| Revision as of 10:49, 7 March 2024 editMinden500 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users926 edits Citation← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:36, 19 January 2025 edit undoJingiby (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Rollbackers62,567 editsm Reverted edit by 46.126.48.65 (talk) to last version by JingibyTag: Rollback | ||
| (58 intermediate revisions by 30 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description| |
{{Short description|none}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see ] --> | ||
| {{Cleanup|reason=Refs must be updated and using the same format and language.|date=September 2019}} | {{Cleanup|reason=Refs must be updated and using the same format and language.|date=September 2019}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2021}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2021}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| | official = German, French, Italian, Romansh | | official = German, French, Italian, Romansh | ||
| | national = {{ublist| | | national = {{ublist| | ||
| {{legend|#F7C7B5|] 62. |
{{legend|#F7C7B5|] 62.3%|outline=gray}}| | ||
| {{legend|#D9D4E9|] 22. |
{{legend|#D9D4E9|] 22.6%|outline=gray}}| | ||
| {{legend|#B6DDC7|] 8. |
{{legend|#B6DDC7|] 8.0%|outline=gray}}| | ||
| {{legend|#FFFCC8|] 0.5%|outline=gray}}}} | {{legend|#FFFCC8|] 0.5%|outline=gray}}}} | ||
| | vernacular = ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | | vernacular = ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | ||
| | immigrant = {{ublist|] 5.4%|] 3.7%|] 2 |
| immigrant = {{ublist|] 5.4%|] 3.7%|] 3.2%|] 2.5%|] 2.4%|others 7.7%}} | ||
| | foreign = ]<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1111/j.1083-6101.2003.tb00359.x |title=Language Choice on a Swiss Mailing List |date=2006 |last1=Durham |first1=Mercedes |journal=Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication |volume=9 }}</ref> | |||
| | sign = ], ], ]<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090410065554/http://www.vpod-ticino.ch/Articoli/Leggi_articolo.php?art_id=202 |date=10 April 2009 }}</ref> | | sign = ], ], ]<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090410065554/http://www.vpod-ticino.ch/Articoli/Leggi_articolo.php?art_id=202 |date=10 April 2009 }}</ref> | ||
| | keyboard = ] | | keyboard = ] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Culture of Switzerland}} | {{Culture of Switzerland}} | ||
| The four national '''languages of |
The four national '''languages of Switzerland''' are ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a4.html |title=SR 101 The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation of 18 April 1999 (Status as of 12 February 2017): Art. 4 National languages |date=12 February 2017 |publisher=The Federal Council |location=Berne, Switzerland |website=The portal of the Swiss government |type=Federal Law collection |access-date=13 June 2017 |archive-date=23 October 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141023100747/http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a4.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> German, French, and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the ] of the ], while Romansh is used in dealings with people who speak it.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.admin.ch/opc/de/classified-compilation/20062545/index.html#a5 |title=SR 441.1 Bundesgesetz über die Landessprachen und die Verständigung zwischen den Sprachgemeinschaften (Sprachengesetz, SpG) vom 5. Oktober 2007 (Stand am 1. Januar 2017): Art. 5 Amtssprachen |date=1 January 2017 |website=The portal of the Swiss government |publisher=The Federal Council |location=Berne, Switzerland |language=de, fr, it, rm |type=Federal Law collection |access-date=13 June 2017}} | ||
| </ref> ] is occasionally used in some formal contexts, particularly to denote the country (''Confoederatio Helvetica)''.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.dailyresearch.co.uk/business/languages-of-instruction-in-switzerland/43/|title=Languages of instruction in Switzerland - Daily Research|website=www.dailyresearch.co.uk|publisher=Daily Research|access-date=January 20, 2022|archive-date=21 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220521220409/https://www.dailyresearch.co.uk/business/languages-of-instruction-in-switzerland/43/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | </ref> ] is occasionally used in some formal contexts, particularly to denote the country (''Confoederatio Helvetica)''.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.dailyresearch.co.uk/business/languages-of-instruction-in-switzerland/43/|title=Languages of instruction in Switzerland - Daily Research|website=www.dailyresearch.co.uk|publisher=Daily Research|access-date=January 20, 2022|archive-date=21 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220521220409/https://www.dailyresearch.co.uk/business/languages-of-instruction-in-switzerland/43/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
| In 2020, 62.3% of the population of Switzerland were native speakers of German (either ] or ]) at home; 22.8% French (mostly ], but including some ] ]s); 8% Italian (mostly ], but including ]); and 0.5% Romansh.<ref name="Languages_2020">{{Cite web |last= |first= |title=Languages |url=https://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/en/home/statistiken/bevoelkerung/sprachen-religionen/sprachen.html |access-date=2022-07-07 |website=Office Federal Statistical |language=en}}</ref> The German region (''Deutschschweiz'') is roughly in the east, north, and centre; the French part (''la Romandie'') in the west; and the Italian area (''Svizzera italiana'') in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in ] in the east. The cantons of ], ], and ] are officially bilingual; ] is officially trilingual. | In 2020, 62.3% of the population of Switzerland were native speakers of German (either ] or ]) at home; 22.8% French (mostly ], but including some ] ]s); 8% Italian (mostly ], but including ]); and 0.5% Romansh.<ref name="Languages_2020">{{Cite web |last= |first= |title=Languages |url=https://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/en/home/statistiken/bevoelkerung/sprachen-religionen/sprachen.html |access-date=2022-07-07 |website=Office Federal Statistical |language=en}}</ref> The German region (''Deutschschweiz'') is roughly in the east, north, and centre; the French part (''la Romandie'') in the west; and the Italian area (''Svizzera italiana'') in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in ] in the east. The cantons of ], ], and ] are officially bilingual; ] is officially trilingual. | ||
| ] is widely spoken as a second language across Switzerland, and many Anglophone migrants live in Switzerland. It is often used as a ] as Switzerland has four official languages. Because of this, English is often used in advertisements in Switzerland,<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1080/01434632.1994.9994584 |title=English as a cultural symbol: The case of advertisements in French-speaking Switzerland |date=1994 |last1=Cheshire |first1=Jenny |last2=Moser |first2=Lise-Marie |journal=Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development |volume=15 |issue=6 |pages=451–469 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241736163 }}</ref> and many businesses and companies in Switzerland, even if they only operate domestically, have names that use English words. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 63: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| In 2012, for the first time, respondents could indicate more than one language, causing the percentages to exceed 100%.<ref name=FSOML/> | In the 2012 survey, for the first time, respondents could indicate more than one language, causing the percentages to exceed 100%.<ref name=FSOML/> | ||
| == Federal authorities == | |||
| While the ] offers simultaneous translation to and from German, French and Italian, the ] does not translate debates – its members are expected to understand at least German and French. | |||
| Employees of the federal government are expected to write documents in their native tongue. 77% of the original official documents were edited in German, 20% in French, and 1.98% in Italian. More than half of the Italian speakers employed by the federal government are translators.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.swissinfo.ch/ger/leben-und-altern/bundesverwaltung-ist-eigentlich-zweisprachig/7241630 |title=Bundesverwaltung ist eigentlich zweisprachig |date=2009-03-01 |access-date=2024-03-17 |publisher=Swissinfo}}</ref> | |||
| The ] publishes its decisions only in one language, usually in the language used in the earlier instance. The so-called ] – a summary of the decision – will be offered in German, French and Italian, but only in important and influential cases (German "Leitentscheide").<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.bger.ch/index/federal/federal-inherit-template/federal-faq/federal-faq-38.htm |title=Werden die Urteile des Bundesgerichts übersetzt? |access-date=2024-03-17 |publisher=Supreme Federal Court of Switzerland |language=de |trans-title=Are the decisions of the Federal Court translated?}}</ref> | |||
| ==National languages and linguistic regions== | ==National languages and linguistic regions== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 77: | ||
| {{Further|Swiss German|Swiss Standard German|German-speaking Switzerland|Walser German}} | {{Further|Swiss German|Swiss Standard German|German-speaking Switzerland|Walser German}} | ||
| ] dialects. Marked in red is the ].]] | ] dialects. Marked in red is the ].]] | ||
| ] dialects |
] dialects]] | ||
| The German-speaking part of Switzerland ({{ |
The German-speaking part of Switzerland ({{langx|de|Deutschschweiz}}, {{langx|fr|Suisse alémanique}}, {{langx|it|Svizzera tedesca}}, {{langx|rm|Svizra tudestga}}) constitutes about 65% of ] (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switzerland, most of the ] and the greater part of the ]). | ||
| In seventeen of the Swiss cantons, German is the only official language (], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a1.html |title=SR 101 The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation of 18 April 1999 (Status as of 12 February 2017): Art. 1: The Swiss Confederation |date=12 February 2017 |publisher=The Federal Council |location=Berne, Switzerland |website=The portal of the Swiss government |type=Federal Law collection |access-date=13 June 2017 |archive-date=4 October 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141004144901/http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a1.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | In seventeen of the Swiss cantons, German is the only official language (], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a1.html |title=SR 101 The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation of 18 April 1999 (Status as of 12 February 2017): Art. 1: The Swiss Confederation |date=12 February 2017 |publisher=The Federal Council |location=Berne, Switzerland |website=The portal of the Swiss government |type=Federal Law collection |access-date=13 June 2017 |archive-date=4 October 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141004144901/http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a1.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| Line 76: | Line 86: | ||
| While the French-speaking Swiss prefer to call themselves ''Romands'' and their part of the country is ], the German-speaking Swiss used to (and, colloquially, still do) refer to the French-speaking Swiss as "Welsche", and to their area as ''Welschland'', which has the same etymology as the English ] (see '']'').<ref>{{cite web | While the French-speaking Swiss prefer to call themselves ''Romands'' and their part of the country is ], the German-speaking Swiss used to (and, colloquially, still do) refer to the French-speaking Swiss as "Welsche", and to their area as ''Welschland'', which has the same etymology as the English ] (see '']'').<ref>{{cite web | ||
| | url = https://www.reddit.com/r/todayilearned/comments/48ajo6/til_that_the_swiss_german_word_for_a_swiss_french/?rdt=33694 | title = TIL | website = Reddit | access-date = 7 March 2024}} | | url = https://www.reddit.com/r/todayilearned/comments/48ajo6/til_that_the_swiss_german_word_for_a_swiss_french/?rdt=33694 | title = TIL | website = Reddit | date = 29 February 2016 | access-date = 7 March 2024}} | ||
| </ref> Research shows that individuals with a French-sounding name in the German-speaking part suffer from social discrimination.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Nesseler|first1=Cornel|last2=Carlos|first2=Gomez-Gonzalez|last3=Dietl|first3=Helmut|date=2019|title=What's in a name? Measuring access to social activities with a field experiment|journal=Palgrave Communications|volume=5|pages=1–7|doi=10.1057/s41599-019-0372-0|doi-access=free|hdl=11250/2635691|hdl-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Dietl|first1=Helmut|last2=Carlos|first2=Gomez-Gonzalez|last3=Moretti|first3=Paolo|last4=Nesseler|first4=Cornel|date=2020|title=Does persistence pay off? Accessing social activities with a foreign-sounding name|journal=Applied Economic Letters|volume=28|issue=10|pages=881–885|doi= 10.1080/13504851.2020.1784381|doi-access=free|hdl=11250/2659779|hdl-access=free}}</ref> | </ref> Research shows that individuals with a French-sounding name in the German-speaking part suffer from social discrimination.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Nesseler|first1=Cornel|last2=Carlos|first2=Gomez-Gonzalez|last3=Dietl|first3=Helmut|date=2019|title=What's in a name? Measuring access to social activities with a field experiment|journal=Palgrave Communications|volume=5|pages=1–7|doi=10.1057/s41599-019-0372-0|doi-access=free|hdl=11250/2635691|hdl-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Dietl|first1=Helmut|last2=Carlos|first2=Gomez-Gonzalez|last3=Moretti|first3=Paolo|last4=Nesseler|first4=Cornel|date=2020|title=Does persistence pay off? Accessing social activities with a foreign-sounding name|journal=Applied Economic Letters|volume=28|issue=10|pages=881–885|doi= 10.1080/13504851.2020.1784381|doi-access=free|hdl=11250/2659779|hdl-access=free}}</ref> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 98: | ||
| ===French=== | ===French=== | ||
| ] language area map with place names in |
] language area map with place names in Arpitan and historic political divisions]] | ||
| {{Main article|Swiss French|Suisse romande}} | {{Main article|Swiss French|Suisse romande}} | ||
| ] ({{ |
] ({{langx|fr|Romandie, la Suisse romande}}, {{langx|de|Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz}},{{efn|name=Welsch|"]" is an old German word for "Foreign" and is the same word the ] used for the original British inhabitants which today are the ].{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}}}} {{langx|it|Svizzera romanda}}) is the French-speaking part of ]. It covers the area of the ] of ], ], ], and ] as well as the French-speaking parts of the cantons of ] (German-speaking majority), ] (French-speaking majority), and ] (French-speaking majority). 1.9 million people (or 24.4% of the Swiss population) live in Romandy.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/02/blank/data/01.Document.67224.xls |format=XLS |title=Bilan de la population résidante permanente (total) selon les districts et les communes |date=2 January 2015 |publisher=Swiss Federal Statistical Office |location=Neuchâtel, Switzerland |access-date=24 October 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110806213408/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/02/blank/data/01.Document.67224.xls |archive-date= 6 August 2011 }}</ref> | ||
| Standard ] and the ] of ] are highly mutually intelligible, though some differences exist. For example, like most Francophone Belgians, speakers of Swiss French use ''septante'' (seventy) instead of ''soixante-dix'' (literally, "sixty ten") and ''nonante'' (ninety) instead of "quatre-vingt-dix" ("four twenty ten"). In the cantons of ], ] and ], speakers use ''huitante'' (eighty) instead of "quatre-vingts" (four twenties) used in the rest of the ]; the cantons of Geneva, Bern and Jura use "quatre-vingts".<ref>{{cite web |author=Dominique Didier |url=http://monsu.desiderio.free.fr/curiosites/septante.html |title=Septante, octante ou huitante, nonante |publisher=Monsu.desiderio.free.fr |access-date=22 October 2015}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|first=Mathieu|last=Avanzi|url=https://francaisdenosregions.com/2017/03/26/comment-dit-on-80-en-belgique-et-en-suisse/|title=Comment dit-on 80 en Belgique et en Suisse ?|website=francaisdenosregions.com|date=26 March 2017|access-date=12 October 2021}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Thibault|first=André|title=Dictionnaire suisse romand : particularités lexicales du français contemporain|publisher=Zoé|others=Pierre Knecht|year=2004|isbn=978-2-88182-870-6|edition=Nouvelle éd. revue et augmentée|location=Carouge (Geneva)|pages=457|language=French|trans-title=Swiss French Dictionary: lexical particularities of contemporary French|chapter=huitante|oclc=828226325|quote=Local. VD, VS, FR ; les autres cantons emploient ''quatre-vingt(s)'', comme en français de référence.|trans-quote=Local. VD, VS, FR; the other cantons use {{lang|fr|quatre-vingt(s)}} like in Standard French.}}</ref> "]" is used throughout Romandy for a ], as is "tune" (or "thune") when referring to a 5-Swiss-franc piece. Swiss French also uses "déjeuner, dîner, souper" for breakfast, lunch and dinner instead of "petit-déjeuner, déjeuner, dîner" used in France. | Standard ] and the ] of ] are highly mutually intelligible, though some differences exist. For example, like most Francophone Belgians, speakers of Swiss French use ''septante'' (seventy) instead of ''soixante-dix'' (literally, "sixty ten") and ''nonante'' (ninety) instead of "quatre-vingt-dix" ("four twenty ten"). In the cantons of ], ] and ], speakers use ''huitante'' (eighty) instead of "quatre-vingts" (four twenties) used in most of the rest of the ]; the cantons of Geneva, Bern and Jura use "quatre-vingts".<ref>{{cite web |author=Dominique Didier |url=http://monsu.desiderio.free.fr/curiosites/septante.html |title=Septante, octante ou huitante, nonante |publisher=Monsu.desiderio.free.fr |access-date=22 October 2015}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|first=Mathieu|last=Avanzi|url=https://francaisdenosregions.com/2017/03/26/comment-dit-on-80-en-belgique-et-en-suisse/|title=Comment dit-on 80 en Belgique et en Suisse ?|website=francaisdenosregions.com|date=26 March 2017|access-date=12 October 2021}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Thibault|first=André|title=Dictionnaire suisse romand : particularités lexicales du français contemporain|publisher=Zoé|others=Pierre Knecht|year=2004|isbn=978-2-88182-870-6|edition=Nouvelle éd. revue et augmentée|location=Carouge (Geneva)|pages=457|language=French|trans-title=Swiss French Dictionary: lexical particularities of contemporary French|chapter=huitante|oclc=828226325|quote=Local. VD, VS, FR ; les autres cantons emploient ''quatre-vingt(s)'', comme en français de référence.|trans-quote=Local. VD, VS, FR; the other cantons use {{lang|fr|quatre-vingt(s)}} like in Standard French.}}</ref> "]" is used throughout Romandy for a ], as is "tune" (or "thune") when referring to a 5-Swiss-franc piece. Swiss French also uses "déjeuner, dîner, souper" for breakfast, lunch and dinner instead of "petit-déjeuner, déjeuner, dîner" used in France. | ||
| Historically, the vernacular language used by inhabitants of most parts of Romandy was ]. Franco-Provençal (also called Arpitan) is a language sometimes considered to be halfway between the ] (the historical language of northern France and ancestor of French) and Occitan (the ], spoken in southern France). Standard French and Franco-Provençal/Arpitan, linguistically, are distinct and mutual intelligibility is limited. Increasingly, Franco-Provençal/Arpitan is used only by members of the older generations.{{ |
Historically, the vernacular language used by inhabitants of most parts of Romandy was ]. Franco-Provençal (also called Arpitan) is a language sometimes considered to be halfway between the ] (the historical language of northern France and ancestor of French) and Occitan (the ], spoken in southern France). Standard French and Franco-Provençal/Arpitan, linguistically, are distinct and mutual intelligibility is limited. Increasingly, Franco-Provençal/Arpitan is used only by members of the older generations.<ref>{{cite journal |last= Meune|first= Manuel |date= 18 December 2018|title= From Little Fatherlands to Imagined Protonation: The Discourse on Francoprovençal in the Journal de Genève and the Gazette de Lausanne (1826–1998) | ||
| |url= https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/64815|journal= Advances in Discourse Analysis|pages= |doi= 10.5772/intechopen.81502|access-date=7 March 2024|doi-access= free|isbn= 978-1-78985-757-3 }} | |||
| </ref> In parts of Jura ] dialects are also spoken; these belong to the same ] bloc as Standard French. | |||
| The term ''Romandy'' does not formally exist in the political system, but is used to distinguish and unify the French-speaking population of Switzerland. The ] channel ] (TSR) served the ''Romande'' community across Switzerland and worldwide through ] until it was merged with the ] (RSR) and renamed ] (Radio Télévision Suisse) in 2010. | The term ''Romandy'' does not formally exist in the political system, but is used to distinguish and unify the French-speaking population of Switzerland. The ] channel ] (TSR) served the ''Romande'' community across Switzerland and worldwide through ] until it was merged with the ] (RSR) and renamed ] (Radio Télévision Suisse) in 2010. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 114: | ||
| {{main article|Swiss Italian|Ticino|Italian Graubünden}} | {{main article|Swiss Italian|Ticino|Italian Graubünden}} | ||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| Italian Switzerland ({{ |
Italian Switzerland ({{langx|it|Svizzera italiana}}, {{langx|rm|Svizra taliana}}, {{langx|fr|Suisse italienne}}, {{langx|de|italienische Schweiz}}) is the ], which includes the canton of ] and ]. Italian is also spoken in the ] Valley (leading to the ], on the southern part of the watershed) in Valais. The traditional vernacular of this region is the ], specifically its ]. | ||
| The linguistic region covers an area of about 3,500 km<sup>2</sup> and has a total population of around 350,000,<ref>{{in lang|fr}} {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090920100559/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/02/blank/data/01.Document.67126.xls |date=20 September 2009 }}; calculated adding up the inhabitants in ] and 11% of the inhabitants of ], Swiss Federal Statistical Office</ref> with the number of Italophones residing in Switzerland being 545,274 (about 7% of the Swiss population).<ref name="CHLangHome2012">{{cite web |title=Bevölkerung, Strukturerhebung der eidgenössischen Volkszählung 2011: Bevölkerung nach Sprache und Religion, Ständige Wohnbevölkerung ab 15 Jahren nach zuhause gesprochenen Sprachen, 2011 |url=http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/news/04/01.Document.169329.xls |type=Statistics |format=XLS |date=30 May 2013 |publisher=Swiss Federal Statistical Office |location=Neuchâtel, Switzerland |language=de, fr, it |access-date=22 December 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131114071643/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/news/04/01.Document.169329.xls |archive-date=14 November 2013 }}</ref> | The linguistic region covers an area of about 3,500 km<sup>2</sup> and has a total population of around 350,000,<ref>{{in lang|fr}} {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090920100559/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/02/blank/data/01.Document.67126.xls |date=20 September 2009 }}; calculated adding up the inhabitants in ] and 11% of the inhabitants of ], Swiss Federal Statistical Office</ref> with the number of Italophones residing in Switzerland being 545,274 (about 7% of the Swiss population).<ref name="CHLangHome2012">{{cite web |title=Bevölkerung, Strukturerhebung der eidgenössischen Volkszählung 2011: Bevölkerung nach Sprache und Religion, Ständige Wohnbevölkerung ab 15 Jahren nach zuhause gesprochenen Sprachen, 2011 |url=http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/news/04/01.Document.169329.xls |type=Statistics |format=XLS |date=30 May 2013 |publisher=Swiss Federal Statistical Office |location=Neuchâtel, Switzerland |language=de, fr, it |access-date=22 December 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131114071643/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/news/04/01.Document.169329.xls |archive-date=14 November 2013 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 120: | Line 132: | ||
| Romansh speakers remain predominant in the ], the ], and the ]. | Romansh speakers remain predominant in the ], the ], and the ]. | ||
| == |
== English == | ||
| ⚫ | While learning one of the other national languages at school is important, many Swiss nowadays find it easier to use ] as a ] with other Swiss people of different linguistic backgrounds.<ref> from Swissinfo.ch</ref> In 2022, Switzerland ranked 23rd in Europe in the ].<ref name="SWI swissinfo.ch 2023 l777">{{cite web | title=Swiss are not as good at English as they might think, study finds | website=SWI swissinfo.ch | date=2023-07-16 | url=https://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/culture/swiss-are-not-as-good-at-english-as-they-might-think--study-finds/48666690 | access-date=2023-08-18}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | Besides the national languages and the many varieties of ], several regional Romance languages are spoken natively in Switzerland: ] and ]. |
||
| Swissinfo, a multilingual outlet of ], reported in 2021 that interview subjects are often asked technical questions in English, given that interviewers are often not proficient enough to do so in the local language. The interviewees then answer in their own local language. The interviews are later translated and dubbed over at the studio. A 2003 study on the online communication behavior of Swiss medical students showed that they quickly changed to English as soon as students from other languages were involved. The main drivers behind using English were the Italian-speaking students from Ticino, as students from other parts of the country rarely understood their messages.<ref>{{Cite news |title=English as a common language in Switzerland: a positive or a problem? |url=https://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/culture/english-as-a-common-language-in-switzerland-a-positive-or-a-problem/46494332 |last=Stephens |first=Thomas |date=2021-04-07 |access-date=2024-03-17 |publisher=Swissinfo}}</ref> | |||
| About 20,000 ] speak ], an ]. | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| ⚫ | While learning one of the other national languages at school is important, many Swiss nowadays find it easier to use ] as a ] |
||
| |+ Inhabitants who mainly speak English in everyday life | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Area !! Percentage | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || 14.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ], village in the Canton of Zug || 27.3 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || 20.0 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || 12.5 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || 11.8 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] || 10.8 | |||
| |- | |||
| |colspan=2|Residents aged 15 or above; according to 2022 census data<ref>{{Cite news |title=In Walchwil und Zug spricht man hauptsächlich Englisch – im Arbeitsleben ist die Sprache nicht mehr wegzudenken |url=https://www.zugerzeitung.ch/zentralschweiz/zug/statistik-in-walchwil-und-zug-spricht-man-hauptsaechlich-englisch-im-arbeitsleben-ist-die-sprache-nicht-mehr-wegzudenken-ld.2571507 |date=2024-01-26 |access-date=2024-04-09 |work=] |language=de |trans-title=In Walchwil and Zug people mainly seak English - in the working life, English is indispensable}}</ref> | |||
| |} | |||
| In advertising and sports, English slogans and labels are frequently used, as it reduces the need for regional branding. For example, Swiss railways sell tourism offers through the "RailAway" label since 1999, and many national sport federations have English names (e.g. ] and ]), with their German or French names almost never being used. | |||
| == Other languages == | |||
| ;Franco-Provençal and Lombard | |||
| ⚫ | Besides the national languages and the many varieties of ], several regional Romance languages are spoken natively in Switzerland: ] and ]. | ||
| ;Sinte | |||
| ⚫ | Five ] are used: ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name=Wittmann>{{cite web |author=Wittmann, Henri |date=1991 |title=Classification linguistique des langues signées non vocalement |publisher=Revue québécoise de linguistique théorique et appliquée 10:1.215–88 |url=http://www.nou-la.org/ling/1991a-class.pdf |language=fr |access-date=22 October 2015|author-link=Henri Wittmann }}</ref> |
||
| About 20,000 ] speak ], an ]. ], in the four national languages of Switzerland]] | |||
| ;Sign languages | |||
| ⚫ | Five ] are used: ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name=Wittmann>{{cite web |author=Wittmann, Henri |date=1991 |title=Classification linguistique des langues signées non vocalement |publisher=Revue québécoise de linguistique théorique et appliquée 10:1.215–88 |url=http://www.nou-la.org/ling/1991a-class.pdf |language=fr |access-date=22 October 2015|author-link=Henri Wittmann }}</ref> | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right" | ||
| Line 435: | Line 474: | ||
| ==Neo-Latin== | ==Neo-Latin== | ||
| {{See also|Name of Switzerland}} | {{See also|Name of Switzerland}} | ||
| ] with the ] inscription ''Confoederatio Helvetica |
] with the ] inscription ''Confoederatio Helvetica'']] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| To avoid having to translate the ] into the four national languages,{{efn|name=Name of Switzerland|When there is no room to use the four official languages, unlike on the ], on the logo of the ] and on the ].}} ] is used on the ] ('']'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on ] (''Helvetia''). The ] for Switzerland on the internet is ], the abbreviation of the Latin name, ''Confoederatio Helvetica'' (Swiss Confederation); similarly, the ] for Swiss automobiles is "CH". The ] bears the inscription ''{{Smallcaps|Curia Confoederationis Helveticae}}''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://commons.wikimedia.org/File:Bern_Parliament_Pediment_Inscription_2019-09-14_00-09.jpg |last=Tschentscher |first=Axel |title=File:Bern Parliament Pediment Inscription 2019-09-14 00-09.jpg |website=commons.wikimedia.org |date=14 September 2019 |access-date=22 March 2020 }}</ref> | To avoid having to translate the ] into the four national languages,{{efn|name=Name of Switzerland|When there is no room to use the four official languages, unlike on the ], on the logo of the ] and on the ].}} ] is used on the ] ('']'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on ] (''Helvetia''). The ] for Switzerland on the internet is ], the abbreviation of the Latin name, ''Confoederatio Helvetica'' (Swiss Confederation); similarly, the ] for Swiss automobiles is "CH". The ] bears the inscription ''{{Smallcaps|Curia Confoederationis Helveticae}}''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://commons.wikimedia.org/File:Bern_Parliament_Pediment_Inscription_2019-09-14_00-09.jpg |last=Tschentscher |first=Axel |title=File:Bern Parliament Pediment Inscription 2019-09-14 00-09.jpg |website=commons.wikimedia.org |date=14 September 2019 |access-date=22 March 2020 }}</ref> | ||
| To have a unique name across the country (without favoring German, French or any other language), several Swiss foundations and associations have Latin names, such as ], Pro Infirmis, ], ], ], Pro Senectute, ], |
To have a unique name across the country (without favoring German, French or any other language), several Swiss foundations and associations have Latin names, such as ], Pro Infirmis, ], ], ], Pro Senectute, ], ], and many more. | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 452: | Line 491: | ||
| {{notelist}} | {{notelist}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Clear}} | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| Line 461: | Line 501: | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * Information portal on current linguistic research in Switzerland | |||
| * Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities | * Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities | ||
| * Pimsleur Swiss German Course | * Pimsleur Swiss German Course | ||
| Line 470: | Line 509: | ||
| {{Portal bar|Language|Switzerland}} | {{Portal bar|Language|Switzerland}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of Switzerland}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of Switzerland}} | ||
| Line 478: | Line 519: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:36, 19 January 2025
| This article may require cleanup to meet Misplaced Pages's quality standards. The specific problem is: Refs must be updated and using the same format and language. Please help improve this article if you can. (September 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Languages of Switzerland | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Official | German, French, Italian, Romansh |
| National | |
| Vernacular | Swiss German, Swiss Standard German, Swiss French, Swiss Italian, Franco-Provençal, Lombard, Walser German, Frainc-Comtou, Bavarian |
| Immigrant |
|
| Foreign | English |
| Signed | Swiss German Sign Language, French Sign Language, Italian Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | QWERTZ |
| Source | FSO |
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Switzerland |
|---|
 |
| History |
| People |
| Languages |
| Mythology and folklore |
| Cuisine |
| Festivals |
| Religion |
| Art |
| Literature |
| Music |
| Media |
| Sport |
| Monuments |
| Symbols |
The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian, and Romansh. German, French, and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the federal administration of the Swiss Confederation, while Romansh is used in dealings with people who speak it. Latin is occasionally used in some formal contexts, particularly to denote the country (Confoederatio Helvetica).
In 2020, 62.3% of the population of Switzerland were native speakers of German (either Swiss or Standard German) at home; 22.8% French (mostly Swiss French, but including some Franco-Provençal dialects); 8% Italian (mostly Swiss Italian, but including Lombard); and 0.5% Romansh. The German region (Deutschschweiz) is roughly in the east, north, and centre; the French part (la Romandie) in the west; and the Italian area (Svizzera italiana) in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in Grisons in the east. The cantons of Freiburg, Bern, and Valais are officially bilingual; Grisons is officially trilingual.
English is widely spoken as a second language across Switzerland, and many Anglophone migrants live in Switzerland. It is often used as a lingua franca as Switzerland has four official languages. Because of this, English is often used in advertisements in Switzerland, and many businesses and companies in Switzerland, even if they only operate domestically, have names that use English words.
History
The main languages of Swiss residents from 1950 to 2015, in percentages, were as follows:
| Year | German | French | Italian | Romansh | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 63.7 | 22.7 | 8.4 | 0.6 | 5.3 |
| 2000 | 63.7 | 20.4 | 6.5 | 0.5 | 9.0 |
| 1990 | 63.6 | 19.2 | 7.6 | 0.6 | 8.9 |
| 1980 | 65.0 | 18.4 | 9.8 | 0.8 | 6.0 |
| 1970 | 64.9 | 18.1 | 11.9 | 0.8 | 4.3 |
| 1960 | 69.4 | 18.9 | 9.5 | 0.9 | 1.4 |
| 1950 | 72.1 | 20.3 | 5.9 | 1.0 | 0.7 |
In the 2012 survey, for the first time, respondents could indicate more than one language, causing the percentages to exceed 100%.
Federal authorities
While the National Council offers simultaneous translation to and from German, French and Italian, the Council of States does not translate debates – its members are expected to understand at least German and French.
Employees of the federal government are expected to write documents in their native tongue. 77% of the original official documents were edited in German, 20% in French, and 1.98% in Italian. More than half of the Italian speakers employed by the federal government are translators.
The Federal Supreme Court publishes its decisions only in one language, usually in the language used in the earlier instance. The so-called regest – a summary of the decision – will be offered in German, French and Italian, but only in important and influential cases (German "Leitentscheide").
National languages and linguistic regions
German
Further information: Swiss German, Swiss Standard German, German-speaking Switzerland, and Walser German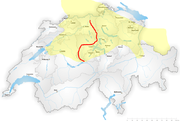

The German-speaking part of Switzerland (German: Deutschschweiz, French: Suisse alémanique, Italian: Svizzera tedesca, Romansh: Svizra tudestga) constitutes about 65% of Switzerland (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switzerland, most of the Swiss Plateau and the greater part of the Swiss Alps).
In seventeen of the Swiss cantons, German is the only official language (Aargau, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Appenzell Innerrhoden, Basel-Stadt, Basel-Landschaft, Glarus, Luzern, Nidwalden, Obwalden, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, Solothurn, St. Gallen, Thurgau, Uri, Zug, and Zürich).
In the cantons of Bern, Fribourg and Valais, French is co-official; in the trilingual canton of Graubünden, more than half of the population speaks German, while the rest speak Romansh or Italian. In each case, all languages are official languages of the respective canton.
While the French-speaking Swiss prefer to call themselves Romands and their part of the country is Romandy, the German-speaking Swiss used to (and, colloquially, still do) refer to the French-speaking Swiss as "Welsche", and to their area as Welschland, which has the same etymology as the English Welsh (see Walha). Research shows that individuals with a French-sounding name in the German-speaking part suffer from social discrimination.
Nevertheless, in 2017, 11.1%, or about 920,600 of the Swiss residents speak Standard German ("Hochdeutsch") at home, but this figure likely includes numerous German (and Austrian) immigrants.

By the Middle Ages, a marked difference had developed within the German-speaking part of Switzerland between the rural cantons (Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Glarus, Zug, Appenzell, Schaffhausen) and the city cantons (Lucerne, Berne, Zurich, Solothurn, Fribourg, Basel, St. Gallen), divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant, and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, when all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farmhouses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
In addition to this more widespread notion of Swiss German dialect, there is also Walser German, another Highest Alemannic speech brought by Walser emigrants from Valais.
Because the largest part of Switzerland is German-speaking, many French, Italian, and Romansh speakers migrate to the rest of Switzerland, and the children of those non-German-speaking Swiss-born within the rest of Switzerland speak German.
French
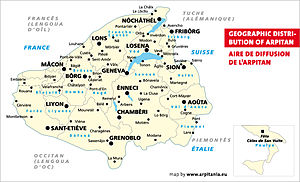
Romandy (French: Romandie, la Suisse romande, German: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz, Italian: Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of Switzerland. It covers the area of the cantons of Geneva, Vaud, Neuchâtel, and Jura as well as the French-speaking parts of the cantons of Bern (German-speaking majority), Valais (French-speaking majority), and Fribourg (French-speaking majority). 1.9 million people (or 24.4% of the Swiss population) live in Romandy.
Standard Swiss French and the French of France are highly mutually intelligible, though some differences exist. For example, like most Francophone Belgians, speakers of Swiss French use septante (seventy) instead of soixante-dix (literally, "sixty ten") and nonante (ninety) instead of "quatre-vingt-dix" ("four twenty ten"). In the cantons of Vaud, Valais and Fribourg, speakers use huitante (eighty) instead of "quatre-vingts" (four twenties) used in most of the rest of the French-speaking world; the cantons of Geneva, Bern and Jura use "quatre-vingts". "Sou" is used throughout Romandy for a 5-centime coin, as is "tune" (or "thune") when referring to a 5-Swiss-franc piece. Swiss French also uses "déjeuner, dîner, souper" for breakfast, lunch and dinner instead of "petit-déjeuner, déjeuner, dîner" used in France.
Historically, the vernacular language used by inhabitants of most parts of Romandy was Franco-Provençal. Franco-Provençal (also called Arpitan) is a language sometimes considered to be halfway between the langue d'oïl (the historical language of northern France and ancestor of French) and Occitan (the langue d'oc, spoken in southern France). Standard French and Franco-Provençal/Arpitan, linguistically, are distinct and mutual intelligibility is limited. Increasingly, Franco-Provençal/Arpitan is used only by members of the older generations. In parts of Jura Franc-Comtois dialects are also spoken; these belong to the same Oïl bloc as Standard French.
The term Romandy does not formally exist in the political system, but is used to distinguish and unify the French-speaking population of Switzerland. The television channel Télévision Suisse Romande (TSR) served the Romande community across Switzerland and worldwide through TV5Monde until it was merged with the Radio Suisse Romande (RSR) and renamed RTS (Radio Télévision Suisse) in 2010.
Italian
Main articles: Swiss Italian, Ticino, and Italian Graubünden
Italian Switzerland (Italian: Svizzera italiana, Romansh: Svizra taliana, French: Suisse italienne, German: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of Switzerland, which includes the canton of Ticino and the southern part of Grisons. Italian is also spoken in the Gondo Valley (leading to the Simplon Pass, on the southern part of the watershed) in Valais. The traditional vernacular of this region is the Lombard language, specifically its Ticinese dialect.
The linguistic region covers an area of about 3,500 km and has a total population of around 350,000, with the number of Italophones residing in Switzerland being 545,274 (about 7% of the Swiss population).
The proportion of Italian-speaking inhabitants had been decreasing since the 1970s, after reaching a high of 12% of the population during the same decade. This was entirely because of the reduced number of immigrants from Italy to Switzerland. However it has increased again during the last decade.
Romansh
Main articles: Romansh language and Canton of Grisons
Romansh school Bilingual Romansh-German school German school, Romansh as a subject German schooling only
Romansh is an official language in the trilingual Canton of Grisons, where the municipalities in turn are free to specify their own official languages. Romansh has been recognized as one of four "national languages" by the Swiss Federal Constitution since 1938. It was also declared an "official language" of the Confederation in 1996, meaning that Romansh speakers may use their language for correspondence with the federal government and expect to receive a Romansh response. Although Romansh is split into several dialects, the federal and cantonal authorities use the standardized version (Romansh Grischun) exclusively.
Romansh speakers remain predominant in the Surselva, the Albula Region, and the Engiadina Bassa/Val Müstair Region.
English
While learning one of the other national languages at school is important, many Swiss nowadays find it easier to use English as a lingua franca with other Swiss people of different linguistic backgrounds. In 2022, Switzerland ranked 23rd in Europe in the English Proficiency Index of EF language school.
Swissinfo, a multilingual outlet of Swiss Radio and Television, reported in 2021 that interview subjects are often asked technical questions in English, given that interviewers are often not proficient enough to do so in the local language. The interviewees then answer in their own local language. The interviews are later translated and dubbed over at the studio. A 2003 study on the online communication behavior of Swiss medical students showed that they quickly changed to English as soon as students from other languages were involved. The main drivers behind using English were the Italian-speaking students from Ticino, as students from other parts of the country rarely understood their messages.
| Area | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Canton of Zug | 14.1 |
| Walchwil, village in the Canton of Zug | 27.3 |
| City of Zug | 20.0 |
| Canton of Basel-City | 12.5 |
| Canton of Geneva | 11.8 |
| Canton of Zurich | 10.8 |
| Residents aged 15 or above; according to 2022 census data | |
In advertising and sports, English slogans and labels are frequently used, as it reduces the need for regional branding. For example, Swiss railways sell tourism offers through the "RailAway" label since 1999, and many national sport federations have English names (e.g. Swiss Olympic and Swiss Super League), with their German or French names almost never being used.
Other languages
- Franco-Provençal and Lombard
Besides the national languages and the many varieties of Swiss German, several regional Romance languages are spoken natively in Switzerland: Franco-Provençal and Lombard.
- Sinte
About 20,000 Romani speak Sinte, an Indic language.

- Sign languages
Five sign languages are used: Swiss-German, French, Italian, Austrian, and German.
| Language | 2000 Mother tongue |
2015 Main language |
2018 Main language |
2020 Main language | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| German | 4,639,762 | 63.7% | 4,424,150 | 64% | 4,458,156 | 62.9% | 4,477,946 | 62.3% |
| French | 1,484,411 | 20.4% | 1,567,197 | 22.7% | 1,619,708 | 22.9% | 1,624,424 | 22.6% |
| Italian | 470,961 | 6.5% | 581,381 | 8.4% | 593,646 | 8.4% | 575,017 | 8% |
| Romansch | 35,072 | 0.5% | 40,299 | 0.6% | 36,709 | 0.5% | 35,938 | 0.5% |
| English | 73,422 | 1% | 374,642 | 5.4% | 471,056 | 5.9% | 416,887 | 5.8% |
| Portuguese | 89,527 | 1.2% | 256,560 | 3.7% | 251,570 | 3.5% | ||
| Albanian | 94,937 | 1.3% | 188,125 | 2.7% | 230,007 | 3.2% | ||
| Serbo-Croatian | 103,350 | 1.4% | 161,882 | 2.3% | 165,317 | 2.3% | ||
| Spanish | 76,750 | 1.1% | 159,859 | 2.3% | 172,505 | 2.4% | ||
| Turkish | 44,523 | 0.6% | 78,015 | 1.1% | ||||
| Arabic | 14,345 | 0.2% | 36,857 | 0.5% | ||||
| Russian | 8,570 | 0.1% | 32,244 | 0.5% | ||||
| Tamil | 21,816 | 0.3% | 31,145 | 0.5% | ||||
| Polish | 5,206 | 0.1% | 24,881 | 0.4% | ||||
| Dutch | 11,840 | 0.2% | 22,357 | 0.3% | ||||
| Hungarian | 6,194 | 0.1% | 20,597 | 0.3% | ||||
| Kurdish | 7,531 | 0.1% | 19,401 | 0.3% | ||||
| Thai | 7,569 | 0.1% | 14,528 | 0.2% | ||||
| Greek | 4,792 | 0.1% | 13,763 | 0.2% | ||||
| Czech | 5,444 | 0.1% | 13,433 | 0.2% | ||||
| Romanian | 3,397 | 0% | 12,738 | 0.2% | ||||
| Chinese | 8,279 | 0.1% | 12,324 | 0.2% | ||||
| Slovak | 2,018 | 0% | 12,072 | 0.2% | ||||
| Persian | 3,467 | 0% | 11,108 | 0.2% | ||||
| Macedonian | 6,415 | 0.1% | 10,698 | 0.2% | ||||
| Swedish | 5,560 | 0.1% | 8,771 | 0.1% | ||||
| Vietnamese | 4,226 | 0.1% | 6,720 | 0.1% | ||||
| Tagalog | 3,019 | 0% | 6,275 | 0.1% | ||||
| Japanese | 4,100 | 0.1% | 6,001 | 0.1% | ||||
| Danish | 2,739 | 0% | 5,272 | 0.1% | ||||
| Tibetan | 1,108 | 0% | 5,219 | 0.1% | ||||
| Bulgarian | 1,579 | 0% | 4,583 | 0.1% | ||||
| Finnish | 2,628 | 0% | 4,299 | 0.1% | ||||
| Hindi-Urdu | 1,407 | 0% | 3,846 | 0.1% | ||||
| Slovene | 1,601 | 0% | 3,690 | 0.1% | ||||
| Somali | 2,661 | 0% | 3,607 | 0.1% | ||||
| Aramaic | 1,333 | 0% | 2,465 | 0% | ||||
| Hebrew | 1,176 | 0% | 2,159 | 0% | ||||
| Norwegian | 1,361 | 0% | 2,108 | 0% | ||||
| Korean | 1,202 | 0% | 1,816 | 0% | ||||
| Other languages | 77,751 | 1.1% | 1,255,656 | 17.7% | 589,393 | 8.2% | ||
Neo-Latin
See also: Name of Switzerland

To avoid having to translate the name of Switzerland into the four national languages, Latin is used on the coins of the Swiss franc (Helvetia or Confoederatio Helvetica) and on Swiss stamps (Helvetia). The country code top-level domain for Switzerland on the internet is .ch, the abbreviation of the Latin name, Confoederatio Helvetica (Swiss Confederation); similarly, the International vehicle registration code for Swiss automobiles is "CH". The Federal Palace of Switzerland bears the inscription Curia Confoederationis Helveticae.
To have a unique name across the country (without favoring German, French or any other language), several Swiss foundations and associations have Latin names, such as Pro Helvetia, Pro Infirmis, Pro Juventute, Pro Natura, Pro Patria, Pro Senectute, Pro Specie Rara, Helvetia Nostra, and many more.
See also
- Swiss people
- Demographics of Switzerland
- Röstigraben, referring to the asserted difference in mentality between German Swiss and the French-speaking Romands
- Swiss literature
- List of multilingual countries and regions
Notes
- "Welsch" is an old German word for "Foreign" and is the same word the Anglo-Saxons used for the original British inhabitants which today are the Welsh people.
- Since 2010, statistics of languages in Switzerland provided by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office are based on a national structural survey of 200,000 people aged 15 years and older (corresponding to 2.5% of the total resident population). Data are extrapolated to obtain statistical results for the whole population (aged 15 years and older). These results are estimates subject to some degree of uncertainty indicated by a confidence interval. Therefore, the figures of the structural survey may not be entirely comparable to data collection before 2010 based on census figures (counting every person living in Switzerland).
- When there is no room to use the four official languages, unlike on the banknotes of the Swiss franc, on the logo of the Federal administration of Switzerland and on the Swiss passport.
References
- Durham, Mercedes (2006). "Language Choice on a Swiss Mailing List". Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication. 9. doi:10.1111/j.1083-6101.2003.tb00359.x.
- Archived 10 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sprachen 2015" (in German, French, and Italian). Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Federal Statistical Office FSO. 31 January 2017. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- "SR 101 The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation of 18 April 1999 (Status as of 12 February 2017): Art. 4 National languages". The portal of the Swiss government (Federal Law collection). Berne, Switzerland: The Federal Council. 12 February 2017. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- "SR 441.1 Bundesgesetz über die Landessprachen und die Verständigung zwischen den Sprachgemeinschaften [Federal Act on the National Languages and Understanding between the Linguistic Communities] (Sprachengesetz, SpG) vom 5. Oktober 2007 (Stand am 1. Januar 2017): Art. 5 Amtssprachen". The portal of the Swiss government (Federal Law collection) (in German, French, Italian, and Romansh). Berne, Switzerland: The Federal Council. 1 January 2017. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- "Languages of instruction in Switzerland - Daily Research". www.dailyresearch.co.uk. Daily Research. Archived from the original on 21 May 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ "Languages". Office Federal Statistical. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
- Cheshire, Jenny; Moser, Lise-Marie (1994). "English as a cultural symbol: The case of advertisements in French-speaking Switzerland". Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development. 15 (6): 451–469. doi:10.1080/01434632.1994.9994584.
- ^ "Die zehn häufigsten Hauptsprachen der ständigen Wohnbevölkerung" (official website) (in German, French, and Italian). Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Statistical Office FSO. 28 February 2018. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- "Bundesverwaltung ist eigentlich zweisprachig". Swissinfo. 1 March 2009. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- "Werden die Urteile des Bundesgerichts übersetzt?" [Are the decisions of the Federal Court translated?] (in German). Supreme Federal Court of Switzerland. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- "SR 101 The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation of 18 April 1999 (Status as of 12 February 2017): Art. 1: The Swiss Confederation". The portal of the Swiss government (Federal Law collection). Berne, Switzerland: The Federal Council. 12 February 2017. Archived from the original on 4 October 2014. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- "TIL". Reddit. 29 February 2016. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- Nesseler, Cornel; Carlos, Gomez-Gonzalez; Dietl, Helmut (2019). "What's in a name? Measuring access to social activities with a field experiment". Palgrave Communications. 5: 1–7. doi:10.1057/s41599-019-0372-0. hdl:11250/2635691.
- Dietl, Helmut; Carlos, Gomez-Gonzalez; Moretti, Paolo; Nesseler, Cornel (2020). "Does persistence pay off? Accessing social activities with a foreign-sounding name". Applied Economic Letters. 28 (10): 881–885. doi:10.1080/13504851.2020.1784381. hdl:11250/2659779.
- Statistik, Bundesamt für (29 January 2019). "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung ab 15 Jahren nach zuhause gesprochenen Sprachen - 2017 | Tabelle". Bundesamt für Statistik (in German). Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- "Bilan de la population résidante permanente (total) selon les districts et les communes". Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Statistical Office. 2 January 2015. Archived from the original (XLS) on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- Dominique Didier. "Septante, octante ou huitante, nonante". Monsu.desiderio.free.fr. Retrieved 22 October 2015.
- Avanzi, Mathieu (26 March 2017). "Comment dit-on 80 en Belgique et en Suisse ?". francaisdenosregions.com. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- Thibault, André (2004). "huitante". Dictionnaire suisse romand : particularités lexicales du français contemporain [Swiss French Dictionary: lexical particularities of contemporary French] (in French). Pierre Knecht (Nouvelle éd. revue et augmentée ed.). Carouge (Geneva): Zoé. p. 457. ISBN 978-2-88182-870-6. OCLC 828226325.
Local. VD, VS, FR ; les autres cantons emploient quatre-vingt(s), comme en français de référence.
[Local. VD, VS, FR; the other cantons use quatre-vingt(s) like in Standard French.] - Meune, Manuel (18 December 2018). "From Little Fatherlands to Imagined Protonation: The Discourse on Francoprovençal in the Journal de Genève and the Gazette de Lausanne (1826–1998)". Advances in Discourse Analysis. doi:10.5772/intechopen.81502. ISBN 978-1-78985-757-3. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- (in French) Bilan de la population résidante permanente selon les cantons Archived 20 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine; calculated adding up the inhabitants in Ticino and 11% of the inhabitants of Grigioni, Swiss Federal Statistical Office
- "Bevölkerung, Strukturerhebung der eidgenössischen Volkszählung 2011: Bevölkerung nach Sprache und Religion, Ständige Wohnbevölkerung ab 15 Jahren nach zuhause gesprochenen Sprachen, 2011" (Statistics) (in German, French, and Italian). Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Statistical Office. 30 May 2013. Archived from the original (XLS) on 14 November 2013. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- English as a common language in Switzerland: a positive or a problem? from Swissinfo.ch
- "Swiss are not as good at English as they might think, study finds". SWI swissinfo.ch. 16 July 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- Stephens, Thomas (7 April 2021). "English as a common language in Switzerland: a positive or a problem?". Swissinfo. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- "In Walchwil und Zug spricht man hauptsächlich Englisch – im Arbeitsleben ist die Sprache nicht mehr wegzudenken" [In Walchwil and Zug people mainly seak English - in the working life, English is indispensable]. Zuger Zeitung (in German). 26 January 2024. Retrieved 9 April 2024.
- Wittmann, Henri (1991). "Classification linguistique des langues signées non vocalement" (PDF) (in French). Revue québécoise de linguistique théorique et appliquée 10:1.215–88. Retrieved 22 October 2015.
- "Methodological basis for research and regional partners [Accuracy of results; Cumulated data-pooling]". Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Statistical Office.
- "Tableau 7: Population résidante selon la langue principale avec au moins 600 locuteurs, en nombres absolus, en 2000". Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Statistical Office.
according to the 2000 census (over 1,000 speakers)
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - "Population résidante permanente de 15 ans et plus, selon les langues principales, en 2018" (XLS) (in French). Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Federal Statistical Office - FSO. 29 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- "Langues principales depuis 1910: Population résidante permanente âgée de 15 ans ou plus" (XLS) (in French). Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Federal Statistical Office - FSO. 24 January 2022. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- Tschentscher, Axel (14 September 2019). "File:Bern Parliament Pediment Inscription 2019-09-14 00-09.jpg". commons.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
External links
- Swiss German
- A quick guide to the Swiss German language
- Characteristics of Swiss German dialects
- sieps.ch Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities
- Pimsleur Swiss German Pimsleur Swiss German Course
| Languages of Switzerland | |
|---|---|
| Official languages | |
| Major dialect groups | |
| Sign languages | |
| Switzerland articles | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major topics | |||||||||
| History |  | ||||||||
| Geography |
| ||||||||
| Politics | |||||||||
| Economy | |||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||
| Languages of Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |