| Revision as of 07:52, 28 April 2024 editElias Ziade (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers25,672 edits Importing Wikidata short description: "Musical instrument"Tag: Shortdesc helper← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:29, 31 October 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1);Tag: AWB | ||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| | related = ], ], ] | | related = ], ], ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''nevel''', '''nebel''' ({{ |
The '''nevel''', '''nebel''' ({{langx|he|]}} ''nēḇel''), was a ] used by the ] and the ]. The Greeks translated the name as ] (νάβλα, "Phoenician harp").<ref name="ATH">], '']'' </ref><ref name=OED>{{cite OED | nabla}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Rich, Anthony |title=A Dictionary of Roman and Greek Antiquities |url=https://archive.org/details/adictionaryroma01richgoog |location=New York |publisher=D. Appleton & Company |year=1874 |page= }}</ref> | ||
| A number of possibilities have been proposed for what kind of instrument the ''nevel'' was; these include the ] and the ], both of which are strummed instruments like the ], with strings running across the ], like the modern ] and ]. Most scholars believe the ''nevel'' was a ], a plucked instrument with strings rising up from its sound box.<ref name="Braun2002">{{cite book |author=Joachim Braun |title=Music in Ancient Israel/Palestine: Archaeological, Written, and Comparative Sources |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AXrHi31KN9YC&pg=PA24 |year=2002 |publisher=Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing |isbn=978-0-8028-4477-4 |page=23}}</ref> | A number of possibilities have been proposed for what kind of instrument the ''nevel'' was; these include the ] and the ], both of which are strummed instruments like the ], with strings running across the ], like the modern ] and ]. Most scholars believe the ''nevel'' was a ], a plucked instrument with strings rising up from its sound box.<ref name="Braun2002">{{cite book |author=Joachim Braun |title=Music in Ancient Israel/Palestine: Archaeological, Written, and Comparative Sources |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AXrHi31KN9YC&pg=PA24 |year=2002 |publisher=Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing |isbn=978-0-8028-4477-4 |page=23}}</ref> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| == In the Phoenician context == | == In the Phoenician context == | ||
| The ''nabla'', mentioned by ] in his work "]", is described as "an invention of the Phoenicians". He cites Sopater of Paphos who writes<ref name="ATH"/> |
The ''nabla'', mentioned by ] in his work "]", is described as "an invention of the Phoenicians". He cites Sopater of Paphos who writes:<ref name="ATH"/> | ||
| {{Poemquote|text=Nor is the noise of the ] nablas , | {{Poemquote|text=Nor is the noise of the ] nablas , | ||
Latest revision as of 20:29, 31 October 2024
Musical instrument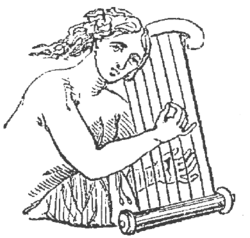 Ancient Nevel (Harp) as imagined in 19th century woodcut Ancient Nevel (Harp) as imagined in 19th century woodcut | |
| Classification | String instrument |
|---|---|
| Related instruments | |
| Lyre, Kinnor, Kithara | |
The nevel, nebel (Hebrew: נֵבֶל nēḇel), was a stringed instrument used by the Phoenicians and the Israelites. The Greeks translated the name as nabla (νάβλα, "Phoenician harp").
A number of possibilities have been proposed for what kind of instrument the nevel was; these include the psaltery and the kithara, both of which are strummed instruments like the kinnor, with strings running across the sound box, like the modern guitar and zither. Most scholars believe the nevel was a frame harp, a plucked instrument with strings rising up from its sound box.
The King James Version renders the word into English as psaltery or viol, and the Book of Common Prayer renders it lute.
The word nevel has been adopted for "harp" in Modern Hebrew.
In the Phoenician context
The nabla, mentioned by Athenaeus in his work "The Deipnosophists", is described as "an invention of the Phoenicians". He cites Sopater of Paphos who writes:
Nor is the noise of the Sidonian nablas ,
— Sopater of Paphos, Pylae
Which from the throat doth flow, at all impaired.
Atheneus reports that Mystacus described the nablas as an instrument of harmony, having a lotus fixed to its long sides. The instrument produces lively music that is not soft or sweet but rather merry, similar to singing in a Bacchic style:
Among the instruments of harmony
— The Salve by Mystacus, in Athenaeus, Deipnosophistae 4.174
The nablas comes, not over soft or sweet;
By its long sides a lifeless lotus fixed
Sends forth a breathed music; and excites men,
Singing in Bacchic strain a merry song.
Atheneus also copies Philemon's The Adulterer, where one of the play characters teases another character, Parmenon, for not knowing what a nablas is:
(A) There should, O Parmenon, be here among us
— The Adulterer by Philemon, in Athenaeus, Deipnosophistae 4.174
A nablas or a female flute-player.
(B) What is a nablas?
(A) Don't you know? you idiot!
(B) Indeed I don't.
(A) What, do not know a nablas?
You know no good; perhaps a sambuca-player
You never have heard of either!
See also
References
- ^ Athenaeus, Deipnosophistae 4.174
- "nabla". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Rich, Anthony (1874). A Dictionary of Roman and Greek Antiquities. New York: D. Appleton & Company. p. 439.
- Joachim Braun (2002). Music in Ancient Israel/Palestine: Archaeological, Written, and Comparative Sources. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-8028-4477-4.
- Neil, James (1913). Everyday Life in the Holy Land. London, UK: Cassel & Company, Ltd. p. 218.