite magazine}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - "The Murder of Ofir Rahum". Israel Government Portal., Inc. Archived from the original on 22 October 2007. Retrieved 22 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Katz, Yaakov (7 March 2008). ""Eight killed at Jerusalem school"". BBC News. Archived from the original on 9 March 2008. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ""Terror Attack At Jerusalem Seminary – Merkaz HaRav Yeshiva – 8 Dead"". National Terror Alert Response Center. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ""Jerusalem seminary attacked"". United Press International. Archived from the original on 8 March 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- Assaf Zohar (17 October 2001). "Minister of Tourism Rehavam Zeevi assassinated at point-blank range in Jerusalem Hyatt". Globes. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Phil Reeves. "'Get tough' call to Sharon as Jewish boys stoned to death". Irish Independent. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
-
- Alan, Philips (13 October 2020). "A day of rage, revenge and bloodshed". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - "Get tough' call to Sharon as Jewish boys stoned to death". Irish Independent. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- Smith, John (13 October 2000). "Lynch mob's brutal attack". BBC News. Archived from the original on 29 January 2008. Retrieved 16 June 2004.
- Raymond, Whitaker (14 October 2000). "A strange voice said: I just killed your husband". The Independent London. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- Alan, Philips (13 October 2020). "A day of rage, revenge and bloodshed". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- Luft, Gal (July–August 2002). "The Palestinian H-Bomb: Terror's Winning Strategy". Foreign Affairs. 81 (4): 2–7. doi:10.2307/20033234. JSTOR 20033234. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "Terrorist organizations exploit UNRWA vehicles: during the Israeli army operation in the Zeitun quarter of Gaza, UNWRA vehicles were used to smuggle armed terrorists out of the area and in all probability remains of Israeli soldiers as well". Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center at the Center for Special Studies (C.S.S). May 2004. Archived from the original on 3 June 2004.
- Snitz, Kobi (15 December 2004). "We are all Ahmed Awwad: Lessons in Popular Resistance". Znet. Archived from the original on 18 April 2005.
- "Palestinian Nonviolent Resistance to Occupation Since 1967" (PDF). Faces of Hope. American Friends Service Committee. Fall 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 November 2005.
- "Palestinian non-violent resistance". Mazin Qumsiyeh. Archived from the original on 27 August 2004.
- Kaufman, Maxine. "Peace Magazine v20n4p22: A Glimpse of Palestinian Nonviolence". Peace Magazine. Archived from the original on 7 December 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- Elmer, Jon. "Protest, Grief as Barrier Segregates Palestinian Village from Farms". The NewStandard. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- "News From Within-> Home Numbers". 13 June 2001. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2014.
- "Budrus has a hammer". ZNet. 17 March 2005. Archived from the original on 18 April 2005.
- "Palestinian non-violent resistance continues: the experience of Beit Sira". Palestine Monitor. 21 February 2006. Archived from the original on 27 May 2006.
- Jumá, Jamal (26 March 2005). "The great divide". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- Jamal Jumá (7–13 April 2005). "Palestine is not for sale!". Al-Ahram. Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- "Palestinian Christians Call for Non-Violent Resistance". National Council of Churches. 10 May 2002. Archived from the original on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- "Israel and the Occupied Territories and the Palestinian Authority: Act Now to Stop the Killing of Children!". Amnesty International. 20 November 2004. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- Gabi Siboni, Defeating Suicide Terrorism in Judea and Samaria, 2002–2005 Archived 20 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine, "Military and Strategic Affairs", Volume 2, No. 2, October 2010.
- "School of Politics and International Studies – Site Homepage" (PDF). School of Politics and International Studies.
- Bergman, Ronen (3 February 2018). "How Israel Won a War but Paid a High Moral Price". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- Milanovic, Marko (June 2007). "Lessons for human rights and humanitarian law in the war on terror: comparing Hamdan and the Israeli Targeted Killings case" (PDF). International Review of the Red Cross. 89 (866): 375. doi:10.1017/S181638310700104X. S2CID 146130526. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- "UN envoy condemns Israel's extra-judicial assassinations". UN News Centre. 25 August 2003. Archived from the original on 12 July 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Wilson, Scott (15 December 2006). "Israeli High Court Backs Military On Its Policy of 'Targeted Killings'". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 20 October 2017. Retrieved 11 September 2017.
- Tavernise, Sabrina (26 January 2009). "In Gaza, the Wait to Rebuild Lingers". The New York Times. p. A6. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- "EU warns against 'collective punishment' in Gaza". Reuters. 29 October 2007. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Ruebner, Josh (26 February 2010). "U.S. Can't Afford Military Aid to Israel". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 18 June 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ Mearsheimer, John; Walt, Stephen (2008). The Israel Lobby and U.S. Foreign Policy. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-53150-8.
- O'Sullivan, Arieh; Friedson, Felice (3 March 2010). "Jewish-Agency-style 'Palestine Network; launched in Bethleh". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- Concepcion, Juan Carlos (9 September 2013). "Top 10 recipients of EU aid". Devex. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- Zanotti, Jim (3 July 2014). "U.S. Foreign Aid to the Palestinians" (PDF). Federation of American Scientists. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 August 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- Sela, Avraham. "Arab Summit Conferences". The Continuum Political Encyclopedia of the Middle East. Ed. Sela. New York: Continuum, 2002. pp. 158–160
- מכון ב.י. ולוסיל כהן למחקרי דעת קהל. social-sciences.tau.ac.il. Archived from the original on 2 June 2006.
- מדד השלום (PDF) (in Hebrew). The Tami Steinmetz Center for Peace Research. May 2004. Archived from the original on 8 November 2006.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Tabarani, Gabriel G. (2008). Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: From Balfour Promise to Bush Declaration: THE COMPLICATIONS AND THE ROAD FOR A LASTING PEACE. AuthorHouse. pp. 242–243. ISBN 978-1-4343-7237-6. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
Sources
Books
- Bregman, Ahron (29 September 2005). Elusive Peace: How the Holy Land Defeated America. Penguin Books Limited. pp. 160–. ISBN 978-0-14-190613-3. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- Byman, Daniel (15 June 2011). A High Price: The Triumphs and Failures of Israeli Counterterrorism. Oxford University Press. pp. 114–. ISBN 978-0-19-983045-9. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- Catignani, Sergio (2008). Israeli Counter-Insurgency and the Intifadas: Dilemmas of a Conventional Army. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-93069-4. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- Mattar, Philip (2005). Encyclopedia of the Palestinians. Infobase Publishing. pp. 40–. ISBN 978-0-8160-6986-6. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- Reinhart, Tanya (2006). The Road Map to Nowhere: Israel/Palestine Since 2003. Verso Books. ISBN 978-1-84467-076-5.
- Schulz, Helena Lindholm; Hammer, Juliane (2003). The Palestinian Diaspora: Formation of Identities and Politics of Homeland. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26820-2.
- Shindler, Colin (25 March 2013). A History of Modern Israel. Cambridge University Press. pp. 283–. ISBN 978-1-107-31121-3. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- Tucker, Spencer C. (31 August 2019). Middle East Conflicts from Ancient Egypt to the 21st Century: An Encyclopedia and Document Collection [4 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. pp. 958–. ISBN 978-1-4408-5353-1. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- Yousef, Mosab Hassan (2011). Son of Hamas: A Gripping Account of Terror, Betrayal, Political Intrigue, and Unthinkable Choices. Tyndale House. ISBN 978-1-85078-985-7. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- Cohen, Hillel (2013). The Rise and Fall of Arab Jerusalem: Palestinian Politics and the City Since 1967. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-85266-4.
Journal articles
- Pressman, Jeremy (21 February 2006). "The Second Intifada: Background and Causes of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict". Journal of Conflict Studies. 23 (2). ISSN 1715-5673. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
Articles
- "Al-Aqsa Intifada timeline". BBC News. 29 September 2004. Archived from the original on 2 July 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "Full text of Abbas declaration". BBC News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 8 March 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "Full text of Sharon declaration". BBC News. 8 February 2005. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "A Feud That Lasted A Lifetime: Ariel Sharon Vs. Yasser Arafat". NPR.org. 11 January 2014. Archived from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
External links
- [REDACTED] Media related to Second Intifada at Wikimedia Commons
| Arab–Israeli conflict | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Post–Cold War conflicts in Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| East Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Southeast Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter-continental conflict | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wars and conflicts involving Israel | |
|---|---|
|
- Second Intifada
- Anti-Israeli sentiment in Palestine
- 2000s in Israel
- 2000s in the Palestinian territories
- Riots and civil disorder in Israel
- Riots and civil disorder in the Palestinian territories
- Protests in the Palestinian territories
- Stone-throwing in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
- Intifadas
- 2000s conflicts