| Revision as of 01:03, 27 June 2010 editAhunt (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers229,437 edits In English the plural of "aircraft" is "aircraft", not "aircrafts"← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:20, 10 December 2024 edit undoFrost (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers55,660 editsm Reverted edits by Noahhyf (talk) (HG) (3.4.13)Tags: Huggle Rollback | ||
| (639 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Engine designed for use in powered aircraft}} | |||
| {|{{Infobox Aircraft Begin | |||
| {{Redirect|Aero-engine|the use of aircraft engines in cars|Aero-engined car}} | |||
| |parameters go here | |||
| ] installed in a preserved ] ]] | |||
| }}{{Seriesbox Aircraft Propulsion}} | |||
| {{Seriesbox aircraft propulsion}} | |||
| |} | |||
| An '''aircraft engine''' is |
An '''aircraft engine''', often referred to as an '''aero engine''', is the power component of an ] ]. Aircraft using power components are referred to as '''powered flight'''.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Dictionary of Aviation |first=David W. |last=Wragg |isbn=9780850451634 |edition=first |publisher=Osprey |year=1973 |page=215}}</ref> Most aircraft engines are either ] or ]s, although a few have been ] and in recent years many small ]s have used ]s. | ||
| ==Manufacturing industry== | |||
| ==Engine design considerations== | |||
| {{see also|List of aircraft engines}} | |||
| In commercial aviation the major Western manufacturers of ] engines are ] (a subsidiary of ]), ], ], and ] (a joint venture of ] and General Electric). Russian manufacturers include the ], ] and ]. ] was formed in 2016 with the merger of several smaller companies.{{cn|date=July 2024}} | |||
| The largest manufacturer of ] engines for ] is Pratt & Whitney.<ref name="turbopropmanufacturer">{{cite news|title=GE Pushes Into Turboprop Engines, Taking on Pratt|url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/ge-pushes-into-turboprop-engines-taking-on-pratt-1447700601|agency=Wall Street Journal|date=November 16, 2015}}</ref> General Electric announced in 2015 entrance into the market.<ref name="turbopropmanufacturer"/> | |||
| The process of developing an engine is one of compromises. Engineers design specific attributes into engines to achieve specific goals. Aircraft are one of the most demanding applications for an engine, presenting multiple design requirements, many of which conflict with each other. An aircraft engine must be: | |||
| * ''reliable'', as losing power in an airplane is a substantially greater problem than in an automobile. Aircraft engines operate at temperature, pressure, and speed extremes, and therefore need to perform reliably and safely under all reasonable conditions. | |||
| * ], as a heavy engine increases the empty weight of the aircraft and reduces its payload. | |||
| * ], to overcome the weight and drag of the aircraft. | |||
| * ''small'' and ''easily streamlined''; large engines with substantial surface area, when installed, create too much drag. | |||
| * ''field repairable'', to keep the cost of replacement down. Minor repairs should be relatively inexpensive and possible outside of specialized shops. | |||
| * ] to give the aircraft the range the design requires. | |||
| * capable of operating at sufficient altitude for the aircraft | |||
| ==Development history== | |||
| Unlike ] engines, aircraft engines are often operated at high ] settings for extended periods of time. In general, the engine runs at maximum power for a few minutes during taking off, then power is slightly reduced for climb, and then spends the majority of its time at a cruise setting—typically 65 percent to 75 percent of full power. In contrast, an automobile engine might spend 20 percent of its time at 65 percent power while accelerating, followed by 80 percent of its time at 20 percent power while cruising. | |||
| ] | |||
| {{See also|Timeline of jet power}} | |||
| * 1848: ] made a steam engine for a 10-foot wingspan model aircraft which achieved the first powered flight, albeit with negligible payload. | |||
| The power of an ] reciprocating or ] aircraft engine is rated in units of power delivered to the propeller (typically ]) which is ] multiplied by ] revolutions per minute (]). The propeller converts the engine power to thrust horsepower or '''thp''' in which the ] is a function of the ] of the propeller relative to the ] of the aircraft. ]s are rated in terms of thrust, usually the maximum amount achieved during takeoff. | |||
| * 1903: ] built an ], mostly of aluminum, for the ] (12 horsepower). | |||
| * 1903: ] sets standards for later ]s.<ref name=e>{{cite book|title= Encyclopedia of the History of Technology |year=1990|publisher=Routledge|location=London|isbn= 978-0-203-19211-5|pages=–21|url= https://archive.org/details/encyclopaediaofh00mcne|url-access= registration | editor= Ian McNeil}}</ref> | |||
| * 1906: ] produces a successful water-cooled ] for aircraft use. | |||
| * 1908: ] patents a design for the ]. | |||
| * 1908: ] designed the ], the world's first ] to be produced in quantity. In 1909 a Gnome powered ] aircraft won the prize for the greatest non-stop distance flown at the Reims '']'' setting a world record for endurance of {{convert|180|km|mi}}. | |||
| * 1910: ], an unsuccessful ] aircraft exhibited at Paris Aero Salon, powered by a piston engine. The aircraft never flew, but a patent was filed for routing exhaust gases into the duct to augment thrust.<ref>{{cite book |last=Gibbs-Smith |first=Charles Harvard |title=Aviation: an historical survey from its origins to the end of World War II |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hxEOAQAAIAAJ |year=1970 |location=London |publisher=]|isbn=9780112900139 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Gibbs-Smith |first=Charles Harvard |author-link=Charles Harvard Gibbs-Smith | title=The Aeroplane: An Historical Survey of Its Origins and Development |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mzcZAAAAIAAJ |year=1960 |location=London |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Winter |first=Frank H. |title=Ducted Fan or the World's First Jet Plane? The Coanda claim re-examined |journal=The Aeronautical Journal |publisher=Royal Aeronautical Society |volume=84 |date=December 1980|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XkBWAAAAMAAJ}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Henri Coandă and his technical work during 1906–1918 |last1=Antoniu |first1=Dan |last2=Cicoș |first2=George |last3=Buiu |first3=Ioan-Vasile |last4=Bartoc |first4=Alexandru |last5=Șutic |first5=Robert |language=ro |publisher=Editura Anima |location=Bucharest |isbn=978-973-7729-61-3|year=2010 }}</ref> | |||
| * 1914: ] suggests using exhaust-powered compressor – a ] – to improve high-altitude performance;<ref name=e/> not accepted after the tests<ref>{{cite book|last=Guttman|first=Jon|title=SPAD XIII vs. Fokker D VII: Western Front 1918|year=2009|publisher=Osprey|location=Oxford|isbn= 978-1-84603-432-9|pages=24–25|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=8TBE5nGmxbEC&pg=PA25|edition=1st}}</ref> | |||
| * 1915: The ] - an eighteen-cylinder liquid-cooled ] aircraft engine - (517 hp/380 kW) was the most powerful engine during WW1. | |||
| * 1917–18: The ]-numbered R.30/16 example of the ] '']'s'' ] heavy bomber becomes the earliest known supercharger-equipped aircraft to fly, with a ] straight-six engine in the central fuselage driving a Brown-Boveri mechanical supercharger for the R.30/16's four ] engines. | |||
| * 1918: ] picks up Rateau's idea and creates the first successful turbocharger<ref name=e/><ref name=p>{{cite journal |last=Powell|first=Hickman|title=He Harnessed a Tornado...|journal=Popular Science|date=Jun 1941|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=UycDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA66}}</ref> | |||
| * 1926: ] IV (S), the first series-produced supercharged engine for aircraft use;<ref name=a>{{cite book|last=Anderson|first=John D |title=The airplane: A history of its technology.|year=2002|publisher=American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics|location=Reston, VA, USA |isbn= 978-1-56347-525-2|pages= 252–53|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=FrvrkXYDCL8C&pg=PA253}}</ref><ref group="nb">The world's first series-produced cars with superchargers came earlier than aircraft. These were ] 6/25/40 hp and Mercedes 10/40/65 hp, both models introduced in 1921 and used Roots superchargers. {{cite book|title= The new encyclopedia of motorcars 1885 to the present|year= 1982|publisher= Dutton|location= New York|isbn= 978-0-525-93254-3|pages= |edition= 3rd|editor= G.N. Georgano|editor-link= G.N. Georgano|url= https://archive.org/details/newencyclopediao0000unse_v2r4/page/415}}</ref> two-row radial with a gear-driven ]. | |||
| * 1930: ] submitted his first patent for a ]. | |||
| * June 1939: ] is the first successful aircraft to fly powered solely by a liquid-fueled rocket engine. | |||
| * August 1939: ] turbojet propels the pioneering German ] aircraft. | |||
| * 1940: ], the world's first run of a ] engine. It is not put into service. | |||
| * 1943 ], first turbofan runs | |||
| * 1944: ]B ''Komet'', the world's first rocket-propelled combat aircraft deployed. | |||
| * 1945: First turboprop-powered aircraft flies, a modified ] with two ] engines. | |||
| * 1947: ] rocket-propelled aircraft exceeds the speed of sound. | |||
| * 1948: 100 shp 782, the first ] engine to be applied to aircraft use; in 1950 used to develop the larger {{convert|280|shp|abbr=on}} ]. | |||
| * 1949: ], the world's first ]-powered aircraft flight. | |||
| * 1950: ], the world's first production ], enters service. | |||
| * 1968: ] ] enters service delivering greater thrust and much better efficiency. | |||
| * 2002: ] ] flew in dive. | |||
| * 2004: ], the first scramjet to maintain altitude. | |||
| * 2020: ] is the first electric aircraft engine to be awarded a type certificate by ]. It powers the ], the first fully electric EASA type-certified aeroplane.<ref name="E811_Flyer" /> | |||
| ==Shaft engines== | |||
| The design of aircraft engines tends to favor reliability over performance. Long engine operation times and high power settings, combined with the requirement for high-reliability means that engines must be constructed to support this type of operation with ease. Aircraft engines tend to use the simplest parts possible and include two sets of anything needed for reliability. Independence of function lessens the likelihood of a single malfunction causing an entire engine to fail. For example, reciprocating engines have two independent ] ignition systems, and the engine's mechanical engine-driven ] is always backed-up by an electric pump. | |||
| ===Reciprocating (piston) engines=== | |||
| {{main|reciprocating engine}} | |||
| ====In-line engine==== | |||
| Aircraft spend the vast majority of their time travelling at high speed. This allows an aircraft engine to be air cooled, as opposed to requiring a ]. With the absence of a radiator, aircraft engines can boast lower weight and less complexity. The amount of air flow an engine receives is usually carefully designed according to expected speed and altitude of the aircraft in order to maintain the engine at the optimal temperature. | |||
| {{main|Straight engine}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| In this section, for clarity, the term "inline engine" refers only to engines with a single row of cylinders, as used in automotive language, but ] (as described below), and is not limited to engines with a single row of cylinders. This is typically to differentiate them from ]s. | |||
| A straight engine typically has an even number of cylinders, but there are instances of three- and five-cylinder engines. The greatest advantage of an inline engine is that it allows the aircraft to be designed with a low frontal area to minimize drag. If the engine crankshaft is located above the cylinders, it is called an inverted inline engine: this allows the propeller to be mounted high up to increase ground clearance, enabling shorter landing gear. The disadvantages of an inline engine include a poor ], because the crankcase and crankshaft are long and thus heavy. An in-line engine may be either air-cooled or liquid-cooled, but liquid-cooling is more common because it is difficult to get enough air-flow to cool the rear cylinders directly. | |||
| Aircraft operate at higher altitudes where the air is less dense than at ground level. As engines need oxygen to burn fuel, a ] system such as ] or ] is especially appropriate for aircraft use. This does bring along the usual drawbacks of additional cost, weight and complexity. | |||
| Inline engines were common in early aircraft; one was used in the ], the aircraft that made the first controlled powered flight. However, the inherent disadvantages of the design soon became apparent, and the inline design was abandoned, becoming a rarity in modern aviation. | |||
| ==History of aircraft engines== | |||
| {{inc-transport}} | |||
| ''For other configurations of aviation inline engine, such as ], ], ], etc., see ].'' | |||
| * 1633: ] took off with what was described to be a cone shaped rocket and then glided with wings into a successful landing | |||
| * 1848: ] made a steam engine capable of powering a model, albeit with negligible payload | |||
| * 1903: The ] commissioned ] to build an inline aeroengine (12 horsepower) for the ] | |||
| * 1906:] flew his first airplane "Vuia I" at Montesson on 18 March, achieving the first ever "only by on-board means" flight, without any "outside assistance", be it an incline, rails, a catapult, etc. | |||
| * 1908: ] patents a design for the ] | |||
| * 1909: Roger Ravaud' ] rotary engine in ]'s aircraft won the Grand Prix for the greatest non-stop distance flown - 180 kilometres (110 mi) - and created a world record for endurance flight | |||
| * 1910: ] displays the first jet powered aircraft at the second International Aeronautic Salon in Paris; he also tries to pilot the jet aircraft however he crashlands. | |||
| * 1911: ]'s rotary engines powered fixed-wing aircraft in the US | |||
| * 1916: Auguste Rateau suggests using exhaust-powered compressors to improve high-altitude performance, the first example of the turbocharger. | |||
| * 1930: ] submitted his first patent | |||
| * 1938: The German ] turbojet propels the ] into the air | |||
| * 1939-1942: The world's first turboprop - the ] - is designed by the Hungarian mechanical engineer György Jendrassik | |||
| * 1944: ] Komet, the world's first rocket propelled aircraft deployed | |||
| * 1947: ] rocket propelled aircraft exceeds the speed of sound | |||
| * 1948: the first turboshaft engine, the 100 shp 782. In 1950 this work was used to develop the larger {{convert|280|shp|abbr=on}} ] | |||
| * 1949: The ] the world's first ] powered aircraft flies | |||
| * 1950(late): ], the world's first production ], enters service | |||
| * 1960s: ] ] enters service delivering greater thrust and much better efficiency | |||
| * 1960s: ] rocket plane flies at more than {{convert|50|mi|km}} altitude at more than {{convert|3000|mi/h|km/h|abbr=on}}. | |||
| * 2002: ] scramjet flew in dive | |||
| * 2004: ] first scramjet to maintain altitude | |||
| ====V-type engine==== | |||
| ==Fuel== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|V engine}} | |||
| Cylinders in this engine are arranged in two in-line banks, typically tilted 60–90 degrees apart from each other and driving a common crankshaft. The vast majority of V engines are water-cooled. The V design provides a higher power-to-weight ratio than an inline engine, while still providing a small frontal area. Perhaps the most famous example of this design is the legendary ] engine, a 27-litre (1649 in<sup>3</sup>) 60° V12 engine used in, among others, the ] that played a major role in the ]. | |||
| ====Horizontally opposed engine==== | |||
| All aviation fuel is produced to stringent quality standards to avoid fuel-related engine failures. Aviation standards are much more strict than those for road vehicle fuel because an aircraft engine must meet a strictly defined level of performance under known conditions. These high standards mean that aviation fuel costs much more than fuel used for road vehicles. | |||
| {{main|Flat engine}} | |||
| ]350iS horizontally opposed air-cooled aero engine]] | |||
| A horizontally opposed engine, also called a flat or boxer engine, has two banks of cylinders on opposite sides of a centrally located crankcase. The engine is either air-cooled or liquid-cooled, but air-cooled versions predominate. Opposed engines are mounted with the crankshaft horizontal in ]s, but may be mounted with the crankshaft vertical in ]. Due to the cylinder layout, reciprocating forces tend to cancel, resulting in a smooth running engine. Opposed-type engines have high power-to-weight ratios because they have a comparatively small, lightweight crankcase. In addition, the compact cylinder arrangement reduces the engine's frontal area and allows a streamlined installation that minimizes aerodynamic drag. These engines always have an even number of cylinders, since a cylinder on one side of the crankcase "opposes" a cylinder on the other side. | |||
| Opposed, air-cooled four- and six-cylinder piston engines are by far the most common engines used in small ] aircraft requiring up to {{convert|400|hp}} per engine. Aircraft that require more than {{convert|400|hp}} per engine tend to be powered by ]. | |||
| Aircraft reciprocating (piston) engines are typically designed to run on ]. Avgas has a higher octane rating as compared to automotive ], allowing the use of higher ]s, increasing power output and efficiency at higher altitudes. Currently the most common Avgas is 100LL, which refers to the ] (100 octane) and the lead content (LL = low lead). | |||
| ====H configuration engine==== | |||
| Avgas is blended with ] (TEL) to achieve these high octane ratings, a practice no longer permitted with road vehicle gasoline. The shrinking supply of TEL, and the possibility of environmental legislation banning its use, has made a search for replacement fuels for ] aircraft a priority for pilot's organizations.<ref>{{ cite press release | url=http://www.eaa.org/communications/eaanews/pr/011207_lawrence.html | title = EAA'S Earl Lawrence Elected Secretary of International Aviation Fuel Committee}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|H engine}} | |||
| An H configuration engine is essentially a pair of horizontally opposed engines placed together, with the two crankshafts geared together. | |||
| ====Radial engine==== | |||
| Turbine engines burn various grades of ], a relatively heavy and less volatile ] derivative similar to ]. | |||
| ] engine]] | |||
| {{main|Radial engine}} | |||
| This type of engine has one or more rows of cylinders arranged around a centrally located ]. Each row generally has an odd number of cylinders to produce smooth operation. A radial engine has only one ] per row and a relatively small crankcase, resulting in a favorable ]. Because the cylinder arrangement exposes a large amount of the engine's heat-radiating surfaces to the air and tends to cancel reciprocating forces, radials tend to cool evenly and run smoothly. The lower cylinders, which are under the crankcase, may collect oil when the engine has been stopped for an extended period. If this oil is not cleared from the cylinders prior to starting the engine, serious damage due to ] may occur. | |||
| ==Shaft engines== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Most radial engines have the cylinders arranged evenly around the crankshaft, although some early engines, sometimes called semi-radials or fan configuration engines, had an uneven arrangement. The best known engine of this type is the Anzani engine, which was fitted to the ] used for the first flight across the ] in 1909. This arrangement had the drawback of needing a heavy counterbalance for the crankshaft, but was used to avoid the ] oiling up. | |||
| ===In-line engine=== | |||
| {{main|Straight engine}} | |||
| In military aircraft designs, the large frontal area of the engine acted as an extra layer of armor for the pilot. Also air-cooled engines, without vulnerable radiators, are slightly less prone to battle damage, and on occasion would continue running even with one or more cylinders shot away. However, the large frontal area also resulted in an aircraft with an ] increased frontal area. | |||
| This type of engine has cylinders lined up in one row. It typically has an even number of cylinders, but there are instances of three- and five- cylinder engines. The biggest advantage of an inline engine is that it allows the aircraft to be designed with a narrow frontal area for low drag. If the engine crankshaft is located above the cylinders, it is called an inverted inline engine, which allows the propeller to be mounted up high for ground clearance even with short landing gear. The disadvantages of an inline engine include a poor ], because the crankcase and crankshaft are long and thus heavy. An in-line engine may be either air cooled or liquid cooled, but liquid-cooling is more common because it is difficult to get enough air-flow to cool the rear cylinders directly. Inline engines were common in early aircraft, including the ], the aircraft that made the first controlled powered flight. However, the inherent disadvantages of the design soon became apparent, and the inline design was abandoned, becoming a rarity in modern aviation. | |||
| ===Rotary engine=== | ====Rotary engine==== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| {{main|Rotary engine}} | {{main|Rotary engine}} | ||
| Rotary engines have the cylinders in a circle around the crankcase, as in a radial engine, (see above), but the crankshaft is fixed to the airframe and the propeller is fixed to the engine case, so that the crankcase and cylinders rotate. The advantage of this arrangement is that a satisfactory flow of cooling air is maintained even at low airspeeds, retaining the weight advantage and simplicity of a conventional air-cooled engine without one of their major drawbacks. | |||
| Early in ], when aircraft were first being used for military purposes, it became apparent that existing inline engines were too heavy for the amount of power needed. Aircraft designers needed an engine that was lightweight, powerful, cheap, and easy to manufacture in large quantities. The rotary engine met these goals. Rotary engines have all the cylinders in a circle around the crankcase like a radial engine (see below), but the difference is that the crankshaft is bolted to the airframe, and the propeller is bolted to the engine case. The entire engine rotates with the propeller, providing plenty of airflow for cooling regardless of the aircraft's forward speed. Some of these engines were a ] design, giving them a high ] and power-to-weight ratio. Unfortunately, the severe ] from the heavy rotating engine made the aircraft very difficult to fly. The engines also consumed large amounts of ], spreading it all over the airframe and creating fumes which were nauseating to the pilots. | |||
| The first practical rotary engine was the ] designed by the Seguin brothers and first flown in 1909. Its relative reliability and good power to weight ratio changed aviation dramatically. <!--I'm not saying revolutionised!--><ref>{{cite book|title=Aviation|last=Gibbs-Smith|first= C.H.|publisher=NMSO|location=London|year=2003|isbn= 1-9007-4752-9 |page=175}}</ref> Before the ] most speed records were gained using Gnome-engined aircraft, and in the early years of the war rotary engines were dominant in aircraft types for which speed and agility were paramount. To increase power, engines with two rows of cylinders were built. | |||
| Engine designers had always been aware of the many limitations of the rotary engine. When the static style engines became more reliable, gave better specific weights and fuel consumption, the days of the rotary engine were numbered. | |||
| However, the ] of the heavy rotating engine produced handling problems in aircraft and the engines also consumed large amounts of oil since they used total loss lubrication, the oil being mixed with the fuel and ejected with the exhaust gases. ] was used for lubrication, since it is not soluble in petrol, and the resultant fumes were nauseating to the pilots. Engine designers had always been aware of the many limitations of the rotary engine so when the static style engines became more reliable and gave better specific weights and fuel consumption, the days of the rotary engine were numbered. | |||
| ], a V-type, liquid-cooled aircraft engine.]] | |||
| === |
====Wankel engine==== | ||
| {{main| |
{{main|Wankel engine}} | ||
| ]e self-launching ], removed from the glider and mounted on a test stand for maintenance at the ] in ], ]. Counter-clockwise from top left: propeller hub, mast with belt guide, radiator, Wankel engine, muffler shroud.]] | |||
| The ] is a type of rotary engine. The ] is about one half the weight and size of a traditional ] ] of equal power output, and much lower in complexity. In an aircraft application, the power-to-weight ratio is very important, making the Wankel engine a good choice. Because the engine is typically constructed with an aluminium housing and a steel rotor, and aluminium expands more than steel when heated, a Wankel engine does not seize when overheated, unlike a piston engine. This is an important safety factor for aeronautical use. Considerable development of these designs started after ], but at the time the aircraft industry favored the use of ] engines. It was believed that ] or ] engines could power all aircraft, from the largest to smallest designs. The Wankel engine did not find many applications in aircraft, but was used by ] in a popular line of ]. The French company ] had developed Wankel powered {{Interlanguage link multi|Citroën RE-2|fr|3=Citroën RE-2|lt=RE-2}} ] in 1970's.<ref name="PBoulay">{{Cite book|language=fr|first=Pierre|last=Boulay|title=Les hélicoptères français|editor=Guides Larivière|year=1998|isbn=978-2-907051-17-0}}</ref> | |||
| Cylinders in this engine are arranged in two in-line banks, tilted 30-60 degrees apart from each other. The vast majority of V engines are water-cooled. The V design provides a higher power-to-weight ratio than an inline engine, while still providing a small frontal area. Perhaps the most famous example of this design is the legendary ] engine, a 27-litre (1649 in<sup>3</sup>) 60° V12 engine used in, among others, the ] that played a major role in the ]. | |||
| In modern times the Wankel engine has been used in ]s where the compactness, light weight, and smoothness are crucially important.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| ===Radial engine=== | |||
| |url = http://www.alexander-schleicher.de/englisch/produkte/ash26/e_ash26_main.htm | |||
| ]]] | |||
| | publisher = Alexander Schleicher | title = ASH 26 E Information | |||
| {{main|Radial engine}} | |||
| |access-date = 2006-11-24 | location = DE | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20061008125929/http://www.alexander-schleicher.de/englisch/produkte/ash26/e_ash26_main.htm |archive-date = 2006-10-08}}</ref> | |||
| The now-defunct ] firm MidWest designed and produced single- and twin-rotor aero engines, the ]. These engines were developed from the motor in the ] ]. The twin-rotor version was fitted into ]s and the ]. The single-rotor engine was put into a ] and into the ] motor-gliders. After the demise of MidWest, all rights were sold to ] of Austria, who have since developed a MkII version of the engine. | |||
| This type of engine has one or more rows of cylinders arranged in a circle around a centrally-located ]. Each row must have an odd number of cylinders in order to produce smooth operation. A radial engine has only one ] per row and a relatively small crankcase, resulting in a favorable ]. Because the cylinder arrangement exposes a large amount of the engine's heat radiating surfaces to the air and tends to cancel reciprocating forces, radials tend to cool evenly and run smoothly. | |||
| As a cost-effective alternative to certified aircraft engines some Wankel engines, removed from automobiles and converted to aviation use, have been fitted in homebuilt ]. Mazda units with outputs ranging from {{convert|100|hp}} to {{convert|300|hp}} can be a fraction of the cost of traditional engines. Such conversions first took place in the early 1970s;{{citation needed|date=February 2016}} and as of 10 December 2006 the ] has only seven reports of incidents involving aircraft with Mazda engines, and none of these is of a failure due to design or manufacturing flaws. | |||
| The lower cylinders, which are under the crankcase, may collect oil when the engine has been stopped for an extended period. If this oil is not cleared from the cylinders prior to starting the engine, serious damage due to ] may occur. | |||
| ====Combustion cycles==== | |||
| In military aircraft designs, the large frontal area of the engine acted as an extra layer of armor for the pilot. However, the large frontal area also resulted in an aircraft with a blunt and ] profile. | |||
| The most common combustion cycle for aero engines is the four-stroke with spark ignition. Two-stroke spark ignition has also been used for small engines, while the compression-ignition ] is seldom used. | |||
| Starting in the 1930s attempts were made to produce a practical ]. In general, Diesel engines are more reliable and much better suited to running for long periods of time at medium power settings. The lightweight alloys of the 1930s were not up to the task of handling the much higher ]s of diesel engines, so they generally had poor power-to-weight ratios and were uncommon for that reason, although the Clerget 14F Diesel radial engine (1939) has the same power to weight ratio as a gasoline radial. Improvements in Diesel technology in automobiles (leading to much better power-weight ratios), the Diesel's much better fuel efficiency and the high relative taxation of AVGAS compared to Jet A1 in Europe have all seen a revival of interest in the use of diesels for aircraft. ] Aircraft Engines converted Mercedes Diesel automotive engines, certified them for aircraft use, and became an OEM provider to Diamond Aviation for their light twin. Financial problems have plagued Thielert, so Diamond's affiliate — Austro Engine — developed the new ], also based on a Mercedes engine.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| ===Opposed engine=== | |||
| |url = http://www.flyingmag.com/pilot-reports/pistons/diamond-twins-reborn | |||
| {{main|flat engine}} | |||
| |title = Diamond Twins Reborn | |||
| ]<br />horizontally-opposed,<br />air-cooled, aero engine.]] | |||
| |publisher = Flying Mag | |||
| |access-date = 2010-06-14 | |||
| An opposed-type engine has two banks of cylinders on opposite sides of a centrally located crankcase. The engine is either air cooled or liquid cooled, but air cooled versions predominate. Opposed engines are mounted with the crankshaft horizontal in ]s, but may be mounted with the crankshaft vertical in ]. Due to the cylinder layout, reciprocating forces tend to cancel, resulting in a smooth running engine. Unlike a ], an opposed engine does not experience any problems with ]. | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140618032748/http://www.flyingmag.com/pilot-reports/pistons/diamond-twins-reborn | |||
| |archive-date = 2014-06-18 | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| }}</ref> Competing new Diesel engines may bring fuel efficiency and lead-free emissions to small aircraft, representing the biggest change in light aircraft engines in decades. | |||
| ===Power turbines=== | |||
| Opposed, air-cooled four and six cylinder piston engines are by far the most common engines used in small ] aircraft requiring up to {{convert|400|hp}} per engine. Aircraft which require more than {{convert|400|hp}} per engine tend to be powered by ]. | |||
| ===Turboprop=== | ====Turboprop==== | ||
| ] turboprop engine |
] turboprop engine showing the gearbox at the front of the engine]] | ||
| {{main|Turboprop}} | {{main|Turboprop}} | ||
| While military fighters require very high speeds, many civil airplanes do not. Yet, civil aircraft designers wanted to benefit from the high power and low maintenance that a ] engine offered. Thus was born the idea to mate a turbine engine to a traditional propeller. Because gas turbines optimally spin at high speed, a turboprop features a ] to lower the speed of the shaft so that the propeller tips don't reach supersonic speeds. Often the turbines |
While military fighters require very high speeds, many civil airplanes do not. Yet, civil aircraft designers wanted to benefit from the high power and low maintenance that a ] engine offered. Thus was born the idea to mate a turbine engine to a traditional propeller. Because gas turbines optimally spin at high speed, a turboprop features a ] to lower the speed of the shaft so that the propeller tips don't reach supersonic speeds. Often the turbines that drive the propeller are separate from the rest of the rotating components so that they can rotate at their own best speed (referred to as a free-turbine engine). A turboprop is very efficient when operated within the realm of cruise speeds it was designed for, which is typically {{convert|200|to|400|mph|km/h|abbr=on}}. | ||
| ===Turboshaft=== | ====Turboshaft==== | ||
| ] turboshaft engine common to many types of helicopters |
] turboshaft engine common to many types of helicopters]] | ||
| {{main|Turboshaft}} | {{main|Turboshaft}} | ||
| Turboshaft engines are used primarily for ]s and ]s. A turboshaft engine is |
Turboshaft engines are used primarily for ]s and ]s. A turboshaft engine is similar to a turboprop in principle, but in a turboprop the propeller is supported by the engine and the engine is bolted to the ]: in a turboshaft, the engine does not provide any direct physical support to the helicopter's rotors. The rotor is connected to a transmission which is bolted to the airframe, and the turboshaft engine drives the transmission. The distinction is seen by some as slim, as in some cases aircraft companies make both turboprop and turboshaft engines based on the same design. | ||
| == |
===Electric power=== | ||
| A number of electrically powered aircraft, such as the ], have been designed since the 1960s.<ref name = french /><ref>{{Citation|url=http://www.physorg.com/printnews.php?newsid=101391900 |title=Superconducting Turbojet |publisher=] |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080223113129/http://www.physorg.com/printnews.php?newsid=101391900 |archive-date=2008-02-23 }}.</ref> Some are used as military ]s.<ref>{{Citation|url=http://www.litemachines.com/mil/mil_main.htm |publisher=Litemachines |title=Voyeur |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091231174446/http://www.litemachines.com//mil//mil_main.htm |archive-date=2009-12-31 }}.</ref> In ] in late 2007, a conventional light aircraft powered by an 18 kW electric motor using lithium polymer batteries was flown, covering more than {{convert|50|km|mi|sp=us}}, the first electric airplane to receive a ].<ref name=french>{{Citation|url=http://www.apame.eu/AA%20Projects.html|title=Worldwide première: first aircraft flight with electrical engine |publisher=Association pour la Promotion des Aéronefs à Motorisation Électrique |date=December 23, 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080110092518/http://www.apame.eu/AA%20Projects.html |archive-date=2008-01-10}}.</ref> | |||
| {{main|jet engine}} | |||
| ]-GE-17A turbojet engine. This cutaway clearly shows the 8 stages of ] at the front (left side of the picture), the ]s in the middle, and the two stages of ]s at the rear of the engine.]] | |||
| On 18 May 2020, the ] was the first electric aircraft engine to be awarded a ] by ] for use in ]. The E-811 powers the ].<ref name="E811_TCDS">{{cite web |title=TCDS for E811 engine, model 268MVLC |url=https://www.easa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/dfu/E.234%20TCDS%20Pipistrel%20electric%20engine%20E-811_Issue%2001.pdf |website=European Union Aviation Safety Agency |access-date=18 August 2020 |date=18 May 2020}}</ref><ref name="E811_Flyer">{{cite news |last1=Calderwood |first1=Dave |title=Pipistrel offers type certified electric motor |url=https://www.flyer.co.uk/pipistrel-offers-type-certified-electric-motor-to-others/ |access-date=18 August 2020 |agency=FLYER Magazine |publisher=Seager Publishing |date=9 July 2020}}</ref> | |||
| The key part of a jet engine is the exhaust nozzle. This is the part which produces thrust for the jet; the hot airflow from the engine is accelerated when exiting the nozzle, creating ], which, in conjunction with the pressures acting inside the engine which are maintained and increased by the constriction of the nozzle, pushes the aircraft forward. | |||
| Limited experiments with ] propulsion have been performed, notably the manned ] and ] and the unmanned ] aircraft. | |||
| The most common jet propulsion engines flown are turbojet, turbofan and rocket. Other types such as ]s, ], ]s and ]s have also flown. | |||
| Many big companies, such as Siemens, are developing high performance electric engines for aircraft use, also, SAE shows new developments in elements as pure Copper core electric motors with a better efficiency. A hybrid system as emergency back-up and for added power in take-off is offered for sale by Axter Aerospace, Madrid, Spain.<ref></ref> | |||
| ===Turbojet=== | |||
| {{main|turbojet}} | |||
| Small ] UAVs are almost always powered by electric motors. | |||
| A turbojet is a type of ] engine that was originally developed for military ] during ]. A turbojet is the simplest of all aircraft gas turbines. It features a compressor to draw air in and compress it, a combustion section which adds fuel and ignites it, one or more turbines that extract power from the expanding exhaust gases to drive the compressor, and an exhaust nozzle which accelerates the exhaust out the back of the engine to create thrust. When turbojets were introduced, the top speed of fighter aircraft equipped with them was at least 100 ] faster than competing piston-driven aircraft. The relative simplicity of turbojet designs lent themselves to wartime production, but the war ended before any turbojets could be mass-produced. In the years after the war, the drawbacks of the turbojet gradually became apparent. Below about Mach 2, turbojets are very fuel inefficient and create tremendous amounts of noise. The early designs also respond very slowly to power changes, a fact which killed many experienced pilots when they attempted the transition to jets. These drawbacks eventually led to the downfall of the pure turbojet, and only a handful of types are still in production. The last airliner that used turbojets was the ], whose Mach 2 flight crossed the threshold into efficient turbojet operation. | |||
| ==Reaction engines== | |||
| ===Turbofan=== | |||
| {{main| |
{{main|Jet engine}} | ||
| Reaction engines generate the ] to propel an aircraft by ejecting the exhaust gases at high velocity from the engine, the resultant ] driving the aircraft forwards. The most common reaction propulsion engines flown are turbojets, turbofans and rockets. Other types such as ]s, ], ]s and ]s have also flown. In jet engines the ] necessary for fuel combustion comes from the air, while rockets carry an ] (usually oxygen in some form) as part of the fuel load, permitting their use in space. | |||
| A turbofan engine is much the same as a turbojet, but with an enlarged fan at the front which provides thrust in much the same way as a ]. A turbofan has extra turbine stages to turn the fan. Thus, more power is extracted from the exhaust gases before they leave the engine. This operation is a more efficient way to provide thrust than the ] alone, resulting in improved fuel-efficiency. Turbofans were the first engines to use multiple ''spools''; concentric shafts which are free to rotate at their own speed; in order to allow the engine to react more quickly to changing power requirements. Although the fan creates thrust like a propeller, the surrounding duct frees it from many of the restrictions which limit propeller performance. Turbofans are more efficient than propellers in the trans-sonic range of aircraft speeds, and can operate in the ] realm. Turbofans are coarsely split into low-bypass and high-bypass categories. Bypass air flows through the fan, but around the jet core, not mixing with fuel and burning. The ratio of this air to the amount of air flowing through the engine core is the bypass ratio. Low-bypass engines are preferred for military applications such as fighters due to high thrust-to-weight ratio, while high-bypass engines are preferred for civil use for good fuel efficiency and low noise. High-bypass turbofans are usually most efficient when the aircraft is traveling at 500 to 550 miles per hour (800 to 885 km/h), the cruise speed of most large airliners. Low-bypass turbofans can reach supersonic speeds, though normally only when fitted with ]s. | |||
| === |
===Jet turbines=== | ||
| {{main|Rocket engine}} | |||
| ====Turbojet==== | |||
| A few aircraft have used rocket engines for main thrust or attitude control, notably the ] and ]. | |||
| ]-GE-17A turbojet engine. This cutaway clearly shows the 8 stages of ] at the front (left side of the picture), the ]s in the middle, and the two stages of ]s at the rear of the engine.]] | |||
| {{main|Turbojet}} | |||
| A turbojet is a type of ] engine that was originally developed for military ] during ]. A turbojet is the simplest of all aircraft gas turbines. It consists of a compressor to draw air in and compress it, a combustion section where fuel is added and ignited, one or more turbines that extract power from the expanding exhaust gases to drive the compressor, and an exhaust nozzle that accelerates the exhaust gases out the back of the engine to create thrust. When turbojets were introduced, the top speed of fighter aircraft equipped with them was at least 100 miles per hour faster than competing piston-driven aircraft. In the years after the war, the drawbacks of the turbojet gradually became apparent. Below about Mach 2, turbojets are very fuel inefficient and create tremendous amounts of noise. Early designs also respond very slowly to power changes, a fact that killed many experienced pilots when they attempted the transition to jets. These drawbacks eventually led to the downfall of the pure turbojet, and only a handful of types are still in production. The last airliner that used turbojets was the ], whose Mach 2 airspeed permitted the engine to be highly efficient. | |||
| Rocket engines are not used for most aircraft as the energy and propellant efficiency is very poor except at high speeds, but have been employed for short bursts of speed and takeoff. | |||
| ====Turbofan==== | |||
| Rocket engines are very efficient only at very high speeds, although are useful because they produce very large thrust and weigh very little. | |||
| ] turbofan engine]] | |||
| {{main|Turbofan}} | |||
| A turbofan engine is much the same as a turbojet, but with an enlarged fan at the front that provides thrust in much the same way as a ducted ], resulting in improved ]. Though the fan creates thrust like a propeller, the surrounding duct frees it from many of the restrictions that limit propeller performance. This operation is a more efficient way to provide thrust than simply using the ] alone, and turbofans are more efficient than propellers in the transsonic range of aircraft speeds and can operate in the ] realm. A turbofan typically has extra turbine stages to turn the fan. Turbofans were among the first engines to use multiple '']''—concentric shafts that are free to rotate at their own speed—to let the engine react more quickly to changing power requirements. Turbofans are coarsely split into low-bypass and high-bypass categories. Bypass air flows through the fan, but around the jet core, not mixing with fuel and burning. The ratio of this air to the amount of air flowing through the engine core is the bypass ratio. Low-bypass engines are preferred for military applications such as fighters due to high thrust-to-weight ratio, while high-bypass engines are preferred for civil use for good fuel efficiency and low noise. High-bypass turbofans are usually most efficient when the aircraft is traveling at {{convert|500|to|550|mph|km/h|abbr=off}}, the cruise speed of most large airliners. Low-bypass turbofans can reach supersonic speeds, though normally only when fitted with ]s. | |||
| ==New designs== | |||
| ===Economics of new designs=== | |||
| ==== Advanced technology engine ==== | |||
| Throughout most of the history of aircraft engine design, they tended to be more advanced than their automobile counterparts. High-strength ] ]s were used in these engines decades before they became common in cars. Likewise, those engines adopted ] instead of ] quite early. Similarly, ] and multiple valves per cylinder were introduced, while automobile engines continued to use ] and didn't widely use more than two valves per cylinder until the 1990s. | |||
| {{Main article|Advanced technology engine}} | |||
| The term ''advanced technology engine'' refers to the modern generation of jet engines.<ref>{{cite book |title=A Dictionary of Aviation |first=David W. |last=Wragg |isbn=9780850451634 |edition=first |publisher=Osprey |year=1973 |page=4}}</ref> The principle is that a turbine engine will function more efficiently if the various sets of turbines can revolve at their individual optimum speeds, instead of at the same speed. The true advanced technology engine has a triple spool, meaning that instead of having a single drive shaft, there are three, in order that the three sets of blades may revolve at different speeds. An interim state is a twin-spool engine, allowing only two different speeds for the turbines. | |||
| ===Pulsejets=== | |||
| Today the ] aviation market is so small that there is essentially no commercial money for new design work. Most aviation engines flying are based on a design from the 1960s, or before, using original materials, tooling and parts. Meanwhile the financial power of the automobile industry has continued improvement. A new car design is likely to use an engine designed no more than a few years ago, built with the latest alloys and advanced electronic engine controls. Modern car engines require very little maintenance apart from oil changes, aircraft engines are now, in comparison and paradoxically, rather heavy, dirty and unreliable. | |||
| {{Main|Pulsejet}} | |||
| Pulsejets are mechanically simple devices that—in a repeating cycle—draw air through a no-return valve at the front of the engine into a combustion chamber and ignite it. The combustion forces the exhaust gases out the back of the engine. It produces power as a series of pulses rather than as a steady output, hence the name. The only application of this type of engine was the German unmanned ] of ]. Though the same engines were also used experimentally for ersatz fighter aircraft, the extremely loud noise generated by the engines caused mechanical damage to the airframe that was sufficient to make the idea unworkable. | |||
| ====Gluhareff Pressure Jet==== | |||
| Much of the innovation (and most newly constructed planes flying) in the past two decades in private aviation has been in ] and ], and so has innovation in powerplants. ], amongst others, has introduced a number of new small production engine designs for this type of craft. The smallest of these mostly use two-stroke designs, but the larger models are four-strokes. For the reasons discussed above, some hobbyists and experimenters prefer to adapt automotive engines for their home-built aircraft, instead of using certified aircraft engines. | |||
| {{Main|Gluhareff Pressure Jet}} | |||
| The Gluhareff Pressure Jet (or tip jet) is a type of jet engine that, like a valveless pulsejet, has no moving parts. Having no moving parts, the engine works by having a coiled pipe in the combustion chamber that superheats the fuel (propane) before being injected into the air-fuel inlet. In the combustion chamber, the fuel/air mixture ignites and burns, creating thrust as it leaves through the exhaust pipe. Induction and compression of the fuel/air mixture is done both by the pressure of propane as it is injected, along with the sound waves created by combustion acting on the intake stacks. It was intended as a power plant for personal helicopters and compact aircraft such as Microlights. | |||
| ===Rocket=== | |||
| Over the history of the development of aircraft engines, the ], that is, conventional gasoline powered, reciprocating-piston engines have been by far the most common type. That is not because they are the best but simply because they were there first and type-certification of new designs is an expensive, time-consuming process. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{main|Rocket engine}} | |||
| A few aircraft have used rocket engines for main thrust or attitude control, notably the ] and ]. | |||
| ===Wankel engine=== | |||
| Rocket engines are not used for most aircraft as the energy and propellant efficiency is very poor, but have been employed for short bursts of speed and takeoff. Where fuel/propellant efficiency is of lesser concern, rocket engines can be useful because they produce very large amounts of thrust and weigh very little. | |||
| {{main|Wankel engine}} | |||
| ]e self-launching ], removed from the glider and mounted on a test stand for maintenance at the ] in ], ]. Counter-clockwise from top left: propeller hub, mast with belt guide, radiator, Wankel engine, muffler shroud.]] | |||
| ====Rocket turbine engine==== | |||
| Another promising design for aircraft use was the ] rotary engine. The ] is about one half the weight and size of a traditional ] ] of equal power output, and much lower in complexity. In an aircraft application, the power to weight ratio is very important, making the Wankel engine a good choice. Because the engine is typically constructed with an aluminium housing and a steel rotor, and aluminium expands more than steel when heated, unlike a piston engine, a Wankel engine will not seize when overheated. This is an important safety factor for aeronautical use. Considerable development of these designs started after ], but at the time the aircraft industry favored the use of ] engines. It was believed that ] or ] engines could power all aircraft, from the largest to smallest designs. The Wankel engine did not find many applications in aircraft, but was used by ] in a popular line of ]. Recently, the Wankel engine has been developed for use in ]s where the small size, light weight, and low vibration are especially important.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| {{main|Rocket turbine engine}} | |||
| |url = http://www.alexander-schleicher.de/englisch/produkte/ash26/e_ash26_main.htm | |||
| A rocket turbine engine is a combination of two types of propulsion engines: a ] and a turbine jet engine. Its ] is a little higher than a regular jet engine, and works at higher altitudes.<ref>"Analysis of the effect of factors on the efficiency of liquid rocket turbine" by Zu, Guojun; Zhang, Yuanjun ''Journal of Propulsion Technology '' no. 6, p. 38-43, 58.</ref> | |||
| |title = Alexander Schleicher GmbH & Co., ASH 26 E Information | |||
| |accessdate = 2006-11-24 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ===Precooled jet engines=== | |||
| Wankel engines are becoming increasingly popular in homebuilt ], due to a number of factors. Most are Mazda 12A and 13B engines, removed from automobiles and converted to aviation use. This is a very cost-effective alternative to certified aircraft engines, providing engines ranging from 100 to {{convert|300|hp}} at a fraction of the cost of traditional engines. These conversions first took place in the early 1970s, and with hundreds or even thousands of these engines mounted on aircraft, as of 10 December 2006 the ] has only seven reports of incidents involving aircraft with Mazda engines, and none of these is of a failure due to design or manufacturing flaws. During the same time frame, they have reports of several thousand reports of broken crankshafts and connecting rods, failed pistons and incidents caused by other components which are not found in the Wankel engines. Rotary engine enthusiasts refer to piston aircraft engines as "Reciprosaurs," and point out that their designs are essentially unchanged since the 1930s, with only minor differences in manufacturing processes and variation in engine displacement. | |||
| {{main|Precooled jet engine}} | |||
| For very high supersonic/low hypersonic flight speeds, inserting a cooling system into the air duct of a hydrogen jet engine permits greater fuel injection at high speed and obviates the need for the duct to be made of refractory or actively cooled materials. This greatly improves the thrust/weight ratio of the engine at high speed. | |||
| Peter Garrison, contributing editor for ], has said that "the most promising engine for aviation use is the Mazda rotary." Garrison lost an airplane which he had designed and built (and missed death literally by inches), when a piston-powered plane had engine failure and crashed into Garrison's plane, which was waiting to take off. | |||
| It is thought that this design of engine could permit sufficient performance for antipodal flight at Mach 5, or even permit a single stage to orbit vehicle to be practical. The hybrid air-breathing ] is a pre-cooled engine under development. | |||
| ===Diesel engine=== | |||
| {{main|Aircraft diesel engine}} | |||
| ===Piston-turbofan hybrid=== | |||
| The ] is another engine design that has been examined for aviation use. In general diesel engines are more reliable and much better suited to running for long periods of time at medium power settings—this is why they are widely used in trucks for instance. Several attempts to produce diesel aircraft engines were made in the 1930s but, at the time, the alloys were not up to the task of handling the much higher ]s used in these designs. They generally had poor power-to-weight ratios and were uncommon for that reason , but for exemple the Clerget 14F diesel radial engine (1939) has the same power to weight as a gazoline radial . Improvements in diesel technology in automobiles (leading to much better power-weight ratios), the diesel's much better fuel efficiency (particularly compared to the old gasoline designs currently being used in light aircraft) and the high relative taxation of AVGAS compared to Jet A1 in Europe have all seen a revival of interest in the concept. ] Aircraft Engines converted Mercedes diesel automotive engines, certified them for aircraft use, and became an OEM provider to Diamond Aviation for their light twin. Financial problems have plagued Thielert, so Diamond's affiliate—Austro Engine—developed the new ], also based on a Mercedes engine.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url = http://www.flyingmag.com/pilot-reports/pistons/diamond-twins-reborn | |||
| |title = Diamond Twins Reborn | |||
| |accessdate = 2010-06-14 | |||
| }}</ref> Competing new diesel engines may bring fuel efficiency and lead-free emissions to small aircraft, representing the biggest change in light aircraft engines in decades. | |||
| Wilksch Airmotive build 2 stroke diesel engine (same power to weight as a gazoline engine) for experimental aircraft: WAM 100 (100hp), WAM 120 (120hp) and WAM 160 (160hp) | |||
| At the April 2018 ], ]-based research institute ] presented a high-efficiency composite cycle engine for 2050, combining a ] with a ] core.<!--<ref name=Flight24apr2018>--> | |||
| ===Precooled jet engines=== | |||
| The 2.87 m diameter, 16-blade fan gives a 33.7 ultra-high ], driven by a geared low-pressure turbine but the high-pressure compressor drive comes from a piston-engine with two 10 piston banks without a high-pressure turbine, increasing efficiency with non-stationary ]-] combustion for higher peak pressures and temperatures.<!--<ref name=Flight24apr2018>--> | |||
| {{main|precooled jet engine}} | |||
| The 11,200 lb (49.7 kN) engine could power a 50-seat ].<ref name=Flight24apr2018>{{cite news |url= https://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/hybrid-geared-fan-and-piston-concept-could-slash-fue-447955/ |title= Hybrid geared-fan and piston concept could slash fuel-burn |date= 24 April 2018 |author= David Kaminski-Morrow |work= Flightglobal}}</ref> | |||
| Its cruise ] would be 11.5 g/kN/s (0.406 lb/lbf/hr) for an overall ] of 48.2%, for a burner temperature of {{cvt|1700|K|C}}, an ] of 38 and a peak pressure of {{cvt|30|MPa|bar}}.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.bauhaus-luftfahrt.net/fileadmin/user_upload/CCE_Data_Sheet.pdf |title= Composite Cycle Engine concept technical data sheet |publisher= Bauhaus Luftfahrt}}</ref> | |||
| For very high supersonic/low hypersonic flight speeds inserting a cooling system into the air duct of a hydrogen jet engine permits greater fuel injection at high speed and obviates the need for the duct to be made of refractory or actively cooled materials. This greatly improves the thrust/weight ratio of the engine at high speed. | |||
| Although engine weight increases by 30%, ] is reduced by 15%.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.bauhaus-luftfahrt.net/en/research/energy-technologies-power-systems/the-composite-cycle-engine-concept/ |title= The composite cycle engine concept |publisher= Bauhaus Luftfahrt}}</ref> | |||
| Sponsored by the ] under Framework 7 project {{abbr|LEMCOTEC|Low Emission Core Engine Technologies}}, Bauhaus Luftfahrt, ] and ] presented the concept in 2015, raising the overall engine pressure ratio to over 100 for a 15.2% fuel burn reduction compared to 2025 engines.<ref>{{cite journal |url= https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278674579 |title= A Composite Cycle Engine Concept with Hecto-Pressure Ratio |date= July 2015 |doi= 10.2514/6.2015-4028 |journal= AIAA Propulsion and Energy Conference |author= Sascha Kaiser|isbn= 978-1-62410-321-6 |display-authors=et al}}</ref> | |||
| ==Engine position numbering== | |||
| It is thought that this design of engine could permit sufficient performance for ], or even permit a ] to be practical. | |||
| ]s of a three-engine ], each one bearing the respective engine number]] | |||
| On multi-engine aircraft, engine positions are numbered from left to right from the point of view of the pilot looking forward, so for example on a four-engine aircraft such as the ], engine No. 1 is on the left side, farthest from the fuselage, while engine No. 3 is on the right side nearest to the fuselage.<ref>{{cite book | |||
| | title = Skyways for business | |||
| | author = ((National Business Aircraft Association)) | |||
| | publisher = Henry Publications | |||
| | year = 1952 | |||
| | volume = 11 | |||
| | page = 52 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=t20PAAAAIAAJ&q=inboard | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| In the case of the twin-engine ], which has two fuselage-mounted jet engines one above the other, engine No. 1 is below and to the front of engine No. 2, which is above and behind.<ref>{{cite web |title=English Electric Lightning F53 (53-671) – Power Plants |url=http://www.gatwick-aviation-museum.co.uk/lightning/power_plants.htm |website=Gatwick Aviation Museum |access-date=9 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180612141820/http://www.gatwick-aviation-museum.co.uk/lightning/power_plants.htm |archive-date=12 June 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In the ], a ] twin-engine airplane, engine No. 1 is the one at the front of the fuselage, while engine No. 2 is aft of the cabin. | |||
| ==Fuel== | |||
| Aircraft reciprocating (piston) engines are typically designed to run on ]. Avgas has a higher octane rating than automotive ] to allow higher ]s, power output, and efficiency at higher altitudes. Currently the most common Avgas is 100LL. This refers to the ] (100 octane) and the lead content (LL = low lead, relative to the historic levels of lead in pre-regulation Avgas).{{citation needed|date=March 2016}} | |||
| Refineries blend Avgas with ] (TEL) to achieve these high octane ratings, a practice that governments no longer permit for gasoline intended for road vehicles. The shrinking supply of TEL and the possibility of environmental legislation banning its use have made a search for replacement fuels for ] aircraft a priority for pilots’ organizations.<ref>{{cite press release|url=http://www.eaa.org/communications/eaanews/pr/011207_lawrence.html |title=EAA'S Earl Lawrence Elected Secretary of International Aviation Fuel Committee |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130303034122/http://www.eaa.org/communications/eaanews/pr/011207_lawrence.html |archive-date=March 3, 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Electric=== | |||
| Turbine engines and ]s burn various grades of ]. Jet fuel is a relatively less volatile ] derivative based on ], but certified to strict aviation standards, with additional additives.{{citation needed|date=March 2016}} | |||
| About 60 electrically powered aircraft, such as the ], have been designed since the 1960s,<ref name = french/><ref>"", ]</ref> Some are used as military ]s.<ref>""</ref> In ] in late 2007, a conventional light aircraft powered by an 18 kW electric motor using lithium polymer batteries was flown, covering more than 50 kilometers (31 miles), the first electric airplane to receive a ].<ref name = french>"", '']'', December 23, 2007</ref> | |||
| ] typically use ]s (also known as "glow engines" due to the use of a ]) powered by ], a mixture of ], ], and lubricant. Electrically powered model airplanes<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nitroplanes.com/rtf.html|title=Electric Airplanes - RTF|website=www.nitroplanes.com}}</ref> and helicopters are also commercially available. Small ] ]s are almost always powered by electricity,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.amazon.com/Photography-Drones-Store-Buying-Guide/b?ie=UTF8&node=13407343011|title=Amazon.com: Photography Drones Store: Buying Guide: Electronics|website=Amazon}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nitroplanes.com/quadcopters.html|title=RC Quadcopters|website=www.nitroplanes.com}}</ref> but larger gasoline-powered designs are under development.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gizmag.com/yeair-hybrid-two-stroke-combustion-quadcopter-drone/37713/|title=Yeair! hybrid gasoline/electric quadcopter boasts impressive numbers|website=www.gizmag.com|date=27 May 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://hackaday.io/project/1230-goliath-a-gas-powered-quadcopter|title=Goliath – A Gas Powered Quadcopter|website=hackaday.io}}</ref> | |||
| Limited experiments with ] propulsion have been performed, notably the manned ] and unmanned ] aircraft. | |||
| <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.industrytap.com/heavy-lifting-quadcopter-lifts-50-pound-loads-its-a-gas-powered-hulk-hlq/2182|title=Heavy Lifting Quadcopter Lifts 50 Pound Loads. It's a Gas Powered HULK (HLQ)|website=Industry Tap|date=2013-03-11}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{Reflist|group=nb}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{Commons category|Aircraft engines}} | ||
| {{wiktionary}} | {{wiktionary}} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * a 1954 ''Flight'' article by ] | |||
| * {{cite magazine |url= https://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1997/1997%20-%202471.html |title= Engine Directory |magazine= Flight International |date= 24 September 1997}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Authority control}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Aircraft Engine}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Aircraft Engine}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:20, 10 December 2024
Engine designed for use in powered aircraft "Aero-engine" redirects here. For the use of aircraft engines in cars, see Aero-engined car.
| Part of a series on |
| Aircraft propulsion |
|---|
|
Shaft engines: driving propellers, rotors, ducted fans or propfans |
| Reaction engines |
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.
Manufacturing industry
See also: List of aircraft enginesIn commercial aviation the major Western manufacturers of turbofan engines are Pratt & Whitney (a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies), General Electric, Rolls-Royce, and CFM International (a joint venture of Safran Aircraft Engines and General Electric). Russian manufacturers include the United Engine Corporation, Aviadvigatel and Klimov. Aeroengine Corporation of China was formed in 2016 with the merger of several smaller companies.
The largest manufacturer of turboprop engines for general aviation is Pratt & Whitney. General Electric announced in 2015 entrance into the market.
Development history

- 1848: John Stringfellow made a steam engine for a 10-foot wingspan model aircraft which achieved the first powered flight, albeit with negligible payload.
- 1903: Charlie Taylor built an inline engine, mostly of aluminum, for the Wright Flyer (12 horsepower).
- 1903: Manly-Balzer engine sets standards for later radial engines.
- 1906: Léon Levavasseur produces a successful water-cooled V8 engine for aircraft use.
- 1908: René Lorin patents a design for the ramjet engine.
- 1908: Louis Seguin designed the Gnome Omega, the world's first rotary engine to be produced in quantity. In 1909 a Gnome powered Farman III aircraft won the prize for the greatest non-stop distance flown at the Reims Grande Semaine d'Aviation setting a world record for endurance of 180 kilometres (110 mi).
- 1910: Coandă-1910, an unsuccessful ducted fan aircraft exhibited at Paris Aero Salon, powered by a piston engine. The aircraft never flew, but a patent was filed for routing exhaust gases into the duct to augment thrust.
- 1914: Auguste Rateau suggests using exhaust-powered compressor – a turbocharger – to improve high-altitude performance; not accepted after the tests
- 1915: The Mercedes D.VI - an eighteen-cylinder liquid-cooled W-18 type aircraft engine - (517 hp/380 kW) was the most powerful engine during WW1.
- 1917–18: The Idflieg-numbered R.30/16 example of the Imperial German Luftstreitkräfte's Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI heavy bomber becomes the earliest known supercharger-equipped aircraft to fly, with a Mercedes D.II straight-six engine in the central fuselage driving a Brown-Boveri mechanical supercharger for the R.30/16's four Mercedes D.IVa engines.
- 1918: Sanford Alexander Moss picks up Rateau's idea and creates the first successful turbocharger
- 1926: Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar IV (S), the first series-produced supercharged engine for aircraft use; two-row radial with a gear-driven centrifugal supercharger.
- 1930: Frank Whittle submitted his first patent for a turbojet engine.
- June 1939: Heinkel He 176 is the first successful aircraft to fly powered solely by a liquid-fueled rocket engine.
- August 1939: Heinkel HeS 3 turbojet propels the pioneering German Heinkel He 178 aircraft.
- 1940: Jendrassik Cs-1, the world's first run of a turboprop engine. It is not put into service.
- 1943 Daimler-Benz DB 670, first turbofan runs
- 1944: Messerschmitt Me 163B Komet, the world's first rocket-propelled combat aircraft deployed.
- 1945: First turboprop-powered aircraft flies, a modified Gloster Meteor with two Rolls-Royce Trent engines.
- 1947: Bell X-1 rocket-propelled aircraft exceeds the speed of sound.
- 1948: 100 shp 782, the first turboshaft engine to be applied to aircraft use; in 1950 used to develop the larger 280 shp (210 kW) Turbomeca Artouste.
- 1949: Leduc 010, the world's first ramjet-powered aircraft flight.
- 1950: Rolls-Royce Conway, the world's first production turbofan, enters service.
- 1968: General Electric TF39 high bypass turbofan enters service delivering greater thrust and much better efficiency.
- 2002: HyShot scramjet flew in dive.
- 2004: NASA X-43, the first scramjet to maintain altitude.
- 2020: Pipistrel E-811 is the first electric aircraft engine to be awarded a type certificate by EASA. It powers the Pipistrel Velis Electro, the first fully electric EASA type-certified aeroplane.
Shaft engines
Reciprocating (piston) engines
Main article: reciprocating engineIn-line engine
Main article: Straight engine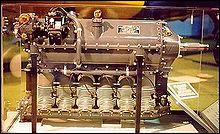
In this section, for clarity, the term "inline engine" refers only to engines with a single row of cylinders, as used in automotive language, but in aviation terms, the phrase "inline engine" also covers V-type and opposed engines (as described below), and is not limited to engines with a single row of cylinders. This is typically to differentiate them from radial engines.
A straight engine typically has an even number of cylinders, but there are instances of three- and five-cylinder engines. The greatest advantage of an inline engine is that it allows the aircraft to be designed with a low frontal area to minimize drag. If the engine crankshaft is located above the cylinders, it is called an inverted inline engine: this allows the propeller to be mounted high up to increase ground clearance, enabling shorter landing gear. The disadvantages of an inline engine include a poor power-to-weight ratio, because the crankcase and crankshaft are long and thus heavy. An in-line engine may be either air-cooled or liquid-cooled, but liquid-cooling is more common because it is difficult to get enough air-flow to cool the rear cylinders directly.
Inline engines were common in early aircraft; one was used in the Wright Flyer, the aircraft that made the first controlled powered flight. However, the inherent disadvantages of the design soon became apparent, and the inline design was abandoned, becoming a rarity in modern aviation.
For other configurations of aviation inline engine, such as X-engines, U-engines, H-engines, etc., see Inline engine (aeronautics).
V-type engine

Cylinders in this engine are arranged in two in-line banks, typically tilted 60–90 degrees apart from each other and driving a common crankshaft. The vast majority of V engines are water-cooled. The V design provides a higher power-to-weight ratio than an inline engine, while still providing a small frontal area. Perhaps the most famous example of this design is the legendary Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, a 27-litre (1649 in) 60° V12 engine used in, among others, the Spitfires that played a major role in the Battle of Britain.
Horizontally opposed engine
Main article: Flat engine
A horizontally opposed engine, also called a flat or boxer engine, has two banks of cylinders on opposite sides of a centrally located crankcase. The engine is either air-cooled or liquid-cooled, but air-cooled versions predominate. Opposed engines are mounted with the crankshaft horizontal in airplanes, but may be mounted with the crankshaft vertical in helicopters. Due to the cylinder layout, reciprocating forces tend to cancel, resulting in a smooth running engine. Opposed-type engines have high power-to-weight ratios because they have a comparatively small, lightweight crankcase. In addition, the compact cylinder arrangement reduces the engine's frontal area and allows a streamlined installation that minimizes aerodynamic drag. These engines always have an even number of cylinders, since a cylinder on one side of the crankcase "opposes" a cylinder on the other side.
Opposed, air-cooled four- and six-cylinder piston engines are by far the most common engines used in small general aviation aircraft requiring up to 400 horsepower (300 kW) per engine. Aircraft that require more than 400 horsepower (300 kW) per engine tend to be powered by turbine engines.
H configuration engine
Main article: H engineAn H configuration engine is essentially a pair of horizontally opposed engines placed together, with the two crankshafts geared together.
Radial engine

This type of engine has one or more rows of cylinders arranged around a centrally located crankcase. Each row generally has an odd number of cylinders to produce smooth operation. A radial engine has only one crank throw per row and a relatively small crankcase, resulting in a favorable power-to-weight ratio. Because the cylinder arrangement exposes a large amount of the engine's heat-radiating surfaces to the air and tends to cancel reciprocating forces, radials tend to cool evenly and run smoothly. The lower cylinders, which are under the crankcase, may collect oil when the engine has been stopped for an extended period. If this oil is not cleared from the cylinders prior to starting the engine, serious damage due to hydrostatic lock may occur.
Most radial engines have the cylinders arranged evenly around the crankshaft, although some early engines, sometimes called semi-radials or fan configuration engines, had an uneven arrangement. The best known engine of this type is the Anzani engine, which was fitted to the Bleriot XI used for the first flight across the English Channel in 1909. This arrangement had the drawback of needing a heavy counterbalance for the crankshaft, but was used to avoid the spark plugs oiling up.
In military aircraft designs, the large frontal area of the engine acted as an extra layer of armor for the pilot. Also air-cooled engines, without vulnerable radiators, are slightly less prone to battle damage, and on occasion would continue running even with one or more cylinders shot away. However, the large frontal area also resulted in an aircraft with an aerodynamically inefficient increased frontal area.
Rotary engine

Rotary engines have the cylinders in a circle around the crankcase, as in a radial engine, (see above), but the crankshaft is fixed to the airframe and the propeller is fixed to the engine case, so that the crankcase and cylinders rotate. The advantage of this arrangement is that a satisfactory flow of cooling air is maintained even at low airspeeds, retaining the weight advantage and simplicity of a conventional air-cooled engine without one of their major drawbacks. The first practical rotary engine was the Gnome Omega designed by the Seguin brothers and first flown in 1909. Its relative reliability and good power to weight ratio changed aviation dramatically. Before the first World War most speed records were gained using Gnome-engined aircraft, and in the early years of the war rotary engines were dominant in aircraft types for which speed and agility were paramount. To increase power, engines with two rows of cylinders were built.
However, the gyroscopic effects of the heavy rotating engine produced handling problems in aircraft and the engines also consumed large amounts of oil since they used total loss lubrication, the oil being mixed with the fuel and ejected with the exhaust gases. Castor oil was used for lubrication, since it is not soluble in petrol, and the resultant fumes were nauseating to the pilots. Engine designers had always been aware of the many limitations of the rotary engine so when the static style engines became more reliable and gave better specific weights and fuel consumption, the days of the rotary engine were numbered.
Wankel engine
Main article: Wankel engine
The Wankel is a type of rotary engine. The Wankel engine is about one half the weight and size of a traditional four-stroke cycle piston engine of equal power output, and much lower in complexity. In an aircraft application, the power-to-weight ratio is very important, making the Wankel engine a good choice. Because the engine is typically constructed with an aluminium housing and a steel rotor, and aluminium expands more than steel when heated, a Wankel engine does not seize when overheated, unlike a piston engine. This is an important safety factor for aeronautical use. Considerable development of these designs started after World War II, but at the time the aircraft industry favored the use of turbine engines. It was believed that turbojet or turboprop engines could power all aircraft, from the largest to smallest designs. The Wankel engine did not find many applications in aircraft, but was used by Mazda in a popular line of sports cars. The French company Citroën had developed Wankel powered RE-2 [fr] helicopter in 1970's.
In modern times the Wankel engine has been used in motor gliders where the compactness, light weight, and smoothness are crucially important.
The now-defunct Staverton-based firm MidWest designed and produced single- and twin-rotor aero engines, the MidWest AE series. These engines were developed from the motor in the Norton Classic motorcycle. The twin-rotor version was fitted into ARV Super2s and the Rutan Quickie. The single-rotor engine was put into a Chevvron motor glider and into the Schleicher ASH motor-gliders. After the demise of MidWest, all rights were sold to Diamond of Austria, who have since developed a MkII version of the engine.
As a cost-effective alternative to certified aircraft engines some Wankel engines, removed from automobiles and converted to aviation use, have been fitted in homebuilt experimental aircraft. Mazda units with outputs ranging from 100 horsepower (75 kW) to 300 horsepower (220 kW) can be a fraction of the cost of traditional engines. Such conversions first took place in the early 1970s; and as of 10 December 2006 the National Transportation Safety Board has only seven reports of incidents involving aircraft with Mazda engines, and none of these is of a failure due to design or manufacturing flaws.
Combustion cycles
The most common combustion cycle for aero engines is the four-stroke with spark ignition. Two-stroke spark ignition has also been used for small engines, while the compression-ignition diesel engine is seldom used.
Starting in the 1930s attempts were made to produce a practical aircraft diesel engine. In general, Diesel engines are more reliable and much better suited to running for long periods of time at medium power settings. The lightweight alloys of the 1930s were not up to the task of handling the much higher compression ratios of diesel engines, so they generally had poor power-to-weight ratios and were uncommon for that reason, although the Clerget 14F Diesel radial engine (1939) has the same power to weight ratio as a gasoline radial. Improvements in Diesel technology in automobiles (leading to much better power-weight ratios), the Diesel's much better fuel efficiency and the high relative taxation of AVGAS compared to Jet A1 in Europe have all seen a revival of interest in the use of diesels for aircraft. Thielert Aircraft Engines converted Mercedes Diesel automotive engines, certified them for aircraft use, and became an OEM provider to Diamond Aviation for their light twin. Financial problems have plagued Thielert, so Diamond's affiliate — Austro Engine — developed the new AE300 turbodiesel, also based on a Mercedes engine. Competing new Diesel engines may bring fuel efficiency and lead-free emissions to small aircraft, representing the biggest change in light aircraft engines in decades.
Power turbines
Turboprop

While military fighters require very high speeds, many civil airplanes do not. Yet, civil aircraft designers wanted to benefit from the high power and low maintenance that a gas turbine engine offered. Thus was born the idea to mate a turbine engine to a traditional propeller. Because gas turbines optimally spin at high speed, a turboprop features a gearbox to lower the speed of the shaft so that the propeller tips don't reach supersonic speeds. Often the turbines that drive the propeller are separate from the rest of the rotating components so that they can rotate at their own best speed (referred to as a free-turbine engine). A turboprop is very efficient when operated within the realm of cruise speeds it was designed for, which is typically 200 to 400 mph (320 to 640 km/h).
Turboshaft

Turboshaft engines are used primarily for helicopters and auxiliary power units. A turboshaft engine is similar to a turboprop in principle, but in a turboprop the propeller is supported by the engine and the engine is bolted to the airframe: in a turboshaft, the engine does not provide any direct physical support to the helicopter's rotors. The rotor is connected to a transmission which is bolted to the airframe, and the turboshaft engine drives the transmission. The distinction is seen by some as slim, as in some cases aircraft companies make both turboprop and turboshaft engines based on the same design.
Electric power
A number of electrically powered aircraft, such as the QinetiQ Zephyr, have been designed since the 1960s. Some are used as military drones. In France in late 2007, a conventional light aircraft powered by an 18 kW electric motor using lithium polymer batteries was flown, covering more than 50 kilometers (31 mi), the first electric airplane to receive a certificate of airworthiness.
On 18 May 2020, the Pipistrel E-811 was the first electric aircraft engine to be awarded a type certificate by EASA for use in general aviation. The E-811 powers the Pipistrel Velis Electro.
Limited experiments with solar electric propulsion have been performed, notably the manned Solar Challenger and Solar Impulse and the unmanned NASA Pathfinder aircraft.
Many big companies, such as Siemens, are developing high performance electric engines for aircraft use, also, SAE shows new developments in elements as pure Copper core electric motors with a better efficiency. A hybrid system as emergency back-up and for added power in take-off is offered for sale by Axter Aerospace, Madrid, Spain.
Small multicopter UAVs are almost always powered by electric motors.
Reaction engines
Main article: Jet engineReaction engines generate the thrust to propel an aircraft by ejecting the exhaust gases at high velocity from the engine, the resultant reaction of forces driving the aircraft forwards. The most common reaction propulsion engines flown are turbojets, turbofans and rockets. Other types such as pulsejets, ramjets, scramjets and pulse detonation engines have also flown. In jet engines the oxygen necessary for fuel combustion comes from the air, while rockets carry an oxidizer (usually oxygen in some form) as part of the fuel load, permitting their use in space.
Jet turbines
Turbojet

A turbojet is a type of gas turbine engine that was originally developed for military fighters during World War II. A turbojet is the simplest of all aircraft gas turbines. It consists of a compressor to draw air in and compress it, a combustion section where fuel is added and ignited, one or more turbines that extract power from the expanding exhaust gases to drive the compressor, and an exhaust nozzle that accelerates the exhaust gases out the back of the engine to create thrust. When turbojets were introduced, the top speed of fighter aircraft equipped with them was at least 100 miles per hour faster than competing piston-driven aircraft. In the years after the war, the drawbacks of the turbojet gradually became apparent. Below about Mach 2, turbojets are very fuel inefficient and create tremendous amounts of noise. Early designs also respond very slowly to power changes, a fact that killed many experienced pilots when they attempted the transition to jets. These drawbacks eventually led to the downfall of the pure turbojet, and only a handful of types are still in production. The last airliner that used turbojets was the Concorde, whose Mach 2 airspeed permitted the engine to be highly efficient.
Turbofan

A turbofan engine is much the same as a turbojet, but with an enlarged fan at the front that provides thrust in much the same way as a ducted propeller, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. Though the fan creates thrust like a propeller, the surrounding duct frees it from many of the restrictions that limit propeller performance. This operation is a more efficient way to provide thrust than simply using the jet nozzle alone, and turbofans are more efficient than propellers in the transsonic range of aircraft speeds and can operate in the supersonic realm. A turbofan typically has extra turbine stages to turn the fan. Turbofans were among the first engines to use multiple spools—concentric shafts that are free to rotate at their own speed—to let the engine react more quickly to changing power requirements. Turbofans are coarsely split into low-bypass and high-bypass categories. Bypass air flows through the fan, but around the jet core, not mixing with fuel and burning. The ratio of this air to the amount of air flowing through the engine core is the bypass ratio. Low-bypass engines are preferred for military applications such as fighters due to high thrust-to-weight ratio, while high-bypass engines are preferred for civil use for good fuel efficiency and low noise. High-bypass turbofans are usually most efficient when the aircraft is traveling at 500 to 550 miles per hour (800 to 890 kilometres per hour), the cruise speed of most large airliners. Low-bypass turbofans can reach supersonic speeds, though normally only when fitted with afterburners.
Advanced technology engine
Main article: Advanced technology engineThe term advanced technology engine refers to the modern generation of jet engines. The principle is that a turbine engine will function more efficiently if the various sets of turbines can revolve at their individual optimum speeds, instead of at the same speed. The true advanced technology engine has a triple spool, meaning that instead of having a single drive shaft, there are three, in order that the three sets of blades may revolve at different speeds. An interim state is a twin-spool engine, allowing only two different speeds for the turbines.
Pulsejets
Main article: PulsejetPulsejets are mechanically simple devices that—in a repeating cycle—draw air through a no-return valve at the front of the engine into a combustion chamber and ignite it. The combustion forces the exhaust gases out the back of the engine. It produces power as a series of pulses rather than as a steady output, hence the name. The only application of this type of engine was the German unmanned V1 flying bomb of World War II. Though the same engines were also used experimentally for ersatz fighter aircraft, the extremely loud noise generated by the engines caused mechanical damage to the airframe that was sufficient to make the idea unworkable.
Gluhareff Pressure Jet
Main article: Gluhareff Pressure JetThe Gluhareff Pressure Jet (or tip jet) is a type of jet engine that, like a valveless pulsejet, has no moving parts. Having no moving parts, the engine works by having a coiled pipe in the combustion chamber that superheats the fuel (propane) before being injected into the air-fuel inlet. In the combustion chamber, the fuel/air mixture ignites and burns, creating thrust as it leaves through the exhaust pipe. Induction and compression of the fuel/air mixture is done both by the pressure of propane as it is injected, along with the sound waves created by combustion acting on the intake stacks. It was intended as a power plant for personal helicopters and compact aircraft such as Microlights.
Rocket

A few aircraft have used rocket engines for main thrust or attitude control, notably the Bell X-1 and North American X-15. Rocket engines are not used for most aircraft as the energy and propellant efficiency is very poor, but have been employed for short bursts of speed and takeoff. Where fuel/propellant efficiency is of lesser concern, rocket engines can be useful because they produce very large amounts of thrust and weigh very little.
Rocket turbine engine
Main article: Rocket turbine engineA rocket turbine engine is a combination of two types of propulsion engines: a liquid-propellant rocket and a turbine jet engine. Its power-to-weight ratio is a little higher than a regular jet engine, and works at higher altitudes.
Precooled jet engines
Main article: Precooled jet engineFor very high supersonic/low hypersonic flight speeds, inserting a cooling system into the air duct of a hydrogen jet engine permits greater fuel injection at high speed and obviates the need for the duct to be made of refractory or actively cooled materials. This greatly improves the thrust/weight ratio of the engine at high speed.
It is thought that this design of engine could permit sufficient performance for antipodal flight at Mach 5, or even permit a single stage to orbit vehicle to be practical. The hybrid air-breathing SABRE rocket engine is a pre-cooled engine under development.
Piston-turbofan hybrid
At the April 2018 ILA Berlin Air Show, Munich-based research institute de:Bauhaus Luftfahrt presented a high-efficiency composite cycle engine for 2050, combining a geared turbofan with a piston engine core. The 2.87 m diameter, 16-blade fan gives a 33.7 ultra-high bypass ratio, driven by a geared low-pressure turbine but the high-pressure compressor drive comes from a piston-engine with two 10 piston banks without a high-pressure turbine, increasing efficiency with non-stationary isochoric-isobaric combustion for higher peak pressures and temperatures. The 11,200 lb (49.7 kN) engine could power a 50-seat regional jet.
Its cruise TSFC would be 11.5 g/kN/s (0.406 lb/lbf/hr) for an overall engine efficiency of 48.2%, for a burner temperature of 1,700 K (1,430 °C), an overall pressure ratio of 38 and a peak pressure of 30 MPa (300 bar). Although engine weight increases by 30%, aircraft fuel consumption is reduced by 15%. Sponsored by the European Commission under Framework 7 project LEMCOTEC, Bauhaus Luftfahrt, MTU Aero Engines and GKN Aerospace presented the concept in 2015, raising the overall engine pressure ratio to over 100 for a 15.2% fuel burn reduction compared to 2025 engines.
Engine position numbering

On multi-engine aircraft, engine positions are numbered from left to right from the point of view of the pilot looking forward, so for example on a four-engine aircraft such as the Boeing 747, engine No. 1 is on the left side, farthest from the fuselage, while engine No. 3 is on the right side nearest to the fuselage.
In the case of the twin-engine English Electric Lightning, which has two fuselage-mounted jet engines one above the other, engine No. 1 is below and to the front of engine No. 2, which is above and behind.
In the Cessna 337 Skymaster, a push-pull twin-engine airplane, engine No. 1 is the one at the front of the fuselage, while engine No. 2 is aft of the cabin.
Fuel
Aircraft reciprocating (piston) engines are typically designed to run on aviation gasoline. Avgas has a higher octane rating than automotive gasoline to allow higher compression ratios, power output, and efficiency at higher altitudes. Currently the most common Avgas is 100LL. This refers to the octane rating (100 octane) and the lead content (LL = low lead, relative to the historic levels of lead in pre-regulation Avgas).
Refineries blend Avgas with tetraethyllead (TEL) to achieve these high octane ratings, a practice that governments no longer permit for gasoline intended for road vehicles. The shrinking supply of TEL and the possibility of environmental legislation banning its use have made a search for replacement fuels for general aviation aircraft a priority for pilots’ organizations.
Turbine engines and aircraft diesel engines burn various grades of jet fuel. Jet fuel is a relatively less volatile petroleum derivative based on kerosene, but certified to strict aviation standards, with additional additives.
Model aircraft typically use nitro engines (also known as "glow engines" due to the use of a glow plug) powered by glow fuel, a mixture of methanol, nitromethane, and lubricant. Electrically powered model airplanes and helicopters are also commercially available. Small multicopter UAVs are almost always powered by electricity, but larger gasoline-powered designs are under development.
See also
- Aviation safety
- Engine configuration
- Federal Aviation Regulations
- Hyper engine
- Model engine
- United States military aircraft engine designations
Notes
- The world's first series-produced cars with superchargers came earlier than aircraft. These were Mercedes 6/25/40 hp and Mercedes 10/40/65 hp, both models introduced in 1921 and used Roots superchargers. G.N. Georgano, ed. (1982). The new encyclopedia of motorcars 1885 to the present (3rd ed.). New York: Dutton. pp. 415. ISBN 978-0-525-93254-3.
References
- Wragg, David W. (1973). A Dictionary of Aviation (first ed.). Osprey. p. 215. ISBN 9780850451634.
- ^ "GE Pushes Into Turboprop Engines, Taking on Pratt". Wall Street Journal. November 16, 2015.
- ^ Ian McNeil, ed. (1990). Encyclopedia of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. pp. 315–21. ISBN 978-0-203-19211-5.
- Gibbs-Smith, Charles Harvard (1970). Aviation: an historical survey from its origins to the end of World War II. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN 9780112900139.
- Gibbs-Smith, Charles Harvard (1960). The Aeroplane: An Historical Survey of Its Origins and Development. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office.
- Winter, Frank H. (December 1980). "Ducted Fan or the World's First Jet Plane? The Coanda claim re-examined". The Aeronautical Journal. 84. Royal Aeronautical Society.
- Antoniu, Dan; Cicoș, George; Buiu, Ioan-Vasile; Bartoc, Alexandru; Șutic, Robert (2010). Henri Coandă and his technical work during 1906–1918 (in Romanian). Bucharest: Editura Anima. ISBN 978-973-7729-61-3.
- Guttman, Jon (2009). SPAD XIII vs. Fokker D VII: Western Front 1918 (1st ed.). Oxford: Osprey. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-1-84603-432-9.
- Powell, Hickman (Jun 1941). "He Harnessed a Tornado..." Popular Science.
- Anderson, John D (2002). The airplane: A history of its technology. Reston, VA, USA: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. pp. 252–53. ISBN 978-1-56347-525-2.
- ^ Calderwood, Dave (9 July 2020). "Pipistrel offers type certified electric motor". Seager Publishing. FLYER Magazine. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- Gibbs-Smith, C.H. (2003). Aviation. London: NMSO. p. 175. ISBN 1-9007-4752-9.
- Boulay, Pierre (1998). Guides Larivière (ed.). Les hélicoptères français (in French). ISBN 978-2-907051-17-0.
- "ASH 26 E Information". DE: Alexander Schleicher. Archived from the original on 2006-10-08. Retrieved 2006-11-24.
- "Diamond Twins Reborn". Flying Mag. Archived from the original on 2014-06-18. Retrieved 2010-06-14.
- ^ Worldwide première: first aircraft flight with electrical engine, Association pour la Promotion des Aéronefs à Motorisation Électrique, December 23, 2007, archived from the original on 2008-01-10.
- Superconducting Turbojet, Physorg.com, archived from the original on 2008-02-23.
- Voyeur, Litemachines, archived from the original on 2009-12-31.
- "TCDS for E811 engine, model 268MVLC" (PDF). European Union Aviation Safety Agency. 18 May 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- Axter Aerospace
- Wragg, David W. (1973). A Dictionary of Aviation (first ed.). Osprey. p. 4. ISBN 9780850451634.
- "Analysis of the effect of factors on the efficiency of liquid rocket turbine" by Zu, Guojun; Zhang, Yuanjun Journal of Propulsion Technology no. 6, p. 38-43, 58.
- David Kaminski-Morrow (24 April 2018). "Hybrid geared-fan and piston concept could slash fuel-burn". Flightglobal.
- "Composite Cycle Engine concept technical data sheet" (PDF). Bauhaus Luftfahrt.
- "The composite cycle engine concept". Bauhaus Luftfahrt.
- Sascha Kaiser; et al. (July 2015). "A Composite Cycle Engine Concept with Hecto-Pressure Ratio". AIAA Propulsion and Energy Conference. doi:10.2514/6.2015-4028. ISBN 978-1-62410-321-6.
- National Business Aircraft Association (1952). Skyways for business. Vol. 11. Henry Publications. p. 52.
- "English Electric Lightning F53 (53-671) – Power Plants". Gatwick Aviation Museum. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- "EAA'S Earl Lawrence Elected Secretary of International Aviation Fuel Committee" (Press release). Archived from the original on March 3, 2013.
- "Electric Airplanes - RTF". www.nitroplanes.com.
- "Amazon.com: Photography Drones Store: Buying Guide: Electronics". Amazon.
- "RC Quadcopters". www.nitroplanes.com.
- "Yeair! hybrid gasoline/electric quadcopter boasts impressive numbers". www.gizmag.com. 27 May 2015.
- "Goliath – A Gas Powered Quadcopter". hackaday.io.
- "Heavy Lifting Quadcopter Lifts 50 Pound Loads. It's a Gas Powered HULK (HLQ)". Industry Tap. 2013-03-11.
External links
- Aircraft Engines and Aircraft Engine Theory (includes links to diagrams)
- The Aircraft Engine Historical Society
- Jet Engine Specification Database
- Aircraft Engine Efficiency: Comparison of Counter-rotating and Axial Aircraft LP Turbines
- The History of Aircraft Power Plants Briefly Reviewed : From the " 7 lb. per h.p" Days to the " 1 lb. per h.p" of To-day
- "The Quest for Power" a 1954 Flight article by Bill Gunston
- "Engine Directory". Flight International. 24 September 1997.