| Revision as of 20:08, 1 August 2008 editDpotop (talk | contribs)3,882 edits →Conquest of Transylvania and integration into the Kingdom of Hungary: What region? You see, you are not forced to copy every stupidity from every encyclopedia. Or be consistent with Magyars← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:34, 22 January 2025 edit undoProcrastineur49 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,295 editsm Outdated page name, replaced: Luxembourg → LuxembourgTag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Historical region in Central Europe}} | |||
| {{pp-move-vandalism|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| ] marked in dark yellow, corresponding to Maramureş, Crişana and the Romanian Banat, are sometimes considered part of Transylvania.]] | |||
| {{Redirect|Siebenbürgen|the band|Siebenbürgen (band)}} | |||
| ] of the ] at the end of the 19th century.]] | |||
| {{Distinguish|Transnistria}} | |||
| {{Infobox country | |||
| | conventional_long_name = Transylvania | |||
| | common_name = Transylvania | |||
| | native_name = {{lang|ro|Transilvania}} / {{native name|ro|Ardeal}}<br/>{{native name|hu|Erdély}}<br/>{{native name|de|Siebenbürgen}}<br /> ''Siweberjen'' (]) | |||
| | image_flag = File:Flag of Transylvania (Local).svg | |||
| | image_coat = Coat of arms of Transylvania.svg | |||
| | coa_size = 70 | |||
| | national_anthem = | |||
| | image_map = Transylvania, Banat, Crisana and Maramures.svg | |||
| | map_caption = {{legend|#FF9955|Transylvania}}{{legend|#FFCCAA|], ] and ]}}{{legend|#FFF6D5|], ], ], ], and ]}} | |||
| | capital = | |||
| | largest_city = ] | |||
| | official_languages = ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cdep.ro/pls/dic/site.page?den=act2_2&par1=1#t1c0s0a13|title=Constitution of Romania|publisher=Cdep.ro|access-date=2 October 2013|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170907214119/http://www.cdep.ro/pls/dic/site.page?den=act2_2&par1=1#t1c0s0a13|archive-date=7 September 2017}}</ref> | |||
| | languages2_type = Recognised minority<br />languages<!--Protected and/or co-official (regional) languages--><ref>{{cite web|title=Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No. 148 – European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages|url=http://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations?p_auth=63PpH3zN|website=Council of Europe|access-date=3 December 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208122308/http://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/148/declarations?p_auth=63PpH3zN|archive-date=8 December 2015}}</ref> | |||
| | languages2 = {{Collapsible list | |||
| | titlestyle=background:transparent;text-align:left;font-weight:normal; | |||
| | title= ''See here'' | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] | |||
| }} | |||
| | ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | |||
| | 76.42% ] | |||
| | 17.36% ] | |||
| | 4.53% ] | |||
| | 1.69% ] | |||
| }} | |||
| | ethnic_groups_year = ] | |||
| | ethnic_groups_ref = <ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Tabel-2.02.1-si-Tabel-2.02.2.xlsx |title=Populaţia rezidentă după etnie (Recensământ 2021) |publisher=INS |website=www.insse.ro |access-date=2023-09-24|language=ro}}</ref> | |||
| | demonym = Transylvanian | |||
| | religion = {{ublist |item_style=white-space; | |||
| |{{Tree list}} | |||
| * 90.42% ] | |||
| ** 65.96% ] | |||
| ** 15.04% ] | |||
| ** 9.32% ] | |||
| ** 2.10% other ] | |||
| {{Tree list/end}} | |||
| |0.27% undeclared / <br/>no religion | |||
| |0.0% no data | |||
| |8.31% ] | |||
| }} | |||
| | religion_year = ] | |||
| | religion_ref = <ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Tabel-2.04.1-si-Tabel-2.04.2.xlsx |title=Populaţia rezidentă după religie (Recensământ 2021) |publisher=INS |website=www.insse.ro |access-date=2023-09-24|language=ro}}</ref> | |||
| | government_type = | |||
| | leader_title1 = | |||
| | leader_name1 = | |||
| | leader_title2 = | |||
| | leader_name2 = | |||
| | legislature = | |||
| | upper_house = | |||
| | lower_house = | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| | established_event1 = | |||
| | established_date1 = | |||
| | established_event2 = | |||
| | established_date2 = | |||
| | established_event3 = | |||
| | established_date3 = | |||
| | established_event4 = | |||
| | established_date4 = | |||
| | established_event5 = ] | |||
| | established_date5 = 1 December 1918/1923 | |||
| | established_event6 = | |||
| | established_date6 = | |||
| | established_event7 = | |||
| | established_date7 = | |||
| | established_event8 = | |||
| | established_date8 = | |||
| | established_event9 = ] | |||
| | established_date9 = 27 December 1989<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IsJADwAAQBAJ&pg=PA218|title=Political Leadership: A Pragmatic Institutionalist Approach|first=Robert|last=Elgie|date= 2017|publisher=Springer|isbn=9781137346223|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Qu3TAAAAMAAJ&q=emblem|title=Romania Directory|date=1990|publisher=Editura Cronos|isbn=9789739000000|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/20050|title=DECRET-LEGE 2 27/12/1989 – Portal Legislativ|website=legislatie.just.ro}}</ref> | |||
| | established_event13 = | |||
| | established_date13 = | |||
| | established_event14 = ] the ] | |||
| | established_date14 = 1 January 2007 | |||
| | area_km2 = 100,390 | |||
| | area_footnote = <ref>{{Cite web |url=https://insse.ro/cms/sites/default/files/field/publicatii/anuarul_statistic_al_romaniei_carte-ed.2022.pdf |title=Romanian Statistical Yearbook (2022) – 1.8 Administrative organisation of Romanian territory, on December 31, 2021 (p.17)|publisher=] |access-date=20 March 2023 |url-status=live|archive-date=20 March 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320054533/https://insse.ro/cms/sites/default/files/field/publicatii/anuarul_statistic_al_romaniei_carte-ed.2022.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| | area_rank = 106th <!-- Area rank should match ]--> | |||
| | area_sq_mi = 38,720 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | percent_water = 3 | |||
| | population_estimate = 6,478,126<ref>{{cite web |url=http://statistici.insse.ro:8077/tempo-online/#/pages/tables/insse-table |title=POP105A – Populația rezidentă la 1 Ianuarie pe grupe de vârste, sexe și medii de rezidență, macroregiuni, regiuni de dezvoltare și județe |publisher=] (TEMPO –statiscal data) |website=www.insse.ro/cms/en |date=5 September 2023 |access-date=24 September 2023 |language=ro}}</ref> | |||
| | population_census = {{decreaseNeutral}} 6,461,780{{efn|name=data1|The sixteen counties that form the historical region of Transylvania.}}<ref name="Census2021">{{cite web|url=https://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Tabel-1.01.xls |title=Populația la Recensămintele 1948–2021 |publisher=INS |website=www.insse.ro |access-date=2023-09-24|language=ro}}</ref> | |||
| | population_estimate_year = January 2023 | |||
| | population_estimate_rank = 107th | |||
| | population_census_year = ] | |||
| | population_census_rank = | |||
| | population_density_km2 = 64.5 | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | population_density_rank = 122nd | |||
| | GDP_PPP = | |||
| | GDP_PPP_year = | |||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $41,633<ref name="IMFWEORO"/> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $194.00 billion<ref name="IMFWEORO">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/April/weo-report?c=968,&s=NGDPD,%20PPPGDP,%20NGDPDPC,%20PPPPC,&sy=2019&ey=2025&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, April 2023 Edition. (Romania) |publisher=] |website=IMF.org |access-date=11 April 2023 }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = 2023 | |||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = 57th | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $28,574<ref name="IMFWEORO"/> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 39th | |||
| | Gini = <!--number only--> | |||
| | Gini_year = | |||
| | Gini_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | Gini_ref = <ref name=eurogini>{{cite web |url=https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/tessi190/default/table?lang=en |title=Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey|publisher=] |website=ec.europa.eu |access-date=16 August 2022}}</ref> | |||
| | Gini_rank = | |||
| | HDI = 0.829 <!--number only--> | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2021/2022|language=en|publisher=]|date=8 September 2022|access-date=8 September 2022}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 33rd | |||
| | currency = ] | |||
| | currency_code = RON | |||
| | time_zone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = +2 | |||
| | utc_offset_DST = +3 | |||
| | time_zone_DST = ] | |||
| | date_format = dd.mm.yyyy (]) | |||
| | drives_on = Right | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | patron_saint = | |||
| | iso3166code = RO | |||
| | cctld = ]<sup>a</sup> | |||
| | footnote_a = Also ], shared with other ] member states. | |||
| | today = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Transylvania''' ({{ |
'''Transylvania''' ({{langx|ro|Transilvania}} {{IPA|ro|transilˈvani.a|}} or {{lang|ro|Ardeal}}; or {{langx|hu|Erdély}} {{IPA|hu|ˈɛrdeːj|}}; {{langx|de|Siebenbürgen}} {{IPA|de|ˌziːbm̩ˈbʏʁɡn̩||De-Siebenbürgen.ogg}} or {{lang|de|Transsilvanien}}, historically {{lang|de|Überwald}}; ]: ''Siweberjen'') is a ] in ], encompassing central ]. To the east and south its ] is the ] and to the west the ]. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of ] and ], and occasionally ]. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring ] and even a small part of south-western neighbouring ] to its north east (represented by ]). | ||
| Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history, coupled with its multi-cultural character. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, ], and other very well preserved medieval iconic cities and towns such as ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. It is also the home of some of Romania's ] such as the ], the ], the ] and the ]. | |||
| After forming part of Hungary (11th–16th century), it was an autonomous principality within the Ottoman Empire (16th–17th century) and then once again became part of Hungary at the end of the 17th century; later it was incorporated into Romania (1918–20).<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Transylvania|url=http://britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/603323/Transylvania|encyclopedia=]|publisher=]|date=2008|accessdate=2008-08-01}}</ref> | |||
| It was under the rule of the ], part of the ] (168 BC – 106 AD), ] (106–271), the ], the ] (4th–5th centuries), the ] (5th–6th centuries), the ] (6th–9th centuries), the ], and the 9th century ]. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and ], and ] family from the ] ruled it in the 10th century. King ] asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle ] and Transylvania became part of the ] in 1002. | |||
| Outside Romania, it is strongly associated with the novel '']'',<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> while within Romania and Hungary the region is known for the scenic beauty of its ] landscape and its rich ]. | |||
| After the ] in 1526 it belonged to the ], from which the ] emerged in 1570 by the ]. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a ] of the ]; however, the principality had dual ]ty (] and ]).<ref>Dennis P. Hupchick, , Palgrave Macmillan, 1995, p. 62</ref><ref>Peter F. Sugar, , University of Washington Press, 1993, pp. 150–154</ref> | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| ], ] and ] in ].]] | |||
| In 1690, the ] gained possession of Transylvania through the ].<ref>{{cite book |author=Béla Köpeczi |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VElpAAAAMAAJ&q=%22+in+1690%2C+the+Habsburgs+gained+possession+of+Transylvania+by+right+of+the+Hungarian+crown.%22 |title=History of Transylvania: From 1606 to 1830 |date=2008 |publisher=Social Science Monographs |isbn=978-0-88033-491-4 |access-date=2017-07-10}}</ref><ref>Peter F. Sugar. (''History of East Central Europe''), University of Washington Press, July 1983, p. 163</ref><ref name="books.google.com2">Paul Lendvai, Ann Major. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2003, p. 146;</ref> After the failure of ] in 1711,<ref>{{cite book |last1=Glockner |first1=Peter G. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FAAMAQAAMAAJ&q=%22+In+1711,+after+the+Peace+Treaty+of+Szatmar,+Austrian+control+was+firmly+established+over+all+of+Hungary+and+Erdely,+and+the+princes+of+Transylvania+were+replaced+by+Austrian+governors.+%22 |title=Encyclopaedia Hungarica: English |last2=Bagossy |first2=Nora Varga |date=2007 |publisher=Hungarian Ethnic Lexicon Foundation |isbn=978-1-55383-178-5 |language=en}}</ref> Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian ] were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors.<ref name="Britannica3"> (2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009</ref><ref name="Leopoldinum2"> (2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009</ref> During the ], the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the ] of 1848.<ref>Laszlo Péter, , Brill, 2012, p. 56</ref> After the failure of the revolution, the ] decreed that the ] be a separate crown land entirely independent of ].<ref name="hoelseth.com">. (Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV)</ref> The separate status of Transylvania ended with the ],<ref>John F. Cadzow, Andrew Ludanyi, Louis J. Elteto, , Kent State University Press, 1983, p. 79</ref> and it was reincorporated into the ] (]) as part of the ].<ref>James Minahan: , Greenwood Press, Westport, CT</ref> It was also during this period that Romanians experienced the awakening of self-consciousness as a nation, manifested in cultural and ideological movements such as ],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Pavel |first=Eugen |date=2018 |title=The Transylvanian School – Premises Underlying the Critical Editions of Texts |page=1 |url=https://www.academia.edu/70072431 |access-date=6 August 2023 |website=Academia.edu}}</ref> and drafted political petitions such as | |||
| {{main|Historical names of Transylvania}} | |||
| ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Török |first=Borbála Zsuzsanna |date=27 October 2015 |title="1 Landeskunde, honismeret – Patriotic Scholarship and Vernacular Languages". In Exploring Transylvania |url=https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004303058_003 |access-date=6 August 2023 |website=brill.com|doi=10.1163/9789004303058_003 }}</ref> After ], the National Assembly of Romanians from Transylvania proclaimed the ] on 1 December 1918, and Transylvania became part of the ] by the ] in 1920. In 1940, ] reverted to ] as a result of the ], but it was returned to ] after the end of ]. | |||
| Transylvania was first referred to in a ] document in 1075 as ''ultra silvam'', meaning "exceedingly forested" (''ultra'' meaning "excessively or beyond what is common" and the ] of ''sylva'' (sylvam) meaning "wood or forest"). | |||
| In popular culture, Transylvania is commonly associated with ] because of the influence of ]'s 1897 novel '']'' and the many subsequent books and films that the story has inspired.<ref name="query.nytimes.com">{{cite news |url=https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9F0CE6DE143BF931A1575BC0A965958260 |work=The New York Times |title=Travel Advisory; Lure of Dracula In Transylvania |date=1993-08-22}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.icromania.com/infoTransylvania.asp |title=Romania Transylvania |website= Icromania.com |date=2007-04-15 |access-date=2012-07-30}}</ref> Many ] were furious with ] for strengthening the borders of ], which interfered with their control of trade routes, and his extreme sadism and barbarity, which by a collection of credible historical accounts of diverse origins, most of which were non-Saxon, led to the industrial-scale execution of over 100,000 people{{citation needed|date=October 2023}} by impaling, some of whom were Saxons. The victims were often arranged in grotesque displays intended to terrorize various groups, including the Saxons. In retaliation, the Saxons distributed poems of cruelty and other propaganda characterising the sadistic Vlad III Dracula as a drinker of blood.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.scribd.com/document/298070110/Die-Geschichte-Dracole-Waide|title=Consuming News: Newspapers and Print Culture in Early Modern Europe (1500–1800)|editor=Gerhild Scholz Williams |editor2=William Layher |pages=14–34 | |||
| The modern English name is probably taken from the ] ''Erdély,'' which is derived from ''Erdő-elve'' meaning ''"beyond the forest"'' (a meaning first referred to in its Medieval Latin version in a 12th century document - '']''). "Transylvania" means "beyond the forest" (''trans'' meaning "across, over, beyond"). | |||
| |access-date=23 July 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| The ] name ''Siebenbürgen'' means "seven fortresses", after the seven (]) ]' cities in the region (], ], ], ], ], ] and ]). This is also the origin of many other language's name for the region, such as the ] ''siedmiogród''. | |||
| {{Main|Historical names of Transylvania}} | |||
| The earliest known reference to Transylvania appears in a ] document of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1078 as {{lang|la|ultra silvam}}, meaning "beyond the forest" ({{lang|la|ultra}} meaning "beyond" or "on the far side of" and the ] of {{lang|la|Sylva}} ({{lang|la|sylvam}}) "woods, forest"). Transylvania, with an alternative Latin prepositional prefix, means "on the other side of the woods". The Medieval Latin form {{Lang|la-x-medieval|Ultrasylvania}}, later {{Lang|la-x-medieval|Transylvania}}, was a direct translation from the ] form {{lang|hu|Erdő-elve}}, later {{lang|hu|Erdély}}, from which also the Romanian name, {{lang|ro|Ardeal}}, comes.<ref name=engel>Engel, Pál (2001). ''Realm of St. Stephen: History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526 (International Library of Historical Studies)'', p. 24, London: I.B. Taurus. {{ISBN|1-86064-061-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Pop|first=Ion-Aurel|trans-title=The Medieval History of Transylvania: from the Romanian Ethnogenesis until Michael the Brave|url=https://www.scribd.com/doc/30886268/Istoria-Transilvaniei-Medievale|title=Istoria Transilvaniei Medievale: De la Etnogeneza Romanilor pana la Mihai Viteazul|accessdate=2013-10-03 |year=1997|language=ro}}</ref> That also was used as an alternative name in ] {{lang|gmh|überwald}} ("beyond the forest") (13th–14th centuries) and ] {{lang|uk|Залісся}} ({{lang|uk-Latn|Zalissia}}). | |||
| Historical names of Transylvania are: | |||
| The origin of the ] name ''Ardeal'' is controversial. The first known occurrence of the Romanian name appeared in a document in 1432 as ''Ardeliu''.<ref name="Ardeliu">{{citation | last= Pascu | first= Ştefan | title= Voievodatul Transilvaniei | volume= I | year= 1972 | pages= 22}}</ref> It may be a result of an ] from the Romanian words ''aur'' and ''deal'' ("gold" and "hill", respectively), resulting in ''Ardeal'' from the composed word ''Aur-deal''. It may also take its origin from the ] word “Ardil-land” (] „Eretz Ardil”, „ארדיל”), from the Celtic "Arduenna" (forest), reflected in other names such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ], or from the ] ''Har-Deal''. Another hypothesis is that the name is borrowing of the Hungarian name ''Erdély'', as is the ] name ''Ardyalo'' - in old Hungarian, ''Erdély'' was pronounced as ''Erdél''. The initial ''e-'' in Hungarian occasionally changes to ''a'' in Romanian (cf. Hung. ''egres'' "gooseberry" and ''Egyed'', which became ''agriş'' and '']'' in Romanian). | |||
| * {{langx|bg|Седмиградско|Sedmigradsko}}, {{lang|bg|Трансилвания}} {{lang|bg-Latn|Transilvanija}} | |||
| * {{langx|hr|Sedmogradska}}, {{lang|hr|Erdelj}} (hist.), {{lang|hu|Transilvanija}} | |||
| * {{langx|de|Siebenbürgen}} ({{IPA|de|ziːbm̩ˈbʏʁɡŋ̍||De-Siebenbürgen.ogg}}), {{lang|de|Transsilvanien}} | |||
| * {{langx|hu|Erdély}} ({{IPA|hu|ˈɛrdeːj|}}) | |||
| * {{langx|la|Ultrasilvania}}, {{lang|la|Transsilvania}} | |||
| * {{langx|pl|Siedmiogród}}, {{lang|pl|Transylwania}} | |||
| * {{langx|rom|Transilvaniya}} | |||
| * {{langx|ro|Ardeal}} ({{IPA|ro|arˈde̯al|}}), {{lang|ro|Transilvania}} ({{IPA|ro|transilˈvani.a|}}) | |||
| * {{langx|ru|Трансильвания|Transil'vaniya}}, {{lang|ru|Седмиградье}} | |||
| * {{langx|sr|Ердељ/Erdelj}}, {{langx|sr|Трансилванија/Transilvanija}} | |||
| * {{langx|sk|Ardieľ, Sedmohradsko}} | |||
| * ]: ''Siweberjen'' | |||
| * {{langx|tr|Erdel}} | |||
| * {{langx|uk|Семигород|Semyhorod}}, {{lang|uk|Залісся}} {{lang|uk-Latn|Zalissiya}}, {{lang|uk|Трансильванія}} {{lang|uk-Latn|Transyl'vaniya}} | |||
| * {{langx|yi|זיבנבערגן|Zibnbergn}}, {{lang|yi|זימבערגן}} {{lang|yi-Latn|Zimbergn}}, {{lang|yi|טראַנסילוואַניע}} {{lang|yi-Latn|Transilvanye}} | |||
| * The German name {{lang|de|Siebenbürgen}} means "seven castles", after the seven (]) ]' cities in the region. This is also the origin of the region's name in many other languages, such as the ] {{lang|hr|Sedmogradska}}, the ] {{lang|bg|Седмиградско}} ({{lang|bg-Latn|Sedmigradsko}}), ] {{lang|pl|Siedmiogród}}, ] {{lang|yi|זיבנבערגן}} ({{lang|yi-Latn|Zibnbergn}}), and ] {{lang|uk|Семигород}} ({{lang|uk-Latn|Semyhorod}}). | |||
| * The Hungarian form {{lang|hu|Erdély}} was first mentioned in the 12th-century {{lang|la|]|italic=yes}} as {{lang|hu|Erdeuleu}} (in modern script {{lang|hu|Erdeüleü}}) or {{lang|hu|Erdő-elve}}. The word {{lang|hu|erdő}} means forest in Hungarian, and the word {{lang|hu|elve}} denotes a region in connection with this, similarly to the Hungarian name for Muntenia ({{lang|hu|Havas-elve}}, or land lying ahead of the snow-capped mountains). {{lang|ota-Latn|Erdel}}, {{lang|ota-Latn|Erdil}}, {{lang|ota-Latn|Erdelistan}} are derived from Hungarian {{lang|hu|Erdély}}. | |||
| * An occurrence of the form ''Ardeliu'' in a ] document written by a Romanian chancellery is attested in 1432. The Romanian {{lang|ro|Ardeal}} is derived from the Hungarian {{lang|hu|Erdély}}.<ref name=Ardeliu>{{Cite journal |last=Pascu |first=Ștefan |title=Voievodatul Transilvaniei |volume=I |year=1972 |page=22 }}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Kristó |first=Gyula |title=A korai Erdély |publisher=Szegedi Középkorász Műhely |year=2002 |isbn=9634825583 |page=24 |trans-title=The early Transylvania}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite book |last=Drăganu |first=Nicolae |url=https://documente.bcucluj.ro/web/bibdigit/periodice/anuarulinstitutuluideistorienationala/1923/BCUCLUJ_FP_BALP_42_1923_002_001.pdf |title=Anuarul Institutului de Istorie Națională |year=1924 |volume=II |location=] |page=237}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| See also ]. | |||
| {{Main|History of Transylvania}} | |||
| {{main|History of Transylvania}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| In its early history, the territory of Transylvania belonged to a variety of empires and states, including ], the ], the ] and the ]<ref>{{cite web |title=History of Transylvania |url=http://mek.oszk.hu/03400/03407/html/33.html |publisher=Atlantic Research and Publications, Inc. |author=Béla Köpeczi (editor) |accessdate=2007-01-29}}</ref>. There were also periods when autonomus political entities raised under the control of the Byzantine and the ]<ref></ref>. As a political entity, (Southern) Transylvania is mentioned from the 12th century as a ](Alba) of the ] (''M. princeps ultrasilvanus - comes Bellegratae''). Transylvania's seven counties were brought under the voivode's (count of ]) rule in 1263. | |||
| It then became an autonomous ] under nominal ] ] in 1571. A few centuries later, in 1688, it was added to the expanding territories of ], then became again a part of the ] within the newly established ] in 1867. Since ], it has been part of ], apart from a brief period of Hungarian occupation during ]. | |||
| The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the ], of the ]. From the 4th century BC, ] ] came to domination. The indigenous ] engaged in politics from the 1st century BC and united under ], forming their kingdom ].<ref>] (2000): ]</ref> | |||
| ] is today considered to be the region's spiritual capital, although Transylvania was also ruled from ] during its period as an autonomous principality within the Ottoman Empire, and from ], where the ] governor was located from 1711 to 1848. The seat of the ] was itself moved to Sibiu for some time in the 19th century. | |||
| The ] made heavy efforts to seize the territory from ], resulting in the formation of ] in 106, after ]'s ]. During Roman rule, the territory, depleted of its indigenous population, was repopulated with Latin colonists and its rich resource stock was systematically exploited. However, the growing threat of ] and ] invasions made Emperor ] withdraw his legions and evacuate the citizens south of the ] in 275, when the province became occupied by the ].<ref>Tóth, Endre (1994): </ref> In 376, a powerful nomadic people, the ], defeated and shattered the Goths, and settled in the area. After the death of Hun ], their empire disintegrated and the ] conquered the region in 455, under ].<ref>Gündisch, Konrad: </ref> For two centuries, the Gepids controlled Transylvania. The ] systematically pushed the Gepids out of ]. ], on the other hand, successfully fought battles against the Eastern Roman Empire.<ref name=":2" /> They were defeated by the ] and ] in 567.<ref name=":2">Bóna, István (1994): </ref> In the following years, the Avars took full control over Transylvania, heavily settling the area with ] who accepted their suzerainty. The expansion of the ], however, imposed a growing threat on them and their khaganate was crushed in the ].<ref>] (2006): ]</ref><ref>Bóna, István (1994): </ref> The Avars and Slavs, although substantially depleted in number, continued to inhabit the ].<ref>] (1962): ]</ref> The ] expanded into ] in the 9th century.<ref>Bóna, István (1994): </ref> Smaller Slavic polities were also present, nevertheless they could hardly keep their independence.<ref>Makkai, László (1975): ]</ref> | |||
| Since medieval times, the population of the region has been a mixture of ethnic ] (historically known as ]), ], the ethnic Hungarian<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Szekler|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/579333/Szekler|encyclopedia=]|publisher=]|date=2008|accessdate=2008-06-30}}</ref> ] people, ] (known as ]), ] (especially in ], ] and ]), ] and ] (known as ] or "tatars" - ''Tatern'' in ] or ''tătăraşi'' in ]). | |||
| In the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the ]. There is an ongoing scholarly debate over the demographics in Transylvania at the time. According to the theory of Daco-Roman continuity, ] continuously lived on the territory. Opponents of that hypothesis point to the lack of written, archaeological and linguistic evidence to support it.<ref>Farkas, Zoltán (2007): ]</ref> Hungarian medieval chronicles claimed that the ] people descended from the ], who remained in Transylvania, and later, in combination with the returning ], ] the ].<ref>]: </ref><ref>Veszprémy, László; Schaer, Frank (1999): </ref><ref>Geréb, László (1993): (in Hungarian)</ref><ref>Geréb, László (1957): (in Hungarian)</ref> According to the '']'', the Vlach (''Blacorum, Blacus'') leader ] ruled part of Transylvania before the ] arrived. Historians debate whether he was a historical person or an imaginary figure. The ] from the ] governed Transylvania in the 10th century. ] asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle ] and Transylvania became part of the ] in 1002.<ref name="Engel 2005 27">{{cite book |title=The Realm of St Stephen |last=Engel |first=Pal |author2=Andrew Ayton |year=2005 |publisher= Tauris|location= London|isbn=1-85043-977-X |page=27 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vEJNBqanT_8C&pg=PA27}}</ref> Place names derived from the ] evidence that major Hungarian groups settled in Transylvania from the 950s.<ref>{{cite book |last=Bóna |first=István |editor1-last=Köpeczi |editor1-first=Béla |editor2-last=Barta |editor2-first=Gábor |editor3-last=Bóna |editor3-first=István |editor4-last=Makkai |editor4-first=László |editor5-last=Szász |editor5-first=Zoltán |editor6-last=Borus |editor6-first=Judit | title=History of Transylvania |publisher=Akadémiai Kiadó |year=1994 |pages=62–177 |chapter=From Dacia to Transylvania: The Period of the Great Migrations (271–895); The Hungarian–Slav Period (895–1172) |isbn=963-05-6703-2}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Kristó |first=Gyula |year=2003 |title=Early Transylvania (895-1324) |publisher= Lucidus Kiadó |isbn=963-9465-12-7}}</ref> In the 12th and 13th centuries, Southeast and Northeast Transylvania was settled by Saxon colonists. In Romanian historiography, ] constituted an important part of Transylvania's population even on the eve of the ].<ref name="Sedlar">{{cite book |author=Jean W Sedlar |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3o5lrvuwOVwC&pg=PA9 |title=East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500 |publisher=University of Washington Press |year=1994 |isbn=978-0-295-97291-6 |pages=9–}}</ref><ref name="=De Medio Aevo">{{cite journal |author=Madgearu |first=Alexandru |date=2018 |title=The Mongol domination and the detachment of the Romanians of Wallachia from the domination of the Hungarian Kingdom |url=https://revistas.ucm.es/index.php/DMAE/article/download/76013/4564456556992 |journal=De Medio Aevo |pages=219–220 |access-date=}}</ref> Hungarian historiography claims that the Vlach population entered Transylvania from the ] only in the 12th century,<ref name="Sedlar2">{{cite book |author=Jean W Sedlar |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3o5lrvuwOVwC&pg=PA9 |title=East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500 |publisher=University of Washington Press |year=1994 |isbn=978-0-295-97291-6 |pages=9–}}</ref> and the devastating invasion of Mongols had also as consequence the large-scale immigration by Romanians, however the immigration of Romanians did not happen all at once, the process of settlement stretched over several centuries.<ref name=":252">{{Cite book |last=Makkai |first=László |title=History of Transylvania Volume I. From the Beginnings to 1606 - III. Transylvania in the Medieval Hungarian Kingdom (896–1526) - 3. From the Mongol Invasion to the Battle of Mohács |publisher=Columbia University Press, (The Hungarian original by Institute of History Of The Hungarian Academy of Sciences) |year=2001 |isbn=0-88033-479-7 |language=English |chapter=The Mongol Invasion and Its Consequences |chapter-url=http://mek.niif.hu/03400/03407/html/76.html}}</ref> After the ] and Ottoman arrival at the Hungarian border, thousands of ] and ] refugees came to Transylvania. | |||
| === The Roman province of Dacia, 105-271=== | |||
| ]'s in color]] | |||
| The ] was in existence at least as early as the beginning of the 2nd century ], and it reached its maximum extent under the rule of ]. The area now constituting Transylvania was the political center of the ancient kingdom, where several important fortified cities were built, among them ], near today's ]. | |||
| ] in 1190, during the rule of ]]]Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the ], led by a ] appointed by the ].<ref>{{Cite journal|date=2004|title=Stephen I|url=http://link.galegroup.com/apps/doc/CX3404706129/GVRL?u=aubu98092&sid=GVRL&xid=fed217b4|journal=Encyclopedia of World Biography|volume=14|pages=427–428|via=Gale Virtual Reference Library}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|title=Merriam-Webster's geographical dictionary|publisher=CREDO|year=2007|edition= 3rd |chapter=Hungary}}</ref> After the ] in 1526, Transylvania became part of the ]. Later, in 1570, the kingdom became the ] by the ], which was ruled primarily by ] ]. The Eastern Hungarian king became the first ], according to the treaty. The ] continued to be part of the ] in the sense of public law, which stressed in a highly significant way that ] possessions belonged to the ] and he was not permitted to alienate them.<ref>Anthony Endrey, , Hungarian Institute, 1978, p. 70</ref> | |||
| ] in 1606–60]] | |||
| The ] acquired the territory shortly after the ] in 1683. In 1687, the rulers of Transylvania recognized the suzerainty of the Habsburg emperor ], and the region was officially attached to the Habsburg Empire. The Habsburgs acknowledged the Principality of Transylvania as one of the ],<ref name="boundary">{{cite web|title=''International Boundary Study'' – No. 47 – April 15, 1965 – Hungary – Romania (Rumania) Boundary|publisher=US Bureau of Intelligence and Research|url=http://www.law.fsu.edu/library/collection/LimitsinSeas/IBS047.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090303212328/http://www.law.fsu.edu/library/collection/LimitsinSeas/IBS047.pdf|archive-date=March 3, 2009}}</ref> but the territory of the principality was administratively separated<ref name="britannica_a">{{cite encyclopedia|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1459175/Diploma-Leopoldinum |title=Diploma Leopoldinum (Transylvanian history) |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |access-date=2012-07-30}}</ref><ref name="britannica.com">{{cite encyclopedia|url=http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/603323/Transylvania |title=Transylvania (region, Romania) |encyclopedia=Britannica.com |access-date=2012-07-30}}</ref> from Habsburg Hungary,<ref>{{Cite book|last=Sugar|first=Peter F.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LOln4TGdDHYC&dq=independent+principality+that+was+not+reunited+with+Hungary&pg=PA163|title=Southeastern Europe under Ottoman Rule, 1354-1804|date=2012-07-01|publisher=University of Washington Press|isbn=978-0-295-80363-0|page=163|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last1=Cadzow|first1=John F.|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fX5pAAAAMAAJ&q=diploma+leopoldinum+transylvania|title=Transylvania: The Roots of Ethnic Conflict|last2=Ludanyi|first2=Andrew|last3=Elteto|first3=Louis J.|date=1983|publisher=Kent State University Press|isbn=978-0-87338-283-0|page=79|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Lendvai|first=Paul|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9yCmAQGTW28C&dq=diploma+leopoldinum+transylvania&pg=PA146|title=The Hungarians: A Thousand Years of Victory in Defeat|date=2003|publisher=C. Hurst|isbn=978-1-85065-682-1|page=146|language=en}}</ref> and subjected to the direct rule of the emperor's governors.<ref name="encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com">{{cite web|url=http://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/Grand+Principality+of+Transylvania |title=Definition of Grand Principality of Transylvania in the Free Online Encyclopedia |publisher=Encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com |access-date=2012-07-30}}</ref> In 1699 the Ottomans legally acknowledged their loss of Transylvania in the ]; however, some ] elements within the principality submitted to the emperor only in the 1711 ], when Habsburg control over Principality of Transylvania was consolidated. The ] was reintroduced 54 years later in 1765. | |||
| In 101-102 and 105-106, ] forces under the Emperor ] fought a series of ] to subjugate Dacia. After the suicide of the Dacian ruler ], parts of Dacia were incorporated into the Roman Empire. According to ] <ref>Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh Edition</ref> '''Breviarium historiae Romanae''', after Decebals death the romans destroyed and killed allmost the whole local population. Dacia had to be repopulated all over again, ("ex toto Orbe Romano"), from the whole Roman Empire. | |||
| Hadrian (117-135) the current territory of Transylvania was included in Dacia Superior. During Antoninus Pius (138-161) the same territory was included in the provinces Dacia Porolissensis (capital at Porolissum) and Dacia Apulensis (capital at Apulum).The Romans built mines, roads and forts in the province. Colonists from other Roman provinces were brought in to settle the land and cities like ''Apulum'' (now ]), ''Napoca'' (now ]), Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa and Aquae appeared. During the Roman administration also Christianity entered the current territory of Transylvania from the neighbouring Roman provinces where according to the tradition of the Romanian Orthodox Church St. Peter preached. | |||
| The ] against the Habsburgs started in 1848, and grew into a war for the total independence of the ] from the ]. ], the leader of the Austrian army, was appointed plenipotentiary to restore order in Hungary after the conflict. He ordered the execution of ] of ], and Prime Minister ] was executed the same day in ]. After a series of serious Austrian defeats in 1849, the ] came close to the brink of collapse. Thus, the new young emperor ] had to call for Russian help under the Holy Alliance. Czar Nicholas I answered, and sent an army of 200,000 men with 80,000 auxiliary forces. Finally, the joint army of Russian and Austrian forces defeated the Hungarian forces. After the restoration of Habsburg power, Hungary was placed under martial law. Following the Hungarian Army's surrender at Világos (now ], Romania) in 1849, their revolutionary banners were taken to Russia by the Tsarist troops and were kept there both under the Tsarist and Communist systems (in 1940 the Soviet Union offered the banners to the Horthy government). | |||
| Due to increasing pressure from the Visigoths, <ref>Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh Edition</ref> the Romans abandoned the province during the reign of the Emperor ] in 271. As across much of Europe, a period of chaos and conquests followed after the collapse of Roman rule. However, as shown by the archeological research, many of the Roman cities continued to exist, building fortifications. Also Christianity survived as proved by the many artifacts discovered. Among the most famous is the donarium from Biertan (4th century) having the inscription 'Ego Zenovius votvm posui' (I, Zenovie, offered this). The territory fell under the control of the Visigoths and ] until they were in turn displaced and subdued by the ] in 376, under the leadership of their infamous warlord ]. After the disintegration of Attila's empire, the Huns were succeeded by Gepids of ] descent. The region was also influenced during this period by massive ] immigration. | |||
| After the ] of 1867, the Principality of Transylvania was once again abolished. The territory then became part of ],<ref name=Britannica/><ref name="MSNEncarta">"Transylvania", Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2008.</ref> an addition to the newly established ]. Romanian intellectuals issued the ] in protest.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070424202011/http://www.hungarian-history.hu/lib/pas/pas14.htm |date=2007-04-24 }} in Pașcu, Ștefan. ''A History of Transylvania''. Dorset Press, New York, 1990.</ref> | |||
| At the beginning of the 9th century, Transylvania, along with eastern ], was under the control of the ]{{Fact|date=June 2008}}. After a brief period of Bulgarian rule, the territory, was partially under Byzantine control. | |||
| The region was the site of an important ] during World War I, which caused the replacement of the German Chief of Staff, temporarily ceased German offensives on all the other fronts and created a unified Central Powers command under the German Kaiser. Following defeat in ], Austria-Hungary disintegrated. Elected representatives of the ] from Transylvania, Banat, Crișana and Maramureș backed by the ], proclaimed ] on 1 December 1918. The ''Proclamation of Union'' of Alba Iulia was adopted by the Deputies of the Romanians from Transylvania and supported one month later by the vote of the Deputies of the Saxons from Transylvania. | |||
| Between 10th-12th centuries A.D. Transylvania was slowly conquered by the ], during a period of 300 years. <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref>. The most powerfull local leaders who opposed the Magyars were ] / ], ] and ]. <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref>. | |||
| ] being ceded to ]. The region was returned to Romania after ]]] | |||
| The ] of ], the ] (also called ''Unification Day'',<ref>CIA World Factbook, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200505143044/http://www.cia.gov/publications/factbook/geos/ro.html#Govt |date=2020-05-05 }}</ref>) occurring on December 1, celebrates this event. The holiday was established after the ], and marks the unification not only of Transylvania but also of the provinces of ], ] and ] with the ]. These other provinces had all joined with the Kingdom of Romania a few months earlier. In 1920, the ] established new borders and much of the proclaimed territories became part of Romania. Hungary protested against the new state borders, as they did not follow the real ethnic boundaries, for over 1.3 or 1.6 million Hungarian people, representing 25.5 or 31.6% of the Transylvanian population (depending on statistics used),<ref name="Történelmi világatlasz">{{cite book|title = Történelmi világatlasz|language=hu|trans-title=World Atlas of History|publisher = Cartographia|year = 1998|isbn = 963-352-519-5}}</ref><ref name="Varga">Varga, E. Árpád, , Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999, pp. 30-34</ref> were living on the Romanian side of the border, mainly in the ] of Eastern Transylvania, and along the newly created border.]]] | |||
| In August 1940, with the arbitration of Germany and Italy under the ], Hungary gained ] (including parts of ] and ]), and over 40% of the territory lost in 1920. This award did not solve the nationality problem, as over 1.15–1.3 million Romanians (or 48% to more than 50% of the population of the ceded territory) remained in Northern Transylvania while 0.36–0.8 million Hungarians (or 11% to more than 20% of the population) continued to reside in ].<ref>{{cite book|author=Keith Hitchins|author-link=Keith Hitchins|title=Romania|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=eKkegAiLtzMC&pg=PA486|year=1994|publisher=Clarendon Press|isbn=978-0-19-822126-5|pages=486–}}</ref> The Second Vienna Award was voided on 12 September 1944 by the ] through (Article 19), and the 1947 ] reaffirmed the borders between Romania and Hungary as originally defined in the Treaty of Trianon, 27 years earlier, thus confirming the return of Northern Transylvania to Romania.<ref name=Britannica>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Transylvania|url=http://britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/603323/Transylvania|encyclopedia=]|publisher=]|year=2008|access-date=2008-08-01}}</ref> | |||
| ===Conquest of Transylvania and integration into the Kingdom of Hungary=== | |||
| From 1947 to 1989, Transylvania, along with the rest of Romania, was ]. The ] between ethnic ] and ] in March 1990 took place after the ] and became the most notable inter-ethnic incident in the post-communist era. | |||
| At the beginning of the 9th century the Hungarian tribes were located in the north of the Black Sea. In 895 as a result of a planned 'conquest' and a massive withdrawal caused by a ] they established in the Upper-] region and Transylvania and started to expand their territories towards west only in 899. According to ] describing among others the conquest of Transylvania, three statal structures ruled by <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> ], ] and ] were encountered and defeated by the Magyars. <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> | |||
| <gallery class="center"> | |||
| ] (Gelu in Romanian, Gyalu in Hungarian) leader of the ]<ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> (ancient ]) in Transylvania was ruling over the Middle part of Transylvania <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> and had his capital at Dăbâca. He was defeated by the warriors of the Magyar chieftain Tétény (also called Töhötöm; in the original Latin: Tuhutum) sometime during the 10th century. | |||
| File:Sarmisegetusa Regia - Templele patrulatere mici - Zona sacra – Gradistea Muntelui, Muntii Sureanu, Hunedoara, Romania 19.JPG|Ruins of ] | |||
| File:Castrum Apulum 2011 - Porta Principalis Dextra-1.jpg|Roman city of ] | |||
| File:Lanzedelli - Târg în Transilvania 3.jpg|A market scene in Transylvania, 1818 | |||
| File:Original_Photo_National_Museum_of_Union-Alba_Iulia.jpg|The National Assembly in ] (December 1, 1918), declaring the ] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Geography and ethnography== | |||
| ] (Bulgarian and Serbian Cyrillic: Глад) rulled over the South-West of Trabsylvania, <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> having authority over the Slavs and Vlachs, which consisted most of the population of mentioned regions at the time. He was, according to the ], a voivod (dux) from Bundyn (Vidin), ruler of the territory of Banat, during the 9th and 10th centuries. He also ruled part of south Transylvania, and Vidin region, and was a local governor or vassal of the First Bulgarian Empire under Bulgarian tsar Simeon. Glad was defeated by the Hungarians during the 10th century{{Fact|date=July 2008}}. One of his descendants, Ahtum, was a duke of Banat and the last ruler{{Fact|date=July 2008}} who opposed to the establishment of the Hungarian Kingdom in the 11th century, but he was too, defeated by the Hungarian Crown. | |||
| ] seen from the west end, in ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The ], {{convert|300|to(-)|500|m|ft|abbr=off}} high, is drained by the ], ], ], and ] rivers, as well as other tributaries of the ]. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the ], ] and ] branches of the ]. The area includes the ]. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania; in common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, although geographically the two are not identical. | |||
| ], a vassal of Byzantium <ref name=Encyclopedia>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=gelou+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1457,M1|page=1457|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> ruled the lands between the River Tisza and the Ygfon Forest{{Fact|date=July 2008}} in the direction of Ultrasilvania (Transylvania), from the Mureş river to the Someş river. He declined the request of the Magyar ruler Árpád (907) to cede his territory between the Someş river and the Meses Mountains, and in the negotiations with the ambassadors Usubuu and Veluc of Árpád he invoked the sovereignty of the Byzantine Emperor Leo VI the Wise. The Magyars first besieged the citadel of Zotmar (Romanian: Satu Mare, Hungarian: Szatmár) and then Menumorut's castle in Bihar, and were able to defeat him. The Gesta Hungarorum then retells the story{{Fact|date=July 2008}} of Menumorut. In the second telling, he married his daughter into the Árpád dynasty. Her son Taksony, the grandson of{{Fact|date=July 2008}} Menumorut, became ruler of the Magyars and father of Mihály and Géza, whose son Vajk became the first King of Hungary in 1001 under the Christian baptismal name Stephen. | |||
| Ethnographic areas: | |||
| The early 11th century was marked by the conflict between ] ] and his uncle ], the ruler of Transylvania. The Hungarian ruler was successful in these wars, and Transylvania was incorporated into the Christian Kingdom of Hungary. The Transylvanian ] ] and the ] were organised. By the early 11th century the ethnic ] ] were established in southeastern Transylvania as a border population of ready warriors, and in the 12th and 13th centuries, the areas in the south and northeast were settled by ] colonists called ]. Romanians maintained control over a few autonomous regions called 'terrae': Fagaras, Amlas. Hateg, Maramures, Lapus. However the autonomy was taken by the end of ] in 1301. | |||
| * Transylvania proper: | |||
| ** ] (Szeben-hegyalja) | |||
| ** ] (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség) | |||
| ** ] (Burzenland/Barcaság) | |||
| ** {{Interlanguage link|Țara Buzaielor|ro}} | |||
| ** ] (Kalotaszeg) | |||
| ** ] (Kővár) | |||
| ** ] (Fogaras) | |||
| ** ] (Hátszeg) | |||
| ** {{ill|Țara Hălmagiului|ro}} | |||
| ** {{ill|Țara Mocanilor|ro}} | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke) | |||
| ** {{Interlanguage link|Țara Silvaniei|ro}} | |||
| ** {{Interlanguage link|Ținutul Pădurenilor|ro}} | |||
| ** ] (Székelyföld/Székely Land) | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** {{ill|Țara Almăjului|ro}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** {{ill|Țara Zarandului|ro}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** ] (Avasság) | |||
| ** {{ill|Țara Lăpușului|ro}} (Lápos-vidék) | |||
| ==Administrative divisions== | |||
| In 1241-1242, during the ], Transylvania was among the territories devastated by the Golden Horde. A large portion of the population perished. This was followed by a second Mongol invasion in 1285, led by ]. | |||
| {{Transylvania Labelled Map|float=right}} | |||
| The area of the historical Voivodeship is {{convert|55146|km2|0|abbr=on}}.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200228094241/http://romaniatraveltourism.com/node/326 |date=2020-02-28 }} at romaniatraveltourism.com</ref>{{sfn|Chisholm|1911}} | |||
| The regions granted to Romania in 1920 covered 23 counties including nearly {{convert|102200|km2|0|abbr=on}} (102,787–103,093 km<sup>2</sup> in Hungarian sources and 102,282 km<sup>2</sup> in contemporary Romanian documents). Nowadays, several administrative reorganisations make the territory cover 16 ] (]: '']''), with an area of {{convert|100290|km2|0|abbr=on}}, in central and northwest Romania. | |||
| Following this devastation, Transylvania was reorganized according to a ] system of ], which established privileged groups (''universitates'') with power and influence in economic and political life, as well as along ethnic lines. The first Estate was the lay and ecclesiastic aristocracy, ethnically heterogeneous, but undergoing a process of homogenization around its Hungarian nucleus. The other Estates were Saxons, Szeklers and Romanians (or ] - '']''), all with an ethnic and ethno-linguistic basis (''Universis nobilibus, Saxonibus, Syculis et Olachis''). The general assembly (''congregatio generalis'') of the four Estates had few genuine legislative powers in Transylvania, but it sometimes took measures regarding order in the country. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The 16 counties are: ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| A key figure to emerge in Transylvania in the first half of the 15th century was ]/]<ref name=EB>{{cite web|title=János Hunyadi|url=http://britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/277182/Janos-Hunyadi|encyclopedia=]|publisher=]|date=2008|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref><ref name=Encarta/>/], a native of Transylvania born in a family of Romanian origins. <ref>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=qtgotOF0MKQC&pg=PA705&dq=john+hunyadi+Romanian&lr=&hl=ro&sig=ACfU3U3UpXF3LNv55OGmlyI2E_jfhOjRWw#PPA705,M1|page=705|accessdate=2008-08-01}}</ref>. He was one of the greatest military figures of the time, being ] general<ref name=EB/><ref name=Encarta>{{cite encyclopedia|title=János Hunyadi|url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761557950/Janos_Hunyadi.html|encyclopedia=]|date=2008|accessdate=2008-08-01}}</ref>, voivode of Transylvania and then governor of the ]<ref name=EB/><ref>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=iancu%20de%20hunedoara+Romanian+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1458,M1|page=1458|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> from 1446 to 1452. He was a Transylvanian noble of ] origin <ref>{{cite web|title=Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=om4olQhrE84C&printsec=frontcover&dq=iancu%20de%20hunedoara+Romanian+transylvania&lr=&hl=ro&source=gbs_summary_r&cad=0#PPA1458,M1|page=1458|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref> some sources indicating him as the son of Voicu/Vajk, a Romanian ] from ]<ref>Enea Silvius Piccolomini, (]), ''In Europa'' - ''Historia Austrialis'', BAV, URB, LAT. 405, ff.245, IIII kal. Aprilis MCCCCLVIII, Ex Urbe ]</ref> though other sources are telling that his father was ''a Transylvanian ]/]''<ref> {{cite web|title=Jean W. Sedlar, ''East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500'', Uniiversity of Washington Press, 1994|url=http://books.google.hu/books?id=ANdbpi1WAIQC&pg=PA41&dq=%22Transylvanian+Vlach%22&hl=ro&sig=ACfU3U3Y-_A50x6WX4HqGLL-fyfHUI-4oA|accessdate=2008-07-31}}</ref>. Hungarian historians claim that his mother was Erzsébet Morzsinay the daughter of a ] noble family<ref name="Balassa">{{cite web|title=A Hunyadiaktól karácsonyig|language=Hungarian|publisher=''Zoltán Balassa''|url=http://web.axelero.hu/kesz/jel/01_12/hunyadiak.htm#10|accessdate=2008-04-25}}</ref>. | |||
| His fame was built in the effective wars of defence against the Turkish attacks, waged from 1439. With his private mercenary army John rapidly rose to the heights of power. His military campaigns against the ] brought him the status of Transylvanian ] in 1446 and ] recognition as the ] of Transylvania in 1448. Continuing his military activity, he won an important victory at Belgrade in 1456, which halted the Ottomans advance for several decades, but died shortly afterwards during an epidemic. | |||
| Transylvania contains both largely urban counties, such as Brașov and Hunedoara counties, as well as largely rural ones, such as Bistrița-Năsăud and Sălaj counties.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/REZULTATE-DEFINITIVE-RPL_2011.pdf |title=Microsoft Word – REZULTATE DEFINITIVE RPL2011.doc |access-date=2018-04-17 |archive-date=2013-07-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130717125951/http://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/REZULTATE-DEFINITIVE-RPL_2011.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| After the suppression of the ]-revolt in 1437, the political system was based on '']'' (''The Union of the Three Nations''). According to the Union, which was explicitly directed against ] and other peasants, society was ruled by three ]d ] of the ] (mostly ethnic Hungarians), the ]s, also an ethnic Hungarian people who primarily served as warriors, and the ethnic German, Saxon ]. | |||
| Since 1998, Romania has been divided into eight ], acting as divisions that coordinate and implement socio-economic development at regional level. Six counties (Alba, Brașov, Covasna, Harghita, Mureș and Sibiu) form the ], another six (Bihor, Bistrița-Năsăud, Cluj, Maramureș, Satu Mare, Sălaj) form the ], while four (Arad, Caraș-Severin, Hunedoara, Timiș) form the ]. | |||
| The only possibility for Romanians to retain or access nobility in Hungarian Transylvania was through ] to ]. Some ] Romanian nobles converted, becoming integrated into the Hungarian nobility. These circumstances marked the beginning of a conflict between ethnic Hungarian Catholics and ethnic Romanian Orthodox in the territory of Transylvania which in some regions remains unresolved to this very day.<ref></ref> | |||
| == Cities and towns == | |||
| ===Transylvania as an Independent Principality=== | |||
| {{Largest cities | |||
| The 16th century in ] was marked by the struggle between the ] ] and the ] ]. After the Ottoman Sultan ] overran central Hungary (see ]), Transylvania became a semi-independent principality where ] and Turkish influences vied for supremacy for nearly two centuries. It is this period of independence and Turkish influence that contributed to Transylvania being seen as ] in the eyes of ]s such as ], whose novel '']'' was published in 1897.<ref></ref> | |||
| | country = Romania | |||
| | kind = cities of Transylvania, Banat, Crișana and Maramureș historical regions | |||
| | stat_ref = (2021 population by place of residence) | |||
| | list_by_pop = | |||
| | div_name = | |||
| | div_link = Counties of Romania{{!}}County | |||
| |city_1 = Cluj-Napoca | |||
| ] | |||
| |div_1 = Cluj County{{!}}Cluj | |||
| |pop_1 = 286,598 | |||
| |img_1 = Biserica romano-catolică "Sfântul Mihail".jpg | |||
| |city_2 = Timișoara | |||
| Due to the fact that Transylvania was now beyond the reach of ] religious authority, ] preaching such as ]ism and ] were able to flourish in the region. In 1568 the ] proclaimed four religious expressions in Transylvania - ], ]ism, ] and ], while ], which was the confession of the Romanian population, was proclaimed as "tolerated" (''tolerata''). | |||
| |div_2 = Timiș County{{!}}Timiș | |||
| |pop_2 = 250,849 | |||
| |img_2 = Piața Victoriei Timișoara.jpg | |||
| |city_3 = Brașov | |||
| The ] family began to rule Transylvania as princes under the Ottomans in 1571, and briefly under ] suzerainty until 1600. The latter period of their rule saw a four-sided conflict in Transylvania involving the Transylvanian Báthorys, the emerging ], the Ottoman Empire, and the Romanian voivoideship (province) of ]. This included a brief period of Romanian rule after the conquest of the territory by ]n voivod ]. As he subsequently extended his rule over ], Michael the Brave unified for the first time in history all the territories where Romanians lived, rebuilding the mainland of the ancient Kingdom of ] <ref> Rezachevici, Constantin, Mihai Viteazul et la "Dacie" de Sigismund Báthory en 1595, Ed. Argessis, 2003, 12, p.155-164 </ref> | |||
| |div_3 = Brașov County{{!}}Brașov | |||
| ]]] | |||
| |pop_3 = 237,589 | |||
| The ] magnate of ] ] managed to obtain, through the Peace of ] (], ]), religious liberty and political autonomy for the region, the restoration of all confiscated estates, the repeal of all "unrighteous" judgments, as well as his own recognition as independent sovereign prince of an enlarged Transylvania. Under Bocskai's successors, most notably ] and ], Transylvania passed through a ] for many religious movements and for the arts and culture. Transylvania became one of the few European States where ]s, ]s, ]s and ]s lived in peace, although ] ] continued to be denied equal recognition. | |||
| |img_3 = BVCouncilSquare0.jpg | |||
| |city_4 = Oradea | |||
| This golden age and relative independence of Transylvania ended with the reign of ]. The prince, coveting the Polish crown, allied with Sweden and invaded ] in spite of the Turkish ] clearly prohibiting any military action. Rákóczi's defeat in Poland, combined with the subsequent invasions of Transylvania by the Turks and their Crimean Tatar allies, the ensuing loss of territory (most importantly, the loss of the most important Transylvanian stronghold, ]) and diminishing manpower led to the complete subordination of Transylvania, which now became a powerless vassal of the Ottoman Empire. | |||
| |div_4 = Bihor County{{!}}Bihor | |||
| |pop_4 = 183,105 | |||
| |img_4 = Primăria și Centrul Municipiului Oradea.JPG | |||
| |city_5 = Arad, Romania{{!}}Arad | |||
| ===Within the Habsburg Empire=== | |||
| |div_5 = Arad County{{!}}Arad | |||
| ]]] | |||
| |pop_5 = 145,078 | |||
| |city_6 = Sibiu | |||
| After the defeat of the Ottomans at the ] in 1683, the Habsburgs gradually began to impose their rule on the formerly autonomous Transylvania. Apart from strengthening the central government and administration, the Habsburgs also promoted the Roman Catholic Church, both as a uniting force and also as an instrument to reduce the influence of the Protestant nobility. In addition, they tried to persuade Romanian Orthodox clergymen to join the ]. As a response to this policy, several peaceful movements of the Romanian Orthodox population advocated for freedom of worship for all the Transylvanian population, most notably being the movements led by Visarion Sarai, Nicolae Oprea Miclăuş and ]. | |||
| |div_6 = Sibiu County{{!}}Sibiu | |||
| |pop_6 = 134,309 | |||
| |city_7 = Târgu Mureș | |||
| From 1711 onward, the princes of Transylvania were replaced with Austrian governors and in 1765 Transylvania was declared a grand principality. | |||
| |div_7 = Mureș County{{!}}Mureș | |||
| |pop_7 = 116,033 | |||
| |city_8 = Baia Mare | |||
| The ] was marked by a great struggle between the Hungarians, the Romanians and the Habsburg Empire. Warfare erupted in November with both Romanian and Saxon troops, under Austrian command, battling the Hungarians led by the Polish born general ]. He carried out a sweeping offensive through Transylvania, and ] managed to retreat to the harsh terrain of the ], mounting a ] campaign on Bem's forces. After the intervention by the armies of Tsar ], Bem's army was defeated decisively at the Battle of ] (Temesvár, Hun.) on ] ]. | |||
| |div_8 = Maramureș County{{!}}Maramureș | |||
| |pop_8 = 108,759 | |||
| |city_9 = Satu Mare | |||
| Having quashed the revolution, Austria imposed a repressive regime on Hungary, ruled Transylvania directly through a military governor <!-- ? and many medieval privileges ?-->and granted citizenship to the Romanians.{{Fact|date=July 2008}} | |||
| |div_9 = Satu Mare County{{!}}Satu Mare | |||
| |pop_9 = 91,520 | |||
| |city_10 = Bistrița | |||
| The 300-year long special separate status came to an end by the ], which established the ] and reincorporated Transylvania into the ]. On 20 June 1867, the ] was dissolved by royal decree, and an ordinance abrogated the legislative acts of the ] provincial assembly. The department of the interior inherited the responsibilities of the ], and the government reserved the right to name Transylvania's royal magistrates as well the Saxon bailiff of the Universitas Saxorum. Hungarian legislation also came to supersede the Austrian code of civil procedure, penal law, commercial law, and regulations for bills of exchange. The new unity of Austria-Hungary created a process of Magyarization affecting Transylvania's Romanians and German Saxons. | |||
| |div_10 = Bistrița-Năsăud County{{!}}Bistrița-Năsăud | |||
| |pop_10 = 78,877 | |||
| |city_11 = Alba Iulia | |||
| ===Part of Romania=== | |||
| |div_11 = Alba County{{!}}Alba | |||
| ]]] | |||
| |pop_11 = 64,227 | |||
| Since the ] empire had begun to disintegrate after the end of ], the nationalities living inside proclaimed their independence from the empire. The 1228-member National Assembly of Romanians of Transylvania and Hungary, headed by leaders of Transylvania's ] and ], passed a resolution calling for unification of all Romanians in a single state on 1 December in ].<ref name="nationalday">{{cite web | title= December 1 - Romania National Day | publisher= Honorary Consul of Romania in Boston | url= http://www.roconsulboston.com/Pages/InfoPages/History/December1.html | accessdate= 2008-01-12}}</ref> This was approved by the National Council of the Germans from Transylvania and the Council of the ] from the ], on ] in ]. In response, the Hungarian General Assembly of ] reaffirmed the loyalty of Hungarians from Transylvania to Hungary on ], 1918. (''See also: ]'') | |||
| |city_12 = Reșița | |||
| The ] placed Transylvania under the sovereignty of Romania, an ally of the ], and after the defeat in 1919 of ]'s ] by the Romanian army the ] (1919) and the ] (signed in June 1920) further elaborated the status of Transylvania and defined the new border between the states of Hungary and Romania.<ref name="treaties">{{cite web | last= Bachman | first= Robert D. | title= Romania: A Country Study | date= 1989 | url= http://countrystudies.us/romania/20.htm | accessdate= 2008-01-12}}</ref><ref name="Trianon">{{cite web | title= Trianon, Treaty of | publisher= ] | url= http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9073332/Treaty-of-Trianon | accessdate= 2008-01-12}}</ref> King ] and Queen ] were crowned at Alba Iulia in 1922 as King and Queen of all Romania. | |||
| |div_12 = Caraș-Severin County{{!}}Caraș-Severin | |||
| |pop_12 = 58,393 | |||
| |city_13 = Deva, Romania{{!}}Deva | |||
| In August 1940, the second ] granted the ] to ]. After the ] (1947), at the end of ], the territory was returned to ]. The post-WWII borders with ], agreed on at the Treaty of Paris, were identical with those set out in 1920. | |||
| |div_13 = Hunedoara County{{!}}Hunedoara | |||
| |pop_13 = 53,113 | |||
| |city_14 = Zalău | |||
| After World War II and especially after the fall of Communism, Transylvania lost almost all of the German-speaking population, most of them left for Germany. | |||
| |div_14 = Sălaj County{{!}}Sălaj | |||
| |pop_14 = 52,359 | |||
| |city_15 = Hunedoara | |||
| A Hungarian minority group is pressing for greater autonomy in that region where its members outnumber Romanians<ref>{{cite web|title=BREAKAWAY ROLE MODEL - Romania: The Magyars in Székely Land|url=http://www.spiegel.de/international/europe/0,1518,537008-2,00.html|work=]|date=2008-02-22|accessdate=2008-07-29}}</ref><ref name="NYT"/>. There are tensions in Transylvania between Romanians and ethnic Hungarians who want autonomy. The Hungarians say they are the target of attacks by Romanian politicians and news organizations.<ref name=Hung>{{cite web|title=Hungarians and Romanians At Odds in Transylvania|url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C02E4DB1E3EF935A15751C1A961958260|work=]|date=1997-12-26|accessdate=2008-08-01}}</ref> They say the aim is to forcibly assimilate the ] of 1.7 million people, or 7.1 percent of the Romanian population.<ref name=Hung/> | |||
| |div_15 = Hunedoara County{{!}}Hunedoara | |||
| |pop_15 = 50,457 | |||
| |city_16 = Sfântu Gheorghe | |||
| The Szekler National Council is a local Hungarian group founded in 2003 with ] as its stated goal<ref name="NYT"/>. Unlike the Kosovars, the Szeklers are asking for autonomy within Romania rather than complete independence, leaving ] and ] in the hands of the government in Bucharest<ref name="NYT"/>. | |||
| |div_16 = Covasna County{{!}}Covasna | |||
| |pop_16 = 50,080 | |||
| |city_17 = Turda | |||
| A new and more radical organization, the Hungarian Civic Party, has risen to challenge the establishment Hungarian party and has advocated for the autonomy of the Szekler region. <ref name="NYT">{{cite web|title=Kosovo’s Actions Hearten a Hungarian Enclave|publisher='']''|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2008/04/07/world/europe/07hungarians.html?_r=1&scp=1&sq=Szekler&st=nyt&oref=slogin|date=2008-04-07|accessdate=2008-06-30}}</ref>. | |||
| |div_17 = Cluj County{{!}}Cluj | |||
| |pop_17 = 43,319 | |||
| |city_18 = Mediaș | |||
| The Hungarian politician, László Tőkés, one of the party leaders, is pressing for greater autonomy, saying that Romanian and Hungarian authorities have to reach an agreement regarding the statute of the Hungarian community, the Szeckler county respectively. <ref name="Laszlo Tokes">{{cite web | title= Magyar Autonomy, An Issue Romania Needs To Deal With| publisher= ] | url= http://www.mediafax.ro/engleza/magyar-autonomy-an-issue-romania-needs-to-deal-with-official.html?6966;2411796 | accessdate= 2008-02-24}}</ref>. | |||
| |div_18 = Sibiu County{{!}}Sibiu | |||
| |pop_18 = 39,505 | |||
| |city_19 = Lugoj | |||
| ==Historical coat of arms of Transylvania== | |||
| |div_19 = Timiș County{{!}}Timiș | |||
| {{main|Coat of arms of Transylvania}} | |||
| |pop_19 = 35,450 | |||
| |city_20 = Miercurea Ciuc | |||
| The first heraldic representation of Transylvania is found{{Fact|date=July 2008}} on the coat of arms of ]. Besides the Walachian eagle and the Moldavian auroch, Transylvania is here represented by two afronted lions holding a sword (elements referring to the ]), standing upon seven hills. | |||
| |div_20 = Harghita County{{!}}Harghita | |||
| |pop_20 = 34,484 | |||
| }} | |||
| ], commonly known as Cluj, is the second most populous city in Romania (as of the 2021 census), after the national capital ], and is the seat of ]. From 1790 to 1848 and from 1861 to 1867, it was the official capital of the ]. ] is an important tourist destination, being the largest city in a mountain resorts area, and a central location, suitable for exploring Romania, with the distances to several tourist destinations (including the ] resorts, the monasteries in northern ], and the wooden churches of ]) being similar. | |||
| The ] of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations in Transylvania's ]. It depicts: | |||
| ] is one of the most important cultural centres of Romania and was designated the ] for the year 2007, along with the city of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sibiu2007.ro/index_en.php|title=Sibiu Cultural Capital Website|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061015213159/http://www.sibiu2007.ro/index_en.php|archive-date=2006-10-15}}</ref> It was formerly the centre of the ] culture and between 1692 and 1791 and 1849–65 was the capital of the ]. | |||
| * A black ] on a blue background, representing the medieval nobility, which was mainly ]. | |||
| * The ] and the ] representing the ]s. | |||
| * Seven red towers on a yellow background representing the seven fortified cities of the ] | |||
| (The red dividing band was originally not part of the coat of arms.) | |||
| ], a city located on the ] in Alba County, has since the ] been the seat of Transylvania's ]. Between 1541 and 1690 it was the capital of the ] and the later ]. Alba Iulia also has historical importance: after the end of World War I, representatives of the Romanian population of Transylvania gathered in Alba Iulia on 1 December 1918 to proclaim the ] with the ]. In Transylvania, there are many medieval smaller towns such as ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| Image:Stema Mihai Viteazul.jpg|Coat of arms of Michael the Brave, ruller of Transylvania, Wallachia and Moldova, 1600 | |||
| <gallery class="center"> | |||
| Image:Coat of arms of Transylvania.svg|Coat of Arms of 1659 | |||
| File:Cluj-Napoca_(Biserica_Romano-Catolică_Sfântul_Mihail).jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Kolozsvár}}, {{langx|de|Klausenburg}}) | |||
| Image:Flag of Transylvania before 1918.svg|''Landesfarben'' of Transylvania in ], reflecting the ] of the coat-of-arms | |||
| File:Brasov, Romania (26523347959).jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Brassó}}, {{langx|de|Kronstadt}}) | |||
| Image:Coat of Arms Kingdom of Hungary.jpg|As part of the ] before the ] in 1920 | |||
| File:Sibiu 200811 800px.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Nagyszeben}}, {{langx|de|Hermannstadt}}) | |||
| Image:Coat_of_arms_of_Romania.svg|As in the ] at present | |||
| File:Arad City Hall (30112380741).jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Arad}}, {{langx|de|Arad}}) | |||
| File:Cetatea_Alba_Iulia_din_aer_toamna.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Gyulafehérvár}}, {{langx|de|Karlsburg}}) defense wall of ] | |||
| File:Palatul Culturii (Targu Mures).jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Marosvásárhely}}, {{langx|de|Neumarkt am Mieresch}}) | |||
| File:Timisoara - Catholic Dome in Union Square.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Temesvár}}, {{langx|de|Temeschburg}}) | |||
| File:Primăria și Centrul Municipiului Oradea.JPG|] ({{langx|hu|Nagyvárad}}, {{langx|de|Großwardein}}) | |||
| File:Sighisoara. Biserica din deal.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Segesvár}}, {{langx|de|Schäßburg}}) | |||
| File:Biserica Sfânta Margareta.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Medgyes}}, {{langx|de|Mediasch}}) | |||
| File:Bistrița de sus.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Beszterce}}, {{langx|de|Bistritz}}) | |||
| File:Sebes evangelical church 3.JPG|] ({{langx|hu|Szászsebes}}, {{langx|de|Mülbach}}) | |||
| File:Centrul Vechi Baia Mare.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Nagybánya}}, {{langx|de|Frauenbach}}) | |||
| File:Dévai vármegyeház.jpeg|] ({{langx|hu|Déva}}, {{langx|de|Diemrich}}) | |||
| File:Miercurea_Ciuc_2010,_The_Petőfi_Street.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Csíkszereda}}, {{langx|de|Szeklerburg}}) | |||
| File:2011-IMG 4425.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Torda}}, {{langx|de|Thorenburg}}) | |||
| File:Sepsiszentgyorgyi reformatus vartemplom.jpg|] ({{langx|hu|Sepsiszentgyörgy}}, {{langx|de|Gergen}}) | |||
| File:Aiud-Turnul dogarilor si biserica reformata-2.JPG|Aiud Citadel in ] ({{langx|hu|Nagyenyed}}, {{langx|de|Straßburg am Mieresch}}) | |||
| </gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| ==Population== | |||
| ==Geography and ethnography== | |||
| {{See also|Demographics of Romania}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The Transylvanian plateau, 300 to 500 metres (1,000-1,600 feet) high, is drained by the ], ], ], and ] rivers, as well as other tributaries of the ]. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. Other areas to the west and north, which also united with Romania in 1918 (inside the border established by peace treaties in 1919-20), are since that time widely considered part of Transylvania. | |||
| ===Historical population=== | |||
| *Transylvania proper: | |||
| {{See also|History of Transylvania#Historical population|Hungarian minority in Romania|Székelys|Transylvanian Saxons|List of Transylvanians}} | |||
| **] | |||
| ], 1910.]] | |||
| **] | |||
| Official censuses with information on Transylvania's population have been conducted since the 18th century. On May 1, 1784 the Emperor ] called for the first official census of the ], including Transylvania. The data was published in 1787, and this census showed only the overall population (1,440,986 inhabitants).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hungarian-history.hu/lib/transy/transy03.htm |title=www.hungarian-history.hu |access-date=2017-07-10 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202185918/http://www.hungarian-history.hu/lib/transy/transy03.htm |archive-date=2017-02-02 }}</ref> ], a 19th-century Hungarian statistician, estimated in 1842 that in the population of Transylvania for the years 1830–1840 the majority were 62.3% ] and 23.3% ].<ref>Elek Fényes, ''Magyarország statistikája'', Vol. 1, Trattner-Károlyi, Pest. VII, 1842</ref> | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| In the last quarter of the 19th century, the Hungarian population of Transylvania increased from 24.9% in 1869 to 31.6%, as indicated in the 1910 Hungarian census (the majority of the ] reported Hungarian as their primary language, so they were also counted as ethnically Hungarian in the 1910 census). At the same time, the percentage of the Romanian population decreased from 59.0% to 53.8% and the percentage of the German population decreased from 11.9% to 10.7%, for a total population of 5,262,495. ] policies greatly contributed to this shift.<ref name="ia">{{cite journal|title=The Problem of Treaty Revision and the Hungarian Frontiers|journal=International Affairs|year=1933|first=Robert William|last=Seton-Watson|volume=12|issue=4|pages=481–503 |doi=10.2307/2603603|jstor=2603603}}</ref> | |||
| ''See also ]''. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present ]n-] border, settled in the Treaty of Trianon, although geographically the two are not identical. | |||
| The percentage of the Romanian majority has significantly increased since the declaration of the union of Transylvania with Romania after World War I in 1918. The proportion of Hungarians in Transylvania was in steep decline as more of the region's inhabitants moved into urban areas, where the pressure to assimilate and Romanianize was greater.<ref name="Varga"/> The expropriation of the estates of Magyar ]s, the distribution of the lands to the Romanian peasants, and the policy of cultural ] that followed the ] were major causes of friction between Hungary and Romania.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Transylvania|url=http://www.bartleby.com/65/tr/Transylv.html|encyclopedia=]|access-date=2008-11-18|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080905190712/http://bartleby.com/65/tr/Transylv.html|archive-date=2008-09-05}}</ref> Other factors include the emigration of non-Romanian peoples, assimilation and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people moved from the ] to Transylvania, and 280,000 from Transylvania to the Old Kingdom, most notably to ]).<ref name="Varga"/> | |||
| ==Administrative divisions== | |||
| {{Transylvania Labelled Map|float=right}} | |||
| === Current population === | |||
| The historical region granted to Romania in ] covered 23 counties including nearly 102,200 km² (102,787 - 103,093 in Hungarian sources and 102,200 in contemporany Romanian documents) now due to the several administrative reorganisations Transylvania covers 16 present-day ] (]: '']'') which include nearly 99,837 km² of central and northwest Romania. The 16 counties are: | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| According to the results of the ], the total population of Transylvania was 6,789,250 inhabitants and the ethnic groups were: Romanians – 70.62%, Hungarians – 17.92%, Roma – 3.99%, Ukrainians – 0.63%, Germans (mostly Transylvanian Saxons and Banat Swabians, but also Zipsers, Sathmar Swabians, or Landlers) – 0.49%, other – 0.77%. Some 378,298 inhabitants (5.58%) have not declared their ethnicity.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.recensamantromania.ro/rezultate-2 |title=RPL 2011 – VOLUMUL I: POPULAŢIA STABILĂ (REZIDENTĂ) – STRUCTURA DEMOGRAFICĂ, Table no. 7 |website=recensamantromania.ro}}</ref> The ethnic Hungarian population of Transylvania form a majority in the counties of ] (73.6%) and ] (84.8%). The Hungarians are also numerous in the following counties: Mureș (37.8%), Satu Mare (34.5%), Bihor (25.2%), and Sălaj (23.2%). | |||
| The most populous cities are: | |||
| * ] (318,027) | |||
| * ] (317,651) | |||
| * ] (283,901) | |||
| * ] (206,527) | |||
| * ] (172,824) | |||
| * ] (155,045) | |||
| * ] (149,577) | |||
| * ] (137,976) | |||
| * ] (115,630) | |||
| == |
== Economy == | ||
| ], now repurposed as a tourist attraction]] | |||
| Historic definitions of Transylvania vary geographically. The 2002 Romanian census classified Transylvania as the entire region of ] west of the ]. This region has a population of 7,221,733, with a large Romanian majority (75,9%). There are also sizeable ] (20%), ] (3.3%), ] (0.7%) and ] (0.1%) communities. <ref>2002 Census official results: </ref> <ref>''Ethnocultural Diversity Resource Centre'' database:</ref> The ethnic Hungarian population of Transylvania, largely composed of ], form a majority in the counties of ] and ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} | |||
| The percentage of Romanian majority has increased since the union of Transylvania with Romania after ] in ] (the 1910 Census indicates a total population of 5,262,495, Romanians 53.8%; Hungarians 31.6%; Germans 10.7%). This is due to the emigration of non-Romanian peoples, assimilation and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people moved from the ] to Transylvania, and 280,000 from Transylvania to the Old Kingdom, most notably to ]).<ref>Varga, E. Árpád, , Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999 , p. 27.</ref> The assimilation process for Hungarians slowed during the first stages of the communist era, when most of the region's ethnic Hungarian population was granted nominal ], but accelerated under the ]. | |||
| Transylvania's GDP (nominal) is $194 billion and its GDP per capita measures around $28,574.{{when|date=October 2022}} Transylvania's Human Development Index is ranked 0.829, which makes Transylvania the 2nd most developed region in Romania after ] and makes it comparable to countries like the Czech Republic, Poland and Estonia.{{citation needed|date=October 2022}} | |||
| ''For people connected to Transylvania's cultural life see: ].'' | |||
| There are large iron and ], chemical, and ] industries. Stock raising, ], ] production and fruit growing are important occupations. Agriculture is widespread in the ], including growing cereals, vegetables, viticulture and breeding cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry. ] is another valuable resource. | |||
| == Economy == | |||
| {{main|Economy of Transylania}} | |||
| Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| ], ] and ] industries are important in urban and university centers like ] (], ]), ] (], ] and ]), ], ], ] and ]. The cities of ] and ] are connected with a strong ] tradition, and according to the same classifications top performance hospitals exist there.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ms.ro/upload/CLASIFICAREA%20SPITALELOR-1.pdf |title=Clasificarea spitalelor |access-date=2016-01-21 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304035718/http://www.ms.ro/upload/CLASIFICAREA%20SPITALELOR-1.pdf |archive-date=2016-03-04 }}</ref> | |||
| There are large iron and ], chemical, and ] industries. Stock raising, ], ] production and fruit growing are important occupations. ] is another valuable resource. | |||
| Native brands include: ] of ] (trucks and buses), ] of ] (fertilizers), ] of ] (pharmaceuticals), ] of ] (finance), ] and ] of ] (natural gas), ] of ] (alcoholic beverages), ] of ] (alcoholic beverages), the state owned ],<ref>{{cite web | url=http://romarm.ro/en/informatii-despre-companie/exhibitions/subsidiaries-sub2/ | title=ROMARM | National Defense Company in Romania | call us 40213171971 }}</ref> and others. | |||
| Transylvania accounts for around 35% of Romania's GDP, and has a GDP per capita (PPP) of around $11,500, around 10% higher than the Romanian average. | |||
| The ], located in the south of ], has been a major ] throughout the second half of the 19th century and the 20th century, but many mines were closed down in the years following the collapse of the communist regime, forcing the region to diversify its economy. | |||
| ==Tourist attractions== | |||
| During the Second World War, Transylvania (the Southern/Romanian half, as the region was divided during the war) was crucial to the Romanian defense industry. Transylvanian factories built until 1945 over 1,000 warplanes and over 1,000 artillery pieces of all types, among ].<ref>Mark Axworthy, London: Arms and Armour, 1995, ''Third Axis, Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces in the European War, 1941–1945'', pp. 29-30, 75, 149, 222-227 and 239-272</ref> | |||
| * The ] cities of ], ], ] (European Capital Of Culture-2007) , ] and ] | |||
| * The city of ] and the nearby ] ski resort | |||
| * The city of ] with the 14th century ] | |||
| * The citadel and the ] city centre of ] | |||
| * The ] of the ] | |||
| * The ], including ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] traditions and folk culture | |||
| * The ] , ] and ] of ] | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| <center><gallery> | |||
| ], Romanian poet, translator, teacher, and journalist, best known for his verses describing, praising and eulogizing rural life]] | |||
| image:Timisoara cathedral.jpg|Orthodox Cathedral in ] | |||
| The culture of Transylvania is complex because of its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, which has incorporated significant Hungarian (see ]) and German (see ]) influences.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.itcnet.ro/folk_festival/culture.htm |title=Cultura |date=2007-12-31 |access-date=2016-05-08 |url-status=unfit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071231125142/http://www.itcnet.ro/folk_festival/culture.htm |archive-date=December 31, 2007 }}</ref> | |||
| Image:Arad cultural center.jpg|] cultural center | |||
| Image:Sârbi Josani.jpg|] | |||
| image:CJROothodox.jpg|] in ] | |||
| Image:Arad evangelic church.jpg|Arad Evangelical church | |||
| Image:Bran Castle.jpg|] | |||
| image:Biserica neagra 1.JPG|Black Church in ] | |||
| image:Centru bv.JPG|Braşov Council Square (Piaţa Sfatului) | |||
| image:CJROcatholic.jpg|] in ] | |||
| Image:Oradea theatre.jpg|The Theatre in ] | |||
| Image:OradeaTownHall.jpg|The town hall in ] | |||
| Image:DaciaSatuMare.jpg|Dacia Hotel in ] | |||
| image:Sibiu.jpg|View of ] | |||
| Image:Sighişoara clock tower.jpg|] clock tower | |||
| Image:Sighisoara IMG 5624.jpg|View of ] | |||
| Image:Timisoara Dome.jpg|The Catholic Cathedral in ] | |||
| </gallery></center> | |||
| The region was the birthplace of the ] movement, its members, namely ], ], and ], being responsible for the early version of ].<ref></ref> | |||
| ==Transylvania in fiction== | |||
| {{Main|Transylvania in fiction}} | |||
| With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian ] is preserved to this day in monuments such as the ] in ] (14th and 15th centuries) and a number of other ], as well as the ] in ] (14th century), and the ] in ] (15th century). | |||
| Transylvania's long history of Muslim Turkish influence{{Clarifyme|date=May 2008}}, as well as its late ] (which meant that in the late 19th century, Transylvania was still mostly covered with wilderness{{Fact|date=May 2008}}), created an ] fascination with the region by a number of notable ] writers. Following the publication of ]'s ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), ] wrote his ] novel '']'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. Due to the success of the latter work, Transylvania became associated in the English-speaking world with ]s. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in ]'s novel ], the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a ] mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by ], ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th and early 20th century social and political history of the country. | |||
| Notable writers such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] were born in Transylvania. Liviu Rebreanu wrote the novel ''Ion'', which introduces the reader to a depiction of the life of Romanian peasants and intellectuals of Transylvania at the turn of the 20th century. Károly Kós was one of the most important writers supporting the movement of ]. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| Another novel featuring transyvania would be 'The Sight,' by author David Clement-Davies. | |||
| == |
== Religion == | ||
| Transylvania has a very rich and unique religious history. Since the ], different Christian denominations have coexisted in this religious melting pot, including ], other ], ] and ], ], ], and ] branches. ] is the largest religion, but other faiths also are present, including ] and ]. Under the ], Transylvania served as a place for "religious undesirables". People who arrived in Transylvania included those that did not conform to the ] and were sent here forcibly, as well as many religious refugees. Transylvania has a long history of religious tolerance, ensured by its religious pluralism. | |||
| * {{1911}} | |||
| * ], '']'' (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ISBN 1-59017-166-7). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986. | |||
| * Zoltán Farkas and Judit Sós, | |||
| Transylvania has also been (and still is) a center for Christian denominations other than ], the form of Christianity that most Romanians currently follow. As such, there are significant numbers of inhabitants of Transylvania that follow ] and ], and ]. Even though before 1948, the population of Transylvania split between Eastern Orthodox, Greek Catholic and other forms of Christianity, during the Communist Period the Orthodox Church was much more favored by the state which has led to Eastern Orthodoxy being the religion of the majority of Transylvanians.<ref name="poperamet">Earl A. Pope, "Protestantism in Romania", in Sabrina Petra Ramet (ed.), ''Protestantism and Politics in Eastern Europe and Russia: The Communist and Postcommunist Eras'', ], Durham, 1992, p.158-160. {{ISBN|0-8223-1241-7}}</ref><ref>. cnewa.org</ref> However, among the Hungarian and German minorities only a small part are Eastern Orthodox. The main two religions of the Hungarian minority are Reformed (Calvinism) and Roman Catholicism;<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nyugatijelen.com/allaspont/reszleges_kozossegi_radiografia_1.php|title=Részleges közösségi radiográfia|language=ro|work=Nyugati Jelen|access-date=19 March 2023|date=19 January 2023|author=Chirmiciu András|archive-date=26 March 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230326032617/https://www.nyugatijelen.com/allaspont/reszleges_kozossegi_radiografia_1.php|url-status=dead}}</ref> among Germans the main religions are Roman Catholicism (slightly over half of ]), followed by Lutheranism and Eastern Orthodox.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.recensamantromania.ro/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Date-provizorii-RPL_cu-anexe_30122022.pdf|title=Primele date provizorii pentru Recensământul Populației și Locuințelor, runda 2021|language=ro|website=recensamantromania.ro|access-date=19 March 2023}}</ref> There are also ] and ], particularly in Banat and Crișana. ], located in ] is the only university in ] that has four faculties of ] (Orthodox, Reformed, Roman Catholic, and Greek Catholic).<ref>{{cite book |url=http://admitere.ubbcluj.ro/ro/info/brosuri/ |title=Ghidul studentului din Universitatea Babeș-Bolyai |page=5 |website=Admitere.ubbcluj.ro |access-date=2016-05-09 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160426170927/http://admitere.ubbcluj.ro/ro/info/brosuri |archive-date=2016-04-26 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | |||
| * | |||
| |- | |||
| *, Katherine Lovatt, in Central Europe Review, Vol 1, No 14 27 September 1999. | |||
| ! || colspan=2 | 1930 ||colspan=2 | 2011 | |||
| * by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany | |||
| |- | |||
| *{{de icon}} by Klaus Popa, Germany | |||
| ! Denomination | |||
| * | |||
| | Number || Percent | |||
| *{{hu icon}} | |||
| | Number || Percent | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 1,933,589 || 34.85 | |||
| | 4,478,532 || 65.96 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 1,385,017 || 24.96 | |||
| | 142,862 || 2.10 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 946,100 || 17.05 | |||
| | 632,948 || 9.32 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 1,038,464 || 18.72 | |||
| | 675,107 || 9.34 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 37,061 || 0.66 | |||
| | 339,472 || 4.70 | |||
| |} | |||
| There are also small denominations like ], ] and more. | |||
| '''<u>Others</u>''' | |||
| * Nowadays, there is a very small number of Muslims (]) and Jews (]), but back in 1930, with 191,877 inhabitants, Jews represented 3.46% of Transylvania's population.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.etnosfera.ro/pdf/2009/2/04.pdf|title=Situatia demografica a cultelor dupa 1918|access-date=2018-04-16|archive-date=2017-12-15|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171215064621/http://www.etnosfera.ro/pdf/2009/2/04.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| * Atheists, agnostics and unaffiliated account for 0.27% of Transylvania's population. | |||
| ''Data refers to extended Transylvania (with ], ] and ]).''<ref>{{cite web| url = http://dspace.bcucluj.ro/bitstream/123456789/64159/1/BCUCLUJ_FP_186593_1937-1938.pdf| title = Anuarul statistic al Romaniei, 1937 si 1938}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.recensamantromania.ro/rezultate-2/ |title=Populația stabilă după religie – județe, municipii, orașe, comune |work=Institutul Național de Statistică}}</ref> | |||
| == Tourist attractions == | |||
| ] ({{langx|hu|Déva vára}}, {{langx|de|Diemricher Burg}})]] | |||
| ], ] ({{langx|hu|Vajdahunyad}}, {{langx|de|Eisenmarkt}})]] | |||
| ], ] ({{langx|hu|Barcarozsnyó}}, {{langx|de|Rosenau}})]] | |||
| ], ] ({{langx|hu|Berethalom}}, {{langx|de|Birthälm}})]] | |||
| ], ] ({{langx|hu|Törcsvár}}, {{langx|de|Die Törzburg}})]] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| * ], also known as ]'s Castle | |||
| * ] | |||
| * The very well preserved medieval towns of ], ] (] 2015), ] (] in 2007), ], and ] (] and alleged birthplace of ]) | |||
| * The city of ] and the nearby ] ski resort | |||
| * The town of ] with the 14th century ] | |||
| * The citadel and the ] city centre of ] | |||
| * The ], the oldest church in Romania that still holds services<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.romanianmonasteries.org/other-monasteries/densus |title=Travel to Romania – Densuș Church (Hunedoara) |publisher=Romanianmonasteries.org |date=2006-05-31 |access-date=2012-07-30}}</ref> | |||
| * The ], including ] (]) | |||
| * The Roman forts including ], ], ], ], and ] | |||
| * The ] (also known as Lake Ghilcoș) | |||
| * The ] ] | |||
| * The ] in ] | |||
| * The ] region | |||
| ** The ] (the only one of that kind in the world) | |||
| ** The ] (]) | |||
| ** The cities of ] and ] | |||
| ** The villages in the ], ], and ] valleys | |||
| * ] (]) | |||
| * The ]: | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** The ]<ref name=itsromania.com>{{cite web |url=http://www.itsromania.com/apuseni-caves.html |title=Apuseni Caves |publisher=Itsromania.com |access-date=2012-07-30 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120316120700/http://www.itsromania.com/apuseni-caves.html |archive-date=2012-03-16 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ** ] in ], the third largest glacier cave in the world<ref name=itsromania.com/> | |||
| * The ] | |||
| * The ] Salt Mine: according to Business Insider, it is one of the ten "coolest underground places in the world". | |||
| * The ] hiking and biking trail | |||
| === Festivals and events === | |||
| ==== Film festivals ==== | |||
| * ], ] – Romania's biggest film festival | |||
| * ], Cluj-Napoca | |||
| * ], Cluj-Napoca | |||
| * Humor Film Festival, ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.timisoreni.ro/despre/zilele_filmului_de_umor/|title=Zilele Filmului de Umor 2014|work=timisoreni.ro|access-date=25 January 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hotnews.ro/stiri-film-17557648-noua-editie-zilelor-filmului-umor-timisoara.htm|title=O nouă ediție a Zilelor Filmului de Umor la Timișoara|work=HotNewsRo|date=26 June 2014|access-date=25 January 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Music festivals ==== | |||
| * ], ] | |||
| * ], ] | |||
| * ], Târgu-Mureș | |||
| * ], Cluj-Napoca – Romania's biggest music festival | |||
| * ], Cluj-Napoca | |||
| * ], Sibiu | |||
| * Rockstadt Extreme Fest, ] | |||
| * ], Bontida, Cluj-Napoca | |||
| ==== Others ==== | |||
| * ], Sighișoara | |||
| * ] | |||
| * Festivalul Medieval Cetăți Transilvane Sibiu | |||
| == Historical coat of arms of Transylvania == | |||
| {{Main|Coat of arms of Transylvania}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The first heraldic representations of Transylvania date from the 16th century. The ] of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations (] (Union of the Three Nations)) in ]. It depicted a black eagle (]) on a blue background, representing the ], the Sun and the Moon representing the ], and seven red towers on a yellow background representing the ] of the ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Ströhl |first=Hugo Gerard |url=http://www.austria-lexikon.at/attach/Wissenssammlungen/Symbole/Wappenrolle_Str%C3%B6hl_1890/Wappenrolle_1890_Text.pdf |title=Oesterreichish-Ungarische Wappenrolle |publisher=Verlag vom Anton Schroll & Co |year=1890 |location=Vienna |page=XV |author-link=Hugo Gerard Ströhl |access-date=24 November 2011}}</ref> The ] were granted by Queen ] in 1765, when she established a ] within the ]. | |||
| In 1596, ] created a coat of arms for Transylvania, consisting of a shield with a rising eagle in the upper field and seven hills with towers on top in the lower field. He published it in his work "''Chronologia''", issued in ] the same year.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hulsius |first=Levinus |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bsA9AAAAcAAJ |title=Chronologia in qua provinciae... |year=1596 |location=Nuremberg |language=Latin}}</ref> The seal from 1597 of ], ], reproduced the new coat of arms with some slight changes: in the upper field the eagle was flanked by a sun and a moon and in the lower field the hills were replaced by simple towers. The coat of arms of ] beside the coat of arms of the ], included the Transylvanian, Wallachia and Moldavian coat of arms, he used the title ], ] and ]. A short-lived heraldic representation of Transylvania is found on the seal of ]. Besides the Wallachian eagle and the ], Transylvania is represented by two lions holding a sword standing on seven hills. Hungarian ] used the symbols of the ] usually with the ] since the 16th century because ] maintained their claims to the throne of the ]. | |||
| While neither symbol has official status in present-day ], the ] is marshalled within the national ], it was also a component of the ]. | |||
| <gallery class="center"> | |||
| File:Coa Transylvania Country History v4.svg|Coat of arms of Transylvania by ] (1596) | |||
| File:SigismundBathory1597.jpg|Coat of arm of ], Prince of Transylvania (1586–1598, 1598–1599, 1601–1602) | |||
| File:Stema Mihai Viteazul.jpg|Seal of ] during his personal union of ], ] and Transylvania (1599–1600) | |||
| File:COA Bathory Zsofia.jpg|Coat of arms of ], ] (1642–1657, 1657–1658, 1659–1660) | |||
| File:Coat of arms of Transilvania in Stematographia.jpg|Coat of arms of Transylvania by ] (1741) | |||
| File:Wappen Großfürstentum Siebenbürgen.png|Coat of arms of Transylvania by ] | |||
| File:Erdely-Cimere-1765.jpg|Coat of arms of Transylvania (1765) | |||
| File:Kreisregierung Vorarlberg.jpg|Coat of arms of Transylvania in an ] coat of arms (1850) | |||
| File:Coa Hungary Country History Mid (1867).svg|alt=kingdom hungary 1867|Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the ] (1867–1915) | |||
| File:Wappen Ungarische Länder 1867 (Mittel).png|Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the ] (1867–1915) | |||
| File:Wappen Ungarische Länder 1915 (Mittel).png|Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the ] (1915–1918) | |||
| File:Kingdom of Romania - Medium CoA.svg|Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the ] (1921–1947) | |||
| File:Coat of arms of Romania.svg|Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of ] (2016) | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==In popular culture== | |||
| {{Main|Transylvania in popular culture}} | |||
| ] as ]]] | |||
| Following the publication of ]'s ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), ] wrote his ] novel '']'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with ]s. Among the first actors to portray ] ] was ], who was born in Lugos (now ]), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called '']'', which plays on the association of Transylvania and Dracula. | |||
| Transylvania has also been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in ]'s novel '']'', the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a ] mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique.{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by ], ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in '']''. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], an unofficial anthem of Transylvania and the anthem of the ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| * ], ''Erdély történetének atlasza'' (''Historical Atlas of Transylvania''), with text and 102 map plates, the first ever historical atlas of Transylvania (Méry Ratio, 2011; {{ISBN|978-80-89286-45-4}}) | |||
| * {{Cite EB1911|wstitle=Transylvania|volume=27|pages=210–211}} | |||
| * Zoltán Farkas and Judit Sós, | |||
| * ], '']'' (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; {{ISBN|1-59017-166-7}}). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986. | |||
| * {{Cite book|last1=Pop|first1=Ioan-Aurel|last2=Nägler|first2=Thomas|last3=Magyari|first3=András|title=The History of Transylvania, vol. I–III|publisher=Romanian Academy, Center for Transylvanian Studies – Romanian Cultural Institute|location=Cluj-Napoca|year=2018|isbn=978-606-8694-78-8}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|last1=Köpeczi|first1=Béla|last2=Makkai|first2=László|last3=Mócsy|first3=András|title=History of Transylvania|publisher=Atlantic Research and Publications|location=New Jersey|year=1994|isbn=963-05-6703-2|language=en|volume=I-III|url=https://mek.oszk.hu/03400/03407/html/index.html|last4=Szász|first4=Zoltán|translator-last=Kovrig|translator-first=Benett}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{wikivoyage}} | |||
| {{Commons category|Transylvania}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{usurped|1=}}, Katherine Lovatt, in ''Central Europe Review'', Vol. 1, No. 14, 27 September 1999. | |||
| * by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180505040138/http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/boner/toc_pag.shtml |date=2018-05-05 }}, by ], 1865 | |||
| * {{in lang|hu}} | |||
| {{Romanian historical regions}} | {{Romanian historical regions}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Coord|46.5|N|25|E|display=title}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:34, 22 January 2025
Historical region in Central Europe For other uses, see Transylvania (disambiguation). "Siebenbürgen" redirects here. For the band, see Siebenbürgen (band). Not to be confused with Transnistria.| TransylvaniaTransilvania / Ardeal (Romanian) Erdély (Hungarian) Siebenbürgen (German) Siweberjen (Transylvanian Saxon) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
 Transylvania Banat, Crișana and Maramureș Bukovina, Dobruja, Moldavia, Muntenia, and Oltenia Transylvania Banat, Crișana and Maramureș Bukovina, Dobruja, Moldavia, Muntenia, and Oltenia | |
| Largest city | Cluj-Napoca |
| Official languages | Romanian |
| Recognised minority languages | See here |
| Ethnic groups (2021) |
|
| Religion (2021) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Transylvanian |
| Establishment history | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 100,390 km (38,760 sq mi) (106th) |
| • Water (%) | 3 |
| Population | |
| • January 2023 estimate | 6,478,126 (107th) |
| • 2021 census | |
| • Density | 64.5/km (167.1/sq mi) (122nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| HDI (2022) | very high (33rd) |
| Currency | Romanian leu (RON) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (AD) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +40 |
| ISO 3166 code | RO |
| Internet TLD | .ro |
| |
Transylvania (Romanian: Transilvania [transilˈvani.a] or Ardeal; or Hungarian: Erdély [ˈɛrdeːj]; German: Siebenbürgen [ˌziːbm̩ˈbʏʁɡn̩] or Transsilvanien, historically Überwald; Transylvanian Saxon: Siweberjen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring Western Moldavia and even a small part of south-western neighbouring Bukovina to its north east (represented by Suceava County).
Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history, coupled with its multi-cultural character. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other very well preserved medieval iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Bistrița, Alba Iulia, Mediaș, and Sighișoara. It is also the home of some of Romania's UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains and the Roșia Montană Mining Cultural Landscape.
It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom (168 BC – 106 AD), Roman Dacia (106–271), the Goths, the Hunnic Empire (4th–5th centuries), the Kingdom of the Gepids (5th–6th centuries), the Avar Khaganate (6th–9th centuries), the Slavs, and the 9th century First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the Hungarian tribes, and Gyula's family from the seven chieftains of the Hungarians ruled it in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002.
After the Battle of Mohács in 1526 it belonged to the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged in 1570 by the Treaty of Speyer. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire; however, the principality had dual suzerainty (Ottoman and Habsburg).
In 1690, the Habsburg monarchy gained possession of Transylvania through the Hungarian crown. After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary. The separate status of Transylvania ended with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, and it was reincorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary (Transleithania) as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It was also during this period that Romanians experienced the awakening of self-consciousness as a nation, manifested in cultural and ideological movements such as Transylvanian School, and drafted political petitions such as Supplex Libellus Valachorum. After World War I, the National Assembly of Romanians from Transylvania proclaimed the Union of Transylvania with Romania on 1 December 1918, and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Romania by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. In 1940, Northern Transylvania reverted to Hungary as a result of the Second Vienna Award, but it was returned to Romania after the end of World War II.
In popular culture, Transylvania is commonly associated with vampires because of the influence of Bram Stoker's 1897 novel Dracula and the many subsequent books and films that the story has inspired. Many Transylvanian Saxons were furious with Vlad the Impaler for strengthening the borders of Wallachia, which interfered with their control of trade routes, and his extreme sadism and barbarity, which by a collection of credible historical accounts of diverse origins, most of which were non-Saxon, led to the industrial-scale execution of over 100,000 people by impaling, some of whom were Saxons. The victims were often arranged in grotesque displays intended to terrorize various groups, including the Saxons. In retaliation, the Saxons distributed poems of cruelty and other propaganda characterising the sadistic Vlad III Dracula as a drinker of blood.
Etymology
Main article: Historical names of TransylvaniaThe earliest known reference to Transylvania appears in a Medieval Latin document of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1078 as ultra silvam, meaning "beyond the forest" (ultra meaning "beyond" or "on the far side of" and the accusative case of Sylva (sylvam) "woods, forest"). Transylvania, with an alternative Latin prepositional prefix, means "on the other side of the woods". The Medieval Latin form Ultrasylvania, later Transylvania, was a direct translation from the Hungarian form Erdő-elve, later Erdély, from which also the Romanian name, Ardeal, comes. That also was used as an alternative name in German überwald ("beyond the forest") (13th–14th centuries) and Ukrainian Залісся (Zalissia).
Historical names of Transylvania are:
- Bulgarian: Седмиградско, romanized: Sedmigradsko, Трансилвания Transilvanija
- Croatian: Sedmogradska, Erdelj (hist.), Transilvanija
- German: Siebenbürgen ([ziːbm̩ˈbʏʁɡŋ̍] ), Transsilvanien
- Hungarian: Erdély ([ˈɛrdeːj])
- Latin: Ultrasilvania, Transsilvania
- Polish: Siedmiogród, Transylwania
- Romani: Transilvaniya
- Romanian: Ardeal ([arˈde̯al]), Transilvania ([transilˈvani.a])
- Russian: Трансильвания, romanized: Transil'vaniya, Седмиградье
- Serbian: Ердељ/Erdelj, Serbian: Трансилванија/Transilvanija
- Slovak: Ardieľ, Sedmohradsko
- Transylvanian Saxon: Siweberjen
- Turkish: Erdel
- Ukrainian: Семигород, romanized: Semyhorod, Залісся Zalissiya, Трансильванія Transyl'vaniya
- Yiddish: זיבנבערגן, romanized: Zibnbergn, זימבערגן Zimbergn, טראַנסילוואַניע Transilvanye
- The German name Siebenbürgen means "seven castles", after the seven (ethnic German) Transylvanian Saxons' cities in the region. This is also the origin of the region's name in many other languages, such as the Croatian Sedmogradska, the Bulgarian Седмиградско (Sedmigradsko), Polish Siedmiogród, Yiddish זיבנבערגן (Zibnbergn), and Ukrainian Семигород (Semyhorod).
- The Hungarian form Erdély was first mentioned in the 12th-century Gesta Hungarorum as Erdeuleu (in modern script Erdeüleü) or Erdő-elve. The word erdő means forest in Hungarian, and the word elve denotes a region in connection with this, similarly to the Hungarian name for Muntenia (Havas-elve, or land lying ahead of the snow-capped mountains). Erdel, Erdil, Erdelistan are derived from Hungarian Erdély.
- An occurrence of the form Ardeliu in a Church Slavonic document written by a Romanian chancellery is attested in 1432. The Romanian Ardeal is derived from the Hungarian Erdély.
History
Main article: History of Transylvania
The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the Agathyrsi, of the Scythic cultures. From the 4th century BC, Celtic La Tène culture came to domination. The indigenous Dacian tribes engaged in politics from the 1st century BC and united under King Burebista, forming their kingdom Dacia.
The Roman Empire made heavy efforts to seize the territory from King Decebalus, resulting in the formation of Roman Dacia in 106, after Trajan's costly and bloody wars. During Roman rule, the territory, depleted of its indigenous population, was repopulated with Latin colonists and its rich resource stock was systematically exploited. However, the growing threat of East Germanic and Carpic invasions made Emperor Aurelian withdraw his legions and evacuate the citizens south of the Lower Danube in 275, when the province became occupied by the Goths. In 376, a powerful nomadic people, the Huns, defeated and shattered the Goths, and settled in the area. After the death of Hun King Attila, their empire disintegrated and the Gepids conquered the region in 455, under King Ardaric. For two centuries, the Gepids controlled Transylvania. The Ostrogoths systematically pushed the Gepids out of Pannonia. King Elemund, on the other hand, successfully fought battles against the Eastern Roman Empire. They were defeated by the Lombards and Avars in 567. In the following years, the Avars took full control over Transylvania, heavily settling the area with Slavic tribes who accepted their suzerainty. The expansion of the Frankish Empire, however, imposed a growing threat on them and their khaganate was crushed in the Avar Wars. The Avars and Slavs, although substantially depleted in number, continued to inhabit the Carpathian Basin. The First Bulgarian Empire expanded into Southern Transylvania in the 9th century. Smaller Slavic polities were also present, nevertheless they could hardly keep their independence.
In the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the Hungarian conquerors. There is an ongoing scholarly debate over the demographics in Transylvania at the time. According to the theory of Daco-Roman continuity, Romanians continuously lived on the territory. Opponents of that hypothesis point to the lack of written, archaeological and linguistic evidence to support it. Hungarian medieval chronicles claimed that the Székely people descended from the Huns, who remained in Transylvania, and later, in combination with the returning Hungarians, conquered the Carpathian Basin. According to the Gesta Hungarorum, the Vlach (Blacorum, Blacus) leader Gelou ruled part of Transylvania before the Hungarians arrived. Historians debate whether he was a historical person or an imaginary figure. The gyulas from the seven chieftains of the Hungarians governed Transylvania in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002. Place names derived from the Hungarian tribes evidence that major Hungarian groups settled in Transylvania from the 950s. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Southeast and Northeast Transylvania was settled by Saxon colonists. In Romanian historiography, Romanians constituted an important part of Transylvania's population even on the eve of the Mongol Invasions. Hungarian historiography claims that the Vlach population entered Transylvania from the Balkans only in the 12th century, and the devastating invasion of Mongols had also as consequence the large-scale immigration by Romanians, however the immigration of Romanians did not happen all at once, the process of settlement stretched over several centuries. After the Battle of Kosovo and Ottoman arrival at the Hungarian border, thousands of Vlach and Serbian refugees came to Transylvania.


Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the Kingdom of Hungary, led by a voivode appointed by the King of Hungary. After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, Transylvania became part of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom. Later, in 1570, the kingdom became the Principality of Transylvania by the Treaty of Speyer, which was ruled primarily by Calvinist Hungarian princes. The Eastern Hungarian king became the first prince of Transylvania, according to the treaty. The Principality of Transylvania continued to be part of the Kingdom of Hungary in the sense of public law, which stressed in a highly significant way that John Sigismund's possessions belonged to the Holy Crown of Hungary and he was not permitted to alienate them.
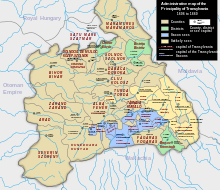
The Habsburgs acquired the territory shortly after the Battle of Vienna in 1683. In 1687, the rulers of Transylvania recognized the suzerainty of the Habsburg emperor Leopold I, and the region was officially attached to the Habsburg Empire. The Habsburgs acknowledged the Principality of Transylvania as one of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, but the territory of the principality was administratively separated from Habsburg Hungary, and subjected to the direct rule of the emperor's governors. In 1699 the Ottomans legally acknowledged their loss of Transylvania in the Treaty of Karlowitz; however, some anti-Habsburg elements within the principality submitted to the emperor only in the 1711 Peace of Szatmár, when Habsburg control over Principality of Transylvania was consolidated. The Grand Principality of Transylvania was reintroduced 54 years later in 1765.
The Hungarian revolution against the Habsburgs started in 1848, and grew into a war for the total independence of the Kingdom of Hungary from the Habsburg dynasty. Julius Jacob von Haynau, the leader of the Austrian army, was appointed plenipotentiary to restore order in Hungary after the conflict. He ordered the execution of The 13 Hungarian Martyrs of Arad, and Prime Minister Batthyány was executed the same day in Pest. After a series of serious Austrian defeats in 1849, the empire came close to the brink of collapse. Thus, the new young emperor Franz Joseph I had to call for Russian help under the Holy Alliance. Czar Nicholas I answered, and sent an army of 200,000 men with 80,000 auxiliary forces. Finally, the joint army of Russian and Austrian forces defeated the Hungarian forces. After the restoration of Habsburg power, Hungary was placed under martial law. Following the Hungarian Army's surrender at Világos (now Șiria, Romania) in 1849, their revolutionary banners were taken to Russia by the Tsarist troops and were kept there both under the Tsarist and Communist systems (in 1940 the Soviet Union offered the banners to the Horthy government).
After the Ausgleich of 1867, the Principality of Transylvania was once again abolished. The territory then became part of Transleithania, an addition to the newly established Austro-Hungarian Empire. Romanian intellectuals issued the Blaj Pronouncement in protest.
The region was the site of an important battle during World War I, which caused the replacement of the German Chief of Staff, temporarily ceased German offensives on all the other fronts and created a unified Central Powers command under the German Kaiser. Following defeat in World War I, Austria-Hungary disintegrated. Elected representatives of the ethnic Romanians from Transylvania, Banat, Crișana and Maramureș backed by the mobilization of Romanian troops, proclaimed Union with Romania on 1 December 1918. The Proclamation of Union of Alba Iulia was adopted by the Deputies of the Romanians from Transylvania and supported one month later by the vote of the Deputies of the Saxons from Transylvania.

The national holiday of Romania, the Great Union Day (also called Unification Day,) occurring on December 1, celebrates this event. The holiday was established after the Romanian Revolution, and marks the unification not only of Transylvania but also of the provinces of Banat, Bessarabia and Bukovina with the Romanian Kingdom. These other provinces had all joined with the Kingdom of Romania a few months earlier. In 1920, the Treaty of Trianon established new borders and much of the proclaimed territories became part of Romania. Hungary protested against the new state borders, as they did not follow the real ethnic boundaries, for over 1.3 or 1.6 million Hungarian people, representing 25.5 or 31.6% of the Transylvanian population (depending on statistics used), were living on the Romanian side of the border, mainly in the Székely Land of Eastern Transylvania, and along the newly created border.

In August 1940, with the arbitration of Germany and Italy under the Second Vienna Award, Hungary gained Northern Transylvania (including parts of Crișana and Maramureș), and over 40% of the territory lost in 1920. This award did not solve the nationality problem, as over 1.15–1.3 million Romanians (or 48% to more than 50% of the population of the ceded territory) remained in Northern Transylvania while 0.36–0.8 million Hungarians (or 11% to more than 20% of the population) continued to reside in Southern Transylvania. The Second Vienna Award was voided on 12 September 1944 by the Allied Commission through the Armistice Agreement with Romania (Article 19), and the 1947 Treaty of Paris reaffirmed the borders between Romania and Hungary as originally defined in the Treaty of Trianon, 27 years earlier, thus confirming the return of Northern Transylvania to Romania.
From 1947 to 1989, Transylvania, along with the rest of Romania, was under a communist regime. The ethnic clashes of Târgu Mureș between ethnic Romanians and Hungarians in March 1990 took place after the fall of the communist regime and became the most notable inter-ethnic incident in the post-communist era.
-
Ruins of Sarmizegetusa Regia
-
 Roman city of Apulum
Roman city of Apulum
-
 A market scene in Transylvania, 1818
A market scene in Transylvania, 1818
-
 The National Assembly in Alba Iulia (December 1, 1918), declaring the Union of Transylvania with Romania
The National Assembly in Alba Iulia (December 1, 1918), declaring the Union of Transylvania with Romania
Geography and ethnography



The Transylvanian Plateau, 300 to 500 metres (980–1,640 feet) high, is drained by the Mureș, Someș, Criș, and Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern, Southern and Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains. The area includes the Transylvanian Plain. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania; in common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, although geographically the two are not identical.
Ethnographic areas:
- Transylvania proper:
- Mărginimea Sibiului (Szeben-hegyalja)
- Transylvanian Plain (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség)
- Țara Bârsei (Burzenland/Barcaság)
- Țara Buzaielor [ro]
- Țara Călatei (Kalotaszeg)
- Țara Chioarului (Kővár)
- Țara Făgărașului (Fogaras)
- Țara Hațegului (Hátszeg)
- Țara Hălmagiului [ro]
- Țara Mocanilor [ro]
- Țara Moților
- Țara Năsăudului (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke)
- Țara Silvaniei [ro]
- Ținutul Pădurenilor [ro]
- Ținutul Secuiesc (Székelyföld/Székely Land)
- Banat
- Crișana
- Maramureș
- Țara Oașului (Avasság)
- Țara Lăpușului [ro] (Lápos-vidék)
Administrative divisions
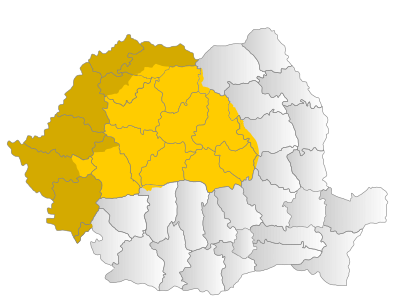 Bihor
Arad
Timiș
Caraș-Severin
Hunedoara
Satu Mare
Sălaj
Alba
Sibiu
Brașov
Covasna
Harghita
Mureș
Cluj
Bistrița-Năsăud
Maramureș
Bihor
Arad
Timiș
Caraș-Severin
Hunedoara
Satu Mare
Sălaj
Alba
Sibiu
Brașov
Covasna
Harghita
Mureș
Cluj
Bistrița-Năsăud
Maramureș
Light yellow – historical region of Transylvania
Dark yellow – historical regions of Banat, Crișana and Maramureș
Grey – historical regions of Wallachia, Moldavia and Dobruja
The area of the historical Voivodeship is 55,146 km (21,292 sq mi).
The regions granted to Romania in 1920 covered 23 counties including nearly 102,200 km (39,460 sq mi) (102,787–103,093 km in Hungarian sources and 102,282 km in contemporary Romanian documents). Nowadays, several administrative reorganisations make the territory cover 16 counties (Romanian: județ), with an area of 100,290 km (38,722 sq mi), in central and northwest Romania.
The 16 counties are: Alba, Arad, Bihor, Bistrița-Năsăud, Brașov, Caraș-Severin, Cluj, Covasna, Harghita, Hunedoara, Maramureș, Mureș, Sălaj, Satu Mare, Sibiu, and Timiș.
Transylvania contains both largely urban counties, such as Brașov and Hunedoara counties, as well as largely rural ones, such as Bistrița-Năsăud and Sălaj counties.
Since 1998, Romania has been divided into eight development regions, acting as divisions that coordinate and implement socio-economic development at regional level. Six counties (Alba, Brașov, Covasna, Harghita, Mureș and Sibiu) form the Centru development region, another six (Bihor, Bistrița-Năsăud, Cluj, Maramureș, Satu Mare, Sălaj) form the Nord-Vest development region, while four (Arad, Caraș-Severin, Hunedoara, Timiș) form the Vest development region.
Cities and towns
| Largest cities of Transylvania, Banat, Crișana and Maramureș historical regions in Romania "NIS 2021 Census" (2021 population by place of residence) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | County | Pop. | Rank | Name | County | Pop. | ||
 Cluj-Napoca  Timișoara |
1 | Cluj-Napoca | Cluj | 286,598 | 11 | Alba Iulia | Alba | 64,227 |  Brașov  Oradea |
| 2 | Timișoara | Timiș | 250,849 | 12 | Reșița | Caraș-Severin | 58,393 | ||
| 3 | Brașov | Brașov | 237,589 | 13 | Deva | Hunedoara | 53,113 | ||
| 4 | Oradea | Bihor | 183,105 | 14 | Zalău | Sălaj | 52,359 | ||
| 5 | Arad | Arad | 145,078 | 15 | Hunedoara | Hunedoara | 50,457 | ||
| 6 | Sibiu | Sibiu | 134,309 | 16 | Sfântu Gheorghe | Covasna | 50,080 | ||
| 7 | Târgu Mureș | Mureș | 116,033 | 17 | Turda | Cluj | 43,319 | ||
| 8 | Baia Mare | Maramureș | 108,759 | 18 | Mediaș | Sibiu | 39,505 | ||
| 9 | Satu Mare | Satu Mare | 91,520 | 19 | Lugoj | Timiș | 35,450 | ||
| 10 | Bistrița | Bistrița-Năsăud | 78,877 | 20 | Miercurea Ciuc | Harghita | 34,484 | ||
Cluj-Napoca, commonly known as Cluj, is the second most populous city in Romania (as of the 2021 census), after the national capital Bucharest, and is the seat of Cluj County. From 1790 to 1848 and from 1861 to 1867, it was the official capital of the Grand Principality of Transylvania. Brașov is an important tourist destination, being the largest city in a mountain resorts area, and a central location, suitable for exploring Romania, with the distances to several tourist destinations (including the Black Sea resorts, the monasteries in northern Moldavia, and the wooden churches of Maramureș) being similar.
Sibiu is one of the most important cultural centres of Romania and was designated the European Capital of Culture for the year 2007, along with the city of Luxembourg. It was formerly the centre of the Transylvanian Saxon culture and between 1692 and 1791 and 1849–65 was the capital of the Principality of Transylvania.
Alba Iulia, a city located on the Mureș River in Alba County, has since the High Middle Ages been the seat of Transylvania's Roman Catholic diocese. Between 1541 and 1690 it was the capital of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and the later Principality of Transylvania. Alba Iulia also has historical importance: after the end of World War I, representatives of the Romanian population of Transylvania gathered in Alba Iulia on 1 December 1918 to proclaim the union of Transylvania with the Kingdom of Romania. In Transylvania, there are many medieval smaller towns such as Sighișoara, Mediaș, Sebeș, and Bistrița.
-
 Cluj-Napoca (Hungarian: Kolozsvár, German: Klausenburg)
Cluj-Napoca (Hungarian: Kolozsvár, German: Klausenburg)
-
 Brașov (Hungarian: Brassó, German: Kronstadt)
Brașov (Hungarian: Brassó, German: Kronstadt)
-
 Sibiu (Hungarian: Nagyszeben, German: Hermannstadt)
Sibiu (Hungarian: Nagyszeben, German: Hermannstadt)
-
 Arad (Hungarian: Arad, German: Arad)
Arad (Hungarian: Arad, German: Arad)
-
 Alba Iulia (Hungarian: Gyulafehérvár, German: Karlsburg) defense wall of Alba Carolina Citadel
Alba Iulia (Hungarian: Gyulafehérvár, German: Karlsburg) defense wall of Alba Carolina Citadel
-
 Târgu Mureș (Hungarian: Marosvásárhely, German: Neumarkt am Mieresch)
Târgu Mureș (Hungarian: Marosvásárhely, German: Neumarkt am Mieresch)
-
 Timișoara (Hungarian: Temesvár, German: Temeschburg)
Timișoara (Hungarian: Temesvár, German: Temeschburg)
-
Oradea (Hungarian: Nagyvárad, German: Großwardein)
-
 Sighișoara (Hungarian: Segesvár, German: Schäßburg)
Sighișoara (Hungarian: Segesvár, German: Schäßburg)
-
 Mediaș (Hungarian: Medgyes, German: Mediasch)
Mediaș (Hungarian: Medgyes, German: Mediasch)
-
 Bistrița (Hungarian: Beszterce, German: Bistritz)
Bistrița (Hungarian: Beszterce, German: Bistritz)
-
Sebeș (Hungarian: Szászsebes, German: Mülbach)
-
 Baia Mare (Hungarian: Nagybánya, German: Frauenbach)
Baia Mare (Hungarian: Nagybánya, German: Frauenbach)
-
 Deva (Hungarian: Déva, German: Diemrich)
Deva (Hungarian: Déva, German: Diemrich)
-
 Miercurea Ciuc (Hungarian: Csíkszereda, German: Szeklerburg)
Miercurea Ciuc (Hungarian: Csíkszereda, German: Szeklerburg)
-
 Turda (Hungarian: Torda, German: Thorenburg)
Turda (Hungarian: Torda, German: Thorenburg)
-
 Sfântu Gheorghe (Hungarian: Sepsiszentgyörgy, German: Gergen)
Sfântu Gheorghe (Hungarian: Sepsiszentgyörgy, German: Gergen)
-
Aiud Citadel in Aiud (Hungarian: Nagyenyed, German: Straßburg am Mieresch)
Population
See also: Demographics of RomaniaHistorical population
See also: History of Transylvania § Historical population, Hungarian minority in Romania, Székelys, Transylvanian Saxons, and List of Transylvanians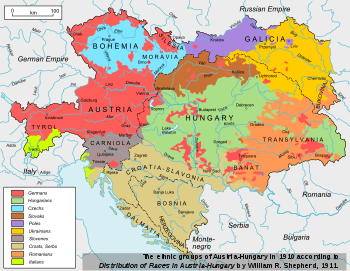
Official censuses with information on Transylvania's population have been conducted since the 18th century. On May 1, 1784 the Emperor Joseph II called for the first official census of the Habsburg Empire, including Transylvania. The data was published in 1787, and this census showed only the overall population (1,440,986 inhabitants). Fényes Elek, a 19th-century Hungarian statistician, estimated in 1842 that in the population of Transylvania for the years 1830–1840 the majority were 62.3% Romanians and 23.3% Hungarians.
In the last quarter of the 19th century, the Hungarian population of Transylvania increased from 24.9% in 1869 to 31.6%, as indicated in the 1910 Hungarian census (the majority of the Jewish population reported Hungarian as their primary language, so they were also counted as ethnically Hungarian in the 1910 census). At the same time, the percentage of the Romanian population decreased from 59.0% to 53.8% and the percentage of the German population decreased from 11.9% to 10.7%, for a total population of 5,262,495. Magyarization policies greatly contributed to this shift.
The percentage of the Romanian majority has significantly increased since the declaration of the union of Transylvania with Romania after World War I in 1918. The proportion of Hungarians in Transylvania was in steep decline as more of the region's inhabitants moved into urban areas, where the pressure to assimilate and Romanianize was greater. The expropriation of the estates of Magyar magnates, the distribution of the lands to the Romanian peasants, and the policy of cultural Romanianization that followed the Treaty of Trianon were major causes of friction between Hungary and Romania. Other factors include the emigration of non-Romanian peoples, assimilation and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people moved from the Old Kingdom to Transylvania, and 280,000 from Transylvania to the Old Kingdom, most notably to Bucharest).
Current population
According to the results of the 2011 census, the total population of Transylvania was 6,789,250 inhabitants and the ethnic groups were: Romanians – 70.62%, Hungarians – 17.92%, Roma – 3.99%, Ukrainians – 0.63%, Germans (mostly Transylvanian Saxons and Banat Swabians, but also Zipsers, Sathmar Swabians, or Landlers) – 0.49%, other – 0.77%. Some 378,298 inhabitants (5.58%) have not declared their ethnicity. The ethnic Hungarian population of Transylvania form a majority in the counties of Covasna (73.6%) and Harghita (84.8%). The Hungarians are also numerous in the following counties: Mureș (37.8%), Satu Mare (34.5%), Bihor (25.2%), and Sălaj (23.2%).
Economy


Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably lignite, iron, lead, manganese, gold, copper, natural gas, salt, and sulfur.
Transylvania's GDP (nominal) is $194 billion and its GDP per capita measures around $28,574. Transylvania's Human Development Index is ranked 0.829, which makes Transylvania the 2nd most developed region in Romania after Bucharest-Ilfov and makes it comparable to countries like the Czech Republic, Poland and Estonia.
There are large iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries. Stock raising, agriculture, wine production and fruit growing are important occupations. Agriculture is widespread in the Transylvanian Plateau, including growing cereals, vegetables, viticulture and breeding cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry. Timber is another valuable resource.
IT, electronics and automotive industries are important in urban and university centers like Cluj-Napoca (Robert Bosch GmbH, Emerson Electric), Timișoara (Alcatel-Lucent, Flextronics and Continental AG), Brașov, Sibiu, Oradea and Arad. The cities of Cluj Napoca and Târgu Mureș are connected with a strong medical tradition, and according to the same classifications top performance hospitals exist there.
Native brands include: Roman of Brașov (trucks and buses), Azomureș of Târgu Mureș (fertilizers), Terapia of Cluj-Napoca (pharmaceuticals), Banca Transilvania of Cluj-Napoca (finance), Romgaz and Transgaz of Mediaș (natural gas), Jidvei of Alba county (alcoholic beverages), Timișoreana of Timișoara (alcoholic beverages), the state owned Cugir Arms Factory, and others.
The Jiu Valley, located in the south of Hunedoara County, has been a major mining area throughout the second half of the 19th century and the 20th century, but many mines were closed down in the years following the collapse of the communist regime, forcing the region to diversify its economy.
During the Second World War, Transylvania (the Southern/Romanian half, as the region was divided during the war) was crucial to the Romanian defense industry. Transylvanian factories built until 1945 over 1,000 warplanes and over 1,000 artillery pieces of all types, among others.
Culture

The culture of Transylvania is complex because of its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, which has incorporated significant Hungarian (see Hungarians in Romania) and German (see Germans of Romania) influences.
The region was the birthplace of the Transylvanian School movement, its members, namely Samuil Micu-Klein, Petru Maior, and Gheorghe Șincai, being responsible for the early version of Romanian alphabet.
With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian Gothic style is preserved to this day in monuments such as the Black Church in Brașov (14th and 15th centuries) and a number of other cathedrals, as well as the Bran Castle in Brașov County (14th century), and the Hunyad Castle in Hunedoara (15th century).
Notable writers such as Emil Cioran, Lucian Blaga, George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici, Octavian Goga, Liviu Rebreanu, Endre Ady, Elie Wiesel, Elek Benedek and Károly Kós were born in Transylvania. Liviu Rebreanu wrote the novel Ion, which introduces the reader to a depiction of the life of Romanian peasants and intellectuals of Transylvania at the turn of the 20th century. Károly Kós was one of the most important writers supporting the movement of Transylvanianism.
Religion
Transylvania has a very rich and unique religious history. Since the Protestant Reformation, different Christian denominations have coexisted in this religious melting pot, including Romanian Orthodox, other Eastern Orthodox, Latin Catholic and Romanian Greek Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed, and Unitarian branches. Christianity is the largest religion, but other faiths also are present, including Jews and Muslims. Under the Habsburgs, Transylvania served as a place for "religious undesirables". People who arrived in Transylvania included those that did not conform to the Catholic Church and were sent here forcibly, as well as many religious refugees. Transylvania has a long history of religious tolerance, ensured by its religious pluralism.
Transylvania has also been (and still is) a center for Christian denominations other than Eastern Orthodoxy, the form of Christianity that most Romanians currently follow. As such, there are significant numbers of inhabitants of Transylvania that follow Latin Catholicism and Greek Catholicism, and Protestantism. Even though before 1948, the population of Transylvania split between Eastern Orthodox, Greek Catholic and other forms of Christianity, during the Communist Period the Orthodox Church was much more favored by the state which has led to Eastern Orthodoxy being the religion of the majority of Transylvanians. However, among the Hungarian and German minorities only a small part are Eastern Orthodox. The main two religions of the Hungarian minority are Reformed (Calvinism) and Roman Catholicism; among Germans the main religions are Roman Catholicism (slightly over half of Germans in Romania), followed by Lutheranism and Eastern Orthodox. There are also Pentecostals and Baptists, particularly in Banat and Crișana. Babeș-Bolyai University, located in Cluj-Napoca is the only university in Europe that has four faculties of theology (Orthodox, Reformed, Roman Catholic, and Greek Catholic).
| 1930 | 2011 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denomination | Number | Percent | Number | Percent |
| Eastern Orthodoxy | 1,933,589 | 34.85 | 4,478,532 | 65.96 |
| Greek Catholicism | 1,385,017 | 24.96 | 142,862 | 2.10 |
| Latin Catholicism | 946,100 | 17.05 | 632,948 | 9.32 |
| Mainline Protestantism | 1,038,464 | 18.72 | 675,107 | 9.34 |
| Evangelical Protestantism | 37,061 | 0.66 | 339,472 | 4.70 |
There are also small denominations like Adventism, Jehovah's Witnesses and more.
Others
- Nowadays, there is a very small number of Muslims (Islam) and Jews (Judaism), but back in 1930, with 191,877 inhabitants, Jews represented 3.46% of Transylvania's population.
- Atheists, agnostics and unaffiliated account for 0.27% of Transylvania's population.
Data refers to extended Transylvania (with Banat, Crișana and Maramureș).
Tourist attractions





- Bran Castle, also known as Dracula's Castle
- Fortress of Deva
- The very well preserved medieval towns of Alba Iulia, Cluj-Napoca (European Youth Capital 2015), Sibiu (European Capital of Culture in 2007), Târgu Mureș, and Sighișoara (UNESCO World Heritage Site and alleged birthplace of Vlad Dracula)
- The city of Brașov and the nearby Poiana Brașov ski resort
- The town of Hunedoara with the 14th century Corvin Castle
- The citadel and the Art Nouveau city centre of Oradea
- The Densuș Church, the oldest church in Romania that still holds services
- The Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains, including Sarmizegetusa Regia (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- The Roman forts including Sarmizegetusa Ulpia Traiana, Porolissum, Apulum, Potaissa, and Drobeta
- The Red Lake (also known as Lake Ghilcoș)
- The Turda Gorge natural reserve
- The Râșnov Citadel in Râșnov
- The Maramureș region
- The Merry Cemetery of Săpânța (the only one of that kind in the world)
- The Wooden Churches (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- The cities of Baia Mare and Sighetu Marmației
- The villages in the Iza, Mara, and Vișeu valleys
- The Saxon fortified churches (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- The Apuseni Mountains:
- Țara Moților
- The Bears' Cave
- Scărișoara Cave in Alba County, the third largest glacier cave in the world
- The Rodna Mountains
- The Salina Turda Salt Mine: according to Business Insider, it is one of the ten "coolest underground places in the world".
- The Via Transilvanica hiking and biking trail
Festivals and events
Film festivals
- Transilvania International Film Festival, Cluj-Napoca – Romania's biggest film festival
- Gay Film Nights, Cluj-Napoca
- Comedy Cluj, Cluj-Napoca
- Humor Film Festival, Timișoara
Music festivals
- Golden Stag Festival, Brașov
- Gărâna Jazz Festival, Gărâna
- Peninsula / Félsziget Festival, Târgu-Mureș
- Untold Festival, Cluj-Napoca – Romania's biggest music festival
- Toamna Muzicală Clujeană, Cluj-Napoca
- Artmania Festival, Sibiu
- Rockstadt Extreme Fest, Râșnov
- Electric Castle Festival, Bontida, Cluj-Napoca
Others
- Sighișoara Medieval Festival, Sighișoara
- Sibiu International Theatre Festival
- Festivalul Medieval Cetăți Transilvane Sibiu
Historical coat of arms of Transylvania
Main article: Coat of arms of Transylvania
The first heraldic representations of Transylvania date from the 16th century. The Diet of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations (Unio Trium Nationum (Union of the Three Nations)) in Transylvania's coat of arms. It depicted a black eagle (Turul) on a blue background, representing the Hungarians, the Sun and the Moon representing the Székelys, and seven red towers on a yellow background representing the seven fortified cities of the Transylvanian Saxons. The flag and coat of arms of Transylvania were granted by Queen Maria Theresa in 1765, when she established a Grand Principality within the Habsburg monarchy.
In 1596, Levinus Hulsius created a coat of arms for Transylvania, consisting of a shield with a rising eagle in the upper field and seven hills with towers on top in the lower field. He published it in his work "Chronologia", issued in Nuremberg the same year. The seal from 1597 of Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, reproduced the new coat of arms with some slight changes: in the upper field the eagle was flanked by a sun and a moon and in the lower field the hills were replaced by simple towers. The coat of arms of Sigismund Báthory beside the coat of arms of the Báthory family, included the Transylvanian, Wallachia and Moldavian coat of arms, he used the title Prince of Transylvania, Wallachia and Moldavia. A short-lived heraldic representation of Transylvania is found on the seal of Michael the Brave. Besides the Wallachian eagle and the Moldavian aurochs, Transylvania is represented by two lions holding a sword standing on seven hills. Hungarian Transylvanian princes used the symbols of the Transylvanian coat of arms usually with the Hungarian coat of arms since the 16th century because Transylvanian princes maintained their claims to the throne of the Kingdom of Hungary.
While neither symbol has official status in present-day Romania, the Transylvanian coat of arms is marshalled within the national Coat of arms of Romania, it was also a component of the Coat of arms of Hungary.
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania by Levinus Hulsius (1596)
Coat of arms of Transylvania by Levinus Hulsius (1596)
-
 Coat of arm of Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania (1586–1598, 1598–1599, 1601–1602)
Coat of arm of Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania (1586–1598, 1598–1599, 1601–1602)
-
 Seal of Michael the Brave during his personal union of Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania (1599–1600)
Seal of Michael the Brave during his personal union of Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania (1599–1600)
-
 Coat of arms of Sophia Báthory, Princess of Transylvania (1642–1657, 1657–1658, 1659–1660)
Coat of arms of Sophia Báthory, Princess of Transylvania (1642–1657, 1657–1658, 1659–1660)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hristofor Žefarović (1741)
Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hristofor Žefarović (1741)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hugo Gerard Ströhl
Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hugo Gerard Ströhl
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania (1765)
Coat of arms of Transylvania (1765)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in an Austrian coat of arms (1850)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in an Austrian coat of arms (1850)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1915)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1915)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1915)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1867–1915)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1915–1918)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary (1915–1918)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Romania (1921–1947)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Romania (1921–1947)
-
 Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of Romania (2016)
Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of Romania (2016)
In popular culture
Main article: Transylvania in popular culture
Following the publication of Emily Gerard's The Land Beyond the Forest (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his gothic horror novel Dracula in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with vampires. Among the first actors to portray Dracula in film was Bela Lugosi, who was born in Lugos (now Lugoj), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called Hotel Transylvania, which plays on the association of Transylvania and Dracula.
Transylvania has also been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel The Witch of Portobello, the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklós Bánffy, The Writing on the Wall, is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in Europa Universalis IV.
See also
- Prehistory of Transylvania
- Siebenbürgenlied, an unofficial anthem of Transylvania and the anthem of the Transylvanian Saxon community
- Transylvanianism
Notes
- The sixteen counties that form the historical region of Transylvania.
References
- "Constitution of Romania". Cdep.ro. Archived from the original on 7 September 2017. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- "Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No. 148 – European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- "Populaţia rezidentă după etnie (Recensământ 2021)". www.insse.ro (in Romanian). INS. Retrieved 2023-09-24.
- "Populaţia rezidentă după religie (Recensământ 2021)". www.insse.ro (in Romanian). INS. Retrieved 2023-09-24.
- "Romanian Statistical Yearbook (2022) – 1.8 Administrative organisation of Romanian territory, on December 31, 2021 (p.17)" (PDF). INS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 March 2023. Retrieved 20 March 2023.
- "POP105A – Populația rezidentă la 1 Ianuarie pe grupe de vârste, sexe și medii de rezidență, macroregiuni, regiuni de dezvoltare și județe". www.insse.ro/cms/en (in Romanian). INS (TEMPO –statiscal data). 5 September 2023. Retrieved 24 September 2023.
- "Populația la Recensămintele 1948–2021". www.insse.ro (in Romanian). INS. Retrieved 2023-09-24.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2023 Edition. (Romania)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- Elgie, Robert (2017). Political Leadership: A Pragmatic Institutionalist Approach. Springer. ISBN 9781137346223 – via Google Books.
- Romania Directory. Editura Cronos. 1990. ISBN 9789739000000 – via Google Books.
- "DECRET-LEGE 2 27/12/1989 – Portal Legislativ". legislatie.just.ro.
- "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- Dennis P. Hupchick, Conflict and chaos in Eastern Europe, Palgrave Macmillan, 1995, p. 62
- Peter F. Sugar, Southeastern Europe under Ottoman rule, 1354–1804, University of Washington Press, 1993, pp. 150–154
- Béla Köpeczi (2008). History of Transylvania: From 1606 to 1830. Social Science Monographs. ISBN 978-0-88033-491-4. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- Peter F. Sugar. "Southeastern Europe Under Ottoman Rule, 1354–1804" (History of East Central Europe), University of Washington Press, July 1983, p. 163
- Paul Lendvai, Ann Major. The Hungarians: A Thousand Years of Victory in Defeat C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2003, p. 146;
- "In 1711, after the Peace Treaty of Szatmar, Austrian control was firmly established over all of Hungary and Erdely, and the princes of Transylvania were replaced by Austrian governors." (Google Search)Glockner, Peter G.; Bagossy, Nora Varga (2007). Encyclopaedia Hungarica: English. Hungarian Ethnic Lexicon Foundation. ISBN 978-1-55383-178-5.
- "Transylvania" (2009). Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 7, 2009
- "Diploma Leopoldinum" (2009). Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 7, 2009
- Laszlo Péter, Hungary's Long Nineteenth Century: Constitutional and Democratic Traditions in a European Perspective, Brill, 2012, p. 56
- Austrian Constitution of 4 March 1849. (Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV)
- John F. Cadzow, Andrew Ludanyi, Louis J. Elteto, Transylvania: The Roots of Ethnic Conflict, Kent State University Press, 1983, p. 79
- James Minahan: One Europe, many nations: an historical dictionary of European national groups, Greenwood Press, Westport, CT
- Pavel, Eugen (2018). "The Transylvanian School – Premises Underlying the Critical Editions of Texts". Academia.edu. p. 1. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- Török, Borbála Zsuzsanna (27 October 2015). ""1 Landeskunde, honismeret – Patriotic Scholarship and Vernacular Languages". In Exploring Transylvania". brill.com. doi:10.1163/9789004303058_003. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- "Travel Advisory; Lure of Dracula In Transylvania". The New York Times. 1993-08-22.
- "Romania Transylvania". Icromania.com. 2007-04-15. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- Gerhild Scholz Williams; William Layher (eds.). Consuming News: Newspapers and Print Culture in Early Modern Europe (1500–1800). pp. 14–34. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- Engel, Pál (2001). Realm of St. Stephen: History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526 (International Library of Historical Studies), p. 24, London: I.B. Taurus. ISBN 1-86064-061-3
- Pop, Ion-Aurel (1997). "Istoria Transilvaniei Medievale: De la Etnogeneza Romanilor pana la Mihai Viteazul" [The Medieval History of Transylvania: from the Romanian Ethnogenesis until Michael the Brave] (in Romanian). Retrieved 2013-10-03.
- Pascu, Ștefan (1972). "Voievodatul Transilvaniei". I: 22.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Kristó, Gyula (2002). A korai Erdély [The early Transylvania]. Szegedi Középkorász Műhely. p. 24. ISBN 9634825583.
- Drăganu, Nicolae (1924). Anuarul Institutului de Istorie Națională (PDF). Vol. II. Bucharest. p. 237.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Vékony, Gábor (2000): Dacians, Romans, Romanians
- Tóth, Endre (1994): The Roman Province of Dacia
- Gündisch, Konrad: Transylvania and the Transylvanian Saxons
- ^ Bóna, István (1994): The Kingdom of the Gepids
- Curta, Florin (2006): Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250
- Bóna, István (1994): The period of Avar rule
- Macartney, Carlile Aylmer (1962): Hungary: a short history
- Bóna, István (1994): Southern Transylvania under Bulgar rule
- Makkai, László (1975): The origins of the Hungarian people and state
- Farkas, Zoltán (2007): Transylvania
- Rady, Martyn: The Gesta Hungarorum of Anonymus, the anonymous notary of King Béla
- Veszprémy, László; Schaer, Frank (1999): Gesta Hungarorum: The Deeds of the Hungarians
- Geréb, László (1993): Képes Krónika (in Hungarian)
- Geréb, László (1957): Magyar Krónika (in Hungarian)
- Engel, Pal; Andrew Ayton (2005). The Realm of St Stephen. London: Tauris. p. 27. ISBN 1-85043-977-X.
- Bóna, István (1994). "From Dacia to Transylvania: The Period of the Great Migrations (271–895); The Hungarian–Slav Period (895–1172)". In Köpeczi, Béla; Barta, Gábor; Bóna, István; Makkai, László; Szász, Zoltán; Borus, Judit (eds.). History of Transylvania. Akadémiai Kiadó. pp. 62–177. ISBN 963-05-6703-2.
- Kristó, Gyula (2003). Early Transylvania (895-1324). Lucidus Kiadó. ISBN 963-9465-12-7.
- Jean W Sedlar (1994). East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500. University of Washington Press. pp. 9–. ISBN 978-0-295-97291-6.
- Madgearu, Alexandru (2018). "The Mongol domination and the detachment of the Romanians of Wallachia from the domination of the Hungarian Kingdom". De Medio Aevo: 219–220.
- Jean W Sedlar (1994). East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500. University of Washington Press. pp. 9–. ISBN 978-0-295-97291-6.
- Makkai, László (2001). "The Mongol Invasion and Its Consequences". History of Transylvania Volume I. From the Beginnings to 1606 - III. Transylvania in the Medieval Hungarian Kingdom (896–1526) - 3. From the Mongol Invasion to the Battle of Mohács. Columbia University Press, (The Hungarian original by Institute of History Of The Hungarian Academy of Sciences). ISBN 0-88033-479-7.
- "Stephen I". Encyclopedia of World Biography. 14: 427–428. 2004 – via Gale Virtual Reference Library.
- "Hungary". Merriam-Webster's geographical dictionary (3rd ed.). CREDO. 2007.
- Anthony Endrey, The Holy Crown of Hungary, Hungarian Institute, 1978, p. 70
- "International Boundary Study – No. 47 – April 15, 1965 – Hungary – Romania (Rumania) Boundary" (PDF). US Bureau of Intelligence and Research. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 3, 2009.
- "Diploma Leopoldinum (Transylvanian history)". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- "Transylvania (region, Romania)". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- Sugar, Peter F. (2012-07-01). Southeastern Europe under Ottoman Rule, 1354-1804. University of Washington Press. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-295-80363-0.
- Cadzow, John F.; Ludanyi, Andrew; Elteto, Louis J. (1983). Transylvania: The Roots of Ethnic Conflict. Kent State University Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-87338-283-0.
- Lendvai, Paul (2003). The Hungarians: A Thousand Years of Victory in Defeat. C. Hurst. p. 146. ISBN 978-1-85065-682-1.
- "Definition of Grand Principality of Transylvania in the Free Online Encyclopedia". Encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ^ "Transylvania". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- "Transylvania", Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2008.
- The Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy and Romanian Political Autonomy Archived 2007-04-24 at the Wayback Machine in Pașcu, Ștefan. A History of Transylvania. Dorset Press, New York, 1990.
- CIA World Factbook, Romania – Government Archived 2020-05-05 at the Wayback Machine
- Történelmi világatlasz [World Atlas of History] (in Hungarian). Cartographia. 1998. ISBN 963-352-519-5.
- ^ Varga, E. Árpád, Hungarians in Transylvania between 1870 and 1995, Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999, pp. 30-34
- Keith Hitchins (1994). Romania. Clarendon Press. pp. 486–. ISBN 978-0-19-822126-5.
- Transilvania Archived 2020-02-28 at the Wayback Machine at romaniatraveltourism.com
- Chisholm 1911.
- "Microsoft Word – REZULTATE DEFINITIVE RPL2011.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-07-17. Retrieved 2018-04-17.
- "Sibiu Cultural Capital Website". Archived from the original on 2006-10-15.
- "www.hungarian-history.hu". Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- Elek Fényes, Magyarország statistikája, Vol. 1, Trattner-Károlyi, Pest. VII, 1842
- Seton-Watson, Robert William (1933). "The Problem of Treaty Revision and the Hungarian Frontiers". International Affairs. 12 (4): 481–503. doi:10.2307/2603603. JSTOR 2603603.
- "Transylvania". Columbia Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 2008-09-05. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- "RPL 2011 – VOLUMUL I: POPULAŢIA STABILĂ (REZIDENTĂ) – STRUCTURA DEMOGRAFICĂ, Table no. 7". recensamantromania.ro.
- "Clasificarea spitalelor" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
- "ROMARM | National Defense Company in Romania | call us 40213171971".
- Mark Axworthy, London: Arms and Armour, 1995, Third Axis, Fourth Ally: Romanian Armed Forces in the European War, 1941–1945, pp. 29-30, 75, 149, 222-227 and 239-272
- "Cultura". 2007-12-31. Archived from the original on December 31, 2007. Retrieved 2016-05-08.
- N. Felecan - Considerations on the First Books of Romanian Grammar
- Earl A. Pope, "Protestantism in Romania", in Sabrina Petra Ramet (ed.), Protestantism and Politics in Eastern Europe and Russia: The Communist and Postcommunist Eras, Duke University Press, Durham, 1992, p.158-160. ISBN 0-8223-1241-7
- The Eastern Catholic Churches 2017. cnewa.org
- Chirmiciu András (19 January 2023). "Részleges közösségi radiográfia". Nyugati Jelen (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- "Primele date provizorii pentru Recensământul Populației și Locuințelor, runda 2021" (PDF). recensamantromania.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- Ghidul studentului din Universitatea Babeș-Bolyai. p. 5. Archived from the original on 2016-04-26. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - "Situatia demografica a cultelor dupa 1918" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-12-15. Retrieved 2018-04-16.
- "Anuarul statistic al Romaniei, 1937 si 1938" (PDF).
- "Populația stabilă după religie – județe, municipii, orașe, comune". Institutul Național de Statistică.
- "Travel to Romania – Densuș Church (Hunedoara)". Romanianmonasteries.org. 2006-05-31. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ^ "Apuseni Caves". Itsromania.com. Archived from the original on 2012-03-16. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- "Zilele Filmului de Umor 2014". timisoreni.ro. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- "O nouă ediție a Zilelor Filmului de Umor la Timișoara". HotNewsRo. 26 June 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- Ströhl, Hugo Gerard (1890). Oesterreichish-Ungarische Wappenrolle (PDF). Vienna: Verlag vom Anton Schroll & Co. p. XV. Retrieved 24 November 2011.
- Hulsius, Levinus (1596). Chronologia in qua provinciae... (in Latin). Nuremberg.
Further reading
- András Bereznay, Erdély történetének atlasza (Historical Atlas of Transylvania), with text and 102 map plates, the first ever historical atlas of Transylvania (Méry Ratio, 2011; ISBN 978-80-89286-45-4)
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Transylvania" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 27 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 210–211.
- Zoltán Farkas and Judit Sós, Transylvania Guidebook
- Patrick Leigh Fermor, Between the Woods and the Water (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ISBN 1-59017-166-7). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986.
- Pop, Ioan-Aurel; Nägler, Thomas; Magyari, András (2018). The History of Transylvania, vol. I–III. Cluj-Napoca: Romanian Academy, Center for Transylvanian Studies – Romanian Cultural Institute. ISBN 978-606-8694-78-8.
- Köpeczi, Béla; Makkai, László; Mócsy, András; Szász, Zoltán (1994). History of Transylvania. Vol. I–III. Translated by Kovrig, Benett. New Jersey: Atlantic Research and Publications. ISBN 963-05-6703-2.
External links
- Radio Transsylvania International
- "Tolerant Transylvania – Why Transylvania will not become another Kosovo", Katherine Lovatt, in Central Europe Review, Vol. 1, No. 14, 27 September 1999.
- The History of Transylvania and the Transylvanian Saxons by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany
- Transylvania,Its Products and its People Archived 2018-05-05 at the Wayback Machine, by Charles Boner, 1865
- Transylvanian Family History Database (in Hungarian)
| Banat |
|
|---|---|
| Dobruja |
|
| Moldavia |
|
| Transylvania | |
| Wallachia | |
| |
46°30′N 25°00′E / 46.5°N 25°E / 46.5; 25
Categories: