| Revision as of 15:55, 10 January 2009 editHipal (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers137,994 edits Undid revision 263173540 by 84.64.50.128 (talk) take it to talk← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 08:28, 5 January 2025 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,435,862 edits Add: newspaper, bibcode, doi-broken-date, work, authors 1-1. Removed parameters. Some additions/deletions were parameter name changes. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Misplaced Pages articles in need of updating from December 2024 | #UCB_Category 564/784 | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Program that simulates conversation}} | |||
| {{external links}} | |||
| {{For2|the bot-creation software|ChatBot|bots on Internet Relay Chat|IRC bot}} | |||
| A '''chatterbot''' (or chatbot) is a type of conversational agent, a ] designed to simulate an intelligent ] with one or more human users via auditory or textual methods. The computer programmes are also known as ] and, though many appear to be intelligently interpreting the human input prior to providing a response, most chatterbots simply scan for keywords within the input and pull a reply with the most matching keywords or the most similar wording pattern from a local ]. Chatterbots may also be referred to as ''talk bots'', ''chat bots'', or ''chatterboxes''. | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2024}} | |||
| However, 2008 ] entry, Eugene Goostman is able to respond in an impressive manner. For example, with this interrogation, by Loebner 2008 preliminary phase judge Scott Jensen: "My car is red. What color is my car?" Eugene later remembered its answer when only asked: "What is the color of my car?". | |||
| ] chatbot]] | |||
| == Method of operation == | |||
| {{examplefarm}} | |||
| A good understanding of a conversation is required to carry on a meaningful dialog but most chatterbots do not attempt this. Instead they "converse" by recognizing cue words or phrases from the human user, which allows them to use pre-prepared or pre-calculated responses which can move the conversation on in an apparently meaningful way without requiring them to know what they are talking about. | |||
| ] chatbot]] | |||
| For example, if a human types, "I am feeling very worried lately," the chatterbot may be programmed to recognize the phrase "I am" and respond by replacing it with "Why are you" plus a question mark at the end, giving the answer, "Why are you feeling very worried lately?" A similar approach using keywords would be for the program to answer any comment including ''(Name of celebrity)'' with "I think they're great, don't you?" Humans, especially those unfamiliar with chatterbots, sometimes find the resulting conversations engaging. Critics of chatterbots call this engagement the ]. | |||
| {{Machine learning|Artificial neural network}} | |||
| Some programs classified as chatterbots use other principles. One example is ], which attempts to model the way humans learn new facts and language. ] attempts to use ] to make more useful responses from a human's input. Some programs like ] use natural language conversation while others such as ], are not generally classified as chatterbots because they link their speech ability to knowledge of a simulated world. This type of link requires a more complex ] (eg., a "vision" system) than standard chatterbots have. | |||
| A '''chatbot''' (originally '''chatterbot''')<ref name="Mauldin" /> is a ] application or web interface designed to have textual or spoken conversations.<ref>{{cite web |title=What is a chatbot? |url=http://searchdomino.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid4_gci935566,00.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101102170613/http://searchdomino.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid4_gci935566,00.html |archive-date=2 November 2010 |access-date=30 January 2017 |website=techtarget.com}}</ref><ref name="Caldarini-20223">{{Cite journal |last1=Caldarini |first1=Guendalina |last2=Jaf |first2=Sardar |last3=McGarry |first3=Kenneth |year=2022 |title=A Literature Survey of Recent Advances in Chatbots |journal=Information |publisher=MDPI |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=41 |arxiv=2201.06657 |doi=10.3390/info13010041 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Adamopoulou |first1=Eleni |last2=Moussiades |first2=Lefteris |date=2020 |title=Chatbots: History, technology, and applications |journal=Machine Learning with Applications |volume=2 |pages=100006 |doi=10.1016/j.mlwa.2020.100006 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Modern chatbots are typically ] and use ] systems that are capable of maintaining a conversation with a user in ] and simulating the way a human would behave as a conversational partner. Such chatbots often use ] and ], but simpler chatbots have existed for decades. | |||
| == Early chatterbots == | |||
| The classic early chatterbots are ] (1966) and ] (1972).<ref name="Güzeldere">{{Harvnb|GüzeldereFranchi|1995}}</ref><ref name="comphis">{{Harvnb|Computer History Museum|2006}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Sondheim|1997}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Network Working Group|1973}}- Transcript of a session between Parry and Eliza. (This is ''not'' the dialogue from the ICCC, which took place October 24-26, 1972, whereas this session is from September 18, 1972.)</ref> More recent programs are ],<ref name="Güzeldere"/> ]s, ], and ]. | |||
| Although chatbots have existed since the late 1960s, the field ] due to the popularity of ]'s ],<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.reuters.com/technology/chatgpt-sets-record-fastest-growing-user-base-analyst-note-2023-02-01/ | title=ChatGPT sets record for fastest-growing user base - analyst note | newspaper=Reuters | date=2 February 2023 | last1=Hu | first1=Krystal }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Hines |first=Kristi |date=4 June 2023 |title=History Of ChatGPT: A Timeline Of The Meteoric Rise Of Generative AI Chatbots |url=https://www.searchenginejournal.com/history-of-chatgpt-timeline/488370/ |access-date=17 November 2023 |website=Search Engine Journal |language=en}}</ref> followed by alternatives such as ]'s ] and ]'s ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.cnet.com/tech/services-and-software/chatgpt-vs-bing-vs-google-bard-which-ai-is-the-most-helpful/ | title=ChatGPT vs. Bing vs. Google Bard: Which AI is the Most Helpful? }}</ref> Such examples reflect the recent practice of basing such products upon broad ] ], such as ] or the ], that get ] so as to target specific tasks or applications (i.e., simulating human conversation, in the case of chatbots). Chatbots can also be designed or customized to further target even more specific situations and/or particular subject-matter domains.<ref name="livemint.com">{{cite web | url=https://www.livemint.com/technology/tech-news/gpt4-takes-the-world-by-storm-list-of-companies-that-integrated-the-chatbot-11679293885004.html | title=GPT-4 takes the world by storm - List of companies that integrated the chatbot | work=mint | date=21 March 2023 | last1=Gupta | first1=Aman }}</ref> | |||
| The growth of chatterbots as a research field has created an expansion in their purposes. While ELIZA and PARRY were used exclusively to simulate typed conversation, ] was used to "write" a story called ''The Policeman's Beard is Half Constructed''. ELLA includes a collection of games and functional features to further extend the potential of chatterbots. | |||
| A major area where chatbots have long been used is in ] and ], with various sorts of ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://cai.tools.sap/blog/2017-messenger-bot-landscape/|title=2017 Messenger Bot Landscape, a Public Spreadsheet Gathering 1000+ Messenger Bots|date=3 May 2017|access-date=1 February 2019|archive-date=2 February 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190202041707/https://cai.tools.sap/blog/2017-messenger-bot-landscape/|url-status=live}}</ref> Companies spanning a wide range of industries have begun using the latest ] technologies to power more advanced developments in such areas.<ref name="livemint.com"/> | |||
| The term "ChatterBot" was coined by ] (Creator of the first ], Julia) in 1994 to describe these conversational programs.<ref>{{Harvnb|Mauldin|1994}}</ref> | |||
| == |
== History == | ||
| === Turing test === | |||
| Malicious chatterbots are frequently used to fill chat rooms with spam and advertising, or to entice people into revealing personal information, such as bank account numbers. They are commonly found on ], ], ] and other ] protocols. There has been a published report of a chatterbot used in a fake personal ad on a dating service's website.<ref> | |||
| In 1950, ]'s famous article "]" was published,<ref name="Turing" /> which proposed what is now called the ] as a criterion of ]. This criterion depends on the ability of a ] to impersonate a human in a ] written conversation with a human judge to the extent that the judge is unable to distinguish reliably—on the basis of the conversational content alone—between the program and a real human. | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| | url = http://drrobertepstein.com/downloads/FROM_RUSSIA_WITH_LOVE-Epstein-Sci_Am_Mind-Oct-Nov2007.pdf | |||
| | title = From Russia With Love | |||
| | format = | |||
| | accessdate = 2007-12-09 | |||
| }} Psychologist and ''Scientific American: Mind'' contributing editor ] reports how he was initially fooled by a chatterbot posing as an attractive girl in a personal ad he answered on a dating website. In the ad, the girl portrayed herself as being in Southern California and then soon revealed, in poor English, that she was actually in Russia. He became suspicious after a couple of months of email exchanges, sent her an email test of gibberish, and she still replied in general terms. The dating website is not named. ''Scientific American: Mind'', October-November 2007, page 16-17, "From Russia With Love: How I got fooled (and somewhat humiliated) by a computer''. Also available online.</ref> | |||
| === Eliza === | |||
| ==Chatterbots in modern AI== | |||
| The notoriety of Turing's proposed test stimulated great interest in ]'s program ], published in 1966, which seemed to be able to fool users into believing that they were conversing with a real human. However Weizenbaum himself did not claim that ELIZA was genuinely intelligent, and the introduction to his paper presented it more as a debunking exercise:<blockquote>In artificial intelligence, machines are made to behave in wondrous ways, often sufficient to dazzle even the most experienced observer. But once a particular program is unmasked, once its inner workings are explained, its magic crumbles away; it stands revealed as a mere collection of procedures. The observer says to himself "I could have written that". With that thought, he moves the program in question from the shelf marked "intelligent", to that reserved for curios. The object of this paper is to cause just such a re-evaluation of the program about to be "explained". Few programs ever needed it more.<ref name="Weizenbaum" /></blockquote>ELIZA's key method of operation involves the recognition of clue words or phrases in the input, and the output of the corresponding pre-prepared or pre-programmed responses that can move the conversation forward in an apparently meaningful way (e.g. by responding to any input that contains the word 'MOTHER' with 'TELL ME MORE ABOUT YOUR FAMILY').<ref name="Weizenbaum" /> Thus an illusion of understanding is generated, even though the processing involved has been merely superficial. ELIZA showed that such an illusion is surprisingly easy to generate because human judges are ready to give the benefit of the doubt when conversational responses are ''capable of being interpreted'' as "intelligent". | |||
| {{Unreferencedsection|date=August 2008}} | |||
| {{Original research|date=August 2008}} | |||
| {{Expert|date=August 2008}} | |||
| Interface designers have come to appreciate that humans' readiness to interpret computer output as genuinely conversational—even when it is actually based on rather simple pattern-matching—can be exploited for useful purposes. Most people prefer to engage with programs that are human-like, and this gives chatbot-style techniques a potentially useful role in interactive systems that need to elicit information from users, as long as that information is relatively straightforward and falls into predictable categories. Thus, for example, online help systems can usefully employ chatbot techniques to identify the area of help that users require, potentially providing a "friendlier" interface than a more formal search or menu system. This sort of usage holds the prospect of moving chatbot technology from Weizenbaum's "shelf ... reserved for curios" to that marked "genuinely useful computational methods". | |||
| Most modern AI research focuses on practical engineering tasks. This is known as weak AI and is distinguished from ], which would require ] and reasoning abilities. | |||
| === Early chatbots === | |||
| One pertinent field of AI research is natural language. Usually weak AI fields employ specialized software or programming languages created for them. For example, one of the 'most-human' natural language chatterbots, ], uses a programming language called AIML that is specific to its program, and its various clones, named Alicebots. Nevertheless, A.L.I.C.E. is still based on pattern matching without any reasoning. This is the same technique ], the first chatterbot, was using back in 1966. | |||
| Among the most notable early chatbots are ELIZA (1966) and ] (1972).<ref name="Güzeldere" /><ref name="comphis" /><ref name="Sondheim" /><ref name="rfc0439" /> More recent notable programs include ], ] and D.U.D.E (] and ] 2006). While ELIZA and PARRY were used exclusively to simulate typed conversation, many chatbots now include other functional features, such as games and ] abilities. In 1984, a book called ''The Policeman's Beard is Half Constructed'' was published, allegedly written by the chatbot ] (though the program as released would not have been capable of doing so).<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100204175415/http://everything2.com/title/the+policeman%2527s+beard+is+half+constructed|date=4 February 2010}}. everything2.com. 13 November 1999</ref> | |||
| From 1978<ref>Kolodner, Janet L. ''''. Advanced Research Projects Agency, 1978.</ref> to some time after 1983,<ref name="Kolodner-19832">{{Cite journal |last=Kolodner |first=Janet L. |date=1 October 1983 |title=Maintaining organization in a dynamic long-term memory |journal=Cognitive Science |language=en |volume=7 |issue=4 |pages=243–280 |doi=10.1016/S0364-0213(83)80001-9 |doi-broken-date=5 January 2025 |issn=0364-0213 |doi-access=free}}</ref> the CYRUS project led by ] constructed a chatbot simulating ] (57th ]). It used ], and updated its database daily by parsing wire news from ]. The program was unable to process the news items subsequent to the surprise resignation of Cyrus Vance in April 1980, and the team constructed another chatbot simulating his successor, ].<ref>{{Citation |last=Dennett |first=Daniel C. |title=Can Machines Think? |date=2004 |work=Alan Turing: Life and Legacy of a Great Thinker |pages=295–316 |editor-last=Teuscher |editor-first=Christof |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05642-4_12 |access-date=23 July 2023 |place=Berlin, Heidelberg |publisher=Springer |language=en |doi=10.1007/978-3-662-05642-4_12 |isbn=978-3-662-05642-4}}</ref><ref name="Kolodner-19832" /> | |||
| Australian company ] also deals in strong AI, allowing users to create and sustain their own virtual personalities online. MyCyberTwin.com also works in a corporate setting, allowing companies to set up Virtual AI Assistants. Another notable program, known as ], also deals in strong AI, as it is claimed to learn new responses based on user interactions, rather than being driven from a static database like many other existing chatterbots. Although such programs show initial promise, many of the existing results in trying to tackle the problem of natural language still appear fairly poor, and it seems reasonable to state that there is currently no general purpose conversational artificial intelligence. This has led some software developers to focus more on the practical aspect of chatterbot technology - information retrieval. | |||
| One pertinent field of AI research is ]. Usually, ] fields employ specialized software or programming languages created specifically for the narrow function required. For example, A.L.I.C.E. uses a ] called AIML,<ref name="Caldarini-20223" /> which is specific to its function as a ], and has since been adopted by various other developers of, so-called, ]. Nevertheless, A.L.I.C.E. is still purely based on ] techniques without any reasoning capabilities, the same technique ELIZA was using back in 1966. This is not strong AI, which would require ] and ] abilities. | |||
| A common rebuttal often used within the AI community against criticism of such approaches asks, "How do we know that humans don't also just follow some cleverly devised rules?" (in the way that Chatterbots do). Two famous examples of this line of argument against the rationale for the basis of the Turing test are John Searle's ] argument and Ned Block's ]. | |||
| Jabberwacky learns new responses and context based on ] ], rather than being driven from a static ]. Some more recent chatbots also combine real-time learning with ] that optimize their ability to communicate based on each conversation held. | |||
| ==Chatterbots/virtual assistants in commercial environments== | |||
| Automated Conversational Systems have progressed and evolved far from the original designs of the first widely used chatbots. In the UK, large commercial entities such as Lloyds TSB, Royal Bank of Scotland, Renault, Citroën and One Railway are already utilizing Virtual Assistants to reduce expenditures on Call Centres and provide a first point of contact that can inform the user exactly of points of interest, provide support, capture data from the user and promote products for sale. | |||
| Chatbot competitions focus on the Turing test or more specific goals. Two such annual contests are the ] and The Chatterbox Challenge (the latter has been offline since 2015, however, materials can still be found from web archives).<ref>{{Cite web |date=11 October 2015 |title=Chat Robots Simiulate People |url=https://pcsite.co.uk/chat-robots-simulate-people/}}</ref> | |||
| In the UK, new projects and research are being conducted to introduce a Virtual Assistant into the classroom to assist the teacher. This project is the first of its kind and the chatbot VA in question is based on the Yhaken {{Failed verification|date=May 2008}}<!-- need a cite that supports this; I asked the elzware bot but it replied "I have no idea what you are asking me about here." --> chatbot design. | |||
| ] created a chatbot during the ] of 2017.<ref>{{Cite web |title=DBpedia Chatbot |url=https://chat.dbpedia.org/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190908054646/http://chat.dbpedia.org/ |archive-date=8 September 2019 |access-date=9 September 2019 |website=chat.dbpedia.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=22 August 2018 |title=Meet the DBpedia Chatbot | DBpedia |url=https://wiki.dbpedia.org/blog/meet-dbpedia-chatbot |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190902144929/https://wiki.dbpedia.org/blog/meet-dbpedia-chatbot |archive-date=2 September 2019 |access-date=2 September 2019 |website=wiki.dbpedia.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=22 August 2018 |title=Meet the DBpedia Chatbot |url=https://blog.dbpedia.org/2018/08/22/dbpedia-chatbot-2/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190902144945/https://blog.dbpedia.org/2018/08/22/dbpedia-chatbot-2/ |archive-date=2 September 2019 |access-date=2 September 2019 |publisher=dbpedia.org}}</ref> It can communicate through ] (see ] article). | |||
| The Yhaken template provides a further move forward in Automated Conversational Systems with features such as complex conversational routing and responses, well defined personality, a complex hierarchical construct with additional external reference points, emotional responses and in depth small talk, all to make the experience more interactive and involving for the user. | |||
| === Modern chatbots based on large language models === | |||
| ==Annual contests for chatterbots== | |||
| Modern chatbots like ] are often based on ] called ] (GPT). They are based on a ] architecture called the ], which contains ]. They learn how to generate text by being trained on a large ], which provides a solid foundation for the model to perform well on downstream tasks with limited amounts of task-specific data. Despite criticism of its accuracy and tendency to "hallucinate"—that is, to confidently output false information and even cite non-existent sources—ChatGPT has gained attention for its detailed responses and historical knowledge. Another example is BioGPT, developed by ], which focuses on answering ] questions.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Luo |first1=Renqian |last2=Sun |first2=Liai |last3=Xia |first3=Yingce |last4=Qin |first4=Tao |last5=Zhang |first5=Sheng |last6=Poon |first6=Hoifung |last7=Liu |first7=Tie-Yan |display-authors=etal |year=2022 |title=BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining |journal=Brief Bioinform |volume=23 |issue=6 |pages= |arxiv=2210.10341 |doi=10.1093/bib/bbac409 |pmid=36156661}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Bastian, Matthias |date=29 January 2023 |title=BioGPT is a Microsoft language model trained for biomedical tasks |url=https://the-decoder.com/biogpt-is-a-microsoft-language-model-trained-for-biomedical-tasks/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230207174627/https://the-decoder.com/biogpt-is-a-microsoft-language-model-trained-for-biomedical-tasks/ |archive-date=7 February 2023 |access-date=7 February 2023 |website=The Decoder}}</ref> In November 2023, Amazon announced a new chatbot, called Q, for people to use at work.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Novet |first=Jordan |date=28 November 2023 |title=Amazon announces Q, an AI chatbot for businesses |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2023/11/28/amazon-announces-q-an-ai-chatbot-for-businesses.html |access-date=28 November 2023 |website=CNBC |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Many organizations try to encourage and support developers all over the world to develop chatterbots that able to do variety of tasks and compete with each other through ]s and more. Annual contests are organized at the following links: | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| == Application == | |||
| ==Chatterbots in culture== | |||
| {{Update section|date=December 2024}}{{See also|Virtual assistant}} | |||
| * Bots generated by ] since the mid-2000s have randomly connected people by seeding messages with opposing usernames. | |||
| === Messaging apps === | |||
| Many companies' chatbots run on ] or simply via ]. They are used for ] customer service, sales and marketing.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Beaver|first1=Laurie|title=The Chatbots Explainer|newspaper=Business Insider |date=July 2016|publisher=BI Intelligence|url=https://www.businessinsider.com/chatbots-explained-why-businesses-should-be-paying-attention-to-the-chatbot-revolution-2016-7?IR=T|access-date=4 November 2019|archive-date=3 May 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190503111645/https://www.businessinsider.com/chatbots-explained-why-businesses-should-be-paying-attention-to-the-chatbot-revolution-2016-7?IR=T|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In 2016, Facebook Messenger allowed developers to place chatbots on their platform. There were 30,000 bots created for Messenger in the first six months, rising to 100,000 by September 2017.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://venturebeat.com/2017/04/18/facebook-messenger-hits-100000-bots/|title=Facebook Messenger Hits 100,000 bots|access-date=22 September 2017|date=18 April 2017|archive-date=22 September 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170922195723/https://venturebeat.com/2017/04/18/facebook-messenger-hits-100000-bots/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| Since September 2017, this has also been as part of a pilot program on WhatsApp. Airlines ] and ] both announced their participation in the testing;<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.phocuswire.com/KLM-claims-airline-first-with-WhatsApp-Business-Platform|title=KLM claims airline first with WhatsApp Business Platform|website=www.phocuswire.com|access-date=12 December 2021|archive-date=5 February 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200205211831/https://www.phocuswire.com/KLM-claims-airline-first-with-WhatsApp-Business-Platform|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.forbes.com.mx/aeromexico-te-respondera-por-whatsapp-durante-2018/|title=Aeroméxico te atenderá por WhatsApp durante 2018|author=Forbes Staff|date=26 October 2017|access-date=2 July 2018|archive-date=2 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180702180522/https://www.forbes.com.mx/aeromexico-te-respondera-por-whatsapp-durante-2018/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.huffingtonpost.com.mx/2017/10/27/podras-hacer-check-in-y-consultar-tu-vuelo-con-aeromexico-a-traves-de-whatsapp_a_23258181/|title=Podrás hacer 'check in' y consultar tu vuelo con Aeroméxico a través de WhatsApp|date=27 October 2017|access-date=2 July 2018|newspaper=Huffington Post|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180310135702/https://www.huffingtonpost.com.mx/2017/10/27/podras-hacer-check-in-y-consultar-tu-vuelo-con-aeromexico-a-traves-de-whatsapp_a_23258181/|archive-date=10 March 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://blog.whatsapp.com/10000633/Building-for-People-and-Now-Businesses|title=Building for People, and Now Businesses|website=WhatsApp.com|access-date=2 July 2018|archive-date=9 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180209031529/https://blog.whatsapp.com/10000633/Building-for-People-and-Now-Businesses|url-status=live}}</ref> both airlines had previously launched customer services on the Facebook Messenger platform. | |||
| ==Citations== | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| The bots usually appear as one of the user's contacts, but can sometimes act as participants in a ]. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| <!-- alphabetical order --> | |||
| Many banks, insurers, media companies, e-commerce companies, airlines, hotel chains, retailers, health care providers, government entities, and restaurant chains have used chatbots to ], increase ],<ref>{{cite web|title=She is the company's most effective employee|work=Nordea News|url=https://nordeanews-no.translate.goog/2017/09/hun-er-bankens-mest-effektive-medarbeider/?_x_tr_sl=no&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=no|date=September 2017|access-date=23 March 2023|archive-date=23 March 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230323165008/https://www-nordea-com.translate.goog/no?_x_tr_sl=no&_x_tr_tl=en&_x_tr_hl=no|url-status=live}}</ref> for promotion, and to offer additional ways to order from them.<ref>{{cite web|title=Better believe the bot boom is blowing up big for B2B, B2C businesses|url=https://venturebeat.com/2016/07/24/better-believe-the-bot-boom-is-blowing-up-big-for-b2b-b2c-businesses-vb-live/|website=VentureBeat|date=24 July 2016|access-date=30 August 2017|archive-date=3 August 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170803182306/https://venturebeat.com/2016/07/24/better-believe-the-bot-boom-is-blowing-up-big-for-b2b-b2c-businesses-vb-live/|url-status=live}}</ref> Chatbots are also used in ] to collect short survey responses.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Dandapani |first=Arundati |url=https://www.rti.org/rti-press-publication/language-survey-research |title=The Essential Role of Language in Survey Research |date=30 April 2020 |publisher=RTI Press |isbn=978-1-934831-24-3 |editor-last=Sha |editor-first=Mandy |pages=221–230 |chapter=Redesigning Conversations with Artificial Intelligence (Chapter 11) |doi=10.3768/rtipress.bk.0023.2004 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| |author=Computer History Museum | |||
| A 2017 study showed 4% of companies used chatbots.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.pm360online.com/the-ai-revolution-is-underway/|title=The AI Revolution is Underway! |website=www.PM360online.com|date=18 October 2017|author=Capan, Faruk|access-date=7 March 2018|archive-date=8 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180308043007/https://www.pm360online.com/the-ai-revolution-is-underway/|url-status=live}}</ref> According to a 2016 study, 80% of businesses said they intended to have one by 2020.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.businessinsider.com/80-of-businesses-want-chatbots-by-2020-2016-12|title=80% of businesses want chatbots by 2020|website=]|date=15 December 2016|access-date=7 March 2018|archive-date=8 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180308042224/http://www.businessinsider.com/80-of-businesses-want-chatbots-by-2020-2016-12|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| |title=Exhibits | |||
| |chapter=Internet History - 1970's | |||
| ==== As part of company apps and websites ==== | |||
| |year=2006 | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| Previous generations of chatbots were present on company websites, e.g. Ask Jenn from ] which debuted in 2008<ref name="nytimes.com">{{cite web|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/04/business/04road.html|title=A Virtual Travel Agent With All the Answers|date=4 March 2008|website=The New York Times|access-date=3 August 2017|archive-date=15 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170615183749/http://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/04/business/04road.html|url-status=live}}</ref> or ]'s virtual customer service agent which launched in 2011.<ref name="nytimes.com" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hypergridbusiness.com/2011/10/chatbot-vendor-directory-released/|title=Chatbot vendor directory released|date=October 2011|website=www.hypergridbusiness.com|access-date=23 April 2017|archive-date=23 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170423153332/http://www.hypergridbusiness.com/2011/10/chatbot-vendor-directory-released/|url-status=live}}</ref> The newer generation of chatbots includes ]-powered "Rocky", introduced in February 2017 by the New York City-based ] company Rare Carat to provide information to prospective diamond buyers.<ref>{{cite news |title=Rare Carat's Watson-powered chatbot will help you put a diamond ring on it |date=15 February 2017 |url=https://techcrunch.com/2017/02/15/rare-carats-watson-powered-chat-bot-will-help-you-put-a-diamond-ring-on-it/ |agency=TechCrunch |access-date=22 August 2017 |archive-date=22 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170822133420/https://techcrunch.com/2017/02/15/rare-carats-watson-powered-chat-bot-will-help-you-put-a-diamond-ring-on-it/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |date=10 March 2017 |title=10 ways you may have already used IBM Watson |url=https://venturebeat.com/2017/03/10/10-ways-you-may-have-already-used-ibm-watson/ |agency=VentureBeat |access-date=22 August 2017 |archive-date=22 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170822101320/https://venturebeat.com/2017/03/10/10-ways-you-may-have-already-used-ibm-watson/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |contribution-url=http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_70s.shtml | |||
| |accessdate=2008-03-05 | |||
| ==== Chatbot sequences ==== | |||
| }} | |||
| Used by marketers to script sequences of messages, very similar to an ] sequence. Such sequences can be triggered by user opt-in or the use of keywords within user interactions. After a trigger occurs a sequence of messages is delivered until the next anticipated user response. Each user response is used in the decision tree to help the chatbot navigate the response sequences to deliver the correct response message. | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| | url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/SHR/4-2/text/dialogues.html | |||
| === Company internal platforms === | |||
| | contribution=dialogues with colorful personalities of early ai | |||
| Companies have used chatbots for customer support, human resources, or in ] (IoT) projects. ], for one, has reportedly launched a chatbot named Mila to attempt to automate certain processes when customer service employees request sick leave.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Greenfield|first1=Rebecca|title=Chatbots Are Your Newest, Dumbest Co-Workers|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-05-05/chatbots-are-your-newest-dumbest-co-workers|newspaper=Bloomberg.com|date=5 May 2016|access-date=6 March 2017|archive-date=6 April 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170406040807/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-05-05/chatbots-are-your-newest-dumbest-co-workers|url-status=live}}</ref> Other large companies such as ], ], ] and ] are now using chatbots instead of ] with humans to provide a first point of contact.{{cn|date=December 2024}} In large companies, like in hospitals and aviation organizations, chatbots are also used to share information within organizations, and to assist and replace service desks.{{cn|date=December 2024}} | |||
| | last=Güzeldere | |||
| | first=Güven | |||
| === Customer service === | |||
| | author-link=<!-- Güven Güzeldere --> | |||
| Chatbots have been proposed as a replacement for ] departments.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Følstad |first1=Asbjørn |last2=Nordheim |first2=Cecilie Bertinussen |last3=Bjørkli |first3=Cato Alexander |chapter=What Makes Users Trust a Chatbot for Customer Service? An Exploratory Interview Study |series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science |date=2018 |volume=11193 |editor-last=Bodrunova |editor-first=Svetlana S. |title=Internet Science |chapter-url=https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-01437-7_16 |language=en |location=Cham |publisher=Springer International Publishing |pages=194–208 |doi=10.1007/978-3-030-01437-7_16 |isbn=978-3-030-01437-7|hdl=11250/2571164 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| | last2=Franchi | |||
| | first2=Stefano | |||
| ] techniques can be incorporated into chatbot applications to allow them to map conversations between users and customer service agents, especially in social media.<ref name="Xu-2017">{{Cite book |last1=Xu |first1=Anbang |last2=Liu |first2=Zhe |last3=Guo |first3=Yufan |last4=Sinha |first4=Vibha |last5=Akkiraju |first5=Rama |chapter=A New Chatbot for Customer Service on Social Media |date=2017-05-02 |title=Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems |chapter-url=https://doi.org/10.1145/3025453.3025496 |series=CHI '17 |location=New York, NY, USA |publisher=Association for Computing Machinery |pages=3506–3510 |doi=10.1145/3025453.3025496 |isbn=978-1-4503-4655-9}}</ref> | |||
| | author2-link=<!-- Stefano Franchi --> | |||
| | title=Constructions of the Mind | |||
| In 2019, ] predicted that by 2021, 15% of all customer service interactions globally will be handled completely by AI.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/27297-2/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191211081442/https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/27297-2/|url-status=dead|archive-date=11 December 2019|title=How to Manage Customer Service Technology Innovation|website=www.gartner.com|access-date=2 January 2020}}</ref> A study by ] in 2019 estimates retail sales resulting from chatbot-based interactions will reach $112 billion by 2023.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.juniperresearch.com/press/press-releases/chatbot-interactions-retail-reach-22-billion-2023|title=Chatbot Interactions to Reach 22 Billion by 2023, as AS AI Offers Compelling New Engagement Solutions |publisher=Juniper Research|author=Smith, Sam|date=8 May 2019|access-date=2 January 2020|archive-date=2 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200102180434/https://www.juniperresearch.com/press/press-releases/chatbot-interactions-retail-reach-22-billion-2023|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | journal=Stanford Humanities Review | |||
| | series=SEHR | |||
| In 2016, Russia-based Tochka Bank launched a chatbot on ] for a range of financial services, including a possibility of making payments.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.vedomosti.ru/technology/articles/2016/07/13/649035-rossiiskii-bank-zapustil-chatbota-v-facebook|title=Российский банк запустил чат-бота в Facebook|date=13 July 2016|work=Vedomosti.ru|access-date=1 April 2019|archive-date=1 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190401194126/https://www.vedomosti.ru/technology/articles/2016/07/13/649035-rossiiskii-bank-zapustil-chatbota-v-facebook|url-status=live}}</ref> In July 2016, ] also launched a Facebook chatbot.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fin24.com/Tech/Companies/absa-launches-world-first-facebook-messenger-banking-20160719|title=Absa launches 'world-first' Facebook Messenger banking|date=19 July 2016|access-date=1 April 2019|archive-date=1 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190401192552/https://www.fin24.com/Tech/Companies/absa-launches-world-first-facebook-messenger-banking-20160719|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | volume=4 | |||
| | issue=2 | |||
| In 2023, US-based ] replaced its human ] staff with a chatbot but had to take it offline after users reported receiving harmful advice from it.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Crimmins |first=Tricia |date=2023-05-30 |title='This robot causes harm': National Eating Disorders Association's new chatbot advises people with disordering eating to lose weight |url=https://www.dailydot.com/irl/neda-chatbot-weight-loss/ |access-date=2023-06-02 |website=The Daily Dot |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Knight |first=Taylor |date=May 31, 2023 |title=Eating disorder helpline fires AI for harmful advice after sacking humans |url=https://nypost.com/2023/05/31/eating-disorder-helpline-fires-ai-for-harmful-advice-after-sacking-humans/}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Aratani |first=Lauren |date=2023-05-31 |title=US eating disorder helpline takes down AI chatbot over harmful advice |url=https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2023/may/31/eating-disorder-hotline-union-ai-chatbot-harm |access-date=2023-06-01 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> | |||
| | year=1995 | |||
| | date=1995-07-24 | |||
| === Healthcare === | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| {{See also|Artificial intelligence in healthcare}}Chatbots are also appearing in the healthcare industry.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Larson |first=Selena |date=11 October 2016 |title=Baidu is bringing AI chatbots to healthcare |url=https://money.cnn.com/2016/10/11/technology/baidu-doctor-ai-melody/index.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200103124942/https://money.cnn.com/2016/10/11/technology/baidu-doctor-ai-melody/index.html |archive-date=3 January 2020 |access-date=3 January 2020 |work=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |title=AI chatbots have a future in healthcare, with caveats |url=https://www.aiin.healthcare/topics/robotics/ai-chatbots-have-future-healthcare-caveats |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230323165017/https://healthexec.com/topics/artificial-intelligence/ai-chatbots-have-future-healthcare-caveats |archive-date=23 March 2023 |access-date=17 September 2019 |website=AI in Healthcare}}</ref> A study suggested that physicians in the United States believed that chatbots would be most beneficial for scheduling doctor appointments, locating health clinics, or providing medication information.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Palanica |first1=Adam |last2=Flaschner |first2=Peter |last3=Thommandram |first3=Anirudh |last4=Li |first4=Michael |last5=Fossat |first5=Yan |date=3 January 2019 |title=Physicians' Perceptions of Chatbots in Health Care: Cross-Sectional Web-Based Survey |journal=Journal of Medical Internet Research |volume=21 |issue=4 |pages=e12887 |doi=10.2196/12887 |pmc=6473203 |pmid=30950796 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| | accessdate=2008-03-05 | |||
| }} | |||
| ] is able to answer user queries related to health promotion and disease prevention such as screening and ].<ref name="Biswas-20233">{{Cite journal |last=Biswas |first=Som S. |date=2023-05-01 |title=Role of Chat GPT in Public Health |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03172-7 |journal=Annals of Biomedical Engineering |language=en |volume=51 |issue=5 |pages=868–869 |doi=10.1007/s10439-023-03172-7 |issn=1573-9686 |pmid=36920578}}</ref> ] has teamed up with the ] (WHO) to make a chatbot service that answers users' questions on ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ahaskar |first=Abhijit |date=27 March 2020 |title=How WhatsApp chatbots are helping in the fight against Covid-19 |url=https://www.livemint.com/technology/tech-news/how-whatsapp-chatbots-are-helping-in-the-fight-against-covid-19-11585310168911.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723154947/https://www.livemint.com/technology/tech-news/how-whatsapp-chatbots-are-helping-in-the-fight-against-covid-19-11585310168911.html |archive-date=23 July 2020 |access-date=23 July 2020 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| | url=http://www.aaai.org/Library/AAAI/aaai94contents.php | |||
| In 2020, the ] launched a chatbot called MyGov Corona Helpdesk,<ref>{{Cite web |date=April 2020 |title=India's Coronavirus Chatbot on WhatsApp Crosses 1.7 Crore Users in 10 Days |url=https://gadgets.ndtv.com/apps/news/coronavirus-mygov-corona-helpdesk-chatbot-whatsapp-indian-government-total-users-haptik-2204458 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200621183924/https://gadgets.ndtv.com/apps/news/coronavirus-mygov-corona-helpdesk-chatbot-whatsapp-indian-government-total-users-haptik-2204458 |archive-date=21 June 2020 |access-date=23 July 2020 |website=NDTV Gadgets 360}}</ref> that worked through WhatsApp and helped people access information about the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kurup |first=Rajesh |date=21 March 2020 |title=COVID-19: Govt of India launches a WhatsApp chatbot |url=https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/covid-19-india-launches-a-whatsapp-chatbot/article31127438.ece |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723224134/https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/covid-19-india-launches-a-whatsapp-chatbot/article31127438.ece |archive-date=23 July 2020 |access-date=23 July 2020 |website=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=7 April 2020 |title=In focus: Mumbai-based Haptik which developed India's official WhatsApp chatbot for Covid-19 |url=https://tech.hindustantimes.com/tech/news/in-focus-mumbai-based-haptik-which-developed-india-s-official-whatsapp-chatbot-for-covid-19-story-SkSTENvrXVmvfM9YWEKXBP.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723162256/https://tech.hindustantimes.com/tech/news/in-focus-mumbai-based-haptik-which-developed-india-s-official-whatsapp-chatbot-for-covid-19-story-SkSTENvrXVmvfM9YWEKXBP.html |archive-date=23 July 2020 |access-date=23 July 2020 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| | contribution=ChatterBots, TinyMuds, and the Turing Test: Entering the Loebner Prize Competition | |||
| | last=Mauldin | |||
| Certain patient groups are still reluctant to use chatbots. A mixed-methods 2019 study showed that people are still hesitant to use chatbots for their healthcare due to poor understanding of the technological complexity, the lack of empathy, and concerns about cyber-security. The analysis showed that while 6% had heard of a health chatbot and 3% had experience of using it, 67% perceived themselves as likely to use one within 12 months. The majority of participants would use a health chatbot for seeking general health information (78%), booking a medical appointment (78%), and looking for local health services (80%). However, a health chatbot was perceived as less suitable for seeking results of medical tests and seeking specialist advice such as sexual health.<ref name=":02">{{Cite journal |last1=Nadarzynski |first1=Tom |last2=Miles |first2=Oliver |last3=Cowie |first3=Aimee |last4=Ridge |first4=Damien |date=1 January 2019 |title=Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-led chatbot services in healthcare: A mixed-methods study |journal=Digital Health |volume=5 |pages=2055207619871808 |doi=10.1177/2055207619871808 |pmc=6704417 |pmid=31467682}}</ref> | |||
| | first=Michael | |||
| | author-link=<!-- Michael Mauldin --> | |||
| The analysis of attitudinal variables showed that most participants reported their preference for discussing their health with doctors (73%) and having access to reliable and accurate health information (93%). While 80% were curious about new technologies that could improve their health, 66% reported only seeking a doctor when experiencing a health problem and 65% thought that a chatbot was a good idea. 30% reported dislike about talking to computers, 41% felt it would be strange to discuss health matters with a chatbot and about half were unsure if they could trust the advice given by a chatbot. Therefore, perceived trustworthiness, individual attitudes towards bots, and dislike for talking to computers are the main barriers to health chatbots.<ref name=":02" /><ref name="Biswas-20233" /> | |||
| | title=Proceedings of the Eleventh National Conference on Artificial Intelligence | |||
| | year=1994 | |||
| === Politics === | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| {{See also|Government by algorithm#AI politicians}} | |||
| | accessdate=2008-03-05 | |||
| }} () | |||
| In New Zealand, the chatbot SAM – short for ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://tuiainnovation.com/sam%2c-the-virtual-politician|title=Sam, the virtual politician|website=Tuia Innovation|access-date=9 September 2019|archive-date=1 September 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190901151417/https://tuiainnovation.com/sam%2c-the-virtual-politician|url-status=live}}</ref> – has been developed by Nick Gerritsen of Touchtech.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/news/2017/12/meet-the-worlds-first-virtual-politician|title=Meet the world's first virtual politician|first=Victoria University of|last=Wellington|date=15 December 2017|website=Victoria University of Wellington|access-date=3 January 2020|archive-date=3 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200103124942/https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/news/2017/12/meet-the-worlds-first-virtual-politician|url-status=live}}</ref> It is designed to share its political thoughts, for example on topics such as climate change, healthcare and education, etc. It talks to people through Facebook Messenger.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cnn.com/2017/11/23/tech/first-virtual-politician-trnd/index.html|title=This virtual politician wants to run for office|first=Meg|last=Wagner|website=CNN|date=23 November 2017|access-date=9 September 2019|archive-date=1 September 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190901151408/https://www.cnn.com/2017/11/23/tech/first-virtual-politician-trnd/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.engadget.com/2017/11/25/talk-with-the-first-ever-robot-politician-on-facebook-messenger/|title=Talk with the first-ever robot politician on Facebook Messenger|date=25 November 2017|website=Engadget|access-date=9 September 2019|archive-date=4 August 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190804024102/http://www.engadget.com/2017/11/25/talk-with-the-first-ever-robot-politician-on-facebook-messenger/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://medium.com/politics-ai/ai-politicians-a-revolution-in-politics-11a7e4ce90b0|title=AI-Politicians: A Revolution In Politics|first=Abishur|last=Prakash|date=8 August 2018|website=Medium|access-date=1 September 2019|archive-date=10 August 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190810020417/https://medium.com/politics-ai/ai-politicians-a-revolution-in-politics-11a7e4ce90b0|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.politiciansam.nz/ |title=SAM website |access-date=23 May 2021 |archive-date=11 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210511215358/http://politiciansam.nz/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| *{{Citation | |||
| | url=http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc439 | |||
| In 2022, the chatbot "Leader Lars" or "Leder Lars" was nominated for ] to run in the ] parliamentary election,<ref>{{cite news |last=Sternberg |first=Sarah |date=20 June 2022 |title=Danskere vil ind på den politiske scene med kunstig intelligens |trans-title=Danes want to enter the political scene with artificial intelligence |newspaper=] |url=https://jyllands-posten.dk/kultur/ECE14145385/danskere-vil-ind-paa-den-politiske-scene-med-kunstig-intelligens/ |accessdate=20 June 2022 |archive-date=20 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220620113705/https://jyllands-posten.dk/kultur/ECE14145385/danskere-vil-ind-paa-den-politiske-scene-med-kunstig-intelligens/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and was built by the artist collective Computer Lars.<ref>{{cite news |last=Diwakar |first=Amar |date=22 August 2022 |title=Can an AI-led Danish party usher in an age of algorithmic politics? |trans-title= |newspaper=] |url=https://www.trtworld.com/magazine/can-an-ai-led-danish-party-usher-in-an-age-of-algorithmic-politics-60008 |accessdate=22 August 2022 |archive-date=22 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220822173530/https://www.trtworld.com/magazine/can-an-ai-led-danish-party-usher-in-an-age-of-algorithmic-politics-60008 |url-status=live }}</ref> Leader Lars differed from earlier virtual politicians by leading a ] and by not pretending to be an objective candidate.<ref>{{cite news |last=Xiang |first=Chloe |date=13 October 2022 |title=This Danish Political Party Is Led by an AI |trans-title= |newspaper=] |url=https://www.vice.com/en/article/jgpb3p/this-danish-political-party-is-led-by-an-ai |accessdate=13 October 2022 |archive-date=13 October 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221013143116/https://www.vice.com/en/article/jgpb3p/this-danish-political-party-is-led-by-an-ai |url-status=live }}</ref> This chatbot engaged in critical discussions on politics with users from around the world.<ref>{{cite web |last=Hearing |first=Alice |date=14 October 2022 |title=A.I. chatbot is leading a Danish political party and setting its policies. Now users are grilling it for its stance on political landmines |url=https://fortune.com/2022/10/14/ai-chatbot-leader-lars-the-synthetic-party-discord-russia-ukraine-crimea-policy/ |work=Fortune |publisher= |access-date=8 December 2022 |archive-date=22 December 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221222013913/https://fortune.com/2022/10/14/ai-chatbot-leader-lars-the-synthetic-party-discord-russia-ukraine-crimea-policy/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | title=RFC 439, PARRY Encounters the DOCTOR | |||
| In ], the state government has launched a chatbot for its Aaple Sarkar platform,<ref>{{Cite web|title=Maharashtra government launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot to provide info on 1,400 public services|url=https://www.cnbctv18.com/technology/maharashtra-government-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot-to-provide-info-on-1400-public-services-2490621.htm|access-date=23 July 2020|website=]|date=5 March 2019|archive-date=23 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723165459/https://www.cnbctv18.com/technology/maharashtra-government-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot-to-provide-info-on-1400-public-services-2490621.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> which provides conversational access to information regarding public services managed.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Government of Maharashtra launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot with Haptik|work=The Economic Times|url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/government-of-maharashtra-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot-with-haptik/articleshow/68268917.cms?from=mdr|access-date=23 July 2020|archive-date=16 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201216043739/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/government-of-maharashtra-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot-with-haptik/articleshow/68268917.cms?from=mdr|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Aggarwal|first=Varun|title=Maharashtra launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot|url=https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/maharashtra-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot/article26438199.ece|access-date=23 July 2020|website=]|date=5 March 2019|archive-date=23 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723160158/https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/maharashtra-launches-aaple-sarkar-chatbot/article26438199.ece|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Toys === | |||
| Chatbots have also been incorporated into devices not primarily meant for computing, such as toys.<ref name="virtualagentchat">{{Cite web|url=https://virtualagentchat.com/2015/02/23/conversational-toys-the-latest-trend-in-speech-technology/|title=Conversational Toys – The Latest Trend in Speech Technology|last=Amy|date=23 February 2015|website=Virtual Agent Chat|access-date=11 August 2016|archive-date=21 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180221035430/https://virtualagentchat.com/2015/02/23/conversational-toys-the-latest-trend-in-speech-technology/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ''Hello ]'' is an Internet-connected version of the doll that uses a chatbot provided by the company ToyTalk,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fastcompany.com/3042430/most-creative-people/using-toytalk-technology-new-hello-barbie-will-have-real-conversations-|title=Using Toy-talk Technology, New Hello Barbie Will Have Real Conversations With Kids |website=Fast Company|last1=Nagy|first1=Evie|date=13 February 2015|access-date=18 March 2015|archive-date=15 March 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150315034733/http://www.fastcompany.com/3042430/most-creative-people/using-toytalk-technology-new-hello-barbie-will-have-real-conversations-|url-status=live}}</ref> which previously used the chatbot for a range of smartphone-based characters for children.<ref>{{Triangulation|179|Oren Jacob, the co-founder and CEO of ToyTalk}}</ref> These characters' behaviors are constrained by a set of rules that in effect emulate a particular character and produce a storyline.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://patents.google.com/patent/US20140032471/en|title=Artificial intelligence script tool|access-date=12 December 2021|archive-date=12 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211212003052/https://patents.google.com/patent/US20140032471/en|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] doll was marketed as a line of {{convert|18|in|cm|adj=on}} dolls which uses ] technology in conjunction with an ] or ] mobile app to recognize the child's speech and have a conversation. Like the Hello Barbie doll, it attracted controversy due to vulnerabilities with the doll's ] stack and its use of data collected from the child's speech. | |||
| IBM's ] has been used as the basis for chatbot-based educational toys for companies such as ''CogniToys,''<ref name="virtualagentchat" /> intended to interact with children for educational purposes.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Takahashi|first1=Dean|title=Elemental's smart connected toy taps IBM's Watson supercomputer for its brains|url=https://venturebeat.com/2015/02/23/elementals-smart-connected-toy-cognitoys-taps-ibms-watson-supercomputer-for-its-brains/|website=Venture Beat|date=23 February 2015|access-date=15 May 2015|archive-date=20 May 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150520103335/http://venturebeat.com/2015/02/23/elementals-smart-connected-toy-cognitoys-taps-ibms-watson-supercomputer-for-its-brains/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Malicious use === | |||
| Malicious chatbots are frequently used to fill ] with spam and advertisements by mimicking human behavior and conversations or to entice people into revealing personal information, such as bank account numbers. They were commonly found on ], ], ] and other ] protocols. There has also been a published report of a chatbot used in a fake personal ad on a dating service's website.<ref>{{cite web|work=Scientific American: Mind|date=October 2007|pages=16–17|url=http://drrobertepstein.com/downloads/FROM_RUSSIA_WITH_LOVE-Epstein-Sci_Am_Mind-Oct-Nov2007.pdf|title=From Russia With Love: How I got fooled (and somewhat humiliated) by a computer|access-date=9 December 2007|author=Epstein, Robert|archive-date=19 October 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101019210430/http://drrobertepstein.com/downloads/FROM_RUSSIA_WITH_LOVE-Epstein-Sci_Am_Mind-Oct-Nov2007.pdf|url-status=live}} | |||
| Psychologist ] reports how he was initially fooled by a chatterbot posing as an attractive girl in a personal ad he answered on a dating website. In the ad, the girl portrayed herself as being in Southern California and then soon revealed, in poor English, that she was actually in Russia. He became suspicious after a couple of months of email exchanges, sent her an email test of gibberish, and she still replied in general terms. The dating website is not named.</ref> | |||
| ], an AI chatbot designed to learn from previous interaction, caused major controversy due to it being targeted by internet trolls on Twitter. Soon after its launch, the bot was exploited, and with its "repeat after me" capability, it started releasing racist, sexist, and controversial responses to Twitter users.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Neff |first1=Gina |last2=Nagy |first2=Peter |date=2016-10-12 |title=Automation, Algorithms, and Politics{{!}} Talking to Bots: Symbiotic Agency and the Case of Tay |url=https://ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/6277 |journal=International Journal of Communication |language=en |volume=10 |pages=17 |issn=1932-8036}}</ref> This suggests that although the bot learned effectively from experience, adequate protection was not put in place to prevent misuse.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Bird |first1=Jordan J. |last2=Ekart |first2=Aniko |last3=Faria |first3=Diego R. |title=Advances in Computational Intelligence Systems |chapter=Learning from Interaction: An Intelligent Networked-Based Human-Bot and Bot-Bot Chatbot System |series=Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing |date=June 2018 |volume=840 |publisher=Springer |location=Nottingham, UK |isbn=978-3-319-97982-3 |pages=179–190 |doi=10.1007/978-3-319-97982-3_15 |s2cid=52069140 |edition=1st}}</ref> | |||
| If a text-sending ] can pass itself off as a human instead of a chatbot, its message would be more credible. Therefore, human-seeming chatbots with well-crafted online identities could start scattering fake news that seems plausible, for instance making false claims during an election. With enough chatbots, it might be even possible to achieve artificial ].<ref>{{cite web | url= https://www.sciencenews.org/article/twitter-bots-fake-news-2016-election | author= Temming, Maria | title= How Twitter bots get people to spread fake news | work= Science News | date= 20 November 2018 | access-date= 20 November 2018 | archive-date= 27 November 2018 | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20181127191003/https://www.sciencenews.org/article/twitter-bots-fake-news-2016-election | url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | |||
| | author = Epp, Len | |||
| | url = https://lenepp.medium.com/five-potential-malicious-uses-for-chatbots-a15f4955fba7 | |||
| | title = Five Potential Malicious Uses For Chatbots | |||
| | date = 11 May 2016 | access-date = 24 February 2023 | archive-date = 24 February 2023 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230224041222/https://lenepp.medium.com/five-potential-malicious-uses-for-chatbots-a15f4955fba7 | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| === Data security === | |||
| ] is one of the major concerns of chatbot technologies. Security threats and system vulnerabilities are weaknesses that are often exploited by malicious users. Storage of user data and past communication, that is highly valuable for training and development of chatbots, can also give rise to security threats.<ref name="Hasal-2021">{{Cite journal |last1=Hasal |first1=Martin |last2=Nowaková |first2=Jana |last3=Ahmed Saghair |first3=Khalifa |last4=Abdulla |first4=Hussam |last5=Snášel |first5=Václav |last6=Ogiela |first6=Lidia |date=2021-10-10 |title=Chatbots: Security, privacy, data protection, and social aspects |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cpe.6426 |journal=Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience |language=en |volume=33 |issue=19 |doi=10.1002/cpe.6426 |issn=1532-0626|hdl=10084/145153 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> Chatbots operating on third-party networks may be subject to various security issues if owners of the third-party applications have policies regarding user data that differ from those of the chatbot.<ref name="Hasal-2021" /> Security threats can be reduced or prevented by incorporating protective mechanisms. User ], chat ], and self-destructing messages are some effective solutions to resist potential security threats.<ref name="Hasal-2021" /> | |||
| == Limitations of chatbots == | |||
| {{expand section|date=December 2024}} | |||
| Chatbots have difficulty managing non-linear conversations that must go back and forth on a topic with a user.<ref>{{citation |last1=Grudin |first1=Jonathan |title=Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems – CHI '19 |pages=209–219 |year=2019 |chapter=Chatbots, Humbots, and the Quest for Artificial General Intelligence |publisher=ACM CHI 2020 |doi=10.1145/3290605.3300439 |isbn=978-1-4503-5970-2 |s2cid=140274744 |last2=Jacques |first2=Richard |author-link=Jonathan Grudin}}</ref> | |||
| ]s are more versatile, but require a large amount of conversational data to train. These modeles generate new responses word by word based on user input, are usually trained on a large dataset of natural-language phrases.<ref name="Caldarini-20223" /> They sometimes provide plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers. They can make up names, dates, historical events, and even simple math problems.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Stover |first=Dawn |date=2023-09-03 |title=Will AI make us crazy? |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00963402.2023.2245247 |journal=Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists |language=en |volume=79 |issue=5 |pages=299–303 |doi=10.1080/00963402.2023.2245247 |bibcode=2023BuAtS..79e.299S |issn=0096-3402}}</ref> When large language models produce coherent-sounding but inaccurate or fabricated content, this is referred to as "]". When humans use and apply chatbot content contaminated with hallucinations, this results in "botshit".<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Hannigan |first1=Timothy R. |last2=McCarthy |first2=Ian P. |last3=Spicer |first3=André |date=2024-03-20 |title=Beware of botshit: How to manage the epistemic risks of generative chatbots |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0007681324000272 |journal=Business Horizons |volume=67 |issue=5 |pages=471–486 |doi=10.1016/j.bushor.2024.03.001 |issn=0007-6813}}</ref> Given the increasing adoption and use of chatbots for generating content, there are concerns that this technology will significantly reduce the cost it takes humans to generate ].<ref>{{Cite news |date=2023-01-06 |title=Transcript: Ezra Klein Interviews Gary Marcus |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2023/01/06/podcasts/transcript-ezra-klein-interviews-gary-marcus.html |access-date=2024-04-21 |work=The New York Times |language=en-US |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> | |||
| == Impact on jobs == | |||
| Chatbots and technology in general used to automate repetitive tasks. But advanced chatbots like ChatGPT are also targeting high-paying, creative, and knowledge-based jobs, raising concerns about workforce disruption and quality trade-offs in favor of cost-cutting.<ref>{{Cite news |date=June 2, 2023 |title=ChatGPT took their jobs. Now they walk dogs and fix air conditioners. |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/06/02/ai-taking-jobs/ |newspaper=The Washington Post}}</ref> | |||
| Chatbots are increasingly used by ], to handle customer interactions efficiently, reducing reliance on large ] and lowering operational costs.{{cn|date=December 2024}} | |||
| ], the task of designing and refining prompts (inputs) leading to desired AI-generated responses has quickly gained significant demand with the advent of large language models,<ref>{{Cite news |date=March 12, 2024 |title=The Future Belongs to Prompt Engineers |url=https://www.inc.com/howard-tullman/the-future-belongs-to-prompt-engineers.html |work=Inc.}}</ref> although the viability of this job is questioned due to new techniques for automating prompt engineering.<ref>{{Cite web |date=November 19, 2024 |title=Is The End of Prompt Engineering Here? |url=https://www.theinformation.com/articles/is-the-end-of-prompt-engineering-here |access-date=2024-12-14 |website=The Information |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| == Impact on the environment == | |||
| {{see also|Environmental impacts of artificial intelligence|Data_center#Energy_use|}} | |||
| Generative AI uses a high amount of ]. Due to reliance on ]s in its ], this increases ], ], and ]. In 2023, a question to ] consumed on average 10 times as much energy as a Google search.<ref>{{cite web |title=AI is poised to drive 160% increase in data center power demand |url=https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/AI-poised-to-drive-160-increase-in-power-demand |date=14 May 2024 |publisher=] |access-date=2 December 2024}}</ref> Data centres in general, and those used for AI tasks specifically, consume significant amounts of water for cooling.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Sreedhar |first1=Nitin |title=AI and its carbon footprint: How much water does ChatGPT consume? |url=https://lifestyle.livemint.com/news/big-story/ai-carbon-footprint-openai-chatgpt-water-google-microsoft-111697802189371.html |website=Mint Lounge}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Crownhart |first1=Casey |title=AI is an energy hog. This is what it means for climate change. |url=https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/05/23/1092777/ai-is-an-energy-hog-this-is-what-it-means-for-climate-change/ |website=MIT Technology Review}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{Portal|Linguistics|Programming}} | |||
| <!-- Please keep entries in alphabetical order & add a short description ] --> | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <!-- please keep entries in alphabetical order --> | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{Reflist|refs= | |||
| <ref name="comphis">{{Citation | author=Computer History Museum | title=Exhibits | chapter=Internet History – 1970's | year=2006 | publisher=] | access-date=5 March 2008 | chapter-url=http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_70s.shtml | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080221093646/http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_70s.shtml | archive-date=21 February 2008 }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Güzeldere">{{Citation | last1=Güzeldere | first1=Güven | title=Constructions of the Mind | date=24 July 1995 | url=http://www.stanford.edu/group/SHR/4-2/text/dialogues.html | last2=Franchi | first2=Stefano | author-link=<!--Güven Güzeldere--> | series=SEHR | journal=Stanford Humanities Review | volume=4 | issue=2 | publisher=] | access-date=5 March 2008 | archive-date=11 July 2007 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070711204557/http://www.stanford.edu/group/SHR/4-2/text/dialogues.html | url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Mauldin>{{Citation | url=http://www.aaai.org/Library/AAAI/1994/aaai94-003.php | contribution=ChatterBots, TinyMuds, and the Turing Test: Entering the Loebner Prize Competition | last=Mauldin | first=Michael | author-link=<!--same--> | title=Proceedings of the Eleventh National Conference on Artificial Intelligence | year=1994 | publisher=] | access-date=5 March 2008 | archive-date=13 December 2007 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071213172751/http://www.aaai.org/Library/AAAI/1994/aaai94-003.php | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="rfc0439">{{cite IETF | |||
| | rfc=439 | |||
| | title=PARRY Encounters the DOCTOR | |||
| | author=Network Working Group | | author=Network Working Group | ||
| | work=] | | work=] | ||
| | publisher=] | |||
| | year=1973 | | year=1973 | ||
| | publisher=] | |||
| | accessdate=2008-03-05 | |||
| }} – Transcript of a session between Parry and Eliza. (This is ''not'' the dialogue from the ICCC, which took place 24–26 October 1972, whereas this session is from 18 September 1972.)</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Sondheim>{{Citation | |||
| |url = http://www.nettime.org/Lists-Archives/nettime-l-9707/msg00059.html | |||
| |title = <nettime> Important Documents from the Early Internet (1972) | |||
| |last = Sondheim | |||
| |first = Alan J | |||
| |year = 1997 | |||
| |publisher = nettime.org | |||
| |access-date = 5 March 2008 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080613072047/http://www.nettime.org/Lists-Archives/nettime-l-9707/msg00059.html | |||
| |archive-date = 13 June 2008 | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Turing>{{Citation | |||
| | last = Turing | first = Alan | author-link=Alan Turing | year=1950 | |||
| | title = Computing Machinery and Intelligence | |||
| | journal = Mind | volume = 59 | issue = 236 | pages = 433–460 | doi=10.1093/mind/lix.236.433 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Weizenbaum>{{Citation | |||
| | last = Weizenbaum | first = Joseph | author-link = Joseph Weizenbaum | title = ELIZA – A Computer Program For the Study of Natural Language Communication Between Man And Machine | |||
| | journal = ] | volume = 9| issue = 1 |date = January 1966| pages = 36–45 | doi = 10.1145/365153.365168 | |||
| | s2cid = 1896290 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| == Further reading == | |||
| * Gertner, Jon. (2023) "Misplaced Pages's Moment of Truth: Can the online encyclopedia help teach A.I. chatbots to get their facts right — without destroying itself in the process?" ''New York Times Magazine'' (18 July 2023) | |||
| *{{Citation | *{{Citation | ||
| | last=Searle| first=John | author-link=John Searle | year=1980 | |||
| | url=http://www.nettime.org/Lists-Archives/nettime-l-9707/msg00059.html | |||
| | url = http://members.aol.com/NeoNoetics/MindsBrainsPrograms.html | |||
| | title=<nettime> Important Documents from the Early Internet (1972) | |||
| | title = Minds, Brains and Programs | |||
| | last=Sondheim | |||
| | journal = Behavioral and Brain Sciences | volume = 3| issue = 3| pages= 417–457 | |||
| | first=Alan J | |||
| | doi=10.1017/S0140525X00005756 | |||
| | year=1997 | |||
| | s2cid=55303721 | |||
| | publisher=nettime.org | |||
| | accessdate=2008-03-05 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| *{{Cite book|title=Designing bots: Creating conversational experiences|last=Shevat|first=Amir|publisher=O'Reilly Media|year=2017|isbn=978-1-4919-7482-7|edition=First|location=Sebastopol, CA|oclc=962125282}} | |||
| * Vincent, James, "Horny Robot Baby Voice: James Vincent on AI chatbots", '']'', vol. 46, no. 19 (10 October 2024), pp. 29–32. " programs are made possible by new technologies but rely on the timelelss human tendency to ]." (p. 29.) | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| *{{commons category-inline}} | |||
| *{{dmoz|Computers/Artificial_Intelligence/Natural_Language/Chatterbots/|Chatterbots}} | |||
| *{{wikibooks inline|Conversational bots}} | |||
| * International chatterbots directory | |||
| {{Natural Language Processing}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:28, 5 January 2025
Program that simulates conversation For the bot-creation software, see ChatBot. For bots on Internet Relay Chat, see IRC bot.
| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
| Paradigms |
Problems
|
|
Supervised learning (classification • regression) |
| Clustering |
| Dimensionality reduction |
| Structured prediction |
| Anomaly detection |
| Artificial neural network |
| Reinforcement learning |
| Learning with humans |
| Model diagnostics |
| Mathematical foundations |
| Journals and conferences |
| Related articles |
A chatbot (originally chatterbot) is a software application or web interface designed to have textual or spoken conversations. Modern chatbots are typically online and use generative artificial intelligence systems that are capable of maintaining a conversation with a user in natural language and simulating the way a human would behave as a conversational partner. Such chatbots often use deep learning and natural language processing, but simpler chatbots have existed for decades.
Although chatbots have existed since the late 1960s, the field gained widespread attention in the early 2020s due to the popularity of OpenAI's ChatGPT, followed by alternatives such as Microsoft's Copilot and Google's Gemini. Such examples reflect the recent practice of basing such products upon broad foundational large language models, such as GPT-4 or the Gemini language model, that get fine-tuned so as to target specific tasks or applications (i.e., simulating human conversation, in the case of chatbots). Chatbots can also be designed or customized to further target even more specific situations and/or particular subject-matter domains.
A major area where chatbots have long been used is in customer service and support, with various sorts of virtual assistants. Companies spanning a wide range of industries have begun using the latest generative artificial intelligence technologies to power more advanced developments in such areas.
History
Turing test
In 1950, Alan Turing's famous article "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" was published, which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence. This criterion depends on the ability of a computer program to impersonate a human in a real-time written conversation with a human judge to the extent that the judge is unable to distinguish reliably—on the basis of the conversational content alone—between the program and a real human.
Eliza
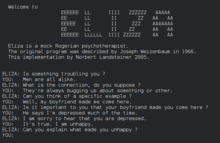
The notoriety of Turing's proposed test stimulated great interest in Joseph Weizenbaum's program ELIZA, published in 1966, which seemed to be able to fool users into believing that they were conversing with a real human. However Weizenbaum himself did not claim that ELIZA was genuinely intelligent, and the introduction to his paper presented it more as a debunking exercise:
In artificial intelligence, machines are made to behave in wondrous ways, often sufficient to dazzle even the most experienced observer. But once a particular program is unmasked, once its inner workings are explained, its magic crumbles away; it stands revealed as a mere collection of procedures. The observer says to himself "I could have written that". With that thought, he moves the program in question from the shelf marked "intelligent", to that reserved for curios. The object of this paper is to cause just such a re-evaluation of the program about to be "explained". Few programs ever needed it more.
ELIZA's key method of operation involves the recognition of clue words or phrases in the input, and the output of the corresponding pre-prepared or pre-programmed responses that can move the conversation forward in an apparently meaningful way (e.g. by responding to any input that contains the word 'MOTHER' with 'TELL ME MORE ABOUT YOUR FAMILY'). Thus an illusion of understanding is generated, even though the processing involved has been merely superficial. ELIZA showed that such an illusion is surprisingly easy to generate because human judges are ready to give the benefit of the doubt when conversational responses are capable of being interpreted as "intelligent".
Interface designers have come to appreciate that humans' readiness to interpret computer output as genuinely conversational—even when it is actually based on rather simple pattern-matching—can be exploited for useful purposes. Most people prefer to engage with programs that are human-like, and this gives chatbot-style techniques a potentially useful role in interactive systems that need to elicit information from users, as long as that information is relatively straightforward and falls into predictable categories. Thus, for example, online help systems can usefully employ chatbot techniques to identify the area of help that users require, potentially providing a "friendlier" interface than a more formal search or menu system. This sort of usage holds the prospect of moving chatbot technology from Weizenbaum's "shelf ... reserved for curios" to that marked "genuinely useful computational methods".
Early chatbots
Among the most notable early chatbots are ELIZA (1966) and PARRY (1972). More recent notable programs include A.L.I.C.E., Jabberwacky and D.U.D.E (Agence Nationale de la Recherche and CNRS 2006). While ELIZA and PARRY were used exclusively to simulate typed conversation, many chatbots now include other functional features, such as games and web searching abilities. In 1984, a book called The Policeman's Beard is Half Constructed was published, allegedly written by the chatbot Racter (though the program as released would not have been capable of doing so).
From 1978 to some time after 1983, the CYRUS project led by Janet Kolodner constructed a chatbot simulating Cyrus Vance (57th United States Secretary of State). It used case-based reasoning, and updated its database daily by parsing wire news from United Press International. The program was unable to process the news items subsequent to the surprise resignation of Cyrus Vance in April 1980, and the team constructed another chatbot simulating his successor, Edmund Muskie.
One pertinent field of AI research is natural-language processing. Usually, weak AI fields employ specialized software or programming languages created specifically for the narrow function required. For example, A.L.I.C.E. uses a markup language called AIML, which is specific to its function as a conversational agent, and has since been adopted by various other developers of, so-called, Alicebots. Nevertheless, A.L.I.C.E. is still purely based on pattern matching techniques without any reasoning capabilities, the same technique ELIZA was using back in 1966. This is not strong AI, which would require sapience and logical reasoning abilities.
Jabberwacky learns new responses and context based on real-time user interactions, rather than being driven from a static database. Some more recent chatbots also combine real-time learning with evolutionary algorithms that optimize their ability to communicate based on each conversation held.
Chatbot competitions focus on the Turing test or more specific goals. Two such annual contests are the Loebner Prize and The Chatterbox Challenge (the latter has been offline since 2015, however, materials can still be found from web archives).
DBpedia created a chatbot during the GSoC of 2017. It can communicate through Facebook Messenger (see Master of Code Global article).
Modern chatbots based on large language models
Modern chatbots like ChatGPT are often based on large language models called generative pre-trained transformers (GPT). They are based on a deep learning architecture called the transformer, which contains artificial neural networks. They learn how to generate text by being trained on a large text corpus, which provides a solid foundation for the model to perform well on downstream tasks with limited amounts of task-specific data. Despite criticism of its accuracy and tendency to "hallucinate"—that is, to confidently output false information and even cite non-existent sources—ChatGPT has gained attention for its detailed responses and historical knowledge. Another example is BioGPT, developed by Microsoft, which focuses on answering biomedical questions. In November 2023, Amazon announced a new chatbot, called Q, for people to use at work.
Application
| This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (December 2024) |
Messaging apps
Many companies' chatbots run on messaging apps or simply via SMS. They are used for B2C customer service, sales and marketing.
In 2016, Facebook Messenger allowed developers to place chatbots on their platform. There were 30,000 bots created for Messenger in the first six months, rising to 100,000 by September 2017.
Since September 2017, this has also been as part of a pilot program on WhatsApp. Airlines KLM and Aeroméxico both announced their participation in the testing; both airlines had previously launched customer services on the Facebook Messenger platform.
The bots usually appear as one of the user's contacts, but can sometimes act as participants in a group chat.
Many banks, insurers, media companies, e-commerce companies, airlines, hotel chains, retailers, health care providers, government entities, and restaurant chains have used chatbots to answer simple questions, increase customer engagement, for promotion, and to offer additional ways to order from them. Chatbots are also used in market research to collect short survey responses.
A 2017 study showed 4% of companies used chatbots. According to a 2016 study, 80% of businesses said they intended to have one by 2020.
As part of company apps and websites
Previous generations of chatbots were present on company websites, e.g. Ask Jenn from Alaska Airlines which debuted in 2008 or Expedia's virtual customer service agent which launched in 2011. The newer generation of chatbots includes IBM Watson-powered "Rocky", introduced in February 2017 by the New York City-based e-commerce company Rare Carat to provide information to prospective diamond buyers.
Chatbot sequences
Used by marketers to script sequences of messages, very similar to an autoresponder sequence. Such sequences can be triggered by user opt-in or the use of keywords within user interactions. After a trigger occurs a sequence of messages is delivered until the next anticipated user response. Each user response is used in the decision tree to help the chatbot navigate the response sequences to deliver the correct response message.
Company internal platforms
Companies have used chatbots for customer support, human resources, or in Internet-of-Things (IoT) projects. Overstock.com, for one, has reportedly launched a chatbot named Mila to attempt to automate certain processes when customer service employees request sick leave. Other large companies such as Lloyds Banking Group, Royal Bank of Scotland, Renault and Citroën are now using chatbots instead of call centres with humans to provide a first point of contact. In large companies, like in hospitals and aviation organizations, chatbots are also used to share information within organizations, and to assist and replace service desks.
Customer service
Chatbots have been proposed as a replacement for customer service departments.
Deep learning techniques can be incorporated into chatbot applications to allow them to map conversations between users and customer service agents, especially in social media.
In 2019, Gartner predicted that by 2021, 15% of all customer service interactions globally will be handled completely by AI. A study by Juniper Research in 2019 estimates retail sales resulting from chatbot-based interactions will reach $112 billion by 2023.
In 2016, Russia-based Tochka Bank launched a chatbot on Facebook for a range of financial services, including a possibility of making payments. In July 2016, Barclays Africa also launched a Facebook chatbot.
In 2023, US-based National Eating Disorders Association replaced its human helpline staff with a chatbot but had to take it offline after users reported receiving harmful advice from it.
Healthcare
See also: Artificial intelligence in healthcareChatbots are also appearing in the healthcare industry. A study suggested that physicians in the United States believed that chatbots would be most beneficial for scheduling doctor appointments, locating health clinics, or providing medication information.
ChatGPT is able to answer user queries related to health promotion and disease prevention such as screening and vaccination. WhatsApp has teamed up with the World Health Organization (WHO) to make a chatbot service that answers users' questions on COVID-19.
In 2020, the Government of India launched a chatbot called MyGov Corona Helpdesk, that worked through WhatsApp and helped people access information about the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
Certain patient groups are still reluctant to use chatbots. A mixed-methods 2019 study showed that people are still hesitant to use chatbots for their healthcare due to poor understanding of the technological complexity, the lack of empathy, and concerns about cyber-security. The analysis showed that while 6% had heard of a health chatbot and 3% had experience of using it, 67% perceived themselves as likely to use one within 12 months. The majority of participants would use a health chatbot for seeking general health information (78%), booking a medical appointment (78%), and looking for local health services (80%). However, a health chatbot was perceived as less suitable for seeking results of medical tests and seeking specialist advice such as sexual health.
The analysis of attitudinal variables showed that most participants reported their preference for discussing their health with doctors (73%) and having access to reliable and accurate health information (93%). While 80% were curious about new technologies that could improve their health, 66% reported only seeking a doctor when experiencing a health problem and 65% thought that a chatbot was a good idea. 30% reported dislike about talking to computers, 41% felt it would be strange to discuss health matters with a chatbot and about half were unsure if they could trust the advice given by a chatbot. Therefore, perceived trustworthiness, individual attitudes towards bots, and dislike for talking to computers are the main barriers to health chatbots.
Politics
See also: Government by algorithm § AI politiciansIn New Zealand, the chatbot SAM – short for Semantic Analysis Machine – has been developed by Nick Gerritsen of Touchtech. It is designed to share its political thoughts, for example on topics such as climate change, healthcare and education, etc. It talks to people through Facebook Messenger.
In 2022, the chatbot "Leader Lars" or "Leder Lars" was nominated for The Synthetic Party to run in the Danish parliamentary election, and was built by the artist collective Computer Lars. Leader Lars differed from earlier virtual politicians by leading a political party and by not pretending to be an objective candidate. This chatbot engaged in critical discussions on politics with users from around the world.
In India, the state government has launched a chatbot for its Aaple Sarkar platform, which provides conversational access to information regarding public services managed.
Toys
Chatbots have also been incorporated into devices not primarily meant for computing, such as toys.
Hello Barbie is an Internet-connected version of the doll that uses a chatbot provided by the company ToyTalk, which previously used the chatbot for a range of smartphone-based characters for children. These characters' behaviors are constrained by a set of rules that in effect emulate a particular character and produce a storyline.
The My Friend Cayla doll was marketed as a line of 18-inch (46 cm) dolls which uses speech recognition technology in conjunction with an Android or iOS mobile app to recognize the child's speech and have a conversation. Like the Hello Barbie doll, it attracted controversy due to vulnerabilities with the doll's Bluetooth stack and its use of data collected from the child's speech.
IBM's Watson computer has been used as the basis for chatbot-based educational toys for companies such as CogniToys, intended to interact with children for educational purposes.
Malicious use
Malicious chatbots are frequently used to fill chat rooms with spam and advertisements by mimicking human behavior and conversations or to entice people into revealing personal information, such as bank account numbers. They were commonly found on Yahoo! Messenger, Windows Live Messenger, AOL Instant Messenger and other instant messaging protocols. There has also been a published report of a chatbot used in a fake personal ad on a dating service's website.
Tay, an AI chatbot designed to learn from previous interaction, caused major controversy due to it being targeted by internet trolls on Twitter. Soon after its launch, the bot was exploited, and with its "repeat after me" capability, it started releasing racist, sexist, and controversial responses to Twitter users. This suggests that although the bot learned effectively from experience, adequate protection was not put in place to prevent misuse.
If a text-sending algorithm can pass itself off as a human instead of a chatbot, its message would be more credible. Therefore, human-seeming chatbots with well-crafted online identities could start scattering fake news that seems plausible, for instance making false claims during an election. With enough chatbots, it might be even possible to achieve artificial social proof.
Data security
Data security is one of the major concerns of chatbot technologies. Security threats and system vulnerabilities are weaknesses that are often exploited by malicious users. Storage of user data and past communication, that is highly valuable for training and development of chatbots, can also give rise to security threats. Chatbots operating on third-party networks may be subject to various security issues if owners of the third-party applications have policies regarding user data that differ from those of the chatbot. Security threats can be reduced or prevented by incorporating protective mechanisms. User authentication, chat End-to-end encryption, and self-destructing messages are some effective solutions to resist potential security threats.
Limitations of chatbots
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2024) |
Chatbots have difficulty managing non-linear conversations that must go back and forth on a topic with a user.
Large language models are more versatile, but require a large amount of conversational data to train. These modeles generate new responses word by word based on user input, are usually trained on a large dataset of natural-language phrases. They sometimes provide plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers. They can make up names, dates, historical events, and even simple math problems. When large language models produce coherent-sounding but inaccurate or fabricated content, this is referred to as "hallucinations". When humans use and apply chatbot content contaminated with hallucinations, this results in "botshit". Given the increasing adoption and use of chatbots for generating content, there are concerns that this technology will significantly reduce the cost it takes humans to generate misinformation.
Impact on jobs
Chatbots and technology in general used to automate repetitive tasks. But advanced chatbots like ChatGPT are also targeting high-paying, creative, and knowledge-based jobs, raising concerns about workforce disruption and quality trade-offs in favor of cost-cutting.
Chatbots are increasingly used by small and medium enterprises, to handle customer interactions efficiently, reducing reliance on large call centers and lowering operational costs.
Prompt engineering, the task of designing and refining prompts (inputs) leading to desired AI-generated responses has quickly gained significant demand with the advent of large language models, although the viability of this job is questioned due to new techniques for automating prompt engineering.
Impact on the environment
See also: Environmental impacts of artificial intelligence and Data_center § Energy_useGenerative AI uses a high amount of electric power. Due to reliance on fossil fuels in its generation, this increases air pollution, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. In 2023, a question to ChatGPT consumed on average 10 times as much energy as a Google search. Data centres in general, and those used for AI tasks specifically, consume significant amounts of water for cooling.
See also
- Applications of artificial intelligence
- Artificial human companion
- Artificial intelligence and elections
- Autonomous agent
- Conversational user interface
- Dead Internet theory
- Friendly artificial intelligence
- Hybrid intelligent system
- Intelligent agent
- Internet bot
- List of chatbots
- Multi-agent system
- Social bot
- Software agent
- Software bot
- Stochastic parrot
- Technological unemployment
- Twitterbot
References
- Mauldin, Michael (1994), "ChatterBots, TinyMuds, and the Turing Test: Entering the Loebner Prize Competition", Proceedings of the Eleventh National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, archived from the original on 13 December 2007, retrieved 5 March 2008
- "What is a chatbot?". techtarget.com. Archived from the original on 2 November 2010. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- ^ Caldarini, Guendalina; Jaf, Sardar; McGarry, Kenneth (2022). "A Literature Survey of Recent Advances in Chatbots". Information. 13 (1). MDPI: 41. arXiv:2201.06657. doi:10.3390/info13010041.
- Adamopoulou, Eleni; Moussiades, Lefteris (2020). "Chatbots: History, technology, and applications". Machine Learning with Applications. 2: 100006. doi:10.1016/j.mlwa.2020.100006.
- Hu, Krystal (2 February 2023). "ChatGPT sets record for fastest-growing user base - analyst note". Reuters.
- Hines, Kristi (4 June 2023). "History Of ChatGPT: A Timeline Of The Meteoric Rise Of Generative AI Chatbots". Search Engine Journal. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- "ChatGPT vs. Bing vs. Google Bard: Which AI is the Most Helpful?".
- ^ Gupta, Aman (21 March 2023). "GPT-4 takes the world by storm - List of companies that integrated the chatbot". mint.
- "2017 Messenger Bot Landscape, a Public Spreadsheet Gathering 1000+ Messenger Bots". 3 May 2017. Archived from the original on 2 February 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- Turing, Alan (1950), "Computing Machinery and Intelligence", Mind, 59 (236): 433–460, doi:10.1093/mind/lix.236.433
- ^ Weizenbaum, Joseph (January 1966), "ELIZA – A Computer Program For the Study of Natural Language Communication Between Man And Machine", Communications of the ACM, 9 (1): 36–45, doi:10.1145/365153.365168, S2CID 1896290
- Güzeldere, Güven; Franchi, Stefano (24 July 1995), "Constructions of the Mind", Stanford Humanities Review, SEHR, 4 (2), Stanford University, archived from the original on 11 July 2007, retrieved 5 March 2008
- Computer History Museum (2006), "Internet History – 1970's", Exhibits, Computer History Museum, archived from the original on 21 February 2008, retrieved 5 March 2008
- Sondheim, Alan J (1997), <nettime> Important Documents from the Early Internet (1972), nettime.org, archived from the original on 13 June 2008, retrieved 5 March 2008
- Network Working Group (1973). "PARRY Encounters the DOCTOR". Internet Engineering Task Force. Internet Society. doi:10.17487/RFC0439. RFC 439. – Transcript of a session between Parry and Eliza. (This is not the dialogue from the ICCC, which took place 24–26 October 1972, whereas this session is from 18 September 1972.)
- The Policeman's Beard is Half Constructed Archived 4 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine. everything2.com. 13 November 1999
- Kolodner, Janet L. Memory organization for natural language data-base inquiry. Advanced Research Projects Agency, 1978.
- ^ Kolodner, Janet L. (1 October 1983). "Maintaining organization in a dynamic long-term memory". Cognitive Science. 7 (4): 243–280. doi:10.1016/S0364-0213(83)80001-9 (inactive 5 January 2025). ISSN 0364-0213.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2025 (link) - Dennett, Daniel C. (2004), Teuscher, Christof (ed.), "Can Machines Think?", Alan Turing: Life and Legacy of a Great Thinker, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 295–316, doi:10.1007/978-3-662-05642-4_12, ISBN 978-3-662-05642-4, retrieved 23 July 2023
- "Chat Robots Simiulate People". 11 October 2015.
- "DBpedia Chatbot". chat.dbpedia.org. Archived from the original on 8 September 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
- "Meet the DBpedia Chatbot | DBpedia". wiki.dbpedia.org. 22 August 2018. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Meet the DBpedia Chatbot". dbpedia.org. 22 August 2018. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- Luo, Renqian; Sun, Liai; Xia, Yingce; Qin, Tao; Zhang, Sheng; Poon, Hoifung; Liu, Tie-Yan; et al. (2022). "BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining". Brief Bioinform. 23 (6). arXiv:2210.10341. doi:10.1093/bib/bbac409. PMID 36156661.
- Bastian, Matthias (29 January 2023). "BioGPT is a Microsoft language model trained for biomedical tasks". The Decoder. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- Novet, Jordan (28 November 2023). "Amazon announces Q, an AI chatbot for businesses". CNBC. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- Beaver, Laurie (July 2016). "The Chatbots Explainer". Business Insider. BI Intelligence. Archived from the original on 3 May 2019. Retrieved 4 November 2019.
- "Facebook Messenger Hits 100,000 bots". 18 April 2017. Archived from the original on 22 September 2017. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- "KLM claims airline first with WhatsApp Business Platform". www.phocuswire.com. Archived from the original on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- Forbes Staff (26 October 2017). "Aeroméxico te atenderá por WhatsApp durante 2018". Archived from the original on 2 July 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- "Podrás hacer 'check in' y consultar tu vuelo con Aeroméxico a través de WhatsApp". Huffington Post. 27 October 2017. Archived from the original on 10 March 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- "Building for People, and Now Businesses". WhatsApp.com. Archived from the original on 9 February 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- "She is the company's most effective employee". Nordea News. September 2017. Archived from the original on 23 March 2023. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- "Better believe the bot boom is blowing up big for B2B, B2C businesses". VentureBeat. 24 July 2016. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 30 August 2017.
- Dandapani, Arundati (30 April 2020). "Redesigning Conversations with Artificial Intelligence (Chapter 11)". In Sha, Mandy (ed.). The Essential Role of Language in Survey Research. RTI Press. pp. 221–230. doi:10.3768/rtipress.bk.0023.2004. ISBN 978-1-934831-24-3.
- Capan, Faruk (18 October 2017). "The AI Revolution is Underway!". www.PM360online.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2018. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
- "80% of businesses want chatbots by 2020". Business Insider. 15 December 2016. Archived from the original on 8 March 2018. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
- ^ "A Virtual Travel Agent With All the Answers". The New York Times. 4 March 2008. Archived from the original on 15 June 2017. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- "Chatbot vendor directory released". www.hypergridbusiness.com. October 2011. Archived from the original on 23 April 2017. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- "Rare Carat's Watson-powered chatbot will help you put a diamond ring on it". TechCrunch. 15 February 2017. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- "10 ways you may have already used IBM Watson". VentureBeat. 10 March 2017. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- Greenfield, Rebecca (5 May 2016). "Chatbots Are Your Newest, Dumbest Co-Workers". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- Følstad, Asbjørn; Nordheim, Cecilie Bertinussen; Bjørkli, Cato Alexander (2018). "What Makes Users Trust a Chatbot for Customer Service? An Exploratory Interview Study". In Bodrunova, Svetlana S. (ed.). Internet Science. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 11193. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 194–208. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-01437-7_16. hdl:11250/2571164. ISBN 978-3-030-01437-7.
- Xu, Anbang; Liu, Zhe; Guo, Yufan; Sinha, Vibha; Akkiraju, Rama (2 May 2017). "A New Chatbot for Customer Service on Social Media". Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI '17. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 3506–3510. doi:10.1145/3025453.3025496. ISBN 978-1-4503-4655-9.
- "How to Manage Customer Service Technology Innovation". www.gartner.com. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- Smith, Sam (8 May 2019). "Chatbot Interactions to Reach 22 Billion by 2023, as AS AI Offers Compelling New Engagement Solutions". Juniper Research. Archived from the original on 2 January 2020. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- "Российский банк запустил чат-бота в Facebook". Vedomosti.ru. 13 July 2016. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- "Absa launches 'world-first' Facebook Messenger banking". 19 July 2016. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- Crimmins, Tricia (30 May 2023). "'This robot causes harm': National Eating Disorders Association's new chatbot advises people with disordering eating to lose weight". The Daily Dot. Retrieved 2 June 2023.
- Knight, Taylor (31 May 2023). "Eating disorder helpline fires AI for harmful advice after sacking humans".
- Aratani, Lauren (31 May 2023). "US eating disorder helpline takes down AI chatbot over harmful advice". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- Larson, Selena (11 October 2016). "Baidu is bringing AI chatbots to healthcare". CNN Money. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- "AI chatbots have a future in healthcare, with caveats". AI in Healthcare. Archived from the original on 23 March 2023. Retrieved 17 September 2019.
- Palanica, Adam; Flaschner, Peter; Thommandram, Anirudh; Li, Michael; Fossat, Yan (3 January 2019). "Physicians' Perceptions of Chatbots in Health Care: Cross-Sectional Web-Based Survey". Journal of Medical Internet Research. 21 (4): e12887. doi:10.2196/12887. PMC 6473203. PMID 30950796.
- ^ Biswas, Som S. (1 May 2023). "Role of Chat GPT in Public Health". Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 51 (5): 868–869. doi:10.1007/s10439-023-03172-7. ISSN 1573-9686. PMID 36920578.
- Ahaskar, Abhijit (27 March 2020). "How WhatsApp chatbots are helping in the fight against Covid-19". Mint. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- "India's Coronavirus Chatbot on WhatsApp Crosses 1.7 Crore Users in 10 Days". NDTV Gadgets 360. April 2020. Archived from the original on 21 June 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- Kurup, Rajesh (21 March 2020). "COVID-19: Govt of India launches a WhatsApp chatbot". Business Line. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- "In focus: Mumbai-based Haptik which developed India's official WhatsApp chatbot for Covid-19". Hindustan Times. 7 April 2020. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- ^ Nadarzynski, Tom; Miles, Oliver; Cowie, Aimee; Ridge, Damien (1 January 2019). "Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-led chatbot services in healthcare: A mixed-methods study". Digital Health. 5: 2055207619871808. doi:10.1177/2055207619871808. PMC 6704417. PMID 31467682.
- "Sam, the virtual politician". Tuia Innovation. Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
- Wellington, Victoria University of (15 December 2017). "Meet the world's first virtual politician". Victoria University of Wellington. Archived from the original on 3 January 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- Wagner, Meg (23 November 2017). "This virtual politician wants to run for office". CNN. Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
- "Talk with the first-ever robot politician on Facebook Messenger". Engadget. 25 November 2017. Archived from the original on 4 August 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
- Prakash, Abishur (8 August 2018). "AI-Politicians: A Revolution In Politics". Medium. Archived from the original on 10 August 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- "SAM website". Archived from the original on 11 May 2021. Retrieved 23 May 2021.
- Sternberg, Sarah (20 June 2022). "Danskere vil ind på den politiske scene med kunstig intelligens" [Danes want to enter the political scene with artificial intelligence]. Jyllands-Posten. Archived from the original on 20 June 2022. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- Diwakar, Amar (22 August 2022). "Can an AI-led Danish party usher in an age of algorithmic politics?". TRT World. Archived from the original on 22 August 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- Xiang, Chloe (13 October 2022). "This Danish Political Party Is Led by an AI". Vice: Motherboard. Archived from the original on 13 October 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- Hearing, Alice (14 October 2022). "A.I. chatbot is leading a Danish political party and setting its policies. Now users are grilling it for its stance on political landmines". Fortune. Archived from the original on 22 December 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- "Maharashtra government launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot to provide info on 1,400 public services". CNBC TV18. 5 March 2019. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- "Government of Maharashtra launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot with Haptik". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- Aggarwal, Varun (5 March 2019). "Maharashtra launches Aaple Sarkar chatbot". Business Line. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2020.
- ^ Amy (23 February 2015). "Conversational Toys – The Latest Trend in Speech Technology". Virtual Agent Chat. Archived from the original on 21 February 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- Nagy, Evie (13 February 2015). "Using Toy-talk Technology, New Hello Barbie Will Have Real Conversations With Kids". Fast Company. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Oren Jacob, the co-founder and CEO of ToyTalk interviewed on the TV show Triangulation on the TWiT.tv network
- "Artificial intelligence script tool". Archived from the original on 12 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- Takahashi, Dean (23 February 2015). "Elemental's smart connected toy taps IBM's Watson supercomputer for its brains". Venture Beat. Archived from the original on 20 May 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- Epstein, Robert (October 2007). "From Russia With Love: How I got fooled (and somewhat humiliated) by a computer" (PDF). Scientific American: Mind. pp. 16–17. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2007. Psychologist Robert Epstein reports how he was initially fooled by a chatterbot posing as an attractive girl in a personal ad he answered on a dating website. In the ad, the girl portrayed herself as being in Southern California and then soon revealed, in poor English, that she was actually in Russia. He became suspicious after a couple of months of email exchanges, sent her an email test of gibberish, and she still replied in general terms. The dating website is not named.
- Neff, Gina; Nagy, Peter (12 October 2016). "Automation, Algorithms, and Politics| Talking to Bots: Symbiotic Agency and the Case of Tay". International Journal of Communication. 10: 17. ISSN 1932-8036.
- Bird, Jordan J.; Ekart, Aniko; Faria, Diego R. (June 2018). "Learning from Interaction: An Intelligent Networked-Based Human-Bot and Bot-Bot Chatbot System". Advances in Computational Intelligence Systems. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Vol. 840 (1st ed.). Nottingham, UK: Springer. pp. 179–190. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-97982-3_15. ISBN 978-3-319-97982-3. S2CID 52069140.
- Temming, Maria (20 November 2018). "How Twitter bots get people to spread fake news". Science News. Archived from the original on 27 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- Epp, Len (11 May 2016). "Five Potential Malicious Uses For Chatbots". Archived from the original on 24 February 2023. Retrieved 24 February 2023.
- ^ Hasal, Martin; Nowaková, Jana; Ahmed Saghair, Khalifa; Abdulla, Hussam; Snášel, Václav; Ogiela, Lidia (10 October 2021). "Chatbots: Security, privacy, data protection, and social aspects". Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience. 33 (19). doi:10.1002/cpe.6426. hdl:10084/145153. ISSN 1532-0626.
- Grudin, Jonathan; Jacques, Richard (2019), "Chatbots, Humbots, and the Quest for Artificial General Intelligence", Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems – CHI '19, ACM CHI 2020, pp. 209–219, doi:10.1145/3290605.3300439, ISBN 978-1-4503-5970-2, S2CID 140274744
- Stover, Dawn (3 September 2023). "Will AI make us crazy?". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 79 (5): 299–303. Bibcode:2023BuAtS..79e.299S. doi:10.1080/00963402.2023.2245247. ISSN 0096-3402.
- Hannigan, Timothy R.; McCarthy, Ian P.; Spicer, André (20 March 2024). "Beware of botshit: How to manage the epistemic risks of generative chatbots". Business Horizons. 67 (5): 471–486. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2024.03.001. ISSN 0007-6813.
- "Transcript: Ezra Klein Interviews Gary Marcus". The New York Times. 6 January 2023. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 21 April 2024.
- "ChatGPT took their jobs. Now they walk dogs and fix air conditioners". The Washington Post. 2 June 2023.
- "The Future Belongs to Prompt Engineers". Inc. 12 March 2024.
- "Is The End of Prompt Engineering Here?". The Information. 19 November 2024. Retrieved 14 December 2024.
- "AI is poised to drive 160% increase in data center power demand". Goldman Sachs. 14 May 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Sreedhar, Nitin. "AI and its carbon footprint: How much water does ChatGPT consume?". Mint Lounge.
- Crownhart, Casey. "AI is an energy hog. This is what it means for climate change". MIT Technology Review.
Further reading
- Gertner, Jon. (2023) "Misplaced Pages's Moment of Truth: Can the online encyclopedia help teach A.I. chatbots to get their facts right — without destroying itself in the process?" New York Times Magazine (18 July 2023) online
- Searle, John (1980), "Minds, Brains and Programs", Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 3 (3): 417–457, doi:10.1017/S0140525X00005756, S2CID 55303721
- Shevat, Amir (2017). Designing bots: Creating conversational experiences (First ed.). Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-1-4919-7482-7. OCLC 962125282.
- Vincent, James, "Horny Robot Baby Voice: James Vincent on AI chatbots", London Review of Books, vol. 46, no. 19 (10 October 2024), pp. 29–32. " programs are made possible by new technologies but rely on the timelelss human tendency to anthropomorphise." (p. 29.)
External links
 Media related to Chatbots at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chatbots at Wikimedia Commons Conversational bots at Wikibooks
Conversational bots at Wikibooks