| Revision as of 08:41, 28 September 2023 editCycloneYoris (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers83,719 edits Reverted 1 pending edit by 95.53.160.157 to revision 1177053433 by Annh07: Unexplained removal.Tags: Manual revert Reverted← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:44, 6 January 2025 edit undoSeltaeb Eht (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,703 edits Undid revision 1267662927 by VelvetEcho 21 (talk) undo Good faith edit which removes citationsTag: Undo | ||
| (966 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| {{Other uses}} | {{Other uses}} | ||
| {{pp-move}} | {{pp-move}} | ||
| {{good article}} | |||
| {{pp-pc}} | {{pp-pc}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Use dmy dates|date=July 2024}}{{Use British English|date=November 2024}} | ||
| {{EngvarB|date=May 2017}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2022}} | |||
| {{Infobox royalty | {{Infobox royalty | ||
| | name = Charlemagne | | name = Charlemagne | ||
| | more = Carolus Magnus | | more = Carolus Magnus | ||
| | image = Charlemagne denier Mayence 812 814.jpg | | image = Charlemagne denier Mayence 812 814.jpg | ||
| | caption = A ] of Charlemagne dated {{c.|812–814}} with the inscription {{sqc|KAROLVS IMP AVG}}<br>(''Karolus Imperator Augustus'') | | caption = A ] of Charlemagne dated {{c.|812–814}} with the inscription {{sqc|KAROLVS IMP AVG}}<br />(''Karolus Imperator Augustus'') | ||
| | succession2 = ] of the ] | | succession2 = ] of the ] | ||
| | title = ] | |||
| | reign2 = 25 December 800 – 28 January 814 | | reign2 = 25 December 800 – 28 January 814 | ||
| | coronation2 = 25 December 800<br />], Rome | | coronation2 = 25 December 800<br />], Rome | ||
| | predecessor2 = <!-- Do not add Constantine VI here; a claim of spiritual inheritance not recognised in modern scholarship has no place here --> | | predecessor2 = <!-- Do not add Constantine VI here; a claim of spiritual inheritance not recognised in modern scholarship has no place here --> | ||
| | successor2 = ] | | successor2 = ] | ||
| | birth_date = {{birth date|748|4|2|df=y}}{{Efn|name=birth|Alternative birth years for Charlemagne include 742 and 747. There has been scholarly debate over this topic, see ]. For full treatment of the debate, see {{harvnb|Nelson|2019|pp=28–29}}. See further Karl Ferdinand Werner, ''Das Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen'', in ''Francia'' 1, 1973, pp. 115–157 ( {{webarchive|url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131117074120/http://mdzx.bib-bvb.de/francia/Blatt_bsb00016275%2C00115.html |date=17 November 2013 }});<br />Matthias Becher: ''Neue Überlegungen zum Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen'', in: ''Francia'' 19/1, 1992, pp. 37–60 ( {{webarchive|url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131117074146/http://mdzx.bib-bvb.de/francia/Blatt_bsb00016296%2C00047.html |date=17 November 2013 }})}} | |||
| | birth_date = 2 April 747{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=72}}<ref name="Charlemagne Britannica" /> | |||
| | birth_place = ] | |||
| | birth_name = Karl<ref name="Fried" /> | |||
| | death_date = {{death date<!-- and age -->|814|1|28|<!-- 748|4|2| -->df=y}} | |||
| | birth_place = ] (]) or ] | |||
| | death_place = ], Francia | |||
| | death_date = 28 January 814 {{nowrap|(aged 66)}}<ref name="Charlemagne Britannica" /> | |||
| | death_place = Aachen, ] | |||
| | spouses = {{Plainlist| | | spouses = {{Plainlist| | ||
| * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|770}}; annulled 771)}} | * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|770}}; annulled 771)}} | ||
| * {{longitem|]<br />(m. 771; d. 783)}} | * {{longitem|]<br />(m. 771; d. 783)}} | ||
| * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|783}}; d. 794)}} | * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|783}}; d. 794)}} | ||
| * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|794}}; d. 800)}} | * {{longitem|]<br />(m. {{circa|794}}; d. 800)}} | ||
| Line 44: | Line 41: | ||
| | type = King | | type = King | ||
| | image_size = 225 | | image_size = 225 | ||
| | succession1 = ] | | succession1 = ] {{nobold|(])}} | ||
| | reign1 = |
| reign1 = June 774 – 28 January 814 | ||
| | coronation1 = 10 July 774<br />] | |||
| | predecessor1 = ] | | predecessor1 = ] | ||
| | successor1 = ] | | successor1 = ] | ||
| | regent1 = ] (781–810) | |||
| | reg-type1 = Co-ruler | |||
| | succession = ] | | succession = ] | ||
| | reign = 9 October 768 – 28 January 814 | | reign = 9 October 768 –<br />28 January 814 | ||
| | coronation = 9 October 768<br />] | | coronation = 9 October 768<br />] | ||
| | regent = ] (768–771)<br />] (800–811) | |||
| | reg-type = Co-ruler | |||
| | predecessor = ] | | predecessor = ] | ||
| | successor = ] | | successor = ] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
| {{carolingians|268px}} | {{carolingians|268px}} | ||
| '''Charlemagne''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|ʃ|ɑːr|l|ə|m|eɪ|n}} {{respell|SHAR|lə|mayn}}; 2 April 748{{Efn|name=birth}} – 28 January 814) was ] from 768, ] from 774, and ] of what is now known as the ] from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of ] and ], and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the ] approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the ]. | |||
| '''Charlemagne''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|ʃ|ɑːr|l|ə|m|eɪ|n|,_|ˌ|ʃ|ɑːr|l|ə|ˈ|m|eɪ|n}} {{respell|SHAR|lə|mayn|,_-|MAYN}}) or '''Charles the Great''' ({{lang-la|Carolus Magnus}}, ]: ''Karl'';<ref name="Fried">{{harvnb|Fried|2016|p=2}}: "...his name in his native Germanic language was Karl (Charles), but he is better known to history by his Latinized name, Carolus Magnus, or Charlemagne."</ref> 2 April 747{{Efn|Alternative birth years for Charlemagne include 742 and 748. There is scholarly debate over this topic, summarised in {{harvnb|Nelson|2019|pp=28–29}}. See further Karl Ferdinand Werner, ''Das Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen'', in ''Francia'' 1, 1973, pp. 115–57 ( {{webarchive|url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131117074120/http://mdzx.bib-bvb.de/francia/Blatt_bsb00016275%2C00115.html |date=17 November 2013 }});<br />Matthias Becher: ''Neue Überlegungen zum Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen'', in: ''Francia'' 19/1, 1992, pp. 37–60 ( {{webarchive|url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131117074146/http://mdzx.bib-bvb.de/francia/Blatt_bsb00016296%2C00047.html |date=17 November 2013 }})}} – 28 January 814), a member of the ], was ] from 768, ] from 774, and was crowned as the ] by ] in 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of ] and ] and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the ] approximately three centuries earlier.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=}} The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the ], which is considered the first phase in the history of the ]. He was ] by ]—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as ] (which is a step on the path to ]hood) in the ]. | |||
| Charlemagne was the eldest son of ] and ]. |
A member of the Frankish ], Charlemagne was the eldest son of ] and ]. With his brother, ], he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, removing the ] from power in ] in 774. His reign saw a period of expansion that led to the conquests of ], ], and ], as well as other campaigns that led Charlemagne to extend his rule over a large part of Europe. Charlemagne spread Christianity to his new conquests (often by force), as seen at the ] against the ]. He also sent envoys and initiated diplomatic contact with the ] ] in the 790s, due to their mutual interest in Iberian affairs. | ||
| In 800, Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by ]. Although historians debate the coronation's significance, the title represented the height of his prestige and authority. Charlemagne's position as the first emperor in the West in over 300 years brought him into conflict with the ] in ]. Through his assumption of the imperial title, he is considered the forerunner to the line of ]s, which persisted into the nineteenth century. As king and emperor, Charlemagne engaged in a number of reforms in administration, law, education, military organisation, and religion, which shaped Europe for centuries. The stability of his reign began a period of cultural activity known as the ]. | |||
| Charlemagne has been called the "Father of Europe" (''Pater Europae''),<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.karlspreis.de/preistraeger/seine_heiligkeit_papst_johannes_paul_ii/ansprache_von_seiner_heiligkeit_papst_johannes_paul_ii.html |title=Ansprache von seiner Heiligkeit Papst Johannes Paul II |year=2004 |author=Papst Johannes Paul II |publisher=Internationaler Karlspreis zu Aachen |language=de |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120117151907/http://www.karlspreis.de/preistraeger/seine_heiligkeit_papst_johannes_paul_ii/ansprache_von_seiner_heiligkeit_papst_johannes_paul_ii.html |archive-date=17 January 2012 }}</ref> as he united most of Western Europe for the first time since the ] of the ], as well as uniting parts of Europe that had never been under Frankish or Roman rule. His reign spurred the ], a period of energetic cultural and intellectual activity within the ]. The ] viewed Charlemagne less favourably, due to his support of the ] and the Pope's preference of him as emperor over the ]'s first female monarch, ]. These and other disputes led to the eventual split of ] and ] in the ].{{sfn|Gregory|2005|pp=251–52}}{{Efn| Also see: or }} | |||
| Charlemagne died in 814 and was buried at ] in ], his imperial capital city. He was succeeded by his only surviving legitimate son, ]. After Louis, the Frankish kingdom was divided and eventually coalesced into ] and ], which later became ] and ], respectively. Charlemagne's profound influence on the Middle Ages and influence on the territory he ruled has led him to be called the "Father of Europe" by many historians. He is seen as a founding figure by multiple European states and a number of historical royal houses of Europe trace their lineage back to him. Charlemagne has been the subject of artworks, monuments and literature during and after the medieval period and is ] by the ]. | |||
| Charlemagne died in 814 after contracting an infectious lung disease.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Schleifring |first1=Joachim H. |last2=Galassi |first2=Francesco M. |last3=Habicht |first3=Michael E. |last4=Rühli |first4=Frank J. |date=2019 |title=Autopsing history: The mummy of Charlemagne (c. 747 – 814 AD), father of Europe |journal=Economics & Human Biology |language=en |volume=32 |pages=11–17 |doi=10.1016/j.ehb.2018.11.002|pmid=30544097 |s2cid=56484821 }}</ref> He was laid to rest in the ], in his imperial capital city of ]. He married at least four times,<ref name="Will Durant Chronique" /><ref name="Charlemagne Britannica" /> and three of his legitimate sons lived to adulthood. Only the youngest of them, ], survived to succeed him. Charlemagne is a direct ancestor of many of Europe's ], including the ],{{Efn|Through ], great-great granddaughter of ] and grandmother of ].<ref name="ESII-10.11">Detlev Schwennicke, ''Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der Europäischen Staaten'', Neue Folge, Band II (Marburg, Germany: J. A. Stargardt, 1984), Tafeln 10, 11</ref><ref>], 'Dynastic Structures and Capetian Throne-Right: the Views of Giles of Paris', ''Traditio'', Vol. 33 (1977), pp. 246-47 n.94</ref>}} the ],{{efn|Through ], great-great granddaughter of ] and mother of ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Jackman|first=Donald C.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZI4NV16sGrUC&pg=PA9|title=Ius hereditarium Encountered III: Ezzo's Chess Match|date=2010|publisher=Editions Enlaplage|isbn=978-1-936466-54-2|pages=9–12}}</ref>}} the ],{{Efn|Through ], great-grandson of ] and great-great grandfather of ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Tanner |first=Heather |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oRNYEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA265 |title=Families, Friends and Allies: Boulogne and Politics in Northern France and England |publisher=Brill |year=2004 |isbn=9789047402558 |pages=263–265}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Tanner |first=Heather J. |year=1992 |editor-last=Chibnall |editor-first=Marjorie |title=The Expansion of the Power and Influence of the Counts of Boulogne under Eustace II |journal=Anglo-Norman Studies - XIV.Proceeding of the Battle Conference 1991 |publisher=The Boydell Press |pages=251–286}}</ref>}} the ]{{Efn|] was a great-great-great grandson of ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Bouchard |first=Constance |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yxSxikFnSU8C&pg=PA129 |title=Those of My Blood: Creating Noble Families in Medieval Francia |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=9780812201406 |pages=129–131}}</ref>}} and the ].{{efn|], the founder of the House of Habsburg, married Ida of Lorraine, who descended from Charlemagne through both of her parents; from ] on ] side and through the Capetians on ] side.}} | |||
| == |
== Name == | ||
| Several languages were spoken in Charlemagne's world, and he was known to contemporaries as {{lang|goh|Karlus}} in the ] he spoke; as {{lang|fro|Karlo}} to ] (or ]) speakers; and as {{lang|la|Carolus}} (or {{lang|la|Karolus}}){{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=116}} in ], the formal language of writing and diplomacy.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=2, 68}} ''Charles'' is the modern English form of these names. The name {{lang|fr|Charlemagne}}, as the emperor is normally known in English, comes from the French {{lang|fr|Charles-le-magne}} ('Charles the Great').{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=2}} In modern German, he is known as {{lang|de|Karl der Große}}.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=529}} The Latin ] {{lang|la|magnus}} ('great') may have been associated with him during his lifetime, but this is not certain. The contemporary '']'' routinely call him {{lang|la|Carolus magnus rex}} ("Charles the great king").{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=413}} That epithet is attested in the works of the ] around 900, and it had become commonly applied to him by 1000.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=4}} | |||
| Charlemagne was named after his grandfather, ].{{sfn|Becher|2005|pp=42–43}} That name, and its derivatives, are unattested before their use by Charles Martel and Charlemagne.{{sfn|Nonn|2008|p=575}} ''Karolus'' was adapted by Slavic languages as their word for "king" ({{langx|ru|korol'}}, {{langx|pl|król}} and {{langx|sk|král}}) through Charlemagne's influence or that of his great-grandson, ].{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=5}} | |||
| The nickname ''magnus'' (great) may have been associated with him already in his lifetime, but this is not certain. The contemporary Latin '']'' routinely call him ''Carolus magnus rex'', "Charles the great king".{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=413}} As a nickname, it is only certainly attested in the works of the ] around 900 and it only became standard in all the lands of his former empire around 1000.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=4}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Charles' achievements gave a new meaning to ]. In many ], the very word for "king" derives from his name; e.g., {{lang-pl|król}}, {{lang-uk|король (korol')}}, {{lang-cs|král}}, {{lang-sk|kráľ}}, {{lang-lt|karalius}}, {{lang-lv|karalis}}, {{lang-ru|король}}, {{lang-mk|крал}}, {{lang-bg|крал}}, {{lang-sh-Cyrl|краљ/kralj}}, {{lang-tr|kral}}. This development parallels that of the name of the ] in the original Roman Empire, which became ''kaiser'' and ''tsar'' (or ''czar''), among others.<ref name="Anderson2013">{{cite book|first=Perry |last=Anderson|title=Passages from Antiquity to Feudalism|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=NE9qw3_yCRgC}}|date=2013|publisher=Verso Books|isbn=978-1-78168-008-7}}</ref> | |||
| ==Early life and rise to power== | |||
| ==Political background== | |||
| ===Political background and ancestry=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| By the |
By the sixth century, the western ] tribe of the ] had been ]; this was due in considerable measure to the conversion of their king, ], to Catholicism.{{sfn|Waldman|Mason|2006|pp=270, 274–275}} The Franks had established a kingdom in ] in the wake of the ].{{sfn|Heather|2009|pp=305–306}} This kingdom, ], grew to encompass nearly all of present-day France and Switzerland, along with parts of modern Germany and the ] under the rule of the ].{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=35}} Francia was often divided under different Merovingian kings, due to the ] practised by the Franks.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=35–37}} The late seventh century saw a period of war and instability following the murder of King ], which led to factional struggles among the Frankish aristocrats.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=38}} | ||
| ], ] of ], ended the strife between various kings and their mayors with his 687 victory at the ].{{sfn|Frassetto|2003|p=292}} Pepin was the grandson of two important figures of Austrasia: ] and ].{{sfn|Frassetto|2003|pp=292–293}} The mayors of the palace had gained influence as the Merovingian kings' power waned due to divisions of the kingdom and several succession crises.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=16}} Pepin was eventually succeeded by his son Charles, later known as Charles Martel.{{sfn|Waldman|Mason|2006|p=271}} Charles did not support a Merovingian successor upon the death of King ] in 737, leaving the throne vacant.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=65}} He made plans to divide the kingdom between his sons, ] and ], who succeeded him after his death in 741.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=51–52}} The brothers placed the Merovingian ] on the throne in 743.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=71}} Pepin married ], a member of an influential Austrasian noble family, in 744.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=61–65}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=17}} In 747, Carloman abdicated and entered a monastery in Rome. He had at least two sons; the elder, ], took his place.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=55}} | |||
| ===Birth=== | |||
| After 737, Charles governed the Franks in lieu of a king and declined to call himself ''king''. Charles was succeeded in 741 by his sons ] and ], the father of Charlemagne. In 743, the brothers placed ] on the throne to curb separatism in the periphery. He was the last Merovingian king. Carloman resigned office in 746, preferring to enter the church as a monk. Pepin brought the question of the kingship before ], asking whether it was logical for a king to have no royal power. The pope handed down his decision in 749, decreeing that it was better for Pepin to be called king, as he had the powers of high office as Mayor, so as not to confuse the hierarchy. He, therefore, ordered him to become the ''true king''.<ref name="France/Pippin">{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/215768/France/40284/Pippin-III |title=France :: Pippin III – Encyclopædia Britannica |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |date=24 April 2013 |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne's year of birth is uncertain, although it was most likely in 748.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=29}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=56}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=15}}{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=32}} An older tradition based on three sources, however, gives a birth year of 742. The ninth-century biographer ] reports Charlemagne as being 72 years old at the time of his death; the ''Royal Frankish Annals'' imprecisely gives his age at death as about 71, and his original epitaph called him a septuagenarian.{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=11}} Einhard said that he did not know much about Charlemagne's early life; some modern scholars believe that, not knowing the emperor's true age, he still sought to present an exact date in keeping with the Roman imperial biographies of ], which he used as a model.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=41}}{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=28–28}} All three sources may have been influenced by ]: "The days of our years are threescore years and ten".{{sfn|Hägermann|2011|p=xxx}} | |||
| Historian ] challenged the acceptance of 742 as the Frankish king's birth year, citing an addition to the '']'' which records Charlemagne's birth in 747.{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=350 n7}}{{efn|"At 747 the scribe had written: {{lang|la|'Et ipso anno fuit natus Karolus rex'}} ('and in that year, King Charles was born')."{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=29}}}} ] commemorated Charlemagne's date of birth as 2 April from the mid-ninth century, and this date is likely to be genuine.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=28}}{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=12}} Matthias Becher built on Werner's work and showed that 2 April in the year recorded would have actually been in 748, since the annalists recorded the start of the year from Easter rather than 1 January.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=29}} Presently, most scholars accept April 748 for Charlemagne's birth.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=15–16}}{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=29}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=56}} Charlemagne's place of birth is unknown. The Frankish palaces in ] and ] are among the places suggested by scholars.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=68}} Pepin the Short held an assembly in ] in 748, but it cannot be proved that it took place in April or if Bertrada was with him.{{sfn|Hägermann|2011|p=xxxiii}} | |||
| In 750, Pepin was elected by an assembly of the Franks, anointed by the archbishop, and then raised to the office of king. The Pope branded Childeric III as "the false king" and ordered him into a monastery. The Merovingian dynasty was thereby replaced by the ] dynasty, named after Charles Martel. In 753, ] fled from Italy to Francia, appealing to Pepin for assistance for the rights of St. Peter. He was supported in this appeal by Carloman, Charles' brother<!---should this be Pepin's brother?- Apparently not; Pepin's brother only left the monastery (Monte Cassino), to plead that Pepin NOT provide aid to Stephen II, and was then imprisoned. Carloman, son of Pepin and brother to Charles, supported Stephen II, and was named along with his father and brother as kings.-->. In return, the pope could provide only legitimacy. He did this by again anointing and confirming Pepin, this time adding his young sons Carolus (Charlemagne) and Carloman to the royal patrimony. They thereby became heirs to the realm that already covered most of western Europe. In 754, Pepin accepted the Pope's invitation to visit Italy on behalf of St. Peter's rights, dealing successfully with the ].<ref name="France/Pippin" /><ref>The background relies heavily on {{harvnb|Einhard, putative|741–829|loc=Years 745–755}}</ref> | |||
| ===Language and education=== | |||
| Under the Carolingians, the Frankish kingdom spread to encompass an area including most of Western Europe; the later east–west division of the kingdom formed the basis for modern ] and ]. Orman{{sfn|Oman|1914|pp=409–10}} portrays the ] (843) between the warring grandsons of Charlemagne as the foundation event of an independent ] under its first king ]; an independent Germany under its first king ]; and an independent intermediate state stretching from the ] along the borderlands to south of Rome under ], who retained the title of emperor and the capitals ] and Rome without the jurisdiction. The middle kingdom had broken up by 890 and partly absorbed into the Western kingdom (later France) and the Eastern kingdom (Germany) and the rest developing into smaller "buffer" states that exist between France and Germany to this day, namely ] and ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| Einhard refers to Charlemagne's {{lang|la|patrius sermo}} ("native tongue").{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=68}} Most scholars have identified this as a form of ], probably a ] ].{{sfn|Chambers|Wilkie|2014|p=33}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=318}} Due to the prevalence in Francia of "]", he was probably functionally bilingual in Germanic and Romance dialects at an early age.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=68}} Charlemagne also spoke Latin and, according to Einhard, could understand and (perhaps) speak some Greek.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=24}} | |||
| Charlemagne's father Pepin had been educated at the abbey of ], although the extent of Charlemagne's formal education is unknown.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=71–72}} He almost certainly was trained in military matters as a youth in Pepin's court,{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=72}} which was ].{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=14–15}} Charlemagne also asserted his own education in the ] in encouraging their study by his children and others, although it is unknown whether his study was as a child or at court during his later life.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=72}} The question of Charlemagne's literacy is debated, with little direct evidence from contemporary sources. He normally had texts read aloud to him and dictated responses and decrees, but this was not unusual even for a literate ruler at the time.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=75–80}} Historian ] considers it likely that Charlemagne would have been able to read,{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=271}} but the medievalist Paul Dutton writes that "the evidence for his ability to read is circumstantial and inferential at best"{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=75}} and concludes that it is likely that he never properly mastered the skill.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=91}} Einhard makes no direct mention of Charlemagne reading, and recorded that he only attempted to learn to write later in life.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=120}} | |||
| ==Rise to power== | |||
| ===<span class="anchor" id="Accession and joint reign with Carloman"></span>Accession and reign with Carloman=== | |||
| === Early life === | |||
| There are only occasional references to Charlemagne in the Frankish ] during his father's lifetime.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=73}} By 751 or 752, Pepin had deposed Childeric and replaced him as king.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=71–72}} Early Carolingian-influenced sources claim that Pepin's seizure of the throne was sanctioned beforehand by ],{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=32}} but modern historians dispute this.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=34}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=71}} It is possible that papal approval came only when Stephen travelled to Francia in 754 (apparently to request Pepin's aid against the Lombards), and on this trip ] Pepin as king; this legitimised his rule.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=72}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=34}} Charlemagne was sent to greet and escort the Pope, and he and his younger brother ] were anointed with their father.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=72–73}} Pepin sidelined Drogo around the same time, sending him and his brother to a monastery.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=62}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Charlemagne began issuing charters in his own name in 760. The following year, he joined his father's campaign against ].{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=74}} Aquitaine, led by Dukes ] and ], was constantly in rebellion during Pepin's reign.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=64}} Pepin fell ill on campaign there and died on 24 September 768, and Charlemagne and Carloman succeeded their father.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=75}} They had separate coronations, Charlemagne at ] and Carloman at ], on 9 October.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=91}} The brothers maintained separate palaces and spheres of influence, although they were considered joint rulers of a single Frankish kingdom.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=77}} The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' report that Charlemagne ruled Austrasia and Carloman ruled ], ], Aquitaine, and ], with no mention made of which brother received Neustria.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=77}} The immediate concern of the brothers was the ongoing uprising in Aquitaine.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}} They marched into Aquitaine together, but Carloman returned to Francia for unknown reasons and Charlemagne completed the campaign on his own.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}} Charlemagne's capture of Duke Hunald marked the end of ten years of war that had been waged in the attempt to bring Aquitaine into line.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}} | |||
| The most likely date of Charlemagne's birth is reconstructed from several sources. The date of 742—calculated from ]'s date of death of January 814 at age 72—predates the marriage of his parents in 744. The year given in the '']'', 747, would be more likely, except that it contradicts Einhard and a few other sources in making Charlemagne sixty-seven years old at his death. The month and day of 2 April are based on a calendar from ].<ref name="Baldwin">{{cite web | first=Stewart | last=Baldwin | title=Charlemagne | date=2007–2009 | publisher=The Henry Project | url=http://sbaldw.home.mindspring.com/hproject/prov/charl000.htm | access-date=7 January 2009 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171210084325/http://sbaldw.home.mindspring.com/hproject/prov/charl000.htm | archive-date=10 December 2017 | url-status=dead }}</ref> Charlemagne claimed descent from the Roman emperor, ].<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9DXZY2giQOAC&pg=PA34|page=34|title=The Italian Romance Epic in the Age of Humanism: The Matter of Italy and the World of Rome|author=Jane E. Everson|publisher=Oxford University Press|date=2001|isbn=978-0-19-816015-1 }}</ref> | |||
| Carloman's refusal to participate in the war against Aquitaine led to a rift between the kings.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=79}} It is uncertain why Carloman abandoned the campaign; the brothers may have disagreed about control of the territory,{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=80}} or Carloman was focused on securing his rule in the north of Francia.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=80}} Regardless of the strife between the kings, they maintained a joint rule for practical reasons.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=81}} Charlemagne and Carloman worked to obtain the support of the clergy and local elites to solidify their positions.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=82}} | |||
| In 747, ] fell on 2 April, a coincidence that likely would have been remarked upon by chroniclers.<ref>{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=rETxD8KcnUIC|page=145}}|title=Icons of the Middle Ages: Rulers, Writers, Rebels, and Saints|last=Matheson|first=Lister M.|publisher=ABC-CLIO|year=2012|isbn=978-0-313-34080-2|pages=145–}}</ref> If Easter was being used as the beginning of the calendar year, then 2 April 747 could have been, by modern reckoning, April 748 (not on Easter). The date favoured by the preponderance of evidence{{sfn|Barbero|2004|pp=12–}} is 2 April 742, based on Charlemagne's age at the time of his death.<ref name="Baldwin"/> This date supports the concept that Charlemagne was technically an ] child, although that is not mentioned by Einhard in either since he was born out of wedlock; Pepin and Bertrada were bound by a private contract or ]{{sfn|Barbero|2004|pp=12–}} at the time of his birth, but did not marry until 744.<ref>{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=CurSh3Sh_KMC|page=226}}|title=Dictionary of World Biography: The Middle Ages |last1=Northen Magill|first1=Frank|last2=Aves|first2=Alison|publisher=Routledge|year=1998|isbn=978-1-57958-041-4|pages=226–}}</ref> | |||
| ] was elected in 768, but was briefly deposed by ] before being restored to Rome.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=99}} Stephen's papacy experienced continuing factional struggles, so he sought support from the Frankish kings.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=99, 101}} Both brothers sent troops to Rome, each hoping to exert his own influence.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=100–101}} The Lombard king ] also had interests in Roman affairs, and Charlemagne attempted to enlist him as an ally.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=101}} Desiderius already had alliances with ] and ] through the marriages of his daughters to their dukes,{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=84–85, 101}} and an alliance with Charlemagne would add to his influence.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=101}} Charlemagne's mother, Bertrada, went on his behalf to Lombardy in 770 and brokered a marriage alliance before returning to Francia with his new bride.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=106}} Desiderius's daughter is traditionally known as ], although she may have been named Gerperga.{{sfn|Nelson|2007|p=31}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=65}} Anxious about the prospect of a Frankish–Lombard alliance, Pope Stephen sent a letter to both Frankish kings decrying the marriage and separately sought closer ties with Carloman.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=104–106}} | |||
| Charlemagne's exact birthplace is unknown, although historians have suggested Aachen in modern-day Germany, and ] (]) in present-day ] as possible locations.{{citation needed|date=November 2022}} Aachen and ] are close to the region whence the Merovingian and Carolingian families originated. Other cities have been suggested, including ], ], ],<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170702123542/http://www.route-gottfried-von-bouillon.de/index.php?rid=1307&cid=5&area=content |date=2 July 2017 }}. Route-gottfried-von-bouillon.de. Retrieved on 7 September 2013.</ref> ], and ]. No definitive evidence resolves the question. | |||
| Charlemagne had already had a relationship with the Frankish noblewoman ], and they had a son in 769 named ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=91}} ] wrote in his 784 {{lang|la|Gesta Episcoporum Mettensium}} that Pepin was born "before legal marriage", but does not say whether Charles and Himiltrude ever married, were joined in a non-canonical marriage ({{lang|de|]}}), or married after Pepin was born.{{sfn|Goffart|1986}} Pope Stephen's letter described the relationship as a legitimate marriage, but he had a vested interest in preventing Charlemagne from marrying Desiderius's daughter.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=84}} | |||
| === Ancestry === | |||
| Charlemagne was the eldest child of ] (714 – 24 September 768, reigned from 751) and his wife ] (720 – 12 July 783), daughter of ]. Many historians consider Charlemagne (Charles) to have been illegitimate, although some state that this is arguable,<ref>{{cite book|title=Dictionary of World Biography: The Middle Ages, Volume 2|page=226|isbn=978-1-579-58041-4 |publisher=Routledge|date=1998|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=CurSh3Sh_KMC|page=226}}}}</ref> because Pepin did not marry Bertrada until 744, which was after Charles' birth; this status did not exclude him from the succession.{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=}}<ref>{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=rETxD8KcnUIC|page=152}}|title=Icons of the Middle Ages: Rulers, Writers, Rebels, and Saints |last=Matheson|first=Lister M.|publisher=ABC-CLIO|year=2012|isbn=978-0-313-34080-2|pages=152–}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=Eo6UrwfmwqUC|page=39}}|title=The Carolingian Empire|last=Fichtenau |first=Heinrich |publisher=University of Toronto Press|year=1957|isbn=978-0-8020-6367-0|pages=39–}}</ref> | |||
| Carloman died suddenly on 4 December 771, leaving Charlemagne sole king of the Franks.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=87}} He moved immediately to secure his hold on his brother's territory, forcing Carloman's widow ] to flee to Desiderius's court in Lombardy with their children.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=108–109}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=66}} Charlemagne ended his marriage to Desiderius's daughter and married ], daughter of count ], a powerful magnate in Carloman's kingdom.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=66}} This was a reaction to Desiderius's sheltering of Carloman's family{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=109–110}} and a move to secure Gerold's support.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=89}}{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=110–111}} | |||
| Records name only ], ], and three short-lived children named Pepin, Chrothais and Adelais as his younger siblings. | |||
| ==King of the Franks and the Lombards== | |||
| {{Blockquote|It would be folly, I think, to write a word concerning Charles' birth and infancy, or even his boyhood, for nothing has ever been written on the subject, and there is no one alive now who can give information on it.|]{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 4. Plan of This Work}}}} | |||
| ===Annexation of the Lombard Kingdom=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Charlemagne's first campaigning season as sole king of the Franks was spent on the eastern frontier in his first ], who had been engaging in border raids on the Frankish kingdom when Charlemagne responded by destroying the pagan ] at ] and seizing their gold and silver.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=99}} The success of the war helped secure Charlemagne's reputation among his brother's former supporters and funded further military action.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=116}} The campaign was the beginning of over thirty years of nearly-continuous warfare against the Saxons by Charlemagne.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=122}} | |||
| ] succeeded Stephen III in 772, and sought the return of papal control of cities that had been captured by Desiderius.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=117}} Unsuccessful in dealing with the Lombard king directly, Adrian sent emissaries to Charlemagne to gain his support for recovering papal territory. Charlemagne, in response to this appeal and the dynastic threat of Carloman's sons in the Lombard court, gathered his forces to intervene.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=117–118}} He first sought a diplomatic solution, offering gold to Desiderius in exchange for the return of the papal territories and his nephews.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=131–132}} This overture was rejected, and Charlemagne's army (commanded by himself and his uncle, ]) crossed the Alps to ] the Lombard capital of ] in late 773.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=133}} | |||
| ===Ambiguous high office=== | |||
| {{further|Mayor of the palace}} | |||
| Charlemagne's second son (also named ]) was born in 772, and Charlemagne brought the child and his wife to the camp at Pavia. Hildegard was pregnant, and gave birth to a daughter named Adelhaid. The baby was sent back to Francia, but died on the way.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=133}} Charlemagne left Bernard to maintain the siege at Pavia while he took a force to capture Verona, where Desiderius's son ] had taken Carloman's sons.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=133, 134}} Charlemagne captured the city; no further record exists of his nephews or of Carloman's wife, and their fate is unknown.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=134–135}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=67}} Recent biographer, ] compares them to the ] in the ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=130}} Fried suggests that the boys were forced into a monastery (a common solution of dynastic issues), or "an act of murder smooth Charlemagne's ascent to power."{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=100}} Adalgis was not captured by Charlemagne, and fled to Constantinople.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=146}} | |||
| The most powerful officers of the Frankish people, the ] (''Maior Domus'') and one or more kings (''rex'', ''reges''), were appointed by the election of the people. Elections were not periodic, but were held as required to elect officers ''ad quos summa imperii pertinebat'', "to whom the highest matters of state pertained". Evidently, interim decisions could be made by the Pope, which ultimately needed to be ratified using an assembly of the people that met annually.{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 1. The Merovingian Family}} | |||
| ] receiving Charlemagne at Rome, 1493]] | |||
| Before he was elected king in 751, Pepin was initially a mayor, a high office he held "as though hereditary" (''velut hereditario fungebatur''). Einhard explains that "the honour" was usually "given by the people" to the distinguished, but Pepin the Great and his brother Carloman the Wise received it as though hereditary, as had their father, ]. There was, however, a certain ambiguity about quasi-inheritance. The office was treated as joint property: one Mayorship held by two brothers jointly.<ref>The ''Annales'' uses maiores domus, a plural followed by a singular: one house, two chief officers. {{harvnb|Einhard, putative|741–829|loc=Year 742}}</ref> Each, however, had his own geographic jurisdiction. When Carloman decided to resign, becoming ultimately a Benedictine at ],{{sfn|Einhard, putative|741–829|loc=Years 745, 746}} the question of the disposition of his quasi-share was settled by the pope. He converted the mayorship into a kingship and awarded the joint property to Pepin, who gained the right to pass it on by inheritance.{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 6. Lombard War}} | |||
| Charlemagne left the siege in April 774 to celebrate Easter in Rome.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=101}} Pope Adrian arranged a formal welcome for the Frankish king, and they swore oaths to each other over the relics of St. Peter.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=135–138}} Adrian presented a copy of the ] outlining the papal lands and rights Pepin had agreed to protect and restore.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=139–140}} It is unclear which lands and rights the agreement involved, which remained a point of dispute for centuries.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=112}} Charlemagne placed a copy of the agreement in the chapel above St. Peter's tomb as a symbol of his commitment, and left Rome to continue the siege.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=139–141}} | |||
| Disease struck the Lombards shortly after his return to Pavia, and they surrendered the city by June 774.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=142–144}} Charlemagne deposed Desiderius and took the title of King of the Lombards.{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=61–63}} The takeover of one kingdom by another was "extraordinary",{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=62}} and the authors of ''The Carolingian World'' call it "without parallel".{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=67}} Charlemagne secured the support of the Lombard nobles and Italian urban elites to seize power in a mainly-peaceful annexation.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=62}}{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=147}} Historian ] suggests that the elective nature of the Lombard monarchy eased Charlemagne's takeover,{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=109}} and ] attributes the easy conquest to the Lombard elite's "presupposition that rightful authority was in the hands of the one powerful enough to seize it".{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=62}} Charlemagne soon returned to Francia with the Lombard royal treasury and with Desiderius and his family, who would be confined to a monastery for the rest of their lives.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=147–148}} | |||
| This decision was not accepted by all family members. Carloman had consented to the temporary tenancy of his own share, which he intended to pass on to his son, Drogo, when the inheritance should be settled at someone's death. By the Pope's decision, in which Pepin had a hand, Drogo was to be disqualified as an heir in favour of his cousin Charles. He took up arms in opposition to the decision and was joined by ], a half-brother of Pepin and Carloman, who had been given a share by Charles Martel, but was stripped of it and held under loose arrest by his half-brothers after an attempt to seize their shares by military action. Grifo perished in combat in the Battle of ] while Drogo was hunted down and taken into custody.{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=32–33}} | |||
| ===Frontier wars in Saxony and Spain=== | |||
| According to the ''Life'', Pepin died in Paris on 24 September 768, whereupon the kingship passed jointly to his sons, "with divine assent" (''divino nutu'').{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 3. Charlemagne's Accession}} The Franks "in general assembly" (''generali conventu'') gave them both the rank of a king (''reges'') but "partitioned the whole body of the kingdom equally" (''totum regni corpus ex aequo partirentur''). The ''annals''{{sfn|Einhard, putative|741–829|loc=Year 768}} tell a slightly different version, with the king dying at ], near Paris. The two "lords" (''domni'') were "elevated to kingship" (''elevati sunt in regnum''), Charles on 9 October in ], Carloman on an unspecified date in ]. If born in 742, Charles was 26 years old, but he had been campaigning at his father's right hand for several years, which may help to account for his military skill. ] was 17. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The Saxons took advantage of Charlemagne's absence in Italy to raid the Frankish borderlands, leading to a Frankish counter-raid in the autumn of 774 and a reprisal campaign the following year.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=154–156}} Charlemagne was soon drawn back to Italy as Duke ] rebelled against him.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=157–159}} He quickly crushed the rebellion, distributing Hrodgaud's lands to the Franks to consolidate his rule in Lombardy.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=159}} Charlemagne wintered in Italy, consolidating his power by issuing charters and legislation and taking Lombard hostages.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=159–161}} Amid the 775 Saxon and ]an campaigns, his daughter ] was born in Francia.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=157}} | |||
| Returning north, Charlemagne waged another brief, destructive campaign against the Saxons in 776.{{efn|Charlemagne's third son (]) was also born in 776, based on the four-year-old's 780 baptism in Pavia.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=136}} }} This led to the submission of many Saxons, who turned over captives and lands and submitted to ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=162–163}} In 777, Charlemagne held an assembly at ] with Frankish and Saxon men; many more Saxons came under his rule, but the Saxon magnate ] fled to Denmark to prepare for a new rebellion.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=164–165}} | |||
| The language, in either case, suggests that there were not two inheritances, which would have created distinct kings ruling over distinct kingdoms, but a single joint inheritance and a joint kingship tenanted by two equal kings, Charles and his brother Carloman. As before, distinct jurisdictions were awarded. Charles received Pepin's original share as Mayor: the outer parts of the kingdom bordering on the sea, namely ], western ], and the northern parts of ]; while Carloman was awarded his uncle's former share, the inner parts: southern Austrasia, ], eastern Aquitaine, ], Provence, and ], lands bordering ]. The question of whether these jurisdictions were joint shares reverting to the other brother if one brother died or were inherited property passed on to the descendants of the brother who died was never definitely settled. It came up repeatedly over the succeeding decades until the grandsons of Charlemagne created distinct sovereign kingdoms.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2022-01-20 |title=Who was Charlemagne? - Boot Camp & Military Fitness Institute |url=https://bootcampmilitaryfitnessinstitute.com/2022/01/20/who-was-charlemagne-2/ |access-date=2023-05-16 |website=bootcampmilitaryfitnessinstitute.com |language=en-GB}}</ref> | |||
| Also at the Paderborn assembly were representatives of dissident factions from ] (Muslim Spain). They included the son and son-in-law of ], the former governor of ] ousted by Caliph ] in 756, who sought Charlemagne's support for al-Fihri's restoration. Also present was ], governor of Barcelona and Girona, who wanted to become part of the Frankish kingdom and receive Charlemagne's protection rather than remain under the rule of Córdoba.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=164–166}} Charlemagne, seeing an opportunity to strengthen the security of the kingdom's southern frontier and extend his influence, agreed to intervene.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=166}} Crossing the Pyrenees, his army found little resistance until an ambush by ] forces in 778 at the ]. The Franks, defeated in the battle, withdrew with most of their army intact.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=167–170, 173}} | |||
| ===Aquitainian rebellion=== | |||
| ====Formation of a new Aquitaine==== | |||
| {{main|Aquitaine}} | |||
| ===Building the dynasty=== | |||
| In southern ], ] had been Romanised and people spoke a ]. Similarly, ] had been populated by peoples who spoke various languages, including ], but these had now been mostly replaced by Romance languages. Between Aquitaine and Hispania were the ], Latinised to ], or ],{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=32}} whose country, Vasconia, extended, according to the distributions of place names attributable to the Basques, mainly in the western ] but also as far south as the upper river ] in Spain and as far north as the river ] in France.{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=105}} The French name ] derives from ]. The Romans were never able to subjugate the whole of Vasconia. The soldiers they recruited for the Roman legions from those parts that did submit, and where they founded the region's first cities, were valued for their fighting abilities. The border with Aquitaine was at ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| Charlemagne returned to Francia to greet his newborn twin sons, ] and Lothair, who were born while he was in Spain;{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=168, 172}} Lothair died in infancy.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=181}} Again, Saxons had seized on the king's absence to raid. Charlemagne sent an army to Saxony in 779{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=172–173}} while he held assemblies, legislated, and addressed a famine in Francia.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=175–179}} Hildegard gave birth to another daughter, ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=181}} Charlemagne returned to Saxony in 780, holding assemblies at which he received hostages from Saxon nobles and oversaw their baptism.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=173}} | |||
| He and Hildegard travelled with their four younger children to Rome in the spring of 781, leaving Pepin and Charles at ], to make a journey first requested by Adrian in 775.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=181}} Adrian baptised Carloman and renamed him Pepin, a name he shared with his half-brother.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=182–186}} Louis and the newly renamed Pepin were then anointed and crowned. Pepin was appointed king of the Lombards, and Louis king of Aquitaine.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=136}} This act was not nominal, since the young kings were sent to live in their kingdoms under the care of regents and advisers.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=186}} A delegation from the ], the remnant of the Roman Empire in the East, met Charlemagne during his stay in Rome; Charlemagne agreed to betroth his daughter Rotrude to ]'s son, Emperor ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=191}} | |||
| In about 660, the ] united with the ] to form a single realm under ], ruling from Toulouse. This was a joint kingship with a Basque Duke, ]. ''Lupus'' is the Latin translation of Basque Otsoa, "wolf".{{sfn|Douglass|Bilbao|2005|pp=36–37}} At Felix's death in 670 the joint property of the kingship reverted entirely to Lupus. As the Basques had no law of joint inheritance but relied on ], ] in effect founded a hereditary dynasty of Basque rulers of an expanded Aquitaine.{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=100}} | |||
| Hildegard gave birth to her eighth child, ], during this trip to Italy.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=182–183}} After the royal family's return to Francia, she had her final pregnancy and died from its complications on 30 April 783. The child, named after her, died shortly thereafter.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=203}} Charlemagne commissioned epitaphs for his wife and daughter, and arranged for a ] to be said daily at Hildegard's tomb.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=203}} Charlemagne's mother Bertrada died shortly after Hildegard, on 12 July 783.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=204–205}} Charlemagne was remarried to ], daughter of the East Frankish count Radolf, by the end of the year.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=205}} | |||
| ====Acquisition of Aquitaine by the Carolingians==== | |||
| {{further|Umayyad conquest of Hispania}} | |||
| ] in 732]] | |||
| ===Saxon resistance and reprisal=== | |||
| The Latin chronicles of the end of ] ] omit many details, such as identification of characters, filling in the gaps and reconciliation of numerous contradictions.<ref>{{harvnb|Collins|2004|pp=130–31}}, "The sequence of events...has not been assisted by the tendency of the historians to take all the information...from all the available sources and combine it to produce a single synthetic account...As a rule of thumb, reliability, and also brevity of narrative, are usually in direct proportion to chronological proximity."</ref> Muslim sources, however, present a more coherent view, such as in the ''Ta'rikh iftitah al-Andalus'' ("History of the Conquest of al-Andalus") by ] ("the son of the Gothic woman", referring to the granddaughter of ], the last Visigothic king of a united Hispania, who married a Moor). Ibn al-Qūṭiyya, who had another, much longer name, must have been relying to some degree on family oral tradition. | |||
| In summer 782, Widukind returned from Denmark to attack the Frankish positions in Saxony.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=193}} He defeated a Frankish army, possibly due to rivalry among the Frankish counts leading it.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=193–195}} Charlemagne came to ] after learning of the defeat, but Widukind fled before his arrival. Charlemagne summoned the Saxon magnates to an assembly and compelled them to turn prisoners over to him, since he regarded their previous acts as treachery. The annals record that Charlemagne had 4,500 Saxon prisoners beheaded in the ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=195–196}} Fried writes, "Although this figure may be exaggerated, the basic truth of the event is not in doubt",{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=126}} and ] calls it "perhaps the greatest stain on his reputation."{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=46}} Charlemagne issued the '']'', probably in the immediate aftermath of (or as a precursor of) the massacre.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=196–197}} With a harsh set of laws which included the death penalty for pagan practices, the ''Capitulatio'' "constituted a program for the forced ]"{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=47}} and was "aimed ... at suppressing Saxon identity".{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=197}} | |||
| Charlemagne's focus for the next several years would be on his attempt to complete the subjugation of the Saxons. Concentrating first in ] in 783, he pushed into ] in 784 as his son ] continued operations in the west. At each stage of the campaigns, the Frankish armies seized wealth and carried Saxon captives into slavery.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=200-202}} Unusually, Charlemagne campaigned through the winter instead of resting his army.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=55}} By 785, he had suppressed the Saxon resistance and completely commanded Westphalia. That summer, he met Widukind and persuaded him to end his resistance. Widukind agreed to be baptised with Charlemagne as his godfather, ending this phase of the ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=208–209}} | |||
| According to Ibn al-Qūṭiyya{{sfn|James|Ibn al-Qūṭiyya|2009|p=49}} ], the last Visigothic king of a united Hispania, died before his three sons, Almund, Romulo, and Ardabast reached maturity. Their mother was ] at ], but ], army chief of staff, staged a rebellion, capturing ]. He chose to impose a joint rule over distinct jurisdictions on the true heirs. Evidence of a division of some sort can be found in the distribution of coins imprinted with the name of each king and in the king lists.{{sfn|Collins|2004|pp=131–32}} Wittiza was succeeded by Roderic, who reigned for seven and a half years, followed by Achila (Aquila), who reigned three and a half years. If the reigns of both terminated with the incursion of the ], then Roderic appears to have reigned a few years before the majority of Achila. The latter's kingdom was securely placed to the northeast, while Roderic seems to have taken the rest, notably modern ]. | |||
| ===Benevento, Bavaria, and Pepin's revolt=== | |||
| The Saracens crossed the mountains to claim Ardo's ], only to encounter the Basque dynasty of Aquitaine, always the allies of the Goths. ] of ] was at first victorious at the ] in 721.{{sfn|Douglass|Bilbao|2005|p=40}} Saracen troops gradually massed in Septimania and, in 732, an army under Emir ] advanced into Vasconia, and Odo was defeated at the ]. They took ] and were advancing towards ] when Odo, powerless to stop them, appealed to his arch-enemy, ], mayor of the Franks. In one of the first of the lightning marches for which the Carolingian kings became famous, Charles and his army appeared in the path of the Saracens between Tours and ], and in the ] decisively defeated and killed al-Ghafiqi. The Moors returned twice more, each time suffering defeat at Charles' hands—at the River Berre near Narbonne in 737{{sfn|Einhard|1880|p=24}} and in the ] in 740.<ref name="Lewis2009">{{cite book|first=David Levering |last=Lewis|title=God's Crucible: Islam and the Making of Europe, 570–1215|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=NwA7mQEACAAJ|page=177}}|date=2009|publisher=W.W. Norton|isbn=978-0-393-33356-5|page=177}}</ref> Odo's price for salvation from the Saracens was incorporation into the Frankish kingdom, a decision that was repugnant to him and also to his heirs. | |||
| Charlemagne travelled to Italy in 786, arriving by Christmas. Aiming to extend his influence further into southern Italy, he marched into the Duchy of Benevento.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=139–140}} ] fled to a fortified position at ] before offering Charlemagne his fealty. Charlemagne accepted his submission and hostages, who included Arechis's son ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=228}} In Italy, Charlemagne also met with envoys from Constantinople. Empress Irene had called the 787 ], but did not inform Charlemagne or invite any Frankish bishops. Charlemagne, probably in reaction to the perceived slight of the exclusion, broke the betrothal of his daughter Rotrude and Constantine VI.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=225–226, 230}} | |||
| ]'' from Benevento, with Grimoald's effigy and Charlemagne's name (DOMS CAR RX, the Lord King Charles)]] | |||
| ====Loss and recovery of Aquitaine==== | |||
| After Charlemagne left Italy, Arechis sent envoys to Irene to offer an alliance; he suggested that she send a Byzantine army with Adalgis, the exiled son of Desiderus, to remove the Franks from power in Lombardy.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=234}} Before his plans could be finalised, Aldechis and his elder son Romuald died of illness within weeks of each other.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=142}} Charlemagne sent Grimoald back to Benevento to serve as duke and return it to Frankish suzerainty.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=240}} The Byzantine army ], but were repulsed by the Frankish and Lombard forces.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=240–241}} | |||
| After the death of his father, ] allied himself with free ]. However, Odo had ambiguously left the kingdom jointly to his two sons, Hunald and Hatto. The latter, loyal to Francia, now went to war with his brother over full possession. Victorious, Hunald blinded and imprisoned his brother, only to be so stricken by conscience that he resigned and entered the church as a monk to do penance. The story is told in ].<ref name="Freeman1904">{{cite book|first=Edward Augustus |last=Freeman|title=Western Europe in the Eighth Century & Onward: An Aftermath|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=5HCIvgAACAAJ|page=74}}|year=1904|publisher=Macmillan and Company, limited| page=74}}</ref> His son ] took an early inheritance, becoming duke of Aquitaine and ratifying the alliance with Lombardy. Waifer, deciding to honour it, repeated his father's decision, which he justified by arguing that any agreements with Charles Martel became invalid on Martel's death. Since ] was now Pepin's inheritance because of the earlier assistance given by Charles Martel, according to some, the latter and his son, the young Charles, hunted down Waifer, who could only conduct a guerrilla war, and executed him.{{sfn|Russell|1930|p=88}} | |||
| As affairs were being settled in Italy, Charlemagne turned his attention to Bavaria. Bavaria was ruled by Duke ], Charlemagne's first cousin, who had been installed by Pepin the Short in 748.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=186–187}} Tassilo's sons were also grandsons of Desiderius, and a potential threat to Charlemagne's rule in Lombardy.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=152}} The neighbouring rulers had a growing rivalry throughout their reigns, but had sworn oaths of peace to each other in 781.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=188–190}} In 784, Rotpert (Charlemagne's viceroy in Italy) accused Tassilo of conspiring with Widukind in Saxony and unsuccessfully attacked the Bavarian city of ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=213–214}} Charlemagne gathered his forces to prepare for an invasion of Bavaria in 787. Dividing the army, the Franks launched a three-pronged attack. Quickly realizing his poor position, Tassilo agreed to surrender and recognise Charlemagne as his overlord.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=243–244}} The following year, Tassilo was accused of plotting with the ] to attack Charlemagne. He was deposed and sent to a monastery, and Charlemagne absorbed Bavaria into his kingdom.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=251–254}} Charlemagne spent the next few years based in ], largely focused on consolidating his rule of Bavaria and ] the Avars.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=294}} Successful campaigns against them were launched from Bavaria and Italy in 788,{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=257}} and Charlemagne led campaigns in 791 and 792.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=157}} | |||
| Among the contingents of the Frankish army were ]ns under ], an ], the hereditary Bavarian ducal family. ] had installed himself as Duke of Bavaria, but Pepin replaced him with a member of the ducal family yet a child, Tassilo, whose protector he had become after the death of his father. The loyalty of the Agilolfings was perpetually in question, but Pepin exacted numerous oaths of loyalty from Tassilo. However, the latter had married ], a daughter of ], king of ]. At a critical point in the campaign, Tassilo left the field with all his Bavarians. Out of reach of Pepin, he repudiated all loyalty to Francia.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=118–25}} Pepin had no chance to respond as he grew ill and died within a few weeks after Waifer's execution. | |||
| Charlemagne gave Charles the Younger rule of ] in Neustria in 789, leaving Pepin the Hunchback his only son without lands.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=270}} His relationship with Himiltrude was now apparently seen as illegitimate at his court, and Pepin was sidelined from the succession.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=270, 274–275}} In 792, as his father and brothers were gathered in Regensburg, Pepin conspired with Bavarian nobles to assassinate them and install himself as king. The plot was discovered and revealed to Charlemagne before it could proceed; Pepin was sent to a monastery, and many of his co-conspirators were executed.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=285–287, 438}} | |||
| The first event of the brothers' reign was the uprising of the Aquitainians and ] in 769, in that territory split between the two kings. One year earlier, Pepin had finally defeated ], ], after waging a destructive, ten-year war against Aquitaine. Now, ] led the Aquitainians as far north as ]. Charles met Carloman, but Carloman refused to participate and returned to Burgundy. Charles went to war, leading an army to ], where he built a fortified camp on the mound at ]. Hunald was forced to flee to the court of Duke ]. Lupus, fearing Charles, turned Hunald over in exchange for peace, and Hunald was put in a monastery. Gascon lords also surrendered, and Aquitaine and ] were finally fully subdued by the Franks. | |||
| The early 790s saw a marked focus on ecclesiastical affairs by Charlemagne. He summoned a council in Regensburg in 792 to address the theological controversy over the ] doctrine in the Spanish church and formulate a response to the Second Council of Nicea.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=283–284}} The council condemned adoptionism as ] and led to the production of the '']'', a detailed argument against Nicea's canons.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=289–292}} In 794, Charlemagne called another ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=302}} The council confirmed Regensburg's positions on adoptionism and Nicea, recognised the deposition of Tassilo, set grain prices, reformed Frankish coinage, forbade abbesses from blessing men, and endorsed prayer in vernacular languages.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=306–314}} Soon after the council, Fastrada fell ill and died;{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=304}} Charlemagne married the Alamannian noblewoman ] shortly afterwards.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=340, 377–379}}{{sfn|Riché|1993|p=135}} | |||
| ===Marriage to Desiderata=== | |||
| The brothers maintained lukewarm relations with the assistance of their mother Bertrada, but in 770 Charles signed a treaty with Duke ] and married a Lombard Princess (commonly known today as ]), the daughter of King Desiderius, to surround Carloman with his own allies. Though ] first opposed the marriage with the Lombard princess, he found little to fear from a Frankish-Lombard alliance. | |||
| ===Continued wars with the Saxons and Avars=== | |||
| Less than a year after his marriage, Charlemagne repudiated Desiderata and married a 13-year-old Swabian named ]. The repudiated Desiderata returned to her father's court at ]. Her father's wrath was now aroused, and he would have gladly allied with Carloman to defeat Charles. Before any open hostilities could be declared, however, Carloman died on 5 December 771, apparently of natural causes. Carloman's widow ] fled to Desiderius' court with her sons for protection. | |||
| Charlemagne gathered an army after the council of Frankfurt as Saxon resistance continued, beginning a series of annual campaigns which lasted through 799.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=319–321}} The campaigns of the 790s were even more destructive than those of earlier decades, with the annal writers frequently noting Charlemagne "burning", "ravaging", "devastating", and "laying waste" the Saxon lands.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=323–324}} Charlemagne forcibly removed a large number of Saxons to Francia, installing Frankish elites and soldiers in their place.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=325–326, 329–331}} His extended wars in Saxony led to his establishing his court in ], which had easy access to the frontier. He built a large ] there, including a chapel which is now part of the ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=356–359}} Einhard joined the court at that time.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=340}} ] (Carloman) engaged in further wars against the Avars in the south, which led to the collapse of their kingdom and the eastward expansion of Frankish rule.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=326, 333}} | |||
| Charlemagne also worked to expand his influence through diplomatic means during the 790s wars, focusing on the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Britain. Charles the Younger proposed a marriage pact with the daughter of King ], but Offa insisted that Charlemagne's daughter Bertha also be given as a bride for his son.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=270–271}} Charlemagne refused the arrangement, and the marriage did not take place.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=83}} Charlemagne and Offa entered into a formal peace in 796, protecting trade and securing the rights of English pilgrims to pass through Francia on their way to Rome.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=84–85}} Charlemagne was also the host and protector of several deposed English rulers who were later restored: ], ], and ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=352, 400, 460}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=466}} Nelson writes that Charlemagne treated the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms "like satellite states," establishing direct relations with English bishops.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=353}} Charlemagne also forged an alliance with ], although Einhard calls Alfonso his "dependent".{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=74}} Following his ] in 798, Alfonso sent Charlemagne trophies of his victory, including armour, mules and prisoners.{{sfn|Reuter|1985|p=85}} | |||
| == Wives, concubines, and children == | |||
| {{further|Carolingian dynasty}} | |||
| Charlemagne had eighteen children with seven of his ten known wives or concubines.<ref name="Will Durant Chronique">Durant, Will. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111224205023/http://www.chronique.com/Library/MedHistory/charlemagne.htm|date=24 December 2011}}. Story of Civilization, Vol III, ''The Age of Faith''. Online version in the Knighthood, Tournaments & Chivalry Resource Library, Ed. Brian R. Price.</ref><ref name="Charlemagne Britannica">{{Cite web|url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Charlemagne|title=Charlemagne – King of the Franks|website=Encyclopedia Britannica|language=en|access-date=12 April 2020}}</ref> Nonetheless, he had only four legitimate grandsons, the four sons of his fourth son, Louis. In addition, he had a grandson (], the only son of his third son, ]), who was illegitimate but included in the line of inheritance. Among his descendants are several royal dynasties, including the ], and ] dynasties. By consequence, most if not all established European noble families ever since can genealogically trace some of their background to Charlemagne. | |||
| ==Reign as emperor== | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ===Coronation=== | |||
| |- | |||
| After ] became pope in 795, he faced political opposition. His enemies accused him of a number of crimes and physically attacked him in April 799, attempting to remove his eyes and tongue.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=160}} Leo escaped and fled north to seek Charlemagne's help.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=152}} Charlemagne continued his campaign against the Saxons before breaking off to meet Leo at ] in September.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=115}}{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=143}} Hearing evidence from the pope and his enemies, he sent Leo back to Rome with royal legates who were instructed to reinstate the pope and conduct a further investigation.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=161}} In August of the following year, Charlemagne made plans to go to Rome after an extensive tour of his lands in Neustria.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=161}}{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=145}} Charlemagne met Leo in November near ] at the twelfth milestone outside Rome, the traditional location where Roman emperors began their ] into the city.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=145}} Charlemagne presided over an assembly to hear the charges, but believed that no one could sit in judgement of the pope. Leo swore an oath on 23 December, declaring his innocence of all charges.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=381}} At mass in ] on Christmas Day 800, Leo proclaimed Charlemagne "emperor of the Romans" (''Imperator Romanorum'') and crowned him.{{efn|The Latin title '']'', meaning "commander", used to denote successful generals in ancient Rome, but eventually came to denote the position of ] and his successors.{{sfn|Hornblower|2012|p=728}} In German, the title was rendered as '']'', after ]. In Greek, it was rendered as '']'' and used alongside the traditional title of '']''. For a discussion of Charlemagne's title and Constantinople's reaction, see {{harvnb|Sarti|2024|pp=7–39}}.}} Charlemagne was the first reigning emperor in the west since the deposition of ] in 476.{{sfn|Heather|2009|p=368}} His son, ], was anointed king by Leo at the same time.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=96}} | |||
| ! Start date | |||
| ! Wives and their children | |||
| ! Concubines and their children | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|768}} | |||
| | His first relationship was with ]. The nature of this relationship is variously described as ], a legal marriage, or a ].{{efn|The nature of Himiltrude's relationship to Charlemagne is a matter of dispute. Charlemagne's biographer ] calls her a "concubine"<ref>Einhard, '']'', ch. 20</ref> and ] speaks of Pippin's birth "before legal marriage",{{citation needed|date=February 2022}} A letter by ] seemingly referring to Charlemagne and his brother Carloman as being already married (to Himiltrude and ]), and advising them not to dismiss their wives has led many historians to believe that Himiltrude and Charlemagne were legally married.{{citation needed|date=February 2022}} However, the words employed by the pope could also mean that there had only been a promise of marriage. The acts of Saint ] supports this hypothesis, for the monastic vocation of that Saint is described as due to the scruple he had regarding Charlemagne's dismissal of Princess ] which occurred before any consummation of the marriage and possibly before any religious ceremony. (It is unclear whether the marriage ever took place or if Desiderata only received the homage of the nobility in accordance with her planned future position of Queen of the Franks.) If Saint Adalard was scandalised by this dismissal, it is highly unlikely he would have been unfazed about Himiltrude's dismissal, had she truly been married to Charlemagne.<ref>Joseph-Épiphane Darras, ''Histoire Générale de l'Église'', Tome 17, p.434-441.</ref> Historians have interpreted the information in different ways. Some, such as ], follow Einhard in describing Himiltrude as a concubine.<ref>Pierre Riché, ''The Carolingians'', p.86.</ref> Others, Dieter Hägemann for example, consider Himiltrude a wife in the full sense.{{citation needed|date=February 2022}} Still others subscribe to the idea that the relationship between the two was "something more than concubinage, less than marriage" and describe it as a ], a supposed form of marriage unrecognized by the Church and easily dissolvable. This form of relationship is often seen in a conflict between Christian marriage and more flexible Germanic concepts.{{citation needed|date=February 2022}}}} (Charlemagne put her aside when he married Desiderata.) The union with Himiltrude produced a son: | |||
| ] | |||
| *] ({{circa|769}}–811) | |||
| Historians differ about the intentions of the imperial coronation, the extent to which Charlemagne was aware of it or participated in its planning, and the significance of the events for those present and for Charlemagne's reign.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=115}} Contemporary Frankish and papal sources differ in their emphasis on, and representation of, events.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=161, 163, 165}} Einhard writes that Charlemagne would not have entered the church if he knew about the pope's plan; modern historians have regarded his report as truthful or rejected it as a literary device demonstrating Charlemagne's humility.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=165–166}} Collins says that the actions surrounding the coronation indicate that it was planned by Charlemagne as early as his meeting with Leo in 799,{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=147}} and Fried writes that Charlemagne planned to adopt the title of emperor by 798 "at the latest."{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=408}} During the years before the coronation, Charlemagne's courtier ] referred to his realm as an ''Imperium Christianum'' ("Christian Empire") in which "just as the inhabitants of the Roman Empire had been united by a common Roman citizenship", the new empire would be united by a common Christian faith.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=151}} This is the view of ], who says that "Charles was the Emperor of the ''ecclesia'' as the Pope conceived it, of the Roman Church, regarded as the universal Church".{{sfn|Pirenne|2012|p=233}} | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|770}} | |||
| | After her, his first wife was ], daughter of ], king of the ]; married in 770, annulled in 771. | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|771}} | |||
| | His second wife was ] (757/758–783), married 771, died 783. By her he had nine children: | |||
| The Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire remained a significant contemporary power in European politics for Leo and Charlemagne, especially in Italy. The Byzantines continued to hold a substantial portion of Italy, with their borders not far south of Rome. Empress Irene had seized the throne from her son Constantine VI in 797, deposing and blinding him.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=361}} Irene, the first Byzantine empress, faced opposition in Constantinople because of her gender and her means of accession.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=370}} One of the earliest narrative sources for the coronation, the '']'', presented a female ruler in Constantinople as a vacancy in the imperial title which justified Leo's coronation of Charlemagne.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=384}} Pirenne disagrees, saying that the coronation "was not in any sense explained by the fact that at this moment a woman was reigning in Constantinople."{{sfn|Pirenne|2012|p=234n}} Leo's main motivations may have been the desire to increase his standing after his political difficulties, placing himself as a power broker and securing Charlemagne as a powerful ally and protector.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=167}} The Byzantine Empire's lack of ability to influence events in Italy and support the papacy were also important to Leo's position.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=167}} According to the ''Royal Frankish Annals'', Leo ] himself before Charlemagne after crowning him (an act of submission standard in Roman coronation rituals from the time of ]). This account presents Leo not as Charlemagne's superior, but as the agent of the Roman people who acclaimed Charlemagne as emperor.{{sfn|Muldoon|1999|p=24}} | |||
| *] ({{circa|772}}–811), Duke of Maine | |||
| * Adalhaid (774), who was born whilst her parents were on campaign in Italy. She was sent back to Francia, but died before reaching Lyons | |||
| *] (or Hruodrud) (775–810) | |||
| *] (777–810), ] | |||
| *] (778–840), twin of Lothair, ] since 781, crowned ] in 813, senior Emperor from 814 | |||
| * Lothair (778–779/780), twin of Louis, he died in infancy<ref>{{cite book |quote=By Charlemagne had four sons and four daughters, according to Paul the Deacon: one son, the twin of Lewis, called Lothar, died as a baby and is not mentioned by Einhard; two daughters, Hildigard and Adelhaid, died as babies, so that Einhard appears to err in one of his names, unless there were really five daughters. |last=Thorpe |first=Lewis |title=Two Lives of Charlemagne |page=185}}</ref> | |||
| *] (779–826) | |||
| * ] (781–808) | |||
| * Hildegarde (782–783) | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|773}} | |||
| | | |||
| | His first known concubine was ]. By her he had: | |||
| Historian Henry Mayr-Harting claims that the assumption of the imperial title by Charlemagne was an effort to incorporate the Saxons into the Frankish realm, since they did not have a native tradition of kingship.{{sfn|Mayr-Harting|1996}} However, Costambeys ''et al.'' note in ''The Carolingian World'' that "since Saxony had not been in the Roman empire it is hard to see on what basis an emperor would have been any more welcomed."{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=167}} These authors write that the decision to take the title of emperor was aimed at furthering Charlemagne's influence in Italy, as an appeal to traditional authority recognised by Italian elites within and (especially) outside his control.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=167}} | |||
| * Adaltrude (b. 774) | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|774}} | |||
| | | |||
| | His second known concubine was Madelgard. By her he had: | |||
| Collins also writes that becoming emperor gave Charlemagne "the right to try to impose his rule over the whole of ", considering this a motivation for the coronation.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=148}} He notes the "element of political and military risk"{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=148}} inherent in the affair due to the opposition of the Byzantine Empire and potential opposition from the Frankish elite, as the imperial title could draw him further into Mediterranean politics.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=149}} Collins sees several of Charlemagne's actions as attempts to ensure that his new title had a distinctly-Frankish context.{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=150–151}} | |||
| * Ruodhaid (775–), ] of ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|784}} | |||
| | His third wife was ], married 784, died 794. By her he had: | |||
| Charlemagne's coronation led to a centuries-long ideological conflict between his successors and Constantinople known as the ],{{efn|{{langx|de|Zweikaiserproblem}}, "two-emperors problem"}} which could be seen as a rejection or usurpation of the Byzantine emperors' claim to be the universal, preeminent rulers of Christendom.{{sfn|Muldoon|1999|p=21}} Historian James Muldoon writes that Charlemagne may have had a more limited view of his role, seeing the title as representing dominion over lands he already ruled.{{sfn|Muldoon|1999|pp=25–26}} However, the title of emperor gave Charlemagne enhanced prestige and ideological authority.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=168}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=115–116}} He immediately incorporated his new title into documents he issued, adopting the formula "Charles, most serene ], crowned by God, great peaceful emperor governing the Roman empire, and who is by the mercy of God king of the Franks and the Lombards"{{efn|{{langx|la|Karolus serenissimus augustus a deo coronatus magnus pacificus imperator Romanum gubernans imperium, qui et per misercordiam dei rex francorum atque langobardorum}}}} instead of the earlier form "Charles, by the grace of God king of the Franks and Lombards and ] of the Romans."{{efn|{{langx|la|Carolus gratia dei rex francorum et langobardorum ac patricius Romanorum}}}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=116}} Leo acclaimed Charlemagne as "emperor of the Romans" during the coronation, but Charlemagne never used this title.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=382, 385}} The avoidance of the specific claim of being a "Roman emperor", as opposed to the more-neutral "emperor governing the Roman empire", may have been to improve relations with the Byzantines.{{sfn|Muldoon|1999|p=26}}{{sfn|Sarti|2024|pp=7-39}} This formulation (with the continuation of his earlier royal titles) may also represent a view of his role as emperor as being the ruler of the people of the city of Rome, as he was of the Franks and the Lombards.{{sfn|Muldoon|1999|p=26}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=168–169}} | |||
| *] (b. 784), ] of ] | |||
| * Hiltrude (b. 787) | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | c. 794 | |||
| | His fourth wife was ], married 794, died childless. | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|800}} | |||
| | | |||
| | His fourth known concubine was Regina. By her he had: | |||
| ===Governing the empire=== | |||
| *] (801–855), ] from 823 and abbot of ] | |||
| ] in Aachen Cathedral]] | |||
| *] (802–844), ] of the Empire | |||
| Charlemagne left Italy in the summer of 801 after adjudicating several ecclesiastical disputes in Rome and experiencing ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=387-389}} He never returned to the city.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=168}} Continuing trends and a ruling style established in the 790s,{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=173–174}} Charlemagne's reign from 801 onward is a "distinct phase"{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=472}} characterised by more sedentary rule from Aachen.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=168}} Although conflict continued until the end of his reign, the relative peace of the imperial period allowed for attention on internal governance. The Franks continued to wage war, though these wars were defending and securing the empire's frontiers,{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=170}}{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=462}} and Charlemagne rarely led armies personally.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=169}} A significant expansion of the ] was achieved with a series of campaigns by Louis against the Emirate of Cordoba, culminating in the ].{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=74–75}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Circa|804}} | |||
| | | |||
| | His fifth known concubine was Ethelind. By her he had: | |||
| The 802 '']'' was an expansive piece of legislation, with provisions governing the conduct of royal officials and requiring that all free men take an ] to Charlemagne.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=495–496}}{{sfn|Ganshof|1965}} The ] reformed the institution of the {{lang|la|]}}, officials who would now be assigned in pairs (a cleric and a lay aristocrat) to administer justice and oversee governance in defined territories.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=450–451}} The emperor also ordered the revision of the Lombard and Frankish legal codes.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=448–449}} | |||
| * Richbod (805–844), ] of ] | |||
| * Theodoric (b. 807) | |||
| |} | |||
| In addition to the {{lang|la|missi}}, Charlemagne also ruled parts of the empire with his sons as sub-kings.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=409, 411}} Although Pepin and Louis had some authority as kings in Italy and Aquitaine, Charlemagne had the ultimate authority and directly intervened.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=410–415}} Charles, their elder brother, had been given lands in Neustria in 789 or 790 and made a king in 800.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=157}} | |||
| ===Children=== | |||
| ] (10th-century copy of 9th-century original)]] | |||
| The 806 charter {{lang|la|Divisio Regnorum}} (''Division of the Realm'') set the terms of Charlemagne's succession.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=429}} Charles, as his eldest son in good favour, was given the largest share of the inheritance: rule of Francia, Saxony, ], and parts of Alemannia. The two younger sons were confirmed in their kingdoms and gained additional territories; most of Bavaria and Alemmannia was given to Pepin, and Provence, Septimania, and parts of Burgundy were given to Louis.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=477}} Charlemagne did not address the inheritance of the imperial title.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=157}} The {{lang|la|Divisio}} also provided that if any of the brothers predeceased Charlemagne, their sons would inherit their share; peace was urged among his descendants.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=432–435}} | |||
| During the first peace of any substantial length (780–782), Charles began to appoint his sons to positions of authority. In 781, during a visit to Rome, he made his two youngest sons kings, crowned by the Pope.{{efn|From 781 Adrian began dating papal documents by the years of Charlemagne's reign, instead of the reign of the ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Asimov |first=I. |year=1968 |title=The Dark Ages |location=Boston |publisher=Houghton Mifflin |page=157}}</ref>}}{{efn|It was during this visit to Rome that Charlemagne met ] and invited him to join his court.{{sfn|Asimov|1968|p=168}}}} The elder of these two, ], was made the ], taking the Iron Crown that his father had first worn in 774, and in the same ceremony was renamed "Pepin"{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 6. Lombard War}}<ref name="Campaigns">{{Cite encyclopedia | |||
| | last = Sullivan | first = Richard E. | |||
| | display-authors=etal | |||
| | year= 2023 | |||
| |title=Charlemagne | encyclopedia= Britannica | |||
| |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Charlemagne|access-date=2023-01-23}}</ref> (not to be confused with Charlemagne's eldest, possibly illegitimate son, ]). The younger of the two, ], became ]. Charlemagne ordered Pepin and Louis to be raised in the customs of their kingdoms, and he gave their regents some control of their subkingdoms, but kept the real power, though he intended his sons to inherit their realms. He did not tolerate insubordination in his sons: in 792, he banished Pepin the Hunchback to ] because the young man had joined a rebellion against him. | |||
| ===Conflict and diplomacy with the east=== | |||
| Charles was determined to have his children educated, including his daughters, as his parents had instilled the importance of learning in him at an early age.<ref>{{Cite book|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=hbnY8GTet_kC}}|title=Charlemagne |last=Gelfand|first=Dale Evva|date=2003|publisher=Infobase Publishing|isbn=978-1438117850|language=en}}</ref> His children were also taught skills in accord with their aristocratic status, which included training in riding and weaponry for his sons, and embroidery, spinning and weaving for his daughters.<ref>{{Cite book|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=bQlJP9O9hKkC}}|title=Daily Life in the Age of Charlemagne|last=Butt|first=John J.|date=2002|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-0313316685|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| After his coronation, Charlemagne sought recognition of his imperial title from Constantinople.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=167–168}} Several delegations were exchanged between Charlemagne and Irene in 802 and 803. According to the contemporary Byzantine chronicler ], Charlemagne made an offer of marriage to Irene which she was close to accepting.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=153}} Irene was deposed and replaced by ], who was unwilling to recognise Charlemagne as emperor.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=153}} The two empires conflicted over control of the ] (especially ] and ]) several times during Nikephoros' reign. Charlemagne sent envoys to Constantinople in 810 to make peace, giving up his claims to Veneto. Nikephoros died in battle before the envoys could leave Constantinople but his son-in-law and successor ] confirmed the peace, sending his own envoys to Aachen to recognise Charlemagne as emperor.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=458–459}} Charlemagne soon issued the first Frankish coins bearing his imperial title, although papal coins minted in Rome had used the title as early as 800.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=116–117}} | |||
| He sent envoys and initiated diplomatic contact with the ] caliph ] during the 790s, due to their mutual interest in Spanish affairs.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=60}} As an early sign of friendship, Charlemagne requested an elephant as a gift from Harun. Harun later provided an elephant named ], which arrived at Aachen in 802.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=60–61}} Harun also sought to undermine Charlemagne's relations with the Byzantines, with whom he was at war. As part of his outreach, Harun gave Charlemagne nominal rule of the ] in Jerusalem and other gifts.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=441}} According to Einhard, Charlemagne "zealously strove to make friendships with kings beyond the seas" in order "that he might get some help and relief to the Christians living under their rule." A surviving administrative document, the ], shows the work done by his agents in Palestine in furtherance of this goal.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=449–452}}{{efn|For more on the Basel roll, see {{harvnb|McCormick|2011}}. }} | |||
| The sons fought many wars on behalf of their father. ] was mostly preoccupied with the Bretons, whose border he shared and who insurrected on at least two occasions and were easily put down. He also fought the Saxons on multiple occasions. In 805 and 806, he was sent into the Böhmerwald (modern ]) to deal with the Slavs living there (Bohemian tribes, ancestors of the modern ]). He subjected them to Frankish authority and devastated the valley of the Elbe, forcing tribute from them. Pippin had to hold the ] and Beneventan borders and fought the ] to his north. He was uniquely poised to fight the ] when that conflict arose after Charlemagne's imperial coronation and a ] rebellion. Finally, Louis was in charge of the ] and fought the Duke of Benevento in southern Italy on at least one occasion. He took ] in ] in 801. | |||
| Harun's death lead to a succession crisis and, under his successors, churches and synagogues were destroyed in the caliphate.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=442}} Unable to intervene directly, Charlemagne sent specially-minted coins and arms to the eastern Christians to defend and restore their churches and monasteries. The coins with their inscriptions were also an important tool of imperial propaganda.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=442–446}} Johannes Fried writes that deteriorating relations with Baghdad after Harun's death may have been the impetus for renewed negotiations with Constantinople which led to Charlemagne's peace with Michael in 811.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=444}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| As emperor, Charlemagne became involved in a religious dispute between Eastern and Western Christians over the recitation of the ], the fundamental statement of orthodox Christian belief. The original text of the creed, adopted at the ], professed that the ] proceeded from ]. A tradition developed in Western Europe that the Holy Spirit proceeded from the Father "and the ]", inserting the Latin term {{lang|la|]}} into the creed.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=449}} The difference did not cause significant conflict until 807, when Frankish monks in Bethlehem were denounced as heretics by a Greek monk for using the {{lang|la|filioque}} form.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=449}} The Frankish monks appealed the dispute to Rome, where Pope Leo affirmed the text of the creed omitting the phrase and passed the report on to Charlemagne.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=449–450}} Charlemagne summoned a ] which defended the use of {{lang|la|filioque}}, and sent the decision to Rome. Leo said that the Franks could maintain their tradition, but asserted that the canonical creed did not include {{lang|la|filioque}}.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=452–453}} He commissioned two silver shields with the creed in Latin and Greek (omitting the {{lang|la|filioque}}), which he hung in ].{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=449}}{{sfn|Sterk|1988}} Another product of the 809 Aachen council was the '']'', an illustrated ] and astronomical compendium.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=488–490}} | |||
| Charlemagne kept his daughters at home with him and refused to allow them to contract ] (though he originally condoned an engagement between his eldest daughter Rotrude and ] of Byzantium, this engagement was annulled when Rotrude was 11).<ref>Runciman, Steven. "The Empress Irene the Athenian." Medieval Women. Ed. Derek Baker. Oxford: Ecclesiastical History Society, 1978.</ref> Charlemagne's opposition to his daughters' marriages may possibly have intended to prevent the creation of ]es of the family to challenge the main line, as had been the case with ]. However, he tolerated their extramarital relationships, even rewarding their common-law husbands and treasuring the illegitimate grandchildren they produced for him. He also refused to believe stories of their wild behaviour. After his death the surviving daughters were banished from the court by their brother, the pious Louis, to take up residence in the convents they had been bequeathed by their father. At least one of them, Bertha, had a recognised relationship, if not a marriage, with ], a member of Charlemagne's court circle.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=}}{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=91}} | |||
| ===Wars with the Danes=== | |||
| ==Italian campaigns== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] had been brought into contact with the Frankish world through Charlemagne's wars with the Saxons.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=461}} Raids on Charlemagne's lands by the ] began around 800.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=167}} Charlemagne engaged in his final campaign in Saxony in 804, seizing Saxon territory east of the ], removing its Saxon population, and giving the land to his ] allies.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=163}} The Danish king ], uneasy at the extension of Frankish power, offered to meet with Charlemagne to arrange peace and (possibly) hand over Saxons who had fled to him;{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=167}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=462}} the talks were unsuccessful.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=462}} | |||
| The northern frontier was quiet until 808, when Gudfred and some allied Slavic tribes led an incursion into the Obotrite lands and extracted tribute from over half the territory.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=462–463}}{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=167}} Charles the Younger led an army across the Elbe in response, but only attacked some of Gudfred's Slavic allies.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=459}} Gudfred again attempted diplomatic overtures in 809, but no peace was apparently made.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=168}} Danish pirates raided Frisia in 810, although it is uncertain if they were connected to Gudfred.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=463}} Charlemagne sent an army to secure Frisia while he led a force against Gudfred, who had reportedly challenged the emperor to face him in battle.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=169}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=463}} The battle never took place, since Gudfred was murdered by two of his own men before Charlemagne's arrival.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=462}} Gudfred's nephew and successor ] immediately sued for peace, and a commission led by Charlemagne's cousin ] reached a settlement with the Danes in 811.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=169}} The Danes did not pose a threat for the remainder of Charlemagne's reign, but the effects of this war and their earlier expansion in Saxony helped set the stage for the intense ] raids across Europe later in the ninth century.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=171}}{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=170}} | |||
| ===Conquest of the Lombard kingdom=== | |||
| ] was threatened by invaders, the king rushed to Rome to provide assistance. Shown here, the pope asks Charlemagne for help at a meeting near Rome.]] | |||
| ===Final years and death=== | |||
| At his succession in 772, ] demanded the return of certain cities in the former ] in accordance with a promise at the succession of Desiderius. Instead, Desiderius took over certain papal cities and invaded the ], heading for Rome. Adrian sent ambassadors to Charlemagne in autumn requesting he enforce the policies of his father, Pepin. Desiderius sent his own ambassadors denying the pope's charges. The ambassadors met at ], and Charlemagne upheld the pope's side. Charlemagne demanded what the pope had requested, but Desiderius swore never to comply. Charlemagne and his uncle ] crossed the Alps in 773 and chased the Lombards back to ].<ref name="Kohn2006">{{cite book|last=Kohn|first=George C.|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=OIzreCGlHxIC&|page=125}}|title=Dictionary of Wars|publisher=Infobase Publishing|year=2006|isbn=978-1-4381-2916-7|pages=125–}}</ref> Charlemagne temporarily left the siege to deal with ], son of Desiderius, who was raising an army at ]. The young prince was chased to the ] littoral and fled to ] to plead for assistance from ], who was waging war with ].{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 6. Lombard War}}<ref>{{cite book |last=Einhard |author-link=Einhard |chapter-url= http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/source/einhard-wars1.asp |chapter=Einhard: The Wars of Charlemagne, c. 770–814 |via=Medieval Sourcebook, Fordham University |editor=William Stearns Davis |title=Readings in Ancient History: Illustrative Extracts from the Sources, 2 Vols. |location=Boston |publisher=Allyn and Bacon |date=1912–1913 |pages=373–375}}</ref> | |||
| ]. Illustrating a ] (a four-horse chariot), it was manufactured in ].]] | |||
| The Carolingian dynasty experienced a number of losses in 810 and 811, when Charlemagne's sister ], his daughter Rotrude, and his sons Pepin the Hunchback, Pepin of Italy, and Charles the Younger died.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=440, 453}} The deaths of Charles and Pepin of Italy left Charlemagne's earlier plans for succession in disarray. He declared Pepin of Italy's son ] ruler of Italy and made his own only surviving son, Louis, heir to the rest of the empire.{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=158}} Charlemagne also made a new ] detailing the disposal of his property at his death, with bequests to the church, his children, and his grandchildren.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=468–470}} Einhard (possibly relying on ] from Suetonius's '']'') says that Charlemagne viewed the deaths of his family members, his fall from a horse, astronomical phenomena, and the collapse of part of the palace in his last years as signs of his impending death.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=480–481}} Charlemagne continued to govern with energy during his final year, ordering bishops to assemble in five ecclesiastical councils.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=478–480}} These culminated in a large assembly at Aachen, where Charlemagne crowned Louis as his co-emperor and Bernard as king in a ceremony on 11 September 813.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=476}} | |||
| Charlemagne became ill in the autumn of 813 and spent his last months praying, fasting, and studying the ]s.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=480–481}} He developed ], and was bedridden for seven days before dying on the morning of 28 January 814.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=514}} ], a biographer of Louis, records the emperor's last words as "Into your hands, Lord, I commend my spirit" (quoting from {{Bibleverse|Luke|23:46}}).{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=481}} Charlemagne's body was prepared and buried in the ] by his daughters and palace officials that day.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=482–483}} Louis arrived at Aachen thirty days after his father's death, making a formal {{lang|la|]}} and taking charge of the palace and the empire.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=483–484}} Charlemagne's remains were exhumed by Holy Roman Emperor ] in 1165, and reinterred in a new casket by ] in 1215.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=520}} | |||
| The siege lasted until the spring of 774 when Charlemagne visited the pope in Rome. There he confirmed ],<ref name="Campaigns" /> with some later chronicles falsely claiming that he also expanded them, granting ], ], Venice and ]. The pope granted him the title '']''. He then returned to Pavia, where the Lombards were on the verge of surrendering. In return for their lives, the Lombards surrendered and opened the gates in early summer. Desiderius was sent to the ] of ], and his son Adelchis died in Constantinople, a patrician. Charles, unusually, had himself crowned with the ] and made the magnates of Lombardy pay homage to him at Pavia. Only Duke ] refused to submit and proclaimed independence. Charlemagne was then master of Italy as king of the Lombards. He left Italy with a garrison in Pavia and a few Frankish counts in place the same year. | |||
| ] and the duchies of ] and ]]] | |||
| Instability continued in Italy. In 776, Dukes ] and ] rebelled. Charlemagne rushed back from ] and defeated the Duke of Friuli in battle; the Duke was slain.{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 6. Lombard War}} The Duke of Spoleto signed a treaty. Their co-conspirator, Arechis, was not subdued, and Adelchis, their candidate in ], never left that city. Northern Italy was now faithfully his. | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| ===Southern Italy=== | |||
| | total_width = 1000 | |||
| In 787, Charlemagne directed his attention towards the ],{{sfn|Hodgkin|1889|p=69}} where ] was reigning independently with the self-given title of ]. Charlemagne's siege of ] forced Arechis into submission, and in return for peace, Arechis recognized Charlemagne's ] and handed his son ] over as a hostage. After Arechis' death in 787, Grimoald was allowed to return to Benevento. In 788, the principality was invaded by Byzantine troops led by Adelchis, but his attempts were thwarted by Grimoald. The Franks assisted in the repulsion of Adelchis, but, in turn, attacked Benevento's territories several times,{{sfn|Hodgkin|1889|pp=85–86}} obtaining small gains, notably the annexation of ] to the ].{{sfn|Bathurst|1782|p=358}} Later, Grimoald tried to throw off Frankish suzerainty, but Charles' sons, ] and ], forced him to submit in 792.{{sfn|Abel|1883|pp=50–51}} | |||
| | align = center | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| ==Carolingian expansion to the south== | |||
| | background color = | |||
| ===Vasconia and the Pyrenees=== | |||
| | width = | |||
| The destructive war led by Pepin in Aquitaine, although brought to a satisfactory conclusion for the Franks, proved the Frankish power structure south of the ] was feeble and unreliable. After the defeat and death of ] in 768, while Aquitaine submitted again to the Carolingian dynasty, a new rebellion broke out in 769 led by Hunald II, a possible son of Waifer. He took refuge with the ally Duke ], but probably out of fear of Charlemagne's reprisal, Lupus handed him over to the new King of the Franks to whom he pledged loyalty, which seemed to confirm the peace in ] south of the ].<ref name="Lewis">{{cite book |last=Lewis |first=Archibald Ross |year=1965 |title=The Development of Southern French and Catalan Society 718–1050 |publisher=University of Texas Press}}</ref> In the campaign of 769, Charlemagne seems to have followed a policy of "overwhelming force" and avoided a major pitched battle<ref>Bachrach, Bernard (2013). Charlemagne's Early Campaigns (768–777): A Diplomatic and Military Analysis. Leiden: Brill. 2013, p. 234</ref> | |||
| | image1 = AachenerDomSarg.jpg | |||
| | width1 = | |||
| Wary of new Basque uprisings, Charlemagne seems to have tried to contain Duke Lupus's power by appointing ] as the Count of Bordeaux (778) and other counts of Frankish background in bordering areas (], ]). The ] Duke, in turn, seems to have contributed decisively or schemed the ] (referred to as "Basque treachery"). The defeat of Charlemagne's army in Roncevaux (778) confirmed his determination to rule directly by establishing the Kingdom of Aquitaine (ruled by ]) based on a power base of Frankish officials, distributing lands among colonisers and allocating lands to the Church, which he took as an ally. A Christianisation programme was put in place across the high ] (778).<ref name=Lewis/> | |||
| | alt1 = An ornate marble sarcophagus | |||
| | caption1 = The ] in which Charlemagne is thought to have been originally buried | |||
| The new political arrangement for Vasconia did not sit well with local lords. As of 788 ] was fighting and capturing ], Carolingian Count of Toulouse. He was eventually released, but Charlemagne, enraged at the compromise, decided to depose him and appointed his trustee ]. William, in turn, fought the Basques and defeated them after banishing Adalric (790).<ref name=Lewis/> | |||
| | image2 = Regione mosana, karlsschrein, reliquiario a cassa di carlomagno, 1182-1215, 06.jpg | |||
| | width2 = | |||
| From 781 (], ]) to 806 (] under Frankish influence), taking the County of Toulouse for a power base, Charlemagne asserted Frankish authority over the Pyrenees by subduing the south-western marches of Toulouse (790) and establishing vassal counties on the southern Pyrenees that were to make up the ].{{sfn|Lewis|1965|p=40}} As of 794, a Frankish vassal, the Basque lord Belasko (''al-Galashki'', 'the Gaul') ruled ], but Pamplona remained under Cordovan and local control up to 806. Belasko and the counties in the Marca Hispánica provided the necessary base to attack the ] (an expedition led by ] and Louis the Pious to capture Barcelona in 801). Events in the Duchy of Vasconia (rebellion in Pamplona, ], Duke Seguin of Bordeaux deposed, uprising of the Basque lords, etc.) were to prove it ephemeral upon Charlemagne's death. | |||
| | alt2 = Another ornate, darker sarcophagus | |||
| | caption2 = The ], in which Frederick II reinterred Charlemagne in 1215 | |||
| ===Roncesvalles campaign=== | |||
| {{See also|Abbasid-Carolingian Alliance}} | |||
| According to the Muslim historian ], the ] of ] had received the representatives of the Muslim rulers of ], ], ] and ]. Their masters had been cornered in the ] by ], the ] ]. These "Saracen" (] and ]) rulers offered their homage to the king of the Franks in return for military support. Seeing an opportunity to extend ] and his own power, and believing the Saxons to be a fully conquered nation, Charlemagne agreed to go to Spain. | |||
| In 778, he led the Neustrian army across the Western ], while the Austrasians, Lombards, and Burgundians passed over the Eastern Pyrenees. The armies met at ] and Charlemagne received the homage of the Muslim rulers, Sulayman al-Arabi and Kasmin ibn Yusuf, but the city did not fall for him. Indeed, Charlemagne faced the toughest battle of his career. The Muslims forced him to retreat, so he decided to go home, as he could not trust the ], whom he had subdued by conquering ]. He turned to leave Iberia, but as his army was crossing back through the Pass of ], one of the most famous events of his reign occurred: the Basques attacked and destroyed his rearguard and baggage train. The ], though less a battle than a skirmish, left many famous dead, including the ] Eggihard, the count of the palace Anselm, and the ] of the ], ], inspiring the subsequent creation of '']'' (''La Chanson de Roland''), regarded as the first major work in the ]. | |||
| ===Contact with Muslims=== | |||
| ] receiving a delegation of Charlemagne in ], by Julius Köckert (1864)]] | |||
| The conquest of Italy brought Charlemagne in contact with Muslims who, at the time, controlled the ]. Charlemagne's eldest son, ], was much occupied with Muslims in Italy. Charlemagne conquered ] and ] at an unknown date and in 799 the ]. The islands were often attacked by Muslim pirates, but the counts of ] and Tuscany (]) controlled them with large fleets until the end of Charlemagne's reign. Charlemagne even had contact with the ]al court in ]. In 797 (or possibly 801), the caliph of Baghdad, ], presented Charlemagne with an ] named ] and a ].<ref name="Heck2007">{{cite book|first=Gene W. |last=Heck|title=When Worlds Collide: Exploring the Ideological and Political Foundations of the Clash of Civilizations|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=dtAyMXqaozwC|page=172}}|year=2007|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield|isbn=978-0-7425-5856-4|pages=172–}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Ottewill-Soulsby |first=Sam |title=The Emperor and the Elephant: Christians and Muslims in the Age of Charlemagne |date=2023 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-22938-6 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Wars with the Moors=== | |||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=December 2018}} | |||
| In ], the struggle against Islam continued unabated throughout the latter half of his reign. Louis was in charge of the Spanish border. In 785, his men captured Girona permanently and extended Frankish control into the ] littoral for the duration of Charlemagne's reign (the area remained nominally Frankish until the ] in 1258). The Muslim chiefs in the northeast of ] were constantly rebelling against Cordovan authority, and they often turned to the Franks for help. The Frankish border was slowly extended until 795, when Girona, ], ] and ] were united into the new ], within the old duchy of ]. | |||
| In 797, ], the greatest city of the region, fell to the Franks when Zeid, its governor, rebelled against Cordova and, failing, handed it to them. The ] authority recaptured it in 799. However, Louis of Aquitaine marched the entire army of his kingdom over the ] and besieged it for two years, wintering there from 800 to 801, when it capitulated. The Franks continued to press forward against the ]. They probably took ] and ] in 809. The last conquest brought them to the mouth of the ] and gave them raiding access to ], prompting the Emir ] to recognise their conquests in 813. | |||
| ==Eastern campaigns== | |||
| ===Saxon Wars=== | |||
| {{Further|Saxon Wars}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Charlemagne was engaged in almost constant warfare throughout his reign,<ref>France, John, "The Composition and Raising of the Armies of Charlemagne", in Journal of Medieval Military History, ed. B. Bachrach (2002), pp. 63–65</ref> often at the head of his elite '']'' bodyguard squadrons. In the ], spanning thirty years and eighteen battles, he conquered ] and proceeded to convert it to Christianity. | |||
| The Germanic ] were divided into four subgroups in four regions. Nearest to ] was ] and farthest away was ]. Between them was ] and north of these three, at the base of the ] peninsula, was ]. | |||
| In his first campaign, in 773, Charlemagne forced the Engrians to submit and cut down an ] pillar near ].<ref>Revised annals of the kingdom of the Franks, ed. and trans. King, Sources, p. 110</ref> The campaign was cut short by his first expedition to Italy. He returned in 775, marching through Westphalia and conquering the Saxon fort at ]. He then crossed Engria, where he defeated the Saxons again. Finally, in Eastphalia, he defeated a Saxon force, and its leader {{ill|Hessi|de|Hessi (Ostfale)}} converted to Christianity. Charlemagne returned through Westphalia, leaving encampments at Sigiburg and ], which had been important Saxon bastions. He then controlled Saxony with the exception of Nordalbingia, but Saxon resistance had not ended. | |||
| Following his subjugation of the Dukes of Friuli and Spoleto, Charlemagne returned rapidly to Saxony in 776, where a rebellion had destroyed his fortress at Eresburg. The Saxons were once again defeated, but their main leader, ], escaped to Denmark, his wife's home. Charlemagne built a new camp at ]. In 777, he called a national diet at Paderborn to integrate Saxony fully into the Frankish kingdom. Many Saxons were baptised as Christians. | |||
| In the summer of 779, he again invaded Saxony and reconquered Eastphalia, Engria and Westphalia. At a diet near ], he divided the land into missionary districts and himself assisted in several mass baptisms (780). He then returned to Italy and, for the first time, the Saxons did not immediately revolt. Saxony was peaceful from 780 to 782. | |||
| ] at ] in 785, painted {{Circa|1840|lk=no}} by ]]] | |||
| He returned to Saxony in 782 and instituted a code of law and appointed counts, both Saxon and Frank. The laws were draconian on religious issues; for example, the '']'' prescribed death to Saxon pagans who refused to convert to Christianity. This led to renewed conflict. That year, in autumn, Widukind returned and led a new revolt. In response, at ] in Lower Saxony, Charlemagne is recorded as having ordered the execution of 4,500 Saxon prisoners by beheading, known as the ] ("Verdener Blutgericht"). The killings triggered three years of renewed bloody warfare. During this war, the ]ns between the ] and the ] joined the Saxons in revolt and were finally subdued.<ref>Oebele Vries, "Friesland", ''Medieval Germany: An Encyclopedia'' (Routledge, 2001), pp. 252–56.</ref> The war ended with Widukind accepting baptism.{{sfn|Frassetto|2003|loc=}} The Frisians afterwards asked for missionaries to be sent to them and a bishop of their own nation, ], was sent. Charlemagne also promulgated a law code, the '']'', as he did for most subject peoples.<ref>A. M. L. Fadda (2000), "The Vernacular and the Propagation of the Faith in Anglo-Saxon Missionary Activity", ''Studies in Church History''. Subsidia, '''13''', 1–15.</ref> | |||
| Thereafter, the Saxons maintained the peace for seven years, but in 792 Westphalia again rebelled. The Eastphalians and Nordalbingians joined them in 793, but the insurrection was unpopular and was put down by 794. An Engrian rebellion followed in 796, but the presence of Charlemagne, Christian Saxons and ] quickly crushed it. The last insurrection occurred in 804, more than thirty years after Charlemagne's first campaign against them, but also failed. According to Einhard: | |||
| {{blockquote| | |||
| The war that had lasted so many years was at length ended by their acceding to the terms offered by the King; which were renunciation of their national religious customs and the worship of devils, acceptance of the sacraments of the Christian faith and religion, and union with the Franks to form one people. | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| ===Submission of Bavaria=== | |||
| ===Political legacy=== | |||
| ]'' by ] (1725), ], ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| The stability and peace of Charlemagne's reign did not long outlive him. Louis' reign was marked by strife, including a number of rebellions by his sons. After Louis' death, the empire was divided among his sons into ], ], and ] by the ].{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=379–381}} Middle Francia was divided several more times over the course of subsequent generations.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=394}} Carolingians would rule{{snd}}with some interruptions{{snd}}in East Francia (later the ]) until 911,{{sfn|Heather|2009|p=368}} and in West Francia (which would become ]) until 987.{{sfn|Riché|1993|p=278}} After 887, the imperial title was held sporadically by a series of non-dynastic Italian rulers{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=424–427}} before it lapsed in 924.{{sfn|Arnold|1997|p=83}} The East Frankish king ] conquered ], and was crowned emperor in 962.{{sfn|Heather|2009|p=369}} By this time, the eastern and western parts of Charlemagne's former empire had already developed distinct languages and cultures.{{sfn|Scales|2012|pp=155–182}} Otto founded (or re-established) the Holy Roman Empire, which would last until its ] in 1806, during the ].{{sfn|Davies|1996|pp=316–317}} | |||
| According to historian Jennifer Davis, Charlemagne "invented medieval rulership" and his influence can be seen at least into the nineteenth century.{{sfn|Davis|2015|p=434}} Charlemagne is often known as "the father of Europe" because of the influence of his reign and the legacy he left across the large area of the continent.{{sfn|Freeman|2017|p=19}} The political structures he established remained in place through his Carolingian successors, and continued to exert influence into the eleventh century.{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|pp=407, 432}} | |||
| By 774, Charlemagne had invaded the ], and he later annexed the Lombardian territories and assumed its crown, placing the ] under Frankish protection.<ref name="autogenerated30">Historical Atlas of Knights and Castles, Cartographica, Dr Ian Barnes, 2007 pp. 30, 31</ref> The ] south of Rome was acquired in 774, while in the central western parts of Europe, the ] was absorbed and the Bavarian policy continued of establishing tributary ], (borders protected in return for tribute or taxes) among the ] Sorbs and Czechs. The remaining power confronting the Franks in the east were the ]. However, Charlemagne acquired other Slavic areas, including ], ], ] and ].<ref name="autogenerated30"/> | |||
| Charlemagne was an ancestor of several European ruling houses, including the ],{{efn|Through ], great-great granddaughter of ] and grandmother of ],{{sfn|Lewis|1977|pp=246–247, n 94}} }} the ],{{efn|Through ], great-great granddaughter of ] and mother of ]{{sfn|Jackman|2010|pp=9–12}} }} the ],{{Efn|Through ], great-grandson of ] and great-great-grandfather of ]{{sfn|Tanner|2004|pp=263–265}} }} and the ].{{Efn|] was a great-great-great grandson of ].{{sfn|Bouchard|2010|pp=129–131}} The House of Ivrea later came to rule Spain and intermarried with the ] and the royal families of Portugal.}} The Ottonians and Capetians, direct successors of the Carolingans, drew on the legacy of Charlemagne to bolster their legitimacy and prestige; the Ottonians and their successors held their German coronations in Aachen through the Middle Ages.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=528}} The marriage of ] to ] (a direct descendant of Charlemagne) was seen as a sign of increased legitimacy for their son, ], and the French kings' association with Charlemagne's legacy was stressed until the monarchy's end.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=527–528}} German and French rulers, such as Frederick Barbarossa and ], cited the influence of Charlemagne and associated themselves with him.{{sfn|Davis|2015|p=433}} Both German and French monarchs considered themselves as successors of Charlemagne, enumerating him as "Charles I" in their regnal lists.{{sfn|Williams|1885|pp=446–47}} | |||
| In 789, Charlemagne turned to ]. He claimed that ] was an unfit ruler, due to his oath-breaking. The charges were exaggerated, but Tassilo was deposed anyway and put in the monastery of ].<ref>{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=oyiTg0wgl58C|page=48}} |title=Struggle for Empire: Kingship and Conflict Under Louis the German, 817–876|last=Goldberg|first=Eric Joseph|publisher=Cornell University Press|year=2006|isbn=978-0-8014-3890-5|pages=48–}}</ref> In 794, Tassilo was made to renounce any claim to Bavaria for himself and his family (the ]) at the ] of ]; he formally handed over to the king all of the rights he had held.{{sfn|Collins|1998|pp=}} Bavaria was subdivided into Frankish counties, as had been done with Saxony. | |||
| The city of Aachen has, since 1949, awarded an international prize (the ] der Stadt Aachen) in honour of Charlemagne. It is awarded annually to those who promote European unity.{{sfn|Davis|2015|p=433}} Recipients of the prize include ] (founder of the pan-European movement), ], and ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.karlspreis.de/en/laureates | title=Laureates }}</ref> | |||
| ===Avar campaigns=== | |||
| ===Carolingian Renaissance=== | |||
| {{Main|Avar Wars}} | |||
| Contacts with the wider Mediterranean world through Spain and Italy, the influx of foreign scholars at court, and the relative stability and length of Charlemagne's reign led to a cultural revival known as the ].{{sfn|Contreni|1984|p=60}} Although the beginnings of this revival can be seen under his predecessors, Charles Martel and Pepin, Charlemagne took an active and direct role in shaping intellectual life which led to the revival's zenith.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|pp=59, 61, 64}} Charlemagne promoted learning as a matter of policy and direct patronage, with the aim of creating a more effective clergy.{{sfn|Contreni|1995|p=709}} The '']'' and ''Epistola de litteris colendis'' outlined his policies and aims for education.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|p=64}} | |||
| Intellectual life at court was dominated by Irish, Anglo-Saxon, Visigothic and Italian scholars, including ], Alcuin of York, ], and ]; Franks such as Einhard and ] also made substantial contributions.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|pp=61, 68}} Aside from the intellectual activity at the palace, Charlemagne promoted ecclesiastical schools and publicly funded schools for the children of the elite and future clergy.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|pp=65-66}} Students learned basic Latin literacy and grammar, arithmetic, and other subjects of the medieval liberal arts.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|pp=66–67}} From their education, it was expected that even rural priests could provide their parishioners with basic instruction in religious matters and (possibly) the literacy required for worship.{{sfn|Contreni|1995|p=715}} Latin was standardised and its use brought into territories well beyond the former Roman Empire, forming a second language community of speakers and writers and sustaining Latin creativity in the Middle Ages.{{sfn|Leonhardt|2016|pp=160–162}} | |||
| In 788, the ], an Asian nomadic group that had settled down in what is today ] (Einhard called them ]), invaded Friuli and Bavaria. Charlemagne was preoccupied with other matters until 790 when he marched down the ] and ravaged Avar territory to the ]. A Lombard army under Pippin then marched into the ] valley and ravaged ]. The campaigns ended when the Saxons revolted again in 792. | |||
| Carolingian authors produced extensive works, including legal treatises, histories, poetry, and religious texts.{{sfn|Contreni|1995|pp=748–756}}{{sfn|Contreni|1984|pp=70}} ] in monasteries and cathedrals focused on copying new and old works, producing an estimated 90,000 manuscripts during the ninth century.{{sfn|Contreni|1995|p=711}} The ] script was developed and popularised in medieval copying, influencing ] and modern typefaces.{{sfn|Contreni|1984|p=73}} Scholar John J. Contreni considers the educational and learning revival under Charlemagne and his successors "one of the most durable and resilient elements of the Carolingian legacy".{{sfn|Contreni|1984|p=73}} | |||
| For the next two years, Charlemagne was occupied, along with the Slavs, against the Saxons. Pippin and Duke ] continued, however, to assault the Avars' ring-shaped strongholds. The great Ring of the Avars, their capital fortress, was taken twice. The booty was sent to Charlemagne at his capital, Aachen, and redistributed to his followers and to foreign rulers, including King ]. Soon the Avar ]s had lost the will to fight and travelled to Aachen to become vassals to Charlemagne and to become Christians. Charlemagne accepted their surrender and sent one native chief, baptised Abraham, back to Avaria with the ancient title of ]. Abraham kept his people in line, but in 800, the ] under ] attacked the remains of the Avar state. | |||
| ===Memory and historiography=== | |||
| In 803, Charlemagne sent a Bavarian army into ], defeating and bringing an end to the ].<ref name="Rogers">{{cite book|first1=Bernard S. |last1=Bachrach|author2=Clifford J. Rogers|author3=Kelly DeVries|title=Journal of Medieval Military History|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=0E-LTZ2n_2EC}}|date=2002|publisher=Boydell Press|isbn=978-0-85115-909-6}}</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne was a frequent subject of, and inspiration for, medieval writers after his death. Einhard's '']'', according to Johannes Fired, "can be said to have revived the defunct literary genre of the secular biography."{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=277}} Einhard drew on classical sources, such as Suetonius' ''The Twelve Caesars'', the orations of Cicero, and ]' '']'' to frame his work's structure and style.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=15–20}} The Carolingian period also saw a revival of the ] genre.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=518–519}} The author of the Latin poem '']'', written {{circa|865}}, uses facts (apparently from Einhard) and his own observations on the decline of Charlemagne's family after their civil wars later in the ninth century as the bases of a visionary tale about Charles meeting a prophetic spectre in a dream.{{sfn|Geary|1987|pp=275–283}} ]'s ''Gesta Karoli Magni'', written for Charlemagne's great-grandson Charles the Fat, presents moral anecdotes ('']'') to highlight the emperor's qualities as a ruler.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=20}} | |||
| ] depicted as Charlemagne (], 1420s)]] | |||
| In November of the same year, Charlemagne went to Regensburg where the Avar leaders acknowledged him as their ruler.<ref name="Rogers"/> In 805, the Avar khagan, who had already been baptised, went to Aachen to ask permission to settle with his people south-eastward from ].<ref name="Rogers"/> The ]n territories became integral parts of the Frankish realm, which was abolished by the ] in 899–900. | |||
| Charlemagne, as a figure of myth and emulation, grew over the centuries; Matthias Becher writes that over 1,000 legends are recorded about him, far outstripping subsequent emperors and kings.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=138}} Later medieval writers depicted Charlemagne as a crusader and Christian warrior.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=138}}{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=539}} Charlemagne is the main figure of the medieval ] known as the ]. Works in this cycle, which originated during the ], centre on characterisations of the emperor as a leader of Christian knights in wars against Muslims. The cycle includes {{lang|fr|]}} (epic poems) such as the '']'' and chronicles such as the '']'', also known as the ''(Pseudo-)Turpin Chronicle''.{{sfn|Hardman|Ailes|2017|pp=1–9}} Charlemagne was depicted as one of the ], a fixture in medieval literature and art as an exemplar of a Christian king.{{sfn|Kuskin|1999|pp=513, 547–548 fn24}} Despite his central role in these legends, author ] noted that "romancers represent him as often weak and passionate, the victim of treacherous counsellors, and at the mercy of turbulent barons, on whose prowess he depends for the maintenance of his throne."{{sfn|Bulfinch|1864|pp=xxii–xxiv}} | |||
| Attention to Charlemagne became more scholarly in the early modern period as Eindhard's ''Vita'' and other sources began to be published.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=142–144}} Political philosophers debated his legacy; ] viewed him as the first constitutional monarch and protector of freemen, but ] saw him as a despotic ruler and representative of the medieval period as a ].{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=144}} As early as the sixteenth century, debate between German and French writers began about Charlemagne's "nationality".{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=142}} These contrasting portraits—a French Charlemagne versus a German ''Karl der Große''—became especially pronounced during the nineteenth century with Napoleon's use of Charlemagne's legacy and the rise of German nationalism.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=539}}{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=146}} German historiography and popular perception focused on the ], emphasised with Charlemagne as the "butcher" of the Germanic Saxons or downplayed as an unfortunate part of the legacy of a great German ruler.{{sfn|Becher|2005|pp=146–148}} ] initially portrayed Charlemagne as an enemy of Germany, a French ruler who worked to take away the freedom and native religion of the German people.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=541–542}} This quickly shifted as ] endorsed a portrait of Charlemagne as a great unifier of disparate German tribes into a common nation, allowing Hitler to co-opt Charlemagne's legacy as an ideological model for his expansionist policies.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=542–546}} | |||
| ===Northeast Slav expeditions=== | |||
| In 789, in recognition of his new pagan neighbours, the ], Charlemagne marched an Austrasian-Saxon army across the ] into ] territory. The Slavs ultimately submitted, led by their leader Witzin. Charlemagne then accepted the surrender of the ] under Dragovit and demanded many hostages. He also demanded permission to send missionaries into this pagan region unmolested. The army marched to the ] before turning around and marching to the Rhine, winning much booty with no harassment. The tributary Slavs became loyal allies. In 795, when the Saxons broke the peace, the Abotrites and Veleti rebelled with their new ruler against the Saxons. Witzin died in battle and Charlemagne avenged him by harrying the Eastphalians on the Elbe. Thrasuco, his successor, led his men to conquest over the Nordalbingians and handed their leaders over to Charlemagne, who honoured him. The Abotrites remained loyal until Charles' death and fought later against the Danes. | |||
| Historiography after World War II focused on Charlemagne as "the father of Europe" rather than a nationalistic figure,{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=148}} a view first advanced during the nineteenth century by German romantic philosopher ].{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=539}} This view has led to Charlemagne's adoption as a political symbol of ].{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=548}} Modern historians increasingly place Charlemagne in the context of the wider Mediterranean world, following the work of Henri Pirenne.{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=549–551}} | |||
| ===Southeast Slav expeditions=== | |||
| When Charlemagne incorporated much of Central Europe, he brought the Frankish state face to face with the Avars and Slavs in the southeast.<ref name="Bruce Ross">{{cite journal | last=Bruce Ross | first=James | pages=212–35 | jstor=2854596 | title=Two Neglected Paladins of Charlemagne: Erich of Friuli and Gerold of Bavaria Speculum, Vol. 20, No. 2 | journal=Speculum | volume=20 | issue=2 |date = April 1945| doi=10.2307/2854596 | s2cid=163300685 }}</ref> The most southeast Frankish neighbours were ], who settled in ] and ]. While fighting the Avars, the Franks had called for their support.<ref name="Denis Sinor">{{cite book|first=Denis |last=Sinor|title=The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=ST6TRNuWmHsC| page=219}}|date=1990|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-24304-9 | page=219 | location=New York }}</ref> During the 790s, he won a major victory over them in 796.<ref name=JohnVanAntwerpFinep257>{{cite book | last=Fine | first=John Van Antwerp | page=78 | url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=Y0NBxG9Id58C|page=242}} | title=The early medieval Balkans: a critical survey from the sixth to the late twelfth century | year=1991 | publisher=University of Michigan Press | isbn=978-0-472-08149-3}}</ref> Duke ] of Lower Pannonia aided Charlemagne, and the Franks made themselves overlords over the Croats of northern Dalmatia, ] and Pannonia.<ref name=JohnVanAntwerpFinep257/> | |||
| ===Religious influence and veneration=== | |||
| The Frankish commander ] wanted to extend his dominion by conquering the Littoral Croat Duchy. During that time, Dalmatian Croatia was ruled by Duke ]. In the ], the forces of Eric fled their positions and were routed by the forces of Višeslav.<ref name="Vjekoslav Klaić"/> Eric was among those killed which was a great blow for the Carolingian Empire.<ref name="Bruce Ross"/>{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc={{full citation needed|date=September 2020}}}}<ref name="Vjekoslav Klaić">{{cite book | last=Klaić | first=Vjekoslav |title=Povijest Hrvata: od najstarijih vremena do svršetka XIX stoljeća. Treće doba: vladanje kraljeva iz raznih porodica (1301–1526). Knj. 2|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=WohQvgAACAAJ}}|year=1988|publisher=Nakladni zavod Matice Hrvatske|isbn=978-86-401-0051-9| pages=63–64 | location=Zagreb | language=hr }}</ref> | |||
| {{further|Charlemagne and church music}} | |||
| ], built by Charlemagne at the Aachen palace]] | |||
| Charlemagne gave much attention to religious and ecclesiastical affairs, holding 23 ]s during his reign. His synods were called to address specific issues at particular times, but generally dealt with church administration and organisation, education of the clergy, and the proper forms of liturgy and worship.{{sfn|Noble|2015|p=294}} Charlemagne used the Christian faith as a unifying factor in the realm and, in turn, worked to impose unity on the church.{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=289–290, 295–296}}{{sfn|McKitterick|1996|p=61}} He implemented an edited version of the '']'' book of ] acquired from Pope Adrian, required use of the ] in monasteries throughout the empire, and promoted a standardised liturgy adapted from the ] to conform with Frankish practices.{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=269–297}} Carolingian policies promoting unity did not eliminate the diverse practices throughout the empire, but created a shared ecclesiastical identity—according to Rosamond McKitterick, "unison, not unity."{{sfn|McKitterick|1996|p=82}} | |||
| The condition of all his subjects as a "Christian people" was an important concern.{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=287–288}} Charlemagne's policies encouraged preaching to the laity, particularly in ] languages they would understand.{{sfn|Noble|2015|p=294–295}} He believed it essential to be able to recite the ] and the ], and made efforts to ensure that the clergy taught them and other basics of Christian morality.{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=301–302}} | |||
| Charlemagne also directed his attention to the ] to the west of the Avar khaganate: the ]ns and ]ns. These people were subdued by the Lombards and Bavarii and made tributaries, but were never fully incorporated into the Frankish state. | |||
| Thomas{{nbsp}}F.{{nbsp}}X.{{nbsp}}Noble writes that the efforts of Charlemagne and his successors to standardise Christian doctrine and practices and harmonise Frankish practices were essential steps in the development of Christianity in Europe, and the Roman Catholic or ] "as a historical phenomenon, not as a theological or ecclesiological one, is a Carolingian construction."{{sfn|Noble|2015|p=287}}{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=306–307}} He says that the medieval European concept of ] as an overarching community of Western Christians, rather than a collection of local traditions, is the result of Carolingian policies and ideology.{{sfn|Noble|2015|pp=292, 306–307}} Charlemagne's doctrinal policies promoting the use of {{lang|la|filioque}} and opposing the Second Council of Nicea were key steps in the ].{{sfn|Siecienski|2010|p=87}} | |||
| ==Imperium== | |||
| Emperor ] attempted to have Charlemagne ] in 1000.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=537}} In 1165, Frederick Barbarossa persuaded ] to elevate Charlemagne to sainthood.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=537}} Since Paschal's acts were not considered valid, Charlemagne was not recognised as a saint by the ].{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=143}} Despite this lack of official recognition, his ] was observed in Aachen, Reims, Frankfurt, Zurich and Regensburg, and he has been venerated in France since the reign of ].{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=538}} | |||
| ===Coronation=== | |||
| ], 1861]] | |||
| Charlemagne also drew attention from figures of the Protestant ], with ] criticising his apparent subjugation to the papacy by accepting his coronation from Leo.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=144}} ] and other Protestant thinkers viewed him as a forerunner of the Reformation, however, noting the ''Libri Carolini''{{'s}} condemnation of the worship of images and relics and conflicts by Charlemagne and his successors with the temporal power of the popes.{{sfn|Becher|2005|p=143}} | |||
| In 799, ] had been assaulted by some of the Romans, who tried to pull out his eyes and tear out his tongue.<ref>Einhard ''Life of Charles the Great''.{{full citation needed|date=September 2020}}</ref> Leo escaped and fled to Charlemagne at ].<ref name=shahan>{{cite encyclopedia |last1=Shahan |first1=Thomas |last2=Macpherson |first2=Ewan |date=1908 |title=Charlemagne |encyclopedia=] |location=New York |publisher=Robert Appleton Company |url=http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/03610c.htm |access-date=1 January 2013 |via=New Advent}}</ref> Charlemagne, advised by scholar ], travelled to Rome, in November 800 and held a synod. On 23 December, Leo swore an oath of innocence to Charlemagne. His position having thereby been weakened, the Pope sought to restore his status. Two days later, at ], on Christmas Day (25 December), when Charlemagne knelt at the altar to pray, the Pope ] him ''Imperator Romanorum'' ("Emperor of the Romans") in ]. In so doing, the Pope rejected the legitimacy of ] of Constantinople: | |||
| ], crowning Charlemagne from ''Chroniques de France ou de Saint Denis'', vol. 1; France, second quarter of 14th century.]] | |||
| {{blockquote|When ] compelled the abdication of ], he did not abolish the Western Empire as a separate power, but caused it to be reunited with or sink into the Eastern, so that from that time there was a single undivided Roman Empire ... , like their predecessors, held the Roman Empire to be one and indivisible, and proposed by the coronation of not to proclaim a severance of the East and West ... they were not revolting against a reigning sovereign, but legitimately filling up the place of the deposed ] ... was held to be the legitimate successor, not of Romulus Augustulus, but of Constantine VI ...<ref>], ''The Holy Roman Empire'', 1864, pp. 62–64</ref>}}Charlemagne's coronation as Emperor, though intended to represent the continuation of the unbroken line of Emperors from ] to Constantine VI, had the effect of setting up two separate (and often opposing) Empires and two separate claims to imperial authority. It led to war in 802, and for centuries to come, ] | |||
| == Wives, concubines, and children == | |||
| Einhard says that Charlemagne was ignorant of the Pope's intent and did not want any such coronation: | |||
| {{further|Carolingian dynasty}} | |||
| {{blockquote|e at first had such an aversion that he declared that he would not have set foot in the Church the day that they were conferred, although it was a great feast-day, if he could have foreseen the design of the Pope.<ref>Einhard ''Vita Karoli Magni '' ch. 28.</ref>}} | |||
| {{col-begin}} | |||
| {{col-2}} | |||
| '''Wives and their children'''{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=xxxiv–xxxv}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=xxi}} | |||
| * ]{{efn|The nature of Himiltrude's relationship to Charlemagne is uncertain. A 770 letter by ] describes both Carloman and Charlemagne "by will and decision...joined in lawful marriage... wives of great beauty from the same fatherland as yourselves."{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=105}} Stephen wrote this in the context of attempting to dissuade either king from entering into a marriage alliance with Desiderius.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=84}} By 784, at Charlemagne's court, Paul the Deacon wrote that their son Pepin was born "before legal marriage", but whether he means Charles and Himiltrude were never married, were joined in a non-canonical marriage or {{lang|de|]}}, or if they married after Pepin was born is unclear.{{sfn|Goffart|1986}} Roger Collins,{{sfn|Collins|1998|p=40}} Johannes Fried,{{sfn|Fried|2016|pp=50–51}} and Janet Nelson{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp= 91, 107, 285–286}} all portray Himiltrude as a wife of Charlemagne in some capacity. Fried also dates the beginning of their relationship to 763 or even earlier.{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=50}}}} (768–770) | |||
| ** ] ({{circa|769}}/770–811) | |||
| * ], daughter of ], king of the ] (m. 770–771) | |||
| * ] (m. 771–783) daughter of ] | |||
| ** ] ({{circa|772/773}}–811), Duke of Maine | |||
| ** Adalhaid (773/4–774), born while her parents were on campaign in Italy. She was sent back to Francia, but died before reaching Lyons{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=133}} | |||
| ** ] (or Hruodrud) ({{circa|775}}–810) | |||
| ** ] (777–810, Baptised "Pepin" 15 April 781), ] | |||
| ** ] (778–840), ] since 781, crowned co-emperor in 813, senior Emperor from 814 | |||
| ** Lothair (778–779/780), twin of Louis, he died in infancy{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=181}} | |||
| ** ] (779/780–826) | |||
| ** ] (b. 782) | |||
| ** Hildegard (782–783) | |||
| * ] (m. 783–794) | |||
| ** ] (b. 785), Abbess of ] | |||
| ** Hiltrude (b. 787, d. after 808) | |||
| * ] (m. 794–800) | |||
| {{col-2}} | |||
| '''Concubines and their children'''{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=xxxiv–xxxv}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=xxi}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** Adaltrude | |||
| * Madelgard | |||
| ** Ruodhaid (d. 852), Abbess of ] | |||
| * Regina | |||
| ** ] (801–855), ] | |||
| ** ] ({{circa|802}}–844), ] of the Empire | |||
| * Adallind | |||
| ** Theodoric (b. 807) | |||
| * Unknown partners | |||
| ** Hroudhaid (b. 784) | |||
| ** Richbod (805–844), Abbot of ] | |||
| ** Bernard (fl. 843), Abbot of ] | |||
| ** Chrothais (d 814) | |||
| {{col-end}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| A number of modern scholars, however,<ref>Tierney, Brian. ''The Crisis of the Church and State 1050–1300''. University of Toronto Press, 1964. p. 17.</ref> suggest that Charlemagne was indeed aware of the coronation; certainly, he cannot have missed the bejewelled crown waiting on the altar when he came to pray—something even contemporary sources support.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Meek|first=Harry|title=Charlemagne's Imperial Coronation: The Enigma of Sources and Use to Historians|url=https://www.academia.edu/6266377 |website=www.academia.edu}}</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne had at least twenty children with his wives and other partners.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=xxxiv–xxxv}}{{sfn|Costambeys|Innes|MacLean|2011|p=xxi}} After the death of his wife Luitgard in 800, he did not remarry, but had children with unmarried partners.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=440}} He was determined that all his children, including his daughters, should receive an education in the liberal arts. His children were taught in accordance with their aristocratic status, which included training in riding and weaponry for his sons, and embroidery, spinning and weaving for his daughters.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=443}} | |||
| Rosamond McKitterick writes that Charlemagne exercised "a remarkable degree of patriarchal control ... over his progeny," noting that only a handful of his children and grandchildren were raised outside his court.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=93}} Pepin of Italy and Louis reigned as kings from childhood and lived at their courts.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=186}} Careers in the church were arranged for his illegitimate sons.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=91}} His daughters were resident at court or at ] (where Charlemagne's sister was abbess), and those at court may have fulfilled the duties of queen after 800.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=94–95}} | |||
| ==== Debate ==== | |||
| ] and the subsequent German Kings in ], Germany]] | |||
| Louis and Pepin of Italy married and had children during their father's lifetime, and Charlemagne brought Pepin's daughters into his household after Pepin's death.{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|pp=91–93}} Rotrude had been betrothed to Emperor Constantine VI, but the betrothal was ended.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=225–226}} None of Charlemagne's daughters married, although several had children with unmarried partners. Bertha had two sons, ] and Hartnid, with Charlemagne's courtier ]; Rotrude had a son named ], possibly with Count ]; and Hiltrude had a son named Richbod, possibly with a count named Richwin.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=441}} The {{lang|la|Divisio Regnorum}} issued by Charlemagne in 806 provided that his legitimate daughters be allowed to marry or become nuns after his death. Theodrada entered a convent, but the decisions of his other daughters are unknown.{{sfn|Nelson|2019|p=435}} | |||
| Historians have debated for centuries whether Charlemagne was aware before the coronation of the Pope's intention to crown him Emperor (Charlemagne declared that he would not have entered Saint Peter's had he known, according to chapter twenty-eight of Einhard's ''Vita Karoli Magni''),<ref>Einhard ''Vita Karoli Magni '' ch. 28. " he said that he would have refused to enter the church that day, although it was a major festival, had he been aware of the Pope's plans".</ref> but that debate obscured the more significant question of ''why'' the Pope granted the title and why Charlemagne accepted it. | |||
| ==Appearance and iconography== | |||
| ] points out "hat the motivation behind the acceptance of the imperial title was a romantic and antiquarian interest in reviving the Roman Empire is highly unlikely."{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=147}} For one thing, such romance would not have appealed either to Franks or Roman Catholics at the turn of the ninth century, both of whom viewed the ] heritage of the Roman Empire with distrust. The Franks took pride in having "fought against and thrown from their shoulders the heavy yoke of the Romans" and "from the knowledge gained in baptism, clothed in gold and precious stones the bodies of the holy martyrs whom the Romans had killed by fire, by the sword and by wild animals", as ] described it in a law of 763 or 764.{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=151}} | |||
| {{Further|Iconography of Charlemagne}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| Furthermore, the new title—carrying with it the risk that the new emperor would "make drastic changes to the traditional styles and procedures of government" or "concentrate his attentions on Italy or on Mediterranean concerns more generally"—risked alienating the Frankish leadership.{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=149}} | |||
| | total_width = 200 | |||
| | align = right | |||
| For both the Pope and Charlemagne, the Roman Empire remained a significant power in European politics at this time. The ], based in Constantinople, continued to hold a substantial portion of Italy, with borders not far south of Rome. Charles' sitting in judgment of the Pope could be seen as usurping the prerogatives of the Emperor in Constantinople: | |||
| | direction = vertical | |||
| | background color = | |||
| {{blockquote|By whom, however, could he be tried? Who, in other words, was qualified to pass judgement on the Vicar of Christ? In normal circumstances the only conceivable answer to that question would have been the Emperor at Constantinople; but the imperial throne was at this moment occupied by ]. That the Empress was notorious for having blinded and murdered her own son was, in the minds of both Leo and Charles, almost immaterial: it was enough that she was a woman. The female sex was known to be incapable of governing, and by the old Salic tradition was debarred from doing so. As far as Western Europe was concerned, the Throne of the Emperors was vacant: Irene's claim to it was merely an additional proof, if any were needed, of the degradation into which the so-called Roman Empire had fallen.|]{{sfn|Norwich|1992b|p=378}}|}} | |||
| | width = | |||
| | image1 = Charles Marville, Hôtel Carnavalet, statue of Charlemagne, ca. 1853–70 (cropped).jpg | |||
| ]]] | |||
| | width1 = | |||
| For the Pope, then, there was "no living Emperor at that time"{{sfn|Norwich|1992b|p=379}} though ]{{sfn|Pirenne|2012|p=234n}} disputes this saying that the coronation "was not in any sense explained by the fact that at this moment a woman was reigning in Constantinople". Nonetheless, the Pope took the extraordinary step of creating one. The papacy had since 727 been in conflict with Irene's predecessors in Constantinople over a number of issues, chiefly the continued Byzantine adherence to the doctrine of ], the destruction of Christian images; while from 750, the secular power of the Byzantine Empire in central Italy had been nullified. | |||
| | alt1 = Statue of Charlemagne on a horse, holding a sword | |||
| | caption1 = | |||
| ] ({{Circa|870|lk=no}})]] | |||
| | image2 = Bust of Charlemagne.png | |||
| | width2 = | |||
| By bestowing the Imperial crown upon Charlemagne, the Pope arrogated to himself "the right to appoint ... the Emperor of the Romans, ... establishing the imperial crown as his own personal gift but simultaneously granting himself implicit superiority over the Emperor whom he had created." And "because the Byzantines had proved so unsatisfactory from every point of view—political, military and doctrinal—he would select a westerner: the one man who by his wisdom and statesmanship and the vastness of his dominions ... stood out head and shoulders above his contemporaries."<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Popes: A History|last=Norwich|first=John Julius|publisher=Random House|year=2011|isbn=978-0701182908|page=55}}</ref> | |||
| | alt2 = A bust of Charlemagne | |||
| | caption2 = | |||
| With Charlemagne's coronation, therefore, "the Roman Empire remained, so far as either of them were concerned, one and indivisible, with Charles as its Emperor", though there can have been "little doubt that the coronation, with all that it implied, would be furiously contested in Constantinople".{{sfn|Norwich|1992a|p=3}} | |||
| | footer = ''Top'': Carolingian-era ] depicting Charlemagne or Charles the Bald. ''Bottom'': ], an idealised portrayal and reliquary said to contain Charlemagne's ], produced in the 14th century. | |||
| ] writes hopefully in his letters of an ''Imperium Christianum'' ("Christian Empire"), wherein, "just as the inhabitants of the had been united by a common Roman citizenship", presumably this new empire would be united by a common Christian faith.{{sfn|Collins|1987|p=151}} This is the view of Pirenne when he says "Charles was the Emperor of the ''ecclesia'' as the Pope conceived it, of the Roman Church, regarded as the universal Church".{{sfn|Pirenne|2012|p=233}} The ''Imperium Christianum'' was further supported at a number of ]s all across Europe by Paulinus of Aquileia.<ref name="Butler1995">{{cite book |chapter-url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=XIEAD2MC1YkC|page=74}} |title=Butler's Lives of the Saints: New Full Edition |first1=Alban |last1=Butler |first2=David |last2=Hugh Farmer |chapter=St Paulinus of Aquileia, Bishop (c. 726–804) |pages=74–75 |publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-86012-250-0}}</ref> | |||
| What is known, from the Byzantine chronicler ],{{sfn|Collins|1987|p= 153}} is that Charlemagne's reaction to his coronation was to take the initial steps towards securing the Constantinopolitan throne by sending envoys of marriage to Irene, and that Irene reacted somewhat favourably to them. | |||
| ]'', by assistants of ], {{Circa|1516–1517|lk=no}}]] | |||
| Distinctions between the universalist and localist conceptions of the empire remain controversial among historians. According to the former, the empire was a universal monarchy, a "commonwealth of the whole world, whose sublime unity transcended every minor distinction"; and the emperor "was entitled to the obedience of ]". According to the latter, the emperor had no ambition for universal dominion; his realm was limited in the same way as that of every other ruler, and when he made more far-reaching claims his object was normally to ward off the attacks either of the Pope or of the Byzantine emperor. According to this view, also, the origin of the empire is to be explained by specific local circumstances rather than by overarching theories.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/269851/Holy-Roman-Empire |title=Holy Roman Empire |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |date=2013 |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref> | |||
| According to Ohnsorge, for a long time, it had been the custom of Byzantium to designate the German princes as spiritual "sons" of the Romans. What might have been acceptable in the fifth century had become provoking and insulting to the Franks in the eighth century. Charles came to believe that the Roman emperor, who claimed to head the world hierarchy of states, was, in reality, no greater than Charles himself, a king as other kings, since beginning in 629 he had entitled himself "Basileus" (translated literally as "king"). Ohnsorge finds it significant that the chief wax seal of Charles, which bore only the inscription: "Christe, protege Carolum regem Francorum" , was used from 772 to 813, even during the imperial period and was not replaced by a special imperial seal; indicating that Charles felt himself to be just the king of the Franks. Finally, Ohnsorge points out that in the spring of 813 at Aachen, Charles crowned his only surviving son, Louis, as the emperor without recourse to Rome with only the acclamation of his Franks. The form in which this acclamation was offered was Frankish-Christian rather than Roman. This implies both independence from Rome and a Frankish (non-Roman) understanding of empire.<ref>{{cite book|author=Ohnsorge, Werner |chapter=Das Zweikaiserproblem im früheren Mittelalter. Die Bedeutung des byzantinischen Reiches für die Entwicklung der Staatsidee in Europa |pages=15–31 |editor=Richard E. Sullivan |title=The coronation of Charlemagne: what did it signify? |publisher=D.C. Heath and Company |location=Boston |date=1959 |lccn=59014499}}</ref> | |||
| Mayr-Harting argues that the Imperial title was Charlemagne's face-saving offer to incorporate the recently conquered Saxons. Since the Saxons did not have an institution of kingship for their own ethnicity, claiming the right to rule them as King of the Saxons was not possible. Hence, it is argued, Charlemagne used the supra-ethnic Imperial title to incorporate the Saxons, which helped to cement the diverse peoples under his rule.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Henry Mayr-Harting |title=Charlemagne, the Saxons, and the Imperial Coronation of 800 |journal=The English Historical Review |date=1996|volume=111 |issue=444 November |pages=1113–1133}}</ref> | |||
| ===Imperial title=== | |||
| Charlemagne used these circumstances to claim that he was the ], which had declined under the ]. In his official charters, Charles preferred the style ''Karolus serenissimus Augustus a Deo coronatus magnus pacificus imperator Romanum gubernans imperium''<ref>Cf. '']'', Diplomata Karolinorum I, 77ff.; title used from 801 onward.</ref> ("Charles, most serene Augustus crowned by God, the great, peaceful emperor ruling the Roman empire") to the more direct ''Imperator Romanorum'' ("Emperor of the Romans"). | |||
| The title of Emperor remained in the Carolingian family for years to come, but divisions of territory and in-fighting over supremacy of the Frankish state weakened its significance.{{sfn|Cantor|2015|pp=194–95, 212}} The papacy itself never forgot the title nor abandoned the right to bestow it. When the family of Charles ceased to produce worthy heirs, the Pope gladly crowned whichever Italian magnate could best protect him from his local enemies. The empire would remain in continuous existence for over a millennium, as the ], a true imperial successor to Charles.{{sfn|Davies1996|pp=316–17}} | |||
| ===Imperial diplomacy=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] ] was endorsed by the Franks.<ref name=Becher2011>{{cite journal|title=Die Außenpolitik Karls des Großen. Zwischen Krieg und Diplomatie |language=de |first=Matthias |last=Becher |journal=] |issue=2011 Special Volume |year=2011 |pages=33–46}}</ref> The ] reintroduced the veneration of icons under Empress ]. The council was not recognised by Charlemagne since no Frankish emissaries had been invited, even though Charlemagne ruled more than three provinces of the classical Roman empire and was considered equal in rank to the Byzantine emperor. And while the Pope supported the reintroduction of the iconic veneration, he politically digressed from Byzantium.<ref name=Becher2011/> He certainly desired to increase the influence of the papacy, to honour his saviour Charlemagne, and to solve the constitutional issues then most troubling to European jurists in an era when Rome was not in the hands of an emperor. Thus, Charlemagne's assumption of the imperial title was not a usurpation in the eyes of the Franks or Italians. It was, however, seen as such in Byzantium, where it was protested by Irene and her successor ]—neither of whom had any great effect in enforcing their protests. | |||
| The East Romans, however, still held several territories in Italy: Venice (what was left of the ]), ] (in ]), ] (in ]), and ] (the '']''). These regions remained outside of Frankish hands until 804, when the Venetians, torn by infighting, transferred their allegiance to the Iron Crown of Pippin, Charles' son. The '']'' ended. Nicephorus ravaged the coasts with a fleet, initiating the only instance of war between the Byzantines and the Franks. The conflict lasted until 810 when the pro-Byzantine party in Venice gave their city back to the Byzantine Emperor, and the two emperors of Europe made peace: Charlemagne received the ]n peninsula and in 812 the emperor ] recognised his status as Emperor,<ref>''eum imperatorem et basileum appellantes'', cf. '']'', a. 812.</ref> although not necessarily as "Emperor of the Romans".<ref name="Eichmann1942">{{cite book|first=Eduard |last=Eichmann|title=Die Kaiserkrönung im Abendland: ein Beitrag zur Geistesgeschichte des Mittelalters, mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des kirchlichen Rechte, der Liturgie und der Kirchenpolitik|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=6S00AAAAIAAJ|page=33}}|page=33|year=1942|publisher=Echter-Verlag}}</ref> | |||
| ===Danish attacks=== | |||
| After the conquest of Nordalbingia, the Frankish frontier was brought into contact with Scandinavia. The ] Danes, "a race almost unknown to his ancestors, but destined to be only too well known to his sons"<ref>{{Cite book |last=Oman |first=Charles |url=https://www.gutenberg.org/files/61536/61536-h/61536-h.htm |title=The Dark Ages, Period 1, 476-918 |year=2020 |isbn=9781973427377 |pages=367 |publisher=Independently Published |language=en}}</ref> as ] described them, inhabiting the ] peninsula, had heard many stories from Widukind and his allies who had taken refuge with them about the dangers of the Franks and the fury which their Christian king could direct against pagan neighbours. | |||
| In 808, the king of the Danes, ], expanded the vast ] across the isthmus of ]. This defence, last employed in the Danish-Prussian War of 1864, was at its beginning a {{convert|30|km|0|abbr=on}} long earthenwork rampart. The Danevirke protected Danish land and gave Godfred the opportunity to harass ] and ] with pirate raids. He also subdued the Frank-allied Veleti and fought the Abotrites. | |||
| Godfred invaded Frisia, joked of visiting Aachen, but was murdered before he could do any more, either by a Frankish assassin or by one of his own men. Godfred was succeeded by his nephew ], who concluded the ] with Charlemagne in late 811. | |||
| ===Death=== | |||
| {{See also|Testament of Charlemagne}} | |||
| ] of Charlemagne in the ]]] | |||
| ] of Charlemagne. It represents a ] and was manufactured in ]. ], Paris.]] | |||
| In 813, Charlemagne called ], king of ], his only surviving legitimate son, to his court. There Charlemagne crowned his son as co-emperor and sent him back to Aquitaine. He then spent the autumn hunting before returning to Aachen on 1 November. In January, he fell ill with ].<ref>{{cite book | |||
| | translator= A. J. Grant | |||
| | year = 1905 | orig-date= c. 820–830 | |||
| | title= The Early Lives of Charlemagne by Eginhard and the Monk of St Gall | |||
| | author1= Einhard | author1-link= Einhard | |||
| | author2= Notker Balbulus | |||
| | title-link =Vita Karoli Magni | |||
| | chapter= Private Life and Character of Charlemagne. 30| page = 39 | |||
| | chapter-url=https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/48870/pg48870.pdf | |||
| | via= ] | |||
| | publisher= Alexander Moring Limited }}</ref> In deep depression (mostly because many of his plans were not yet realised), he took to his bed on 21 January and as ] tells it: | |||
| {{blockquote|He died January twenty-eighth, the seventh day from the time that he took to his bed, at nine o'clock in the morning, after partaking of the ], in the seventy-second year of his age and the forty-seventh of his reign.}} | |||
| ] gold and silver casket for Charlemagne, the ]]] | |||
| He was buried that same day, in ]. The earliest surviving '']'', the '']'', was composed by a monk of ], which he had patronised.<ref name="Godman1985">{{cite book|first=Peter |last=Godman|title=Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=OD9QAQAAIAAJ |page=206}}|year=1985|publisher=Duckworth|isbn=978-0-7156-1768-7|pages=206–11}}</ref> A later story, told by Otho of Lomello, Count of the Palace at Aachen in the time of ], would claim that he and Otto had discovered Charlemagne's tomb: Charlemagne, they claimed, was seated upon a throne, wearing a crown and holding a sceptre, his flesh almost entirely incorrupt. In 1165, ] re-opened the tomb again and placed the emperor in a sarcophagus beneath the floor of the cathedral.<ref>{{cite book|first=Russell |last=Chamberlin|title=The Emperor, Charlemagne|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=x-HtHAAACAAJ|pages=222–24 |year=1986 |publisher=F. Watts|isbn=978-0-531-15004-7}}}}</ref> In 1215 ] re-interred him in a casket made of gold and silver known as the ]. | |||
| Charlemagne's death emotionally affected many of his subjects, particularly those of the literary clique who had surrounded him at Aachen. An anonymous monk of Bobbio lamented:{{sfn|Dutton|2004}} | |||
| {{blockquote|From the lands where the sun rises to western shores, people are crying and wailing ... the Franks, the Romans, all Christians, are stung with mourning and great worry ... the young and old, glorious nobles, all lament the loss of their Caesar ... the world laments the death of Charles ... O Christ, you who govern the heavenly host, grant a peaceful place to Charles in your kingdom. Alas for miserable me.}} | |||
| Louis succeeded him as Charles had intended. He left ] allocating his assets in 811 that was not updated prior to his death. He left most of his wealth to the Church, to be used for charity. His empire lasted only another generation in its entirety; its division, according to custom, between Louis's own sons after their father's death laid the foundation for the modern states of Germany and France.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,,3840415,00.html |title=Die Geburt zweier Staaten – Die Straßburger Eide vom 14. Februar 842 |language=de |first=Matthias |last=von Hellfeld |work=] |access-date=22 October 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ==Administration== | |||
| {{Further|Carolingian Empire#Government}} | |||
| ===Organisation=== | |||
| The Carolingian king exercised the '']'', the right to rule and command. Under the ], it was a royal prerogative but could be delegated.<ref name=Evergates1983>Theodore Evergates, "Ban, Banalité", in ] (ed.), ''Dictionary of the Middle Ages'' (New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1983), vol. 2, p. 69.</ref> He had supreme jurisdiction in judicial matters, made legislation, led the army, and protected both the Church and the poor.{{Citation needed|date=January 2019}} His administration was an attempt to organise the kingdom, church and nobility around him. As an administrator, Charlemagne stands out for his many reforms: ], governmental, military, cultural and ]al. He is the main protagonist of the "Carolingian Renaissance". | |||
| ===Military=== | |||
| Charlemagne's success rested primarily on novel ] technologies and excellent logistics<ref name="Bowlus2006">{{cite book|first=Charles R. |last=Bowlus|title=The Battle of Lechfeld and Its Aftermath, August 955: The End of the Age of Migrations in the Latin West|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=0XBtVwukIogC|page=49}}|year=2006|publisher=Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.|isbn=978-0-7546-5470-4|pages=49–}}</ref> rather than the long-claimed "] revolution" led by ] in 730s. However, the ], which made the "shock cavalry" ] charge possible, was not introduced to the Frankish kingdom until the late eighth century.<ref name="books.google.com" /> | |||
| Horses were used extensively by the Frankish military because they provided a quick, long-distance method of ], which was critical to building and maintaining the large empire.<ref name="books.google.com">{{cite book|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=Sf8UIynR0koC|page=12}}|title=The Cambridge Illustrated Atlas of Warfare: The Middle Ages, 768–1487|last2=Bennett|first2=Matthew|date=1996|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-44049-3|pages=12–|first1=Nicholas|last1=Hooper}}</ref> | |||
| ===Economic and monetary reforms=== | |||
| ] of Charlemagne, including {{lang|la|]}}, from the subscription of a royal diploma: {{lang|la|Signum}} (monogr.: KAROLVS) {{lang|la|Karoli gloriosissimi regis}}]] | |||
| Charlemagne had an important role in determining Europe's immediate economic future. Pursuing his father's reforms, Charlemagne abolished the monetary system based on the gold {{lang|fr|]}}. Instead, he and the ] ] took up Pippin's system for pragmatic reasons, notably a shortage of the metal. | |||
| The gold shortage was a direct consequence of the conclusion of peace with Byzantium, which resulted in ceding Venice and Sicily to the East and losing their trade routes to Africa. The resulting standardisation economically harmonised and unified the complex array of currencies that had been in use at the commencement of his reign, thus simplifying trade and commerce. | |||
| ], 793–812]] | |||
| Charlemagne established a new standard, the {{lang|fr|]}} (from the Latin {{lang|la|]}}, the modern ]), which was based upon a pound of silver—a unit of both money and weight—worth 20 sous (from the Latin {{lang|la|]}} , the modern ]) or 240 {{lang|fr|]}} (from the Latin {{lang|la|]}}, the modern ]). During this period, the {{lang|fr|livre}} and the {{lang|fr|sou}} were counting units; only the {{lang|fr|denier}} was a coin of the realm. | |||
| Charlemagne instituted principles for ] by means of the ] of 802, which laid down strict rules for the way in which incomes and expenses were to be recorded. | |||
| Charlemagne applied this system to much of the European continent, and Offa's standard was voluntarily adopted by much of England. After Charlemagne's death, continental coinage degraded, and most of Europe resorted to using the continued high-quality English coin until about 1100. | |||
| ===Jews in Charlemagne's realm=== | |||
| Early in Charlemagne's rule he tacitly allowed Jews to monopolise ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.worldology.com/Europe/early_dark_ages_3.htm |title=Charlemagne created a peaceful environment for Jews in his kingdom. Charlemagne fostered a system where the Christian majority could procure credit through Jewish constituents. Christians were forbidden to loan money at an interest rate, a restriction not shared by the Jews. |publisher=Worldology.com |date=25 April 2013 |access-date=14 January 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131103180546/http://www.worldology.com/Europe/early_dark_ages_3.htm |archive-date=3 November 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> He invited Italian Jews to immigrate, as royal clients independent of the feudal landowners, and form trading communities in the agricultural regions of ] and the ]. Their trading activities augmented the otherwise almost exclusively agricultural economies of these regions.<ref>Scheindlin, Raymond P., ''A Short History of the Jewish People'', Oxford University Press, 1998, pp. 101–04</ref> His personal ] was Jewish,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/4250-charlemagne |title=Charlemagne |publisher=JewishEncyclopedia.com |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref> and he employed a Jew named Isaac as his personal representative to the ] of ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/4250-charlemagne|title=Charlemagne |website=www.jewishencyclopedia.com|access-date=11 October 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ===Education reforms=== | |||
| ] hairstyle.]] | |||
| Part of Charlemagne's success as a warrior, an administrator and ruler can be traced to his admiration for learning and education. His reign is often referred to as the ] because of the flowering of scholarship, literature, art and architecture that characterise it. Charlemagne came into contact with the culture and learning of other countries (especially Moorish Spain, Anglo-Saxon England,<ref>''Charlemagne and Anglo-Saxon England'', Joanna Story, ''Charlemagne: Empire and Society'', ed. Joanna Story, (Manchester University Press, 2005), 195.</ref> and Lombard Italy) due to his vast conquests. He greatly increased the provision of monastic schools and scriptoria (centres for book-copying) in Francia. | |||
| Charlemagne was a lover of books, sometimes having them read to him during meals. He was thought to enjoy the works of ].<ref name="onlinelibrary.wiley.com">{{cite journal |last=Bullough |first=Donald A. |author-link=Donald A. Bullough |date = December 2003|title=Charlemagne's court library revisited |journal=] |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=339–63 |doi=10.1111/j.0963-9462.2004.00141.x |s2cid=247668930 }}</ref> His court played a key role in producing books that taught elementary Latin and different aspects of the church. It also played a part in creating a royal library that contained in-depth works on language and Christian faith.<ref>{{Cite web|title = Charlemagne {{!}} Holy Roman emperor |url = https://www.britannica.com/biography/Charlemagne|website = Encyclopædia Britannica|access-date = 17 November 2015}}</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne encouraged clerics to translate Christian creeds and prayers into their respective vernaculars as well to teach grammar and music. Due to the increased interest of intellectual pursuits and the urging of their king, the monks accomplished so much copying that almost every manuscript from that time was preserved. At the same time, at the urging of their king, scholars were producing more secular books on many subjects, including history, poetry, art, music, law, theology, etc. Due to the increased number of titles, private libraries flourished. These were mainly supported by aristocrats and churchmen who could afford to sustain them. At Charlemagne's court, a library was founded and a number of copies of books were produced, to be distributed by Charlemagne.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Charlemagne's court library revisited|journal=Early Medieval Europe|year=2003|volume=12|issue=4|pages=339–63|doi=10.1111/j.0963-9462.2004.00141.x|s2cid=247668930}}</ref><ref name="Anderson2013" /> Book production was completed slowly by hand and took place mainly in large monastic libraries. Books were so in demand during Charlemagne's time that these libraries lent out some books, but only if that borrower offered valuable collateral in return.<ref name="Anderson2013" /> | |||
| ] (containing the ] of Charlemagne), dated 782]] | |||
| Most of the surviving works of classical Latin were copied and preserved by Carolingian scholars. Indeed, the earliest manuscripts available for many ancient texts are Carolingian. It is almost certain that a text which survived to the Carolingian age survives still. | |||
| The pan-European nature of Charlemagne's influence is indicated by the origins of many of the men who worked for him: ], an ] from ]; ], a ], probably from ]; ], Lombard; ] ] and ]; and Franks ], Angilram, ] and ]. | |||
| Charlemagne promoted the ] at court, ordering that his children and grandchildren be well-educated, and even studying himself (in a time when even leaders who promoted education did not take time to learn themselves) under the tutelage of Peter of Pisa, from whom he learned grammar; Alcuin, with whom he studied rhetoric, dialectic (logic), and astronomy (he was particularly interested in the movements of the stars); and Einhard, who tutored him in arithmetic.{{sfn|Dutton|2016}} | |||
| His great scholarly failure, as Einhard relates, was his inability to write: when in his old age he attempted to learn—practising the formation of letters in his bed during his free time on books and wax tablets he hid under his pillow—"his effort came too late in life and achieved little success", and his ability to read—which Einhard is silent about, and which no contemporary source supports—has also been called into question.{{sfn|Dutton|2016}} | |||
| In 800, Charlemagne enlarged the hostel at the ] in ] and added a library to it. He certainly had not been personally in Jerusalem.<ref>Karl der Grosse und das Erbe der Kulturen, Band 1999, Franz-Reiner Erkens, Akademie Verlag, 2001.</ref><ref>Saint-Denis zwischen Adel und König, Rolf Große, Thorbecke, Stuttgart 2002.</ref> | |||
| ===Church reforms=== | |||
| {{See also|Charlemagne and church music}} | |||
| ] at ]]] | |||
| Charlemagne expanded the reform Church's programme unlike his father, Pippin, and uncle, Carloman. The deepening of the spiritual life was later to be seen as central to public policy and royal governance. His reform focused on strengthening the church's power structure, improving clergy's skill and moral quality, standardising liturgical practices, improvements on the basic tenets of the faith and the rooting out of paganism. His authority extended over church and state. He could discipline clerics, control ecclesiastical property and define orthodox doctrine. Despite the harsh legislation and sudden change, he had developed support from clergy who approved his desire to deepen the piety and morals of his subjects.<ref name=britannica>{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/106546/Charlemagne |title=Charlemagne |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |date= 2012 |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref> | |||
| In 809–810, Charlemagne called a church council in ], which confirmed the unanimous belief in the West that the Holy Spirit proceeds from the Father and the Son (''ex Patre ]'') and sanctioned inclusion in the ] of the phrase ''Filioque'' (and the Son). For this Charlemagne sought the approval of ]. The Pope, while affirming the doctrine and approving its use in teaching, opposed its inclusion in the text of the Creed as adopted in the 381 ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Sterk |first=Andrea |date=1 October 1988 |title=The Silver Shields of Pope Leo III: A Reassessment of the Evidence |url=https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3859m82c |journal=Comitatus: A Journal of Medieval and Renaissance Studies |volume=19|pages=62–79}}</ref> This spoke of the procession of the Holy Spirit from the Father, without adding phrases such as "and the Son", "through the Son", or "alone". Stressing his opposition, the Pope had the original text inscribed in Greek and Latin on two heavy shields that were displayed in ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.usccb.org/beliefs-and-teachings/dialogue-with-others/ecumenical/orthodox/filioque-church-dividing-issue-english.cfm |title=The Filioque: A Church-Dividing Issue?: An Agreed Statement of the North American Orthodox-Catholic Consultation |publisher=Usccb.org |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |chapter-url=http://www.ccel.org/ccel/harnack/dogma5.ii.ii.i.vi.iv.html |author=Adolf Harnack |title=History of Dogma – Volume V |chapter=2. The Controversy regarding the Filioque and Pictures |via=CCEL.org |date=1 June 2005 |access-date=14 January 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.tyndalehouse.com/TynBul/Library/TynBull_1983_34_04_Bray_FilioqueInHistory.pdf |author=Gerald Bray |title=The ''Filioque'' Clause in History and Theology |journal=Tyndale Bulletin |volume=34 |date=1983 |pages=91–144 |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110716095849/http://www.tyndalehouse.com/TynBul/Library/TynBull_1983_34_04_Bray_FilioqueInHistory.pdf |archive-date=16 July 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ===Writing reforms=== | |||
| ] of Charlemagne's reign]] | |||
| During Charles' reign, the ] script and its cursive version, which had given rise to various continental ] scripts, were combined with features from the ]s in use in Irish and English monasteries. ] was created partly under the patronage of Charlemagne. ], who ran the palace school and ] at Aachen, was probably a chief influence. | |||
| The revolutionary character of the Carolingian reform, however, can be overemphasised; efforts at taming Merovingian and Germanic influence had been underway before Alcuin arrived at Aachen. The new minuscule was disseminated first from Aachen and later from the influential scriptorium at ], where Alcuin retired as an abbot. | |||
| ===Political reforms=== | |||
| Charlemagne engaged in many reforms of Frankish governance while continuing many traditional practices, such as the division of the kingdom among sons.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The rise of the medieval world, 500–1300: a biographical dictionary|last=Schulman|first=Jana K.|publisher=Greenwood Press|year=2002|isbn=978-0313011085|location=Westport, CN|page=xx}}</ref> | |||
| ====Divisio regnorum==== | |||
| In 806, Charlemagne first made provision for the traditional division of the empire on his death. For Charles the Younger he designated Austrasia and Neustria, Saxony, Burgundy and ]. To Pippin, he gave Italy, Bavaria, and ]. Louis received Aquitaine, the Spanish March and ]. The imperial title was not mentioned, which led to the suggestion that, at that particular time, Charlemagne regarded the title as an honorary achievement that held no hereditary significance. | |||
| Pepin died in 810 and Charles in 811. Charlemagne then reconsidered the matter, and in 813, crowned his youngest son, Louis, co-emperor and co-King of the Franks, granting him a half-share of the empire and the rest upon Charlemagne's own death. The only part of the Empire that Louis was not promised was Italy, which Charlemagne specifically bestowed upon Pippin's illegitimate son ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Noble|first=Thomas F. X.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LUCPcwybApIC&q=Bernard%2520of%2520Italy&pg=PA10|title=Charlemagne and Louis the Pious: The Lives by Einhard, Notker, Ermoldus, Thegan, and the Astronomer|date=2009|publisher=Penn State Press|isbn=978-0-271-03573-4|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Appearance== | |||
| ===Manner=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Einhard tells in his twenty-fourth chapter: {{blockquote|Charles was temperate in eating, and particularly so in drinking, for he abominated drunkenness in anybody, much more in himself and those of his household; but he could not easily abstain from food, and often complained that fasts injured his health. He very rarely gave entertainments, only on great feast-days, and then to large numbers of people. His meals ordinarily consisted of four courses, not counting the roast, which his huntsmen used to bring in on the spit; he was more fond of this than of any other dish. While at table, he listened to reading or music. The subjects of the readings were the stories and deeds of olden time: he was fond, too, of St. Augustine's books, and especially of the one titled "]".{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 24. Habits}}}}Charlemagne threw grand banquets and feasts for special occasions such as religious holidays and four of his weddings. When he was not working, he loved Christian books, horseback riding, swimming, bathing in natural hot springs with his friends and family, and hunting.<ref name="Bhote"/> Franks were well known for horsemanship and hunting skills.<ref name="Bhote"/> Charles was a light sleeper and would stay in his bed chambers for entire days at a time due to restless nights. During these days, he would not get out of bed when a quarrel occurred in his kingdom, instead summoning all members of the situation into his bedroom to be given orders. Einhard tells again in the twenty-fourth chapter: "In summer after the midday meal, he would eat some fruit, drain a single cup, put off his clothes and shoes, just as he did for the night, and rest for two or three hours. He was in the habit of awaking and rising from bed four or five times during the night."<ref name="Bhote">{{Cite book|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=BgDrUuug9c0C}}|title=Charlemagne: The Life and Times of an Early Medieval Emperor|last=Bhote|first=Tehmina|date=2005|publisher=The Rosen Publishing Group|isbn=978-1404201613|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Language=== | |||
| {{main|Theodiscus}} | |||
| Charlemagne probably spoke a Rhenish ] dialect.<ref>{{cite journal | first=R.E. | last=Keller | title=The Language of the Franks | journal= Bulletin of the John Rylands Library| volume=47 |number=1 | year=1964 | pages=101–22 | doi=10.7227/BJRL.47.1.6 }}</ref><ref name="ChambersWilkie2014">{{cite book|first1=William Walker |last1=Chambers|first2=John Ritchie |last2=Wilkie|title=A Short History of the German Language (RLE Linguistics E: Indo-European Linguistics)|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=eY7FBQAAQBAJ}}|date=2014|isbn=978-1-317-91852-3 |location=London | publisher=Routledge| page=33}}</ref>{{sfn|McKitterick|2008|p=318}} | |||
| He also spoke ] and had at least some understanding of Greek, according to Einhard (''Grecam vero melius intellegere quam pronuntiare poterat'', "he could understand Greek better than he could speak it").{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 25. Studies}} | |||
| The largely fictional account of Charlemagne's Iberian campaigns by ], written some three centuries after his death, gave rise to the legend that the king also spoke ].<ref name="Herwaarden2003">{{cite book|first=J. |last=Van Herwaarden|title=Between Saint James and Erasmus: Studies in Late-Medieval Religious Life : Devotions and Pilgrimages in the Netherlands|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=BTZfHERxuCQC|p=475}}|date=2003|publisher=Brill|isbn=978-90-04-12984-9 | page=475}}</ref> | |||
| ===Physical appearance=== | |||
| ] thought to represent Charlemagne (from ], now in the Louvre)]] | |||
| Charlemagne's personal appearance is known from a good description by Einhard after his death in the biography '']''. Einhard states:{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=116}} | |||
| {{blockquote|He was heavily built, sturdy, and of considerable stature, although not exceptionally so, since his height was seven times the length of his own foot. He had a round head, large and lively eyes, a slightly larger nose than usual, white but still attractive hair, a bright and cheerful expression, a short and fat neck, and he enjoyed good health, except for the fevers that affected him in the last few years of his life. Towards the end, he dragged one leg. Even then, he stubbornly did what he wanted and refused to listen to doctors, indeed he detested them, because they wanted to persuade him to stop eating roast meat, as was his wont, and to be content with boiled meat.}} | |||
| The physical portrait provided by Einhard is confirmed by contemporary depictions such as coins and his {{convert|8|in|cm|adj=on}} ] kept in the ]. In 1861, Charlemagne's tomb was opened by scientists who reconstructed his skeleton and estimated it to be measured {{convert|1.95|m|ftin}}.{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=118}} A 2010 estimate of his height from an ] and ] of his ] was {{convert|1.84|m|ftin}}. This puts him in the 99th ] of height for his period, given that average male height of his time was {{convert|1.69|m|ftin}}. The width of the bone suggested he was ] in body build.<ref>{{cite journal| last1=Ruhli | first1=F.J. | last2=Blumich | first2=B. | last3=Henneberg | first3=M. | year=2010 | title=Charlemagne was very tall, but not robust | journal=Economics and Human Biology | volume=8 | issue=2 | pages=289–90 | doi=10.1016/j.ehb.2009.12.005| pmid=20153271 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Dress=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Charlemagne wore the traditional ], described by Einhard thus:{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 23. Dress}} | |||
| {{blockquote|He used to wear the national, that is to say, the Frank, dress—next his skin a linen shirt and linen breeches, and above these a tunic fringed with silk; while hose fastened by bands covered his lower limbs, and shoes his feet, and he protected his shoulders and chest in winter by a close-fitting coat of otter or marten skins.}} | |||
| He wore a blue cloak and always carried a sword typically of a golden or silver hilt. He wore intricately jeweled swords to banquets or ambassadorial receptions. Nevertheless:{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 23. Dress}} | |||
| {{blockquote|He despised foreign costumes, however handsome, and never allowed himself to be robed in them, except twice in Rome, when he donned the Roman tunic, ], and shoes; the first time at the request of Pope Hadrian, the second to gratify Leo, Hadrian's successor.}} | |||
| On great feast days, he wore embroidery and jewels on his clothing and shoes. He had a golden buckle for his cloak on such occasions and would appear with his great ], but he despised such apparel according to Einhard, and usually dressed like the common people.{{sfn|Einhard|1880|loc=ch. 23. Dress}} | |||
| === Homes === | |||
| Charlemagne had residences across his kingdom, including numerous private estates that were governed in accordance with the ]. A 9th-century document detailing the inventory of an estate at Asnapium listed amounts of livestock, plants and vegetables and kitchenware including cauldrons, drinking cups, brass kettles and firewood. The manor contained seventeen houses built inside the courtyard for nobles and family members and was separated from its supporting villas.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://legacy.fordham.edu/halsall/source/800Asnapium.asp|title=Internet History Sourcebooks Project|website=legacy.fordham.edu|access-date=2 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| == Beatification == | |||
| {{Infobox saint | |||
| | honorific_prefix = ] | |||
| | name = Charlemagne the Great | |||
| | honorific_suffix = | |||
| | image = Louis-Félix Amiel - Charlemagne empereur d'Occident (742-814).jpg | |||
| | imagesize = | |||
| | alt = | |||
| | caption = Charlemagne Empereur d'Occident by Louis-Félix Amiel, circa 1837. | |||
| | titles = ] and ] | |||
| | birth_name = | |||
| | birth_date = | |||
| | birth_place = | |||
| | home_town = | |||
| | residence = | |||
| | death_date = | |||
| | death_place = | |||
| | venerated_in = ] | |||
| | beatified_date = 1179 | |||
| | beatified_place = ], ], ] | |||
| | beatified_by = ] ''(cultus approved)'' | |||
| | canonized_date = | |||
| | canonized_place = | |||
| | canonized_by = | |||
| | major_shrine = ], ], ] | |||
| | feast_day = 28 January | |||
| | attributes = Crown<br>Sword | |||
| | patronage = | |||
| | issues = | |||
| | suppressed_date = | |||
| | suppressed_by = | |||
| | influences = | |||
| | influenced = | |||
| | tradition = | |||
| | major_works = | |||
| | module = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| Einhard gives a first-hand description of Charlemagne's appearance later in life:{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=116}} | |||
| Charlemagne was revered as a saint in the ] and some other locations after the twelfth century. The ] did not recognise his invalid ] by ], done to gain the favour of ] in 1165. The Apostolic See annulled all of Paschal's ordinances at the ] in 1179.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |last1=Shahan |first1=Thomas |last2=Macpherson |first2=Ewan |date=1908 |title=Charlemagne|encyclopedia=] |location=New York |publisher=Robert Appleton Company |url=http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/03610c.htm |access-date=1 January 2013 |via=New Advent |quote=In some parts of the empire popular affection placed him among the saints. For political purposes and to please Frederick Barbarossa he was canonised (1165) by the antipope Paschal III, but this act was never ratified by insertion of his feast in the Roman Breviary or by the Universal Church; his cultus, however, was permitted at Aachen }}</ref> He is not enumerated among the 28 saints named "Charles" in the '']''.<ref>{{cite book|title=Martyrologium Romanum, Ad Formam Editionis Typicae Scholiis Historicis Instructum|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=SglLjwEACAAJ|page=685}}|page=685|year=1940}}</ref> His ] has been acknowledged as '']'' and is celebrated on 28 January.<ref name=shahan /><ref name=Hoche>{{cite book|last=Hoche|first=Dominique T|title=Icons of the Middle Ages: Rulers, Writers, Rebels, and Saints|year=2012|publisher=Greenwood|location=Santa Barbara, CA|isbn=978-0-313-34080-2 |pages=143–74 |chapter-url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=rETxD8KcnUIC|page=172}}|editor=Lister M. Matheson|access-date=1 January 2013|chapter=Charlemagne}}</ref> | |||
| ==Cultural impact== | |||
| {{See also|Iconography of Charlemagne}} | |||
| === Middle Ages === | |||
| The author of the '']'' written around 865 uses facts gathered apparently from Einhard and his own observations on the decline of Charlemagne's family after the dissensions war (840–43) as the basis for a visionary tale of Charles' meeting with a prophetic spectre in a dream. | |||
| ] legends about Charlemagne: ''Ystorya de Carolo Magno'' from the '']'' (], MS 111), 14th century]] | |||
| Charlemagne was a model ] as one of the ] who enjoyed an important legacy in European culture. One of the great medieval ]s, the Charlemagne cycle or the '']'', centres on his deeds—the Emperor with the Flowing Beard of '']'' fame—and his historical commander of the border with ], ], and the 12 ]s. These are analogous to, and inspired the myth of, the ] of ]'s court.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Arthurian-legend|title=Arthurian legend|website=Encyclopedia Britannica|date=25 August 2023 }}</ref> Their tales constitute the first '']''. | |||
| In the 12th century, ] based his stories of Arthur largely on stories of Charlemagne.<ref>{{Cite book|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=pnxdCwAAQBAJ|page=44}}|title=Arthur: King of Britain|last=Fraley|first=Michael|date=1993|publisher=Caliber Comics|isbn=978-1626657984|language=en}}<br />"To anyone familiar with the early Medieval Period of European history, Geoffrey's story begins to sound familiar here. It should. It seems to be based, in large part, on the historical adventures of Charlemagne, the Frankish King of the Ninth Century, who eventually became Emperor. Looking at Charlemagne's life and personality, it becomes clear that he and Geoffrey's Arthur are practically twins."</ref> During the ] in the 14th century, there was considerable cultural conflict in England, where the ] rulers were aware of their French roots and identified with Charlemagne, Anglo-Saxon natives felt more affinity for Arthur, whose own legends were relatively primitive. Therefore, storytellers in England adapted legends of Charlemagne and his 12 Peers to the Arthurian tales.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Charlemagne, King Arthur and Contested National Identity in English Romances | Memento Medievalia|url=https://www.mementomedievalia.com/charlemagne-king-arthur-and-contested-national-identity-in-english-romances/|access-date=2023-01-23|language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| In the '']'', the spirit of Charlemagne appears to ] in the ], among the other "warriors of the faith".<ref name="DLS17">], ''Paradise'', notes on Canto XVII.</ref> | |||
| === 19th century === | |||
| ], 1511–1513, ]]] | |||
| Charlemagne's capitularies were quoted by ] in his apostolic constitution 'Providas' against freemasonry: "For in no way are we able to understand how they can be faithful to us, who have shown themselves unfaithful to God and disobedient to their Priests".<ref>Benedict XIV, Providas, 1751</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne appears in '']'', the second tragedy by Italian writer ], first published in 1822.{{sfn|Banham|1998|p=678}} | |||
| In 1867, an ] was made by ] and was inaugurated in 1868 on the Boulevard d'Avroy in ]. In the niches of the neo-roman ] are six statues of Charlemagne's ancestors (Sainte Begge, Pépin de Herstal, Charles Martel, Bertrude, Pépin de Landen and Pépin le Bref). | |||
| The North Wall ] in the courtroom of the ] depicts Charlemagne as a legal reformer.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.supremecourt.gov/about/northandsouthwalls.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.supremecourt.gov/about/northandsouthwalls.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=US Supreme Court Courtroom Friezes|access-date=19 February 2019}}</ref> | |||
| === 20th century === | |||
| The city of Aachen has, since 1949, awarded an international prize (called the ''] der Stadt Aachen'') in honour of Charlemagne. It is awarded annually to "personages of merit who have promoted the idea of Western unity by their political, economic and literary endeavours."<ref>Chamberlin, Russell, ''The Emperor Charlemagne'', p. ???{{page needed|date=September 2020}}</ref> Winners of the prize include ], the founder of the pan-European movement, ], and ]. | |||
| In its national anthem, "]", the microstate of ] credits Charlemagne with its independence. | |||
| In 1964, young French singer ] released the hit song "]" in which the lyrics blame the great king for imposing the burden of compulsory education on French children. | |||
| Charlemagne is quoted by Dr Henry Jones, Sr. in '']''. After using his umbrella to induce a flock of seagulls to smash through the glass cockpit of a pursuing German fighter plane, Henry Jones remarks, "I suddenly remembered my Charlemagne: 'Let my armies be the rocks and the trees and the birds in the sky.{{'"}} Despite the quote's popularity since the movie, there is no evidence that Charlemagne actually said this.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.quidplura.com/?p=29 |title=Quid plura? {{pipe}} "Flying birds, excellent birds ..." |publisher=Quidplura.com |date=5 August 2007 |access-date=14 January 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200729122546/http://www.quidplura.com/?p=29|archive-date=29 July 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ===21st century=== | |||
| A 2010 episode of '']'' discussed the mathematics completed by Mark Humphrys that calculated that all modern Europeans are highly likely to share Charlemagne as a common ancestor (see ]).<ref>{{Cite web|title=Common ancestors of all humans|url=https://humphrysfamilytree.com/ca.html|access-date=2023-01-23|website=humphrysfamilytree.com}}</ref> | |||
| '']'' featured a weekly column entitled "Charlemagne", focusing generally on European affairs and, more usually and specifically, on the ] and its politics.<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.economist.com/blogs/economist-explains/2013/09/economist-explains-itself-3|title=Where do The Economist's unusual names come from?|newspaper=The Economist|access-date=26 March 2017|date=5 September 2013}}</ref> | |||
| Actor and singer ]'s ] ] '']''<ref name=Michaels>{{cite news|last=Michaels|first=Sean|title=Christopher Lee to release 'symphonic metal' album, The man who played Dracula and Saruman is to tell the story of Charlemagne, the first Holy Roman Emperor, through the universal language of metal|url=https://www.theguardian.com/music/2010/jan/05/christopher-lee-symphonic-metal-album|access-date=1 January 2013|newspaper=The Guardian|date=5 January 2010|quote=The man who played Dracula, Saruman and the Man with the Golden Gun is now to portray Charlemagne—through the medium of song. Actor Christopher Lee is to release an album of 'symphonic metal', telling the story of his own direct ancestor, the first Holy Roman Emperor.}}</ref> and its ] follow-up '']'' feature the events of Charlemagne's life.<ref name=Farrell>{{cite news|last=Farrell|first=John|title=Christopher Lee Celebrates 90th Birthday By Recording Heavy Metal|url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/johnfarrell/2012/05/28/christopher-lee-celebrates-90th-birthday-by-recording-heavy-metal/|access-date=1 January 2013|newspaper=Forbes|date=28 May 2012|quote='Let Legend Mark Me As King;' and 'The Ultimate Sacrifice', arranged by Judas Priest lead guitarist Richie Falkner, are part of a new album, Charlemagne: The Omens of Death.}}</ref> | |||
| In April 2014, on the occasion of the 1200th anniversary of Charlemagne's death, public art ''Mein Karl'' by ] at Katschhof place was installed between city hall and the Aachen cathedral, displaying 500 Charlemagne statues.<ref>{{cite web |website=Euregio Aachen |url=http://euregio-aachen.de/mein-karl-2014/ |title=Mein Karl |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140423080431/http://euregio-aachen.de/mein-karl-2014/ |archive-date=23 April 2014 |url-status=dead |date=18 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| {{blockquote|He was heavily built, sturdy, and of considerable stature, although not exceptionally so, since his height was seven times the length of his own foot. He had a round head, large and lively eyes, a slightly larger nose than usual, white but still attractive hair, a bright and cheerful expression, a short and fat neck, and he enjoyed good health, except for the fevers that affected him in the last few years of his life.}} | |||
| Charlemagne features as a playable character in the 2014 ''Charlemagne'' expansion for the ] video game '']''.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Crusader Kings II: Charlemagne {{!}} Paradox Interactive|url=https://www.paradoxinteractive.com/games/crusader-kings-ii/add-ons/crusader-kings-ii-charlemagne|access-date=16 April 2023|website=www.paradoxinteractive.com|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Charlemagne's tomb was opened in 1861 by scientists who reconstructed his skeleton and measured it at {{convert|1.92|m|ftin}} in length, roughly equivalent to Einhard's seven feet.{{sfn|Barbero|2004|p=118}} A 2010 estimate of his height from an ] and ] of his ] was {{convert|1.84|m|ftin}}; this puts him in the 99th ] of height for his period, given that average male height of his time was {{convert|1.69|m|ftin}}. The width of the bone suggested that he was slim.{{sfn|Ruhli|Blumich|Henneberg|2010}} | |||
| Charlemagne is a playable character in the Mobile/PC Game Rise of Kingdoms. | |||
| Charlemagne wore his hair short, abandoning the Merovingian tradition of long-haired monarchs.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=21–22}} He had a moustache (possibly imitating the Ostrogothic king ]), in contrast with the bearded Merovingian kings;{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=24–26}} future Carolingian monarchs would adopt this style.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=24, 26}} Paul Dutton notes the ubiquitous crown in portraits of Charlemagne and other Carolingian rulers, replacing the earlier Merovingian long hair.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=22–23}} A ninth-century statuette depicts Charlemagne or his grandson, ]{{efn|Janet Nelson considers it a depiction of Charlemagne;{{sfn|Nelson|2019|pp=xxxvi, 495}} Paul Dutton says that it was "long thought to depict Charlemagne and now attributed by most to Charles the Bald,"{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=35}} and Johannes Fried presents both as possibilities{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=216}} but considers it "highly contentious."{{sfn|Fried|2016|p=516}}}} and shows the subject as moustachioed with short hair;{{sfn|Dutton|2016|p=35}} this also appears on contemporary coinage.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=24–25}} | |||
| In the 2018 video game '']'', Charlemagne appears as a Heroic Spirit separated into two Saint Graphs: the adventurous hero Charlemagne, who embodies the fantasy aspect as leader of the Twelve Paladins, and the villain Karl de Große, who embodies the historical aspect as Holy Roman Emperor.<ref>{{cite web|title=Rex Magnus: Servant|url = http://fateextellalink.com/characters/rexmagnus/|access-date=9 November 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Charlemagne: Servant|url = http://fateextellalink.com/characters/charlemagne/|access-date=9 November 2021}}</ref> | |||
| By the twelfth century, Charlemagne was described as bearded rather than moustachioed in literary sources such as the ''Song of Roland'', the ''Pseudo-Turpin Chronicle'', and other works in Latin, French, and German.{{sfn|Coxon|2021|pp=31, 196}} The ''Pseudo-Turpin'' uniquely says that his hair was brown.{{sfn|Coxon|2021|p=196}} Later art and iconography of Charlemagne followed suit, generally depicting him in a later medieval style as bearded with longer hair.{{sfn|Dutton|2016|pp=27–30}} | |||
| In July 2022, Charlemagne featured as a character in an episode of The Family Histories Podcast, and it references his role as an ancestor of all modern Europeans. He is portrayed here in later life, and is speaking Latin, which is translated by a device. He is returned to 9th Century Aquitaine by the end of the episode after a DNA sample has been extracted.<ref>{{cite web |title=S03EP08: The Great (Bonus) |url=https://familyhistoriespodcast.com/2022/07/19/s03ep08-the-great-bonus-episode/ |website=familyhistoriespodcast.com |date=19 July 2022 |publisher=The Family Histories Podcast |access-date=19 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 636: | Line 341: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| ===Citations=== | ===Citations=== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist|23em}} | ||
| === |
=== Works cited === | ||
| {{ |
{{Sfn whitelist|CITEREFEinhard,_putative741–829}} | ||
| <!-- Please order books alphabetically by the author's last name --> | <!-- Please order books alphabetically by the author's last name --> | ||
| {{Refbegin|30em}} | {{Refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Arnold |first=Benjamin |title=Medieval Germany , 500–1300 A Political Interpretation |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-3336-1091-6}} | |||
| * , from '']'', full-article, latest edition. | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Barbero |first=Alessandro |title=Charlemagne: Father of a Continent |publisher=University of California Press |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-5202-3943-2 |location=Berkeley |translator-last=Allan Cameron}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Becher |first=Matthias |title=Charlemagne |date=2005 |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-3000-9796-2 |location=New Haven |translator-last=Bachrach |translator-first=David S.}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Bouchard |first=Constance |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yxSxikFnSU8C&pg=PA129 |title=Those of My Blood: Creating Noble Families in Medieval Francia |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-8122-0140-6 }} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Bulfinch |first=Thomas |url=https://archive.org/details/legendsofcharle00bulf/page/n5/mode/2up |title=Legends of Charlemagne |publisher=Boston, J. E. Tilton and Co. |year=1864 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Bathurst|first=Charles|title=An Universal History from the Earliest Accounts to the Present Time|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=EtY-AAAAYAAJ}}|year=1782|volume=24 |location=London |publisher=C. Bathurst}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Chambers |first1=William Walker |title=A Short History of the German Language (RLE Linguistics E: Indo-European Linguistics) |last2=Wilkie |first2=John Ritchie |date=2014 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-3179-1852-3 |location=London}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Matthias |last=Becher|title=Charlemagne|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=KbbMcYpuQswC}} |date=2005 |translator-first= David S. |translator-last=Bachrach |publisher=Yale University Press |location=New Haven |isbn=978-0-300-09796-2}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Collins |first=Roger |title=Charlemagne |publisher=University of Toronto Press |year=1998 |isbn=978-0-3336-5055-4 |location=Toronto}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Norman F. |last=Cantor|title=Civilization of the Middle Ages: Completely Revised and Expanded Edition, A|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=d1rHCgAAQBAJ}}|date=2015|publisher=HarperCollins |isbn=978-0-06-244460-8}} | |||
| * {{Citation |last=Contreni |first=John J. |title=Renaissances before the Renaissance: Cultural Revivals of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages |date=1984 |editor-last=Treadgold |editor-first=Warren T. |chapter=The Carolingian Renaissance |place=Stanford |publisher=Stanford University Press |isbn=0-8047-1198-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last=Collins | first=Roger | year=1987 | title=The Basques | location=New York | publisher=Basil Blackwell Inc | orig-year=1986}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Contreni |first=John J. |title=The New Cambridge Medieval History Volume II: c. 700–900 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1995 |isbn=978-1-1390-5571-0 |editor-last=McKitterick |editor-first=Rosamond |location=Cambridge |chapter=The Carolingian Renaissance: Education and Literary Culture}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last=Collins | first=Roger | year=1998 | title=Charlemagne | location=Toronto | publisher=University of Toronto Press}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last1=Costambeys |first1=Marios |title=The Carolingian World |last2=Innes |first2=Matthew |last3=MacLean |first3=Simon |date=2011 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-5215-6366-6 |location=Cambridge}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Coxon |first=Sebastian |url=https://directory.doabooks.org/handle/20.500.12854/74778 |title=Beards and Texts: Images of Masculinity in Medieval German Literature |date=2021 |publisher=UCL Press |isbn=978-1-7873-5221-6 |location=London |doi=10.2307/j.ctv1hggknc |jstor=j.ctv1hggknc |s2cid=239135035 |access-date=6 March 2024 |archive-date=11 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240411223400/https://directory.doabooks.org/handle/20.500.12854/74778 |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last=Collins | first=Roger | year=2004 | title=Visigothic Spain, 409–711 | location=Malden, MA; Oxford | publisher=Blackwell Pub. | series=History of Spain}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Davies |first=Norman |url={{Google books|plainurl=y|id=jrVW9W9eiYMC}} |title=Europe: A History |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-1982-0171-7 }} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Davis |first=Jennifer R. |title=Charlemagne's Practice of Empire |date=2015 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-1070-7699-0 |location=Cambridge}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Dutton |first=Paul |url={{Google books|plainurl=y|id=WGgYDAAAQBAJ}} |title=Charlemagne's Mustache: And Other Cultural Clusters of a Dark Age |date=2016 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=978-1-1370-6228-4 }} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Frassetto |first=Michael |title=Encyclopedia of Barbarian Europe: Society in Transformation |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2003 |isbn=978-1-5760-7263-9 |location=Santa Barbara, CA}} | ||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Freeman |first=Elizabeth |date=2017 |title="Charles the Great, or Just Plain Charles: Was Charlemagne a Great Medieval Leader?" |journal=Agora |volume=52 |issue=1 |pages=10–19}} | |||
| * {{cite book| author=Einhard, putative | year=741–829 | title=Annales Regni Francorum (Annales Laurissenses Maiores) | work=Medieval Latin | publisher=The Latin Library | url=http://www.thelatinlibrary.com/annalesregnifrancorum.html}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Fried |first=Johannes |title=Charlemagne |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=2016 |isbn=978-0-6747-3739-6 |location=Cambridge, MA |translator-last=Lewis |translator-first=Peter}} | ||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Ganshof |first=François L. |date=1965 |title=The Impact of Charlemagne on the Institutions of the Frankish Realm. |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/2856463 |journal=Speculum |volume=40 |issue=1 |pages=49 |doi=10.2307/2856463 |jstor=2856463 |access-date=17 August 2024 |archive-date=17 August 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240817150723/https://www.jstor.org/stable/2856463 |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Fouracre|first=Paul|chapter=The Long Shadow of the Merovingians| editor=Joanna Story |title=Charlemagne: Empire and Society|year=2005|publisher=Manchester University Press|location=Manchester|isbn=978-0-71907-089-1}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Geary |first=Patrick J. |date=1987 |title=Germanic Tradition and Royal Ideology in the Ninth Century: The ''Visio Karoli Magni'' |journal=Frühmittelalterliche Studien |volume=21 |pages=274–294 |doi=10.1515/9783110242195.274 |issn=0071-9706 |s2cid=165699647}} | |||
| * {{cite book| last=Frassetto | first=Michael | year=2003 | title=Encyclopedia of Barbarian Europe: Society in Transformation | place=Santa Barbara, CA | publisher=ABC-CLIO | isbn=978-1-57607-263-9}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Goffart |first=Walter |date=1986 |title=]'s 'Gesta Episcoporum Mettensium' and the Early Design of Charlemagne's Succession |journal=Traditio |volume=42 |pages=59–93 |doi=10.1017/S0362152900004049 |s2cid=151941720}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Fried|first=Johannes|title=Charlemagne|year=2016|others=trans. Peter Lewis|publisher=Harvard University Press|location=Cambridge, MA|isbn=978-0674737396}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Hägermann |first=Dieter |title=Carlo Magno: Il signore dell'Occidente |publisher=Arnoldo Mondadori Editore |year=2011 |translator-last=Giuseppe Albertoni |trans-title=Karl der Grosse: Herrscher des Abendlandes |orig-year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Ganshof|first=F. L.|author-link=François-Louis Ganshof|title=The Carolingians and the Frankish Monarchy: Studies in Carolingian History|year=1971|others=trans. Janet Sondheimer|publisher=Cornell University Press|location=Ithaca, NY|isbn=978-0-8014-0635-5|url=https://archive.org/details/carolingiansfran0000gans}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last1=Hardman |first1=Philipa |title=The Legend of Charlemagne in Medieval England |last2=Ailes |first2=Marianne |date=2017 |publisher=DS Brewer |isbn=978-1-8438-4472-3 |location=Cambridge |pages=1–9}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Heather |first=Peter |title=Empires and Barbarians:The Fall of Rome and the birth of Europe |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-1998-9226-6 |location=New York}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Thomas |last=Hodgkin|title=Italy and Her Invaders|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=_zlpAAAAMAAJ}}|year=1889|author-link=Thomas Hodgkin |volume=8 |location=Oxford |publisher=Clarendon Press}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Hornblower |first=Simon |title=Oxford Classical Dictionary |date=2012 |isbn=978-0-1995-4556-8 |publisher=Oxford University Press |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bVWcAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA728 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last1=James |first1=David |last2=Ibn al-Qūṭiyya |first2=Muḥammad b ʻUmar |title=Early Islamic Spain: The History of Ibn al-Qūṭiyya: a study of the unique Arabic manuscript in the Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris, with a translation, notes and comments |location=London and New York |publisher=Routledge |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-41547-552-5}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Jackman |first=Donald C. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZI4NV16sGrUC&pg=PA9 |title=Ius hereditarium Encountered III: Ezzo's Chess Match |publisher=Editions Enlaplage |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-9364-6654-2 |pages=9–12 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|editor-last=Lewers Langston|editor-first=Aileen|editor2-last=Buck|editor2-first=J. Orton Jr.|title=Pedigrees of Some of the Emperor Charlemagne's Descendants|year=1974|publisher=Genealogical Pub. Co. |location=Baltimore}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Kuskin |first=William |date=1999 |title=Caxton's Worthies Series: The Production of Literary Culture |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/30032085 |journal=ELH |volume=66 |issue=3 |pages=511–551 |doi=10.1353/elh.1999.0027 |jstor=30032085 |s2cid=162260451 |access-date=2 December 2023 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Rosamond |last=McKitterick|title=Charlemagne: The Formation of a European Identity|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=kxb8kR4hvbQC|page=91}}|date=2008|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-139-47285-2|author-link=Rosamond McKitterick|location=Cambridge}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Leonhardt |first=Jürgen |title=Latin: story of a World Language |date=2016 |publisher=Harvard |isbn=978-0-6746-5996-4 |translator-last=Kenneth Kronenberg |ol=OL35499574M |orig-date=2009}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Molina Figueras |first=Joan |year=2004 |title= Arnau de Montrodon y la catedral de San Carlomagno: sobre la imagen y el culto al emperador carolingio en Gerona |language=es |journal=Anuario de Estudios Medievales |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages= 417–54 |doi=10.3989/aem.2004.v34.i1.190|doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Lewis |first=Andrew W. |date=1977 |title=Dynastic Structures and Capetian Throne-Right: the Views of Giles of Paris |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/27831029 |journal=Traditio |volume=33 |issue=1 |pages=225–252 |doi=10.1017/S0362152900009119 |jstor=27831029 |access-date=9 March 2024 |archive-date=10 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240310003051/https://www.jstor.org/stable/27831029 |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Janet L.|last=Nelson|author-link=Janet Nelson|title=King and Emperor: A New Life of Charlemagne|location=London|year=2019}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Mayr-Harting |first=Henry |date=1996 |title=Charlemagne, the Saxons, and the Imperial Coronation of 800 |journal=The English Historical Review |volume=111 |issue=444 November |pages=1113–1133 |doi=10.1093/ehr/CXI.444.1113}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=John Julius |last=Norwich|title=Byzantium: The Apogee|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=4JsTAQAAIAAJ}}|year=1992a|publisher=Knopf|isbn=978-0-394-53779-5}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=McCormick |first=Michael |title=Charlemagne's Survey of the Holy Land: Wealth, Personnel, and Buildings of a Mediterranean Church between Antiquity and the Middle Ages |publisher=Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection |year=2011}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=John Julius |last=Norwich|author-link=John Julius Norwich |title=Byzantium: The Early Centuries|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=jEMNrgEACAAJ}}|year=1992b|publisher=Penguin Books}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=McKitterick |first=Rosamond |date=1996 |title=Unity and Diversity in the Carolingian Church |journal=Studies in Church History |volume=32 |pages=59–82 |doi=10.1017/S0424208400015333 |s2cid=163254629}} | |||
| * {{cite book| last=Oman|first=Charles|author-link=Charles Oman|title=The Dark Ages, 476–918|year=1914 |edition=6th |publisher=Rivingtons|location=London}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=McKitterick |first=Rosamond |author-link=Rosamond McKitterick |url={{Google books|plainurl=y|id=kxb8kR4hvbQC|page=91}} |title=Charlemagne: The Formation of a European Identity |date=2008 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-1394-7285-2 |location=Cambridge }} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Muldoon |first=James |title=Empire and Order:Concepts of Empire 800-1800 |publisher=St. Martin's Press |year=1999 |isbn=0-3122-2226-2 |location=New York}} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Henri |last=Pirenne|title=Mohammed and Charlemagne|url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=nfPBAgAAQBAJ}}|date=2012|isbn=978-0-486-12225-0| author-link=Henri Pirenne| publisher=Dover| location=Mineola, NY| orig-year=1937 posthumous}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Nelson |first=Janet L. |title=Courts, elites, and gendered power in the early Middle Ages Charlemagne and others |publisher=Ashgate |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7546-5933-4 |oclc=1039829293}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Nelson |first=Janet L. |author-link=Janet Nelson |title=King and Emperor: A New Life of Charlemagne |publisher=University of California Press |year=2019 |isbn=978-0-5203-1420-7 |location=Oakland |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nesjEAAAQBAJ }} | |||
| * {{cite book| first=Charles Edward | last=Russell | title=Charlemagne, first of the moderns | year=1930 | location=Boston and New York | publisher=Houghton Mifflin Co.}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Noble |first=Thomas F. X. |date=2015 |title=Carolingian Religion |journal=Church History |volume=84 |issue=2 |pages=287–307 |doi=10.1017/S0009640715000104 |s2cid=231888268}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Santosuosso|first=Antonio|author-link=Antonio Santosuosso|title=Barbarians, Marauders, and Infidels: The Ways of Medieval Warfare|year=2004|publisher=Westview Press|location=Boulder, CO|isbn=978-0-8133-9153-3}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Nonn |first=Ulrich |url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9783110210477.3.575/html?lang=en |title=Nomen et Fraternitas |date=2008 |publisher=DeGruyter |isbn=978-3-1102-0238-0 |editor-last=Ludwig |editor-first=Uwe |series=Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde – Ergänzungsbände |volume=62 |location=Berlin, New York |pages=575–586 |chapter=Karl Martell – Name und Beiname |doi=10.1515/9783110210477.3.575 |editor-last2=Schlipp |editor-first2=Thomas |access-date=29 January 2024 |archive-date=23 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240123174400/https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9783110210477.3.575/html?lang=en |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Sarti|first=Laury|title=Frankish Romanness and Charlemagne's Empire|journal=Speculum |volume=91 |issue=4|year=2016|pages=1040–58|doi=10.1086/687993|s2cid=163283337}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Pirenne |first=Henri |author-link=Henri Pirenne |title=Mohammed and Charlemagne |date=2012 |publisher=Dover |isbn=978-0-4861-2225-0 |location=Mineola, NY |orig-year=1937 posthumous}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Scholz|first=Bernhard Walter|author2=Barbara Rogers|title=Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories|year=1970|publisher=University of Michigan Press|location=Ann Arbor |isbn=978-0-472-08790-7}} Comprises the ''Annales regni Francorum'' and ''The History of the Sons of Louis the Pious'' | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Reuter |first=Timothy |author-link=Timothy Reuter |year=1985 |title=Plunder and Tribute in the Carolingian Empire |journal=Transactions of the Royal Historical Society |series=Fifth Series |volume=35 |pages=75–94 |doi=10.1017/S0080440100017710 |doi-broken-date=2 January 2025 |jstor=3679177}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Sypeck|first=Jeff|title=Becoming Charlemagne: Europe, Baghdad, and The Empires of A.D. 800|year=2006|publisher=Ecco/HarperCollins|location=New York|isbn=978-0-06-079706-5|url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/becomingcharlema0000sype}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite book |last=Riché |first=Pierre |title=The Carolingians: A Family Who Forged Europe |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-8122-1096-5 |series=Middle Ages Series |location=Philadelphia |translator-last=Allen |translator-first=Michael Idomir}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Cite journal |last1=Ruhli |first1=F.J. |last2=Blumich |first2=B. |last3=Henneberg |first3=M. |year=2010 |title=Charlemagne was very tall, but not robust |journal=Economics and Human Biology |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=289–290 |doi=10.1016/j.ehb.2009.12.005 |pmid=20153271}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Sarti |first=Laury |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KTAFEQAAQBAJ |title=Orbis Romanus: Byzantium and the Legacy of Rome in the Carolingian World |date=2024 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-774654-7 |access-date=3 September 2024 |archive-date=3 September 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240903015325/https://books.google.com/books?id=KTAFEQAAQBAJ |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Wilson|first=Derek|title=Charlemagne: The Great Adventure|year=2005|publisher=Hutchinson |location=London|isbn=978-0-09-179461-3}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Scales |first=Len |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-qICADV-G-EC&pg=PA159 |title=The Shaping of German Identity: Authority and Crisis |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2012 |isbn=9780521573337 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Siecienski |first=Anthony Edward |title=The Filioque: History of a Doctrinal Controversy |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-1953-7204-5}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Sterk |first=Andrea |date=1 October 1988 |title=The Silver Shields of Pope Leo III: A Reassessment of the Evidence |url=https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3859m82c |journal=Comitatus: A Journal of Medieval and Renaissance Studies |volume=19 |pages=62–79 |access-date=22 February 2019 |archive-date=27 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190327090129/https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3859m82c |url-status=live }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Tanner |first=Heather |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oRNYEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA265 |title=Families, Friends and Allies: Boulogne and Politics in Northern France and England |publisher=Brill |year=2004 |isbn=978-9-0474-0255-8 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Waldman |first1=Carl |title=Encyclopedia of European Peoples |last2=Mason |first2=Catherine |publisher=Facts on File |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-8160-4964-6 |location=New York}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Williams |first=J.D. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hGFRAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA447 |title=Chambers's New Handy Volume American Encyclopædia |date=1885 |publisher=Arundel |volume=3 |pages=446–7 }} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| ===Primary sources in English translation=== | |||
| {{Refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Alcuin |author-link=Alcuin |title=The Rhetoric of Alcuin and Charlemagne: A Translation, with an Introduction, the Latin Text, and Notes |date=1941 |publisher=Princeton University Press |location=Princeton |translator-last=Howell |translator-first=Wilbur Samuel}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Alcuin |author-link=Alcuin |title=Alcuin of York, c. AD 732 to 804: His life and letters |date=1974 |publisher=Sessions Book Trust |isbn=0-9006-5721-9 |editor-last=Alcott |editor-first=Stephen |location=York |translator-last=Alcott |translator-first=Stephen}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Liber Historiae Francorum |date=1973 |publisher=Coronodo Press |isbn=978-0-8729-1058-4 |editor-last=Bachrach |editor-first=Bernard S. |location=Lawrence, KS |translator-last=Bachrach |translator-first=Bernard S.}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The Lives of the Eighth-Century Popes |date=1992 |publisher=Liverpool University Press |isbn=978-0-8532-3018-2 |editor-last=Davis |editor-first=Raymond |location=Liverpool |translator-last=Davis |translator-first=Raymond}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Einhard |author-link=Einhard |title=Two Lives of Charlemagne |last2=Notker |author-link2=Notker the Stammerer |date=1969 |publisher=Penguin |isbn=978-0-1404-4213-7 |location=London |translator-last=Thorpe |translator-first=Lewis}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Einhard |author-link=Einhard |title=Charlemagne's Courtier: The Complete Einhard |date=1998 |publisher=Broadview Press |isbn=1-5511-1134-9 |editor-last=Dutton |editor-first=Paul |series=Readings in Medieval Civilizations and Cultures |location=Petersborough, ON |translator-last=Dutton |translator-first=Paul}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Carolingian Civilization: A Reader |publisher=Broadview Press |date=2004 |isbn=978-1-5511-1492-7 |editor-last=Dutton |editor-first=Paul |location=Petersborough, ON}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance |date=1985 |publisher=University of Oklahoma Press |isbn=978-0-8061-1939-7 |editor-last=Goodman |editor-first=Peter |location=Norman |translator-last=Goodman |translator-first=Peter}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Charlemagne: Translated Sources |date=1997 |publisher=P.D. King |isbn=978-0-9511-5030-6 |editor-last=King |editor-first=P.D. |location=Lancaster |translator-last=King |translator-first=P.D.}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Codex Epistolaris Carolinus: Letters from the popes to the Frankish rulers, 739–791 |publisher=Liverpool University Press |date=2021 |isbn=978-1-8003-4871-4 |editor-last=McKitterick |editor-first=Rosamond |location=Liverpool |translator-last=McKitterick |translator-first=Rosamond |editor-last2=van Espelo |editor-first2=Dorine |editor-last3=Pollard |editor-first3=Richard |editor-last4=Price |editor-first4=Richard |translator-last2=van Espelo |translator-first2=Dorine |translator-last3=Pollard |translator-first3=Richard |translator-last4=Price |translator-first4=Richard}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The Reign of Charlemagne: Documents on Carolingian Government and Administration |date=1975 |publisher=Arnold |isbn=978-0-7131-5813-7 |editor-last=Lyon |editor-first=H.R. |series=Documents of Medieval History |location=London |translator-last=Lyon |translator-first=H.R. |editor-last2=Percival |editor-first2=John |translator-last2=Percival |translator-first2=John}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories |publisher=University of Michigan Press |date=1970 |isbn=978-0-4720-8790-7 |editor-last=Scholz |editor-first=Bernhard Walter |location=Ann Arbor |translator-last=Scholz |translator-first=Bernhard Walter |editor-last2=Rogers |editor-first2=Barbara |translator-last2=Rogers |translator-first2=Barbara}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ===Secondary works=== | |||
| {{Refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Bachrach |first=Bernard S. |author-link=Bernard Bachrach |title=Early Carolingian Warfare Prelude to Empire |date=2011 |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |isbn=978-0-8122-2144-2}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Cantor |first=Norman F. |title=Civilization of the Middle Ages: A Completely Revised and Expanded Edition |date=2015 |publisher=HarperCollins |isbn=978-0-0624-4460-8}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Collins |first=Roger |title=Early Medieval Europe, 300–1000 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |date=1999 |isbn=978-0-3336-5808-6 |location=New York}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Collins |first=Roger |title=Visigothic Spain, 409–711 |publisher=Blackwell Pub. |date=2004 |series=History of Spain |location=Malden, MA; Oxford}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Fouracre |first=Paul |title=Charlemagne: Empire and Society |publisher=Manchester University Press |date=2005 |isbn=978-0-7190-7089-1 |editor-last=Joanna Story |location=Manchester |chapter=The Long Shadow of the Merovingians}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Ganshof |first=F. L. |author-link=François-Louis Ganshof |url=https://archive.org/details/carolingiansfran0000gans |title=The Carolingians and the Frankish Monarchy: Studies in Carolingian History |publisher=Cornell University Press |others=trans. Janet Sondheimer |date=1971 |isbn=978-0-8014-0635-5 |location=Ithaca, NY}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Gregory |first=Timothy E. |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofbyzanti00greg |title=A History of Byzantium |publisher=Blackwell Publishing |date=2005 |isbn=978-0-6312-3513-2 |location=Malden, MA; Oxford, UK}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=James |first1=David |title=Early Islamic Spain: The History of Ibn al-Qūṭiyya: a study of the unique Arabic manuscript in the Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris, with a translation, notes and comments |last2=Ibn al-Qūṭiyya |first2=Muḥammad b ʻUmar |publisher=Routledge |date=2009 |isbn=978-0-4154-7552-5 |location=London and New York}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Pedigrees of Some of the Emperor Charlemagne's Descendants |publisher=Genealogical Pub. Co. |date=1974 |editor-last=Lewers Langston |editor-first=Aileen |location=Baltimore |editor-last2=Buck |editor-first2=J. Orton Jr.}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=McKitterick |first=Rosamond |title=The Frankish Kingdoms under the Carolingians, 751–987 |publisher=Logman |date=1983 |isbn=978-0-5824-9005-5 |location=London}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The New Cambridge Medieval History |volume= II: c. 700–900 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |date=1995 |isbn=978-1-1390-5571-0 |editor-last=McKitterick |editor-first=Rosamond |location=Cambridge}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Riché |first=Pierre |title=Daily Life in the World of Charlemagne |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |date=1978 |isbn=978-0-8122-1342-3 |series=Middle Ages Series |location=Philadelphia |translator-last=McNamara |translator-first=Jo Ann}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Santosuosso |first=Antonio |author-link=Antonio Santosuosso |title=Barbarians, Marauders, and Infidels: The Ways of Medieval Warfare |publisher=Westview Press |date=2004 |isbn=978-0-8133-9153-3 |location=Boulder, CO}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Sarti |first=Laury |date=2016 |title=Frankish Romanness and Charlemagne's Empire |journal=Speculum |volume=91 |issue=4 |pages=1040–58 |doi=10.1086/687993 |s2cid=163283337}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Sypeck |first=Jeff |url=https://archive.org/details/becomingcharlema0000sype |title=Becoming Charlemagne: Europe, Baghdad, and The Empires of A.D. 800 |publisher=Ecco/HarperCollins |date=2006 |isbn=978-0-0607-9706-5 |location=New York |url-access=registration}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | {{Refend}} | ||
| Line 689: | Line 436: | ||
| {{Sister project links |commons=Carolus_Magnus |wikt=Charlemagne |q=Charlemagne |b=Saylor.org's Ancient Civilizations of the World/Charlemagne and the Carolingian Empire |v=Middle Ages/Week 1 |s=Charlemagne }} | {{Sister project links |commons=Carolus_Magnus |wikt=Charlemagne |q=Charlemagne |b=Saylor.org's Ancient Civilizations of the World/Charlemagne and the Carolingian Empire |v=Middle Ages/Week 1 |s=Charlemagne }} | ||
| * (freely available database of prosopographical and socio-economic data from legal documents dating to Charlemagne's reign, produced by ]) | * (freely available database of prosopographical and socio-economic data from legal documents dating to Charlemagne's reign, produced by ]) | ||
| * , a collection of primary sources of Charlemagne's reign edited by Paul Halsall of Fordham University | |||
| * {{cite web | url=http://www.thelatinlibrary.com/ein.html | title= ''Vita Karoli Magni'' | author=Einhard | work=Medieval Latin | publisher=] |language=la}} | * {{cite web | url=http://www.thelatinlibrary.com/ein.html | title= ''Vita Karoli Magni'' | author=Einhard | work=Medieval Latin | publisher=] |language=la}} | ||
| * {{cite web | first=Marco | last=Bakker | title=Charlemagne | date=2003–2011 | publisher=Reportret | url=http://www.reportret.info/gallery/charlemagne1.html}} | |||
| * (myArmoury.com article) | |||
| * {{cite web | first=Melissa | last=Snell | title=Charlemagne Picture Gallery | url=http://www.historymedren.about.com/od/carolingianempire/ig/Charlemagne-Picture-Gallery/index_t.htm | publisher=About.com | work=Medieval History | year=2011 | access-date=3 July 2008 | archive-date=21 February 2014 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140221205835/http://historymedren.about.com/od/carolingianempire/ig/Charlemagne-Picture-Gallery/index_t.htm | url-status=dead }} | |||
| * for ] showing the Emperor's seal, 22.2.794 . Taken from the collections of the at ] | |||
| * {{Internet Archive author |search=( "Charles the Great" OR Charlemagne )}} | * {{Internet Archive author |search=( "Charles the Great" OR Charlemagne )}} | ||
| * {{Librivox author |id=8397}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| * {{Cite EB1911|wstitle= Charlemagne | volume= 5 |last1= Holland |first1= Arthur William |author1-link= |last2= Bryant |first2= Margaret |author2-link= | pages = 891–897 |short=1}} | |||
| * {{Geschichtsquellen Person|118560034|Carolus Magnus imperator}} | |||
| {{s-start}} | {{s-start}} | ||
| Line 704: | Line 445: | ||
| {{s-reg|}} | {{s-reg|}} | ||
| {{s-bef | {{s-bef | ||
| | before = ] | | before = ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{s-ttl | {{s-ttl | ||
| Line 711: | Line 452: | ||
| | regent1 = ] | | regent1 = ] | ||
| | years1 = 768–771 | | years1 = 768–771 | ||
| | regent2 = |
| regent2 = with ] | ||
| | years2 = 800–811 | | years2 = 800–811 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{s-aft | {{s-aft | ||
| | rows = |
| rows = 2 | ||
| | after = ] | | after = ] | ||
| }} | |||
| {{s-break}} | |||
| {{s-new|creation|reason=''']'''<br /><small>''] as undisputed<br>Byzantine emperor''</small>}} | |||
| {{s-ttl | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | years = 800–814 | |||
| | regent1 = ] | |||
| | years1 = 813–814 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| Line 725: | Line 474: | ||
| | title = ] | | title = ] | ||
| | years = 774–814 | | years = 774–814 | ||
| | regent1 = ] | | regent1 = ] | ||
| | years1 = 781–810 | | years1 = 781–810 | ||
| | regent2 = ] | | regent2 = with ] | ||
| | years2 = |
| years2 = 810–814 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{s- |
{{s-aft | ||
| | rows = 1 | |||
| {{s-new|creation|reason=''']'''<br /><small>''] as undisputed<br>Byzantine emperor''</small>}} | |||
| | after = ] | |||
| {{s-ttl | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | years = 800–814 | |||
| | regent1 = ] | |||
| | years1 = 813–814 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{s-end}} | {{s-end}} | ||
| Line 757: | Line 502: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Line 772: | Line 513: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:44, 6 January 2025
King of the Franks, first Holy Roman Emperor For other uses, see Charlemagne (disambiguation).
| Charlemagne | |
|---|---|
 A denarius of Charlemagne dated c. 812–814 with the inscription KAROLVS IMP AVG A denarius of Charlemagne dated c. 812–814 with the inscription KAROLVS IMP AVG(Karolus Imperator Augustus) | |
| King of the Franks | |
| Reign | 9 October 768 – 28 January 814 |
| Coronation | 9 October 768 Noyon |
| Predecessor | Pepin the Short |
| Successor | Louis the Pious |
| Co-ruler | Carloman I (768–771) Charles (800–811) |
| King of the Lombards (Italy) | |
| Reign | June 774 – 28 January 814 |
| Predecessor | Desiderius |
| Successor | Bernard |
| Co-ruler | Pepin of Italy (781–810) |
| Emperor of the Carolingian Empire | |
| Reign | 25 December 800 – 28 January 814 |
| Coronation | 25 December 800 Old St. Peter's Basilica, Rome |
| Successor | Louis the Pious |
| Born | (748-04-02)2 April 748 Francia |
| Died | (814-01-28)28 January 814 Aachen, Francia |
| Burial | Aachen Cathedral |
| Spouses |
|
| Issue Among others | |
| Dynasty | Carolingian |
| Father | Pepin the Short |
| Mother | Bertrada of Laon |
| Religion | Chalcedonian Christianity |
| Signum manus | |
| Carolingian dynasty |
|---|
 |
Pippinids
|
Arnulfings
|
Carolingians
|
After the Treaty of Verdun (843)
|
Charlemagne (/ˈʃɑːrləmeɪn/ SHAR-lə-mayn; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages.
A member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. With his brother, Carloman I, he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, removing the Lombards from power in northern Italy in 774. His reign saw a period of expansion that led to the conquests of Bavaria, Saxony, and northern Spain, as well as other campaigns that led Charlemagne to extend his rule over a large part of Europe. Charlemagne spread Christianity to his new conquests (often by force), as seen at the Massacre of Verden against the Saxons. He also sent envoys and initiated diplomatic contact with the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid in the 790s, due to their mutual interest in Iberian affairs.
In 800, Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III. Although historians debate the coronation's significance, the title represented the height of his prestige and authority. Charlemagne's position as the first emperor in the West in over 300 years brought him into conflict with the Eastern Roman Empire in Constantinople. Through his assumption of the imperial title, he is considered the forerunner to the line of Holy Roman Emperors, which persisted into the nineteenth century. As king and emperor, Charlemagne engaged in a number of reforms in administration, law, education, military organisation, and religion, which shaped Europe for centuries. The stability of his reign began a period of cultural activity known as the Carolingian Renaissance.
Charlemagne died in 814 and was buried at Aachen Cathedral in Aachen, his imperial capital city. He was succeeded by his only surviving legitimate son, Louis the Pious. After Louis, the Frankish kingdom was divided and eventually coalesced into West and East Francia, which later became France and Germany, respectively. Charlemagne's profound influence on the Middle Ages and influence on the territory he ruled has led him to be called the "Father of Europe" by many historians. He is seen as a founding figure by multiple European states and a number of historical royal houses of Europe trace their lineage back to him. Charlemagne has been the subject of artworks, monuments and literature during and after the medieval period and is venerated by the Catholic Church.
Name
Several languages were spoken in Charlemagne's world, and he was known to contemporaries as Karlus in the Old High German he spoke; as Karlo to Early Old French (or Proto-Romance) speakers; and as Carolus (or Karolus) in Medieval Latin, the formal language of writing and diplomacy. Charles is the modern English form of these names. The name Charlemagne, as the emperor is normally known in English, comes from the French Charles-le-magne ('Charles the Great'). In modern German, he is known as Karl der Große. The Latin epithet magnus ('great') may have been associated with him during his lifetime, but this is not certain. The contemporary Royal Frankish Annals routinely call him Carolus magnus rex ("Charles the great king"). That epithet is attested in the works of the Poeta Saxo around 900, and it had become commonly applied to him by 1000.
Charlemagne was named after his grandfather, Charles Martel. That name, and its derivatives, are unattested before their use by Charles Martel and Charlemagne. Karolus was adapted by Slavic languages as their word for "king" (Russian: korol', Polish: król and Slovak: král) through Charlemagne's influence or that of his great-grandson, Charles the Fat.
Early life and rise to power
Political background and ancestry

By the sixth century, the western Germanic tribe of the Franks had been Christianised; this was due in considerable measure to the conversion of their king, Clovis I, to Catholicism. The Franks had established a kingdom in Gaul in the wake of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire. This kingdom, Francia, grew to encompass nearly all of present-day France and Switzerland, along with parts of modern Germany and the Low Countries under the rule of the Merovingian dynasty. Francia was often divided under different Merovingian kings, due to the partible inheritance practised by the Franks. The late seventh century saw a period of war and instability following the murder of King Childeric II, which led to factional struggles among the Frankish aristocrats.
Pepin of Herstal, mayor of the palace of Austrasia, ended the strife between various kings and their mayors with his 687 victory at the Battle of Tertry. Pepin was the grandson of two important figures of Austrasia: Arnulf of Metz and Pepin of Landen. The mayors of the palace had gained influence as the Merovingian kings' power waned due to divisions of the kingdom and several succession crises. Pepin was eventually succeeded by his son Charles, later known as Charles Martel. Charles did not support a Merovingian successor upon the death of King Theuderic IV in 737, leaving the throne vacant. He made plans to divide the kingdom between his sons, Carloman and Pepin the Short, who succeeded him after his death in 741. The brothers placed the Merovingian Childeric III on the throne in 743. Pepin married Bertrada, a member of an influential Austrasian noble family, in 744. In 747, Carloman abdicated and entered a monastery in Rome. He had at least two sons; the elder, Drogo, took his place.
Birth
Charlemagne's year of birth is uncertain, although it was most likely in 748. An older tradition based on three sources, however, gives a birth year of 742. The ninth-century biographer Einhard reports Charlemagne as being 72 years old at the time of his death; the Royal Frankish Annals imprecisely gives his age at death as about 71, and his original epitaph called him a septuagenarian. Einhard said that he did not know much about Charlemagne's early life; some modern scholars believe that, not knowing the emperor's true age, he still sought to present an exact date in keeping with the Roman imperial biographies of Suetonius, which he used as a model. All three sources may have been influenced by Psalm 90: "The days of our years are threescore years and ten".
Historian Karl Ferdinand Werner challenged the acceptance of 742 as the Frankish king's birth year, citing an addition to the Annales Petaviani which records Charlemagne's birth in 747. Lorsch Abbey commemorated Charlemagne's date of birth as 2 April from the mid-ninth century, and this date is likely to be genuine. Matthias Becher built on Werner's work and showed that 2 April in the year recorded would have actually been in 748, since the annalists recorded the start of the year from Easter rather than 1 January. Presently, most scholars accept April 748 for Charlemagne's birth. Charlemagne's place of birth is unknown. The Frankish palaces in Vaires-sur-Marne and Quierzy are among the places suggested by scholars. Pepin the Short held an assembly in Düren in 748, but it cannot be proved that it took place in April or if Bertrada was with him.
Language and education

Einhard refers to Charlemagne's patrius sermo ("native tongue"). Most scholars have identified this as a form of Old High German, probably a Rhenish Franconian dialect. Due to the prevalence in Francia of "rustic Roman", he was probably functionally bilingual in Germanic and Romance dialects at an early age. Charlemagne also spoke Latin and, according to Einhard, could understand and (perhaps) speak some Greek.
Charlemagne's father Pepin had been educated at the abbey of Saint-Denis, although the extent of Charlemagne's formal education is unknown. He almost certainly was trained in military matters as a youth in Pepin's court, which was itinerant. Charlemagne also asserted his own education in the liberal arts in encouraging their study by his children and others, although it is unknown whether his study was as a child or at court during his later life. The question of Charlemagne's literacy is debated, with little direct evidence from contemporary sources. He normally had texts read aloud to him and dictated responses and decrees, but this was not unusual even for a literate ruler at the time. Historian Johannes Fried considers it likely that Charlemagne would have been able to read, but the medievalist Paul Dutton writes that "the evidence for his ability to read is circumstantial and inferential at best" and concludes that it is likely that he never properly mastered the skill. Einhard makes no direct mention of Charlemagne reading, and recorded that he only attempted to learn to write later in life.
Accession and reign with Carloman
There are only occasional references to Charlemagne in the Frankish annals during his father's lifetime. By 751 or 752, Pepin had deposed Childeric and replaced him as king. Early Carolingian-influenced sources claim that Pepin's seizure of the throne was sanctioned beforehand by Pope Stephen II, but modern historians dispute this. It is possible that papal approval came only when Stephen travelled to Francia in 754 (apparently to request Pepin's aid against the Lombards), and on this trip anointed Pepin as king; this legitimised his rule. Charlemagne was sent to greet and escort the Pope, and he and his younger brother Carloman were anointed with their father. Pepin sidelined Drogo around the same time, sending him and his brother to a monastery.
Charlemagne began issuing charters in his own name in 760. The following year, he joined his father's campaign against Aquitaine. Aquitaine, led by Dukes Hunald and Waiofar, was constantly in rebellion during Pepin's reign. Pepin fell ill on campaign there and died on 24 September 768, and Charlemagne and Carloman succeeded their father. They had separate coronations, Charlemagne at Noyon and Carloman at Soissons, on 9 October. The brothers maintained separate palaces and spheres of influence, although they were considered joint rulers of a single Frankish kingdom. The Royal Frankish Annals report that Charlemagne ruled Austrasia and Carloman ruled Burgundy, Provence, Aquitaine, and Alamannia, with no mention made of which brother received Neustria. The immediate concern of the brothers was the ongoing uprising in Aquitaine. They marched into Aquitaine together, but Carloman returned to Francia for unknown reasons and Charlemagne completed the campaign on his own. Charlemagne's capture of Duke Hunald marked the end of ten years of war that had been waged in the attempt to bring Aquitaine into line.
Carloman's refusal to participate in the war against Aquitaine led to a rift between the kings. It is uncertain why Carloman abandoned the campaign; the brothers may have disagreed about control of the territory, or Carloman was focused on securing his rule in the north of Francia. Regardless of the strife between the kings, they maintained a joint rule for practical reasons. Charlemagne and Carloman worked to obtain the support of the clergy and local elites to solidify their positions.
Pope Stephen III was elected in 768, but was briefly deposed by Antipope Constantine II before being restored to Rome. Stephen's papacy experienced continuing factional struggles, so he sought support from the Frankish kings. Both brothers sent troops to Rome, each hoping to exert his own influence. The Lombard king Desiderius also had interests in Roman affairs, and Charlemagne attempted to enlist him as an ally. Desiderius already had alliances with Bavaria and Benevento through the marriages of his daughters to their dukes, and an alliance with Charlemagne would add to his influence. Charlemagne's mother, Bertrada, went on his behalf to Lombardy in 770 and brokered a marriage alliance before returning to Francia with his new bride. Desiderius's daughter is traditionally known as Desiderata, although she may have been named Gerperga. Anxious about the prospect of a Frankish–Lombard alliance, Pope Stephen sent a letter to both Frankish kings decrying the marriage and separately sought closer ties with Carloman.
Charlemagne had already had a relationship with the Frankish noblewoman Himiltrude, and they had a son in 769 named Pepin. Paul the Deacon wrote in his 784 Gesta Episcoporum Mettensium that Pepin was born "before legal marriage", but does not say whether Charles and Himiltrude ever married, were joined in a non-canonical marriage (friedelehe), or married after Pepin was born. Pope Stephen's letter described the relationship as a legitimate marriage, but he had a vested interest in preventing Charlemagne from marrying Desiderius's daughter.
Carloman died suddenly on 4 December 771, leaving Charlemagne sole king of the Franks. He moved immediately to secure his hold on his brother's territory, forcing Carloman's widow Gerberga to flee to Desiderius's court in Lombardy with their children. Charlemagne ended his marriage to Desiderius's daughter and married Hildegard, daughter of count Gerold, a powerful magnate in Carloman's kingdom. This was a reaction to Desiderius's sheltering of Carloman's family and a move to secure Gerold's support.
King of the Franks and the Lombards
Annexation of the Lombard Kingdom
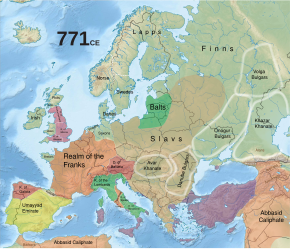
Charlemagne's first campaigning season as sole king of the Franks was spent on the eastern frontier in his first war against the Saxons, who had been engaging in border raids on the Frankish kingdom when Charlemagne responded by destroying the pagan Irminsul at Eresburg and seizing their gold and silver. The success of the war helped secure Charlemagne's reputation among his brother's former supporters and funded further military action. The campaign was the beginning of over thirty years of nearly-continuous warfare against the Saxons by Charlemagne.
Pope Adrian I succeeded Stephen III in 772, and sought the return of papal control of cities that had been captured by Desiderius. Unsuccessful in dealing with the Lombard king directly, Adrian sent emissaries to Charlemagne to gain his support for recovering papal territory. Charlemagne, in response to this appeal and the dynastic threat of Carloman's sons in the Lombard court, gathered his forces to intervene. He first sought a diplomatic solution, offering gold to Desiderius in exchange for the return of the papal territories and his nephews. This overture was rejected, and Charlemagne's army (commanded by himself and his uncle, Bernard) crossed the Alps to besiege the Lombard capital of Pavia in late 773.
Charlemagne's second son (also named Charles) was born in 772, and Charlemagne brought the child and his wife to the camp at Pavia. Hildegard was pregnant, and gave birth to a daughter named Adelhaid. The baby was sent back to Francia, but died on the way. Charlemagne left Bernard to maintain the siege at Pavia while he took a force to capture Verona, where Desiderius's son Adalgis had taken Carloman's sons. Charlemagne captured the city; no further record exists of his nephews or of Carloman's wife, and their fate is unknown. Recent biographer, Janet Nelson compares them to the Princes in the Tower in the Wars of the Roses. Fried suggests that the boys were forced into a monastery (a common solution of dynastic issues), or "an act of murder smooth Charlemagne's ascent to power." Adalgis was not captured by Charlemagne, and fled to Constantinople.

Charlemagne left the siege in April 774 to celebrate Easter in Rome. Pope Adrian arranged a formal welcome for the Frankish king, and they swore oaths to each other over the relics of St. Peter. Adrian presented a copy of the agreement between Pepin and Stephen III outlining the papal lands and rights Pepin had agreed to protect and restore. It is unclear which lands and rights the agreement involved, which remained a point of dispute for centuries. Charlemagne placed a copy of the agreement in the chapel above St. Peter's tomb as a symbol of his commitment, and left Rome to continue the siege.
Disease struck the Lombards shortly after his return to Pavia, and they surrendered the city by June 774. Charlemagne deposed Desiderius and took the title of King of the Lombards. The takeover of one kingdom by another was "extraordinary", and the authors of The Carolingian World call it "without parallel". Charlemagne secured the support of the Lombard nobles and Italian urban elites to seize power in a mainly-peaceful annexation. Historian Rosamond McKitterick suggests that the elective nature of the Lombard monarchy eased Charlemagne's takeover, and Roger Collins attributes the easy conquest to the Lombard elite's "presupposition that rightful authority was in the hands of the one powerful enough to seize it". Charlemagne soon returned to Francia with the Lombard royal treasury and with Desiderius and his family, who would be confined to a monastery for the rest of their lives.
Frontier wars in Saxony and Spain

The Saxons took advantage of Charlemagne's absence in Italy to raid the Frankish borderlands, leading to a Frankish counter-raid in the autumn of 774 and a reprisal campaign the following year. Charlemagne was soon drawn back to Italy as Duke Hrodgaud of Friuli rebelled against him. He quickly crushed the rebellion, distributing Hrodgaud's lands to the Franks to consolidate his rule in Lombardy. Charlemagne wintered in Italy, consolidating his power by issuing charters and legislation and taking Lombard hostages. Amid the 775 Saxon and Friulian campaigns, his daughter Rotrude was born in Francia.
Returning north, Charlemagne waged another brief, destructive campaign against the Saxons in 776. This led to the submission of many Saxons, who turned over captives and lands and submitted to baptism. In 777, Charlemagne held an assembly at Paderborn with Frankish and Saxon men; many more Saxons came under his rule, but the Saxon magnate Widukind fled to Denmark to prepare for a new rebellion.
Also at the Paderborn assembly were representatives of dissident factions from al-Andalus (Muslim Spain). They included the son and son-in-law of Yusuf ibn Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri, the former governor of Córdoba ousted by Caliph Abd al-Rahman in 756, who sought Charlemagne's support for al-Fihri's restoration. Also present was Sulayman al-Arabi, governor of Barcelona and Girona, who wanted to become part of the Frankish kingdom and receive Charlemagne's protection rather than remain under the rule of Córdoba. Charlemagne, seeing an opportunity to strengthen the security of the kingdom's southern frontier and extend his influence, agreed to intervene. Crossing the Pyrenees, his army found little resistance until an ambush by Basque forces in 778 at the Battle of Roncevaux Pass. The Franks, defeated in the battle, withdrew with most of their army intact.
Building the dynasty

Charlemagne returned to Francia to greet his newborn twin sons, Louis and Lothair, who were born while he was in Spain; Lothair died in infancy. Again, Saxons had seized on the king's absence to raid. Charlemagne sent an army to Saxony in 779 while he held assemblies, legislated, and addressed a famine in Francia. Hildegard gave birth to another daughter, Bertha. Charlemagne returned to Saxony in 780, holding assemblies at which he received hostages from Saxon nobles and oversaw their baptism.
He and Hildegard travelled with their four younger children to Rome in the spring of 781, leaving Pepin and Charles at Worms, to make a journey first requested by Adrian in 775. Adrian baptised Carloman and renamed him Pepin, a name he shared with his half-brother. Louis and the newly renamed Pepin were then anointed and crowned. Pepin was appointed king of the Lombards, and Louis king of Aquitaine. This act was not nominal, since the young kings were sent to live in their kingdoms under the care of regents and advisers. A delegation from the Byzantine Empire, the remnant of the Roman Empire in the East, met Charlemagne during his stay in Rome; Charlemagne agreed to betroth his daughter Rotrude to Empress Irene's son, Emperor Constantine VI.
Hildegard gave birth to her eighth child, Gisela, during this trip to Italy. After the royal family's return to Francia, she had her final pregnancy and died from its complications on 30 April 783. The child, named after her, died shortly thereafter. Charlemagne commissioned epitaphs for his wife and daughter, and arranged for a Mass to be said daily at Hildegard's tomb. Charlemagne's mother Bertrada died shortly after Hildegard, on 12 July 783. Charlemagne was remarried to Fastrada, daughter of the East Frankish count Radolf, by the end of the year.
Saxon resistance and reprisal
In summer 782, Widukind returned from Denmark to attack the Frankish positions in Saxony. He defeated a Frankish army, possibly due to rivalry among the Frankish counts leading it. Charlemagne came to Verden after learning of the defeat, but Widukind fled before his arrival. Charlemagne summoned the Saxon magnates to an assembly and compelled them to turn prisoners over to him, since he regarded their previous acts as treachery. The annals record that Charlemagne had 4,500 Saxon prisoners beheaded in the massacre of Verden. Fried writes, "Although this figure may be exaggerated, the basic truth of the event is not in doubt", and Alessandro Barbero calls it "perhaps the greatest stain on his reputation." Charlemagne issued the Capitulatio de partibus Saxoniae, probably in the immediate aftermath of (or as a precursor of) the massacre. With a harsh set of laws which included the death penalty for pagan practices, the Capitulatio "constituted a program for the forced conversion of the Saxons" and was "aimed ... at suppressing Saxon identity".
Charlemagne's focus for the next several years would be on his attempt to complete the subjugation of the Saxons. Concentrating first in Westphalia in 783, he pushed into Thuringia in 784 as his son Charles the Younger continued operations in the west. At each stage of the campaigns, the Frankish armies seized wealth and carried Saxon captives into slavery. Unusually, Charlemagne campaigned through the winter instead of resting his army. By 785, he had suppressed the Saxon resistance and completely commanded Westphalia. That summer, he met Widukind and persuaded him to end his resistance. Widukind agreed to be baptised with Charlemagne as his godfather, ending this phase of the Saxon Wars.
Benevento, Bavaria, and Pepin's revolt
Charlemagne travelled to Italy in 786, arriving by Christmas. Aiming to extend his influence further into southern Italy, he marched into the Duchy of Benevento. Duke Arechis fled to a fortified position at Salerno before offering Charlemagne his fealty. Charlemagne accepted his submission and hostages, who included Arechis's son Grimoald. In Italy, Charlemagne also met with envoys from Constantinople. Empress Irene had called the 787 Second Council of Nicaea, but did not inform Charlemagne or invite any Frankish bishops. Charlemagne, probably in reaction to the perceived slight of the exclusion, broke the betrothal of his daughter Rotrude and Constantine VI.

After Charlemagne left Italy, Arechis sent envoys to Irene to offer an alliance; he suggested that she send a Byzantine army with Adalgis, the exiled son of Desiderus, to remove the Franks from power in Lombardy. Before his plans could be finalised, Aldechis and his elder son Romuald died of illness within weeks of each other. Charlemagne sent Grimoald back to Benevento to serve as duke and return it to Frankish suzerainty. The Byzantine army invaded, but were repulsed by the Frankish and Lombard forces.
As affairs were being settled in Italy, Charlemagne turned his attention to Bavaria. Bavaria was ruled by Duke Tassilo, Charlemagne's first cousin, who had been installed by Pepin the Short in 748. Tassilo's sons were also grandsons of Desiderius, and a potential threat to Charlemagne's rule in Lombardy. The neighbouring rulers had a growing rivalry throughout their reigns, but had sworn oaths of peace to each other in 781. In 784, Rotpert (Charlemagne's viceroy in Italy) accused Tassilo of conspiring with Widukind in Saxony and unsuccessfully attacked the Bavarian city of Bolzano. Charlemagne gathered his forces to prepare for an invasion of Bavaria in 787. Dividing the army, the Franks launched a three-pronged attack. Quickly realizing his poor position, Tassilo agreed to surrender and recognise Charlemagne as his overlord. The following year, Tassilo was accused of plotting with the Avars to attack Charlemagne. He was deposed and sent to a monastery, and Charlemagne absorbed Bavaria into his kingdom. Charlemagne spent the next few years based in Regensburg, largely focused on consolidating his rule of Bavaria and warring against the Avars. Successful campaigns against them were launched from Bavaria and Italy in 788, and Charlemagne led campaigns in 791 and 792.
Charlemagne gave Charles the Younger rule of Maine in Neustria in 789, leaving Pepin the Hunchback his only son without lands. His relationship with Himiltrude was now apparently seen as illegitimate at his court, and Pepin was sidelined from the succession. In 792, as his father and brothers were gathered in Regensburg, Pepin conspired with Bavarian nobles to assassinate them and install himself as king. The plot was discovered and revealed to Charlemagne before it could proceed; Pepin was sent to a monastery, and many of his co-conspirators were executed.
The early 790s saw a marked focus on ecclesiastical affairs by Charlemagne. He summoned a council in Regensburg in 792 to address the theological controversy over the adoptionism doctrine in the Spanish church and formulate a response to the Second Council of Nicea. The council condemned adoptionism as heresy and led to the production of the Libri Carolini, a detailed argument against Nicea's canons. In 794, Charlemagne called another council in Frankfurt. The council confirmed Regensburg's positions on adoptionism and Nicea, recognised the deposition of Tassilo, set grain prices, reformed Frankish coinage, forbade abbesses from blessing men, and endorsed prayer in vernacular languages. Soon after the council, Fastrada fell ill and died; Charlemagne married the Alamannian noblewoman Luitgard shortly afterwards.
Continued wars with the Saxons and Avars
Charlemagne gathered an army after the council of Frankfurt as Saxon resistance continued, beginning a series of annual campaigns which lasted through 799. The campaigns of the 790s were even more destructive than those of earlier decades, with the annal writers frequently noting Charlemagne "burning", "ravaging", "devastating", and "laying waste" the Saxon lands. Charlemagne forcibly removed a large number of Saxons to Francia, installing Frankish elites and soldiers in their place. His extended wars in Saxony led to his establishing his court in Aachen, which had easy access to the frontier. He built a large palace there, including a chapel which is now part of the Aachen Cathedral. Einhard joined the court at that time. Pepin of Italy (Carloman) engaged in further wars against the Avars in the south, which led to the collapse of their kingdom and the eastward expansion of Frankish rule.
Charlemagne also worked to expand his influence through diplomatic means during the 790s wars, focusing on the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Britain. Charles the Younger proposed a marriage pact with the daughter of King Offa of Mercia, but Offa insisted that Charlemagne's daughter Bertha also be given as a bride for his son. Charlemagne refused the arrangement, and the marriage did not take place. Charlemagne and Offa entered into a formal peace in 796, protecting trade and securing the rights of English pilgrims to pass through Francia on their way to Rome. Charlemagne was also the host and protector of several deposed English rulers who were later restored: Eadbehrt of Kent, Ecgberht, King of Wessex, and Eardwulf of Northumbria. Nelson writes that Charlemagne treated the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms "like satellite states," establishing direct relations with English bishops. Charlemagne also forged an alliance with Alfonso II of Asturias, although Einhard calls Alfonso his "dependent". Following his sack of Lisbon in 798, Alfonso sent Charlemagne trophies of his victory, including armour, mules and prisoners.
Reign as emperor
Coronation
After Leo III became pope in 795, he faced political opposition. His enemies accused him of a number of crimes and physically attacked him in April 799, attempting to remove his eyes and tongue. Leo escaped and fled north to seek Charlemagne's help. Charlemagne continued his campaign against the Saxons before breaking off to meet Leo at Paderborn in September. Hearing evidence from the pope and his enemies, he sent Leo back to Rome with royal legates who were instructed to reinstate the pope and conduct a further investigation. In August of the following year, Charlemagne made plans to go to Rome after an extensive tour of his lands in Neustria. Charlemagne met Leo in November near Mentana at the twelfth milestone outside Rome, the traditional location where Roman emperors began their formal entry into the city. Charlemagne presided over an assembly to hear the charges, but believed that no one could sit in judgement of the pope. Leo swore an oath on 23 December, declaring his innocence of all charges. At mass in St. Peter's Basilica on Christmas Day 800, Leo proclaimed Charlemagne "emperor of the Romans" (Imperator Romanorum) and crowned him. Charlemagne was the first reigning emperor in the west since the deposition of Romulus Augustulus in 476. His son, Charles the Younger, was anointed king by Leo at the same time.

Historians differ about the intentions of the imperial coronation, the extent to which Charlemagne was aware of it or participated in its planning, and the significance of the events for those present and for Charlemagne's reign. Contemporary Frankish and papal sources differ in their emphasis on, and representation of, events. Einhard writes that Charlemagne would not have entered the church if he knew about the pope's plan; modern historians have regarded his report as truthful or rejected it as a literary device demonstrating Charlemagne's humility. Collins says that the actions surrounding the coronation indicate that it was planned by Charlemagne as early as his meeting with Leo in 799, and Fried writes that Charlemagne planned to adopt the title of emperor by 798 "at the latest." During the years before the coronation, Charlemagne's courtier Alcuin referred to his realm as an Imperium Christianum ("Christian Empire") in which "just as the inhabitants of the Roman Empire had been united by a common Roman citizenship", the new empire would be united by a common Christian faith. This is the view of Henri Pirenne, who says that "Charles was the Emperor of the ecclesia as the Pope conceived it, of the Roman Church, regarded as the universal Church".
The Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire remained a significant contemporary power in European politics for Leo and Charlemagne, especially in Italy. The Byzantines continued to hold a substantial portion of Italy, with their borders not far south of Rome. Empress Irene had seized the throne from her son Constantine VI in 797, deposing and blinding him. Irene, the first Byzantine empress, faced opposition in Constantinople because of her gender and her means of accession. One of the earliest narrative sources for the coronation, the Annals of Lorsch, presented a female ruler in Constantinople as a vacancy in the imperial title which justified Leo's coronation of Charlemagne. Pirenne disagrees, saying that the coronation "was not in any sense explained by the fact that at this moment a woman was reigning in Constantinople." Leo's main motivations may have been the desire to increase his standing after his political difficulties, placing himself as a power broker and securing Charlemagne as a powerful ally and protector. The Byzantine Empire's lack of ability to influence events in Italy and support the papacy were also important to Leo's position. According to the Royal Frankish Annals, Leo prostrated himself before Charlemagne after crowning him (an act of submission standard in Roman coronation rituals from the time of Diocletian). This account presents Leo not as Charlemagne's superior, but as the agent of the Roman people who acclaimed Charlemagne as emperor.
Historian Henry Mayr-Harting claims that the assumption of the imperial title by Charlemagne was an effort to incorporate the Saxons into the Frankish realm, since they did not have a native tradition of kingship. However, Costambeys et al. note in The Carolingian World that "since Saxony had not been in the Roman empire it is hard to see on what basis an emperor would have been any more welcomed." These authors write that the decision to take the title of emperor was aimed at furthering Charlemagne's influence in Italy, as an appeal to traditional authority recognised by Italian elites within and (especially) outside his control.
Collins also writes that becoming emperor gave Charlemagne "the right to try to impose his rule over the whole of ", considering this a motivation for the coronation. He notes the "element of political and military risk" inherent in the affair due to the opposition of the Byzantine Empire and potential opposition from the Frankish elite, as the imperial title could draw him further into Mediterranean politics. Collins sees several of Charlemagne's actions as attempts to ensure that his new title had a distinctly-Frankish context.
Charlemagne's coronation led to a centuries-long ideological conflict between his successors and Constantinople known as the problem of two emperors, which could be seen as a rejection or usurpation of the Byzantine emperors' claim to be the universal, preeminent rulers of Christendom. Historian James Muldoon writes that Charlemagne may have had a more limited view of his role, seeing the title as representing dominion over lands he already ruled. However, the title of emperor gave Charlemagne enhanced prestige and ideological authority. He immediately incorporated his new title into documents he issued, adopting the formula "Charles, most serene augustus, crowned by God, great peaceful emperor governing the Roman empire, and who is by the mercy of God king of the Franks and the Lombards" instead of the earlier form "Charles, by the grace of God king of the Franks and Lombards and patrician of the Romans." Leo acclaimed Charlemagne as "emperor of the Romans" during the coronation, but Charlemagne never used this title. The avoidance of the specific claim of being a "Roman emperor", as opposed to the more-neutral "emperor governing the Roman empire", may have been to improve relations with the Byzantines. This formulation (with the continuation of his earlier royal titles) may also represent a view of his role as emperor as being the ruler of the people of the city of Rome, as he was of the Franks and the Lombards.
Governing the empire

Charlemagne left Italy in the summer of 801 after adjudicating several ecclesiastical disputes in Rome and experiencing an earthquake in Spoleto. He never returned to the city. Continuing trends and a ruling style established in the 790s, Charlemagne's reign from 801 onward is a "distinct phase" characterised by more sedentary rule from Aachen. Although conflict continued until the end of his reign, the relative peace of the imperial period allowed for attention on internal governance. The Franks continued to wage war, though these wars were defending and securing the empire's frontiers, and Charlemagne rarely led armies personally. A significant expansion of the Spanish March was achieved with a series of campaigns by Louis against the Emirate of Cordoba, culminating in the 801 capture of Barcelona.
The 802 Capitulare missorum generale was an expansive piece of legislation, with provisions governing the conduct of royal officials and requiring that all free men take an oath of loyalty to Charlemagne. The capitulary reformed the institution of the missi dominici, officials who would now be assigned in pairs (a cleric and a lay aristocrat) to administer justice and oversee governance in defined territories. The emperor also ordered the revision of the Lombard and Frankish legal codes.
In addition to the missi, Charlemagne also ruled parts of the empire with his sons as sub-kings. Although Pepin and Louis had some authority as kings in Italy and Aquitaine, Charlemagne had the ultimate authority and directly intervened. Charles, their elder brother, had been given lands in Neustria in 789 or 790 and made a king in 800.
The 806 charter Divisio Regnorum (Division of the Realm) set the terms of Charlemagne's succession. Charles, as his eldest son in good favour, was given the largest share of the inheritance: rule of Francia, Saxony, Nordgau, and parts of Alemannia. The two younger sons were confirmed in their kingdoms and gained additional territories; most of Bavaria and Alemmannia was given to Pepin, and Provence, Septimania, and parts of Burgundy were given to Louis. Charlemagne did not address the inheritance of the imperial title. The Divisio also provided that if any of the brothers predeceased Charlemagne, their sons would inherit their share; peace was urged among his descendants.
Conflict and diplomacy with the east

After his coronation, Charlemagne sought recognition of his imperial title from Constantinople. Several delegations were exchanged between Charlemagne and Irene in 802 and 803. According to the contemporary Byzantine chronicler Thophanes, Charlemagne made an offer of marriage to Irene which she was close to accepting. Irene was deposed and replaced by Nikephoros I, who was unwilling to recognise Charlemagne as emperor. The two empires conflicted over control of the Adriatic Sea (especially Istria and Veneto) several times during Nikephoros' reign. Charlemagne sent envoys to Constantinople in 810 to make peace, giving up his claims to Veneto. Nikephoros died in battle before the envoys could leave Constantinople but his son-in-law and successor Michael I confirmed the peace, sending his own envoys to Aachen to recognise Charlemagne as emperor. Charlemagne soon issued the first Frankish coins bearing his imperial title, although papal coins minted in Rome had used the title as early as 800.
He sent envoys and initiated diplomatic contact with the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid during the 790s, due to their mutual interest in Spanish affairs. As an early sign of friendship, Charlemagne requested an elephant as a gift from Harun. Harun later provided an elephant named Abul-Abbas, which arrived at Aachen in 802. Harun also sought to undermine Charlemagne's relations with the Byzantines, with whom he was at war. As part of his outreach, Harun gave Charlemagne nominal rule of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem and other gifts. According to Einhard, Charlemagne "zealously strove to make friendships with kings beyond the seas" in order "that he might get some help and relief to the Christians living under their rule." A surviving administrative document, the Basel roll, shows the work done by his agents in Palestine in furtherance of this goal.
Harun's death lead to a succession crisis and, under his successors, churches and synagogues were destroyed in the caliphate. Unable to intervene directly, Charlemagne sent specially-minted coins and arms to the eastern Christians to defend and restore their churches and monasteries. The coins with their inscriptions were also an important tool of imperial propaganda. Johannes Fried writes that deteriorating relations with Baghdad after Harun's death may have been the impetus for renewed negotiations with Constantinople which led to Charlemagne's peace with Michael in 811.
As emperor, Charlemagne became involved in a religious dispute between Eastern and Western Christians over the recitation of the Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed, the fundamental statement of orthodox Christian belief. The original text of the creed, adopted at the Council of Constantinople, professed that the Holy Spirit proceeded from the Father. A tradition developed in Western Europe that the Holy Spirit proceeded from the Father "and the Son", inserting the Latin term filioque into the creed. The difference did not cause significant conflict until 807, when Frankish monks in Bethlehem were denounced as heretics by a Greek monk for using the filioque form. The Frankish monks appealed the dispute to Rome, where Pope Leo affirmed the text of the creed omitting the phrase and passed the report on to Charlemagne. Charlemagne summoned a council at Aachen in 809 which defended the use of filioque, and sent the decision to Rome. Leo said that the Franks could maintain their tradition, but asserted that the canonical creed did not include filioque. He commissioned two silver shields with the creed in Latin and Greek (omitting the filioque), which he hung in St. Peter's Basilica. Another product of the 809 Aachen council was the Handbook of 809, an illustrated calendrical and astronomical compendium.
Wars with the Danes
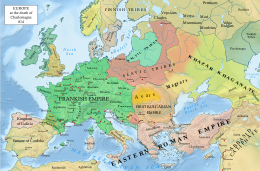
Scandinavia had been brought into contact with the Frankish world through Charlemagne's wars with the Saxons. Raids on Charlemagne's lands by the Danes began around 800. Charlemagne engaged in his final campaign in Saxony in 804, seizing Saxon territory east of the Elbe, removing its Saxon population, and giving the land to his Obotrite allies. The Danish king Gudfred, uneasy at the extension of Frankish power, offered to meet with Charlemagne to arrange peace and (possibly) hand over Saxons who had fled to him; the talks were unsuccessful.
The northern frontier was quiet until 808, when Gudfred and some allied Slavic tribes led an incursion into the Obotrite lands and extracted tribute from over half the territory. Charles the Younger led an army across the Elbe in response, but only attacked some of Gudfred's Slavic allies. Gudfred again attempted diplomatic overtures in 809, but no peace was apparently made. Danish pirates raided Frisia in 810, although it is uncertain if they were connected to Gudfred. Charlemagne sent an army to secure Frisia while he led a force against Gudfred, who had reportedly challenged the emperor to face him in battle. The battle never took place, since Gudfred was murdered by two of his own men before Charlemagne's arrival. Gudfred's nephew and successor Hemming immediately sued for peace, and a commission led by Charlemagne's cousin Wala reached a settlement with the Danes in 811. The Danes did not pose a threat for the remainder of Charlemagne's reign, but the effects of this war and their earlier expansion in Saxony helped set the stage for the intense Viking raids across Europe later in the ninth century.
Final years and death

The Carolingian dynasty experienced a number of losses in 810 and 811, when Charlemagne's sister Gisela, his daughter Rotrude, and his sons Pepin the Hunchback, Pepin of Italy, and Charles the Younger died. The deaths of Charles and Pepin of Italy left Charlemagne's earlier plans for succession in disarray. He declared Pepin of Italy's son Bernard ruler of Italy and made his own only surviving son, Louis, heir to the rest of the empire. Charlemagne also made a new will detailing the disposal of his property at his death, with bequests to the church, his children, and his grandchildren. Einhard (possibly relying on tropes from Suetonius's The Twelve Caesars) says that Charlemagne viewed the deaths of his family members, his fall from a horse, astronomical phenomena, and the collapse of part of the palace in his last years as signs of his impending death. Charlemagne continued to govern with energy during his final year, ordering bishops to assemble in five ecclesiastical councils. These culminated in a large assembly at Aachen, where Charlemagne crowned Louis as his co-emperor and Bernard as king in a ceremony on 11 September 813.
Charlemagne became ill in the autumn of 813 and spent his last months praying, fasting, and studying the gospels. He developed pleurisy, and was bedridden for seven days before dying on the morning of 28 January 814. Thegan, a biographer of Louis, records the emperor's last words as "Into your hands, Lord, I commend my spirit" (quoting from Luke 23:46). Charlemagne's body was prepared and buried in the chapel at Aachen by his daughters and palace officials that day. Louis arrived at Aachen thirty days after his father's death, making a formal adventus and taking charge of the palace and the empire. Charlemagne's remains were exhumed by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1165, and reinterred in a new casket by Frederick II in 1215.
 The Proserpina sarcophagus in which Charlemagne is thought to have been originally buried
The Proserpina sarcophagus in which Charlemagne is thought to have been originally buried The Karlsschrein, in which Frederick II reinterred Charlemagne in 1215
The Karlsschrein, in which Frederick II reinterred Charlemagne in 1215
Legacy
Political legacy

The stability and peace of Charlemagne's reign did not long outlive him. Louis' reign was marked by strife, including a number of rebellions by his sons. After Louis' death, the empire was divided among his sons into West, East, and Middle Francia by the Treaty of Verdun. Middle Francia was divided several more times over the course of subsequent generations. Carolingians would rule – with some interruptions – in East Francia (later the Kingdom of Germany) until 911, and in West Francia (which would become France) until 987. After 887, the imperial title was held sporadically by a series of non-dynastic Italian rulers before it lapsed in 924. The East Frankish king Otto the Great conquered Italy, and was crowned emperor in 962. By this time, the eastern and western parts of Charlemagne's former empire had already developed distinct languages and cultures. Otto founded (or re-established) the Holy Roman Empire, which would last until its dissolution in 1806, during the Napoleonic Wars.
According to historian Jennifer Davis, Charlemagne "invented medieval rulership" and his influence can be seen at least into the nineteenth century. Charlemagne is often known as "the father of Europe" because of the influence of his reign and the legacy he left across the large area of the continent. The political structures he established remained in place through his Carolingian successors, and continued to exert influence into the eleventh century.
Charlemagne was an ancestor of several European ruling houses, including the Capetian dynasty, the Ottonian dynasty, the House of Luxembourg, and the House of Ivrea. The Ottonians and Capetians, direct successors of the Carolingans, drew on the legacy of Charlemagne to bolster their legitimacy and prestige; the Ottonians and their successors held their German coronations in Aachen through the Middle Ages. The marriage of Philip II of France to Isabella of Hainault (a direct descendant of Charlemagne) was seen as a sign of increased legitimacy for their son, Louis VIII, and the French kings' association with Charlemagne's legacy was stressed until the monarchy's end. German and French rulers, such as Frederick Barbarossa and Napoleon, cited the influence of Charlemagne and associated themselves with him. Both German and French monarchs considered themselves as successors of Charlemagne, enumerating him as "Charles I" in their regnal lists.
The city of Aachen has, since 1949, awarded an international prize (the Karlspreis der Stadt Aachen) in honour of Charlemagne. It is awarded annually to those who promote European unity. Recipients of the prize include Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi (founder of the pan-European movement), Alcide De Gasperi, and Winston Churchill.
Carolingian Renaissance
Contacts with the wider Mediterranean world through Spain and Italy, the influx of foreign scholars at court, and the relative stability and length of Charlemagne's reign led to a cultural revival known as the Carolingian Renaissance. Although the beginnings of this revival can be seen under his predecessors, Charles Martel and Pepin, Charlemagne took an active and direct role in shaping intellectual life which led to the revival's zenith. Charlemagne promoted learning as a matter of policy and direct patronage, with the aim of creating a more effective clergy. The Admonitio generalis and Epistola de litteris colendis outlined his policies and aims for education.
Intellectual life at court was dominated by Irish, Anglo-Saxon, Visigothic and Italian scholars, including Dungal of Bobbio, Alcuin of York, Theodulf of Orléans, and Peter of Pisa; Franks such as Einhard and Angelbert also made substantial contributions. Aside from the intellectual activity at the palace, Charlemagne promoted ecclesiastical schools and publicly funded schools for the children of the elite and future clergy. Students learned basic Latin literacy and grammar, arithmetic, and other subjects of the medieval liberal arts. From their education, it was expected that even rural priests could provide their parishioners with basic instruction in religious matters and (possibly) the literacy required for worship. Latin was standardised and its use brought into territories well beyond the former Roman Empire, forming a second language community of speakers and writers and sustaining Latin creativity in the Middle Ages.
Carolingian authors produced extensive works, including legal treatises, histories, poetry, and religious texts. Scriptoria in monasteries and cathedrals focused on copying new and old works, producing an estimated 90,000 manuscripts during the ninth century. The Carolingian minuscule script was developed and popularised in medieval copying, influencing Renaissance and modern typefaces. Scholar John J. Contreni considers the educational and learning revival under Charlemagne and his successors "one of the most durable and resilient elements of the Carolingian legacy".
Memory and historiography
Charlemagne was a frequent subject of, and inspiration for, medieval writers after his death. Einhard's Vita Karoli Magni, according to Johannes Fired, "can be said to have revived the defunct literary genre of the secular biography." Einhard drew on classical sources, such as Suetonius' The Twelve Caesars, the orations of Cicero, and Tacitus' Agricola to frame his work's structure and style. The Carolingian period also saw a revival of the mirrors for princes genre. The author of the Latin poem Visio Karoli Magni, written c. 865, uses facts (apparently from Einhard) and his own observations on the decline of Charlemagne's family after their civil wars later in the ninth century as the bases of a visionary tale about Charles meeting a prophetic spectre in a dream. Notker's Gesta Karoli Magni, written for Charlemagne's great-grandson Charles the Fat, presents moral anecdotes (exempla) to highlight the emperor's qualities as a ruler.

Charlemagne, as a figure of myth and emulation, grew over the centuries; Matthias Becher writes that over 1,000 legends are recorded about him, far outstripping subsequent emperors and kings. Later medieval writers depicted Charlemagne as a crusader and Christian warrior. Charlemagne is the main figure of the medieval literary cycle known as the Matter of France. Works in this cycle, which originated during the Crusades, centre on characterisations of the emperor as a leader of Christian knights in wars against Muslims. The cycle includes chansons de geste (epic poems) such as the Song of Roland and chronicles such as the Historia Caroli Magni, also known as the (Pseudo-)Turpin Chronicle. Charlemagne was depicted as one of the Nine Worthies, a fixture in medieval literature and art as an exemplar of a Christian king. Despite his central role in these legends, author Thomas Bulfinch noted that "romancers represent him as often weak and passionate, the victim of treacherous counsellors, and at the mercy of turbulent barons, on whose prowess he depends for the maintenance of his throne."
Attention to Charlemagne became more scholarly in the early modern period as Eindhard's Vita and other sources began to be published. Political philosophers debated his legacy; Montesquieu viewed him as the first constitutional monarch and protector of freemen, but Voltaire saw him as a despotic ruler and representative of the medieval period as a Dark Age. As early as the sixteenth century, debate between German and French writers began about Charlemagne's "nationality". These contrasting portraits—a French Charlemagne versus a German Karl der Große—became especially pronounced during the nineteenth century with Napoleon's use of Charlemagne's legacy and the rise of German nationalism. German historiography and popular perception focused on the Massacre of Verden, emphasised with Charlemagne as the "butcher" of the Germanic Saxons or downplayed as an unfortunate part of the legacy of a great German ruler. Propaganda in Nazi Germany initially portrayed Charlemagne as an enemy of Germany, a French ruler who worked to take away the freedom and native religion of the German people. This quickly shifted as Adolf Hitler endorsed a portrait of Charlemagne as a great unifier of disparate German tribes into a common nation, allowing Hitler to co-opt Charlemagne's legacy as an ideological model for his expansionist policies.
Historiography after World War II focused on Charlemagne as "the father of Europe" rather than a nationalistic figure, a view first advanced during the nineteenth century by German romantic philosopher Friedrich Schlegel. This view has led to Charlemagne's adoption as a political symbol of European integration. Modern historians increasingly place Charlemagne in the context of the wider Mediterranean world, following the work of Henri Pirenne.
Religious influence and veneration
Further information: Charlemagne and church music
Charlemagne gave much attention to religious and ecclesiastical affairs, holding 23 synods during his reign. His synods were called to address specific issues at particular times, but generally dealt with church administration and organisation, education of the clergy, and the proper forms of liturgy and worship. Charlemagne used the Christian faith as a unifying factor in the realm and, in turn, worked to impose unity on the church. He implemented an edited version of the Dionysio-Hadriana book of canon law acquired from Pope Adrian, required use of the Rule of St. Benedict in monasteries throughout the empire, and promoted a standardised liturgy adapted from the rites of the Roman Church to conform with Frankish practices. Carolingian policies promoting unity did not eliminate the diverse practices throughout the empire, but created a shared ecclesiastical identity—according to Rosamond McKitterick, "unison, not unity."
The condition of all his subjects as a "Christian people" was an important concern. Charlemagne's policies encouraged preaching to the laity, particularly in vernacular languages they would understand. He believed it essential to be able to recite the Lord's Prayer and the Apostles' Creed, and made efforts to ensure that the clergy taught them and other basics of Christian morality.
Thomas F. X. Noble writes that the efforts of Charlemagne and his successors to standardise Christian doctrine and practices and harmonise Frankish practices were essential steps in the development of Christianity in Europe, and the Roman Catholic or Latin Church "as a historical phenomenon, not as a theological or ecclesiological one, is a Carolingian construction." He says that the medieval European concept of Christendom as an overarching community of Western Christians, rather than a collection of local traditions, is the result of Carolingian policies and ideology. Charlemagne's doctrinal policies promoting the use of filioque and opposing the Second Council of Nicea were key steps in the growing divide between Western and Eastern Christianity.
Emperor Otto II attempted to have Charlemagne canonised in 1000. In 1165, Frederick Barbarossa persuaded Antipope Paschal III to elevate Charlemagne to sainthood. Since Paschal's acts were not considered valid, Charlemagne was not recognised as a saint by the Holy See. Despite this lack of official recognition, his cult was observed in Aachen, Reims, Frankfurt, Zurich and Regensburg, and he has been venerated in France since the reign of Charles V.
Charlemagne also drew attention from figures of the Protestant Reformation, with Martin Luther criticising his apparent subjugation to the papacy by accepting his coronation from Leo. John Calvin and other Protestant thinkers viewed him as a forerunner of the Reformation, however, noting the Libri Carolini's condemnation of the worship of images and relics and conflicts by Charlemagne and his successors with the temporal power of the popes.
Wives, concubines, and children
Further information: Carolingian dynasty|
Wives and their children
|
Concubines and their children
|

Charlemagne had at least twenty children with his wives and other partners. After the death of his wife Luitgard in 800, he did not remarry, but had children with unmarried partners. He was determined that all his children, including his daughters, should receive an education in the liberal arts. His children were taught in accordance with their aristocratic status, which included training in riding and weaponry for his sons, and embroidery, spinning and weaving for his daughters.
Rosamond McKitterick writes that Charlemagne exercised "a remarkable degree of patriarchal control ... over his progeny," noting that only a handful of his children and grandchildren were raised outside his court. Pepin of Italy and Louis reigned as kings from childhood and lived at their courts. Careers in the church were arranged for his illegitimate sons. His daughters were resident at court or at Chelles Abbey (where Charlemagne's sister was abbess), and those at court may have fulfilled the duties of queen after 800.
Louis and Pepin of Italy married and had children during their father's lifetime, and Charlemagne brought Pepin's daughters into his household after Pepin's death. Rotrude had been betrothed to Emperor Constantine VI, but the betrothal was ended. None of Charlemagne's daughters married, although several had children with unmarried partners. Bertha had two sons, Nithard and Hartnid, with Charlemagne's courtier Angilbert; Rotrude had a son named Louis, possibly with Count Rorgon; and Hiltrude had a son named Richbod, possibly with a count named Richwin. The Divisio Regnorum issued by Charlemagne in 806 provided that his legitimate daughters be allowed to marry or become nuns after his death. Theodrada entered a convent, but the decisions of his other daughters are unknown.
Appearance and iconography
Further information: Iconography of Charlemagne
 Top: Carolingian-era equestrian statuette depicting Charlemagne or Charles the Bald. Bottom: Bust of Charlemagne, an idealised portrayal and reliquary said to contain Charlemagne's skull cap, produced in the 14th century.
Top: Carolingian-era equestrian statuette depicting Charlemagne or Charles the Bald. Bottom: Bust of Charlemagne, an idealised portrayal and reliquary said to contain Charlemagne's skull cap, produced in the 14th century.
Einhard gives a first-hand description of Charlemagne's appearance later in life:
He was heavily built, sturdy, and of considerable stature, although not exceptionally so, since his height was seven times the length of his own foot. He had a round head, large and lively eyes, a slightly larger nose than usual, white but still attractive hair, a bright and cheerful expression, a short and fat neck, and he enjoyed good health, except for the fevers that affected him in the last few years of his life.
Charlemagne's tomb was opened in 1861 by scientists who reconstructed his skeleton and measured it at 1.92 metres (6 ft 4 in) in length, roughly equivalent to Einhard's seven feet. A 2010 estimate of his height from an X-ray and CT scan of his tibia was 1.84 metres (6 ft 0 in); this puts him in the 99th percentile of height for his period, given that average male height of his time was 1.69 metres (5 ft 7 in). The width of the bone suggested that he was slim.
Charlemagne wore his hair short, abandoning the Merovingian tradition of long-haired monarchs. He had a moustache (possibly imitating the Ostrogothic king Theoderic the Great), in contrast with the bearded Merovingian kings; future Carolingian monarchs would adopt this style. Paul Dutton notes the ubiquitous crown in portraits of Charlemagne and other Carolingian rulers, replacing the earlier Merovingian long hair. A ninth-century statuette depicts Charlemagne or his grandson, Charles the Bald and shows the subject as moustachioed with short hair; this also appears on contemporary coinage.
By the twelfth century, Charlemagne was described as bearded rather than moustachioed in literary sources such as the Song of Roland, the Pseudo-Turpin Chronicle, and other works in Latin, French, and German. The Pseudo-Turpin uniquely says that his hair was brown. Later art and iconography of Charlemagne followed suit, generally depicting him in a later medieval style as bearded with longer hair.
Notes
- ^ Alternative birth years for Charlemagne include 742 and 747. There has been scholarly debate over this topic, see Birth and early life. For full treatment of the debate, see Nelson 2019, pp. 28–29. See further Karl Ferdinand Werner, Das Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen, in Francia 1, 1973, pp. 115–157 (online Archived 17 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine);
Matthias Becher: Neue Überlegungen zum Geburtsdatum Karls des Großen, in: Francia 19/1, 1992, pp. 37–60 (online Archived 17 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine) - "At 747 the scribe had written: 'Et ipso anno fuit natus Karolus rex' ('and in that year, King Charles was born')."
- Historian Johannes Fried writes that "Comparisons with other images allow us to interpret it as a sketch of an ancient emperor or king, or even of Charlemagne himself. However sketchy and unaccomplished the drawing is, its message and its moral could not be clearer: the ruler appears here as a powerful protector, guarding the Church with his weapons and—as the following text emphasises—restoring it according to the dictates of the faith and the Church Fathers in preparation for the impending end time."
- Charlemagne's third son (Carloman) was also born in 776, based on the four-year-old's 780 baptism in Pavia.
- The Latin title imperator, meaning "commander", used to denote successful generals in ancient Rome, but eventually came to denote the position of Augustus and his successors. In German, the title was rendered as kaiser, after Caesar. In Greek, it was rendered as autokrator and used alongside the traditional title of basileus. For a discussion of Charlemagne's title and Constantinople's reaction, see Sarti 2024, pp. 7–39.
- German: Zweikaiserproblem, "two-emperors problem"
- Latin: Karolus serenissimus augustus a deo coronatus magnus pacificus imperator Romanum gubernans imperium, qui et per misercordiam dei rex francorum atque langobardorum
- Latin: Carolus gratia dei rex francorum et langobardorum ac patricius Romanorum
- For more on the Basel roll, see McCormick 2011.
- Through Beatrice of Vermandois, great-great granddaughter of Pepin of Italy and grandmother of Hugh Capet,
- Through Hedwiga, great-great granddaughter of Louis the Pious and mother of Henry the Fowler
- Through Albert II, Count of Namur, great-grandson of Louis IV of France and great-great-grandfather of Henry the Blind
- Berengar II of Italy was a great-great-great grandson of Louis the Pious. The House of Ivrea later came to rule Spain and intermarried with the Habsburgs and the royal families of Portugal.
- The nature of Himiltrude's relationship to Charlemagne is uncertain. A 770 letter by Pope Stephen III describes both Carloman and Charlemagne "by will and decision...joined in lawful marriage... wives of great beauty from the same fatherland as yourselves." Stephen wrote this in the context of attempting to dissuade either king from entering into a marriage alliance with Desiderius. By 784, at Charlemagne's court, Paul the Deacon wrote that their son Pepin was born "before legal marriage", but whether he means Charles and Himiltrude were never married, were joined in a non-canonical marriage or friedelehe, or if they married after Pepin was born is unclear. Roger Collins, Johannes Fried, and Janet Nelson all portray Himiltrude as a wife of Charlemagne in some capacity. Fried also dates the beginning of their relationship to 763 or even earlier.
- Janet Nelson considers it a depiction of Charlemagne; Paul Dutton says that it was "long thought to depict Charlemagne and now attributed by most to Charles the Bald," and Johannes Fried presents both as possibilities but considers it "highly contentious."
References
Citations
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 116.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 2, 68.
- Nelson 2019, p. 2.
- Fried 2016, p. 529.
- Barbero 2004, p. 413.
- Fried 2016, p. 4.
- Becher 2005, pp. 42–43.
- Nonn 2008, p. 575.
- Fried 2016, p. 5.
- Waldman & Mason 2006, pp. 270, 274–275.
- Heather 2009, pp. 305–306.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 35.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 35–37.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 38.
- Frassetto 2003, p. 292.
- Frassetto 2003, pp. 292–293.
- Nelson 2019, p. 16.
- Waldman & Mason 2006, p. 271.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 65.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 51–52.
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 71.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 61–65.
- Fried 2016, p. 17.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 55.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 29.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 56.
- Fried 2016, p. 15.
- Collins 1998, p. 32.
- Barbero 2004, p. 11.
- Becher 2005, p. 41.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 28–28.
- Hägermann 2011, p. xxx.
- Barbero 2004, p. 350 n7.
- Nelson 2019, p. 28.
- Barbero 2004, p. 12.
- Fried 2016, pp. 15–16.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 68.
- Hägermann 2011, p. xxxiii.
- Fried 2016, pp. 262–263.
- Chambers & Wilkie 2014, p. 33.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 318.
- Fried 2016, p. 24.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 71–72.
- ^ Dutton 2016, p. 72.
- Fried 2016, pp. 14–15.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 75–80.
- Fried 2016, p. 271.
- Dutton 2016, p. 75.
- Dutton 2016, p. 91.
- Collins 1998, p. 120.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 73.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 71–72.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 32.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 34.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 72.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 72–73.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 62.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 74.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 64.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 75.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 91.
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 77.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 65.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 79.
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 80.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 81.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 82.
- Nelson 2019, p. 99.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 99, 101.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 100–101.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 101.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 84–85, 101.
- Nelson 2019, p. 106.
- Nelson 2007, p. 31.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 104–106.
- ^ Goffart 1986.
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 84.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 87.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 108–109.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 66.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 109–110.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 89.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 110–111.
- Fried 2016, p. 99.
- Nelson 2019, p. 116.
- Fried 2016, p. 122.
- Nelson 2019, p. 117.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 117–118.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 131–132.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 133.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 133, 134.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 134–135.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 67.
- Nelson 2019, p. 130.
- Fried 2016, p. 100.
- Nelson 2019, p. 146.
- Fried 2016, p. 101.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 135–138.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 139–140.
- Fried 2016, p. 112.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 139–141.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 142–144.
- Collins 1998, pp. 61–63.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 62.
- Nelson 2019, p. 147.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 109.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 147–148.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 154–156.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 157–159.
- Nelson 2019, p. 159.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 159–161.
- Nelson 2019, p. 157.
- ^ Fried 2016, p. 136.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 162–163.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 164–165.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 164–166.
- Nelson 2019, p. 166.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 167–170, 173.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 168, 172.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 181.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 172–173.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 175–179.
- Nelson 2019, p. 173.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 182–186.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 186.
- Nelson 2019, p. 191.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 182–183.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 203.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 204–205.
- Nelson 2019, p. 205.
- Nelson 2019, p. 193.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 193–195.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 195–196.
- Fried 2016, p. 126.
- Barbero 2004, p. 46.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 196–197.
- Barbero 2004, p. 47.
- Nelson 2019, p. 197.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 200–202.
- Collins 1998, p. 55.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 208–209.
- Fried 2016, pp. 139–140.
- Nelson 2019, p. 228.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 225–226, 230.
- Nelson 2019, p. 234.
- Fried 2016, p. 142.
- Nelson 2019, p. 240.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 240–241.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 186–187.
- Fried 2016, p. 152.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 188–190.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 213–214.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 243–244.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 251–254.
- Nelson 2019, p. 294.
- Nelson 2019, p. 257.
- Fried 2016, p. 157.
- Nelson 2019, p. 270.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 270, 274–275.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 285–287, 438.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 283–284.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 289–292.
- Nelson 2019, p. 302.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 306–314.
- Nelson 2019, p. 304.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 340, 377–379.
- Riché 1993, p. 135.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 319–321.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 323–324.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 325–326, 329–331.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 356–359.
- Nelson 2019, p. 340.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 326, 333.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 270–271.
- Fried 2016, p. 83.
- Fried 2016, pp. 84–85.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 352, 400, 460.
- Fried 2016, p. 466.
- Nelson 2019, p. 353.
- Collins 1998, p. 74.
- Reuter 1985, p. 85.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 160.
- Collins 1998, p. 152.
- ^ McKitterick 2008, p. 115.
- Collins 1998, p. 143.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 161.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 145.
- Nelson 2019, p. 381.
- Hornblower 2012, p. 728.
- ^ Heather 2009, p. 368.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 96.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 161, 163, 165.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 165–166.
- Collins 1998, p. 147.
- Fried 2016, p. 408.
- Collins 1998, p. 151.
- Pirenne 2012, p. 233.
- Nelson 2019, p. 361.
- Nelson 2019, p. 370.
- Nelson 2019, p. 384.
- Pirenne 2012, p. 234n.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 167.
- Muldoon 1999, p. 24.
- Mayr-Harting 1996.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 148.
- Collins 1998, p. 149.
- Collins 1998, pp. 150–151.
- Muldoon 1999, p. 21.
- Muldoon 1999, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 168.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 115–116.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 382, 385.
- ^ Muldoon 1999, p. 26.
- Sarti 2024, pp. 7–39.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 168–169.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 387–389.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 173–174.
- Nelson 2019, p. 472.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 170.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 462.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 169.
- Collins 1998, pp. 74–75.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 495–496.
- Ganshof 1965.
- Fried 2016, pp. 450–451.
- Fried 2016, pp. 448–449.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 409, 411.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 410–415.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 157.
- Nelson 2019, p. 429.
- Fried 2016, p. 477.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 432–435.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 167–168.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 153.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 458–459.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 116–117.
- Dutton 2016, p. 60.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 60–61.
- Fried 2016, p. 441.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 449–452.
- Fried 2016, p. 442.
- Fried 2016, pp. 442–446.
- Fried 2016, p. 444.
- ^ Nelson 2019, p. 449.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 449–450.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 452–453.
- Sterk 1988.
- Fried 2016, pp. 488–490.
- Fried 2016, p. 461.
- ^ Collins 1998, p. 167.
- Collins 1998, p. 163.
- ^ Fried 2016, p. 462.
- Fried 2016, pp. 462–463.
- Nelson 2019, p. 459.
- Collins 1998, p. 168.
- ^ Fried 2016, p. 463.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 171.
- Collins 1998, p. 170.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 440, 453.
- Collins 1998, p. 158.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 468–470.
- ^ Nelson 2019, pp. 480–481.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 478–480.
- Nelson 2019, p. 476.
- Fried 2016, p. 514.
- Nelson 2019, p. 481.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 482–483.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 483–484.
- Fried 2016, p. 520.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 379–381.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. 394.
- Riché 1993, p. 278.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 424–427.
- Arnold 1997, p. 83.
- Heather 2009, p. 369.
- Scales 2012, pp. 155–182.
- Davies 1996, pp. 316–317.
- Davis 2015, p. 434.
- Freeman 2017, p. 19.
- Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, pp. 407, 432.
- Lewis 1977, pp. 246–247, n 94.
- Jackman 2010, pp. 9–12.
- Tanner 2004, pp. 263–265.
- Bouchard 2010, pp. 129–131.
- Fried 2016, p. 528.
- Fried 2016, pp. 527–528.
- ^ Davis 2015, p. 433.
- Williams 1885, pp. 446–47.
- "Laureates".
- Contreni 1984, p. 60.
- Contreni 1984, pp. 59, 61, 64.
- Contreni 1995, p. 709.
- Contreni 1984, p. 64.
- Contreni 1984, pp. 61, 68.
- Contreni 1984, pp. 65–66.
- Contreni 1984, pp. 66–67.
- Contreni 1995, p. 715.
- Leonhardt 2016, pp. 160–162.
- Contreni 1995, pp. 748–756.
- Contreni 1984, pp. 70.
- Contreni 1995, p. 711.
- ^ Contreni 1984, p. 73.
- Fried 2016, p. 277.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 15–20.
- Fried 2016, pp. 518–519.
- Geary 1987, pp. 275–283.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 20.
- ^ Becher 2005, p. 138.
- ^ Fried 2016, p. 539.
- Hardman & Ailes 2017, pp. 1–9.
- Kuskin 1999, pp. 513, 547–548 fn24.
- Bulfinch 1864, pp. xxii–xxiv.
- Becher 2005, p. 142–144.
- ^ Becher 2005, p. 144.
- Becher 2005, p. 142.
- Becher 2005, p. 146.
- Becher 2005, pp. 146–148.
- Fried 2016, p. 541–542.
- Fried 2016, pp. 542–546.
- Becher 2005, p. 148.
- Fried 2016, p. 548.
- Fried 2016, pp. 549–551.
- Noble 2015, p. 294.
- Noble 2015, pp. 289–290, 295–296.
- McKitterick 1996, p. 61.
- Noble 2015, pp. 269–297.
- McKitterick 1996, p. 82.
- Noble 2015, pp. 287–288.
- Noble 2015, p. 294–295.
- Noble 2015, pp. 301–302.
- Noble 2015, p. 287.
- Noble 2015, pp. 306–307.
- Noble 2015, pp. 292, 306–307.
- Siecienski 2010, p. 87.
- ^ Fried 2016, p. 537.
- ^ Becher 2005, p. 143.
- Fried 2016, p. 538.
- ^ Nelson 2019, pp. xxxiv–xxxv.
- ^ Costambeys, Innes & MacLean 2011, p. xxi.
- Nelson 2019, p. 105.
- Collins 1998, p. 40.
- Fried 2016, pp. 50–51.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 91, 107, 285–286.
- Fried 2016, p. 50.
- Nelson 2019, p. 440.
- Nelson 2019, p. 443.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 93.
- McKitterick 2008, p. 91.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 94–95.
- McKitterick 2008, pp. 91–93.
- Nelson 2019, pp. 225–226.
- Nelson 2019, p. 441.
- Nelson 2019, p. 435.
- Barbero 2004, p. 116.
- Barbero 2004, p. 118.
- Ruhli, Blumich & Henneberg 2010.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 21–22.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 24–26.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 24, 26.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 22–23.
- Nelson 2019, pp. xxxvi, 495.
- ^ Dutton 2016, p. 35.
- Fried 2016, p. 216.
- Fried 2016, p. 516.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 24–25.
- Coxon 2021, pp. 31, 196.
- Coxon 2021, p. 196.
- Dutton 2016, pp. 27–30.
Works cited
- Arnold, Benjamin (1997). Medieval Germany , 500–1300 A Political Interpretation. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-3336-1091-6.
- Barbero, Alessandro (2004). Charlemagne: Father of a Continent. Translated by Allan Cameron. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-5202-3943-2.
- Becher, Matthias (2005). Charlemagne. Translated by Bachrach, David S. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-3000-9796-2.
- Bouchard, Constance (2010). Those of My Blood: Creating Noble Families in Medieval Francia. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-0140-6.
- Bulfinch, Thomas (1864). Legends of Charlemagne. Boston, J. E. Tilton and Co.
- Chambers, William Walker; Wilkie, John Ritchie (2014). A Short History of the German Language (RLE Linguistics E: Indo-European Linguistics). London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-3179-1852-3.
- Collins, Roger (1998). Charlemagne. Toronto: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-0-3336-5055-4.
- Contreni, John J. (1984), "The Carolingian Renaissance", in Treadgold, Warren T. (ed.), Renaissances before the Renaissance: Cultural Revivals of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Stanford: Stanford University Press, ISBN 0-8047-1198-4
- Contreni, John J. (1995). "The Carolingian Renaissance: Education and Literary Culture". In McKitterick, Rosamond (ed.). The New Cambridge Medieval History Volume II: c. 700–900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-1390-5571-0.
- Costambeys, Marios; Innes, Matthew; MacLean, Simon (2011). The Carolingian World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5215-6366-6.
- Coxon, Sebastian (2021). Beards and Texts: Images of Masculinity in Medieval German Literature. London: UCL Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctv1hggknc. ISBN 978-1-7873-5221-6. JSTOR j.ctv1hggknc. S2CID 239135035. Archived from the original on 11 April 2024. Retrieved 6 March 2024.
- Davies, Norman (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1982-0171-7.
- Davis, Jennifer R. (2015). Charlemagne's Practice of Empire. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-1070-7699-0.
- Dutton, Paul (2016). Charlemagne's Mustache: And Other Cultural Clusters of a Dark Age. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-1370-6228-4.
- Frassetto, Michael (2003). Encyclopedia of Barbarian Europe: Society in Transformation. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-5760-7263-9.
- Freeman, Elizabeth (2017). ""Charles the Great, or Just Plain Charles: Was Charlemagne a Great Medieval Leader?"". Agora. 52 (1): 10–19.
- Fried, Johannes (2016). Charlemagne. Translated by Lewis, Peter. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-6747-3739-6.
- Ganshof, François L. (1965). "The Impact of Charlemagne on the Institutions of the Frankish Realm". Speculum. 40 (1): 49. doi:10.2307/2856463. JSTOR 2856463. Archived from the original on 17 August 2024. Retrieved 17 August 2024.
- Geary, Patrick J. (1987). "Germanic Tradition and Royal Ideology in the Ninth Century: The Visio Karoli Magni". Frühmittelalterliche Studien. 21: 274–294. doi:10.1515/9783110242195.274. ISSN 0071-9706. S2CID 165699647.
- Goffart, Walter (1986). "Paul the Deacon's 'Gesta Episcoporum Mettensium' and the Early Design of Charlemagne's Succession". Traditio. 42: 59–93. doi:10.1017/S0362152900004049. S2CID 151941720.
- Hägermann, Dieter (2011) . Carlo Magno: Il signore dell'Occidente [Karl der Grosse: Herrscher des Abendlandes]. Translated by Giuseppe Albertoni. Arnoldo Mondadori Editore.
- Hardman, Philipa; Ailes, Marianne (2017). The Legend of Charlemagne in Medieval England. Cambridge: DS Brewer. pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-1-8438-4472-3.
- Heather, Peter (2009). Empires and Barbarians:The Fall of Rome and the birth of Europe. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1998-9226-6.
- Hornblower, Simon (2012). Oxford Classical Dictionary. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1995-4556-8.
- Jackman, Donald C. (2010). Ius hereditarium Encountered III: Ezzo's Chess Match. Editions Enlaplage. pp. 9–12. ISBN 978-1-9364-6654-2.
- Kuskin, William (1999). "Caxton's Worthies Series: The Production of Literary Culture". ELH. 66 (3): 511–551. doi:10.1353/elh.1999.0027. JSTOR 30032085. S2CID 162260451. Retrieved 2 December 2023.
- Leonhardt, Jürgen (2016) . Latin: story of a World Language. Translated by Kenneth Kronenberg. Harvard. ISBN 978-0-6746-5996-4. OL 35499574M.
- Lewis, Andrew W. (1977). "Dynastic Structures and Capetian Throne-Right: the Views of Giles of Paris". Traditio. 33 (1): 225–252. doi:10.1017/S0362152900009119. JSTOR 27831029. Archived from the original on 10 March 2024. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- Mayr-Harting, Henry (1996). "Charlemagne, the Saxons, and the Imperial Coronation of 800". The English Historical Review. 111 (444 November): 1113–1133. doi:10.1093/ehr/CXI.444.1113.
- McCormick, Michael (2011). Charlemagne's Survey of the Holy Land: Wealth, Personnel, and Buildings of a Mediterranean Church between Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection.
- McKitterick, Rosamond (1996). "Unity and Diversity in the Carolingian Church". Studies in Church History. 32: 59–82. doi:10.1017/S0424208400015333. S2CID 163254629.
- McKitterick, Rosamond (2008). Charlemagne: The Formation of a European Identity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-1394-7285-2.
- Muldoon, James (1999). Empire and Order:Concepts of Empire 800-1800. New York: St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-3122-2226-2.
- Nelson, Janet L. (2007). Courts, elites, and gendered power in the early Middle Ages Charlemagne and others. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-5933-4. OCLC 1039829293.
- Nelson, Janet L. (2019). King and Emperor: A New Life of Charlemagne. Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-5203-1420-7.
- Noble, Thomas F. X. (2015). "Carolingian Religion". Church History. 84 (2): 287–307. doi:10.1017/S0009640715000104. S2CID 231888268.
- Nonn, Ulrich (2008). "Karl Martell – Name und Beiname". In Ludwig, Uwe; Schlipp, Thomas (eds.). Nomen et Fraternitas. Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde – Ergänzungsbände. Vol. 62. Berlin, New York: DeGruyter. pp. 575–586. doi:10.1515/9783110210477.3.575. ISBN 978-3-1102-0238-0. Archived from the original on 23 January 2024. Retrieved 29 January 2024.
- Pirenne, Henri (2012) . Mohammed and Charlemagne. Mineola, NY: Dover. ISBN 978-0-4861-2225-0.
- Reuter, Timothy (1985). "Plunder and Tribute in the Carolingian Empire". Transactions of the Royal Historical Society. Fifth Series. 35: 75–94. doi:10.1017/S0080440100017710 (inactive 2 January 2025). JSTOR 3679177.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2025 (link) - Riché, Pierre (1993). The Carolingians: A Family Who Forged Europe. Middle Ages Series. Translated by Allen, Michael Idomir. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-1096-5.
- Ruhli, F.J.; Blumich, B.; Henneberg, M. (2010). "Charlemagne was very tall, but not robust". Economics and Human Biology. 8 (2): 289–290. doi:10.1016/j.ehb.2009.12.005. PMID 20153271.
- Sarti, Laury (2024). Orbis Romanus: Byzantium and the Legacy of Rome in the Carolingian World. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-774654-7. Archived from the original on 3 September 2024. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- Scales, Len (2012). The Shaping of German Identity: Authority and Crisis. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521573337.
- Siecienski, Anthony Edward (2010). The Filioque: History of a Doctrinal Controversy. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1953-7204-5.
- Sterk, Andrea (1 October 1988). "The Silver Shields of Pope Leo III: A Reassessment of the Evidence". Comitatus: A Journal of Medieval and Renaissance Studies. 19: 62–79. Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- Tanner, Heather (2004). Families, Friends and Allies: Boulogne and Politics in Northern France and England. Brill. ISBN 978-9-0474-0255-8.
- Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2006). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. New York: Facts on File. ISBN 978-0-8160-4964-6.
- Williams, J.D. (1885). Chambers's New Handy Volume American Encyclopædia. Vol. 3. Arundel. pp. 446–7.
Further reading
Primary sources in English translation
- Alcuin (1941). The Rhetoric of Alcuin and Charlemagne: A Translation, with an Introduction, the Latin Text, and Notes. Translated by Howell, Wilbur Samuel. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Alcuin (1974). Alcott, Stephen (ed.). Alcuin of York, c. AD 732 to 804: His life and letters. Translated by Alcott, Stephen. York: Sessions Book Trust. ISBN 0-9006-5721-9.
- Bachrach, Bernard S., ed. (1973). Liber Historiae Francorum. Translated by Bachrach, Bernard S. Lawrence, KS: Coronodo Press. ISBN 978-0-8729-1058-4.
- Davis, Raymond, ed. (1992). The Lives of the Eighth-Century Popes. Translated by Davis, Raymond. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. ISBN 978-0-8532-3018-2.
- Einhard; Notker (1969). Two Lives of Charlemagne. Translated by Thorpe, Lewis. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-1404-4213-7.
- Einhard (1998). Dutton, Paul (ed.). Charlemagne's Courtier: The Complete Einhard. Readings in Medieval Civilizations and Cultures. Translated by Dutton, Paul. Petersborough, ON: Broadview Press. ISBN 1-5511-1134-9.
- Dutton, Paul, ed. (2004). Carolingian Civilization: A Reader. Petersborough, ON: Broadview Press. ISBN 978-1-5511-1492-7.
- Goodman, Peter, ed. (1985). Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance. Translated by Goodman, Peter. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-1939-7.
- King, P.D., ed. (1997). Charlemagne: Translated Sources. Translated by King, P.D. Lancaster: P.D. King. ISBN 978-0-9511-5030-6.
- McKitterick, Rosamond; van Espelo, Dorine; Pollard, Richard; Price, Richard, eds. (2021). Codex Epistolaris Carolinus: Letters from the popes to the Frankish rulers, 739–791. Translated by McKitterick, Rosamond; van Espelo, Dorine; Pollard, Richard; Price, Richard. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. ISBN 978-1-8003-4871-4.
- Lyon, H.R.; Percival, John, eds. (1975). The Reign of Charlemagne: Documents on Carolingian Government and Administration. Documents of Medieval History. Translated by Lyon, H.R.; Percival, John. London: Arnold. ISBN 978-0-7131-5813-7.
- Scholz, Bernhard Walter; Rogers, Barbara, eds. (1970). Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories. Translated by Scholz, Bernhard Walter; Rogers, Barbara. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-4720-8790-7.
Secondary works
- Bachrach, Bernard S. (2011). Early Carolingian Warfare Prelude to Empire. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-2144-2.
- Cantor, Norman F. (2015). Civilization of the Middle Ages: A Completely Revised and Expanded Edition. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-0624-4460-8.
- Collins, Roger (1999). Early Medieval Europe, 300–1000. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-3336-5808-6.
- Collins, Roger (2004). Visigothic Spain, 409–711. History of Spain. Malden, MA; Oxford: Blackwell Pub.
- Fouracre, Paul (2005). "The Long Shadow of the Merovingians". In Joanna Story (ed.). Charlemagne: Empire and Society. Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0-7190-7089-1.
- Ganshof, F. L. (1971). The Carolingians and the Frankish Monarchy: Studies in Carolingian History. trans. Janet Sondheimer. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-0635-5.
- Gregory, Timothy E. (2005). A History of Byzantium. Malden, MA; Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-0-6312-3513-2.
- James, David; Ibn al-Qūṭiyya, Muḥammad b ʻUmar (2009). Early Islamic Spain: The History of Ibn al-Qūṭiyya: a study of the unique Arabic manuscript in the Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris, with a translation, notes and comments. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-4154-7552-5.
- Lewers Langston, Aileen; Buck, J. Orton Jr., eds. (1974). Pedigrees of Some of the Emperor Charlemagne's Descendants. Baltimore: Genealogical Pub. Co.
- McKitterick, Rosamond (1983). The Frankish Kingdoms under the Carolingians, 751–987. London: Logman. ISBN 978-0-5824-9005-5.
- McKitterick, Rosamond, ed. (1995). The New Cambridge Medieval History. Vol. II: c. 700–900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-1390-5571-0.
- Riché, Pierre (1978). Daily Life in the World of Charlemagne. Middle Ages Series. Translated by McNamara, Jo Ann. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-1342-3.
- Santosuosso, Antonio (2004). Barbarians, Marauders, and Infidels: The Ways of Medieval Warfare. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-8133-9153-3.
- Sarti, Laury (2016). "Frankish Romanness and Charlemagne's Empire". Speculum. 91 (4): 1040–58. doi:10.1086/687993. S2CID 163283337.
- Sypeck, Jeff (2006). Becoming Charlemagne: Europe, Baghdad, and The Empires of A.D. 800. New York: Ecco/HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-0607-9706-5.
External links
- The Making of Charlemagne's Europe (freely available database of prosopographical and socio-economic data from legal documents dating to Charlemagne's reign, produced by King's College London)
- Internet Medieval Sourcebook, a collection of primary sources of Charlemagne's reign edited by Paul Halsall of Fordham University
- Einhard. "Vita Karoli Magni". Medieval Latin (in Latin). The Latin Library.
- Works by or about Charlemagne at the Internet Archive
- An interactive map of Charlemagne's travels
| Emperor Charles I the GreatCarolingian dynasty Died: 28 January 814 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byPepin the Short | King of the Franks 768–814 with Carloman I (768–771) with Charles the Younger (800–811) |
Succeeded byLouis the Pious |
| New creation Problem of two emperors Constantine VI as undisputed Byzantine emperor |
Holy Roman Emperor 800–814 with Louis the Pious (813–814) | |
| Preceded byDesiderius | King of the Lombards 774–814 with Pepin of Italy (781–810) with Bernard of Italy (810–814) |
Succeeded byBernard of Italy |
| Holy Roman emperors | |
|---|---|
| |
| Kings of Italy between 476 and 1556 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Non-dynastic |  | |
| Ostrogoths | ||
| Lombards |
| |
| Carolingians | ||
| Non-dynastic (title disputed 887–933) | ||
| Kingdom of Italy within the Holy Roman Empire (962–1556) |
| |
| Monarchs of France | |
|---|---|
| Merovingians (509–751) | |
| Carolingians, Robertians and Bosonids (751–987) | |
| House of Capet (987–1328) | |
| House of Valois (1328–1589) | |
| House of Lancaster (1422–1453) | |
| House of Bourbon (1589–1792) | |
| House of Bonaparte (1804–1814; 1815) | |
| House of Bourbon (1814–1815; 1815–1830) | |
| House of Orléans (1830–1848) | |
| House of Bonaparte (1852–1870) | |
| Debatable or disputed rulers are in italics. | |
| King Charlemagne and the Matter of France | |
|---|---|
| Key people | |
| Paladins and other characters |
|
| Horses and other animals | |
| Swords and other objects | |
| Places | |
| Chansons de geste and other works | |
| Pippinids, Arnulfings and Carolingians | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legend: → ≡ "father of", · ≡ "brother of" Begga, the daughter of Pepin I, married Ansegisel, the son of Arnulf of Metz, and was the mother of Pepin II. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pippinids |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Arnulfings |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Early Carolingians |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Carolingian Empire |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| West Francia |
| ||||||||||||||||||
- Charlemagne
- 740s births
- 814 deaths
- 8th-century dukes of Bavaria
- 8th-century Frankish kings
- 8th-century Lombard monarchs
- 9th-century dukes of Bavaria
- 9th-century Holy Roman Emperors
- 9th-century kings of Italy
- Carolingian dynasty
- Characters in The Song of Roland
- Frankish Christian royal saints
- Deaths from respiratory disease
- Founding monarchs
- Frankish warriors
- French bibliophiles
- French Christians
- German bibliophiles
- German Christians
- Matter of France
- Medieval history of the Low Countries
- People of ancient Roman descent



