| Revision as of 17:31, 29 August 2003 editYanyang1985 (talk | contribs)413 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 01:09, 10 January 2025 edit undoThehistorianisaac (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,982 edits →See alsoTag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Prefecture-level city in Guangxi}} | |||
| '''Guilin'''(桂林 ]: gui1 lin2) is ]'s most picturesque city, situated in the northeast of ] on the west bank of the beautiful ]. | |||
| {{More citations needed|date=April 2011}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2017}} | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | |||
| <!-- Basic info ----------------> | |||
| |name = Guilin | |||
| |official_name = <!-- Official name in English if different from 'name' --> | |||
| |native_name = {{lang|zh|桂林市 • {{lang|za|Gveilinz Si}}}} | |||
| |other_name = Kweilin | |||
| |nickname = | |||
| |settlement_type = ] | |||
| |total_type = <!-- to set a non-standard label for total area and population rows --> | |||
| |motto = | |||
| <!-- images and maps -----------> | |||
| |image_skyline = {{multiple image | |||
| |border = infobox | |||
| |total_width = 280px | |||
| |image_style = border:1; | |||
| |perrow = 1/2/3/1 | |||
| |image1 = View of Guilin from Elephant Trunk Hill (cropped).jpg | |||
| |image2 = Xiangshan Scenic Area 89468-Guilin (31130832628).jpg | |||
| |image3 = Lake Shanhu pagodas at night.jpg | |||
| |image4 = Longsheng rice terraces 87849-Longsheng (49040768916).jpg | |||
| |image5 = Jingjiang Princes City 89785-Guilin (49040802591).jpg | |||
| |image6 = Flickr - archer10 (Dennis) - China-7516.jpg | |||
| |image7 = 1 aerial yangshuo panorama 2017.jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| |image_caption = From left to right, top to bottom: View of Guilin city; ], ]; ], ], ]; ] scenery | |||
| |image_size = 280px | |||
| |image_seal = | |||
| |seal_size = | |||
| |image_shield = | |||
| |shield_size = | |||
| |image_blank_emblem = | |||
| |blank_emblem_type = ] | |||
| |blank_emblem_size = | |||
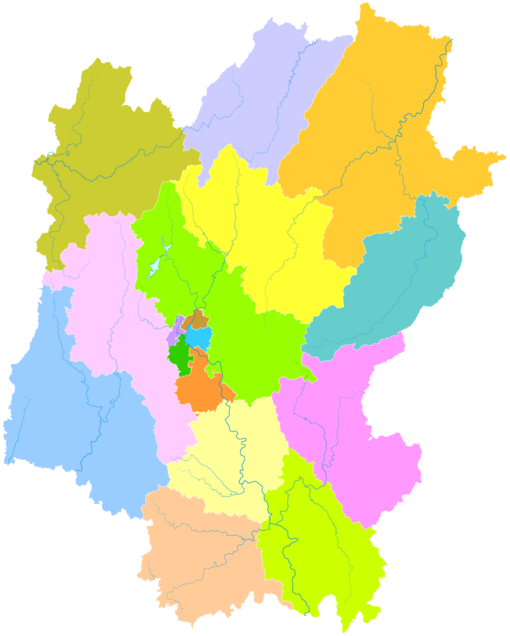
| |image_map = Guangxi subdivisions - Guilin.svg | |||
| |mapsize = | |||
| |map_caption = Location of Guilin City jurisdiction in Guangxi | |||
| |image_map1 = | |||
| |mapsize1 = | |||
| |map_caption1 = | |||
| |image_dot_map = | |||
| |dot_mapsize = | |||
| |dot_map_caption = | |||
| |dot_x = | |||
| |dot_y = | |||
| |pushpin_map = China | |||
| |pushpin_label_position = | |||
| |pushpin_map_caption = Location in China | |||
| |pushpin_mapsize = | |||
| <!-- Location ------------------> | |||
| | subdivision_type = Country | |||
| |subdivision_name = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type2 = | |||
| |subdivision_name2 = | |||
| |seat_type = | |||
| |seat = | |||
| |parts_type = | |||
| |parts_style = <!-- =list (for list), coll (for collapsed list), para (for paragraph format) | |||
| Default is list if up to 5 items, coll if more than 5--> | |||
| |parts = <!-- parts text, or header for parts list --> | |||
| |p1 = | |||
| |p2 = <!-- etc. up to p50: for separate parts to be listed--> | |||
| <!-- Politics -----------------> | |||
| |government_footnotes = | |||
| |government_type = | |||
| |leader_title = | |||
| |leader_name = | |||
| |leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager --> | |||
| |leader_name1 = | |||
| |leader_title2 = | |||
| |leader_name2 = | |||
| |leader_title3 = | |||
| |leader_name3 = | |||
| |leader_title4 = | |||
| |leader_name4 = | |||
| |established_title = <!-- Settled --> | |||
| |established_date = | |||
| |established_title1 = <!-- Incorporated (town) --> | |||
| |established_date1 = | |||
| |established_title2 = <!-- Incorporated (city) --> | |||
| |established_date2 = | |||
| |established_title3 = | |||
| |established_date3 = | |||
| |founder = | |||
| |named_for = | |||
| <!-- Area ---------------------> | |||
| |area_magnitude = <!-- use only to set a special wikilink --> | |||
| |unit_pref = <!--Enter: Imperial, to display imperial before metric--> | |||
| |area_footnotes = | |||
| |area_total_km2 = 27797<!-- ALL fields with measurements are subject to automatic unit conversion--> | |||
| |area_land_km2 = <!--See table @ Template:Infobox Settlement for details on unit conversion--> | |||
| |area_water_km2 = | |||
| |area_water_percent = | |||
| |area_urban_km2 = 2753 | |||
| |area_metro_km2 = 5041 | |||
| |area_blank1_title = | |||
| |area_blank1_km2 = | |||
| <!-- Elevation --------------------------> | |||
| |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> tags--> | |||
| |elevation_m = 153 | |||
| |elevation_max_m = | |||
| |elevation_min_m = | |||
| <!-- Population -----------------------> | |||
| |population_as_of = 2020 census | |||
| |population_footnotes = <ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.citypopulation.de/en/china/guangxi/admin/|title = China: Guăngxī (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map}}</ref> | |||
| |population_note = | |||
| |population_total = 4931137 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = auto <!--For automatic calculation, any density field may contain: auto --> | |||
| |population_metro = 2148641 | |||
| |population_density_metro_km2 = auto | |||
| |population_urban = 1725865 | |||
| |population_density_urban_km2 = auto | |||
| |population_blank1_title = | |||
| |population_blank1 = | |||
| |population_density_blank1_km2 = | |||
| | demographics_type2 = GDP<ref>{{citation|title=广西统计年鉴-2021|url=http://tjj.gxzf.gov.cn//tjsj/tjnj/material/tjnj20200415/2022/indexch.htm|website=tjj.gxzf.gov.cn}}</ref> | |||
| | demographics2_title1 = ] | |||
| | demographics2_info1 = ] 231.1 billion<br />] 35.8 billion | |||
| | demographics2_title2 = Per capita | |||
| | demographics2_info2 = CN¥ 46,767<br />US$ 7,249 | |||
| <!-- General information ---------------> | |||
| |timezone = ] | |||
| |utc_offset = +8 | |||
| |coor_pinpoint = Guilin Central Square ({{lang|zh-Hans|桂林中心广场}}) | |||
| |coordinates = {{coord|25.275|N|110.296|E|type:adm2nd_region:CN-45_source:Gaode|format=dms|display=it}} | |||
| |postal_code_type = ] | |||
| |postal_code = 541XXX | |||
| |area_code = 0773 | |||
| |iso_code = ] | |||
| |blank_name = ] | |||
| |blank_info = {{lang|zh-cn|桂C}} for Guilin's city proper, Yangshuo, and Lingui; all others {{lang|zh-cn|桂H}} | |||
| |website = {{URL|www.guilin.gov.cn/}} | |||
| |footnotes = | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Infobox Chinese | |||
| |pic=Guilin_(Chinese_characters).svg | |||
| |piccap= "Guìlín" in Chinese characters | |||
| |picupright=0.45 | |||
| |c = {{linktext|lang=zh|桂林}} | |||
| |p = Guìlín|showflag=p | |||
| |bpmf = ㄍㄨㄟˋ ㄌㄧㄣˊ | |||
| |gr = Gueylin | |||
| |w = Kuei<sup>4</sup>-lin<sup>2</sup> | |||
| |mi = {{IPAc-cmn|g|ui|4|.|l|in|2}} | |||
| |myr = Gwèilín | |||
| |y =Gwailàhm | |||
| |j = Gwai3lam4 | |||
| |ci = {{IPAc-yue|gw|ai|3|.|l|am|4}} | |||
| |h = Kui-lìm | |||
| |zha = Gveilinz | |||
| |zha57 = Gveilinƨ | |||
| |psp = Kweilin | |||
| |l="] Forest" | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Guilin'''<!--Chinese in infobox--> (]: ''Gveilinz''), ] ] as '''Kweilin''', is a ] in the northeast of ]'s ]. It is situated on the west bank of the ] and borders ] to the north. Its name means "forest of ]", owing to the large number of fragrant sweet osmanthus trees located in the region. The city has long been renowned for its ] of ] topography. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| 190,000,000 ago, the area around present-day Guilin was a vast water, a part of the ancient sea. Due to the movement of ], it rose and became land. | |||
| Guilin is one of China's most popular tourist destinations,<ref>{{cite book |last=Foster |first=Simon |title=Frommer's China |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9781118094198 |url-access=registration |year=2012 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |isbn=9781118223529 |pages=}}</ref> and the epithet "By water, by mountains, most lovely, Guilin" ({{zh|labels=no|c=山水甲天下}})<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://language.chinadaily.com.cn/trans/2009-01/24/content_7414726.htm|script-title=zh:“桂林山水甲天下”之英译 |work=] |language=zh-cn |access-date=2019-06-11}}</ref> is often associated with the city. The State Council of China has designated Guilin a ], doing so in the first edition of the list. | |||
| ], the city of Guilin was founded in the ] as a small settlement along the bank of ]. | |||
| == History == | |||
| ], during the reign of ] of the ], Guilin was named Shi An County. | |||
| Before the ], the Guilin region was settled by the ].<ref name="people" /> In 314 BC, a small settlement was established along the banks of the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.discoverchina.com/article/cruise-through-the-beautiful-scenery-of-the-li-river-in-guilin|title=Cruise Through The Beautiful Scenery Of The Li River In Guilin|website=Discover China|access-date=2020-01-25}}</ref> | |||
| During the Qin dynasty's (221–206 BC) campaigns against the state of ], the first administration was set up in the area around Guilin.<ref name="Encyclopædia Britannica Online">{{cite web | url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/324390/Guilin | title=Guilin (China) Encyclopædia Britannica | publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica (Online) | access-date=11 July 2013}}</ref> The modern city was located within the ], which is the origin of the modern name "Guilin". | |||
| The city prospered in ] and ] ] and became the political, economic and cultural centre of ]. The city was also a nexus between the central government and the southwest border where the regular armies were placed to guard the border. The ]s were built through the city so that the food supplies could be directly transported from the food-productive ] plain to the farthest southwestern point of the empire. | |||
| In 111 BC, during the reign of ] of the ], Shi'an County ({{zh|links=no|s=始安县|t=始安縣}}) was established, which could be regarded as the beginning of the city. | |||
| In the ], Guilin became the provincial capital due to its immense role in the province. | |||
| In AD 507, the town was renamed Guizhou (Gui Prefecture, {{zh|labels=no|c=桂州}}).<ref name="people" /> | |||
| In 634, ] was established at the modern site of Guilin, under Gui Prefecture. In 868, ] rebelled against the Tang from Gui Prefecture.<ref name="people" /> | |||
| In ], Guilin ceased to be the capital of the province. Instead, ], another center of the provence and a heroic city with more than 1,600 years of history, became the capital. | |||
| Guilin prospered in the ] and ] dynasties but remained a county. The city was also a nexus between the central government and the southwest border, and it was where regular armies were placed to guard that border. ]s were built through the city so that food supplies could be directly transported from the food-productive ] plain to the farthest southwestern point of the empire. | |||
| In ], Guilin became one of the headquarters of the ] led by ]. | |||
| In 997, ], the predecessor of modern Guangxi, was established, with Guizhou as the capital. In 1133, Guizhou was renamed Jingjiang Prefecture ({{zh|links=no|s=静江路|t=靜江路}}). In 1367, the name was changed to Guilin Prefecture ({{zh|labels=no|c=桂林府}}).<ref name="people">{{cite web |script-title=zh:桂林概况 |url=http://politics.people.com.cn/GB/8198/53318/53322/3707531.html |website=people.com.cn |language=zh-cn |access-date=29 October 2018 |archive-date=29 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181029191712/http://politics.people.com.cn/GB/8198/53318/53322/3707531.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In ], the city acquired its present name. | |||
| In 1921, Guilin became one of the headquarters of the Northern Expeditionary Army led by ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/travel/2011-03/09/content_12142923.htm|title=Guilin never ceases to amaze|access-date=19 April 2016}}</ref> In 1940, Guilin City was established.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.justchina.org/china/guilin/guilin-history.asp |title=History of Guilin |access-date=18 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120509193825/http://www.justchina.org/china/guilin/guilin-history.asp |archive-date=9 May 2012 |url-status=dead |df=dmy-all }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.travelchinaguide.com/cityguides/guangxi/guilin/|title=Guilin History|access-date=19 April 2016}}</ref> Guilin was the provincial capital of Guangxi before 1912 and from 1936 to 1949. | |||
| In ], this ancient city was listed by the ] as one of the four cities (the other three being ], ] and ]) where the protection of historical and cultural heritage as well as natural scenery should be treated as a prior project. | |||
| Guilin became one of the most important military, transport, and cultural centers of China during World War II. The city drastically expanded as refugees from all over China poured in, and by 1944 its population had grown from 70,000 pre-war to more than 500,000. It hosted intellectuals and artists including ], ], ], ], ], ] and many others.<ref>{{cite news |title=初心50城|广西桂林:"抗战文化城"的新文旅之路 |url=https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_12355661 |access-date=7 December 2021 |agency=thepaper.cn |date=23 April 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ==Neighboring ]== | |||
| ], ], ] and ] | |||
| In 1950, the provincial capital of Guangxi was moved from Guilin to ]. | |||
| ==Physical setting== | |||
| *Area: 27,809 sq km | |||
| *subtropical region | |||
| *the typical ] | |||
| *Mountains: ], ], ], ], ] and ] | |||
| *Rivers: ] | |||
| In 1981, Guilin was listed by the ] as one of the four cities (the other three being ], ], and ]) where the protection of historical and cultural heritage, as well as ], should be treated as a priority project.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.greatwall-of-china-beijing.com/guilin-travel.html#.UUc8KxeG1Lo|title=Beijing Hotels 【 #1 Ranked Hotel in Beijing 】 - Nehow.com|work=Nehow.com|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-date=25 May 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130525161725/http://www.greatwall-of-china-beijing.com/guilin-travel.html#.UUc8KxeG1Lo|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.chinatourguide.com/guilin/guilin_history.html|title=Guilin History|access-date=19 April 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ==People== | |||
| *Population: 1.34 million | |||
| == Administrative divisions == | |||
| *Urban Population: 600,000 | |||
| ] at Fuboshan, Guilin.]] | |||
| *]: ], ], ], ], ] and ] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Guilin administers seventeen ], including 6 ], 8 ], 2 ], and 1 ]. | |||
| *]: | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|秀峰区}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|象山区}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|叠彩区}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|七星区}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|雁山区}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|临桂区}}) | |||
| * ]: | |||
| **] city ({{lang|zh|荔浦市}}) | |||
| * ]: | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|阳朔县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|灵川县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|兴安县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh|全州县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh|永福县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|资源县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|灌阳县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|平乐县}}) | |||
| * ]: | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|恭城瑶族自治县}}) | |||
| **] ({{lang|zh-hans|龙胜各族自治县}}) | |||
| {| class="wikitable | |||
| ! Map | |||
| |- | |||
| | align="center"|<div style="position: relative" class="center"> | |||
| {{Image label begin|image=Administrative Division Guilin.png|width={{{1|510}}}|link=}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=550|y=1200|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=680|y=1150|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=600|y=1270|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=710|y=1210|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=670|y=1420|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=380|y=1230|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=750|y=1670|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=640|y=1040|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1220|y=450|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=910|y=860|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=230|y=1540|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1320|y=1020|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=300|y=570|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=860|y=380|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1110|y=1980|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1070|y=1530|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=690|y=2030|scale={{{1|510}}}/1820|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label end}} | |||
| </div> | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| ], 1954)]] | |||
| <!-- | |||
| {{climate chart | |||
| | Guilin | |||
| | 5.4 | 11.5 | 64 | |||
| | 7.0 | 12.7 | 97 | |||
| | 10.4 | 16.5 | 137 | |||
| | 15.9 | 22.7 | 247 | |||
| | 20.1 | 27.1 | 352 | |||
| | 23.4 | 30.4 | 347 | |||
| | 24.8 | 32.6 | 231 | |||
| | 24.5 | 32.8 | 173 | |||
| | 21.9 | 30.3 | 82 | |||
| | 17.3 | 25.6 | 66 | |||
| | 12.1 | 20.2 | 64 | |||
| | 7.3 | 15.2 | 43 | |||
| |float=left | |||
| |clear=right | |||
| |source = CMA<REF NAME = CMA /> }}--> | |||
| Guilin is located in northern Guangxi, bordering ] to the west, ] to the southwest, ] to the south, ] to the southeast, and within neighbouring ], ] to the northwest, ] to the north, and ] to the east. It has a total area of {{convert|27809|km2}}. The topography of the area is marked by ]. The karsts surrounding Guilin are made of ] period ] and ]s. The ] flows through the city. | |||
| *Hills and mountains: Diecai Hill ({{lang|zh-hans-CN|叠彩山}}), ], Wave-Subduing Hill ({{lang|zh-hans-CN|伏波山}}), Lipu Mountains, ], the highest peak of Guangxi, and Yao Hill ({{lang|zh-hans-CN|尧山}}) | |||
| *Caves: ], ] | |||
| ==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
| ]]] | |||
| *damp monsoon climate | |||
| Guilin has a monsoon-influenced ] (] ''Cfa'', bordering on ''Cwa''), with short, mild winters, and long, hot, humid summers. Winter begins dry but becomes progressively wetter and cloudier. Spring is generally overcast and often rainy, while summer continues to be rainy though is the sunniest time of year. Autumn is sunny and dry. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from {{convert|8.1|°C|1}} in January to {{convert|28.2|°C|1}} in July, and the annual mean is {{convert|19.12|°C|1}}. The annual rainfall is just under {{convert|1890|mm|in|abbr=on}} and is delivered in bulk (~50%) from April to June, when the ]s occur and often create the risk of flooding. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 14% in March to 53% in September, the city receives 1,487 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from {{convert|−4.9|°C|0}} (though an unofficial record low of {{convert|−5.0|°C|0}} was recorded on 25 January 1940)<ref>{{Cite web |title=中国各地城市的历史最低气温 |url=https://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309404203050792315805 |access-date=2024-09-15 |website=weibo.com}}</ref> to {{convert|40.3|°C|0}}.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Extreme Temperatures Around the World |url=https://www.mherrera.org/temp.htm |access-date=2024-09-15 |website=www.mherrera.org}}</ref> | |||
| *warm and rainy | |||
| *plenty of sunshine and clear division of four seasons | |||
| *Average Temperature: 19C annually | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| ==Products== | |||
| | width = auto | |||
| ]s, ]s, ], ]s, ], | |||
| | metric first = y | |||
| ], ], ], ], ], | |||
| | single line = y | |||
| ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] | |||
| | collapsed = Y | |||
| | location = Guilin (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–present) | |||
| | Jan high C = 11.7 | |||
| | Feb high C = 14.2 | |||
| | Mar high C = 17.5 | |||
| | Apr high C = 23.7 | |||
| | May high C = 27.9 | |||
| | Jun high C = 30.5 | |||
| | Jul high C = 32.8 | |||
| | Aug high C = 33.2 | |||
| | Sep high C = 30.8 | |||
| | Oct high C = 26.3 | |||
| | Nov high C = 20.8 | |||
| | Dec high C = 14.9 | |||
| | Jan mean C = 8.4 | |||
| | Feb mean C = 10.6 | |||
| | Mar mean C = 13.9 | |||
| | Apr mean C = 19.6 | |||
| | May mean C = 23.7 | |||
| | Jun mean C = 26.6 | |||
| | Jul mean C = 28.4 | |||
| | Aug mean C = 28.4 | |||
| | Sep mean C = 26.0 | |||
| | Oct mean C = 21.5 | |||
| | Nov mean C = 16.2 | |||
| | Dec mean C = 10.8 | |||
| | Jan low C = 6.1 | |||
| | Feb low C = 8.3 | |||
| | Mar low C = 11.4 | |||
| | Apr low C = 16.6 | |||
| | May low C = 20.7 | |||
| | Jun low C = 23.8 | |||
| | Jul low C = 25.2 | |||
| | Aug low C = 25.0 | |||
| | Sep low C = 22.6 | |||
| | Oct low C = 18.3 | |||
| | Nov low C = 13.1 | |||
| | Dec low C = 8.0 | |||
| | Jan record high C = 27.6 | |||
| | Jan record low C = −4.9 | |||
| | Feb record high C = 32.8 | |||
| | Feb record low C = −3.6 | |||
| | Mar record high C = 33.7 | |||
| | Mar record low C = 0.0 | |||
| | Apr record high C = 35.6 | |||
| | Apr record low C = 4.0 | |||
| | May record high C = 36.6 | |||
| | May record low C = 10.7 | |||
| | Jun record high C = 37.4 | |||
| | Jun record low C = 13.0 | |||
| | Jul record high C = 40.3 | |||
| | Jul record low C = 18.2 | |||
| | Aug record high C = 39.4 | |||
| | Aug record low C = 18.3 | |||
| | Sep record high C = 38.5 | |||
| | Sep record low C = 12.9 | |||
| | Oct record high C = 35.6 | |||
| | Oct record low C = 6.1 | |||
| | Nov record high C = 32.6 | |||
| | Nov record low C = 0.7 | |||
| | Dec record high C = 27.6 | |||
| | Dec record low C = −3.3 | |||
| | precipitation colour = green | |||
| | Jan precipitation mm = 68.9 | |||
| | Feb precipitation mm = 83.9 | |||
| | Mar precipitation mm = 153.0 | |||
| | Apr precipitation mm = 226.7 | |||
| | May precipitation mm = 321.1 | |||
| | Jun precipitation mm = 448.7 | |||
| | Jul precipitation mm = 266.3 | |||
| | Aug precipitation mm = 147.6 | |||
| | Sep precipitation mm = 80.9 | |||
| | Oct precipitation mm = 54.9 | |||
| | Nov precipitation mm = 81.9 | |||
| | Dec precipitation mm = 54.1 | |||
| | Jan humidity = 71 | |||
| | Feb humidity = 73 | |||
| | Mar humidity = 78 | |||
| | Apr humidity = 78 | |||
| | May humidity = 78 | |||
| | Jun humidity = 81 | |||
| | Jul humidity = 77 | |||
| | Aug humidity = 75 | |||
| | Sep humidity = 70 | |||
| | Oct humidity = 66 | |||
| | Nov humidity = 67 | |||
| | Dec humidity = 65 | |||
| | unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm | |||
| | Jan precipitation days = 13.5 | |||
| | Feb precipitation days = 13.6 | |||
| | Mar precipitation days = 19.3 | |||
| | Apr precipitation days = 18.5 | |||
| | May precipitation days = 18.2 | |||
| | Jun precipitation days = 18.5 | |||
| | Jul precipitation days = 16.1 | |||
| | Aug precipitation days = 12.5 | |||
| | Sep precipitation days = 7.9 | |||
| | Oct precipitation days = 7.1 | |||
| | Nov precipitation days = 9.2 | |||
| | Dec precipitation days = 10.1 | |||
| | year precipitation days = | |||
| | Jan sun = 58.4 | |||
| | Feb sun = 52.2 | |||
| | Mar sun = 55.0 | |||
| | Apr sun = 78.7 | |||
| | May sun = 113.1 | |||
| | Jun sun = 113.3 | |||
| | Jul sun = 180.6 | |||
| | Aug sun = 197.2 | |||
| | Sep sun = 180.3 | |||
| | Oct sun = 157.1 | |||
| | Nov sun = 122.9 | |||
| | Dec sun = 102.1 | |||
| | year sun = | |||
| | Jan percentsun = 18 | |||
| | Feb percentsun = 16 | |||
| | Mar percentsun = 15 | |||
| | Apr percentsun = 21 | |||
| | May percentsun = 27 | |||
| | Jun percentsun = 28 | |||
| | Jul percentsun = 43 | |||
| | Aug percentsun = 49 | |||
| | Sep percentsun = 49 | |||
| | Oct percentsun = 44 | |||
| | Nov percentsun = 38 | |||
| | Dec percentsun = 31 | |||
| | year percentsun = | |||
| | Jan snow days = 1.1 | |||
| | Feb snow days = 0.4 | |||
| | Mar snow days = 0 | |||
| | Apr snow days = 0 | |||
| | May snow days = 0 | |||
| | Jun snow days = 0 | |||
| | Jul snow days = 0 | |||
| | Aug snow days = 0 | |||
| | Sep snow days = 0 | |||
| | Oct snow days = 0 | |||
| | Nov snow days = 0 | |||
| | Dec snow days = 0.5 | |||
| | year snow days = | |||
| | source 1 = ]<ref name="cma graphical">{{cite web |url=http://data.cma.cn/data/weatherBk.html |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data |publisher=] |language = zh-hans |access-date=28 May 2023}}</ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite web|url=https://experience.arcgis.com/template/e724038fda394e9d9b7921f10fd1aa55/page/%E7%BA%AF%E8%A1%A8%E6%A0%BC%E7%BB%9F%E8%AE%A1-(%E5%AF%B9%E6%AF%948110%E5%8F%98%E5%8C%96)/?org=UQmaps |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网|publisher=] |language = zh-hans | access-date =28 May 2023}}</ref><ref name="CMA old"> | |||
| {{cite web|url=http://old-cdc.cma.gov.cn/shuju/search1.jsp?dsid=SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MMON_19712000_CES&tpcat=SURF&type=table&pageid=3 |script-title=zh:中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年)|publisher=] |accessdate=2010-05-25 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130921055035/http://old-cdc.cma.gov.cn/shuju/search1.jsp?dsid=SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MMON_19712000_CES&tpcat=SURF&type=table&pageid=3 |archivedate=2013-09-21 | |||
| }}</ref>all-time extreme temperature<ref name = Mherrera>{{cite web | |||
| |url= http://www.mherrera.org/temp.htm | |||
| |title= Extreme Temperatures Around the World | |||
| |access-date= 2024-09-09 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| | source = | |||
| }} | |||
| == |
==Demographics== | ||
| According to the ] its population was 4,931,137 inhabitants and 2,148,641 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 6 urban Districts plus Lingchuan County now being conurbated. | |||
| There are more than 30 noted scenic spots within the boundaries of Guilin Peak. | |||
| According to the ], the largest ethnic group in the prefecture-level city was ], accounting for 84.53% of the total population. This was followed by ] at 7.79% and ] at 4.81%.<ref>广西壮族自治区统计局、广西壮族自治区人口普查办公室. 《广西壮族自治区2010年人口普查资料》. 中国统计出版社. 2012年7月. ISBN 978-7-5037-6549-0.</ref> Citizens of Guilin's urban area speak a dialect of ], while ] is predominantly spoken in suburbs and surrounding areas.<ref>{{cite web |title=桂林市志 方言志 |url=http://lib.gxdfz.org.cn/view-b10-389.html |publisher=广西壮族自治区地方志编纂委员会办公室}}</ref> | |||
| *the Ludi (Reed-Flute) Cave | |||
| *the Elephant Trunk Hill | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| *the Piled Festoon Hill | |||
| ] | |||
| *the Crescent Hill | |||
| * The GDP per capita was ¥41891 (ca. US$6569) in 2020, ranked no. 134 among 659 Chinese cities.{{Citation needed|date=November 2021}} | |||
| *the seven-star-rock cave | |||
| * Local industries: ], ] goods, ]s, ], ], ], perfume, wine, tea, ], ] | |||
| *the Fubo Hill | |||
| *Local agricultural products: ], summer orange, ], ], moon persimmon, Lipu Taro, Sanhua Alcohol, ], ], Guilin Rice Noodle, ], ], fish and dried bean milk cream in tight rolls | |||
| *Nanxi Hill | |||
| *the Erlang Gorge | |||
| Until 1949 only a thermal power plant, a cement works, and some small textile mills existed as signs of industrialization in Guilin.<ref name="Encyclopædia Britannica Online"/> However, since the 1950s Guilin has added electronics, engineering, and agricultural equipment, medicine, rubber, buses, textile, and cotton yarn factories. Food processing, including the processing of local agricultural produce, remains the most important industry. More recent and modern industry features high technology, and the tertiary industry is characterized by tourism trading and service.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.china-window.com/china_economy/china_economy_guide/china-economy-guilin.shtml | title=Guilin Economy; china Window | access-date=11 July 2013 | archive-date=12 September 2015 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150912072531/http://www.china-window.com/china_economy/china_economy_guide/china-economy-guilin.shtml | url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| *Huangbu (Yellow Cloth) Beach | |||
| Citizens of ] states do not need a visa to visit Guilin if part of a tour lasting a maximum of 144 hours (not including the day of arrival).<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3242168/4-visa-free-ways-travel-china-land-sea-and-air-72-hours-30-days |title=5 visa-free ways to travel to China by land, sea and air for 72 hours and up to 30 days |author=Ralph Jennings |publisher=South China Morning Post |date=21 November 2023 |access-date=16 January 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ==Transportation== | |||
| ===Air=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The airport is ] (ICAO:ZGKL, IATA:KWL). Airlines that fly to the airport are: | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ===Rail=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Guilin has several high-speed rail stations, {{rws|Guilin North}}, {{rws|Guilin West}}, Guilin, and a new station in the ]. | |||
| Guilin station and Guilin North station are on the ], ] and ], the main railways connecting Guangxi with central and southern China. Arriving at North Station, high-speed trains between Guilin and ] and ] came into operation in December 2013. In December 2014, high-speed operations began connecting ], ], ], and ]. This made it more convenient for people to come to Guilin. It takes only about 2 or 3 hours from Guangzhou to Guilin, 9 hours from Shanghai to Guilin, and 13 hours from Beijing to Guilin.<ref name=Guilin> | |||
| Accessed 2014-12-29</ref> Trains traveling between ] and ] stations (for example) stop at ].<ref name=GuilinWest> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190213005725/https://uk.trip.com/trains/ScheduleResult/Index?=1&DepartureCity=Kunming+South+%28%E6%98%86%E6%98%8E%E5%8D%97%29%2C+Yunnan&ArrivalCity=Hong+Kong+West+Kowloon+%28%E9%A6%99%E6%B8%AF%E8%A5%BF%E4%B9%9D%E9%BE%99%29%2C+Hong+Kong&DepartureStation=&TrainNo=&DepartureCityPinyin=%E6%98%86%E6%98%8E%E5%8D%97&ArrivalCityPinyin=%E9%A6%99%E6%B8%AF%E8%A5%BF%E4%B9%9D%E9%BE%99&DepartureStationPinyin=&hidSearchType=1 |date=13 February 2019 }} Accessed 2019-02-12</ref> | |||
| ===Urban=== | |||
| ] double decker bus operating in Guilin]] | |||
| The city's public transportation includes bus routes and taxis. Guilin is the leading city in Mainland China operating ]es regularly on major routes; in its main street, the double-deckers run one by one almost every minute. Sightseeing boats also run on the city's canals and lakes. | |||
| A ] is planned for 7 lines by 2040 with 117 stations and a total length of 273.2 kilometres. Line 1 is planned to have been opened by 2025, and it will be 29.23 km with 13 stations. | |||
| ==Public colleges and universities== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] ({{lang|zh-hans|桂林航天工业学院}}) | |||
| *] | |||
| ''Note:'' Institutions without full-time bachelor programs are not listed. | |||
| ==Scenic spots== | |||
| {{Main|Guilin Scenic Area}} | |||
| <gallery heights="150px" perrow="5" mode="packed"> | |||
| 1 li jiang guilin yangshuo 2011.jpg|The ] connects Guilin and ] | |||
| 87340-Li-River (29881879337).jpg|Ship tour on Li River | |||
| 1 ping an longji terrace 2011.jpg|] (Ping An) | |||
| 1 pano cuiping yangshuo 2016.jpg|Cuiping Village | |||
| 1 pano xinping yangshupo.jpg|Xingping Village | |||
| 1 aerial yangshuo panorama 2017.jpg|Rafts sailing down the Yulong River in Yangshuo, a county of Guilin | |||
| Sun and Moon Pagodas Guilin November 2017 HDR panorama.jpg|] in Shan Lake | |||
| Reed flute cave.jpg|Reed flute cave | |||
| Guilin scenic.jpg|Scenic view of the town from Seven-star Park | |||
| Longji rice terraces - 2023 10 11 Kaur Virunurm.jpg|Longji rice terraces | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| {{right|{{Commons category|Guilin}}}} | |||
| ] around Guilin include: | |||
| *], a royal complex dating from the ] that lies near the center of modern Guilin | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] and ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.discoverchina.com/guilin-tours|title=Guilin Tours - Best Tour Packages For Guilin, China in 2019|website=Discover China|access-date=2020-01-25}}</ref> ({{lang|zh-hans|七星公园}}) | |||
| *Camel Mountain ({{lang|zh-hans|骆驼山}}) and ] | |||
| *Piled Festoon Hill ({{lang|zh-hans|堆花彩山}}) | |||
| *Crescent Hill ({{lang|zh|月牙山}}) | |||
| *Fubo Hill ({{lang|zh|伏波山}}) | |||
| *Nanxi Hill ({{lang|zh|南溪山}}) | |||
| *Erlang Gorge ({{lang|zh-hans|二郎山峡谷}}) | |||
| *Huangbu (Yellow Cloth) Beach ({{lang|zh-hans|黄埔滩}}) | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *Daxu Ancient Town ({{lang|zh-hans|大圩古市镇}}) | |||
| *Xingping Ancient Town ({{lang|zh-hans|兴坪古镇}}) | |||
| *Duxiu, Solitary Beauty Peak ({{lang|zh-hans|独秀峰}}) | |||
| *Liusanjie Landscape Garden ({{lang|zh-hans|刘三姐景观园}}) | |||
| *Yao Hill ({{lang|zh-hans|尧山}}) | |||
| *] ({{lang|zh-hans|日月双塔}}) | |||
| ==Cuisine== | |||
| ] | |||
| Guilin cuisine is a mixture of Cantonese cuisine and Zhuang cuisine. It is known for its snacks and the use of spices, especially chili. Guilin chili sauce ({{lang|zh-hans|桂林辣椒酱}}), used widely in cooking by locals, is made of fresh chili, garlic, and fermented soybeans, and is considered one of the city's Three Treasures ({{lang|zh-hans|桂林三宝}}). The other two of the Three Treasures are Guilin Sanhua Jiu ({{lang|zh|桂林三花酒}}), a variety of '']'', or liquor distilled from rice; and Guilin ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| Guilin ] have been the local breakfast staple since the Qin dynasty and are renowned for their delicate taste. Legend has it that when Qin troops suffering from diarrhea entered this region, a cook created the Guilin rice noodles for the army because they had trouble eating the local food. Specifically, the local specialty is noodles with ], but this dish can also be ordered without the horse meat. '']'', a dumpling made from ] and mung bean paste wrapped in a bamboo or banana leaf is another popular delicacy in Guilin. | |||
| == Military == | |||
| Guilin is the garrision of the {{ill|122nd Medium Combined Arms Brigade|zh|中国人民解放军陆军合成第一二二旅}}, ] which is equipped with the ] and ] | |||
| ==Quotes== | ==Quotes== | ||
| : |
:"I often sent pictures of the hills of Guilin which I painted to friends back home, but few believed what they saw." | ||
| ::- ] (Chinese ] scholar)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.chinavista.com/travel/guilin/main.html|title=Guilin Tours, Guilin Tour Packages, China Travel Agency|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-date=29 July 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190729015350/http://www.chinavista.com/travel/guilin/main.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ::- ] (Chinese ] scholar) | |||
| :"] is best among ]." ({{zh|s=桂林山水甲天下|hp=Guìlín shānshuǐ jiǎ tiānxià|links=no}}) | |||
| :''桂林山水甲天下 "Guilin’s scenery bests all others in the world."'' | |||
| ::- Popular Chinese quote<ref>{{cite web|url=http://en.glut.edu.cn/english/011guilin%20tour/001%20guilin%201.htm|title=Learn Chinese, Study Chinese, Language, Study in China, Travel in China, Guilin|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-date=29 December 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151229232340/http://en.glut.edu.cn/english/011guilin%20tour/001%20guilin%201.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ::- popular Chinese saying | |||
| ==International relations== | |||
| {{See also|List of twin towns and sister cities in China}} | |||
| ===Twin towns—Sister cities=== | |||
| Guilin is ] with: | |||
| *{{flagdeco|JPN}} – ], Japan<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.pref.yamanashi.jp/english/profile/documents/2008yamanashifactsandfigures.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=1 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924081143/http://www.pref.yamanashi.jp/english/profile/documents/2008yamanashifactsandfigures.pdf |archive-date=24 September 2015 |url-status=dead |df=dmy-all }}</ref> – Lingchuan County | |||
| *{{flagdeco|JPN}} – ], Japan<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.kumamoto-if.or.jp/info/s_detail.asp?LC=e&PageID=3&l_id=3|title=Kumamoto International Foundation|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-date=27 May 2024|archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527195246/https://www.webcitation.org/6gkE2pvnD?url=http://www.kumamoto-if.or.jp/info/s_detail.asp%3FLC=e|url-status=dead}}</ref> – Guilin | |||
| *{{flagdeco|JPN}} – ], Japan – Guilin | |||
| *{{flagdeco|JPN}} – ], Japan – Lingui | |||
| *{{flagdeco|ROK}} – ], South Korea | |||
| *{{flagdeco|NZL}} – ] | |||
| *{{flagdeco|POL}} – ], Poland<ref name="Toruń twinnings">{{cite web|url=http://www.torun.pl/pl/node/1700|title=Miasta bliźniacze Torunia|access-date=2013-08-22|work=Urząd Miasta Torunia |language=pl|trans-title=Toruń's twin towns}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagdeco|US}} – ], United States<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.cityoforlando.net/international/global_connex/asia.htm |title=City of Orlando International Affairs |access-date=18 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130412060509/http://www.cityoforlando.net/international/global_connex/asia.htm |archive-date=12 April 2013 |url-status=dead |df=dmy-all }}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagdeco|MEX}} – ], ], Mexico<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oem.com.mx/elsoldehidalgo/notas/n2042191.htm|title=Tlaxcoapan se hermana con Guilin, China|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-date=21 October 2013|archive-url=https://archive.today/20131021063012/http://www.oem.com.mx/elsoldehidalgo/notas/n2042191.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagdeco|MYS}} – ], ] | |||
| The Guilin relationship with the New Zealand city Hastings started in 1977, after a research scientist, Stuart Falconer, identified several common areas of interest between the two cities, including horticulture and their rural-urban mix.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hastingsdc.govt.nz/sister-city|title=Hastings-Guilin Sister City relationship|access-date=19 April 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100323033839/http://www.hastingsdc.govt.nz/sister-city|archive-date=23 March 2010|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In 1997 Guilin commenced an exchange relationship with ], Japan.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.city.ota.gunma.jp/005gyosei/0020-007kikaku-kouryu/kokusaikouryu/keirin.html |script-title=ja:中華人民共和国広西壮族自治区桂林市 |trans-title=Guilin, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China |language=ja |access-date=20 June 2016 |archive-date=15 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200315091714/https://www.city.ota.gunma.jp/005gyosei/0020-007kikaku-kouryu/kokusaikouryu/keirin.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==Notable people== | |||
| * ], general and politician | |||
| * ], badminton player | |||
| * ], general and ], vice-president and ] ] | |||
| * ], scientist, educator and politician | |||
| * ], climate activist | |||
| * ], news anchor for ] | |||
| * ], writer | |||
| * ], actor and dancer | |||
| * ], weightlifter | |||
| * ], general and politician, first president of the ] | |||
| * ], Israeli professor of ] at the ] | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], a popular tourist destination in Vietnam with similar karst formations | |||
| * ] - 2 ships | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| * —'']'' | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons|2=Guilin}} | |||
| {{Wikivoyage}} | |||
| * {{in lang|zh}} | |||
| {{Guangxi topics}} | |||
| {{Guangxi}} | |||
| {{Prefectural-level divisions of the People's Republic of China}} | |||
| {{Major cities along the Pearl River}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ==External Link== | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:09, 10 January 2025
Prefecture-level city in Guangxi| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Guilin" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Prefecture-level city in Guangxi, People's Republic of China
| Guilin 桂林市 • Gveilinz SiKweilin | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
       From left to right, top to bottom: View of Guilin city; Elephant Trunk Hill, Sun and Moon Pagodas; Longsheng Rice Terraces, Jingjiang Princes' Palace, Reed Flute Cave; Yangshuo scenery From left to right, top to bottom: View of Guilin city; Elephant Trunk Hill, Sun and Moon Pagodas; Longsheng Rice Terraces, Jingjiang Princes' Palace, Reed Flute Cave; Yangshuo scenery | |
 Location of Guilin City jurisdiction in Guangxi Location of Guilin City jurisdiction in Guangxi | |
 | |
| Coordinates (Guilin Central Square (桂林中心广场)): 25°16′30″N 110°17′46″E / 25.275°N 110.296°E / 25.275; 110.296 | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Autonomous region | Guangxi |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 27,797 km (10,732 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,753 km (1,063 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 5,041 km (1,946 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 153 m (502 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,931,137 |
| • Density | 180/km (460/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,725,865 |
| • Urban density | 630/km (1,600/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,148,641 |
| • Metro density | 430/km (1,100/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 231.1 billion US$ 35.8 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 46,767 US$ 7,249 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 541XXX |
| Area code | 0773 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GX-03 |
| License plate prefixes | 桂C for Guilin's city proper, Yangshuo, and Lingui; all others 桂H |
| Website | www |
| Guilin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 桂林 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Guìlín | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Kweilin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Sweet Osmanthus Forest" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang | Gveilinz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1957 orthography | Gveilinƨ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Guilin (Standard Zhuang: Gveilinz), formerly romanized as Kweilin, is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. It is situated on the west bank of the Li River and borders Hunan to the north. Its name means "forest of sweet osmanthus", owing to the large number of fragrant sweet osmanthus trees located in the region. The city has long been renowned for its scenery of karst topography.
Guilin is one of China's most popular tourist destinations, and the epithet "By water, by mountains, most lovely, Guilin" (山水甲天下) is often associated with the city. The State Council of China has designated Guilin a National Famous Historical and Cultural City, doing so in the first edition of the list.
History
Before the Qin dynasty, the Guilin region was settled by the Baiyue people. In 314 BC, a small settlement was established along the banks of the Li River.
During the Qin dynasty's (221–206 BC) campaigns against the state of Nanyue, the first administration was set up in the area around Guilin. The modern city was located within the Guilin Commandery, which is the origin of the modern name "Guilin".
In 111 BC, during the reign of Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty, Shi'an County (simplified Chinese: 始安县; traditional Chinese: 始安縣) was established, which could be regarded as the beginning of the city.
In AD 507, the town was renamed Guizhou (Gui Prefecture, 桂州).
In 634, Lingui County was established at the modern site of Guilin, under Gui Prefecture. In 868, Pang Xun rebelled against the Tang from Gui Prefecture.
Guilin prospered in the Tang and Song dynasties but remained a county. The city was also a nexus between the central government and the southwest border, and it was where regular armies were placed to guard that border. Canals were built through the city so that food supplies could be directly transported from the food-productive Yangtze plain to the farthest southwestern point of the empire.
In 997, Guangnan West Circuit, the predecessor of modern Guangxi, was established, with Guizhou as the capital. In 1133, Guizhou was renamed Jingjiang Prefecture (simplified Chinese: 静江路; traditional Chinese: 靜江路). In 1367, the name was changed to Guilin Prefecture (桂林府).
In 1921, Guilin became one of the headquarters of the Northern Expeditionary Army led by Sun Yat-sen. In 1940, Guilin City was established. Guilin was the provincial capital of Guangxi before 1912 and from 1936 to 1949.
Guilin became one of the most important military, transport, and cultural centers of China during World War II. The city drastically expanded as refugees from all over China poured in, and by 1944 its population had grown from 70,000 pre-war to more than 500,000. It hosted intellectuals and artists including Guo Moruo, Mao Dun, Ba Jin, Tian Han, Xu Beihong, Feng Zikai and many others.
In 1950, the provincial capital of Guangxi was moved from Guilin to Nanning.
In 1981, Guilin was listed by the State Council as one of the four cities (the other three being Beijing, Hangzhou, and Suzhou) where the protection of historical and cultural heritage, as well as natural scenery, should be treated as a priority project.
Administrative divisions


Guilin administers seventeen county-level divisions, including 6 districts, 8 counties, 2 autonomous counties, and 1 county-level city.
- District:
- Xiufeng District (秀峰区)
- Xiangshan District (象山区)
- Diecai District (叠彩区)
- Qixing District (七星区)
- Yanshan District (雁山区)
- Lingui District (临桂区)
- County-level city:
- Lipu city (荔浦市)
- County:
- Yangshuo County (阳朔县)
- Lingchuan County (灵川县)
- Xing'an County (兴安县)
- Quanzhou County (全州县)
- Yongfu County (永福县)
- Ziyuan County (资源县)
- Guanyang County (灌阳县)
- Pingle County (平乐县)
- Autonomous county:
- Gongcheng Yao Autonomous County (恭城瑶族自治县)
- Longsheng Various Nationalities Autonomous County (龙胜各族自治县)
Geography

Guilin is located in northern Guangxi, bordering Liuzhou to the west, Laibin to the southwest, Wuzhou to the south, Hezhou to the southeast, and within neighbouring Hunan, Huaihua to the northwest, Shaoyang to the north, and Yongzhou to the east. It has a total area of 27,809 square kilometres (10,737 sq mi). The topography of the area is marked by karst formations. The karsts surrounding Guilin are made of Triassic period limestone and dolomite rocks. The Li River flows through the city.
- Hills and mountains: Diecai Hill (叠彩山), Elephant Trunk Hill, Wave-Subduing Hill (伏波山), Lipu Mountains, Kitten Mountain, the highest peak of Guangxi, and Yao Hill (尧山)
- Caves: Reed Flute Cave, Seven-star Cave
Climate

Guilin has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa, bordering on Cwa), with short, mild winters, and long, hot, humid summers. Winter begins dry but becomes progressively wetter and cloudier. Spring is generally overcast and often rainy, while summer continues to be rainy though is the sunniest time of year. Autumn is sunny and dry. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 8.1 °C (46.6 °F) in January to 28.2 °C (82.8 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 19.12 °C (66.4 °F). The annual rainfall is just under 1,890 mm (74 in) and is delivered in bulk (~50%) from April to June, when the plum rains occur and often create the risk of flooding. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 14% in March to 53% in September, the city receives 1,487 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from −4.9 °C (23 °F) (though an unofficial record low of −5.0 °C (23 °F) was recorded on 25 January 1940) to 40.3 °C (105 °F).
| Climate data for Guilin (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.6 (81.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.6 (96.1) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.4 (99.3) |
40.3 (104.5) |
39.4 (102.9) |
38.5 (101.3) |
35.6 (96.1) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.6 (81.7) |
40.3 (104.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 11.7 (53.1) |
14.2 (57.6) |
17.5 (63.5) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.2 (91.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
26.3 (79.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
14.9 (58.8) |
23.7 (74.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
13.9 (57.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.4 (83.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
26.0 (78.8) |
21.5 (70.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
10.8 (51.4) |
19.5 (67.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.7 (69.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.0 (77.0) |
22.6 (72.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
16.6 (61.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.9 (23.2) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
4.0 (39.2) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
12.9 (55.2) |
6.1 (43.0) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 68.9 (2.71) |
83.9 (3.30) |
153.0 (6.02) |
226.7 (8.93) |
321.1 (12.64) |
448.7 (17.67) |
266.3 (10.48) |
147.6 (5.81) |
80.9 (3.19) |
54.9 (2.16) |
81.9 (3.22) |
54.1 (2.13) |
1,988 (78.26) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 13.5 | 13.6 | 19.3 | 18.5 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 16.1 | 12.5 | 7.9 | 7.1 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 164.5 |
| Average snowy days | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71 | 73 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 81 | 77 | 75 | 70 | 66 | 67 | 65 | 73 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 58.4 | 52.2 | 55.0 | 78.7 | 113.1 | 113.3 | 180.6 | 197.2 | 180.3 | 157.1 | 122.9 | 102.1 | 1,410.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 18 | 16 | 15 | 21 | 27 | 28 | 43 | 49 | 49 | 44 | 38 | 31 | 32 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administrationall-time extreme temperature | |||||||||||||
Demographics
According to the 2020 Chinese census its population was 4,931,137 inhabitants and 2,148,641 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 6 urban Districts plus Lingchuan County now being conurbated. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the largest ethnic group in the prefecture-level city was Han Chinese, accounting for 84.53% of the total population. This was followed by Yao at 7.79% and Zhuang at 4.81%. Citizens of Guilin's urban area speak a dialect of Mandarin, while Pinghua is predominantly spoken in suburbs and surrounding areas.
Economy

- The GDP per capita was ¥41891 (ca. US$6569) in 2020, ranked no. 134 among 659 Chinese cities.
- Local industries: condoms, pharmaceutical goods, tires, machinery, fertilizer, silk, perfume, wine, tea, cinnamon, herbal medicine
- Local agricultural products: Shatian Pomelo, summer orange, Fructus Momordicae, ginkgo, moon persimmon, Lipu Taro, Sanhua Alcohol, pepper sauce, fermented bean curd, Guilin Rice Noodle, water chestnut, grain, fish and dried bean milk cream in tight rolls
Until 1949 only a thermal power plant, a cement works, and some small textile mills existed as signs of industrialization in Guilin. However, since the 1950s Guilin has added electronics, engineering, and agricultural equipment, medicine, rubber, buses, textile, and cotton yarn factories. Food processing, including the processing of local agricultural produce, remains the most important industry. More recent and modern industry features high technology, and the tertiary industry is characterized by tourism trading and service.
Citizens of ASEAN states do not need a visa to visit Guilin if part of a tour lasting a maximum of 144 hours (not including the day of arrival).
Transportation
Air

The airport is Guilin Liangjiang International Airport (ICAO:ZGKL, IATA:KWL). Airlines that fly to the airport are:
- China Eastern
- Asiana Airlines
- China Southern
- Air China
- Hainan Airlines
- Shanghai Airlines
- Shandong Airlines
- Xiamen Airlines
- Tianjin Airlines
- EVA Air
- Air Asia
- Beijing Capital Airlines
- Hebei Airlines
Rail

Guilin has several high-speed rail stations, Guilin North, Guilin West, Guilin, and a new station in the Lingui District. Guilin station and Guilin North station are on the Hunan–Guangxi railway, Hengyang–Liuzhou intercity railway and Guiyang–Guangzhou high-speed railway, the main railways connecting Guangxi with central and southern China. Arriving at North Station, high-speed trains between Guilin and Changsha and Beijing came into operation in December 2013. In December 2014, high-speed operations began connecting Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Guiyang, and Shanghai. This made it more convenient for people to come to Guilin. It takes only about 2 or 3 hours from Guangzhou to Guilin, 9 hours from Shanghai to Guilin, and 13 hours from Beijing to Guilin. Trains traveling between Kunming South and West Kowloon stations (for example) stop at Guilin West railway station.
Urban

The city's public transportation includes bus routes and taxis. Guilin is the leading city in Mainland China operating double-decker buses regularly on major routes; in its main street, the double-deckers run one by one almost every minute. Sightseeing boats also run on the city's canals and lakes.
A Guilin Metro is planned for 7 lines by 2040 with 117 stations and a total length of 273.2 kilometres. Line 1 is planned to have been opened by 2025, and it will be 29.23 km with 13 stations.
Public colleges and universities
- Guilin University of Technology
- Guilin Medical University
- Guilin University of Electronic Technology
- Guangxi Normal University
- Guilin University of Aerospace Technology (桂林航天工业学院)
- Guilin University
Note: Institutions without full-time bachelor programs are not listed.
Scenic spots
Main article: Guilin Scenic Area-
 The Li River connects Guilin and Yangshuo County
The Li River connects Guilin and Yangshuo County
-
 Ship tour on Li River
Ship tour on Li River
-
 Longsheng Rice Terrace (Ping An)
Longsheng Rice Terrace (Ping An)
-
 Cuiping Village
Cuiping Village
-
 Xingping Village
Xingping Village
-
 Rafts sailing down the Yulong River in Yangshuo, a county of Guilin
Rafts sailing down the Yulong River in Yangshuo, a county of Guilin
-
 Sun and Moon Pagodas in Shan Lake
Sun and Moon Pagodas in Shan Lake
-
 Reed flute cave
Reed flute cave
-
 Scenic view of the town from Seven-star Park
Scenic view of the town from Seven-star Park
-
 Longji rice terraces
Longji rice terraces
Scenic spots around Guilin include:
- Jingjiang Princes City, a royal complex dating from the Ming dynasty that lies near the center of modern Guilin
- Reed Flute Cave
- Silver Cave
- Li River
- Yangshuo
- Seven-star Cave and Seven Star Park (七星公园)
- Camel Mountain (骆驼山) and Elephant Trunk Hill
- Piled Festoon Hill (堆花彩山)
- Crescent Hill (月牙山)
- Fubo Hill (伏波山)
- Nanxi Hill (南溪山)
- Erlang Gorge (二郎山峡谷)
- Huangbu (Yellow Cloth) Beach (黄埔滩)
- Moon Hill
- Longsheng Rice Terrace
- Daxu Ancient Town (大圩古市镇)
- Xingping Ancient Town (兴坪古镇)
- Duxiu, Solitary Beauty Peak (独秀峰)
- Liusanjie Landscape Garden (刘三姐景观园)
- Yao Hill (尧山)
- Sun and Moon Pagodas (日月双塔)
Cuisine

Guilin cuisine is a mixture of Cantonese cuisine and Zhuang cuisine. It is known for its snacks and the use of spices, especially chili. Guilin chili sauce (桂林辣椒酱), used widely in cooking by locals, is made of fresh chili, garlic, and fermented soybeans, and is considered one of the city's Three Treasures (桂林三宝). The other two of the Three Treasures are Guilin Sanhua Jiu (桂林三花酒), a variety of rice baijiu, or liquor distilled from rice; and Guilin pickled tofu.

Guilin rice noodles have been the local breakfast staple since the Qin dynasty and are renowned for their delicate taste. Legend has it that when Qin troops suffering from diarrhea entered this region, a cook created the Guilin rice noodles for the army because they had trouble eating the local food. Specifically, the local specialty is noodles with horse meat, but this dish can also be ordered without the horse meat. Zongzi, a dumpling made from glutinous rice and mung bean paste wrapped in a bamboo or banana leaf is another popular delicacy in Guilin.
Military
Guilin is the garrision of the 122nd Medium Combined Arms Brigade [zh], 75th Group Army which is equipped with the ZBL-08 and ZTL-11
Quotes
- "I often sent pictures of the hills of Guilin which I painted to friends back home, but few believed what they saw."
- - Fan Chengda (Chinese Song dynasty scholar)
- "Guilin's scenery is best among all under heaven." (Chinese: 桂林山水甲天下; pinyin: Guìlín shānshuǐ jiǎ tiānxià)
- - Popular Chinese quote
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in ChinaTwin towns—Sister cities
Guilin is twinned with:
 – Nishikatsura, Yamanashi, Japan – Lingchuan County
– Nishikatsura, Yamanashi, Japan – Lingchuan County – Kumamoto City, Japan – Guilin
– Kumamoto City, Japan – Guilin – Toride City, Japan – Guilin
– Toride City, Japan – Guilin – Miho, Ibaraki, Japan – Lingui
– Miho, Ibaraki, Japan – Lingui – Jeju, South Korea
– Jeju, South Korea – Hastings, New Zealand
– Hastings, New Zealand – Toruń, Poland
– Toruń, Poland – Orlando, United States
– Orlando, United States – Tlaxcoapan, Hidalgo, Mexico
– Tlaxcoapan, Hidalgo, Mexico – Langkawi, Malaysia
– Langkawi, Malaysia
The Guilin relationship with the New Zealand city Hastings started in 1977, after a research scientist, Stuart Falconer, identified several common areas of interest between the two cities, including horticulture and their rural-urban mix. In 1997 Guilin commenced an exchange relationship with Ōta, Gunma, Japan.
Notable people
- Bai Chongxi, general and politician
- Jiang Zhenbang, badminton player
- Li Zongren, general and warlord, vice-president and acting president of the Republic of China
- Ma Junwu, scientist, educator and politician
- Ou Hongyi, climate activist
- Ouyang Xiadan, news anchor for China Central Television
- Pai Hsien-yung, writer
- Qiao Zhenyu, actor and dancer
- Shi Zhiyong, weightlifter
- Tang Jingsong, general and politician, first president of the Republic of Formosa
- Daniel Weihs, Israeli professor of aeronautical engineering at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology
See also
- Bai Chongxi
- Alcoholic drinks in China
- Li Zongren
- Hạ Long Bay, a popular tourist destination in Vietnam with similar karst formations
- CNS Guilin - 2 ships
References
- "China: Guăngxī (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- "广西统计年鉴-2021", tjj.gxzf.gov.cn
- Foster, Simon (2012). Frommer's China. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 612. ISBN 9781118223529.
- “桂林山水甲天下”之英译. China Daily (in Chinese (China)). Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ^ 桂林概况. people.com.cn (in Chinese (China)). Archived from the original on 29 October 2018. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
- "Cruise Through The Beautiful Scenery Of The Li River In Guilin". Discover China. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ^ "Guilin (China) Encyclopædia Britannica". Encyclopædia Britannica (Online). Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- "Guilin never ceases to amaze". Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "History of Guilin". Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- "Guilin History". Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "初心50城|广西桂林:"抗战文化城"的新文旅之路". thepaper.cn. 23 April 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- "Beijing Hotels 【 #1 Ranked Hotel in Beijing 】 - Nehow.com". Nehow.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "Guilin History". Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "中国各地城市的历史最低气温". weibo.com. Retrieved 15 September 2024.
- "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". www.mherrera.org. Retrieved 15 September 2024.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 25 May 2010.
- "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 9 September 2024.
- 广西壮族自治区统计局、广西壮族自治区人口普查办公室. 《广西壮族自治区2010年人口普查资料》. 中国统计出版社. 2012年7月. ISBN 978-7-5037-6549-0.
- "桂林市志 方言志". 广西壮族自治区地方志编纂委员会办公室.
- "Guilin Economy; china Window". Archived from the original on 12 September 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- Ralph Jennings (21 November 2023). "5 visa-free ways to travel to China by land, sea and air for 72 hours and up to 30 days". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- "High-speed Trains Available in Guilin" ChinaTour.Net Accessed 2014-12-29
- "G314 timetable" Archived 13 February 2019 at the Wayback Machine Accessed 2019-02-12
- "Guilin Tours - Best Tour Packages For Guilin, China in 2019". Discover China. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- "Guilin Tours, Guilin Tour Packages, China Travel Agency". Archived from the original on 29 July 2019. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "Learn Chinese, Study Chinese, Language, Study in China, Travel in China, Guilin". Archived from the original on 29 December 2015. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Kumamoto International Foundation". Archived from the original on 27 May 2024. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "Miasta bliźniacze Torunia" [Toruń's twin towns]. Urząd Miasta Torunia (in Polish). Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- "City of Orlando International Affairs". Archived from the original on 12 April 2013. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- "Tlaxcoapan se hermana con Guilin, China". Archived from the original on 21 October 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- "Hastings-Guilin Sister City relationship". Archived from the original on 23 March 2010. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- 中華人民共和国広西壮族自治区桂林市 [Guilin, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China] (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
Further reading
External links
- Guilin Government Official website (in Chinese)
| Guangxi topics | |
|---|---|
| Nanning (capital) | |
| General | |
| Geography | |
| Education | |
| Culture | |
| Cuisine | |
| Visitor attractions | |
| Notes: *Provincial capitals, ★Sub-provincial cities, ☆Sub-provincial autonomous prefecture *Sub prefectural-level divisions, ✧"Comparatively larger city [zh]" (较大的市) as approved by the State Council | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also: List of prefectures in China, List of cities in China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major cities along the Pearl River | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cities (from upper reaches to lower reaches) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major tributaries |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pearl River | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pearl |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shiziyang | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lingdingyang | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jiuzhouyang | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major cities along the Yangtze River · Major cities along the Yellow River | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||