| Revision as of 13:54, 19 June 2011 editDcirovic (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers253,275 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:15, 13 December 2024 edit undoAlith Anar (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users11,734 editsm Reverted 1 edit by Reckfulonelove (talk) to last revision by Yoshi24517Tags: Twinkle Undo | ||
| (140 intermediate revisions by 84 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Experimental drug}} | |||
| {{drugbox | |||
| {{cs1 config |name-list-style=vanc }} | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| {{Drugbox | |||
| | IUPAC_name = 1'-(2-methylalanyl-''O''-benzyl-<small>D</small>-seryl)-1-(methylsulfonyl)-1,2-dihydrospiro | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 435091605 | ||
| ⚫ | | image = |
||
| ⚫ | | IUPAC_name = 2-amino-2-methyl-''N''--1'-yl)-1-oxo-3-phenylmethoxypropan-2-yl]propanamide | ||
| ⚫ | | CAS_number = | ||
| ⚫ | | image = Ibutamoren skeletal.svg | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | |
| width = 250px | ||
| <!--Clinical data--> | |||
| | tradename = | |||
| ⚫ | | pregnancy_AU = | ||
| ⚫ | | pregnancy_US = | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_AU = | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_UK = | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_US = | ||
| | legal_status = ] | |||
| ⚫ | | routes_of_administration = ] | ||
| <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = | ||
| ⚫ | | protein_bound = | ||
| ⚫ | | metabolism = | ||
| | elimination_half-life = 4–6 hours (in ]s);<ref name="SmithThorner2000">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Unf5BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA45 |title=Human Growth Hormone: Research and Clinical Practice |vauthors=Smith RG, Thorner MO |date=28 January 2000 |publisher=Springer Science & Business Media |isbn=978-1-59259-015-5 |pages=45–}}</ref> ] levels remain elevated in humans with a single oral dose for up to 24 hours<ref name="Smith Ploeg Howard Feighner 1997 pp. 621–645">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Smith RG, Van der Ploeg LH, Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cheng K, Hickey GJ, Wyvratt MJ, Fisher MH, Nargund RP, Patchett AA |date=October 1997 |title=Peptidomimetic regulation of growth hormone secretion |journal=Endocrine Reviews |publisher=The Endocrine Society |volume=18 |issue=5 |pages=621–645 |doi=10.1210/edrv.18.5.0316 |pmid=9331545 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | | excretion = | ||
| <!--Identifiers--> | |||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| ⚫ | | CAS_number = 159634-47-6 | ||
| | CAS_supplemental = <br />159752-10-0 (]) | |||
| | ATC_prefix = | | ATC_prefix = | ||
| | ATC_suffix = | | ATC_suffix = | ||
| | ATC_supplemental = | | ATC_supplemental = | ||
| | UNII = GJ0EGN38UL | |||
| | PubChem = 9939050 | | PubChem = 9939050 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| | DrugBank = | | DrugBank = | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 154975 | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | synonyms = MK-677; MK-0677; L-163,191; Oratrope | |||
| ⚫ | | C |
||
| | molecular_weight = 528.662 g/mol | |||
| <!--Chemical data--> | |||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = | ||
| ⚫ | | C=27 | H=36 | N=4 | O=5 | S=1 | ||
| ⚫ | | protein_bound = | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = O=S(C)(=O)N(C2)c1ccccc1C23CCN(CC3)C(=O)C(NC(=O)C(N)(C)C)COCc4ccccc4 | ||
| ⚫ | | metabolism = | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C27H36N4O5S/c1-26(2,28)25(33)29-22(18-36-17-20-9-5-4-6-10-20)24(32)30-15-13-27(14-16-30)19-31(37(3,34)35)23-12-8-7-11-21(23)27/h4-12,22H,13-19,28H2,1-3H3,(H,29,33)/t22-/m1/s1 | |||
| | elimination_half-life = | |||
| | StdInChIKey = UMUPQWIGCOZEOY-JOCHJYFZSA-N | |||
| ⚫ | | pregnancy_AU = | ||
| ⚫ | | pregnancy_US = | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_AU = |
||
| ⚫ | | legal_UK = | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_US = | ||
| ⚫ | | routes_of_administration = | ||
| ⚫ | | excretion = |
||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Ibutamoren''' ({{abbrlink|INN|International Nonproprietary Name}}) (developmental code names '''MK-677''', '''MK-0677''', '''LUM-201''', '''L-163,191'''; former tentative brand name '''Oratrope''') is a ], long-acting, ], ], and ] ] of the ] and a ], mimicking the ] (GH)-stimulating action of the ] ] ].<ref name="AdisInsight">{{Cite web |title=Ibutamoren - Lumos Pharma/Merck |url=http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800007434 |website=AdisInsight |access-date=2017-12-14 |archive-date=2018-09-27 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180927005555/https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800007434 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Patchett AA, Nargund RP, Tata JR, Chen MH, Barakat KJ, Johnston DB, Cheng K, Chan WW, Butler B, Hickey G |date=July 1995 |title=Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677): a potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America |volume=92 |issue=15 |pages=7001–7005 |bibcode=1995PNAS...92.7001P |doi=10.1073/pnas.92.15.7001 |pmc=41459 |pmid=7624358 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Pong SS, Chaung LY, Dean DC, Nargund RP, Patchett AA, Smith RG |date=January 1996 |title=Identification of a new G-protein-linked receptor for growth hormone secretagogues |journal=Molecular Endocrinology |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=57–61 |doi=10.1210/mend.10.1.8838145 |pmid=8838145 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Cassoni P, Papotti M, Ghè C, Catapano F, Sapino A, Graziani A, Deghenghi R, Reissmann T, Ghigo E, Muccioli G |date=April 2001 |title=Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines |journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism |volume=86 |issue=4 |pages=1738–1745 |doi=10.1210/jcem.86.4.7402 |pmid=11297611 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Holst B, Frimurer TM, Mokrosinski J, Halkjaer T, Cullberg KB, Underwood CR, Schwartz TW |date=January 2009 |title=Overlapping binding site for the endogenous agonist, small-molecule agonists, and ago-allosteric modulators on the ghrelin receptor |journal=Molecular Pharmacology |volume=75 |issue=1 |pages=44–59 |doi=10.1124/mol.108.049189 |pmid=18923064 |s2cid=2218638}}</ref> It has been shown to increase the ] of several hormones including GH and ] (IGF-1) and produces sustained increases in the plasma levels of these hormones while also raising ] levels.<ref>{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Nass R, Pezzoli SS, Oliveri MC, Patrie JT, Harrell FE Jr, Clasey JL, Heymsfield SB, Bach MA, Vance ML, Thorner MO |date=November 2008 |title=Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: a randomized trial |journal=Annals of Internal Medicine |volume=149 |issue=9 |pages=601–611 |doi=10.7326/0003-4819-149-9-200811040-00003 |pmc=2757071 |pmid=18981485 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| '''MK-677''' ('''L-163,191''') is a drug which acts as a potent, orally active ] secretagogue,<ref>Patchett AA, Nargund RP, Tata JR, Chen MH, Barakat KJ, Johnston DB, Cheng K, Chan WW, Butler B, Hickey G, et al. Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677): a potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA''. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):7001-5. PMID 7624358</ref><ref>Pong SS, Chaung LY, Dean DC, Nargund RP, Patchett AA, Smith RG. Identification of a new G-protein-linked receptor for growth hormone secretagogues. ''Molecular Endocrinology''. 1996 Jan;10(1):57-61. PMID 8838145</ref> mimicking the GH stimulating action of the endogenous hormone ].<ref>Cassoni P, Papotti M, Ghè C, Catapano F, Sapino A, Graziani A, Deghenghi R, Reissmann T, Ghigo E, Muccioli G. Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 2001 Apr;86(4):1738-45. PMID 11297611</ref><ref>Holst B, Frimurer TM, Mokrosinski J, Halkjaer T, Cullberg KB, Underwood CR, Schwartz TW. Overlapping Binding Site for the Endogenous Agonist, Small Molecule Agonists and Ago-allosteric Modulators on the Ghrelin Receptor. ''Molecular Pharmacology''. 2008 Oct 15. PMID 18923064</ref> It has been demonstrated to increase the release of, and produces sustained increases in plasma levels of several hormones including growth hormone and ], but without affecting ] levels.<ref>Copinschi G, Van Onderbergen A, L'Hermite-Balériaux M, Mendel CM, Caufriez A, Leproult R, Bolognese JA, De Smet M, Thorner MO, Van Cauter E. Effects of a 7-day treatment with a novel, orally active, growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, MK-677, on 24-hour GH profiles, insulin-like growth factor I, and adrenocortical function in normal young men. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 1996 Aug;81(8):2776-82. PMID 8768828</ref> It is currently under development as a potential treatment for reduced levels of these hormones, such as in growth hormone deficient children or elderly adults,<ref>Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, Schilling LM, Cole KY, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Gormley GJ, Thorner MO. Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 1996 Dec;81(12):4249-57. PMID 8954023</ref><ref>Thorner MO, Chapman IM, Gaylinn BD, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML. Growth hormone-releasing hormone and growth hormone-releasing peptide as therapeutic agents to enhance growth hormone secretion in disease and aging. ''Recent Progress in Hormone Research''. 1997;52:215-46. PMID 9238854</ref><ref>Chapman IM, Pescovitz OH, Murphy G, Treep T, Cerchio KA, Krupa D, Gertz B, Polvino WJ, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Thorner MO. Oral administration of growth hormone (GH) releasing peptide-mimetic MK-677 stimulates the GH/insulin-like growth factor-I axis in selected GH-deficient adults. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 1997 Oct;82(10):3455-63. PMID 9329386</ref> and human studies have shown it to increase both muscle mass and bone mineral density,<ref>Murphy MG, Bach MA, Plotkin D, Bolognese J, Ng J, Krupa D, Cerchio K, Gertz BJ. Oral administration of the growth hormone secretagogue MK-677 increases markers of bone turnover in healthy and functionally impaired elderly adults. The MK-677 Study Group. ''Journal of Bone and Mineral Research''. 1999 Jul;14(7):1182-8. PMID 10404019</ref><ref>Murphy MG, Weiss S, McClung M, Schnitzer T, Cerchio K, Connor J, Krupa D, Gertz BJ; MK-677/Alendronate Study Group. Effect of alendronate and MK-677 (a growth hormone secretagogue), individually and in combination, on markers of bone turnover and bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 2001 Mar;86(3):1116-25. PMID 11238495</ref> making it a promising therapy for the treatment of ].<ref>Smith RG, Sun Y, Jiang H, Albarran-Zeckler R, Timchenko N. Ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1A) agonists show potential as interventive agents during aging. ''Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences''. 2007 Nov;1119:147-64. PMID 18056963</ref><ref></ref> It also alters metabolism of body fat and so may have application in the treatment of ].<ref>Svensson J, Lönn L, Jansson JO, Murphy G, Wyss D, Krupa D, Cerchio K, Polvino W, Gertz B, Boseaus I, Sjöström L, Bengtsson BA. Two-month treatment of obese subjects with the oral growth hormone (GH) secretagogue MK-677 increases GH secretion, fat-free mass, and energy expenditure. ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 1998 Feb;83(2):362-9. PMID 9467542</ref><ref>Svensson J, Jansson JO, Ottosson M, Johannsson G, Taskinen MR, Wiklund O, Bengtsson BA. Treatment of obese subjects with the oral growth hormone secretagogue MK-677 affects serum concentrations of several lipoproteins, but not lipoprotein(a). ''Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism''. 1999 Jun;84(6):2028-33. PMID 10372705</ref> | |||
| == Effect on lean mass == | |||
| ⚫ | ==See also== | ||
| Ibutamoren has been shown to sustain activation of the ], increasing growth hormone secretion by up to 97%,<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Chapman |first=I. M. |year=1996 |title=Stimulation of the growth hormone (gh)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by Daily Oral Administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects |journal=Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism |volume=81 |issue=12 |pages=4249–4257 |pmid=8954023 }}</ref> and to increase ] with no change in ] or ]. It is under investigation as a potential treatment for reduced levels of these hormones, such as in children or elderly adults with ],<ref name="AdisInsight" /><ref name="pmid8954023">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, Schilling LM, Cole KY, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Gormley GJ, Thorner MO |date=December 1996 |title=Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects |journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism |volume=81 |issue=12 |pages=4249–4257 |doi=10.1210/jcem.81.12.8954023 |pmid=8954023 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |vauthors=Thorner MO, Chapman IM, Gaylinn BD, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML |year=1997 |title=Growth hormone-releasing hormone and growth hormone-releasing peptide as therapeutic agents to enhance growth hormone secretion in disease and aging |journal=Recent Progress in Hormone Research |volume=52 |pages=215–44; discussion 244–6 |pmid=9238854}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Chapman IM, Pescovitz OH, Murphy G, Treep T, Cerchio KA, Krupa D, Gertz B, Polvino WJ, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Thorner MO |date=October 1997 |title=Oral administration of growth hormone (GH) releasing peptide-mimetic MK-677 stimulates the GH/insulin-like growth factor-I axis in selected GH-deficient adults |journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism |volume=82 |issue=10 |pages=3455–3463 |doi=10.1210/jcem.82.10.4297 |pmid=9329386 |doi-access=free}}</ref> and human studies have shown it to increase both ] and ],<ref>{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Murphy MG, Bach MA, Plotkin D, Bolognese J, Ng J, Krupa D, Cerchio K, Gertz BJ |date=July 1999 |title=Oral administration of the growth hormone secretagogue MK-677 increases markers of bone turnover in healthy and functionally impaired elderly adults. The MK-677 Study Group |journal=Journal of Bone and Mineral Research |volume=14 |issue=7 |pages=1182–1188 |doi=10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1182 |pmid=10404019 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="pmid11238495">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Murphy MG, Weiss S, McClung M, Schnitzer T, Cerchio K, Connor J, Krupa D, Gertz BJ |date=March 2001 |title=Effect of alendronate and MK-677 (a growth hormone secretagogue), individually and in combination, on markers of bone turnover and bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporotic women |journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism |volume=86 |issue=3 |pages=1116–1125 |doi=10.1210/jcem.86.3.7294 |pmid=11238495 |doi-access=free}}</ref> making it a promising potential therapy for the treatment of ].<ref name="pmid18056963">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Smith RG, Sun Y, Jiang H, Albarran-Zeckler R, Timchenko N |date=November 2007 |title=Ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1A) agonists show potential as interventive agents during aging |journal=Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences |volume=1119 |issue=1 |pages=147–164 |bibcode=2007NYASA1119..147S |doi=10.1196/annals.1404.023 |pmid=18056963 |s2cid=3220799}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=5 November 2008 |title=An Anti-frailty Pill For Seniors? New Drug Increases Muscle Mass In Arms And Legs Of Older Adults. |url=https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/11/081104132902.htm |website=ScienceDaily |access-date=28 February 2018 |archive-date=7 November 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171107111853/https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/11/081104132902.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> As of June 2017, ibutamoren is in the ] stage of development for growth hormone deficiency.<ref name="AdisInsight" /> | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Effect on sleep architecture == | |||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| In a small study of 14 subjects, MK-677 dosed at 25mg/day at bedtime was shown to increase ] by 20% and 50% in young and older subjects respectively.<ref name=":4">{{Cite journal |display-authors=6 |vauthors=Copinschi G, Leproult R, Van Onderbergen A, Caufriez A, Cole KY, Schilling LM, Mendel CM, De Lepeleire I, Bolognese JA, Van Cauter E |date=October 1997 |title=Prolonged oral treatment with MK-677, a novel growth hormone secretagogue, improves sleep quality in man |journal=Neuroendocrinology |language=english |volume=66 |issue=4 |pages=278–286 |doi=10.1159/000127249 |pmid=9349662}}</ref> Treatment with MK-677 also resulted in an approximate 50% increase in ] in young subjects.<ref name=":4" /> | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==Growth hormone deficiency== | |||
| {{Neuropeptide agonists and antagonists}} | |||
| In a study of children with ], MK-677 performed better than other growth hormone secretagogues at improving growth hormone levels.<ref>{{Cite journal |vauthors=Bright GM, Thorner MO |date=30 March 2022 |title=A GH Secretagogue Receptor Agonist (LUM-201) Elicits Greater GH Responses than Standard GH Secretagogues in Subjects of a Pediatric GH Deficiency Trial |journal=Hormone Research in Paediatrics |volume=95 |issue=1 |pages=76–81 |doi=10.1159/000524244 |pmc=9227666 |pmid=35354138}}</ref> An ongoing study compares MK-677 directly to injectable hGH in terms of ] in this population.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Phase 2 Study of LUM-201 in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency (OraGrowtH210 Trial) - Full Text View |url=https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04614337 |access-date=4 September 2023 |website=clinicaltrials.gov |language=en |archive-date=4 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230904074031/https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04614337 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| == Non-research use == | |||
| Since MK-677 is still an ], it has not yet been approved to be marketed for consumption by humans in the United States.<ref name="AdisInsight" /> However, it has been used experimentally by some in the bodybuilding community. The use of MK-677 is banned in most sports.<ref>{{Cite web |date=23 May 2022 |title=Ibutamoren (MK 677) not OK - Don't be fooled by marketing! |url=https://www.sportintegrity.gov.au/news/integrity-blog/2022-05/ibutamoren-mk-677-not-ok-dont-be-fooled-marketing |website=Sport Integrity Australia |language=en-AU |department=Integrity Blog |access-date=9 April 2024 |archive-date=9 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240409060603/https://www.sportintegrity.gov.au/news/integrity-blog/2022-05/ibutamoren-mk-677-not-ok-dont-be-fooled-marketing |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | == See also == | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ⚫ | == References == | ||
| ] | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{GH/IGF-1 axis signaling modulators}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:15, 13 December 2024
Experimental drugPharmaceutical compound
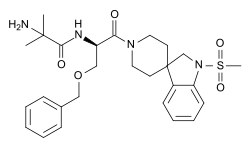 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MK-677; MK-0677; L-163,191; Oratrope |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 4–6 hours (in beagles); IGF-1 levels remain elevated in humans with a single oral dose for up to 24 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.734 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H36N4O5S |
| Molar mass | 528.67 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ibutamoren (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name) (developmental code names MK-677, MK-0677, LUM-201, L-163,191; former tentative brand name Oratrope) is a potent, long-acting, orally-active, selective, and non-peptide agonist of the ghrelin receptor and a growth hormone secretagogue, mimicking the growth hormone (GH)-stimulating action of the endogenous hormone ghrelin. It has been shown to increase the secretion of several hormones including GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and produces sustained increases in the plasma levels of these hormones while also raising cortisol levels.
Effect on lean mass
Ibutamoren has been shown to sustain activation of the GH–IGF-1 axis, increasing growth hormone secretion by up to 97%, and to increase lean body mass with no change in total fat mass or visceral fat. It is under investigation as a potential treatment for reduced levels of these hormones, such as in children or elderly adults with growth hormone deficiency, and human studies have shown it to increase both muscle mass and bone mineral density, making it a promising potential therapy for the treatment of frailty in the elderly. As of June 2017, ibutamoren is in the preclinical stage of development for growth hormone deficiency.
Effect on sleep architecture
In a small study of 14 subjects, MK-677 dosed at 25mg/day at bedtime was shown to increase rapid eye movement sleep by 20% and 50% in young and older subjects respectively. Treatment with MK-677 also resulted in an approximate 50% increase in slow-wave sleep in young subjects.
Growth hormone deficiency
In a study of children with growth hormone deficiency, MK-677 performed better than other growth hormone secretagogues at improving growth hormone levels. An ongoing study compares MK-677 directly to injectable hGH in terms of height velocity in this population.
Non-research use
Since MK-677 is still an Investigational New Drug, it has not yet been approved to be marketed for consumption by humans in the United States. However, it has been used experimentally by some in the bodybuilding community. The use of MK-677 is banned in most sports.
See also
References
- Smith RG, Thorner MO (28 January 2000). Human Growth Hormone: Research and Clinical Practice. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 45–. ISBN 978-1-59259-015-5.
- Smith RG, Van der Ploeg LH, Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cheng K, Hickey GJ, et al. (October 1997). "Peptidomimetic regulation of growth hormone secretion". Endocrine Reviews. 18 (5). The Endocrine Society: 621–645. doi:10.1210/edrv.18.5.0316. PMID 9331545.
- ^ "Ibutamoren - Lumos Pharma/Merck". AdisInsight. Archived from the original on 2018-09-27. Retrieved 2017-12-14.
- Patchett AA, Nargund RP, Tata JR, Chen MH, Barakat KJ, Johnston DB, et al. (July 1995). "Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677): a potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (15): 7001–7005. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.7001P. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.15.7001. PMC 41459. PMID 7624358.
- Pong SS, Chaung LY, Dean DC, Nargund RP, Patchett AA, Smith RG (January 1996). "Identification of a new G-protein-linked receptor for growth hormone secretagogues". Molecular Endocrinology. 10 (1): 57–61. doi:10.1210/mend.10.1.8838145. PMID 8838145.
- Cassoni P, Papotti M, Ghè C, Catapano F, Sapino A, Graziani A, et al. (April 2001). "Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 86 (4): 1738–1745. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.4.7402. PMID 11297611.
- Holst B, Frimurer TM, Mokrosinski J, Halkjaer T, Cullberg KB, Underwood CR, Schwartz TW (January 2009). "Overlapping binding site for the endogenous agonist, small-molecule agonists, and ago-allosteric modulators on the ghrelin receptor". Molecular Pharmacology. 75 (1): 44–59. doi:10.1124/mol.108.049189. PMID 18923064. S2CID 2218638.
- Nass R, Pezzoli SS, Oliveri MC, Patrie JT, Harrell FE Jr, Clasey JL, et al. (November 2008). "Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: a randomized trial". Annals of Internal Medicine. 149 (9): 601–611. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-149-9-200811040-00003. PMC 2757071. PMID 18981485.
- Chapman IM (1996). "Stimulation of the growth hormone (gh)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by Daily Oral Administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 81 (12): 4249–4257. PMID 8954023.
- Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, et al. (December 1996). "Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 81 (12): 4249–4257. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.12.8954023. PMID 8954023.
- Thorner MO, Chapman IM, Gaylinn BD, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML (1997). "Growth hormone-releasing hormone and growth hormone-releasing peptide as therapeutic agents to enhance growth hormone secretion in disease and aging". Recent Progress in Hormone Research. 52: 215–44, discussion 244–6. PMID 9238854.
- Chapman IM, Pescovitz OH, Murphy G, Treep T, Cerchio KA, Krupa D, et al. (October 1997). "Oral administration of growth hormone (GH) releasing peptide-mimetic MK-677 stimulates the GH/insulin-like growth factor-I axis in selected GH-deficient adults". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 82 (10): 3455–3463. doi:10.1210/jcem.82.10.4297. PMID 9329386.
- Murphy MG, Bach MA, Plotkin D, Bolognese J, Ng J, Krupa D, et al. (July 1999). "Oral administration of the growth hormone secretagogue MK-677 increases markers of bone turnover in healthy and functionally impaired elderly adults. The MK-677 Study Group". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 14 (7): 1182–1188. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1182. PMID 10404019.
- Murphy MG, Weiss S, McClung M, Schnitzer T, Cerchio K, Connor J, et al. (March 2001). "Effect of alendronate and MK-677 (a growth hormone secretagogue), individually and in combination, on markers of bone turnover and bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporotic women". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 86 (3): 1116–1125. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.3.7294. PMID 11238495.
- Smith RG, Sun Y, Jiang H, Albarran-Zeckler R, Timchenko N (November 2007). "Ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1A) agonists show potential as interventive agents during aging". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1119 (1): 147–164. Bibcode:2007NYASA1119..147S. doi:10.1196/annals.1404.023. PMID 18056963. S2CID 3220799.
- "An Anti-frailty Pill For Seniors? New Drug Increases Muscle Mass In Arms And Legs Of Older Adults". ScienceDaily. 5 November 2008. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- ^ Copinschi G, Leproult R, Van Onderbergen A, Caufriez A, Cole KY, Schilling LM, et al. (October 1997). "Prolonged oral treatment with MK-677, a novel growth hormone secretagogue, improves sleep quality in man". Neuroendocrinology. 66 (4): 278–286. doi:10.1159/000127249. PMID 9349662.
- Bright GM, Thorner MO (30 March 2022). "A GH Secretagogue Receptor Agonist (LUM-201) Elicits Greater GH Responses than Standard GH Secretagogues in Subjects of a Pediatric GH Deficiency Trial". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 95 (1): 76–81. doi:10.1159/000524244. PMC 9227666. PMID 35354138.
- "Phase 2 Study of LUM-201 in Children With Growth Hormone Deficiency (OraGrowtH210 Trial) - Full Text View". clinicaltrials.gov. Archived from the original on 4 September 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- "Ibutamoren (MK 677) not OK - Don't be fooled by marketing!". Integrity Blog. Sport Integrity Australia. 23 May 2022. Archived from the original on 9 April 2024. Retrieved 9 April 2024.
External links
- Ibutamoren - AdisInsight
- MK-677 and A Potential Dementia Link - Loungecity.org
- Ghrelin Over-Stimulation, Molecular Psychiatry Study - Nature.org