| Revision as of 15:13, 28 April 2007 editAnomaly1 (talk | contribs)175 editsm Revert vandilism← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:41, 20 December 2024 edit undo100.36.106.199 (talk) Undid revision 1263995588 by Dark Flow (talk) already linked in articleTag: Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Scientific law that a closed system's mass remains constant}} | |||
| The '''law of conservation of mass/matter''', also known as '''law of mass/matter conservation '''(or the ]-] law), states that the ] of a ] of substances will remain constant, regardless of the processes acting inside the system. An equivalent statement is that ] changes form, but cannot be created nor destroyed. This implies that for any chemical process in a closed system, the mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products.''' | |||
| {{more references|date=May 2020}} | |||
| In chemistry, so long as no nuclear reactions take place, a special form the conservation of mass also holds in regard to the conservation of the mass (and number of atoms) of each ]. In most basic chemical reactions and equations, no atoms of any element may be created or destroyed. They must only come out exactly as found in the reactant side of an equation, with a different location in regard to their new chemical formula, as may be found on the product side of an equation. | |||
| ]. Where 4 atoms of hydrogen, 4 atoms of oxygen, and 1 of carbon are present before and after the reaction. The total mass after the reaction is the same as before the reaction.]] | |||
| {{Continuum mechanics |laws}} | |||
| In ] and ], the '''law of conservation of mass''' or '''principle of mass conservation''' states that for any ] to all transfers of ] the ] of the system must remain constant over time.<ref>{{cite book |title=Chemistry: The Molecular Science |author1=John Olmsted |author2=Gregory M. Williams |edition=illustrated |publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-8151-8450-8 |page=69 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1vnk6J8knKkC}} </ref> | |||
| The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form. For example, in ]s, the mass of the chemical components before the reaction is equal to the mass of the components after the reaction. Thus, during any chemical reaction and low-energy ]es in an isolated system, the total mass of the ]s, or starting materials, must be equal to the mass of the products. | |||
| The conservation of mass is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, mechanics, and fluid dynamics. According to ], the conservation of mass is a statement of conservation of energy. The ] of a system of particles is equivalent to its ] energy. Energy is conserved according to any inertial frame and so this system mass defined this way is conserved even under nuclear reactions. It is the sum of the masses of a system's constituent particles that is changed in such a reaction. The decrease in the sum of the masses of the constituent particles becomes an increase in the kinetic energies of the constituents which is what is referred to as a mass-energy conversion, but although the ''sum'' of (rest) masses is not conserved - the system's mass which includes the kinetic energies of the constituents according to the ] ''is'' conserved. | |||
| The concept of mass conservation is widely used in many fields such as ], ], and ]. Historically, mass conservation in chemical reactions was primarily demonstrated in the 17th century<ref></ref> and finally confirmed by ] in the late 18th century. The formulation of this law was of crucial importance in the progress from ] to the modern ] of chemistry. | |||
| Also, for example, several forms of ] are popularly said to show mass to energy conversion in which matter may be converted into ]/] and vice versa. Calculating that the net mass changes in such situations, results from the Newtonian addition of rest masses (see "mass defect" in ]), to get total mass--an operation not allowed once the system's mass has been defined relativistically as its ] energy, instead of the sum of the constituent masses. The ''entire system'' in such conversions continues to have mass, and this mass is conserved in nuclear reactions, unless energy is allowed to escape. | |||
| In reality, the conservation of mass only holds approximately and is considered part of a series of assumptions in ]. The law has to be modified to comply with the laws of ] and ] under the principle of ], which states that energy and mass form one conserved quantity. For very energetic systems the conservation of mass only is shown not to hold, as is the case in ]s and particle-antiparticle ] in ]. | |||
| Tiny amounts of mass are thus gained or lost from systems when they lose or gain heat, or any kind of radiation, and this gain or loss may not be taken into account. However, in many practical (low-energy and chemical) contexts, the assumption of conservation of mass is true to a high degree of approximation, even for systems that are not closed to radiation. | |||
| Mass is also not generally conserved in ]s. Such is the case when any energy or matter is allowed into, or out of, the system. However, unless ] or nuclear reactions are involved, the amount of energy entering or escaping such systems (as ], ], or ]) is usually too small to be measured as a change in the mass of the system. | |||
| ==Historical development and importance== | |||
| For systems that include large gravitational fields, ] has to be taken into account; thus mass–energy conservation becomes a more complex concept, subject to different definitions, and neither mass nor energy is as strictly and simply conserved as is the case in special relativity. | |||
| The law of conservation of mass (which is effectively conservation of weight when weights are properly taken) was clearly formulated by ] in ], who is often for this reason (see below) referred to as the father of modern ]. However, ] (]) had previously expressed similar ideas and proved them in experiments. Historically, the conservation of mass and weight was kept obscure for millennia by the buoyant effect of the Earth's atmosphere on quantities of gases, an effect not understood until the vacuum pump first allowed the effective weighing of gases using scales. Once understood, conservation of mass was of key importance in changing alchemy to modern chemistry. When scientists realized that substances never disappeared from measurement with the scales (once buoyancy had been accounted for), they could for the first time embark on quantitative studies of the transformations of substances. This in turn led to ideas of chemical elements, as well as the idea that all chemical processes and transformations (including both fire and metabolism) are simple reactions between invariant amounts/weights of these elements. | |||
| == Formulation and examples == | |||
| ===Approximate conservation vs. serious violation=== | |||
| The law of conservation of mass can only be formulated in ], in which the energy scales associated with an isolated system are much smaller than <math>mc^2</math>, where <math>m</math> is the mass of a typical object in the system, measured in the ] where the object is at rest, and <math>c</math> is the ]. | |||
| The law can be formulated mathematically in the fields of ] and ], where the conservation of mass is usually expressed using the ], given in ] as <math display="block">\frac{\partial \rho}{\partial t} + \nabla\cdot(\rho \mathbf{v}) = 0,</math> where <math display="inline">\rho</math> is the ] (mass per unit volume), <math display="inline">t</math> is the time, <math display="inline">\nabla\cdot</math> is the ], and <math display="inline">\mathbf{v}</math> is the ] field. | |||
| Even when energy such as heat or light is allowed to enter a system, or escape it, the law of conservation of mass holds to high approximation in cases when neglected. Even in higher energy chemical reactions, the mass-energy of the reactants is huge in comparison to the energy absorbed, retained, or released when they react. By way of example, a gram of TNT releases 4.16 kJ of energy when exploded. However, the rest-energy of a gram of TNT is 90 TJ, or about 20 billion times as much. This means that even if the products of a TNT explosion were stopped and allowed to cool to the original temperature, they would only lose 1 part in 20 billion in weight. This amount would be very difficult to measure. | |||
| The interpretation of the continuity equation for mass is the following: For a given closed surface in the system, the change, over any time interval, of the mass enclosed by the surface is equal to the mass that traverses the surface during that time interval: positive if the matter goes in and negative if the matter goes out. For the whole isolated system, this condition implies that the total mass <math display="inline">M</math>, the sum of the masses of all components in the system, does not change over time, i.e. <math display="block">\frac{\text{d}M}{\text{d}t} = \frac{\text{d}}{\text{d}t} \int \rho \, \text{d}V = 0,</math> where <math display="inline">\text{d}V</math> is the ] that defines the ] over the whole volume of the system. | |||
| ===Serious violations=== | |||
| The continuity equation for the mass is part of the ] of fluid dynamics. Many other ]s describe the conservation and flow of mass and matter in a given system. | |||
| ⚫ | {{main| |
||
| {{main|Conservation_of_energy#Modern physics}} | |||
| In chemistry, the calculation of the amount of ] and ] in a chemical reaction, or ], is founded on the principle of conservation of mass. The principle implies that during a chemical reaction the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. For example, in the following reaction | |||
| Drastic violations of the conservation of mass can occur in systems open to escape of energy, for relativistic processes involving very high speeds or very strong fields, such as ] and very large astronomical objects. In these situations, whenever a system loses potential energy, and this energy ''is allowed to escape'' the system as radiation or heat, the system also loses the corresponding amount of mass with an appropriate factor of ''c''<sup>2</sup>. Essentially, this loss in mass is ponderable in such systems, because a very great amount of radiation or heat is involved (enough to have appreciable mass). Even here, however, it must be again emphasized that the loss or gain in mass would ''not'' appear if the energy associated with it were not allowed to enter or escape the system. | |||
| {{block indent | em = 1.5 | text = {{chem|CH|4}} + 2 {{chem|O|2}} → {{chem|CO|2}} + 2 {{chem|H|2|O}},}} | |||
| where one ] of ] ({{chem|CH|4}}) and two ] molecules {{chem|O|2}} are converted into one molecule of ] ({{chem|CO|2}}) and two of ] ({{chem|H|2|O}}). The number of molecules resulting from the reaction can be derived from the principle of conservation of mass, as initially four ] atoms, 4 oxygen atoms and one carbon atom are present (as well as in the final state); thus the number water molecules produced must be exactly two per molecule of carbon dioxide produced. | |||
| Many ] problems are solved by following the mass distribution of a given system over time; this methodology is known as ]. | |||
| From the non-system view, large violations of conservation of mass in nuclear reactions occur when the total mass of the reaction products is erroneously derived in Newtonian fashion from the sum (addition) of their "rest masses". Such derivation can be accomplished either from allowing energy to escape (i.e., being able to measure all products at "rest," or with zero momentum, because their energy of motion or heat has been removed); or else is equivalent to changing observers (i.e., the "rest mass" of products is calculated by using the value for the mass of each product in its own frame of rest, meaning that the observer has moved multiple times, to look at each particle). None of these operations are correct in special relativity, although they result in no great errors in Newtonian mechanics so long as speeds (and energies) are relatively small (for speeds, this means small in comparison to the speed of light). | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] formulated the law of mass conservation in 1756 and came to the conclusion that the ] is incorrect.<ref>{{cite book |title=Entropy and Information |edition=illustrated |first1=Mikhail V. |last1=Volkenstein |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-3-0346-0078-1 |page=20 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=v6noGJ4YJz4C}} </ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Energy and Mass in Relativity Theory |first1=Lev Borisovič |last1=Okuň |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-981-281-412-8 |page=253 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OjgTS12V0VUC}} </ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Early Russian Organic Chemists and Their Legacy |edition=illustrated |first1=David |last1=Lewis |publisher=Springer Science & Business Media |year=2012 |isbn=978-3-642-28219-5 |page=29 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KaDEDmzwhlsC}} </ref>]] | |||
| ]'s discovery of the law of conservation of mass led to many new findings in the 19th century. ]'s ] and ]'s ] branched from the discoveries of Antoine Lavoisier. Lavoisier's quantitative experiments revealed that combustion involved ] rather than what was previously thought to be ].]] | |||
| As early as 520 BCE, ], a ] based on the teachings of ],<ref>Mahavira is dated 598 BC - 526 BC. See: {{cite book | last =Dundas | first =Paul |author-link=Paul Dundas |series=book series, Library of Religious Beliefs and Practices, edited by John R. Hinnels & ] | title =The Jains | publisher =] | year =2002 | location =London | isbn =978-0-415-26606-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jdjNkZoGFCgC&pg=PA24}} p. 24</ref> stated that the universe and its constituents such as matter cannot be destroyed or created. The ] ] (2nd century CE) states that a substance is permanent, but its modes are characterised by creation and destruction.<ref>Devendra (Muni.), T. G. Kalghatgi, T. S. Devadoss (1983) ''A source-book in Jaina philosophy'' Udaipur:Sri Tarak Guru Jain Gran. p.57. Also see Tattvarthasutra verses 5.29 and 5.37</ref> | |||
| An important idea in ] was that "]", so that what exists now has always existed: no new matter can come into existence where there was none before. An explicit statement of this, along with the further principle that nothing can pass away into nothing, is found in ] (c.{{nbsp}}4th century BCE): "For it is impossible for anything to come to be from what is not, and it cannot be brought about or heard of that what is should be utterly destroyed."<ref>Fr. 12; see pp.291–2 of {{Cite book| edition = 2| publisher = ]| isbn = 978-0-521-27455-5| last = Kirk| first = G. S.|author2=J. E. Raven |author3=Malcolm Schofield | title = The Presocratic Philosophers| location = Cambridge| year = 1983}}</ref> | |||
| A further principle of conservation was stated by ] around the 3rd century BCE, who wrote in describing the nature of the Universe that "the totality of things was always such as it is now, and always will be".<ref>{{Cite book| publisher = Cambridge University Press| isbn = 978-0-521-27556-9| pages = 25–26| last = Long| first = A. A.|author2=D. N. Sedley| title = The Hellenistic Philosophers. Vol 1: Translations of the principal sources with philosophical commentary| chapter = Epicureanism: The principals of conservation| location = Cambridge| year = 1987}}</ref> | |||
| ===Discoveries in chemistry=== | |||
| By the 18th century the principle of conservation of mass during chemical reactions was widely used and was an important assumption during experiments, even before a definition was widely established,<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Whitaker|first=Robert D.|date=1975-10-01|title=An historical note on the conservation of mass|journal=Journal of Chemical Education|volume=52|issue=10|pages=658|doi=10.1021/ed052p658|issn=0021-9584|bibcode=1975JChEd..52..658W}}</ref> though an expression of the law can be dated back to Hero of Alexandria’s time,<ref>{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dUQtlF6pDdQC&dq=Conservation+of+mass+dioptra&pg=PA2 | title=Rheology: An Historical Perspective | isbn=9780444829467 | last1=Tanner | first1=R. I. | last2=Walters | first2=K. | year=1998 | publisher=Elsevier }}</ref> as can be seen in the works of ], ], and ].<ref>Robert D. Whitaker, "", '']'', 52, 10, 658-659, Oct 75</ref> One of the first to outline the principle was ] in 1756. He may have demonstrated it by experiments and certainly had discussed the principle in 1748 in correspondence with ],<ref>{{cite book |last1=Pismen |first1=Len |title=The Swings of Science: From Complexity to Simplicity and Back |date=2018 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-3-319-99777-3 |page=41 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rvx9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA41}}</ref> though his claim on the subject is sometimes challenged.<ref>{{Cite journal | volume = 10 | issue = 3 | pages = 119–127 | last = Pomper | first = Philip | title = Lomonosov and the Discovery of the Law of the Conservation of Matter in Chemical Transformations | journal = Ambix | date = October 1962| doi = 10.1179/amb.1962.10.3.119 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | publisher = ] | last = Lomonosov | first = Mikhail Vasil’evich | others = ] (trans.) | title = Mikhail Vasil'evich Lomonosov on the Corpuscular Theory | location = Cambridge, Mass. | year = 1970 | at = Introduction, p. 25}}</ref> According to the Soviet physicist Yakov Dorfman:<blockquote>The universal law was formulated by Lomonosov on the basis of general philosophical materialistic considerations, it was never questioned or tested by him, but on the contrary, served him as a solid starting position in all research throughout his life. <ref>{{Cite book|last=Дорфман|first=Яков|title=Закон сохранения массы при химических реакциях и физические воззрения Ломоносова // Ломоносов М.В. Сборник статей и материалов, T.5|publisher=М.-Л.: Издательство АН СССР|year=1961|url=http://gidropraktikum.narod.ru/Lomonosov-Dorfman.djvu|pages=193}}</ref> </blockquote>A more refined series of experiments were later carried out by ] who expressed his conclusion in 1773 and popularized the principle of conservation of mass.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |last1=Agnew |first1=Henry |last2=Alviar-Agnew |first2=Marisa |title=3.7 Conservation of Mass - There is No New Matter |url=https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Arkansas_Northeastern_College/CH14133%3A_Chemistry_for_General_Education/03%3A_Matter_and_Energy/3.07%3A_Conservation_of_Mass_-_There_is_No_New_Matter#:~:text=If%20you%20witness%20a%20300%20kg%20tree%20burn%20to%20the%20ground,%20there%20are%20only%20ashes%20left%20after%20the%20burn,%20and%20all%20of%20them%20together%20weigh%2010%20kg.%20It%20may%20make%20you%20wonder%20where%20the%20other%20290%20kg%20went.%20The%20missing%20290%20kg%20was%20released%20into%20the%20atmosphere%20as%20smoke,%20so%20the%20only%20thing%20left%20that%20you%20can%20see%20is%20the%2010%20kg%20of%20ash. |access-date=10 January 2024 |website=LibreTexts™ Chemistry|date=7 January 2020 }}</ref> The demonstrations of the principle disproved the then popular ] that said that mass could be gained or lost in ] and heat processes. | |||
| The conservation of mass was obscure for millennia because of the buoyancy effect of the Earth's atmosphere on the weight of gases. For example, a piece of wood weighs less after burning;<ref name=":0" /> this seemed to suggest that some of its mass disappears, or is transformed or lost. Careful experiments were performed in which chemical reactions such as rusting were allowed to take place in sealed glass ampoules; it was found that the chemical reaction did not change the weight of the sealed container and its contents. Weighing of gases using scales was not possible until the invention of the ] in the 17th century. | |||
| Once understood, the conservation of mass was of great importance in progressing from ] to modern chemistry. Once early chemists realized that chemical substances never disappeared but were only transformed into other substances with the same weight, these scientists could for the first time embark on quantitative studies of the transformations of substances. The idea of mass conservation plus a surmise that certain "elemental substances" also could not be transformed into others by chemical reactions, in turn led to an understanding of ]s, as well as the idea that all chemical processes and transformations (such as burning and metabolic reactions) are reactions between invariant amounts or weights of these chemical elements. | |||
| Following the pioneering work of Lavoisier, the exhaustive experiments of ] supported the consistency of this law in chemical reactions,<ref>Matthew Moncrieff Pattison Muir, (1904)</ref> even though they were carried out with other intentions. His research<ref>''Nouv. Recherches sur les lois des proportions chimiques'' (1865) 152, 171, 189</ref><ref>"Conservation of Mass in Chemical Changes", Part 2 Chemical Society (Great Britain)</ref> indicated that in certain reactions the loss or gain could not have been more than 2 to 4 parts in 100,000.<ref>William Edwards Henderson, (1921)</ref> The difference in the accuracy aimed at and attained by Lavoisier on the one hand, and by ] and Stas on the other, is enormous.<ref>], (1904)</ref> | |||
| === Modern physics === | |||
| ⚫ | {{main|Mass–energy equivalence|Mass in general relativity}} | ||
| The law of conservation of mass was challenged with the advent of special relativity. In one of the ] of ] in 1905, he suggested an equivalence between mass and energy. This theory implied several assertions, like the idea that internal energy of a system could contribute to the mass of the whole system, or that mass could be converted into ]. However, as ] pointed out, a change in mass as a result of extraction or addition of chemical energy, as predicted by Einstein's theory, is so small that it could not be measured with the available instruments and could not be presented as a test of special relativity. Einstein speculated that the energies associated with newly discovered ] were significant enough, compared with the mass of systems producing them, to enable their change of mass to be measured, once the energy of the reaction had been removed from the system. This later indeed proved to be possible, although it was eventually to be the first artificial ] reaction in 1932, demonstrated by ], that proved the first successful test of Einstein's theory regarding mass loss with energy gain. | |||
| The law of conservation of mass and the analogous law of ] were finally generalized and unified into the principle of ], described by ]'s equation <math qid=Q35875>E = mc^2</math>. Special relativity also redefines the concept of mass and energy, which can be used interchangeably and are defined relative to the frame of reference. Several quantities had to be defined for consistency, such as the '']'' of a particle (mass in the rest frame of the particle) and the ''relativistic mass'' (in another frame). The latter term is usually less frequently used. | |||
| In ], conservation of both mass and energy is not globally conserved and its definition is more complicated. | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Conservation Of Mass}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:41, 20 December 2024
Scientific law that a closed system's mass remains constant| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Conservation of mass" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Part of a series on | |||||||
| Continuum mechanics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fick's laws of diffusion | |||||||
Laws
|
|||||||
| Solid mechanics | |||||||
Fluid mechanics
|
|||||||
Rheology
|
|||||||
| Scientists | |||||||
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter the mass of the system must remain constant over time.
The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form. For example, in chemical reactions, the mass of the chemical components before the reaction is equal to the mass of the components after the reaction. Thus, during any chemical reaction and low-energy thermodynamic processes in an isolated system, the total mass of the reactants, or starting materials, must be equal to the mass of the products.
The concept of mass conservation is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, mechanics, and fluid dynamics. Historically, mass conservation in chemical reactions was primarily demonstrated in the 17th century and finally confirmed by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century. The formulation of this law was of crucial importance in the progress from alchemy to the modern natural science of chemistry.
In reality, the conservation of mass only holds approximately and is considered part of a series of assumptions in classical mechanics. The law has to be modified to comply with the laws of quantum mechanics and special relativity under the principle of mass–energy equivalence, which states that energy and mass form one conserved quantity. For very energetic systems the conservation of mass only is shown not to hold, as is the case in nuclear reactions and particle-antiparticle annihilation in particle physics.
Mass is also not generally conserved in open systems. Such is the case when any energy or matter is allowed into, or out of, the system. However, unless radioactivity or nuclear reactions are involved, the amount of energy entering or escaping such systems (as heat, mechanical work, or electromagnetic radiation) is usually too small to be measured as a change in the mass of the system.
For systems that include large gravitational fields, general relativity has to be taken into account; thus mass–energy conservation becomes a more complex concept, subject to different definitions, and neither mass nor energy is as strictly and simply conserved as is the case in special relativity.
Formulation and examples
The law of conservation of mass can only be formulated in classical mechanics, in which the energy scales associated with an isolated system are much smaller than , where is the mass of a typical object in the system, measured in the frame of reference where the object is at rest, and is the speed of light.
The law can be formulated mathematically in the fields of fluid mechanics and continuum mechanics, where the conservation of mass is usually expressed using the continuity equation, given in differential form as where is the density (mass per unit volume), is the time, is the divergence, and is the flow velocity field.
The interpretation of the continuity equation for mass is the following: For a given closed surface in the system, the change, over any time interval, of the mass enclosed by the surface is equal to the mass that traverses the surface during that time interval: positive if the matter goes in and negative if the matter goes out. For the whole isolated system, this condition implies that the total mass , the sum of the masses of all components in the system, does not change over time, i.e. where is the differential that defines the integral over the whole volume of the system.
The continuity equation for the mass is part of the Euler equations of fluid dynamics. Many other convection–diffusion equations describe the conservation and flow of mass and matter in a given system.
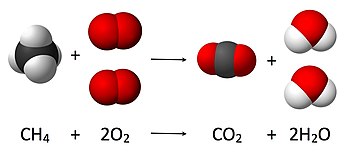
In chemistry, the calculation of the amount of reactant and products in a chemical reaction, or stoichiometry, is founded on the principle of conservation of mass. The principle implies that during a chemical reaction the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. For example, in the following reaction
CH4 + 2 O
2 → CO
2 + 2 H
2O,
where one molecule of methane (CH
4) and two oxygen molecules O
2 are converted into one molecule of carbon dioxide (CO
2) and two of water (H
2O). The number of molecules resulting from the reaction can be derived from the principle of conservation of mass, as initially four hydrogen atoms, 4 oxygen atoms and one carbon atom are present (as well as in the final state); thus the number water molecules produced must be exactly two per molecule of carbon dioxide produced.
Many engineering problems are solved by following the mass distribution of a given system over time; this methodology is known as mass balance.
History


As early as 520 BCE, Jain philosophy, a non-creationist philosophy based on the teachings of Mahavira, stated that the universe and its constituents such as matter cannot be destroyed or created. The Jain text Tattvarthasutra (2nd century CE) states that a substance is permanent, but its modes are characterised by creation and destruction.
An important idea in ancient Greek philosophy was that "Nothing comes from nothing", so that what exists now has always existed: no new matter can come into existence where there was none before. An explicit statement of this, along with the further principle that nothing can pass away into nothing, is found in Empedocles (c. 4th century BCE): "For it is impossible for anything to come to be from what is not, and it cannot be brought about or heard of that what is should be utterly destroyed."
A further principle of conservation was stated by Epicurus around the 3rd century BCE, who wrote in describing the nature of the Universe that "the totality of things was always such as it is now, and always will be".
Discoveries in chemistry
By the 18th century the principle of conservation of mass during chemical reactions was widely used and was an important assumption during experiments, even before a definition was widely established, though an expression of the law can be dated back to Hero of Alexandria’s time, as can be seen in the works of Joseph Black, Henry Cavendish, and Jean Rey. One of the first to outline the principle was Mikhail Lomonosov in 1756. He may have demonstrated it by experiments and certainly had discussed the principle in 1748 in correspondence with Leonhard Euler, though his claim on the subject is sometimes challenged. According to the Soviet physicist Yakov Dorfman:
The universal law was formulated by Lomonosov on the basis of general philosophical materialistic considerations, it was never questioned or tested by him, but on the contrary, served him as a solid starting position in all research throughout his life.
A more refined series of experiments were later carried out by Antoine Lavoisier who expressed his conclusion in 1773 and popularized the principle of conservation of mass. The demonstrations of the principle disproved the then popular phlogiston theory that said that mass could be gained or lost in combustion and heat processes.
The conservation of mass was obscure for millennia because of the buoyancy effect of the Earth's atmosphere on the weight of gases. For example, a piece of wood weighs less after burning; this seemed to suggest that some of its mass disappears, or is transformed or lost. Careful experiments were performed in which chemical reactions such as rusting were allowed to take place in sealed glass ampoules; it was found that the chemical reaction did not change the weight of the sealed container and its contents. Weighing of gases using scales was not possible until the invention of the vacuum pump in the 17th century.
Once understood, the conservation of mass was of great importance in progressing from alchemy to modern chemistry. Once early chemists realized that chemical substances never disappeared but were only transformed into other substances with the same weight, these scientists could for the first time embark on quantitative studies of the transformations of substances. The idea of mass conservation plus a surmise that certain "elemental substances" also could not be transformed into others by chemical reactions, in turn led to an understanding of chemical elements, as well as the idea that all chemical processes and transformations (such as burning and metabolic reactions) are reactions between invariant amounts or weights of these chemical elements.
Following the pioneering work of Lavoisier, the exhaustive experiments of Jean Stas supported the consistency of this law in chemical reactions, even though they were carried out with other intentions. His research indicated that in certain reactions the loss or gain could not have been more than 2 to 4 parts in 100,000. The difference in the accuracy aimed at and attained by Lavoisier on the one hand, and by Edward W. Morley and Stas on the other, is enormous.
Modern physics
Main articles: Mass–energy equivalence and Mass in general relativityThe law of conservation of mass was challenged with the advent of special relativity. In one of the Annus Mirabilis papers of Albert Einstein in 1905, he suggested an equivalence between mass and energy. This theory implied several assertions, like the idea that internal energy of a system could contribute to the mass of the whole system, or that mass could be converted into electromagnetic radiation. However, as Max Planck pointed out, a change in mass as a result of extraction or addition of chemical energy, as predicted by Einstein's theory, is so small that it could not be measured with the available instruments and could not be presented as a test of special relativity. Einstein speculated that the energies associated with newly discovered radioactivity were significant enough, compared with the mass of systems producing them, to enable their change of mass to be measured, once the energy of the reaction had been removed from the system. This later indeed proved to be possible, although it was eventually to be the first artificial nuclear transmutation reaction in 1932, demonstrated by Cockcroft and Walton, that proved the first successful test of Einstein's theory regarding mass loss with energy gain.
The law of conservation of mass and the analogous law of conservation of energy were finally generalized and unified into the principle of mass–energy equivalence, described by Albert Einstein's equation . Special relativity also redefines the concept of mass and energy, which can be used interchangeably and are defined relative to the frame of reference. Several quantities had to be defined for consistency, such as the rest mass of a particle (mass in the rest frame of the particle) and the relativistic mass (in another frame). The latter term is usually less frequently used.
In general relativity, conservation of both mass and energy is not globally conserved and its definition is more complicated.
See also
- Charge conservation
- Conservation law
- Fick's laws of diffusion
- Law of definite proportions
- Law of multiple proportions
References
- John Olmsted; Gregory M. Williams (1997). Chemistry: The Molecular Science (illustrated ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-8151-8450-8. Extract of page 69
- Lavoisier's Method
- Volkenstein, Mikhail V. (2009). Entropy and Information (illustrated ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 20. ISBN 978-3-0346-0078-1. Extract of page 20
- Okuň, Lev Borisovič (2009). Energy and Mass in Relativity Theory. World Scientific. p. 253. ISBN 978-981-281-412-8. Extract of page 253
- Lewis, David (2012). Early Russian Organic Chemists and Their Legacy (illustrated ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 29. ISBN 978-3-642-28219-5. Extract of page 29
- Mahavira is dated 598 BC - 526 BC. See: Dundas, Paul (2002). The Jains. book series, Library of Religious Beliefs and Practices, edited by John R. Hinnels & Ninian Smart. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26606-2. p. 24
- Devendra (Muni.), T. G. Kalghatgi, T. S. Devadoss (1983) A source-book in Jaina philosophy Udaipur:Sri Tarak Guru Jain Gran. p.57. Also see Tattvarthasutra verses 5.29 and 5.37
- Fr. 12; see pp.291–2 of Kirk, G. S.; J. E. Raven; Malcolm Schofield (1983). The Presocratic Philosophers (2 ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27455-5.
- Long, A. A.; D. N. Sedley (1987). "Epicureanism: The principals of conservation". The Hellenistic Philosophers. Vol 1: Translations of the principal sources with philosophical commentary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 25–26. ISBN 978-0-521-27556-9.
- Whitaker, Robert D. (1975-10-01). "An historical note on the conservation of mass". Journal of Chemical Education. 52 (10): 658. Bibcode:1975JChEd..52..658W. doi:10.1021/ed052p658. ISSN 0021-9584.
- Tanner, R. I.; Walters, K. (1998). Rheology: An Historical Perspective. Elsevier. ISBN 9780444829467.
- Robert D. Whitaker, "An Historical Note on the Conservation of Mass", Journal of Chemical Education, 52, 10, 658-659, Oct 75
- Pismen, Len (2018). The Swings of Science: From Complexity to Simplicity and Back. Springer. p. 41. ISBN 978-3-319-99777-3.
- Pomper, Philip (October 1962). "Lomonosov and the Discovery of the Law of the Conservation of Matter in Chemical Transformations". Ambix. 10 (3): 119–127. doi:10.1179/amb.1962.10.3.119.
- Lomonosov, Mikhail Vasil’evich (1970). Mikhail Vasil'evich Lomonosov on the Corpuscular Theory. Henry M. Leicester (trans.). Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press. Introduction, p. 25.
- Дорфман, Яков (1961). Закон сохранения массы при химических реакциях и физические воззрения Ломоносова // Ломоносов М.В. Сборник статей и материалов, T.5. М.-Л.: Издательство АН СССР. p. 193.
- ^ Agnew, Henry; Alviar-Agnew, Marisa (7 January 2020). "3.7 Conservation of Mass - There is No New Matter". LibreTexts™ Chemistry. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- Matthew Moncrieff Pattison Muir, The Elements of Chemistry (1904)
- Nouv. Recherches sur les lois des proportions chimiques (1865) 152, 171, 189
- "Conservation of Mass in Chemical Changes"Journal - Chemical Society, London, Vol.64, Part 2 Chemical Society (Great Britain)
- William Edwards Henderson, A Course in General Chemistry (1921)
- Ida Freund, The study of Chemical Composition: an account of its method and historical development, with illustrative quotations (1904)

 , where
, where  is the mass of a typical object in the system, measured in the
is the mass of a typical object in the system, measured in the  is the
is the  where
where  is the
is the  is the time,
is the time,  is the
is the  is the
is the  , the sum of the masses of all components in the system, does not change over time, i.e.
, the sum of the masses of all components in the system, does not change over time, i.e.  where
where  is the
is the 