| Revision as of 20:57, 13 November 2007 editU.S.A.U.S.A.U.S.A. (talk | contribs)4,018 edits Undid revision 171281832 by 209.137.220.73 (talk)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:50, 1 January 2025 edit undoOmphalographer (talk | contribs)333 edits rv - not a useful illustrationTag: Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Visual artwork on two-dimensional surface}} | |||
| {{for|scale drawings or plans|Plans (drawings)}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| ], 16th century]] | |||
| ]'s '']'' ({{circa|1485}}) ]]] | |||
| '''Drawing''' is a ] which makes use of any number of drawing instruments to mark a two-dimensional medium. Common instruments include ] ]s, ], ]ed ]es, wax ]s, ]s, ]s, ], ]s, ]s, ], or various metals like ]. An artist who practices or works in drawing may be referred to as a draftsman or draughtsman. | |||
| '''Drawing''' is a ] that uses an instrument to mark ] or another ] surface. The instruments used to make a drawing are ]s, ]s, ]s with ]s, ]es with ]s, or combinations of these, and in more modern times, ] with ]s or ]s in ] drawing software. | |||
| A small amount of material |
A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is ], although other materials, such as ], ], ], plastic, ], ], and ], have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a ] or ]. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. It is one of the simplest and most efficient means of communicating ideas.<ref name=SBTCModule6>{{cite web|last=www.sbctc.edu (adapted)|title=Module 6: Media for 2-D Art|url=http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Module-6.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120809171125/http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Module-6.pdf |archive-date=2012-08-09 |url-status=live|publisher=Saylor.org|access-date=2 April 2012}}</ref> The wide availability of drawing instruments makes drawing one of the most common artistic activities. | ||
| In addition to its more artistic forms, drawing is frequently used in commercial ], ], ], ], and ]. A quick, freehand drawing, usually not intended as a finished work, is sometimes called a ]. An ] who practices or works in technical drawing may be called a ], draftsman, or draughtsman.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/draftsman|title=Draftsman Definition & Meaning|work = Dictionary.com|access-date=}}</ref> | |||
| ==Definitions== | |||
| {{Unreferencedsection|date=September 2007}} | |||
| Drawing is a form of visual expression and is one of the major forms within the visual arts. There are a number of subcategories of drawing, including ], and certain drawing methods or approaches, such as "]," may or may not be considered as part of "drawing" as a "fine art." | |||
| ==Overview== | |||
| The word 'drawing' is used as both a verb and a noun: | |||
| ]]]Drawing is one of the oldest forms of human expression within the visual arts. It is generally concerned with the marking of lines and areas of tone onto paper/other material, where the accurate representation of the visual world is expressed upon a plane surface.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=McManus |first1=I. C. |last2=Chamberlain |first2=R |last3=Loo |first3=P-W |last4=Riley |first4=H |last5=Rankin |first5=Q |last6=Brunswick |first6=N |date=2010 |title=Art Students Who Cannot Draw: Exploring the Relations Between Drawing Ability, Visual Memory, Accuracy of Copying, and Dyslexia |url=http://www.ucl.ac.uk/medical-education/publications/Reprints2010/2010-PACA-ArtStudentsWhoCannotDraw.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303223647/http://www.ucl.ac.uk/medical-education/publications/Reprints2010/2010-PACA-ArtStudentsWhoCannotDraw.pdf |archive-date=2016-03-03 |access-date=2014-03-11 |website=University College London |series=Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, vol. 4, no. 1, 18 –30}}</ref> Traditional drawings were ], or at least had little colour,<ref>See ] and ]</ref> while modern colored-pencil drawings may approach or cross a boundary between drawing and ]. In Western terminology, drawing is distinct from painting, even though similar ] often are employed in both tasks. Dry media, normally associated with drawing, such as chalk, may be used in ] paintings. Drawing may be done with a liquid medium, applied with brushes or pens. Using a brush for drawing is very widespread and here it is more the process of using lines and hatching, that characterises something as a drawing. Similar supports likewise can serve both: painting generally involves the application of liquid paint onto prepared canvas or panels, but sometimes an ] is drawn first on that same support. | |||
| * Drawing (verb) is the act of making marks on a surface so as to create an image, form or shape. | |||
| Drawing is often exploratory, with considerable emphasis on observation, problem-solving and composition. Drawing is also regularly used in preparation for a painting, further obfuscating their distinction. Drawings created for these purposes are called sketches. | |||
| * The produced image is also called a drawing (noun). A quick, unrefined drawing may be defined as a ]. | |||
| There are several categories of drawing, including ], ], ], and ]. There are also many drawing methods, such as ], stippling, ], the surrealist method of ] (in which dots are made at the sites of impurities in a blank sheet of paper, and lines are then made between the dots), and tracing (drawing on a translucent paper, such as '']'', around the outline of preexisting shapes that show through the paper). | |||
| In simplistic terms, drawing is distinct from painting, perhaps more so in the Western view; East Asian art, which generally only uses brushes, has historically made less distinction between the two. Critics may praise a painter's ability to draw well, meaning that the shapes, especially of the human body, are well-articulated, or a drawing may be considered ]. | |||
| A quick, unrefined drawing may be called a '']''. | |||
| Adding confusion, similar tools and media may be used in both tasks. Dry media normally associated with drawing, such as chalk, may be used in ] painting. Drawing may be done with liquid media applied with brushes or pens. Similar supports likewise can serve both: painting generally involves the application of liquid paint onto prepared canvas or panels, but sometimes an ] is drawn first on that same support. Drawing is generally concerned with the marking of lines and areas of tone onto paper, but ] painting uses a paper support. Traditional drawings were monochrome, or at least had little colour,<ref>See ] and ]</ref> while modern coloured-pencil drawings may approach or cross the boundary (if there is one) between drawing and painting. | |||
| In fields outside art, ]s or plans of buildings, machinery, circuitry and other things are often called "drawings" even when they have been transferred to another medium by printing. | |||
| The term drawing suggests a process and intent that is distinct from the traditional act of painting. While there are drawings that are finished artworks, drawing is often exploratory, with considerable emphasis on observation, problem solving and composition, often as a means of preparation for a painting. In contrast, traditional painting is often a means of execution or finishing an artwork. It is fair to note that modern painters often incorporate methods of drawing in their painting process. | |||
| == |
==History== | ||
| {{Unreferencedsection|date=September 2007}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Drawings may be representational, depicting objects, living beings, or scenes which the artist views, remembers, or imagines. They may be realistic to the point of lifelike resemblance (e.g. traditional ]s), architectural drawing or looser approximations of reality (e.g. ]es), and highly stylized (e.g. ]s, ]s), or ] (e.g. ], ]). | |||
| === In communication === | |||
| ==Media== | |||
| Drawing is one of the oldest forms of human expression, with evidence for its existence preceding that of written communication.<ref name="Tversky 2011 499–535">{{cite journal|last=Tversky|first=B|title=Visualizing thought|journal=Topics in Cognitive Science|year=2011|volume=3|issue=3|pages=499–535|doi=10.1111/j.1756-8765.2010.01113.x|pmid=25164401}}</ref> It is believed that drawing was used as a specialised form of communication before the invention of the written language,<ref name="Tversky 2011 499–535"/><ref>{{cite web|last=Farthing|first=S|title=The Bigger Picture of Drawing|url=http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|year=2011|access-date=2014-03-11|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317224618/http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|archive-date=2014-03-17|url-status=dead}}</ref> demonstrated by the production of ] around 30,000 years ago (]).<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317224618/http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf |date=2014-03-17 }} 2011c{{page needed|date=December 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The medium is the means by which ink, pigment, or color are delivered onto the drawing surface. Most drawing media are either dry (e.g. graphite, charcoal, ], ], ]), or water-based (marker, pen and ink).<ref>{{cite book |last=Mayer |first=Ralph |title=The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques |publisher=Viking |isbn=0-670-83701-6 }}</ref> Watercolor pencils can be used dry like ordinary pencil, then moistened with a wet brush to get various painterly effects. Very rarely, artists have drawn with (usually decoded) ]. | |||
| These drawings, known as pictograms, depicted objects and abstract concepts.<ref>{{cite book|last=Robinson|first=A|title=Writing and script: a very short introduction|year=2009|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=New York}}</ref> The sketches and paintings produced by Neolithic times were eventually stylised and simplified in to symbol systems (]) and eventually into early ]. | |||
| === In manuscripts === | |||
| Before the widespread availability of paper in Europe, ] in European monasteries used drawings, either as ]s for ]s on vellum or parchment, or as the final image. Drawing has also been used extensively in the field of science, as a method of discovery, understanding and explanation. | |||
| === In science === | |||
| ], ''Phases of the Moon'', 1609 or 1610, brown ink and wash on paper. 208 × 142 mm. ], Gal. 48, fol. 28r]]Drawing diagrams of observations is an important part of scientific study. | |||
| In 1609, astronomer ] explained the changing phases of Venus and also the ] through his observational telescopic drawings.<ref name="Kovats 2005" /> In 1924, geophysicist ] used illustrations to visually demonstrate the origin of the continents.<ref name="Kovats 2005" /> | |||
| === As artistic expression === | |||
| Drawing is one of the easiest ways to visualise ideas and to express one's creativity; therefore it has been prominent in the world of art. Throughout much of history, drawing was regarded as the foundation for artistic practice.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Walker|first1=J. F|title=Drawing- The Process|year=2005|publisher=]|location=Bristol|author2=Duff, L|author3=Davies, J|chapter=Old Manuals and New Pencils}}</ref> Initially, artists used and reused wooden tablets for the production of their drawings.<ref>See the discussion on erasable drawing boards and 'tafeletten' in {{cite book|last=van de Wetering|first=Ernst|title=Rembrandt: The Painter at Work}}</ref> Following the widespread availability of paper in the 14th century, the use of drawing in the arts increased. At this point, drawing was commonly used as a tool for thought and investigation, acting as a study medium whilst artists were preparing for their final pieces of work.<ref>{{cite web|last=Burton|first=J|title=Preface|url=http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|access-date=2014-03-11|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317224618/http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|archive-date=2014-03-17|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite thesis|last=Chamberlain|first=R|title=Drawing Conclusions: An exploration of the cognitive and neuroscientific foundations of representational drawing.|year=2013|url=http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1408829/|type=Doctoral}}</ref> The ] brought about a great sophistication in drawing techniques, enabling artists to represent things more realistically than before,<ref>{{cite book |last1=Davis |first1=P|title=Drawing – The Process|url=https://archive.org/details/drawingprocess00davi |url-access=limited |year=2005|publisher=Intellect Books|location=Bristol|pages=–25|author2=Duff, L |author3=Davies, J|chapter=Drawing a Blank|isbn=9781841500768}}</ref> and revealing an interest in geometry and philosophy.<ref>{{cite web |last=Simmons |first=S |title=Philosophical Dimension of Drawing Instruction |url=http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf |year=2011 |access-date=2014-03-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317224618/http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf |archive-date=2014-03-17 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The invention of the first widely available form of ] led to a shift in the hierarchy of the arts.<ref>{{cite book|last=Poe|first=E. A.|title=The Daguerreotype. Classic Essays on Photography|year=1840|publisher=Leete's Island Books|location=New Haven, CN|pages=37–38}}</ref> Photography offered an alternative to drawing as a method for accurately representing visual phenomena, and traditional drawing practice was given less emphasis as an essential skill for artists, particularly so in Western society.<ref name="Kovats 2005">{{cite book|last=Kovats|first=T|title=The Drawing Book|year=2005|publisher=Black Dog Publishing|location=London|isbn = 9781904772330}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notable artists and draftsmen== | |||
| Drawing became significant as an art form around the late 15th century, with artists and master engravers such as ] and ] ({{circa|1448}}–1491), the first Northern engraver known by name. Schongauer came from Alsace, and was born into a family of goldsmiths. Albrecht Dürer, a master of the next generation, was also the son of a goldsmith.<ref>{{Cite news|date = 1 July 2020|url=https://www.christies.com/features/Old-Master-Prints-Collecting-Guide-8021-1.aspx |title= Collecting guide: Old Master prints |website = Christie's|access-date=|language=en}}</ref><ref>. Accessed 20 February 2016</ref> | |||
| Old Master Drawings often reflect the history of the country in which they were produced, and the fundamental characteristics of a nation at that time. In 17th-century Holland, a Protestant country, there were almost no religious artworks, and, with no King or court, most art was bought privately. Drawings of landscapes or genre scenes were often viewed not as sketches but as highly finished works of art. Italian drawings, however, show the influence of Catholicism and the Church, which played a major role in artistic patronage. The same is often true of French drawings, although in the 17th century the disciplines of French Classicism<ref>Barbara Hryszko, A Painter as a Draughtsman. Typology and Terminology of Drawings in Academic Didactics and Artistic Practice in France in 17th Century Metodologia, metoda i terminologia grafiki i rysunku. Teoria i praktyka, ed. Jolanta Talbierska, Warszawa 2014, pp. 169–176.</ref> meant drawings were less Baroque than the more free Italian counterparts, which conveyed a greater sense of movement.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.christies.com/features/Old-Master-Drawings-Collecting-Guide-7455-1.aspx|title= Collecting guide: Old Master drawings |website= Christie's|access-date=|language=en|date = 23 June 2021}}</ref> | |||
| In the 20th century ] encouraged "imaginative originality"<ref>{{cite book|title=Drawing – The Process|last1=Duff|first1=L|last2=Davies|first2= J|publisher=Intellect Books|year=2005|location=Bristol|isbn = 9781841509075}}</ref> and some artists' approach to drawing became less literal, more abstract. World-renowned artists such as ], ] and ] helped challenge the status quo, with drawing being very much at the centre of their practice, and often re-interpreting traditional technique.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2009/feb/12/life-art-jean-michel-basquiat|title=My life in art: How Jean-Michel Basquiat taught me to forget about technique|last=Gompertz|first=Will|date=2009-02-12|website=the Guardian|language=en|access-date=2018-04-20}}</ref> | |||
| Basquiat's drawings were produced in many different mediums, most commonly ink, pencil, felt-tip or marker, and oil-stick, and he drew on any surface that came to hand, such as doors, clothing, refrigerators, walls and baseball helmets.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://i-d.vice.com/en_uk/article/zm3z7j/a-dictionary-of-jean-michel-basquiat|title=boom for real: a dictionary of basquiat|date=2017-09-26|work=I-d|access-date=2018-04-20|language=en-uk}}</ref> | |||
| The centuries have produced a canon of notable artists and draftsmen, each with their own distinct language of drawing, including: | |||
| * 14th, 15th and 16th: ]<ref>. Accessed 20 February 2016</ref> • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| * 17th: ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| * 18th: ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| * 19th: ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| * 20th: ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| ==Materials== | ==Materials== | ||
| The ''medium'' is the means by which ink, pigment, or color are delivered onto the drawing surface. Most drawing media either are dry (e.g. ], ], ], ], ]), or use a fluid solvent or carrier (], ]). Watercolor pencils can be used dry like ordinary pencils, then moistened with a wet brush to get various painterly effects. Very rarely, artists have drawn with (usually decoded) ]. Metalpoint drawing usually employs either silver or lead.<ref>lara Broecke, ''Cennino Cennini's ''Il Libro dell'Arte'': a new English Translation and Commentary with Italian Transcription'', Archetype 2015</ref> More rarely used are gold, platinum, copper, brass, bronze, and tinpoint. | |||
| Paper comes in a variety of different sizes and qualities, ranging from newspaper grade for practice up to high quality and relatively expensive paper sometimes sold as individual sheets.<ref>{{cite book |last=Mayer |first=Ralph |title=The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques |publisher=Viking |isbn=0-670-83701-6 }}</ref> Papers can vary in texture, hue, acidity, and strength when wet. Smooth paper is good for rendering fine detail, but a more "toothy" paper will hold the drawing material better. Thus a more coarse material is useful for producing deeper contrast. | |||
| Paper comes in a variety of different sizes and qualities, ranging from newspaper grade up to high quality and relatively expensive paper sold as individual sheets.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Mayer |first=Ralph |title=The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques |publisher=Viking |isbn=978-0-670-83701-4 |year=1991 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/artistshandbooko00maye_0 }}</ref> Papers vary in texture, hue, acidity, and strength when wet. Smooth paper is good for rendering fine detail, but a more "toothy" paper holds the drawing material better. Thus a coarser material is useful for producing deeper contrast. | |||
| For pen and ink work, typing paper is often used for practice drawings, but heavier paper holds up better. Bristol board makes a hard surface that is especially good for ink or fine detailed graphite drawing. Coldpressed watercolor paper is sometimes favored for ink drawing due to its texture. Tracing vellum is often used for experimenting on top of a pencil drawing, prior to committing a technique to the final page. | |||
| Newsprint and typing paper may be useful for practice and rough ]. ] is used to experiment over a half-finished drawing, and to transfer a design from one sheet to another. ] is the basic type of drawing paper sold in pads. ] and even heavier acid-free boards, frequently with smooth finishes, are used for drawing fine detail and do not distort when wet media (ink, washes) are applied. Vellum is extremely smooth and suitable for very fine detail. Coldpressed watercolor paper may be favored for ink drawing due to its texture. | |||
| Various tools are routinely used in the process of drawing. These include a ], ], ], ]s, and ]. Other tools that sometimes prove useful are ], a ], ], ], ], and ]. The use of an easel or slanted table reduces the distorting effects of perspective. Metalpointing can include ], ], and even ] some of which metals can change color over time and produce interesting results. | |||
| Acid-free, archival quality paper keeps its color and texture far longer than ] based paper such as ], which turns yellow and becomes brittle much sooner. | |||
| <!--This paragraph is messy and unfocused. Work in progress... 2007 Nov 7 -->One new tool for drawing is the computer's 'drawing option'. Contemporary artists have broadened the sphere of associations the term 'drawing' encompasses to include performance and multimedia work, employing the branches of trees as drawing instruments, and fashioning images with carbon deposit from smoke,{{Fact|date=August 2007}} in addition to working in a number of unconventional drawing mediums, such as blood.<ref>{{cite web|title=my blood drawings|url=http://pavewalkdelune.spaces.live.com/|accessdate=2007-10-14}}</ref> | |||
| The basic tools are a ] or table, ] and ], and for ink drawing, ]. Other tools used are ], ], and ]. ] is used to prevent pencil and crayon marks from smudging. ] is used to secure paper to drawing surface, and also to mask an area to keep it free of accidental marks, such as sprayed or spattered materials and washes. An easel or slanted table is used to keep the drawing surface in a suitable position, which is generally more horizontal than the position used in painting. | |||
| ==Aspects of the drawing process== | |||
| {{Unreferencedsection|date=September 2007}} | |||
| ===Applying media=== | |||
| Prior to working on an image, the artist will likely want to gain an understanding of how the various media will work. The different drawing implements can be tried on practice sheets in order to determine value and texture, and how to apply the implement in order to produce various effects. | |||
| ==Technique== | |||
| ] by ]]] | |||
| ], '']'' technique]] | |||
| The stroke of the drawing implement can be used to control the appearance of the image. Ink drawings typically use ], which consists of groups of parallel lines. <ref>This use of hatching is to be distinguished from the use of a ] in heraldry to indicate ] (i.e. what "color," in layman's language, the arms are) in a monochromatic context.)</ref> Cross-hatching uses hatching in two or more different directions to create a darker tone. Broken hatching, or lines with intermittent breaks, is used to form lighter tones, and by controlling the density of the breaks a graduation of tone can be achieved. ], uses dots to produce tone, ] or ]. | |||
| Almost all draftsmen use their hands and fingers to apply the media, with the exception of some disabled individuals who draw with their mouth or feet.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.webdesignerdepot.com/2010/03/the-amazing-art-of-disabled-artists/|title=The Amazing Art of Disabled Artists |publisher= Webdesigner Depot|date=16 March 2010|access-date=1 January 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ] drawings use similar techniques, although with pencils and drawing sticks continuous variations in tone can be achieved. For best results the lines in a sketch are typically drawn to follow the contour curves of the surface, thus producing a depth effect. When drawing hair, the lines of the sketch follow the direction of the hair growth. | |||
| Prior to working on an image, the artist typically explores how various media work. They may try different drawing implements on practice sheets to determine value and texture, and how to apply the implement to produce various effects. | |||
| Typically a drawing will be filled in based on which hand the artist favors. A right-handed artist will want to draw from left to right in order to avoid smearing the image. Sometimes the artist will want to leave a section of the image blank while filling in the remainder of the picture. A frisket can be used for this purpose. The shape of the area to be preserved is cut out of the ], and the resulting shape is then applied to the drawing surface. This will protect the surface from receiving any stray marks before it is ready to be filled in. | |||
| ], study for what became the '']'', with other sketches]] | |||
| Another method to preserve a section of the image is to apply a spray-on ''fixative'' to the surface. This will hold loose material more firmly to the sheet and prevent it from smearing. However the fixative spray typically uses chemicals that can negatively affect the respiratory system, so it should be employed in a well-ventilated area such as outdoors. | |||
| The artist's choice of drawing strokes affects the appearance of the image. Pen and ink drawings often use ] – groups of parallel lines.<ref>This is unrelated to the ] in heraldry that indicates ] (i.e., the color of arms depicted in monochrome.)</ref> Cross-hatching uses hatching in two or more different directions to create a darker tone. Broken hatching, or lines with intermittent breaks, form lighter tones – and controlling the density of the breaks achieves a gradation of tone. ] uses dots to produce ], ] and ]. Different textures can be achieved depending on the method used to build tone.<ref>{{cite book|last=Guptill|first=Arthur L.|title=Drawing with Pen and Ink|year=1930|publisher=Reinhold Publishing Corporation|location=New York}}</ref> | |||
| Drawings in dry media often use similar techniques, though pencils and drawing sticks can achieve continuous variations in tone. Typically a drawing is filled in based on which hand the artist favors. A right-handed artist draws from left to right to avoid smearing the image. ] can remove unwanted lines, lighten tones, and clean up stray marks. In a sketch or outline drawing, lines drawn often follow the contour of the subject, creating depth by looking like shadows cast from a light in the artist's position. | |||
| ===Tone=== | |||
| Shading is the technique of varying the tonal values on the paper to represent the shade of the material as well as the placement of the shadows. Careful attention to reflected light, shadows, and highlights can result in a very realistic rendition of the image. | |||
| Sometimes the artist leaves a section of the image untouched while filling in the remainder. The shape of the area to preserve can be painted with ] or cut out of a ] and applied to the drawing surface, protecting the surface from stray marks until the mask is removed. | |||
| Blending uses an implement to soften or spread the original drawing strokes. Blending is most easily done with a medium that does not immediately ] itself, such as graphite, chalk, or charcoal, although freshly applied ink can be smudged, wet or dry, for some effects. For shading and blending, the artist can use a ], ], a ], a fingertip, or any combination of them. A piece of ] is useful for creating smooth textures, and for removing material to lighten the tone. Continuous tone can be achieved with graphite on a smooth surface without blending, but the technique is laborious, involving small circular or oval strokes with a somewhat blunt point. | |||
| Another method to preserve a section of the image is to apply a spray-on ''fixative'' to the surface. This holds loose material more firmly to the sheet and prevents it from smearing. However the fixative spray typically uses chemicals that can harm the respiratory system, so it should be employed in a well-ventilated area such as outdoors. | |||
| Shading techniques that also introduce texture to the drawing include ] and ]. There are a number of other methods for producing texture in the picture: in addition to choosing a suitable paper, the type of drawing material and the drawing technique will result in different textures. Texture can be made to appear more realistic when it is drawn next to a contrasting texture; a coarse texture will be more obvious when placed next to a smoothly blended area. A similar effect can be achieved by drawing different tones in close proximity; a light edge next to a dark background will stand out to the eye, and almost appear to float above the surface. | |||
| Another technique is ] in which the drawing surface is covered with graphite or charcoal and then erased to make the image.<ref>South, Helen, ''The Everything Drawing Book'', Adams Media, Avon, MA, 2004, pp. 152–53, {{ISBN|1-59337-213-2}}</ref> | |||
| ===Layout=== | |||
| Measuring the dimensions of a subject while blocking in the drawing is an important step in producing a realistic rendition of the aertically can be used to measure the angles of different sides. These angles can be reproduced on the drawing surface and then rechecked to make sure they are accurate. Another form of measurement is to compare the relative sizes of different parts of the subject with each other. A finger placed at a point along the drawing implement can be used to compare that dimension with other parts of the image. | |||
| ==Tone== | |||
| When attempting to draw a complicated shape such as a human figure, it is helpful at first to represent the form with a set of primitive shapes. Almost any form can be represented by some combination of the cube, sphere, cylinder, and cone. Once these basic shapes have been assembled into a likeness, then the drawing can be refined into a more accurate and polished form. The lines of the primitive shapes are removed and replaced by the final likeness. | |||
| ], with hatching and shading (1909)]] | |||
| Shading is the technique of varying the tonal values on the paper to represent the shade of the material as well as the placement of the shadows. Careful attention to reflected light, shadows and highlights can result in a very realistic rendition of the image. | |||
| Blending uses an implement to soften or spread the original drawing strokes. Blending is most easily done with a medium that does not immediately ] itself, such as graphite, chalk, or charcoal, although freshly applied ink can be smudged, wet or dry, for some effects. For shading and blending, the artist can use a ], ], a ], a fingertip, or any combination of them. A piece of ] is useful for creating smooth textures, and for removing material to lighten the tone. Continuous tone can be achieved with graphite on a smooth surface without blending, but the technique is laborious, involving small circular or oval strokes with a somewhat blunt point. | |||
| Shading techniques that also introduce texture to the drawing include ] and ]. A number of other methods produce texture. In addition to the choice of paper, drawing material and technique affect texture. Texture can be made to appear more realistic when it is drawn next to a contrasting texture; a coarse texture is more obvious when placed next to a smoothly blended area. A similar effect can be achieved by drawing different tones close together. A light edge next to a dark background stands out to the eye, and almost appears to float above the surface. | |||
| ==Form and proportion== | |||
| ] | |||
| Measuring the dimensions of a subject while blocking in the drawing is an important step in producing a realistic rendition of the subject. Tools such as a ] can be used to measure the angles of different sides. These angles can be reproduced on the drawing surface and then rechecked to make sure they are accurate. Another form of measurement is to compare the relative sizes of different parts of the subject with each other. A finger placed at a point along the drawing implement can be used to compare that dimension with other parts of the image. A ] can be used both as a ] and a device to compute proportions. | |||
| ] | |||
| When attempting to draw a complicated shape such as a human figure, it is helpful at first to represent the form with a set of primitive volumes. Almost any form can be represented by some combination of the cube, sphere, cylinder, and cone. Once these basic volumes have been assembled into a likeness, then the drawing can be refined into a more accurate and polished form. The lines of the primitive volumes are removed and replaced by the final likeness. Drawing the underlying construction is a fundamental skill for representational art, and is taught in many books and schools. Its correct application resolves most uncertainties about smaller details, and makes the final image look consistent.<ref name=drawinghale>{{cite book|last=Hale|first=Robert Beverly|title=Drawing Lessons from the Great Masters|url=https://archive.org/details/drawinglessonsfr0000hale|url-access=registration|year=1964|publication-date=2009|edition=45th Anniversary|publisher=Watson-Guptill Publications|isbn=978-0-8230-1401-9}}</ref> | |||
| A more refined art of ] relies upon the artist possessing a deep understanding of anatomy and the human proportions. A trained artist is familiar with the skeleton structure, joint location, muscle placement, tendon movement, and how the different parts work together during movement. This allows the artist to render more natural poses that do not appear artificially stiff. The artist is also familiar with how the proportions vary depending on the age of the subject, particularly when drawing a portrait. | A more refined art of ] relies upon the artist possessing a deep understanding of anatomy and the human proportions. A trained artist is familiar with the skeleton structure, joint location, muscle placement, tendon movement, and how the different parts work together during movement. This allows the artist to render more natural poses that do not appear artificially stiff. The artist is also familiar with how the proportions vary depending on the age of the subject, particularly when drawing a portrait. | ||
| ==Perspective== | |||
| {{Main|Perspective (graphical)|l1=Perspective}} | |||
| ] is a method of portraying objects on a flat surface so that the dimensions shrink with distance. The parallel, straight edges of any object, whether a building or a table, will follow lines that eventually converge at infinity. Typically this point of convergence will be along the horizon, as buildings are built level with the flat surface. When multiple structures are aligned with each other, such as buildings along a street, the horizontal tops and bottoms of the structures will all typically converge at a vanishing point. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Linear perspective is a method of portraying objects on a flat surface so that the dimensions shrink with distance. Each set of parallel, straight edges of any object, whether a building or a table, follows lines that eventually converge at a vanishing point. Typically this convergence point is somewhere along the horizon, as buildings are built level with the flat surface. When multiple structures are aligned with each other, such as buildings along a street, the horizontal tops and bottoms of the structures typically converge at a vanishing point. | |||
| ] | |||
| When both the fronts and sides of a building are drawn, then the parallel lines forming a side converge at a second point along the horizon (which may be off the drawing paper.) This is a "two-point perspective". Converging the vertical lines to a point in the sky then produces a "three-point perspective". | |||
| When both the fronts and sides of a building are drawn, then the parallel lines forming a side converge at a second point along the horizon (which may be off the drawing paper.) This is a two-point perspective.<ref>{{cite book|last=Watson|first=Ernest W.|title=Course in Pencil Sketching: Four Books in One|year=1978|publisher=Van Nostrand Reinhold Company|location=New York|isbn=978-0-442-29229-4|pages=167–75}}</ref> Converging the vertical lines to a third point above or below the horizon then produces a three-point perspective. | |||
| Depth can also be portrayed by several techniques in addition to the perspective approach above. Objects of similar '''size''' should appear ever smaller the further they are from the viewer. Thus the back wheel of a cart will appear slightly smaller than the front wheel. Depth can be portrayed through the use of '''texture'''. As the texture of an object gets further away it becomes more compressed and busy, taking on an entirely different character than if it was close. Depth can also be portrayed by reducing the amount of contrast of more distant objects, and also by making the colors more pale. This will reproduce the effect of '''atmospheric''' haze, and cause the eye to focus primarily on objects drawn in the foreground. | |||
| ] from ]]] | |||
| ===Artistry=== | |||
| Depth can also be portrayed by several techniques in addition to the perspective approach above. Objects of similar '''size''' should appear ever smaller the further they are from the viewer. Thus the back wheel of a cart appears slightly smaller than the front wheel. Depth can be portrayed through the use of '''texture'''. As the texture of an object gets further away it becomes more compressed and busy, taking on an entirely different character than if it was close. Depth can also be portrayed by reducing the contrast in more distant objects, and by making their colors less saturated. This reproduces the effect of '''atmospheric''' haze, and cause the eye to focus primarily on objects drawn in the foreground. | |||
| ] ] by ]]] | |||
| The ] of the image is an important element in producing an interesting work of ]. The artist plans the placement of elements in the art in order to communicate ideas and feelings with the viewer. The composition can determine the focus of the art, and result in a harmonious whole that is aesthetically appealing and stimulating. | |||
| ==Composition== | |||
| ] with white highlights by ]]] | |||
| The ] of the image is an important element in producing an interesting work of ]. The artist plans element placement in the art to communicate ideas and feelings with the viewer. The composition can determine the focus of the art, and result in a harmonious whole that is aesthetically appealing and stimulating. | |||
| The ] of the subject is also a key element in creating an artistic piece, and the interplay of ] is a valuable method in the artist's toolbox. The ] can make a considerable difference in the type of message that is being presented. Multiple light sources can wash out any wrinkles in a person's face, for instance, and give a more youthful appearance. In contrast, a single light source, such as harsh daylight, can serve to highlight any texture or interesting features. | The ] of the subject is also a key element in creating an artistic piece, and the interplay of ] is a valuable method in the artist's toolbox. The ] can make a considerable difference in the type of message that is being presented. Multiple light sources can wash out any wrinkles in a person's face, for instance, and give a more youthful appearance. In contrast, a single light source, such as harsh daylight, can serve to highlight any texture or interesting features. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 120: | ||
| When drawing an object or figure, the skilled artist pays attention to both the area within the silhouette and what lies outside. The exterior is termed the ], and can be as important in the representation as the figure. Objects placed in the background of the figure should appear properly placed wherever they can be viewed. | When drawing an object or figure, the skilled artist pays attention to both the area within the silhouette and what lies outside. The exterior is termed the ], and can be as important in the representation as the figure. Objects placed in the background of the figure should appear properly placed wherever they can be viewed. | ||
| A ] is a draft drawing that is made in preparation for a planned final image. Studies can be used to determine the |
A ] is a draft drawing that is made in preparation for a planned final image. Studies can be used to determine the appearances of specific parts of the completed image, or for experimenting with the best approach for accomplishing the end goal. However a well-crafted study can be a piece of art in its own right, and many hours of careful work can go into completing a study. | ||
| ==Process== | |||
| ==History: masters of drawing== | |||
| ] in ]]]Individuals display differences in their ability to produce visually accurate drawings.<ref>{{cite web|last=Ostrofsky|first=J|title=A Multi-Stage Attention Hypothesis of Drawing Ability|url=http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|year=2011|access-date=2014-03-11|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317224618/http://ttd2011.pressible.org/files/2012/05/Thinking-through-Drawing_Practice-into-Knowledge.pdf|archive-date=2014-03-17|url-status=dead}}</ref> A visually accurate drawing is described{{By whom|date=October 2024}} as being "recognized as a particular object at a particular time and in a particular space, rendered with little addition of visual detail that can not be seen in the object represented or with little deletion of visual detail."<ref name="Cohen 1997 609–621">{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=D. J|author2=Bennett, S.|title=Why can't most people draw what they see?|journal=Journal of Experimental Psychology|year=1997|volume=67|issue=6|pages=609–21|doi=10.1037/0096-1523.23.3.609 |pmid=9180037 }}</ref> | |||
| People have made ] since ] times. This art form first gained widespread popularity among ] artists during the 1400s{{Fact|date=September 2007}}, when ] became generally available, although ] for paintings already existed. Since that time, each century has produced artists who have created great drawings. | |||
| Investigative studies have aimed to explain the reasons why some individuals draw better than others. | |||
| * Masters of drawing in the 1400s and 1500s included ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| One study posited four key abilities in the drawing process: motor skills required for mark-making, the drawer's own perception of their drawing, perception of objects being drawn, and the ability to make good representational decisions.<ref name="Cohen 1997 609–621" /> Following this hypothesis, several studies have sought to conclude which of these processes are most significant in affecting the accuracy of drawings. | |||
| * During the 1600s, ], ], ], ], and ] created important drawings. | |||
| * In the 1700s, great drawings were produced by ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| * The masters of drawing during the 1800s included ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| * Great drawings in the 1900s have been created by ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ] (1801, ])]] | |||
| ==Digital illustration== | |||
| {{Unreferencedsection|date=September 2007}} | |||
| {{main|digital illustration|digital art}} | |||
| Drawing may also be done on a ]. '''Computer illustration''' or '''digital illustration''' is the use of digital tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a ] or a ]. It is distinguished from ], which is produced by a computer using mathematical models created by the artist. It is also distinct from ], in that it is an original construction "from scratch". (Photographic elements may be incorporated into such works, but they are not the primary basis or source for them.) | |||
| ;] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| Motor control is an important physical component in the 'Production Phase' of the drawing process.<ref>{{cite journal|last=van Somers|first=P|title=A system for drawing and drawing-related neuropsychology.|journal=Cognitive Neuropsychology|year=1989|volume=6|issue=2|pages=117–64|doi=10.1080/02643298908253416}}</ref> It has been suggested that motor control plays a role in drawing ability, though its effects are not significant.<ref name="Cohen 1997 609–621"/> | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <references/> | |||
| </div> | |||
| ;] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| It has been suggested that an individual's ability to perceive an object they are drawing is the most important stage in the drawing process.<ref name="Cohen 1997 609–621"/> This suggestion is supported by the discovery of a robust relationship between perception and drawing ability.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=D. J.|author2=Jones, H. E.|title=How shape constanct related to drawing accuracy|journal=Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts|year=2008|volume=2|issue=1|pages=8–19|doi=10.1037/1931-3896.2.1.8|url=http://people.uncw.edu/cohend/research/papers/cohen%20and%20jones%20-%20aca-2-1-8.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170809060155/http://people.uncw.edu/cohend/research/papers/cohen%20and%20jones%20-%20aca-2-1-8.pdf |archive-date=2017-08-09 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{wiktionary}} | |||
| * J. D. Hillberry, ''Drawing Realistic Textures in Pencil'', North Light Books, ], ISBN 0-89134-868-9. | |||
| * Frank Lohan, ''Pen & Ink Techniques'', Contemporary Books, ], ISBN 0-8092-7438-8. | |||
| * World Book, Inc. ''The World Book Encyclopedia Volume 5'', ], ISBN 0-7166-0089-7. | |||
| * Bodley Gallery, New York, N.Y., ''Modern master drawings'', ], OCLC 37498294. | |||
| * Betty Edwards, ''The New Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain'', HarperCollins Publishers Ltd; 3Rev Ed edition, ], ISBN 978-0007116454 | |||
| This evidence acted as the basis of ]' how-to-draw book, '']''.<ref>{{cite book|last=Edwards|first=B|year=1989|title=Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain|publisher=Putnam|location=New York|isbn=978-1-58542-920-2}}</ref> Edwards aimed to teach her readers how to draw, based on the development of the reader's perceptual abilities. | |||
| ==External link== | |||
| * | |||
| Furthermore, the influential artist and art critic ] emphasised the importance of perception in the drawing process in his book ''The Elements of Drawing''.<ref>{{cite book|last=Ruskin|first=John|title=The Elements of Drawing|year=1857|publisher=Dover Publishcations Inc|location=Mineola, NY}}</ref> He stated, "For I am nearly convinced, that once we see keenly enough, there is very little difficult in drawing what we see." | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| ;] | |||
| * ] | |||
| This has also been shown to influence one's ability to create visually accurate drawings. ] plays an important part in drawing as one's gaze shifts between the object they are drawing and the drawing itself.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=McManus|first1=I. C.|last2=Chamberlain|first2=R. S.|last3=Loo|first3=P.-K.|last4=Rankin|first4=Q.|last5=Riley|first5=H.|last6=Brunswick|first6=N.|title=Art students who cannot draw: exploring the relations between drawing ability, visual memory, accuracy of copying, and dyslexia.|journal=Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts|year=2010|volume=4|pages=18–30|doi=10.1037/a0017335|url=http://dspace.smu.ac.uk:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10875/226/PACApaper2010.pdf?sequence%3D1|citeseerx=10.1.1.654.5263|access-date=2017-10-25|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171026001726/http://dspace.smu.ac.uk:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10875/226/PACApaper2010.pdf?sequence%3D1|archive-date=2017-10-26|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| ;] | |||
| Some studies comparing artists to non-artists have found that artists spend more time thinking strategically while drawing. In particular, artists spend more time on 'metacognitive' activities such as considering different hypothetical plans for how they might progress with a drawing.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Fayena-Tawil|first1=F.|last2=Kozbelt|first2=A.|last3=Sitaras|first3=S.|title=Think global, act local: A protocol analysis comparison of artists' and nonartists' cognitions, metacognitions, and evaluations while drawing.|journal=Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts|year=2011|volume=5|issue=2|pages=135–45|doi=10.1037/a0021019}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=22em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] |
* ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ] | |||
| '''Notes''' | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| '''Further reading''' | |||
| <!--Interlanguage links--> | |||
| * Edwards, Betty. ''The New Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain'', HarperCollins Publishers Ltd; 3Rev Ed edition, 2001, {{ISBN|978-0-00-711645-4}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * Brommer, Gerald F. ''Exploring Drawing''. Worcester, Massachusetts: Davis Publications. 1988. | |||
| ] | |||
| * Bodley Gallery, New York, ''Modern master drawings'', 1971, {{OCLC|37498294}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| * {{cite book |author=Holcomb, M.| title=''Pen and Parchment : Drawing in the Middle Ages'' | location=New York | publisher=The Metropolitan Museum of Art | year=2009 | url=http://cdm16028.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p15324coll10/id/95658 |ref=none}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * Hillberry, J.D. ''Drawing Realistic Textures in Pencil'', North Light Books, 1999, {{ISBN|0-89134-868-9}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| * Landa, Robin. Take a line for a walk: A Creativity Journal. Boston: Wadsworth, 2011. {{ISBN|978-1-111-83922-2}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * Lohan, Frank. ''Pen & Ink Techniques'', Contemporary Books, 1978, {{ISBN|0-8092-7438-8}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| * Ruskin, J. (1857). The Elements of Drawing. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications Inc. {{ISBN|978-1-4538-4264-5}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * Spears, Heather. ''The Creative Eye.'' London: Arcturus. 2007. {{ISBN|978-0-572-03315-6}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| * World Book, Inc. ''The World Book Encyclopedia Volume 5'', 1988, {{ISBN|0-7166-0089-7}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| * ''Drawing/Thinking: Confronting an Electronic Age'', edited by Marc Treib, 2008, {{ISBN|0-415-77560-4}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Wiktionary}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Wikiversity}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| * , an essay about the craft of drawing, by artist Norman Nason. Archived from the on April 25, 2012.{{Gutenberg|no=25290|name=Line and Form (1900) by Walter Crane}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * , exhibition catalog fully online as PDF from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (a great drawing resource). | |||
| ] | |||
| * , exhibition catalog fully online as PDF from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (a great drawing resource). | |||
| ] | |||
| * A summary of how drawing was used as part of the artistic process in the Middle Ages. | |||
| ] | |||
| * Ganesh is a popular drawing technique used in India that usually involves drawing a full-body illustration of Ganesh drawing is often practiced in the presence of Ganesh statues and devotees. | |||
| {{Branches of the visual arts}} | |||
| {{Art world}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:50, 1 January 2025
Visual artwork on two-dimensional surface For other uses, see Drawing (disambiguation).
Drawing is a visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface. The instruments used to make a drawing are pencils, crayons, pens with inks, brushes with paints, or combinations of these, and in more modern times, computer styluses with graphics tablets or gamepads in VR drawing software.
A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as cardboard, vellum, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. It is one of the simplest and most efficient means of communicating ideas. The wide availability of drawing instruments makes drawing one of the most common artistic activities.
In addition to its more artistic forms, drawing is frequently used in commercial illustration, animation, architecture, engineering, and technical drawing. A quick, freehand drawing, usually not intended as a finished work, is sometimes called a sketch. An artist who practices or works in technical drawing may be called a drafter, draftsman, or draughtsman.
Overview

Drawing is one of the oldest forms of human expression within the visual arts. It is generally concerned with the marking of lines and areas of tone onto paper/other material, where the accurate representation of the visual world is expressed upon a plane surface. Traditional drawings were monochrome, or at least had little colour, while modern colored-pencil drawings may approach or cross a boundary between drawing and painting. In Western terminology, drawing is distinct from painting, even though similar media often are employed in both tasks. Dry media, normally associated with drawing, such as chalk, may be used in pastel paintings. Drawing may be done with a liquid medium, applied with brushes or pens. Using a brush for drawing is very widespread and here it is more the process of using lines and hatching, that characterises something as a drawing. Similar supports likewise can serve both: painting generally involves the application of liquid paint onto prepared canvas or panels, but sometimes an underdrawing is drawn first on that same support.
Drawing is often exploratory, with considerable emphasis on observation, problem-solving and composition. Drawing is also regularly used in preparation for a painting, further obfuscating their distinction. Drawings created for these purposes are called sketches.
There are several categories of drawing, including figure drawing, cartooning, doodling, and freehand. There are also many drawing methods, such as line drawing, stippling, shading, the surrealist method of entopic graphomania (in which dots are made at the sites of impurities in a blank sheet of paper, and lines are then made between the dots), and tracing (drawing on a translucent paper, such as tracing paper, around the outline of preexisting shapes that show through the paper).
A quick, unrefined drawing may be called a sketch.
In fields outside art, technical drawings or plans of buildings, machinery, circuitry and other things are often called "drawings" even when they have been transferred to another medium by printing.
History
In communication
Drawing is one of the oldest forms of human expression, with evidence for its existence preceding that of written communication. It is believed that drawing was used as a specialised form of communication before the invention of the written language, demonstrated by the production of cave and rock paintings around 30,000 years ago (Art of the Upper Paleolithic). These drawings, known as pictograms, depicted objects and abstract concepts. The sketches and paintings produced by Neolithic times were eventually stylised and simplified in to symbol systems (proto-writing) and eventually into early writing systems.
In manuscripts
Before the widespread availability of paper in Europe, monks in European monasteries used drawings, either as underdrawings for illuminated manuscripts on vellum or parchment, or as the final image. Drawing has also been used extensively in the field of science, as a method of discovery, understanding and explanation.
In science

Drawing diagrams of observations is an important part of scientific study.
In 1609, astronomer Galileo Galilei explained the changing phases of Venus and also the sunspots through his observational telescopic drawings. In 1924, geophysicist Alfred Wegener used illustrations to visually demonstrate the origin of the continents.
As artistic expression
Drawing is one of the easiest ways to visualise ideas and to express one's creativity; therefore it has been prominent in the world of art. Throughout much of history, drawing was regarded as the foundation for artistic practice. Initially, artists used and reused wooden tablets for the production of their drawings. Following the widespread availability of paper in the 14th century, the use of drawing in the arts increased. At this point, drawing was commonly used as a tool for thought and investigation, acting as a study medium whilst artists were preparing for their final pieces of work. The Renaissance brought about a great sophistication in drawing techniques, enabling artists to represent things more realistically than before, and revealing an interest in geometry and philosophy.
The invention of the first widely available form of photography led to a shift in the hierarchy of the arts. Photography offered an alternative to drawing as a method for accurately representing visual phenomena, and traditional drawing practice was given less emphasis as an essential skill for artists, particularly so in Western society.
Notable artists and draftsmen
Drawing became significant as an art form around the late 15th century, with artists and master engravers such as Albrecht Dürer and Martin Schongauer (c. 1448–1491), the first Northern engraver known by name. Schongauer came from Alsace, and was born into a family of goldsmiths. Albrecht Dürer, a master of the next generation, was also the son of a goldsmith.
Old Master Drawings often reflect the history of the country in which they were produced, and the fundamental characteristics of a nation at that time. In 17th-century Holland, a Protestant country, there were almost no religious artworks, and, with no King or court, most art was bought privately. Drawings of landscapes or genre scenes were often viewed not as sketches but as highly finished works of art. Italian drawings, however, show the influence of Catholicism and the Church, which played a major role in artistic patronage. The same is often true of French drawings, although in the 17th century the disciplines of French Classicism meant drawings were less Baroque than the more free Italian counterparts, which conveyed a greater sense of movement.
In the 20th century Modernism encouraged "imaginative originality" and some artists' approach to drawing became less literal, more abstract. World-renowned artists such as Pablo Picasso, Andy Warhol and Jean-Michel Basquiat helped challenge the status quo, with drawing being very much at the centre of their practice, and often re-interpreting traditional technique.
Basquiat's drawings were produced in many different mediums, most commonly ink, pencil, felt-tip or marker, and oil-stick, and he drew on any surface that came to hand, such as doors, clothing, refrigerators, walls and baseball helmets.
The centuries have produced a canon of notable artists and draftsmen, each with their own distinct language of drawing, including:
- 14th, 15th and 16th: Leonardo da Vinci • Albrecht Dürer • Hans Holbein the Younger • Michelangelo • Pisanello • Raphael
- 17th: Claude • Jacques de Gheyn II • Guercino • Nicolas Poussin • Rembrandt • Peter Paul Rubens • Pieter Saenredam
- 18th: François Boucher • Jean-Honoré Fragonard • Giovanni Battista Tiepolo • Antoine Watteau
- 19th: Aubrey Beardsley • Paul Cézanne • Jacques-Louis David • Honoré Daumier • Edgar Degas • Théodore Géricault • Francisco Goya • Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres • Pierre-Paul Prud'hon • Odilon Redon • John Ruskin • Georges Seurat • Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec • Vincent van Gogh
- 20th: Max Beckmann • Jean Dubuffet • M. C. Escher • Arshile Gorky • George Grosz • Paul Klee • Oskar Kokoschka • Käthe Kollwitz • Alfred Kubin • André Masson • Alphonse Mucha • Jules Pascin • Pablo Picasso • Egon Schiele • Jean-Michel Basquiat • Andy Warhol
Materials
The medium is the means by which ink, pigment, or color are delivered onto the drawing surface. Most drawing media either are dry (e.g. graphite, charcoal, pastels, Conté, silverpoint), or use a fluid solvent or carrier (marker, pen and ink). Watercolor pencils can be used dry like ordinary pencils, then moistened with a wet brush to get various painterly effects. Very rarely, artists have drawn with (usually decoded) invisible ink. Metalpoint drawing usually employs either silver or lead. More rarely used are gold, platinum, copper, brass, bronze, and tinpoint.
Paper comes in a variety of different sizes and qualities, ranging from newspaper grade up to high quality and relatively expensive paper sold as individual sheets. Papers vary in texture, hue, acidity, and strength when wet. Smooth paper is good for rendering fine detail, but a more "toothy" paper holds the drawing material better. Thus a coarser material is useful for producing deeper contrast.
Newsprint and typing paper may be useful for practice and rough sketches. Tracing paper is used to experiment over a half-finished drawing, and to transfer a design from one sheet to another. Cartridge paper is the basic type of drawing paper sold in pads. Bristol board and even heavier acid-free boards, frequently with smooth finishes, are used for drawing fine detail and do not distort when wet media (ink, washes) are applied. Vellum is extremely smooth and suitable for very fine detail. Coldpressed watercolor paper may be favored for ink drawing due to its texture.
Acid-free, archival quality paper keeps its color and texture far longer than wood pulp based paper such as newsprint, which turns yellow and becomes brittle much sooner.
The basic tools are a drawing board or table, pencil sharpener and eraser, and for ink drawing, blotting paper. Other tools used are circle compass, ruler, and set square. Fixative is used to prevent pencil and crayon marks from smudging. Drafting tape is used to secure paper to drawing surface, and also to mask an area to keep it free of accidental marks, such as sprayed or spattered materials and washes. An easel or slanted table is used to keep the drawing surface in a suitable position, which is generally more horizontal than the position used in painting.
Technique

Almost all draftsmen use their hands and fingers to apply the media, with the exception of some disabled individuals who draw with their mouth or feet.
Prior to working on an image, the artist typically explores how various media work. They may try different drawing implements on practice sheets to determine value and texture, and how to apply the implement to produce various effects.

The artist's choice of drawing strokes affects the appearance of the image. Pen and ink drawings often use hatching – groups of parallel lines. Cross-hatching uses hatching in two or more different directions to create a darker tone. Broken hatching, or lines with intermittent breaks, form lighter tones – and controlling the density of the breaks achieves a gradation of tone. Stippling uses dots to produce tone, texture and shade. Different textures can be achieved depending on the method used to build tone.
Drawings in dry media often use similar techniques, though pencils and drawing sticks can achieve continuous variations in tone. Typically a drawing is filled in based on which hand the artist favors. A right-handed artist draws from left to right to avoid smearing the image. Erasers can remove unwanted lines, lighten tones, and clean up stray marks. In a sketch or outline drawing, lines drawn often follow the contour of the subject, creating depth by looking like shadows cast from a light in the artist's position.
Sometimes the artist leaves a section of the image untouched while filling in the remainder. The shape of the area to preserve can be painted with masking fluid or cut out of a frisket and applied to the drawing surface, protecting the surface from stray marks until the mask is removed.
Another method to preserve a section of the image is to apply a spray-on fixative to the surface. This holds loose material more firmly to the sheet and prevents it from smearing. However the fixative spray typically uses chemicals that can harm the respiratory system, so it should be employed in a well-ventilated area such as outdoors.
Another technique is subtractive drawing in which the drawing surface is covered with graphite or charcoal and then erased to make the image.
Tone

Shading is the technique of varying the tonal values on the paper to represent the shade of the material as well as the placement of the shadows. Careful attention to reflected light, shadows and highlights can result in a very realistic rendition of the image.
Blending uses an implement to soften or spread the original drawing strokes. Blending is most easily done with a medium that does not immediately fix itself, such as graphite, chalk, or charcoal, although freshly applied ink can be smudged, wet or dry, for some effects. For shading and blending, the artist can use a blending stump, tissue, a kneaded eraser, a fingertip, or any combination of them. A piece of chamois is useful for creating smooth textures, and for removing material to lighten the tone. Continuous tone can be achieved with graphite on a smooth surface without blending, but the technique is laborious, involving small circular or oval strokes with a somewhat blunt point.
Shading techniques that also introduce texture to the drawing include hatching and stippling. A number of other methods produce texture. In addition to the choice of paper, drawing material and technique affect texture. Texture can be made to appear more realistic when it is drawn next to a contrasting texture; a coarse texture is more obvious when placed next to a smoothly blended area. A similar effect can be achieved by drawing different tones close together. A light edge next to a dark background stands out to the eye, and almost appears to float above the surface.
Form and proportion

Measuring the dimensions of a subject while blocking in the drawing is an important step in producing a realistic rendition of the subject. Tools such as a compass can be used to measure the angles of different sides. These angles can be reproduced on the drawing surface and then rechecked to make sure they are accurate. Another form of measurement is to compare the relative sizes of different parts of the subject with each other. A finger placed at a point along the drawing implement can be used to compare that dimension with other parts of the image. A ruler can be used both as a straightedge and a device to compute proportions.
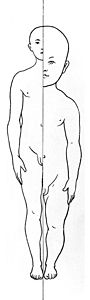
When attempting to draw a complicated shape such as a human figure, it is helpful at first to represent the form with a set of primitive volumes. Almost any form can be represented by some combination of the cube, sphere, cylinder, and cone. Once these basic volumes have been assembled into a likeness, then the drawing can be refined into a more accurate and polished form. The lines of the primitive volumes are removed and replaced by the final likeness. Drawing the underlying construction is a fundamental skill for representational art, and is taught in many books and schools. Its correct application resolves most uncertainties about smaller details, and makes the final image look consistent.
A more refined art of figure drawing relies upon the artist possessing a deep understanding of anatomy and the human proportions. A trained artist is familiar with the skeleton structure, joint location, muscle placement, tendon movement, and how the different parts work together during movement. This allows the artist to render more natural poses that do not appear artificially stiff. The artist is also familiar with how the proportions vary depending on the age of the subject, particularly when drawing a portrait.
Perspective
Main article: Perspective
Linear perspective is a method of portraying objects on a flat surface so that the dimensions shrink with distance. Each set of parallel, straight edges of any object, whether a building or a table, follows lines that eventually converge at a vanishing point. Typically this convergence point is somewhere along the horizon, as buildings are built level with the flat surface. When multiple structures are aligned with each other, such as buildings along a street, the horizontal tops and bottoms of the structures typically converge at a vanishing point.
When both the fronts and sides of a building are drawn, then the parallel lines forming a side converge at a second point along the horizon (which may be off the drawing paper.) This is a two-point perspective. Converging the vertical lines to a third point above or below the horizon then produces a three-point perspective.

Depth can also be portrayed by several techniques in addition to the perspective approach above. Objects of similar size should appear ever smaller the further they are from the viewer. Thus the back wheel of a cart appears slightly smaller than the front wheel. Depth can be portrayed through the use of texture. As the texture of an object gets further away it becomes more compressed and busy, taking on an entirely different character than if it was close. Depth can also be portrayed by reducing the contrast in more distant objects, and by making their colors less saturated. This reproduces the effect of atmospheric haze, and cause the eye to focus primarily on objects drawn in the foreground.
Composition

The composition of the image is an important element in producing an interesting work of artistic merit. The artist plans element placement in the art to communicate ideas and feelings with the viewer. The composition can determine the focus of the art, and result in a harmonious whole that is aesthetically appealing and stimulating.
The illumination of the subject is also a key element in creating an artistic piece, and the interplay of light and shadow is a valuable method in the artist's toolbox. The placement of the light sources can make a considerable difference in the type of message that is being presented. Multiple light sources can wash out any wrinkles in a person's face, for instance, and give a more youthful appearance. In contrast, a single light source, such as harsh daylight, can serve to highlight any texture or interesting features.
When drawing an object or figure, the skilled artist pays attention to both the area within the silhouette and what lies outside. The exterior is termed the negative space, and can be as important in the representation as the figure. Objects placed in the background of the figure should appear properly placed wherever they can be viewed.
A study is a draft drawing that is made in preparation for a planned final image. Studies can be used to determine the appearances of specific parts of the completed image, or for experimenting with the best approach for accomplishing the end goal. However a well-crafted study can be a piece of art in its own right, and many hours of careful work can go into completing a study.
Process

Individuals display differences in their ability to produce visually accurate drawings. A visually accurate drawing is described as being "recognized as a particular object at a particular time and in a particular space, rendered with little addition of visual detail that can not be seen in the object represented or with little deletion of visual detail."
Investigative studies have aimed to explain the reasons why some individuals draw better than others. One study posited four key abilities in the drawing process: motor skills required for mark-making, the drawer's own perception of their drawing, perception of objects being drawn, and the ability to make good representational decisions. Following this hypothesis, several studies have sought to conclude which of these processes are most significant in affecting the accuracy of drawings.

Motor control is an important physical component in the 'Production Phase' of the drawing process. It has been suggested that motor control plays a role in drawing ability, though its effects are not significant.
It has been suggested that an individual's ability to perceive an object they are drawing is the most important stage in the drawing process. This suggestion is supported by the discovery of a robust relationship between perception and drawing ability.
This evidence acted as the basis of Betty Edwards' how-to-draw book, Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain. Edwards aimed to teach her readers how to draw, based on the development of the reader's perceptual abilities.
Furthermore, the influential artist and art critic John Ruskin emphasised the importance of perception in the drawing process in his book The Elements of Drawing. He stated, "For I am nearly convinced, that once we see keenly enough, there is very little difficult in drawing what we see."
This has also been shown to influence one's ability to create visually accurate drawings. Short-term memory plays an important part in drawing as one's gaze shifts between the object they are drawing and the drawing itself.
Some studies comparing artists to non-artists have found that artists spend more time thinking strategically while drawing. In particular, artists spend more time on 'metacognitive' activities such as considering different hypothetical plans for how they might progress with a drawing.
See also
- Academy figure
- Architectural drawing
- Composition
- Contour drawing
- Diagram
- Digital illustration
- Engineering drawing
- Figure drawing
- Geometric drawing
- Graphic design
- Illustration
- Landscape painting
- Negro (lead pencil)
- Painting
- Plumbago drawing
- Sketch (drawing)
- Subtractive drawing
- Technical drawing
- Visual arts
- Image
References
Notes
- www.sbctc.edu (adapted). "Module 6: Media for 2-D Art" (PDF). Saylor.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-08-09. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- "Draftsman Definition & Meaning". Dictionary.com.
- McManus, I. C.; Chamberlain, R; Loo, P-W; Riley, H; Rankin, Q; Brunswick, N (2010). "Art Students Who Cannot Draw: Exploring the Relations Between Drawing Ability, Visual Memory, Accuracy of Copying, and Dyslexia" (PDF). University College London. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, vol. 4, no. 1, 18 –30. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- See grisaille and chiaroscuro
- ^ Tversky, B (2011). "Visualizing thought". Topics in Cognitive Science. 3 (3): 499–535. doi:10.1111/j.1756-8765.2010.01113.x. PMID 25164401.
- Farthing, S (2011). "The Bigger Picture of Drawing" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- Thinking Through Drawing: Practice into Knowledge Archived 2014-03-17 at the Wayback Machine 2011c
- Robinson, A (2009). Writing and script: a very short introduction. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Kovats, T (2005). The Drawing Book. London: Black Dog Publishing. ISBN 9781904772330.
- Walker, J. F; Duff, L; Davies, J (2005). "Old Manuals and New Pencils". Drawing- The Process. Bristol: Intellect Books.
- See the discussion on erasable drawing boards and 'tafeletten' in van de Wetering, Ernst. Rembrandt: The Painter at Work.
- Burton, J. "Preface" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- Chamberlain, R (2013). Drawing Conclusions: An exploration of the cognitive and neuroscientific foundations of representational drawing (Doctoral).
- Davis, P; Duff, L; Davies, J (2005). "Drawing a Blank". Drawing – The Process. Bristol: Intellect Books. pp. 15–25. ISBN 9781841500768.
- Simmons, S (2011). "Philosophical Dimension of Drawing Instruction" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- Poe, E. A. (1840). The Daguerreotype. Classic Essays on Photography. New Haven, CN: Leete's Island Books. pp. 37–38.
- "Collecting guide: Old Master prints". Christie's. 1 July 2020.
- Hinrich Sieveking, "German Draughtsmanship in the Ages of Dürer and Goethe", British Museum. Accessed 20 February 2016
- Barbara Hryszko, A Painter as a Draughtsman. Typology and Terminology of Drawings in Academic Didactics and Artistic Practice in France in 17th Century Metodologia, metoda i terminologia grafiki i rysunku. Teoria i praktyka, ed. Jolanta Talbierska, Warszawa 2014, pp. 169–176.
- "Collecting guide: Old Master drawings". Christie's. 23 June 2021.
- Duff, L; Davies, J (2005). Drawing – The Process. Bristol: Intellect Books. ISBN 9781841509075.
- Gompertz, Will (2009-02-12). "My life in art: How Jean-Michel Basquiat taught me to forget about technique". the Guardian. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- "boom for real: a dictionary of basquiat". I-d. 2017-09-26. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- ArtCyclopedia, February 2003, "Masterful Leonardo and Graphic Dürer". Accessed 20 February 2016
- lara Broecke, Cennino Cennini's Il Libro dell'Arte: a new English Translation and Commentary with Italian Transcription, Archetype 2015
- Mayer, Ralph (1991). The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques. Viking. ISBN 978-0-670-83701-4.
- "The Amazing Art of Disabled Artists". Webdesigner Depot. 16 March 2010. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- This is unrelated to the hatching system in heraldry that indicates tincture (i.e., the color of arms depicted in monochrome.)
- Guptill, Arthur L. (1930). Drawing with Pen and Ink. New York: Reinhold Publishing Corporation.
- South, Helen, The Everything Drawing Book, Adams Media, Avon, MA, 2004, pp. 152–53, ISBN 1-59337-213-2
- Hale, Robert Beverly (1964). Drawing Lessons from the Great Masters (45th Anniversary ed.). Watson-Guptill Publications (published 2009). ISBN 978-0-8230-1401-9.
- Watson, Ernest W. (1978). Course in Pencil Sketching: Four Books in One. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. pp. 167–75. ISBN 978-0-442-29229-4.
- Ostrofsky, J (2011). "A Multi-Stage Attention Hypothesis of Drawing Ability" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-17. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ Cohen, D. J; Bennett, S. (1997). "Why can't most people draw what they see?". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 67 (6): 609–21. doi:10.1037/0096-1523.23.3.609. PMID 9180037.
- van Somers, P (1989). "A system for drawing and drawing-related neuropsychology". Cognitive Neuropsychology. 6 (2): 117–64. doi:10.1080/02643298908253416.
- Cohen, D. J.; Jones, H. E. (2008). "How shape constanct related to drawing accuracy" (PDF). Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts. 2 (1): 8–19. doi:10.1037/1931-3896.2.1.8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-09.
- Edwards, B (1989). Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain. New York: Putnam. ISBN 978-1-58542-920-2.
- Ruskin, John (1857). The Elements of Drawing. Mineola, NY: Dover Publishcations Inc.
- McManus, I. C.; Chamberlain, R. S.; Loo, P.-K.; Rankin, Q.; Riley, H.; Brunswick, N. (2010). "Art students who cannot draw: exploring the relations between drawing ability, visual memory, accuracy of copying, and dyslexia" (PDF). Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts. 4: 18–30. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.654.5263. doi:10.1037/a0017335. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-10-26. Retrieved 2017-10-25.
- Fayena-Tawil, F.; Kozbelt, A.; Sitaras, S. (2011). "Think global, act local: A protocol analysis comparison of artists' and nonartists' cognitions, metacognitions, and evaluations while drawing". Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts. 5 (2): 135–45. doi:10.1037/a0021019.
Further reading
- Edwards, Betty. The New Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain, HarperCollins Publishers Ltd; 3Rev Ed edition, 2001, ISBN 978-0-00-711645-4
- Brommer, Gerald F. Exploring Drawing. Worcester, Massachusetts: Davis Publications. 1988.
- Bodley Gallery, New York, Modern master drawings, 1971, OCLC 37498294.
- Holcomb, M. (2009). Pen and Parchment : Drawing in the Middle Ages. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- Hillberry, J.D. Drawing Realistic Textures in Pencil, North Light Books, 1999, ISBN 0-89134-868-9.
- Landa, Robin. Take a line for a walk: A Creativity Journal. Boston: Wadsworth, 2011. ISBN 978-1-111-83922-2
- Lohan, Frank. Pen & Ink Techniques, Contemporary Books, 1978, ISBN 0-8092-7438-8.
- Ruskin, J. (1857). The Elements of Drawing. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications Inc. ISBN 978-1-4538-4264-5
- Spears, Heather. The Creative Eye. London: Arcturus. 2007. ISBN 978-0-572-03315-6.
- World Book, Inc. The World Book Encyclopedia Volume 5, 1988, ISBN 0-7166-0089-7.
- Drawing/Thinking: Confronting an Electronic Age, edited by Marc Treib, 2008, ISBN 0-415-77560-4
External links
- Timeline of Drawing Development in Children
- On Drawing, an essay about the craft of drawing, by artist Norman Nason. Archived from the original on April 25, 2012.
- Line and Form (1900) by Walter Crane at Project Gutenberg
- Leonardo da Vinci: anatomical drawings from the Royal Library, Windsor Castle, exhibition catalog fully online as PDF from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (a great drawing resource).
- Leonardo da Vinci, Master Draftsman, exhibition catalog fully online as PDF from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (a great drawing resource).
- Drawing in the Middle Ages A summary of how drawing was used as part of the artistic process in the Middle Ages.
- Ganesh drawing is a popular drawing technique used in India that usually involves drawing a full-body illustration of Ganesh drawing is often practiced in the presence of Ganesh statues and devotees.
| Visual arts | |
|---|---|