| Revision as of 14:32, 4 December 2005 editTheMadBaron (talk | contribs)12,744 editsm →Forster and nations: link repair← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:38, 10 January 2025 edit undoGiantSnowman (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators601,627 editsm script-assisted date audit and style fixes per MOS:NUM | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|German naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist, and revolutionary}} | |||
| {{NPOV}} | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| {{for-multi|the German Renaissance editor and composer|Georg Forster (composer)|other people named George Forster|George Forster (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Featured article}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2025}} | |||
| {{Use British English|date=November 2024}} | |||
| {{Infobox scientist | |||
| | name = Georg Forster | |||
| | image = Georg Forster.jpg | |||
| | caption = Georg Forster at age 26, by ], 1781 | |||
| | honorific_suffix = FRS | |||
| | birth_date = {{birth-date|27 November 1754}} | |||
| | birth_name = Johann George Adam Forster | |||
| | birth_place = ], ], ] | |||
| | death_date = {{death date and age|1794|1|10|1754|11|27|df=y}} | |||
| | death_place = ], ] | |||
| | education = ], ] | |||
| | known_for = Founding modern travel literature | |||
| | parents = ] and Justina Elisabeth, née Nicolai | |||
| | spouse = ] | |||
| | children = ] | |||
| | awards = ], 1777 | |||
| | field = ], ] | |||
| | workplaces = ], ], ] | |||
| | patrons = ] | |||
| | signature = Georg Forster signature.png | |||
| | author_abbrev_bot = '''G.Forst.''' | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Johann George Adam Forster''', also known as '''Georg Forster'''{{refn|group=nb|Forster was baptised "Johann George Adam Forster", with the English spelling "George", widely used in the Danzig area at the time,{{sfn|Gordon|1975|p=9}} possibly chosen commemorating the family's ancestors from Yorkshire.{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|p=425}} The German form of his name is also common in English (for example, ]'s English-language biography is titled "Georg Forster"),{{sfn|Saine|1972}} which helps to distinguish him from ], a contemporaneous English traveller.{{sfn|Rosove|2015}}}} ({{IPA|de|ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfɔʁstɐ}}, 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German ], ], ], ], journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, ], on several scientific expeditions, including ]'s ] to the ]. His report of that journey, '']'', contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of ] and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the ] at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature. | |||
| ], ].]] | |||
| After returning to continental Europe, Forster turned toward academia. He taught natural history at the ] in the ], ] (1778–84), and later at the ] (1784–87). In 1788, he became ] at the ]. Most of his scientific work during this time consisted of essays on ] and ethnology, but he also prefaced and translated many books about travel and exploration, including a German translation of Cook's diaries. | |||
| '''Johann Georg Adam Forster''' (], ] – ], ]) was a ] ] ], ], ], and ]. He took part in ]'s second expedition to the ]. | |||
| Forster was a central figure of the ] in Germany, and corresponded with most of its adherents, including his close friend ]. His ideas, travelogues and personality influenced ], one of the great scientists of the 19th century{{sfn|Daum|2019b|pp=19–21, 43}} who hailed Forster as the founder of both comparative ethnology (''Völkerkunde'') and regional geography (''Länderkunde'').<ref>Alexander von Humboldt in ''Kosmos'' (1874), quoted in Jovanović, Lazar, 2020. “The Cosmopolitan Circumnavigator of the South Seas: A Biography of Georg Forster”, in Bérose – ''Encyclopédie internationale des histoires de l'anthropologie'', Paris.</ref> | |||
| ==Biography== | |||
| When the French took control of ] in 1792, Forster played a leading role in the ], the earliest ] state in Germany. During July 1793 and while he was in Paris as a delegate of the young Mainz Republic, ] and ] coalition forces regained control of the city and Forster was declared an outlaw. Unable to return to Germany and separated from his friends and family, he died in Paris of illness in early 1794, not yet 40. | |||
| {{botanist|G.Forst.|inline=y}} | |||
| === Childhood and first journeys === | |||
| == Early life == | |||
| Georg Forster was born in the small village of ] (] ''Nassenhuben''), near ] (''Danzig'') in the ] province of ]. | |||
| Georg Forster was born in ]{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|p=xix}}{{refn|group=nb|Some sources indicate that the birth took place in the rectory of ], a village very close to Nassenhuben on the other side of the ] river.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=15–16}}}} (now Mokry Dwór, Poland), a small village near Danzig, on 27 November 1754.{{sfn|Enzensberger|1996|p=10}}{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=18}}{{refn|group=nb|Some variants of the date of birth exist in the literature, with 26 November common in earlier literature.{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=18}}{{sfn|Hoare|1976|p=18}} The baptism registries of Nassenhuben and of {{ill|St Peter and Paul, Gdańsk|de|St. Peter und Paul (Danzig)|pl|Kościół św. Piotra i Pawła w Gdańsku}} list 27 November as date of birth and 5 December as date of baptism.{{sfn|Strehlke|1861|pp=201–203}}{{sfn|Enzensberger|1996|p=15}} The date of 27 November is claimed by both father and son;{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=353}} for example, Reinhold's diary entry for 27 November 1772 starts "This day was George's birthday & we were all very happy."{{sfn|Forster|1982|p=184}}<ref>{{Cite web |last=Forster |first=Johann Reinhold |title=Continuation of a Journal of a Voyage on board his Majesties Ship Resolution |url=https://digital.staatsbibliothek-berlin.de/werkansicht/?PPN=PPN833628925&PHYSID=PHYS_0007 |access-date=31 December 2024 |website=Digitalisierte Sammlungen der Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin}}</ref>}} Georg was the oldest of seven surviving children of ], a ] pastor and scholar, and his wife Justina Elisabeth, {{nee|Nicolai}}.{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|p=xix}}{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=15–16}} From an early age, Georg was interested in the study of nature, and his father first learned natural history from the books of ] and then taught his son biology as well as Latin, French, and religion.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=21–22}}{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|pp=19–20}} In 1765, Reinhold obtained a commission by the Russian government to inspect the recently founded colonies near ] on the ], which were mostly settled by ].{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=25–26}} Ten-year old Georg accompanied his father on the {{convert|4000|km|mi|-2|abbr=on}} journey, which reached the ] and ], and collected hundreds of specimens of plants, helping his father with naming and identification.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|p=31}} From October 1765, he attended ] in St Petersburg,{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=26}} while his father prepared a report about the state of the colony.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=32–33}} Reinhold's report was critical of the voivode of Saratov and of the conditions in the colony, and the Forsters left Russia without payment amidst quarrel with ].{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=26}}{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=33–36}} After a sea journey from Kronstadt, during which Georg learned English and practiced Russian, they arrived in London on 4 October 1766.{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=27}}{{sfn|Hoare|1976|p=36}} Twelve-year old Georg competently translated ]'s history of Russia into English and continued it until the present, and the printed book was presented to the ] on 21 May 1767.{{sfn|Gordon|1975|pp=30–31}}{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=28}} His father took up a teaching position at ] in June 1767, succeeding ], leaving Georg behind in London as apprentice with a London merchant until the rest of the family arrived in England in September 1767.{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=29}}{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=50–51}} In Warrington, Georg learned classics and religion from ], mathematics from John Holt and French and natural history from his father.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|p=52}}{{sfn|Steiner|1977|p=12}} | |||
| He was the first child of ] and Justina Elisabeth (de domo Nicolai). His father was a naturalist, scientist and a ] ]. In ], the Russian ] gave the pastor an assignment to travel in ] on a research journey and investigate the situation of a German colony at the ]. Georg, then ten years old, joined him. They reached the ] ] at the lower ]. The young Forster learned there how to conduct scientific research and how to practise cartography. He also learnt ] and became fluent in this language. A critical report from the journey was refused by the tsar, so the Forsters did not obtain fair payment for their work and had to move. They chose to settle in England which they did in ]. The father took up teaching and translation work there. The young Forster, only thirteen years old, published his first book: a translation of ]'s history of ], which was well received in scientific circles. | |||
| == Around the world with Captain Cook == | |||
| ], Greenwich]] | |||
| The Forsters moved back to London in 1770,{{sfn|Hoare|1976|p=67}} where Reinhold Forster cultivated scientific contacts and became a member of the ] in 1772.{{sfn|Hoare|1976|pp=68–69}} After the withdrawal of ], he was invited by the ] to join ]'s ] to the ] (1772–75). Georg Forster joined his father in the expedition again and was appointed as a ] to his father. Johann Reinhold Forster's task was to work on a scientific report of the journey's discoveries that was to be published after their return.{{sfn|Aulie|1999a}}<!-- replace --> | |||
| They embarked ] on 13 July 1772, in ]. The ship's route led first to the ], then through the Indian Ocean and the ] to the islands of ] and finally around ] back to England, returning on 30 July 1775. During the three-year journey, the explorers visited New Zealand, the ] islands, ], ], the ] and ]. They went further south than anybody before them, almost discovering ]. The journey conclusively disproved the ''] Incognita'' theory, which claimed there was a big, habitable continent in the South.{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|p=xxii}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Supervised by his father, Georg Forster first undertook studies of the ] and ] of the southern seas, mostly by drawing animals and plants. However, Georg also pursued his own interests, which led to completely independent explorations in comparative ] and ].{{sfn|Daum|2019a}}<!-- check--> He quickly learned the languages of the Polynesian islands. His reports on the people of Polynesia are well regarded today, as they describe the inhabitants of the southern islands with empathy, sympathy and largely without ] or Christian bias.{{sfn|Ackerknecht|1955|pp=85–86}}<!-- modernise--> | |||
| They embarked on the board of the '']'' on July 13th, 1772 in ]. The route led first to the ] then through the ] and ] waters in ] to the island of ] and finally around the ] to reach England, where the ] arrived on ], ]. During the three years long travel the explorers visited ], the ] islands, ], ], the ] and the ]. They went as much to the south as nobody before them. The journey disproved conclusively the theory which said that there is a big, habitable continent in the south, although the ships did not reach ]. | |||
| ] and ] in ]'' by ]]] | |||
| Georg Forster took up first, mostly as a draughtsman, the studies of ] and ] in the southern seas. This research was done under the supervision of his father. However he had also his own interests which led to completely independent exploration in the fields of comparative ] and ]. He quickly learned the languages of the Polynesia islands. His reports on people of ] are approved even today, as they show Forster's endavours to describe the habitants of southern islands with empathy, sympathy and to great extent without western christian prejudices. Conversely, he even tries to idealise the 'noble wild people'. Forster, with this kind of attitude, was much ahead of the other ] of his times. | |||
| Unlike ], whose reports from a journey to Tahiti a few years earlier had initiated uncritical '']'' romanticism, Forster developed a sophisticated picture of the societies of the South Pacific islands.{{sfn|Ackerknecht|1955|pp=86–87}} He described various ]s and religions that he encountered on the ], Easter Island and in Tonga and New Zealand, and ascribed this diversity to the difference in living conditions of these people. At the same time, he also observed that the languages of these fairly widely scattered islands were similar. About the inhabitants of the ] islands (in the ] island group of present-day Tonga), he wrote that their languages, vehicles, weapons, furniture, clothes, tattoos, style of beard, in short all of their being matched perfectly with what he had already seen while studying tribes on ]. However, he wrote, "we could not observe any subordination among them, though this had strongly characterised the natives of Tonga-Tabboo, who seemed to descend even to servility in their obeisance to the king."<ref name="VTW TT">Forster, Georg. ''A Voyage Round the World'', Book II, Chapter VIII</ref> | |||
| :''Their languages, vehicles, weapons, home furniture, cloths, tatoos, type of beard lopping; in short all of their being matched perfectly with what we had already seen studying tribes on Tonga. We could not only (...) find any kind of subordination which was very apparent among Tonga tribes and recognisable in their respect to the king that reached even extreme forms of servitude.'' | |||
| The journey was rich in scientific results. However, the relationship between the Forsters and Cook and his officers was often problematic, due to the elder Forster's fractious temperament{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|pp=xxii–xxvi}}<!-- it would be great to have some quotes from Michael Hoare: "The Tactless Philosopher", a bio of JR Forster--> as well as Cook's refusal to allow more time for botanical and other scientific observation. Cook refused scientists on his third journey after his experiences with the Forsters.{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=22}} | |||
| The ] items that were collected by Georg and Reinhold Forster are currently presented as ''Cook-Forster-Sammlung'' (''Cook-Forster-Collection'') in ] in ]. | |||
| == Founder of modern travel literature == | |||
| The journey was very fruitful scientifically. However, the relations between Forsters and Captain Cook and his officers were problematic. This was a result of both the Prussian pride of the Forsters and their justifiable feeling of independence on one hand, and Cook's need to warrant an orderly course of the journey on the other hand. | |||
| ], also known as Forster's dove of Tanna]] | |||
| These conflicts continued after the journey with the problem of who should write the official account of the travels. ], although willing to pay the promised money, was irritated with Johann Reinhold Forster's opening chapter and tried to have it edited. However, Forster did not want to have his writing corrected "like a theme of a School-boy", and stubbornly refused any compromise.{{sfn|Aulie|1999a}}<!-- replace--> As a result, the official account was written by Cook, and the Forsters were deprived of the right to compile the account and did not obtain payment for their work. During the negotiations, the younger Forster decided to release an unofficial account of their travels. In 1777, his book '']'' was published. This report was the first account of Cook's second voyage (it appeared six weeks before the official publication) and was intended for the general public. The English version and his own translation into German (published 1778–80) earned the young author real fame. The poet ] praised the book as the most important one of his time, and even today it remains one of the most important journey descriptions ever written. The book also had a significant impact on German literature, culture and science, influencing such scientists as ]{{sfn|Smith|1990|p=218}} and it inspired many ] of later times. | |||
| Forster wrote well-polished German prose, which was not only scientifically accurate and objective, but also exciting and easy to read. This differed from conventional ] of the time, insofar as it presented more than a mere collection of data – it also demonstrated coherent, colourful and reliable ] facts that resulted from detailed and sympathetic observation. He often interrupted the description to enrich it with philosophical remarks about his observations.{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|pp=xiii–xiv}} His main focus was always on the people he encountered: their behavior, customs, habits, religions and forms of social organization. In ''A Voyage Round the World'' he even presented the songs sung by the people of ], complete with lyrics and ]. The book is one of the most important sources concerning the societies of the Southern Pacific from the times before European influence had become significant.<ref name="Dawson2011">Ruth P. Dawson, “Navigating Gender: Georg Forster in the Pacific and Emilie von Berlepsch in Scotland.“ In: ''Weimar Classicism'', ed. David Gallagher. Lampeter, Wales: Edwin Mellen Press, 2011. 39–64.</ref><!-- find other source --> | |||
| === A founder of the modern travel literature === | |||
| Both Forsters also published descriptions of their South Pacific travels in the Berlin-based ''Magazin von merkwürdigen neuen Reisebeschreibungen'' ("''Magazine of strange new travel accounts''"), and Georg published a translation of "''A Voyage to the South Sea, by Lieutenant ], London 1792''" in 1791–93.<!-- use Steiner or Uhlig --> | |||
| These conflicts continued after the journey when the problem of who should write the official account of the travel arised. ], although willing to pay the promised money for the final account, was dissatisfied with Senior Forster's English and tried to establish an editor over him. However, this was interpreted by Forster as a censorship and he refused all compromises in this direction. As a result of that the official account was to be written by ] and Forsters were deprived of the right to compile the account and they did not get their payment for the work. During the negotiations, young Forster decided to release an unofficial account of the travel. In ], a book ''A Voyage round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5'' (from which the expression ''a voyage round the world'' stems) was published. This report was the first account of the second Cook's voyage (it occurred six weeks before the official relation) and was intended for the wide public. The English version and his own translation to German which was published in ]-] earned the young author a real fame. Poet ] praised the book as the most important book of his time and it still today remains one of the most important journey descriptions that were ever written. The book had also significant impact on German literature, culture and science. For instance ] was under its great influence and it inspired many ] at the later date. | |||
| == Forster at universities == | |||
| Forster composed a well polished German ]. When he presented scientific facts he did not forget to make the book interesting. His work distinguished itself from conventional ], because he did not present only bare data, but instead he demonstrated coherent, colourful and reliable ] facts which were the result of observations took by a person who participated in the events. He also quite often interrupted the description to enrich it with ] remarks concerning the observed objects and situations. | |||
| The publication of ''A Voyage Round the World'' brought Forster scientific recognition all over Europe.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Gray|first=Sally Hatch|url=http://openinquiryarchive.net/2012/04/28/disinterested-pleasure-and-aesthetic-autonomy/|title=Disinterested Pleasure and Aesthetic Autonomy in Georg Forster's Voyage 'round the World|journal=Open Inquiry Archive|volume=1|issue=5|year=2012|access-date=23 May 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121024105542/http://openinquiryarchive.net/2012/04/28/disinterested-pleasure-and-aesthetic-autonomy/|archive-date=24 October 2012|url-status=live}}</ref> The respectable ] made him a member on 9 January 1777,<ref>{{Cite web|url = http://www.royalsoc.co.uk/downloaddoc.asp?id=778|title = Fellows of the Royal Society – F|access-date = 8 May 2015|publisher = Royal Society|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20071008133318/http://www.royalsoc.co.uk/downloaddoc.asp?id=778|archive-date = 8 October 2007}}</ref> though he was not even 23 years old. He was granted similar titles from academies ranging from ] to ].{{sfn|Uhlig|2004|p=75}} These appointments, however, were unpaid. | |||
| He travelled to Paris to seek out a discussion with the American revolutionary ] in 1777.<ref>{{Cite magazine|url = http://harpers.org/blog/2008/04/georg-forsters-recollection-of-benjamin-franklin/|title = Georg Forster's Recollection of Benjamin Franklin|date = 13 April 2008|access-date = 8 May 2015|magazine = Harper's Magazine|last1 = Horton|first1 = Scott|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150708031910/http://harpers.org/blog/2008/04/georg-forsters-recollection-of-benjamin-franklin/|archive-date = 8 July 2015|url-status = live}}</ref> In 1778, he went to Germany to take a teaching position as a Natural History professor at the ] in ], where he met ], the daughter of classicist ]. They married in 1785 (which was after he left Kassel) and had two surviving children, ] and Clara Forster, but an unhappy marriage. She would eventually leave him for ] and became one of the first independent female writers in Germany. . From his time in Kassel on, Forster actively corresponded with important figures of the ], including ], ], ] and ]. He also initiated cooperation between the Carolinum in Kassel and the ] where his friend ] worked. Together, they founded and published the scientific and literary journal ''Göttingisches Magazin der Wissenschaften und Litteratur''.{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=27}} Forster's closest friend, ], arrived in Kassel shortly after Forster, and both were soon involved with the ]s in Kassel, where Forster took the secret name ''Amadeus Sragorisinus Segenitor''.<ref name="harp_intro">{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Das Abenteuer der Freiheit und die Liebe zur Welt |encyclopedia=Georg Forster: Reise um die Welt : illustriert von eigener Hand |publisher=Eichborn |location=Frankfurt am Main |last=Harpprecht |first=Klaus |date=2007 |page=22 |isbn=978-3-8218-6203-3 |oclc=173842524}}</ref> | |||
| His main point of focus was always on people he encountered, their ], their ]s, ]s, ]s and forms of social organisation. In ''A Voyage round the World'' he even presented texts of songs sang by people of ]. The book is even today one of the most imprtant sources concerning the societies of the southern seas, especially as the book comes from the times before the European influence started to be significant there. | |||
| ], with a commemorative plaque next to the door]] | |||
| Both Forsters published also travel descriptions to the ] in the ''Magazin von merkwürdigen neuen Reisebeschreibungen'' ("''Magazine of notable new travel accounts''") in ]; and Georg, a translation of "''A Voyage to the South Sea, by Lieutenant ], ] ]''" in ] and ]. The innovative descriptions of those travels were the basis for many books and films, like '']''. | |||
| However, by 1783 Forster saw that his involvement with the Rosicrucians not only led him away from real science, but also deeper into debt{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=33}} (it is said he was not good at money{{sfn|Thomas|Berghof|2000|p=xx}}); for these reasons Forster was happy to accept a proposal by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth ] and became Chair of Natural History at ] in 1784.{{sfn|Reintjes|1953|p=50}} Initially, he was accepted well in ], but he felt more and more isolated with time. Most of his contacts were still with scientists in Germany; especially notable is his dispute with ] about the definition of ].{{sfn|Saine|1972|pp=43–48}} In 1785, Forster traveled to ] where he submitted his thesis on the plants of the South Pacific for a doctorate in medicine.<ref name="OnTheContinent">{{cite book |last1=Aulie |first1=Richard P. |author-link=Richard P. Aulie |date=1999 |title=The Voyages of Captain James Cook |chapter-url=http://www.captaincooksociety.com/home/detail/on-the-continent |publisher=Captain Cook Study Unit |access-date=14 May 2015 |chapter=On the Continent}}</ref> Back in Vilnius, Forster's ambitions to build a real natural history scientific centre could not get appropriate financial support from the authorities in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Moreover, his famous speech on natural history in 1785 went almost unnoticed and was not printed until 1843. These events led to high tensions between him and the local community.<ref name="Bodi">{{cite book|last=Bodi|first=Leslie|chapter=Georg Forster: The "Pacific Expert" of eighteenth-century Germany|title=Literatur, Politik, Identität – Literature, Politics, Cultural Identity|pages=29, 54|publisher=Röhrig Universitätsverlag|year=2002|isbn=3-86110-332-X}}</ref> Eventually, he broke the contract six years short of its completion as ] had offered him a place on a journey around the world (the ]) for a high honorarium and a position as a professor in ].<ref name="King">{{cite journal|last=King|first=Robert J.|year=2008|title=The Mulovsky expedition and Catherine II's North Pacific empire|journal=Australian Slavonic and East European Studies|volume=21|issue=1/2|pages=101–126|url=http://miskinhill.com.au/journals/asees/21:1-2/mulovsky-expedition|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091025062759/http://miskinhill.com.au/journals/asees/21:1-2/mulovsky-expedition|archive-date=25 October 2009}}</ref> This resulted in a conflict between Forster and the influential Polish scientist ]. However, the Russian proposal was withdrawn and Forster left Vilnius. He then settled in ], where he became head librarian of the ], a position held previously by his friend ], who made sure Forster would succeed him when Müller moved to the administration of ] ].{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=59}} | |||
| Forster regularly published essays on contemporary explorations and continued to be a very prolific translator; for instance, he wrote about Cook's third journey to the South Pacific, and about the ] expedition, as well as translating Cook's and ]'s diaries from these journeys into German.<ref>{{cite journal|last=King|first=Robert J.|title=The Call of the South Seas: Georg Forster and the expeditions to the Pacific of Lapérouse, Mulovsky and Malaspina|journal=Georg-Forster-Studien|volume=XIII|year=2008}}</ref> From his London years, Forster was in contact with Sir ], the initiator of the Bounty expedition and a participant in Cook's first journey. While at the University of Vilnius he wrote the article "Neuholland und die brittische Colonie in Botany-Bay", published in the ''Allgemeines historisches Taschenbuch'' (Berlin, December 1786), an essay on the future prospects of the English colony founded in ] in 1788.<ref>{{Cite book|title = Neuholland und die brittische Colonie in Botany-Bay|last = Sprengel|first = Matthias Christian|publisher = Australasian Hydrographic Society|year = 2008|url = http://www.australiaonthemap.org.au/content/view/47/59/|orig-year = 1787|trans-title = New Holland and the British Colony at Botany Bay|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080719062302/http://www.australiaonthemap.org.au/content/view/47/59/|archive-date = 19 July 2008|chapter = German text (Google Books)|chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=MvM9AAAAcAAJ&q=Taschenbuch+1787+Forster&pg=PA11|others = Translated by Robert J. King}}</ref> | |||
| === Forster as a professor === | |||
| Another interest of his was ] – one of the main goals of his failed expedition to be financed by Catherine II had been to reach India. He translated the ] play '']'' using a ] version provided by Sir ]; this strongly influenced ], and triggered German interest in the culture of India.{{sfn|Ackerknecht|1955|p=85}} | |||
| The publication of ''A Voyage round the World'' gave Forster scientific distinctions around the Europe. Respectable ] nominated him as its member although he was not even 23 years old. He was granted similar titles from Academies ranging from ] to ]. These achievements did not give him money though. In ] he went to ] to take a position of a professor in ]. He met ], a daughter of a professor of classical ], there. Later, she became one of the first free female writers in Germany. Forster married her in ] and they had three children, but the marriage was not happy. | |||
| == ''Views from the Lower Rhine'' == | |||
| On initiative of the Polish ], Forster became Professor of ] at ] in ]. Despite his notable scientific record he was not accepted well in Wilno. His famous speech on natural history from ] went unnoticed and was not printed before ]. He broke the contract 6 years short of its completion, after ] gave him an offer to take part in a journey around the world for a high honorarium. This resulted in a conflict between Forster and ]. However, the Russian proposal was withdrawn and Forster left ]. He settled in ] where he worked as librarian of the ]. In ] he made a tour of the ] with ]. This resulted in a book ''Ansichten von Niederrhein, von Brabant, Flandern, Holland, England und Frankreich''. | |||
| ], which was praised in ''Ansichten vom Niederrhein'']] | |||
| In the second quarter of 1790, Forster and the young ] started from Mainz on a long journey through the ], the ], and England, eventually finishing in Paris. The impressions from the journey were described in a three volume publication ''Ansichten vom Niederrhein, von Brabant, Flandern, Holland, England und Frankreich im April, Mai und Juni 1790'' (''Views of the Lower Rhine, from Brabant, Flanders, Holland, England, and France in April, May and June 1790''), published 1791–94. Goethe said about the book: "One wants, after one has finished reading, to start it over, and wishes to travel with such a good and knowledgeable observer." The book includes comments on the ] that were as influential for the discipline as ''A Voyage Round the world'' was for ]. Forster was, for example, one of the first writers who gave just treatment to the ] of ],{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=103}} which was widely perceived as "barbarian" at that time. The book conformed well to the early ] intellectual movements in German-speaking Europe.<ref>{{Cite book|title = Encyclopedia of the Romantic Era, 1760–1850: A-L|last = Murray|first = Christopher John|publisher = Taylor & Francis|year = 2003|isbn = 978-1-57958-423-8|pages = |url = https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofro002unse_v8y9/page/365}}</ref> | |||
| Forster's main interest, however, was again focused on the social behavior of people, as 15 years earlier in the Pacific. The national uprisings in ] and ] and the ] sparked his curiosity. The journey through these regions, together with the Netherlands and England, where citizens' freedoms were equally well developed, in the end helped him to resolve his own political opinions. From that time on he was to be a confident opponent of the ]. With other German scholars, he welcomed the outbreak of the revolution as a clear consequence of the Enlightenment. As early as 30 July 1789, shortly after he heard about the ], he wrote to his father-in-law, philologist ], that it was beautiful to see what philosophy had nurtured in people's minds and then had realized in the state. To educate people about their rights in this way, he wrote, was after all the surest way; the rest would then result as if by itself.<ref name="zeit">{{cite journal|last=Schweigard|first=Jörg|title=Freiheit oder Tod!|trans-title=Liberty or Death!|journal=]|issue=29|year=2001|url=http://www.zeit.de/2001/29/200129_a-14_juli_xml|language=de|access-date=30 May 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050905224929/http://www.zeit.de/2001/29/200129_a-14_juli_xml|archive-date=5 September 2005|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| == Life as a revolutionary == | |||
| === Forster and the French Revolution === | |||
| === Foundation of the Mainz Republic === | |||
| Forster was a co-founder and the vice chairman of the Mainz ] club in ] and was an active participant in the founding of the ], the first democratic state in Germany. He later became vice president of the provisory administration and a member of the Rhenish-German National Convent, the parliament of the Mainz Republic. He also worked as a newspaper editor, and wrote in his first article: | |||
| ], a symbol of revolutionary France as used in the ]. Watercolor by ]]] | |||
| :''The ] finally reigns within these walls where the ] was invented.'' | |||
| The French revolutionary army under ] gained control over ] on 21 October 1792. Two days later, Forster joined others in establishing a ] called "Freunde der Freiheit und Gleichheit" ("Friends of Freedom and Equality") in the ]. From early 1793 he was actively involved in organizing the ]. This first republic located on German soil was constituted on the principles of democracy, and encompassed areas on the left bank of the ] between ] and ]. Forster became vice-president of the republic's temporary administration and a candidate in the elections to the local parliament, the {{lang|de|Rheinisch-Deutscher Nationalkonvent}} (''Rhenish-German National Convention''). From January to March 1793, he was an editor of {{lang|de|Die neue Mainzer Zeitung oder Der Volksfreund}} (''The new Mainz newspaper or The People's Friend''), a name chosen in reference to ]'s {{lang|fr|L'Ami du peuple}}.<ref>Harpprecht, ''Das Abenteuer der Freiheit'', p. 33</ref> In his first article he wrote: | |||
| Forster was sent to ] as representative of the Mainz Republic and applied for Mainz to become part of the ]. This was granted, but had no effect, since Mainz was conquered by Prussian and Austrian troops in ], and the old order was restored. | |||
| {{blockquote|''Die Pressefreiheit herrscht endlich innerhalb dieser Mauern, wo die Buchdruckerpresse erfunden ward.''<ref name="SZ">{{cite journal|last=Lepenies|first=Wolf|title=Freiheit, das Riesenkind|trans-title=Freedom, the giant child|journal=]|date=May 17, 2010|url=http://www.sueddeutsche.de/kultur/aufmacher-xv-freiheit-das-riesenkind-1.423586|language=de|access-date=February 20, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708135125/http://www.sueddeutsche.de/kultur/aufmacher-xv-freiheit-das-riesenkind-1.423586|archive-date=July 8, 2015|url-status=live}}</ref>}} | |||
| Forster was expelled from Germany as a ] and died in Paris in January ], from ]. | |||
| {{blockquote|The ] finally reigns within these walls where the ] was invented.}} | |||
| This freedom did not last long, though. The Mainz Republic existed only until the retreat of the French troops in July 1793 after the ]. | |||
| == Forster and nations == | |||
| Forster was not present in Mainz during the siege. As representatives of the Mainz National Convention, he and ] had been sent to Paris to apply for Mainz – which was unable to exist as an independent state – to become a part of the ]. The application was accepted, but had no effect, since Mainz was conquered by Prussian and Austrian troops, and the old order was restored.<ref name="WHKMLA">{{cite web|url=http://www.zum.de/whkmla/region/germany/mainzrep.html|title=The Mainz Republic|publisher=World History at KMLA (WHKLMA)|access-date=22 May 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303202218/http://www.zum.de/whkmla/region/germany/mainzrep.html|archive-date=3 March 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> Forster lost his library and collections and decided to remain in Paris.<ref name="nie">{{Cite NIE|wstitle=Forster, Georg|year=1906}}</ref> | |||
| Forster had Scottish roots and was born in Polish ]. He worked in Russia, England, Poland and in several German countries of his times. Finally, he finished his life in France. He worked in different milieu and travelled a lot from his young age on. This together with the scientific upbringing based on the principles of the ], in his view gave him a cosmopolitan perspective on different ethnic and national communities: | |||
| ] and Georg Forster in ], by ], ].]] | |||
| :''All peoples of the earth have equal claims to my good will..., and my praise and blame are independent of national prejudice.''{{ref|Forster1}} | |||
| In his opinion all humans have the same abilities with regard to reason, feelings and imagination, but these basic ingredients are used in a different ways and in different environments which gives rise to different cultures and civilisations. According to him it is obvious that the culture on Tierra del Fuego is on a lower level of development than the European culture, but he also admits that the conditions of life there are much more difficult and this gives people very little chances to develop a higher culture.{{ref|SixVarieties}} | |||
| === Death in revolutionary Paris === | |||
| In contrast to the attitude expressed in these writings and to his Enlightenment background, he used insulting terms against Poles in his private letters. For example he compared {{ref|Lawaty}} Poles {{ref|Krause}} to animals ( "''cattle in human form''"{{ref|Booksbooks}}). He also used the term ''"Polnische Wirtschaft"''{{ref|Stasiewski}} in one of his letters in ], a stereotype that became widely used in Germany to pejoratively describe Polish disorganization as compared to purported German order. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The rise of the nationalist ideas at the end of the 18th and in the 19th century resulted in him and his cosmopolitan ideas being nowhere welcome. For Englishmen he was a proud Prussian who started conflicts, for Germans he was too unpatriotic, being able to give away a part of his fatherland to France, for Poles he was unacceptable due to his attitude towards them, and for French people he was not significant enough politically. | |||
| Based on a decree by Emperor ] inflicting punishments on German subjects who collaborated with the French revolutionary government, Forster was declared an outlaw and placed under the ]; a prize of 100 ducats was set on his head and he could not return to Germany.{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=154}} Devoid of all means of making a living and without his wife, who had stayed in Mainz with their children and her later husband ], he remained in Paris. At this point the revolution in Paris had entered the ] introduced by the ] under the rule of ]. Forster had the opportunity to experience the difference between the promises of the revolution of happiness for all and its cruel practice. In contrast to many other German supporters of the revolution, like for instance ], Forster did not turn back from his revolutionary ideals under the pressure of the terror. He viewed the events in France as a force of nature that could not be slowed and that had to release its own energies to avoid being even more destructive.{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=152}} | |||
| == Forster's heritage == | |||
| Before the reign of terror reached its climax, Forster died after a rheumatic illness{{sfn|Reintjes|1953|p=136}} in his small attic apartment at Rue des Moulins<ref name="hr">{{cite AV media|url=http://www.hr-online.de/servlet/de.blueorange.xred.util.GetFile/04-165.rtf?db=hrmysql&tbl=int_xredfile&key=id&keyval=11787328&imgcol=xred_file|medium=radio script (RTF)|last=Schell|first=Christa|title=Die Revolution ist ein Orkan|trans-title=The Revolution is a Hurricane|date=26 November 2004|access-date=12 April 2012|language=de|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071001051325/http://www.hr-online.de/servlet/de.blueorange.xred.util.GetFile/04-165.rtf?db=hrmysql&tbl=int_xredfile&key=id&keyval=11787328&imgcol=xred_file|archive-date=1 October 2007|url-status=dead}}</ref> in Paris on 10 January 1794,{{sfn|Saine|1972|p=154}} at the age of thirty-nine. At the time, he was making plans to visit India.<ref name=nie /> | |||
| After the death of Forster his works were almost completely forgotten, except in professional circles. This was partly due to his involvement in the ]. However, his reception was changing with the changes in politics. | |||
| == Views on nations and their culture == | |||
| In the time of nationalism after the Napoleonic times he was regarded in Germany as a "traitor of the nation", notably among the literats and scientists. This attitude rose even though the philosopher ] wrote about Forster at the beginning of 19th century: "Among all the real writers no one breathes so much the spirit of free progression as Georg Forster“. In the Germany of ] and even more so in the ], his memory was ostracized. The ], in turn, profited from his memory and tried to connect him as a scientist and revolutionary to its tradition. For instance, the GDR research station on ] was given Forster's name on July 1st, 1987. The search for democratic traditions in German history led also to a more diversified picture of him in ]. His reputation as one of first and one of the most outstanding German ] is indisputable. His works testify that he developed ethnology in Germany so that it could stand as a separate branch of science. | |||
| Forster had partial Scottish roots and was born in Polish ], and therefore was by birth a Polish subject. He worked in Russia, England, Poland and in several German countries of his time. Finally, he finished his life in France. He worked in different milieus and traveled a lot from his youth on. It was his view that this, together with his scientific upbringing based on the principles of the Enlightenment, gave him a wide perspective on different ethnic and national communities: | |||
| ], London 1780.<ref name="npg">{{Cite web |url=http://www.portrait.gov.au/portraits/2009.55/portrait-of-dr-johann-reinhold-forster-and-his-son-george-forster/ |title=Portrait of Dr Johann Reinhold Forster and his son George Forster, c. 1780 |website=National Portrait Gallery|publisher = portrait.gov.au |access-date=}}</ref> The plant in the brim of the hat is a '']'' and the bird in Johann Forster's hand a ], locating the scene in New Zealand.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VIirDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA12 |title=Johann Reinhold Forster and the Making of Natural History on Cook's Second Voyage, 1772–1775 |last=Mariss |first=Anne |date=9 September 2019 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |isbn=978-1-4985-5615-6 |language=en|page=166}}</ref> However, the painting has been commonly called "Reinhold and George Forster at Tahiti" or similar.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mIk8x6lsusQC |title=The Life of Captain James Cook |last=Beaglehole |first=J. C. |author-link=John Beaglehole|date=1 April 1992 |publisher=Stanford University Press |isbn=978-0-8047-2009-0 |language=en|page=viii}}</ref>]] | |||
| In ], the standard ] '''G.Forst.''' is applied to ] described by him. | |||
| {{blockquote|All peoples of the earth have equal claims to my good will ... and my praise and blame are independent of national prejudice.<ref>{{cite book|last=Forster|first=Johann Georg|title=Georg Forsters Werke, Sämtliche Schriften, Tagebücher, Briefe|trans-title=Georg Forster's works, all writings, diaries, letters|publisher=Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin|editor-first1=Gerhard|editor-last1=Steiner|year=1958|volume=II|pages=13–14|language=de}}</ref>}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| In his opinion all human beings have the same abilities with regard to reason, feelings and imagination, but these basic ingredients are used in different ways and in different environments, which gives rise to different cultures and civilizations. According to him it is obvious that the culture on ] is at a lower level of development than European culture, but he also admits that the conditions of life there are much more difficult and this gives people very little chance to develop a higher culture. Based on these opinions he was classified as one of the main examples of 18th-century German ].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Kleingeld |first=Pauline |title=Six Varieties of Cosmopolitanism in Late Eighteenth-Century Germany |journal=Journal of the History of Ideas |date=1999 |volume=60 |issue=3 |page=515 |issn=0022-5037 |url=http://www.filosofie.leidenuniv.nl/content_docs/publicaties/Kleingeld/six_varieties_of_cosmopolitanism.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080228091212/http://www.filosofie.leidenuniv.nl/content_docs/publicaties/Kleingeld/six_varieties_of_cosmopolitanism.pdf |archive-date=28 February 2008 |doi=10.1353/jhi.1999.0025 |hdl=1887/8607 |s2cid=59415888 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| *''A Voyage round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5'' (]) | |||
| *''Journal of travels in Poland'' (August-November, ]), The Warsaw Voice, 1990 31 8-9 | |||
| *''Dissertatio botanico-medica de plantis esculentis insularum oceani Australis'' (]) | |||
| *''Essays on the moral and natural geography, natural history and phylosophy'' (]-]) | |||
| *''Views of the Lower Rhine, Brabant, Flanders'' (three volumes, ]-]) | |||
| *''Letters'' (posthumous compilation of his correspondence, ]) | |||
| In contrast to the attitude expressed in these writings and to his Enlightenment background, he used insulting terms expressing prejudice against Poles in his private letters during his stay in Vilnius and in a diary from the journey through Poland,<ref>{{cite book|last=Lawaty|first=Andreas|contribution="Polnische Wirtschaft" und "deutsche Ordnung": Nachbarbilder und ihr Eigenleben|title=Der Fremde, Interdisziplinäre Beiträge zu Aspekten von Fremdheit|trans-title=The Stranger, Interdisciplinary Contributions to Aspects of Foreignness|editor-first1=Bernhard|editor-last1=Oestreich|publisher=Peter Lang Verlag|year=2003|pages=156–166|language=de}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Krause|first=Hans-Thomas|contribution=Georg Forster und Polen|title=Georg Forster (1754–1794). Ein Leben für den wissenschaftlichen und politischen Fortschritt|trans-title=Georg Forster (1754–1794). A Life of Scientific and Political Progress|series=Wissenschaftliche Beiträge der Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg|year=1981|pages=79–85|language=de}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~sarmatia/902/223books.html|title=Books and Periodicals Received: "Czarna legenda Polski: Obraz Polski i Polaków w Prusach 1772–1815"|access-date=1 September 2005|journal=The Sarmatian Review|volume=XXII|issue=3|date=September 2002|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050920052622/http://www.ruf.rice.edu/%7Esarmatia/902/223books.html|archive-date=20 September 2005|url-status=live}}</ref> but he never published any manifestation of this attitude.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Bömelburg|first=Hans-Jürgen|title=Georg Forster und das negative deutsche Polenbild. Ein Kosmopolit als Architekt von nationalen Feindbildern?|trans-title=Georg Forster and the negative German image of Poland. A cosmopolitan as an architect of national bogeymen?|journal=Mainzer Geschichtsblätter|volume=8|year=1993|pages=79–90|language=de}}</ref> These insults only became known after his death, when his private correspondence and diaries were released to the public. Since Forster's published descriptions of other nations were seen as impartial scientific observations, Forster's disparaging description of Poland in his letters and diaries was often taken at face value in Imperial and Nazi Germany, where it was used as a means of science-based support for a purported German superiority.<ref>{{cite book |first1=Michael|last1=Burleigh|first2=Wolfgang|last2=Wippermann|title=The Racial State: Germany 1933–1945|url=https://archive.org/details/racialstate00mich|url-access=registration|year=1991|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=0-521-39802-9|page=26}}</ref> The spreading of the ''"Polnische Wirtschaft"'' (Polish economy) stereotype<ref>{{cite book|last=Orłowski|first=Hubert|year=1996|title="Polnische Wirtschaft": Zum deutschen Polendiskurs der Neuzeit|series=Studien der Forschungsstelle Ostmitteleuropa an der Universität Dortmund|volume=21|isbn=3-447-03877-2|language=de}}</ref><ref name="Salmonowicz" /> is most likely due to the influence of his letters.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Stasiewski|first=Bernhard|title="Polnische Wirtschaft" und Johann Georg Forster, eine wortgeschichtliche Studie|trans-title="Polish economy" and Johann Georg Forster, a word historical study|journal=Deutsche Wissenschaftliche Zeitschrift im Wartheland|volume=2|year=1941|issue=3/4|pages=207–216|language=de}}</ref><ref name="Salmonowicz">{{cite journal|last=Salmonowicz|first=Stanisław|title=Jerzy Forster a narodziny stereotypu Polaka w Niemczech XVIII/XIX wieku|journal=Zapiski Historyczne|volume=52|year=1987|issue=4|pages=135–147|language=pl}}<br />*{{cite journal|first=Stanisław|last=Salmonowicz|title=Georg Forster und sein Polenbild: Kosmopolitismus und nationales Stereotyp|trans-title=Georg Forster and his image of Poland: cosmopolitanism and national stereotype|journal=Medizenhistorisches Journal|volume=23|issue=3–4|year=1988|pages=277–290|language=de}}</ref> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Forster's attitude brought him into conflict with the people of the different nations he encountered and made him welcome nowhere, as he was too revolutionary and antinational for Germans,<ref name=":0">{{cite journal|last=Craig|first=Gordon A.|title=Engagement and Neutrality in Germany: The Case of Georg Forster, 1754–94|journal=Journal of Modern History|volume=41|issue=1|date=March 1969|pages=2–16|doi=10.1086/240344|s2cid=143853614}}</ref> proud and opposing in his dealings with Englishmen,<ref>{{cite journal|first1=Allan|last1=Arlidge|title=Cook As A Commander – Cook and His Supernumeraries|journal=Cook's Log|page=5|volume=28|number=1|year=2005|url=http://www.captaincooksociety.com/home/detail/cook-as-a-commander-cook-and-his-supernumeraries|publisher=Captain Cook Society|access-date=14 July 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923200519/http://www.captaincooksociety.com/home/detail/cook-as-a-commander-cook-and-his-supernumeraries|archive-date=23 September 2015|url-status=live}}</ref> too unconcerned about Polish science for Poles,<ref name="Salmonowicz" /><ref>{{cite book|last=Grębecka|first=Wanda|title=Stanisław Bonifacy Jundziłł (1761–1847)|series=Wybitni Polacy na Ziemi Lidzkiej|oclc=749967908|year=2003|language=pl}}</ref> and too insignificant politically and ignored while in France.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| {{note|Lawaty}} | |||
| Lawaty, Andreas, ''„Polnische Wirtschaft“ und „deutsche Ordnung“: Nachbarbilder und ihr Eigenleben'', in: Der Fremde, Interdisziplinäre Beiträge zu Aspekten von Fremdheit, Hg. Bernhard Oestreich, Peter Lang Verlag 2003, p. 156–166. | |||
| == Legacy == | |||
| {{note|Bömelburg}} | |||
| After Forster's death, his works were mostly forgotten, except in professional circles. This was partly due to his involvement in the French revolution. However, his reception changed with the politics of the times, with different periods focusing on different parts of his work. In the period of rising nationalism after the Napoleonic era he was regarded in Germany as a "traitor to his country", overshadowing his work as an author and scientist. This attitude rose even though the philosopher ] wrote about Forster at the beginning of the 19th century: | |||
| Bömelburg, Hans-Jürgen, ''Georg Forster und das negative deutsche Polenbild. Ein Kosmopolit als Architekt von nationalen Feindbildern?'', in: Mainzer Geschichtsblätter 8 (1993), p. 79-90. | |||
| {{blockquote|Among all those authors of prose who are justified in laying claim to a place in the ranks of German classics, none breathes the spirit of free progress more than Georg Forster.<ref name="Schlegel">Schlegel, Friedrich. ''Kritische Schriften'', ed. W. Rasch, 2nd ed., Munich: Hanser 1964, translated by T. Saine in the preface to ''Georg Forster''</ref>}} | |||
| {{note|Forster1}} | |||
| Forster, Johann Georg, ''Georg Forsters Werke'', 11, 13-14. | |||
| Some interest in Forster's life and revolutionary actions was revived in the context of the liberal sentiments leading up to the ].{{sfn|Saine|1972|pp=14–15}} But he was largely forgotten in the Germany of ] and more so in ],<ref name="hr" /> where interest in Forster was limited to his stance on Poland from his private letters. Interest in Forster resumed in the 1960s in ], where he was interpreted as a champion of ].<ref name="wurzner">{{cite book|last=Würzner|first=M. H.|chapter=The Effect of the French Revolution in Germany: Christoph Martin Wieland and Georg Forster|title=Tropes of Revolution: Writers' Reactions to Real and Imagined Revolutions 1789–1989|editor-first1=Cedric Charles|editor-last1=Barfoot|editor-first2=Theo|editor-last2=D'haen|publisher=Rodopi |year=1991|isbn=90-5183-292-3}}</ref> The ] in Antarctica that was opened on 25 October 1987, was named after him.<ref name="polarpost">{{cite journal|url=http://www.earth-syst-sci-data.net/1/1/2009/essd-1-1-2009.html|doi=10.5194/essd-1-1-2009|title=Compilation of ozonesonde profiles from the Antarctic Georg-Forster-Station from 1985 to 1992|first1=Gert|last1=König-Langlo|first2=Hartwig|last2=Gernandt|journal=Earth System Science Data|date=12 January 2009|volume=1|issue= 1|issn= 1866-3516 |oclc=277823257|publisher=Copernicus GmbH|pages=1–5|bibcode=2009ESSD....1....1K|access-date=12 April 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140512215149/http://www.earth-syst-sci-data.net/1/1/2009/essd-1-1-2009.html|archive-date=12 May 2014|url-status=live|doi-access=free}}</ref> In ], the search for democratic traditions in German history also led to a more diversified picture of him in the 1970s. The Alexander von Humboldt foundation named a scholarship program for foreign scholars from developing countries after him.<ref name= "avh">{{Cite web|url = https://www.humboldt-foundation.de/en/apply/sponsorship-programmes/georg-forster-research-fellowship|title = Georg Forster Research Fellowship |access-date = |publisher = ]|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230512035411/https://www.humboldt-foundation.de/en/apply/sponsorship-programmes/georg-forster-research-fellowship |archive-date =12 May 2023|url-status = live}}</ref> His reputation as one of the first and most outstanding German ethnologists is indisputable, and his works are seen as crucial in the development of ethnology in Germany into a separate branch of science.<ref name="Bast">{{cite web|first1=Bianca |last1= Bast |title=Georg Forster – Die Wiederentdeckung eines Genies|trans-title=Georg Forster – The Rediscovery of a Genius|url=http://www.uni-protokolle.de/nachrichten/id/61496/ |language=de |publisher=uni-protokolle.de|date=31 July 2000|access-date=29 May 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050514185855/http://www.uni-protokolle.de/nachrichten/id/61496/|archive-date=14 May 2005|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{note|SixVarieties}} | |||
| Pauline Kleingeld, ''Six Varieties of Cosmopolitanism in Late Eighteenth-Century Germany'', in Journal of the History of Ideas, 1999 | |||
| The ethnographical items collected by Georg and Johann Reinhold Forster are now presented as the ''Cook-Forster-Sammlung'' (Cook–Forster Collection) in the ] anthropological collection in ].<ref name="goettingen">{{cite web|first1=Frank|last1=Witzel|first2=Andreas|last2=Riechel|url=http://www.uni-goettingen.de/en/sh/28899.html|title=Ethnographical Collection of the University of Göttingen|publisher=Uni-goettingen.de|access-date=21 March 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100518210640/http://www.uni-goettingen.de/en/sh/28899.html|archive-date=18 May 2010|url-status=live}}</ref> Another collection of items collected by the Forsters is on display at the ] in Oxford.<ref name="oxford">{{cite journal|last1=Coote|first1=Jeremy|last2=Gathercole|first2=Peter|last3=Meister|first3=Nicolette|url=http://web.prm.ox.ac.uk/forster/curios-sent.html|title='Curiosities sent to Oxford': The Original Documentation of the Forster Collection at the Pitt Rivers Museum|journal=Journal of the History of Collections|volume=XII|issue=2|year=2000|pages=177–192|doi=10.1093/jhc/12.2.177|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150508202353/http://web.prm.ox.ac.uk/forster/curios-sent.html|archive-date=8 May 2015}}</ref> | |||
| {{note|Krause}} | |||
| Krause, Hans-Thomas, ''Georg Forster und Polen. In: Georg Forster (1754-1794). Ein Leben für den wissenschaftlichen und politischen Fortschritt'', in: Wissenschaftliche Beiträge der Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg T 42, Beiträge zur Universitätsgeschichte). Halle/S. 1981, p. 79-85. | |||
| == Works == | |||
| {{note|Stasiewski}} | |||
| *'']'' (1777) ] scans: and ; modern publication with commentary: | |||
| Stasiewski, Bernhard, ''"Polnische Wirtschaft" und Johann Georg Forster, eine wortgeschichtliche Studie.'', in: Deutsche Wissenschaftliche Zeitschrift im Wartheland 2 (1941), H. 3/4, p. 207-216. | |||
| *'']'' (1775/76), | |||
| *''De Plantis Esculentis Insularum Oceani Australis Commentatio Botanica'' (1786) available online at | |||
| *''Florulae Insularum Australium Prodromus '' (1786) available online at and Biodiversity Heritage Library (DOI:10.5962/bhl.title.10725) | |||
| *''Essays on moral and natural geography, natural history and philosophy'' (1789–97) | |||
| *''Views of the Lower Rhine, Brabant, Flanders'' (three volumes, 1791–94) | |||
| *'' Georg Forsters Werke, Sämtliche Schriften, Tagebücher, Briefe'', Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, G. Steiner et al. Berlin: Akademie 1958 | |||
| *''Werke in vier Bänden'', Gerhard Steiner (editor). Leipzig: Insel 1965. ASIN: B00307GDQ0 | |||
| *''Reise um die Welt'', Gerhard Steiner (editor). Frankfurt am Main: Insel, 1983. {{ISBN|3-458-32457-7}} | |||
| *''Ansichten vom Niederrhein'', Gerhard Steiner (editor). Frankfurt am Main: Insel, 1989. {{ISBN|3-458-32836-X}} | |||
| *''Georg Forster, Briefe an Ernst Friedrich Hector Falcke. Neu aufgefundene Forsteriana aus der Gold- und Rosenkreuzerzeit'', Michael Ewert, Hermann Schüttler (editors). Georg-Forster-Studien Beiheft 4. Kassel: Kassel University Press 2009. {{ISBN|978-3-89958-485-1}} | |||
| {{botanist|G.Forst.|Forster, Georg}} | |||
| {{note|Booksbooks}} (accessed on September 1st, 2005). In the review of: ''"Czarna legenda Polski: Obraz Polski i Polaków w Prusach 1772-1815" (The black legend of Poland: the image of Poland and Poles in Prussia between 1772-1815)'', by Dariusz Łukasiewicz. Poznań: Wydawnictwo Poznańskiego Towarzystwa Przyjaciół Nauk, 1995. Vol. 51 of the history and social sciences series (English and German summaries). ISBN 8370631487. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| ---- | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| <div class="notice metadata" id="spoiler" style="border-top:2px solid #ddd; border-bottom:2px solid #ddd;"><center >The standard ] '''G.Forst.''' is applied to ] described by this ], who should also appear on ].</center ></div > | |||
| {{reflist|group=nb}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| === Sources === | |||
| {{Link FA|de}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|last=Ackerknecht|first=Erwin H.|title=George Forster, Alexander von Humboldt, and Ethnology|journal=]|volume=46|issue=2|date=June 1955|publisher=University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society|pages=83–95|jstor=227120|doi=10.1086/348401|pmid=13242231|s2cid=26981757}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Aulie |first1=Richard P. |author-link=Richard P. Aulie |date=1999 |title=The Voyages of Captain James Cook |chapter-url=http://www.captaincooksociety.com/home/detail/the-forsters-at-home |publisher=Captain Cook Study Unit |access-date=14 May 2015 |chapter=The Forsters at Home |ref={{sfnRef|Aulie|1999a}} }} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Daum |first=Andreas|author-link=Andreas Daum |editor-last=Berghoff |editor-first=Hartmut |title=Explorations and Entanglements: Germans in Pacific Worlds from the Early Modern Period to World War I |publisher=Berghahn Books |date=2019 |pages=79–102 |chapter=German Naturalists in the Pacific around 1800: Entanglement, Autonomy, and a Transnational Culture of Expertise |ref={{sfnRef|Daum|2019a}} }} | |||
| *{{cite book | last=Daum | first=Andreas|author-link=Andreas Daum | year=2019 | title=Alexander von Humboldt | location=Munich | publisher=C. H. Beck |pages=19–21, 43 | isbn=978-3-406-73436-6 |ref={{sfnRef|Daum|2019b}} }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=j20gAQAAIAAJ |title=Georg Forster: ein Leben in Scherben |last=Enzensberger |first=Ulrich |date=1996 |publisher=Eichborn |isbn=978-3-8218-4139-7 |language=de}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Forster |first=Johann Reinhold |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/58633015 |title=The "Resolution" journal of Johann Reinhold Forster, 1772–1775 Vol. 2 |date=1982 |publisher=Hakluyt Society |isbn=978-0-904180-10-7 |oclc=58633015|editor-last=Hoare|editor-first=Michael E.}} | |||
| *{{Cite thesis |last=Gordon |first=Joseph Stuart |title=Reinhold and Georg Forster in England, 1766–1780 |date=1975 |publisher=Duke University |oclc=732713365 |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/732713365 |place=Ann Arbor |language=English}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hcYLAQAAIAAJ&q=%2522Cook+told+his%2522 |title=The Tactless Philosopher: Johann Reinhold Forster (1729–98) |last=Hoare |first=Michael Edward |date=1976 |publisher=Hawthorne Press |isbn=978-0-7256-0121-8 |language=en}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last=Rosove |first=Michael H. |year=2015 |title=The folio issues of the Forsters' Characteres Generum Plantarum (1775 and 1776): a census of copies |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/polar-record/article/abs/folio-issues-of-the-forsters-characteres-generum-plantarum-1775-and-1776-a-census-of-copies/31B125C55EA7ED14D748363A73BF8B76 |journal=Polar Record |language=en |volume=51 |issue=6 |pages=611–623 |doi=10.1017/S0032247414000722 |bibcode=2015PoRec..51..611R |s2cid=129922206 |issn=0032-2474}} | |||
| *{{cite book |author-link1=Thomas P. Saine|last1=Saine |first1=Thomas P. |date=1972 |title=Georg Forster |url=https://archive.org/details/georgforster00sain|url-access=registration|location=New York, NY |publisher=Twayne Publishers |isbn=0-8057-2316-1}} | |||
| *{{cite book |first1=Alexander|last1=Smith |title=Explorers of the Amazon |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3VP8usYq7XEC&pg=PA218 |year= 1990 |isbn= 0-226-76337-4 |publisher= University of Chicago Press }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Steiner |first=Gerhard |url=https://archive.org/details/georgforster0000stei |title=Georg Forster |date=1977 |publisher=J.B. Metzler |isbn=978-3-476-10156-3 |location=Stuttgart |language=German |oclc=462099778}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last=Strehlke |first=F. |date=1861 |title=Georg Forster's Geburtsort |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=J9sXAAAAYAAJ |journal=Neue Preußische Provinzialblätter |series=3 Folge |volume=8 |pages=189–212}} | |||
| *{{cite book |others=Forster, Georg|title=A Voyage Round the World|editor-first1=Nicholas|editor-last1=Thomas |editor-first2=Oliver|editor-last2=Berghof |year=2000 |publisher=University of Hawai'i Press |jstor=j.ctvvn739|isbn=0-8248-2091-6|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctvvn739}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/georgforsterlebe0000uhli |url-access=registration |page= |title=Georg Forster: Lebensabenteuer eines gelehrten Weltbürgers (1754–1794) |last=Uhlig |first=Ludwig |date=2004 |publisher=Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht |isbn=978-3-525-36731-5 |language=de}} | |||
| *Jovanović, Lazar, (2020). , in ''BEROSE – International Encyclopaedia of the Histories of Anthropology'', Paris. | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Reintjes|first1=Heinrich|date=1953|title=Weltreise nach Deutschland|location=Düsseldorf|publisher=Progress-Verlag|language=de}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Wikisource author}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{EB1911 poster|Forster, Johann Georg Adam|Georg Forster}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| * {{in lang|de}} | |||
| * recommending Georg Forster to the ] (archived link, 21 October 2006) | |||
| * at the ] | |||
| * {{Gutenberg author | id=37318}} | |||
| * {{Internet Archive author |sname=Georg Forster}} | |||
| * {{Librivox author |id=310}} | |||
| * Resources related to research : . , Paris, 2020. (ISSN 2648-2770) | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Forster, Georg}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:38, 10 January 2025
German naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist, and revolutionary For the German Renaissance editor and composer, see Georg Forster (composer). For other people named George Forster, see George Forster (disambiguation).
| Georg ForsterFRS | |
|---|---|
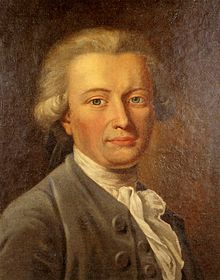 Georg Forster at age 26, by J. H. W. Tischbein, 1781 Georg Forster at age 26, by J. H. W. Tischbein, 1781 | |
| Born | Johann George Adam Forster 27 November 1754 (1754-11-27) Nassenhuben, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland |
| Died | 10 January 1794(1794-01-10) (aged 39) Paris, French Republic |
| Education | Saint Peter's School (Saint Petersburg), Warrington Academy |
| Known for | Founding modern travel literature |
| Spouse | Therese Heyne |
| Children | Therese Forster |
| Parent(s) | Johann Reinhold Forster and Justina Elisabeth, née Nicolai |
| Awards | Fellow of the Royal Society, 1777 |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | natural history, ethnology |
| Institutions | Vilnius University, University of Mainz, Collegium Carolinum (Kassel) |
| Patrons | Catherine the Great |
| Author abbrev. (botany) | G.Forst. |
| Signature | |
Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster (German pronunciation: [ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfɔʁstɐ], 27 November 1754 – 10 January 1794), was a German geographer, naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold Forster, on several scientific expeditions, including James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific. His report of that journey, A Voyage Round the World, contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of Polynesia and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the Royal Society at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature.
After returning to continental Europe, Forster turned toward academia. He taught natural history at the Collegium Carolinum in the Ottoneum, Kassel (1778–84), and later at the Academy of Vilna (Vilnius University) (1784–87). In 1788, he became head librarian at the University of Mainz. Most of his scientific work during this time consisted of essays on botany and ethnology, but he also prefaced and translated many books about travel and exploration, including a German translation of Cook's diaries.
Forster was a central figure of the Enlightenment in Germany, and corresponded with most of its adherents, including his close friend Georg Christoph Lichtenberg. His ideas, travelogues and personality influenced Alexander von Humboldt, one of the great scientists of the 19th century who hailed Forster as the founder of both comparative ethnology (Völkerkunde) and regional geography (Länderkunde). When the French took control of Mainz in 1792, Forster played a leading role in the Mainz Republic, the earliest republican state in Germany. During July 1793 and while he was in Paris as a delegate of the young Mainz Republic, Prussian and Austrian coalition forces regained control of the city and Forster was declared an outlaw. Unable to return to Germany and separated from his friends and family, he died in Paris of illness in early 1794, not yet 40.
The standard author abbreviation G.Forst. is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
Early life
Georg Forster was born in Nassenhuben (now Mokry Dwór, Poland), a small village near Danzig, on 27 November 1754. Georg was the oldest of seven surviving children of Johann Reinhold Forster, a Reformed Protestant pastor and scholar, and his wife Justina Elisabeth, née Nicolai. From an early age, Georg was interested in the study of nature, and his father first learned natural history from the books of Carl Linnaeus and then taught his son biology as well as Latin, French, and religion. In 1765, Reinhold obtained a commission by the Russian government to inspect the recently founded colonies near Saratov on the Volga River, which were mostly settled by German colonists. Ten-year old Georg accompanied his father on the 4,000 km (2,500 mi) journey, which reached the Kalmyk Steppe and Lake Elton, and collected hundreds of specimens of plants, helping his father with naming and identification. From October 1765, he attended Saint Peter's School in St Petersburg, while his father prepared a report about the state of the colony. Reinhold's report was critical of the voivode of Saratov and of the conditions in the colony, and the Forsters left Russia without payment amidst quarrel with Grigory Orlov. After a sea journey from Kronstadt, during which Georg learned English and practiced Russian, they arrived in London on 4 October 1766. Twelve-year old Georg competently translated Lomonosov's history of Russia into English and continued it until the present, and the printed book was presented to the Society of Antiquaries on 21 May 1767. His father took up a teaching position at Warrington Academy in June 1767, succeeding Joseph Priestley, leaving Georg behind in London as apprentice with a London merchant until the rest of the family arrived in England in September 1767. In Warrington, Georg learned classics and religion from John Aikin, mathematics from John Holt and French and natural history from his father.
Around the world with Captain Cook

The Forsters moved back to London in 1770, where Reinhold Forster cultivated scientific contacts and became a member of the Royal Society in 1772. After the withdrawal of Joseph Banks, he was invited by the British Admiralty to join James Cook's second expedition to the Pacific (1772–75). Georg Forster joined his father in the expedition again and was appointed as a draughtsman to his father. Johann Reinhold Forster's task was to work on a scientific report of the journey's discoveries that was to be published after their return.
They embarked HMS Resolution on 13 July 1772, in Plymouth. The ship's route led first to the South Atlantic, then through the Indian Ocean and the Southern Ocean to the islands of Polynesia and finally around Cape Horn back to England, returning on 30 July 1775. During the three-year journey, the explorers visited New Zealand, the Tonga islands, New Caledonia, Tahiti, the Marquesas Islands and Easter Island. They went further south than anybody before them, almost discovering Antarctica. The journey conclusively disproved the Terra Australis Incognita theory, which claimed there was a big, habitable continent in the South.
Supervised by his father, Georg Forster first undertook studies of the zoology and botanics of the southern seas, mostly by drawing animals and plants. However, Georg also pursued his own interests, which led to completely independent explorations in comparative geography and ethnology. He quickly learned the languages of the Polynesian islands. His reports on the people of Polynesia are well regarded today, as they describe the inhabitants of the southern islands with empathy, sympathy and largely without Western or Christian bias.

Unlike Louis Antoine de Bougainville, whose reports from a journey to Tahiti a few years earlier had initiated uncritical noble savage romanticism, Forster developed a sophisticated picture of the societies of the South Pacific islands. He described various social structures and religions that he encountered on the Society Islands, Easter Island and in Tonga and New Zealand, and ascribed this diversity to the difference in living conditions of these people. At the same time, he also observed that the languages of these fairly widely scattered islands were similar. About the inhabitants of the Nomuka islands (in the Ha'apai island group of present-day Tonga), he wrote that their languages, vehicles, weapons, furniture, clothes, tattoos, style of beard, in short all of their being matched perfectly with what he had already seen while studying tribes on Tongatapu. However, he wrote, "we could not observe any subordination among them, though this had strongly characterised the natives of Tonga-Tabboo, who seemed to descend even to servility in their obeisance to the king."
The journey was rich in scientific results. However, the relationship between the Forsters and Cook and his officers was often problematic, due to the elder Forster's fractious temperament as well as Cook's refusal to allow more time for botanical and other scientific observation. Cook refused scientists on his third journey after his experiences with the Forsters.
Founder of modern travel literature

These conflicts continued after the journey with the problem of who should write the official account of the travels. Lord Sandwich, although willing to pay the promised money, was irritated with Johann Reinhold Forster's opening chapter and tried to have it edited. However, Forster did not want to have his writing corrected "like a theme of a School-boy", and stubbornly refused any compromise. As a result, the official account was written by Cook, and the Forsters were deprived of the right to compile the account and did not obtain payment for their work. During the negotiations, the younger Forster decided to release an unofficial account of their travels. In 1777, his book A Voyage Round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5 was published. This report was the first account of Cook's second voyage (it appeared six weeks before the official publication) and was intended for the general public. The English version and his own translation into German (published 1778–80) earned the young author real fame. The poet Christoph Martin Wieland praised the book as the most important one of his time, and even today it remains one of the most important journey descriptions ever written. The book also had a significant impact on German literature, culture and science, influencing such scientists as Alexander von Humboldt and it inspired many ethnologists of later times.
Forster wrote well-polished German prose, which was not only scientifically accurate and objective, but also exciting and easy to read. This differed from conventional travel literature of the time, insofar as it presented more than a mere collection of data – it also demonstrated coherent, colourful and reliable ethnographical facts that resulted from detailed and sympathetic observation. He often interrupted the description to enrich it with philosophical remarks about his observations. His main focus was always on the people he encountered: their behavior, customs, habits, religions and forms of social organization. In A Voyage Round the World he even presented the songs sung by the people of Polynesia, complete with lyrics and notation. The book is one of the most important sources concerning the societies of the Southern Pacific from the times before European influence had become significant.
Both Forsters also published descriptions of their South Pacific travels in the Berlin-based Magazin von merkwürdigen neuen Reisebeschreibungen ("Magazine of strange new travel accounts"), and Georg published a translation of "A Voyage to the South Sea, by Lieutenant William Bligh, London 1792" in 1791–93.
Forster at universities
The publication of A Voyage Round the World brought Forster scientific recognition all over Europe. The respectable Royal Society made him a member on 9 January 1777, though he was not even 23 years old. He was granted similar titles from academies ranging from Berlin to Madrid. These appointments, however, were unpaid.
He travelled to Paris to seek out a discussion with the American revolutionary Benjamin Franklin in 1777. In 1778, he went to Germany to take a teaching position as a Natural History professor at the Collegium Carolinum in Kassel, where he met Therese Heyne, the daughter of classicist Christian Gottlob Heyne. They married in 1785 (which was after he left Kassel) and had two surviving children, Therese Forster and Clara Forster, but an unhappy marriage. She would eventually leave him for Ludwig Ferdinand Huber and became one of the first independent female writers in Germany. . From his time in Kassel on, Forster actively corresponded with important figures of the Enlightenment, including Lessing, Herder, Wieland and Goethe. He also initiated cooperation between the Carolinum in Kassel and the University of Göttingen where his friend Georg Christoph Lichtenberg worked. Together, they founded and published the scientific and literary journal Göttingisches Magazin der Wissenschaften und Litteratur. Forster's closest friend, Samuel Thomas von Sömmering, arrived in Kassel shortly after Forster, and both were soon involved with the Rosicrucians in Kassel, where Forster took the secret name Amadeus Sragorisinus Segenitor.

However, by 1783 Forster saw that his involvement with the Rosicrucians not only led him away from real science, but also deeper into debt (it is said he was not good at money); for these reasons Forster was happy to accept a proposal by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Commission of National Education and became Chair of Natural History at Vilnius University in 1784. Initially, he was accepted well in Vilnius, but he felt more and more isolated with time. Most of his contacts were still with scientists in Germany; especially notable is his dispute with Immanuel Kant about the definition of race. In 1785, Forster traveled to Halle where he submitted his thesis on the plants of the South Pacific for a doctorate in medicine. Back in Vilnius, Forster's ambitions to build a real natural history scientific centre could not get appropriate financial support from the authorities in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Moreover, his famous speech on natural history in 1785 went almost unnoticed and was not printed until 1843. These events led to high tensions between him and the local community. Eventually, he broke the contract six years short of its completion as Catherine II of Russia had offered him a place on a journey around the world (the Mulovsky expedition) for a high honorarium and a position as a professor in Saint Petersburg. This resulted in a conflict between Forster and the influential Polish scientist Jędrzej Śniadecki. However, the Russian proposal was withdrawn and Forster left Vilnius. He then settled in Mainz, where he became head librarian of the University of Mainz, a position held previously by his friend Johannes von Müller, who made sure Forster would succeed him when Müller moved to the administration of Elector Friedrich Karl Josef von Erthal.
Forster regularly published essays on contemporary explorations and continued to be a very prolific translator; for instance, he wrote about Cook's third journey to the South Pacific, and about the Bounty expedition, as well as translating Cook's and Bligh's diaries from these journeys into German. From his London years, Forster was in contact with Sir Joseph Banks, the initiator of the Bounty expedition and a participant in Cook's first journey. While at the University of Vilnius he wrote the article "Neuholland und die brittische Colonie in Botany-Bay", published in the Allgemeines historisches Taschenbuch (Berlin, December 1786), an essay on the future prospects of the English colony founded in New South Wales in 1788.
Another interest of his was indology – one of the main goals of his failed expedition to be financed by Catherine II had been to reach India. He translated the Sanskrit play Shakuntala using a Latin version provided by Sir William Jones; this strongly influenced Johann Gottfried Herder, and triggered German interest in the culture of India.
Views from the Lower Rhine

In the second quarter of 1790, Forster and the young Alexander von Humboldt started from Mainz on a long journey through the Southern Netherlands, the United Provinces, and England, eventually finishing in Paris. The impressions from the journey were described in a three volume publication Ansichten vom Niederrhein, von Brabant, Flandern, Holland, England und Frankreich im April, Mai und Juni 1790 (Views of the Lower Rhine, from Brabant, Flanders, Holland, England, and France in April, May and June 1790), published 1791–94. Goethe said about the book: "One wants, after one has finished reading, to start it over, and wishes to travel with such a good and knowledgeable observer." The book includes comments on the history of art that were as influential for the discipline as A Voyage Round the world was for ethnology. Forster was, for example, one of the first writers who gave just treatment to the Gothic architecture of Cologne Cathedral, which was widely perceived as "barbarian" at that time. The book conformed well to the early Romantic intellectual movements in German-speaking Europe.
Forster's main interest, however, was again focused on the social behavior of people, as 15 years earlier in the Pacific. The national uprisings in Flanders and Brabant and the revolution in France sparked his curiosity. The journey through these regions, together with the Netherlands and England, where citizens' freedoms were equally well developed, in the end helped him to resolve his own political opinions. From that time on he was to be a confident opponent of the ancien régime. With other German scholars, he welcomed the outbreak of the revolution as a clear consequence of the Enlightenment. As early as 30 July 1789, shortly after he heard about the Storming of the Bastille, he wrote to his father-in-law, philologist Christian Gottlob Heyne, that it was beautiful to see what philosophy had nurtured in people's minds and then had realized in the state. To educate people about their rights in this way, he wrote, was after all the surest way; the rest would then result as if by itself.
Life as a revolutionary
Foundation of the Mainz Republic

The French revolutionary army under General Custine gained control over Mainz on 21 October 1792. Two days later, Forster joined others in establishing a Jacobin Club called "Freunde der Freiheit und Gleichheit" ("Friends of Freedom and Equality") in the Electoral Palace. From early 1793 he was actively involved in organizing the Mainz Republic. This first republic located on German soil was constituted on the principles of democracy, and encompassed areas on the left bank of the Rhine between Landau and Bingen. Forster became vice-president of the republic's temporary administration and a candidate in the elections to the local parliament, the Rheinisch-Deutscher Nationalkonvent (Rhenish-German National Convention). From January to March 1793, he was an editor of Die neue Mainzer Zeitung oder Der Volksfreund (The new Mainz newspaper or The People's Friend), a name chosen in reference to Marat's L'Ami du peuple. In his first article he wrote:
Die Pressefreiheit herrscht endlich innerhalb dieser Mauern, wo die Buchdruckerpresse erfunden ward.
The freedom of the press finally reigns within these walls where the printing press was invented.
This freedom did not last long, though. The Mainz Republic existed only until the retreat of the French troops in July 1793 after the siege of Mainz.
Forster was not present in Mainz during the siege. As representatives of the Mainz National Convention, he and Adam Lux had been sent to Paris to apply for Mainz – which was unable to exist as an independent state – to become a part of the French Republic. The application was accepted, but had no effect, since Mainz was conquered by Prussian and Austrian troops, and the old order was restored. Forster lost his library and collections and decided to remain in Paris.
Death in revolutionary Paris

Based on a decree by Emperor Francis II inflicting punishments on German subjects who collaborated with the French revolutionary government, Forster was declared an outlaw and placed under the Imperial ban; a prize of 100 ducats was set on his head and he could not return to Germany. Devoid of all means of making a living and without his wife, who had stayed in Mainz with their children and her later husband Ludwig Ferdinand Huber, he remained in Paris. At this point the revolution in Paris had entered the Reign of Terror introduced by the Committee of Public Safety under the rule of Maximilien Robespierre. Forster had the opportunity to experience the difference between the promises of the revolution of happiness for all and its cruel practice. In contrast to many other German supporters of the revolution, like for instance Friedrich Schiller, Forster did not turn back from his revolutionary ideals under the pressure of the terror. He viewed the events in France as a force of nature that could not be slowed and that had to release its own energies to avoid being even more destructive.
Before the reign of terror reached its climax, Forster died after a rheumatic illness in his small attic apartment at Rue des Moulins in Paris on 10 January 1794, at the age of thirty-nine. At the time, he was making plans to visit India.
Views on nations and their culture
Forster had partial Scottish roots and was born in Polish Royal Prussia, and therefore was by birth a Polish subject. He worked in Russia, England, Poland and in several German countries of his time. Finally, he finished his life in France. He worked in different milieus and traveled a lot from his youth on. It was his view that this, together with his scientific upbringing based on the principles of the Enlightenment, gave him a wide perspective on different ethnic and national communities:

All peoples of the earth have equal claims to my good will ... and my praise and blame are independent of national prejudice.
In his opinion all human beings have the same abilities with regard to reason, feelings and imagination, but these basic ingredients are used in different ways and in different environments, which gives rise to different cultures and civilizations. According to him it is obvious that the culture on Tierra del Fuego is at a lower level of development than European culture, but he also admits that the conditions of life there are much more difficult and this gives people very little chance to develop a higher culture. Based on these opinions he was classified as one of the main examples of 18th-century German cosmopolitanism.
In contrast to the attitude expressed in these writings and to his Enlightenment background, he used insulting terms expressing prejudice against Poles in his private letters during his stay in Vilnius and in a diary from the journey through Poland, but he never published any manifestation of this attitude. These insults only became known after his death, when his private correspondence and diaries were released to the public. Since Forster's published descriptions of other nations were seen as impartial scientific observations, Forster's disparaging description of Poland in his letters and diaries was often taken at face value in Imperial and Nazi Germany, where it was used as a means of science-based support for a purported German superiority. The spreading of the "Polnische Wirtschaft" (Polish economy) stereotype is most likely due to the influence of his letters.
Forster's attitude brought him into conflict with the people of the different nations he encountered and made him welcome nowhere, as he was too revolutionary and antinational for Germans, proud and opposing in his dealings with Englishmen, too unconcerned about Polish science for Poles, and too insignificant politically and ignored while in France.
Legacy
After Forster's death, his works were mostly forgotten, except in professional circles. This was partly due to his involvement in the French revolution. However, his reception changed with the politics of the times, with different periods focusing on different parts of his work. In the period of rising nationalism after the Napoleonic era he was regarded in Germany as a "traitor to his country", overshadowing his work as an author and scientist. This attitude rose even though the philosopher Karl Wilhelm Friedrich Schlegel wrote about Forster at the beginning of the 19th century:
Among all those authors of prose who are justified in laying claim to a place in the ranks of German classics, none breathes the spirit of free progress more than Georg Forster.
Some interest in Forster's life and revolutionary actions was revived in the context of the liberal sentiments leading up to the 1848 revolution. But he was largely forgotten in the Germany of Wilhelm II and more so in Nazi Germany, where interest in Forster was limited to his stance on Poland from his private letters. Interest in Forster resumed in the 1960s in East Germany, where he was interpreted as a champion of class struggle. The GDR research station in Antarctica that was opened on 25 October 1987, was named after him. In West Germany, the search for democratic traditions in German history also led to a more diversified picture of him in the 1970s. The Alexander von Humboldt foundation named a scholarship program for foreign scholars from developing countries after him. His reputation as one of the first and most outstanding German ethnologists is indisputable, and his works are seen as crucial in the development of ethnology in Germany into a separate branch of science.
The ethnographical items collected by Georg and Johann Reinhold Forster are now presented as the Cook-Forster-Sammlung (Cook–Forster Collection) in the Sammlung für Völkerkunde anthropological collection in Göttingen. Another collection of items collected by the Forsters is on display at the Pitt Rivers Museum in Oxford.
Works
- A Voyage Round the World in His Britannic Majesty's Sloop Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years, 1772, 3, 4, and 5 (1777) Internet Archive scans: Vol. I and II; modern publication with commentary: (preview)
- Characteres generum plantarum, quas in Itinere ad Insulas Maris Australis, Collegerunt, Descripserunt, Delinearunt, annis MDCCLXXII-MDCCLXXV Joannes Reinoldus Forster et Georgius Forster (1775/76), archive.org
- De Plantis Esculentis Insularum Oceani Australis Commentatio Botanica (1786) available online at Project Gutenberg
- Florulae Insularum Australium Prodromus (1786) available online at Project Gutenberg and Biodiversity Heritage Library (DOI:10.5962/bhl.title.10725)
- Essays on moral and natural geography, natural history and philosophy (1789–97)
- Views of the Lower Rhine, Brabant, Flanders (three volumes, 1791–94)
- Georg Forsters Werke, Sämtliche Schriften, Tagebücher, Briefe, Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, G. Steiner et al. Berlin: Akademie 1958
- Werke in vier Bänden, Gerhard Steiner (editor). Leipzig: Insel 1965. ASIN: B00307GDQ0
- Reise um die Welt, Gerhard Steiner (editor). Frankfurt am Main: Insel, 1983. ISBN 3-458-32457-7
- Ansichten vom Niederrhein, Gerhard Steiner (editor). Frankfurt am Main: Insel, 1989. ISBN 3-458-32836-X
- Georg Forster, Briefe an Ernst Friedrich Hector Falcke. Neu aufgefundene Forsteriana aus der Gold- und Rosenkreuzerzeit, Michael Ewert, Hermann Schüttler (editors). Georg-Forster-Studien Beiheft 4. Kassel: Kassel University Press 2009. ISBN 978-3-89958-485-1
See also
- Category:Taxa named by Georg Forster
- European and American voyages of scientific exploration
- List of important publications in anthropology
Notes
- Forster was baptised "Johann George Adam Forster", with the English spelling "George", widely used in the Danzig area at the time, possibly chosen commemorating the family's ancestors from Yorkshire. The German form of his name is also common in English (for example, Thomas P. Saine's English-language biography is titled "Georg Forster"), which helps to distinguish him from George Forster, a contemporaneous English traveller.
- Some sources indicate that the birth took place in the rectory of Hochzeit, a village very close to Nassenhuben on the other side of the Motława river.
- Some variants of the date of birth exist in the literature, with 26 November common in earlier literature. The baptism registries of Nassenhuben and of St Peter and Paul, Gdańsk [de; pl] list 27 November as date of birth and 5 December as date of baptism. The date of 27 November is claimed by both father and son; for example, Reinhold's diary entry for 27 November 1772 starts "This day was George's birthday & we were all very happy."
References
- Gordon 1975, p. 9.
- Thomas & Berghof 2000, p. 425.
- Saine 1972.
- Rosove 2015.
- Daum 2019b, pp. 19–21, 43.
- Alexander von Humboldt in Kosmos (1874), quoted in Jovanović, Lazar, 2020. “The Cosmopolitan Circumnavigator of the South Seas: A Biography of Georg Forster”, in Bérose – Encyclopédie internationale des histoires de l'anthropologie, Paris.
- International Plant Names Index. G.Forst.
- ^ Thomas & Berghof 2000, p. xix.
- ^ Hoare 1976, pp. 15–16.
- Enzensberger 1996, p. 10.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 18.
- Saine 1972, p. 18.
- Hoare 1976, p. 18.
- Strehlke 1861, pp. 201–203.
- Enzensberger 1996, p. 15.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 353.
- Forster 1982, p. 184.
- Forster, Johann Reinhold. "Continuation of a Journal of a Voyage on board his Majesties Ship Resolution". Digitalisierte Sammlungen der Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin. Retrieved 31 December 2024.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 21–22.
- Uhlig 2004, pp. 19–20.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 25–26.
- Hoare 1976, p. 31.
- ^ Uhlig 2004, p. 26.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 32–33.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 33–36.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 27.
- Hoare 1976, p. 36.
- Gordon 1975, pp. 30–31.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 28.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 29.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 50–51.
- Hoare 1976, p. 52.
- Steiner 1977, p. 12.
- Hoare 1976, p. 67.
- Hoare 1976, pp. 68–69.
- ^ Aulie 1999a.
- Thomas & Berghof 2000, p. xxii.
- Daum 2019a.
- Ackerknecht 1955, pp. 85–86.
- Ackerknecht 1955, pp. 86–87.
- Forster, Georg. A Voyage Round the World, Book II, Chapter VIII
- Thomas & Berghof 2000, pp. xxii–xxvi.
- Saine 1972, p. 22.
- Smith 1990, p. 218.
- Thomas & Berghof 2000, pp. xiii–xiv.
- Ruth P. Dawson, “Navigating Gender: Georg Forster in the Pacific and Emilie von Berlepsch in Scotland.“ In: Weimar Classicism, ed. David Gallagher. Lampeter, Wales: Edwin Mellen Press, 2011. 39–64.
- Gray, Sally Hatch (2012). "Disinterested Pleasure and Aesthetic Autonomy in Georg Forster's Voyage 'round the World". Open Inquiry Archive. 1 (5). Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- "Fellows of the Royal Society – F". Royal Society. Archived from the original on 8 October 2007. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- Uhlig 2004, p. 75.
- Horton, Scott (13 April 2008). "Georg Forster's Recollection of Benjamin Franklin". Harper's Magazine. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- Saine 1972, p. 27.
- Harpprecht, Klaus (2007). "Das Abenteuer der Freiheit und die Liebe zur Welt". Georg Forster: Reise um die Welt : illustriert von eigener Hand. Frankfurt am Main: Eichborn. p. 22. ISBN 978-3-8218-6203-3. OCLC 173842524.
- Saine 1972, p. 33.
- Thomas & Berghof 2000, p. xx.
- Reintjes 1953, p. 50.
- Saine 1972, pp. 43–48.
- Aulie, Richard P. (1999). "On the Continent". The Voyages of Captain James Cook. Captain Cook Study Unit. Retrieved 14 May 2015.
- Bodi, Leslie (2002). "Georg Forster: The "Pacific Expert" of eighteenth-century Germany". Literatur, Politik, Identität – Literature, Politics, Cultural Identity. Röhrig Universitätsverlag. pp. 29, 54. ISBN 3-86110-332-X.
- King, Robert J. (2008). "The Mulovsky expedition and Catherine II's North Pacific empire". Australian Slavonic and East European Studies. 21 (1/2): 101–126. Archived from the original on 25 October 2009.
- Saine 1972, p. 59.
- King, Robert J. (2008). "The Call of the South Seas: Georg Forster and the expeditions to the Pacific of Lapérouse, Mulovsky and Malaspina". Georg-Forster-Studien. XIII.
- Sprengel, Matthias Christian (2008) . "German text (Google Books)". Neuholland und die brittische Colonie in Botany-Bay [New Holland and the British Colony at Botany Bay]. Translated by Robert J. King. Australasian Hydrographic Society. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008.
- Ackerknecht 1955, p. 85.
- Saine 1972, p. 103.
- Murray, Christopher John (2003). Encyclopedia of the Romantic Era, 1760–1850: A-L. Taylor & Francis. pp. 365. ISBN 978-1-57958-423-8.
- Schweigard, Jörg (2001). "Freiheit oder Tod!" [Liberty or Death!]. Die Zeit (in German) (29). Archived from the original on 5 September 2005. Retrieved 30 May 2006.
- Harpprecht, Das Abenteuer der Freiheit, p. 33
- Lepenies, Wolf (17 May 2010). "Freiheit, das Riesenkind" [Freedom, the giant child]. Süddeutsche Zeitung (in German). Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- "The Mainz Republic". World History at KMLA (WHKLMA). Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2015.
- ^ Gilman, D. C.; Peck, H. T.; Colby, F. M., eds. (1906). "Forster, Georg" . New International Encyclopedia (1st ed.). New York: Dodd, Mead.
- ^ Saine 1972, p. 154.
- Saine 1972, p. 152.
- Reintjes 1953, p. 136.
- ^ Schell, Christa (26 November 2004). Die Revolution ist ein Orkan [The Revolution is a Hurricane] (radio script (RTF)) (in German). Archived from the original on 1 October 2007. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- "Portrait of Dr Johann Reinhold Forster and his son George Forster, c. 1780". National Portrait Gallery. portrait.gov.au.
- Mariss, Anne (9 September 2019). Johann Reinhold Forster and the Making of Natural History on Cook's Second Voyage, 1772–1775. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 166. ISBN 978-1-4985-5615-6.
- Beaglehole, J. C. (1 April 1992). The Life of Captain James Cook. Stanford University Press. p. viii. ISBN 978-0-8047-2009-0.
- Forster, Johann Georg (1958). Steiner, Gerhard (ed.). Georg Forsters Werke, Sämtliche Schriften, Tagebücher, Briefe [Georg Forster's works, all writings, diaries, letters] (in German). Vol. II. Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin. pp. 13–14.
- Kleingeld, Pauline (1999). "Six Varieties of Cosmopolitanism in Late Eighteenth-Century Germany" (PDF). Journal of the History of Ideas. 60 (3): 515. doi:10.1353/jhi.1999.0025. hdl:1887/8607. ISSN 0022-5037. S2CID 59415888. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2008.
- Lawaty, Andreas (2003). ""Polnische Wirtschaft" und "deutsche Ordnung": Nachbarbilder und ihr Eigenleben". In Oestreich, Bernhard (ed.). Der Fremde, Interdisziplinäre Beiträge zu Aspekten von Fremdheit [The Stranger, Interdisciplinary Contributions to Aspects of Foreignness] (in German). Peter Lang Verlag. pp. 156–166.
- Krause, Hans-Thomas (1981). "Georg Forster und Polen". Georg Forster (1754–1794). Ein Leben für den wissenschaftlichen und politischen Fortschritt [Georg Forster (1754–1794). A Life of Scientific and Political Progress]. Wissenschaftliche Beiträge der Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg (in German). pp. 79–85.
- "Books and Periodicals Received: "Czarna legenda Polski: Obraz Polski i Polaków w Prusach 1772–1815"". The Sarmatian Review. XXII (3). September 2002. Archived from the original on 20 September 2005. Retrieved 1 September 2005.
- Bömelburg, Hans-Jürgen (1993). "Georg Forster und das negative deutsche Polenbild. Ein Kosmopolit als Architekt von nationalen Feindbildern?" [Georg Forster and the negative German image of Poland. A cosmopolitan as an architect of national bogeymen?]. Mainzer Geschichtsblätter (in German). 8: 79–90.
- Burleigh, Michael; Wippermann, Wolfgang (1991). The Racial State: Germany 1933–1945. Cambridge University Press. p. 26. ISBN 0-521-39802-9.
- Orłowski, Hubert (1996). "Polnische Wirtschaft": Zum deutschen Polendiskurs der Neuzeit. Studien der Forschungsstelle Ostmitteleuropa an der Universität Dortmund (in German). Vol. 21. ISBN 3-447-03877-2.
- ^ Salmonowicz, Stanisław (1987). "Jerzy Forster a narodziny stereotypu Polaka w Niemczech XVIII/XIX wieku". Zapiski Historyczne (in Polish). 52 (4): 135–147.
*Salmonowicz, Stanisław (1988). "Georg Forster und sein Polenbild: Kosmopolitismus und nationales Stereotyp" [Georg Forster and his image of Poland: cosmopolitanism and national stereotype]. Medizenhistorisches Journal (in German). 23 (3–4): 277–290. - Stasiewski, Bernhard (1941). ""Polnische Wirtschaft" und Johann Georg Forster, eine wortgeschichtliche Studie" ["Polish economy" and Johann Georg Forster, a word historical study]. Deutsche Wissenschaftliche Zeitschrift im Wartheland (in German). 2 (3/4): 207–216.
- ^ Craig, Gordon A. (March 1969). "Engagement and Neutrality in Germany: The Case of Georg Forster, 1754–94". Journal of Modern History. 41 (1): 2–16. doi:10.1086/240344. S2CID 143853614.
- Arlidge, Allan (2005). "Cook As A Commander – Cook and His Supernumeraries". Cook's Log. 28 (1). Captain Cook Society: 5. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- Grębecka, Wanda (2003). Stanisław Bonifacy Jundziłł (1761–1847). Wybitni Polacy na Ziemi Lidzkiej (in Polish). OCLC 749967908.
- Schlegel, Friedrich. Kritische Schriften, ed. W. Rasch, 2nd ed., Munich: Hanser 1964, translated by T. Saine in the preface to Georg Forster
- Saine 1972, pp. 14–15.
- Würzner, M. H. (1991). "The Effect of the French Revolution in Germany: Christoph Martin Wieland and Georg Forster". In Barfoot, Cedric Charles; D'haen, Theo (eds.). Tropes of Revolution: Writers' Reactions to Real and Imagined Revolutions 1789–1989. Rodopi. ISBN 90-5183-292-3.
- König-Langlo, Gert; Gernandt, Hartwig (12 January 2009). "Compilation of ozonesonde profiles from the Antarctic Georg-Forster-Station from 1985 to 1992". Earth System Science Data. 1 (1). Copernicus GmbH: 1–5. Bibcode:2009ESSD....1....1K. doi:10.5194/essd-1-1-2009. ISSN 1866-3516. OCLC 277823257. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2012.
- "Georg Forster Research Fellowship". Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Archived from the original on 12 May 2023.
- Bast, Bianca (31 July 2000). "Georg Forster – Die Wiederentdeckung eines Genies" [Georg Forster – The Rediscovery of a Genius] (in German). uni-protokolle.de. Archived from the original on 14 May 2005. Retrieved 29 May 2006.
- Witzel, Frank; Riechel, Andreas. "Ethnographical Collection of the University of Göttingen". Uni-goettingen.de. Archived from the original on 18 May 2010. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- Coote, Jeremy; Gathercole, Peter; Meister, Nicolette (2000). "'Curiosities sent to Oxford': The Original Documentation of the Forster Collection at the Pitt Rivers Museum". Journal of the History of Collections. XII (2): 177–192. doi:10.1093/jhc/12.2.177. Archived from the original on 8 May 2015.
- International Plant Names Index. G.Forst.
Sources
- Ackerknecht, Erwin H. (June 1955). "George Forster, Alexander von Humboldt, and Ethnology". Isis. 46 (2). University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society: 83–95. doi:10.1086/348401. JSTOR 227120. PMID 13242231. S2CID 26981757.
- Aulie, Richard P. (1999). "The Forsters at Home". The Voyages of Captain James Cook. Captain Cook Study Unit. Retrieved 14 May 2015.
- Daum, Andreas (2019). "German Naturalists in the Pacific around 1800: Entanglement, Autonomy, and a Transnational Culture of Expertise". In Berghoff, Hartmut (ed.). Explorations and Entanglements: Germans in Pacific Worlds from the Early Modern Period to World War I. Berghahn Books. pp. 79–102.
- Daum, Andreas (2019). Alexander von Humboldt. Munich: C. H. Beck. pp. 19–21, 43. ISBN 978-3-406-73436-6.
- Enzensberger, Ulrich (1996). Georg Forster: ein Leben in Scherben (in German). Eichborn. ISBN 978-3-8218-4139-7.
- Forster, Johann Reinhold (1982). Hoare, Michael E. (ed.). The "Resolution" journal of Johann Reinhold Forster, 1772–1775 Vol. 2. Hakluyt Society. ISBN 978-0-904180-10-7. OCLC 58633015.
- Gordon, Joseph Stuart (1975). Reinhold and Georg Forster in England, 1766–1780 (Thesis). Ann Arbor: Duke University. OCLC 732713365.
- Hoare, Michael Edward (1976). The Tactless Philosopher: Johann Reinhold Forster (1729–98). Hawthorne Press. ISBN 978-0-7256-0121-8.
- Rosove, Michael H. (2015). "The folio issues of the Forsters' Characteres Generum Plantarum (1775 and 1776): a census of copies". Polar Record. 51 (6): 611–623. Bibcode:2015PoRec..51..611R. doi:10.1017/S0032247414000722. ISSN 0032-2474. S2CID 129922206.
- Saine, Thomas P. (1972). Georg Forster. New York, NY: Twayne Publishers. ISBN 0-8057-2316-1.
- Smith, Alexander (1990). Explorers of the Amazon. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-76337-4.
- Steiner, Gerhard (1977). Georg Forster (in German). Stuttgart: J.B. Metzler. ISBN 978-3-476-10156-3. OCLC 462099778.
- Strehlke, F. (1861). "Georg Forster's Geburtsort". Neue Preußische Provinzialblätter. 3 Folge. 8: 189–212.
- Thomas, Nicholas; Berghof, Oliver, eds. (2000). A Voyage Round the World. Forster, Georg. University of Hawai'i Press. ISBN 0-8248-2091-6. JSTOR j.ctvvn739.
- Uhlig, Ludwig (2004). Georg Forster: Lebensabenteuer eines gelehrten Weltbürgers (1754–1794) (in German). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht. p. 107. ISBN 978-3-525-36731-5.
- Jovanović, Lazar, (2020). “The Cosmopolitan Circumnavigator of the South Seas: A Biography of Georg Forster”, in BEROSE – International Encyclopaedia of the Histories of Anthropology, Paris.
- Reintjes, Heinrich (1953). Weltreise nach Deutschland (in German). Düsseldorf: Progress-Verlag.
External links
- The Forster Collection at the Pitt Rivers Museum
- Georg Forster society in Kassel (in German)
- Letter recommending Georg Forster to the Royal Society (archived link, 21 October 2006)
- Biography at the Australian Dictionary of Biography
- Works by Georg Forster at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Georg Forster at the Internet Archive
- Works by Georg Forster at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Resources related to research : BEROSE – International Encyclopaedia of the Histories of Anthropology. "Forster, Georg (1754–1794)", Paris, 2020. (ISSN 2648-2770)
- 1754 births
- 1794 deaths
- 18th-century German explorers
- 18th-century German botanists
- 18th-century German writers
- 18th-century German male writers
- 18th-century German zoologists
- Botanists active in the Pacific
- Enlightenment scientists
- Fellows of the Royal Society
- German entomologists
- German librarians
- German male non-fiction writers
- German mycologists
- German ornithologists
- German people from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
- German people of Scottish descent
- German revolutionaries
- German taxonomists
- German travel writers
- James Cook
- Academic staff of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
- Members of the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina
- People from Gdańsk County
- People from Royal Prussia
- People of the French Revolution
- Pteridologists
- Saint Peter's School (Saint Petersburg) alumni
- Academic staff of Vilnius University
- 18th-century German naturalists