| Revision as of 22:50, 11 September 2009 view sourceWBardwin (talk | contribs)Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers20,628 edits →Reconstruction to present: "over time"← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:46, 5 January 2025 view source Milo8505 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,328 editsm →Distribution of slaveholders: clean up, fixed census overcapitalizationTag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|none}} | |||
| {{slavery}} | |||
| {{About|slavery from the founding of the United States in 1776|the colonial period|Slavery in the colonial history of the United States|modern illegal slavery|Human trafficking in the United States|modern legal forced labor|Penal labor in the United States}} | |||
| ], 1863, whose scars resulted from violent abuse by a plantation overseer. Photo on file with U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, online at nara.gov along others. .]] | |||
| {{Redirect|Peculiar institution|the book|The Peculiar Institution{{!}}''The Peculiar Institution''}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{See also|Abolitionism in the United States}} | |||
| '''Slavery in the United States''' had its origins with the first ] of North America in ] in 1607, although African slaves were brought to ] as early as the 1560s.<ref>], ''Inhuman Bondage: The Rise and Fall of Slavery in the New World.'' Oxford University Press. 2006. p. 124.</ref> Historian ] "begins with what he calls the 'charter generations.' These 17th-century black settlers entered areas like Dutch New Netherland, the English Chesapeake, French Louisiana or Spanish Florida with an indeterminate status that only gradually evolved into slavery. Their debasement was driven by the European demand for workers who could be used to exploit the economic opportunities offered by the New World." <ref>] review of ''Generations Of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves'' by Ira Berlin. Belknap Press/Harvard University Press: 2003]</ref> | |||
| {{Pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=February 2017}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=June 2023}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | border = | |||
| | total_width = 300 | |||
| | image_style = border:none; | |||
| | perrow = 2/2/2/2/1 | |||
| | image1 = Torturing American citizens page 129.jpg | |||
| | image2 = Detail of Wilson Chinn photograph "VBM".jpg | |||
| | image3 = Adam Crosswhite.jpg | |||
| | image4 = Franklin and Armfield slave prison Alexandria Virginia 1836.png | |||
| | image5 = Detail of Contrabands Aboard U.S. Ship Vermont, Port Royal, South Carolina MET DP254888.jpg | |||
| | image6 = DeliaGarlic.jpg | |||
| | image8 = Ezra Greenleaf Weld (American - Fugitive Slave Law Convention, Cazenovia, New York - Google Art Project.jpg | |||
| | image7 = J Allentharp.jpg | |||
| | image9 = MS-Indianola-Bettersworth0001 DESTROYED 1960s White Gold in the Delta.jpg | |||
| | footer = ], wood-engraving made 1834; ], showing a slave collar and facial branding of the initials of his enslaver, Valsin B. Marmillion; slavery survivor ] photographed 1878; ]'s slave jail in the ], 1836; freedmen leaving South Carolina on the ] in 1862; ] at age 100; 1818 Kentucky ]'s ad; daguerreotype made at the 1850 ]; ''White Gold in the Delta'', painted 1939 by Beulah Bettersworth for the ] post office, mural destroyed 1960s | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Slavery|sp=us}} | |||
| ] lasted as a legal institution in the U.S. until the passage of the ] in 1865. On the economic value of slaves, historian ] has written: | |||
| {{African American topics sidebar|collapsed}} | |||
| <blockquote>On the eve of the Civil War, the economic value of slaves in the United States was $3 billion in 1860 currency, more than the combined value of all the factories, railroads and banks in the country. Much of the North's economic prosperity derived from what Abraham Lincoln, in his second inaugural address, called ''the bondman's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil.'' Lincoln was asking Americans to consider the obligations created by slavery. The first of those obligations is to acknowledge the full truth.<ref>]'' July 13, 2000]</ref> </blockquote> | |||
| {{Native American topics sidebar}} | |||
| The legal institution of human ], comprising the enslavement primarily of ] and ], was prevalent in the ] from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the ]. Slavery was established throughout ]. From 1526, during the early ], it was practiced in what became ], including the ] that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of ]s until ] in 1865, and issues concerning slavery seeped into every aspect of national politics, economics, and social custom.<ref>{{cite book | |||
| Before the widespread establishment of ], much labor was organized under a system of bonded labor known as ''].'' This typically lasted for several years for ] and ] alike, and it was a means of using labor to pay the costs of transporting people to the colonies.<ref name="usnews.com"></ref> By the 18th century, court rulings established the racial basis of the American incarnation of ] to apply chiefly to ] ]ns and people of African descent, and occasionally to ]. A 1705 Virginia law stated slavery would apply to those peoples from nations that were not Christian.<ref></ref> In part because of the success of tobacco as a ] in the ], its labor-intensive character caused planters to import more slaves for labor by the end of the 17th century than did the ]. The South had a significantly high number and proportion of slaves in the population.<ref name="usnews.com"/> Religious differences contributed to this geographic disparity as well.{{Fact|date=March 2009}} | |||
| |page=87 | |||
| |title=Passionate Liberator. Theodore Dwight Weld and the Dilemma of Reform | |||
| |first=Robert H. | |||
| |last=Abzug | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |year=1980 | |||
| |isbn=0-19-502771-X}}</ref> In the decades after the end of ] in 1877, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through ], ], and ]. Involuntary servitude as a punishment for crime is still legal in the United States. | |||
| By the time of the ] (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial ] associated with African ancestry.<ref>{{cite magazine |url= http://www.slate.com/articles/life/the_history_of_american_slavery/2015/05/why_america_adopted_race_based_slavery.html |title= The Birth of Race-Based Slavery |last=Wood |first=Peter |date=2003 |magazine=Slate |id= (May 19, 2015): Reprinted from ''Strange New Land: Africans in Colonial America'' by Peter H. Wood with permission from Oxford University Press. 1996, 2003}}</ref> During and immediately following the Revolution, ] laws were passed in most ] and a movement developed to abolish slavery. The role of slavery under the ] (1789) was the most contentious issue during its drafting. The ] of the Constitution gave slave states disproportionate political power,<ref>{{cite web|first=Frederick|last=Douglass|title=The Constitution and Slavery|url=https://teachingamericanhistory.org/library/document/the-constitution-and-slavery/|year=1849}}</ref> while the Fugitive Slave Clause (]) provided that, if a slave escaped to another state, the other state could not prevent the return of the slave to the person claiming to be his or her owner. All Northern states had abolished slavery to some degree by 1805, sometimes with completion at a future date, sometimes with an intermediary status of unpaid indentured servant. | |||
| From 1654 until 1865, slavery for life was legal within the boundaries of much of the present ].<ref></ref> Most slaves were black and were held by whites, although some Native Americans and free blacks also held slaves; there was a small number of white slaves as well. The majority of slaveholders were in the ], where most slaves were engaged in an efficient machine-like gang system of agriculture, with farms of fifteen or more slaves proving to be far more productive than farms without slaves. According to the 1860 U.S. census, nearly four million slaves were held in a total population of just over 12 million in the 15 states in which slavery was legal.<ref name=CWHP-1860c>, The Civil War Home Page. This source derived numbers for "Percent of Families Owning Slaves" by assuming only one slaveholder per family, a presumption with evidence only to the contrary.</ref> Of all 8,289,782 free persons in the 15 ]s, 393,967 people (4.8%) held slaves, with the average number of slaves held by any single owner being 10.<ref name=CWHP-1860c /><ref> This source derived numbers for "% of Families Owning Slaves" by assuming only one slaveholder per family, a presumption with evidence only to the contrary. The summary numbers also include 17 slaves and 8 slaveowners counted by census-takers in Nebraska and Kansas, where slavery was illegal.</ref> The majority of slaves were held by planters, defined by historians as those who held 20 or more slaves.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.southernhistory.net/modules.php?op=modload&name=News&file=article&sid=9406 |title=Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States |accessdate=2007-11-23 |author=Otto H. Olsen |year=2004 |month=December |work=Civil War History |publisher=Southernhistory.net }}</ref> Ninety-five percent of black people lived in the South, comprising one-third of the population there, as opposed to 2% of the population of the ].<ref>{{cite book |last=] |title=Drawn with the Sword: Reflections on the American Civil War |year=1996 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |isbn=0-19-509679-7 |pages=15 }}</ref> Despite being an efficient economic system, slavery did not spread northward due to the nature of the soil in the region and the types of crops typically produced there. At the time, principal importers of slaves were sugar and cotton growing regions. Both of these crops were more suitably farmed on plantations and in the soil of the southern regions. Thus, when land more suitable for these crops was discovered towards the west, slavery spread westward and not to the north. The wealth of the United States in the first half of the 19th century was greatly enhanced by the labor of African Americans.<ref>{{cite book |last=James Oliver Horton |coauthors=Lois E. Horton |title=Slavery and the Making of America |year=2005 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |isbn=0-19-517903-X |pages=7 |quote=The slave trade and the products created by slaves' labor, particularly ], provided the basis for America's wealth as a nation. Such wealth provided some of the capital for the country's ] and enabled the United States to project its power into the rest of the world. }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.digitalhistory.uh.edu/historyonline/con_economic.cfm |title=Was slavery the engine of economic growth? |accessdate=2007-11-23 |publisher=Digital History }}</ref> | |||
| Abolition was in many cases a gradual process. Some slaveowners, primarily in the ], ] their slaves, and charitable groups bought and freed others. The ] began to be outlawed by individual states during the American Revolution. The import trade was ], although smuggling was common thereafter,<ref name="Julia Floyd Smith 1973, pp. 44–46">{{cite book |first=Julia Floyd |last=Smith |title= Slavery and Plantation Growth in Antebellum Florida, 1821–1860 |location= Gainesville |publisher= University of Florida Press |year=1973 |isbn= 978-0-8130-0323-8 |pages=44–46 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=BKIDcAAACAAJ&pg=PA44 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title= The Florida Negro. A Federal Writers' Project Legacy |publisher= University Press of Mississippi |year=1993 |isbn= 978-0-87805-588-3 |first=Gary W. |last=McDonough|page=7}}</ref> at which point the ] (Coast Guard) began enforcing the law on the high seas.<ref name=USCG1808> on the USCG official history website.</ref> It has been estimated that before 1820 a majority of serving ] owned slaves, and that about 30 percent of congressmen who were born before 1840 (some of whom served into the 20th century) owned slaves at some time in their lives.<ref name="WP-20220110">{{cite news |last1=Weil |first1=Julie Zauzmer |last2=Blanco |first2=Adrian |last3=Dominguez |first3=Leo |title=More than 1,700 congressmen once enslaved Black people. This is who they were, and how they shaped the nation. |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/history/interactive/2022/congress-slaveowners-names-list/ |date=January 10, 2022 |newspaper=] |access-date=January 11, 2022 }}</ref> | |||
| Slavery was the major issue of the ] in which the ] emerged victorious, after which the slave-labor system was abolished in the South.<ref></ref> This contributed to the decline of the postbellum Southern economy, but it was most affected by the continuing decline in the price of cotton through the end of the century.<ref>''Without Consent or Contract: The Rise and Fall of American Slavery'', 1994, Robert William Fogel</ref> That made it difficult for the region to recover from the war, as did its comparative lack of infrastructure, which kept products from markets. The South faced ] from foreign cotton producers such as ] and ]. Northern ], which had expanded rapidly before and during the war, surged even further ahead of the ]. Industrialists from ] came to dominate many aspects of the nation's life, including social and some aspects of ]. The planter class of the South lost power temporarily. The rapid economic development following the Civil War accelerated the development of the modern ].<!-- most of this paragraph is off-topic for the lede--> | |||
| The rapid expansion of the ] in the ] after the invention of the ] greatly increased demand for slave labor, and the ] continued as slave societies. The U.S., divided into ], became ever more polarized over the issue of slavery. Driven by labor demands from new cotton ], the Upper South sold more than a million slaves who were taken to the Deep South. The total slave population in the South eventually reached four million.<ref name="Stephen1999">{{Cite book|last1=Appiah|first1=Anthony|url=http://archive.org/details/africanaencyclop00appi|title=Africana: the encyclopedia of the African and African American experience|last2=Gates|first2=Henry Louis|date=1999|publisher=New York : Basic Civitas Books|others=Internet Archive|isbn=978-0-465-00071-5}}</ref>{{page needed|date=July 2024}}<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070714073725/http://www.itd.nps.gov/cwss/manassas/social/introsoc.htm |date=July 14, 2007 }}, National Park Service.</ref> As the U.S. expanded, the Southern states attempted to extend slavery into the new Western territories to allow ] forces to maintain power in Congress. The new ] acquired by the ] and the ] were the subject of major political crises and compromises.<ref>"n 1854, the passage of the ] ... overturned the policy of containment and effectively unlocked the gates of the Western territories (including both the old Louisiana Purchase lands and the Mexican Cession) to the legal expansion of slavery...." ], ''] as a Man of Ideas'', Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press (2009), p. 80.</ref> ], and the largest religious denominations split over the slavery issue into regional organizations of the North and South. | |||
| Twelve million Africans were shipped to the ] from the 16th to the 19th centuries.<ref>{{cite book |last=Ronald Segal |title=The Black Diaspora: Five Centuries of the Black Experience Outside Africa |year=1995 |publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux |location=New York |isbn=0-374-11396-3 |pages=4 |quote=It is now estimated that 11,863,000 slaves were shipped across the Atlantic. ... It is widely conceded that further revisions are more likely to be upward than downward. }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/6445941.stm |title=Quick guide: The slave trade |accessdate=2007-11-23 |date=March 15, 2007 |publisher=bbc.co.uk }}</ref> Of these, an estimated 645,000 were brought to what is now the United States. The largest number were shipped to ] (see ]).<ref>Stephen D. Behrendt, David Richardson, and David Eltis, ], ]. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". {{cite book |last=Stephen Behrendt |title=Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience |year=1999 |publisher=Basic Civitas Books |location=New York |isbn=0-465-00071-1 |chapter=Transatlantic Slave Trade |quote=}}</ref> The slave population in the United States had grown to four million by the 1860 Census.<ref></ref> | |||
| By 1850, the newly rich, cotton-growing South threatened to secede from the ]. ] broke out over slavery in the ]. When ] won the ] on a platform of halting the expansion of slavery, slave states seceded to form the ]. Shortly afterward, the ] began when Confederate forces attacked the U.S. Army's ] in Charleston, South Carolina. During the war some ] and, due to Union measures such as the ] and the ], the war effectively ended slavery in most places. After the Union victory, the ] was ratified on December 6, 1865, prohibiting "slavery involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime."<ref>{{Cite web |title=The 13th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution |url=https://constitutioncenter.org/interactive-constitution/amendment/amendment-xiii |access-date=2022-03-01 |website=National Constitution Center – The 13th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Colonial America== | |||
| {{Main|Slavery in Colonial United States}} | |||
| {{African American topics sidebar}} | |||
| The first record of African slavery in Colonial America was made in 1619. A British pirate ship under the ] flag, the ''White Lion'', had captured 20 ]n slaves in a battle with a ] ship, the San Juan Bautista, bound for ], ]<ref name=WP> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/09/02/AR2006090201097_pf.html | |||
| |title=Mystery of Va.'s First Slaves Is Unlocked 400 Years Later | |||
| |publisher=www.washingtonpost.com | |||
| |accessdate=2009-04-19 | |||
| |last= | |||
| |first= | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref>. The Angolans were from the kingdoms of ] and ], and spoke languages of the ] group<ref name=WP/>. The ''White Lion'' had been damaged first by the battle and then more severely in a great storm during the late summer when it came ashore at Old Point Comfort, site of present day ] in ]. Though the colony was in the middle of a period later known as "The Great Migration" (1618-1623), during which its population grew from 450 to 4,000 residents, extremely high mortality rates from ], ], and ] kept the population of able-bodied laborers low<ref> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.virtualjamestown.org/timeline2.html | |||
| |title=Virtual Jamestown--Timeline | |||
| |publisher=www.virtualjamestown.org | |||
| |accessdate=2009-04-19 | |||
| |last= | |||
| |first= | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref>. With the Dutch ship being in severe need of repairs and supplies and the colonists being in need of able-bodied workers, the human cargo was traded for food and services. | |||
| ==Background== | |||
| In addition to African slaves, Europeans, mostly ],<ref></ref> ],<ref></ref> ], and ],<ref>, Faulkner University</ref> were brought over in substantial numbers as ]s,<ref>, By Deanna Barker, Frontier Resources</ref> particularly in the British ].<ref>, ''A Short History of Northern Ireland'', BBC. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> Over half of all white immigrants to the English colonies of North America during the 17th and 18th centuries might have been indentured servants.<ref></ref> In the 18th century numerous Europeans traveled to the colonies as ]s.<ref></ref> The white citizens of Virginia, who had arrived from Britain, decided to treat the first Africans in Virginia as indentured servants. As with European indentured servants, the Africans were freed after a stated period and given the use of land and supplies by their former owners. ], a former indentured servant from Africa, became a landowner on the ] and a slave-owner.<ref></ref> The major problem with indentured servants was that, in time, they would be freed, but they were unlikely to become prosperous. The best lands in the ] regions were already in the hands of wealthy plantation families by 1650, and the former servants became an underclass. ] showed that the poor laborers and farmers could prove a dangerous element to the wealthy landowners. By switching to pure chattel slavery, new white laborers and small farmers were mostly limited to those who could afford to immigrate and support themselves. In addition, improving economic conditions in England meant that fewer laborers wanted to migrate to the colonies as indentured servants, so the planters needed to find new sources of labor. | |||
| {{Main|Slavery in the colonial history of the United States|Slavery among Native Americans in the United States|History of unfree labor in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|Atlantic slave trade|Slavery in New France|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#Colonial period, 1607–1775}} | |||
| {{For|the related topic of indentured servitude in the United States|Indentured servitude in British America|Indentured servitude in Pennsylvania|Indentured servitude in Virginia|Engagé system in Louisiana}} | |||
| ] (Colonial Williamsburg Foundation)]] | |||
| <!-- NOTE: The primary focus of this encyclopedia article is slavery in the United States, which got going in 1776. Content about slavery that time should generally be added to the colonial slavery article. This section is meant to be an introductory overview and background, and should be mere summary. --> | |||
| ]'', c. 1790)]] | |||
| During most of the British colonial period, slavery existed in all the colonies. People enslaved in ] typically worked as house servants, artisans, laborers and craftsmen, with the greater number in cities. Many men worked on the docks and in shipping. In 1703, more than 42 percent of New York City households held enslaved people in bondage, the second-highest proportion of any city in the colonies, behind only ].<ref name="Nation">, ''The Nation'', November 7, 2005</ref> Enslaved people were also used as agricultural workers in farm communities, especially in ], but also in ] and ], ], and ]. By 1770, there were 397,924 blacks out of a population of 2.17 million in what would soon become the United States. The slaves of the colonial era were unevenly distributed: 14,867 lived in ], where they were three percent of the population; 34,679 lived in the ], where they were six percent of the population; and 347,378 in the five ], where they were 31 percent of the population.<ref>Ira Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves'', 2003. {{ISBN|0674010612}}{{page needed|date=April 2022}}</ref> | |||
| The South developed an ] dependent on ]. Its planters rapidly acquired a significantly higher number and proportion of enslaved people in the population overall, as its commodity crops were labor-intensive.<ref name="usnews.com"> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110202205901/http://www.usnews.com/usnews/news/articles/070121/29african.htm |date=February 2, 2011 }}, Hashaw, Tim; ''U.S. News & World Report'', 1/21/07</ref> Early on, enslaved people in ] worked primarily on farms and plantations growing ], ] and ] (] did not become a major crop until after the 1790s). In 1720, about 65 percent of ] population was enslaved.<ref>{{Cite web|title=South Carolina - African-Americans - Slave Population|url=https://www.sciway.net/afam/slavery/population.html|access-date=2022-12-29|website=www.sciway.net}}</ref> Planters (defined by historians in the Upper South as those who held 20 or more slaves) used enslaved workers to cultivate commodity crops. They also worked in the artisanal trades on large plantations and in many Southern port cities. The later wave of settlers in the 18th century who settled along the ] and ] were backwoods ], and they seldom held enslaved people. | |||
| The transformation from indentured servitude to racial slavery happened gradually. There were no laws regarding slavery early in Virginia's history. However, by 1640, the Virginia courts had sentenced at least one black servant to slavery. | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1654, ], a black man, became the first legally recognized slave in the present United States. A court in ] ruled against Casor, declaring him ] for life, "owned" by the black colonist Anthony Johnson. Since persons with African origins were not English citizens by birth, they were not necessarily covered by ]. ] successfully gained her freedom in the Virginia courts in 1656 by making her case as the baptized Christian daughter of free Englishman Thomas Key.<ref>, Digital Commons Law, University of Maryland Law School, accessed 21 Apr 2009</ref> | |||
| Beginning in the second half of the 18th century, a debate emerged over the continued importation of African slaves to the American colonies. Many in the colonies, including the Southern ], opposed further importation of slaves due to fears that it would destabilize colonies and lead to further ]s. In 1772, prominent Virginians submitted a petition to ], requesting that the slave trade to Virginia be abolished; it was rejected.<ref>{{cite book|last=Smith|first=Howard W.|title=Benjamin Harrison and the American Revolution|editor-first=Edward M.|editor-last=Riley|location=Williamsburg|publisher= Virginia Independence Bicentennial Commission|year=1978|oclc=4781472}}</ref> ] forbade the importation of slaves in 1774. The influential revolutionary ] called for an end to the "wicked, cruel and unnatural" Atlantic slave trade.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Foner |first1=Eric |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tZeHAgAAQBAJ&q=the+influential+fairfax+resolves+called+for+the+end+of+the+slave+trade&pg=PT728 |title=The Reader's Companion to American History |last2=Garraty |first2=John A. |year=2014 |publisher=Houghton Mifflin |isbn=978-0-547-56134-9 |page=705 |language=en |access-date=4 July 2021 |archive-date=7 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210707115029/https://books.google.com/books?id=tZeHAgAAQBAJ&newbks=0&printsec=frontcover&pg=PT728&dq=the+influential+fairfax+resolves+called+for+the+end+of+the+slave+trade&hl=en |url-status=live }}</ref> All of the colonies banned slave importations during the Revolutionary War.<ref>Morison and Commager: ''Growth of the American Republic'', pp. 212–220.</ref> | |||
| ==Slavery in the American Revolution and early republic== | |||
| Shortly after the Elizabeth Key trial, in 1662 Virginia passed a law on '']'', stating that any children of an enslaved mother would follow her status and automatically be slaves, no matter if the father was a freeborn Englishman. This institutionalized the power relationships and confined the possible scandal of mixed-race children to within the slave quarters. The Virginia ] of 1705 further defined as slaves those people imported from nations that were not ], as well as Native Americans who were sold to colonists by other ]. | |||
| {{Main|African Americans in the Revolutionary War|Slavery and the United States Constitution}} | |||
| {{Further|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#American Revolution and Confederation period, 1776–1787|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#Early Constitutional period, 1787–1811}} | |||
| ]'', watercolor attributed to John Rose, possibly painted 1785–1795 in the ] of South Carolina (]) ]] | |||
| Slavery had existed for thousands of years, all around the world. In the United States and many parts of the world it was a legal practise and had become entrenched socially and economically in many societies. The ideals and principles promoted in the ] and the American Revolution helped to put slavery and the desire for its ] on the political agenda. As historian ] put it, slavery "had never been on the agenda in a serious way before", but the ] "forced it to be a public question from there forward".<ref>Brown, Christopher. PBS Video "Liberty! The American Revolution", Episode 6, "Are We to be a Nation?", Twin Cities Public Television, Inc., 1997.</ref><ref>Brown, Christopher Leslie (2006). ''Moral Capital: Foundations of British Abolitionism,'' pp. 105–106, Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. {{ISBN|978-0-8078-3034-5}}.</ref><ref>]. "An Interview with Historian Gordon Wood on the New York Times "1619 Project," World Socialist Web Site, wsws.org, November 28, 2019.</ref><ref>Bailyn, Bernard. ''Faces of the Revolution: Personalities and Themes in the Struggle for American Independence,'' pp. 221-4, Vintage Books, New York, New York, 1992. {{ISBN|0-679-73623-9}}.</ref><ref>Wood, Gordon S. ''The Radicalism of the American Revolution,'' pp. 3-8, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, New York, 1992. {{ISBN|0-679-40493-7}}.</ref> | |||
| During the British colonial period, every colony had slavery. People enslaved in ] typically worked as house servants, artisans, laborers and craftsmen, with the greater number in cities. Early on, slaves in ] worked primarily in agriculture, on farms and ]s growing ], ], and ]; ] became a major crop after the 1790s. Tobacco was very labor intensive, as was rice cultivation.<ref name="britannica">, ''Encyclopedia Britannica's Guide to Black History''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> In ] in 1720 about 65% of the population consisted of slaves.<ref>Trinkley, M. , ''South Carolina Information Highway''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> Slaves were used by rich farmers and plantation owners who cultivate crops for commercial export operations. Backwoods subsistence farmers, a later wave of settlers, seldom owned slaves. | |||
| After the new country's independence was secure, slavery was a topic of contention at the 1787 ]. Many of ] were plantation owners who owned large numbers of enslaved laborers; the original Constitution preserved their right to own slaves, and they further gained a political advantage in owning slaves. Although the enslaved of the early Republic were considered sentient property, were not permitted to vote, and had no rights to speak of, they were to be enumerated in population censuses and counted as ] of a person for the purposes of representation in the national legislature, the ]. | |||
| Some of the British colonies attempted to abolish the ], fearing that the importation of new Africans would be disruptive. Virginia bills to that effect were vetoed by the ]; ] forbade the import of slaves in 1774. All of the colonies except ] had banned or limited the African slave trade by 1786; Georgia did so in 1798 - although some of these laws were later repealed.<ref>Morison and Commager: ''Growth of the American Republic'', pp. 212-220.</ref> | |||
| <br clear=left> | |||
| ===Slaves and free blacks who supported the Continental Army=== | |||
| The British ]'s slave trade suppression activities were assisted by forces from the ], starting in 1820 with the ]. Initially, this consisted of a few ships. With the ] of 1842, the relationship was formalised and they jointly ran the ].<ref></ref> | |||
| {{Main|Black Patriot}} | |||
| ], who was an enslaved African-American man who purchased his freedom, became a soldier, and rose to fame as a war hero during the ].<ref name=Hubbard>Hubbard, Robert Ernest (2017). ''Major General Israel Putnam: Hero of the American Revolution'', p. 98, McFarland & Company, Inc., Jefferson, NC. {{ISBN|978-1-4766-6453-8}}.</ref>]] | |||
| The rebels began to offer freedom as an incentive to motivate slaves to fight on their side. Washington authorized slaves to be freed who fought with the American ]. Rhode Island started enlisting slaves in 1778, and promised compensation to owners whose slaves enlisted and survived to gain freedom.<ref>{{cite book|last=Nell|first=William C.|chapter=IV, Rhode Island|title=The Colored Patriots of the American Revolution|publisher=Robert F. Wallcut|year=1855|isbn=978-0-557-53528-6|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Jy8OAAAAIAAJ}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery|publisher=W.W. Norton & Company, Inc|author=Foner, Eric|year=2010|location=New York|page=205}}</ref> During the course of the war, about one-fifth of the Northern army was black.<ref>] (Documentary), Episode II:''Blows Must Decide: 1774–1776''. 1997 ] {{ISBN|1-4157-0217-9}}</ref> In 1781, Baron Closen, a ] in the French ] at the ], estimated the American army to be about one-quarter black.<ref>{{Cite web|title=The Revolution's Black Soldiers|url=https://www.americanrevolution.org/blk.php|access-date=2022-12-29|website=www.americanrevolution.org}}</ref> These men included both former slaves and free-born blacks. Thousands of free blacks in the Northern states fought in the state militias and Continental Army. In the South, both sides offered freedom to slaves who would perform military service. Roughly 20,000 slaves fought in the American Revolution.<ref name=Hubbard/><ref>Hoock, Holger. ''Scars of Independence: America's Violent Birth,'' pp. 95, 300–303, 305, 308–310, Crown Publishing Group, New York, 2017. {{ISBN|978-0-8041-3728-7}}.</ref><ref>O'Reilly, Bill and Dugard, Martin. ''Killing England: The Brutal Struggle for American Independence,'' pp. 96, 308, Henry Holt and Company, New York, 2017. {{ISBN|978-1-62779-064-2}}.</ref><ref>Ayres, Edward. , Jamestown Settlement and American Revolution Museum at Yorktown website. Retrieved October 21, 2020.</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Digital History|url=http://www.digitalhistory.uh.edu/active_learning/explorations/revolution/revolution_slavery.cfm#:~:text=Slavery,%2520the%2520American%2520Revolution,%2520and%2520the%2520Constitution%2520African,sensitivity%2520to%2520the%2520opinion%2520of%2520southern%2520slave%2520holders|access-date=2022-12-29|website=www.digitalhistory.uh.edu}}</ref> | |||
| ==1776 to 1850== | |||
| ===Second Middle Passage=== | |||
| As the ], so did the cultivation of cotton<ref>Kolchin p. 96. In 1834, ], ], and ] grew half the nation's cotton; by 1859, along with ], they grew 78%. By 1859 cotton growth in the ] had fallen to just 10% of the national total. Berlin p. 166. At the end of the ] there were less than 300,000 bales of cotton produced nationally. By 1820 this figure had increased to 600,000, and by 1850 it had reached 4,000,000.</ref> and the institution of slavery. Historian Peter Kolchin wrote, "By breaking up existing families and forcing slaves to relocate far from everyone and everything they knew" this migration "replicated (if on a reduced level) many of horrors" of the Atlantic slave trade.<ref>Kolchin p. 96</ref> Historian Ira Berlin called this forced migration the Second ]. Characterizing it as the "central event” in the life of a slave between the ] and the Civil War, Berlin wrote that whether they were uprooted themselves or simply lived in fear that they or their families would be involuntarily moved, "the massive deportation traumatized black people, both slave and free."<ref> Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 161-162</ref> | |||
| ===Black Loyalists=== | |||
| Although complete statistics are lacking, it is estimated that 1,000,000 slaves moved west from the ] between 1790 and 1860. Most of the slaves were moved from ], ], and the ]. Originally the points of destination were ] and ], but after 1810 the states of the Deep South: ], ], ], ] and ] received the most. This corresponded to the massive expansion of cotton cultivation in that region, which needed labor. In the 1830s, almost 300,000 were transported, with Alabama and Mississippi receiving 100,000 each. Every decade between 1810 and 1860 had at least 100,000 slaves moved from their state of origin. In the final decade before the Civil War, 250,000 were moved. Michael Tadman, in a 1989 book ''Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South'', indicates that 60-70% of interregional migrations were the result of the sale of slaves. In 1820 a child in the Upper South had a 30% chance of being sold south by 1860.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 168-169. Kolchin p. 96. Kolchin notes that Fogel and Engerman maintained that 84% of slaves moved with their families but "most other scholars assign far greater weight ... to slave sales." Ransome (p. 582) notes that Fogel and Engermann based their conclusions on the study of some counties in Maryland in the 1830s and attempt to extrapolate that as reflective of the entire South over the entire period.</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Black Loyalist|Dunmore's Proclamation}} | |||
| {{See also|Book of Negroes}} | |||
| ]s in the ].]] | |||
| After the Revolutionary War broke out, the British realized they lacked the manpower necessary to prosecute the war. In response, British commanders began issuing proclamations to Patriot-owned slaves, offering freedom if they fled to British lines and assisted the British war effort.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://blogs.bl.uk/untoldlives/2020/10/tracing-the-lives-and-letters-of-the-black-loyalists-part-1-the-journey-to-sierra-leone-1.html|title=Tracing the lives and letters of the Black Loyalists – Part 1 The Journey to Sierra Leone - Untold lives blog}}</ref> Such proclamations were repeatedly issued over the course of the conflict, which resulted in up to 100,000 American slaves fleeing to British lines.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/black-loyalists-in-british-north-america | title=Black Loyalists in British North America }}</ref> Self-emancipated slaves who reached British lines were organized into a variety of military units, which served in all theaters of the war. Formerly enslaved women and children, in lieu of military service, worked instead as laborers and domestic servants. At the end of the war, freed slaves in British lines either evacuated to other British colonies or to Britain itself, were re-enslaved by the victorious Americans, or fled into the countryside.<ref>{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kZfOjZ65WecC&q=Black+Patriots+and+Loyalists:+Fighting+for+Emancipation+in+the+War+for+Independence+by+Alan+Gilbert | title=Black Patriots and Loyalists: Fighting for Emancipation in the War for Independence | isbn=978-0-226-29309-7 | last1=Gilbert | first1=Alan | date=March 19, 2012 | publisher=University of Chicago Press }}</ref> | |||
| Slave traders were responsible for the majority of the slaves that moved west. Only a minority moved with their families and existing owner. Slave traders had little interest in purchasing or transporting intact slave families, although in the interest of creating a "self-reproducing labor force", equal numbers of men and women were transported. Berlin wrote, "The internal slave trade became the largest enterprise in the South outside the plantation itself, and probably the most advanced in its employment of modern transportation, finance, and publicity." The slave trade industry developed its own unique language with terms such as "prime hands, bucks, breeding wenches, and fancy girls" coming into common use.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 166-169</ref> The expansion of the interstate slave trade contributed to the "economic revival of once depressed seaboard states" as demand accelerated the value of the slaves who were subject to sale.<ref>Kolchin p. 98</ref> | |||
| In early 1775, the ], ], wrote to the ] of his intention to free slaves owned by ] in case they staged a rebellion.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.americanrevolution.org/blk.html |title=The Revolution's Black Soldiers |access-date=October 18, 2007 |first=Robert A. |last=Selig |publisher=AmericanRevolution.org}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Frey|first=Sylvia R.|title=Water From the Rock: Black Resistance in a Revolutionary Age|date=1991|publisher=Princeton University Press|location=Princeton, New Jersey|page=63}}</ref> On November 7, 1775, Dunmore issued ], which promised freedom to any slaves of American patriots who would leave their masters and join the British forces.<ref>{{cite book |last=Scribner |first=Robert L. |title=Revolutionary Virginia, the Road to Independence |publisher=University of Virginia Press |year=1983 |page=xxiv |isbn=978-0-8139-0748-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/revolutionaryvir0000unse }}</ref> Historians agree that the proclamation was chiefly designed for practical rather than moral reasons, and slaves owned by American Loyalists were unaffected by the proclamation. About 1,500 slaves owned by patriots escaped and joined Dunmore's forces. A total of 18 slaves fled ]'s plantation, one of whom, Harry, served in Dunmore's all-black loyalist regiment called "the Black Pioneers".<ref name=PBS/> Escapees who joined Dunmore had "Liberty to Slaves" stitched on to their jackets.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Hartmann |first1=Thom |title=The Hidden History of Guns and the Second Amendment |date=2019 |publisher=Berrett-Koehler Publishers |page=48}}</ref> Most died of disease before they could do any fighting, but three hundred of these freed slaves made it to freedom in Britain.<ref>{{cite book|first=James L.|last=Roark|title=The American Promise, Volume I: To 1877: A History of the United States|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F7bVy_eUYYwC&pg=PA206 |year=2008|publisher=Macmillan|page=206|isbn=978-0-312-58552-5|display-authors=etal}}</ref> Historian Jill Lepore writes that "between eighty and a hundred thousand (nearly one in five black slaves) left their homes ... betting on British victory", but Cassandra Pybus states that between 20,000 and 30,000 is a more realistic number of slaves who defected to the British side during the war.<ref name=PBS>{{cite news |title=George Washington's Runaway Slave, Harry |url=https://www.pbs.org/wnet/african-americans-many-rivers-to-cross/history/george-washingtons-runaway-slave-harry/ |access-date=March 29, 2023 |work=PBS}}</ref> | |||
| Some traders moved their "chattels" by sea, with ] to ] being the most common route, but most slaves were forced to walk. Regular migration routes were established and were served by a network of slave pens, yards, and warehouses needed as temporary housing for the slaves. As the trek advanced, some slaves were sold and new ones purchased. Berlin concluded, "In all, the slave trade, with its hubs and regional centers, its spurs and circuits, reached into every cranny of southern society. Few southerners, black or white, were untouched."<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 168-171</ref> | |||
| Many slaves took advantage of the disruption of war to escape from their plantations to British lines or to fade into the general population. Upon their first sight of British vessels, thousands of slaves in Maryland and Virginia fled from their owners.<ref name=Clavin>{{cite book|title=The Battle of Negro Fort. The rise and fall of a fugitive slave community|isbn=978-1-4798-1110-6|first=Matthew J.|last=Clavin|year=2019|location=New York|publisher=New York University Press}}</ref>{{rp|21}} Throughout the South, losses of slaves were high, with many due to escapes.<ref>Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1994, p. 73.</ref> Slaves also escaped throughout New England and the mid-Atlantic, with many joining the British who had occupied New York.<ref name=PBS/> In the closing months of the war, the British evacuated ] and also removed slaves owned by loyalists. Around 15,000 ] left with the British, most of them ending up as free people in England or its colonies.<ref name="Duke Law">{{cite book |last1=Finkelman |first1=Paul |title=Slavery in the United States |date=2012 |page=116 |url=https://scholarship.law.duke.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=5386&context=faculty_scholarship|publisher=Duke University School of Law}}</ref> Washington hired a ] during the war, and at its end he pressed the British to return the slaves to their masters.<ref name=PBS/> With the British certificates of freedom in their belongings, the black loyalists, including Washington's slave Harry, sailed with their white counterparts out of New York harbor to ].<ref name=PBS/> More than 3,000 were resettled in Nova Scotia, where they were eventually granted land and formed the community of the ]. | |||
| The death rate for the slaves on their way to their new destination across the American South was much less than that of the captives across the Atlantic Ocean. Mortality was still higher than the normal death rate. Berlin summarizes the experience: | |||
| ===Early abolitionism in the United States=== | |||
| {{quote|... the Second Middle Passage was extraordinarily lonely, debilitating, and dispiriting. Capturing the mournful character of one southward marching coffle, an observer characterized it as "a procession of men, women, and children resembling that of a funeral." Indeed, with men and women dying on the march or being sold and resold, slaves became not merely commodified but cut off from nearly every human attachment.... | |||
| {{Main|Abolitionism in the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In the first two decades after the American Revolution, state legislatures and individuals took actions to free slaves. Northern states passed new constitutions that contained language about equal rights or specifically abolished slavery; some states, such as New York and New Jersey, where slavery was more widespread, passed laws by the end of the 18th century to abolish slavery incrementally. By 1804, all the Northern states had passed laws outlawing slavery, either immediately or over time. In New York, the last slaves were freed in 1827 (celebrated with a big July{{spaces}}5 parade). ], which had been widespread in the colonies (half the population of ] had once been ]), dropped dramatically, and disappeared by 1800. However, there were still forcibly indentured servants in New Jersey in 1860. No Southern state abolished slavery, but some individual owners, more than a handful, freed their slaves by personal decision, often providing for ] in wills but sometimes filing deeds or court papers to free individuals. Numerous slaveholders who freed their slaves cited revolutionary ideals in their documents; others freed slaves as a promised reward for service. From 1790 to 1810, the proportion of ] increased from 8 to 13.5 percent, and in the ] from less than one to nearly ten percent as a result of these actions.<ref>{{cite book|last=Painter|first=Nell Irvin|title=Creating Black Americans: African-American History and Its Meanings, 1619 to the Present|year=2007|page=72}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=An interview with historian Gordon Wood on the New York Times' 1619 Project|url=https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2019/11/28/wood-n28.html|access-date=2022-12-29|website=World Socialist Web Site|date=November 28, 2019 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Interview with Gordon Wood on the American Revolution|url=https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2015/03/03/wood-m03.html|access-date=2022-12-29|website=World Socialist Web Site|date=March 3, 2015 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Murder and mayhem made the Second Middle Passage almost as dangerous for traders as it was for slaves, which was why the men were chained tightly and guarded closely. ... The coffles that marched slaves southward – like the slave ships that carried their ancestors westward – became mobile fortresses, and under such circumstances, flight was more common than revolt. Slaves found it easier – and far less perilous – to slip into the night and follow the North Star to the fabled land of freedom than to confront their heavily armed overlords.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 172-173</ref>}} | |||
| Starting in 1777, the rebels outlawed the importation of slaves state by state. They all acted to end the international trade, but, after the war, it was reopened in North Carolina (opened until 1794) and Georgia (opened until 1798) and South Carolina (opened until 1787, and then reopened again in 1803.)<ref name="O'Malley">{{Cite journal|last=O'Malley|first=Gregory E.|year=2009|title=Beyond the Middle Passage: Slave Migration from the Caribbean to North America, 1619–1807|journal=The William and Mary Quarterly|volume=66|issue=1|pages=145, 150}}</ref> In 1807, the ] acted on President ]'s advice and, without controversy, made importing slaves from abroad a federal crime, effective the first day that the ] permitted this prohibition: January 1, 1808.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://abolition.nypl.org/print/us_constitution/|title=The Abolition of The Slave Trade|publisher=New York Public Library|date=2007|access-date=June 25, 2014|author=Finkelman, Paul}}</ref> | |||
| Once the trip was ended, slaves faced a life on the frontier significantly different from their experiences back east. Clearing trees and starting crops on virgin fields was harsh and backbreaking work. A combination of inadequate nutrition, bad water, and exhaustion from both the journey and the work weakened the newly arrived slaves and produced casualties. The preferred locations of the new plantations at rivers' edges, with ]es and other environmental challenges, threatened the survival of slaves. They had acquired only limited immunities in their previous homes. The death rate was such that, in the first few years of hewing a plantation out of the wilderness, some planters preferred whenever possible to use rented slaves rather than their own.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" p. 174</ref> | |||
| During the Revolution and in the following years, all states north of Maryland ( the ]) took steps towards abolishing slavery. In 1777, the ], which was still unrecognized by the United States, passed a ]. The ], led in part by ], was founded in 1775, and Pennsylvania began ] in 1780. In 1783, the ] ruled in '']'' that slavery was unconstitutional under the state's new ]. New Hampshire began ] in 1783, while Connecticut and Rhode Island followed suit in 1784. The ], which was led by ], ], and ], was founded in 1785. New York state began gradual emancipation in 1799, and New Jersey did the same in 1804. | |||
| The harsh conditions on the frontier increased slave resistance and led to much more reliance on violence by the owners and overseers. Many of the slaves were new to cotton fields and unaccustomed to the "sunrise-to-sunset gang labor" required by their new life. Slaves were driven much harder than when they were involved in growing tobacco or ] back east. Slaves also had less time and opportunity to improve the quality of their lives by raising their own ] or tending vegetable gardens, for either their own consumption or trade, as they could in the eastern south.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" p. 175-177</ref> | |||
| Shortly after the Revolution, the ] was established, by ] and ] (who had been George Washington's chief engineer). Both Cutler and Putnam came from ] New England. The Puritans strongly believed that slavery was morally wrong. Their influence on the issue of slavery was long-lasting, and this was provided significantly greater impetus by the Revolution. The Northwest Territory (which became Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin, and part of Minnesota) doubled the size of the United States, and it was established at the insistence of Cutler and Putnam as "free soil"{{snd}}no slavery. This was to prove crucial a few decades later. Had those states been slave states, and their electoral votes gone to Abraham Lincoln's main opponent, Lincoln would not have become president. The Civil War would not have been fought. Even if it eventually had been, the North might well have lost.<ref name="Hubbard, Robert Ernest pp. 1">Hubbard, Robert Ernest. ''General Rufus Putnam: George Washington's Chief Military Engineer and the "Father of Ohio"'', pp. 1–4, 105–106, McFarland & Company, Inc., Jefferson, North Carolina, 2020. {{ISBN|978-1-4766-7862-7}}.</ref><ref name="McCullough, David pp. 11, 13">McCullough, David. ''The Pioneers: The Heroic Story of the Settlers Who Brought the American Ideal West,'' pp. 11, 13, 29–30, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2019. {{ISBN|978-1-5011-6868-0}}.</ref><ref name="McCullough, David p. 132-3">McCullough, David. ''John Adams,'' pp. 132–133, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2001. {{ISBN|0-684-81363-7}}.</ref><ref>Bennett, William J. ''America: The Last Best Hope,'' Vol. I, p. 110, Tomas Nelson, Inc., Nashville, Tennessee, 2006. {{ISBN|978-1-59555-111-5}}.</ref><ref>Gradert, Kenyon. ''Puritan Spirits in the Abolitionist Imagination,'' pp. 1-3, 26, 74-5, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois, 2020. {{ISBN|978-0-226-69402-3}}</ref> | |||
| In Louisiana it was ], rather than cotton, that was the main crop. Between 1810 and 1830 the number of slaves increased from under 10,000 to over 42,000. New Orleans became nationally important as a slave port and by the 1840s had the largest slave market in the country. Dealing with sugar cane was even more physically demanding than growing cotton. Planters preferred young males, who represented two-thirds of the slave purchases. The largely young, unmarried male slave force made the reliance on violence by the owners “especially savage.”<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity" pp. 179-180</ref> | |||
| === |
===Constitution of the United States=== | ||
| {{Main|Slavery and the United States Constitution}} | |||
| Historian ] describes the role of coercion in slavery, | |||
| {{Further|Fugitive Slave Clause}} | |||
| :"Without the power to punish, which the state conferred upon the master, bondage could not have existed. By comparison, all other techniques of control were of secondary importance."<ref name=Stamp171/> | |||
| ]'', May 24, 1796, seeking the return of ], a ] who had escaped from the household of ]]] | |||
| Slavery was a contentious issue in the ] of the ].<ref>Keith L. Dougherty, and Jac C. Heckelman. "Voting on slavery at the Constitutional Convention." ''Public Choice'' 136.3–4 (2008): 293.</ref> The words "slave" and "slavery" did not appear in the Constitution as originally adopted, although several provisions clearly referred to slaves and slavery. Until the adoption of the ] in 1865, the Constitution did not prohibit slavery.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Mason | first1 = Matthew | year = 2006 | title = Slavery and the Founding | journal = History Compass | volume = 4 | issue = 5| pages = 943–955 | doi = 10.1111/j.1478-0542.2006.00345.x | issn=1478-0542}}</ref> | |||
| Stampp further notes that while rewards sometimes led slaves to perform adequately, most agreed with an Arkansas slaveholder, who wrote: | |||
| Section 9 of ] forbade the federal government from prohibiting the importation of slaves, described as "such Persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit", for twenty years after the Constitution's ratification (until January 1, 1808). The ], passed by Congress and signed into law by President ] (who had called for its enactment in his 1806 State of the Union address), went into effect on January 1, 1808, the earliest date on which the importation of slaves could be prohibited under the Constitution.<ref>Joseph R. Conlin, ''The American Past: A Survey of American History'' (Cengage Learning, 2008)</ref> | |||
| {{quote|Now, I speak what I know, when I say it is like ‘casting pearls before swine' to try to persuade a negro to work. He must be made to work, and should always be given to understand that if he fails to perform his duty he will be punished for it.<ref name=Stamp171>Stampp, The Peculiar Institution p. 171</ref>}} | |||
| The delegates approved the ] of the Constitution (]), which prohibited states from freeing those "held to Service or Labour" (meaning slaves, indentures, and apprentices) who fled to them from another state and required that they be returned to their owners.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Baker | first1 = H. Robert | year = 2012 | title = The Fugitive Slave Clause and the Antebellum Constitution | journal = Law and History Review | volume = 30 | issue = 4| pages = 1133–1174 | doi = 10.1017/s0738248012000697 | s2cid = 145241006 }}</ref> The ] and the ] gave effect to the Fugitive Slave Clause.<ref>{{cite news |title=Fugitive Slave Laws |url=https://encyclopediavirginia.org/entries/fugitive-slave-laws/ |access-date=February 19, 2022 |work=Encyclopedia Virginia}}</ref> ] considered the Fugitive Slave Acts unconstitutional because "The Fugitive Slave Clause was a compact among the states, not a grant of power to the federal government".<ref>Stahr, Walter, ''Salmon P. Chase: Lincoln's Vital Rival'', New York: Simon & Schuster, 2021, p. 67.</ref> | |||
| According to both the ]-winning historian ] and historian ], treatment of slaves was both harsh and inhumane. Whether laboring or walking about in public, people living as slaves were regulated by legally authorized violence. Davis makes the point that, while some aspects of slavery took on a "welfare capitalist" look, | |||
| ====Three-fifths Compromise==== | |||
| {{quote|Yet we must never forget that these same "welfare capitalist" plantations in the Deep South were essentially ruled by terror. Even the most kindly and humane masters knew that only the threat of violence could force gangs of field hands to work from dawn to dusk "with the discipline," as one contemporary observer put it, "of a regular trained army." Frequent public floggings reminded every slave of the penalty for inefficient labor, disorderly conduct, or refusal to accept the authority of a superior.<ref>Davis p. 196</ref>}} | |||
| {{Main|Three-fifths Compromise}} | |||
| {{See also|Slave Trade Act of 1794|Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves}} | |||
| ]'s 1780 portrait '']'' also depicts a man believed to be Washington's enslaved valet ] (] 24.109.88)]] | |||
| In a section negotiated by ] of Virginia, Section{{spaces}}2 of Article{{spaces}}I designated "other persons" (slaves) to be added to the total of the state's free population, at the rate of ] of their total number, to establish the state's official population for the purposes of apportionment of congressional representation and federal taxation.<ref>Section{{spaces}}2 of Article{{spaces}}I provides in part: "Representatives and direct taxes shall be apportioned among the several states{{spaces}}...by adding to the whole number of free persons, including those bound to service for a term of years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three-fifths of all other persons."</ref> The "Three-Fifths Compromise" was reached after a debate in which delegates from Southern (slaveholding) states argued that slaves should be counted in the census just as all other persons were while delegates from Northern (free) states countered that slaves should not be counted at all. The compromise strengthened the political power of Southern states, as three-fifths of the (non-voting) slave population was counted for congressional apportionment and in the ], although it did not strengthen Southern states as much as it would have had the Constitution provided for counting all persons, whether slave or free, equally. | |||
| ]On large plantations, slave overseers were authorized to ] and brutalize non-compliant slaves. According to an account by a plantation overseer to a visitor, "'some negroes are determined never to let a white man whip them and will resist you, when you attempt it; of course you must kill them in that case"<ref>] ''A People’s History of the United States''. New York, New York: Harper Collins Publications, 2003.</ref> By law, slave owners could be fined for not punishing recaptured runaway slaves. Slave codes authorized, ] or even required the use of violence, and were denounced by ] for their brutality. Both slaves and free blacks were regulated by the ] and had their movements monitored by ]s conscripted from the white population which were allowed to use summary punishment against escapees, sometimes maiming or killing them. In addition to physical abuse and murder, slaves were at constant risk of losing members of their families if their owners decided to trade them for profit, punishment, or to pay debts. A few slaves retaliated by murdering owners and overseers, burning barns, killing horses, or staging work slowdowns.<ref name="Genovese 1967">Genovese (1967)</ref> Stampp, without contesting Genovese's assertions concerning the violence and ] faced by slaves, does question the appropriateness of a Marxian approach in analyzing the owner-slave relationship.<ref>Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." Stampp writes, "Genovese writes with verve, and certainly he is never dull. But, in my opinion, his attempt to demonstrate the superiority of the Marxian interpretation of history must be adjudged a failure. Some may explain this by arguing that the book's point of view is not in fact very Marxian. My own explanation is that the antebellum South, with its essentially racial defense of slavery, and with its emphasis on caste rather than class, is just about as unpromising a place for the application of a Marxian interpretation of history as one can imagine."</ref> | |||
| In addition, many parts of the country were tied to the Southern economy. As the historian James Oliver Horton noted, prominent slaveholder politicians and the commodity crops of the South had a strong influence on United States politics and economy. Horton said, | |||
| Genovese claims that because the slaves were the legal property of their owners, it was not unusual for enslaved black women to be raped by their owners, members of their owner's families, or their owner's friends. Children who resulted from such rapes were slaves as well because they took the status of their mothers, unless freed by the slaveholder. Nell Irwin Painter and other historians have also documented that Southern history went "across the color line." Contemporary accounts by ] and ], both married in the planter class, as well as accounts by former slaves gathered under the ] (WPA), all attested to the abuse of women slaves by white men of the owning and overseer class. | |||
| <blockquote>in the 72 years between the election of George Washington and the election of Abraham Lincoln, 50 of those years a ], and, for that whole period of time, there was never a person elected to a second term who was not a slaveholder.<ref name="pbs.org" /></blockquote> | |||
| However, the Nobel economist ] controversially describes as a myth the belief that slave-breeding and sexual exploitation destroyed black families. He argues that the family was the basic unit of social organization under slavery, and to the economic interest of slave owners to encourage the stability of slave families, and most of them did so. Most slave sales were either of whole families or of individuals at an age when it would have been normal for them to leave the family.<ref name="weiss">Weiss, T. , ''Economic History News Services - Book Reviews'', November 16, 2001. Book review. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> However, eyewitness testimony from former slaves does not support Fogel's view. ], who grew up as a slave in Maryland, reported the systematic separation of slave families and widespread rape of slave women to boost slave numbers. <ref name="douglas">Douglass, Frederick , ''Autobiography of Frederick Douglass'', 1845. Book. Retrieved June 10, 2008.</ref> | |||
| The power of Southern states in Congress lasted until the ], affecting national policies, legislation, and appointments.<ref name="pbs.org"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131223050216/http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/social_issues/jan-june07/divided_01-25.html |date=December 23, 2013 }}, PBS ''Newshour'', January 25, 2007. Retrieved February 11, 2012.</ref> One result was that most of the justices appointed to the ] were slave owners. The planter elite dominated the Southern congressional delegations and the United States presidency for nearly fifty years.<ref name="pbs.org" /> | |||
| In the early 1930s, members of the ] interviewed former slaves, and in doing so, produced the only known original recordings of former slaves. In 2007, the interviews were remastered and reproduced on modern CDs and in book form in conjunction with the ], ] and a national radio project. In the book and CD oral history project called ''Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk About Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Emancipation'', the editors wrote, | |||
| <blockquote>As masters applied their stamp to the domestic life of the slave quarter, slaves struggled to maintain the integrity of their families. Slaveholders had no legal obligation to respect the sanctity of the slave's marriage bed, and slave women—married or single — had no formal protection against their owners' sexual advances. ...Without legal protection and subject to the master's whim, the slave family was always at risk." <ref>>''Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk About Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Emancipation'' edited by ], Marc Favreau, and Steven F. Miller, p. 122-3. ISBN 978-1595582287 </ref> </blockquote> | |||
| ==Slavery in the 19th century== | |||
| The book includes examples of enslaved families torn apart when family members were sold out of state and it contains examples of sexual violations of the enslaved people by individuals who held power over them. | |||
| {{Main|Slave and free states|History of slavery in the United States by state}} | |||
| {{Further|List of court cases in the United States involving slavery|Fugitive slaves in the United States|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#1812 1849|Female slavery in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Slave labor on United States military installations 1799–1863| Slavery at American colleges and universities}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Slavery in the United States was a variable thing, in "constant flux, driven by the violent pursuit of ever-larger profits."<ref>{{cite journal |last=Regan |first=Joe |date=2020-09-01 |title=The large Irish enslavers of antebellum Louisiana |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14664658.2020.1841939 |journal=American Nineteenth Century History |language=en |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=211–235 |doi=10.1080/14664658.2020.1841939 |s2cid=228097042 |issn=1466-4658}}</ref> According to demographic calculations by J. David Hacker of the University of Minnesota, approximately four out of five of all of the slaves who ever lived in the United States or the territory that became the United States (beginning in 1619 and including all colonies that were eventually acquired or conquered by the United States) were born in or imported to the United States in the 19th century.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Hacker |first=J. David |date=2020-10-01 |title=From '20. and odd' to 10 million: the growth of the slave population in the United States |journal=Slavery & Abolition |language=en |volume=41 |issue=4 |pages=840–855 |doi=10.1080/0144039X.2020.1755502 |issn=0144-039X |pmc=7716878 |pmid=33281246}}</ref> Slaves were the labor force of the South, but slave ownership was also the foundation upon which American ] was constructed. Historian ] argues that "one of the many miraculous things a slave could do was make a household white...", meaning that the value of whiteness in America was in some ways measured by the ability to purchase and maintain black slaves.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
| "|thumb|right|300px]] | |||
| According to Genovese, slaves were fed, clothed, housed and provided medical care in the most minimal manner. It was common to pay small bonuses during the ] season, and some slave owners permitted their slaves to keep earnings and gambling profits. (One slave, ], is known to have won a lottery and bought his freedom.) In many households, treatment of slaves varied with the slave's skin color. Darker-skinned slaves worked in the fields, while lighter-skinned house servants had comparatively better clothing, food and housing.<ref name="Genovese 1967"/> | |||
| ] described slavery in the United States in 1853:<ref name="Stowe1853">{{cite book |last=Stowe |first=Harriet Beecher |title=] |publisher=J. P. Jewett & Co. |year=1853 |location=Boston |pages=291–292 |language=en-us |lccn=02004230 |oclc=317690900 |ol=21879838M |author-link=Harriet Beecher Stowe}}</ref> | |||
| As in President ]'s household, the presence of lighter-skinned slaves as household servants was not merely an issue of skin color. Sometimes planters used mixed-race slaves as house servants or favored artisans because they were their children or other relatives. Several of Jefferson's household slaves were children of his father-in-law ] and the enslaved woman ], who were brought to the marriage by Jefferson's wife. In turn the widower Jefferson had a long relationship with Betty and John Wayle's daughter ], a much younger enslaved woman who was mostly of white ancestry and half-sister to his late wife. The Hemings children grew up to be closely involved in Jefferson's household staff activities; one became his chef. Two sons trained as carpenters. Three of his four surviving mixed-race children with Sally Hemings passed into white society as adults.<ref>], '']'', New York: W.W. Norton, 2008</ref> | |||
| {{blockquote|What, then, is American slavery, as we have seen it exhibited by law, and by the decision of Courts? Let us begin by stating what it is not: | |||
| Planters who had mixed-race children sometimes arranged for their education, even in schools in the North, or as apprentices in crafts. Others settled property on them. Some freed the children and their mothers. While fewer than in the Upper South, ] in the ] were more often mixed-race children of planters and were sometimes the recipients of transfers of property and social capital. For instance, ], founded by ] and ] (AME) representatives in ] in 1856 for the education of African-American youth, was in its first years largely supported by wealthy southern planters who paid for the education of their mixed-race children. When the war broke out, the school lost most of its 200 students.<ref>, New York: Oxford University Press, 1995, p.259-260, accessed 13 Jan 2009</ref> The college closed for a couple of years before the AME Church bought it and began to operate it. | |||
| 1. It is not apprenticeship. | |||
| Fogel argues that the material conditions of the lives of slaves compared favorably with those of free industrial workers. They were not good by modern standards, but this fact emphasizes the hard lot of all workers, free or slave, during the first half of the 19th century. Over the course of his lifetime, the typical slave field hand received about 90% of the income he produced.<ref name="weiss"/> In a survey, 58% of historians and 42% of economists disagreed with the proposition that the material condition of slaves compared favorably with those of free industrial workers.<ref name="weiss"/> | |||
| 2. It is not guardianship. | |||
| Slaves were considered legal non-persons except if they committed crimes. An Alabama court asserted that slaves "are rational beings, they are capable of committing crimes; and in reference to acts which are crimes, are regarded as persons. Because they are slaves, they are incapable of performing civil acts, and, in reference to all such, they are things, not persons."<ref>Catterall, Helen T., Ed. 1926. ''Judicial Cases Concerning Slavery and the Negro'', Washington, D.C.: Carnegie Institute, p. 247</ref> | |||
| 3. It is in no sense a system for the education of a weaker race by a stronger. | |||
| In 1811, ] was the first slave owner executed for the murder of a slave in the ].<ref>John Andrew, '''', ], 2000, ISBN 0-7388-1930-1. The assertion is probably correct; there appear to be no other records of any British slave owners being executed for holding slaves, and, given the excitement which the Hodge trial created, it seems improbable that another execution could have occurred without attracting attention. Slavery as an institution in the British West Indies only continued for another 23 years after Hodge's death.</ref> However, he was not, as some have claimed, the first white person to have been ] for the killing of a slave.<ref>Vernon Pickering, ''A Concise History of the British Virgin Islands'', ISBN 10-0934139059, page 48</ref> Records indicate at least two earlier incidents. On November 23, 1739, in ], two white men, Charles Quin and David White, were hanged for the murder of another white man's black slave; and on April 21, 1775, the ] newspaper, the '']'' reported that a white man, William Pitman, had been hanged for the murder of his own black slave.''<ref>'', p101, Oscar Reiss, McFarland & Company, 1997; '', ] Department of Historic Preservation archives</ref> | |||
| 4. The happiness of the governed is in no sense its object. | |||
| ===Slave Codes=== | |||
| To help regulate the relationship between slave and owner, including legal support for keeping the slave as property, ] were established. While each state would have their own, most of the ideas were shared throughout the slave states. In the codes for the District of Columbia, a slave is defined as “a human being, who is by law deprived of his or her liberty for life, and is the property of another.”<ref> The Library of Congress. Retrieved on July 19, 2008</ref> A paragraph from the Black Code of South Carolina, still valid in 1863, declared death as the penalty for him who dared " to aid any slave in running away or departing from his master's or employer's service."<ref>Mee, Arthur; Hammerton, J. A.; Innes, Arthur D., , 1907, Carmelite House, London; (at section: "Social Fabric of the Ancient World, IV": in article: William Romaine Paterson: "The effects of the slave system: man's inhumanity to man its own retribution"); at page 2834; where the author cites this excerpt from the South Carolina Black Code after saying:"Christian slave states in the nineteenth century passed laws which are identical in spirit and almost in letter with the slave laws of Babylon. We saw that in Babylon death was the penalty for anyone who assisted a slave to escape. The Code declared that ' if a man has induced either a male or female slave from the house of a patrician or plebeian to leave the city, he shall be put to death.'"</ref> Codes from other states placed limits on relations allowed between black and white people. Louisiana's Code Noir did not allow interracial marriage, and if children were a result a fine of three hundred livres would have to be paid. This code also stated children of a slave "shall share the condition of their mother”<ref> Copyright: Blackpast.org. Retrieved on July 19, 2009</ref> if the child’s parents had different masters they would stay with the mother, and if the father was free and the mother a slave the children would also be slaves. | |||
| 5. The temporal improvement or the eternal well-being of the governed is in no sense its object. | |||
| ===Women's rights=== | |||
| While working on plantations and farms, women and men had equal labor-intensive work. However, much of the hard labor was taken care of by men or by women who were past the child-bearing stage. Some of the labor-intensive jobs given to women were: cooking for the owner's household as well as the slaves themselves, sewing, midwifery, pruning fields, and many other laborious occupations. | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1837, an Antislavery Convention of American Women met in ] with both black and white women participating. ] and ] had first met at the convention and realized the need for a separate ] movement. At the ] gathering Stanton also met other women delegates such as Emily Winslow, Abby Southwick, Elizabeth Neal, ], Abby Kimber, as well as many other women. However, during the ] Anti-slavery Society meetings, which Stanton and Winslow attended, the hosts refused to seat the women delegates. This resulted in a convention of their own to form a "society to advocate the rights of women". In 1848 at ], Stanton and Winslow launched the women's rights movement, becoming one of the most diverse and social forces in American life.<ref>Sklar, Kathryn. "Women who speak for an Entire Nation". American British Women Compared at the World Anti-slavery Convention, London 1840. The Pacific Historical Review, Vol. 59, Wo. 4, November 1990. pp. 453-499.</ref> | |||
| The object of it has been distinctly stated in one sentence by ],— "The end is the profit of the master, his security, and the public safety." | |||
| ===Abolitionist movement=== | |||
| Beginning in the 1750s, there was widespread sentiment during the ] that slavery was a social evil (for the country as a whole and for the whites) and should eventually be abolished. All the Northern states passed emancipation acts between 1780 and 1804; most of these arranged for gradual emancipation and a special status for freedmen, so there were still a dozen "permanent apprentices" in ] in 1860.<ref>Richard S. Newman, ''Transformation of American abolitionism: fighting slavery in the early Republic'' chapter 1</ref> | |||
| Slavery, then, is absolute despotism, of the most unmitigated form.}} | |||
| The ] of 1780 declared all men "born free and equal"; the slave ] sued for his freedom on this basis and won his freedom, thus abolishing slavery in Massachusetts. | |||
| ===Justifications in the South=== | |||
| Throughout the first half of the 19th century, a movement to end slavery grew in strength throughout the United States. This struggle took place amid strong support for slavery among white Southerners, who profited greatly from the system of enslaved labor. These slave owners began to refer to slavery as the "]" in a defensive attempt to differentiate it from other examples of forced labor. | |||
| {{Further|American proslavery movement|Fire-Eaters}} | |||
| {{See also|Field slaves in the United States|Gang system|Task system|Plantation complexes in the Southern United States|American gentry|Planter class|List of plantations in the United States}} | |||
| ]" of planters was beneficial or necessary<ref>{{Citation |last=Ford |first=Lacy K. Jr.|title=Chapter Five Paternalism Emerges |date=2009-11-01 |url=https://academic.oup.com/book/289/chapter/134863692 |work=Deliver Us from Evil: The Slavery Question in the Old South |pages=143–172 |access-date=2023-08-22 |edition= |publisher=Oxford University PressNew York |language=en |doi=10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195118094.003.0006 |isbn=978-0-19-511809-4}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last= Broussard |first=Joyce L. |date=2018 |title=Paternalism |url=https://mississippiencyclopedia.org/entries/paternalism/ |access-date=2023-08-22 |website=Mississippi Encyclopedia |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Cole |first=Josh |title=THE EXCUSE OF PATERNALISM IN THE ANTEBELLUM SOUTH: IDEOLOGY OR PRACTICE? |url=https://www.eiu.edu/historia/Cole.pdf}}</ref> (Detail, '']'', 1840)]] | |||
| ====American slavery as "a necessary evil"==== | |||
| ] (1777–1852), one of three founders of the ] the vehicle for returning black Americans to greater freedom in Afica, founding ].<ref name=AFP/>]] | |||
| In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". At that time, it was feared that emancipation of black slaves would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. On April 22, 1820, ], one of the ], wrote in a letter to ], that with slavery, | |||
| In the early part of the 19th century, a variety of organizations were established advocating the movement of black people from the United States to locations where they would enjoy greater freedom; some endorsed ], while others advocated ]. During the 1820s and 1830s the ] (A.C.S.) was the primary vehicle for proposals to return black Americans to greater freedom and equality in Africa,<ref name=AFP>{{cite web|url=http://www.fcnl.org/issues/item.php?item_id=731&issue_id=75|title=Background on conflict in Liberia ], advocated settling freed slaves in Africa. He gained support from free black leaders in the U.S., and members of Congress for an early emigration plan. From 1815-1816, he financed and captained a successful voyage to British-ruled Sierra Leone where he helped a small group of African-American immigrants establish themselves. Cuffee believed that African Americans could more easily "rise to be a people" in Africa than in the U.S. where slavery and legislated limits on black freedom were still in place. Although Cuffee died in 1817, his early efforts to help repatriate African Americans encouraged the ] (ACS) to lead further settlements. The ACS was made up mostly of Quakers and slaveholders, who disagreed on the issue of slavery but found common ground in support of repatriation. Friends opposed slavery but believed blacks would face better chances for freedom in Africa than in the U.S. The slaveholders opposed freedom for blacks, but saw ] as a way of avoiding rebellions}}.</ref> and in 1821 the A.C.S. established colony of ], assisting thousands of former African-American slaves and free black people (with legislated limits) to move there from the United States. Many white people saw this as preferable to ] in America, with A.C.S founder ] believing; "unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country". Slaveholders opposed freedom for blacks, but saw ] as a way of avoiding rebellions. | |||
| {{blockquote|We have the wolf by the ear, and we can neither hold him, nor safely let him go. Justice is in one scale, and self-preservation in the other.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Jefferson |first1=Thomas |title=Like a fire bell in the night |url=https://www.loc.gov/exhibits/jefferson/159.html |website=Library of Congress |access-date=2007-10-24}}</ref>}} | |||
| After 1830, a religious movement led by ] declared slavery to be a personal ] and demanded the owners repent immediately and start the process of emancipation. The movement was highly controversial and was a factor in ]. | |||
| The French writer and traveler ], in his influential '']'' (1835), expressed opposition to slavery while observing its effects on American society. He felt that a multiracial society without slavery was untenable, as he believed that prejudice against blacks increased as they were granted more rights (for example, in Northern states). He believed that the attitudes of white Southerners, and the concentration of the black population in the South, were bringing the white and black populations to a state of equilibrium, and were a danger to both races. Because of the racial differences between master and slave, he believed that the latter could not be emancipated.<ref name="Alexis de Tocqueville">{{cite book|title=Democracy in America (Volume 1)|last=de Tocqueville |first=Alexise|chapter=Chapter XVIII: Future Condition Of Three Races In The United States|year=2007 |publisher=Digireads.com |isbn=978-1-4209-2910-2}}</ref> | |||
| Very few abolitionists, such as ], favored the use of armed force to foment uprisings among the slaves; others tried to use the legal system. | |||
| In a letter to his wife dated December 27, 1856, in reaction to a message from President ], ] wrote, | |||
| Influential leaders of the '''abolition movement''' (1810-60) included: | |||
| * ] - published '']'' newspaper | |||
| * ] - author of '']'' | |||
| * ] - nation's most powerful anti-slavery speaker, a former slave. Most famous for his book ''Narrative in the Life of Frederick Douglass''. | |||
| * ] - helped 350 slaves escape from the South, became known as a "conductor" on the ]. | |||
| * ] - mixed-race abolitionist who used wealth for the black race, active in Philadelphia and Anti-Slavery Society, helped hundreds of slaves on Underground Railroad | |||
| * ] - mixed-race abolitionist in ]; one of two people tried for ], which gained national attention | |||
| {{blockquote|There are few, I believe, in this enlightened age, who will not acknowledge that slavery as an institution is a moral and political evil. It is idle to expatiate on its disadvantages. I think it is a greater evil to the white than to the colored race. While my feelings are strongly enlisted in behalf of the latter, my sympathies are more deeply engaged for the former. The blacks are immeasurably better off here than in Africa, morally, physically, and socially. The painful discipline they are undergoing is necessary for their further instruction as a race, and will prepare them, I hope, for better things. How long their servitude may be necessary is known and ordered by a merciful Providence.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Lee |first1=Robert E. |title=Robert E. Lee's opinion regarding slavery |url=https://www.civilwarhome.com/leepierce.htm |website=Shotgun's Home of the American Civil War |access-date=2007-10-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Emory M.|last=Thomas|author-link=Emory M. Thomas|title=Robert E. Lee|page=173|publisher=]|year=1997|isbn=978-0-393-31631-5|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jJWR80JZ_hsC}}</ref>}} | |||
| Slave uprisings that used '''armed force''' (1700 - 1859) include: | |||
| * New York Revolt of 1712 | |||
| * The ] (1739) in South Carolina | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (1800) in Virginia | |||
| * Louisiana Territory Slave Rebellion, led by ] (1811) | |||
| * ] (1815) in Virginia | |||
| * ] (1822) | |||
| * ] (1831) in Virginia | |||
| * ] Seizure (1839) on a Spanish ship | |||
| ====American slavery as "a positive good"==== | |||
| {{seealso|List of notable opponents of slavery}} | |||
| {{Main|Slavery as a positive good in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|Eugenics in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Mudsill theory}} | |||
| ], ])]] | |||
| ] in New Orleans; donated to the ] museum]] | |||
| However, as the abolitionist movement's agitation increased and the area developed for plantations expanded, apologies for slavery became more faint in the South. Leaders then described slavery as a beneficial scheme of labor management. ], in a famous speech in the ] in 1837, declared that slavery was "instead of an evil, a good{{snd}}a positive good". Calhoun supported his view with the following reasoning: in every civilized society one portion of the community must live on the labor of another; learning, science, and the arts are built upon leisure; the African slave, kindly treated by his master and mistress and looked after in his old age, is better off than the free laborers of Europe; and under the slave system conflicts between capital and labor are avoided. The advantages of slavery in this respect, he concluded, "will become more and more manifest, if left undisturbed by interference from without, as the country advances in wealth and numbers".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Beard |first1=Charles A. |author-link1=Charles A. Beard |last2=Beard |first2=Mary R. |author-link2=Mary Ritter Beard |year=1921 |url=http://www.gutenberg.org/files/16960/16960-h/16960-h.htm#Page_316 |title=History of the United States |publisher=The Macmillan Company |location=New York |page=316}}</ref> | |||
| ===Rising tensions=== | |||
| The economic value of plantation slavery was magnified in 1793 with the invention of the ] by ], a device designed to separate cotton fibers from seedpods and the sometimes sticky seeds. The invention revolutionized the cotton industry by increasing fiftyfold the quantity of cotton that could be processed in a day. The result was the explosive growth of the cotton industry and greatly increased the demand for slave labor in the South.<ref>The People's Chronology, 1994 by James Trager</ref> | |||
| ] at Barrone and ], and at 54, 58, 68, and 78 Barrone represented but a slim fraction of the trade in the city<ref> | |||
| At the same time, the northern states banned slavery, though, as ] noted in '']'' (1835), the prohibition did not always mean that the slaves were freed. Toqueville noted that as Northern states provided for gradual emancipation, they generally outlawed the sale of slaves within the state. This meant that the only way to sell slaves before they were freed was to move them South. Toqueville does not document that such transfers actually occurred much.<ref>de Toqueville p. 367.</ref> In fact, the emancipation of slaves in the North led to the growth in the population of northern free blacks, from several hundreds in the 1770s to nearly 50,000 by 1810.<ref>Berlin, "Generations of Captivity" p. 104</ref> | |||
| {{cite journal |last=McInnis |first=Maurie D. |author-link=Maurie D. McInnis |title=Mapping the slave trade in Richmond and New Orleans |url=https://www.academia.edu/17316662 |journal=Building & Landscapes |volume=20 |issue=2 |doi=10.5749/buildland.20.2.0102 |jstor=10.5749/buildland.20.2.0102 |date=Fall 2013 |pages=102–125 |s2cid=160472953 |url-access=registration}}</ref> (''New Orleans Crescent'', January 10, 1861)]] | |||
| South Carolina army officer, ], and railroad executive ] called slavery "a social blessing" and abolitionists "the greatest curse of the nation".<ref>{{cite book |last=Richards |first=Leonard L. |title=The California Gold Rush and the Coming of the Civil War |page= |year=2007 |location=New York |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |isbn=978-0-307-26520-3 |url=https://archive.org/details/californiagoldru00ric_923/page/125 }}</ref> Gadsden was in favor of South Carolina's ] in 1850, and was a leader in efforts to split California into two states, ]. | |||
| Just as demand for slaves was increasing, the supply was restricted. The ], adopted in 1787, prevented ] from banning the ]ation of slaves until 1808. On January 1, 1808, Congress banned further imports. Any new slaves would have to be descendants of ones currently in the United States. However, the internal American slave trade and the involvement in the international slave trade or the outfitting of ships for that trade by U.S. citizens were not banned. Though there were certainly violations of this law, slavery in America became, more or less, self-sustaining. | |||
| Other Southern writers who also began to portray slavery as a positive good were ] and ]. They presented several arguments to defend the practice of slavery in the South.<ref name="Mudsill Theory">{{cite web|last=Hammond|first=James Henry|author-link=James Henry Hammond|title=The 'Mudsill' Theory|website=]|date=March 4, 1858|url=http://pbs.org/wgbh/aia/part4/4h3439t.html|access-date=December 10, 2017}}</ref> Hammond, like Calhoun, believed that slavery was needed to build the rest of society. In a speech to the Senate on March 4, 1858, Hammond developed his "Mudsill Theory", defending his view on slavery by stating: "Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement. It constitutes the very mud-sill of society and of political government; and you might as well attempt to build a house in the air, as to build either the one or the other, except on this mud-sill." Hammond believed that in every class one group must accomplish all the menial duties, because without them the leaders in society could not progress.<ref name="Mudsill Theory"/> He argued that the hired laborers of the North were slaves too: "The difference{{spaces}}... is, that our slaves are hired for life and well compensated; there is no starvation, no begging, no want of employment," while those in the North had to search for employment.<ref name="Mudsill Theory"/> | |||
| ===The War of 1812 and slavery=== | |||
| During the ], British ] commanders of the blockading fleet, based at the ], were given instructions to encourage the defection of American slaves by offering freedom, as they did during the Revolutionary War. Thousands of black slaves went over to the Crown with their families, and were recruited into the (3rd Colonial Battalion) ] on occupied ], in the Chesapeake. A further company of colonial marines was raised at the Bermuda dockyard, where many freed slaves, men women and children, had been given refuge and employment. It was kept as a defensive force in case of an attack. | |||
| George Fitzhugh used assumptions about white superiority to justify slavery, writing that, "the Negro is but a grown up child, and must be governed as a child." In ''The Universal Law of Slavery'', Fitzhugh argues that slavery provides everything necessary for life and that the slave is unable to survive in a free world because he is lazy, and cannot compete with the intelligent European white race. He states that "The negro slaves of the South are the happiest, and in some sense, the freest people in the world."<ref name="Universal Law">{{cite web|last=Fitzhugh|first=George|author-link=George Fitzhugh|title=The Universal Law of Slavery|website=]|url=http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aia/part4/4h3141t.html|access-date=December 10, 2017}}</ref> Without the South, "He (slave) would become an insufferable burden to society" and "Society has the right to prevent this, and can only do so by subjecting him to domestic slavery."<ref name="Universal Law"/> | |||
| These former slaves fought for Britain throughout the Atlantic campaign, including the attack on Washington D.C.and the Louisiana Campaign, and most were later re-enlisted into British West India regiments, or settled in ] in August, 1816, where seven hundred of these ex-marines were granted land (they reportedly organised themselves in villages along the lines of military companies). Many other freed American slaves were recruited directly into existing West Indian regiments, or newly created British Army units. A few thousand freed slaves were later settled at Nova Scotia by the British. | |||
| On March 21, 1861, ], Vice President of the Confederacy, delivered his ]. He explained the differences between the ] and the ], laid out the cause for the American Civil War, as he saw it, and defended slavery:<ref name="Schott, Thomas E. 1996, page 334">Schott, Thomas E. ''Alexander H. Stephens of Georgia: A Biography'', 1996, p. 334.</ref> | |||
| Slaveholders primarily in the South experienced considerable "loss of property" as tens of thousands of slaves escaped to British lines or ships for freedom, despite the difficulties. The planters' complacency about slave "contentment" was shocked by seeing slaves would risk so much to be free.<ref>Simon Schama, ''Rough Crossings: Britain, the Slaves and the American Revolution'', New York: HarperCollins, 2006, p.406</ref> Afterward, when some freed slaves had been settled at Bermuda, slaveholders such as Major ] of ] tried to persuade them to return to the United States, to no avail. | |||
| {{Blockquote|The new Constitution has put at rest forever all the agitating questions relating to our peculiar institutions{{snd}}African slavery as it exists among us{{snd}}the proper status of the negro in our form of civilization. This was the immediate cause of the late rupture and present revolution. Jefferson, in his forecast, had anticipated this, as the "rock upon which the old Union would split." He was right. What was conjecture with him, is now a realized fact. But whether he fully comprehended the great truth upon which that rock stood and stands, may be doubted. The prevailing ideas entertained by him and most of the leading statesmen at the time of the formation of the old Constitution were, that the enslavement of the African was in violation of the laws of nature; that it was wrong in principle, socially, morally and politically. It was an evil they knew not well how to deal with; but the general opinion of the men of that day was, that, somehow or other, in the order of Providence, the institution would be evanescent and pass away{{spaces}}... Those ideas, however, were fundamentally wrong. They rested upon the assumption of the equality of races. This was an error. It was a sandy foundation, and the idea of a Government built upon it{{snd}}when the "storm came and the wind blew, it fell".<br /><br />Our new Government is founded upon exactly the opposite ideas; its foundations are laid, its cornerstone rests, upon the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery, subordination to the superior race, is his natural and moral condition.<ref name="Schott, Thomas E. 1996, page 334" />}} | |||
| ===Internal Slave Trade=== | |||
| ], ], 1864. (Note building with sign reading "Auction & Negro Sales".)|thumb]] | |||
| With the movement in Virginia and the Carolinas away from tobacco cultivation and toward mixed agriculture, which was less labor intensive, planters in those states had excess slave labor. They hired out some slaves for occasional labor, but planters also began to sell enslaved African Americans to traders who took them to markets in the Deep South for their expanding plantations. The internal slave trade and forced migration of enslaved African Americans continued for another half-century. Tens of thousands of slaves were transported from the ], including Kentucky and Tennessee which became slave-selling states in these decades, to the ]. Thousands of African American families were broken up in the sales, which first concentrated on male laborers. The scale of the internal slave trade contributed substantially to the wealth of the Deep South. In 1840, New Orleans—which had the largest slave market and important shipping—was the third largest city in the country and the wealthiest. | |||
| This view of the "Negro race" was backed by ].<ref>{{cite book|contribution=Men but Not Brothers|first=William C.|last=Davis|title=Look Away!: A History of the Confederate States of America|pages=130–162|date=2002|publisher=]}}</ref> The leading researcher was Dr. ], a Southerner and the inventor of the mental illnesses of ] (the desire of a slave to run away) and ] ("rascality"), both cured, according to him, by whipping. The Medical Association of Louisiana set up a committee, of which he was chair, to investigate "the Diseases and Physical Peculiarities of the Negro Race". Their report, first delivered to the Medical Association in an address, was published in their journal in 1851,<ref>{{cite journal|title=Report on the Diseases and Physical Peculiarities of the Negro Race|first=Samuel A.|last=Cartwright|author-link=Samuel A. Cartwright|journal=New Orleans Medical and Surgical Journal|date=May 1851|pages=691–715|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mjkCAAAAYAAJ&pg=RA2-PA707|access-date=May 15, 2018}}</ref> and then reprinted in part in the widely circulated '']''.<ref name=Cartwright>{{cite journal|last=Cartwright|first=Samuel A.|author-link=Samuel A. Cartwright|title=Diseases and Peculiarities of the Negro Race|journal=]|year=1851|volume=XI|url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aia/part4/4h3106t.html|access-date=16 November 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Because of the ] in the U.S. Constitution, slaveholders exerted their power through the Federal Government and passed Federal ]. Refugees from slavery fled the South across the ] and other parts of the ] dividing North from South, to the North via the ]. The physical presence of African Americans in ], ], and other Northern towns agitated some white Northerners, though others helped hide former slaves from their former owners, and others helped them reach freedom in ]. After 1854, ] fumed that ], especially the pro-slavery ], controlled two of the three branches of the Federal government. | |||
| ====Proposed expansion of slavery==== | |||
| Most Northeastern states became free states through local emancipation. The settlement of the ] states after the Revolution led to their decisions in the 1820s not to allow slavery. A Northern block of free states united into one contiguous geographic area which shared an anti-slavery culture. The boundary was the Mason-Dixon Line (between slave-state ] and free-state ]) and the Ohio River. | |||
| ], an aspirational empire for American slave owners]] | |||
| <!--] with handwritten caption in ink: "Charleston S.C. 4th March 1833 The land of the free & home of the brave" (] 1981-42-42)]]--> | |||
| Whether slavery was to be limited to the Southern states that already had it, or whether it was to be permitted in new states made from the lands of the ] and ], was a major issue in the 1840s and 1850s. It was addressed by the ] and during the ] period. | |||
| The slave trade (though not the legality of slavery) was abolished by Congress in the ] as part of the ]. | |||
| Also relatively well-known are the proposals, including the ], to ], as well as the privately funded invasion of Cuba by ]. There was also talk of making slave states of Mexico, Nicaragua (see ] and ]) and other lands around the so-called ]. Less well known today, though well known at the time, is that pro-slavery Southerners: | |||
| ===Religious institutions=== | |||
| * Actively ]<ref>{{cite news|title=The Slave Trade Meeting|newspaper=] (])|date=October 22, 1859|via=]|url=https://www.newspapers.com/clip/63220535/meeting-of-those-who-wanted-to-reopen/|page=1}}</ref> | |||
| North and South grew further apart in 1845 when the Baptist Church and other denominations split into Northern and Southern organizations. The ] formed on the premise that the ] sanctions slavery and that it was acceptable for ] to own slaves. (In the 20th century, the Southern Baptist Convention renounced this interpretation.) Currently American Baptist numerical strength is greatest in the former slave-holding states.<ref>Department of Geography and Meteorology, ], Valparaiso, Indiana.</ref> Northern Baptists opposed slavery. In 1844, the ] declared that a person could not be a ] and still keep slaves as property. The ] and ] churches likewise divided north and south. By the late 1850s only the Democratic Party was a national institution, although it split in the ]. | |||
| * Funded ] from the Caribbean and Africa, such as the '']'' slave shipment to Georgia in 1858<ref>{{Cite book|last=Wells|first=Tom Henderson |title=The Slave Ship Wanderer|publisher=University of Georgia Press|year=2009|isbn=9-780-8203-3457-8}}</ref> | |||
| * Wanted to reintroduce slavery in the Northern states, through federal action or ] making slavery legal nationwide, thus overriding state anti-slavery laws.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Review of ''The Slave Power Conspiracy and the Paranoid Style'', by David Brion Davis|first=James|last=Rabun|journal=]|volume=49|number=2|date=October 1970|pages=174–175|jstor=30140388}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=John Brown and His Friends|author-link=Franklin Benjamin Sanborn|first=Franklin Benjamin|last=Sanborn|page=2|date=c. 1900|url=https://archive.org/details/aberpa.sanbornfb.1900.johnbrown/page/n2/mode/1up}}</ref> (See ].) This was described as "well underway" by 1858.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Abraham Lincoln and the Fruitage of his Proclamation|first=Archibald|last=Grimké|author-link=Archibald Grimké|journal=]|date=February 1909|volume=63|number=2|pages=51–53|url=https://archive.org/details/americanmissiona00bear/page/50/mode/2up?q=Archibald}}</ref> | |||
| * Said openly that slavery should by no means be limited to black people, since in their view it was beneficial. Northern white workers, who were allegedly "]" already, would allegedly have better lives if they were enslaved.<ref>{{cite journal|title=The Slave Power Conspiracy: 1830–1860|first=Russel B.|last=Nye|journal=]|volume=10|number=3|date=Summer 1946|pages=262–274|jstor=40399768}}</ref> | |||
| None of these ideas got very far, but they alarmed Northerners and contributed to the growing polarization of the country. | |||
| ===Abolitionism in the North=== | |||
| {{Main|Abolitionism in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|List of abolitionists|Underground Railroad|African American founding fathers of the United States|Radical Republicans}} | |||
| {{Blockquote|Slavery is a volcano, the fires of which cannot be quenched, nor its ravishes controlled. We already feel its convulsions, and if we sit idly gazing upon its flames, as they rise higher and higher, our happy republic will be buried in ruin, beneath its overwhelming energies.|author=], attorney for ], 1834<ref name=Williams>{{cite book|first=James|last=Williams|title=Narrative of James Williams, an American slave: who was for several years a driver on a cotton plantation in Alabama|year=1838|page=iv|location=Boston|publisher=Published by the ]|others=] coordinated the publication.|series=Authentic narrative of James Williams, an American slave|url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=emu.010002634169&view=1up&seq=1}}</ref>{{rp|193–194}}}} | |||
| ] and ] (with British abolitionist ]), ], ], 1851 meeting of the ] (including ], ], ], and ]), ], and ]]] | |||
| Beginning during the Revolution and in the first two decades of the postwar era, every state in the North abolished slavery. These were the first abolitionist laws in the ].<ref>Arthur Zilversmit, ''The First Emancipation: The Abolition of Slavery in the North'' (1967).</ref><ref>{{cite book|editor-first=Junius P.|editor-last=Rodriguez|title=Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DXysBwAAQBAJ&pg=PR34|year=2015|publisher=Routledge|pages=34–35|isbn=978-1-317-47180-6}}</ref> However, the abolition of slavery did not necessarily mean that existing slaves became free. In some states they were forced to remain with their former owners as ]: free in name only, although they could not be sold and thus families could not be split, and their children were born free. The end of slavery did not come in New York until July 4, 1827, when it was celebrated (on July 5) with a big parade.<ref>David Nathaniel Gellman, ''Emancipating New York: The politics of slavery and freedom, 1777-1827'' (LSU Press, 2006) pp. 1–11.</ref> However, in the ], the only state with no slaves was Vermont. In the ], there were still slaves in New Hampshire (1), Rhode Island (5), Connecticut (17), New York (4), Pennsylvania (64), Ohio (3), Indiana (3), Illinois (331), Iowa (16), and Wisconsin (11). There were none in these states in the ].<ref>{{cite book|title=Statistical View of the United States|author=J. D. B. DeBow, Superintendent of the United States Census|chapter=Slave Population of the United States|page=82|publisher=United States Senate|chapter-url=https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/1850/1850c/1850c-04.pdf|year=1854}}</ref> | |||
| Most Northern states passed legislation for gradual abolition, first freeing children born to slave mothers (and requiring them to serve lengthy indentures to their mother's owners, often into their 20s as young adults). In 1845, the ] received lengthy arguments towards "the deliverance of four thousand persons from bondage".<ref>{{cite book|title=A legal argument before the Supreme court of the state of New Jersey, at the May term, 1845, at Trenton, for the deliverance of four thousand persons from bondage|first=Alvan|last=Stewart|author-link=Alvan Stewart|location=New York|publisher=Finch & Weed|year=1845|url=https://archive.org/details/legalargumentbef00stew/page/n6/mode/1up}}</ref> Pennsylvania's last slaves were freed in 1847, Connecticut's in 1848, and while neither New Hampshire nor New Jersey had any slaves in the ], and New Jersey only one and New Hampshire none in the ], slavery was never prohibited in either state until ratification of the ] in 1865<ref>{{cite book|first1=Randall M.|last1=Miller|first2=John David|last2=Smith|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=idktzKdgb7YC&pg=PA471|chapter=Gradual abolition|title=Dictionary of Afro-American Slavery|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|year=1997|page=471|isbn=978-0-275-95799-5}}</ref> (and New Jersey was one of the last states to ratify it). | |||
| ] and ] proved to be crucial to the outcome of the Civil War<ref name="Hubbard, Robert Ernest pp. 1"/><ref name="McCullough, David pp. 11, 13"/> (] artist, 3¢ stamp issued July 13, 1937)]] | |||
| None of the Southern states abolished slavery before 1865, but it was not unusual for individual slaveholders in the South to free numerous slaves, often citing revolutionary ideals, in their wills. ], ], and ] preachers traveled in the South, appealing to slaveholders to ] their slaves, and there were "manumission societies" in some Southern states. By 1810, the number and proportion of free blacks in the population of the United States had risen dramatically. Most free blacks lived in the North, but even in the Upper South, the proportion of free blacks went from less than one percent of all blacks to more than ten percent, even as the total number of slaves was increasing through imports.<ref name="Peter Kolchin 1993 pp. 77–78">Peter Kolchin (1993), ''American Slavery'', pp. 77–78, 81.</ref> | |||
| ] was chief justice of the ], the highest court in Massachusetts. (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Massachusetts)]] | |||
| African slaves arrived in the ] in the 1630s, and slavery was legally sanctioned by the Puritans in 1641.<ref name="Mass Col"/> Massachusetts residents participated in the slave trade, and laws were passed regulating the movement and marriage among slaves.<ref name="Mass Col">{{cite news |title=Massachusetts Constitution and the Abolition of Slavery |url=https://www.mass.gov/guides/massachusetts-constitution-and-the-abolition-of-slavery |access-date=February 8, 2024 |agency=Mass.gov}}</ref> In 1700, ], Puritan abolitionist and associate justice of the ], wrote ''The Selling of Joseph'', within which he condemned slavery and the slave trade and refuted many of the era's typical justifications for slavery.<ref>Sewall, Samuel. ''The Selling of Joseph,'' pp. 1–3, Bartholomew Green & John Allen, Boston, Massachusetts, 1700.</ref><ref>McCullough, David. ''John Adams'', pp. 132–133, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2001. {{ISBN|0-684-81363-7}}.</ref> The Puritan influence on slavery was still strong at the time of the ] and up until the Civil War. Of America's first seven presidents, the two who did not own slaves, ] and his son ], came from Puritan New England. They were wealthy enough to own slaves, but they chose not to because they believed that it was morally wrong to do so. In 1765, colonial leader ] and his wife were given a slave girl as a gift. They immediately freed her. Just after the Revolution, in 1787, the ] (which became the states of Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin and part of Minnesota) was opened up for settlement. The two men responsible for establishing this territory were ] and ]. They came from Puritan New England, and they insisted that this new territory, which doubled the size of the United States, was going to be "free soil"{{snd}}no slavery. This was to prove crucial in the coming decades. If those states had become slave states, and their electoral votes had gone to ]'s main opponent, Lincoln would not have been elected president.<ref name="Hubbard, Robert Ernest pp. 1"/><ref name="McCullough, David pp. 11, 13"/><ref name="McCullough, David p. 132-3"/> | |||
| ] was ] in the ] in 1842 for introducing anti-slavery resolution deemed to be incendiary, and in violation of the House's ] prohibiting discussion of slavery.<ref>{{cite news |title=The House Censured Rashida Tlaib for Political Speech Plain and Simple |url=https://www.esquire.com/news-politics/politics/a45781154/rashida-tlaib-house-censure/ |access-date=November 10, 2023 |work=Esquire}}</ref>]] | |||
| In the decades leading up to the Civil War, the abolitionists, such as ], ], ] and ], repeatedly used the Puritan heritage of the country to bolster their cause. The most radical anti-slavery newspaper, ''],'' invoked the Puritans and Puritan values over a thousand times. Parker, in urging New England Congressmen to support the abolition of slavery, wrote that "The son of the Puritan{{spaces}}... is sent to Congress to stand up for Truth and Right{{spaces}}..."<ref>Gradert, Kenyon. ''Puritan Spirits in the Abolitionist Imagination,'' pp. 1–3, 14–15, 24, 29–30, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, and London, 2020. {{ISBN|978-0-226-69402-3}}.</ref><ref>Commager, Henry Steele. ''Theodore Parker,'' pp. 206, 208–209, 210, The Beacon Press, Boston, Massachusetts, 1947.</ref> | |||
| Northerners predominated in the westward movement into the ] territory after the American Revolution; as the states were organized, they voted to prohibit slavery in their constitutions when they achieved statehood: Ohio in 1803, Indiana in 1816, and Illinois in 1818. What developed was a Northern block of free states united into one contiguous geographic area that generally shared an anti-slavery culture. The exceptions were the areas along the Ohio River settled by Southerners: the southern portions of Indiana, Ohio, and Illinois. Residents of those areas generally shared in Southern culture and attitudes. In addition, these areas were devoted to agriculture longer than the industrializing northern parts of these states, and some farmers used slave labor. In Illinois, for example, while the trade in slaves was prohibited, it was legal to bring slaves from ] into Illinois and use them there, as long as the slaves left Illinois one day per year (they were "visiting"). The emancipation of slaves in the North led to the growth in the population of Northern free blacks, from several hundred in the 1770s to nearly 50,000 by 1810.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', p. 104.</ref> | |||
| ]'' (1852), an influential abolitionist novel]] | |||
| Throughout the first half of the 19th century, abolitionism, a movement to end slavery, grew in strength; most abolitionist societies and supporters were in the North. They worked to raise awareness about the evils of slavery, and to build support for abolition. After 1830, abolitionist and newspaper publisher ] promoted emancipation, characterizing slaveholding as a personal sin. He demanded that slaveowners repent and start the process of emancipation. His position increased defensiveness on the part of some Southerners, who noted the long history of slavery among many cultures. A few abolitionists, such as ], favored the use of armed force to foment uprisings among the slaves, as he attempted to do at ]. Most abolitionists tried to raise public support to change laws and to challenge slave laws. Abolitionists were active on the lecture circuit in the North, and often featured escaped slaves in their presentations. Writer and orator ] became an important abolitionist leader after escaping from slavery. ]'s novel '']'' (1852) was an international bestseller, and along with the non-fiction companion ''],'' aroused popular sentiment against slavery.<ref>] ''Mightier Than the Sword:'' Uncle Tom's Cabin ''and the Battle for America''. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2011.</ref> It also provoked the publication of numerous ] by Southerners in the years before the American Civil War. | |||
| ] routes, as mapped by a historian of 1898]] | |||
| This struggle took place amid strong support for slavery among white Southerners, who profited greatly from the system of enslaved labor. But slavery was entwined with the national economy; for instance, the banking, shipping, insurance, and manufacturing industries of New York City all had strong economic interests in slavery, as did similar industries in other major port cities in the North. The Northern textile mills in New York and New England processed Southern cotton and manufactured clothes to outfit slaves. By 1822, half of New York City's exports were related to cotton.<ref name="divided">{{Cite web |title=New York Divided: King Cotton |url=http://nydivided.org/VirtualExhibit/T1/G1/G1ReadMore.php |access-date=2022-12-29 |website=nydivided.org}}</ref> | |||
| Slaveholders began to refer to slavery as the "peculiar institution" to differentiate it from other examples of ]. They justified it as less cruel than the free labor of the North. | |||
| ]'' (1846–1849)]] | |||
| The principal organized bodies to advocate abolition and anti-slavery reforms in the north were the ] and the ]. Before the 1830s the antislavery groups called for gradual emancipation.<ref>Gilbert Hobbs Barnes, ''The antislavery impulse: 1830–1844'' (1933)</ref> By the late 1820s, under the impulse of religious evangelicals such as ], the sense emerged that owning slaves was a sin and the owner had to immediately free himself from this grave sin by immediate emancipation.<ref>{{Cite journal |jstor = 2204556|title = Evangelicalism and "Immediate Emancipation" in American Antislavery Thought|journal = The Journal of Southern History|volume = 32|issue = 2|pages = 172–188|last1 = Loveland|first1 = Anne C.|year = 1966|doi = 10.2307/2204556}}</ref> | |||
| ===Prohibiting the international trade=== | |||
| {{Main|Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves}} | |||
| ], ], and ], plus cotton shipping out for ], and a delivery of ] cloth, which was traded for "prime negroes" in regions of Africa where ] made American ] undesirable<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Kelley |first=Sean M. |date=2018 |title=American Rum, African Consumers, and the Transatlantic Slave Trade |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1353/aeh.2018.0004 |journal=African Economic History |volume=46 |issue=2 |pages=1–29 |doi=10.1353/aeh.2018.0004 |issn=2163-9108}}</ref>]] | |||
| Under the Constitution, Congress could not prohibit the import slave trade that was allowed in South Carolina until 1808. However, the third Congress regulated against it in the ], which prohibited American shipbuilding and outfitting for the trade. Subsequent acts ] and 1803 sought to discourage the trade by banning American investment in the trade, and American employment on ships in the trade, as well as prohibiting importation into states that had abolished slavery, which all states except South Carolina had by 1807.<ref name="Regulation of the Trade">{{cite web | url=http://abolition.nypl.org/essays/us_constitution/4/ | title=Regulation of the Trade | publisher=] | access-date=June 23, 2014 | archive-date=July 8, 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180708232800/http://abolition.nypl.org/essays/us_constitution/4/ }}</ref><ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Finkelman |first=Paul |date=2004 |title=Suppressing American Slave Traders in the 1790s |magazine=OAH Magazine of History |volume=18 |issue=3 |pages=51–55 |issn=0882-228X}}</ref> The final ] was adopted in 1807 and went into effect in 1808. However, illegal importation of African slaves (smuggling) was common.<ref name="Julia Floyd Smith 1973, pp. 44–46" /> The Cuban slave trade between 1796 and 1807 was dominated by American slave ships. Despite the 1794 Act, Rhode Island slave ship owners found ways to continue supplying the slave-owning states. The overall U.S. slave-ship fleet in 1806 was estimated to be almost 75% the size of that of the British.<ref name="Grindal 2016">{{cite book |last1=Grindal |first1=Peter |title=Opposing the Slavers. The Royal Navy's Campaign against the Atlantic Slave Trade |date=2016 |publisher=I.B. Tauris & Co. Ltd |location=London |isbn=978-0-85773-938-4 |edition=Kindle}}</ref>{{rp|63, 65}} | |||
| After Great Britain and the United States outlawed the international slave trade in 1807, British slave trade suppression activities began in 1808 through diplomatic efforts and the formation of the ]'s ] in 1809. The United States denied the Royal Navy the right to stop and search U.S. ships suspected as slave ships, so not only were American ships unhindered by British patrols, but slavers from other countries would fly the American flag to try to avoid being stopped. Co-operation between the United States and Britain was not possible during the ] or the period of poor relations in the following years. In 1820, the ] sent {{USS|Cyane|1815|6}} under the command of Captain ] to patrol the slave coasts of West Africa. ''Cyane'' seized four American slave ships in her first year on station. Trenchard developed a good level of co-operation with the Royal Navy. Four additional U.S. warships were sent to the African coast in 1820 and 1821. A total of 11 American slave ships were taken by the U.S. Navy over this period. Then American enforcement activity reduced. There was still no agreement between the United States and Britain on a mutual right to board suspected slave traders sailing under each other's flag. Attempts to reach such an agreement stalled in 1821 and 1824 in the ]. A U.S. Navy presence, however sporadic, did result in American slavers sailing under the Spanish flag, but still as an extensive trade. The ] of 1842 set a guaranteed minimum level of patrol activity by the U.S. Navy and the Royal Navy, and formalized the level of co-operation that had existed in 1820. Its effects, however, were minimal{{efn|The United States continued to prohibit Royal Navy ships from investigating U.S.-flagged vessels{{snd}}even in instances when the U.S. flag was being used fraudulently. The British still insisted on the right to impress (i.e. force to serve in the Royal Navy) British citizens found on American ships{{snd}}something that was a continued cause of grievance. Despite the intent of the treaty, the opportunity for additional co-operation was missed.}} while opportunities for greater co-operation were not taken. The U.S. transatlantic slave trade was not effectively suppressed until 1861, during Lincoln's presidency, when a treaty with Britain was signed whose provisions included allowing the Royal Navy to board, search and arrest slavers operating under the American flag.{{r|Grindal 2016|pp=399–400, 449, 1144, 1149}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.potomacbooksinc.com/Books/BookDetail.aspx?productID=63330|title=Potomac Books – University of Nebraska Press – University of Nebraska Press|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071015130620/http://www.potomacbooksinc.com/Books/BookDetail.aspx?productID=63330|archive-date=October 15, 2007|df=mdy-all}}</ref> | |||
| ===War of 1812=== | |||
| {{See also|Black refugee (War of 1812)}} | |||
| ]: Jackson, soon to be the "Hero of New Orleans," explains how much it should cost to take a shipment of slaves to Natchez for sale ('' The Correspondence of Andrew Jackson'', 1926)]] | |||
| During the ], British ] commanders of the blockading fleet were instructed to offer freedom to defecting American slaves, as the Crown had during the Revolutionary War. Thousands of ] went over to the Crown with their families.<ref>Gene Allen Smith, ''The Slaves' Gamble: Choosing Sides in the War of 1812'' (St. Martin's Press, 2013) pp. 1–11.</ref> Men were recruited into the ] on occupied ], in the ]. Many freed American slaves were recruited directly into existing West Indian regiments, or newly created ] units. The British later resettled a few thousand freed slaves to Nova Scotia. Their descendants, together with descendants of the black people resettled there after the Revolution, have established the Black Loyalist Heritage Museum.<ref name="schama" /> | |||
| Slaveholders, primarily in the South, had considerable "loss of property" as thousands of slaves escaped to the British lines or ships for freedom, despite the difficulties.<ref name="schama" /> The planters' complacency about slave "contentment" was shocked by seeing that slaves would risk so much to be free.<ref name="schama">{{cite book |first=Simon |last=Schama |author-link=Simon Schama |chapter=Endings, Beginnings |title=Rough Crossings: Britain, the Slaves and the American Revolution |location=New York |publisher=HarperCollins |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-06-053916-0 |pages= |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=w6P8FSfh7GwC&pg=PA406 |title-link=Rough Crossings: Britain, the Slaves and the American Revolution }}</ref> Afterward, when some freed slaves had been settled at ], slaveholders such as Major ] of ] tried to persuade them to return to the United States, to no avail. | |||
| The Americans protested that Britain's failure to return all slaves violated the ]. After arbitration by the ], the British paid $1,204,960 in damages (about ${{Inflation|US|1.204960|1826|r=1}} million in today's money) to Washington, which reimbursed the slaveowners.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Lindsay |first=Arnett G. |title=Diplomatic Relations Between the United States and Great Britain Bearing on the Return of Negro Slaves, 1783–1828 |journal=] |volume=5 |issue=4 |year=1920 |pages=391–419 |jstor=2713676 |doi=10.2307/2713676 |s2cid=149894983 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Slave rebellions=== | |||
| {{Main|Slave rebellion and resistance in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Slavery in the colonial United States#Slave rebellions}} | |||
| , an 1881 ] by {{ill|William Henry Shelton|WD=Q52155231|short=yes}}]] | |||
| According to ], "there were few phases of ante-bellum Southern life and history that were not in some way influenced by the fear of, or the actual outbreak of, militant concerted slave action."<ref>{{citation|isbn=978-0-7178-0605-8|page=|date=1993|edition=50th Anniversary|place=New York|title=American Negro Slave Revolts|author=Aptheker, Herbert|url=https://archive.org/details/americannegrosla00apth/page/368|author-link=Herbert Aptheker|publisher=International Publishers}}</ref> | |||
| Historians in the 20th century identified 250 to 311 slave uprisings in U.S. and colonial history.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.pbs.org/wnet/african-americans-many-rivers-to-cross/history/did-african-american-slaves-rebel/|title=The Five Greatest Slave Rebellions in the United States {{!}} African American History Blog {{!}} The African Americans: Many Rivers to Cross|date=January 12, 2013|newspaper=The African Americans: Many Rivers to Cross|author= Gates, Henry Louis|publisher=]|language=en-US|access-date=October 11, 2016|author-link=Henry Louis Gates}}</ref> Those after 1776 include: | |||
| * ]'s conspiracy (1800) | |||
| * ] slave escape and mass suicide (1803) | |||
| * ] Rebellion (1805) | |||
| * ], (1811)<ref>{{cite book|last=Rasmussen|first=Daniel|title=American Uprising: The Untold Story of America's Largest Slave Revolt|url=https://archive.org/details/americanuprising00dani|url-access=registration|year=2011|publisher=HarperCollins|page=288|isbn=978-0-06-199521-7}}</ref> | |||
| * ] Rebellion (1815) | |||
| * ]'s conspiracy (1822) | |||
| * ] (1831) | |||
| * ] (1835–1838)<ref>{{cite web|author=J.B. Bird |url=http://www.johnhorse.com/black-seminoles/black-seminole-slave-rebellion.htm |title=The slave rebellion the country tried to forget |website=John Horse |access-date=October 4, 2013}}</ref> | |||
| * ] (1839)<ref name="WDLAmistad">{{cite web |url = http://www.wdl.org/en/item/3080/ |title = Unidentified Young Man |website = ] |date = 1839–1840 |access-date = July 28, 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| * ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.okhistory.org/publications/enc/entry.php?entry=SL002|title=Slave Revolt of 1842 {{pipe}} The Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture|website=www.okhistory.org}}</ref> | |||
| * ] (1849) | |||
| In 1831, ], a literate slave who claimed to have spiritual ], organized a ] in ]; it was sometimes called the Southampton Insurrection. Turner and his followers killed nearly sixty white inhabitants, mostly women and children. Many of the men in the area were attending a religious event in North Carolina.<ref name="Foner 2009 406–407">{{cite book|last=Foner|first=Eric|title=Give Me Liberty|year=2009|publisher=Seagull Edition|location=London|pages=406–407}}</ref> Eventually Turner was captured with 17 other rebels, who were subdued by the militia.<ref name="Foner 2009 406–407" /> Turner and his followers were ], and Turner's body was ]. In a frenzy of fear and retaliation, the militia killed more than 100 slaves who had not been involved in the rebellion. Planters whipped hundreds of innocent slaves to ensure resistance was quelled.<ref name="Foner 2009 406–407" /> | |||
| This rebellion prompted Virginia and other slave states to pass more restrictions on slaves and free people of color, controlling their movement and requiring more white supervision of gatherings. In 1835, North Carolina withdrew the franchise for free people of color, and they lost their vote. | |||
| There are four known mutinies on vessels involved in the coastwise slave trade: '']'' (1826), ''Governor Strong'' (1826), ''Lafayette'' (1829), and the ] (1841).<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Williams |first=Jennie K. |date=2020-04-02 |title=Trouble the water: The Baltimore to New Orleans coastwise slave trade, 1820–1860 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0144039X.2019.1660509 |journal=Slavery & Abolition |language=en |volume=41 |issue=2 |pages=275–303 |doi=10.1080/0144039X.2019.1660509 |s2cid=203494471 |issn=0144-039X}}</ref> | |||
| ===Post-revolution Southern manumissions=== | |||
| ])]] | |||
| Although Virginia, Maryland and ] were slave states, the latter two already had a high proportion of free blacks by the outbreak of war. Following the Revolution, the three legislatures made ] easier, allowing it by deed or will. Quaker and Methodist ministers in particular urged slaveholders to free their slaves. The number and proportion of freed slaves in these states rose dramatically until 1810. More than half of the number of free blacks in the United States were concentrated in the Upper South. The proportion of free blacks among the black population in the Upper South rose from less than 1 percent in 1792 to more than 10 percent by 1810.<ref name="Peter Kolchin 1993 pp. 77–78" /> In Delaware, nearly 75 percent of black people were free by 1810.<ref>Kolchin (1993), ''American Slavery'', p. 78.</ref> | |||
| In the United States as a whole, the number of free blacks reached 186,446, or 13.5 percent of all black people by 1810.<ref name="PeterKolchin">Peter Kolchin (1993), ''American Slavery'', p. 81.</ref> After that period, few slaves were freed, as the development of ] featuring short-staple cotton in the Deep South drove up the internal demand for slaves in the domestic slave trade and high prices being paid for them.<ref>Kolchin (1993), ''American Slavery'', p. 87.</ref> | |||
| South Carolina made manumission more difficult, requiring legislative approval of every manumission.{{Citation needed|date=August 2023}} Alabama banned free black people from the state beginning in 1834; free people of color who crossed the state line were subject to enslavement.<ref>{{Cite web |last=MADEO |title=Jan. 17, 1834 {{!}} Alabama Legislature Bans Free Black People from Living in the State |url=https://calendar.eji.org/racial-injustice/jan/17 |access-date=2023-08-22 |website=calendar.eji.org |language=en}}</ref> Free black people in Arkansas after 1843 had to buy a $500 good-behavior bond, and no unenslaved black person was legally allowed to move into the state.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Cathey |first=Clyde W. |date=1944 |title=Slavery in Arkansas |journal=The Arkansas Historical Quarterly |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=66–90 |doi=10.2307/40027465 |jstor=40027465 |issn=0004-1823}}</ref> | |||
| ===Female slave owners=== | |||
| ] a profitable criminal business{{mdash}}the ] gang was at work in Northwest Fork Hundred, Delaware until 1829, when four bodies were found buried on property they had owned ("Kidnapping 250 Dollars Reward" ''Constitutional Whig'', April 27, 1827)]] | |||
| Women exercised their right to own and control human property without their husbands' interference or permission, and they were active participants in the slave trade.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Jones-Rogers |first1=Stephanie E. |title=They Were Her Property: White Women as Slave Owners in the American South |date=2019 |publisher=Yale University Press |location=New Haven London |isbn=978-0-300-25183-8|pages=37, 134|quote="Throughout the antebellum period, married women consistently asserted their rights to own and control human property without their husband's interference, and they exercised those rights as well." "White women were not anomalies at local slave auctions, either, and no group could testify more powerfully to white women's presence at and involvement in slave auctions than the enslaved people who were there.}}</ref> For example, in South Carolina 40% of bills of sale for slaves from the 1700s to the present included a female buyer or seller.<ref name=mcdonald2019>{{Cite web|last=McDonald|first=Soraya Nadia|date=2019-03-15|title=In 'They Were Her Property,' a historian shows that white women were deeply involved in the slave economy|url=https://andscape.com/features/in-they-were-her-property-a-historian-shows-that-white-women-were-deeply-involved-in-the-slave-economy/|access-date=2020-07-14|website=Andscape|language=en-US|quote=South Carolina has bills of sale for property transactions from the 1700s to pretty recently. I looked at a sample of 3,000 bills of sale involving enslaved people being purchased or sold. Close to 40 percent of the bills of sale included either a female buyer or a female seller.}}</ref> Women also governed their slaves in a manner similar to men, engaging in the same levels of physical disciplining. Like men, they brought lawsuits against those who jeopardized their ownership to their slaves.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Jones-Rogers |first1=Stephanie E. |title=They Were Her Property: White Women as Slave Owners in the American South |date=2019 |publisher=Yale University Press |location=New Haven London |isbn=978-0-300-25183-8|pages=xv-xvi|quote=When we listen to what enslaved people had to say about white women and slave mastery, we find that articulated quite clearly their belief that slave-owning women governed their slaves in the same ways that white men did, sometimes they were more effective at slave management or they used more brutal methods of discipline than their husbands did...White southern women conducted transactions with slave traders...and they were not meek in their bargaining...slave-owning women brought legal suits against individuals, both male and female, who jeopardized their claims to human property, and others sued them in kind. They bought and sold slaves for profit, and, on rare occasions owned slave yards.}}</ref> | |||
| ===Black slave owners=== | |||
| {{Main|African-American slave owners}} | |||
| Despite the longstanding color line in the United States, some African Americans were slave owners themselves, some in cities and others as plantation owners in the country.<ref name=":5">{{Cite journal |date=2006-01-01 |title=Class |journal=Encyclopedia of African American History, 1619–1895: From the Colonial Period to the Age of Frederick Douglass |doi=10.1093/acref/9780195167771.001.0001|isbn=978-0-19-516777-1 }}</ref> Slave ownership signified both wealth and increased social status.<ref name=":5" /> Black slave owners were uncommon, however, as "of the two and a half million African Americans living in the United States in 1850, the vast majority enslaved."<ref name=":5" /> | |||
| ===Native American slave owners=== | |||
| {{Main|Amerindian slave ownership}} | |||
| After 1800, some of the ] and the other ] of the Southeast started buying and using black slaves as labor. They continued this practice after removal to ] in the 1830s, when as many as 15,000 enslaved blacks were taken with them.<ref>A history of the descendants of the slaves of Cherokee can be found at {{cite journal |last=Sturm |first=Circe |title=Blood Politics, Racial Classification, and Cherokee National Identity: The Trials and Tribulations of the Cherokee Freedmen |journal=] |volume=22 |issue=1/2 |year=1998 |pages=230–258 |jstor=1185118}} In 1835, 7.4% of Cherokee families held slaves. In comparison, nearly one-third of white families living in Confederate states owned slaves in 1860. Further analysis of the 1835 Federal Cherokee Census can be found in {{cite journal |last1=McLoughlin |first1=W. G. |first2=W. H. |last2=Conser |title=The Cherokees in Transition: a Statistical Analysis of the Federal Cherokee Census of 1835 |journal=] |volume=64 |issue=3 |pages=678–703 |year=1977 |jstor=1887236|doi=10.2307/1887236 }} A discussion on the total number of Slave holding families can be found in {{cite web |last=Olsen |first=Otto H. |title=Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States |work=Civil War History |date=December 2004 |url=http://www.southernhistory.net/modules.php?op=modload&name=News&file=article&sid=9406&mode=thread&order=0&thold=0 |access-date=June 8, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070720231457/http://www.southernhistory.net/modules.php?op=modload&name=News&file=article&sid=9406&mode=thread&order=0&thold=0 |archive-date=July 20, 2007 |url-status=dead |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| The nature of ] often mirrored that of white slave-owning society. The law barred intermarriage of Cherokees and enslaved African Americans, but Cherokee men had unions with enslaved women, resulting in mixed-race children.<ref name="tperdue1">{{cite book |last1=Perdue |first1=Theda |title=Slavery and the Evolution of Cherokee Society, 1540–1866 |date=1979 |publisher=University of Tennessee Press |page= |isbn=978-0-87049-530-4 }}</ref><ref name="katover">{{cite book |last1=Katz |first1=William Loren |title=Black Indians: A Hidden Heritage |date=3 January 2012 |publisher=Simon and Schuster |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/blackindianshidd0000katz |url-access=registration |quote=black indians. |access-date=1 March 2019|isbn=978-1-4424-4637-3 }}</ref> Cherokee who aided slaves were punished with one hundred lashes on the back. In Cherokee society, persons of African descent were barred from holding office even if they were also racially and culturally Cherokee. They were also barred from bearing arms and owning property. The Cherokee prohibited the teaching of African Americans to read and write.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Duncan |first=J. W. |year=1928 |url=http://digital.library.okstate.edu/chronicles/v006/v006p178.html |title=Interesting ante-bellum laws of the Cherokee, now Oklahoma history |journal=Chronicles of Oklahoma |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=178–180 |access-date=July 13, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071219043621/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/chronicles/v006/v006p178.html |archive-date=December 19, 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Davis |first=J. B. |year=1933 |url=http://digital.library.okstate.edu/Chronicles/v011/v011p1056.html |title=Slavery in the Cherokee nation |journal=Chronicles of Oklahoma |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=1056–1072 |access-date=July 13, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150310044812/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/Chronicles/v011/v011p1056.html |archive-date=March 10, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| By contrast, the ] welcomed into their nation African Americans who had ] slavery (]). Historically, the Black Seminoles lived mostly in distinct bands near the Native American Seminole. Some were held as slaves of particular Seminole leaders. Seminole practice in Florida had acknowledged slavery, though not the chattel slavery model common elsewhere. It was, in fact, more like feudal dependency and taxation.<ref name="Jennison2012">{{cite book|first=Watson W.|last=Jennison|title=Cultivating Race: The Expansion of Slavery in Georgia, 1750–1860|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ImNeFi-wt6IC&pg=PA132|year=2012|publisher=University Press of Kentucky|isbn=978-0-8131-4021-6|page=132}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=McCall |first=George A. |title=Letters from the Frontiers |year =1868 |publisher=J.B. Lippincott |place=Philadelphia |page=160 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bA0EZPPKc_QC&q=%22melons+pumpkins%22+mccall&pg=PA160 |isbn=978-1-4290-2158-6}}</ref><ref name="Mulroy2016">{{cite book|first=Kevin|last=Mulroy|title=The Seminole Freedmen: A History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=b--eCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25|year= 2016|publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|isbn=978-0-8061-5588-3|page=25}}</ref> The relationship between Seminole blacks and natives changed following their relocation in the 1830s to territory controlled by the ] who had a system of chattel slavery. Pro slavery pressure from Creek and pro-Creek Seminole and slave raiding led to many Black Seminoles escaping to Mexico.<ref name="DeloriaSalisbury2008">{{cite book|first1=Philip|last1=Deloria|first2=Neal|last2=Salisbury|title=A Companion to American Indian History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BMenL80QO0kC&pg=PA348|year= 2008|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-4051-4378-3|pages=348–349}}</ref><ref name="TriggerWashburn1996">{{cite book|first1=Bruce G.|last1=Trigger|first2=Wilcomb E.|last2=Washburn|title=The Cambridge History of the Native Peoples of the Americas|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DRGVjLiyXEwC&pg=PA525|year=1996|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-57392-4|page=525}}</ref><ref name="Binder1987">{{cite book|first=Wolfgang|last=Binder|title=Westward Expansion in America (1803–1860)|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=k7F1AAAAMAAJ&q=%22Marcellus%20Duval%22|year=1987|publisher=Palm & Enke|isbn=978-3-7896-0171-2|page=147}}</ref><ref name="Buchanan1955">{{cite book|author=James Shannon Buchanan|title=Chronicles of Oklahoma|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6i8UAAAAYAAJ&q=%22Siah%20Hardridge%22|year=1955|publisher=Oklahoma Historical Society.|page=522}}</ref><ref name="Mulroy2007p79">{{cite book|first=Kevin|last=Mulroy|title=The Seminole Freedmen: A History|url=https://archive.org/details/seminolefreedmen0000mulr|url-access=registration|year=2007|publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|isbn=978-0-8061-3865-7|page=}}</ref> | |||
| ===High demand and smuggling=== | |||
| {{Further|Post-1808 importation of slaves to the United States|Movement to reopen the transatlantic slave trade}} | |||
| ]'' confronting the ] ''Martha'' off ] on June 6, 1850 (] lithograph, ]'s ''Africa and the American Flag'', 1854)]] | |||
| The ], adopted in 1787, prevented ] from completely banning the ]ation of slaves until 1808, although Congress regulated against the trade in the ], and in subsequent Acts ] and 1803.<ref name="Regulation of the Trade" /><ref>{{Cite magazine|last=Finkelman|first=Paul|date=2004|title=Suppressing American Slave Traders in the 1790s|magazine=OAH Magazine of History|volume=18|issue=3|pages=51–55|issn=0882-228X}}</ref> During and after the Revolution, the ] individually passed laws against importing slaves. By contrast, the states of Georgia and South Carolina reopened their trade due to demand by their upland planters, who were developing new cotton plantations: Georgia from 1800 until December 31, 1807, and South Carolina from 1804. In that period, Charleston traders imported about 75,000 slaves, more than were brought to South Carolina in the 75 years before the Revolution.<ref>James A. McMillin, ''The Final Victims: Foreign Slave Trade to North America, 1783–1810, Volume 2'', Univ of South Carolina Press, 2004, p. 86</ref> Approximately 30,000 were imported to Georgia. | |||
| By January 1, 1808, when Congress ], South Carolina was the only state that still allowed importation of enslaved people. The domestic trade became extremely profitable as demand rose with the expansion of cultivation in the Deep South for cotton and sugar cane crops. Slavery in the United States became, more or less, self-sustaining by natural increase among the current slaves and their descendants. Maryland and Virginia viewed themselves as slave producers, seeing "producing slaves" as resembling animal husbandry. Workers, including many children, were relocated by force from the upper to the lower South. | |||
| Despite the ban, slave imports continued through smugglers bringing in slaves past the U.S. Navy's ] to South Carolina, and overland from Texas and Florida, both under Spanish control.<ref>{{cite book |first=Hugh |last=Thomas |title=The Slave Trade. The Story of the Atlantic Slave Trade: 1440–1870 |location=New York |publisher=Simon and Schuster |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-684-81063-8 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/slavetradestoryo00thom |url-access=registration }}</ref> Congress increased the punishment associated with importing slaves, classifying it in 1820 as an act of piracy, with smugglers subject to harsh penalties, including death if caught. After that, "it is unlikely that more than 10,000 were successfully landed in the United States."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://abolition.nypl.org/print/us_constitution/ |first=Paul |last=Finkelman |title=The Abolition of the Slave Trade |work=New York Public Library |date=2007 |access-date=February 14, 2012}}</ref> But, some smuggling of slaves into the United States continued until just before the start of the Civil War. | |||
| ===Colonization movement=== | |||
| {{Main|American Colonization Society|History of Liberia}} | |||
| ] shows colonial settlements including ], ], ], ], and ] ]] | |||
| ] | |||
| In the early part of the 19th century, other organizations were founded to take action on the future of black Americans. Some advocated removing free black people from the United States to places where they would enjoy greater freedom; some endorsed ] in Africa, while others advocated ], usually to Haiti. During the 1820s and 1830s, the ] (ACS) was the primary organization to implement the "return" of black Americans to Africa.<ref name=AFP>{{cite web|url=http://www.fcnl.org/issues/item.php?item_id=731&issue_id=75|title=Background on Conflict in Liberia|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110108042234/http://www.fcnl.org/issues/item.php?item_id=731&issue_id=75|archive-date=January 8, 2011|df=mdy-all}} ], a successful New England black shipping man, financed and captained a voyage for American blacks in 1815–1816 to British-ruled ]. Cuffe believed that African Americans could more easily "rise to be a people" in Africa than in the United States because of the latter's slavery, racial discrimination, and limits on black rights. Although Cuffee died in 1817, his early efforts encouraged the ACS to promote further settlements. The ] opposed slavery, but they believed that blacks would face better chances for freedom in Africa than in the United States. Slaveholders opposed abolition, but they wanted to get rid of ], whom they saw as potential leaders of rebellions and people who encouraged slaves to run away.</ref> The ACS was made up mostly of ] and slaveholders, and they found uneasy common ground in support of what was incorrectly called "repatriation". By this time, however, most black Americans were native-born and did not want to emigrate, saying they were no more African than white Americans were British. Rather, they wanted full rights in the United States, where their families had lived and worked for generations. | |||
| In 1822, the ACS and affiliated state societies established what would become the colony of ], in West Africa.<ref name="WDLMap">{{cite web |url = http://www.wdl.org/en/item/446/ |title = Map of Liberia, West Africa |work = ] |year = 1830 |access-date = June 3, 2013}}</ref> The ACS assisted thousands of freedmen and free blacks (with legislated limits) to emigrate there from the United States. Many white people considered this preferable to ] in the United States. ], one of the founders and a prominent slaveholder politician from Kentucky, said that blacks faced: | |||
| {{Blockquote|text=...unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off.<ref name=ATH>{{cite book |first=Maggie Montesinos |last=Sale |title=The Slumbering Volcano: American Slave Ship Revolts and the Production of Rebellious Masculinity |publisher=Duke University Press |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-8223-1992-4 |page=45 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1yQowl-nEh8C&pg=PA45 }}</ref>}} | |||
| Deportation would also be a way to prevent reprisals against former slaveholders and white people in general, as had occurred in the ], which had contributed to a consuming fear amongst whites of retributive black violence, a phobia dubbed ]. | |||
| ===Domestic slave trade and forced migration=== | |||
| {{Main|Slave trade in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|List of slave traders of the United States|Slave markets and slave jails in the United States|Kidnapping into slavery in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Bibliography of the slave trade in the United States|Family separation in American slavery}} | |||
| ] based on a sketch made 1853 while visiting the United States with ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] barred the federal government from prohibiting the importation of slaves for twenty years. Various states passed bans on the international slave trade during that period; by 1808, the only state still allowing the importation of African slaves was South Carolina. After 1808, legal importation of slaves ceased, although there was smuggling via ] and the disputed Gulf Coast to the west.<ref name=Florida>{{cite book|title=The African American Heritage of Florida|contribution=African Religious Retentions in Florida|first=Robert L.|last=Hall|publisher=University Press of Florida|year=1995|isbn=978-0-8130-1332-9|pages=42–70|editor1-first=David R.|editor1-last=Colburn|editor2-first=Jane L.|editor2-last=Landers}}</ref>{{rp|48–49}}<ref name=Peoples>{{cite book|title=A People's History of Florida 1513–1876. How Africans, Seminoles, Women, and Lower Class Whites Shaped the Sunshine State|first=Adam|last=Wasserman|isbn=978-1-4421-6709-4|year=2010|publisher=Adam Wasserman|edition=Revised 4th}}</ref>{{rp|138}} This route all but ended after Florida ] in 1821 (but see ]s ] and ]). | |||
| The replacement for the importation of slaves from abroad was increased domestic production. Virginia and Maryland had little new agricultural development, and their need for slaves was mostly for replacements for decedents. Normal reproduction more than supplied these: Virginia and Maryland had surpluses of slaves. Their tobacco farms were "worn out"<ref name=Sweig>{{cite web|title=Alexandria to New Orleans: The Human Tragedy of the Interstate Slave Trade|newspaper=]|first=Donald|last=Sweig|date=October 2014|access-date=February 13, 2018|url=http://connectionarchives.com/PDF/2014/Slave%20Trader/Slave%20Trader.PDF}}</ref> and the climate was not suitable for cotton or sugar cane. The surplus was even greater because ] (though ]). The pro-slavery Virginian ] wrote in 1832 that Virginia was a "negro-raising state"; i.e. Virginia "produced" slaves.<ref>{{cite book|first=Charles B.|last=Dew|title=The Making of a Racist|publisher=]|year=2016|isbn=978-0-8139-3887-5|page=2}}</ref> According to him, in 1832 Virginia exported "upwards of 6,000 slaves" per year, "a source of wealth to Virginia".<ref name=Curry>{{cite book|title=Slavery in America: Theodore Weld's ''American Slavery As It Is''|first1=Richard O.|last1=Curry|first2=Joanna Dunlop|last2=Cowden|location=]|publisher=F. E. Peacock|year=1972|oclc=699102217}}</ref>{{rp|198}} A newspaper from 1836 gives the figure as 40,000, earning for Virginia an estimated $24,000,000 per year.<ref>{{cite news|title=(Untitled)|newspaper=]|location=]|date=10 Dec 1836|page=2|via=]|url=https://www.newspapers.com/clip/103141201/slaves-exported-from-virginia/}}</ref><ref name=Curry/>{{rp|201}} Demand for slaves was the strongest in what was then the southwest of the country: Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana, and, later, Texas, Arkansas, and Missouri. Here there was abundant land suitable for plantation agriculture, which young men with some ] established. This was expansion of the white, monied population: younger men seeking their fortune. | |||
| The most valuable crop that could be grown on a plantation in that climate was cotton. That crop was labor-intensive, and the least-costly laborers were slaves. Demand for slaves exceeded the supply in the southwest; therefore slaves, never cheap if they were productive, went for a higher price. As portrayed in '']'' (the "original" cabin was in Maryland),<ref>{{cite episode|series=All Things Considered|title=A Visit to the Real 'Uncle Tom's Cabin'|date=February 4, 2006|access-date=February 28, 2018|first=Debbie|last=Elliot|url=https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5188487|network=]}}</ref> "selling South" was greatly feared. A recently (2018) publicized example of the practice of "selling South" is the ] by ] of 272 slaves from Maryland, to plantations in Louisiana, to benefit ], which has been described as "ow its existence" to this transaction.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Swarns|first1=Rachel|title=272 Slaves Were Sold to Save Georgetown. What Does It Owe Their Descendants?|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/17/us/georgetown-university-search-for-slave-descendants.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160416193641/http://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/17/us/georgetown-university-search-for-slave-descendants.html|archive-date=2016-04-16|url-access=subscription|url-status=live|access-date=February 15, 2018|newspaper=]|date=February 14, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=A Glimpse Into the Life of a Slave Sold to Save Georgetown|first=Rachel L.|last=Swarns|date=March 12, 2017|newspaper=]|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/03/12/us/georgetown-university-slaves-life-campbell.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170312203811/https://www.nytimes.com/2017/03/12/us/georgetown-university-slaves-life-campbell.html|archive-date=2017-03-12|url-access=subscription|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Georgetown Students Agree to Create Reparations Fund|first=Adeel|last=Hassan|date=April 12, 2019|newspaper=]|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/04/12/us/georgetown-reparations.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190412174603/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/04/12/us/georgetown-reparations.html|archive-date=2019-04-12|url-access=subscription |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The growing international demand for cotton led many plantation owners further west in search of suitable land. In addition, the invention of the ] in 1793 enabled profitable processing of short-staple cotton, which could readily be grown in the uplands. The invention revolutionized the cotton industry by increasing fifty-fold the quantity of cotton that could be processed in a day. At the end of the ], fewer than 300,000 bales of cotton were produced nationally. By 1820, the amount of cotton produced had increased to 600,000 bales, and by 1850 it had reached 4,000,000. There was an explosive growth of cotton cultivation throughout the Deep South and greatly increased demand for slave labor to support it.<ref>''The People's Chronology'', 1994, by James Trager.</ref> As a result, manumissions decreased dramatically in the South.<ref>Kolchin p. 96. | |||
| Through the domestic slave trade, about one million enslaved African Americans were forcibly removed from the Upper South to the Deep South, with some transported by ship in the coastwise trade. In 1834, ], ], and ] grew half the nation's cotton; by 1859, along with ], they grew 78%. By 1859, cotton growth in the ] had fallen to just 10% of the national total. Berlin p. 166.</ref> | |||
| Most of the slaves sold from the Upper South were from ], ] and the ], where changes in agriculture decreased the need for their labor and the demand for slaves. Before 1810, primary destinations for the slaves who were sold were ] and ], but, after 1810, the Deep South states of ], ], ], ] and ] received the most slaves. This is where cotton became "king".<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 168–169. Kolchin p. 96.</ref> Meanwhile, the Upper South states of Kentucky and Tennessee joined the slave-exporting states. | |||
| By 1815, the domestic slave trade had become a major economic activity in the United States; it lasted until the 1860s.<ref name="CUP">{{Cite book|last=Morgan|first=Marcyliena|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mhJcsiydNe8C&pg=PA20|title=Language, Discourse and Power in African American Culture|date=2002-07-04|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-00149-6|language=en}}</ref> Between 1830 and 1840, nearly 250,000 slaves were taken across state lines.<ref name="CUP" /> In the 1850s, more than 193,000 enslaved persons were transported, and historians estimate nearly one million in total took part in the forced migration of this new "Middle Passage". By 1860, the slave population in the United States had reached four million.<ref name="CUP" /> Of the 1,515,605 free families in the fifteen slave states in 1860, nearly 400,000 held slaves (roughly one in four, or 25%),<ref>{{Cite web|title=Gun Reviews Archives|url=https://thegunzone.com/gun-reviews/|access-date=2022-12-29|website=TheGunZone|language=en-US}}</ref> amounting to 8% of all American families.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.civil-war.net/census.asp?census=Total |title=American Civil War Census Data |publisher=Civil-war.net |access-date=May 27, 2014 |archive-date=March 22, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160322110116/http://www.civil-war.net/census.asp?census=Total }}</ref> | |||
| ] is a cloth that recounts a slave sale separating a mother and her daughter. The sack belonged to a nine-year-old girl Ashley and was a parting gift from her mother, Rose, after Ashley had been sold. Rose filled the sack with a dress, braid of her hair, pecans, and "my love always". (], South Carolina)]] | |||
| The historian ] called this forced migration of slaves the "Second Middle Passage" because it reproduced many of the same horrors as the ] (the name given to the transportation of slaves from Africa to North America). These sales of slaves broke up many families and caused much hardship. Characterizing it as the "central event" in the life of a slave between the ] and the Civil War, Berlin wrote that, whether slaves were directly uprooted or lived in fear that they or their families would be involuntarily moved, "the massive deportation traumatized black people, both slave and free".<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 161–162.</ref> Individuals lost their connection to families and clans. Added to the earlier colonists combining slaves from different tribes, many ethnic Africans lost their knowledge of varying tribal origins in Africa. Most were descended from families that had been in the United States for many generations.<ref name="CUP" /> | |||
| The firm of ] was a leader in this trade. In the 1840s, almost 300,000 slaves were transported, with Alabama and Mississippi receiving 100,000 each. During each decade between 1810 and 1860, at least 100,000 slaves were moved from their state of origin. In the final decade before the Civil War, 250,000 were transported. Michael Tadman wrote in ''Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South'' (1989) that 60–70% of inter-regional migrations were the result of the sale of slaves. In 1820, a slave child in the Upper South had a 30 percent chance of being sold South by 1860.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 168–169. Kolchin p. 96. Kolchin notes that Fogel and Engerman maintained that 84% of slaves moved with their families but "most other scholars assign far greater weight{{spaces}}... to slave sales." Ransome (p. 582) notes that Fogel and Engerman based their conclusions on the study of some counties in Maryland in the 1830s and attempted to extrapolate that analysis as reflective of the entire South over the entire period.</ref> The death rate for the slaves on their way to their new destination across the American South was less than that suffered by captives shipped across the Atlantic Ocean, but mortality nevertheless was higher than the normal death rate. | |||
| ] transported two-thirds of the slaves who moved West.<ref>{{cite book |first=Allan |last=Kulikoff |title=The Agrarian Origins of American Capitalism |location=Charlottesville |publisher=University of Virginia Press |year=1992 |isbn=978-0-8139-1388-9 |pages=–269 |url=https://archive.org/details/agrarianoriginso00kuli |url-access=registration }}</ref> Only a minority moved with their families and existing master. Slave traders had little interest in purchasing or transporting intact slave families; in the early years, planters demanded only the young male slaves needed for heavy labor. Later, in the interest of creating a "self-reproducing labor force", planters purchased nearly equal numbers of men and women. Berlin wrote: | |||
| <blockquote>The internal slave trade became the largest enterprise in the South outside the plantation itself, and probably the most advanced in its employment of modern transportation, finance, and publicity. The slave trade industry ], with terms such as "prime hands, bucks, breeding wenches, and "fancy girls" coming into common use.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 166–169.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ] | |||
| The expansion of the interstate slave trade contributed to the "economic revival of once depressed seaboard states" as demand accelerated the value of slaves who were subject to sale.<ref>Kolchin, p. 98.</ref> Some traders moved their "chattels" by sea, with ] to ] being the most common route, but most slaves were forced to walk overland. Others were shipped downriver from such markets as ] on the Ohio River, and ] on the Mississippi. Traders created regular migration routes served by a network of slave pens, yards and warehouses needed as temporary housing for the slaves. In addition, other vendors provided clothes, food and supplies for slaves. As the trek advanced, some slaves were sold and new ones purchased. Berlin concluded, "In all, the slave trade, with its hubs and regional centers, its spurs and circuits, reached into every cranny of southern society. Few southerners, black or white, were untouched."<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 168–171.</ref> | |||
| Once the trip ended, slaves faced a life on the frontier significantly different from most labor in the Upper South. Clearing trees and starting crops on virgin fields was harsh and backbreaking work. A combination of inadequate nutrition, bad water and exhaustion from both the journey and the work weakened the newly arrived slaves and produced casualties. New plantations were located at rivers' edges for ease of transportation and travel. ]es and other environmental challenges spread disease, which took the lives of many slaves. They had acquired only limited immunities to lowland diseases in their previous homes. The death rate was so high that, in the first few years of hewing a plantation out of the wilderness, some planters preferred whenever possible to use rented slaves rather than their own.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', p. 174.</ref> | |||
| The harsh conditions on the frontier increased slave resistance and led owners and overseers to rely on violence for control. Many of the slaves were new to cotton fields and unaccustomed to the "sunrise-to-sunset gang labor" required by their new life. Slaves were driven much harder than when they had been in growing tobacco or ] back East. Slaves had less time and opportunity to improve the quality of their lives by raising their own ] or tending vegetable gardens, for either their own consumption or trade, as they could in the East.<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 175–177.</ref> | |||
| ] in New Orleans (] 2011.155.305)]] | |||
| In ], French colonists had established ] plantations and exported sugar as the chief commodity crop. After the ] in 1803, Americans entered the state and joined the sugar cultivation. Between 1810 and 1830, planters bought slaves from the North and the number of slaves increased from fewer than 10,000 to more than 42,000. Planters preferred young males, who represented two-thirds of the slave purchases. Dealing with sugar cane was even more physically demanding than growing cotton. The largely young, unmarried male slave force made the reliance on violence by the owners "especially savage".<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', pp. 179–180.</ref> | |||
| ], a slave trading business in ], photographed by ] just prior to the 1864 ]]] | |||
| ] became nationally important as a slave market and port, as slaves were shipped from there upriver by ] to plantations on the Mississippi River; it also sold slaves who had been shipped downriver from markets such as Louisville. By 1840, the ] was the largest in North America. It became the wealthiest and the fourth-largest city in the nation, based chiefly on the slave trade and associated businesses.<ref name=":1">Walter Johnson, ''Soul by Soul: Life Inside the Antebellum Slave Market'', Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1999. pages=90 ("miraculous things"), 228 (property law status)</ref> The trading season was from September to May, after the harvest.<ref>Johnson (1999), ''Soul by Soul'', p. 2.</ref> | |||
| The notion that slave traders were social outcasts of low reputation, even in the South, was initially promulgated by defensive southerners and later by figures like historian ].<ref name=":2">{{Cite book |last=Tadman |first=Michael |url=https://academic.oup.com/edited-volume/34514/chapter/292862907 |title=Internal Slave Trades |date=2012-09-18 |publisher=Oxford University Press |editor-last=Smith |editor-first=Mark M. |volume=1 |language=en |doi=10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199227990.013.0029 |isbn=978-0-19-922799-0 |editor-last2=Paquette |editor-first2=Robert L.}}</ref> Historian ], author of '']'' (1931) found — to the contrary of Phillips's position — that many traders were esteemed members of their communities.<ref>{{Cite journal |date=April 1931 |title=Frederic Bancroft, Slave-Trading in the Old South |url=http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/10.2307/2714086 |journal=The Journal of Negro History |language=en |volume=16 |issue=2 |pages=240–241 |doi=10.2307/2714086 |jstor=2714086 |s2cid=153885388 |issn=0022-2992}}</ref> Contemporary researcher ] argues that the "trader's position in society was not unproblematic and owners who dealt with the trader felt the need to satisfy themselves that they acted honorably," while ] contends that "'trader as outcast' operated at the level of propaganda" whereas white slave owners almost universally professed a belief that slaves were not human like them, and thus dismissed the consequences of slave trading as beneath consideration.<ref name=":2" /> Similarly, historian ] read hundreds of letters to slave traders and found virtually zero narrative evidence for guilt, shame, or contrition about the slave trade: "If you begin with the absolute belief in white supremacy—unquestioned white superiority/unquestioned black inferiority—everything falls neatly into place: the African is inferior racial 'stock,' living in sin and ignorance and barbarism and heathenism on the 'Dark Continent' until enslaved...Slavery thus miraculously becomes a form of 'uplift' for this supposedly benighted and brutish race of people. And once notions of white supremacy and black inferiority are in place in the American South, they are passed on from one generation to the next with all the certainty and inevitability of a genetic trait."<ref>{{cite book |last=Dew |first=Charles B. |title=The making of a racist: a southerner reflects on family, history, and the slave trade |publisher=University of Virginia Press |year=2016 |isbn=978-0-8139-3888-2 |location=Charlottesville |page=154 |language=en-us |lccn=2015043815 |oclc=956713856 |author-link=Charles B. Dew}}</ref> | |||
| In the ], candidate ] was strongly criticized by opponents ] who transacted in slaves in defiance of modern standards or morality.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Frontiersman or Southern Gentleman? Newspaper Coverage of Andrew Jackson during the 1828 Presidential Campaign {{pipe}} Readex |url=https://www.readex.com/readex-report/issues/volume-9-issue-3/frontiersman-or-southern-gentleman-newspaper-coverage-andrew |access-date=2022-12-29 |website=www.readex.com}}</ref> | |||
| ===Treatment=== | |||
| {{Main|Treatment of slaves in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Torture of slaves in the United States|Slave health on plantations in the United States|Slave quarters in the United States|Field slaves in the United States}} | |||
| ], formerly enslaved on a cotton plantation along the ], photo taken at ], 1863; after the whipping, Peter's wounds were salted, a common practice;<ref name=":12">{{Cite news |last=Bostonian |date=1863-12-03 |orig-date=1863-11-12 |title=The Realities of Slavery: To the Editor of the N.Y. Tribune |language=en-us |page=4 |work=New-York Tribune |url=https://www.newspapers.com/article/new-york-tribune-the-realities-of-slaver/128982438/ |access-date=2023-07-27 |issn=2158-2661 |via=]}}</ref><ref name=":42">{{cite thesis |last1=Dickman |first1=Michael |title=Honor, Control, and Powerlessness: Plantation Whipping in the Antebellum South |publisher=Boston College |year=2015 |hdl=2345/bc-ir:104219 |url=http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:104219}}</ref> the overseer who whipped Peter was fired by slave owner ]<ref>{{cite news|first=Kathleen|last=Collins|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/10/04/books/review/Letters-t-ASLAVENAMEDG_LETTERS.html?_r=0|title=The Scourged Back|work=]|date=January 9, 1985|pages=43–45}}</ref> (original '']'' by ])]] | |||
| The treatment of slaves in the United States varied widely depending on conditions, time, and place, but in general it was brutal, especially on plantations. Whippings and rape were routine. The power relationships of slavery corrupted many whites that had authority over slaves, with children showing their own cruelty. Masters and overseers resorted to physical punishments to impose their wills. Slaves were punished by whipping, shackling, hanging, beating, burning, mutilation, branding and imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but sometimes abuse was carried out to re-assert the dominance of the master or overseer of the slave.<ref>Moore, p. 114.</ref> Treatment was usually harsher on large plantations, which were often managed by overseers and owned by absentee slaveholders, conditions permitting abuses. | |||
| ], who escaped to freedom, reported that on one plantation, slave men were required to pick eighty pounds per day of cotton, while women were required to pick seventy pounds; if any slave failed in his or her quota, they were subject to whip lashes for each pound they were short. The whipping post stood next to the cotton scales.<ref>Clinton, Catherine, ''Scholastic Encyclopedia of the Civil War'', New York: Scholastic Inc., 1999, p. 8.</ref> A New York man who attended a slave auction in the mid-19th century reported that at least three-quarters of the male slaves he saw at sale had scars on their backs from whipping.<ref name="McInnis2011">{{cite book|first=Maurie D.|last=McInnis|title=Slaves Waiting for Sale: Abolitionist Art and the American Slave Trade|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=R3W4M4UojrEC&pg=PA129|year=2011|publisher=University of Chicago Press|isbn=978-0-226-55933-9|pages=129–}}</ref> By contrast, small slave-owning families had closer relationships between the owners and slaves; this sometimes resulted in a more humane environment but was not a given.<ref>Moore, p. 118.</ref> | |||
| Historian ] wrote: "Ten Southern codes made it a crime to mistreat a slave.{{spaces}}... Under the ] of 1825 (art. 192), if a master was "convicted of cruel treatment", the judge could order the sale of the mistreated slave, presumably to a better master.<ref>] (2005). ''A History of American Law: Third Edition''. Simon and Schuster, p. 163. {{ISBN|0-7432-8258-2}}</ref> Masters and overseers were seldom prosecuted under these laws. No slave could give testimony in the courts. | |||
| ], a branded slave from Louisiana—also exhibiting instruments of torture used to punish slaves (carte de visite by ], Metropolitan Museum of Art 2019.521)]] | |||
| According to Adalberto Aguirre's research, 1,161 slaves were executed in the United States between the 1790s and 1850s.<ref>A. Aguirre, Jr., "", ''The Social Science Journal'', vol. 36, issue 1 (1999), pp. 1–31.</ref> Quick executions of innocent slaves as well as suspects typically followed any attempted slave rebellions, as white militias overreacted with widespread killings that expressed their fears of rebellions, or suspected rebellions. | |||
| Although most slaves had lives that were very restricted in terms of their movements and agency, exceptions existed to virtually every generalization; for instance, there were also slaves who had considerable freedom in their daily lives: slaves allowed to rent out their labor and who might live independently of their master in cities, slaves who employed white workers, and slave doctors who treated upper-class white patients.<ref>Davis, p. 124.</ref> After 1820, in response to the inability to import new slaves from Africa and in part to abolitionist criticism, some slaveholders improved the living conditions of their slaves, to encourage them to be productive and to try to prevent escapes.<ref>Christian, Charles M., and Bennet, Sari, ''Black Saga: The African American Experience: A Chronology'', Basic Civitas Books, 1998, p. 90.</ref> It was part of a paternalistic approach in the ] that was encouraged by ministers trying to use Christianity to improve the treatment of slaves. Slaveholders published articles in Southern agricultural journals to share best practices in treatment and management of slaves; they intended to show that their system was better than the living conditions of northern industrial workers. | |||
| Medical care for slaves was limited in terms of the medical knowledge available to anyone. It was generally provided by other slaves or by slaveholders' family members, although sometimes "plantation physicians", like ], were called by the owners to protect their investment by treating sick slaves. Many slaves possessed medical skills needed to tend to each other, and used folk remedies brought from Africa. They also developed new remedies based on American plants and herbs.<ref>Burke, p. 155.</ref> | |||
| An estimated nine percent of ] due to a physical, sensory, psychological, neurological, or developmental condition. However, slaves were often described as disabled if they were unable to work or bear a child, and were often subjected to harsh treatment as a result.<ref name=":4">Barclay, J. L. (2021). ''The Mark of Slavery: Disability, Race, and Gender in Antebellum America''. University of Illinois Press.</ref> | |||
| According to Andrew Fede, an owner could be held criminally liable for killing a slave only if the slave he killed was "completely submissive and under the master's absolute control".<ref>Andrew Fede (2012). ''People Without Rights (Routledge Revivals): An Interpretation of the Fundamentals of the Law of Slavery in the U.S. South''. Routledge, p. 79. {{ISBN|1-136-71610-6}}</ref> For example, in 1791 the ] defined the willful killing of a slave as criminal ], unless done in resisting or under moderate correction (that is, corporal punishment).<ref>{{cite book |first=Thomas D. |last=Morris |year=1999 |title=Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |page=172 |isbn=978-0-8078-6430-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VmPWCKh0hZAC&pg=PA172 }}</ref> | |||
| ] on the plaza north of the ] in ] on March 10, 1853, of 96 people who had previously been enslaved near the ] (Eyre Crowe, ], Havana, Cuba)]] | |||
| While slaves' living conditions were poor by modern standards, ] argued that all workers, free or slave, during the first half of the 19th century were subject to hardship.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111220190203/http://eh.net/node/2749 |date=December 20, 2011 }}, ''Project 2001: Significant Works in Economic History'', EH.net (Economic History.net)</ref> Unlike free individuals, however, enslaved people were far more likely to be underfed, physically punished, sexually abused, or killed, with no recourse, legal or otherwise, against those who perpetrated these crimes against them. | |||
| ===Commodification of human tissue=== | |||
| In a very grim fashion, the commodification of the human body was legal in the case of African slaves as they were not legally seen as fully human. The most popular means of commodifying slave tissues was through medical experimentation. Slaves were routinely used as medical specimens forced to take part in experimental surgeries, amputations, disease research, and developing medical techniques.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kenney |first1=Stephen |title=Power, opportunism, racism: Human experiments under American slavery |journal=Endeavour |volume=39 |issue=1 |pages=10–20 |date=March 2015 |doi=10.1016/j.endeavour.2015.02.002 |pmid=25824012}}</ref> Many slaves in these routine experiments were not given pain relief or analgesics, resulting in death by shock on the table. The bodies of such slaves were grouped with other medical cadavers, or sold with the bodies of other slaves sold, stolen, or grave robbed for medical experimentation.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Halperin |first=Edward C. |date=July 2007 |title=The poor, the Black, and the marginalized as the source of cadavers in United States anatomical education |url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17226823/ |journal=Clinical Anatomy |volume=20 |issue=5 |pages=489–495 |doi=10.1002/ca.20445 |issn=0897-3806 |pmid=17226823}}</ref> In many cases, slave cadavers were used in demonstrations and dissection tables,<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Savitt |first1=Todd |title=The Use of Blacks for Medical Experimentation and Demonstration in the Old South |journal=The Journal of Southern History |date=August 1982 |volume=48 |issue=3 |pages=331–348 |doi=10.2307/2207450 |jstor=2207450|pmid=11645888 }}</ref> oftentimes resulting in their tissues being sold for profit. | |||
| For the reason of slave punishment, decoration, or self-expression, the skin of slaves was in many instances allowed to be made into leather for furniture, accessories, and clothing,<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Berry |first1=Daina |title=Nat Turner's Skull and My Student's Purse of Skin |journal=The New York Times |date=October 18, 2016 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/18/opinion/nat-turners-skull-and-my-students-purse-of-skin.html |access-date=16 October 2022}}</ref> a common instance of which being that of wealthy clientele sending cadaver skin to tanners and shoemakers under the guise of animal leather.<ref>{{cite news |title=Leather Made From Human Skin |url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/9144128# |access-date=16 October 2022 |agency=The Mercury |publisher=Philadelphia News |date=March 17, 1888}}</ref> Slave hair could be shaved and used for stuffing in pillows and furniture. In some instances, the inner body tissue of slaves (fat, bones, etc.) could be made into soap, medicinal grease, trophies, and other commodities.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Plaisance |first1=Patrick |title=A Museum for Nat Turner |url=https://www.dailypress.com/news/dp-xpm-19980902-1998-09-02-9809020063-story.html |access-date=16 October 2022 |publisher=Daily Press |date=September 2, 1998}}</ref> | |||
| ===Sexual abuse, reproductive exploitation, and breeding farms=== | |||
| {{Main|Slave breeding in the United States|Children of the plantation|Shadow family|Enslaved women's resistance in the United States and Caribbean}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Because of the power relationships at work, ] were at high risk for rape and sexual abuse.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9d9FC-gcWaAC&pg=PA38 |title=Who Is Black?: One Nation's Definition |last=Davis |first=Floyd James |year=2001 |publisher=Penn State Press |page=38 |isbn=978-0-271-04463-7}}</ref><ref name="Moon, p. 234">Moon, p. 234.</ref> Their children were repeatedly taken away from them and sold as chattel; usually they never saw each other again. Many slaves fought back against sexual attacks, and some died resisting. Others carried psychological and physical scars from the attacks.<ref>Marable, p. 74.</ref> Sexual abuse of slaves was partially rooted in a patriarchal Southern culture that treated black women as property or chattel.<ref name="Moon, p. 234" /> Southern culture strongly policed against sexual relations between white women and black men on the purported grounds of racial purity but, by the late 18th century, the many ] slaves and slave children showed that white men had often taken advantage of slave women.<ref name="Moon, p. 234" /> Wealthy planter widowers, notably such as ] and his son-in-law ], took slave women as ]; each had six children with his partner: ] and her daughter ] (the half-sister of Jefferson's late wife), respectively. Both ] and ], wives of planters, wrote about this issue in the antebellum South in the decades before the Civil War. Sometimes planters used mixed-race slaves as house servants or favored artisans because they were their children or other relatives.<ref>{{cite web| title = Memoirs of Madison Hemings | publisher = PBS Frontline |url = https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/jefferson/cron/1873march.html}}</ref> While publicly opposed to race mixing, in his '']'' published in 1785, Jefferson wrote: "The improvement of the blacks in body and mind, in the first instance of their mixture with the whites, has been observed by every one, and proves that their inferiority is not the effect merely of their condition of life".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Higginbotham |first1=A. Leon |title=In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process. The Colonial Period |date=1980 |page=10}}</ref> Historians estimate that 58% of enslaved women in the U.S. aged 15–30 years were sexually assaulted by their slave owners and other white men.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Racism, African American Women, and Their Sexual and Reproductive Health: A Review of Historical and Contemporary Evidence and Implications for Health Equity |date=2018 |publisher=National Institutes of Health (NIH)|pmc=6167003 |last1=Prather |first1=C. |last2=Fuller |first2=T. R. |last3=Jeffries Wl |first3=I. V. |last4=Marshall |first4=K. J. |last5=Howell |first5=A. V. |last6=Belyue-Umole |first6=A. |last7=King |first7=W. |journal=Health Equity |volume=2 |issue=1 |pages=249–259 |doi=10.1089/heq.2017.0045 |pmid=30283874 }}</ref> As a result of centuries of slavery and such relationships, DNA studies have shown that the vast majority of African Americans also have historic European ancestry, generally through paternal lines.<ref name="Bryc 2015">{{cite journal|first1=Katarzyna |last1=Bryc |first2= Eric Y. |last2=Durand |first3=J. Michael |last3=Macpherson |first4=David |last4=Reich |first5=Joanna L. |last5=Mountain|title=The Genetic Ancestry of African Americans, Latinos, and European Americans across the United States|journal=The American Journal of Human Genetics|date=January 8, 2015|volume=96|issue=1|pages=37–53|doi=10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.11.010|pmid=25529636 |doi-access=free|pmc=4289685}}</ref><ref name="Zakharia2009">{{cite journal|first1=Fouad |last1=Zakharia |first2=Analabha |last2=Basu |first3=Devin |last3=Absher |first4=Themistocles L |last4=Assimes |first5=Alan S |last5=Go |first6=Mark A |last6=Hlatky |first7=Carlos |last7=Iribarren |first8=Joshua W |last8=Knowles |first9=Jun |last9=Li |first10=Balasubramanian |last10=Narasimhan |first11=Steven |last11=Sidney |first12=Audrey |last12=Southwick |first13=Richard M |last13=Myers |first14=Thomas |last14=Quertermous |first15=Neil |last15=Risch |first16=Hua |last16=Tang|title=Characterizing the admixed African ancestry of African Americans|journal=Genome Biology|date=2009|volume=10|issue=R141|page=R141 |doi=10.1186/gb-2009-10-12-r141|pmid=20025784 |pmc=2812948 |doi-access=free }}</ref> The average Black American genome is roughly 20-25% European,<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-09-30 |title=Learn About Hidden African DNA & Ancestry |url=https://blog.23andme.com/articles/hidden-african-ancestry |access-date=2024-12-08 |website=23andMe Blog |language=en}}</ref> and it is estimated that as much as one third of their Y chromosomes are of European origin.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Zakharia |first1=Fouad |last2=Basu |first2=Analabha |last3=Absher |first3=Devin |last4=Assimes |first4=Themistocles L. |last5=Go |first5=Alan S. |last6=Hlatky |first6=Mark A. |last7=Iribarren |first7=Carlos |last8=Knowles |first8=Joshua W. |last9=Li |first9=Jun |last10=Narasimhan |first10=Balasubramanian |last11=Sidney |first11=Steven |last12=Southwick |first12=Audrey |last13=Myers |first13=Richard M. |last14=Quertermous |first14=Thomas |last15=Risch |first15=Neil |date=2009-12-22 |title=Characterizing the admixed African ancestry of African Americans |journal=Genome Biology |volume=10 |issue=12 |pages=R141 |doi=10.1186/gb-2009-10-12-r141 |doi-access=free |issn=1474-760X |pmc=2812948 |pmid=20025784}}</ref> | |||
| Portrayals of black men as hypersexual and savage, along with ideals of protecting white women, were predominant during this time<ref>{{Cite book |title=American sexual histories |date=2012 |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=978-1-4443-3929-1 |editor-last=Reis |editor-first=Elizabeth |edition=2. |series=Blackwell readers in American social and cultural history |location=Malden, Mass.}}</ref> and masked the experiences of sexual violence faced by black male slaves, especially by white women. Subject not only to rape and sexual exploitation, slaves faced sexual violence in many forms. A black man could be forced by his slaveowner to rape another slave or even a free black woman.<ref name=":05">{{Cite book |last1=Berry |first1=Daina Ramey |title=Sexuality and slavery: reclaiming intimate histories in the Americas |last2=Harris |first2=Leslie Maria |date=2018 |publisher=University of Georgia Press |isbn=978-0-8203-5403-3 |series=Gender and slavery |location=Athens, Ga}}</ref> Forced pairings with other slaves, including forced breeding, which neither slave might desire, were common.<ref name=":05" /> Despite explicit bans on homosexuality and sodomy, it was not uncommon for male slaves and children to be sexually harassed and assaulted by their masters in secret.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Woodard |first1=Vincent |title=The delectable Negro: human consumption and homoeroticism within U.S. slave culture |last2=Joyce |first2=Justin A. |last3=McBride |first3=Dwight A. |date=2014 |publisher=New York University Press |isbn=978-0-8147-9461-6 |series=Sexual cultures |location=New York}}</ref> Through sexual and reproductive abuse slaveowners could further enforce their control over their slaves. | |||
| The ] into the United States after 1808 limited the supply of slaves in the United States. This came at a time when the invention of the cotton gin enabled the expansion of cultivation in the uplands of short-staple cotton, leading to clearing lands cultivating cotton through large areas of the Deep South, especially the ]. The demand for labor in the area increased sharply and led to an expansion of the internal slave market. At the same time, the ] had an excess number of slaves because of a shift to mixed-crops agriculture, which was less labor-intensive than tobacco. To add to the supply of slaves, slaveholders looked at the fertility of slave women as part of their productivity, and intermittently forced the women to have large numbers of children. During this time period, the terms "breeders", "breeding slaves", "child bearing women", "breeding period", and "too old to breed" became familiar.<ref>Smith, Julia Floyd (1991) ''Slavery and Rice Culture in Low Country Georgia, 1750-1860'' University of Tennessee Press, </ref> | |||
| ] (] 1976.25)]] | |||
| As it became popular on many plantations to breed slaves for strength, fertility, or extra labor, there grew many documented instances of "]" in the United States. Slaves were forced to conceive and birth as many new slaves as possible. The largest farms were located in Virginia and Maryland.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Sublette |first1=Ned |last2=Sublette |first2=Constance |title=The American Slave Coast: A History of the Slave-Breeding Industry |date=October 1, 2015 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iwCKCgAAQBAJ |publisher=Chicago Review Press |isbn=978-1-61373-893-1 |access-date=October 15, 2022}}</ref> Because the industry of slave breeding came from a desire for larger than natural population growth of slaves, slaveowners often turned towards systematic practices for creating more slaves. Female slaves "were subjected to repeated rape or forced sex and became pregnant again and again",<ref>{{cite web |title=Childbirth and Midwifery {{!}} Encyclopedia.com |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/humanities/applied-and-social-sciences-magazines/childbirth-and-midwifery |access-date=2023-05-22 |website=www.encyclopedia.com}}</ref> even by ]. In horrific accounts of former slaves, some stated that hoods or bags were placed over their heads to prevent them from knowing who they were forced to have sex with. Journalist William Spivey wrote, "It could be someone they know, perhaps a niece, aunt, sister, or their own mother. The breeders only wanted a child that could be sold."<ref>{{cite web |last=Spivey |first=William |date=2023-01-23 |title=America's Breeding Farms: What History Books Never Told You |url=https://williamspivey.medium.com/americas-breeding-farms-what-history-books-never-told-you-6704e8b152a4 |access-date=2023-05-22 |website=Medium |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In the United States in the early 19th century, owners of female slaves could freely and legally ]s. This follows free use of female slaves on slaving vessels by the crews.<ref name=Kingsley>{{cite book|title=Zephaniah Kingsley Jr. and the Atlantic World. Slave Trader, Plantation Owner, Emancipator|first=Daniel L.|last=Schafer|year=2013|publisher=University Press of Florida|isbn=978-0-8130-4462-0}}</ref>{{rp|83}} | |||
| <blockquote>The slaveholder has it in his power, to violate the chastity of his slaves. And not a few are beastly enough to exercise such power. Hence it happens that, in some families, it is difficult to distinguish the free children from the slaves. It is sometimes the case, that the largest part of the master's own children are born, not of his wife, but of the wives and daughters of his slaves, whom he has basely prostituted as well as enslaved.<ref name=Rankin>{{cite book|title=Letters on American slavery, addressed to Mr. Thomas Rankin, merchant at Middlebrook, Augusta County, Va|last=Rankin|first=John|author-link=John Rankin (abolitionist)|location=Boston|publisher=] and ]|url=https://archive.org/details/lettersonamerica00rank_0/page/28|date=1833}}</ref>{{rp|38}}</blockquote> | |||
| "This vice, this bane of society, has already become so common, that it is scarcely esteemed a disgrace."<ref>{{cite book|title=The Horrors of Slavery|page=44|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts|year=1817|author-link=John Kenrick, 1755–1833|first=John|last=Kenrick|url=http://ebooks.library.cornell.edu/cgi/t/text/pageviewer-idx?c=mayantislavery;cc=mayantislavery;q1=American;rgn=full%20text;idno=19869004;didno=19869004;view=image;seq=1;node=19869004%3A1}}</ref> | |||
| ], a 70-year-old physician,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Commerce |first=D'Iberville/St Martin Chamber of |title=D'Iberville/St. Martin Chamber of Commerce |url=https://dsmchamber.com/diberville-time-line |access-date=2024-06-21 |website=D'Iberville/St. Martin Chamber of Commerce |language=en-US}}</ref> placed an unusually long and detailed ] in two Alabama newspapers in hopes of recovering a 20-year-old enslaved woman, whom he had purchased four years earlier, and her four-year-old daughter, who sometimes called herself Lolo {{small|("$100 Reward" ''Cahawba Democrat'', ], June 16, 1838)}}]] | |||
| "Fancy" was a code word that indicated that the girl or young woman was suitable for or trained for sexual use.<ref name=Manganelli />{{rp|56}} In some cases, children were also abused in this manner. The sale of a 13-year-old "nearly a fancy" is documented.<ref name="Johnson">{{cite journal |last=Johnson |first=Walter |title=The Slave Trader, the White Slave, and the Politics of Racial Determination in the 1850s |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/2567914 |journal=] |date=2000 |volume=87 |access-date=May 25, 2018 |number=1|pages=13–38 |doi=10.2307/2567914 |jstor=2567914 }}</ref> ], bought his wife when she was 13.<ref name=Allman />{{rp|191}} | |||
| Furthermore, enslaved women who were old enough to bear children were encouraged to procreate, which raised their value as slaves, since their children would eventually provide labor or be sold, enriching the owners. Enslaved women were sometimes medically treated to enable or encourage their fertility.<ref>Schwartz, Marie Jenkins (2004). ''Birthing a Slave: Motherhood and Medicine in the Antebellum South''. Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 10–11.</ref> The variations in skin color found in the United States make it obvious how often black women were impregnated by whites.<ref>{{cite book|title=Blood at the Root. A Racial Cleansing in America|first=Patrick|last=Phillips|pages=78–79|year=2016|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-393-29301-2}}</ref> For example, in the 1850 Census, 75.4% of "free negros" in Florida were described as ]s, of mixed race.<ref>{{cite book|title=Balancing Evils Judiciously: The Proslavery Writings of Zephaniah Kingsley|year=2000|first1=Zephaniah Jr.|last1=Kingsley|first2=Daniel W.|last2=Stowell|contribution=Introduction|page=2|publisher=University Press of Florida|isbn=978-0-8130-1733-4}}{{Dead link|date=February 2019|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}}</ref> Nevertheless, it is only very recently, with ] studies, that any sort of reliable number can be provided, and the research has only begun. Light-skinned girls, who contrasted with the darker field workers, were preferred.<ref name=Johnson /><ref>{{citation|first=Monique|last=Guillory|title=Some Enchanted Evening on the Auction Block: The Cultural Legacy of the New Orleans Quadroon Balls|publisher=PhD dissertation, New York University|year=1999}}</ref> | |||
| As ] was quoted in '']'': "You Want a Confederate Monument? My Body Is a Confederate Monument." "I have rape-colored skin", she added.<ref>{{cite news|title=You Want a Confederate Monument? My Body Is a Confederate Monument. The black people I come from were owned and raped by the white people I come from. Who dares to tell me to celebrate them?|first=Caroline Randall|last=Williams|author-link=Caroline Randall Williams|newspaper=]|date=June 26, 2020|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/26/opinion/confederate-monuments-racism.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200626112011/https://www.nytimes.com/2020/06/26/opinion/confederate-monuments-racism.html|archive-date=2020-06-26|url-access=subscription|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The sexual use of black slaves by either slave owners or by those who could purchase the temporary services of a slave took various forms. A slaveowner, or his teenage son, could go to the ] and do what he wanted, with minimal privacy if any. It was common for a "house" female (housekeeper, maid, cook, laundress, or ]) to be raped by one or more members of the household. ] throughout the slave states were largely staffed by female slaves providing sexual services, to their owners' profit. There were a small number of free black females engaged in prostitution, or concubinage, especially in New Orleans.<ref name=Manganelli />{{rp|41}} | |||
| Slave owners who engaged in sexual activity with female slaves "were often the elite of the community. They had little need to worry about public scorn." These relationships "appear to have been tolerated and in some cases even quietly accepted". "Southern women{{spaces}}... do not trouble themselves about it".<ref>{{cite book|pages=87–88|first=Marvin|last=Dunn|title=A History of Florida through Black Eyes|year=2016|publisher=CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform|isbn=978-1-5193-7267-3}}</ref> Franklin and Armfield, who were definitely the elite of the community, joked frequently in their letters about the black women and girls that they were raping. It never occurred to them that there was anything wrong in what they were doing.<ref name=Wapo>{{cite news|title=They were once America's cruelest, richest slave traders. Why does no one know their names?|first=Hannah|last=Natanson|date=September 14, 2019|newspaper=]|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/history/2019/09/14/they-were-once-americas-cruelest-richest-slave-traders-why-does-no-one-know-their-names/}}</ref> | |||
| Light-skinned young girls were sold openly for sexual use; their price was much higher than that of a field hand.<ref name=Manganelli>{{cite book|title=Transatlantic spectacles of race: the tragic mulatta and the tragic muse|year=2012|publisher=Rutgers University Press|first=Kimberly Snyder|last=Manganelli|isbn=978-0-8135-4987-3}}</ref>{{rp|38, 55}}<ref>{{cite web|title=Clary and the Fancy Girl Trade, 1806|first=Nancy|last=Bercaw|publisher=]|url=https://nmaahc.si.edu/object/nmaahc_2010.1.117ab|access-date=May 15, 2018}}</ref> Special markets for the fancy girl trade existed in New Orleans<ref name=Manganelli />{{rp|55}} and ].<ref>{{cite news|title=Without the Civil War, who knows when Lexington's slave trade might have ended?|first=Tom|last=Eblen|newspaper=]|date=February 1, 2012|url=http://www.kentucky.com/news/local/news-columns-blogs/tom-eblen/article44152383.html|access-date=May 15, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|page=|title=The town that started the Civil War|last=Brandt|first=Nat|year=1990|url=https://archive.org/details/townthatstartedt00bran|url-access=registration|isbn=978-0-8156-0243-9|location=]|publisher=]}}</ref> Historian Philip Shaw describes an occasion when ] and Allen Gentry witnessed such sales in New Orleans in 1828: | |||
| {{Blockquote|Gentry vividly remembered a day in New Orleans when he and the nineteen-year-old Lincoln came upon a slave market. Pausing to watch, Gentry recalled looking down at Lincoln's hands and seeing that he "doubled his fists tightly; his knuckles went white". Men wearing black coats and white hats buy field hands, "black and ugly", for $500 to 800. And then the real horror begins: "When the sale of "fancy girls" began, Lincoln, "unable to stand it any longer", muttered to Gentry "Allen that's a disgrace. If I ever get a lick at that thing I'll hit it hard."<ref>{{cite journal|title=Lincoln and Negro Slavery: I Haven't Got Time for the Pain|first=Phillip Shaw|last=Paludan|journal=Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association|volume=27|issue=2|date=Summer 2006|pages=1–23|hdl=2027/spo.2629860.0027.203}}</ref>}} | |||
| Those girls who were "considered educated and refined, were purchased by the wealthiest clients, usually plantation owners, to become personal sexual companions". "There was a great demand in New Orleans for 'fancy girls'."<ref>{{cite book |author1-link=Eugene Genovese|first=Eugene D.|last=Genovese|title=Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made|year=1974|publisher=]|page=416}}</ref> | |||
| The issue that did come up frequently was the threat of sexual intercourse between black males and white females. Just as the black women were perceived as having "a trace of Africa, that supposedly incited passion and sexual wantonness",<ref name=Manganelli />{{rp|39}} the men were perceived as savages, unable to control their lust, given an opportunity.<ref>{{cite book|contribution=Black Violence in the New South. Patterns of Conflict in Late-Nineteenth-Century Tampa|first=Jeffrey S.|last=Adler|pages=207–239 |title=The African Ameritage Heritage of Florida|editor1-first=David R.|editor1-last=Colburn|editor2-first=Jane L.|editor2-last=Landers|publisher=University Press of Florida|isbn=978-0-8130-1332-9|year=1995}}</ref> | |||
| Another approach to the question was offered by ] and Florida planter ] He advocated, and personally practiced, deliberate racial mixing through marriage, as part of his proposed solution to the slavery issue: ], called "]" at the time. In ], he stated that mixed-race people were healthier and often more beautiful, that interracial sex was hygienic, and slavery made it convenient.<ref name=Allman>{{cite book|title=Finding Florida. The True History of the Sunshine State|first=T.D.|last=Allman|publisher=Atlantic Monthly Press|year=2013|isbn=978-0-8021-2076-2}}</ref>{{rp|190}} Because of these views, tolerated in ], he found it impossible to remain long in ], and moved with his slaves and multiple wives to a plantation, ], in ] (now in the ]). There were many others who less flagrantly practiced interracial, common-law marriages with slaves (see '']''). | |||
| ===Slave codes=== | |||
| {{Main|Slave codes}} | |||
| {{Further|Slave catcher|Slave patrol|Slave pass}} | |||
| {{See also|South Carolina slave codes|New York slave codes}} | |||
| ]'s hand as branded by the ] for having helped 7 men to obtain 'Life Liberty, and Happiness.' SS Slave Saviour Northern Dist. SS Slave Stealer Southern Dist.'' (image by ], ] 1.373)]] | |||
| ] | |||
| To help regulate the relationship between slave and owner, including legal support for keeping the slave as property, states established ], most based on laws existing since the colonial era. The code for the District of Columbia defined a slave as "a human being, who is by law deprived of his or her liberty for life, and is the property of another".<ref>{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} The Library of Congress. Retrieved July 19, 2008.</ref> | |||
| While each state had its own slave code, many concepts were shared throughout the slave states.<ref>{{cite book |title=Nat Turner |url=https://archive.org/details/natturner0000fone |url-access=registration |first=Eric |last=Foner |year=1971 |publisher=Englewood Cliffs, N.J., Prentice-Hall |author-link=Eric Foner}}</ref> According to the slave codes, some of which were passed in reaction to slave rebellions, teaching a slave to read or write was illegal. This prohibition was unique to American slavery, believed to reduce slaves forming aspirations that could lead to escape or rebellion.<ref>Rodriguez, pp. 616–617.</ref> Informal education occurred when white children taught slave companions what they were learning; in other cases, adult slaves learned from free artisan workers, especially if located in cities, where there was more freedom of movement. | |||
| In Alabama, slaves were not allowed to leave their master's premises without written consent or passes. This was a common requirement in other states as well, and locally run patrols (known to slaves as ''pater rollers'') often checked the passes of slaves who appeared to be away from their plantations. In Alabama slaves were prohibited from trading goods among themselves. In Virginia, a slave was not permitted to drink in public within one mile of his master or during public gatherings. Slaves were not permitted to carry firearms in any of the slave states. | |||
| Slaves were generally prohibited by law from associating in groups, with the exception of worship services (a reason why the ] is such a notable institution in black communities today). Following ] in 1831, which raised white fears throughout the South, some states also prohibited or restricted religious gatherings of slaves, or required that they be officiated by white men. Planters feared that group meetings would facilitate communication among slaves that could lead to rebellion.<ref>{{cite book |first=Thomas D. |last=Morris |year=1999 |title=Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |page=347 |isbn=978-0-8078-6430-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VmPWCKh0hZAC&pg=PA347 }}</ref> Slaves held private, secret "brush meetings" in the woods. | |||
| In Ohio, an emancipated slave was prohibited from returning to the state in which he or she had been enslaved. Other Northern states discouraged the settling of free blacks within their boundaries. Fearing the influence of free blacks, Virginia and other Southern states passed laws to require blacks who had been freed to leave the state within a year (or sometimes less time) unless granted a stay by an act of the legislature. | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{Further|Religion of black Americans|Black Catholicism|Marriage of enslaved people (United States)}} | |||
| {{See also|Invisible churches|Hush harbor|Praise house}} | |||
| ]'s 1863 oil painting painting ] (] 1979.5.13)]] | |||
| Africans brought their religions with them from Africa, including Islam,<ref name="Gomez">{{Cite journal |last=Gomez |first=Michael A. |date=1994 |title=Muslims in Early America |journal=The Journal of Southern History |volume=60 |issue=4 |pages=671–710 |doi=10.2307/2211064 |jstor=2211064 |issn=0022-4642 }}</ref> Catholicism,<ref>{{cite web |last=Costello|first=Damian|date=2020-09-01|title=Pray with Our Lady of Stono to heal the wounds of slavery|url=https://uscatholic.org/articles/202009/pray-with-our-lady-of-stono-to-heal-the-wounds-of-slavery/|access-date=2020-10-12|website=U.S. Catholic magazine – Faith in Real Life|language=en-US}}</ref> and traditional religions. | |||
| Prior to the American Revolution, masters and revivalists spread Christianity to slave communities, including Catholicism in ] and ], and in French and Spanish ], and Protestantism in English colonies, supported by the ]. In the ] of the mid-18th century, ] and ] from New England preached a message against slavery, encouraged masters to free their slaves, converted both slaves and free blacks, and gave them active roles in new congregations.<ref>{{cite book |first=J. William |last=Frost |chapter=Christianity and Culture in America |title=Christianity: A Social and Cultural History |editor-first=Howard Clark |editor-last=Kee |location=Upper Saddle River, NJ |publisher=Prentice Hall |year=1998 |isbn=978-0-13-578071-8 |page=446 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8YrYAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA446 }}</ref> The first independent black congregations were started in the South before the Revolution, in South Carolina and Georgia. Believing that, "slavery was contrary to the ethics of Jesus", Christian congregations and church clergy, especially in the North, played a role in the ], especially ], ]s and ]s.<ref name="Smedley2005">{{cite book |last1=Smedley |first1=R. C. |title=History of the Underground Railroad: In Chester and the Neighboring Counties of Pennsylvania |date=2005 |publisher=Stackpole Books |isbn=978-0-8117-3189-8 |page=xvi |language=English}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=History of Salem Township, Washtenaw County, Michigan |date=1976 |publisher=Salem Area Historical Society |page=56 |language=English}}</ref> | |||
| Over the decades and with the growth of slavery throughout the South, some Baptist and Methodist ministers gradually changed their messages to accommodate the institution. After 1830, ] argued for the compatibility of Christianity and slavery, with a multitude of both ] and ] citations.<ref name="J. William Frost 1998">{{cite book |first=J. William |last=Frost |chapter=Christianity and Culture in America |title=Christianity: A Social and Cultural History |editor-first=Howard Clark |editor-last=Kee |location=Upper Saddle River, NJ |publisher=Prentice Hall |year=1998 |isbn=978-0-13-578071-8 |page=447 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8YrYAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA447 }}</ref> They promoted Christianity as encouraging better treatment of slaves and argued for a paternalistic approach. In the 1840s and 1850s, the issue of accepting slavery split the nation's largest religious denominations (the ], ] and ] churches) into separate Northern and Southern organizations (see ], ], and ]).<ref>{{cite book|last=Ahlstrom|first=Sydney E.|title=A Religious History of the American People|publisher=Yale University Press|year=1972|location=New Haven, Connecticut|isbn=978-0-300-01762-5|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=5kFF6a1viGcC}} |pages=648–649}}</ref> Schisms occurred, such as that between the ] and the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Abolition and the Splintering of the Church |url=https://www.pbs.org/thisfarbyfaith/journey_2/p_5.html |publisher=] |access-date=11 May 2021 |language=English |date=2003}}</ref> | |||
| Southern slaves generally attended their masters' white churches, where they often outnumbered the white congregants. They were usually permitted to sit only in the back or in the balcony. They listened to white preachers, who emphasized the obligation of slaves to keep in their place, and acknowledged the slave's identity as both person and property.<ref name="J. William Frost 1998" /> Preachers taught the master's responsibility and the concept of appropriate paternal treatment, using Christianity to improve conditions for slaves, and to treat them "justly and fairly" (Col. 4:1). This included masters having self-control, not disciplining under anger, not threatening, and ultimately fostering Christianity among their slaves by example.<ref name="J. William Frost 1998" /> | |||
| Slaves also created their own religious observances, meeting alone without the supervision of their white masters or ministers. The larger plantations with groups of slaves numbering 20, or more, tended to be centers of nighttime meetings of one or several plantation slave populations.<ref name="J. William Frost 1998" /> These congregations revolved around a singular preacher, often illiterate with limited knowledge of theology, who was marked by his personal piety and ability to foster a spiritual environment. African Americans developed a theology related to Biblical stories having the most meaning for them, including the hope for deliverance from slavery by their own ]. One lasting influence of these secret congregations is the ].<ref>Frost (1998), ''Christianity'', 448.</ref> | |||
| ===Mandatory illiteracy=== | |||
| {{Main|Anti-literacy laws in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|Education during the slave period in the United States|Education of freed people during the Civil War}} | |||
| In a feature unique to American slavery, legislatures across the South enacted new laws to curtail the already limited rights of African Americans. For example, Virginia prohibited blacks, free or slave, from practicing preaching, prohibited them from owning firearms, and forbade anyone to teach slaves or free blacks how to read.<ref name="Foner 2009 406–407" /> It specified heavy penalties for both student and teacher if slaves were taught, including whippings or jail.<ref name="Basu">{{Cite book|last=Basu|first=B.D.|title=History of Education in India under the rule of the East India Company|editor=Chatterjee, R.|url=https://archive.org/details/historyofeducati00basurich|access-date=March 9, 2009|place=Calcutta|publisher=Modern Review Office|pages=–4}}</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>very assemblage of negroes for the purpose of instruction in reading or writing, or in the night time for any purpose, shall be an unlawful assembly. Any justice may issue his warrant to any office or other person, requiring him to enter any place where such assemblage may be, and seize any negro therein; and he, or any other justice, may order such negro to be punished with stripes.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Code of Virginia|pages=747–748|year=1849|place=Richmond|publisher=William F. Ritchie}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Slave owners saw ] as a threat to the institution of slavery and their financial investment in it; as a North Carolina statute passed in 1830-1831 stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and rebellion."<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.historyisaweapon.com/defcon1/slaveprohibit.html|title=Slaves Are Prohibited to Read and Write by Law | North Carolina Law (1830-31)|website=www.historyisaweapon.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=An Inquiry Into the Character and Tendency of the American Colonization, and American Anti-slavery Societies|author-link=William Jay (jurist)|first=William|last=Jay|year=1835|edition=2nd|location=New York|publisher=]|url=https://archive.org/details/aninquiryintoch05jaygoog/page/n6/mode/2up|page=136}}</ref> Literacy enabled the enslaved to read the writings of ]s, which discussed the abolition of slavery and described the ] of 1791–1804 and the ] in 1833. It also allowed slaves to learn that thousands of enslaved individuals had escaped, often with the assistance of the ]. Literacy also was believed to make the enslaved unhappy at best, insolent and sullen at worst. As put by prominent Washington lawyer ] in 1822: | |||
| {{Blockquote|The more you improve the condition of these people, the more you cultivate their minds, the more miserable you make them, in their present state. You give them a higher relish for those privilegies which they can never attain, and turn what we intend for a blessing into a curse. No, if they must remain in their present situation, keep them in the lowest state of degradation and ignorance. The nearer you bring them to the condition of brutes, the better chance do you give them of possessing their apathy.<ref>{{cite book|page=102|url=https://archive.org/details/americanslavetr00torrgoog/page/n118/mode/2up|title=American slave trade; or, An Account of the Manner in which the Slave Dealers take Free People from some of the United States of America, and carry them away, and sell them as Slaves in other of the States; and of the horrible Cruelties practiced in the carrying on of this infamous Traffic: with Reflections on the Project for forming a Colony of American Blacks in Africa, and certain Documents respecting that Project|last=Torrey|first=Jesse|author-link=Jesse Torrey|date=1822|location=London|publisher= M Cobbett]]}}</ref>}} | |||
| Unlike in the South, slave owners in Utah were required to send their slaves to school.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.blackpast.org/primarywest/utah-slave-code-1852|title=The Utah Territory Slave Code (1852) – The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed|website=www.blackpast.org|access-date=August 28, 2017|date=2007-06-27}}</ref> Black slaves did not have to spend as much time in school as Indian slaves.<ref>{{cite book|title=Acts, Resolutions, and Memorials Passed at the ... Annual, and Special Sessions, of the Legislative Assembly of the Territory of Utah|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uNFGAQAAMAAJ|publisher=Brigham H. Young, Printers|year=1866|pages=87–88}}</ref> | |||
| ===Freedom suits and Dred Scott=== | |||
| {{Main|Dred Scott v. Sandford|Freedom suits}} | |||
| ] from '']'', 1849<ref>{{cite web |title=Image 74 of Page view |url=https://www.loc.gov/resource/rbc0001.2019gen05639/?sp=74 |access-date=2023-08-28 |website=Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA}}</ref>]] | |||
| With the development of slave and free states after the American Revolution, and far-flung commercial and military activities, new situations arose in which slaves might be taken by masters into free states. Most free states not only prohibited slavery, but ruled that slaves brought and kept there illegally could be freed. Such cases were sometimes known as transit cases.<ref>Paul Finkelman, '' Dred Scott v. Sandford: A Brief History with Documents'' (Bedford Books, 1997).</ref> ] and his wife Harriet Scott each ] in ] after the death of their master, based on their having been held in a free territory (the northern part of the ] from which slavery was excluded under the terms of the ]). (Later the two cases were combined under Dred Scott's name.) Scott filed suit for freedom in 1846 and went through two state trials, the first denying and the second granting freedom to the couple (and, by extension, their two daughters, who had also been held illegally in free territories). For 28 years, Missouri state precedent had generally respected laws of neighboring free states and territories, ruling for freedom in such transit cases where slaves had been held illegally in free territory. But in the Dred Scott case, the ] ruled against the slaves.<ref>{{cite book |first=Don E. |last=Fehrenbacher |author-link=Don E. Fehrenbacher |title=The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics |location=New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1978 |isbn=978-0-19-502403-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=btkgAQAAIAAJ }}</ref> | |||
| After Scott and his team appealed the case to the ], Chief Justice ], in a sweeping decision, denied Scott his freedom. The 1857 ], decided 7–2, held that a slave did not become free when taken into a free state; Congress could not bar slavery from a territory; and people of African descent imported into the United States and held as slaves, or their descendants, could never be citizens and thus had no status to bring suit in a U.S. court. A state could not bar slaveowners from bringing slaves into that state. Many Republicans, including ], considered the decision unjust and evidence that the ] had seized control of the Supreme Court. Anti-slavery groups were enraged and slave owners encouraged, escalating the tensions that led to civil war.<ref>Fehrenbacher, ''The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics'' (2001).</ref> | |||
| ===1850 to the firing on Fort Sumter=== | |||
| {{Further|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#Compromise of 1850 to the Election of 1860|Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War#Election of 1860 to the Battle of Fort Sumter}} | |||
| {{See also|Bleeding Kansas|1860 United States presidential election}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] of ] seeking to buy slaves to resell in the lucrative the New Orleans market]] | |||
| ]'', oil on paperboard, {{circa|1862}} by Eastman Johnson (] 40.59a-b)]] | |||
| In 1850, Congress passed the ], as part of the ], which required law enforcement and citizens of free states to cooperate in the capture and return of slaves. This met with considerable overt and covert resistance in free states and cities such as Philadelphia, New York, and Boston. Refugees from slavery continued to flee the South across the ] and other parts of the ] dividing North from South, to the North and ] via the ]. Some white Northerners helped hide former slaves from their former owners or helped them reach freedom in Canada.<ref>Larry Gara, '' The Liberty Line: The Legend of the Underground Railroad'' (University Press of Kentucky, 2013).</ref> | |||
| As part of the ], Congress abolished the slave trade (though not the ownership of slaves) in the ]; fearing this would happen, ], regional slave trading center and port, successfully sought ]. After 1854, ] argued that the "]", especially the pro-slavery ], controlled two of the three branches of the Federal government.<ref>Leonard L. Richards, ''The Slave Power: The Free North and Southern Domination, 1780–1860'' (LSU Press, 2000).</ref> | |||
| The abolitionists, realizing that the total elimination of slavery was unrealistic as an immediate goal, worked to prevent the expansion of slavery into the western territories that eventually would become new states. The ], the ], and the ] period dealt with whether new states would be slave or free, or how that was to be decided. Both sides were anxious about effects of these decisions on the balance of power in the ]. | |||
| After the passage of the ] in 1854, border fighting broke out in the ], where the question of whether it would be admitted to the Union as a ] or ] was ]. Migrants from both free and slave states moved into the territory to prepare for the vote on slavery. Abolitionist ], the most famous of the anti-slavery immigrants, was active in the fighting in "Bleeding Kansas", but so too were many white Southerners (many from adjacent Missouri) who opposed abolition. | |||
| Abraham Lincoln's and the Republicans' political platform in 1860 was to stop slavery's expansion. Historian ] says that in his famous "]" speech in 1858, Lincoln said ] can be purified by restricting the further expansion of slavery as the first step to putting it on the road to 'ultimate extinction.' Southerners took Lincoln at his word. When he won the presidency, they left the Union to escape the 'ultimate extinction' of slavery."<ref>{{cite book|first=James M.|last=McPherson|title=Abraham Lincoln and the Second American Revolution|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tYdpAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA134|year=1992|page=134|publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-976270-5}}</ref> | |||
| The divisions became fully exposed with the ]. The electorate split four ways. The ] endorsed slavery, while the ] denounced it. The ] said democracy required the people to decide on slavery locally, state by state and territory by territory. The ] said the survival of the Union was at stake and everything else should be compromised.<ref>David M. Potter, ''The Impending Crisis: America Before the Civil War, 1848–1861'' (Harper & Row, 1976).</ref> | |||
| Lincoln, the Republican, won with a plurality of popular votes and a majority of ]. Lincoln, however, did not appear on the ballots of ten southern slave states. Many slave owners in the South feared that the real intent of the Republicans was the abolition of slavery in states where it already existed, and that the sudden emancipation of four million slaves would be disastrous for the slave owners and for the economy that drew its greatest profits from the labor of people who were not paid. The slave owners feared that ending the balance could lead to the domination of the ] by the northern free states. This led seven southern states to ]. When the ] ], the ] began and four additional slave states seceded. Northern leaders had viewed the slavery interests as a threat politically, but with secession, they viewed the prospect of a new Southern nation, the ], with control over the ] and parts of the ], as politically unacceptable. Most of all, they could not accept this repudiation of ].<ref>Potter, pp. 448–554.</ref> | |||
| ==Civil War and emancipation== | |||
| {{Main|Slavery during the American Civil War}} | |||
| {{Events leading to US Civil War}} | |||
| ]'' graphic, advocating a confederation of slave states, with a quote from ]: "SLAVE STATES, once more let me repeat that the only way of preserving our slave property, or what we prize more than life, our LIBERTY, is by a UNION WITH EACH OTHER." (])]] | |||
| ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] ("Confederate chieftans" engraving by ], 1864) ]] | |||
| ===American Civil War=== | |||
| {{Main|Origins of the American Civil War|American Civil War|Contraband (American Civil War)|Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War}} | |||
| {{See also|Confiscation Acts|Act Prohibiting the Return of Slaves}} | |||
| The ], beginning in 1861, led to the end of chattel slavery in America. Not long after the war broke out, through a legal maneuver by Union General ], a lawyer by profession, slaves who fled to Union lines were considered ]. General Butler ruled that they were not subject to return to Confederate owners as they had been before the war. "Lincoln and his Cabinet discussed the issue on May 30 and decided to support Butler's stance".<ref>Stahr, Walter, ''Samuel Chase: Lincoln's Vital Rival''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2021, p. 342.</ref> Soon word spread, and many slaves sought refuge in Union territory, desiring to be declared "contraband". Many of the "contrabands" joined the ] as workers or troops, forming entire regiments of the ]. Others went to refugee camps such as the ] near ] or fled to northern cities. General Butler's interpretation was reinforced when Congress passed the ], which declared that any property used by the Confederate military, including slaves, could be confiscated by Union forces. | |||
| ] of African-American woman with a flag, "believed to be a washerwoman for Union troops quartered outside Richmond, Virginia" (National Museum of American History 2005.0002)]] | |||
| At the beginning of the war, some Union commanders thought they were supposed to return escaped slaves to their masters. By 1862, when it became clear that this would be a long war, the question of what to do about slavery became more general. The Southern economy and military effort depended on slave labor. It began to seem unreasonable to protect slavery while blockading Southern commerce and destroying Southern production. As Congressman ] of Indiana put it in an 1862 speech in Congress, the slaves "cannot be neutral. As laborers, if not as soldiers, they will be allies of the rebels, or of the Union."<ref>], '']'', p. 495.</ref> Julian and his fellow ] put pressure on Lincoln to rapidly emancipate the slaves, whereas moderate Republicans favored gradual, compensated emancipation and voluntary colonization.<ref>McPherson, ''Battle Cry'', pp. 355, 494–496, quote from ] on 495.</ref> The ], ], and ] opposed emancipation, although the border states and ]s eventually accepted it as part of the ] needed to save the Union. | |||
| ===Emancipation Proclamation=== | |||
| {{Main|Emancipation Proclamation}} | |||
| The Emancipation Proclamation was an ] issued by President ] on January 1, 1863. In a single stroke it changed the legal status of three million slaves in designated areas of the Confederacy from "slave" to "free". It had the practical effect that as soon as a slave escaped the control of his or her owner, by running away or through advances of federal troops, the slave's proclaimed freedom became actual. Plantation owners, realizing that emancipation would destroy their economic system, sometimes moved their slaves as far as possible out of reach of the Union army. By June 1865, the ] controlled all of the Confederacy and had liberated all of the designated slaves.<ref>{{cite book |first=Leon F. |last=Litwack |author-link=Leon Litwack |title=Been in the Storm So Long: The Aftermath of Slavery |location=New York |publisher=Knopf |year=1979 |isbn=978-0-394-50099-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bi2aAAAAIAAJ }}</ref> | |||
| In 1861, Lincoln expressed the fear that premature attempts at emancipation would mean the loss of the border states. He believed that "to lose Kentucky is nearly the same as to lose the whole game."<ref>Lincoln's letter to O. H. Browning, September 22, 1861.</ref> At first, Lincoln reversed attempts at emancipation by Secretary of War ] and Generals ] (in Missouri) and ] (in South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) to keep the loyalty of the border states and the War Democrats. | |||
| ] (unidentified ] "F", '']'', March 18, 1865)]] | |||
| On July 22, 1862, Lincoln told his cabinet of his plan to issue a preliminary Emancipation Proclamation. Secretary of State ] advised Lincoln to wait for a victory before issuing the proclamation, as to do otherwise would seem like "our last shriek on the retreat".<ref>], ''Abraham Lincoln: The Man Behind the Myths'', page 106.</ref> On September 17, 1862, the ] provided this opportunity, and on September 22, 1862, Lincoln issued his preliminary ], which provided that enslaved people in the states in rebellion against the United States on January 1, 1863, "shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free".<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.archives.gov/exhibits/american_originals_iv/sections/transcript_preliminary_emancipation.html|title=The Preliminary Emancipation Proclamation, 1862|website=www.archives.gov}}</ref> On September 24 and 25, the ] added support for the proclamation.<ref>''Images of America: Altoona'', by Sr. Anne Francis Pulling, 2001, 10.</ref> Lincoln issued his final Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863. In his letter to Albert G. Hodges, Lincoln explained his belief that | |||
| {{Blockquote|If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong{{spaces}}... And yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act officially upon this judgment and feeling{{spaces}}... I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me.<ref>{{Cite book|url=http://name.umdl.umich.edu/lincoln7|title=Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln. Volume 7 .|first=Abraham|last=Lincoln|date=June 15, 1953}}</ref>}} | |||
| Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation declared freedom for slaves in the Confederate states and authorized the enlistment of African Americans in the Union Army. The Emancipation Proclamation did not free slaves in the ], which were the slaveholding states that remained in the Union. As a practical matter, the proclamation freed only those slaves who escaped to Union lines. But the proclamation made the abolition of slavery an official war goal and was implemented as the Union took territory from the Confederacy. According to the ], this policy would free nearly four million slaves, or over 12 percent of the total ]. | |||
| Because the Emancipation Proclamation was issued under the president's war powers, it might not have continued in force after the war ended. Therefore, Lincoln played a leading role in getting the constitutionally required two-thirds majority of both houses of Congress to vote for the ],<ref name="Who Freed">James McPherson, "Drawn With the Sword", from the article "Who Freed the Slaves?"</ref> which made emancipation universal and permanent, "except as a punishment for crime". | |||
| ]s of a formerly enslaved family, photographed by ] on J. J. Smith's confiscated plantation at ] (now ]) during the ], 1862]] | |||
| Enslaved African Americans had not waited for Lincoln before escaping and seeking freedom behind Union lines. From the early years of the war, hundreds of thousands of African Americans escaped to Union lines, especially in Union-controlled areas such as ] and the ] region in 1862 Virginia, Tennessee from 1862 on, and the line of Sherman's march. So many African Americans fled to Union lines that commanders created camps and schools for them, where both adults and children learned to read and write. The ] entered the war effort by sending teachers south to such contraband camps, for instance, establishing schools in Norfolk and on nearby plantations. | |||
| In addition, nearly 200,000 African-American men served with distinction in the Union forces as soldiers and sailors; most were escaped slaves. The Confederacy was outraged by armed black soldiers and refused to treat them as ]. They murdered many, as at the ], and re-enslaved others.<ref>{{cite book|last=Doyle |first=Robert C. C.|title=The Enemy in Our Hands: America's Treatment of Prisoners of War from the Revolution to the War on Terror|url=https://archive.org/details/enemyinourhandsa0000doyl |url-access=registration |year= 2010|publisher=University Press of Kentucky|page=|isbn=978-0-8131-3961-6}}</ref> | |||
| On February 24, 1863, the ] abolished slavery in the newly formed ]. ] and all of the border states (except Kentucky and Delaware) abolished slavery by early 1865. Thousands of slaves were freed by the operation of the Emancipation Proclamation as Union armies marched across the South. Emancipation came to the remaining Southern slaves after the surrender of all the Confederate troops in spring 1865. | |||
| In spite of the South's shortage of manpower, until 1865, most Southern leaders opposed arming slaves as soldiers. However, a few Confederates discussed arming slaves. Finally, in early 1865, General ] said that black soldiers were essential, and legislation was passed. The first black units were in training when the war ended in April.<ref>Bruce C. Levine, ''Confederate Emancipation: Southern Plans to Free and Arm Slaves during the Civil War'' (2007).</ref> | |||
| ===End of slavery=== | |||
| {{Main|End of slavery in the United States of America}} | |||
| {{Further|Slave states and free states#End of slavery|Emancipation Day#United States|Compensated emancipation in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Family reunification ads after emancipation}} | |||
| ]'' (1864) oil painting by ] (U.S. Senate Collection 33.00005.000) ]] | |||
| ] remembered ] in early 1863, when he was a boy of nine in Virginia:<ref>''Up from Slavery'' (1901), pp. 19–21.</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote|As the great day drew nearer, there was more singing in the slave quarters than usual. It was bolder, had more ring, and lasted later into the night. Most of the verses of the plantation songs had some reference to freedom.{{spaces}}... Some man who seemed to be a stranger (a United States officer, I presume) made a little speech and then read a rather long paper{{snd}}the Emancipation Proclamation, I think. After the reading we were told that we were all free, and could go when and where we pleased. My mother, who was standing by my side, leaned over and kissed her children, while tears of joy ran down her cheeks. She explained to us what it all meant, that this was the day for which she had been so long praying, but fearing that she would never live to see.}} | |||
| [[File:Abolition of slavery in the United States SVG map.svg|thumb|Abolition of slavery in the various states of the United States over time:{{Legend|#84c6c9|Abolition of slavery during or shortly after the American Revolution}} | |||
| {{Legend|#7be3de|The Northwest Ordinance, 1787}} | |||
| {{Legend|#64e5c5|Gradual emancipation in New York (starting 1799) and New Jersey (starting 1804)}} | |||
| {{Legend|#7ab377|The Missouri Compromise, 1821}} | |||
| {{Legend|#5f9b4a|Effective abolition of slavery by Mexican or joint US/British authority}} | |||
| {{Legend|#97cf2d|Abolition of slavery by Congressional action, 1861}} | |||
| {{Legend|#c7dd47|Abolition of slavery by Congressional action, 1862}} | |||
| {{Legend|#ffe86d|Emancipation Proclamation as originally issued, 1 Jan 1863}} | |||
| {{Legend|#f1c84e|Subsequent operation of the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863}} | |||
| {{Legend|#d39c59|Abolition of slavery by state action during the Civil War}} | |||
| {{Legend|#f7b360|Operation of the Emancipation Proclamation in 1864}} | |||
| {{Legend|#f6a89a|Operation of the Emancipation Proclamation in 1865}} | |||
| {{Legend|#d3595f|Thirteenth Amendment to the U.S. constitution, 18 Dec 1865}} | |||
| {{Legend|#bca4b1|Territory incorporated into the U.S. after the passage of the Thirteenth Amendment}}]] | |||
| The war ended on June 22, 1865, and following that surrender, the ] was enforced throughout remaining regions of the South that had not yet freed the slaves. Slavery officially continued for a couple of months in other locations.<ref>{{cite web|title= History of Juneteenth|url= http://www.juneteenth.com/history.htm|work= Juneteenth World Wide Celebration|access-date= March 9, 2014|archive-date= May 27, 2007|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070527081441/http://www.juneteenth.com/history.htm}}</ref> Federal troops arrived in ], on June 19, 1865, to enforce the emancipation. The commemoration of that event, ], was declared a ] in 2021.<ref>{{Cite AV media|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lUjBhwFcQ4U&t=3811s|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230204195847/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lUjBhwFcQ4U&t=3811s|archive-date=February 4, 2023|url-status=live|title=President Biden Signs the Juneteenth National Independence Day Act Into Law|publisher=The White House|date=June 17, 2021|via=YouTube|access-date=December 3, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| The ], abolishing slavery except as punishment for a crime, had been passed by the Senate in April 1864, and by the House of Representatives in January 1865.<ref name="quote">{{Cite web|url=https://www.archives.gov/founding-docs|title=America's Founding Documents|date=October 30, 2015|website=National Archives}}</ref> | |||
| ]'s 1863 woodblock etching ''Emancipation: The Past and the Future'' (] 1865-3 variant 101540.F) ]] | |||
| The amendment did not take effect until it was ratified by three-fourths of the states, which occurred on December 6, 1865, when Georgia ratified it. On that date, the last 40,000–45,000 enslaved Americans in the remaining two slave states of ] and ], as well as the 200 or so perpetual apprentices in New Jersey left from the very gradual emancipation process begun in 1804, were freed.<ref>E. Merton Coulter. ''The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky'' (1926), pp. 268–270; James J. Gigantino, ''The Ragged Road to Abolition; Slavery and Freedom in New Jersey, 1775–1865''.</ref> The ] known to have been born into legal slavery died in the 1970s. | |||
| ==Reconstruction to the present== | |||
| {{Further|Reconstruction Era|Reconstruction Amendments}} | |||
| {{See also|History of unfree labor in the United States|History of civil rights in the United States}} | |||
| ] like ] and ], and black representatives elected by newly enfranchised former slaves, including ], who took ]' old Senate seat, worked to realize the lofty goals of the abolitionists through Congressional legislation ]] | |||
| Journalist ] reported in his ]-winning book '']'' that many black persons were virtually enslaved under ] programs, which started after the Civil War. Most Southern states had no prisons; they leased convicts to businesses and farms for their labor, and the lessee paid for food and board. Incentives for abuse were present. | |||
| The continued involuntary servitude took various forms, but the primary forms included ], ]age and ], with the latter eventually encompassing ]s as well. By the 1930s, whites constituted most of the sharecroppers in the South. ] had reduced the need for farm labor, and many black people left the South in the ]. Jurisdictions and states created fines and sentences for a wide variety of minor crimes and used these as an excuse to arrest and sentence black people. Under convict-leasing programs, African-American men, often guilty of petty crimes or even no crime at all, were arrested, compelled to work without pay, repeatedly bought and sold, and coerced to do the bidding of the leaseholder. Sharecropping, as it was practiced during this period, often involved severe restrictions on the freedom of movement of sharecroppers, who could be whipped for leaving the plantation. Both sharecropping and convict leasing were legal and tolerated by both the North and South. However, peonage was an illicit form of forced labor. Its existence was ignored by authorities while thousands of African Americans and poor white Americans were subjugated and held in bondage until the mid-1960s to the late 1970s. With the exception of cases of peonage, beyond the ], the federal government took almost no action to enforce the Thirteenth Amendment until December 1941, when President ] summoned his attorney general. Five days after the attack on Pearl Harbor, at the request of the President, Attorney General ] issued ] to all ], instructing them to investigate actively and try any case of involuntary servitude or slavery. Several months later, convict leasing was officially abolished. But aspects have persisted in other forms. Historians argue that other systems of penal labor were all created in 1865, and convict leasing was simply the most oppressive form. Over time, a large ] arose to bring full civil rights and equality under the law to all Americans. | |||
| <ref>Thomas C. Holt, ed. ''Major Problems in African-American History: From Freedom to "Freedom Now", 1865–1990s'' (2000),</ref> | |||
| ===Convict leasing=== | |||
| {{Main|Convict lease|Penal labor in the United States}} | |||
| ] transitioned effortlessly from being a slave trader before the war<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Huebner |first=Timothy S. |date=March 2023 |title=Taking Profits, Making Myths: The Slave Trading Career of Nathan Bedford Forrest |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/879775 |journal=Civil War History |language=en |volume=69 |issue=1 |pages=42–75 |doi=10.1353/cwh.2023.0009 |s2cid=256599213 |issn=1533-6271}}</ref> to using convict labor on his farm on ] near Memphis after the war<ref>{{Cite news |date=1877-05-16 |title=Convict Labor in Georgia and Tennessee |page=2 |work=The Daily Memphis Avalanche |url=https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-daily-memphis-avalanche-convict-labo/130036626/ |access-date=2023-08-24}}</ref> (glass copy negative, Library of Congress LC-BH821-3061)]] | |||
| ] in Louisiana, which was built on land that had formerly been plantations owned by hugely successful interstate slave trader ]<ref>{{Cite news |last=Brockell |first=Gillian |date=2022-11-10 |title=La. voters keep 'slavery' at Angola prison, once and still a plantation |language=en-US |newspaper=Washington Post |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/history/2022/11/10/angola-prison-louisiana-slave-labor/ |access-date=2023-08-24 |issn=0190-8286}}</ref>]] | |||
| With emancipation a legal reality, white Southerners were concerned with both controlling the newly freed slaves and keeping them in the labor force at the lowest level. The system of ] began during Reconstruction and was fully implemented in the 1880s, officially ending in the last state, Alabama, in 1928. It persisted in various forms until it was abolished in 1942 by President ] during ], several months after the attack on ] involved the U.S. in the conflict. This system allowed private contractors to purchase the services of convicts from the state or local governments for a specific time period. African Americans, due to "vigorous and selective enforcement of laws and discriminatory sentencing", made up the vast majority of the convicts leased.<ref>Litwack (1998), p. 271.</ref> Writer Douglas A. Blackmon writes of the system: | |||
| {{Blockquote|It was a form of bondage distinctly different from that of the antebellum South in that for most men, and the relatively few women drawn in, this slavery did not last a lifetime and did not automatically extend from one generation to the next. But it was nonetheless slavery{{snd}}a system in which armies of free men, guilty of no crimes and entitled by law to freedom, were compelled to labor without compensation, were repeatedly bought and sold, and were forced to do the bidding of white masters through the regular application of extraordinary physical coercion.<ref>Blackmon (2008), p. 4.</ref>}} | |||
| The constitutional basis for convict leasing is that the ], while abolishing slavery and involuntary servitude generally, expressly ]. | |||
| ===Educational issues=== | |||
| Historian Mark Summers Wahlgren notes that the estimated literacy rate among formerly enslaved southern blacks at the time of emancipation was five to 10 percent, but had reached a baseline of 40 to 50 percent (and higher in cities) by the turn of the century, representing a "great advance".<ref>The Ordeal of the Reunion: A New History of Reconstruction (Littlefield History of the Civil War Era) by Mark Wahlgren Summers, 978-1-4696-1758-9, page=397</ref> As ] noted, the black colleges were not perfect, but "in a single generation they put thirty thousand black teachers in the South" and "wiped out the illiteracy of the majority of black people in the land".<ref>{{cite book |first=James D. |last=Anderson |title=The Education of Blacks in the South, 1860–1935 |location=Chapel Hill, NC |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |year=1988 |pages=244–245 |isbn=978-0-8078-1793-3 |title-link=The Education of Blacks in the South, 1860–1935 }}</ref>]'', September 22, 1866)]] | |||
| Northern philanthropists continued to support black education in the 20th century, for example of a major donor to Hampton Institute and Tuskegee was ], who also helped fund health programs at colleges and in communities.<ref name="Ford">{{cite book|first=Carin T.|last=Ford|year=2004|title=George Eastman: The Kodak Camera Man|publisher=Enslow Publishers, INC}}</ref> | |||
| ===Apologies=== | |||
| {{Main|Public apologies for slavery in the United States}} | |||
| In the 21st century, various legislative bodies have issued ]. | |||
| ===Political legacy=== | |||
| A 2016 study, published in '']'', finds that "hites who currently live in Southern counties that had high shares of slaves in 1860 are more likely to identify as a Republican, oppose affirmative action, and express racial resentment and colder feelings toward blacks." The study contends that "contemporary differences in political attitudes across counties in the American South in part trace their origins to slavery's prevalence more than 150 years ago. "<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal|last1=Acharya|first1=Avidit|last2=Blackwell|first2=Matthew|last3=Sen|first3=Maya|date=May 19, 2016|title=The Political Legacy of American Slavery|journal=The Journal of Politics|volume=78|issue=3|pages=621–641 |doi=10.1086/686631|issn=0022-3816|citeseerx=10.1.1.397.3549|s2cid=222442945}}</ref> The authors argue that their findings are consistent with the theory that "following the Civil War, Southern whites faced political and economic incentives to reinforce existing racist norms and institutions to maintain control over the newly freed African American population. This amplified local differences in racially conservative political attitudes, which in turn have been passed down locally across generations."<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| ], Mississippi Delta, Mississippi" (] 35mm nitrate negative, ], October 1939)]] | |||
| A 2017 study in the '']'' argued that the British American colonies without slavery adopted better democratic institutions to attract migrant workers to their colonies.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Nikolova|first=Elena|date=January 1, 2017|title=Destined for Democracy? Labour Markets and Political Change in Colonial British America|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-political-science/article/div-classtitledestined-for-democracy-labour-markets-and-political-change-in-colonial-british-americadiv/2A13C0004A17BBFF4C3AD2E710E44F3B|journal=British Journal of Political Science|volume=47|issue=1|pages=19–45|doi=10.1017/S0007123415000101|s2cid=17112994|issn=0007-1234}}</ref> | |||
| An article published in the '']'' in 2022 finds that former slave owners remained politically dominant long after the abolition of slavery. Using data from Texas, the authors find that "n 1900, still around 50 percent of all state legislators came from a slave-owning background."<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Bellani|first1=Luna|last2=Hager|first2=Anselm|last3=Maurer|first3=Stephan|title=The Long Shadow of Slavery: The Persistence of Slave Owners in Southern Lawmaking|journal=Journal of Economic History|year=2022 |volume=82|issue=1|pages=250–283|doi=10.1017/S0022050721000590|s2cid=211165817 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economics== | |||
| ] via ])]] | |||
| ] and ], in their 1974 book '']'', argued that the ] of slavery at the market price was close to ten percent, a number close to investment in other assets. The transition from indentured servants to slaves is cited to show that slaves offered greater profits to their owners. A qualified consensus among economic historians and economists is that "Slave agriculture was efficient compared with free agriculture. Economies of scale, effective management, and intensive utilization of labor and capital made southern slave agriculture considerably more efficient than nonslave southern farming",<ref name="Whaples 1995 No. 16">{{Cite journal|last=Whaples|first=Robert|author-link=Robert Whaples|journal=]|volume=55|issue=1|pages=141, 146–147|jstor=2123771|title=Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions|date=March 1995|doi=10.1017/S0022050700040602|s2cid=145691938 }}</ref> and it is the near-universal consensus among economic historians and economists that slavery was not "a system irrationally kept in existence by plantation owners who failed to perceive or were indifferent to their best economic interests".<ref name="Whaples 1995 139–154">{{cite journal|last=Whaples|first=Robert|author-link=Robert Whaples|title=Where is There Consensus among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions|journal=]|date=March 1995|pages=139–154|jstor=2123771|doi=10.1017/S0022050700040602|volume=55|issue=1|s2cid=145691938}}</ref> | |||
| The relative price of slaves and indentured servants in the antebellum period did decrease.<!--How significant were indentured servants? They are not usually discussed at all in the antebellum period!--> Indentured servants became more costly with the increase in the demand of skilled labor in England.<ref name=Galenson>{{cite journal|last=Galenson|first=D.W.|s2cid=154682898|title=The Rise and Fall of Indentured Servants in the Americas: An Economic Approach |journal=]|date=March 1984|page=1|doi=10.1017/S002205070003134X|volume=44}}</ref> At the same time, slaves were mostly supplied from within the United States and thus language was not a barrier, and the cost of transporting slaves from one state to another was relatively low. However, as in ] and ], slavery at its end in the United States tended to be concentrated in the poorest regions of the United States,<ref name="Sowell 2005 pp. 157–158">{{cite book|last1=Sowell|first1=Thomas|author-link1=Thomas Sowell|title=Black Rednecks and White Liberals|chapter=The Real History of Slavery|publisher=]|place=New York|pages=|isbn=978-1-59403-086-4|year=2005|title-link=Black Rednecks and White Liberals}}</ref> with a qualified consensus among economists and economic historians concluding that the "modern period of the South's economic convergence to the level of the North only began in earnest when the institutional foundations of the southern regional labor market were undermined, largely by ]."<ref name="Whaples 1995 No. 26">{{Cite journal|last=Whaples|first=Robert|author-link=Robert Whaples|journal=]|volume=55|issue=1|pages=142, 147–148|jstor=2123771|title=Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions|date=March 1995|doi=10.1017/S0022050700040602|citeseerx=10.1.1.482.4975|s2cid=145691938 |url=http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/jolson/econ315/whaples2123771.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| In the decades preceding the Civil War, the black population of the United States experienced a rapid ].<ref name=Tadman>{{cite journal|last=Tadman|first=M.|title=The Demographic Cost of Sugar: Debates on Slave Societies and Natural Increase in the Americas |journal=] |date=December 2000|doi=10.2307/2652029|volume=105|issue=5|pages=1534–1575|jstor=2652029}}</ref> Unlike the ] with ], the slave population transported by the ] to the United States was sex-balanced.<ref name="Sowell 2005 p. 156">{{cite book|last1=Sowell|first1=Thomas|author-link1=Thomas Sowell|title=Black Rednecks and White Liberals|chapter=The Real History of Slavery|publisher=]|place=New York|page=|isbn=978-1-59403-086-4|year=2005|title-link=Black Rednecks and White Liberals}}</ref> The slave population multiplied nearly fourfold between 1810 and 1860, despite the passage of the ] signed into law by ] ] in 1807 banning the international slave trade.<ref name="ICPSR Study">{{cite web|title=Historical Demographic, Economic and Social Data: the United States, 1790–1970|url=http://fisher.lib.virginia.edu/census/.|work=Historical Statistics of the United States|publisher=ICPSR Study|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030401083841/http://fisher.lib.virginia.edu/census/|archive-date=April 1, 2003|df=mdy-all}}</ref> Thus, it is also the universal consensus among modern economic historians and economists that slavery in the United States was not "economically moribund on the eve of the Civil War".<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Whaples|first=Robert|author-link=Robert Whaples|journal=]|volume=55|issue=1|pages=139–154|jstor=2123771|title=Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions|date=March 1995|doi=10.1017/S0022050700040602|citeseerx=10.1.1.482.4975|s2cid=145691938 |url=http://www.employees.csbsju.edu/jolson/econ315/whaples2123771.pdf}}</ref> In the 2010s, several historians, among them ], ], ] and Calvin Schermerhorn, have posited that slavery was integral in the development of American ].<ref>{{cite book |last= Baptist|first=Edward E.|date=2016 |title=The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery And The Making Of American Capitalism|url=https://www.basicbooks.com/titles/edward-e-baptist/the-half-has-never-been-told/9780465097685/|publisher=] |isbn=978-0-465-09768-5|author-link=Edward E. Baptist}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Slavery's Capitalism: A New History of American Economic Development|editor1-first=Sven|editor1-last=Beckert|editor2-first=Seth|editor2-last=Rockman|editor1-link=Sven Beckert|url=https://site.pennpress.org/aaihs-2021/9780812224177/slaverys-capitalism/|publisher=]|year=2016|isbn=978-0-8122-2417-7}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{cite book |last=Johnson |first=Walter |title=River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom |publisher=] |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-674-04555-2 |pages=86–87 (credit backed by slave labor) |author-link=Walter Johnson (historian)}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Calvin|last=Schermerhorn|title=The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860|url=https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300192001/business-slavery-and-rise-american-capitalism-1815-1860| publisher=]|year=2015|isbn=978-0-300-19200-1}}</ref> Johnson wrote in ''River of Dark Dreams'' (2013): "The cords of credit and debt—of advance and obligation—that cinched the Atlantic economy together were anchored with the mutually defining values of land and slaves: without land and slaves, there was no credit, and without slaves, land itself was valueless. Promises made in the Mississippi Valley were backed by the value of slaves and fulfilled in their labor."<ref name=":3" /> Other ] have rejected that thesis.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Wright |first=Gavin |date=2022 |title=Slavery and the Rise of the Nineteenth-Century American Economy |journal=Journal of Economic Perspectives |language=en |volume=36 |issue=2 |pages=123–148 |doi=10.1257/jep.36.2.123 |s2cid=248716718 |issn=0895-3309|doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wright|first=Gavin|title=Slavery and Anglo-American capitalism revisited|journal=The Economic History Review|language=en|volume=73|issue=2|doi=10.1111/ehr.12962|issn=1468-0289|year=2020|pages=353–383|s2cid=214142489}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Clegg|first=John J.|date=2015|title=Capitalism and Slavery|journal=Critical Historical Studies|volume=2|issue=2|pages=281–304|doi=10.1086/683036|jstor=10.1086/683036|s2cid=155629580}}{{Cite journal|last1=Murray|first1=John E.|last2=Olmstead|first2=Alan L.|last3=Logan|first3=Trevon D.|last4=Pritchett|first4=Jonathan B.|last5=Rousseau|first5=Peter L.|date=September 2015|title=The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism. By Baptist Edward E. New York: Basic Books, 2014. pp. xxvii, 498. $35.00, cloth.|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-economic-history/article/half-has-never-been-told-slavery-and-the-making-of-american-capitalism-by-baptist-edward-e-new-york-basic-books-2014-pp-xxvii-498-3500-cloth/427A1036B912359C1B5B53A5E7273CC0|journal=The Journal of Economic History|volume=75|issue=3|pages=919–931|doi=10.1017/S0022050715000996|s2cid=154464892|issn=0022-0507}}{{Cite journal|last=Engerman|first=Stanley L.|date=June 2017|title=Review of The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860 by Calvin Schermerhorn and The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism by Edward E. Baptist|journal=Journal of Economic Literature|volume=55|issue=2|pages=637–643|doi=10.1257/jel.20151334|issn=0022-0515|url=https://www.aeaweb.org/articles/attachments?retrieve=xVrFb4bNof4Y_b5EHZBKhsL0-ILuNblZ}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.law.columbia.edu/law-economic-studies/workshops/fall-2016-workshops|title=Cotton, Slavery, and the New History of Capitalism|last1=Alan L. Olmstead|last2=Paul W. Rhode|date=12 September 2016|website=Center for Law and Economic Studies|publisher=Columbia University|access-date=23 June 2019|quote=mishandle historical evidence and mischaracterize important events in ways that affect their major interpretations on the nature of slavery}}{{cite journal|last1=Alan L. Olmstead|last2=Paul W. Rhode|date=January 2018|title=Cotton, slavery, and the new history of capitalism|journal=]|volume=67|pages=1–17|doi=10.1016/j.eeh.2017.12.002}}</ref><ref name=":03">{{Cite news|last=Parry|first=Marc|url=http://www.chronicle.com/article/ShacklesDollars/238598?key=yop9k7-B1QiWD6aZpWTJr3Ge-x6XSRuIwbSFcNhqE7B9uMfC2WvYE1p7I2kjzRzpSkFvXzJQajd5azZCOWUzcUZld1AzVnNoVlpWOXBiOWJEMGgxLUJUX2p4Yw|title=Shackles and Dollars|date=2016-12-08|work=The Chronicle of Higher Education|access-date=2017-06-12|issn=0009-5982}}</ref> | |||
| A 2023 study estimates that prior to the onset of the US Civil War, the enslaved population produced 12.6% of US national product.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Rhode |first=Paul W. |date=2023 |title=What Fraction of Antebellum US National Product did the Enslaved Produce? |journal=Explorations in Economic History |volume=91 |doi=10.1016/j.eeh.2023.101552 |s2cid=262210797 |issn=0014-4983|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| Slavery had a long-lasting impact on wealth and racial inequality in the United States. Black families whose ancestors were freed before the start of the Civil War have substantially better socio-economic outcomes than families who were freed in the Civil War.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Althoff |first1=Lukas |last2=Reichardt |first2=Hugo |date=2024 |title=Jim Crow and Black Economic Progress After Slavery |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/qje/qjae023 |journal=The Quarterly Journal of Economics |volume=139 |issue=4 |pages=2279–2330 |doi=10.1093/qje/qjae023 |issn=0033-5533}}</ref> | |||
| ===Efficiency of slaves=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Scholars disagree on how to quantify the efficiency of slavery. In ''Time on the Cross'' Fogel and Engerman equate efficiency to ] (TFP), the output per average unit of input on a farm. Using this measurement, Southern farms that enslaved black people using the ] were 35% more efficient than Northern farms, which used free labor. Under the gang system, groups of slaves perform synchronized tasks under the constant vigilance of an overseer. Each group was like a part of a machine. If perceived to be working below his capacity, a slave could be punished. Fogel argues that this kind of negative enforcement was not frequent and that slaves and free laborers had a similar quality of life; however, there is controversy on this last point.<ref name="Fogel and Engeman">{{cite book|last=Fogel & Engerman|title=Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery|year=1974|publisher=W.W. Norton and Company|location=New York}}</ref> A critique of Fogel and Engerman's view was published by Paul A. David in 1976.<ref>David, Paul A., Herbert G. Gutman, Richard Sutch, and Peter Temin. "Reckoning with slavery." (1985).</ref> | |||
| In 1995, a random survey of 178 members of the ] sought to study the views of economists and economic historians on the debate. The study found that 72 percent of economists and 65 percent of economic historians would generally agree that "Slave agriculture was efficient compared with free agriculture. Economies of scale, effective management, and intensive utilization of labor and capital made southern slave agriculture considerably more efficient than nonslave southern farming." 48 percent of the economists agreed without provisos, while 24 percent agreed when provisos were included in the statement. On the other hand, 58 percent of economic historians and 42 percent of economists disagreed with Fogel and Engerman's "proposition that the material (not psychological) conditions of the lives of slaves compared favorably with those of free industrial workers in the decades before the Civil War".<ref name="Whaples 1995 No. 16" /> | |||
| ===Prices of slaves=== | |||
| The U.S. has a capitalist economy so the price of slaves was determined by the law of ]. For example, following bans on the import of slaves after the UK's ] and the American 1807 ], the prices for slaves increased. The markets for the products produced by slaves also affected the price of slaves (e.g. the price of slaves fell when the price of cotton fell in 1840). Anticipation of slavery's abolition also influenced prices. During the Civil War the price for slave men in New Orleans dropped from $1,381 in 1861 to $1,116 by 1862 (the ] by U.S. forces in the Spring of 1862).<ref>{{cite journal|last=Kotlikoff|first=L. J.|title=The Structure of Slave prices in New Orleans|journal=Economic Inquiry|date=October 1979|pages=496–518|doi=10.1111/j.1465-7295.1979.tb00544.x|volume=17|issue=4|url=http://www.econ.ucla.edu/workingpapers/wp119.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| ] basin—were purchased at a Portuguese-run African slave market in 1858 for an estimated {{USD|50|1858}} each, and resold in the United States where the fair-market price for a healthy young enslaved male was easily {{USD|1000|1858}}<ref>{{Cite book |last=Calonius |first=Erik |title=The Wanderer: the last American slave ship and the conspiracy that set its sails |date=2006 |publisher=Saint Martin's Press |isbn=978-0-312-34347-7 |location=New York, N.Y |pages=101–102 (Portuguese-African market), 125–126 (prices), 250–253 (origin, biography) |language=en-us}}</ref> (Charles J. Montgomery, '']'', 1908)]] | |||
| Controlling for inflation, prices of slaves rose dramatically in the six decades prior to the Civil War, reflecting demand due to commodity cotton, as well as use of slaves in shipping and manufacturing. Although the prices of slaves relative to indentured servants declined, both got more expensive. Cotton production was rising and relied on the use of slaves to yield high profits. Fogel and Engeman initially argued that if the Civil War had not happened, the slave prices would have increased even more, an average of more than fifty percent by 1890.<ref name="Fogel and Engeman" />{{rp|96}} | |||
| Prices reflected the characteristics of the slave; such factors as sex, age, nature, and height were all taken into account to determine the price of a slave. Over the life-cycle, the price of enslaved women was higher than their male counterparts up to puberty age, as they would likely bear children who their masters could sell as slaves and could be used as slave laborers. Men around the age of 25 were the most valued, as they were at the highest level of productivity and still had a considerable life-span.{{citation needed|date=March 2021}} If slaves had a history of fights or escapes, their price was lowered reflecting what planters believed was risk of repeating such behavior. Slave traders and buyers would examine a slave's back for whipping scars; a large number of injuries would be seen as evidence of laziness or rebelliousness, rather than the previous master's brutality, and would lower the slave's price.<ref name="McInnis2011" /> Taller male slaves were priced at a higher level, as height was viewed as a proxy for fitness and productivity.<ref name="Fogel and Engeman" /> | |||
| ===Effects on Southern economic development=== | |||
| ], 1853. On display at the British Museum in London.]] | |||
| While slavery brought profits in the short run, discussion continues on the economic benefits of slavery in the long run. In 1995, a random anonymous survey of 178 members of the ] found that out of the forty propositions about ] that were surveyed, the group of propositions most disputed by economic historians and economists were those about the postbellum economy of the American South (along with the ]). The only exception was the proposition initially put forward by historian ] that the "modern period of the South's economic convergence to the level of the North only began in earnest when the institutional foundations of the southern regional labor market were undermined, largely by ]." 62 percent of economists (24 percent with and 38 percent without provisos) and 73 percent of historians (23 percent with and 50 percent without provisos) agreed with this statement.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Wright|first=Gavin|author-link=Gavin Wright|journal=]|volume=1|issue=1|pages=161–178|jstor=1942954|title=The Economic Revolution in the American South|date=Summer 1987|doi=10.1257/jep.1.1.161}}</ref><ref name="Whaples 1995 No. 26" /> Wright has also argued that the private investment of monetary resources in the cotton industry, among others, delayed development in the South of commercial and industrial institutions. There was little public investment in railroads or other infrastructure. Wright argues that agricultural technology was far more developed in the South, representing an economic advantage of the South over the North of the United States.<ref>{{cite book|last=Wright|first=Gavin|author-link=Gavin Wright|title=The Political Economy of the Cotton South: Households, Markets, and Wealth in the Nineteenth Century|url=https://archive.org/details/politicaleconomy0000wrig|url-access=registration|year=1978|publisher=]|location=New York|isbn=978-0-393-09038-3}}</ref> | |||
| In '']'', ] noted that "the colonies in which there were no slaves became more populous and more rich than those in which slavery flourished".<ref>{{cite book|title=Democracy in America: The Complete and Unabridged, Volumes I and II|title-link=Democracy in America|last=de Tocqueville|first=Alexise|translator-last=Reeve|translator-first=Henry|translator-link=Henry Reeve (journalist)|author-link=Alexis de Tocqueville|chapter=Volume I, Chapter XVIII: Future Condition Of Three Races In The United States|orig-date=1835|year=2004|page=419|place=New York|publisher=]|edition=Reissue|isbn=978-0-553-21464-2|chapter-url=http://www.gutenberg.org/files/815/815-h/815-h.htm}}</ref> In 1857, in '']: How to Meet It'', ] made the same point.<ref>Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 1968 edition edited by ].</ref> Economists Peter H. Lindert and ], in a pair of articles published in 2012 and 2013, found that, despite the American South initially having per capita income roughly double that of the North in 1774, incomes in the South had declined 27% by 1800 and continued to decline over the next four decades, while the economies in New England and the Mid-Atlantic states vastly expanded. By 1840, per capita income in the South was well behind the Northeast and the national average (Note: this is also true ]).<ref>{{cite journal |first1=Peter H. |last1=Lindert |first2=Jeffrey G. |last2=Williamson |author-link2=Jeffrey G. Williamson |title=American Incomes Before and After the Revolution |journal=] |volume=73 |issue=3 |year=2013 |pages=725–765 |doi=10.1017/S0022050713000594 |url=https://www.nber.org/papers/w17211.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Lindert |first1=Peter H. |last2=Williamson |first2=Jeffrey G. |author-link2=Jeffrey G. Williamson|title=American Incomes 1774–1860 |journal=NBER Working Paper Series No. 18396 |date=September 2012 |doi=10.3386/w18396 |s2cid=153965760 |url=https://www.nber.org/papers/w18396.pdf|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Lindert and Williamson argue that this antebellum period is an example of what economists ], ], and ] call "a reversal of fortune".<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Acemoğlu |first1=Daron |last2=Johnson |first2=Simon |last3=Robinson |first3=James A. |author-link1=Daron Acemoglu |author-link2=Simon Johnson (economist) |author-link3=James A. Robinson (economist) |title=Reversal of Fortune: Geography and Institutions in the Making of the Modern World Income Distribution |journal=] |volume=117 |issue=4 |year=2002 |pages=1231–1294 |doi=10.3386/w18396 |s2cid=153965760 |url=https://www.nber.org/papers/w8460.pdf |doi-access=free }}</ref> In his essay "]", economist ] reiterated and augmented the observation made by de Tocqueville by comparing slavery in the United States to ]. He notes that slave societies reflected similar economic trends in those and other parts of the world, suggesting that the trend Lindert and Williamson identify may have continued until the ]: | |||
| {{blockquote|Both in ] and in the United States{{snd}}the countries with the two largest slave populations in the Western Hemisphere{{snd}}the end of slavery found the regions in which slaves had been concentrated poorer than other regions of these same countries. For the United States, a case could be made that this was due to the Civil War, which did so much damage to the South, but no such explanation would apply to Brazil, which fought no Civil War over this issue. Moreover, even in the United States, the South lagged behind the North in many ways even before the Civil War. | |||
| Although slavery in Europe died out before it was abolished in the Western Hemisphere, as late as 1776 slavery had not yet died out all across the continent when ] wrote in '']'' that it still existed in some eastern regions. But, even then, Eastern Europe was much poorer than Western Europe. The slavery of North Africa and the Middle East, over the centuries, took more slaves from sub-Saharan Africa than the Western Hemisphere did{{spaces}}... But these remained largely poor countries until the discovery and extraction of their vast oil deposits.<ref name="Sowell 2005 pp. 157–158" />}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Sowell also notes in ''Ethnic America: A History'', citing historians ] and ], that three-quarters of Southern white families owned no slaves at all.<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Eaton|first1=Clement|author-link1=Clement Eaton|title=The Freedom-of-Thought Struggle in the Old South|publisher=]|place=New York|pages=39–40|date=1964}}</ref> Most slaveholders lived on farms rather than plantations,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Genovese|first1=Eugene D.|author-link1=Eugene Genovese|title=Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made|publisher=]|place=New York|page=7|date=1974|isbn=978-0-394-71652-7}}</ref> and few plantations were as large as the fictional ones depicted in '']''.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Sowell|first1=Thomas|author-link1=Thomas Sowell|title=Ethnic America: A History|publisher=]|place=New York|page=|date=1981|isbn=978-0-465-02075-1|url=https://archive.org/details/ethnicamericahis00thom/page/190}}</ref> In "The Real History of Slavery", Sowell also notes in comparison to ] (where slaves were seldom used for productive purposes) and ] (where the slaves consumed the entire output they created), Sowell observes that many commercial slaveowners in the antebellum South tended to be ] and many lost their plantations due to creditor ]s, and in Britain, profits by British slave traders only amounted to two percent of British ] at the ].<ref>{{cite book|last1=Sowell|first1=Thomas|author-link1=Thomas Sowell|title=Black Rednecks and White Liberals|chapter=The Real History of Slavery|publisher=]|place=New York|page=|isbn=978-1-59403-086-4|year=2005|title-link=Black Rednecks and White Liberals}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Anstey|first=Roger|editor-first1=Stanley|editor-last1=Engerman|editor-link1=Stanley Engerman|editor-first2=Eugene|editor-last2=Genovese|editor-link2=Eugene Genovese|title=Race and Slavery in the Western Hemisphere|chapter=The Volume and Profitability of the British Slave Trade, 1675–1800|year=1975|pages=22–23|place=]|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-691-04625-9}}</ref> Sowell draws the following conclusion regarding the ] value of slavery: | |||
| <blockquote>In short, even though some individual slaveowners grew rich and some family fortunes were founded on the exploitation of slaves, that is very different from saying that the whole society, or even its non-slave population as a whole, was more economically advanced than it would have been in the absence of slavery. What this means is that, whether employed as domestic servants or producing crops or other goods, millions suffered exploitation and dehumanization for no higher purpose than the{{spaces}}... aggrandizement of slaveowners.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Sowell|first1=Thomas|author-link1=Thomas Sowell|title=Black Rednecks and White Liberals|chapter=The Real History of Slavery|publisher=]|place=New York|pages=|isbn=978-1-59403-086-4|date=2005|title-link=Black Rednecks and White Liberals}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Eric Hilt noted that, while some historians have suggested slavery was necessary for the ] (on the grounds that American slave plantations produced most of the raw cotton for the British textiles market and the British textiles market was the vanguard of the Industrial Revolution), it is not clear if this is actually true; there is no evidence that cotton could not have been mass-produced by ]s rather than slave plantations if the latter had not existed (as their existence tended to force yeoman farmers into ]) and there is some evidence that they certainly could have. The soil and ] were excellent for growing cotton, so it is not unreasonable to postulate that farms without slaves could have produced substantial amounts of cotton; even if they did not produce as much as the plantations did, it could still have been enough to serve the demand of British producers.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hilt|first=Eric|title=Economic History, Historical Analysis, and the "New History of Capitalism"|journal=]|publisher=]|volume=77|issue=2|year=2017|pages=511–536|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/E17BEA48B930F6F25F328B5A79332A6E/S002205071700016Xa.pdf/economic_history_historical_analysis_and_the_new_history_of_capitalism.pdf|doi=10.1017/S002205071700016X|doi-access=free}}</ref> Similar arguments have been made by other historians.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Olmstead|first1=Alan L.|last2=Rhode|first2=Paul W.|title=Cotton, Slavery, and the New History of Capitalism|journal=]|publisher=]|volume=67|year=2018|pages=1–17|doi=10.1016/j.eeh.2017.12.002|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014498317302292}}</ref> | |||
| ===Sexual economy of American slavery=== | |||
| ], Pittsburgh)]] | |||
| Scholar Adrienne Davis articulates how the economics of slavery also can be defined as a sexual economy, specifically focusing on how ] were expected to perform physical, sexual and reproductive labor to provide a consistent enslaved workforce and increase the profits of white slavers. Davis writes that black women were needed for their "sexual and reproductive labor to satisfy the economic, political, and personal interest of white men of the elite class"<ref>{{Cite book|title=Sister Circle: Black Women and Work|last=Davis|first=Adrienne|publisher=Rutgers University Press|year=2002|isbn=978-0-8135-3061-1|page=|chapter="Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/sistercircle00rutg/page/107}}</ref> articulating that black women's reproductive capacity was important in the maintenance of the system of slavery due to its ability to perpetuate an enslaved workforce. She is also drawing attention to black women's labor being needed to maintain the aristocracy of a white ruling class, due to the intimate nature of reproduction and its potential for producing more enslaved peoples. | |||
| Due to the institution of '']'', black women's wombs became the site where slavery was developed and transferred,<ref>{{Cite book|title=Sister Circle: Black Women and Work|last=Davis|first=Adrienne|publisher=Rutgers University Press|year=2002|isbn=978-0-8135-3061-1|page=|chapter="Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" Sexual Economy of American Slavery|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/sistercircle00rutg/page/108}}</ref> meaning that black women were not only used for their physical labor, but for their sexual and reproductive labor as well. | |||
| <blockquote>"The rule that the children's status follows their mothers' was a foundational one for our economy. It converted enslaved women's reproductive capacity into market capital"<ref>{{Cite book|title=Sister Circle: Black Women and Work|last=Davis|first=Adrienne|publisher=Rutgers University Press|year=2002|isbn=978-0-8135-3061-1|page=|chapter="Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/sistercircle00rutg/page/109}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ] postcard: "The Old Slave Block in the ], New Orleans, La. The colored woman standing on the block was sold for $1500.00 on this same block when a little girl."]] | |||
| This articulation by Davis illustrates how black women's reproductive capacity was commodified under slavery, and that an analysis of the economic structures of slavery requires an acknowledgment of how pivotal black women's sexuality was in maintaining slavery's economic power. Davis writes how black women performed labor under slavery, writing: " male when convenient and horrifically female when needed".<ref name=":02">{{Cite book|title=Sister Circle: Black Women and Work|last=Davis|first=Adrienne|publisher=Rutgers University Press|year=2002|isbn=978-0-8135-3061-1|page=|chapter="Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/sistercircle00rutg/page/119}}</ref> The fluctuating expectations of black women's gendered labor under slavery disrupted the white normative roles that were assigned to white men and white women. This ungendering black women received under slavery contributed to the systemic dehumanization experienced by enslaved black women, as they were unable to receive the expectations or experiences of either gender within the white binary. | |||
| Davis's arguments address the fact that, under slavery, black women's sexuality became linked to the economic and public sphere, making their intimate lives into public institutions. Black women's physical labor was gendered as masculine under slavery when they were needed to yield more profit, but their reproductive capacities and sexual labor were equally as important in maintaining white power over black communities and perpetuating an enslaved workforce.<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| ==Geography and demography== | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Slave importation=== | |||
| About 600,000 slaves were transported to the United States, or five percent of the 12 million slaves taken from Africa. About 310,000 of these persons were imported into the Thirteen Colonies before 1776: 40 percent directly, and the rest from the Caribbean. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |+ Slaves trafficked to the British colonies and United States:<ref>Source: Miller and Smith, eds. ''Dictionary of American Slavery'' (1988) p. 678</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Time period !! Quantity | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1620–1700 || 21,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1701–1760 || 189,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1761–1770 || 63,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1771–1790 || 56,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1791–1800 || 79,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1801–1810 || 124,000<ref>Includes 10,000 to Louisiana before 1803.</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1810–1865 || 51,000 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Total || 597,000 | |||
| |} | |||
| The great majority of enslaved Africans were transported to ] and to ]. As life expectancy was short, their numbers had to be continually replenished. Life expectancy was much higher in the United States, and the enslaved population was successful in reproduction, which was called "natural increase" by enslavers. The population of enslaved people in the United States grew to {{nowrap|4 million}} by the ]. Historian J. David Hacker conducted research that estimated that the cumulative number of slaves in colonial America and the United States (1619–1865) was 10 million.<ref name="Hacker 2020 pp. 840–855">{{cite journal | last=Hacker | first=J. David | title=From '20. and odd' to 10 million: the growth of the slave population in the United States | journal=Slavery & Abolition | publisher=Informa UK Limited | volume=41 | issue=4 | date=2020-05-13 | issn=0144-039X | doi=10.1080/0144039x.2020.1755502 | pages=840–855| pmid=33281246 | pmc=7716878 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Origins of American slaves=== | |||
| {{Further|African-American genealogy}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| ! Origins and percentages of Africans<br />imported into British North America<br />and Louisiana (1700–1820)<ref>Gomez, Michael A: ''Exchanging Our Country Marks: The Transformation of African Identities in the Colonial and Antebellum South'', p. 29. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina, 1998.</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=The River Flows On: Black Resistance, Culture, and Identity Formation in Early America |first=Walter C. |last=Rucker |publisher=LSU Press |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-8071-3109-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c2XlG4rRK4QC&pg=PA126 |page=126}}</ref>!! Amount % <br /> (exceeds 100%) | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ], ])</small> ||align=center| 26.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ], ], ], ])</small> ||align=center| 24.4 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ])</small> ||align=center| 15.8 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ], ])</small> ||align=center| 14.5 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ])</small> ||align=center| 13.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ])</small> ||align=center| 5.2 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ], ], ] and ])</small> ||align=center| 4.3 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] <small>(], ])</small> ||align=center| 1.8 | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Distribution of slaves=== | ===Distribution of slaves=== | ||
| ]; Lincoln kept a copy of this map in the White House and studied it often, using it to track Union troop movements<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Susan Schulten |date=2010 |title=The Cartography of Slavery and the Authority of Statistics |journal=Civil War History |language=en |volume=56 |issue=1 |pages=5–32 |doi=10.1353/cwh.0.0141 |s2cid=144587155 |issn=1533-6271|doi-access=free }}</ref>]] | |||
| ] | |||
| {| align=left border=1 cellpadding=6 cellspacing=0 style="margin: 0 0 0 1em; background: #ffffff; border: 1px #aaaaaa solid; border-collapse: collapse; text-align:right; font-size: 95%" | |||
| | |
{| class="wikitable" style="ftext-align:right; font-size:95%;" | ||
| |- style="border-bottom:2px solid gray;" | |||
| ! Census<br>Year !! # Slaves !! # Free<br>blacks !! Total<br>black!! % free<br>blacks!!Total US<br>population!! % black<br>of total | |||
| ! Census<br />Year !! # Slaves !! # Free<br />Africans !! Total<br />Africans!! % Free<br />Africans!!Total US<br />population!! % Africans<br />of total | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1790 || 697,681 || 59,527 || 757,208 || |
| 1790 || 697,681 || 59,527 || 757,208 || 8% || 3,929,214 || 19% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1800 || 893,602 || 108,435 || 1,002,037 || |
| 1800 || 893,602 || 108,435 || 1,002,037 || 11% || 5,308,483 || 19% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1810 || 1,191,362 || 186,446 || 1,377,808 || |
| 1810 || 1,191,362 || 186,446 || 1,377,808 || 14% || 7,239,881 || 19% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1820 || 1,538,022 || 233,634 || 1,771,656 || 13 |
| 1820 || 1,538,022 || 233,634 || 1,771,656 || 13% || 9,638,453 || 18% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1830 || 2,009,043 || 319,599 || 2,328,642 || |
| 1830 || 2,009,043 || 319,599 || 2,328,642 || 14% || 12,860,702 || 18% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1840 || 2,487,355 || 386,293 || 2,873,648 || 13 |
| 1840 || 2,487,355 || 386,293 || 2,873,648 || 13% || 17,063,353 || 17% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1850 || 3,204,313 || 434,495 || 3,638,808 || |
| 1850 || 3,204,313 || 434,495 || 3,638,808 || 12% || 23,191,876 || 16% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1860 || 3,953,760 || 488,070 || 4,441,830 || 11 |
| 1860 || 3,953,760 || 488,070 || 4,441,830 || 11% || 31,443,321 || 14% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1870 || 0 ||4,880,009|| 4,880,009 || 100% || 38,558,371 || 13% | | 1870 || 0 ||4,880,009|| 4,880,009 || 100% || 38,558,371 || 13% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | colspan="7" style="text-align:center;"|Source:{{cite web |url=http://thomaslegioncherokee.tripod.com/distributionofslavesinunitedstateshistory.html |access-date=May 13, 2010 |title=Distribution of Slaves in U.S. History}} | |||
| |colspan=7|Source: http://www.census.gov/population/documentation/twps0056/tab01.xls | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| <br clear=all> | |||
| ] | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable"; style="text-align:right" border=1 cellpadding=6 cellspacing=0 style="margin: 0 0 0 1em; background: #ffffff; border: 1px #aaaaaa solid; border-collapse: collapse; text-align:right; font-size: 95%" | |||
| |+ Total Slave Population in US 1790-1860, by State<ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right; font-size:80%;" | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |+ Total Slave Population in U.S., 1790–1860, by State and Territory<ref>{{Cite web |title=Chapter V: Slave Population of the United States (through 1850) |url=https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/1850/1850c/1850c-04.pdf? |website=census.gov}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Population of Slaves in 1860: Introduction |url=https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/1860/population/1860a-02.pdf |website=census.gov}}</ref> | |||
| |url=http://fisher.lib.virginia.edu/collections/stats/histcensus/php/newlong.php | |||
| |title=Total Slave Population in US, 1790-1860, by State | |||
| |accessdate=2007-12-28}} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| |- style="text-align:center; background: #efefef; border-bottom:2px solid gray;" | |- style="text-align:center; background: #efefef; border-bottom:2px solid gray;" | ||
| ! Census<br>Year !! 1790 !! 1800 !! 1810 !! 1820 !! 1830 !! 1840 !! 1850 !! 1860 | ! Census<br />Year !! 1790 !! 1800 !! 1810 !! 1820 !! 1830 !! 1840 !! 1850 !! 1860 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !align=left| All States || 694,207 || |
!align=left| All States || 694,207 || 893,308 || 1,191,338 || 1,531,490 || 2,009,079 || 2,487,392 || 3,204,215 || 3,953,820 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Alabama || |
|align=left| Alabama || – || 494 || 2,565 || 41,879 || 117,549 || 253,532 || 342,844 || 435,080 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Arkansas || |
|align=left| Arkansas || – || – || 136 || 1,617 || 4,576 || 19,935 || 47,100 || 111,115 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| California || |
|align=left| California || – || – || – || – || – || – || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Connecticut || 2,648 || 951 || 310 || 97 || 25 || 54 || |
|align=left| Connecticut || 2,648 || 951 || 310 || 97 || 25 || 54 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Delaware || 8,887 || 6,153 || 4,177 || 4,509 || 3,292 || 2,605 || 2,290 || 1,798 | |align=left| Delaware || 8,887 || 6,153 || 4,177 || 4,509 || 3,292 || 2,605 || 2,290 || 1,798 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| |
|align=left| District of Columbia || – || 2,072 || 3,554 || 4,520 || 4,505 || 3,320 || 3,687 || 3,185 | ||
| |- | |||
| |align=left| Florida || – || – || – || – || 15,501 || 25,717 || 39,310 || 61,745 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Georgia || 29,264 || 59,699 || 105,218 || 149,656 || 217,531 || 280,944 || 381,682 || 462,198 | |align=left| Georgia || 29,264 || 59,699 || 105,218 || 149,656 || 217,531 || 280,944 || 381,682 || 462,198 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Illinois || |
|align=left| Illinois || – || 107 || 168 || 917 || 747 || 331 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Indiana || |
|align=left| Indiana || – || 28 || 237 || 190 || 3 || 3 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Iowa || |
|align=left| Iowa || – || – || – || – || – || 16 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Kansas || |
|align=left| Kansas || – || – || – || – || – || – || – || 2 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Kentucky || 12,430 || 40,343 || 80,561 || 126,732 || 165,213 || 182,258 || 210,981 || 225,483 | |align=left| Kentucky || 12,430 || 40,343 || 80,561 || 126,732 || 165,213 || 182,258 || 210,981 || 225,483 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Louisiana || |
|align=left| Louisiana || – || – || 34,660 || 69,064 || 109,588 || 168,452 || 244,809 || 331,726 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Maine || |
|align=left| Maine || – || – || – || – || 2 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Maryland || 103,036 || 105,635 || 111,502 || 107,398 || 102,994 || 89,737 || 90,368 || 87,189 | |align=left| Maryland || 103,036 || 105,635 || 111,502 || 107,398 || 102,994 || 89,737 || 90,368 || 87,189 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Massachusetts || |
|align=left| Massachusetts || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 1 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Michigan || |
|align=left| Michigan || – || – || 24 || 0 || 1 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Minnesota || |
|align=left| Minnesota || – || – || – || – || – || – || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Mississippi || |
|align=left| Mississippi || – || 2,995 || 14,523 || 32,814 || 65,659 || 195,211 || 309,878 || 436,631 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Missouri || |
|align=left| Missouri || – || – || – || 10,222 || 25,096 || 58,240 || 87,422 || 114,931 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Nebraska || |
|align=left| Nebraska || – || – || – || – || – || – || – || 15 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Nevada || |
|align=left| Nevada || – || – || – || – || – || – || – || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| New Hampshire || 157 || 8 || |
|align=left| New Hampshire || 157 || 8 || 0 || 0 || 3 || 1 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| New Jersey || 11,423 || 12,422 || 10,851 || 7,557 || 2,254 || 674 || 236 || 18 | |align=left| New Jersey || 11,423 || 12,422 || 10,851 || 7,557 || 2,254 || 674 || 236 || 18 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| New York || 21,193 || 20,613 || 15,017 || 10,088 || 75 || 4 || |
|align=left| New York || 21,193 || 20,613 || 15,017 || 10,088 || 75 || 4 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| North Carolina || 100,783 || 133,296 || 168,824 || 205,017 || 245,601 || 245,817 || 288,548 || 331,059 | |align=left| North Carolina || 100,783 || 133,296 || 168,824 || 205,017 || 245,601 || 245,817 || 288,548 || 331,059 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Ohio || |
|align=left| Ohio || – || 0 || 0 || 0 || 6 || 3 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Oregon || |
|align=left| Oregon || – || – || – || – || – || – || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Pennsylvania || 3,707 || 1,706 || 795 || 211 || 403 || 64 || |
|align=left| Pennsylvania || 3,707 || 1,706 || 795 || 211 || 403 || 64 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Rhode Island || 958 || 380 || 108 || 48 || 17 || 5 || |
|align=left| Rhode Island || 958 || 380 || 108 || 48 || 17 || 5 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| South Carolina || 107,094 || 146,151 || 196,365 || 251,783 || 315,401 || 327,038 || 384,984 || 402,406 | |align=left| South Carolina || 107,094 || 146,151 || 196,365 || 251,783 || 315,401 || 327,038 || 384,984 || 402,406 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Tennessee || |
|align=left| Tennessee || 3,417 || 13,584 || 44,535 || 80,107 || 141,603 || 183,059 || 239,459 || 275,719 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| Texas || |
|align=left| Texas || – || – || – || – || – || – || 58,161 || 182,566 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| |
|align=left| Utah || – || – || – || – || – || – || 26 || 29 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| |
|align=left| Vermont || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 || 0 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |align=left| |
|align=left| Virginia || 287,959 || 339,499 || 383,521 || 411,886 || 453,698 || 431,873 || 452,028 || 472,494 | ||
| |- | |||
| |align=left| West Virginia || 4,668 || 7,172 || 10,836 || 15,178 || 17,673 || 18,488 || 20,428 || 18,371 | |||
| |- | |||
| |align="left" | Wisconsin || – || – || – || – || – || 11 || 4 || 0 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| For various reasons, the census did not always include all of the slaves, especially in the West. California was admitted as a free state and reported no slaves. However, there were many slaves that were brought to work in the mines during the ].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Johnson|first=Jason B.|date=2007-01-27|title=SAN FRANCISCO / Slavery in Gold Rush days / New discoveries prompt exhibition, re-examination of state's involvement|url=https://www.sfgate.com/bayarea/article/SAN-FRANCISCO-Slavery-in-Gold-Rush-days-New-2653800.php|access-date=2022-12-29|website=SFGATE|language=en-US}}</ref> Some Californian communities openly tolerated slavery, such as ], which was mostly made up of transplants from the neighboring slave ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://sbcsentinel.com/2016/07/mormons-created-and-then-abandoned-san-bernardino/|title=Mormons Created And Then Abandoned San Bernardino|first=Mark|last=Gutglueck|publisher=San Bernardino County Sentinel}}</ref> ] never reported any slaves on the census, yet sued the government for compensation for 600 slaves that were freed when Congress outlawed slavery in the territory.<ref name=Snodgrass>{{cite book|title=The Civil War Era and Reconstruction: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural and Economic History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cWysBwAAQBAJ|author=Mary Ellen Snodgrass|page=556|isbn=978-1-317-45791-6|year=2015| publisher=Routledge }}</ref> Utah was actively trying to hide its slave population from Congress<ref>{{cite thesis|last=Ricks |first=Nathaniel R. |date=2007 |title=A Peculiar Place for the Peculiar Institution: Slavery and Sovereignty in Early Territorial Utah |type=MA thesis |publisher=Brigham Young University |url=https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/etd/1007/ |hdl=1877/etd1909}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Mormonism: A Historical Encyclopedia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qLji9wwnaoUC|page=26|author2-link=Ardis E. Parshall|author1-link=W. Paul Reeve|first1= W. Paul |last1=Reeve |first2=Ardis E |last2=Parshall|isbn=978-1-59884-107-7|year=2010| publisher=Bloomsbury Academic }}</ref> and did not report slaves in several communities.<ref>{{cite book|title=Blacks in Utah History: An Unknown Legacy|first=Ronald G.|last=Coleman|url=http://content.lib.utah.edu/utils/getfile/collection/USHSArchPub/id/5295/filename/5330.pdf}}</ref> Additionally, the census did not traditionally include Native Americans, and hence did not include Native American slaves or Native African slaves owned by Native Americans. There were hundreds of Native American slaves in California,<ref>Castillo, E.D. 1998. '''' {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061214031402/http://www.ceres.ca.gov/nahc/califindian.html |date=December 14, 2006 }}, ''California Native American Heritage Commission'', 1998. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> Utah<ref name=morrill>{{cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/congressionalgl41bailgoog|pages=–288|title=The Congressional Globe, Part 2|author=United States. Congress|publisher=Blair & Rives|year=1857}}</ref> and New Mexico<ref name=Snodgrass /> that were never recorded in the census. | |||
| ===Nat Turner, anti-literacy laws=== | |||
| In 1831, a bloody slave rebellion took place in ]. A slave named ], who was able to read and write and had "visions," started what became known as ] or the Southampton Insurrection. With the goal of freeing himself and others, Turner and his followers killed approximately fifty men, women and children, but they were eventually subdued by the militia. | |||
| ===Distribution of slaveholders=== | |||
| Nat Turner and his followers were ], and Turner's body was ]. The militia also killed more than a hundred slaves who had not been involved in the rebellion. Across the South, harsh new laws were enacted in the aftermath of the 1831 Turner Rebellion to curtail the already limited rights of African Americans. Typical was the following Virginia law against educating slaves, free blacks and children of whites and blacks:<ref name="Basu">{{citation|last=Basu|first=B.D.|title=History of Education in India under the rule of the East India Company|editor=Chatterjee, R.|url=http://www.archive.org/details/historyofeducati00basurich|accessdate=2009 March 9|place=Calcutta|publisher=Modern Review Office|pages=3–4}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| As of the ], one may compute the following statistics on slaveholding:<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150905223723/http://freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com/~ajac/|date=September 5, 2015}}, by Tom Blake, 2001–2005.</ref> | |||
| <blockquote><p>. . . very assemblage of negroes for the purpose of instruction in reading or writing, or in the night time for any purpose, shall be an unlawful assembly. Any justice may issue his warrant to any office or other person, requiring him to enter any place where such assemblage may be, and seize any negro therein; and he, or any other justice, may order such negro to be punished with stripes.</p> | |||
| <p>If a white person assemble with negroes for the purpose of instructing them to read or write, or if he associate with them in an unlawful assembly, he shall be confined in jail not exceeding six months and fined not exceeding one hundred dollars; and any justice may require him to enter into a recognizance, with sufficient security, to appear before the circuit, county or corporation court, of the county or corporation where the offence was committed, at its next term, to answer therefor, and in the mean time to keep the peace and be of good behaviour.</p></blockquote><ref name="virginia1849">{{citation|title=The Code of Virginia|pages=747–748|date=1849|place=Richmond|publisher=William F. Ritchie}}</ref> | |||
| * Enumerating slave schedules by county, 393,975 ] held 3,950,546 unnamed slaves, for an average of about ten slaves per holder. As some large holders held slaves in multiple counties and are thus multiply counted, this slightly overestimates the number of slaveholders. | |||
| These laws were often defied by individuals, among whom was noted future ] General ]{{Fact|date=December 2008}}. | |||
| * Excluding slaves, the 1860 U.S. population was 27,167,529; therefore, approximately 1.45% of free persons (roughly one in 69) was a named slaveholder (393,975 named slaveholders among 27,167,529 free persons). By counting only named slaveholders, this approach does not acknowledge people who benefited from slavery by being in a slaveowning household, e.g., the wife and children of an owner; in 1850, there was an average of 5.55 people per household,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/10/01/the-number-of-people-in-the-average-u-s-household-is-going-up-for-the-first-time-in-over-160-years/|title=The number of people in the average U.S. household is going up for the first time in over 160 years|first=Richard|last=Fry|date=October 2019 }}</ref> so on average, around 8.05% of free persons lived in a slave-owning household. In the South, 33% of families owned at least one slave.{{citation needed|date=February 2020}} According to historian Joseph Glatthaar, the number of soldiers of the Confederacy's Army of Northern Virginia who either owned slaves or came from slave owning households is "almost one of every two 1861 recruits". In addition he notes that, "Untold numbers of enlistees rented land from, sold crops to, or worked for slaveholders. In the final tabulation, the vast majority of the volunteers of 1861 had a direct connection to slavery."<ref>{{Cite book|last=Glatthaar |first=Joseph |title=General Lee's Army: From Victory to Collapse |location=New York |publisher=Free Press |year=2009 |pages=20, 474 |isbn=978-1-4165-9697-4}}</ref> | |||
| * It is estimated by the transcriber Tom Blake, that holders of 200 or more slaves, constituting less than 1% of all U.S. slaveholders (fewer than 4,000 persons, one in 7,000 free persons, or 0.015% of the population) held an estimated 20–30% of all slaves (800,000 to 1,200,000 slaves). Nineteen holders of 500 or more slaves have been identified.<ref name="largest"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130719043247/http://freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com/~ajac/biggest16.htm |date=July 19, 2013 }}, Transcribed by Tom Blake, April to July 2001, (updated October 2001 and December 2004; now includes 19 holders)</ref> The largest slaveholder was ], of ], who in 1850 held 1,092 slaves,<ref name="dap2008" /> and whose heirs in 1860 held 1,130 or 1,131 slaves<ref name="largest" /><ref name="dap2008" />{{snd}}he was dubbed "the king of the rice planters",<ref name="dap2008">{{cite journal | last1 = Pargas | first1 = Damian Alan | year = 2008 | title = Boundaries and Opportunities: Comparing Slave Family Formation in the Antebellum South | url = http://jfh.sagepub.com/cgi/reprint/33/3/316.pdf | journal = Journal of Family History | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 316–345 | doi = 10.1177/0363199008318919 | pmid = 18831111 | s2cid = 22302394 }}{{Dead link|date=April 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> and one of his plantations is now part of ]. | |||
| * The percentage of families that owned slaves in 1860 in various groupings of states was as follows:<ref>{{cite book |last=Bonekemper III |first=Edward H. |author-link=Edward H. Bonekemper |title=The Myth of the Lost Cause: Why the South Fought the Civil War and Why the North Won |year=2015 |publisher=Regnery Publishing |location=Washington, D.C. |page=39 }}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| ==1850s== | |||
| |- | |||
| ===Bleeding Kansas=== | |||
| ! Group of States | |||
| After the passage of the ], 1854, the border wars broke out in ], where the question of whether it would be admitted to the Union as a ] or ] was left to the inhabitants. Abolitionist ] was active in the rebellion and killing in "]" as were many white Southerners. At the same time, fears that the Slave Power was seizing full control of the national government swept anti-slavery Republicans into office. | |||
| ! States in Group | |||
| ! Slave-Owning Families | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="width: 325px;"|15 states where slavery was legal | |||
| | style="width: 600px;"|Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia | |||
| | style="width: 50px; padding-left: 2.5em;"|26% | |||
| |- | |||
| | 11 states that seceded | |||
| | Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia | |||
| | style="width: 50px; padding-left: 2.5em;"|31% | |||
| |- | |||
| | 7 states that seceded before Lincoln's inauguration | |||
| | Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Texas | |||
| | style="width: 50px; padding-left: 2.5em;"|37% | |||
| |- | |||
| | 4 states that seceded later | |||
| | Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia | |||
| | style="width: 50px; padding-left: 2.5em;"|25% | |||
| |- | |||
| | 4 slave states that did not secede | |||
| | Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri | |||
| | style="width: 50px; padding-left: 2.5em;"|16% | |||
| |} | |||
| == |
==Historiography== | ||
| {{Main|Historiography of the United States#Slavery and black history}} | |||
| ] was a 46 or 47-year old slave who sued for his freedom after the death of his owner on the grounds that he had lived in a territory where slavery was forbidden (the northern part of the ], from which slavery was excluded under the terms of the ]). Scott filed suit for freedom in 1846 and went through two state trials, the first denying and the second granting freedom. Eleven years later the ] denied Scott his freedom in a sweeping decision that set the United States on course for ]. The court ruled that Dred Scott was not a ] who had a right to sue in the Federal courts, and that Congress had no constitutional power to pass the Missouri Compromise. | |||
| {{See also|Bibliography of slavery in the United States}} | |||
| ], 500–506 Chartres, New Orleans (Richard Koch, ], April 1934)]] | |||
| The historian ], writing in 1993, noted that until the latter decades of the 20th century, historians of slavery had primarily concerned themselves with the culture, practices and economics of the slaveholders, not with the slaves. This was in part due to the circumstance that most slaveholders were literate and left behind written records, whereas slaves were largely illiterate and not in a position to leave written records. Scholars differed as to whether slavery should be considered a benign or a "harshly exploitive" institution.<ref name="Kolchin p. 134">Kolchin p. 134.</ref> | |||
| The 1857 ], decided 7-2, held that a slave did not become free when taken into a free state; Congress could not bar slavery from a territory; and blacks could not be citizens. Furthermore, a state could not bar slaveowners from bringing slaves into that state. This decision, seen as unjust by many Republicans including ], was also seen as proof that the ] had seized control of the Supreme Court. The decision, written by ] ], barred slaves and their descendants from citizenship. The decision enraged abolitionists and encouraged slave owners, helping to push the country towards civil war.<ref>Don E. Fehrenbacher, ''The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics'' (New York: Oxford University Press, 1978)</ref> | |||
| Much of the history written prior to the 1950s had a distinctive racist slant to it.<ref name="Kolchin p. 134" /> By the 1970s and 1980s, historians were using ] records, black ] and statistical data to develop a much more detailed and nuanced picture of slave life. Individuals were shown to have been resilient and somewhat autonomous in many of their activities, within the limits of their situation and despite its precariousness. Historians who wrote in this era include ] ('']''), ] (''Roll, Jordan, Roll''), Leslie Howard Owens (''This Species of Property''), and ] ('']'').<ref>Kolchin pp. 137–143. Horton and Horton p. 9.</ref> | |||
| ==Civil War and Emancipation== | |||
| ===1860 presidential election=== | |||
| The divisions became fully exposed with the ]. The electorate split four ways. The Southern Democrats endorsed slavery, while the Republicans denounced it. The Northern Democrats said democracy required the people to decide on slavery locally. The ] said the survival of the Union was at stake and everything else should be compromised. | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| Lincoln, the Republican, won with a plurality of popular votes and a majority of ]. Lincoln, however, did not appear on the ballots of ten southern states: thus his election necessarily split the nation along sectional lines. Many slave owners in the South feared that the real intent of the Republicans was the abolition of slavery in states where it already existed, and that the sudden emancipation of four million slaves would be problematic for the slave owners and for the economy that drew its greatest profits from the labor of people who were not paid. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| They also argued that banning slavery in new states would upset what they saw as a delicate balance of free states and slave states. They feared that ending this balance could lead to the domination of the industrial North with its preference for high ]s on imported goods. The combination of these factors led the South to ], and thus began the ]. Northern leaders had viewed the slavery interests as a threat politically, and with secession, they viewed the prospect of a new southern nation, the ], with control over the ] and the ], as politically and militarily unacceptable. | |||
| {{Portal|Business|History|United States}} | |||
| {{div col}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (ADOS) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{slink|Historiography of the United States#Slavery and black history}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{slink|Slave narrative#North American slave narratives}} | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ===Histories of slavery in the Western Hemisphere=== | |||
| ===Civil War=== | |||
| * ] | |||
| The consequent ], beginning in 1861, led to the end of chattel slavery in America. Not long after the war broke out, through a legal maneuver credited to Union General ], a lawyer by profession, slaves who came into Union "possession" were considered ]. General Butler ruled that they were not subject to return to Confederate owners as they had been before the war. Soon word spread, and many slaves sought refuge in Union territory, desiring to be declared "contraband." Many of the "contrabands" joined the ] as workers or troops, forming entire regiments of the ]. Others went to refugee camps such as the ] near ] or fled to northern cities. General Butler's interpretation was reinforced when Congress passed the ], which declared that any property used by the Confederate military, including slaves, could be confiscated by Union forces. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| Lincoln's ] of January 1, 1863 was a powerful move that promised freedom for slaves in the Confederacy as soon as the Union armies reached them, and authorized the enlistment of African Americans in the Union Army. The Emancipation Proclamation did not free slaves in the Union-allied slave-holding states that bordered the Confederacy. Since the Confederate States did not recognize the authority of President Lincoln, and the proclamation did not apply in the ], at first the proclamation freed only slaves who had escaped behind Union lines. Still, the proclamation made the abolition of slavery an official war goal that was implemented as the Union took territory from the Confederacy. According to the Census of 1860, this policy would free nearly four million slaves, or over 12% of the total population of the United States. | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ]'', history's most famous ] novel]] | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| The ] abolished slavery on February 24, 1863 in the newly formed ]. ] and all of the border states (except ]) abolished slavery by early 1865. Thousands of slaves were freed by the operation of the Emancipation Proclamation as Union armies marched across the South. Emancipation as a reality came to the remaining southern slaves after the surrender of all Confederate troops in spring 1865. | |||
| {{Main|Bibliography of slavery in the United States}} | |||
| ===National and comparative studies=== | |||
| At the beginning of the war, some Union commanders thought they were supposed to return escaped slaves to their masters. By 1862, when it became clear that this would be a long war, the question of what to do about slavery became more general. The Southern economy and military effort depended on slave labor. It began to seem unreasonable to protect slavery while blockading Southern commerce and destroying Southern production. As one Congressman put it, the slaves "…cannot be neutral. As laborers, if not as soldiers, they will be allies of the rebels, or of the Union."<ref>McPherson, ''Battle Cry of Freedom'' page 495</ref> The same Congressman—and his fellow Radical Republicans—put pressure on Lincoln to rapidly emancipate the slaves, whereas moderate Republicans came to accept gradual, compensated emancipation and colonization.<ref>McPherson, ''Battle Cry'' page 355, 494–6, quote from ] on 495.</ref> ], the ] and ] opposed emancipation, although the border states and War Democrats eventually accepted it as part of ] needed to save the Union. | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Aptheker |first=Herbert |author-link=Herbert Aptheker |title=Negro Slave Revolts in the United States (1526–1860) |publisher=International Publishers |year=1939 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/dli.ernet.734/page/1/mode/2up -->}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Aptheker |first=Herbert |author-mask=2 |title=American Negro Slave Revolts |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=1945 |orig-date=1943 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.84187/page/n7/mode/2up -->}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Arthur |first=John |author-link=John Arthur (philosopher) |title=Race, Equality, and the Burdens of History |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |year=2007 |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/raceequalityburd0000arth/page/n3/mode/2up -->}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Baptist |first=Edward E. |author-link=Edward E. Baptist |title=The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism |publisher=Basic Books |year=2016 |location=New York |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/halfhasneverbeen0000bapt_c1d5--> |isbn=978-0-465-04966-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bateman |first1=Fred |author1-link=Fred Bateman |last2=Weiss |first2=Thomas |title=A Deplorable Scarcity: The Failure of Industrialization in the Slave Economy |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |year=1980 |location=Chapel Hill, NC |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/deplorablescarci0000bate/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8078-1447-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Beckert |first=Sven |author-link=Sven Beckert |title=Empire of Cotton: A Global History |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |year=2014 |location=New York |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/empireofcottongl0000beck--> |isbn=978-0-375-41414-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berlin |first=Ira |author-link=Ira Berlin |title=Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves |publisher=Belknap Press of Harvard University Press |year=2003 |location=Cambridge, MA |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/generationsofcap00berl --> |isbn=0-674-01061-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berlin |first=Ira |author-mask=2 |title=Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America |publisher=Belknap Press of Harvard University Press |year=1998 |location=Cambridge, MA |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/manythousandsgon0000berl_w4u6--> |isbn=0-674-81092-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berlin |first=Ira |author-mask=2 |title=Slaves Without Masters: The Free Negro in the Antebellum South |publisher=The New Press |year=1992 |orig-date=1974 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/slaveswithoutmas00berl/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=1-56584-028-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Berlin |editor1-first=Ira |editor1-mask=2 |editor2-last=Hoffman |editor2-first=Ronald |title=Slavery and Freedom in the Age of the American Revolution |publisher=University Press of Virginia |year=1983 |location=Charlottesville, VA |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/slaveryfreedomin0000unse/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8139-0969-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Blackburn |first=Robin |author-link=Robin Blackburn |title=The American Crucible: Slavery, Emancipation and Human Rights |publisher=Verso |year=2011 |location=London; New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/americancrucible0000blac/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-1-84467-569-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Blackburn |first=Robin |author-mask=2 |title=The Overthrow of Colonial Slavery |publisher=Verso |year=1988 |location=London; New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/overthrowofcolon0000blac/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-86091-188-8}} | |||
| * ] ''Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II'', 2008, {{ISBN|978-0-385-50625-0}}. | |||
| * ] '']: Plantation Life in the Antebellum South'' Oxford University Press, 1979, {{ISBN|0-19-502563-6}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Brewster |first=Francis E. |title=Slavery and the Constitution. Both Sides of the Question |publisher=Unknown Publisher |year=1850 |location=Philadelphia |url=}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Childers |first=Christopher |title=The Failure of Popular Sovereignty: Slavery, Manifest Destiny, and the Radicalization of Southern Politics |publisher=University Press of Kansas |year=2012 |location=Lawrence|url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/failureofpopular0000chil --> |isbn=978-0-7006-1868-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Coughtry |first=Jay |title=The Notorious Triangle: Rhode Island and the African Slave Trade, 1700–1807 |publisher=Temple University Press |year=1981 |location=Philadelphia |url=https://archive.org/details/notorioustriangl0000coug/page/n5/mode/2up |isbn=0-87722-218-5}} | |||
| * ]. '']'', 2006. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Davis |first=David Brion |author-mask=2 |title=The Problem of Slavery in Western Culture |publisher=Pelican Books |year=1970 |orig-date=1966 |location=London |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/problemofslavery0000unse_o0v2-->}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Duberman |editor-first=Martin B. |editor-link=Martin Duberman |title=New Essays on the Abolitionists |date=1965 |location=Princeton, NJ |publisher=Princeton University Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Egerton |first=Douglas R. |title=Death or Liberty: African Americans and Revolutionary America |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2009 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/deathorlibertyaf00eger/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-19-530669-9}} | |||
| * ]. ''Slavery: A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life.'' University of Chicago Press, 1976, {{ISBN|0-226-20477-4}}. | |||
| * ] ''Slavery, Law, and Politics: The Dred Scott Case in Historical Perspective'', Oxford University Press, 1981. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Finkelman |first=Paul |author-link= Paul Finkelman |title=An Imperfect Union: Slavery, Federalism, and Comity |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |year=1981 |location=Chapel Hill|url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/imperfectunionsl0000fink/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8078-1438-5}} | |||
| * ] ''Without Consent or Contract: The Rise and Fall of American Slavery'', W.W. Norton, 1989. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Fogel |first1=Robert William |author1-link=Robert Fogel |author1-mask=2 |last2=Engerman |first2=Stanley L. |author2-link=Stanley Engerman |title=Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery |publisher=W.W. Norton Company, Inc. |year=1995 |location=New York |url= |isbn=0-393-31218-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Foner |first1=Eric |author1-link=Eric Foner |last2=Brown |first2=Joshua |author2-link=Joshua Brown (historian) |title=Forever Free: The Story of Emancipation and Reconstruction |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |year=2005 |location=New York |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/foreverfreestory00fone--> |isbn=0-375-40259-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Foner |first=Eric |author-mask=2 |title=Gateway to Freedom: The Hidden History of the Underground Railroad |publisher=W.W. Norton & Company |year=2015 |location=New York |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/gatewaytofreedom0000fone_a5t8/page/n9/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-393-35219-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Foner |first=Eric |author-mask=2 |title=The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery |publisher=W. W. Norton & Co. |year=2010 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/fierytrialabraha0000fone/page/n7/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-393-06618-0}} Pulitzer Prize. | |||
| * ] and Loren Schweninger. ''Runaway Slaves: Rebels on the Plantation'', 1999, {{ISBN|0-19-508449-7}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fredrickson |first=George M. |author-link=George M. Fredrickson |title=The Black Image in the White Mind: The Debate on Afro-American Character and Destiny, 1817–1914 |publisher=Harper & Row |year=1971 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/blackimageinwh00fred/page/n7/mode/2up --> |sbn=06-011343-X}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Freehling |first=William W. |author-link=William W. Freehling |title=The Road to Disunion, Volume I: Secessionists at Bay |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2007 |orig-date=1990 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/roadtodisunion0000free/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-19-505814-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Freehling |first=William W. |author-mask=2 |title=The Road to Disunion, Volume II: Secessionists Triumph |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2007 |orig-date=1990 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/roadtodisunionvo0000free/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-19-505815-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Frey |first=Sylvia R. |title=Water from the Rock: Black Resistance in a Revolutionary Age |publisher=Princeton University Press |year=1991 |location=Princeton, NJ |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/waterfromrockbla0000frey/page/n7/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-691-04784-7}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Indian Slave Trade'', 2002. | |||
| * ] (1974). ''Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made''. New York: Pantheon Books. {{ISBN|0-394-49131-9}}. | |||
| * —— (1967). ''The Political Economy of Slavery: Studies in the Economy and Society of the Slave South''. New York: Vintage Books. | |||
| * —— and ] (1983). ''Fruits of Merchant Capital: Slavery and Bourgeois Property in the Rise and Expansion of Capitalism''. New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|0-19-503157-1}}. | |||
| * Harrold, Stanley. ''American Abolitionism: Its Direct Political Impact from Colonial Times into Reconstruction'' (U of Virginia Press, 2019) . | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hashaw |first=Tim |title=The Birth of Black America: The First African Americans and the Pursuit of Freedom at Jamestown |publisher=Carroll & Graf Publishers |year=2007 |location=New York |url= |isbn=978-0-7867-1718-7}} | |||
| * ] ''In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period.'' Oxford University Press, 1978, {{ISBN|0-19-502745-0}}. | |||
| * Horton, James Oliver and Horton, Lois E. ''Slavery and the Making of America'', 2005, {{ISBN|0-19-517903-X}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Johnson |first=Walter |author-link=Walter Johnson (historian) |title=River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom |publisher=Belknap Press of Harvard University Press |year=2013 |location=Cambridge, MA |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/riverofdarkdream0000john--> |isbn=978-0-674-04555-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kaplan |first=Sidney |title=The Black Presence in the Era of the American Revolution, 1770–1800 |publisher=New York Graphic Society |year=1973 |location=Greenwich, CT |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/blackpresenceint00kapl/page/n7/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8212-0541-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kolchin |first=Peter |author-link=Peter Kolchin |title=American Slavery, 1619–1877 |publisher=Hill and Wang |year=1999 |orig-date=1992 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780809015542/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8090-1554-4}} | |||
| * ] ''Been in the Storm So Long: The Aftermath of Slavery'' (1979), social history of how slavery ended in the Confederacy. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Litwack |first=Leon F. |author-mask=2 |title=North of Slavery: The Negro in the Free States, 1790–1860 |publisher=University of Chicago Press |year=1961 |location=Chicago |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/northofslavery00leon/page/n5/mode/2up -->}} | |||
| * Mason, Matthew. ''Slavery and Politics in the Early American Republic'', 2006, {{ISBN|978-0-8078-3049-9}}. | |||
| * {{cite book|title=The Complete History of American Slavery|editor-first=James|editor-last=Miller|date=2001|isbn=0737704241|publisher=]|location=San Diego, California}} | |||
| * Moon, Dannell, "Slavery", article in ''Encyclopedia of Rape'', Merril D. Smith (Ed.), Greenwood Publishing Group, 2004. | |||
| * ], ''American Negro Slavery and Abolition: A Sociological Study'', Ayer Publishing, 1980. | |||
| * ] '']: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia '', W.W. Norton, 1975. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Morris |first=Thomas D. |title=Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |year=1996 |location=Chapel Hill |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/southernslavery00thom/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8078-4817-4}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Ruling Race: A History of American Slaveholders'', 1982, {{ISBN|0-393-31705-6}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Palmer |editor-first=Colin A. |editor-link=Colin A. Palmer |title=The Worlds of Unfree Labour: From Indentured Servitude to Slavery |publisher=Ashgate Publishing Company |year=1998 |location=Brookfield, VT |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/worldsofunfreela0000unse/page/n7/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-86078-515-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Robinson |first=Donald L. |title=Slavery in the Structure of American Politics, 1765–1820 |publisher=Harcourt Brace Jovanovich |year=1970 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/slaveryinstructu0000robi/page/n7/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-15-182972-1}} | |||
| * ], ed. ''Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World'', Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2007. | |||
| * ——, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Slave Resistance and Rebellion'', Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. | |||
| * Scarborough, William K. ''The Overseer: Plantation Management in the Old South'', 1984. | |||
| * Schermerhorn, Calvin. ''The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860'', Yale University Press, 2015. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Scott |first1=Daryl Michael |date=2020 |title=The Social and Intellectual Origins of 13thism |journal=Fire!!! |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=2–39 |url=<!-- https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.5323/48573836 -->}} | |||
| * Snyder, Terri L. ''The Power to Die: Slavery and Suicide in British North America'', University of Chicago Press, 2015. | |||
| * ] ''The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South'', 1956. | |||
| * Tadman, Michael. ''Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South'', University of Wisconsin Press, 1989. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Tannenbaum |first=Frank |author-link=Frank Tannenbaum |title=Slave and Citizen, the Negro in the Americas |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |year=1946 |location=New York |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/slavecitizennegr0000tann-->}} | |||
| * ]. ''Negro Population in the United States, 1790–1915'', New York: Arno Press, 1968. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wiecek |first=William M. |title=The Sources of Antislavery Constitutionalism in America, 1760–1848 |publisher=Cornell University Press |year=1977 |location=Ithaca, NY |url=https://archive.org/details/sourcesofantisla00wiec/page/n5/mode/2up |isbn=0-8014-1089-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Williams |first=Eric Eustace |title=Capitalism and Slavery |publisher=G.P. Putnam's Sons |year=1966 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/capitalismslaver00will/page/n1/mode/2up -->}} | |||
| * ] ''Historians and Slavery; A Critical Analysis of Perspectives and Irony in American Slavery and Other Recent Works'', Washington, D.C.: University Press of America, 1978. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Yafa |first=Stephen |author-link=Stephen Yafa |title=Big Cotton |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/bigcottonhowhumb00yafa/page/n5/mode/2up --> |date=2006 |publisher=Viking Penguin |isbn=0-670-03367-7}} Republished as ''Cotton: The Biography of a Revolutionary Fiber'' (2006). | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ====Journal articles==== | |||
| In 1861, Lincoln expressed the fear that premature attempts at emancipation would mean the loss of the border states. He believed that "to lose Kentucky is nearly the same as to lose the whole game."<ref>Lincoln's letter to O. H. Browning, September 22, 1861</ref> At first, Lincoln reversed attempts at emancipation by Secretary of War ] and Generals ] (in Missouri) and ] (in South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) in order to keep the loyalty of the border states and the War Democrats. | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Cohen |first1=William |date=1969 |title=Thomas Jefferson and the Problem of Slavery |url=<!-- https://doi.org/10.2307/1904203 --> |journal=The Journal of American History |volume=56 |issue=3 |pages=503–526 |doi=10.2307/1904203 |jstor=1904203}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Cushing |first1=John D. |date=1961 |title=The Cushing Court and the Abolition of Slavery in Massachusetts: More Notes on the 'Quock Walker Case' |url=<!--https://doi.org/10.2307/844116 --> |journal=The American Journal of Legal History |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=118–144 |doi=10.2307/844116|jstor=844116}} | |||
| * ] and ]. "Review: Slavery: The Progressive Institution?", ''].'' Vol. 34, No.{{spaces}}3 (September 1974) | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Finkelman |first1=Paul |author-link=Paul Finkelman |date=2001 |title=The Founders and Slavery: Little Ventured, Little Gained |url=<!-- https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1432083 --> |journal=Yale Journal of Law & the Humanities |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=413–449}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Lynd |first1=Staughton |author-link=Staughton Lynd |date=October 1963 |title=On Turner, Beard and Slavery |journal=The Journal of Negro History |volume=48 |issue=4 |pages=235–250 |publisher=University of Chicago Press|doi=10.2307/2716327 |jstor=2716327 |s2cid=149624479 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Ohline |first=Howard A. |title=Republicanism and Slavery: Origins of the Three-Fifths Clause in the United States Constitution |journal=The William and Mary Quarterly |pages=563–584 |publisher=Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture |volume=28 |issue=4 |date=October 1971 |jstor=1922187 |doi=10.2307/1922187}} | |||
| * Ransom, Roger L. "Was It Really All That Great to Be a Slave?" ''Agricultural History'', Vol. 48, No.{{spaces}}4, 1974. | |||
| * Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." Agricultural History 1970 44(4): 407–412, {{ISSN|0002-1482}}. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ====Videos==== | |||
| Lincoln mentioned his Emancipation Proclamation to members of his cabinet on July 21, 1862. Secretary of State ] told Lincoln to wait for a victory before issuing the proclamation, as to do otherwise would seem like "our last shriek on the retreat".<ref>Stephen B. Oates, ''Abraham Lincoln: The Man Behind the Myths'', page 106</ref> In September 1862 the ] provided this opportunity, and the subsequent ] added support for the proclamation.<ref>''Images of America: Altoona'', by Sr. Anne Francis Pulling, 2001, 10.</ref> Lincoln had already published a letter<ref>Letter to Greeley, August 22, 1862</ref> encouraging the border states especially to accept emancipation as necessary to save the Union. Lincoln later said that slavery was "somehow the cause of the war".<ref name="Second Inaugural"> Abraham Lincoln, Second Inaugural Address, March 4, 1865</ref> Lincoln issued his preliminary ] on September 22, 1862, and said that a final proclamation would be issued if his gradual plan based on compensated emancipation and voluntary colonization was rejected. Only the District of Columbia accepted Lincoln's gradual plan, and Lincoln issued his final Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863. In his letter to Hodges, Lincoln explained his belief that "If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong … And yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act officially upon this judgment and feeling ... I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me."<ref> Lincoln's Letter to A. G. Hodges, April 4, 1864</ref> | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * ]. '''', ], 2004. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===Slavery and the Constitution=== | |||
| Since the Emancipation Proclamation was based on the President's war powers, it only included territory held by Confederates at the time. However, the Proclamation became a symbol of the Union's growing commitment to add emancipation to the Union's definition of liberty.<ref>James McPherson, The War that Never Goes Away</ref> Lincoln also played a leading role in getting Congress to vote for the Thirteenth Amendment,<ref name="Who Freed">James McPherson, Drawn With the Sword, from the article Who Freed the Slaves?</ref> which made emancipation universal and permanent. | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Second Founding: How the Civil War and Reconstruction Remade the Constitution'' (W. W. Norton & Company, 2019). | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goldstone |first=Lawrence |title=Dark Bargain: Slavery, Profits, and the Struggle for the Constitution |publisher=Walker & Company |year=2005 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/darkbargainslave0000gold/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8027-1460-9 |ref=goldstone2005}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Drake |first=Charles E. |title=The War of Slavery upon the Constitution: Address of Charles E. Drake on the Anniversary of the Constitution Delivered in St. Louis |date=September 17, 1862 |url=}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-link=Robert Goldwin |editor-last1=Goldwin |editor-first1=Robert A. |editor-last2=Kaufman |editor-first2=Art |title=Slavery and Its Consequences: The Constitution, Equality, and Race |publisher=American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research |date=1988 |location=Washington, DC |url=https://archive.org/details/slaveryitsconseq0000unse/page/n3/mode/2up |isbn=0-8447-3649-X |ref=goldwin1988}} | |||
| * {{cite book|editor-last=Kaminski |editor-first=John P. |title=A Necessary Evil?: Slavery and the Debate over the Constitution |publisher=Madison House |year=1995 |location=Madison, WI |url=https://archive.org/details/necessaryevilsla0000unse/page/256/mode/2up |page=256 |isbn=978-0945-61216-2 |ref=kaminski1995}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Crooked Path to Abolition: Abraham Lincoln and the Antislavery Constitution'' (W. W. Norton & Company, 2021). | |||
| * Van Cleve, George William. ''A Slaveholders' Union: Slavery, Politics, and the Constitution in the Early American Republic'' (University of Chicago Press, 2019). | |||
| * ]. ''No Property in Man: Slavery and Antislavery at the Nation's Founding'' (2nd ed. Harvard University Press, 2019). | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Williamson |first=Joel |title=After Slavery: The Negro in South Carolina During Reconstruction, 1861–1877 |publisher=University Press of New England |year=1990 |location=Hanover, NH |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/afterslaverynegr0000will/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8195-6236-X}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ====Journal articles==== | |||
| Enslaved African Americans did not wait for Lincoln's action before escaping and seeking freedom behind Union lines. From early years of the war, hundreds of thousands of African Americans escaped to Union lines, especially in Union-controlled areas like ] and the ] region in 1862 Virginia, Tennessee from 1862 on, the line of Sherman's march, etc. So many African Americans fled to Union lines that commanders created camps and schools for them, where both adults and children learned to read and write. The ] entered the war effort by sending teachers south to such contraband camps, for instance, establishing schools in Norfolk and on nearby plantations. In addition, nearly 200,000 African-American men served with distinction as soldiers and sailors with Union troops. Most of those were escaped slaves. | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=David |first=C. W. A. |title=The Fugitive Slave Law of 1793 and its Antecedents |journal=The Journal of Negro History |pages=18–25 |publisher=The University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History |volume=9 |issue=1 |date=January 1924 |jstor=2713433 |doi=10.2307/2713433 |s2cid=149160543}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Dougherty |first1=Keith L. |last2=Heckelman |first2=Jac C. |date=2008 |title=Voting on Slavery at the Constitutional Convention |url=<!-- http://www.jstor.org/stable/40270762 --> |journal=Public Choice |volume=136 |issue=3/4 |pages=293–313 |doi=10.1007/s11127-008-9297-7 |jstor=40270762|s2cid=14103553 |doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Finkelman |first=Paul |author-link=Paul Finkelman |title=Slavery, the Constitution, and the Origins of the Civil War |journal=OAH Magazine of History |pages=14–18 |publisher=Oxford University Press |volume=25 |issue=2 |date=April 2011 |jstor=23210240 |doi= 10.1093/oahmag/oar004}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Finkelman |first1=Paul |author-mask=2 |date=Winter 2000 |title=Garrison's Constitution: The Covenant with Death and How It Was Made |url=<!-- https://www.archives.gov/publications/prologue/2000/winter/garrisons-constitution-1 --> |journal=Prologue Magazine |volume=32 |issue=4 |pages=14–18}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Freehling |first=William W. |author-link=William W. Freehling |title=The Founding Fathers and Slavery |journal=The American Historical Review |pages=81–93 |publisher=Oxford University Press |volume=77 |issue=1 |date=February 1972 |jstor=1856595 |doi=10.2307/1856595}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Knowles |first=Helen J. |title=Seeing the Light: Lysander Spooner's Increasingly Popular Constitutionalism |journal=Law and History Review |pages=531–558 |publisher=American Society for Legal History |volume=31 |issue=3 |date=August 2013 |jstor=23489502 |doi= 10.1017/S0738248013000242|s2cid=146391068}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Maltz |first=Earl M. |title=Slavery, Federalism, and the Structure of the Constitution |journal=The American Journal of Legal History |pages=466–498 |publisher=Oxford University Press |volume=36 |issue=4 |date=October 1992 |jstor=845555 |doi=10.2307/845555}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Patterson |first=Orlando |author-link=Orlando Patterson |title=The Unholy Trinity: Freedom, Slavery, and the American Constitution |journal=Social Research |pages=543–577 |publisher=The Johns Hopkins University Press |volume=54 |issue=3 |date=Autumn 1987 |jstor=40970472}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===State and local studies=== | |||
| Confederates enslaved captured black Union soldiers, and black soldiers especially were shot when trying to surrender at the ].<ref>Bruce Catton, ''Never Call Retreat'', page 335</ref> This led to a breakdown of the prisoner exchange program, and the growth of prison camps such as ] in Georgia, where almost 13,000 Union prisoners of war died of disease and starvation.<ref>James McPherson, Battle Cry of Freedom, pages 791–798</ref> | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite book|author=Burke, Diane Mutti |title=On Slavery's Border: Missouri's Small Slaveholding Households, 1815–1865|year=2010|publisher=University of Georgia Press|isbn=978-0-8203-3683-1}} | |||
| In spite of the South's shortage of manpower, until 1865, most Southern leaders opposed arming slaves as soldiers. However,a few Confederates discussed arming slaves since the early stages of the war, and some free blacks had even offered to fight for the South. In 1862 Georgian Congressman Warren Akin supported the enrolling of slaves with the promise of emancipation, as did the Alabama legislature. Support for doing so also grew in other Southern states. A few all black Confederate militia units, most notably the ], were formed in Louisiana at the start of the war, but were disbanded in 1862.<ref>Bergeron, Arthur W., Jr. Louisianans in the Civil War, "Louisiana's Free Men of Color in Gray", University of Missouri Press, 2002, p. 107-109.</ref> In early March, 1865, Virginia endorsed a bill to enlist black soldiers, and on March 13 the Confederate Congress did the same.<ref>Jay Winik, ''April 1865. The Month that Saved America'', p.51-59</ref> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fede |first=Andrew |title=People Without Rights: An Interpretation of the Fundamentals of the Law of Slavery in the U.S. South |publisher=Garland Publishing, Inc. |year=1992 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/peoplewithoutrig00fede/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8153-0894-9}} | |||
| * ] ''Slavery and Freedom on the Middle Ground: Maryland During the Nineteenth Century'', Yale University Press, 1985. | |||
| There still were over 250,000 slaves in Texas. Word did not reach Texas about the collapse of the Confederacy until June 19, 1865. African Americans and others celebrate that day as ], the day of freedom, in ], ] and some other states. It commemorates the date when the news finally reached slaves at ]. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Freehling |first=Alice Goodyear |title=Drift Toward Dissolution: The Virginia Slavery Debate of 1831–1832 |publisher=Louisiana State University Press |year=1982 |location=Baton Rouge, LA | url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/drifttowarddisso0000free/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8071-1035-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Holton |first=Woody |author-link=Woody Holton |title=Forced Founders: Indians, Debtors, Slaves, and the Making of the American Revolution in Virginia |publisher=University of North Carolina Press (published for the Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture, Williamsburg, Virginia) |year=1999 |location=Chapel Hill|url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/forcedfoundersin00holt/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-8078-2501-8}} | |||
| Legally, the last 40,000 or so slaves were freed in Kentucky<ref>E. Merton Coulter, ''The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky'' (1926) pp 268-270.</ref> by the final ratification of the ] in December 1865. Slaves still held in New Jersey, ], ], Maryland, Missouri and ] also ]. | |||
| * Jennison, Watson W. ''Cultivating Race: The Expansion of Slavery in Georgia, 1750–1860'', University Press of Kentucky, 2012. | |||
| * Jewett, Clayton E. and John O. Allen; ''Slavery in the South: A State-By-State History'' Greenwood Press, 2004. | |||
| ==Reconstruction to present== | |||
| * Kulikoff, Alan. ''Tobacco and Slaves: The Development of Southern Cultures in the Chesapeake, 1680–1800'' University of North Carolina Press, 1986. | |||
| During ], it was a serious question whether slavery had been permanently abolished or whether some form of semi-slavery would appear after the Union armies left. Over time a large ] arose to bring full civil rights and equality under the law to all Americans. | |||
| * ]; ''Slavery in the Cherokee Nation: The Keetoowah Society and the Defining of a People, 1855–1867'', 2003. | |||
| * Mohr, Clarence L. ''On the Threshold of Freedom: Masters and Slaves in Civil War Georgia'' University of Georgia Press, 1986. | |||
| ===Sharecropping=== | |||
| * Mooney, Chase C. ''Slavery in Tennessee'', Indiana University Press, 1957. | |||
| An 1867 federal law prohibited a descendant form of slavery known as ] or ], which still existed in the ] as a legacy of ]. Between 1903 and 1944, the Supreme Court ruled on several cases involving debt bondage of black Americans, declaring these arrangements unconstitutional. In actual practice, however, sharecropping arrangements often resulted in ] for both black and white farmers in the South. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Morgan |first=Edmund S. |author-link=Edmund Morgan (historian) |title=American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia |publisher=W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. |year=1995 |orig-date=1975 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/americanslaverya0000morg/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-393-31288-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Nash |first=Gary B. |author-link=Gary B. Nash |title=Freedom by Degrees: Emancipation in Pennsylvania and Its Aftermath |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1991 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/freedombydegrees0000nash/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-19-504583-1}} | |||
| ===Educational issues=== | |||
| * Olwell, Robert. ''Masters, Slaves, & Subjects: The Culture of Power in the South Carolina Low Country, 1740–1790'' Cornell University Press, 1998. | |||
| The anti-literacy laws after 1832 contributed greatly to the problem of widespread illiteracy facing the ] and other African Americans after Emancipation and the Civil War 35 years later. The problem of illiteracy and need for education was seen as one of the greatest challenges confronting these people as they sought to join the ] and support themselves during Reconstruction and thereafter. | |||
| * Reidy, Joseph P. ''From Slavery to Agrarian Capitalism in the Cotton Plantation South, Central Georgia, 1800–1880'' University of North Carolina Press, 1992. | |||
| * Ripley, C. Peter. ''Slaves and Freemen in Civil War Louisiana'' Louisiana State University Press, 1976. | |||
| Consequently, many black and white religious organizations, former Union Army officers and soldiers, and wealthy philanthropists were inspired to create and fund educational efforts specifically for the betterment of African Americans in the South. Blacks started their own schools even before the end of the war. Northerners helped create numerous ]s, such as those that became ] and ], to generate teachers. Blacks held teaching as a high calling, with education the first priority for children and adults. Many of the most talented went into the field. Some of the schools took years to reach a high standard, but they managed to get thousands of teachers started. As W. E. B. Du Bois noted, the black colleges were not perfect, but "in a single generation they put thirty thousand black teachers in the South" and "wiped out the illiteracy of the majority of black people in the land."<ref>James D. Anderson, ''The Education of Blacks in the South, 1860-1935'', Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 1988, pp.244-245 </ref> | |||
| * Rivers, Larry Eugene. ''Slavery in Florida: Territorial Days to Emancipation'', University Press of Florida, 2000. | |||
| * Sellers, James Benson; ''Slavery in Alabama'' University of Alabama Press, 1950. | |||
| Northern philanthropists continued to support black education in the 20th century, even as tensions rose within the black community, exemplified by Dr. Booker T. Washington and Dr. ], as to the proper emphasis between industrial and classical academic education at the college level. Collaborating with Dr. ] in the early decades of the 20th century, philanthropist ] provided matching funds for community efforts to build rural schools for black children. He insisted on white and black cooperation in the effort, wanting to ensure that white-controlled school boards made a commitment to maintain the schools. By the 1930s local parents had helped raise funds (sometimes donating labor and land) to create over 5,000 rural schools in the South. Other philanthropists such as ] and ], each of whom had arisen from modest roots to become wealthy, used matching fund grants to stimulate local development of libraries and schools. | |||
| * Sydnor, Charles S. ''Slavery in Mississippi'', 1933. | |||
| * Takagi, Midori. ''Rearing Wolves to Our Own Destruction: Slavery in Richmond, Virginia, 1782–1865'' University Press of Virginia, 1999. | |||
| ===Apologies=== | |||
| * Taylor, Joe Gray. ''Negro Slavery in Louisiana''. Louisiana Historical Society, 1963. | |||
| On February 24, 2007, the ] passed House Joint Resolution Number 728 acknowledging "with profound regret the involuntary servitude of Africans and the exploitation of Native Americans, and call for reconciliation among all Virginians."<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/02/25/AR2007022500470.html |title=Virginia Apologizes for Role in Slavery |publisher=The Washington Post |first=Larry |last=O'Dell |date=]}}</ref> With the passing of this resolution, Virginia became the first state to acknowledge through the state's governing body their state's negative involvement in slavery. The passing of this resolution came on the heels of the 400th anniversary celebration of the city of ], which was one of the first slave ports of the American colonies. | |||
| * Trexler, Harrison Anthony. ''Slavery in Missouri, 1804–1865'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1914. | |||
| * ] ''Black Majority: Negroes in Colonial South Carolina from 1670 through the Stono Rebellion'' W.W. Norton & Company, 1974. | |||
| On July 30, 2008, the ] passed a resolution apologizing for American slavery and subsequent discriminatory laws.<ref></ref> The U.S. Senate unanimously passed a similar resolution on June 18, 2009; it also explicitly states that it cannot be used for restitution claims.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/06/18/AR2009061803877.html|title=Senate Backs Apology for Slavery|last=Thompson|first=Krissah|date=2009-06-19|work=The Washington Post|accessdate=2009-06-21}}</ref> | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Arguments used to justify slavery== | |||
| {{seealso|Proslavery in the antebellum United States}} | |||
| ==="A necessary evil"=== | |||
| In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". It was feared that emancipation would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. In 1820, ] wrote in a letter that with slavery: | |||
| {{quote|We have the wolf by the ear, and we can neither hold him, nor safely let him go. Justice is in one scale, and self-preservation in the other.<ref>Jefferson, Thomas. Letter to ], April 22, 1820. ''Library of Congress''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref>|}} | |||
| ] wrote in 1856: | |||
| {{quote|There are few, I believe, in this enlightened age, who will not acknowledge that slavery as an institution is a moral and political evil. It is idle to expatiate on its disadvantages. I think it is a greater evil to the white than to the colored race. While my feelings are strongly enlisted in behalf of the latter, my sympathies are more deeply engaged for the former. The blacks are immeasurably better off here than in Africa, morally, physically, and socially. The painful discipline they are undergoing is necessary for their further instruction as a race, and will prepare them, I hope, for better things. How long their servitude may be necessary is known and ordered by a merciful Providence.<ref>Lee, R.E. ", letter to president ], December 27, 1856. ''civilwarhome.com''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref>|}} | |||
| ==="A positive good"=== | |||
| However, as the abolition agitation increased and the planting system expanded, apologies for slavery became more faint in the South. Then apologies were superseded by claims that slavery was a beneficial scheme of labor control. ], in a famous speech in the ] in 1837, declared that slavery was "instead of an evil, a good—a positive good." Calhoun supported his view with the following reasoning: in every civilized society one portion of the community must live on the labor of another; learning, science, and the arts are built upon leisure; the African slave, kindly treated by his master and mistress and looked after in his old age, is better off than the free laborers of Europe; and under the slave system conflicts between capital and labor are avoided. The advantages of slavery in this respect, he concluded, "will become more and more manifest, if left undisturbed by interference from without, as the country advances in wealth and numbers."<ref>Beard C.A. and M.R. Beard. 1921. . No copyright in the United States, p. 316.</ref> | |||
| Others who also moved from the idea of necessary evil to positive good are ] and ]. Hammond, like Calhoun, believed slavery was needed to build the rest of society. In a speech to the Senate on March 4, 1858, Hammond developed his Mudsill Theory defending his view on slavery stating, “Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement. It constitutes the very mud-sill of society and of political government; and you might as well attempt to build a house in the air, as to build either the one or the other, except on this mud-sill.” He argued that the hired laborers of the North are slaves too: “The difference… is, that our slaves are hired for life and well compensated; there is no starvation, no begging, no want of employment,” while those in the North had to search for employment.<ref>James Henry Hammond. . Senate floor speech, March 4, 1858. Retrieved July 21, 2008.</ref> George Fitzhugh wrote that, “the Negro is but a grown up child, and must be governed as a child.” In "The Universal Law of Slavery" Fitzhugh argues that slavery provides everything necessary for life and that the slave is unable to survive in a free world because he is lazy, and cannot compete with the intelligent European white race.<ref>George Fitzhugh. in ''The Black American: A Documentary History'', Third Ed. (Leslie H. Fishel, Benjamin Quarles, ed.). 1970. Retrieved July 21, 2008.</ref> | |||
| ==Native Americans== | |||
| {{details|Slavery among Native Americans in the United States}} | |||
| ===Enslavement of Native Americans=== | |||
| During the 17th and 18th century, ], the enslavement of Native Americans by ], was common. Many of these Native slaves were exported to off-shore colonies, especially the "sugar islands" of the ]. Historian Alan Gallay estimates that from 1670-1715, British slave traders sold between 24,000 and 51,000 Native Americans from what is now the southern part of the U.S.<ref>Gallay, Alan. (2002) ''The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670-171''. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7.</ref> | |||
| Slavery of Native Americans was organized in ] and ] through ] missions, theoretically entitled to ten years of Native labor, but in practice maintaining them in perpetual servitude, until their charge was revoked in the mid-1830s. Following the 1847–1848 ], Native Californians were enslaved in the new state from statehood in 1850 to 1867.<ref>Castillo, E.D. 1998. '', ''California Native American Heritage Commission'', 1998. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> Slavery required the posting of a bond by the slave holder and enslavement occurred through raids and a four-month servitude imposed as a punishment for Indian "]".<ref>] (1918). "Slavery in California," ''The Journal of Negro History'', Vol. 3, No. 1. (Jan.), pp. 33-44.</ref> | |||
| ====Videos==== | |||
| ===Slavery among Native Americans=== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| The ] and ] Indians who lived along southeast ]'s coast were traditionally known as fierce warriors and slave-traders, raiding as far as California. Slavery was hereditary after slaves were taken as ]. Among some ] tribes, about a quarter of the population were slaves.<ref>, ''Digital History''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref><ref>, ''civilization.ca''. Retrieved October 24, 2007.</ref> Other slave-owning tribes of North America were, for example, ] of Texas, ] of Georgia, the fishing societies, such as the ], that lived along the coast from what is now Alaska to California, the ], and ].<ref name="britannica"/> | |||
| * Jenkins, Gary (director). ''Negroes To Hire'' ; 52 minutes DVD; on slavery in Missouri | |||
| * {{cite video |title=A Moral Debt: The Legacy of Slavery in the USA |first=James |last=Gannon |work=] |date=October 25, 2018 |quote=Gannon is a descendant of Robert E. Lee |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/aljazeeracorrespondent/2018/10/moral-debt-legacy-slavery-usa-181017093941707.html |ref=none |access-date=October 28, 2018 |archive-date=July 22, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190722120128/https://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/aljazeeracorrespondent/2018/10/moral-debt-legacy-slavery-usa-181017093941707.html}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===Historiography and memory=== | |||
| After 1800, the ]s and some other tribes started buying and using black slaves, a practice they continued after being relocated to ] in the 1830s.<ref>A history of the descendants of the slaves of Cherokee can be found at Sturm, Circe. ''Blood Politics, Racial Classification, and Cherokee National Identity: The Trials and Tribulations of the Cherokee Freedmen''. American Indian Quarterly, Vol. 22, No. 1/2. (Winter - Spring, 1998), pp. 230-258. In 1835, 7.4% of Cherokee families held slaves. In comparison, nearly one-third of white families living in Confederate states owned slaves in 1860. Further analysis of the 1835 Federal Cherokee Census can be found in Mcloughlin, WG. "The Cherokees in Transition: a Statistical Analysis of the Federal Cherokee Census of 1835". 'Journal of American History'', Vol. 64, 3, 1977, p. 678. A discussion on the total number of Slave holding families can be found in Olsen, Otto H. "Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States", ''Civil War History'', December 2004 (Accessed June 8, 2007)</ref> | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * ] "The American Civil War, Emancipation, and Reconstruction on the World Stage," ''OAH Magazine of History'', January 2006, Vol. 20, Issue 1, pp.{{spaces}}54–60 | |||
| * ]. "American Slavery in History and Memory and the Search for Social Justice", ''The Journal of American History'', March 2004, Vol. 90, Issue 4, pp.{{spaces}}1251–1268. | |||
| * Boles, John B. and Evelyn T. Nolen, eds., ''Interpreting Southern History: Historiographical Essays in Honor of Sanford W. Higginbotham'' (1987). | |||
| * ]. "Social Death and Political Life in the Study of Slavery", ''American Historical Review'', December 2009, Vol. 114, Issue 5, pp.{{spaces}}1231–1249, examined historical and sociological studies since the influential 1982 book ''Slavery and Social Death'' by American sociologist ]. | |||
| * Campbell, Gwyn. "Children and slavery in the new world: A review", ''Slavery & Abolition'', August 2006, Vol. 27, Issue 2, pp.{{spaces}}261–285 | |||
| * Collins, Bruce. "Review: American Slavery and Its Consequences" ''Historical Journal'' (1979) 33#4 pp.{{spaces}}997–1015 | |||
| * Dirck, Brian. "Changing Perspectives on Lincoln, Race, and Slavery," ''OAH Magazine of History'', October 2007, Vol. 21, Issue 4, pp.{{spaces}}9–12. | |||
| * Farrow, Anne; Lang, Joel; Frank, Jenifer. ''Complicity: How the North Promoted, Prolonged, and Profited from Slavery'', Ballantine Books, 2006, {{ISBN|0-345-46783-3}}. | |||
| * ] ''The Slavery Debates, 1952–1990: A Retrospective'', 2007. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Deliver Us from Evil. The Slavery Question in the Old South |first=Lacy K. |last=Ford |year=2009 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-511809-4}} | |||
| * Fox-Amato, Matthew. ''Exposing Slavery: Photography, Human Bondage, and the Birth of Modern Visual Politics in America'' (Oxford University Press, 2019). | |||
| * Frey, Sylvia R. "The Visible Church: Historiography of African American Religion since Raboteau", ''Slavery & Abolition'', January 2008, Vol. 29 Issue 1, pp.{{spaces}}83–110 | |||
| * Hettle, Wallace. "White Society in the Old South: The Literary Evidence Reconsidered", ''Southern Studies: An Interdisciplinary Journal of the South'', Fall/Winter 2006, Vol. 13, Issue 3/4, pp. 29–44 | |||
| * King, Richard H. "Review: Marxism and the Slave South", ''American Quarterly'' 29 (1977), 117–131. focus on Genovese. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Klarman |first=Michael J. |author-link=Michael Klarman |title=Unfinished Business: Racial Equality in American History |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2016 |location=New York |isbn=978-0-19-994203-9}} | |||
| * ]. "American Historians and Antebellum Southern Slavery, 1959–1984", in ], Michael F. Holt, and ], eds., ''A Master's Due: Essays in Honor of David Herbert Donald'' (1985), 87–111 | |||
| * Laurie, Bruce. "Workers, Abolitionists, and the Historians: A Historiographical Perspective", ''Labor: Studies in Working Class History of the Americas'', Winter 2008, Vol. 5, Issue 4, pp.{{spaces}}17–55 | |||
| * ] "Lincoln, Slavery, and the Nation," ''The Journal of American History'', September 2009, Vol. 96 Issue 2, pp.{{spaces}}456–458. | |||
| * Parish; Peter J. ''Slavery: History and Historians'' Westview Press. 1989. | |||
| * ]. "Writing Slavery's History", ''OAH Magazine of History'', April 2009, Vol. 23 Issue 2, pp.{{spaces}}13–20. | |||
| * Rael, Patrick. ''Eighty-Eight Years: The Long Death of Slavery in the United States, 1777–1865.'' Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 2015. | |||
| * Sidbury, James. "Globalization, Creolization, and the Not-So-Peculiar Institution", ''Journal of Southern History'', August 2007, Vol. 73, Issue 3, pp.{{spaces}}617–630, on colonial era. | |||
| * Stuckey, P. Sterling. "Reflections on the Scholarship of African Origins and Influence in American Slavery", ''Journal of African American History'', Fall 2006, Vol. 91 Issue 4, pp.{{spaces}}425–443. | |||
| * Sweet, John Wood. "The Subject of the Slave Trade: Recent Currents in the Histories of the Atlantic, Great Britain, and Western Africa," ''Early American Studies, An Interdisciplinary Journal'', Spring 2009, Vol.{{spaces}}7 Issue 1, pp.{{spaces}}1–45 | |||
| * Tadman, Michael. "The Reputation of the Slave Trader in Southern History and the Social Memory of the South", ''American Nineteenth Century History'', September 2007, Vol. 8, Issue 3, pp.{{spaces}}247–271 | |||
| * Tulloch, Hugh. ''The Debate on the American Civil War Era'' (1998), ch. 2–4 | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| The nature of ] often mirrored that of white slave-owning society. The law barred intermarriage of Cherokees and blacks, whether slave or free. Cherokee who aided slaves were punished with one hundred lashes on the back. In Cherokee society, blacks were barred from holding office, bearing arms, and owning property, and they made it illegal to teach blacks to read and write.<ref>Duncan, J.W. 1928. . ''Chronicles of Oklahoma'' '''6(2)''':178-180. Retrieved July 13, 2007.</ref><ref>Davis, J. B. 1933. . ''Chronicles of Oklahoma'' '''11(4)''':1056-1072. Retrieved July 13, 2007.</ref> | |||
| By contrast, the ]s welcomed into their nation African Americans who had ] slavery (]). | |||
| ==Barbary states== | |||
| According to Robert Davis, between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by ] and sold as slaves in ] and ] between the 16th and 19th centuries.<ref>Davis, Robert. ''Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500-1800''. </ref><ref>, ''Research News'', Ohio State University</ref> Because of the large numbers of Britons captured by the Barbary States and in other venues, captivity was the other side of exploration and empire. Captivity narratives originated as a literary form in the 17th century. They were widely published and read, preceding those of colonists captured by American Indians in North America.<ref>Linda Colley, ''Captives: Britain, Empire and the World, 1600-1850'', London: Jonathan Cape, 2002, pp. 9-11</ref> Slave-taking persisted into the 19th century when Barbary pirates would capture ships and enslave the crew. Between 1609 and 1616, ] alone had 466 merchant ships lost to Barbary pirates.<ref>Rees Davies, , ], 1 July 2003</ref> | |||
| ] commercial ships were not immune from pirate attacks. In 1783, the United States made peace with, and gained recognition from, the ]. In 1784 the first American ship was seized by pirates from ]. By late 1793, a dozen American ships had been captured, goods stripped and everyone enslaved. After some serious debate, the government created the ] in March 1794. This new military presence helped to stiffen American resolve to resist the continuation of tribute payments, leading to the two ] along the North African coast: the ] from 1801 to 1805<ref></ref> and the ] in 1815. Payments in ransom and tribute to the Barbary states had amounted to 20% of United States government annual revenues in 1800.<ref>{{cite web|last=Oren|first=Michael B.|title=The Middle East and the Making of the United States, 1776 to 1815|date=2005-11-03|url=http://www.columbia.edu/cu/news/05/11/michaelOren.html|accessdate=2007-02-18}}</ref> It was not until 1815 that naval victories ended tribute payments by the U.S. Some European nations continued annual payments until the 1830s.<ref>Richard Leiby, , '']'', October 15, 2001</ref> | |||
| ==Free black people and slavery== | |||
| Some slaveholders were black or had some black ancestry. In 1830 there were 3,775 such slaveholders in the South, with 80% of them located in Louisiana, South Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland. There were economic differences between free blacks of the Upper South and Deep South, with the latter fewer in number, but wealthier and typically of mixed race. Half of the black slaveholders lived in cities rather than the countryside, with most in New Orleans and ]. Especially New Orleans had a large, relatively wealthy ] population ('']'') composed of people of mixed race, who had become a third class between whites and enslaved blacks under French and Spanish rule. Relatively few slaveholders were “substantial planters.” Of those who were, most were of mixed race, often endowed by white fathers with some property and social capital.<ref>Stampp p. 194. Oakes pp.47-48.</ref> Historians John Hope Franklin and Loren Schweninger wrote: | |||
| {{quote|A large majority of profit-oriented free black slaveholders resided in the Lower South. For the most part, they were persons of mixed racial origin, often women who cohabited or were mistresses of white men, or mulatto men ... . Provided land and slaves by whites, they owned farms and plantations, worked their hands in the rice, cotton, and sugar fields, and like their white contemporaries were troubled with runaways.<ref>Franklin and Schweninger p. 201</ref>}} | |||
| Historian Ira Berlin wrote: | |||
| {{quote|In slave societies, nearly everyone – free and slave – aspired to enter the slaveholding class, and upon occasion some former slaves rose into slaveholders’ ranks. Their acceptance was grudging, as they carried the stigma of bondage in their lineage and, in the case of American slavery, color in their skin.<ref>Berlin, "Generations of Captivity" p. 9</ref>}} | |||
| Free blacks were perceived “as a continual symbolic threat to slaveholders, challenging the idea that ‘black’ and ‘slave’ were synonymous.” Free blacks were seen as potential allies of fugitive slaves and “slaveholders bore witness to their fear and loathing of free blacks in no uncertain terms."<ref>Mason pp. 19-20</ref> For free blacks, who had only a precarious hold on freedom, “slave ownership was not simply an economic convenience but indispensable evidence of the free blacks” determination to break with their slave past and their silent acceptance – if not approval – of slavery.”<ref>Berlin, ''Generations of Captivity'', p. 138</ref> | |||
| Historian James Oakes notes that, “The evidence is overwhelming that the vast majority of black slaveholders were free men who purchased members of their families or who acted out of benevolence.”<ref>Oakes pp. 47-48</ref> After 1810 southern states made it increasingly difficult for any slaveholders to free slaves. Often the purchasers of family members were left with no choice but to maintain, on paper, the owner-slave relationship. In the 1850s “there were increasing efforts to restrict the right to hold bondsmen on the grounds that slaves should be kept ‘as far as possible under the control of white men only.”<ref>Oakes pp. 47-49</ref> | |||
| In his 1985 statewide study of black slaveholders in South Carolina, Larry Koger challenged this benevolent view. He found that the majority of black slaveholders appeared to hold slaves as a commercial decision. For instance, he noted that in 1850 more than 80% of black slaveholders were of mixed race, but nearly 90% of their slaves were classified as black.<ref>Larry Koger, ''Black Slaveowners: Free Black Masters in South Carolina, 1790-1860'', Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press, 1985, Foreword</ref> He also noted the number of small artisans in Charleston who held slaves to help with their businesses. | |||
| ==Historiography of American slavery== | |||
| Historian Peter Kolchin, writing in 1993, noted that until recently historians of slavery concentrated more on the behavior of slaveholders than on slaves. Part of this was related to the fact that most slaveholders were literate and able to leave behind a written record of their perspective. Most slaves were illiterate and unable to create a written record. There were differences among scholars as to whether slavery should be considered a benign or a “harshly exploitive” institution.<ref name="Kolchin p. 134">Kolchin p. 134</ref> | |||
| Kolchin described the state of historiography in the early twentieth century as follows: | |||
| {{quote|During the first half of the twentieth century, a major component of this approach was often simply racism, manifest in the belief that blacks were, at best, imitative of whites. Thus Ulrich B. Phillips, the era's most celebrated and influential expert on slavery, combined a sophisticated portrait of the white planters' life and behavior with crude passing generalizations about the life and behavior of their black slaves.<ref name="Kolchin p. 134"/>}} | |||
| Historians James Oliver Horton and Louise Horton described Phillips' mindset, methodology and influence: | |||
| {{quote|His portrayal of blacks as passive, inferior people, whose African origins made them uncivilized, seemed to provide historical evidence for the theories of racial inferiority that supported racial segregation. Drawing evidence exclusively from plantation records, letters, southern newspapers, and other sources reflecting the slaveholder's point of view, Phillips depicted slave masters who provided for the welfare of their slaves and contended that true affection existed between master and slave.<ref>Horton and Horton p. 9. David and Temin (p. 740) add, "The considerable scholarship of Phillips and his followers was devoted to rehabilitating the progressive image of white supremacist society in the antebellum South; it provided a generally sympathetic and sometimes blatantly apologetic portrayal of slaveholders as a paternalistic breed of men."</ref>}} | |||
| The racist attitude concerning slaves carried over into the historiography of the Dunning School of reconstruction history, which dominated in the early 20th century. Writing in 2005, historian Eric Foner states: | |||
| {{quote|Their account of the era rested, as one member of the Dunning school put it, on the assumption of “negro incapacity.” Finding it impossible to believe that blacks could ever be independent actors on the stage of history, with their own aspirations and motivations, Dunning et al. portrayed African Americans either as “children”, ignorant dupes manipulated by unscrupulous whites, or as savages, their primal passions unleashed by the end of slavery.<ref>Foner p. xxii</ref>}} | |||
| Beginning in the 1930s and 1940s, historiography moved away from the “overt” racism of the Phillips era. However, historians still emphasized the slave as an object. Whereas Phillips presented the slave as the object of benign attention by the owners, historians such as Kenneth Stampp changed the emphasis to the mistreatment and abuse of the slave.<ref>Kolchin p. 135. David and Temin p. 741. The latter wrote, “The vantage point correspondingly shifted from that of the master to that of his slave. The reversal culminated in Kenneth M. Stampp's ‘The Peculiar Institution’ (1956), which rejected both the characterization of blacks as a biologically and culturally inferior, childlike people, and the depiction of the white planters as paternal Cavaliers coping with a vexing social problem that was not of their own making.”</ref> | |||
| In the culmination of the slave as victim, Historian Stanley M. Elkins in his 1959 work “Slavery: A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life” compared United States slavery to the brutality of the ]. He stated the institution destroyed the will of the slave, creating an “emasculated, docile ]” who identified totally with the owner. Elkins' thesis immediately was challenged by historians. Gradually historians recognized that in addition to the effects of the owner-slave relationship, slaves did not live in a “totally closed environment but rather in one that permitted the emergence of enormous variety and allowed slaves to pursue important relationships with persons other than their master, including those to be found in their families, churches and communities.” | |||
| Robert W. Fogel and Stanley L. Engerman in the 1970s, through their work "Time on the Cross," presented the final attempt to salvage a version of the Sambo theory, picturing slaves as having internalized the ] of their owners.<ref>Kolchin p. 136</ref> In portraying the more benign version of slavery, they also argue in their 1974 book that the material conditions under which the slaves lived and worked compared favorably to those of free workers in the agriculture and industry of the time. | |||
| In the 1970s and 1980s, historians made use of archaeological records, black folklore, and statistical data to describe a much more detailed and nuanced picture of slave life. Relying also on autobiographies of ex-slaves and former slave interviews conducted in the 1930s by the Federal Writers' Project, historians described slavery as the slaves experienced it. Far from slaves' being strictly victims or content, historians showed slaves as both resilient and autonomous in many of their activities. Despite the efforts at autonomy and their efforts to make a life within slavery, current historians recognize the precariousness of the slave's situation. Slave children quickly learned that they were subject to the direction of both their parents and their owners. They saw their parents disciplined just as they came to realize that they also could be physically or verbally abused by their owners. Historians writing during this era include John Blassingame (“Slave Community”), Eugene Genovese (“Roll, Jordon, Roll”), Leslie Howard Owens (“This Species of Property”), and Herbert Gutman (“The Black Family in Slavery and Freedom”).<ref>Kolchin pp. 137-143. Horton and Horton p. 9</ref> | |||
| Important work on slavery has continued; for instance, in 2003 Steven Hahn published the Pulitze Prize-winning account (''A Nation under Our Feet: Black Political Struggles in the Rural South from Slavery to the Great Migration''), which examined how slaves built community and political understanding even while enslaved, so they quickly began to form new associations and institutions when emancipated, including a black church separate from white control. | |||
| ==Modern slavery== | |||
| Although slave ownership by private individuals and businesses has been illegal in the United States since 1865, the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution specifically exempts the judiciary, permitting the enslavement of individuals "as a punishment for crime where of the party shall have been duly convicted". | |||
| The ] occasionally prosecutes cases against people for ] and ]. These cases often involve ] who are forced to work as slaves in factories to pay off a debt claimed by the people who transported them into the United States. Other cases have involved ]s.<ref>{{citation |last=Gilmore |first=Janet |title=Press Release: Modern slavery thriving in the U.S. |publisher=] |date=2004-09-23 |url=http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2004/09/23_16691.shtml Modern slavery thriving in the United States }}</ref> | |||
| ''The New York Times''<ref>{{citation |last=Landesman |first=Peter| publisher=] |year=2004 | url=http://www.nytimes.com/2004/01/25/magazine/25SEXTRAFFIC.html |month=Jul |author=Landesman, Ly |title=Does preparedness make a difference? |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=186–7 |issn=0160-6379 |pmid=15596963 |journal=Family & community health}}</ref>, ABC News<ref>{{citation |last=Murphy and Allen |publisher=] |url=http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/AmericanFamily/story?id=2834852&page=1}}</ref>, and ''The San Francisco Chronicle''<ref>{{citation |last=Fitzmaurice |publisher=] |url=http://www.sfgate.com/sextrafficking/}}</ref>, among others, have reported on child and teenage ] in the United States. There are also reports on children working in organized criminal businesses and in legitimate businesses under both human and inhuman conditions. | |||
| In 2002, the ] repeated an earlier ] estimate<ref>{{citation |last=Wright |first=Jennifer |title=Worldwide Tragedy: U.S. Not Immune to Sexual Slavery |publisher=] |year=2000 |url=http://www.now.org/nnt/summer-2000/slavery.html }}</ref> that each year, about 50,000 women and children are brought against their will to the United States for sexual exploitation.<ref>{{citation |title=Victims of Trafficking and Violence Protection Act of 2000: Trafficking in Persons Report |publisher=] |year=2002 |url=http://www.state.gov/g/tip/rls/tiprpt/2002/ }}</ref> Former ] ] said that "Here and abroad, the victims of trafficking toil under inhuman conditions -- in brothels, sweatshops, fields and even in private homes."<ref>{{citation |last=Powell |first=Colin L. |title=Special Briefing on Release of Trafficking in Persons Report, June 2002 |publisher=] |date=2002-06-05 |url=http://www.state.gov/secretary/former/powell/remarks/2002/10748.htm }}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{reflist|3}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| ===Primary sources=== | ===Primary sources=== | ||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * ]. ''The House of Bondage Or Charlotte Brooks and Other Slaves''. Oxford University Press, 1991. Primary sources with commentary. ISBN 0-19-506784-3 | |||
| * ]. ''The House of Bondage Or Charlotte Brooks and Other Slaves''. Oxford University Press, 1991. Primary sources with commentary. {{ISBN|0-19-506784-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Cotton is king: or, The culture of cotton, and its relation to Agriculture, Manufactures and Commerce; to the free colored people; and to those who hold that slavery is in itself sinful |author=An American |location=Cincinnati |year=1855 |publisher=Moore, Wilstach, Keys |url=https://archive.org/details/cottoniskingorcu01chri |ref=none}} | |||
| * Berlin, Ira, Joseph P. Reidy, and Leslie S. Rowlands, eds. ''Freedom: A Documentary History of Emancipation, 1861-1867'' 5 vol Cambridge University Press, 1982. Very large collection of primary sources regarding the end of slavery | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Basker |first=James G. |author-link=James Basker |title=Amazing Grace: An Anthology of Poems About Slavery, 1660–1810 |publisher=Yale University Press |year=2002 |location=New Haven, CT |url=<!--https://archive.org/details/amazinggraceanth0000unse--> |isbn=0-300-09172-9}} | |||
| * Berlin, Ira, Marc Favreau, and Steven F. Miller, eds. ''Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk About Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Emancipation'' The New Press: 2007. ISBN 978-1595582287 | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Berlin |editor1-first=Ira |editor1-link=Ira Berlin |editor2-last=Fields |editor2-first=Barbara J. |editor2-link=Barbara J. Fields |editor3-last=Miller |editor3-first=Steven F. |editor4-last=Reidy |editor4-first=Joseph P. |editor4-link=Joseph P. Reidy |editor5-last=Rowland |editor5-first=Leslie S. |title=Free at Last: A Documentary History of Slavery, Freedom, and the Civil War |publisher=The New Press |year=1992 |location=New York |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9781565841208/page/n3/mode/2up |isbn=1-56584-120-4 |ref=berlin1992}} | |||
| * Blassingame, John W., ed. ''Slave Testimony: Two Centuries of Letters, Speeches, Interviews, and Autobiographies''.Louisiana State University Press, 1977. | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Berlin |editor1-first=Ira |editor1-mask=2 |editor2-last=Rowland |editor2-first=Leslie S. |title=Families and Freedom: A Documentary History of African-American Kinship in the Civil War Era |publisher=The New Press |year=1997 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/familiesfreedomd00irab/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=1-56584-026-7 |ref=berlin1997}} | |||
| * '']'' (1845) (Project Gutenberg: ), (Audio book at FreeAudio.org ) | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Berlin |editor1-first=Ira |editor1-mask=2 |editor2-last=Favreau |editor2-first=Marc |editor3-last=Miller |editor3-first=Steven F. |title=Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk About Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Emancipation |publisher=The New Press |year=1998 |location=New York |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/rememberingslave0000irab_h1y3/page/n5/mode/2up --> |isbn=<!-- no isbn --> |ref=berlin1998}}. | |||
| * "The Heroic Slave." ''Autographs for Freedom''. Ed. Julia Griffiths Boston: Jewett and Company, 1853. 174-239. Available at the Documenting the American South website. | |||
| * ], ed., ''Slave Testimony: Two Centuries of Letters, Speeches, Interviews, and Autobiographies''. Louisiana State University Press, 1977. | |||
| * Frederick Douglass '']'' (1855) (Project Gutenberg: ) | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Douglass |first=Frederick |author-link=Frederick Douglass |editor-last=Morris |editor-first=Kenneth B. Jr. |title=] |publisher=Frederick Douglass Family Initiatives |year=2017 |orig-date=1845 |location=Atlanta, GA |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/narrativeoflifeo0000doug_q4s0/page/n39/mode/2up --> |isbn=978-0-9984730-2-4}} | |||
| * Frederick Douglass ''Life and Times of Frederick Douglass'' (1892) | |||
| * ——, "]." ''Autographs for Freedom'', ], ed., Boston: John P. Jewett and Company, 1853. pp. 174–239. Available at the Documenting the American South website. | |||
| * Frederick Douglass (Project Gutenberg) | |||
| * |
* ——, Collected Articles of Frederick Douglass, A Slave (Project Gutenberg) | ||
| * ] Archives | |||
| * ] ''Been in the Storm So Long: The Aftermath of Slavery.'' (1979) Winner of the 1981 ] for history and the 1980 ]. | |||
| * |
* Morgan, Kenneth, ed. ''Slavery in America: a reader and guide'' (University of Georgia Press, 2005.) | ||
| * ], ed., ''The American Slave: A Composite Autobiography''. 19 vols. Greenwood Publishing Company, 1972. Collection of WPA interviews made in the 1930s with ex-slaves | |||
| * | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * Missouri History Museum Archives | |||
| * Rawick, George P., ed. ''The American Slave: A Composite Autobiography'' . 19 vols. Greenwood Publishing Company, 1972. Collection of WPA interviews made in 1930s with ex-slaves | |||
| === |
===Scholarly books=== | ||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * Berlin, Ira. ''Generations of Captivity: A History of African American Slaves.'' (2003) ISBN 0-674-01061-2. | |||
| * |
* Andrews, William L. (2019) ''Slavery and Class in the American South: A Generation of Slave Narrative Testimony, 1840–1865'' (Oxford University Press). | ||
| * {{cite book |author-link=Edward E. Baptist |last=Baptist |first=Edward E. |title=The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism |publisher=] |year=2014 |isbn=978-0-465-00296-2 |ref=none}} | |||
| * Berlin, Ira and Ronald Hoffman, eds. ''Slavery and Freedom in the Age of the American Revolution'' University Press of Virginia, 1983. essays by scholars | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Beckert |first1=Sven |title=Empire of Cotton: A Global History |url={{google books |plainurl=y |id=UyyOAwAAQBAJ}} |date=2014 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-385-35325-0 |author-link=Sven Beckert |ref=none}} | |||
| * Blassingame, John W. '']'' Oxford University Press, 1979. ISBN 0-19-502563-6. | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-first=Sven |editor1-last=Beckert |editor2-first=Seth |editor2-last=Rockman |editor1-link=Sven Beckert |title=Slavery's Capitalism: A New History of American Economic Development |publisher=] |year=2016 |isbn=978-0-8122-4841-8 |ref=beckert2016}} | |||
| * David, Paul A. and Temin, Peter. ''Slavery:The Progressive Institution?'' The Journal of Economic History. Vol. 34, No. 3 (September 1974) | |||
| * Brady, Steven J. (2022) ''Chained to History: Slavery and US Foreign Relations to 1865'' (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press). | |||
| * David Brion Davis. ''Inhuman Bondage: The Rise and Fall of Slavery in the New World'' (2006) | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Finkelman |first=Paul |author-link=Paul Finkelman |title=Slavery and the Founders: Race and Liberty in the Age of Jefferson |publisher=M.E. Sharpe |year=1996 |location=Armonk, NY |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/slaveryfoundersr0000fink --> |isbn=978-1-56324-590-9 |ref=finkelman1996}} | |||
| * De Tocqueville, Alexis. ''Democracy in America.'' (1994 Edition by Alfred A Knopf, Inc) ISBN 0-679-43134-9 | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Finkelman |editor-first=Paul |author-mask=2 |title=Slavery & The Law |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2002 |location=Lanham, MD |url=<!-- https://archive.org/details/slaverylaw0000unse/page/n3/mode/2up --> |isbn=0-945612-36-2 |ref=finkelman2002}} | |||
| * Elkins, Stanley. ''Slavery : A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life.'' University of Chicago Press, 1976. ISBN 0-226-20477-4 | |||
| * {{cite book |title=New Directions in Slavery Studies: Commodification, Community, and Comparison |first=Jeff |last=Forret |author-link=Jeff Forret |publisher=] |year=2015 |isbn=978-0-8071-6115-9 |ref=forret2015}} | |||
| * Fehrenbacher, Don E. ''Slavery, Law, and Politics: The Dred Scott Case in Historical Perspective'' Oxford University Press, 1981 | |||
| * Gellman, David Nathaniel. ''Emancipating New York: The politics of slavery and freedom, 1777–1827'' (LSU Press, 2006) | |||
| * Fogel, Robert W. ''Without Consent or Contract: The Rise and Fall of American Slavery'' W.W. Norton, 1989. Econometric approach | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Walter |last=Johnson |author-link=Walter Johnson (historian) |title=River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-674-04555-2 |ref=none}} | |||
| * Foner, Eric. ''Forever Free.''(2005) ISBN 0-375-40259-4 | |||
| * Larson, Edward J. (2023) ''American Inheritance: Liberty and Slavery in the Birth of a Nation, 1765–1795'' (W. W. Norton, 2023) | |||
| * Franklin, John Hope and Schweninger. ''Runaway Slaves: Rebels on the Plantation.'' (1999) ISBN 0-19-508449-7. | |||
| * ] (2000) ''Slavery and Servitude in North America, 1607–1800'' (Edinburgh, Scotland: Edinburgh University Press). | |||
| * Gallay, Alan. ''The Indian Slave Trade'' (2002). | |||
| * Parish, Peter J. (2022) ''Slavery: History and Historians'' (New York: Harper & Row). | |||
| * Genovese, Eugene D. ''Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made'' Pantheon Books, 1974. | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Andrés |last=Reséndez |author-link=Andrés Reséndez |title=] |year=2016 |location=New York |publisher=Houghton Mifflin Harcourt |isbn=978-0-544-94710-8}} | |||
| * Genovese, Eugene D. ''The Political Economy of Slavery: Studies in the Economy and Society of the Slave South'' (1967) | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Calvin |last=Schermerhorn |title=The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860 |publisher=] |year=2015 |isbn=978-0-300-19200-1 |ref=schermerhorn2015}} | |||
| * Genovese, Eugene D. and Elizabeth Fox-Genovese, ''Fruits of Merchant Capital: Slavery and Bourgeois Property in the Rise and Expansion of Capitalism'' (1983) | |||
| * Schwalm, Leslie A. (1997) ''A Hard Hight for We: Women's Transition from Slavery to Freedom in South Carolina'' (Chicago: University of Illinois Press). | |||
| * Hahn, Steven. (2004) | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * Higginbotham, A. Leon, Jr. ''In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period.'' Oxford University Press, 1978. ISBN 0-19-502745-0 | |||
| * Horton, James Oliver and Horton, Lois E. ''Slavery and the Making of America.'' (2005) ISBN 0-19-517903-X | |||
| * Kolchin, Peter. ''American Slavery, 1619-1877'' Hill and Wang, 1993. Survey | |||
| * Mason, Matthew. ''Slavery and Politics in the Early American Republic.'' (2006) ISBN 13:978-0-8078-3049-9. | |||
| * Morgan, Edmund S. ''American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia '' W.W. Norton, 1975. | |||
| * Morris, Thomas D. ''Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619-1860'' University of North Carolina Press, 1996. | |||
| * Oakes, James. ''The Ruling Race: A History of American Slaveholders.'' (1982) ISBN 0-393-31705-6. | |||
| * Ransom, Roger L. ''Was It Really All That Great to Be a Slave?'' Agricultural History, Vol. 48, No. 4 (October 1974) | |||
| * Scarborough, William K. ''The Overseer: Plantation Management in the Old South'' (1984) | |||
| * Stampp, Kenneth M. ''The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South'' (1956) Survey | |||
| * Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." Agricultural History 1970 44(4): 407-412. ISSN 0002-1482 | |||
| * Tadman, Michael. ''Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South'' University of Wisconsin Press, 1989. | |||
| * Wright, W. D. ''Historians and Slavery; A Critical Analysis of Perspectives and Irony in American Slavery and Other Recent Works'' Washington, D.C.: University Press of America (1978) | |||
| ===Scholarly articles=== | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Slave Resistance and Rebellion''. Westport, CT: Greenwood, 2007. | |||
| * Baker, Regina S. (2022) "The historical racial regime and racial inequality in poverty in the American south." ''American Journal of Sociology'' 127.6 (2022): 1721–1781. | |||
| * Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World''. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2007. | |||
| * Hilt, Eric. (2010). "Revisiting Time on the Cross After 45 Years: The Slavery Debates and the New Economic History." ''Capitalism: A Journal of History and Economics'', Volume 1, Number 2, pp.{{spaces}}456–483. {{doi|10.1353/cap.2020.0000}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |title=Searching for Climax: Black Erotic Lives in Slavery and Freedom |first1=Treva B. |last1=Lindsey |first2=Jessica Marie |last2=Johnson |journal=Meridians: Feminism, Race, Transnationalism |volume=12 |number=2 |date=Fall 2014 |access-date=March 25, 2018 |pages=169+ |url=http://edb.pbclibrary.org:2084/apps/doc/A388827961/AONE?u=d0_mlpbcls&sid=AONE&xid=5d794dee |ref=none}}{{Dead link|date=June 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes}} | |||
| * Logan, Trevon D. (2022) "American Enslavement and the Recovery of Black Economic History." ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' 36.2 (2022): 81–98. | |||
| * {{cite journal |author-link=Thomas A. McCarthy |last=McCarthy |first=Thomas |s2cid=32786606 |title=Coming to Terms with Our Past, Part II: On the Morality and Politics of Reparations for Slavery |journal=] |volume=32 |number=6 |date=December 2004 |pages=750–772|doi=10.1177/0090591704268924 |ref=none}} | |||
| * Naidu, S. (2020). "American slavery and labour market power." ''Economic History of Developing Regions'', 35(1), 3–22. {{doi|10.1080/20780389.2020.1734312}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Singleton |first=Theresa A. |author-link=Theresa A. Singleton |title=The Archaeology of Slavery in North America |journal=] |volume=24 |year=1995 |pages=119–140 |doi=10.1146/annurev.an.24.100195.001003 |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=phhLAQAAMAAJ |last=Turner |first=Edward Raymond |title=The First Abolition Society in the United States |journal=] |year=1912 |volume=36 |pages=92–109|ref=none}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| === |
===Oral histories and autobiographies of ex-slaves=== | ||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * Fields, Barbara J. ''Slavery and Freedom on the Middle Ground: Maryland During the Nineteenth Century'' Yale University Press, 1985. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Life of William Grimes, the Runaway Slave |editor1-first=William L. |editor1-last=Andrews |editor2-first=Regina E. |editor2-last=Mason |date=2008 |isbn=978-0-19-534331-1 |publisher=]}} | |||
| * Clayton E. Jewett and John O. Allen; ''Slavery in the South: A State-By-State History'' Greenwood Press, 2004 | |||
| * ] (2009). ''A Slave No More: Two Men Who Escaped to Freedom, Including Their Own Narratives of Emancipation''. Boston and New York: Mariner Books, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. {{ISBN|978-0-15-101-232-9}}. | |||
| * Kulikoff, Alan. ''Tobacco and Slaves: The Development of Southern Cultures in the Chesapeake, 1680-1800'' University of North Carolina Press, 1986. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Rambles of a Runaway from Southern Slavery |first=Henry |last=Goings |publisher=] |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-8139-3240-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bpuMd7z3klIC |editor1-first=Calvin |editor1-last=Schermerhorn |editor2-first=Michael |editor2-last=Plunkett |editor3-first=Edward |editor3-last=Gaynor|ref=none}} | |||
| * Minges, Patrick N.; ''Slavery in the Cherokee Nation: The Keetoowah Society and the Defining of a People, 1855-1867'' 2003 deals with Indian slave owners. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Before Freedom When I Just Can Remember: Twenty-seven Oral Histories of Former South Carolina Slaves |editor-first=Belinda |editor-last=Hurmence |date=1989 |isbn=978-0-89587-069-8 |publisher=]|ref=none}} | |||
| * Mohr, Clarence L. ''On the Threshold of Freedom: Masters and Slaves in Civil War Georgia'' University of Georgia Press, 1986. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Before Freedom: Forty-Eight Oral Histories of Former North & South Carolina Slaves |editor-first=Belinda |editor-last=Hurmence |publisher=] |year=1990 |isbn=978-0-451-62781-0|ref=none}} | |||
| * Mooney, Chase C. ''Slavery in Tennessee'' Indiana University Press, 1957. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=My Folks Don't Want Me to Talk about Slavery: Twenty-One Oral Histories of Former North Carolina Slaves |editor-first=Belinda |editor-last=Hurmence |year=1990 |ref=none}} | |||
| * Olwell, Robert. ''Masters, Slaves, & Subjects: The Culture of Power in the South Carolina Low Country, 1740-1790'' Cornell University Press, 1998. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Slavery Time When I Was Chillun |url=https://archive.org/details/slaverytimewheni00beli |url-access=registration |year=1997 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-399-23194-0 |editor-first=Belinda |editor-last=Hurmence |ref=none}} | |||
| * Reidy, Joseph P. ''From Slavery to Agrarian Capitalism in the Cotton Plantation South, Central Georgia, 1800-1880'' University of North Carolina Press, 1992. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=We Lived in a Little Cabin in the Yard: Personal Accounts of Slavery in Virginia |date=1994 |editor-first=Belinda |editor-last=Hurmence |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-89587-118-3|ref=none}} | |||
| * Ripley, C. Peter. ''Slaves and Freemen in Civil War Louisiana'' Louisiana State University Press, 1976. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl, Written by Herself |first=Harriet |last=Jacobs |author-link=Harriet Jacobs |publisher=] |date=1861 |url=http://docsouth.unc.edu/fpn/jacobs/jacobs.html |editor-first=Lydia Maria |editor-last=Child |editor-link=Lydia Maria Child |ref=none}} | |||
| * Rivers, Larry Eugene. ''Slavery in Florida: Territorial Days to Emancipation'' University Press of Florida, 2000. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=God Struck Me Dead: Voices of Ex-Slaves |first=Clifton H. |last=Johnson |year=1993 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-8298-0945-9 |ref=none}} | |||
| * Sellers, James Benson; ''Slavery in Alabama'' University of Alabama Press, 1950 | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * Sydnor, Charles S. ''Slavery in Mississippi''. 1933 | |||
| * Takagi, Midori. ''Rearing Wolves to Our Own Destruction: Slavery in Richmond, Virginia, 1782-1865'' University Press of Virginia, 1999. | |||
| * Taylor, Joe Gray. ''Negro Slavery in Louisiana''. Louisiana Historical Society, 1963. | |||
| * Wood, Peter H. ''Black Majority: Negroes in Colonial South Carolina from 1670 through the Stono Rebellion'' W.W. Norton & Company, 1974. | |||
| === |
===Bibliographies=== | ||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * John B. Boles and Evelyn T. Nolen, eds., ''Interpreting Southern History: Historiographical Essays in Honor of Sanford W. Higginbotham'' (1987). | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Miller |first=Joseph C. |author-link=Joseph C. Miller |title=Slavery and Slaving in World History: A Bibliography, Volume I, 1900–1991 |publisher=Kraus International Publications |year=1993 |location=Millwood, NY | |||
| * Richard H. King, "Marxism and the Slave South", ''American Quarterly'' 29 (1977), 117-31. focus on Genovese | |||
| |url=https://archive.org/details/slaveryslavingin0000mill/page/n5/mode/2up |isbn=0-527-63660-6 |ref=miller1993}} | |||
| * Peter Kolchin, "American Historians and Antebellum Southern Slavery, 1959-1984", in William J. Cooper, Michael F. Holt, and John McCardell, eds., ''A Master's Due: Essays in Honor of David Herbert Donald'' (1985), 87-111 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Miller |first=Joseph C. |author-mask=2 |title=Slavery and Slaving in World History: A Bibliography, Volume II, 1992–1996 |publisher=M.E. Sharpe, Inc. |year=1999 |location=Armonk, NY |url=https://archive.org/details/slaveryslavingin0002mill/page/n5/mode/2up |isbn=0-765-60279-2 |ref=miller1999}} | |||
| * James M. McPherson et al., ''Blacks in America: Bibliographical Essays'' (1971). | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * Peter J. Parish; ''Slavery: History and Historians'' Westview Press. 1989 | |||
| * Tulloch, Hugh. ''The Debate on the American Civil War Era'' (1998) ch 2-4 | |||
| ===Discussions by foreigners=== | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Charles|last=Dickens|author-link=Charles Dickens|chapter=Slavery|url=https://gutenberg.org/files/675/675-h/675-h.htm|title=American Notes for General Circulation|others=First published in 1842. See Louise H. Johnson, "The Source of the Chapter on Slavery in Dickens' ''American Notes''", ''American Literature,'' vol. 14, Jan. 1943, pp. 427–430|location=London|publisher=]|year=1913}} | |||
| ===Oral histories of ex-slaves=== | |||
| * ''Before Freedom When I Just Can Remember: Twenty-seven Oral Histories of Former South Carolina Slaves'' Belinda Hurmence, 1989. ISBN 0-89587-069-X | |||
| * ''Before Freedom: Forty-Eight Oral Histories of Former North & South Carolina Slaves''. Belinda Hurmence. Mentor Books: 1990. ISBN 0-451-62781-4 | |||
| * ''God Struck Me Dead, Voices of Ex-Slaves'' Clifton H. Johnson ISBN 0-8298-0945-7 | |||
| ===Literary and cultural criticism=== | |||
| ===Historical fiction=== | |||
| * Ryan, Tim A. ''Calls and Responses: The American Novel of Slavery Since'' Gone with the Wind. ]: ], 2008. | |||
| * ]. '']''. New York: Harper and Row, 1981. ISBN 0-06-010491-0. An exploration of the long-term effects of slavery, set mainly in Pennsylvania in the 1970s, but also including scenes set in the ] South. | |||
| * ]. ''Slavery and Race in American Popular Culture''. ]: ], 1984. | |||
| * ]. '']''. New York: Amistad, 2003. ISBN 0-06-055755-9. The 2003 winner of the for fiction and 2004 winner of the ]. | |||
| * ]. '']''. New York: Alfred Knopf, 1987. ISBN 1-58060-120-0. The winner of the 1987 ], this novel by ] laureate Morrison examines the effect of slavery on one African-American family. | |||
| * ]. '']''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2001. ISBN 0-618-11309-7. A reimagining of the story of ]'s '']'' (1936) from the point of view of ]'s half-sister Cynara, a ] slave on the O'Hara plantation. | |||
| * ]. '']''. London: Hamish Hamilon, 1992. ISBN 0-241-13003-4. A 1992 winner of the ], this novel by a British novelist centers around a rebellion on a British slave ship bound for America in the mid-18th century. The novel's climactic sequence is set on the coast of colonial Florida. | |||
| ===Documentary films=== | |||
| ==Literary and cultural criticism== | |||
| * {{cite web|url=https://www.tracesofthetrade.org/|title=Traces of the Trade|website=Traces of the Trade|language=en-US|access-date=2019-03-19}} | |||
| * Ryan, Tim A. ''Calls and Responses: The American Novel of Slavery since Gone with the Wind''. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State UP, 2008. | |||
| * Van Deburg, William. ''Slavery and Race in American Popular Culture''. Madsion: U of Wisconsin P, 1984. | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| {{Commonscat}} | |||
| {{wikisource portal|Slavery in the United States}} | |||
| * : Slave Narratives from the Federal Writers' Project, 1936-1938 | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| * , interviews of 23 former slaves recorded between 1932 and 1975, American Folklife Center, Library of Congress | |||
| * , ] | |||
| * | |||
| * , Library of Congress | |||
| * by Ari Kelman: a review in the , February 14, 2007. | |||
| * |
* , audio interviews of former slaves, 1932–1975, Library of Congress | ||
| * at ] | |||
| * of Slavery in America | |||
| * , summaries, lesson plans, documents and illustrations for schools; focus on United States | |||
| * drawn by ] (has background music) | |||
| * , summaries and documents; focus on United States | |||
| * at ] | |||
| * , ] (4-part series) | |||
| * | |||
| * |
* at the History Channel | ||
| * , ''Economic History Encyclopedia'', March 26, 2008 | |||
| * showing free and slave territories. | |||
| * , ''Documenting the American South'', ] | |||
| * collection of old documents available on-line through Dinsmore Documentation | |||
| * has information on almost 36,000 slaving voyages | |||
| * by Nell Irvin Painter, historian and author of Creating Black Americans | |||
| * | |||
| * (Slavery in Antebellum Georgia) | |||
| * . '']''. August 14, 2019. | |||
| * | |||
| * , ]: a searchable database of 25,000 scholarly works on slavery and the slave trade in all western European languages. | |||
| * Manchester: Wm. Irwin, London: Simpkin, Marshall, and Co., 1849. | |||
| * The Emancipator, August 23, September 13, September 20, October 11, October 18, 1838. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * : Stanford researcher finds that slave trade artifacts were designed to convey messages of power, ownership, and even refinement. | |||
| * | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| |state=expanded | |||
| |list = | |list = | ||
| {{History of slavery in the United States}} | {{History of slavery in the United States}} | ||
| {{Underground Railroad}} | |||
| {{North America topic|Slavery in}} | |||
| {{Slave narrative}} | |||
| {{African American topics}} | {{African American topics}} | ||
| {{Gullah topics|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Plantation agriculture in the Southeastern United States}} | |||
| {{American Civil War}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 5 January 2025
This article is about slavery from the founding of the United States in 1776. For the colonial period, see Slavery in the colonial history of the United States. For modern illegal slavery, see Human trafficking in the United States. For modern legal forced labor, see Penal labor in the United States. "Peculiar institution" redirects here. For the book, see The Peculiar Institution. See also: Abolitionism in the United States








 Whipping a slave, wood-engraving made 1834; Wilson Chinn, showing a slave collar and facial branding of the initials of his enslaver, Valsin B. Marmillion; slavery survivor Adam Crosswhite photographed 1878; Franklin & Armfield's slave jail in the District of Columbia, 1836; freedmen leaving South Carolina on the USS Vermont in 1862; Delia Garlic at age 100; 1818 Kentucky slave trader's ad; daguerreotype made at the 1850 Fugitive Slave Convention; White Gold in the Delta, painted 1939 by Beulah Bettersworth for the Indianola, Mississippi post office, mural destroyed 1960s
Whipping a slave, wood-engraving made 1834; Wilson Chinn, showing a slave collar and facial branding of the initials of his enslaver, Valsin B. Marmillion; slavery survivor Adam Crosswhite photographed 1878; Franklin & Armfield's slave jail in the District of Columbia, 1836; freedmen leaving South Carolina on the USS Vermont in 1862; Delia Garlic at age 100; 1818 Kentucky slave trader's ad; daguerreotype made at the 1850 Fugitive Slave Convention; White Gold in the Delta, painted 1939 by Beulah Bettersworth for the Indianola, Mississippi post office, mural destroyed 1960s
| Part of a series on | ||||||||||||
| African Americans | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | ||||||||||||
Culture
|
||||||||||||
Religion
|
||||||||||||
Politics
|
||||||||||||
Civic/economic groups
|
||||||||||||
Sports
|
||||||||||||
Sub-communities
|
||||||||||||
Dialects and languages
|
||||||||||||
Population
|
||||||||||||
Prejudice
|
||||||||||||
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during the early colonial period, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition in 1865, and issues concerning slavery seeped into every aspect of national politics, economics, and social custom. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction in 1877, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. Involuntary servitude as a punishment for crime is still legal in the United States.
By the time of the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately following the Revolution, abolitionist laws were passed in most Northern states and a movement developed to abolish slavery. The role of slavery under the United States Constitution (1789) was the most contentious issue during its drafting. The Three-Fifths Clause of the Constitution gave slave states disproportionate political power, while the Fugitive Slave Clause (Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3) provided that, if a slave escaped to another state, the other state could not prevent the return of the slave to the person claiming to be his or her owner. All Northern states had abolished slavery to some degree by 1805, sometimes with completion at a future date, sometimes with an intermediary status of unpaid indentured servant.
Abolition was in many cases a gradual process. Some slaveowners, primarily in the Upper South, freed their slaves, and charitable groups bought and freed others. The Atlantic slave trade began to be outlawed by individual states during the American Revolution. The import trade was banned by Congress in 1808, although smuggling was common thereafter, at which point the U.S. Revenue Cutter Service (Coast Guard) began enforcing the law on the high seas. It has been estimated that before 1820 a majority of serving congressmen owned slaves, and that about 30 percent of congressmen who were born before 1840 (some of whom served into the 20th century) owned slaves at some time in their lives.
The rapid expansion of the cotton industry in the Deep South after the invention of the cotton gin greatly increased demand for slave labor, and the Southern states continued as slave societies. The U.S., divided into slave and free states, became ever more polarized over the issue of slavery. Driven by labor demands from new cotton plantations in the Deep South, the Upper South sold more than a million slaves who were taken to the Deep South. The total slave population in the South eventually reached four million. As the U.S. expanded, the Southern states attempted to extend slavery into the new Western territories to allow proslavery forces to maintain power in Congress. The new territories acquired by the Louisiana Purchase and the Mexican Cession were the subject of major political crises and compromises. Slavery was defended in the South as a "positive good", and the largest religious denominations split over the slavery issue into regional organizations of the North and South.
By 1850, the newly rich, cotton-growing South threatened to secede from the Union. Bloody fighting broke out over slavery in the Kansas Territory. When Abraham Lincoln won the 1860 election on a platform of halting the expansion of slavery, slave states seceded to form the Confederacy. Shortly afterward, the Civil War began when Confederate forces attacked the U.S. Army's Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. During the war some jurisdictions abolished slavery and, due to Union measures such as the Confiscation Acts and the Emancipation Proclamation, the war effectively ended slavery in most places. After the Union victory, the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution was ratified on December 6, 1865, prohibiting "slavery involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime."
Background
Main articles: Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, Slavery among Native Americans in the United States, and History of unfree labor in the United States Further information: Atlantic slave trade; Slavery in New France; and Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § Colonial period, 1607–1775 For the related topic of indentured servitude in the United States, see Indentured servitude in British America, Indentured servitude in Pennsylvania, Indentured servitude in Virginia, and Engagé system in Louisiana.
During most of the British colonial period, slavery existed in all the colonies. People enslaved in the North typically worked as house servants, artisans, laborers and craftsmen, with the greater number in cities. Many men worked on the docks and in shipping. In 1703, more than 42 percent of New York City households held enslaved people in bondage, the second-highest proportion of any city in the colonies, behind only Charleston, South Carolina. Enslaved people were also used as agricultural workers in farm communities, especially in the South, but also in upstate New York and Long Island, Connecticut, and New Jersey. By 1770, there were 397,924 blacks out of a population of 2.17 million in what would soon become the United States. The slaves of the colonial era were unevenly distributed: 14,867 lived in New England, where they were three percent of the population; 34,679 lived in the mid-Atlantic colonies, where they were six percent of the population; and 347,378 in the five Southern Colonies, where they were 31 percent of the population.
The South developed an agricultural economy dependent on commodity crops. Its planters rapidly acquired a significantly higher number and proportion of enslaved people in the population overall, as its commodity crops were labor-intensive. Early on, enslaved people in the South worked primarily on farms and plantations growing indigo, rice and tobacco (cotton did not become a major crop until after the 1790s). In 1720, about 65 percent of South Carolina's population was enslaved. Planters (defined by historians in the Upper South as those who held 20 or more slaves) used enslaved workers to cultivate commodity crops. They also worked in the artisanal trades on large plantations and in many Southern port cities. The later wave of settlers in the 18th century who settled along the Appalachian Mountains and backcountry were backwoods subsistence farmers, and they seldom held enslaved people.

Beginning in the second half of the 18th century, a debate emerged over the continued importation of African slaves to the American colonies. Many in the colonies, including the Southern slavocracy, opposed further importation of slaves due to fears that it would destabilize colonies and lead to further slave rebellions. In 1772, prominent Virginians submitted a petition to the Crown, requesting that the slave trade to Virginia be abolished; it was rejected. Rhode Island forbade the importation of slaves in 1774. The influential revolutionary Fairfax Resolves called for an end to the "wicked, cruel and unnatural" Atlantic slave trade. All of the colonies banned slave importations during the Revolutionary War.
Slavery in the American Revolution and early republic
Main articles: African Americans in the Revolutionary War and Slavery and the United States Constitution Further information: Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § American Revolution and Confederation period, 1776–1787; and Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § Early Constitutional period, 1787–1811
Slavery had existed for thousands of years, all around the world. In the United States and many parts of the world it was a legal practise and had become entrenched socially and economically in many societies. The ideals and principles promoted in the Enlightenment and the American Revolution helped to put slavery and the desire for its abolition on the political agenda. As historian Christopher L. Brown put it, slavery "had never been on the agenda in a serious way before", but the American Revolution "forced it to be a public question from there forward".
After the new country's independence was secure, slavery was a topic of contention at the 1787 Constitutional Convention. Many of Founding Fathers of the United States were plantation owners who owned large numbers of enslaved laborers; the original Constitution preserved their right to own slaves, and they further gained a political advantage in owning slaves. Although the enslaved of the early Republic were considered sentient property, were not permitted to vote, and had no rights to speak of, they were to be enumerated in population censuses and counted as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of representation in the national legislature, the U.S. Congress.
Slaves and free blacks who supported the Continental Army
Main article: Black Patriot
The rebels began to offer freedom as an incentive to motivate slaves to fight on their side. Washington authorized slaves to be freed who fought with the American Continental Army. Rhode Island started enlisting slaves in 1778, and promised compensation to owners whose slaves enlisted and survived to gain freedom. During the course of the war, about one-fifth of the Northern army was black. In 1781, Baron Closen, a German officer in the French Royal Deux-Ponts Regiment at the Battle of Yorktown, estimated the American army to be about one-quarter black. These men included both former slaves and free-born blacks. Thousands of free blacks in the Northern states fought in the state militias and Continental Army. In the South, both sides offered freedom to slaves who would perform military service. Roughly 20,000 slaves fought in the American Revolution.
Black Loyalists
Main articles: Black Loyalist and Dunmore's Proclamation See also: Book of Negroes
After the Revolutionary War broke out, the British realized they lacked the manpower necessary to prosecute the war. In response, British commanders began issuing proclamations to Patriot-owned slaves, offering freedom if they fled to British lines and assisted the British war effort. Such proclamations were repeatedly issued over the course of the conflict, which resulted in up to 100,000 American slaves fleeing to British lines. Self-emancipated slaves who reached British lines were organized into a variety of military units, which served in all theaters of the war. Formerly enslaved women and children, in lieu of military service, worked instead as laborers and domestic servants. At the end of the war, freed slaves in British lines either evacuated to other British colonies or to Britain itself, were re-enslaved by the victorious Americans, or fled into the countryside.
In early 1775, the royal governor of Virginia, Lord Dunmore, wrote to the Earl of Dartmouth of his intention to free slaves owned by American Patriots in case they staged a rebellion. On November 7, 1775, Dunmore issued Dunmore's Proclamation, which promised freedom to any slaves of American patriots who would leave their masters and join the British forces. Historians agree that the proclamation was chiefly designed for practical rather than moral reasons, and slaves owned by American Loyalists were unaffected by the proclamation. About 1,500 slaves owned by patriots escaped and joined Dunmore's forces. A total of 18 slaves fled George Washington's plantation, one of whom, Harry, served in Dunmore's all-black loyalist regiment called "the Black Pioneers". Escapees who joined Dunmore had "Liberty to Slaves" stitched on to their jackets. Most died of disease before they could do any fighting, but three hundred of these freed slaves made it to freedom in Britain. Historian Jill Lepore writes that "between eighty and a hundred thousand (nearly one in five black slaves) left their homes ... betting on British victory", but Cassandra Pybus states that between 20,000 and 30,000 is a more realistic number of slaves who defected to the British side during the war.
Many slaves took advantage of the disruption of war to escape from their plantations to British lines or to fade into the general population. Upon their first sight of British vessels, thousands of slaves in Maryland and Virginia fled from their owners. Throughout the South, losses of slaves were high, with many due to escapes. Slaves also escaped throughout New England and the mid-Atlantic, with many joining the British who had occupied New York. In the closing months of the war, the British evacuated freedmen and also removed slaves owned by loyalists. Around 15,000 black loyalists left with the British, most of them ending up as free people in England or its colonies. Washington hired a slave catcher during the war, and at its end he pressed the British to return the slaves to their masters. With the British certificates of freedom in their belongings, the black loyalists, including Washington's slave Harry, sailed with their white counterparts out of New York harbor to Nova Scotia. More than 3,000 were resettled in Nova Scotia, where they were eventually granted land and formed the community of the black Nova Scotians.
Early abolitionism in the United States
Main article: Abolitionism in the United States
In the first two decades after the American Revolution, state legislatures and individuals took actions to free slaves. Northern states passed new constitutions that contained language about equal rights or specifically abolished slavery; some states, such as New York and New Jersey, where slavery was more widespread, passed laws by the end of the 18th century to abolish slavery incrementally. By 1804, all the Northern states had passed laws outlawing slavery, either immediately or over time. In New York, the last slaves were freed in 1827 (celebrated with a big July 5 parade). Indentured servitude, which had been widespread in the colonies (half the population of Philadelphia had once been indentured servants), dropped dramatically, and disappeared by 1800. However, there were still forcibly indentured servants in New Jersey in 1860. No Southern state abolished slavery, but some individual owners, more than a handful, freed their slaves by personal decision, often providing for manumission in wills but sometimes filing deeds or court papers to free individuals. Numerous slaveholders who freed their slaves cited revolutionary ideals in their documents; others freed slaves as a promised reward for service. From 1790 to 1810, the proportion of blacks free in the United States increased from 8 to 13.5 percent, and in the Upper South from less than one to nearly ten percent as a result of these actions.
Starting in 1777, the rebels outlawed the importation of slaves state by state. They all acted to end the international trade, but, after the war, it was reopened in North Carolina (opened until 1794) and Georgia (opened until 1798) and South Carolina (opened until 1787, and then reopened again in 1803.) In 1807, the United States Congress acted on President Thomas Jefferson's advice and, without controversy, made importing slaves from abroad a federal crime, effective the first day that the United States Constitution permitted this prohibition: January 1, 1808.
During the Revolution and in the following years, all states north of Maryland ( the Mason–Dixon line) took steps towards abolishing slavery. In 1777, the Vermont Republic, which was still unrecognized by the United States, passed a state constitution prohibiting slavery. The Pennsylvania Abolition Society, led in part by Benjamin Franklin, was founded in 1775, and Pennsylvania began gradual abolition in 1780. In 1783, the Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts ruled in Commonwealth v. Jennison that slavery was unconstitutional under the state's new 1780 constitution. New Hampshire began gradual emancipation in 1783, while Connecticut and Rhode Island followed suit in 1784. The New York Manumission Society, which was led by John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, and Aaron Burr, was founded in 1785. New York state began gradual emancipation in 1799, and New Jersey did the same in 1804.
Shortly after the Revolution, the Northwest Territory was established, by Manasseh Cutler and Rufus Putnam (who had been George Washington's chief engineer). Both Cutler and Putnam came from Puritan New England. The Puritans strongly believed that slavery was morally wrong. Their influence on the issue of slavery was long-lasting, and this was provided significantly greater impetus by the Revolution. The Northwest Territory (which became Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin, and part of Minnesota) doubled the size of the United States, and it was established at the insistence of Cutler and Putnam as "free soil" – no slavery. This was to prove crucial a few decades later. Had those states been slave states, and their electoral votes gone to Abraham Lincoln's main opponent, Lincoln would not have become president. The Civil War would not have been fought. Even if it eventually had been, the North might well have lost.
Constitution of the United States
Main article: Slavery and the United States Constitution Further information: Fugitive Slave Clause
Slavery was a contentious issue in the writing and approval of the Constitution of the United States. The words "slave" and "slavery" did not appear in the Constitution as originally adopted, although several provisions clearly referred to slaves and slavery. Until the adoption of the 13th Amendment in 1865, the Constitution did not prohibit slavery.
Section 9 of Article I forbade the federal government from prohibiting the importation of slaves, described as "such Persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit", for twenty years after the Constitution's ratification (until January 1, 1808). The Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves of 1807, passed by Congress and signed into law by President Thomas Jefferson (who had called for its enactment in his 1806 State of the Union address), went into effect on January 1, 1808, the earliest date on which the importation of slaves could be prohibited under the Constitution.
The delegates approved the Fugitive Slave Clause of the Constitution (Article IV, section 2, clause 3), which prohibited states from freeing those "held to Service or Labour" (meaning slaves, indentures, and apprentices) who fled to them from another state and required that they be returned to their owners. The Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 and the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 gave effect to the Fugitive Slave Clause. Salmon P. Chase considered the Fugitive Slave Acts unconstitutional because "The Fugitive Slave Clause was a compact among the states, not a grant of power to the federal government".
Three-fifths Compromise
Main article: Three-fifths Compromise See also: Slave Trade Act of 1794 and Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves
In a section negotiated by James Madison of Virginia, Section 2 of Article I designated "other persons" (slaves) to be added to the total of the state's free population, at the rate of three-fifths of their total number, to establish the state's official population for the purposes of apportionment of congressional representation and federal taxation. The "Three-Fifths Compromise" was reached after a debate in which delegates from Southern (slaveholding) states argued that slaves should be counted in the census just as all other persons were while delegates from Northern (free) states countered that slaves should not be counted at all. The compromise strengthened the political power of Southern states, as three-fifths of the (non-voting) slave population was counted for congressional apportionment and in the Electoral College, although it did not strengthen Southern states as much as it would have had the Constitution provided for counting all persons, whether slave or free, equally.
In addition, many parts of the country were tied to the Southern economy. As the historian James Oliver Horton noted, prominent slaveholder politicians and the commodity crops of the South had a strong influence on United States politics and economy. Horton said,
in the 72 years between the election of George Washington and the election of Abraham Lincoln, 50 of those years a slaveholder as president of the United States, and, for that whole period of time, there was never a person elected to a second term who was not a slaveholder.
The power of Southern states in Congress lasted until the Civil War, affecting national policies, legislation, and appointments. One result was that most of the justices appointed to the Supreme Court were slave owners. The planter elite dominated the Southern congressional delegations and the United States presidency for nearly fifty years.
Slavery in the 19th century
Main articles: Slave and free states and History of slavery in the United States by state Further information: List of court cases in the United States involving slavery, Fugitive slaves in the United States, Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § 1812 1849, and Female slavery in the United States See also: Slave labor on United States military installations 1799–1863 and Slavery at American colleges and universities
Slavery in the United States was a variable thing, in "constant flux, driven by the violent pursuit of ever-larger profits." According to demographic calculations by J. David Hacker of the University of Minnesota, approximately four out of five of all of the slaves who ever lived in the United States or the territory that became the United States (beginning in 1619 and including all colonies that were eventually acquired or conquered by the United States) were born in or imported to the United States in the 19th century. Slaves were the labor force of the South, but slave ownership was also the foundation upon which American white supremacy was constructed. Historian Walter Johnson argues that "one of the many miraculous things a slave could do was make a household white...", meaning that the value of whiteness in America was in some ways measured by the ability to purchase and maintain black slaves.
Harriet Beecher Stowe described slavery in the United States in 1853:
What, then, is American slavery, as we have seen it exhibited by law, and by the decision of Courts? Let us begin by stating what it is not:
1. It is not apprenticeship.
2. It is not guardianship.
3. It is in no sense a system for the education of a weaker race by a stronger.
4. The happiness of the governed is in no sense its object.
5. The temporal improvement or the eternal well-being of the governed is in no sense its object.
The object of it has been distinctly stated in one sentence by Judge Ruffin,— "The end is the profit of the master, his security, and the public safety."
Slavery, then, is absolute despotism, of the most unmitigated form.
Justifications in the South
Further information: American proslavery movement and Fire-Eaters See also: Field slaves in the United States, Gang system, Task system, Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, American gentry, Planter class, and List of plantations in the United States
American slavery as "a necessary evil"
In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". At that time, it was feared that emancipation of black slaves would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. On April 22, 1820, Thomas Jefferson, one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, wrote in a letter to John Holmes, that with slavery,
We have the wolf by the ear, and we can neither hold him, nor safely let him go. Justice is in one scale, and self-preservation in the other.
The French writer and traveler Alexis de Tocqueville, in his influential Democracy in America (1835), expressed opposition to slavery while observing its effects on American society. He felt that a multiracial society without slavery was untenable, as he believed that prejudice against blacks increased as they were granted more rights (for example, in Northern states). He believed that the attitudes of white Southerners, and the concentration of the black population in the South, were bringing the white and black populations to a state of equilibrium, and were a danger to both races. Because of the racial differences between master and slave, he believed that the latter could not be emancipated.
In a letter to his wife dated December 27, 1856, in reaction to a message from President Franklin Pierce, Robert E. Lee wrote,
There are few, I believe, in this enlightened age, who will not acknowledge that slavery as an institution is a moral and political evil. It is idle to expatiate on its disadvantages. I think it is a greater evil to the white than to the colored race. While my feelings are strongly enlisted in behalf of the latter, my sympathies are more deeply engaged for the former. The blacks are immeasurably better off here than in Africa, morally, physically, and socially. The painful discipline they are undergoing is necessary for their further instruction as a race, and will prepare them, I hope, for better things. How long their servitude may be necessary is known and ordered by a merciful Providence.
American slavery as "a positive good"
Main article: Slavery as a positive good in the United States Further information: Eugenics in the United States See also: Mudsill theory

However, as the abolitionist movement's agitation increased and the area developed for plantations expanded, apologies for slavery became more faint in the South. Leaders then described slavery as a beneficial scheme of labor management. John C. Calhoun, in a famous speech in the Senate in 1837, declared that slavery was "instead of an evil, a good – a positive good". Calhoun supported his view with the following reasoning: in every civilized society one portion of the community must live on the labor of another; learning, science, and the arts are built upon leisure; the African slave, kindly treated by his master and mistress and looked after in his old age, is better off than the free laborers of Europe; and under the slave system conflicts between capital and labor are avoided. The advantages of slavery in this respect, he concluded, "will become more and more manifest, if left undisturbed by interference from without, as the country advances in wealth and numbers".

South Carolina army officer, planter, and railroad executive James Gadsden called slavery "a social blessing" and abolitionists "the greatest curse of the nation". Gadsden was in favor of South Carolina's secession in 1850, and was a leader in efforts to split California into two states, one slave and one free.
Other Southern writers who also began to portray slavery as a positive good were James Henry Hammond and George Fitzhugh. They presented several arguments to defend the practice of slavery in the South. Hammond, like Calhoun, believed that slavery was needed to build the rest of society. In a speech to the Senate on March 4, 1858, Hammond developed his "Mudsill Theory", defending his view on slavery by stating: "Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement. It constitutes the very mud-sill of society and of political government; and you might as well attempt to build a house in the air, as to build either the one or the other, except on this mud-sill." Hammond believed that in every class one group must accomplish all the menial duties, because without them the leaders in society could not progress. He argued that the hired laborers of the North were slaves too: "The difference ... is, that our slaves are hired for life and well compensated; there is no starvation, no begging, no want of employment," while those in the North had to search for employment.
George Fitzhugh used assumptions about white superiority to justify slavery, writing that, "the Negro is but a grown up child, and must be governed as a child." In The Universal Law of Slavery, Fitzhugh argues that slavery provides everything necessary for life and that the slave is unable to survive in a free world because he is lazy, and cannot compete with the intelligent European white race. He states that "The negro slaves of the South are the happiest, and in some sense, the freest people in the world." Without the South, "He (slave) would become an insufferable burden to society" and "Society has the right to prevent this, and can only do so by subjecting him to domestic slavery."
On March 21, 1861, Alexander Stephens, Vice President of the Confederacy, delivered his Cornerstone Speech. He explained the differences between the Constitution of the Confederate States and the United States Constitution, laid out the cause for the American Civil War, as he saw it, and defended slavery:
The new Constitution has put at rest forever all the agitating questions relating to our peculiar institutions – African slavery as it exists among us – the proper status of the negro in our form of civilization. This was the immediate cause of the late rupture and present revolution. Jefferson, in his forecast, had anticipated this, as the "rock upon which the old Union would split." He was right. What was conjecture with him, is now a realized fact. But whether he fully comprehended the great truth upon which that rock stood and stands, may be doubted. The prevailing ideas entertained by him and most of the leading statesmen at the time of the formation of the old Constitution were, that the enslavement of the African was in violation of the laws of nature; that it was wrong in principle, socially, morally and politically. It was an evil they knew not well how to deal with; but the general opinion of the men of that day was, that, somehow or other, in the order of Providence, the institution would be evanescent and pass away ... Those ideas, however, were fundamentally wrong. They rested upon the assumption of the equality of races. This was an error. It was a sandy foundation, and the idea of a Government built upon it – when the "storm came and the wind blew, it fell".
Our new Government is founded upon exactly the opposite ideas; its foundations are laid, its cornerstone rests, upon the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery, subordination to the superior race, is his natural and moral condition.
This view of the "Negro race" was backed by pseudoscience. The leading researcher was Dr. Samuel A. Cartwright, a Southerner and the inventor of the mental illnesses of drapetomania (the desire of a slave to run away) and dysaesthesia aethiopica ("rascality"), both cured, according to him, by whipping. The Medical Association of Louisiana set up a committee, of which he was chair, to investigate "the Diseases and Physical Peculiarities of the Negro Race". Their report, first delivered to the Medical Association in an address, was published in their journal in 1851, and then reprinted in part in the widely circulated DeBow's Review.
Proposed expansion of slavery

Whether slavery was to be limited to the Southern states that already had it, or whether it was to be permitted in new states made from the lands of the Louisiana Purchase and Mexican Cession, was a major issue in the 1840s and 1850s. It was addressed by the Compromise of 1850 and during the Bleeding Kansas period.
Also relatively well-known are the proposals, including the Ostend Manifesto, to annex Cuba as a slave state, as well as the privately funded invasion of Cuba by Narciso López. There was also talk of making slave states of Mexico, Nicaragua (see Walker affair and Filibuster War) and other lands around the so-called Golden Circle. Less well known today, though well known at the time, is that pro-slavery Southerners:
- Actively sought to reopen the transatlantic slave trade
- Funded illegal slave shipments from the Caribbean and Africa, such as the Wanderer slave shipment to Georgia in 1858
- Wanted to reintroduce slavery in the Northern states, through federal action or Constitutional amendment making slavery legal nationwide, thus overriding state anti-slavery laws. (See Crittenden Compromise.) This was described as "well underway" by 1858.
- Said openly that slavery should by no means be limited to black people, since in their view it was beneficial. Northern white workers, who were allegedly "wage slaves" already, would allegedly have better lives if they were enslaved.
None of these ideas got very far, but they alarmed Northerners and contributed to the growing polarization of the country.
Abolitionism in the North
Main article: Abolitionism in the United States Further information: List of abolitionists, Underground Railroad, African American founding fathers of the United States, and Radical RepublicansSlavery is a volcano, the fires of which cannot be quenched, nor its ravishes controlled. We already feel its convulsions, and if we sit idly gazing upon its flames, as they rise higher and higher, our happy republic will be buried in ruin, beneath its overwhelming energies.
— William Ellsworth, attorney for Prudence Crandall, 1834

Beginning during the Revolution and in the first two decades of the postwar era, every state in the North abolished slavery. These were the first abolitionist laws in the Atlantic World. However, the abolition of slavery did not necessarily mean that existing slaves became free. In some states they were forced to remain with their former owners as indentured servants: free in name only, although they could not be sold and thus families could not be split, and their children were born free. The end of slavery did not come in New York until July 4, 1827, when it was celebrated (on July 5) with a big parade. However, in the 1830 census, the only state with no slaves was Vermont. In the 1840 census, there were still slaves in New Hampshire (1), Rhode Island (5), Connecticut (17), New York (4), Pennsylvania (64), Ohio (3), Indiana (3), Illinois (331), Iowa (16), and Wisconsin (11). There were none in these states in the 1850 census.
Most Northern states passed legislation for gradual abolition, first freeing children born to slave mothers (and requiring them to serve lengthy indentures to their mother's owners, often into their 20s as young adults). In 1845, the Supreme Court of New Jersey received lengthy arguments towards "the deliverance of four thousand persons from bondage". Pennsylvania's last slaves were freed in 1847, Connecticut's in 1848, and while neither New Hampshire nor New Jersey had any slaves in the 1850 Census, and New Jersey only one and New Hampshire none in the 1860 Census, slavery was never prohibited in either state until ratification of the 13th Amendment in 1865 (and New Jersey was one of the last states to ratify it).

None of the Southern states abolished slavery before 1865, but it was not unusual for individual slaveholders in the South to free numerous slaves, often citing revolutionary ideals, in their wills. Methodist, Quaker, and Baptist preachers traveled in the South, appealing to slaveholders to manumit their slaves, and there were "manumission societies" in some Southern states. By 1810, the number and proportion of free blacks in the population of the United States had risen dramatically. Most free blacks lived in the North, but even in the Upper South, the proportion of free blacks went from less than one percent of all blacks to more than ten percent, even as the total number of slaves was increasing through imports.

African slaves arrived in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in the 1630s, and slavery was legally sanctioned by the Puritans in 1641. Massachusetts residents participated in the slave trade, and laws were passed regulating the movement and marriage among slaves. In 1700, Samuel Sewall, Puritan abolitionist and associate justice of the Massachusetts Superior Court of Judicature, wrote The Selling of Joseph, within which he condemned slavery and the slave trade and refuted many of the era's typical justifications for slavery. The Puritan influence on slavery was still strong at the time of the American Revolution and up until the Civil War. Of America's first seven presidents, the two who did not own slaves, John Adams and his son John Quincy Adams, came from Puritan New England. They were wealthy enough to own slaves, but they chose not to because they believed that it was morally wrong to do so. In 1765, colonial leader Samuel Adams and his wife were given a slave girl as a gift. They immediately freed her. Just after the Revolution, in 1787, the Northwest Territory (which became the states of Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin and part of Minnesota) was opened up for settlement. The two men responsible for establishing this territory were Manasseh Cutler and Rufus Putnam. They came from Puritan New England, and they insisted that this new territory, which doubled the size of the United States, was going to be "free soil" – no slavery. This was to prove crucial in the coming decades. If those states had become slave states, and their electoral votes had gone to Abraham Lincoln's main opponent, Lincoln would not have been elected president.

In the decades leading up to the Civil War, the abolitionists, such as Theodore Parker, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry David Thoreau and Frederick Douglass, repeatedly used the Puritan heritage of the country to bolster their cause. The most radical anti-slavery newspaper, The Liberator, invoked the Puritans and Puritan values over a thousand times. Parker, in urging New England Congressmen to support the abolition of slavery, wrote that "The son of the Puritan ... is sent to Congress to stand up for Truth and Right ..."
Northerners predominated in the westward movement into the Midwestern territory after the American Revolution; as the states were organized, they voted to prohibit slavery in their constitutions when they achieved statehood: Ohio in 1803, Indiana in 1816, and Illinois in 1818. What developed was a Northern block of free states united into one contiguous geographic area that generally shared an anti-slavery culture. The exceptions were the areas along the Ohio River settled by Southerners: the southern portions of Indiana, Ohio, and Illinois. Residents of those areas generally shared in Southern culture and attitudes. In addition, these areas were devoted to agriculture longer than the industrializing northern parts of these states, and some farmers used slave labor. In Illinois, for example, while the trade in slaves was prohibited, it was legal to bring slaves from Kentucky into Illinois and use them there, as long as the slaves left Illinois one day per year (they were "visiting"). The emancipation of slaves in the North led to the growth in the population of Northern free blacks, from several hundred in the 1770s to nearly 50,000 by 1810.

Throughout the first half of the 19th century, abolitionism, a movement to end slavery, grew in strength; most abolitionist societies and supporters were in the North. They worked to raise awareness about the evils of slavery, and to build support for abolition. After 1830, abolitionist and newspaper publisher William Lloyd Garrison promoted emancipation, characterizing slaveholding as a personal sin. He demanded that slaveowners repent and start the process of emancipation. His position increased defensiveness on the part of some Southerners, who noted the long history of slavery among many cultures. A few abolitionists, such as John Brown, favored the use of armed force to foment uprisings among the slaves, as he attempted to do at Harper's Ferry. Most abolitionists tried to raise public support to change laws and to challenge slave laws. Abolitionists were active on the lecture circuit in the North, and often featured escaped slaves in their presentations. Writer and orator Frederick Douglass became an important abolitionist leader after escaping from slavery. Harriet Beecher Stowe's novel Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852) was an international bestseller, and along with the non-fiction companion A Key to Uncle Tom's Cabin, aroused popular sentiment against slavery. It also provoked the publication of numerous anti-Tom novels by Southerners in the years before the American Civil War.

This struggle took place amid strong support for slavery among white Southerners, who profited greatly from the system of enslaved labor. But slavery was entwined with the national economy; for instance, the banking, shipping, insurance, and manufacturing industries of New York City all had strong economic interests in slavery, as did similar industries in other major port cities in the North. The Northern textile mills in New York and New England processed Southern cotton and manufactured clothes to outfit slaves. By 1822, half of New York City's exports were related to cotton.
Slaveholders began to refer to slavery as the "peculiar institution" to differentiate it from other examples of forced labor. They justified it as less cruel than the free labor of the North.

The principal organized bodies to advocate abolition and anti-slavery reforms in the north were the Pennsylvania Abolition Society and the New York Manumission Society. Before the 1830s the antislavery groups called for gradual emancipation. By the late 1820s, under the impulse of religious evangelicals such as Beriah Green, the sense emerged that owning slaves was a sin and the owner had to immediately free himself from this grave sin by immediate emancipation.
Prohibiting the international trade
Main article: Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves
Under the Constitution, Congress could not prohibit the import slave trade that was allowed in South Carolina until 1808. However, the third Congress regulated against it in the Slave Trade Act of 1794, which prohibited American shipbuilding and outfitting for the trade. Subsequent acts in 1800 and 1803 sought to discourage the trade by banning American investment in the trade, and American employment on ships in the trade, as well as prohibiting importation into states that had abolished slavery, which all states except South Carolina had by 1807. The final Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves was adopted in 1807 and went into effect in 1808. However, illegal importation of African slaves (smuggling) was common. The Cuban slave trade between 1796 and 1807 was dominated by American slave ships. Despite the 1794 Act, Rhode Island slave ship owners found ways to continue supplying the slave-owning states. The overall U.S. slave-ship fleet in 1806 was estimated to be almost 75% the size of that of the British.
After Great Britain and the United States outlawed the international slave trade in 1807, British slave trade suppression activities began in 1808 through diplomatic efforts and the formation of the Royal Navy's West Africa Squadron in 1809. The United States denied the Royal Navy the right to stop and search U.S. ships suspected as slave ships, so not only were American ships unhindered by British patrols, but slavers from other countries would fly the American flag to try to avoid being stopped. Co-operation between the United States and Britain was not possible during the War of 1812 or the period of poor relations in the following years. In 1820, the United States Navy sent USS Cyane under the command of Captain Edward Trenchard to patrol the slave coasts of West Africa. Cyane seized four American slave ships in her first year on station. Trenchard developed a good level of co-operation with the Royal Navy. Four additional U.S. warships were sent to the African coast in 1820 and 1821. A total of 11 American slave ships were taken by the U.S. Navy over this period. Then American enforcement activity reduced. There was still no agreement between the United States and Britain on a mutual right to board suspected slave traders sailing under each other's flag. Attempts to reach such an agreement stalled in 1821 and 1824 in the United States Senate. A U.S. Navy presence, however sporadic, did result in American slavers sailing under the Spanish flag, but still as an extensive trade. The Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842 set a guaranteed minimum level of patrol activity by the U.S. Navy and the Royal Navy, and formalized the level of co-operation that had existed in 1820. Its effects, however, were minimal while opportunities for greater co-operation were not taken. The U.S. transatlantic slave trade was not effectively suppressed until 1861, during Lincoln's presidency, when a treaty with Britain was signed whose provisions included allowing the Royal Navy to board, search and arrest slavers operating under the American flag.
War of 1812
See also: Black refugee (War of 1812)
During the War of 1812, British Royal Navy commanders of the blockading fleet were instructed to offer freedom to defecting American slaves, as the Crown had during the Revolutionary War. Thousands of escaped slaves went over to the Crown with their families. Men were recruited into the Corps of Colonial Marines on occupied Tangier Island, in the Chesapeake Bay. Many freed American slaves were recruited directly into existing West Indian regiments, or newly created British Army units. The British later resettled a few thousand freed slaves to Nova Scotia. Their descendants, together with descendants of the black people resettled there after the Revolution, have established the Black Loyalist Heritage Museum.
Slaveholders, primarily in the South, had considerable "loss of property" as thousands of slaves escaped to the British lines or ships for freedom, despite the difficulties. The planters' complacency about slave "contentment" was shocked by seeing that slaves would risk so much to be free. Afterward, when some freed slaves had been settled at Bermuda, slaveholders such as Major Pierce Butler of South Carolina tried to persuade them to return to the United States, to no avail.
The Americans protested that Britain's failure to return all slaves violated the Treaty of Ghent. After arbitration by the Tsar of Russia, the British paid $1,204,960 in damages (about $32.4 million in today's money) to Washington, which reimbursed the slaveowners.
Slave rebellions
Main article: Slave rebellion and resistance in the United States See also: Slavery in the colonial United States § Slave rebellions
According to Herbert Aptheker, "there were few phases of ante-bellum Southern life and history that were not in some way influenced by the fear of, or the actual outbreak of, militant concerted slave action."
Historians in the 20th century identified 250 to 311 slave uprisings in U.S. and colonial history. Those after 1776 include:
- Gabriel's conspiracy (1800)
- Igbo Landing slave escape and mass suicide (1803)
- Chatham Manor Rebellion (1805)
- 1811 German Coast uprising, (1811)
- George Boxley Rebellion (1815)
- Denmark Vesey's conspiracy (1822)
- Nat Turner's Rebellion (1831)
- Black Seminole Slave Rebellion (1835–1838)
- Amistad seizure (1839)
- 1842 Slave Revolt in the Cherokee Nation
- Charleston Workhouse Slave Rebellion (1849)
In 1831, Nat Turner, a literate slave who claimed to have spiritual visions, organized a slave rebellion in Southampton County, Virginia; it was sometimes called the Southampton Insurrection. Turner and his followers killed nearly sixty white inhabitants, mostly women and children. Many of the men in the area were attending a religious event in North Carolina. Eventually Turner was captured with 17 other rebels, who were subdued by the militia. Turner and his followers were hanged, and Turner's body was flayed. In a frenzy of fear and retaliation, the militia killed more than 100 slaves who had not been involved in the rebellion. Planters whipped hundreds of innocent slaves to ensure resistance was quelled.
This rebellion prompted Virginia and other slave states to pass more restrictions on slaves and free people of color, controlling their movement and requiring more white supervision of gatherings. In 1835, North Carolina withdrew the franchise for free people of color, and they lost their vote.
There are four known mutinies on vessels involved in the coastwise slave trade: Decatur (1826), Governor Strong (1826), Lafayette (1829), and the Creole (1841).
Post-revolution Southern manumissions

Although Virginia, Maryland and Delaware were slave states, the latter two already had a high proportion of free blacks by the outbreak of war. Following the Revolution, the three legislatures made manumission easier, allowing it by deed or will. Quaker and Methodist ministers in particular urged slaveholders to free their slaves. The number and proportion of freed slaves in these states rose dramatically until 1810. More than half of the number of free blacks in the United States were concentrated in the Upper South. The proportion of free blacks among the black population in the Upper South rose from less than 1 percent in 1792 to more than 10 percent by 1810. In Delaware, nearly 75 percent of black people were free by 1810.
In the United States as a whole, the number of free blacks reached 186,446, or 13.5 percent of all black people by 1810. After that period, few slaves were freed, as the development of cotton plantations featuring short-staple cotton in the Deep South drove up the internal demand for slaves in the domestic slave trade and high prices being paid for them.
South Carolina made manumission more difficult, requiring legislative approval of every manumission. Alabama banned free black people from the state beginning in 1834; free people of color who crossed the state line were subject to enslavement. Free black people in Arkansas after 1843 had to buy a $500 good-behavior bond, and no unenslaved black person was legally allowed to move into the state.
Female slave owners

Women exercised their right to own and control human property without their husbands' interference or permission, and they were active participants in the slave trade. For example, in South Carolina 40% of bills of sale for slaves from the 1700s to the present included a female buyer or seller. Women also governed their slaves in a manner similar to men, engaging in the same levels of physical disciplining. Like men, they brought lawsuits against those who jeopardized their ownership to their slaves.
Black slave owners
Main article: African-American slave ownersDespite the longstanding color line in the United States, some African Americans were slave owners themselves, some in cities and others as plantation owners in the country. Slave ownership signified both wealth and increased social status. Black slave owners were uncommon, however, as "of the two and a half million African Americans living in the United States in 1850, the vast majority enslaved."
Native American slave owners
Main article: Amerindian slave ownershipAfter 1800, some of the Cherokee and the other four civilized tribes of the Southeast started buying and using black slaves as labor. They continued this practice after removal to Indian Territory in the 1830s, when as many as 15,000 enslaved blacks were taken with them.
The nature of slavery in Cherokee society often mirrored that of white slave-owning society. The law barred intermarriage of Cherokees and enslaved African Americans, but Cherokee men had unions with enslaved women, resulting in mixed-race children. Cherokee who aided slaves were punished with one hundred lashes on the back. In Cherokee society, persons of African descent were barred from holding office even if they were also racially and culturally Cherokee. They were also barred from bearing arms and owning property. The Cherokee prohibited the teaching of African Americans to read and write.
By contrast, the Seminole welcomed into their nation African Americans who had escaped slavery (Black Seminoles). Historically, the Black Seminoles lived mostly in distinct bands near the Native American Seminole. Some were held as slaves of particular Seminole leaders. Seminole practice in Florida had acknowledged slavery, though not the chattel slavery model common elsewhere. It was, in fact, more like feudal dependency and taxation. The relationship between Seminole blacks and natives changed following their relocation in the 1830s to territory controlled by the Creek who had a system of chattel slavery. Pro slavery pressure from Creek and pro-Creek Seminole and slave raiding led to many Black Seminoles escaping to Mexico.
High demand and smuggling
Further information: Post-1808 importation of slaves to the United States and Movement to reopen the transatlantic slave trade
The United States Constitution, adopted in 1787, prevented Congress from completely banning the importation of slaves until 1808, although Congress regulated against the trade in the Slave Trade Act of 1794, and in subsequent Acts in 1800 and 1803. During and after the Revolution, the states individually passed laws against importing slaves. By contrast, the states of Georgia and South Carolina reopened their trade due to demand by their upland planters, who were developing new cotton plantations: Georgia from 1800 until December 31, 1807, and South Carolina from 1804. In that period, Charleston traders imported about 75,000 slaves, more than were brought to South Carolina in the 75 years before the Revolution. Approximately 30,000 were imported to Georgia.
By January 1, 1808, when Congress banned further imports, South Carolina was the only state that still allowed importation of enslaved people. The domestic trade became extremely profitable as demand rose with the expansion of cultivation in the Deep South for cotton and sugar cane crops. Slavery in the United States became, more or less, self-sustaining by natural increase among the current slaves and their descendants. Maryland and Virginia viewed themselves as slave producers, seeing "producing slaves" as resembling animal husbandry. Workers, including many children, were relocated by force from the upper to the lower South.
Despite the ban, slave imports continued through smugglers bringing in slaves past the U.S. Navy's African Slave Trade Patrol to South Carolina, and overland from Texas and Florida, both under Spanish control. Congress increased the punishment associated with importing slaves, classifying it in 1820 as an act of piracy, with smugglers subject to harsh penalties, including death if caught. After that, "it is unlikely that more than 10,000 were successfully landed in the United States." But, some smuggling of slaves into the United States continued until just before the start of the Civil War.
Colonization movement
Main articles: American Colonization Society and History of Liberia

In the early part of the 19th century, other organizations were founded to take action on the future of black Americans. Some advocated removing free black people from the United States to places where they would enjoy greater freedom; some endorsed colonization in Africa, while others advocated emigration, usually to Haiti. During the 1820s and 1830s, the American Colonization Society (ACS) was the primary organization to implement the "return" of black Americans to Africa. The ACS was made up mostly of Quakers and slaveholders, and they found uneasy common ground in support of what was incorrectly called "repatriation". By this time, however, most black Americans were native-born and did not want to emigrate, saying they were no more African than white Americans were British. Rather, they wanted full rights in the United States, where their families had lived and worked for generations.
In 1822, the ACS and affiliated state societies established what would become the colony of Liberia, in West Africa. The ACS assisted thousands of freedmen and free blacks (with legislated limits) to emigrate there from the United States. Many white people considered this preferable to emancipation in the United States. Henry Clay, one of the founders and a prominent slaveholder politician from Kentucky, said that blacks faced:
...unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off.
Deportation would also be a way to prevent reprisals against former slaveholders and white people in general, as had occurred in the 1804 Haiti massacre, which had contributed to a consuming fear amongst whites of retributive black violence, a phobia dubbed Haitianism.
Domestic slave trade and forced migration
Main article: Slave trade in the United States Further information: List of slave traders of the United States, Slave markets and slave jails in the United States, and Kidnapping into slavery in the United States See also: Bibliography of the slave trade in the United States and Family separation in American slavery

The U.S. Constitution barred the federal government from prohibiting the importation of slaves for twenty years. Various states passed bans on the international slave trade during that period; by 1808, the only state still allowing the importation of African slaves was South Carolina. After 1808, legal importation of slaves ceased, although there was smuggling via Spanish Florida and the disputed Gulf Coast to the west. This route all but ended after Florida became a U.S. territory in 1821 (but see slave ships Wanderer and Clotilda).
The replacement for the importation of slaves from abroad was increased domestic production. Virginia and Maryland had little new agricultural development, and their need for slaves was mostly for replacements for decedents. Normal reproduction more than supplied these: Virginia and Maryland had surpluses of slaves. Their tobacco farms were "worn out" and the climate was not suitable for cotton or sugar cane. The surplus was even greater because slaves were encouraged to reproduce (though they could not marry). The pro-slavery Virginian Thomas Roderick Dew wrote in 1832 that Virginia was a "negro-raising state"; i.e. Virginia "produced" slaves. According to him, in 1832 Virginia exported "upwards of 6,000 slaves" per year, "a source of wealth to Virginia". A newspaper from 1836 gives the figure as 40,000, earning for Virginia an estimated $24,000,000 per year. Demand for slaves was the strongest in what was then the southwest of the country: Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana, and, later, Texas, Arkansas, and Missouri. Here there was abundant land suitable for plantation agriculture, which young men with some capital established. This was expansion of the white, monied population: younger men seeking their fortune.
The most valuable crop that could be grown on a plantation in that climate was cotton. That crop was labor-intensive, and the least-costly laborers were slaves. Demand for slaves exceeded the supply in the southwest; therefore slaves, never cheap if they were productive, went for a higher price. As portrayed in Uncle Tom's Cabin (the "original" cabin was in Maryland), "selling South" was greatly feared. A recently (2018) publicized example of the practice of "selling South" is the 1838 sale by Jesuits of 272 slaves from Maryland, to plantations in Louisiana, to benefit Georgetown University, which has been described as "ow its existence" to this transaction.
The growing international demand for cotton led many plantation owners further west in search of suitable land. In addition, the invention of the cotton gin in 1793 enabled profitable processing of short-staple cotton, which could readily be grown in the uplands. The invention revolutionized the cotton industry by increasing fifty-fold the quantity of cotton that could be processed in a day. At the end of the War of 1812, fewer than 300,000 bales of cotton were produced nationally. By 1820, the amount of cotton produced had increased to 600,000 bales, and by 1850 it had reached 4,000,000. There was an explosive growth of cotton cultivation throughout the Deep South and greatly increased demand for slave labor to support it. As a result, manumissions decreased dramatically in the South.
Most of the slaves sold from the Upper South were from Maryland, Virginia and the Carolinas, where changes in agriculture decreased the need for their labor and the demand for slaves. Before 1810, primary destinations for the slaves who were sold were Kentucky and Tennessee, but, after 1810, the Deep South states of Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas received the most slaves. This is where cotton became "king". Meanwhile, the Upper South states of Kentucky and Tennessee joined the slave-exporting states.
By 1815, the domestic slave trade had become a major economic activity in the United States; it lasted until the 1860s. Between 1830 and 1840, nearly 250,000 slaves were taken across state lines. In the 1850s, more than 193,000 enslaved persons were transported, and historians estimate nearly one million in total took part in the forced migration of this new "Middle Passage". By 1860, the slave population in the United States had reached four million. Of the 1,515,605 free families in the fifteen slave states in 1860, nearly 400,000 held slaves (roughly one in four, or 25%), amounting to 8% of all American families.

The historian Ira Berlin called this forced migration of slaves the "Second Middle Passage" because it reproduced many of the same horrors as the Middle Passage (the name given to the transportation of slaves from Africa to North America). These sales of slaves broke up many families and caused much hardship. Characterizing it as the "central event" in the life of a slave between the American Revolution and the Civil War, Berlin wrote that, whether slaves were directly uprooted or lived in fear that they or their families would be involuntarily moved, "the massive deportation traumatized black people, both slave and free". Individuals lost their connection to families and clans. Added to the earlier colonists combining slaves from different tribes, many ethnic Africans lost their knowledge of varying tribal origins in Africa. Most were descended from families that had been in the United States for many generations.
The firm of Franklin and Armfield was a leader in this trade. In the 1840s, almost 300,000 slaves were transported, with Alabama and Mississippi receiving 100,000 each. During each decade between 1810 and 1860, at least 100,000 slaves were moved from their state of origin. In the final decade before the Civil War, 250,000 were transported. Michael Tadman wrote in Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South (1989) that 60–70% of inter-regional migrations were the result of the sale of slaves. In 1820, a slave child in the Upper South had a 30 percent chance of being sold South by 1860. The death rate for the slaves on their way to their new destination across the American South was less than that suffered by captives shipped across the Atlantic Ocean, but mortality nevertheless was higher than the normal death rate.
Slave traders transported two-thirds of the slaves who moved West. Only a minority moved with their families and existing master. Slave traders had little interest in purchasing or transporting intact slave families; in the early years, planters demanded only the young male slaves needed for heavy labor. Later, in the interest of creating a "self-reproducing labor force", planters purchased nearly equal numbers of men and women. Berlin wrote:
The internal slave trade became the largest enterprise in the South outside the plantation itself, and probably the most advanced in its employment of modern transportation, finance, and publicity. The slave trade industry developed its own unique language, with terms such as "prime hands, bucks, breeding wenches, and "fancy girls" coming into common use.

The expansion of the interstate slave trade contributed to the "economic revival of once depressed seaboard states" as demand accelerated the value of slaves who were subject to sale. Some traders moved their "chattels" by sea, with Norfolk to New Orleans being the most common route, but most slaves were forced to walk overland. Others were shipped downriver from such markets as Louisville on the Ohio River, and Natchez on the Mississippi. Traders created regular migration routes served by a network of slave pens, yards and warehouses needed as temporary housing for the slaves. In addition, other vendors provided clothes, food and supplies for slaves. As the trek advanced, some slaves were sold and new ones purchased. Berlin concluded, "In all, the slave trade, with its hubs and regional centers, its spurs and circuits, reached into every cranny of southern society. Few southerners, black or white, were untouched."
Once the trip ended, slaves faced a life on the frontier significantly different from most labor in the Upper South. Clearing trees and starting crops on virgin fields was harsh and backbreaking work. A combination of inadequate nutrition, bad water and exhaustion from both the journey and the work weakened the newly arrived slaves and produced casualties. New plantations were located at rivers' edges for ease of transportation and travel. Mosquitoes and other environmental challenges spread disease, which took the lives of many slaves. They had acquired only limited immunities to lowland diseases in their previous homes. The death rate was so high that, in the first few years of hewing a plantation out of the wilderness, some planters preferred whenever possible to use rented slaves rather than their own.
The harsh conditions on the frontier increased slave resistance and led owners and overseers to rely on violence for control. Many of the slaves were new to cotton fields and unaccustomed to the "sunrise-to-sunset gang labor" required by their new life. Slaves were driven much harder than when they had been in growing tobacco or wheat back East. Slaves had less time and opportunity to improve the quality of their lives by raising their own livestock or tending vegetable gardens, for either their own consumption or trade, as they could in the East.

In Louisiana, French colonists had established sugar cane plantations and exported sugar as the chief commodity crop. After the Louisiana Purchase in 1803, Americans entered the state and joined the sugar cultivation. Between 1810 and 1830, planters bought slaves from the North and the number of slaves increased from fewer than 10,000 to more than 42,000. Planters preferred young males, who represented two-thirds of the slave purchases. Dealing with sugar cane was even more physically demanding than growing cotton. The largely young, unmarried male slave force made the reliance on violence by the owners "especially savage".

New Orleans became nationally important as a slave market and port, as slaves were shipped from there upriver by steamboat to plantations on the Mississippi River; it also sold slaves who had been shipped downriver from markets such as Louisville. By 1840, the New Orleans slave market was the largest in North America. It became the wealthiest and the fourth-largest city in the nation, based chiefly on the slave trade and associated businesses. The trading season was from September to May, after the harvest.
The notion that slave traders were social outcasts of low reputation, even in the South, was initially promulgated by defensive southerners and later by figures like historian Ulrich B. Phillips. Historian Frederic Bancroft, author of Slave-Trading in the Old South (1931) found — to the contrary of Phillips's position — that many traders were esteemed members of their communities. Contemporary researcher Steven Deyle argues that the "trader's position in society was not unproblematic and owners who dealt with the trader felt the need to satisfy themselves that they acted honorably," while Michael Tadman contends that "'trader as outcast' operated at the level of propaganda" whereas white slave owners almost universally professed a belief that slaves were not human like them, and thus dismissed the consequences of slave trading as beneath consideration. Similarly, historian Charles Dew read hundreds of letters to slave traders and found virtually zero narrative evidence for guilt, shame, or contrition about the slave trade: "If you begin with the absolute belief in white supremacy—unquestioned white superiority/unquestioned black inferiority—everything falls neatly into place: the African is inferior racial 'stock,' living in sin and ignorance and barbarism and heathenism on the 'Dark Continent' until enslaved...Slavery thus miraculously becomes a form of 'uplift' for this supposedly benighted and brutish race of people. And once notions of white supremacy and black inferiority are in place in the American South, they are passed on from one generation to the next with all the certainty and inevitability of a genetic trait."
In the 1828 presidential election, candidate Andrew Jackson was strongly criticized by opponents as a slave trader who transacted in slaves in defiance of modern standards or morality.
Treatment
Main article: Treatment of slaves in the United States See also: Torture of slaves in the United States, Slave health on plantations in the United States, Slave quarters in the United States, and Field slaves in the United States
The treatment of slaves in the United States varied widely depending on conditions, time, and place, but in general it was brutal, especially on plantations. Whippings and rape were routine. The power relationships of slavery corrupted many whites that had authority over slaves, with children showing their own cruelty. Masters and overseers resorted to physical punishments to impose their wills. Slaves were punished by whipping, shackling, hanging, beating, burning, mutilation, branding and imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but sometimes abuse was carried out to re-assert the dominance of the master or overseer of the slave. Treatment was usually harsher on large plantations, which were often managed by overseers and owned by absentee slaveholders, conditions permitting abuses.
William Wells Brown, who escaped to freedom, reported that on one plantation, slave men were required to pick eighty pounds per day of cotton, while women were required to pick seventy pounds; if any slave failed in his or her quota, they were subject to whip lashes for each pound they were short. The whipping post stood next to the cotton scales. A New York man who attended a slave auction in the mid-19th century reported that at least three-quarters of the male slaves he saw at sale had scars on their backs from whipping. By contrast, small slave-owning families had closer relationships between the owners and slaves; this sometimes resulted in a more humane environment but was not a given.
Historian Lawrence M. Friedman wrote: "Ten Southern codes made it a crime to mistreat a slave. ... Under the Louisiana Civil Code of 1825 (art. 192), if a master was "convicted of cruel treatment", the judge could order the sale of the mistreated slave, presumably to a better master. Masters and overseers were seldom prosecuted under these laws. No slave could give testimony in the courts.

According to Adalberto Aguirre's research, 1,161 slaves were executed in the United States between the 1790s and 1850s. Quick executions of innocent slaves as well as suspects typically followed any attempted slave rebellions, as white militias overreacted with widespread killings that expressed their fears of rebellions, or suspected rebellions.
Although most slaves had lives that were very restricted in terms of their movements and agency, exceptions existed to virtually every generalization; for instance, there were also slaves who had considerable freedom in their daily lives: slaves allowed to rent out their labor and who might live independently of their master in cities, slaves who employed white workers, and slave doctors who treated upper-class white patients. After 1820, in response to the inability to import new slaves from Africa and in part to abolitionist criticism, some slaveholders improved the living conditions of their slaves, to encourage them to be productive and to try to prevent escapes. It was part of a paternalistic approach in the antebellum era that was encouraged by ministers trying to use Christianity to improve the treatment of slaves. Slaveholders published articles in Southern agricultural journals to share best practices in treatment and management of slaves; they intended to show that their system was better than the living conditions of northern industrial workers.
Medical care for slaves was limited in terms of the medical knowledge available to anyone. It was generally provided by other slaves or by slaveholders' family members, although sometimes "plantation physicians", like J. Marion Sims, were called by the owners to protect their investment by treating sick slaves. Many slaves possessed medical skills needed to tend to each other, and used folk remedies brought from Africa. They also developed new remedies based on American plants and herbs.
An estimated nine percent of slaves were disabled due to a physical, sensory, psychological, neurological, or developmental condition. However, slaves were often described as disabled if they were unable to work or bear a child, and were often subjected to harsh treatment as a result.
According to Andrew Fede, an owner could be held criminally liable for killing a slave only if the slave he killed was "completely submissive and under the master's absolute control". For example, in 1791 the North Carolina General Assembly defined the willful killing of a slave as criminal murder, unless done in resisting or under moderate correction (that is, corporal punishment).
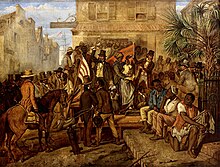
While slaves' living conditions were poor by modern standards, Robert Fogel argued that all workers, free or slave, during the first half of the 19th century were subject to hardship. Unlike free individuals, however, enslaved people were far more likely to be underfed, physically punished, sexually abused, or killed, with no recourse, legal or otherwise, against those who perpetrated these crimes against them.
Commodification of human tissue
In a very grim fashion, the commodification of the human body was legal in the case of African slaves as they were not legally seen as fully human. The most popular means of commodifying slave tissues was through medical experimentation. Slaves were routinely used as medical specimens forced to take part in experimental surgeries, amputations, disease research, and developing medical techniques. Many slaves in these routine experiments were not given pain relief or analgesics, resulting in death by shock on the table. The bodies of such slaves were grouped with other medical cadavers, or sold with the bodies of other slaves sold, stolen, or grave robbed for medical experimentation. In many cases, slave cadavers were used in demonstrations and dissection tables, oftentimes resulting in their tissues being sold for profit.
For the reason of slave punishment, decoration, or self-expression, the skin of slaves was in many instances allowed to be made into leather for furniture, accessories, and clothing, a common instance of which being that of wealthy clientele sending cadaver skin to tanners and shoemakers under the guise of animal leather. Slave hair could be shaved and used for stuffing in pillows and furniture. In some instances, the inner body tissue of slaves (fat, bones, etc.) could be made into soap, medicinal grease, trophies, and other commodities.
Sexual abuse, reproductive exploitation, and breeding farms
Main articles: Slave breeding in the United States, Children of the plantation, Shadow family, and Enslaved women's resistance in the United States and Caribbean
Because of the power relationships at work, slave women in the United States were at high risk for rape and sexual abuse. Their children were repeatedly taken away from them and sold as chattel; usually they never saw each other again. Many slaves fought back against sexual attacks, and some died resisting. Others carried psychological and physical scars from the attacks. Sexual abuse of slaves was partially rooted in a patriarchal Southern culture that treated black women as property or chattel. Southern culture strongly policed against sexual relations between white women and black men on the purported grounds of racial purity but, by the late 18th century, the many mixed-race slaves and slave children showed that white men had often taken advantage of slave women. Wealthy planter widowers, notably such as John Wayles and his son-in-law Thomas Jefferson, took slave women as concubines; each had six children with his partner: Elizabeth Hemings and her daughter Sally Hemings (the half-sister of Jefferson's late wife), respectively. Both Mary Chesnut and Fanny Kemble, wives of planters, wrote about this issue in the antebellum South in the decades before the Civil War. Sometimes planters used mixed-race slaves as house servants or favored artisans because they were their children or other relatives. While publicly opposed to race mixing, in his Notes on the State of Virginia published in 1785, Jefferson wrote: "The improvement of the blacks in body and mind, in the first instance of their mixture with the whites, has been observed by every one, and proves that their inferiority is not the effect merely of their condition of life". Historians estimate that 58% of enslaved women in the U.S. aged 15–30 years were sexually assaulted by their slave owners and other white men. As a result of centuries of slavery and such relationships, DNA studies have shown that the vast majority of African Americans also have historic European ancestry, generally through paternal lines. The average Black American genome is roughly 20-25% European, and it is estimated that as much as one third of their Y chromosomes are of European origin.
Portrayals of black men as hypersexual and savage, along with ideals of protecting white women, were predominant during this time and masked the experiences of sexual violence faced by black male slaves, especially by white women. Subject not only to rape and sexual exploitation, slaves faced sexual violence in many forms. A black man could be forced by his slaveowner to rape another slave or even a free black woman. Forced pairings with other slaves, including forced breeding, which neither slave might desire, were common. Despite explicit bans on homosexuality and sodomy, it was not uncommon for male slaves and children to be sexually harassed and assaulted by their masters in secret. Through sexual and reproductive abuse slaveowners could further enforce their control over their slaves.
The prohibition on the importation of slaves into the United States after 1808 limited the supply of slaves in the United States. This came at a time when the invention of the cotton gin enabled the expansion of cultivation in the uplands of short-staple cotton, leading to clearing lands cultivating cotton through large areas of the Deep South, especially the Black Belt. The demand for labor in the area increased sharply and led to an expansion of the internal slave market. At the same time, the Upper South had an excess number of slaves because of a shift to mixed-crops agriculture, which was less labor-intensive than tobacco. To add to the supply of slaves, slaveholders looked at the fertility of slave women as part of their productivity, and intermittently forced the women to have large numbers of children. During this time period, the terms "breeders", "breeding slaves", "child bearing women", "breeding period", and "too old to breed" became familiar.

As it became popular on many plantations to breed slaves for strength, fertility, or extra labor, there grew many documented instances of "breeding farms" in the United States. Slaves were forced to conceive and birth as many new slaves as possible. The largest farms were located in Virginia and Maryland. Because the industry of slave breeding came from a desire for larger than natural population growth of slaves, slaveowners often turned towards systematic practices for creating more slaves. Female slaves "were subjected to repeated rape or forced sex and became pregnant again and again", even by incest. In horrific accounts of former slaves, some stated that hoods or bags were placed over their heads to prevent them from knowing who they were forced to have sex with. Journalist William Spivey wrote, "It could be someone they know, perhaps a niece, aunt, sister, or their own mother. The breeders only wanted a child that could be sold."
In the United States in the early 19th century, owners of female slaves could freely and legally use them as sexual objects. This follows free use of female slaves on slaving vessels by the crews.
The slaveholder has it in his power, to violate the chastity of his slaves. And not a few are beastly enough to exercise such power. Hence it happens that, in some families, it is difficult to distinguish the free children from the slaves. It is sometimes the case, that the largest part of the master's own children are born, not of his wife, but of the wives and daughters of his slaves, whom he has basely prostituted as well as enslaved.
"This vice, this bane of society, has already become so common, that it is scarcely esteemed a disgrace."

"Fancy" was a code word that indicated that the girl or young woman was suitable for or trained for sexual use. In some cases, children were also abused in this manner. The sale of a 13-year-old "nearly a fancy" is documented. Zephaniah Kingsley, Jr., bought his wife when she was 13.
Furthermore, enslaved women who were old enough to bear children were encouraged to procreate, which raised their value as slaves, since their children would eventually provide labor or be sold, enriching the owners. Enslaved women were sometimes medically treated to enable or encourage their fertility. The variations in skin color found in the United States make it obvious how often black women were impregnated by whites. For example, in the 1850 Census, 75.4% of "free negros" in Florida were described as mulattos, of mixed race. Nevertheless, it is only very recently, with DNA studies, that any sort of reliable number can be provided, and the research has only begun. Light-skinned girls, who contrasted with the darker field workers, were preferred.
As Caroline Randall Williams was quoted in The New York Times: "You Want a Confederate Monument? My Body Is a Confederate Monument." "I have rape-colored skin", she added.
The sexual use of black slaves by either slave owners or by those who could purchase the temporary services of a slave took various forms. A slaveowner, or his teenage son, could go to the slave quarters area of the plantation and do what he wanted, with minimal privacy if any. It was common for a "house" female (housekeeper, maid, cook, laundress, or nanny) to be raped by one or more members of the household. Houses of prostitution throughout the slave states were largely staffed by female slaves providing sexual services, to their owners' profit. There were a small number of free black females engaged in prostitution, or concubinage, especially in New Orleans.
Slave owners who engaged in sexual activity with female slaves "were often the elite of the community. They had little need to worry about public scorn." These relationships "appear to have been tolerated and in some cases even quietly accepted". "Southern women ... do not trouble themselves about it". Franklin and Armfield, who were definitely the elite of the community, joked frequently in their letters about the black women and girls that they were raping. It never occurred to them that there was anything wrong in what they were doing.
Light-skinned young girls were sold openly for sexual use; their price was much higher than that of a field hand. Special markets for the fancy girl trade existed in New Orleans and Lexington, Kentucky. Historian Philip Shaw describes an occasion when Abraham Lincoln and Allen Gentry witnessed such sales in New Orleans in 1828:
Gentry vividly remembered a day in New Orleans when he and the nineteen-year-old Lincoln came upon a slave market. Pausing to watch, Gentry recalled looking down at Lincoln's hands and seeing that he "doubled his fists tightly; his knuckles went white". Men wearing black coats and white hats buy field hands, "black and ugly", for $500 to 800. And then the real horror begins: "When the sale of "fancy girls" began, Lincoln, "unable to stand it any longer", muttered to Gentry "Allen that's a disgrace. If I ever get a lick at that thing I'll hit it hard."
Those girls who were "considered educated and refined, were purchased by the wealthiest clients, usually plantation owners, to become personal sexual companions". "There was a great demand in New Orleans for 'fancy girls'."
The issue that did come up frequently was the threat of sexual intercourse between black males and white females. Just as the black women were perceived as having "a trace of Africa, that supposedly incited passion and sexual wantonness", the men were perceived as savages, unable to control their lust, given an opportunity.
Another approach to the question was offered by Quaker and Florida planter Zephaniah Kingsley, Jr. He advocated, and personally practiced, deliberate racial mixing through marriage, as part of his proposed solution to the slavery issue: racial integration, called "amalgamation" at the time. In an 1829 Treatise, he stated that mixed-race people were healthier and often more beautiful, that interracial sex was hygienic, and slavery made it convenient. Because of these views, tolerated in Spanish Florida, he found it impossible to remain long in Territorial Florida, and moved with his slaves and multiple wives to a plantation, Mayorasgo de Koka, in Haiti (now in the Dominican Republic). There were many others who less flagrantly practiced interracial, common-law marriages with slaves (see Partus sequitur ventrem).
Slave codes
Main article: Slave codes Further information: Slave catcher, Slave patrol, and Slave pass See also: South Carolina slave codes and New York slave codes

To help regulate the relationship between slave and owner, including legal support for keeping the slave as property, states established slave codes, most based on laws existing since the colonial era. The code for the District of Columbia defined a slave as "a human being, who is by law deprived of his or her liberty for life, and is the property of another".
While each state had its own slave code, many concepts were shared throughout the slave states. According to the slave codes, some of which were passed in reaction to slave rebellions, teaching a slave to read or write was illegal. This prohibition was unique to American slavery, believed to reduce slaves forming aspirations that could lead to escape or rebellion. Informal education occurred when white children taught slave companions what they were learning; in other cases, adult slaves learned from free artisan workers, especially if located in cities, where there was more freedom of movement.
In Alabama, slaves were not allowed to leave their master's premises without written consent or passes. This was a common requirement in other states as well, and locally run patrols (known to slaves as pater rollers) often checked the passes of slaves who appeared to be away from their plantations. In Alabama slaves were prohibited from trading goods among themselves. In Virginia, a slave was not permitted to drink in public within one mile of his master or during public gatherings. Slaves were not permitted to carry firearms in any of the slave states.
Slaves were generally prohibited by law from associating in groups, with the exception of worship services (a reason why the Black Church is such a notable institution in black communities today). Following Nat Turner's rebellion in 1831, which raised white fears throughout the South, some states also prohibited or restricted religious gatherings of slaves, or required that they be officiated by white men. Planters feared that group meetings would facilitate communication among slaves that could lead to rebellion. Slaves held private, secret "brush meetings" in the woods.
In Ohio, an emancipated slave was prohibited from returning to the state in which he or she had been enslaved. Other Northern states discouraged the settling of free blacks within their boundaries. Fearing the influence of free blacks, Virginia and other Southern states passed laws to require blacks who had been freed to leave the state within a year (or sometimes less time) unless granted a stay by an act of the legislature.
Religion
Further information: Religion of black Americans, Black Catholicism, and Marriage of enslaved people (United States) See also: Invisible churches, Hush harbor, and Praise house
Africans brought their religions with them from Africa, including Islam, Catholicism, and traditional religions.
Prior to the American Revolution, masters and revivalists spread Christianity to slave communities, including Catholicism in Spanish Florida and California, and in French and Spanish Louisiana, and Protestantism in English colonies, supported by the Society for the Propagation of the Gospel. In the First Great Awakening of the mid-18th century, Baptists and Methodists from New England preached a message against slavery, encouraged masters to free their slaves, converted both slaves and free blacks, and gave them active roles in new congregations. The first independent black congregations were started in the South before the Revolution, in South Carolina and Georgia. Believing that, "slavery was contrary to the ethics of Jesus", Christian congregations and church clergy, especially in the North, played a role in the Underground Railroad, especially Wesleyan Methodists, Quakers and Congregationalists.
Over the decades and with the growth of slavery throughout the South, some Baptist and Methodist ministers gradually changed their messages to accommodate the institution. After 1830, white Southerners argued for the compatibility of Christianity and slavery, with a multitude of both Old and New Testament citations. They promoted Christianity as encouraging better treatment of slaves and argued for a paternalistic approach. In the 1840s and 1850s, the issue of accepting slavery split the nation's largest religious denominations (the Methodist, Baptist and Presbyterian churches) into separate Northern and Southern organizations (see Methodist Episcopal Church, South, Southern Baptist Convention, and Presbyterian Church in the Confederate States of America). Schisms occurred, such as that between the Wesleyan Methodist Church and the Methodist Episcopal Church.
Southern slaves generally attended their masters' white churches, where they often outnumbered the white congregants. They were usually permitted to sit only in the back or in the balcony. They listened to white preachers, who emphasized the obligation of slaves to keep in their place, and acknowledged the slave's identity as both person and property. Preachers taught the master's responsibility and the concept of appropriate paternal treatment, using Christianity to improve conditions for slaves, and to treat them "justly and fairly" (Col. 4:1). This included masters having self-control, not disciplining under anger, not threatening, and ultimately fostering Christianity among their slaves by example.
Slaves also created their own religious observances, meeting alone without the supervision of their white masters or ministers. The larger plantations with groups of slaves numbering 20, or more, tended to be centers of nighttime meetings of one or several plantation slave populations. These congregations revolved around a singular preacher, often illiterate with limited knowledge of theology, who was marked by his personal piety and ability to foster a spiritual environment. African Americans developed a theology related to Biblical stories having the most meaning for them, including the hope for deliverance from slavery by their own Exodus. One lasting influence of these secret congregations is the African American spiritual.
Mandatory illiteracy
Main article: Anti-literacy laws in the United States Further information: Education during the slave period in the United States and Education of freed people during the Civil WarIn a feature unique to American slavery, legislatures across the South enacted new laws to curtail the already limited rights of African Americans. For example, Virginia prohibited blacks, free or slave, from practicing preaching, prohibited them from owning firearms, and forbade anyone to teach slaves or free blacks how to read. It specified heavy penalties for both student and teacher if slaves were taught, including whippings or jail.
very assemblage of negroes for the purpose of instruction in reading or writing, or in the night time for any purpose, shall be an unlawful assembly. Any justice may issue his warrant to any office or other person, requiring him to enter any place where such assemblage may be, and seize any negro therein; and he, or any other justice, may order such negro to be punished with stripes.
Slave owners saw literacy as a threat to the institution of slavery and their financial investment in it; as a North Carolina statute passed in 1830-1831 stated, "Teaching slaves to read and write, tends to excite dissatisfaction in their minds, and to produce insurrection and rebellion." Literacy enabled the enslaved to read the writings of abolitionists, which discussed the abolition of slavery and described the slave revolution in Haiti of 1791–1804 and the end of slavery in the British Empire in 1833. It also allowed slaves to learn that thousands of enslaved individuals had escaped, often with the assistance of the Underground Railroad. Literacy also was believed to make the enslaved unhappy at best, insolent and sullen at worst. As put by prominent Washington lawyer Elias B. Caldwell in 1822:
The more you improve the condition of these people, the more you cultivate their minds, the more miserable you make them, in their present state. You give them a higher relish for those privilegies which they can never attain, and turn what we intend for a blessing into a curse. No, if they must remain in their present situation, keep them in the lowest state of degradation and ignorance. The nearer you bring them to the condition of brutes, the better chance do you give them of possessing their apathy.
Unlike in the South, slave owners in Utah were required to send their slaves to school. Black slaves did not have to spend as much time in school as Indian slaves.
Freedom suits and Dred Scott
Main articles: Dred Scott v. Sandford and Freedom suits
With the development of slave and free states after the American Revolution, and far-flung commercial and military activities, new situations arose in which slaves might be taken by masters into free states. Most free states not only prohibited slavery, but ruled that slaves brought and kept there illegally could be freed. Such cases were sometimes known as transit cases. Dred Scott and his wife Harriet Scott each sued for freedom in St. Louis after the death of their master, based on their having been held in a free territory (the northern part of the Louisiana Purchase from which slavery was excluded under the terms of the Missouri Compromise). (Later the two cases were combined under Dred Scott's name.) Scott filed suit for freedom in 1846 and went through two state trials, the first denying and the second granting freedom to the couple (and, by extension, their two daughters, who had also been held illegally in free territories). For 28 years, Missouri state precedent had generally respected laws of neighboring free states and territories, ruling for freedom in such transit cases where slaves had been held illegally in free territory. But in the Dred Scott case, the Missouri Supreme Court ruled against the slaves.
After Scott and his team appealed the case to the U.S. Supreme Court, Chief Justice Roger B. Taney, in a sweeping decision, denied Scott his freedom. The 1857 decision, decided 7–2, held that a slave did not become free when taken into a free state; Congress could not bar slavery from a territory; and people of African descent imported into the United States and held as slaves, or their descendants, could never be citizens and thus had no status to bring suit in a U.S. court. A state could not bar slaveowners from bringing slaves into that state. Many Republicans, including Abraham Lincoln, considered the decision unjust and evidence that the Slave Power had seized control of the Supreme Court. Anti-slavery groups were enraged and slave owners encouraged, escalating the tensions that led to civil war.
1850 to the firing on Fort Sumter
Further information: Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § Compromise of 1850 to the Election of 1860, and Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War § Election of 1860 to the Battle of Fort Sumter See also: Bleeding Kansas and 1860 United States presidential election


In 1850, Congress passed the Fugitive Slave Act, as part of the Compromise of 1850, which required law enforcement and citizens of free states to cooperate in the capture and return of slaves. This met with considerable overt and covert resistance in free states and cities such as Philadelphia, New York, and Boston. Refugees from slavery continued to flee the South across the Ohio River and other parts of the Mason–Dixon line dividing North from South, to the North and Canada via the Underground Railroad. Some white Northerners helped hide former slaves from their former owners or helped them reach freedom in Canada.
As part of the Compromise of 1850, Congress abolished the slave trade (though not the ownership of slaves) in the District of Columbia; fearing this would happen, Alexandria, regional slave trading center and port, successfully sought its removal from the District of Columbia and devolution to Virginia. After 1854, Republicans argued that the "Slave Power", especially the pro-slavery Democratic Party in the South, controlled two of the three branches of the Federal government.
The abolitionists, realizing that the total elimination of slavery was unrealistic as an immediate goal, worked to prevent the expansion of slavery into the western territories that eventually would become new states. The Missouri Compromise, the Compromise of 1850, and the Bleeding Kansas period dealt with whether new states would be slave or free, or how that was to be decided. Both sides were anxious about effects of these decisions on the balance of power in the Senate.
After the passage of the Kansas–Nebraska Act in 1854, border fighting broke out in the Kansas Territory, where the question of whether it would be admitted to the Union as a slave or free state was left to the inhabitants. Migrants from both free and slave states moved into the territory to prepare for the vote on slavery. Abolitionist John Brown, the most famous of the anti-slavery immigrants, was active in the fighting in "Bleeding Kansas", but so too were many white Southerners (many from adjacent Missouri) who opposed abolition.
Abraham Lincoln's and the Republicans' political platform in 1860 was to stop slavery's expansion. Historian James M. McPherson says that in his famous "House Divided" speech in 1858, Lincoln said American republicanism can be purified by restricting the further expansion of slavery as the first step to putting it on the road to 'ultimate extinction.' Southerners took Lincoln at his word. When he won the presidency, they left the Union to escape the 'ultimate extinction' of slavery."
The divisions became fully exposed with the 1860 presidential election. The electorate split four ways. The Southern Democrats endorsed slavery, while the Republican Party denounced it. The Northern Democrats said democracy required the people to decide on slavery locally, state by state and territory by territory. The Constitutional Union Party said the survival of the Union was at stake and everything else should be compromised.
Lincoln, the Republican, won with a plurality of popular votes and a majority of electoral votes. Lincoln, however, did not appear on the ballots of ten southern slave states. Many slave owners in the South feared that the real intent of the Republicans was the abolition of slavery in states where it already existed, and that the sudden emancipation of four million slaves would be disastrous for the slave owners and for the economy that drew its greatest profits from the labor of people who were not paid. The slave owners feared that ending the balance could lead to the domination of the federal government by the northern free states. This led seven southern states to secede from the Union. When the Confederate Army attacked a U.S. Army installation at Fort Sumter, the American Civil War began and four additional slave states seceded. Northern leaders had viewed the slavery interests as a threat politically, but with secession, they viewed the prospect of a new Southern nation, the Confederate States of America, with control over the Mississippi River and parts of the West, as politically unacceptable. Most of all, they could not accept this repudiation of American nationalism.
Civil War and emancipation
Main article: Slavery during the American Civil War Events leading to the American Civil War- Northwest Ordinance (1787)
- Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions (1798–99)
- End of Atlantic slave trade
- Missouri Compromise (1820)
- Tariff of 1828
- Nat Turner's Rebellion (1831)
- Nullification crisis (1832–33)
- Abolition of slavery across British colonies (1834)
- Texas Revolution (1835–36)
- United States v. Crandall (1836)
- Gag rule (1836–44)
- Commonwealth v. Aves (1836)
- Murder of Elijah Lovejoy (1837)
- Burning of Pennsylvania Hall (1838)
- American Slavery As It Is (1839)
- United States v. The Amistad (1841)
- Prigg v. Pennsylvania (1842)
- Texas annexation (1845)
- Mexican–American War (1846–48)
- Wilmot Proviso (1846)
- Nashville Convention (1850)
- Compromise of 1850
- Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852)
- Recapture of Anthony Burns (1854)
- Kansas–Nebraska Act (1854)
- Ostend Manifesto (1854)
- Bleeding Kansas (1854–61)
- Caning of Charles Sumner (1856)
- Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
- The Impending Crisis of the South (1857)
- Panic of 1857
- Lincoln–Douglas debates (1858)
- Oberlin–Wellington Rescue (1858)
- John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry (1859)
- Virginia v. John Brown (1859)
- 1860 presidential election
- Crittenden Compromise (1860)
- Secession of Southern states (1860–61)
- Peace Conference of 1861
- Corwin Amendment (1861)
- Battle of Fort Sumter (1861)


American Civil War
Main articles: Origins of the American Civil War, American Civil War, Contraband (American Civil War), and Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War See also: Confiscation Acts and Act Prohibiting the Return of SlavesThe American Civil War, beginning in 1861, led to the end of chattel slavery in America. Not long after the war broke out, through a legal maneuver by Union General Benjamin F. Butler, a lawyer by profession, slaves who fled to Union lines were considered "contraband of war". General Butler ruled that they were not subject to return to Confederate owners as they had been before the war. "Lincoln and his Cabinet discussed the issue on May 30 and decided to support Butler's stance". Soon word spread, and many slaves sought refuge in Union territory, desiring to be declared "contraband". Many of the "contrabands" joined the Union Army as workers or troops, forming entire regiments of the U.S. Colored Troops. Others went to refugee camps such as the Grand Contraband Camp near Fort Monroe or fled to northern cities. General Butler's interpretation was reinforced when Congress passed the Confiscation Act of 1861, which declared that any property used by the Confederate military, including slaves, could be confiscated by Union forces.

At the beginning of the war, some Union commanders thought they were supposed to return escaped slaves to their masters. By 1862, when it became clear that this would be a long war, the question of what to do about slavery became more general. The Southern economy and military effort depended on slave labor. It began to seem unreasonable to protect slavery while blockading Southern commerce and destroying Southern production. As Congressman George W. Julian of Indiana put it in an 1862 speech in Congress, the slaves "cannot be neutral. As laborers, if not as soldiers, they will be allies of the rebels, or of the Union." Julian and his fellow Radical Republicans put pressure on Lincoln to rapidly emancipate the slaves, whereas moderate Republicans favored gradual, compensated emancipation and voluntary colonization. The border states, Peace Democrats (Copperheads), and War Democrats opposed emancipation, although the border states and War Democrats eventually accepted it as part of the total war needed to save the Union.
Emancipation Proclamation
Main article: Emancipation ProclamationThe Emancipation Proclamation was an executive order issued by President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863. In a single stroke it changed the legal status of three million slaves in designated areas of the Confederacy from "slave" to "free". It had the practical effect that as soon as a slave escaped the control of his or her owner, by running away or through advances of federal troops, the slave's proclaimed freedom became actual. Plantation owners, realizing that emancipation would destroy their economic system, sometimes moved their slaves as far as possible out of reach of the Union army. By June 1865, the Union Army controlled all of the Confederacy and had liberated all of the designated slaves.
In 1861, Lincoln expressed the fear that premature attempts at emancipation would mean the loss of the border states. He believed that "to lose Kentucky is nearly the same as to lose the whole game." At first, Lincoln reversed attempts at emancipation by Secretary of War Simon Cameron and Generals John C. Frémont (in Missouri) and David Hunter (in South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) to keep the loyalty of the border states and the War Democrats.

On July 22, 1862, Lincoln told his cabinet of his plan to issue a preliminary Emancipation Proclamation. Secretary of State William H. Seward advised Lincoln to wait for a victory before issuing the proclamation, as to do otherwise would seem like "our last shriek on the retreat". On September 17, 1862, the Battle of Antietam provided this opportunity, and on September 22, 1862, Lincoln issued his preliminary Emancipation Proclamation, which provided that enslaved people in the states in rebellion against the United States on January 1, 1863, "shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free". On September 24 and 25, the War Governors' Conference added support for the proclamation. Lincoln issued his final Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863. In his letter to Albert G. Hodges, Lincoln explained his belief that
If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong ... And yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act officially upon this judgment and feeling ... I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me.
Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation declared freedom for slaves in the Confederate states and authorized the enlistment of African Americans in the Union Army. The Emancipation Proclamation did not free slaves in the border states, which were the slaveholding states that remained in the Union. As a practical matter, the proclamation freed only those slaves who escaped to Union lines. But the proclamation made the abolition of slavery an official war goal and was implemented as the Union took territory from the Confederacy. According to the Census of 1860, this policy would free nearly four million slaves, or over 12 percent of the total population of the United States.
Because the Emancipation Proclamation was issued under the president's war powers, it might not have continued in force after the war ended. Therefore, Lincoln played a leading role in getting the constitutionally required two-thirds majority of both houses of Congress to vote for the Thirteenth Amendment, which made emancipation universal and permanent, "except as a punishment for crime".

Enslaved African Americans had not waited for Lincoln before escaping and seeking freedom behind Union lines. From the early years of the war, hundreds of thousands of African Americans escaped to Union lines, especially in Union-controlled areas such as Norfolk and the Hampton Roads region in 1862 Virginia, Tennessee from 1862 on, and the line of Sherman's march. So many African Americans fled to Union lines that commanders created camps and schools for them, where both adults and children learned to read and write. The American Missionary Association entered the war effort by sending teachers south to such contraband camps, for instance, establishing schools in Norfolk and on nearby plantations.
In addition, nearly 200,000 African-American men served with distinction in the Union forces as soldiers and sailors; most were escaped slaves. The Confederacy was outraged by armed black soldiers and refused to treat them as prisoners of war. They murdered many, as at the Fort Pillow massacre, and re-enslaved others.
On February 24, 1863, the Arizona Organic Act abolished slavery in the newly formed Arizona Territory. Tennessee and all of the border states (except Kentucky and Delaware) abolished slavery by early 1865. Thousands of slaves were freed by the operation of the Emancipation Proclamation as Union armies marched across the South. Emancipation came to the remaining Southern slaves after the surrender of all the Confederate troops in spring 1865.
In spite of the South's shortage of manpower, until 1865, most Southern leaders opposed arming slaves as soldiers. However, a few Confederates discussed arming slaves. Finally, in early 1865, General Robert E. Lee said that black soldiers were essential, and legislation was passed. The first black units were in training when the war ended in April.
End of slavery
Main article: End of slavery in the United States of America Further information: Slave states and free states § End of slavery, Emancipation Day § United States, and Compensated emancipation in the United States See also: Family reunification ads after emancipation
Booker T. Washington remembered Emancipation Day in early 1863, when he was a boy of nine in Virginia:
As the great day drew nearer, there was more singing in the slave quarters than usual. It was bolder, had more ring, and lasted later into the night. Most of the verses of the plantation songs had some reference to freedom. ... Some man who seemed to be a stranger (a United States officer, I presume) made a little speech and then read a rather long paper – the Emancipation Proclamation, I think. After the reading we were told that we were all free, and could go when and where we pleased. My mother, who was standing by my side, leaned over and kissed her children, while tears of joy ran down her cheeks. She explained to us what it all meant, that this was the day for which she had been so long praying, but fearing that she would never live to see.
The war ended on June 22, 1865, and following that surrender, the Emancipation Proclamation was enforced throughout remaining regions of the South that had not yet freed the slaves. Slavery officially continued for a couple of months in other locations. Federal troops arrived in Galveston, Texas, on June 19, 1865, to enforce the emancipation. The commemoration of that event, Juneteenth National Independence Day, was declared a national holiday in 2021.
The Thirteenth Amendment, abolishing slavery except as punishment for a crime, had been passed by the Senate in April 1864, and by the House of Representatives in January 1865.

The amendment did not take effect until it was ratified by three-fourths of the states, which occurred on December 6, 1865, when Georgia ratified it. On that date, the last 40,000–45,000 enslaved Americans in the remaining two slave states of Kentucky and Delaware, as well as the 200 or so perpetual apprentices in New Jersey left from the very gradual emancipation process begun in 1804, were freed. The last Americans known to have been born into legal slavery died in the 1970s.
Reconstruction to the present
Further information: Reconstruction Era and Reconstruction Amendments See also: History of unfree labor in the United States and History of civil rights in the United States
Journalist Douglas A. Blackmon reported in his Pulitzer Prize-winning book Slavery By Another Name that many black persons were virtually enslaved under convict leasing programs, which started after the Civil War. Most Southern states had no prisons; they leased convicts to businesses and farms for their labor, and the lessee paid for food and board. Incentives for abuse were present.
The continued involuntary servitude took various forms, but the primary forms included convict leasing, peonage and sharecropping, with the latter eventually encompassing poor whites as well. By the 1930s, whites constituted most of the sharecroppers in the South. Mechanization of agriculture had reduced the need for farm labor, and many black people left the South in the Great Migration. Jurisdictions and states created fines and sentences for a wide variety of minor crimes and used these as an excuse to arrest and sentence black people. Under convict-leasing programs, African-American men, often guilty of petty crimes or even no crime at all, were arrested, compelled to work without pay, repeatedly bought and sold, and coerced to do the bidding of the leaseholder. Sharecropping, as it was practiced during this period, often involved severe restrictions on the freedom of movement of sharecroppers, who could be whipped for leaving the plantation. Both sharecropping and convict leasing were legal and tolerated by both the North and South. However, peonage was an illicit form of forced labor. Its existence was ignored by authorities while thousands of African Americans and poor white Americans were subjugated and held in bondage until the mid-1960s to the late 1970s. With the exception of cases of peonage, beyond the period of Reconstruction, the federal government took almost no action to enforce the Thirteenth Amendment until December 1941, when President Franklin Delano Roosevelt summoned his attorney general. Five days after the attack on Pearl Harbor, at the request of the President, Attorney General Francis Biddle issued Circular No. 3591 to all federal prosecutors, instructing them to investigate actively and try any case of involuntary servitude or slavery. Several months later, convict leasing was officially abolished. But aspects have persisted in other forms. Historians argue that other systems of penal labor were all created in 1865, and convict leasing was simply the most oppressive form. Over time, a large civil rights movement arose to bring full civil rights and equality under the law to all Americans.
Convict leasing
Main articles: Convict lease and Penal labor in the United States

With emancipation a legal reality, white Southerners were concerned with both controlling the newly freed slaves and keeping them in the labor force at the lowest level. The system of convict leasing began during Reconstruction and was fully implemented in the 1880s, officially ending in the last state, Alabama, in 1928. It persisted in various forms until it was abolished in 1942 by President Franklin D. Roosevelt during World War II, several months after the attack on Pearl Harbor involved the U.S. in the conflict. This system allowed private contractors to purchase the services of convicts from the state or local governments for a specific time period. African Americans, due to "vigorous and selective enforcement of laws and discriminatory sentencing", made up the vast majority of the convicts leased. Writer Douglas A. Blackmon writes of the system:
It was a form of bondage distinctly different from that of the antebellum South in that for most men, and the relatively few women drawn in, this slavery did not last a lifetime and did not automatically extend from one generation to the next. But it was nonetheless slavery – a system in which armies of free men, guilty of no crimes and entitled by law to freedom, were compelled to labor without compensation, were repeatedly bought and sold, and were forced to do the bidding of white masters through the regular application of extraordinary physical coercion.
The constitutional basis for convict leasing is that the Thirteenth Amendment, while abolishing slavery and involuntary servitude generally, expressly permits it as a punishment for crime.
Educational issues
Historian Mark Summers Wahlgren notes that the estimated literacy rate among formerly enslaved southern blacks at the time of emancipation was five to 10 percent, but had reached a baseline of 40 to 50 percent (and higher in cities) by the turn of the century, representing a "great advance". As W. E. B. Du Bois noted, the black colleges were not perfect, but "in a single generation they put thirty thousand black teachers in the South" and "wiped out the illiteracy of the majority of black people in the land".

Northern philanthropists continued to support black education in the 20th century, for example of a major donor to Hampton Institute and Tuskegee was George Eastman, who also helped fund health programs at colleges and in communities.
Apologies
Main article: Public apologies for slavery in the United StatesIn the 21st century, various legislative bodies have issued public apologies for slavery in the United States.
Political legacy
A 2016 study, published in The Journal of Politics, finds that "hites who currently live in Southern counties that had high shares of slaves in 1860 are more likely to identify as a Republican, oppose affirmative action, and express racial resentment and colder feelings toward blacks." The study contends that "contemporary differences in political attitudes across counties in the American South in part trace their origins to slavery's prevalence more than 150 years ago. " The authors argue that their findings are consistent with the theory that "following the Civil War, Southern whites faced political and economic incentives to reinforce existing racist norms and institutions to maintain control over the newly freed African American population. This amplified local differences in racially conservative political attitudes, which in turn have been passed down locally across generations."

A 2017 study in the British Journal of Political Science argued that the British American colonies without slavery adopted better democratic institutions to attract migrant workers to their colonies.
An article published in the Journal of Economic History in 2022 finds that former slave owners remained politically dominant long after the abolition of slavery. Using data from Texas, the authors find that "n 1900, still around 50 percent of all state legislators came from a slave-owning background."
Economics

Robert Fogel and Stanley Engerman, in their 1974 book Time on the Cross, argued that the rate of return of slavery at the market price was close to ten percent, a number close to investment in other assets. The transition from indentured servants to slaves is cited to show that slaves offered greater profits to their owners. A qualified consensus among economic historians and economists is that "Slave agriculture was efficient compared with free agriculture. Economies of scale, effective management, and intensive utilization of labor and capital made southern slave agriculture considerably more efficient than nonslave southern farming", and it is the near-universal consensus among economic historians and economists that slavery was not "a system irrationally kept in existence by plantation owners who failed to perceive or were indifferent to their best economic interests".
The relative price of slaves and indentured servants in the antebellum period did decrease. Indentured servants became more costly with the increase in the demand of skilled labor in England. At the same time, slaves were mostly supplied from within the United States and thus language was not a barrier, and the cost of transporting slaves from one state to another was relatively low. However, as in Brazil and Europe, slavery at its end in the United States tended to be concentrated in the poorest regions of the United States, with a qualified consensus among economists and economic historians concluding that the "modern period of the South's economic convergence to the level of the North only began in earnest when the institutional foundations of the southern regional labor market were undermined, largely by federal farm and labor legislation dating from the 1930s."
In the decades preceding the Civil War, the black population of the United States experienced a rapid natural increase. Unlike the trans-Saharan slave trade with Africa, the slave population transported by the Atlantic slave trade to the United States was sex-balanced. The slave population multiplied nearly fourfold between 1810 and 1860, despite the passage of the Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves signed into law by President Thomas Jefferson in 1807 banning the international slave trade. Thus, it is also the universal consensus among modern economic historians and economists that slavery in the United States was not "economically moribund on the eve of the Civil War". In the 2010s, several historians, among them Edward E. Baptist, Sven Beckert, Walter Johnson and Calvin Schermerhorn, have posited that slavery was integral in the development of American capitalism. Johnson wrote in River of Dark Dreams (2013): "The cords of credit and debt—of advance and obligation—that cinched the Atlantic economy together were anchored with the mutually defining values of land and slaves: without land and slaves, there was no credit, and without slaves, land itself was valueless. Promises made in the Mississippi Valley were backed by the value of slaves and fulfilled in their labor." Other economic historians have rejected that thesis.
A 2023 study estimates that prior to the onset of the US Civil War, the enslaved population produced 12.6% of US national product.
Slavery had a long-lasting impact on wealth and racial inequality in the United States. Black families whose ancestors were freed before the start of the Civil War have substantially better socio-economic outcomes than families who were freed in the Civil War.
Efficiency of slaves

Scholars disagree on how to quantify the efficiency of slavery. In Time on the Cross Fogel and Engerman equate efficiency to total factor productivity (TFP), the output per average unit of input on a farm. Using this measurement, Southern farms that enslaved black people using the gang system were 35% more efficient than Northern farms, which used free labor. Under the gang system, groups of slaves perform synchronized tasks under the constant vigilance of an overseer. Each group was like a part of a machine. If perceived to be working below his capacity, a slave could be punished. Fogel argues that this kind of negative enforcement was not frequent and that slaves and free laborers had a similar quality of life; however, there is controversy on this last point. A critique of Fogel and Engerman's view was published by Paul A. David in 1976.
In 1995, a random survey of 178 members of the Economic History Association sought to study the views of economists and economic historians on the debate. The study found that 72 percent of economists and 65 percent of economic historians would generally agree that "Slave agriculture was efficient compared with free agriculture. Economies of scale, effective management, and intensive utilization of labor and capital made southern slave agriculture considerably more efficient than nonslave southern farming." 48 percent of the economists agreed without provisos, while 24 percent agreed when provisos were included in the statement. On the other hand, 58 percent of economic historians and 42 percent of economists disagreed with Fogel and Engerman's "proposition that the material (not psychological) conditions of the lives of slaves compared favorably with those of free industrial workers in the decades before the Civil War".
Prices of slaves
The U.S. has a capitalist economy so the price of slaves was determined by the law of supply and demand. For example, following bans on the import of slaves after the UK's Slave Trade Act 1807 and the American 1807 Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves, the prices for slaves increased. The markets for the products produced by slaves also affected the price of slaves (e.g. the price of slaves fell when the price of cotton fell in 1840). Anticipation of slavery's abolition also influenced prices. During the Civil War the price for slave men in New Orleans dropped from $1,381 in 1861 to $1,116 by 1862 (the city was captured by U.S. forces in the Spring of 1862).

Controlling for inflation, prices of slaves rose dramatically in the six decades prior to the Civil War, reflecting demand due to commodity cotton, as well as use of slaves in shipping and manufacturing. Although the prices of slaves relative to indentured servants declined, both got more expensive. Cotton production was rising and relied on the use of slaves to yield high profits. Fogel and Engeman initially argued that if the Civil War had not happened, the slave prices would have increased even more, an average of more than fifty percent by 1890.
Prices reflected the characteristics of the slave; such factors as sex, age, nature, and height were all taken into account to determine the price of a slave. Over the life-cycle, the price of enslaved women was higher than their male counterparts up to puberty age, as they would likely bear children who their masters could sell as slaves and could be used as slave laborers. Men around the age of 25 were the most valued, as they were at the highest level of productivity and still had a considerable life-span. If slaves had a history of fights or escapes, their price was lowered reflecting what planters believed was risk of repeating such behavior. Slave traders and buyers would examine a slave's back for whipping scars; a large number of injuries would be seen as evidence of laziness or rebelliousness, rather than the previous master's brutality, and would lower the slave's price. Taller male slaves were priced at a higher level, as height was viewed as a proxy for fitness and productivity.
Effects on Southern economic development

While slavery brought profits in the short run, discussion continues on the economic benefits of slavery in the long run. In 1995, a random anonymous survey of 178 members of the Economic History Association found that out of the forty propositions about American economic history that were surveyed, the group of propositions most disputed by economic historians and economists were those about the postbellum economy of the American South (along with the Great Depression). The only exception was the proposition initially put forward by historian Gavin Wright that the "modern period of the South's economic convergence to the level of the North only began in earnest when the institutional foundations of the southern regional labor market were undermined, largely by federal farm and labor legislation dating from the 1930s." 62 percent of economists (24 percent with and 38 percent without provisos) and 73 percent of historians (23 percent with and 50 percent without provisos) agreed with this statement. Wright has also argued that the private investment of monetary resources in the cotton industry, among others, delayed development in the South of commercial and industrial institutions. There was little public investment in railroads or other infrastructure. Wright argues that agricultural technology was far more developed in the South, representing an economic advantage of the South over the North of the United States.
In Democracy in America, Alexis de Tocqueville noted that "the colonies in which there were no slaves became more populous and more rich than those in which slavery flourished". In 1857, in The Impending Crisis of the South: How to Meet It, Hinton Rowan Helper made the same point. Economists Peter H. Lindert and Jeffrey G. Williamson, in a pair of articles published in 2012 and 2013, found that, despite the American South initially having per capita income roughly double that of the North in 1774, incomes in the South had declined 27% by 1800 and continued to decline over the next four decades, while the economies in New England and the Mid-Atlantic states vastly expanded. By 1840, per capita income in the South was well behind the Northeast and the national average (Note: this is also true in the early 21st century).

Lindert and Williamson argue that this antebellum period is an example of what economists Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James A. Robinson call "a reversal of fortune". In his essay "The Real History of Slavery", economist Thomas Sowell reiterated and augmented the observation made by de Tocqueville by comparing slavery in the United States to slavery in Brazil. He notes that slave societies reflected similar economic trends in those and other parts of the world, suggesting that the trend Lindert and Williamson identify may have continued until the American Civil War:
Both in Brazil and in the United States – the countries with the two largest slave populations in the Western Hemisphere – the end of slavery found the regions in which slaves had been concentrated poorer than other regions of these same countries. For the United States, a case could be made that this was due to the Civil War, which did so much damage to the South, but no such explanation would apply to Brazil, which fought no Civil War over this issue. Moreover, even in the United States, the South lagged behind the North in many ways even before the Civil War. Although slavery in Europe died out before it was abolished in the Western Hemisphere, as late as 1776 slavery had not yet died out all across the continent when Adam Smith wrote in The Wealth of Nations that it still existed in some eastern regions. But, even then, Eastern Europe was much poorer than Western Europe. The slavery of North Africa and the Middle East, over the centuries, took more slaves from sub-Saharan Africa than the Western Hemisphere did ... But these remained largely poor countries until the discovery and extraction of their vast oil deposits.

Sowell also notes in Ethnic America: A History, citing historians Clement Eaton and Eugene Genovese, that three-quarters of Southern white families owned no slaves at all. Most slaveholders lived on farms rather than plantations, and few plantations were as large as the fictional ones depicted in Gone with the Wind. In "The Real History of Slavery", Sowell also notes in comparison to slavery in the Arab world and the Middle East (where slaves were seldom used for productive purposes) and China (where the slaves consumed the entire output they created), Sowell observes that many commercial slaveowners in the antebellum South tended to be spendthrift and many lost their plantations due to creditor foreclosures, and in Britain, profits by British slave traders only amounted to two percent of British domestic investment at the height of the Atlantic slave trade in the 18th century. Sowell draws the following conclusion regarding the macroeconomic value of slavery:
In short, even though some individual slaveowners grew rich and some family fortunes were founded on the exploitation of slaves, that is very different from saying that the whole society, or even its non-slave population as a whole, was more economically advanced than it would have been in the absence of slavery. What this means is that, whether employed as domestic servants or producing crops or other goods, millions suffered exploitation and dehumanization for no higher purpose than the ... aggrandizement of slaveowners.
Eric Hilt noted that, while some historians have suggested slavery was necessary for the Industrial Revolution (on the grounds that American slave plantations produced most of the raw cotton for the British textiles market and the British textiles market was the vanguard of the Industrial Revolution), it is not clear if this is actually true; there is no evidence that cotton could not have been mass-produced by yeoman farmers rather than slave plantations if the latter had not existed (as their existence tended to force yeoman farmers into subsistence farming) and there is some evidence that they certainly could have. The soil and climate of the American South were excellent for growing cotton, so it is not unreasonable to postulate that farms without slaves could have produced substantial amounts of cotton; even if they did not produce as much as the plantations did, it could still have been enough to serve the demand of British producers. Similar arguments have been made by other historians.
Sexual economy of American slavery

Scholar Adrienne Davis articulates how the economics of slavery also can be defined as a sexual economy, specifically focusing on how black women were expected to perform physical, sexual and reproductive labor to provide a consistent enslaved workforce and increase the profits of white slavers. Davis writes that black women were needed for their "sexual and reproductive labor to satisfy the economic, political, and personal interest of white men of the elite class" articulating that black women's reproductive capacity was important in the maintenance of the system of slavery due to its ability to perpetuate an enslaved workforce. She is also drawing attention to black women's labor being needed to maintain the aristocracy of a white ruling class, due to the intimate nature of reproduction and its potential for producing more enslaved peoples.
Due to the institution of partus sequitur ventrem, black women's wombs became the site where slavery was developed and transferred, meaning that black women were not only used for their physical labor, but for their sexual and reproductive labor as well.
"The rule that the children's status follows their mothers' was a foundational one for our economy. It converted enslaved women's reproductive capacity into market capital"

This articulation by Davis illustrates how black women's reproductive capacity was commodified under slavery, and that an analysis of the economic structures of slavery requires an acknowledgment of how pivotal black women's sexuality was in maintaining slavery's economic power. Davis writes how black women performed labor under slavery, writing: " male when convenient and horrifically female when needed". The fluctuating expectations of black women's gendered labor under slavery disrupted the white normative roles that were assigned to white men and white women. This ungendering black women received under slavery contributed to the systemic dehumanization experienced by enslaved black women, as they were unable to receive the expectations or experiences of either gender within the white binary.
Davis's arguments address the fact that, under slavery, black women's sexuality became linked to the economic and public sphere, making their intimate lives into public institutions. Black women's physical labor was gendered as masculine under slavery when they were needed to yield more profit, but their reproductive capacities and sexual labor were equally as important in maintaining white power over black communities and perpetuating an enslaved workforce.
Geography and demography

Slave importation
About 600,000 slaves were transported to the United States, or five percent of the 12 million slaves taken from Africa. About 310,000 of these persons were imported into the Thirteen Colonies before 1776: 40 percent directly, and the rest from the Caribbean.
| Time period | Quantity |
|---|---|
| 1620–1700 | 21,000 |
| 1701–1760 | 189,000 |
| 1761–1770 | 63,000 |
| 1771–1790 | 56,000 |
| 1791–1800 | 79,000 |
| 1801–1810 | 124,000 |
| 1810–1865 | 51,000 |
| Total | 597,000 |
The great majority of enslaved Africans were transported to sugar plantations in the Caribbean and to Portuguese Brazil. As life expectancy was short, their numbers had to be continually replenished. Life expectancy was much higher in the United States, and the enslaved population was successful in reproduction, which was called "natural increase" by enslavers. The population of enslaved people in the United States grew to 4 million by the 1860 census. Historian J. David Hacker conducted research that estimated that the cumulative number of slaves in colonial America and the United States (1619–1865) was 10 million.
Origins of American slaves
Further information: African-American genealogy| Origins and percentages of Africans imported into British North America and Louisiana (1700–1820) |
Amount % (exceeds 100%) |
|---|---|
| West-central Africa (Kongo, N. Mbundu, S. Mbundu) | 26.1 |
| Bight of Biafra (Igbo, Tikar, Ibibio, Bamileke, Bubi) | 24.4 |
| Sierra Leone (Mende, Temne) | 15.8 |
| Senegambia (Mandinka, Fula, Wolof) | 14.5 |
| Gold Coast (Akan, Fon) | 13.1 |
| Windward Coast (Mandé, Kru) | 5.2 |
| Bight of Benin (Yoruba, Ewe, Fon, Allada and Mahi) | 4.3 |
| Southeast Africa (Macua, Malagasy) | 1.8 |
Distribution of slaves
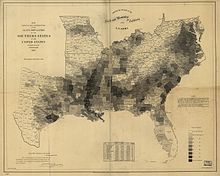
| Census Year |
# Slaves | # Free Africans |
Total Africans |
% Free Africans |
Total US population |
% Africans of total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1790 | 697,681 | 59,527 | 757,208 | 8% | 3,929,214 | 19% |
| 1800 | 893,602 | 108,435 | 1,002,037 | 11% | 5,308,483 | 19% |
| 1810 | 1,191,362 | 186,446 | 1,377,808 | 14% | 7,239,881 | 19% |
| 1820 | 1,538,022 | 233,634 | 1,771,656 | 13% | 9,638,453 | 18% |
| 1830 | 2,009,043 | 319,599 | 2,328,642 | 14% | 12,860,702 | 18% |
| 1840 | 2,487,355 | 386,293 | 2,873,648 | 13% | 17,063,353 | 17% |
| 1850 | 3,204,313 | 434,495 | 3,638,808 | 12% | 23,191,876 | 16% |
| 1860 | 3,953,760 | 488,070 | 4,441,830 | 11% | 31,443,321 | 14% |
| 1870 | 0 | 4,880,009 | 4,880,009 | 100% | 38,558,371 | 13% |
| Source:"Distribution of Slaves in U.S. History". Retrieved May 13, 2010. | ||||||

| Census Year |
1790 | 1800 | 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All States | 694,207 | 893,308 | 1,191,338 | 1,531,490 | 2,009,079 | 2,487,392 | 3,204,215 | 3,953,820 |
| Alabama | – | 494 | 2,565 | 41,879 | 117,549 | 253,532 | 342,844 | 435,080 |
| Arkansas | – | – | 136 | 1,617 | 4,576 | 19,935 | 47,100 | 111,115 |
| California | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 |
| Connecticut | 2,648 | 951 | 310 | 97 | 25 | 54 | 0 | 0 |
| Delaware | 8,887 | 6,153 | 4,177 | 4,509 | 3,292 | 2,605 | 2,290 | 1,798 |
| District of Columbia | – | 2,072 | 3,554 | 4,520 | 4,505 | 3,320 | 3,687 | 3,185 |
| Florida | – | – | – | – | 15,501 | 25,717 | 39,310 | 61,745 |
| Georgia | 29,264 | 59,699 | 105,218 | 149,656 | 217,531 | 280,944 | 381,682 | 462,198 |
| Illinois | – | 107 | 168 | 917 | 747 | 331 | 0 | 0 |
| Indiana | – | 28 | 237 | 190 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Iowa | – | – | – | – | – | 16 | 0 | 0 |
| Kansas | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 |
| Kentucky | 12,430 | 40,343 | 80,561 | 126,732 | 165,213 | 182,258 | 210,981 | 225,483 |
| Louisiana | – | – | 34,660 | 69,064 | 109,588 | 168,452 | 244,809 | 331,726 |
| Maine | – | – | – | – | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Maryland | 103,036 | 105,635 | 111,502 | 107,398 | 102,994 | 89,737 | 90,368 | 87,189 |
| Massachusetts | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Michigan | – | – | 24 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Minnesota | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 |
| Mississippi | – | 2,995 | 14,523 | 32,814 | 65,659 | 195,211 | 309,878 | 436,631 |
| Missouri | – | – | – | 10,222 | 25,096 | 58,240 | 87,422 | 114,931 |
| Nebraska | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 15 |
| Nevada | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 |
| New Hampshire | 157 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| New Jersey | 11,423 | 12,422 | 10,851 | 7,557 | 2,254 | 674 | 236 | 18 |
| New York | 21,193 | 20,613 | 15,017 | 10,088 | 75 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| North Carolina | 100,783 | 133,296 | 168,824 | 205,017 | 245,601 | 245,817 | 288,548 | 331,059 |
| Ohio | – | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Oregon | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 |
| Pennsylvania | 3,707 | 1,706 | 795 | 211 | 403 | 64 | 0 | 0 |
| Rhode Island | 958 | 380 | 108 | 48 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| South Carolina | 107,094 | 146,151 | 196,365 | 251,783 | 315,401 | 327,038 | 384,984 | 402,406 |
| Tennessee | 3,417 | 13,584 | 44,535 | 80,107 | 141,603 | 183,059 | 239,459 | 275,719 |
| Texas | – | – | – | – | – | – | 58,161 | 182,566 |
| Utah | – | – | – | – | – | – | 26 | 29 |
| Vermont | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Virginia | 287,959 | 339,499 | 383,521 | 411,886 | 453,698 | 431,873 | 452,028 | 472,494 |
| West Virginia | 4,668 | 7,172 | 10,836 | 15,178 | 17,673 | 18,488 | 20,428 | 18,371 |
| Wisconsin | – | – | – | – | – | 11 | 4 | 0 |
For various reasons, the census did not always include all of the slaves, especially in the West. California was admitted as a free state and reported no slaves. However, there were many slaves that were brought to work in the mines during the California Gold Rush. Some Californian communities openly tolerated slavery, such as San Bernardino, which was mostly made up of transplants from the neighboring slave territory of Utah. New Mexico Territory never reported any slaves on the census, yet sued the government for compensation for 600 slaves that were freed when Congress outlawed slavery in the territory. Utah was actively trying to hide its slave population from Congress and did not report slaves in several communities. Additionally, the census did not traditionally include Native Americans, and hence did not include Native American slaves or Native African slaves owned by Native Americans. There were hundreds of Native American slaves in California, Utah and New Mexico that were never recorded in the census.
Distribution of slaveholders

As of the 1860 census, one may compute the following statistics on slaveholding:
- Enumerating slave schedules by county, 393,975 named persons held 3,950,546 unnamed slaves, for an average of about ten slaves per holder. As some large holders held slaves in multiple counties and are thus multiply counted, this slightly overestimates the number of slaveholders.
- Excluding slaves, the 1860 U.S. population was 27,167,529; therefore, approximately 1.45% of free persons (roughly one in 69) was a named slaveholder (393,975 named slaveholders among 27,167,529 free persons). By counting only named slaveholders, this approach does not acknowledge people who benefited from slavery by being in a slaveowning household, e.g., the wife and children of an owner; in 1850, there was an average of 5.55 people per household, so on average, around 8.05% of free persons lived in a slave-owning household. In the South, 33% of families owned at least one slave. According to historian Joseph Glatthaar, the number of soldiers of the Confederacy's Army of Northern Virginia who either owned slaves or came from slave owning households is "almost one of every two 1861 recruits". In addition he notes that, "Untold numbers of enlistees rented land from, sold crops to, or worked for slaveholders. In the final tabulation, the vast majority of the volunteers of 1861 had a direct connection to slavery."
- It is estimated by the transcriber Tom Blake, that holders of 200 or more slaves, constituting less than 1% of all U.S. slaveholders (fewer than 4,000 persons, one in 7,000 free persons, or 0.015% of the population) held an estimated 20–30% of all slaves (800,000 to 1,200,000 slaves). Nineteen holders of 500 or more slaves have been identified. The largest slaveholder was Joshua John Ward, of Georgetown, South Carolina, who in 1850 held 1,092 slaves, and whose heirs in 1860 held 1,130 or 1,131 slaves – he was dubbed "the king of the rice planters", and one of his plantations is now part of Brookgreen Gardens.
- The percentage of families that owned slaves in 1860 in various groupings of states was as follows:
| Group of States | States in Group | Slave-Owning Families |
|---|---|---|
| 15 states where slavery was legal | Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia | 26% |
| 11 states that seceded | Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia | 31% |
| 7 states that seceded before Lincoln's inauguration | Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Texas | 37% |
| 4 states that seceded later | Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia | 25% |
| 4 slave states that did not secede | Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri | 16% |
Historiography
Main article: Historiography of the United States § Slavery and black history See also: Bibliography of slavery in the United States
The historian Peter Kolchin, writing in 1993, noted that until the latter decades of the 20th century, historians of slavery had primarily concerned themselves with the culture, practices and economics of the slaveholders, not with the slaves. This was in part due to the circumstance that most slaveholders were literate and left behind written records, whereas slaves were largely illiterate and not in a position to leave written records. Scholars differed as to whether slavery should be considered a benign or a "harshly exploitive" institution.
Much of the history written prior to the 1950s had a distinctive racist slant to it. By the 1970s and 1980s, historians were using archaeological records, black folklore and statistical data to develop a much more detailed and nuanced picture of slave life. Individuals were shown to have been resilient and somewhat autonomous in many of their activities, within the limits of their situation and despite its precariousness. Historians who wrote in this era include John Blassingame (Slave Community), Eugene Genovese (Roll, Jordan, Roll), Leslie Howard Owens (This Species of Property), and Herbert Gutman (The Black Family in Slavery and Freedom).
See also
- Abolition of slavery timeline
- American Descendants of Slavery (ADOS)
- Glossary of American slavery
- Historiography of the United States § Slavery and black history
- List of slave owners
- Lists of United States public officials who owned slaves
- Category:American slave owners
- Reparations for slavery debate in the United States
- Slave insurance in the United States
- Slave narrative § North American slave narratives
- Slavery and Slaving in World History: A Bibliography
- Slavery at American colleges and universities
- Indian removal
- Triangular trade
Histories of slavery in the Western Hemisphere
- Slavery in the Spanish New World colonies
- Slavery in the British and French Caribbean
- Slavery in Cuba
- Slavery in Brazil
- Slavery in Latin America
- Slavery in Canada
Notes
- Slaves were considered personal property in all slave states except Louisiana, which deemed them real estate.
- The United States continued to prohibit Royal Navy ships from investigating U.S.-flagged vessels – even in instances when the U.S. flag was being used fraudulently. The British still insisted on the right to impress (i.e. force to serve in the Royal Navy) British citizens found on American ships – something that was a continued cause of grievance. Despite the intent of the treaty, the opportunity for additional co-operation was missed.
References
- Abzug, Robert H. (1980). Passionate Liberator. Theodore Dwight Weld and the Dilemma of Reform. Oxford University Press. p. 87. ISBN 0-19-502771-X.
- Wood, Peter (2003). "The Birth of Race-Based Slavery". Slate. (May 19, 2015): Reprinted from Strange New Land: Africans in Colonial America by Peter H. Wood with permission from Oxford University Press. 1996, 2003.
- Douglass, Frederick (1849). "The Constitution and Slavery".
- ^ Smith, Julia Floyd (1973). Slavery and Plantation Growth in Antebellum Florida, 1821–1860. Gainesville: University of Florida Press. pp. 44–46. ISBN 978-0-8130-0323-8.
- McDonough, Gary W. (1993). The Florida Negro. A Federal Writers' Project Legacy. University Press of Mississippi. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-87805-588-3.
- Chronology of U.S. Coast Guard history on the USCG official history website.
- Weil, Julie Zauzmer; Blanco, Adrian; Dominguez, Leo (January 10, 2022). "More than 1,700 congressmen once enslaved Black people. This is who they were, and how they shaped the nation". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 11, 2022.
- Appiah, Anthony; Gates, Henry Louis (1999). Africana: the encyclopedia of the African and African American experience. Internet Archive. New York : Basic Civitas Books. ISBN 978-0-465-00071-5.
- Introduction – Social Aspects of the Civil War Archived July 14, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, National Park Service.
- "n 1854, the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act ... overturned the policy of containment and effectively unlocked the gates of the Western territories (including both the old Louisiana Purchase lands and the Mexican Cession) to the legal expansion of slavery...." Guelzo, Allen C., Abraham Lincoln as a Man of Ideas, Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press (2009), p. 80.
- "The 13th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution". National Constitution Center – The 13th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. Retrieved March 1, 2022.
- "Slavery in New York", The Nation, November 7, 2005
- Ira Berlin, Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves, 2003. ISBN 0674010612
- "The First Black Americans" Archived February 2, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Hashaw, Tim; U.S. News & World Report, 1/21/07
- "South Carolina - African-Americans - Slave Population". www.sciway.net. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- Mehr, Emmanuel (November 18, 2023). "City of Brick: Bricks and Early Baltimore". Baltimore Histories Weekly. Retrieved July 12, 2024.
- Smith, Howard W. (1978). Riley, Edward M. (ed.). Benjamin Harrison and the American Revolution. Williamsburg: Virginia Independence Bicentennial Commission. OCLC 4781472.
- Foner, Eric; Garraty, John A. (2014). The Reader's Companion to American History. Houghton Mifflin. p. 705. ISBN 978-0-547-56134-9. Archived from the original on July 7, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- Morison and Commager: Growth of the American Republic, pp. 212–220.
- Brown, Christopher. PBS Video "Liberty! The American Revolution", Episode 6, "Are We to be a Nation?", Twin Cities Public Television, Inc., 1997.
- Brown, Christopher Leslie (2006). Moral Capital: Foundations of British Abolitionism, pp. 105–106, Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-3034-5.
- Mackaman, Tom. "An Interview with Historian Gordon Wood on the New York Times "1619 Project," World Socialist Web Site, wsws.org, November 28, 2019.
- Bailyn, Bernard. Faces of the Revolution: Personalities and Themes in the Struggle for American Independence, pp. 221-4, Vintage Books, New York, New York, 1992. ISBN 0-679-73623-9.
- Wood, Gordon S. The Radicalism of the American Revolution, pp. 3-8, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, New York, 1992. ISBN 0-679-40493-7.
- ^ Hubbard, Robert Ernest (2017). Major General Israel Putnam: Hero of the American Revolution, p. 98, McFarland & Company, Inc., Jefferson, NC. ISBN 978-1-4766-6453-8.
- Nell, William C. (1855). "IV, Rhode Island". The Colored Patriots of the American Revolution. Robert F. Wallcut. ISBN 978-0-557-53528-6.
- Foner, Eric (2010). The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. p. 205.
- Liberty! The American Revolution (Documentary), Episode II:Blows Must Decide: 1774–1776. 1997 Twin Cities Public Television, Inc. ISBN 1-4157-0217-9
- "The Revolution's Black Soldiers". www.americanrevolution.org. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- Hoock, Holger. Scars of Independence: America's Violent Birth, pp. 95, 300–303, 305, 308–310, Crown Publishing Group, New York, 2017. ISBN 978-0-8041-3728-7.
- O'Reilly, Bill and Dugard, Martin. Killing England: The Brutal Struggle for American Independence, pp. 96, 308, Henry Holt and Company, New York, 2017. ISBN 978-1-62779-064-2.
- Ayres, Edward. "African Americans and the American Revolution", Jamestown Settlement and American Revolution Museum at Yorktown website. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
- "Digital History". www.digitalhistory.uh.edu. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- "Tracing the lives and letters of the Black Loyalists – Part 1 The Journey to Sierra Leone - Untold lives blog".
- "Black Loyalists in British North America".
- Gilbert, Alan (March 19, 2012). Black Patriots and Loyalists: Fighting for Emancipation in the War for Independence. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-29309-7.
- Selig, Robert A. "The Revolution's Black Soldiers". AmericanRevolution.org. Retrieved October 18, 2007.
- Frey, Sylvia R. (1991). Water From the Rock: Black Resistance in a Revolutionary Age. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 63.
- Scribner, Robert L. (1983). Revolutionary Virginia, the Road to Independence. University of Virginia Press. p. xxiv. ISBN 978-0-8139-0748-2.
- ^ "George Washington's Runaway Slave, Harry". PBS. Retrieved March 29, 2023.
- Hartmann, Thom (2019). The Hidden History of Guns and the Second Amendment. Berrett-Koehler Publishers. p. 48.
- Roark, James L.; et al. (2008). The American Promise, Volume I: To 1877: A History of the United States. Macmillan. p. 206. ISBN 978-0-312-58552-5.
- Clavin, Matthew J. (2019). The Battle of Negro Fort. The rise and fall of a fugitive slave community. New York: New York University Press. ISBN 978-1-4798-1110-6.
- Peter Kolchin, American Slavery: 1619–1877, New York: Hill and Wang, 1994, p. 73.
- Finkelman, Paul (2012). Slavery in the United States. Duke University School of Law. p. 116.
- Painter, Nell Irvin (2007). Creating Black Americans: African-American History and Its Meanings, 1619 to the Present. p. 72.
- "An interview with historian Gordon Wood on the New York Times' 1619 Project". World Socialist Web Site. November 28, 2019. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- "Interview with Gordon Wood on the American Revolution". World Socialist Web Site. March 3, 2015. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- O'Malley, Gregory E. (2009). "Beyond the Middle Passage: Slave Migration from the Caribbean to North America, 1619–1807". The William and Mary Quarterly. 66 (1): 145, 150.
- Finkelman, Paul (2007). "The Abolition of The Slave Trade". New York Public Library. Retrieved June 25, 2014.
- ^ Hubbard, Robert Ernest. General Rufus Putnam: George Washington's Chief Military Engineer and the "Father of Ohio", pp. 1–4, 105–106, McFarland & Company, Inc., Jefferson, North Carolina, 2020. ISBN 978-1-4766-7862-7.
- ^ McCullough, David. The Pioneers: The Heroic Story of the Settlers Who Brought the American Ideal West, pp. 11, 13, 29–30, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2019. ISBN 978-1-5011-6868-0.
- ^ McCullough, David. John Adams, pp. 132–133, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2001. ISBN 0-684-81363-7.
- Bennett, William J. America: The Last Best Hope, Vol. I, p. 110, Tomas Nelson, Inc., Nashville, Tennessee, 2006. ISBN 978-1-59555-111-5.
- Gradert, Kenyon. Puritan Spirits in the Abolitionist Imagination, pp. 1-3, 26, 74-5, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois, 2020. ISBN 978-0-226-69402-3
- Keith L. Dougherty, and Jac C. Heckelman. "Voting on slavery at the Constitutional Convention." Public Choice 136.3–4 (2008): 293.
- Mason, Matthew (2006). "Slavery and the Founding". History Compass. 4 (5): 943–955. doi:10.1111/j.1478-0542.2006.00345.x. ISSN 1478-0542.
- Joseph R. Conlin, The American Past: A Survey of American History (Cengage Learning, 2008)
- Baker, H. Robert (2012). "The Fugitive Slave Clause and the Antebellum Constitution". Law and History Review. 30 (4): 1133–1174. doi:10.1017/s0738248012000697. S2CID 145241006.
- "Fugitive Slave Laws". Encyclopedia Virginia. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- Stahr, Walter, Salmon P. Chase: Lincoln's Vital Rival, New York: Simon & Schuster, 2021, p. 67.
- Section 2 of Article I provides in part: "Representatives and direct taxes shall be apportioned among the several states ...by adding to the whole number of free persons, including those bound to service for a term of years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three-fifths of all other persons."
- ^ "Interview: James Oliver Horton: Exhibit Reveals History of Slavery in New York City" Archived December 23, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, PBS Newshour, January 25, 2007. Retrieved February 11, 2012.
- Regan, Joe (September 1, 2020). "The large Irish enslavers of antebellum Louisiana". American Nineteenth Century History. 21 (3): 211–235. doi:10.1080/14664658.2020.1841939. ISSN 1466-4658. S2CID 228097042.
- Hacker, J. David (October 1, 2020). "From '20. and odd' to 10 million: the growth of the slave population in the United States". Slavery & Abolition. 41 (4): 840–855. doi:10.1080/0144039X.2020.1755502. ISSN 0144-039X. PMC 7716878. PMID 33281246.
- ^ Walter Johnson, Soul by Soul: Life Inside the Antebellum Slave Market, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1999. pages=90 ("miraculous things"), 228 (property law status)
- Stowe, Harriet Beecher (1853). A key to Uncle Tom's cabin: presenting the original facts and documents upon which the story is founded. Boston: J. P. Jewett & Co. pp. 291–292. LCCN 02004230. OCLC 317690900. OL 21879838M.
- Ford, Lacy K. Jr. (November 1, 2009), "Chapter Five Paternalism Emerges", Deliver Us from Evil: The Slavery Question in the Old South, Oxford University PressNew York, pp. 143–172, doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195118094.003.0006, ISBN 978-0-19-511809-4, retrieved August 22, 2023
- Broussard, Joyce L. (2018). "Paternalism". Mississippi Encyclopedia. Retrieved August 22, 2023.
- Cole, Josh. "THE EXCUSE OF PATERNALISM IN THE ANTEBELLUM SOUTH: IDEOLOGY OR PRACTICE?" (PDF).
- Jefferson, Thomas. "Like a fire bell in the night". Library of Congress. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- de Tocqueville, Alexise (2007). "Chapter XVIII: Future Condition Of Three Races In The United States". Democracy in America (Volume 1). Digireads.com. ISBN 978-1-4209-2910-2.
- Lee, Robert E. "Robert E. Lee's opinion regarding slavery". Shotgun's Home of the American Civil War. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- Thomas, Emory M. (1997). Robert E. Lee. W. W. Norton & Co. p. 173. ISBN 978-0-393-31631-5.
- McCauley, Byron. "The Confederacy was about preserving slavery. The proof? It's on the money". The Enquirer. Retrieved August 24, 2023.
- Levin, Kevin M. (April 21, 2016). "When Dixie Put Slaves on the Money". The Daily Beast. Retrieved August 24, 2023.
- Johnson, Soul by Soul
- Schermerhorn, Calvin (2020). "Chapter 2: 'Cash for Slaves' The African American Trail of Tears". In Bond, Beverly Greene; O'Donovan, Susan Eva (eds.). Remembering the Memphis Massacre: An American Story. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-0-8203-5649-5.
- Beard, Charles A.; Beard, Mary R. (1921). History of the United States. New York: The Macmillan Company. p. 316.
- McInnis, Maurie D. (Fall 2013). "Mapping the slave trade in Richmond and New Orleans". Building & Landscapes. 20 (2): 102–125. doi:10.5749/buildland.20.2.0102. JSTOR 10.5749/buildland.20.2.0102. S2CID 160472953.
- Richards, Leonard L. (2007). The California Gold Rush and the Coming of the Civil War. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 125. ISBN 978-0-307-26520-3.
- ^ Hammond, James Henry (March 4, 1858). "The 'Mudsill' Theory". PBS. Retrieved December 10, 2017.
- ^ Fitzhugh, George. "The Universal Law of Slavery". PBS. Retrieved December 10, 2017.
- ^ Schott, Thomas E. Alexander H. Stephens of Georgia: A Biography, 1996, p. 334.
- Davis, William C. (2002). "Men but Not Brothers". Look Away!: A History of the Confederate States of America. Simon & Schuster. pp. 130–162.
- Cartwright, Samuel A. (May 1851). "Report on the Diseases and Physical Peculiarities of the Negro Race". New Orleans Medical and Surgical Journal: 691–715. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- Cartwright, Samuel A. (1851). "Diseases and Peculiarities of the Negro Race". DeBow's Review. XI. Retrieved November 16, 2011.
- "The Slave Trade Meeting". Charleston Daily Courier (Charleston, South Carolina). October 22, 1859. p. 1 – via newspapers.com.
- Wells, Tom Henderson (2009). The Slave Ship Wanderer. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 9-780-8203-3457-8.
- Rabun, James (October 1970). "Review of The Slave Power Conspiracy and the Paranoid Style, by David Brion Davis". Florida Historical Quarterly. 49 (2): 174–175. JSTOR 30140388.
- Sanborn, Franklin Benjamin (c. 1900). John Brown and His Friends. p. 2.
- Grimké, Archibald (February 1909). "Abraham Lincoln and the Fruitage of his Proclamation". American Missionary. 63 (2): 51–53.
- Nye, Russel B. (Summer 1946). "The Slave Power Conspiracy: 1830–1860". Science & Society. 10 (3): 262–274. JSTOR 40399768.
- Williams, James (1838). Narrative of James Williams, an American slave: who was for several years a driver on a cotton plantation in Alabama. Authentic narrative of James Williams, an American slave. Isaac Knapp coordinated the publication. Boston: Published by the American Anti-Slavery Society. p. iv.
- Arthur Zilversmit, The First Emancipation: The Abolition of Slavery in the North (1967).
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. (2015). Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World. Routledge. pp. 34–35. ISBN 978-1-317-47180-6.
- David Nathaniel Gellman, Emancipating New York: The politics of slavery and freedom, 1777-1827 (LSU Press, 2006) pp. 1–11.
- J. D. B. DeBow, Superintendent of the United States Census (1854). "Slave Population of the United States" (PDF). Statistical View of the United States. United States Senate. p. 82.
- Stewart, Alvan (1845). A legal argument before the Supreme court of the state of New Jersey, at the May term, 1845, at Trenton, for the deliverance of four thousand persons from bondage. New York: Finch & Weed.
- Miller, Randall M.; Smith, John David (1997). "Gradual abolition". Dictionary of Afro-American Slavery. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 471. ISBN 978-0-275-95799-5.
- ^ Peter Kolchin (1993), American Slavery, pp. 77–78, 81.
- ^ "Massachusetts Constitution and the Abolition of Slavery". Mass.gov. Retrieved February 8, 2024.
- Sewall, Samuel. The Selling of Joseph, pp. 1–3, Bartholomew Green & John Allen, Boston, Massachusetts, 1700.
- McCullough, David. John Adams, pp. 132–133, Simon & Schuster, New York, 2001. ISBN 0-684-81363-7.
- "The House Censured Rashida Tlaib for Political Speech Plain and Simple". Esquire. Retrieved November 10, 2023.
- Gradert, Kenyon. Puritan Spirits in the Abolitionist Imagination, pp. 1–3, 14–15, 24, 29–30, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, and London, 2020. ISBN 978-0-226-69402-3.
- Commager, Henry Steele. Theodore Parker, pp. 206, 208–209, 210, The Beacon Press, Boston, Massachusetts, 1947.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, p. 104.
- Reynolds, David S. Mightier Than the Sword: Uncle Tom's Cabin and the Battle for America. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2011.
- "New York Divided: King Cotton". nydivided.org. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- Gilbert Hobbs Barnes, The antislavery impulse: 1830–1844 (1933)
- Loveland, Anne C. (1966). "Evangelicalism and "Immediate Emancipation" in American Antislavery Thought". The Journal of Southern History. 32 (2): 172–188. doi:10.2307/2204556. JSTOR 2204556.
- Kelley, Sean M. (2018). "American Rum, African Consumers, and the Transatlantic Slave Trade". African Economic History. 46 (2): 1–29. doi:10.1353/aeh.2018.0004. ISSN 2163-9108.
- ^ "Regulation of the Trade". New York Public Library. Archived from the original on July 8, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2014.
- Finkelman, Paul (2004). "Suppressing American Slave Traders in the 1790s". OAH Magazine of History. Vol. 18, no. 3. pp. 51–55. ISSN 0882-228X.
- ^ Grindal, Peter (2016). Opposing the Slavers. The Royal Navy's Campaign against the Atlantic Slave Trade (Kindle ed.). London: I.B. Tauris & Co. Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85773-938-4.
- "Potomac Books – University of Nebraska Press – University of Nebraska Press". Archived from the original on October 15, 2007.
- Gene Allen Smith, The Slaves' Gamble: Choosing Sides in the War of 1812 (St. Martin's Press, 2013) pp. 1–11.
- ^ Schama, Simon (2006). "Endings, Beginnings". Rough Crossings: Britain, the Slaves and the American Revolution. New York: HarperCollins. pp. 406–407. ISBN 978-0-06-053916-0.
- Lindsay, Arnett G. (1920). "Diplomatic Relations Between the United States and Great Britain Bearing on the Return of Negro Slaves, 1783–1828". Journal of Negro History. 5 (4): 391–419. doi:10.2307/2713676. JSTOR 2713676. S2CID 149894983.
- Aptheker, Herbert (1993), American Negro Slave Revolts (50th Anniversary ed.), New York: International Publishers, p. 368, ISBN 978-0-7178-0605-8
- Gates, Henry Louis (January 12, 2013). "The Five Greatest Slave Rebellions in the United States | African American History Blog | The African Americans: Many Rivers to Cross". The African Americans: Many Rivers to Cross. WTTW. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- Rasmussen, Daniel (2011). American Uprising: The Untold Story of America's Largest Slave Revolt. HarperCollins. p. 288. ISBN 978-0-06-199521-7.
- J.B. Bird. "The slave rebellion the country tried to forget". John Horse. Retrieved October 4, 2013.
- "Unidentified Young Man". World Digital Library. 1839–1840. Retrieved July 28, 2013.
- "Slave Revolt of 1842 | The Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture". www.okhistory.org.
- ^ Foner, Eric (2009). Give Me Liberty. London: Seagull Edition. pp. 406–407.
- Williams, Jennie K. (April 2, 2020). "Trouble the water: The Baltimore to New Orleans coastwise slave trade, 1820–1860". Slavery & Abolition. 41 (2): 275–303. doi:10.1080/0144039X.2019.1660509. ISSN 0144-039X. S2CID 203494471.
- Kolchin (1993), American Slavery, p. 78.
- Peter Kolchin (1993), American Slavery, p. 81.
- Kolchin (1993), American Slavery, p. 87.
- MADEO. "Jan. 17, 1834 | Alabama Legislature Bans Free Black People from Living in the State". calendar.eji.org. Retrieved August 22, 2023.
- Cathey, Clyde W. (1944). "Slavery in Arkansas". The Arkansas Historical Quarterly. 3 (1): 66–90. doi:10.2307/40027465. ISSN 0004-1823. JSTOR 40027465.
- Jones-Rogers, Stephanie E. (2019). They Were Her Property: White Women as Slave Owners in the American South. New Haven London: Yale University Press. pp. 37, 134. ISBN 978-0-300-25183-8.
"Throughout the antebellum period, married women consistently asserted their rights to own and control human property without their husband's interference, and they exercised those rights as well." "White women were not anomalies at local slave auctions, either, and no group could testify more powerfully to white women's presence at and involvement in slave auctions than the enslaved people who were there.
- McDonald, Soraya Nadia (March 15, 2019). "In 'They Were Her Property,' a historian shows that white women were deeply involved in the slave economy". Andscape. Retrieved July 14, 2020.
South Carolina has bills of sale for property transactions from the 1700s to pretty recently. I looked at a sample of 3,000 bills of sale involving enslaved people being purchased or sold. Close to 40 percent of the bills of sale included either a female buyer or a female seller.
- Jones-Rogers, Stephanie E. (2019). They Were Her Property: White Women as Slave Owners in the American South. New Haven London: Yale University Press. pp. xv–xvi. ISBN 978-0-300-25183-8.
When we listen to what enslaved people had to say about white women and slave mastery, we find that articulated quite clearly their belief that slave-owning women governed their slaves in the same ways that white men did, sometimes they were more effective at slave management or they used more brutal methods of discipline than their husbands did...White southern women conducted transactions with slave traders...and they were not meek in their bargaining...slave-owning women brought legal suits against individuals, both male and female, who jeopardized their claims to human property, and others sued them in kind. They bought and sold slaves for profit, and, on rare occasions owned slave yards.
- ^ "Class". Encyclopedia of African American History, 1619–1895: From the Colonial Period to the Age of Frederick Douglass. January 1, 2006. doi:10.1093/acref/9780195167771.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-516777-1.
- A history of the descendants of the slaves of Cherokee can be found at Sturm, Circe (1998). "Blood Politics, Racial Classification, and Cherokee National Identity: The Trials and Tribulations of the Cherokee Freedmen". American Indian Quarterly. 22 (1/2): 230–258. JSTOR 1185118. In 1835, 7.4% of Cherokee families held slaves. In comparison, nearly one-third of white families living in Confederate states owned slaves in 1860. Further analysis of the 1835 Federal Cherokee Census can be found in McLoughlin, W. G.; Conser, W. H. (1977). "The Cherokees in Transition: a Statistical Analysis of the Federal Cherokee Census of 1835". The Journal of American History. 64 (3): 678–703. doi:10.2307/1887236. JSTOR 1887236. A discussion on the total number of Slave holding families can be found in Olsen, Otto H. (December 2004). "Historians and the extent of slave ownership in the Southern United States". Civil War History. Archived from the original on July 20, 2007. Retrieved June 8, 2007.
- Perdue, Theda (1979). Slavery and the Evolution of Cherokee Society, 1540–1866. University of Tennessee Press. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-87049-530-4.
- Katz, William Loren (January 3, 2012). Black Indians: A Hidden Heritage. Simon and Schuster. p. 254. ISBN 978-1-4424-4637-3. Retrieved March 1, 2019.
black indians.
- Duncan, J. W. (1928). "Interesting ante-bellum laws of the Cherokee, now Oklahoma history". Chronicles of Oklahoma. 6 (2): 178–180. Archived from the original on December 19, 2007. Retrieved July 13, 2007.
- Davis, J. B. (1933). "Slavery in the Cherokee nation". Chronicles of Oklahoma. 11 (4): 1056–1072. Archived from the original on March 10, 2015. Retrieved July 13, 2007.
- Jennison, Watson W. (2012). Cultivating Race: The Expansion of Slavery in Georgia, 1750–1860. University Press of Kentucky. p. 132. ISBN 978-0-8131-4021-6.
- McCall, George A. (1868). Letters from the Frontiers. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott. p. 160. ISBN 978-1-4290-2158-6.
- Mulroy, Kevin (2016). The Seminole Freedmen: A History. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-8061-5588-3.
- Deloria, Philip; Salisbury, Neal (2008). A Companion to American Indian History. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 348–349. ISBN 978-1-4051-4378-3.
- Trigger, Bruce G.; Washburn, Wilcomb E. (1996). The Cambridge History of the Native Peoples of the Americas. Cambridge University Press. p. 525. ISBN 978-0-521-57392-4.
- Binder, Wolfgang (1987). Westward Expansion in America (1803–1860). Palm & Enke. p. 147. ISBN 978-3-7896-0171-2.
- James Shannon Buchanan (1955). Chronicles of Oklahoma. Oklahoma Historical Society. p. 522.
- Mulroy, Kevin (2007). The Seminole Freedmen: A History. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-8061-3865-7.
- Finkelman, Paul (2004). "Suppressing American Slave Traders in the 1790s". OAH Magazine of History. Vol. 18, no. 3. pp. 51–55. ISSN 0882-228X.
- James A. McMillin, The Final Victims: Foreign Slave Trade to North America, 1783–1810, Volume 2, Univ of South Carolina Press, 2004, p. 86
- Thomas, Hugh (1997). The Slave Trade. The Story of the Atlantic Slave Trade: 1440–1870. New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 568. ISBN 978-0-684-81063-8.
- Finkelman, Paul (2007). "The Abolition of the Slave Trade". New York Public Library. Retrieved February 14, 2012.
- "Background on Conflict in Liberia". Archived from the original on January 8, 2011. Paul Cuffe, a successful New England black shipping man, financed and captained a voyage for American blacks in 1815–1816 to British-ruled Sierra Leone. Cuffe believed that African Americans could more easily "rise to be a people" in Africa than in the United States because of the latter's slavery, racial discrimination, and limits on black rights. Although Cuffee died in 1817, his early efforts encouraged the ACS to promote further settlements. The Quakers opposed slavery, but they believed that blacks would face better chances for freedom in Africa than in the United States. Slaveholders opposed abolition, but they wanted to get rid of freedmen, whom they saw as potential leaders of rebellions and people who encouraged slaves to run away.
- "Map of Liberia, West Africa". World Digital Library. 1830. Retrieved June 3, 2013.
- Sale, Maggie Montesinos (1997). The Slumbering Volcano: American Slave Ship Revolts and the Production of Rebellious Masculinity. Duke University Press. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-8223-1992-4.
- Hall, Robert L. (1995). "African Religious Retentions in Florida". In Colburn, David R.; Landers, Jane L. (eds.). The African American Heritage of Florida. University Press of Florida. pp. 42–70. ISBN 978-0-8130-1332-9.
- Wasserman, Adam (2010). A People's History of Florida 1513–1876. How Africans, Seminoles, Women, and Lower Class Whites Shaped the Sunshine State (Revised 4th ed.). Adam Wasserman. ISBN 978-1-4421-6709-4.
- Sweig, Donald (October 2014). "Alexandria to New Orleans: The Human Tragedy of the Interstate Slave Trade" (PDF). Alexandria Gazette-Packet. Retrieved February 13, 2018.
- Dew, Charles B. (2016). The Making of a Racist. University of Virginia Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-8139-3887-5.
- ^ Curry, Richard O.; Cowden, Joanna Dunlop (1972). Slavery in America: Theodore Weld's American Slavery As It Is. Itasca, Illinois: F. E. Peacock. OCLC 699102217.
- "(Untitled)". South Branch Intelligencer. Romney, West Virginia. December 10, 1836. p. 2 – via newspapers.com.
- Elliot, Debbie (February 4, 2006). "A Visit to the Real 'Uncle Tom's Cabin'". All Things Considered. NPR. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- Swarns, Rachel (February 14, 2018). "272 Slaves Were Sold to Save Georgetown. What Does It Owe Their Descendants?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 16, 2016. Retrieved February 15, 2018.
- Swarns, Rachel L. (March 12, 2017). "A Glimpse Into the Life of a Slave Sold to Save Georgetown". The New York Times. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017.
- Hassan, Adeel (April 12, 2019). "Georgetown Students Agree to Create Reparations Fund". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 12, 2019.
- The People's Chronology, 1994, by James Trager.
- Kolchin p. 96. Through the domestic slave trade, about one million enslaved African Americans were forcibly removed from the Upper South to the Deep South, with some transported by ship in the coastwise trade. In 1834, Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana grew half the nation's cotton; by 1859, along with Georgia, they grew 78%. By 1859, cotton growth in the Carolinas had fallen to just 10% of the national total. Berlin p. 166.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 168–169. Kolchin p. 96.
- ^ Morgan, Marcyliena (July 4, 2002). Language, Discourse and Power in African American Culture. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00149-6.
- "Gun Reviews Archives". TheGunZone. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- "American Civil War Census Data". Civil-war.net. Archived from the original on March 22, 2016. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 161–162.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 168–169. Kolchin p. 96. Kolchin notes that Fogel and Engerman maintained that 84% of slaves moved with their families but "most other scholars assign far greater weight ... to slave sales." Ransome (p. 582) notes that Fogel and Engerman based their conclusions on the study of some counties in Maryland in the 1830s and attempted to extrapolate that analysis as reflective of the entire South over the entire period.
- Kulikoff, Allan (1992). The Agrarian Origins of American Capitalism. Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press. pp. 226–269. ISBN 978-0-8139-1388-9.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 166–169.
- Kolchin, p. 98.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 168–171.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, p. 174.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 175–177.
- Berlin, Generations of Captivity, pp. 179–180.
- Johnson (1999), Soul by Soul, p. 2.
- ^ Tadman, Michael (September 18, 2012). Smith, Mark M.; Paquette, Robert L. (eds.). Internal Slave Trades. Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199227990.013.0029. ISBN 978-0-19-922799-0.
- "Frederic Bancroft, Slave-Trading in the Old South". The Journal of Negro History. 16 (2): 240–241. April 1931. doi:10.2307/2714086. ISSN 0022-2992. JSTOR 2714086. S2CID 153885388.
- Dew, Charles B. (2016). The making of a racist: a southerner reflects on family, history, and the slave trade. Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press. p. 154. ISBN 978-0-8139-3888-2. LCCN 2015043815. OCLC 956713856.
- "Frontiersman or Southern Gentleman? Newspaper Coverage of Andrew Jackson during the 1828 Presidential Campaign | Readex". www.readex.com. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- Bostonian (December 3, 1863) . "The Realities of Slavery: To the Editor of the N.Y. Tribune". New-York Tribune. p. 4. ISSN 2158-2661. Retrieved July 27, 2023 – via Newspapers.com.
- Dickman, Michael (2015). Honor, Control, and Powerlessness: Plantation Whipping in the Antebellum South (Thesis). Boston College. hdl:2345/bc-ir:104219.
- Collins, Kathleen (January 9, 1985). "The Scourged Back". The New York Times. pp. 43–45.
- Moore, p. 114.
- Clinton, Catherine, Scholastic Encyclopedia of the Civil War, New York: Scholastic Inc., 1999, p. 8.
- ^ McInnis, Maurie D. (2011). Slaves Waiting for Sale: Abolitionist Art and the American Slave Trade. University of Chicago Press. pp. 129–. ISBN 978-0-226-55933-9.
- Moore, p. 118.
- Lawrence M. Friedman (2005). A History of American Law: Third Edition. Simon and Schuster, p. 163. ISBN 0-7432-8258-2
- A. Aguirre, Jr., "Slave executions in the United States", The Social Science Journal, vol. 36, issue 1 (1999), pp. 1–31.
- Davis, p. 124.
- Christian, Charles M., and Bennet, Sari, Black Saga: The African American Experience: A Chronology, Basic Civitas Books, 1998, p. 90.
- Burke, p. 155.
- Barclay, J. L. (2021). The Mark of Slavery: Disability, Race, and Gender in Antebellum America. University of Illinois Press.
- Andrew Fede (2012). People Without Rights (Routledge Revivals): An Interpretation of the Fundamentals of the Law of Slavery in the U.S. South. Routledge, p. 79. ISBN 1-136-71610-6
- Morris, Thomas D. (1999). Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860. University of North Carolina Press. p. 172. ISBN 978-0-8078-6430-2.
- Thomas Weiss, Review: Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery Archived December 20, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Project 2001: Significant Works in Economic History, EH.net (Economic History.net)
- Kenney, Stephen (March 2015). "Power, opportunism, racism: Human experiments under American slavery". Endeavour. 39 (1): 10–20. doi:10.1016/j.endeavour.2015.02.002. PMID 25824012.
- Halperin, Edward C. (July 2007). "The poor, the Black, and the marginalized as the source of cadavers in United States anatomical education". Clinical Anatomy. 20 (5): 489–495. doi:10.1002/ca.20445. ISSN 0897-3806. PMID 17226823.
- Savitt, Todd (August 1982). "The Use of Blacks for Medical Experimentation and Demonstration in the Old South". The Journal of Southern History. 48 (3): 331–348. doi:10.2307/2207450. JSTOR 2207450. PMID 11645888.
- Berry, Daina (October 18, 2016). "Nat Turner's Skull and My Student's Purse of Skin". The New York Times. Retrieved October 16, 2022.
- "Leather Made From Human Skin". Philadelphia News. The Mercury. March 17, 1888. Retrieved October 16, 2022.
- Plaisance, Patrick (September 2, 1998). "A Museum for Nat Turner". Daily Press. Retrieved October 16, 2022.
- Davis, Floyd James (2001). Who Is Black?: One Nation's Definition. Penn State Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-0-271-04463-7.
- ^ Moon, p. 234.
- Marable, p. 74.
- "Memoirs of Madison Hemings". PBS Frontline.
- Higginbotham, A. Leon (1980). In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process. The Colonial Period. p. 10.
- Prather, C.; Fuller, T. R.; Jeffries Wl, I. V.; Marshall, K. J.; Howell, A. V.; Belyue-Umole, A.; King, W. (2018). "Racism, African American Women, and Their Sexual and Reproductive Health: A Review of Historical and Contemporary Evidence and Implications for Health Equity". Health Equity. 2 (1). National Institutes of Health (NIH): 249–259. doi:10.1089/heq.2017.0045. PMC 6167003. PMID 30283874.
- Bryc, Katarzyna; Durand, Eric Y.; Macpherson, J. Michael; Reich, David; Mountain, Joanna L. (January 8, 2015). "The Genetic Ancestry of African Americans, Latinos, and European Americans across the United States". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 96 (1): 37–53. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.11.010. PMC 4289685. PMID 25529636.
- Zakharia, Fouad; Basu, Analabha; Absher, Devin; Assimes, Themistocles L; Go, Alan S; Hlatky, Mark A; Iribarren, Carlos; Knowles, Joshua W; Li, Jun; Narasimhan, Balasubramanian; Sidney, Steven; Southwick, Audrey; Myers, Richard M; Quertermous, Thomas; Risch, Neil; Tang, Hua (2009). "Characterizing the admixed African ancestry of African Americans". Genome Biology. 10 (R141): R141. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-12-r141. PMC 2812948. PMID 20025784.
- "Learn About Hidden African DNA & Ancestry". 23andMe Blog. September 30, 2023. Retrieved December 8, 2024.
- Zakharia, Fouad; Basu, Analabha; Absher, Devin; Assimes, Themistocles L.; Go, Alan S.; Hlatky, Mark A.; Iribarren, Carlos; Knowles, Joshua W.; Li, Jun; Narasimhan, Balasubramanian; Sidney, Steven; Southwick, Audrey; Myers, Richard M.; Quertermous, Thomas; Risch, Neil (December 22, 2009). "Characterizing the admixed African ancestry of African Americans". Genome Biology. 10 (12): R141. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-12-r141. ISSN 1474-760X. PMC 2812948. PMID 20025784.
- Reis, Elizabeth, ed. (2012). American sexual histories. Blackwell readers in American social and cultural history (2. ed.). Malden, Mass.: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4443-3929-1.
- ^ Berry, Daina Ramey; Harris, Leslie Maria (2018). Sexuality and slavery: reclaiming intimate histories in the Americas. Gender and slavery. Athens, Ga: University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-0-8203-5403-3.
- Woodard, Vincent; Joyce, Justin A.; McBride, Dwight A. (2014). The delectable Negro: human consumption and homoeroticism within U.S. slave culture. Sexual cultures. New York: New York University Press. ISBN 978-0-8147-9461-6.
- Smith, Julia Floyd (1991) Slavery and Rice Culture in Low Country Georgia, 1750-1860 University of Tennessee Press, 104.
- Sublette, Ned; Sublette, Constance (October 1, 2015). The American Slave Coast: A History of the Slave-Breeding Industry. Chicago Review Press. ISBN 978-1-61373-893-1. Retrieved October 15, 2022.
- "Childbirth and Midwifery | Encyclopedia.com". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved May 22, 2023.
- Spivey, William (January 23, 2023). "America's Breeding Farms: What History Books Never Told You". Medium. Retrieved May 22, 2023.
- Schafer, Daniel L. (2013). Zephaniah Kingsley Jr. and the Atlantic World. Slave Trader, Plantation Owner, Emancipator. University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0-8130-4462-0.
- Rankin, John (1833). Letters on American slavery, addressed to Mr. Thomas Rankin, merchant at Middlebrook, Augusta County, Va. Boston: Garrison and Knapp.
- Kenrick, John (1817). The Horrors of Slavery. Cambridge, Massachusetts. p. 44.
- Commerce, D'Iberville/St Martin Chamber of. "D'Iberville/St. Martin Chamber of Commerce". D'Iberville/St. Martin Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved June 21, 2024.
- ^ Manganelli, Kimberly Snyder (2012). Transatlantic spectacles of race: the tragic mulatta and the tragic muse. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-4987-3.
- ^ Johnson, Walter (2000). "The Slave Trader, the White Slave, and the Politics of Racial Determination in the 1850s". The Journal of American History. 87 (1): 13–38. doi:10.2307/2567914. JSTOR 2567914. Retrieved May 25, 2018.
- ^ Allman, T.D. (2013). Finding Florida. The True History of the Sunshine State. Atlantic Monthly Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-2076-2.
- Schwartz, Marie Jenkins (2004). Birthing a Slave: Motherhood and Medicine in the Antebellum South. Cambridge MA: Harvard University Press. pp. 10–11.
- Phillips, Patrick (2016). Blood at the Root. A Racial Cleansing in America. W. W. Norton. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-393-29301-2.
- Kingsley, Zephaniah Jr.; Stowell, Daniel W. (2000). "Introduction". Balancing Evils Judiciously: The Proslavery Writings of Zephaniah Kingsley. University Press of Florida. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-8130-1733-4.
- Guillory, Monique (1999), Some Enchanted Evening on the Auction Block: The Cultural Legacy of the New Orleans Quadroon Balls, PhD dissertation, New York University
- Williams, Caroline Randall (June 26, 2020). "You Want a Confederate Monument? My Body Is a Confederate Monument. The black people I come from were owned and raped by the white people I come from. Who dares to tell me to celebrate them?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 26, 2020.
- Dunn, Marvin (2016). A History of Florida through Black Eyes. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. pp. 87–88. ISBN 978-1-5193-7267-3.
- Natanson, Hannah (September 14, 2019). "They were once America's cruelest, richest slave traders. Why does no one know their names?". The Washington Post.
- Bercaw, Nancy. "Clary and the Fancy Girl Trade, 1806". National Museum of African-American History and Culture. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- Eblen, Tom (February 1, 2012). "Without the Civil War, who knows when Lexington's slave trade might have ended?". Lexington Herald-Leader. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- Brandt, Nat (1990). The town that started the Civil War. Syracuse, New York: Syracuse University Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-8156-0243-9.
- Paludan, Phillip Shaw (Summer 2006). "Lincoln and Negro Slavery: I Haven't Got Time for the Pain". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association. 27 (2): 1–23. hdl:2027/spo.2629860.0027.203.
- Genovese, Eugene D. (1974). Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made. Pantheon Books. p. 416.
- Adler, Jeffrey S. (1995). "Black Violence in the New South. Patterns of Conflict in Late-Nineteenth-Century Tampa". In Colburn, David R.; Landers, Jane L. (eds.). The African Ameritage Heritage of Florida. University Press of Florida. pp. 207–239 . ISBN 978-0-8130-1332-9.
- "Slaves and the Courts, 1740–1860 Slave code for the District of Columbia, 1860." The Library of Congress. Retrieved July 19, 2008.
- Foner, Eric (1971). Nat Turner. Englewood Cliffs, N.J., Prentice-Hall.
- Rodriguez, pp. 616–617.
- Morris, Thomas D. (1999). Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860. University of North Carolina Press. p. 347. ISBN 978-0-8078-6430-2.
- Gomez, Michael A. (1994). "Muslims in Early America". The Journal of Southern History. 60 (4): 671–710. doi:10.2307/2211064. ISSN 0022-4642. JSTOR 2211064.
- Costello, Damian (September 1, 2020). "Pray with Our Lady of Stono to heal the wounds of slavery". U.S. Catholic magazine – Faith in Real Life. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- Frost, J. William (1998). "Christianity and Culture in America". In Kee, Howard Clark (ed.). Christianity: A Social and Cultural History. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. p. 446. ISBN 978-0-13-578071-8.
- Smedley, R. C. (2005). History of the Underground Railroad: In Chester and the Neighboring Counties of Pennsylvania. Stackpole Books. p. xvi. ISBN 978-0-8117-3189-8.
- History of Salem Township, Washtenaw County, Michigan. Salem Area Historical Society. 1976. p. 56.
- ^ Frost, J. William (1998). "Christianity and Culture in America". In Kee, Howard Clark (ed.). Christianity: A Social and Cultural History. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. p. 447. ISBN 978-0-13-578071-8.
- Ahlstrom, Sydney E. (1972). A Religious History of the American People. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. pp. 648–649. ISBN 978-0-300-01762-5.
- "Abolition and the Splintering of the Church". PBS. 2003. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- Frost (1998), Christianity, 448.
- Basu, B.D. Chatterjee, R. (ed.). History of Education in India under the rule of the East India Company. Calcutta: Modern Review Office. pp. 3–4. Retrieved March 9, 2009.
- The Code of Virginia. Richmond: William F. Ritchie. 1849. pp. 747–748.
- "Slaves Are Prohibited to Read and Write by Law | North Carolina Law (1830-31)". www.historyisaweapon.com.
- Jay, William (1835). An Inquiry Into the Character and Tendency of the American Colonization, and American Anti-slavery Societies (2nd ed.). New York: Leavitt, Lord & Co. p. 136.
- Torrey, Jesse (1822). American slave trade; or, An Account of the Manner in which the Slave Dealers take Free People from some of the United States of America, and carry them away, and sell them as Slaves in other of the States; and of the horrible Cruelties practiced in the carrying on of this infamous Traffic: with Reflections on the Project for forming a Colony of American Blacks in Africa, and certain Documents respecting that Project. London: J M Cobbett. p. 102.
- "The Utah Territory Slave Code (1852) – The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed". www.blackpast.org. June 27, 2007. Retrieved August 28, 2017.
- Acts, Resolutions, and Memorials Passed at the ... Annual, and Special Sessions, of the Legislative Assembly of the Territory of Utah. Brigham H. Young, Printers. 1866. pp. 87–88.
- "Image 74 of Page view". Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA. Retrieved August 28, 2023.
- Paul Finkelman, Dred Scott v. Sandford: A Brief History with Documents (Bedford Books, 1997).
- Fehrenbacher, Don E. (1978). The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-502403-6.
- Fehrenbacher, The Dred Scott Case: Its Significance in American Law and Politics (2001).
- Larry Gara, The Liberty Line: The Legend of the Underground Railroad (University Press of Kentucky, 2013).
- Leonard L. Richards, The Slave Power: The Free North and Southern Domination, 1780–1860 (LSU Press, 2000).
- McPherson, James M. (1992). Abraham Lincoln and the Second American Revolution. Oxford University Press. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-19-976270-5.
- David M. Potter, The Impending Crisis: America Before the Civil War, 1848–1861 (Harper & Row, 1976).
- Potter, pp. 448–554.
- Stahr, Walter, Samuel Chase: Lincoln's Vital Rival. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2021, p. 342.
- McPherson, Battle Cry of Freedom, p. 495.
- McPherson, Battle Cry, pp. 355, 494–496, quote from George Julian on 495.
- Litwack, Leon F. (1979). Been in the Storm So Long: The Aftermath of Slavery. New York: Knopf. ISBN 978-0-394-50099-7.
- Lincoln's letter to O. H. Browning, September 22, 1861.
- Stephen B. Oates, Abraham Lincoln: The Man Behind the Myths, page 106.
- "The Preliminary Emancipation Proclamation, 1862". www.archives.gov.
- Images of America: Altoona, by Sr. Anne Francis Pulling, 2001, 10.
- Lincoln, Abraham (June 15, 1953). Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln. Volume 7 [Nov. 5, 1863-Sept. 12, 1864].
- James McPherson, "Drawn With the Sword", from the article "Who Freed the Slaves?"
- Doyle, Robert C. C. (2010). The Enemy in Our Hands: America's Treatment of Prisoners of War from the Revolution to the War on Terror. University Press of Kentucky. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-8131-3961-6.
- Bruce C. Levine, Confederate Emancipation: Southern Plans to Free and Arm Slaves during the Civil War (2007).
- Up from Slavery (1901), pp. 19–21.
- "History of Juneteenth". Juneteenth World Wide Celebration. Archived from the original on May 27, 2007. Retrieved March 9, 2014.
- President Biden Signs the Juneteenth National Independence Day Act Into Law. The White House. June 17, 2021. Archived from the original on February 4, 2023. Retrieved December 3, 2024 – via YouTube.
- "America's Founding Documents". National Archives. October 30, 2015.
- E. Merton Coulter. The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky (1926), pp. 268–270; James J. Gigantino, The Ragged Road to Abolition; Slavery and Freedom in New Jersey, 1775–1865.
- Thomas C. Holt, ed. Major Problems in African-American History: From Freedom to "Freedom Now", 1865–1990s (2000),
- Huebner, Timothy S. (March 2023). "Taking Profits, Making Myths: The Slave Trading Career of Nathan Bedford Forrest". Civil War History. 69 (1): 42–75. doi:10.1353/cwh.2023.0009. ISSN 1533-6271. S2CID 256599213.
- "Convict Labor in Georgia and Tennessee". The Daily Memphis Avalanche. May 16, 1877. p. 2. Retrieved August 24, 2023.
- Brockell, Gillian (November 10, 2022). "La. voters keep 'slavery' at Angola prison, once and still a plantation". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved August 24, 2023.
- Litwack (1998), p. 271.
- Blackmon (2008), p. 4.
- The Ordeal of the Reunion: A New History of Reconstruction (Littlefield History of the Civil War Era) by Mark Wahlgren Summers, 978-1-4696-1758-9, page=397
- Anderson, James D. (1988). The Education of Blacks in the South, 1860–1935. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press. pp. 244–245. ISBN 978-0-8078-1793-3.
- Ford, Carin T. (2004). George Eastman: The Kodak Camera Man. Enslow Publishers, INC.
- ^ Acharya, Avidit; Blackwell, Matthew; Sen, Maya (May 19, 2016). "The Political Legacy of American Slavery". The Journal of Politics. 78 (3): 621–641. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.397.3549. doi:10.1086/686631. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 222442945.
- Nikolova, Elena (January 1, 2017). "Destined for Democracy? Labour Markets and Political Change in Colonial British America". British Journal of Political Science. 47 (1): 19–45. doi:10.1017/S0007123415000101. ISSN 0007-1234. S2CID 17112994.
- Bellani, Luna; Hager, Anselm; Maurer, Stephan (2022). "The Long Shadow of Slavery: The Persistence of Slave Owners in Southern Lawmaking". Journal of Economic History. 82 (1): 250–283. doi:10.1017/S0022050721000590. S2CID 211165817.
- "P.J. Porcher and Baya slave sale broadside – Lowcountry Digital Library Catalog Search". lcdl.library.cofc.edu. Retrieved August 27, 2023.
- ^ Whaples, Robert (March 1995). "Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions". The Journal of Economic History. 55 (1): 141, 146–147. doi:10.1017/S0022050700040602. JSTOR 2123771. S2CID 145691938.
- Whaples, Robert (March 1995). "Where is There Consensus among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions". Journal of Economic History. 55 (1): 139–154. doi:10.1017/S0022050700040602. JSTOR 2123771. S2CID 145691938.
- Galenson, D.W. (March 1984). "The Rise and Fall of Indentured Servants in the Americas: An Economic Approach". Journal of Economic History. 44: 1. doi:10.1017/S002205070003134X. S2CID 154682898.
- ^ Sowell, Thomas (2005). "The Real History of Slavery". Black Rednecks and White Liberals. New York: Encounter Books. pp. 157–158. ISBN 978-1-59403-086-4.
- ^ Whaples, Robert (March 1995). "Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions" (PDF). The Journal of Economic History. 55 (1): 142, 147–148. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.482.4975. doi:10.1017/S0022050700040602. JSTOR 2123771. S2CID 145691938.
- Tadman, M. (December 2000). "The Demographic Cost of Sugar: Debates on Slave Societies and Natural Increase in the Americas". American Historical Review. 105 (5): 1534–1575. doi:10.2307/2652029. JSTOR 2652029.
- Sowell, Thomas (2005). "The Real History of Slavery". Black Rednecks and White Liberals. New York: Encounter Books. p. 156. ISBN 978-1-59403-086-4.
- "Historical Demographic, Economic and Social Data: the United States, 1790–1970". Historical Statistics of the United States. ICPSR Study. Archived from the original on April 1, 2003.
- Whaples, Robert (March 1995). "Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions" (PDF). The Journal of Economic History. 55 (1): 139–154. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.482.4975. doi:10.1017/S0022050700040602. JSTOR 2123771. S2CID 145691938.
- Baptist, Edward E. (2016). The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery And The Making Of American Capitalism. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-09768-5.
- Beckert, Sven; Rockman, Seth, eds. (2016). Slavery's Capitalism: A New History of American Economic Development. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-2417-7.
- ^ Johnson, Walter (2013). River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom. Harvard University Press. pp. 86–87 (credit backed by slave labor). ISBN 978-0-674-04555-2.
- Schermerhorn, Calvin (2015). The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-19200-1.
- Wright, Gavin (2022). "Slavery and the Rise of the Nineteenth-Century American Economy". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 36 (2): 123–148. doi:10.1257/jep.36.2.123. ISSN 0895-3309. S2CID 248716718.
- Wright, Gavin (2020). "Slavery and Anglo-American capitalism revisited". The Economic History Review. 73 (2): 353–383. doi:10.1111/ehr.12962. ISSN 1468-0289. S2CID 214142489.
- Clegg, John J. (2015). "Capitalism and Slavery". Critical Historical Studies. 2 (2): 281–304. doi:10.1086/683036. JSTOR 10.1086/683036. S2CID 155629580.Murray, John E.; Olmstead, Alan L.; Logan, Trevon D.; Pritchett, Jonathan B.; Rousseau, Peter L. (September 2015). "The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism. By Baptist Edward E. New York: Basic Books, 2014. pp. xxvii, 498. $35.00, cloth". The Journal of Economic History. 75 (3): 919–931. doi:10.1017/S0022050715000996. ISSN 0022-0507. S2CID 154464892.Engerman, Stanley L. (June 2017). "Review of The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860 by Calvin Schermerhorn and The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism by Edward E. Baptist". Journal of Economic Literature. 55 (2): 637–643. doi:10.1257/jel.20151334. ISSN 0022-0515.
- Alan L. Olmstead; Paul W. Rhode (September 12, 2016). "Cotton, Slavery, and the New History of Capitalism". Center for Law and Economic Studies. Columbia University. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
mishandle historical evidence and mischaracterize important events in ways that affect their major interpretations on the nature of slavery
Alan L. Olmstead; Paul W. Rhode (January 2018). "Cotton, slavery, and the new history of capitalism". Explorations in Economic History. 67: 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.eeh.2017.12.002. - Parry, Marc (December 8, 2016). "Shackles and Dollars". The Chronicle of Higher Education. ISSN 0009-5982. Retrieved June 12, 2017.
- Rhode, Paul W. (2023). "What Fraction of Antebellum US National Product did the Enslaved Produce?". Explorations in Economic History. 91. doi:10.1016/j.eeh.2023.101552. ISSN 0014-4983. S2CID 262210797.
- Althoff, Lukas; Reichardt, Hugo (2024). "Jim Crow and Black Economic Progress After Slavery". The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 139 (4): 2279–2330. doi:10.1093/qje/qjae023. ISSN 0033-5533.
- Watkins, James L. "King Cotton; a historical and statistical review, 1790 to 1908". HathiTrust. pp. 82–83. hdl:2027/njp.32101058916295. Retrieved July 14, 2024.
- ^ Fogel & Engerman (1974). Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery. New York: W.W. Norton and Company.
- David, Paul A., Herbert G. Gutman, Richard Sutch, and Peter Temin. "Reckoning with slavery." (1985).
- Kotlikoff, L. J. (October 1979). "The Structure of Slave prices in New Orleans" (PDF). Economic Inquiry. 17 (4): 496–518. doi:10.1111/j.1465-7295.1979.tb00544.x.
- Calonius, Erik (2006). The Wanderer: the last American slave ship and the conspiracy that set its sails. New York, N.Y: Saint Martin's Press. pp. 101–102 (Portuguese-African market), 125–126 (prices), 250–253 (origin, biography). ISBN 978-0-312-34347-7.
- Wright, Gavin (Summer 1987). "The Economic Revolution in the American South". The Journal of Economic Perspectives. 1 (1): 161–178. doi:10.1257/jep.1.1.161. JSTOR 1942954.
- Wright, Gavin (1978). The Political Economy of the Cotton South: Households, Markets, and Wealth in the Nineteenth Century. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-09038-3.
- de Tocqueville, Alexise (2004) . "Volume I, Chapter XVIII: Future Condition Of Three Races In The United States". Democracy in America: The Complete and Unabridged, Volumes I and II. Translated by Reeve, Henry (Reissue ed.). New York: Bantam Books. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-553-21464-2.
- Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 1968 edition edited by George M. Fredrickson.
- Lindert, Peter H.; Williamson, Jeffrey G. (2013). "American Incomes Before and After the Revolution" (PDF). Journal of Economic History. 73 (3): 725–765. doi:10.1017/S0022050713000594.
- Lindert, Peter H.; Williamson, Jeffrey G. (September 2012). "American Incomes 1774–1860" (PDF). NBER Working Paper Series No. 18396. doi:10.3386/w18396. S2CID 153965760.
- Acemoğlu, Daron; Johnson, Simon; Robinson, James A. (2002). "Reversal of Fortune: Geography and Institutions in the Making of the Modern World Income Distribution" (PDF). Quarterly Journal of Economics. 117 (4): 1231–1294. doi:10.3386/w18396. S2CID 153965760.
- Eaton, Clement (1964). The Freedom-of-Thought Struggle in the Old South. New York: Harper & Row. pp. 39–40.
- Genovese, Eugene D. (1974). Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made. New York: Pantheon. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-394-71652-7.
- Sowell, Thomas (1981). Ethnic America: A History. New York: Basic Books. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-465-02075-1.
- Sowell, Thomas (2005). "The Real History of Slavery". Black Rednecks and White Liberals. New York: Encounter Books. p. 158. ISBN 978-1-59403-086-4.
- Anstey, Roger (1975). "The Volume and Profitability of the British Slave Trade, 1675–1800". In Engerman, Stanley; Genovese, Eugene (eds.). Race and Slavery in the Western Hemisphere. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. pp. 22–23. ISBN 978-0-691-04625-9.
- Sowell, Thomas (2005). "The Real History of Slavery". Black Rednecks and White Liberals. New York: Encounter Books. pp. 158–159. ISBN 978-1-59403-086-4.
- Hilt, Eric (2017). "Economic History, Historical Analysis, and the "New History of Capitalism"" (PDF). The Journal of Economic History. 77 (2). Cambridge University Press: 511–536. doi:10.1017/S002205071700016X.
- Olmstead, Alan L.; Rhode, Paul W. (2018). "Cotton, Slavery, and the New History of Capitalism". Explorations in Economic History. 67. Elsevier: 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.eeh.2017.12.002.
- Davis, Adrienne (2002). ""Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery". Sister Circle: Black Women and Work. Rutgers University Press. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-8135-3061-1.
- Davis, Adrienne (2002). ""Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" Sexual Economy of American Slavery". Sister Circle: Black Women and Work. Rutgers University Press. p. 108. ISBN 978-0-8135-3061-1.
- Davis, Adrienne (2002). ""Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery". Sister Circle: Black Women and Work. Rutgers University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-8135-3061-1.
- ^ Davis, Adrienne (2002). ""Don't Let Nobody Bother Yo' Principle" The Sexual Economy of American Slavery". Sister Circle: Black Women and Work. Rutgers University Press. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-8135-3061-1.
- Source: Miller and Smith, eds. Dictionary of American Slavery (1988) p. 678
- Includes 10,000 to Louisiana before 1803.
- Hacker, J. David (May 13, 2020). "From '20. and odd' to 10 million: the growth of the slave population in the United States". Slavery & Abolition. 41 (4). Informa UK Limited: 840–855. doi:10.1080/0144039x.2020.1755502. ISSN 0144-039X. PMC 7716878. PMID 33281246.
- Gomez, Michael A: Exchanging Our Country Marks: The Transformation of African Identities in the Colonial and Antebellum South, p. 29. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina, 1998.
- Rucker, Walter C. (2006). The River Flows On: Black Resistance, Culture, and Identity Formation in Early America. LSU Press. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-8071-3109-1.
- Susan Schulten (2010). "The Cartography of Slavery and the Authority of Statistics". Civil War History. 56 (1): 5–32. doi:10.1353/cwh.0.0141. ISSN 1533-6271. S2CID 144587155.
- "Chapter V: Slave Population of the United States (through 1850)" (PDF). census.gov.
- "Population of Slaves in 1860: Introduction" (PDF). census.gov.
- Johnson, Jason B. (January 27, 2007). "SAN FRANCISCO / Slavery in Gold Rush days / New discoveries prompt exhibition, re-examination of state's involvement". SFGATE. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
- Gutglueck, Mark. "Mormons Created And Then Abandoned San Bernardino". San Bernardino County Sentinel.
- ^ Mary Ellen Snodgrass (2015). The Civil War Era and Reconstruction: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural and Economic History. Routledge. p. 556. ISBN 978-1-317-45791-6.
- Ricks, Nathaniel R. (2007). A Peculiar Place for the Peculiar Institution: Slavery and Sovereignty in Early Territorial Utah (MA thesis). Brigham Young University. hdl:1877/etd1909.
- Reeve, W. Paul; Parshall, Ardis E (2010). Mormonism: A Historical Encyclopedia. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 26. ISBN 978-1-59884-107-7.
- Coleman, Ronald G. Blacks in Utah History: An Unknown Legacy (PDF).
- Castillo, E.D. 1998. "Short Overview of California Indian History Archived December 14, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, California Native American Heritage Commission, 1998. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- United States. Congress (1857). The Congressional Globe, Part 2. Blair & Rives. pp. 287–288.
- Large Slaveholders of 1860 and African American Surname Matches from 1870 Archived September 5, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, by Tom Blake, 2001–2005.
- Fry, Richard (October 2019). "The number of people in the average U.S. household is going up for the first time in over 160 years".
- Glatthaar, Joseph (2009). General Lee's Army: From Victory to Collapse. New York: Free Press. pp. 20, 474. ISBN 978-1-4165-9697-4.
- ^ The Sixteen Largest American Slaveholders from 1860 Slave Census Schedules Archived July 19, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Transcribed by Tom Blake, April to July 2001, (updated October 2001 and December 2004; now includes 19 holders)
- ^ Pargas, Damian Alan (2008). "Boundaries and Opportunities: Comparing Slave Family Formation in the Antebellum South" (PDF). Journal of Family History. 33 (3): 316–345. doi:10.1177/0363199008318919. PMID 18831111. S2CID 22302394.
- Bonekemper III, Edward H. (2015). The Myth of the Lost Cause: Why the South Fought the Civil War and Why the North Won. Washington, D.C.: Regnery Publishing. p. 39.
- ^ Kolchin p. 134.
- Kolchin pp. 137–143. Horton and Horton p. 9.
Bibliography
Main article: Bibliography of slavery in the United StatesNational and comparative studies
- Aptheker, Herbert (1939). Negro Slave Revolts in the United States (1526–1860). New York: International Publishers. Preview.
- —— (1945) . American Negro Slave Revolts. New York: Columbia University Press. Preview.
- Arthur, John (2007). Race, Equality, and the Burdens of History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Preview
- Baptist, Edward E. (2016). The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-04966-0. Preview.
- Bateman, Fred; Weiss, Thomas (1980). A Deplorable Scarcity: The Failure of Industrialization in the Slave Economy. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-1447-4. Preview.
- Beckert, Sven (2014). Empire of Cotton: A Global History. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-375-41414-5. Preview.
- Berlin, Ira (2003). Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-01061-2. Preview.
- —— (1998). Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-81092-9. Preview.
- —— (1992) . Slaves Without Masters: The Free Negro in the Antebellum South. New York: The New Press. ISBN 1-56584-028-3. Preview.
- ——; Hoffman, Ronald, eds. (1983). Slavery and Freedom in the Age of the American Revolution. Charlottesville, VA: University Press of Virginia. ISBN 0-8139-0969-4. Preview.
- Blackburn, Robin (2011). The American Crucible: Slavery, Emancipation and Human Rights. London; New York: Verso. ISBN 978-1-84467-569-2. Preview.
- —— (1988). The Overthrow of Colonial Slavery. London; New York: Verso. ISBN 0-86091-188-8. Preview.
- Blackmon, Douglas A. Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II, 2008, ISBN 978-0-385-50625-0. Preview.
- Blassingame, John W. The Slave Community: Plantation Life in the Antebellum South Oxford University Press, 1979, ISBN 0-19-502563-6. Preview.
- Brewster, Francis E. (1850). Slavery and the Constitution. Both Sides of the Question. Philadelphia: Unknown Publisher. Preview.
- Childers, Christopher (2012). The Failure of Popular Sovereignty: Slavery, Manifest Destiny, and the Radicalization of Southern Politics. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-1868-2. Preview.
- Coughtry, Jay (1981). The Notorious Triangle: Rhode Island and the African Slave Trade, 1700–1807. Philadelphia: Temple University Press. ISBN 0-87722-218-5.
- Davis, David Brion. Inhuman Bondage: The Rise and Fall of Slavery in the New World, 2006.
- —— (1970) . The Problem of Slavery in Western Culture. London: Pelican Books. Preview.
- Duberman, Martin B., ed. (1965). New Essays on the Abolitionists. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. Preview.
- Egerton, Douglas R. (2009). Death or Liberty: African Americans and Revolutionary America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530669-9. Preview
- Elkins, Stanley. Slavery: A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life. University of Chicago Press, 1976, ISBN 0-226-20477-4. Preview.
- Fehrenbacher, Don E. Slavery, Law, and Politics: The Dred Scott Case in Historical Perspective, Oxford University Press, 1981. Preview.
- Finkelman, Paul (1981). An Imperfect Union: Slavery, Federalism, and Comity. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-1438-5. Preview.
- Fogel, Robert W. Without Consent or Contract: The Rise and Fall of American Slavery, W.W. Norton, 1989. Preview.
- ——; Engerman, Stanley L. (1995). Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery. New York: W.W. Norton Company, Inc. ISBN 0-393-31218-6. Preview.
- Foner, Eric; Brown, Joshua (2005). Forever Free: The Story of Emancipation and Reconstruction. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-40259-4.Preview.
- —— (2015). Gateway to Freedom: The Hidden History of the Underground Railroad. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-35219-1. Preview.
- —— (2010). The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery. New York: W. W. Norton & Co. ISBN 978-0-393-06618-0. Pulitzer Prize. Preview.
- Franklin, John Hope and Loren Schweninger. Runaway Slaves: Rebels on the Plantation, 1999, ISBN 0-19-508449-7. Preview.
- Fredrickson, George M. (1971). The Black Image in the White Mind: The Debate on Afro-American Character and Destiny, 1817–1914. New York: Harper & Row. SBN 06-011343-X. Preview.
- Freehling, William W. (2007) . The Road to Disunion, Volume I: Secessionists at Bay. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505814-7. Preview.
- —— (2007) . The Road to Disunion, Volume II: Secessionists Triumph. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505815-4.Preview.
- Frey, Sylvia R. (1991). Water from the Rock: Black Resistance in a Revolutionary Age. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-04784-7. Preview.
- Gallay, Alan. The Indian Slave Trade, 2002. Preview.
- Genovese, Eugene D. (1974). Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made. New York: Pantheon Books. ISBN 0-394-49131-9. Preview.
- —— (1967). The Political Economy of Slavery: Studies in the Economy and Society of the Slave South. New York: Vintage Books. Preview.
- —— and Elizabeth Fox-Genovese (1983). Fruits of Merchant Capital: Slavery and Bourgeois Property in the Rise and Expansion of Capitalism. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-503157-1. Preview.
- Harrold, Stanley. American Abolitionism: Its Direct Political Impact from Colonial Times into Reconstruction (U of Virginia Press, 2019) online.
- Hashaw, Tim (2007). The Birth of Black America: The First African Americans and the Pursuit of Freedom at Jamestown. New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7867-1718-7. Preview.
- Higginbotham, A. Leon, Jr. In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period. Oxford University Press, 1978, ISBN 0-19-502745-0. Preview.
- Horton, James Oliver and Horton, Lois E. Slavery and the Making of America, 2005, ISBN 0-19-517903-X. Preview.
- Johnson, Walter (2013). River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-04555-2. Preview.
- Kaplan, Sidney (1973). The Black Presence in the Era of the American Revolution, 1770–1800. Greenwich, CT: New York Graphic Society. ISBN 0-8212-0541-2. Preview.
- Kolchin, Peter (1999) . American Slavery, 1619–1877. New York: Hill and Wang. ISBN 0-8090-1554-4. Preview.
- Litwack, Leon F. Been in the Storm So Long: The Aftermath of Slavery (1979), social history of how slavery ended in the Confederacy. Preview.
- —— (1961). North of Slavery: The Negro in the Free States, 1790–1860. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Preview.
- Mason, Matthew. Slavery and Politics in the Early American Republic, 2006, ISBN 978-0-8078-3049-9.Preview.
- Miller, James, ed. (2001). The Complete History of American Slavery. San Diego, California: Greenhaven Press. ISBN 0737704241.
- Moon, Dannell, "Slavery", article in Encyclopedia of Rape, Merril D. Smith (Ed.), Greenwood Publishing Group, 2004.
- Moore, Wilbert Ellis, American Negro Slavery and Abolition: A Sociological Study, Ayer Publishing, 1980. Preview.
- Morgan, Edmund S. American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia , W.W. Norton, 1975. Preview.
- Morris, Thomas D. (1996). Southern Slavery and the Law, 1619–1860. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-4817-4. Preview.
- Oakes, James. The Ruling Race: A History of American Slaveholders, 1982, ISBN 0-393-31705-6. Preview.
- Palmer, Colin A., ed. (1998). The Worlds of Unfree Labour: From Indentured Servitude to Slavery. Brookfield, VT: Ashgate Publishing Company. ISBN 0-86078-515-7. Preview.
- Robinson, Donald L. (1970). Slavery in the Structure of American Politics, 1765–1820. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. ISBN 0-15-182972-1. Preview.
- Rodriguez, Junius P., ed. Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World, Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2007.
- ——, ed. Encyclopedia of Slave Resistance and Rebellion, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007.
- Scarborough, William K. The Overseer: Plantation Management in the Old South, 1984. Preview.
- Schermerhorn, Calvin. The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860, Yale University Press, 2015.
- Scott, Daryl Michael (2020). "The Social and Intellectual Origins of 13thism". Fire!!!. 5 (2): 2–39. Preview.
- Snyder, Terri L. The Power to Die: Slavery and Suicide in British North America, University of Chicago Press, 2015.
- Stampp, Kenneth M. The Peculiar Institution: Slavery in the Ante-Bellum South, 1956. Preview.
- Tadman, Michael. Speculators and Slaves: Masters, Traders, and Slaves in the Old South, University of Wisconsin Press, 1989. Preview.
- Tannenbaum, Frank (1946). Slave and Citizen, the Negro in the Americas. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. Preview.
- United States Census Bureau. Negro Population in the United States, 1790–1915, New York: Arno Press, 1968. Preview
- Wiecek, William M. (1977). The Sources of Antislavery Constitutionalism in America, 1760–1848. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0-8014-1089-4. Preview.
- Williams, Eric Eustace (1966). Capitalism and Slavery. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons. Preview.
- Wright, W. D. Historians and Slavery; A Critical Analysis of Perspectives and Irony in American Slavery and Other Recent Works, Washington, D.C.: University Press of America, 1978.
- Yafa, Stephen (2006). Big Cotton. Viking Penguin. ISBN 0-670-03367-7. Republished as Cotton: The Biography of a Revolutionary Fiber (2006). Preview
Journal articles
- Cohen, William (1969). "Thomas Jefferson and the Problem of Slavery". The Journal of American History. 56 (3): 503–526. doi:10.2307/1904203. JSTOR 1904203. Preview.
- Cushing, John D. (1961). "The Cushing Court and the Abolition of Slavery in Massachusetts: More Notes on the 'Quock Walker Case'". The American Journal of Legal History. 5 (2): 118–144. doi:10.2307/844116. JSTOR 844116. Preview.
- David, Paul A. and Temin, Peter. "Review: Slavery: The Progressive Institution?", Journal of Economic History. Vol. 34, No. 3 (September 1974)
- Finkelman, Paul (2001). "The Founders and Slavery: Little Ventured, Little Gained". Yale Journal of Law & the Humanities. 13 (2): 413–449. Preview.
- Lynd, Staughton (October 1963). "On Turner, Beard and Slavery". The Journal of Negro History. 48 (4). University of Chicago Press: 235–250. doi:10.2307/2716327. JSTOR 2716327. S2CID 149624479. Preview.
- Ohline, Howard A. (October 1971). "Republicanism and Slavery: Origins of the Three-Fifths Clause in the United States Constitution". The William and Mary Quarterly. 28 (4). Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture: 563–584. doi:10.2307/1922187. JSTOR 1922187. Preview.
- Ransom, Roger L. "Was It Really All That Great to Be a Slave?" Agricultural History, Vol. 48, No. 4, 1974. Preview.
- Stampp, Kenneth M. "Interpreting the Slaveholders' World: a Review." Agricultural History 1970 44(4): 407–412, ISSN 0002-1482. Preview.
Videos
- Hahn, Steven. The Greatest Slave Rebellion in Modern History: Southern Slaves in the American Civil War, Southern Spaces, 2004.
Slavery and the Constitution
- Foner, Eric. The Second Founding: How the Civil War and Reconstruction Remade the Constitution (W. W. Norton & Company, 2019).
- Goldstone, Lawrence (2005). Dark Bargain: Slavery, Profits, and the Struggle for the Constitution. New York: Walker & Company. ISBN 0-8027-1460-9. Preview.
- Drake, Charles E. (September 17, 1862). The War of Slavery upon the Constitution: Address of Charles E. Drake on the Anniversary of the Constitution Delivered in St. Louis. Preview.
- Goldwin, Robert A.; Kaufman, Art, eds. (1988). Slavery and Its Consequences: The Constitution, Equality, and Race. Washington, DC: American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research. ISBN 0-8447-3649-X.
- Kaminski, John P., ed. (1995). A Necessary Evil?: Slavery and the Debate over the Constitution. Madison, WI: Madison House. p. 256. ISBN 978-0945-61216-2.
- Oakes, James. The Crooked Path to Abolition: Abraham Lincoln and the Antislavery Constitution (W. W. Norton & Company, 2021).
- Van Cleve, George William. A Slaveholders' Union: Slavery, Politics, and the Constitution in the Early American Republic (University of Chicago Press, 2019). online
- Wilentz, Sean. No Property in Man: Slavery and Antislavery at the Nation's Founding (2nd ed. Harvard University Press, 2019).
- Williamson, Joel (1990). After Slavery: The Negro in South Carolina During Reconstruction, 1861–1877. Hanover, NH: University Press of New England. ISBN 0-8195-6236-X. Preview.
Journal articles
- David, C. W. A. (January 1924). "The Fugitive Slave Law of 1793 and its Antecedents". The Journal of Negro History. 9 (1). The University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History: 18–25. doi:10.2307/2713433. JSTOR 2713433. S2CID 149160543. Preview.
- Dougherty, Keith L.; Heckelman, Jac C. (2008). "Voting on Slavery at the Constitutional Convention". Public Choice. 136 (3/4): 293–313. doi:10.1007/s11127-008-9297-7. JSTOR 40270762. S2CID 14103553. Preview.
- Finkelman, Paul (April 2011). "Slavery, the Constitution, and the Origins of the Civil War". OAH Magazine of History. 25 (2). Oxford University Press: 14–18. doi:10.1093/oahmag/oar004. JSTOR 23210240. Preview.
- —— (Winter 2000). "Garrison's Constitution: The Covenant with Death and How It Was Made". Prologue Magazine. 32 (4): 14–18. Preview.
- Freehling, William W. (February 1972). "The Founding Fathers and Slavery". The American Historical Review. 77 (1). Oxford University Press: 81–93. doi:10.2307/1856595. JSTOR 1856595. Preview.
- Knowles, Helen J. (August 2013). "Seeing the Light: Lysander Spooner's Increasingly Popular Constitutionalism". Law and History Review. 31 (3). American Society for Legal History: 531–558. doi:10.1017/S0738248013000242. JSTOR 23489502. S2CID 146391068. Preview.
- Maltz, Earl M. (October 1992). "Slavery, Federalism, and the Structure of the Constitution". The American Journal of Legal History. 36 (4). Oxford University Press: 466–498. doi:10.2307/845555. JSTOR 845555. Preview.
- Patterson, Orlando (Autumn 1987). "The Unholy Trinity: Freedom, Slavery, and the American Constitution". Social Research. 54 (3). The Johns Hopkins University Press: 543–577. JSTOR 40970472. Preview.
State and local studies
- Burke, Diane Mutti (2010). On Slavery's Border: Missouri's Small Slaveholding Households, 1815–1865. University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-0-8203-3683-1. Preview.
- Fede, Andrew (1992). People Without Rights: An Interpretation of the Fundamentals of the Law of Slavery in the U.S. South. New York: Garland Publishing, Inc. ISBN 0-8153-0894-9. Preview.
- Fields, Barbara J. Slavery and Freedom on the Middle Ground: Maryland During the Nineteenth Century, Yale University Press, 1985. Preview.
- Freehling, Alice Goodyear (1982). Drift Toward Dissolution: The Virginia Slavery Debate of 1831–1832. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-1035-3. Preview.
- Holton, Woody (1999). Forced Founders: Indians, Debtors, Slaves, and the Making of the American Revolution in Virginia. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press (published for the Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture, Williamsburg, Virginia). ISBN 0-8078-2501-8. Preview.
- Jennison, Watson W. Cultivating Race: The Expansion of Slavery in Georgia, 1750–1860, University Press of Kentucky, 2012. Preview.
- Jewett, Clayton E. and John O. Allen; Slavery in the South: A State-By-State History Greenwood Press, 2004. Preview.
- Kulikoff, Alan. Tobacco and Slaves: The Development of Southern Cultures in the Chesapeake, 1680–1800 University of North Carolina Press, 1986. Preview.
- Minges, Patrick N.; Slavery in the Cherokee Nation: The Keetoowah Society and the Defining of a People, 1855–1867, 2003. Preview.
- Mohr, Clarence L. On the Threshold of Freedom: Masters and Slaves in Civil War Georgia University of Georgia Press, 1986. Preview.
- Mooney, Chase C. Slavery in Tennessee, Indiana University Press, 1957.
- Morgan, Edmund S. (1995) . American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. ISBN 0-393-31288-7. Preview.
- Nash, Gary B. (1991). Freedom by Degrees: Emancipation in Pennsylvania and Its Aftermath. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-504583-1. Preview.
- Olwell, Robert. Masters, Slaves, & Subjects: The Culture of Power in the South Carolina Low Country, 1740–1790 Cornell University Press, 1998.
- Reidy, Joseph P. From Slavery to Agrarian Capitalism in the Cotton Plantation South, Central Georgia, 1800–1880 University of North Carolina Press, 1992. Preview.
- Ripley, C. Peter. Slaves and Freemen in Civil War Louisiana Louisiana State University Press, 1976.
- Rivers, Larry Eugene. Slavery in Florida: Territorial Days to Emancipation, University Press of Florida, 2000. Preview.
- Sellers, James Benson; Slavery in Alabama University of Alabama Press, 1950. Preview.
- Sydnor, Charles S. Slavery in Mississippi, 1933. Preview.
- Takagi, Midori. Rearing Wolves to Our Own Destruction: Slavery in Richmond, Virginia, 1782–1865 University Press of Virginia, 1999. Preview.
- Taylor, Joe Gray. Negro Slavery in Louisiana. Louisiana Historical Society, 1963. Preview.
- Trexler, Harrison Anthony. Slavery in Missouri, 1804–1865, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1914. Preview.
- Wood, Peter H. Black Majority: Negroes in Colonial South Carolina from 1670 through the Stono Rebellion W.W. Norton & Company, 1974. Preview.
Videos
- Jenkins, Gary (director). Negroes To Hire (Lifedocumentaries, 2010); 52 minutes DVD; on slavery in Missouri
- Gannon, James (October 25, 2018). A Moral Debt: The Legacy of Slavery in the USA. Al-Jazeera. Archived from the original on July 22, 2019. Retrieved October 28, 2018.
Gannon is a descendant of Robert E. Lee
Historiography and memory
- Ayers, Edward L. "The American Civil War, Emancipation, and Reconstruction on the World Stage," OAH Magazine of History, January 2006, Vol. 20, Issue 1, pp. 54–60
- Berlin, Ira. "American Slavery in History and Memory and the Search for Social Justice", The Journal of American History, March 2004, Vol. 90, Issue 4, pp. 1251–1268. Preview.
- Boles, John B. and Evelyn T. Nolen, eds., Interpreting Southern History: Historiographical Essays in Honor of Sanford W. Higginbotham (1987). Preview.
- Brown, Vincent. "Social Death and Political Life in the Study of Slavery", American Historical Review, December 2009, Vol. 114, Issue 5, pp. 1231–1249, examined historical and sociological studies since the influential 1982 book Slavery and Social Death by American sociologist Orlando Patterson. Preview.
- Campbell, Gwyn. "Children and slavery in the new world: A review", Slavery & Abolition, August 2006, Vol. 27, Issue 2, pp. 261–285
- Collins, Bruce. "Review: American Slavery and Its Consequences" Historical Journal (1979) 33#4 pp. 997–1015 online
- Dirck, Brian. "Changing Perspectives on Lincoln, Race, and Slavery," OAH Magazine of History, October 2007, Vol. 21, Issue 4, pp. 9–12. Preview.
- Farrow, Anne; Lang, Joel; Frank, Jenifer. Complicity: How the North Promoted, Prolonged, and Profited from Slavery, Ballantine Books, 2006, ISBN 0-345-46783-3. Preview.
- Fogel, Robert W. The Slavery Debates, 1952–1990: A Retrospective, 2007.
- Ford, Lacy K. (2009). Deliver Us from Evil. The Slavery Question in the Old South. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-511809-4. Preview.
- Fox-Amato, Matthew. Exposing Slavery: Photography, Human Bondage, and the Birth of Modern Visual Politics in America (Oxford University Press, 2019).
- Frey, Sylvia R. "The Visible Church: Historiography of African American Religion since Raboteau", Slavery & Abolition, January 2008, Vol. 29 Issue 1, pp. 83–110
- Hettle, Wallace. "White Society in the Old South: The Literary Evidence Reconsidered", Southern Studies: An Interdisciplinary Journal of the South, Fall/Winter 2006, Vol. 13, Issue 3/4, pp. 29–44
- King, Richard H. "Review: Marxism and the Slave South", American Quarterly 29 (1977), 117–131. focus on Genovese. Preview.
- Klarman, Michael J. (2016). Unfinished Business: Racial Equality in American History. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-994203-9. Preview
- Kolchin, Peter. "American Historians and Antebellum Southern Slavery, 1959–1984", in William J. Cooper, Michael F. Holt, and John McCardell, eds., A Master's Due: Essays in Honor of David Herbert Donald (1985), 87–111
- Laurie, Bruce. "Workers, Abolitionists, and the Historians: A Historiographical Perspective", Labor: Studies in Working Class History of the Americas, Winter 2008, Vol. 5, Issue 4, pp. 17–55
- Neely Jr., Mark E. "Lincoln, Slavery, and the Nation," The Journal of American History, September 2009, Vol. 96 Issue 2, pp. 456–458. Preview.
- Parish; Peter J. Slavery: History and Historians Westview Press. 1989. Preview.
- Penningroth, Dylan. "Writing Slavery's History", OAH Magazine of History, April 2009, Vol. 23 Issue 2, pp. 13–20. Preview.
- Rael, Patrick. Eighty-Eight Years: The Long Death of Slavery in the United States, 1777–1865. Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 2015.
- Sidbury, James. "Globalization, Creolization, and the Not-So-Peculiar Institution", Journal of Southern History, August 2007, Vol. 73, Issue 3, pp. 617–630, on colonial era. Preview.
- Stuckey, P. Sterling. "Reflections on the Scholarship of African Origins and Influence in American Slavery", Journal of African American History, Fall 2006, Vol. 91 Issue 4, pp. 425–443. Preview.
- Sweet, John Wood. "The Subject of the Slave Trade: Recent Currents in the Histories of the Atlantic, Great Britain, and Western Africa," Early American Studies, An Interdisciplinary Journal, Spring 2009, Vol. 7 Issue 1, pp. 1–45
- Tadman, Michael. "The Reputation of the Slave Trader in Southern History and the Social Memory of the South", American Nineteenth Century History, September 2007, Vol. 8, Issue 3, pp. 247–271
- Tulloch, Hugh. The Debate on the American Civil War Era (1998), ch. 2–4
Primary sources
- Albert, Octavia V. Rogers. The House of Bondage Or Charlotte Brooks and Other Slaves. Oxford University Press, 1991. Primary sources with commentary. ISBN 0-19-506784-3
- An American (1855). Cotton is king: or, The culture of cotton, and its relation to Agriculture, Manufactures and Commerce; to the free colored people; and to those who hold that slavery is in itself sinful. Cincinnati: Moore, Wilstach, Keys.
- Basker, James G. (2002). Amazing Grace: An Anthology of Poems About Slavery, 1660–1810. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09172-9. Preview.
- Berlin, Ira; Fields, Barbara J.; Miller, Steven F.; Reidy, Joseph P.; Rowland, Leslie S., eds. (1992). Free at Last: A Documentary History of Slavery, Freedom, and the Civil War. New York: The New Press. ISBN 1-56584-120-4. Preview.
- ——; Rowland, Leslie S., eds. (1997). Families and Freedom: A Documentary History of African-American Kinship in the Civil War Era. New York: The New Press. ISBN 1-56584-026-7. Preview.
- ——; Favreau, Marc; Miller, Steven F., eds. (1998). Remembering Slavery: African Americans Talk About Their Personal Experiences of Slavery and Emancipation. New York: The New Press.Preview.
- Blassingame, John W., ed., Slave Testimony: Two Centuries of Letters, Speeches, Interviews, and Autobiographies. Louisiana State University Press, 1977.
- Douglass, Frederick (2017) . Morris, Kenneth B. Jr. (ed.). Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave (Written by Himself). Atlanta, GA: Frederick Douglass Family Initiatives. ISBN 978-0-9984730-2-4. Preview.
- ——, "The Heroic Slave." Autographs for Freedom, Julia Griffiths, ed., Boston: John P. Jewett and Company, 1853. pp. 174–239. Available at the Documenting the American South website.
- ——, Collected Articles of Frederick Douglass, A Slave (Project Gutenberg)
- Missouri History Museum Archives Slavery Collection
- Morgan, Kenneth, ed. Slavery in America: a reader and guide (University of Georgia Press, 2005.)
- Rawick, George P., ed., The American Slave: A Composite Autobiography. 19 vols. Greenwood Publishing Company, 1972. Collection of WPA interviews made in the 1930s with ex-slaves
Scholarly books
- Andrews, William L. (2019) Slavery and Class in the American South: A Generation of Slave Narrative Testimony, 1840–1865 (Oxford University Press).
- Baptist, Edward E. (2014). The Half Has Never Been Told: Slavery and the Making of American Capitalism. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-00296-2. Preview.
- Beckert, Sven (2014). Empire of Cotton: A Global History. Knopf Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-35325-0. Preview.
- Beckert, Sven; Rockman, Seth, eds. (2016). Slavery's Capitalism: A New History of American Economic Development. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-4841-8. Preview.
- Brady, Steven J. (2022) Chained to History: Slavery and US Foreign Relations to 1865 (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press). Online Reviews.
- Finkelman, Paul (1996). Slavery and the Founders: Race and Liberty in the Age of Jefferson. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-1-56324-590-9. Preview.
- Finkelman, Paul, ed. (2002). Slavery & The Law. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-945612-36-2. Preview.
- Forret, Jeff (2015). New Directions in Slavery Studies: Commodification, Community, and Comparison. Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8071-6115-9.
- Gellman, David Nathaniel. Emancipating New York: The politics of slavery and freedom, 1777–1827 (LSU Press, 2006) Online.
- Johnson, Walter (2013). River of Dark Dreams: Slavery and Empire in the Cotton Kingdom. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-04555-2. Preview.
- Larson, Edward J. (2023) American Inheritance: Liberty and Slavery in the Birth of a Nation, 1765–1795 (W. W. Norton, 2023) Excerpt.
- Morgan, Kenneth O. (2000) Slavery and Servitude in North America, 1607–1800 (Edinburgh, Scotland: Edinburgh University Press). Preview.
- Parish, Peter J. (2022) Slavery: History and Historians (New York: Harper & Row). Preview.
- Reséndez, Andrés (2016). The Other Slavery: The Uncovered Story of Indian Enslavement in America. New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-544-94710-8.
- Schermerhorn, Calvin (2015). The Business of Slavery and the Rise of American Capitalism, 1815–1860. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-19200-1.
- Schwalm, Leslie A. (1997) A Hard Hight for We: Women's Transition from Slavery to Freedom in South Carolina (Chicago: University of Illinois Press). Preview.
Scholarly articles
- Baker, Regina S. (2022) "The historical racial regime and racial inequality in poverty in the American south." American Journal of Sociology 127.6 (2022): 1721–1781. online
- Hilt, Eric. (2010). "Revisiting Time on the Cross After 45 Years: The Slavery Debates and the New Economic History." Capitalism: A Journal of History and Economics, Volume 1, Number 2, pp. 456–483. doi:10.1353/cap.2020.0000
- Lindsey, Treva B.; Johnson, Jessica Marie (Fall 2014). "Searching for Climax: Black Erotic Lives in Slavery and Freedom". Meridians: Feminism, Race, Transnationalism. 12 (2): 169+. Retrieved March 25, 2018.
- Logan, Trevon D. (2022) "American Enslavement and the Recovery of Black Economic History." Journal of Economic Perspectives 36.2 (2022): 81–98. online
- McCarthy, Thomas (December 2004). "Coming to Terms with Our Past, Part II: On the Morality and Politics of Reparations for Slavery". Political Theory. 32 (6): 750–772. doi:10.1177/0090591704268924. S2CID 32786606.
- Naidu, S. (2020). "American slavery and labour market power." Economic History of Developing Regions, 35(1), 3–22. doi:10.1080/20780389.2020.1734312
- Singleton, Theresa A. (1995). "The Archaeology of Slavery in North America". Annual Review of Anthropology. 24: 119–140. doi:10.1146/annurev.an.24.100195.001003.
- Turner, Edward Raymond (1912). "The First Abolition Society in the United States". Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography. 36: 92–109.
Oral histories and autobiographies of ex-slaves
- Andrews, William L.; Mason, Regina E., eds. (2008). Life of William Grimes, the Runaway Slave. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-534331-1.
- Blight, David W. (2009). A Slave No More: Two Men Who Escaped to Freedom, Including Their Own Narratives of Emancipation. Boston and New York: Mariner Books, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-15-101-232-9.
- Goings, Henry (2012). Schermerhorn, Calvin; Plunkett, Michael; Gaynor, Edward (eds.). Rambles of a Runaway from Southern Slavery. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-3240-8.
- Hurmence, Belinda, ed. (1989). Before Freedom When I Just Can Remember: Twenty-seven Oral Histories of Former South Carolina Slaves. Blair. ISBN 978-0-89587-069-8.
- Hurmence, Belinda, ed. (1990). Before Freedom: Forty-Eight Oral Histories of Former North & South Carolina Slaves. Mentor Books. ISBN 978-0-451-62781-0.
- Hurmence, Belinda, ed. (1990). My Folks Don't Want Me to Talk about Slavery: Twenty-One Oral Histories of Former North Carolina Slaves.
- Hurmence, Belinda, ed. (1997). Slavery Time When I Was Chillun. G. P. Putnam's Sons. ISBN 978-0-399-23194-0.
- Hurmence, Belinda, ed. (1994). We Lived in a Little Cabin in the Yard: Personal Accounts of Slavery in Virginia. Blair. ISBN 978-0-89587-118-3.
- Jacobs, Harriet (1861). Child, Lydia Maria (ed.). Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl, Written by Herself. Thayer & Eldridge.
- Johnson, Clifton H. (1993). God Struck Me Dead: Voices of Ex-Slaves. Pilgrim Press. ISBN 978-0-8298-0945-9.
Bibliographies
- Miller, Joseph C. (1993). Slavery and Slaving in World History: A Bibliography, Volume I, 1900–1991. Millwood, NY: Kraus International Publications. ISBN 0-527-63660-6.
- —— (1999). Slavery and Slaving in World History: A Bibliography, Volume II, 1992–1996. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, Inc. ISBN 0-765-60279-2.
Discussions by foreigners
- Dickens, Charles (1913). "Slavery". American Notes for General Circulation. First published in 1842. See Louise H. Johnson, "The Source of the Chapter on Slavery in Dickens' American Notes", American Literature, vol. 14, Jan. 1943, pp. 427–430. London: Chapman & Hall.
Literary and cultural criticism
- Ryan, Tim A. Calls and Responses: The American Novel of Slavery Since Gone with the Wind. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2008.
- Van Deburg, William. Slavery and Race in American Popular Culture. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1984.
Documentary films
- "Traces of the Trade". Traces of the Trade. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
External links
- Slavery in America: A Resource Guide, Library of Congress
- "Born in Slavery: Slave Narratives from the Federal Writers' Project, 1936 to 1938", Library of Congress
- "Voices Remembering Slavery: Freed People Tell Their Stories", audio interviews of former slaves, 1932–1975, Library of Congress
- Digital Library on American Slavery at University of North Carolina at Greensboro
- The Abolitionist Seminar, summaries, lesson plans, documents and illustrations for schools; focus on United States
- American Abolitionism, summaries and documents; focus on United States
- "Slavery and the Making of America", WNET (4-part series)
- Slavery in America at the History Channel
- "Slavery in the United States", Economic History Encyclopedia, March 26, 2008
- North American Slave Narratives, Documenting the American South, Louis Round Wilson Library
- The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Database has information on almost 36,000 slaving voyages
- 1850: New Orleans woman and child she held in slavery
- American Capitalism Is Brutal. You Can Trace That to the Plantation. The New York Times Magazine. August 14, 2019.
- The Bibliography of Slavery and World Slaving, University of Virginia: a searchable database of 25,000 scholarly works on slavery and the slave trade in all western European languages.
| Links to related articles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Slavery in the United States
- Pre-emancipation African-American history
- 1776 establishments in the United States
- 1865 disestablishments in the United States
- African-American-related controversies
- Race-related controversies in the United States
- Political controversies in the United States
- African-American cultural history
- Cultural history of the United States
- Economic history of the American Civil War
- Economic history of the United States
- 18th century in the United States
- 19th century in the United States
- Labor history of the United States
- Plantations in the United States
- Politics of the American Civil War
- Slavery of Native Americans
- Social history of the American Civil War
- Social history of the United States
- White supremacy in the United States
- Political compromises in the United States


