| Revision as of 15:11, 8 August 2011 editBeetstra (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators172,071 edits now duplicate← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 21:03, 16 April 2024 edit undoCoolieCoolster (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users49,705 editsm Fixed typo (via WP:JWB) | ||
| (64 intermediate revisions by 46 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Distinguish|text = the psychoactive chemical ], which is also commonly abbreviated as DMT}} | |||
| {{Chembox | {{Chembox | ||
| |Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 415324112 | |||
| |verifiedrevid = 447275147 | |||
| | ImageFile = Dimethylterephthalat.svg | |||
| |ImageFile = Dimethylterephthalat.svg | |||
| | ImageName = Structural formula of dimethyl terephthalate | |||
| | |
|ImageName = Structural formula of dimethyl terephthalate | ||
| | |
|PIN = Dimethyl benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate | ||
| |OtherNames = Dimethyl terephthalate<br />1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester<br />Dimethyl 4-phthalate<br />Dimethyl ''p''-phthalate<br />Di-Me terephthalate<br />Methyl 4-carbomethoxybenzoate<br />Methyl-p-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoate<br />Methyl terephthalate, di-<br />Terephthalic acid dimethyl ester (2:1) | |||
| | OtherNames = 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester<br /> | |||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| Dimethyl 4-phthalate<br /> | |||
| |Abbreviations = DMT | |||
| Dimethyl-p-phthalate<br /> | |||
| |CASNo = 120-61-6 | |||
| Di-Me terephthalate<br /> | |||
| |CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| Methyl 4-carbomethoxybenzoate<br /> | |||
| |UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| Methyl-p-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoate<br /> | |||
| |UNII = IKZ2470UNV | |||
| Methyl terephthalate<br /> | |||
| |PubChem = 8441 | |||
| Terephthalic acid methyl ester<br /> | |||
| |PubChem1 = 12241382 | |||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| |PubChem1_Comment = (<sup>2</sup>''H''<sub>4</sub>) | |||
| | Abbreviations = DMT | |||
| | |
|ChEBI = 156286 | ||
| |ChemSpiderID = 13863300 | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{Cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| |ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | PubChem = 8441 | |||
| |EINECS = 204-411-8 | |||
| | PubChem_Ref = {{Pubchemcite|correct|PubChem}} | |||
| |MeSHName = Dimethyl+4-phthalate | |||
| | PubChem1 = 12241382 | |||
| |RTECS = WZ1225000 | |||
| | PubChem1_Comment = (<sup>2</sup>''H''<sub>4</sub>) | |||
| | |
|StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| |StdInChI = 1S/C10H10O4/c1-13-9(11)7-3-5-8(6-4-7)10(12)14-2/h3-6H,1-2H3 | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 13863300 | |||
| | |
|StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| |StdInChIKey = WOZVHXUHUFLZGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| | EINECS = 204-411-8 | |||
| |SMILES = COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)OC | |||
| | MeSHName = Dimethyl+4-phthalate | |||
| |SMILES1 = O=C(OC)c1ccc(cc1)C(=O)OC | |||
| | RTECS = WZ1225000 | |||
| | |
|InChI = 1/C10H10O4/c1-13-9(11)7-3-5-8(6-4-7)10(12)14-2/h3-6H,1-2H3 | ||
| | |
|InChIKey = WOZVHXUHUFLZGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| |Beilstein = 1107185}} | |||
| | SMILES = COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)OC | |||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |||
| | SMILES1 = O=C(OC)c1ccc(cc1)C(=O)OC | |||
| |C=10 | H=10 | O=4 | |||
| | InChI = 1/C10H10O4/c1-13-9(11)7-3-5-8(6-4-7)10(12)14-2/h3-6H,1-2H3 | |||
| |Appearance = white solid | |||
| | InChIKey = WOZVHXUHUFLZGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| |Density = 1.2 g/cm<sup>3</sup>, ?<!-- 1.2 g/cm<sup>3</sup>, solid / ? g/mL, liquid / ? g/L, gas --> | |||
| | Beilstein = 1107185}} | |||
| |MeltingPtC = 142 | |||
| | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| | |
|BoilingPtC = 288 | ||
| | |
|pKa = -7.21 | ||
| | |
|pKb = -6.60}} | ||
| | ExactMass = 198.083015792 g mol<sup>-1</sup> | |||
| | Appearance = white solid | |||
| | Density = 1.2 g/cm³, ?<!-- 1.2 g/cm³, solid / ? g/ml, liquid / ? g/l, gas --> | |||
| | MeltingPtC = 142 | |||
| | BoilingPtC = 288 | |||
| | pKa = -7.21 | |||
| | pKb = -6.60}} | |||
| | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | ExternalMSDS = | |||
| | MainHazards = | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Dimethyl terephthalate''' (DMT) is an ] with the formula C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>( |
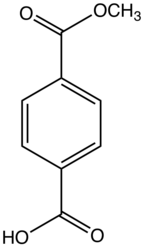
'''Dimethyl terephthalate''' ('''DMT''') is an ] with the formula C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(COOCH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>. It is the ] formed from ] and ]. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.<ref name=Ullmann>Richard J. Sheehan "Terephthalic Acid, Dimethyl Terephthalate, and Isophthalic Acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.{{doi|10.1002/14356007.a26_193}}</ref> | ||
| ==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| DMT has been produced in a number of ways. |
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally, and still of commercial value, is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-] steps from ] via ] (PT).<ref name=Ullmann/> | ||
| ===Dimethyl terephthalate by the Witten process=== | |||
| ==Use== | |||
| The method for the production of DMT from ''p''-xylene (PX) and methanol consists of a multistep process involving both oxidation and esterification. A mixture of p-xylene (PX) and methyl ''p''-toluate is oxidized with air in the presence of cobalt and manganese catalysts. The acid mixture resulting from the oxidation is esterified with methanol to produce a mixture of esters. The crude ester mixture is then distilled to remove all the heavy boilers and residue that are produced; lighter esters such as monomethyl terephthalate are recycled to the oxidation section. The raw DMT is then sent to the crystallization section to remove DMT isomers, residual acids and aromatic aldehydes.<ref>{{Cite web|url = http://www.gtctech.com/technology-licensing/polyester-technologies/dimethyl-terephthalate-technology/|title = Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)|date = 2013-05-02|access-date = 2015-03-05|archive-date = 2017-10-07|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20171007020846/http://www.gtctech.com/technology-licensing/polyester-technologies/dimethyl-terephthalate-technology/|url-status = dead}}</ref> | |||
| DMT is used in the production of ]s, including ] (PET) and ]. It consists of ] substituted with carboxymethyl groups (CO<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub>) at the 1 and 4 positions. Because DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate is some schemes for the recyclic of PET, e.g. from ]s. | |||
| ] | |||
| Oxidation of methyl p-toluate followed by esterification also yields dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) as shown in the below reaction:<ref name=Ullmann/> | |||
| :] | |||
| ===Dimethyl terephthalate by direct esterification=== | |||
| DMT can also be made by a different route, namely direct esterification of terephthalic acid with methanol. The dimethyl terephthalate that is formed is then purified by distillation. Even terephthalic acid of low purity may be used in this method. | |||
| :C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O<sub>4</sub> + 2CH<sub>3</sub>OH → C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>4</sub> + 2 H<sub>2</sub>O | |||
| in the presence of o-xylene at 250–300 °C. | |||
| ==Uses== | |||
| DMT is used in the production of ]s, including ] (PET), ] (PTT), and ] (PBT). Structurally, DMT consists of a ] ring substituted at the 1 and 4 positions with methyl carboxylate (-CO<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub>) groups. Because DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate in some schemes for the recycling of PET, e.g. from ]s. | |||
| Hydrogenation of DMT affords the diol ], which is a useful monomer. | Hydrogenation of DMT affords the diol ], which is a useful monomer. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * Supplier:Teijin Limited https://web.archive.org/web/20150503041344/http://www.teijin.com/products/chemicals/dmt/ | |||
| * http://www.inchem.org/documents/icsc/icsc/eics0262.htm | * http://www.inchem.org/documents/icsc/icsc/eics0262.htm | ||
| * {{ICSC|0262|02}} | * {{ICSC|0262|02}} | ||
| * | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Dimethyl Terephthalate}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{ester-stub}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:03, 16 April 2024
Not to be confused with the psychoactive chemical N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, which is also commonly abbreviated as DMT. | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Dimethyl benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate | |
| Other names
Dimethyl terephthalate 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester Dimethyl 4-phthalate Dimethyl p-phthalate Di-Me terephthalate Methyl 4-carbomethoxybenzoate Methyl-p-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoate Methyl terephthalate, di- Terephthalic acid dimethyl ester (2:1) | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | DMT |
| Beilstein Reference | 1107185 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.011 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Dimethyl+4-phthalate |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H10O4 |
| Molar mass | 194.186 g·mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm, ? |
| Melting point | 142 °C (288 °F; 415 K) |
| Boiling point | 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | -7.21 |
| Basicity (pKb) | -6.60 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COOCH3)2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.
Production
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally, and still of commercial value, is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-esterification steps from p-xylene via methyl p-toluate (PT).
Dimethyl terephthalate by the Witten process
The method for the production of DMT from p-xylene (PX) and methanol consists of a multistep process involving both oxidation and esterification. A mixture of p-xylene (PX) and methyl p-toluate is oxidized with air in the presence of cobalt and manganese catalysts. The acid mixture resulting from the oxidation is esterified with methanol to produce a mixture of esters. The crude ester mixture is then distilled to remove all the heavy boilers and residue that are produced; lighter esters such as monomethyl terephthalate are recycled to the oxidation section. The raw DMT is then sent to the crystallization section to remove DMT isomers, residual acids and aromatic aldehydes.
Oxidation of methyl p-toluate followed by esterification also yields dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) as shown in the below reaction:
Dimethyl terephthalate by direct esterification
DMT can also be made by a different route, namely direct esterification of terephthalic acid with methanol. The dimethyl terephthalate that is formed is then purified by distillation. Even terephthalic acid of low purity may be used in this method.
- C8H6O4 + 2CH3OH → C10H10O4 + 2 H2O
in the presence of o-xylene at 250–300 °C.
Uses
DMT is used in the production of polyesters, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT), and polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). Structurally, DMT consists of a benzene ring substituted at the 1 and 4 positions with methyl carboxylate (-CO2CH3) groups. Because DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate in some schemes for the recycling of PET, e.g. from plastic bottles.
Hydrogenation of DMT affords the diol cyclohexanedimethanol, which is a useful monomer.
References
- ^ Richard J. Sheehan "Terephthalic Acid, Dimethyl Terephthalate, and Isophthalic Acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_193
- "Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)". 2013-05-02. Archived from the original on 2017-10-07. Retrieved 2015-03-05.
External links
- Supplier:Teijin Limited https://web.archive.org/web/20150503041344/http://www.teijin.com/products/chemicals/dmt/
- http://www.inchem.org/documents/icsc/icsc/eics0262.htm
- International Chemical Safety Card 0262
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Hazardous Substances Databank – Dimethyl+terephthalate
