| Revision as of 07:21, 13 February 2023 editSimon-holmes69 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,479 edits →History: it's use doesn't seem noteworthy enough to warrant a specific reference here above other songs← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:51, 10 December 2024 edit undoKvng (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers108,284 editsm simplify link | ||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Synthesizer model}} | {{short description|Synthesizer model}} | ||
| {{More citations needed|reason=inline citations are lacking for several notable users of VCS3 throughout article.|date=August 2024}} | |||
| {{use dmy dates|cs1-dates=ly|date=June 2021}} | {{use dmy dates|cs1-dates=ly|date=June 2021}} | ||
| {{Use British English|date=November 2022}} | {{Use British English|date=November 2022}} | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The '''VCS 3''' (or '''VCS3'''; an ] for ''Voltage Controlled Studio, version #3'') is a portable ] with a flexible modular voice architecture introduced by ] ( |
The '''VCS 3''' (or '''VCS3'''; an ] for ''Voltage Controlled Studio, version #3'') is a portable ] with a flexible modular voice architecture introduced by ] (EMS) in 1969.<ref name=vcs3 group="#"> | ||
| {{cite web | {{cite web | ||
| | title = VCS3 (aka The Putney) – The Products | | title = VCS3 (aka The Putney) – The Products | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| EMS released the product under various names. Logos printed at the console's front left (see photos) say " |
EMS released the product under various names. Logos printed at the console's front left (see photos) say "V.C.S. 3" on the most widely sold version; "The Putney (VCS 3)" on the earlier version; and "The Synthi (VCS 3) II" on the later version "Synthi VCS 3 II".<ref name=vcs3ii group="#"> | ||
| {{cite web | {{cite web | ||
| | title = Synthi VCS3 II – The Products | | title = Synthi VCS3 II – The Products | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
| | publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | | publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | ||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| <div style="float:right;"> | |||
| ⚫ | ==History== | ||
| {{multiple image |align=right |direction=horizontal | {{multiple image |align=right |direction=horizontal | ||
| |header = VCS 3 variations | |||
| |caption1 = Synthi VCS 3 with <!-- printed --> logo:<br/> " |
|caption1 = Synthi VCS 3 with <!-- printed --> logo:<br/> "The Putney (VCS 3)" | ||
| |image1 = EMS_Putney_VCS_3.jpg |width1=150 | |image1 = EMS_Putney_VCS_3.jpg |width1=150 | ||
| |caption2 = Synthi VCS 3 II with <!-- printed --> logo:<br/> " |
|caption2 = Synthi VCS 3 II with <!-- printed --> logo:<br/> "The Synthi (VCS 3) II" | ||
| |image2 = EMS_at_MIM_Synthesizer.jpg |width2=156 | |image2 = EMS_at_MIM_Synthesizer.jpg |width2=156 | ||
| }} |
}} | ||
| ⚫ | The VCS 3 was created in 1969 by ]'s ] company. The electronics were designed largely by ], and its distinctive appearance was the work of electronic composer ]. It was one of the first ''portable'' commercially available synthesizers, in the sense that it was housed entirely in a small wooden case, unlike synths from American manufacturers such as ], ] and ], which had large cabinets and could take up entire rooms. | ||
| ⚫ | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | The VCS 3 was created in 1969 by ]'s ] company. The electronics were designed largely by ], and its distinctive appearance was the work of electronic composer ]. It was one of the first ''portable'' commercially available synthesizers, in the sense that it was housed entirely in a small wooden case, unlike synths from American manufacturers such as ], ] and ], which had large cabinets and could take up entire rooms. | ||
| ⚫ | The VCS 3 cost just under £330 in 1969. Some people found it unsatisfactory as a melodic instrument due to its inherent tuning instability.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Reid |first=Gordon |date=November 2000 |title=All About EMS, Part 1 |journal=] |url=http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/nov00/articles/retrozone.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160303173436/http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/nov00/articles/retrozone.htm |archive-date=2016-03-03}}</ref> This arose from the instrument's reliance on the then |
||
| ⚫ | The VCS 3 cost just under £330 in 1969. Some people found it unsatisfactory as a melodic instrument due to its inherent tuning instability.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Reid |first=Gordon |date=November 2000 |title=All About EMS, Part 1 |journal=] |url=http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/nov00/articles/retrozone.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160303173436/http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/nov00/articles/retrozone.htm |archive-date=2016-03-03}}</ref> This arose from the instrument's reliance on the then current method of exponential conversion of voltage to oscillator frequency—an approach that other companies also implemented with fewer tuning issues. However, the VCS 3 was renowned as an extremely powerful generator of electronic effects and processor of external sounds for its cost.{{according to whom|date=May 2013}} | ||
| The VCS 3 found popularity among artists seeking to create exotic synthesised sounds. As a result, remaining examples sell for far more than their original asking prices.<ref group=note>In August 2010, VCS3 reached £6700 in an ] auction.{{cn|date=November 2022}}</ref> | |||
| The first album recorded using only the VCS 3 was ''The Unusual Classical Synthesizer'' on Westminster Gold.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://sites.google.com/site/krakatack/unusualstuff |title=unusualstuff - krakatack |website=Sites.google.com |access-date=2020-04-12}}</ref> | The first album recorded using only the VCS 3 was ''The Unusual Classical Synthesizer'' on Westminster Gold.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://sites.google.com/site/krakatack/unusualstuff |title=unusualstuff - krakatack |website=Sites.google.com |access-date=2020-04-12}}</ref> | ||
| The |
The VCS 3 was popular among ] bands, and was used on recordings by ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] (with ] and as a solo artist or collaborator), ], ], ], and ], and many others. The VCS 3-generated bass sound at the beginning of Pink Floyd's "]" forms the foundation of the song, with its other parts heard in response. Two VCS 3s and a Sequencer 256 were featured in the 1978 film 'The Shout'.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://pinelectronics.com/2007/07/31/ems-vcs-3-the-shout-1978/|title=EMS VCS 3 "The Shout" 1978 | Pin Electronics}}</ref> | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| The |
The VCS 3 has three oscillators (the first two normal ]s; the third a ]), a ], two input amplifiers, a ], 24 dB/octave low-pass ],{{citation needed|date=September 2011}} a trapezoid ], a joystick controller, a voltage-controlled ] unit, and two stereo output amplifiers. Unlike most ] systems, which used cables to link components, the VCS 3 uses a distinctive patchboard matrix where pins are inserted to connect its components. | ||
| ===Keyboards controller=== | ===Keyboards controller=== | ||
| Line 57: | Line 56: | ||
| | archive-date=2013-10-31 | | archive-date=2013-10-31 | ||
| | publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | | publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | ||
| }}</ref> In 1972 it was extended for ] play as ''DK2''.<ref name=dk2 group="#"> | }}</ref> In 1972 it was extended for ] play as ''DK2''.<ref name=dk2 group="#"> | ||
| {{cite web | {{cite web | ||
| | title = DK2 – The Products | | title = DK2 – The Products | ||
| Line 81: | Line 80: | ||
| ===Related models=== | ===Related models=== | ||
| The VCS 3's basic design was reused by EMS in many other of their own products,{{Citation needed|date=September 2011}} most notably the ] (1971),<ref name=synthi100 group="#"> | The VCS 3's basic design was reused by EMS in many other of their own products,{{Citation needed|date=September 2011}} most notably the ] (1971),<ref name=synthi100 group="#">{{cite web | ||
| {{cite web | |||
| |title = Synthi 100 (formerly Digitana, aka the Delaware) – The Products | |title = Synthi 100 (formerly Digitana, aka the Delaware) – The Products | ||
| |url |
|url = http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/emsprods.html#synthi100 | ||
| |publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | |publisher = Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall) | ||
| |access-date = 2011-09-30 | |||
| ⚫ | }}</ref> the ] (1971),<ref name=synthia group="#"> | ||
| |archive-date = 2013-10-31 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131031040324/http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/emsprods.html#synthi100 | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| ⚫ | }}</ref> the ] (1971),<ref name=synthia group="#"> | ||
| {{cite web | {{cite web | ||
| | title = Synthi A (formerly Portabella) – The Products | | title = Synthi A (formerly Portabella) – The Products | ||
| Line 110: | Line 112: | ||
| <div style="margin-left:1em;"><gallery> | <div style="margin-left:1em;"><gallery> | ||
| File:EMS A.jpg|] (1971), <br/>also called ''Portabella''<ref name=synthia group="#"/> | File:EMS A.jpg|] (1971), <br/>also called ''Portabella''<ref name=synthia group="#"/> | ||
| File:EMS Synthi AKS.jpg|] (1972)<ref name=synthiaks group="#"/> | File:EMS Synthi AKS.jpg|] (1972)<ref name=synthiaks group="#"/> | ||
| File:EMS Synthi 100.jpg|] (1971), <br/>formerly ''Digitana'', also called ''The Delaware''<ref name=synthi100 group="#"/> | File:EMS Synthi 100.jpg|] (1971), <br/>formerly ''Digitana'', also called ''The Delaware''<ref name=synthi100 group="#"/> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 118: | ||
| ====Synthi A==== | ====Synthi A==== | ||
| ] band; underneath are an EMS DK keyboard controller, ], ], and an M400 ]]] | ] band; underneath are an EMS DK keyboard controller, ], ], and an M400 ]]] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| {{main|EMS Synthi A|EMS Synthi AKS}} | {{main|EMS Synthi A|EMS Synthi AKS}} | ||
| The '''EMS Synthi A''' has the same electronics as the VCS 3, but was rehoused in a Spartanite briefcase. Instead of routing signals using ]s, like ] products, it uses a patch matrix with resistive pins. The 2700 ohm resistors soldered inside each pin vary in tolerance, indicated by different colours: red pins have 1% tolerance, white have 5%, and green pins are attenuating pins with a resistance of 68,000 ohms. | The '''EMS Synthi A''' has the same electronics as the VCS 3, but was rehoused in a Spartanite briefcase. Instead of routing signals using ]s, like ] products, it uses a ] with resistive pins. The 2700 ohm resistors soldered inside each pin vary in tolerance, indicated by different colours: red pins have 1% tolerance, white have 5%, and green pins are attenuating pins with a resistance of 68,000 ohms. | ||
| The later Synthi AKS incorporated an early digital 256 event KS (Keyboard Sequencer) ] in the lid, with input provided by a capacitance-sensitive ]-style keyboard. | The later Synthi AKS incorporated an early digital 256 event KS (Keyboard Sequencer) ] in the lid, with input provided by a capacitance-sensitive ]-style keyboard. | ||
| Perhaps its most prominent |
Perhaps its most prominent use is in the introduction to ]'s ''I Robot.'' (1977). VCS 3 synthesisers were also used alongside a traditional chamber music ensemble for the soundtrack to the BBC's '']'' nature documentary series, composed by ].<ref>Power, Mike. '', in ''The Guardian'', 2 November 2009</ref> | ||
| Along with ] and ], other frequent users of the instrument include ], ] & ] of ], ] of ], ], ], ] and ]. | Along with ] and ], other frequent users of the instrument include ], ] & ] of ], ] of ], ], ], ] and ]. | ||
| Line 133: | Line 135: | ||
| ==Notable users== | ==Notable users== | ||
| * ]<ref>{{cite web |last1=Rawlins |first1=Sarah |title=The Birth of the Radiophonic Workshop |url=https://blog.scienceandmediamuseum.org.uk/birth-of-radiophonic-workshop/ |website=National Science and Media Museum blog |publisher=] |access-date=12 August 2024 |date=31 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]<ref name="Eno">{{cite web |title=How Brian Eno Created "Discreet Music" {{!}} Reverb Machine |url=https://reverbmachine.com/blog/deconstructing-brian-enos-discreet-music/ |website=reverbmachine.com |access-date=9 October 2022 |date=3 September 2019}}</ref> | * ]<ref name="Eno">{{cite web |title=How Brian Eno Created "Discreet Music" {{!}} Reverb Machine |url=https://reverbmachine.com/blog/deconstructing-brian-enos-discreet-music/ |website=reverbmachine.com |access-date=9 October 2022 |date=3 September 2019}}</ref> | ||
| * ] on ]'s '']''<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/1997_articles/jul97/flood_u2.html|title=Flood & Howie B: Producing U2's Pop|work=Sound On Sound|date=July 1997|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150607055529/http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/1997_articles/jul97/flood_u2.html|archive-date=7 June 2015}}</ref> | * ] on ]'s '']''<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/1997_articles/jul97/flood_u2.html|title=Flood & Howie B: Producing U2's Pop|work=Sound On Sound|date=July 1997|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150607055529/http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/1997_articles/jul97/flood_u2.html|archive-date=7 June 2015}}</ref> | ||
| * ]<ref name="JMJ">{{cite web |title=Three Questions With Jean-Michel Jarre |url=https://www.synthhistory.com/post/three-questions-with-jean-michel-jarre |website=Synth History |access-date=12 August 2024 |language=en |date=20 October 2022 |quote=EMS VCS 3, my first synth ever, still working and present on each of my albums as a ritual.}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | * ] on ] (1972), ] (1973), and ] (1975)<ref name=PinkFloyd1973>{{cite AV media notes |title=The Dark Side Of The Moon |url={{Discogs master|10362|type=album|pure_url=yes}}|last=The|first=Pink Floyd|date=1973}}: {{smaller|1=“''DAVID GILMOUR Vocals, Guitars, VCS3 / NICK MASON Percussion, Tape Effects / RICHARD WRIGHT Keyboards, Vocals, VCS3 / ROGER WATERS Bass Guitar, Vocals, VCS3, Tape Effects''”}}.<!-- (''See'' on {{cite web|date=2019-03-01|title=20,000 vinyl LPs 171: Pink Floyd ~ The Dark Side Of The Moon |url=https://styrous.blogspot.com/2019/03/20000-vinyl-lps-171-pink-floyd-dark.html|website=The Styrous® Viewfinder}}) --></ref> | ||
| * ] on ''Door Open at 8 AM''<ref>{{cite AV media notes |title=Door Open at 8 AM |url=https://masamiakitamerzbow.bandcamp.com/album/door-open-at-8-am-remastered-bonus-tracks |website=Bandcamp |access-date=2 October 2024 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=EMS Synthesizers: Brits en eigenzinnig |url=https://www.interface.nl/nieuws/artikel/2-23490/ems-synthesizers |website=interface.nl |access-date=4 October 2024 |language=nl |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20241004220412/https://www.interface.nl/nieuws/artikel/2-23490/ems-synthesizers |archive-date=4 October 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Silent Modular Wars!! |url=https://merzbow.net/blog/ems-set-dommune/ |website=merzbow.net |access-date=4 October 2024 |language=ja |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20241004221518/https://merzbow.net/blog/ems-set-dommune/ |archive-date=4 October 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=A short conversation with the legendary noise artist, Merzbow |author=Miron Ghiu |date=26 February 2018 |website=blackrhinoradio.com |url=https://blackrhinoradio.com/interviews/a-short-conversation-with-the-legendary-noise-artist-merzbow |access-date=4 October 2024 |language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20241004221423/https://blackrhinoradio.com/interviews/a-short-conversation-with-the-legendary-noise-artist-merzbow |archive-date=4 October 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | * ]<ref>{{cite book | url=https:// |
||
| * ]<ref>{{cite web |title=Three Questions With Pete Townshend |url=https://www.synthhistory.com/post/three-questions-with-pete-townshend |website=Synth History |access-date=12 August 2024 |language=en |date=27 April 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Marks |first1=Ben |title=Rise of the Synthesizer: How an Electronics Whiz Kid Gave the 1980s Its Signature Sound |url=https://www.collectorsweekly.com/articles/rise-of-the-synthesizer/ |publisher=] |access-date=12 August 2024 |language=en |date=1 October 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | * ] on '']'' (1972), '']'' (1973), and '']'' (1975)<ref name=PinkFloyd1973>{{cite AV media notes |title=The Dark Side Of The Moon |url={{Discogs master|10362|type=album|pure_url=yes}}|last=The|first=Pink Floyd|date=1973}}: {{smaller|1=“''DAVID GILMOUR Vocals, Guitars, VCS3 / NICK MASON Percussion, Tape Effects / RICHARD WRIGHT Keyboards, Vocals, VCS3 / ROGER WATERS Bass Guitar, Vocals, VCS3, Tape Effects''”}}.<!-- (''See'' on {{cite web|date=2019-03-01|title=20,000 vinyl LPs 171: Pink Floyd ~ The Dark Side Of The Moon |url=https://styrous.blogspot.com/2019/03/20000-vinyl-lps-171-pink-floyd-dark.html|website=The Styrous® Viewfinder}}) --></ref> | ||
| ==Note== | |||
| * ] on '']'' (1970) and ] (1972)<ref>{{cite news |last1=Logan |first1=Nick |title=KING CRIMSON — biggest one man band in business |url=https://geirmykl.wordpress.com/2021/06/14/article-about-king-crimson-from-new-musical-express-june-6-1970/ |access-date=12 August 2024 |work=New Musical Express |date=6 June 1970}}</ref><ref>Sleeve notes for ''Earthbound''.</ref> | |||
| <references group=note/> | |||
| * ]<ref>{{cite web |title=Todd Rundgren |url=https://jazzrocksoul.com/artists/todd-rundgren/ |website=Jazz Rock Soul |date=30 March 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Zanca |first1=Nick |title=The Wizard Speaks: An Interview With Todd Rundgren |url=https://reverb.com/news/interview-todd-rundgren |publisher=] |access-date=12 August 2024 |date=23 November 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | * ]<ref>{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bzKUEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA131 | isbn=9781009041591 | title=The Cambridge Companion to Krautrock | date=27 October 2022 | publisher=Cambridge University Press }}</ref> | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 184: | Line 189: | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| ===Official=== | |||
| *http://emssynthesisers.co.uk/ | *http://emssynthesisers.co.uk/ | ||
| * {{cite web|title=An advertisement for the company, "every nun needs a Synthi" |url=http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/snaps/everynun.jpg |publisher=Electronic Music Studios (London), Ltd |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120717010956/http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/snaps/everynun.jpg |archive-date=2012-07-17 }} | * {{cite web|title=An advertisement for the company, "every nun needs a Synthi" |url=http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/snaps/everynun.jpg |publisher=Electronic Music Studios (London), Ltd |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120717010956/http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/snaps/everynun.jpg |archive-date=2012-07-17 }} | ||
| *{{cite web |title=EMS Home |url=http://www.emsrehberg.de/ |publisher=EMS Rehberg (Germany)}} | *{{cite web |title=EMS Home |url=http://www.emsrehberg.de/ |publisher=EMS Rehberg (Germany)}} | ||
| ===Articles=== | |||
| * {{cite web |title=EMS VCS3 in the 1970s, part 1 |url=https://musicaficionado.blog/2020/09/02/ems-vcs3-in-the-1970s-part-1/ |website=The Music Aficionado |access-date=13 August 2024 |date=2 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite web |title=THE EMS SYNTHI BLOG |url=http://www.thesynthi.de/ }} | |||
| * {{cite web |title=EMS VCS3 in the 1970s, part 2 |url=https://musicaficionado.blog/2020/10/14/ems-vcs3-in-the-1970s-part-2/ |website=The Music Aficionado |access-date=13 August 2024 |date=14 October 2020}} | |||
| ===Modification and resources=== | |||
| * {{cite web |author=Graham Hinton |title=A Guide to EMS VCS3 & Synthi A/AKS Modifications & Servicing |url=http://www.hinton-instruments.co.uk/ems/emsmods.html |publisher=Hinton Instruments}} | * {{cite web |author=Graham Hinton |title=A Guide to EMS VCS3 & Synthi A/AKS Modifications & Servicing |url=http://www.hinton-instruments.co.uk/ems/emsmods.html |publisher=Hinton Instruments}} | ||
| * {{cite web |title=Information on the EMS synthi A, KS and VCS3 |url=http://www.burningimage.net/synthesisers/EMS/ }} | * {{cite web |title=Information on the EMS synthi A, KS and VCS3 |url=http://www.burningimage.net/synthesisers/EMS/ }} | ||
| ===Software emulation=== | |||
| * {{cite web |title=XILS 3, 4 and Vocoder 5000 |url=https://www.xils-lab.com/products/synthesizers-c-60.html }} — A VST simulation of a VCS3/VCS4 with Synthi Sequencer, and Vocoder 5000 by XILS-lab | * {{cite web |title=XILS 3, 4 and Vocoder 5000 |url=https://www.xils-lab.com/products/synthesizers-c-60.html }} — A VST simulation of a VCS3/VCS4 with Synthi Sequencer, and Vocoder 5000 by XILS-lab | ||
| * {{cite web |title=Synthi Avs Plug-In |url=http://www.emsrehberg.de/SYNTHI__s/SYNTHI_Avs_plugin/synthi_avs_plugin.html |publisher=EMS Rehberg}} — A (commercial) VST simulation of a VCS3/Synthi A by EMS Rehberg | * {{cite web |title=Synthi Avs Plug-In |url=http://www.emsrehberg.de/SYNTHI__s/SYNTHI_Avs_plugin/synthi_avs_plugin.html |publisher=EMS Rehberg}} — A (commercial) VST simulation of a VCS3/Synthi A by EMS Rehberg | ||
| * {{cite web |title=Cynthia |url=https://freevstplugins.net/cynthia/ }} — A free VST based on the architecture of VCS3/Synthi A by Ninecows | * {{cite web |title=Cynthia |url=https://freevstplugins.net/cynthia/ }} — A free VST based on the architecture of VCS3/Synthi A by Ninecows | ||
| <!-- Commented out (and replaced with line above) because link is currently a broken Wordpress site 10/02/2023. | <!-- Commented out (and replaced with line above) because link is currently a broken Wordpress site 10/02/2023. | ||
| * {{cite web |title=Cynthia |url=http://www.ninecows.dk/cynthia }} — A free VST based on the architecture of VCS3/Synthi A by Ninecows C | * {{cite web |title=Cynthia |url=http://www.ninecows.dk/cynthia }} — A free VST based on the architecture of VCS3/Synthi A by Ninecows C | ||
| --> | --> | ||
| * {{cite web |title=iVCS3 |url=http://www.alessandro-petrolati.it }} — Official EMS iOS emulator by apeSoft, with preface by Peter Zinovieff ({{smaller|1=}}) | * {{cite web |title=iVCS3 |url=http://www.alessandro-petrolati.it }} — Official EMS iOS emulator by apeSoft, with preface by Peter Zinovieff ({{smaller|1=}}) | ||
| <!-- should be capitalized, because "VCS 3" is acronym of "Voltage Controlled Studio with 3 oscillators") --> | <!-- should be capitalized, because "VCS 3" is acronym of "Voltage Controlled Studio with 3 oscillators") --> | ||
| ===EMS Synthi A=== | |||
| *{{cite web <!-- author = Graham Hinton --> | *{{cite web <!-- author = Graham Hinton --> | ||
| | url = http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/ | | url = http://www.ems-synthi.demon.co.uk/ | ||
| Line 238: | Line 242: | ||
| --> | --> | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
Latest revision as of 03:51, 10 December 2024
Synthesizer model| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "EMS VCS 3" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Note: it has printed logo: "V.C.S. 3".
The VCS 3 (or VCS3; an initialism for Voltage Controlled Studio, version #3) is a portable analogue synthesizer with a flexible modular voice architecture introduced by Electronic Music Studios (EMS) in 1969.
EMS released the product under various names. Logos printed at the console's front left (see photos) say "V.C.S. 3" on the most widely sold version; "The Putney (VCS 3)" on the earlier version; and "The Synthi (VCS 3) II" on the later version "Synthi VCS 3 II".
History
VCS 3 variations Synthi VCS 3 with logo:
Synthi VCS 3 with logo:"The Putney (VCS 3)"
 Synthi VCS 3 II with logo:
Synthi VCS 3 II with logo:"The Synthi (VCS 3) II"
The VCS 3 was created in 1969 by Peter Zinovieff's EMS company. The electronics were designed largely by David Cockerell, and its distinctive appearance was the work of electronic composer Tristram Cary. It was one of the first portable commercially available synthesizers, in the sense that it was housed entirely in a small wooden case, unlike synths from American manufacturers such as Moog Music, ARP and Buchla, which had large cabinets and could take up entire rooms.
The VCS 3 cost just under £330 in 1969. Some people found it unsatisfactory as a melodic instrument due to its inherent tuning instability. This arose from the instrument's reliance on the then current method of exponential conversion of voltage to oscillator frequency—an approach that other companies also implemented with fewer tuning issues. However, the VCS 3 was renowned as an extremely powerful generator of electronic effects and processor of external sounds for its cost.
The first album recorded using only the VCS 3 was The Unusual Classical Synthesizer on Westminster Gold.
The VCS 3 was popular among progressive rock bands, and was used on recordings by Franco Battiato, The Moody Blues, The Alan Parsons Project, Jean-Michel Jarre, Todd Rundgren, Hawkwind, Curved Air, Brian Eno (with Roxy Music and as a solo artist or collaborator), King Crimson, The Who, Gong, and Pink Floyd, and many others. The VCS 3-generated bass sound at the beginning of Pink Floyd's "Welcome to the Machine" forms the foundation of the song, with its other parts heard in response. Two VCS 3s and a Sequencer 256 were featured in the 1978 film 'The Shout'.
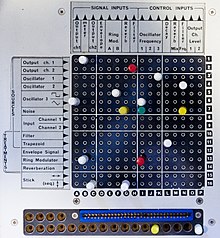
Description
The VCS 3 has three oscillators (the first two normal voltage-controlled oscillators; the third a low-frequency oscillator), a noise generator, two input amplifiers, a ring modulator, 24 dB/octave low-pass voltage-controlled filter, a trapezoid envelope generator, a joystick controller, a voltage-controlled spring reverb unit, and two stereo output amplifiers. Unlike most modular synthesiser systems, which used cables to link components, the VCS 3 uses a distinctive patchboard matrix where pins are inserted to connect its components.
Keyboards controller

connected to VCS 3 (rear)
Although the VCS 3 is often used for generating sound effects due to lack of a built-in keyboard, external keyboard controllers were available for melodic play. The DK1, produced in 1969, is an early velocity-sensitive monophonic keyboard for VCS 3 with an extra VCO and VCA. In 1972 it was extended for duophonic play as DK2. Also in 1972, the Synthi AKS was released, as well as a digital sequencer with a touch-sensitive flat keyboard, the KS sequencer, and its mechanical keyboard version, DKS.
Related models
The VCS 3's basic design was reused by EMS in many other of their own products, most notably the EMS Synthi 100 (1971), the Synthi A (1971), and AKS (1972, essentially a VCS 3 in a plastic briefcase). The AKS also has a sequencer built into the keyboard's lid.
A former agent of EMS in the United States, Ionic Industries in Morristown, New Jersey, released a portable-keyboard VCS 3 clone in 1973. The Ionic Performer, whose circuitry is based on the VCS 3's, replaced the patchboard matrix with over 100 push-buttons, and added a built-in keyboard and effects units.
-
 EMS Synthi A (1971),
EMS Synthi A (1971),
also called Portabella -
 EMS Synthi AKS (1972)
EMS Synthi AKS (1972)
-
 EMS Synthi 100 (1971),
EMS Synthi 100 (1971),
formerly Digitana, also called The Delaware
Synthi A


The EMS Synthi A has the same electronics as the VCS 3, but was rehoused in a Spartanite briefcase. Instead of routing signals using patch cables, like Moog products, it uses a patch matrix with resistive pins. The 2700 ohm resistors soldered inside each pin vary in tolerance, indicated by different colours: red pins have 1% tolerance, white have 5%, and green pins are attenuating pins with a resistance of 68,000 ohms.
The later Synthi AKS incorporated an early digital 256 event KS (Keyboard Sequencer) sequencer in the lid, with input provided by a capacitance-sensitive Buchla-style keyboard.
Perhaps its most prominent use is in the introduction to The Alan Parsons Project's I Robot. (1977). VCS 3 synthesisers were also used alongside a traditional chamber music ensemble for the soundtrack to the BBC's Life On Earth nature documentary series, composed by Edward Williams.
Along with Klaus Schulze and Tangerine Dream, other frequent users of the instrument include Cabaret Voltaire, Tim Blake & Miquette Giraudy of Gong, Richard Pinhas of Heldon, Merzbow, Thomas Lehn, Cor Fuhler and Alva Noto.
Development
The original VCS No.1 was a hand-built rack-mount unit with two oscillators, one filter and one envelope, designed by Cockerell before the formation of EMS. When a benefactor, Don Banks, asked Zinovieff for a synthesiser, Zinovieff and Cockerell decided to work together on an instrument that was small and portable but powerful and flexible.
Notable users
- BBC Radiophonic Workshop
- Brian Eno
- Howie B on U2's Pop
- Jean-Michel Jarre
- Merzbow on Door Open at 8 AM
- Pete Townshend
- Pink Floyd on Obscured by Clouds (1972), The Dark Side of the Moon (1973), and Wish You Were Here (1975)
- King Crimson on Lizard (1970) and Earthbound (1972)
- Todd Rundgren
- Tangerine Dream
References
- Reid, Gordon (November 2000). "All About EMS, Part 1". Sound on Sound. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- "unusualstuff - krakatack". Sites.google.com. Retrieved 2020-04-12.
- "EMS VCS 3 "The Shout" 1978 | Pin Electronics".
- Dennis Bathory-Kitsz. "Killer – My Ionic "Performer" Synth (from Ionic Industories, made by Alfred Mayer)".
- Power, Mike. 'Release of Life On Earth soundtrack delivers music as pioneering as the show', in The Guardian, 2 November 2009
- Rawlins, Sarah (31 March 2021). "The Birth of the Radiophonic Workshop". National Science and Media Museum blog. National Science and Media Museum. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- "How Brian Eno Created "Discreet Music" | Reverb Machine". reverbmachine.com. 3 September 2019. Retrieved 2022-10-09.
- "Flood & Howie B: Producing U2's Pop". Sound On Sound. July 1997. Archived from the original on 2015-06-07.
- "Three Questions With Jean-Michel Jarre". Synth History. 20 October 2022. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
EMS VCS 3, my first synth ever, still working and present on each of my albums as a ritual.
- Door Open at 8 AM. Bandcamp (Media notes). Retrieved 2024-10-02.
- "EMS Synthesizers: Brits en eigenzinnig". interface.nl (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 2024-10-04. Retrieved 2024-10-04.
- "Silent Modular Wars!!". merzbow.net (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2024-10-04. Retrieved 2024-10-04.
- Miron Ghiu (26 February 2018). "A short conversation with the legendary noise artist, Merzbow". blackrhinoradio.com. Archived from the original on 2024-10-04. Retrieved 2024-10-04.
- "Three Questions With Pete Townshend". Synth History. 27 April 2020. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- Marks, Ben (1 October 2015). "Rise of the Synthesizer: How an Electronics Whiz Kid Gave the 1980s Its Signature Sound". Collectors Weekly. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- The, Pink Floyd (1973). The Dark Side Of The Moon (Media notes).: “DAVID GILMOUR Vocals, Guitars, VCS3 / NICK MASON Percussion, Tape Effects / RICHARD WRIGHT Keyboards, Vocals, VCS3 / ROGER WATERS Bass Guitar, Vocals, VCS3, Tape Effects”.
- Logan, Nick (6 June 1970). "KING CRIMSON — biggest one man band in business". New Musical Express. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- Sleeve notes for Earthbound.
- "Todd Rundgren". Jazz Rock Soul. 30 March 2022.
- Zanca, Nick (23 November 2022). "The Wizard Speaks: An Interview With Todd Rundgren". Reverb.com. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- The Cambridge Companion to Krautrock. Cambridge University Press. 27 October 2022. ISBN 9781009041591.
Bibliography
- Hinton, Graham (December 2002). "EMS: The Inside Story". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-05-21. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- Hinton, Graham (December 2002). "A Guide to the EMS Product Range - 1969 to 1979". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- Reid, Gordon (November 2000). "All About EMS, Part 1". Sound on Sound. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- Reid, Gordon (December 2000). "All About EMS, Part 2". Sound on Sound. Archived from the original on 2011-09-08.
- Models
- ^ "VCS3 (aka The Putney) – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- "Synthi VCS3 II – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- "DK1 (aka The Cricklewood) – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- "DK2 – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- "KS – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- "DKS – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- ^ "Synthi 100 (formerly Digitana, aka the Delaware) – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^ "Synthi A (formerly Portabella) – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
- ^ "Synthi AKS – The Products". Electronic Music Studios (Cornwall). Archived from the original on 2013-10-31.
Further reading
- "Retro: VCS3". Future Music. No. 63. Future Publishing. November 1997. p. 55. ISSN 0967-0378. OCLC 1032779031.
External links
Official
- http://emssynthesisers.co.uk/
- "An advertisement for the company, "every nun needs a Synthi"". Electronic Music Studios (London), Ltd. Archived from the original on 2012-07-17.
- "EMS Home". EMS Rehberg (Germany).
Articles
- "EMS VCS3 in the 1970s, part 1". The Music Aficionado. 2 September 2020. Retrieved 2024-08-13.
- "EMS VCS3 in the 1970s, part 2". The Music Aficionado. 14 October 2020. Retrieved 2024-08-13.
Modification and resources
- Graham Hinton. "A Guide to EMS VCS3 & Synthi A/AKS Modifications & Servicing". Hinton Instruments.
- "Information on the EMS synthi A, KS and VCS3".
Software emulation
- "XILS 3, 4 and Vocoder 5000". — A VST simulation of a VCS3/VCS4 with Synthi Sequencer, and Vocoder 5000 by XILS-lab
- "Synthi Avs Plug-In". EMS Rehberg. — A (commercial) VST simulation of a VCS3/Synthi A by EMS Rehberg
- "Cynthia". — A free VST based on the architecture of VCS3/Synthi A by Ninecows
- "iVCS3". — Official EMS iOS emulator by apeSoft, with preface by Peter Zinovieff (screen shot)
EMS Synthi A
- "EMS' homepage (last updated August 1998)". Cornwall: Electronic Music Studios. Archived from the original on 2013-11-25.
- "Every Nun Needs a Synthi" (ad). Archived from the original on 2012-07-17.
- "VCS3 & Synthi A Modifications". Hinton Instruments. (last updated 2013-12-14)
- "Synthi A-VS plugin". Germany: EMS Rehberg. — A commercial VST simulation of a Synthi A by German EMS
- A freeware VST simulation of a Synthi A
- The EMS SYNTHI BLOG