| Revision as of 20:46, 9 October 2022 editJcubic (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users615 edits offical websiteTags: Reverted 2017 wikitext editor← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:12, 6 January 2025 edit undoGray eyes (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users30,541 edits removed Category:Photography companies of Germany; added Category:Photography equipment manufacturers of Germany using HotCat | ||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| | revenue = | | revenue = | ||
| | products = optical lenses, cameras, and other related products | | products = optical lenses, cameras, and other related products | ||
| | homepage = |
| homepage = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Voigtländer''' ({{IPA |
'''Voigtländer''' ({{IPA|de|ˈfoːktlɛndɐ}}) was a significant long-established company within the ] and photographic industry, headquartered in ], ],<ref name="VS1">{{Cite book|title=Voigtländer & Sohn: Die Firmengeschichte von 1756 bis 1914|trans-title=Voigtländer & Son: The company history from 1756 to 1914|url=http://www.appelhans-verlag.de/leseprobe/Voigtlaender+Sohn/files/assets/seo/toc.html|first=Carsten|last=Grabenhorst|publisher=Museum für Photographie – Appelhans Verlag|location=Braunschweig|year=2002|language=de|isbn=978-3-930292-25-7}}</ref> and today continues as a ] for a range of photographic products. | ||
| == History == | == History == | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| === Photography optics and cameras === | === Photography optics and cameras === | ||
| From 1839, the year, when the invention of ] was being published, came ] and from 1840 complete cameras for photography. The ] were revolutionary because they were the first mathematically calculated precision objectives in the history of photography, developed by the ]/] mathematics professor ], with technical advice provided by Peter Voigtländer.<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="BDHT1" /><ref name="DBE1" /> Voigtländer went on to produce the first ] (the fastest lens at that time: f/3.6) in 1840,<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="BDHT1" /> and the world's first all-metal ] camera (''Ganzmetallkamera'') in 1840,<ref name="VS1" /> also bringing out ] cameras shortly afterwards. An original of the 1840 all-metal daguerreotype camera with "No. 84 Voigtländer & Sohn in Vienna" is exhibited in the "]" in Munich. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| From 1839, the year, when the invention of ] was being published, came ] and from 1840 complete cameras for photography. The ] were revolutionary because they were the first mathematically calculated precision objectives in the history of photography, developed by the German-Hungarian mathematics professor ], with technical advice provided by Peter Voigtländer.<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="BDHT1" /><ref name="DBE1" /> Voigtländer went on to produce the first ] (the fastest lens at that time: f/3.6) in 1840,<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="BDHT1" /> and the world's first all-metal ] camera (''Ganzmetallkamera'') in 1840,<ref name="VS1" /> also bringing out ] cameras shortly afterwards. An original of the 1840 all-metal daguerreotype camera with "No. 84 Voigtländer & Sohn in Vienna" is exhibited in the "]" in Munich. | |||
| In 1845, Peter Voigtländer married the daughter of a respected ] lawyer, whom he met on one of his photographic |
In 1845, Peter Voigtländer married the daughter of a respected ] lawyer, whom he had met on one of his photographic sale journeys in Braunschweig.<ref name="VS1" /> Voigtländer had previously set up a branch sales office in ], ], at that time the central hub in the German rail network. Compared to Vienna, Braunschweig offered a location advantage regarding the distribution of Voigtländer objectives and daguerreotype camera products due to the greater proximity to the German overseas ports.<ref name="VS1" /> | ||
| During the rising social and political tensions in the ] leading to the ], Peter Voigtländer had joined the political cause of the Democrats and also became ] to the commander of the Vienna national civil guard—General {{ill|Wenzel Messenhauser|de}}.<ref name="VS1" /> As the revolutions escalated during the ] of October 1848, the counter-revolution had strengthened with full force, and General Messenhauser of the revolting national civil guard, like many others—were executed.<ref name="VS1" /> Voigtländer at that time had in perception of the power relations withdrawn from the Vienna national civil guard and with his family took refuge in a suburb of Vienna.<ref name="VS1" /> On the wishes of Peter Voigtländer's wife and when the March revolutions of 1848 hindered the further development of the young photographic company, the family promptly re-located from Vienna to his wife's hometown Braunschweig, where from 1849 Voigtländer established a subsidiary production site, granted on a provisional "Concession for the pursuit of a trade", issued by the city directorate with a term of five years.<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="DBE1" /> In September 1852, Peter Voigtländer was successfully awarded a so-called "land-cooperative" (German ''Markgenossenschaft'') and issued the desired unrestricted "Concession for the pursuit of a trade" in the city Braunschweig.<ref name="VS1" /> In 1864, Peter Voigtländer was honoured by Emperor ] with the ] of the ]; becoming known as Peter Wilhelm Friedrich ] ] Voigtländer.<ref name="DBE1" /> On the death of Voigtländer's Vienna works manager, the Vienna business was closed in 1868.<ref name="DBE1 |
During the rising social and political tensions in the ] leading to the ], Peter Voigtländer had joined the political cause of the Democrats and also became ] to the commander of the Vienna national civil guard—General {{ill|Wenzel Messenhauser|de}}.<ref name="VS1" /> As the revolutions escalated during the ] of October 1848, the counter-revolution had strengthened with full force, and General Messenhauser of the revolting national civil guard, like many others—were executed.<ref name="VS1" /> Voigtländer at that time had in perception of the power relations withdrawn from the Vienna national civil guard and with his family took refuge in a suburb of Vienna.<ref name="VS1" /> On the wishes of Peter Voigtländer's wife and when the March revolutions of 1848 hindered the further development of the young photographic company, the family promptly re-located from Vienna to his wife's hometown Braunschweig, where from 1849 Voigtländer established a subsidiary production site, granted on a provisional "Concession for the pursuit of a trade", issued by the city directorate with a term of five years.<ref name="VS1" /><ref name="DBE1" /> In September 1852, Peter Voigtländer was successfully awarded a so-called "land-cooperative" (German ''Markgenossenschaft'') and issued the desired unrestricted "Concession for the pursuit of a trade" in the city Braunschweig.<ref name="VS1" /> In 1864, Peter Voigtländer was honoured by Emperor ] with the ] of the ]; becoming known as Peter Wilhelm Friedrich ] ] Voigtländer.<ref name="DBE1" /> On the death of Voigtländer's Vienna works manager, the Vienna business was closed in 1868.<ref name="DBE1" /> | ||
| ===Public corporation=== | |||
| Over the next three decades, Voigtländer became a technology leader and the first manufacturer to introduce several new kinds of product that later became commonplace. These include the first ] for 35 mm still photography (36–82/2.8 Zoomar) in 1959<ref>{{Cite news |last=Deschin |first=Jacob |date=15 March 1959 |title=Zoom Lens For Stills |url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1959/03/15/110085221.html?pageNumber=419 |work=The New York Times |page=X11 |access-date=September 12, 2017 |url-access=subscription }}</ref> and the first 35 mm compact camera with built-in ] (Vitrona) in 1965. | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Voigtländer Braunschweig changed status to a public '']'' (Voigtländer & Sohn AG) in 1898. In 1923 a majority of the shares (99.7%) were acquired by ]'s photo division and large-scale production then took place in 1925.<ref name="VS1" /> | |||
| ] | |||
| Schering sold its share of the company to the ] in 1956, and ''Zeiss-Ikon'' and ''Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft'' integrated in 1965. Due to falling sales, on 4 August 1971 ''Zeiss-Ikon/Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft'' ended producing cameras and closed the Voigtländer factory, which employed at the time 2,037 persons. Subsequently, the company moved to the collective enterprise ''Optische Werke Voigtländer'' (Optical Works Voigtländer), in which ], the state of ] and the ] camera manufacturer ] each participated to one-third; Later Rollei took over all the shares. On the collapse of Rollei in 1982, Plusfoto took over the name, selling it in 1997 to Ringfoto. | |||
| Over the next three decades, Voigtländer became a technology leader and the first manufacturer to introduce several new photographic products that later became commonplace. These include the first ] for 35 mm still photography (36–82/2.8 ]) in 1959<ref>{{Cite news |last=Deschin |first=Jacob |date=15 March 1959 |title=Zoom Lens For Stills |url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1959/03/15/110085221.html?pageNumber=419 |work=The New York Times |page=X11 |access-date=September 12, 2017 |url-access=subscription }}</ref> and the first 35 mm compact camera with built-in ] (Vitrona) in 1965. | |||
| Schering sold its share of the company to the ] in 1956, and '']'' and ''Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft'' integrated in 1965. Due to falling sales, on 4 August 1971 ''Zeiss-Ikon/Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft'' ceased camera production and closed the Voigtländer factory, which employed at the time 2,037 persons. Subsequently, the company was reorganized as the collective enterprise ''Optische Werke Voigtländer'' (Optical Works Voigtländer), in which ], the state of ] and the ] camera manufacturer ] each took an equal one-third share; in 1974, Rollei took over all the shares. On the collapse of Rollei in 1982, Plusfoto took over the name, selling it in 1997 to Ringfoto. | |||
| === Contemporary times === | |||
| === Current Status === | |||
| Since 1999, Voigtländer-branded products have been manufactured and marketed by the Japanese optics and camera company ], under license from Ringfoto GmbH & Co. ALFO Marketing KG; for these, see ]. | Since 1999, Voigtländer-branded products have been manufactured and marketed by the Japanese optics and camera company ], under license from Ringfoto GmbH & Co. ALFO Marketing KG; for these, see ]. | ||
| Line 62: | Line 66: | ||
| {{See also|Cosina Voigtländer}} | {{See also|Cosina Voigtländer}} | ||
| Original Voigtländer lens designs can be divided roughly between pre-war designs, which date back to a series of lenses developed by Dr. Hans Harting as ] and '']'' derivatives at around the start of the 20th century, and post-war designs, which largely are credited to Dr. Albrecht Tronnier. | |||
| Below is a list of original Voigtländer lens designs (in all variants). | |||
| * Voigtar, a three element lens. | |||
| The pre-war designs include: | |||
| * Vaskar | |||
| * ''Heliar'', designed by Dr. Hans Harting originally in 1902 as a symmetric design derived from the '']'' with five elements in three groups consisting of two cemented doublets flanking a central bi-concave element,<ref name=US716035A/> followed quickly by an improved asymmetric design.<ref name=DE143889C/><ref name=Croell>{{cite web |url=https://www.arnecroell.com/voigtlaender.pdf |title=Voigtländer Large Format Lenses from 1949-1972 |author=Cröll, Arne |date=August 10, 2020 |access-date=16 May 2023}}</ref>{{rp|2}} The Heliar was made over many years, and was usually a 5 element lens, the 75 mm versions were of a 6 element design. The 125 mm version actually had 11 elements. | |||
| * Helomar | |||
| ** ''Dynar'' was a similar five-element, three-group lens designed by Harting in 1904, but the cemented doublets were reversed compared to the original ''Heliar''; this design was later renamed ''Heliar''.<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|2}} Robert Richter designed several improved versions of the ''Heliar'' in the 1920s.<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|2}} | |||
| * Skopar, Skoparex, Skoparet, Skopagon, Color-Skopar, Color-Skopar X. The basic Skopar is a 4 element Tessar type lens. | |||
| ** ''Tele-Dynar'', another five-element, three-group design similar to the ''Heliar''<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|3}} | |||
| * Heliar, The Heliar was made over many years, and was usually a 5 element lens, the 75 mm versions were of a 6 element design. The 125 mm version actually had 11 elements. | |||
| ** ''Apo Lanthar'', designed by Tronnier in 1949<ref name=US2645154A/> which shared lens geometries with the improved ''Heliar''<ref name=US2645156A/> that Tronnier developed at the same time.<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|11}} Most are slightly radioactive; the ''Lanthar'' name refers to the ]-doped glass used in its construction, which often included ].<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|12–13}} | |||
| * Dynarex, Dynaret, Color-Dynarex, Super-Dynarex, Super-Dynaret | |||
| * ''Voigtar'', a three-element ] derivative<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|2–3}} | |||
| * Septon | |||
| ** Similar post-war triplet designs include the ''Vaskar'' and ''Color-Lanthar'' | |||
| * Color-Lanthar | |||
| * ''Skopar'', a 4-element, 3-group ] type lens.<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|2}} | |||
| * Color-Ultron | |||
| ** Improved ''Skopar'' designs were sold as ''Skoparex'', ''Skoparet'', ''Skopagon'', ''Color-Skopar'', and ''Color-Skopar X''. | |||
| * Zoomar, usually reckoned to be the first zoom lens specifically designed for a 35 mm "still" camera. | |||
| * ''Heliostigmat'', a reversed ''Tessar''<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|2}} | |||
| * Nokton, Super Nokton | |||
| * ''Radiar'', a ]<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|3}} | |||
| * Apo Lanthar | |||
| Tronnier, who previously had designed several lenses for ], joined Voigtländer as a consultant in 1944 and is credited with several important post-war improvements and original designs,<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|4}} including: | |||
| * ''Ultron'',<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|5}} a fast asymmetric ] ] comparable to the Leitz '']'' and ] designs. This later was reformulated in 1968 with a concave front element for the ] cameras, credited as a Carl Zeiss lens after that company had acquired Voigtländer in 1956.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://lenslegend.com/carl-zeiss-ultron-50mm-f1-8-lens-review/ |title=Carl Zeiss Ultron 50mm f1.8 Lens Review |date=March 27, 2020 |website=Lens Legend |access-date=16 May 2023}}</ref> | |||
| * ''Nokton'',<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|5}} the fastest asymmetric double Gauss lens offered by Voigtländer, comparable to ]'s ''Ernostar'', the Leitz '']'', and ]. | |||
| * ''Ultragon'',<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|16–17}} an asymmetric design coupling the front half of a '']'' with the rear half of a double Gauss design. | |||
| * ''Telomar'',<ref name=Croell/>{{rp|18–20}} a telephoto derived from the ''Heliar''. | |||
| * ''Skoparon'', an ] wide-angle lens design for SLR cameras incorporating the ''Skopar''. | |||
| Additional post-war lenses include: | |||
| * ''Helomar'' | |||
| * Dynarex, Dynaret, Color-Dynarex, Super-Dynarex, Super-Dynaret, telephoto lenses | |||
| * Septon, comparable to the ''Ultron'' | |||
| In addition, Voigtländer offered the ] with its ] starting from 1959. The ''Zoomar'' was designed by Frank G. Back of Zoomar U.S.A and manufactured by Kilfitt in Munich; it is usually reckoned to be the first ] specifically designed for a 35 mm "still" camera. | |||
| <gallery heights=150px widths=200px caption="Voigtländer lens diagrams"> | |||
| File:Harting US716035A (Heliar, 1901).svg|''Heliar I'' (1901, Harting)<ref name=US716035A>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=716035A |title=Lens |inventor=Carl A.H. Harting |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=February 4, 1901 |fdate=February 4, 1901 |pubdate=December 16, 1902}}</ref> | |||
| File:Voigtländer DE143889C (Heliar II, 1902).svg|''Heliar II'' (1902)<ref name=DE143889C>{{cite patent |country=DE |status=Patent |number=143889C |title=Chromatisch, sphärisch und astigmatisch korrigiertes Objektiv |inventor= |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate= |fdate=December 1, 1900 |pubdate=June 10, 1902}}</ref> | |||
| File:Harting US765006A (Dynar, 1904).svg|''Dynar'' (1904, Harting)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=765006A |title=Lens |inventor=Hans Harting |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=February 17, 1904 |fdate=February 17, 1904 |pubdate=July 12, 1904}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2573511A (Color-Skopar, 1949).svg|''Skopar'' (1949, Tronnier)<ref name=US25753511A>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2573511A |title=Four-lens photographic objective |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=April 30, 1949 |fdate=November 17, 1949 |pubdate=October 30, 1951}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2645156A (Color-Heliar, 1949).svg|''Apo Lanthar'' (1949, Tronnier)<ref name=US2645154A>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2645154A |title=Five-lens photographic objective |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=October 17, 1949 |fdate=September 9, 1950 |pubdate=July 14, 1953}}</ref><br/>''Heliar III'' (1949, Tronnier)<ref name=US2645156A>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2645156A |title=Five-lens photographic objective comprising three members separated by air spaces |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=October 17, 1949 |fdate=September 12, 1950 |pubdate=July 14, 1953}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier DE969778C (Ultron, 1950).svg|''Ultron'' (1950, Tronnier)<ref>{{cite patent |country=DE |status=Patent |number=969778C |title=Sphärisch, chromatisch, astigmatisch und komatisch korrigiertes Objektiv |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=January 13, 1950 |fdate=February 4, 1950 |pubdate=August 28, 1958}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2645155A (Nokton, 1950).svg|''Nokton'' (1950, Tronnier)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2645155A |title=Photographic objective of high light-transmitting capacity of the gauss type |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=January 16, 1950 |fdate=September 12, 1950 |pubdate=July 14, 1953}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2670659A (Ultragon, 1951).svg|''Ultragon'' (1951, Tronnier)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2670659A |title=Modified gauss-type photographic objective formed of four components arranged in two groups |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=August 30, 1951 |fdate=July 29, 1952 |pubdate=March 3, 1954}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2662446A (Telomar, 1951).svg|''Telomar'' (1951, Tronnier)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2662446A |title=Photographic teleobjective having a composite positive front part axially spaced from a composite negative rear part |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=December 13, 1951 |fdate=December 13, 1951 |pubdate=December 15, 1953}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US2746351A (Skoparon, 1952).svg|''Skoparon'' (1952, Tronnier)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2746351A |title=Photographic objective of the modified triplet type and a meniscus shaped negative member axially separated therefrom |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=March 5, 1952 |fdate=March 3, 1953 |pubdate=May 22, 1956}}</ref> | |||
| File:Back US2913957A (Zoomar, 1959).svg|''Zoomar'' (1959, Back)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=2913957A |title=Varifocal lens assembly |inventor=Frank G. Back |assign=Zoomar |pridate=June 27, 1958 |fdate=June 27, 1958 |pubdate=November 24, 1959}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US3176582A (Vaskar, 1960).svg|''Vaskar'' (1960, Tronnier & Eggert)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=3176582A |title=Three lens photographic objective |inventor=Ernst Tronnier |invent2=Joachim Eggert |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=January 11, 1960 |fdate=August 25, 1960 |pubdate=April 6, 1965}}</ref> | |||
| File:Tronnier US3612663A (Ultron, 1968).svg|''Ultron II'' (1968, Tronnier, Eggert & Uberhagen)<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |status=Patent |number=3612663A |title=Wide-aperture objective of the expanded double-anastigmat type having an inner biconvex diaphragm-space and a concave front survace toward the distant object |inventor=Albrecht W. Tronnier |invent2=Joachim Eggert |invent3=Fritz Uberhagen |assign=Voigtländer & Sohn AG |pridate=June 14, 1968 |fdate=June 11, 1969 |pubdate=October 12, 1971}}</ref> | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Models == | == Models == | ||
| {|class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:100%;text-align:center;" | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| |+Voigtländer camera lines | |||
| File:150411-Voigtländer-01.jpg|Voigtländer Vitomatic IIa with Ultron 50 mm 1:2 | |||
| | colspan=2 {{diagonal split header|Type|Format}} | |||
| File:Voigtlander Bessa & Bessa RF.jpg|Voigtländer Bessa & Bessa RF | |||
| ! ] | |||
| File:Voigtlander Vito II Camera Digon3.jpg|Voigtländer Vito II | |||
| ! ] | |||
| File:Vitorets.JPG|Voigtländer Vitoret S | |||
| |- | |||
| File:Voigtlaender vitoret sst.jpg|Voigtländer Vitoret DR | |||
| ! colspan=2 | ] | |||
| File:Vitessa T.jpg|Voigtländer Vitessa T with German manual | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| File:Voigtlaender-superb-2.jpg|Voigtländer Superb | |||
| | style="background:#ddd;" | — | |||
| File:Voigtländer Bessy ak.jpg|Voigtländer Bessy | |||
| |- | |||
| File:Voigtländer Vitomatic IIa (Front), 1811111401, ako.jpg|Voigtländer Vitomatic IIa camera with Color Skopar f/2.8 lens | |||
| ! colspan=2 | ] | |||
| File:Voigtländer VF 135.jpg|Voigtländer VF 135 | |||
| | style="background:#ddd;" | — | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan=3 | ] | |||
| | Fixed-lens, rigid | |||
| | ] | |||
| | style="background:#ddd;" | — | |||
| |- | |||
| | Fixed-lens, folding | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | Interchangeable lens | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| | style="background:#ddd;" | — | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan=2 | ] | |||
| | Bessy, ], ], VF 135 | |||
| | style="background:#ddd;" | — | |||
| |} | |||
| <gallery heights=150px widths=200px caption="Voigtländer cameras"> | |||
| File:150411-Voigtländer-01.jpg|Vitomatic IIa with Ultron 50 mm 1:2 | |||
| File:Voigtlander Bessa & Bessa RF.jpg|Bessa & Bessa RF | |||
| File:Voigtlander Vito II Camera Digon3.jpg|Vito II | |||
| File:Vitorets.JPG|Vitoret S | |||
| File:Voigtlaender vitoret sst.jpg|Vitoret DR | |||
| File:Vitessa T.jpg|Vitessa T with German manual | |||
| File:Voigtlaender-superb-2.jpg|Superb | |||
| File:Voigtländer Bessy ak.jpg|Bessy | |||
| File:Voigtländer Vitomatic IIa (Front), 1811111401, ako.jpg|Vitomatic IIa camera with Color Skopar f/2.8 lens | |||
| File:Voigtländer VF 135.jpg|VF 135 | |||
| </gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| {{div col |colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * ] series | |||
| * ] & ] SLR cameras (1958–69) | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] rangefinder cameras (1950–59?) | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| * ] series | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| Line 109: | Line 175: | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| {{Voigtländer}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Voigtlander}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Voigtlander}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:12, 6 January 2025
German optical manufacturer | |
 Replica of the world's first all-metal camera from 1840, the daguerreotype camera No. 84 Voigtländer & Son in Vienna, at the Swedish National Museum of Science and Technology, Stockholm, Sweden. The revolutionary lens is light-fast so that exposure time could be reduced to around one minute. Replica of the world's first all-metal camera from 1840, the daguerreotype camera No. 84 Voigtländer & Son in Vienna, at the Swedish National Museum of Science and Technology, Stockholm, Sweden. The revolutionary lens is light-fast so that exposure time could be reduced to around one minute. | |
| Industry | optics and photography (lens and camera manufacturer) |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1756; 269 years ago (1756) in Vienna, Archduchy of Austria |
| Founder | Johann Christoph Voigtländer |
| Defunct | 1972 (1972) |
| Fate | Brand acquired by Rollei (1973) Plusfoto GmbH & Co. (1983) RINGFOTO GmbH & Co. ALFO Marketing KG (1997) |
| Successor | Schering AG (1923) Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung (1956) Carl Zeiss AG, state of Lower Saxony and Rollei (1972) |
| Headquarters | Braunschweig, Germany |
| Products | optical lenses, cameras, and other related products |
Voigtländer (German pronunciation: [ˈfoːktlɛndɐ]) was a significant long-established company within the optics and photographic industry, headquartered in Braunschweig, Germany, and today continues as a trademark for a range of photographic products.
History
Voigtländer was founded in Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, in 1756, by Johann Christoph Voigtländer [de]. Voigtländer produced mathematical instruments, precision mechanical products, optical instruments, including optical measuring instruments and opera glasses, and is the oldest name in cameras.
Early beginnings
Johann Christoph Voigtländer (November 19, 1732 in Leipzig – June 27, 1797 in Vienna), the son of a carpenter, came to Prague in 1755, and to Vienna in the same year, and worked from 1757 to 1762 in the workshop of Meinicke, who produced mathematical instruments.
Through Johann Voigtländer's skilful achievements, the Minister of State of the Habsburg monarchy—Prince Wenzel von Kaunitz, drew attention to Voigtländer and Empress Maria Theresa of Austria granted Voigtländer in 1763 a so-called trade "Protection Decree" (German Schutzdekret/Schutzdecret): "on the making of mathematical instruments and on an unspecified number of workers", upon which Voigtländer founded his own workshop and whereby he could sell his products relatively unrivalled.
In 1767, Voigtländer invented two important tools: a linear device for natural and tapered gauges, and a circular device for elevation, astrolabe, and cartography etc., including, a screw cutting machine, a metal lathe and finishing rollers for sheep wool and silk factories. The production program was supplemented by compasses, tweezers, levelling devices, dioptres and other fine mechanical products.
In recognition of his achievements and dexterity, Voigtländer received in 1797 a so-called "national commercial license with all advantages and privileges" (German Landesfabriksbefugnis); this license awarded Voigtländer under certain circumstances the prestige to display the imperial eagle of the Habsburg monarchy, but above all the right to establish branch sales offices in all major cities of the empire. In the same year, Voigtländer died, and his successful family business was continued by his widow, their three sons and one daughter.

From 1840, Voigtländer's grandson Peter Wilhelm Friedrich Ritter von Voigtländer [de] established Voigtländer as a leading photographic company of its time on introducing and producing the Petzval objective lens.
Photography optics and cameras
From 1839, the year, when the invention of photography was being published, came objective optics and from 1840 complete cameras for photography. The Voigtländer objectives were revolutionary because they were the first mathematically calculated precision objectives in the history of photography, developed by the Austro-Hungarian/Slovak mathematics professor Josef Maximilian Petzval, with technical advice provided by Peter Voigtländer. Voigtländer went on to produce the first Petzval portrait photographic lens (the fastest lens at that time: f/3.6) in 1840, and the world's first all-metal daguerreotype camera (Ganzmetallkamera) in 1840, also bringing out photographic plate cameras shortly afterwards. An original of the 1840 all-metal daguerreotype camera with "No. 84 Voigtländer & Sohn in Vienna" is exhibited in the "Deutsches Museum" in Munich.
In 1845, Peter Voigtländer married the daughter of a respected Braunschweig lawyer, whom he had met on one of his photographic sale journeys in Braunschweig. Voigtländer had previously set up a branch sales office in Braunschweig, Duchy of Brunswick, at that time the central hub in the German rail network. Compared to Vienna, Braunschweig offered a location advantage regarding the distribution of Voigtländer objectives and daguerreotype camera products due to the greater proximity to the German overseas ports.
During the rising social and political tensions in the Austrian Empire leading to the Revolutions of 1848, Peter Voigtländer had joined the political cause of the Democrats and also became adjutant to the commander of the Vienna national civil guard—General Wenzel Messenhauser [de]. As the revolutions escalated during the Vienna Uprising of October 1848, the counter-revolution had strengthened with full force, and General Messenhauser of the revolting national civil guard, like many others—were executed. Voigtländer at that time had in perception of the power relations withdrawn from the Vienna national civil guard and with his family took refuge in a suburb of Vienna. On the wishes of Peter Voigtländer's wife and when the March revolutions of 1848 hindered the further development of the young photographic company, the family promptly re-located from Vienna to his wife's hometown Braunschweig, where from 1849 Voigtländer established a subsidiary production site, granted on a provisional "Concession for the pursuit of a trade", issued by the city directorate with a term of five years. In September 1852, Peter Voigtländer was successfully awarded a so-called "land-cooperative" (German Markgenossenschaft) and issued the desired unrestricted "Concession for the pursuit of a trade" in the city Braunschweig. In 1864, Peter Voigtländer was honoured by Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria with the Knight's Cross of the Order of Franz Joseph; becoming known as Peter Wilhelm Friedrich Ritter von Voigtländer. On the death of Voigtländer's Vienna works manager, the Vienna business was closed in 1868.
Public corporation



Voigtländer Braunschweig changed status to a public Aktiengesellschaft (Voigtländer & Sohn AG) in 1898. In 1923 a majority of the shares (99.7%) were acquired by Schering AG's photo division and large-scale production then took place in 1925.

Over the next three decades, Voigtländer became a technology leader and the first manufacturer to introduce several new photographic products that later became commonplace. These include the first zoom lens for 35 mm still photography (36–82/2.8 Zoomar) in 1959 and the first 35 mm compact camera with built-in electronic flash (Vitrona) in 1965.
Schering sold its share of the company to the Carl Zeiss Foundation in 1956, and Zeiss-Ikon and Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft integrated in 1965. Due to falling sales, on 4 August 1971 Zeiss-Ikon/Voigtländer-Vertriebsgesellschaft ceased camera production and closed the Voigtländer factory, which employed at the time 2,037 persons. Subsequently, the company was reorganized as the collective enterprise Optische Werke Voigtländer (Optical Works Voigtländer), in which Carl Zeiss AG, the state of Lower Saxony and the Braunschweig camera manufacturer Rollei each took an equal one-third share; in 1974, Rollei took over all the shares. On the collapse of Rollei in 1982, Plusfoto took over the name, selling it in 1997 to Ringfoto.
Current Status
Since 1999, Voigtländer-branded products have been manufactured and marketed by the Japanese optics and camera company Cosina, under license from Ringfoto GmbH & Co. ALFO Marketing KG; for these, see Cosina Voigtländer.
Lenses

Original Voigtländer lens designs can be divided roughly between pre-war designs, which date back to a series of lenses developed by Dr. Hans Harting as Cooke triplet and Tessar derivatives at around the start of the 20th century, and post-war designs, which largely are credited to Dr. Albrecht Tronnier.
The pre-war designs include:
- Heliar, designed by Dr. Hans Harting originally in 1902 as a symmetric design derived from the Cooke triplet with five elements in three groups consisting of two cemented doublets flanking a central bi-concave element, followed quickly by an improved asymmetric design. The Heliar was made over many years, and was usually a 5 element lens, the 75 mm versions were of a 6 element design. The 125 mm version actually had 11 elements.
- Dynar was a similar five-element, three-group lens designed by Harting in 1904, but the cemented doublets were reversed compared to the original Heliar; this design was later renamed Heliar. Robert Richter designed several improved versions of the Heliar in the 1920s.
- Tele-Dynar, another five-element, three-group design similar to the Heliar
- Apo Lanthar, designed by Tronnier in 1949 which shared lens geometries with the improved Heliar that Tronnier developed at the same time. Most are slightly radioactive; the Lanthar name refers to the lanthanum oxide-doped glass used in its construction, which often included thorium dioxide.
- Voigtar, a three-element Cooke Triplet derivative
- Similar post-war triplet designs include the Vaskar and Color-Lanthar
- Skopar, a 4-element, 3-group Tessar type lens.
- Improved Skopar designs were sold as Skoparex, Skoparet, Skopagon, Color-Skopar, and Color-Skopar X.
- Heliostigmat, a reversed Tessar
- Radiar, a Dialyte
Tronnier, who previously had designed several lenses for Schneider Kreuznach, joined Voigtländer as a consultant in 1944 and is credited with several important post-war improvements and original designs, including:
- Ultron, a fast asymmetric double Gauss normal lens comparable to the Leitz Summicron and Zeiss Planar designs. This later was reformulated in 1968 with a concave front element for the Icarex cameras, credited as a Carl Zeiss lens after that company had acquired Voigtländer in 1956.
- Nokton, the fastest asymmetric double Gauss lens offered by Voigtländer, comparable to Ludwig Bertele's Ernostar, the Leitz Summilux, and Zeiss Sonnar.
- Ultragon, an asymmetric design coupling the front half of a Topogon with the rear half of a double Gauss design.
- Telomar, a telephoto derived from the Heliar.
- Skoparon, an inverted telephoto wide-angle lens design for SLR cameras incorporating the Skopar.
Additional post-war lenses include:
- Helomar
- Dynarex, Dynaret, Color-Dynarex, Super-Dynarex, Super-Dynaret, telephoto lenses
- Septon, comparable to the Ultron
In addition, Voigtländer offered the Zoomar with its Bessamatic starting from 1959. The Zoomar was designed by Frank G. Back of Zoomar U.S.A and manufactured by Kilfitt in Munich; it is usually reckoned to be the first zoom lens specifically designed for a 35 mm "still" camera.
- Voigtländer lens diagrams
-
 Heliar I (1901, Harting)
Heliar I (1901, Harting)
-
 Heliar II (1902)
Heliar II (1902)
-
 Dynar (1904, Harting)
Dynar (1904, Harting)
-
 Skopar (1949, Tronnier)
Skopar (1949, Tronnier)
-
 Apo Lanthar (1949, Tronnier)
Apo Lanthar (1949, Tronnier)
Heliar III (1949, Tronnier) -
 Ultron (1950, Tronnier)
Ultron (1950, Tronnier)
-
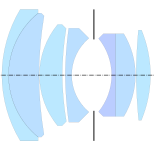 Nokton (1950, Tronnier)
Nokton (1950, Tronnier)
-
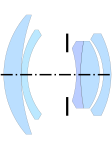 Ultragon (1951, Tronnier)
Ultragon (1951, Tronnier)
-
 Telomar (1951, Tronnier)
Telomar (1951, Tronnier)
-
 Skoparon (1952, Tronnier)
Skoparon (1952, Tronnier)
-
 Zoomar (1959, Back)
Zoomar (1959, Back)
-
 Vaskar (1960, Tronnier & Eggert)
Vaskar (1960, Tronnier & Eggert)
-
 Ultron II (1968, Tronnier, Eggert & Uberhagen)
Ultron II (1968, Tronnier, Eggert & Uberhagen)
Models
| FormatType | 35 mm | Medium format | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLR | Bessamatic, Ultramatic | — | |
| TLR | — | Brillant, Superb | |
| RF | Fixed-lens, rigid | Vito (B/C) | — |
| Fixed-lens, folding | Vito (I/II/III/IIa), Vitessa | Bessa, Perkeo | |
| Interchangeable lens | Vitessa T, Prominent | — | |
| Compact | Bessy, Vitomatic, Vitoret, VF 135 | — | |
- Voigtländer cameras
-
 Vitomatic IIa with Ultron 50 mm 1:2
Vitomatic IIa with Ultron 50 mm 1:2
-
 Bessa & Bessa RF
Bessa & Bessa RF
-
 Vito II
Vito II
-
Vitoret S
-
 Vitoret DR
Vitoret DR
-
 Vitessa T with German manual
Vitessa T with German manual
-
 Superb
Superb
-
 Bessy
Bessy
-
 Vitomatic IIa camera with Color Skopar f/2.8 lens
Vitomatic IIa camera with Color Skopar f/2.8 lens
-
 VF 135
VF 135
- Bessamatic & Ultramatic SLR cameras (1958–69)
- Brillant/Brilliant
- Vitessa rangefinder cameras (1950–59?)
- Vitomatic
References
- ^ Grabenhorst, Carsten (2002). Voigtländer & Sohn: Die Firmengeschichte von 1756 bis 1914 [Voigtländer & Son: The company history from 1756 to 1914] (in German). Braunschweig: Museum für Photographie – Appelhans Verlag. ISBN 978-3-930292-25-7.
- ^ Day, Lance; McNeil, Ian (1996). Biographical Dictionary of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. pp. 958–959. ISBN 0-415-06042-7.
- ^ Deutschen Biographischen Enzyklopädie [German Biographical Encyclopaedia] (in German). Vol. 10. Munich: K.G. Saur Verlag. 2008. p. 292. ISBN 978-3-598-25040-8.
- Deschin, Jacob (15 March 1959). "Zoom Lens For Stills". The New York Times. p. X11. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- Objektiv Voigtländer Super Nokton – Ideal für Aufnahmen im Dunklen – Stiftung Warentest, Stiftung Warentest, 2021-05-06, German
- ^ US Patent 716035A, Carl A.H. Harting, "Lens", published December 16, 1902, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- ^ DE Patent 143889C, "Chromatisch, sphärisch und astigmatisch korrigiertes Objektiv", published June 10, 1902, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- ^ Cröll, Arne (August 10, 2020). "Voigtländer Large Format Lenses from 1949-1972" (PDF). Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ US Patent 2645154A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Five-lens photographic objective", published July 14, 1953, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- ^ US Patent 2645156A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Five-lens photographic objective comprising three members separated by air spaces", published July 14, 1953, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- "Carl Zeiss Ultron 50mm f1.8 Lens Review". Lens Legend. March 27, 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- US Patent 765006A, Hans Harting, "Lens", published July 12, 1904, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2573511A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Four-lens photographic objective", published October 30, 1951, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- DE Patent 969778C, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Sphärisch, chromatisch, astigmatisch und komatisch korrigiertes Objektiv", published August 28, 1958, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2645155A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Photographic objective of high light-transmitting capacity of the gauss type", published July 14, 1953, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2670659A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Modified gauss-type photographic objective formed of four components arranged in two groups", published March 3, 1954, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2662446A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Photographic teleobjective having a composite positive front part axially spaced from a composite negative rear part", published December 15, 1953, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2746351A, Albrecht W. Tronnier, "Photographic objective of the modified triplet type and a meniscus shaped negative member axially separated therefrom", published May 22, 1956, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 2913957A, Frank G. Back, "Varifocal lens assembly", published November 24, 1959, assigned to Zoomar
- US Patent 3176582A, Ernst Tronnier & Joachim Eggert, "Three lens photographic objective", published April 6, 1965, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
- US Patent 3612663A, Albrecht W. Tronnier; Joachim Eggert & Fritz Uberhagen, "Wide-aperture objective of the expanded double-anastigmat type having an inner biconvex diaphragm-space and a concave front survace toward the distant object", published October 12, 1971, assigned to Voigtländer & Sohn AG
Further reading
- Grabenhorst, Carsten (2002). Voigtländer & Sohn: Die Firmengeschichte von 1756 bis 1914 [Voigtländer & Son: The company history from 1756 to 1914] (in German). Braunschweig: Museum für Photographie – Appelhans Verlag. ISBN 978-3-930292-25-7.
External links
- Voigtländer Heliar Lens Article
- http://www.voigtlaender.com/
- Voigtländer Historical Lenses
- Complete list of all Voigtländer cameras and their images
- Documents and clippings about Voigtländer in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
| Voigtländer | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cameras |
| ||||||||||||
| Lenses |
| ||||||||||||