| Revision as of 19:25, 23 April 2007 edit84.36.154.215 (talk) →Sectorisation← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 08:12, 30 November 2024 edit undoGuy Harris (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users76,812 edits rv unexplained removal of linksTag: Undo | ||
| (215 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Section of cellular telephone network}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{More citations needed|date=January 2017}} | |||
| ⚫ | The ''' |
||
| ] base station displayed in ]]] | |||
| ==Base Transceiver Station== | |||
| ⚫ | The '''base station subsystem''' ('''BSS''') is the section of a traditional ] which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a ] and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out ] of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, ], ] and ] over the ] and many other tasks related to the radio network. | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | The ], or BTS, contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving |
||
| ⚫ | A BTS is controlled by a parent BSC via the |
||
| ==Base transceiver station== | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | ], ].]] | ||
| ]]] | |||
| {{Main|Base transceiver station}} | |||
| ⚫ | The ], or BTS, contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving radio signals (]), ], and equipment for ] and decrypting communications with the ] (BSC). Typically a BTS for anything other than a ] will have several transceivers (TRXs) which allow it to serve several different ] and different sectors of the cell (in the case of sectorised base stations). | ||
| ⚫ | A BTS is controlled by a parent BSC via the "base station control function" (BCF). The BCF is implemented as a discrete unit or even incorporated in a TRX in compact base stations. The BCF provides an operations and maintenance (O&M) connection to the network management system (NMS), and manages operational states of each TRX, as well as software handling and alarm collection. | ||
| The BTSs are equipped with radios that are able to modulate layer 1 of interface Um; for GSM 2G+ the modulation type is GMSK, while for EDGE-enabled networks it is GMSK and 8-PSK. | |||
| ⚫ | The functions of a BTS vary depending on the cellular technology used and the cellular telephone provider. There are vendors in which the BTS is a plain transceiver which receives information from the MS (mobile station) through the ] and then converts it to a TDM (PCM) based interface, the Abis interface, and sends it towards the BSC. There are vendors which build their BTSs so the information is preprocessed, target cell lists are generated and even intracell handover (HO) can be fully handled. The advantage in this case is less load on the expensive Abis interface. | ||
| The BTSs are equipped with radios that are able to modulate layer 1 of interface Um; for GSM 2G+ the modulation type is ] (GMSK), while for ]-enabled networks it is GMSK and ]. This modulation is a kind of continuous-phase ]. In GMSK, the signal to be modulated onto the carrier is first smoothed with a ] ] prior to being fed to a ], which greatly reduces the interference to neighboring channels (]). | |||
| Antenna combiners are implemented to use the same antenna for several TRXs (carriers), the more TRXs are combined the greater the combiner loss will be. Up to 8:1 combiners are found in micro and pico cells only. | Antenna combiners are implemented to use the same antenna for several TRXs (carriers), the more TRXs are combined the greater the combiner loss will be. Up to 8:1 combiners are found in micro and pico cells only. | ||
| Frequency hopping is often used to increase overall BTS performance |
] is often used to increase overall BTS performance; this involves the rapid switching of voice traffic between TRXs in a sector. A hopping sequence is followed by the TRXs and handsets using the sector. Several hopping sequences are available, and the sequence in use for a particular cell is continually broadcast by that cell so that it is known to the handsets. | ||
| A TRX transmits and receives according to the GSM standards, which specify eight TDMA timeslots per radio frequency. A TRX may lose some of this capacity as some information is required to be broadcast to handsets in the area that the BTS serves. This information allows the handsets to identify the network and gain access to it. This signalling makes use of a channel known as the |
A TRX transmits and receives according to the ] standards, which specify eight ] timeslots per radio frequency. A TRX may lose some of this capacity as some information is required to be ] to handsets in the area that the BTS serves. This information allows the handsets to identify the network and gain access to it. This signalling makes use of a channel known as the ] (BCCH). | ||
| == |
===Sectorization=== | ||
| {{See|Sector antenna}} | |||
| By using directional antennas on a base station, each pointing in different directions, it is possible to sectorise the base station so that several different cells are served from the same location. Typically these directional |
By using directional antennas on a base station, each pointing in different directions, it is possible to sectorise the base station so that several different cells are served from the same location. Typically these ]s have a beamwidth of 65 to 85 degrees. This increases the traffic capacity of the base station (each frequency can carry eight voice channels) whilst not greatly increasing the ] caused to neighboring cells (in any given direction, only a small number of frequencies are being broadcast). Typically two antennas are used per sector, at spacing of ten or more ]s apart. This allows the operator to overcome the effects of ] due to physical phenomena such as ]. Some ] of the received signal as it leaves the antenna is often used to preserve the balance between uplink and downlink signal.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.abcofnetworks.com/2019/03/4-things-you-need-to-improve-coverage-and-Capacity-in-cellular-system.html|title=4 Things you need to Improve Coverage and Capacity in cellular system|last=Networks|first=Editor ABC of|website=ABC of Networks|access-date=2019-10-09}}</ref> | ||
| ==Base |
==Base station controller== | ||
| The |
The base station controller (BSC) provides, classically, the ''intelligence'' behind the BTSs. Typically a BSC has tens or even hundreds of BTSs under its control. The BSC handles allocation of radio channels, receives measurements from the mobile phones, and controls handovers from BTS to BTS (except in the case of an inter-BSC handover in which case control is in part the responsibility of the ]). A key function of the BSC is to act as a ] where many different low capacity connections to BTSs (with relatively low utilisation) become reduced to a smaller number of connections towards the ] (MSC) (with a high level of utilisation). Overall, this means that networks are often structured to have many BSCs distributed into regions near their BTSs which are then connected to large centralised MSC sites. | ||
| The BSC is undoubtedly the most robust element in the BSS as it is not only a BTS controller but, for some vendors, a full switching center, as well as an SS7 node with connections to the MSC and ] (when using ]). It also provides all the required data to the |
The BSC is undoubtedly the most robust element in the BSS as it is not only a BTS controller but, for some vendors, a full switching center, as well as an ] node with connections to the MSC and ] (SGSN) (when using ]). It also provides all the required data to the operation support subsystem (OSS) as well as to the performance measuring centers. | ||
| A BSC is often based on a distributed computing architecture, with redundancy applied to critical functional units to ensure availability in the event of fault conditions. Redundancy often extends beyond the BSC equipment itself and is commonly used in the power supplies and in the transmission equipment providing the A-ter interface to PCU. | A BSC is often based on a distributed computing architecture, with redundancy applied to critical functional units to ensure availability in the event of fault conditions. Redundancy often extends beyond the BSC equipment itself and is commonly used in the power supplies and in the transmission equipment providing the A-ter interface to PCU. | ||
| The databases for all the sites, including information such as carrier frequencies, frequency hopping lists, power reduction levels, receiving levels for cell border calculation, are stored in the BSC. This data is obtained directly from radio planning engineering which involves modelling of the signal propagation as well as traffic projections. | The databases for all the sites, including information such as ], frequency hopping lists, power reduction levels, receiving levels for cell border calculation, are stored in the BSC. This data is obtained directly from radio planning engineering which involves modelling of the ] as well as traffic projections. | ||
| ==Transcoder== | ===Transcoder=== | ||
| The transcoder is responsible for ] the voice channel coding between the coding used in the mobile network, and the coding used by the world's terrestrial circuit-switched network, the ]. Specifically, GSM uses a ] (RPE-LTP) coder for voice data between the mobile device and the BSS, but ] (] or ] standardized in ]) upstream of the BSS. RPE-LPC coding results in a data rate for voice of 13 kbit/s where standard PCM coding results in 64 kbit/s. Because of this change in data rate ''for the same voice call'', the transcoder also has a buffering function so that PCM 8-bit words can be recoded to construct GSM 20 ms traffic blocks. | |||
| ⚫ | ] in ], ].]] | ||
| Although the Transcoding (compressing/decompressing) function is as standard defined as a BSC function, there are several vendors which have implemented the solution in a stand-alone rack using a proprietary interface. This subsystem is also referred to as the TRAU (Transcoder and Rate Adaptation Unit). The transcoding function converts the voice channel coding between the GSM (Regular Pulse Excited-Long Term Prediction, also known as RPE-LPC) coder and the CCITT standard PCM (G.711 A-law or u-law). Since the PCM coding is 64 ] and the GSM coding is 13 kbit/s, this also involves a buffering function so that PCM 8-bit words can be recoded to construct GSM 20 ms traffic blocks, to compress voice channels from the 64 kbit/s PCM standard to the 13 kbit/s rate used on the air interface. Some networks use 32 kbit/s ADPCM on the terrestrial side of the network instead of 64 kbit/s PCM and the TRAU converts accordingly. When the traffic is not voice but data such as fax or email, the TRAU enables its Rate Adaptation Unit function to give compatibility between the BSS data rates and the MSC capability. | |||
| Although transcoding (compressing/decompressing) functionality is defined as a base station function by the relevant standards, there are several vendors which have implemented the solution outside of the BSC. Some vendors have implemented it in a stand-alone rack using a proprietary interface. In ]' and ]'s architecture, the transcoder is an identifiable separate sub-system which will normally be co-located with the MSC. In some of ]'s systems it is integrated to the MSC rather than the BSC. The reason for these designs is that if the compression of voice channels is done at the site of the MSC, the number of fixed transmission links between the BSS and MSC can be reduced, decreasing network infrastructure costs. | |||
| This subsystem is also referred to as the ''transcoder and rate adaptation unit'' (]). Some networks use 32 kbit/s ] on the terrestrial side of the network instead of 64 kbit/s ] and the TRAU converts accordingly. When the traffic is not voice but data such as fax or email, the TRAU enables its rate adaptation unit function to give compatibility between the BSS and MSC data rates. | |||
| ⚫ | ==Packet |
||
| ⚫ | The |
||
| ⚫ | ==Packet control unit== | ||
| ⚫ | The PCU can be built into the base station, built into the BSC or even, in some proposed architectures, it can be at the SGSN site. | ||
| ⚫ | The packet control unit (PCU) is a late addition to the GSM standard. It performs some of the processing tasks of the BSC, but for packet data. The allocation of channels between voice and data is controlled by the base station, but once a channel is allocated to the PCU, the PCU takes full control over that channel. | ||
| ⚫ | The PCU can be built into the base station, built into the BSC or even, in some proposed architectures, it can be at the SGSN site. In most of the cases, the PCU is a separate node communicating extensively with the BSC on the radio side and the SGSN on the Gb<!--?--> side. | ||
| ==BSS interfaces== | ==BSS interfaces== | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| {{sectstub}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ;]: The air interface between the ] (MS) and the BTS. This interface uses ] protocol for signaling, to conduct call control, measurement reporting, ], ], ], ], location update and so on. Traffic and signaling are sent in bursts of 0.577 ms at intervals of 4.615 ms, to form data blocks each 20 ms. | |||
| ;Abis: The interface between the BTS and BSC. Generally carried by a DS-1, ES-1, or E1 ] circuit. Uses TDM subchannels for traffic (TCH), LAPD protocol for BTS supervision and telecom signaling, and carries synchronization from the BSC to the BTS and MS. | |||
| ;A: The interface between the BSC and MSC. It is used for carrying traffic channels and the BSSAP user part of the ] stack. Although there are usually transcoding units between BSC and MSC, the signaling communication takes place between these two ending points and the transcoder unit doesn't touch the SS7 information, only the voice or CS data are transcoded or rate adapted. | |||
| ;Ater: The interface between the BSC and transcoder. It is a proprietary interface whose name depends on the vendor (for example Ater by Nokia), it carries the A interface information from the BSC leaving it untouched. | |||
| ;Gb: Connects the BSS to the SGSN in the ]. | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * U.S. ] (FCC) | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| * - open source Base Station Controller implementation | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:12, 30 November 2024
Section of cellular telephone network| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Base station subsystem" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
Base transceiver station


The base transceiver station, or BTS, contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving radio signals (transceivers), antennas, and equipment for encrypting and decrypting communications with the base station controller (BSC). Typically a BTS for anything other than a picocell will have several transceivers (TRXs) which allow it to serve several different frequencies and different sectors of the cell (in the case of sectorised base stations).
A BTS is controlled by a parent BSC via the "base station control function" (BCF). The BCF is implemented as a discrete unit or even incorporated in a TRX in compact base stations. The BCF provides an operations and maintenance (O&M) connection to the network management system (NMS), and manages operational states of each TRX, as well as software handling and alarm collection.
The functions of a BTS vary depending on the cellular technology used and the cellular telephone provider. There are vendors in which the BTS is a plain transceiver which receives information from the MS (mobile station) through the Um air interface and then converts it to a TDM (PCM) based interface, the Abis interface, and sends it towards the BSC. There are vendors which build their BTSs so the information is preprocessed, target cell lists are generated and even intracell handover (HO) can be fully handled. The advantage in this case is less load on the expensive Abis interface.
The BTSs are equipped with radios that are able to modulate layer 1 of interface Um; for GSM 2G+ the modulation type is Gaussian minimum-shift keying (GMSK), while for EDGE-enabled networks it is GMSK and 8-PSK. This modulation is a kind of continuous-phase frequency-shift keying. In GMSK, the signal to be modulated onto the carrier is first smoothed with a Gaussian low-pass filter prior to being fed to a frequency modulator, which greatly reduces the interference to neighboring channels (adjacent-channel interference).
Antenna combiners are implemented to use the same antenna for several TRXs (carriers), the more TRXs are combined the greater the combiner loss will be. Up to 8:1 combiners are found in micro and pico cells only.
Frequency hopping is often used to increase overall BTS performance; this involves the rapid switching of voice traffic between TRXs in a sector. A hopping sequence is followed by the TRXs and handsets using the sector. Several hopping sequences are available, and the sequence in use for a particular cell is continually broadcast by that cell so that it is known to the handsets.
A TRX transmits and receives according to the GSM standards, which specify eight TDMA timeslots per radio frequency. A TRX may lose some of this capacity as some information is required to be broadcast to handsets in the area that the BTS serves. This information allows the handsets to identify the network and gain access to it. This signalling makes use of a channel known as the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH).
Sectorization
Further information: Sector antennaBy using directional antennas on a base station, each pointing in different directions, it is possible to sectorise the base station so that several different cells are served from the same location. Typically these directional antennas have a beamwidth of 65 to 85 degrees. This increases the traffic capacity of the base station (each frequency can carry eight voice channels) whilst not greatly increasing the interference caused to neighboring cells (in any given direction, only a small number of frequencies are being broadcast). Typically two antennas are used per sector, at spacing of ten or more wavelengths apart. This allows the operator to overcome the effects of fading due to physical phenomena such as multipath reception. Some amplification of the received signal as it leaves the antenna is often used to preserve the balance between uplink and downlink signal.
Base station controller
The base station controller (BSC) provides, classically, the intelligence behind the BTSs. Typically a BSC has tens or even hundreds of BTSs under its control. The BSC handles allocation of radio channels, receives measurements from the mobile phones, and controls handovers from BTS to BTS (except in the case of an inter-BSC handover in which case control is in part the responsibility of the anchor MSC). A key function of the BSC is to act as a concentrator where many different low capacity connections to BTSs (with relatively low utilisation) become reduced to a smaller number of connections towards the mobile switching center (MSC) (with a high level of utilisation). Overall, this means that networks are often structured to have many BSCs distributed into regions near their BTSs which are then connected to large centralised MSC sites.
The BSC is undoubtedly the most robust element in the BSS as it is not only a BTS controller but, for some vendors, a full switching center, as well as an SS7 node with connections to the MSC and serving GPRS support node (SGSN) (when using GPRS). It also provides all the required data to the operation support subsystem (OSS) as well as to the performance measuring centers.
A BSC is often based on a distributed computing architecture, with redundancy applied to critical functional units to ensure availability in the event of fault conditions. Redundancy often extends beyond the BSC equipment itself and is commonly used in the power supplies and in the transmission equipment providing the A-ter interface to PCU.
The databases for all the sites, including information such as carrier frequencies, frequency hopping lists, power reduction levels, receiving levels for cell border calculation, are stored in the BSC. This data is obtained directly from radio planning engineering which involves modelling of the signal propagation as well as traffic projections.
Transcoder
The transcoder is responsible for transcoding the voice channel coding between the coding used in the mobile network, and the coding used by the world's terrestrial circuit-switched network, the Public Switched Telephone Network. Specifically, GSM uses a regular pulse excited-long term prediction (RPE-LTP) coder for voice data between the mobile device and the BSS, but pulse-code modulation (A-law or μ-law standardized in ITU G.711) upstream of the BSS. RPE-LPC coding results in a data rate for voice of 13 kbit/s where standard PCM coding results in 64 kbit/s. Because of this change in data rate for the same voice call, the transcoder also has a buffering function so that PCM 8-bit words can be recoded to construct GSM 20 ms traffic blocks.
Although transcoding (compressing/decompressing) functionality is defined as a base station function by the relevant standards, there are several vendors which have implemented the solution outside of the BSC. Some vendors have implemented it in a stand-alone rack using a proprietary interface. In Siemens' and Nokia's architecture, the transcoder is an identifiable separate sub-system which will normally be co-located with the MSC. In some of Ericsson's systems it is integrated to the MSC rather than the BSC. The reason for these designs is that if the compression of voice channels is done at the site of the MSC, the number of fixed transmission links between the BSS and MSC can be reduced, decreasing network infrastructure costs.
This subsystem is also referred to as the transcoder and rate adaptation unit (TRAU). Some networks use 32 kbit/s ADPCM on the terrestrial side of the network instead of 64 kbit/s PCM and the TRAU converts accordingly. When the traffic is not voice but data such as fax or email, the TRAU enables its rate adaptation unit function to give compatibility between the BSS and MSC data rates.
Packet control unit
The packet control unit (PCU) is a late addition to the GSM standard. It performs some of the processing tasks of the BSC, but for packet data. The allocation of channels between voice and data is controlled by the base station, but once a channel is allocated to the PCU, the PCU takes full control over that channel.
The PCU can be built into the base station, built into the BSC or even, in some proposed architectures, it can be at the SGSN site. In most of the cases, the PCU is a separate node communicating extensively with the BSC on the radio side and the SGSN on the Gb side.
BSS interfaces
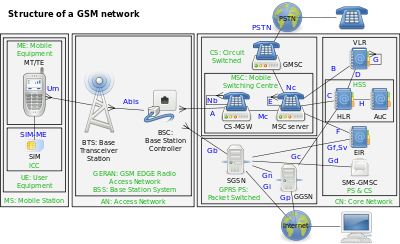
- Um
- The air interface between the mobile station (MS) and the BTS. This interface uses LAPDm protocol for signaling, to conduct call control, measurement reporting, handover, power control, authentication, authorization, location update and so on. Traffic and signaling are sent in bursts of 0.577 ms at intervals of 4.615 ms, to form data blocks each 20 ms.
- Abis
- The interface between the BTS and BSC. Generally carried by a DS-1, ES-1, or E1 TDM circuit. Uses TDM subchannels for traffic (TCH), LAPD protocol for BTS supervision and telecom signaling, and carries synchronization from the BSC to the BTS and MS.
- A
- The interface between the BSC and MSC. It is used for carrying traffic channels and the BSSAP user part of the SS7 stack. Although there are usually transcoding units between BSC and MSC, the signaling communication takes place between these two ending points and the transcoder unit doesn't touch the SS7 information, only the voice or CS data are transcoded or rate adapted.
- Ater
- The interface between the BSC and transcoder. It is a proprietary interface whose name depends on the vendor (for example Ater by Nokia), it carries the A interface information from the BSC leaving it untouched.
- Gb
- Connects the BSS to the SGSN in the GPRS core network.
See also
- Network switching subsystem
- GPRS core network
- Cell site
- U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- Base station
- Cellular repeater
- Telecom infrastructure sharing
- OpenBTS
References
- Networks, Editor ABC of. "4 Things you need to Improve Coverage and Capacity in cellular system". ABC of Networks. Retrieved 2019-10-09.
{{cite web}}:|first=has generic name (help)
External links
- Osmocom OpenBSC - open source Base Station Controller implementation