| Revision as of 15:31, 10 August 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per [[Misplaced Pages:WikiProject Chemicals/Chembox validation|Chem/← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:39, 26 December 2024 edit undoAnomieBOT (talk | contribs)Bots6,591,021 editsm Dating maintenance tags: {{Unreferenced section}} {{Cn}} | ||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 30 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Chemical compound}} | |||
| {{drugbox | |||
| {{More citations needed|date=October 2013}} | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 444075322 | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=December 2024}} | |||
| | IUPAC_name = 1--4--5--1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile | |||
| {{cs1 config |name-list-style=vanc |display-authors=6}} | |||
| | image = Pyriprole.png | |||
| {{Infobox drug | |||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 444077120 | |||
| | image = Pyriprole.svg | |||
| | width = 220 | | width = 220 | ||
| | alt = | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite}} | |||
| | image2 = Pyriprole 3D ball.png | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | alt2 = Ball-and-stick model of the pyriprole molecule | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = | |||
| | InChI = | |||
| <!-- Clinical data --> | |||
| | InChIKey = | |||
| | pronounce = | |||
| | tradename = Prac-tic | |||
| | Drugs.com = | |||
| | MedlinePlus = | |||
| | DailyMedID = <!-- DailyMed may use generic or brand name (generic name preferred) --> | |||
| | pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | |||
| | pregnancy_AU_comment = | |||
| | pregnancy_category = | |||
| | routes_of_administration = ] | |||
| | class = ] | |||
| | ATCvet = yes | |||
| | ATC_prefix = P53 | |||
| | ATC_suffix = AX26 | |||
| | ATC_supplemental = | |||
| <!-- Legal status --> | |||
| | legal_AU = <!-- S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9 or Unscheduled --> | |||
| | legal_AU_comment = | |||
| | legal_BR = <!-- OTC, A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, C1, C2, C3, C5, D1, D2, E, F1, F2, F3, F4 --> | |||
| | legal_BR_comment = | |||
| | legal_CA = <!-- OTC, Rx-only, Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| | legal_CA_comment = | |||
| | legal_DE = <!-- Anlage I, II, III or Unscheduled --> | |||
| | legal_DE_comment = | |||
| | legal_NZ = <!-- Class A, B, C --> | |||
| | legal_NZ_comment = | |||
| | legal_UK = <!-- GSL, P, POM, CD, CD Lic, CD POM, CD No Reg POM, CD (Benz) POM, CD (Anab) POM or CD Inv POM / Class A, B, C --> | |||
| | legal_UK_comment = | |||
| | legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V --> | |||
| | legal_US_comment = | |||
| | legal_EU = | |||
| | legal_EU_comment = <ref>{{cite web | title=Prac-tic EPAR | website=European Medicines Agency (EMA) | date=18 December 2006 | url=https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/veterinary/EPAR/prac-tic | access-date=26 December 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | title=Prac-tic PI | website=Union Register of medicinal products | date=20 December 2006 | url=https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/v066.htm | access-date=26 December 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | legal_UN = <!-- N I, II, III, IV / P I, II, III, IV --> | |||
| | legal_UN_comment = | |||
| | legal_status = <!-- For countries not listed above --> | |||
| <!--Identifiers--> | |||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| | CAS_number = 394730-71-3 | | CAS_number = 394730-71-3 | ||
| | |
| PubChem = 12056859 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| | ATC_suffix = | |||
| | DrugBank = | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 11677344 | |||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| | UNII = 69OX73ZVJN | | UNII = 69OX73ZVJN | ||
| | |
| KEGG = C18580 | ||
| | ChEBI = 81845 | |||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| | DrugBank = | |||
| | C=18|H=10|Cl=2|F=5|N=5|S=1 | |||
| | molecular_weight = 494.268 | |||
| | melting_point = | |||
| | smiles = Clc2cc(C(F)(F)F)cc(Cl)c2-n(nc(C#N)c1SC(F)F)c1NCc3ncccc3 | |||
| | bioavailability = | |||
| | metabolism = | |||
| | elimination_half-life = | |||
| | excretion = | |||
| | pregnancy_category = | |||
| | legal_status = | |||
| | routes_of_administration = | |||
| <!--Chemical data--> | |||
| | IUPAC_name = 1--4--5--1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile | |||
| | C=18 | H=10 | Cl=2 | F=5 | N=5 | S=1 | |||
| | smiles = Clc2cc(C(F)(F)F)cc(Cl)c2-n(nc(C#N)c1SC(F)F)c1NCc3ncccc3 | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI=1S/C18H10Cl2F5N5S/c19-11-5-9(18(23,24)25)6-12(20)14(11)30-16(28-8-10-3-1-2-4-27-10)15(31-17(21)22)13(7-26)29-30/h1-6,17,28H,8H2 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChIKey = MWMQNVGAHVXSPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| | melting_point = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Pyriprole''', sold under the brand name '''Prac-tic''', is a veterinary medication used for dogs against external parasites such as ]s and ]s.<ref name = "Page_2008">{{cite book | vauthors = Page SW | chapter = Antiparasitic Drugs | veditors = Maddison JE, Page SW, Church DB |title=Small Animal Clinical Pharmacology |date=2008 |publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences |location= |isbn=978-0-7020-2858-8 | pages = 198–260 (229) |edition=Second |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RpsROVqemk8C&dq=Pyriprole&pg=PA229 | doi = 10.1016/B978-070202858-8.50012-9 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Londershausen M, Hansen O | chapter = Ectoparasiticides – Antagonists and Modulators of Chloride Channels |veditors = Mehlhorn H |title=Encyclopedia of Parasitology |date=2008 |publisher=Springer Rechtswissenschaft |location=Berlin |isbn=978-3-540-48994-8 |page=431 |edition=3rd | chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Jpg1ysgVn-AC&dq=Pyriprole&pg=PA431}}</ref> | |||
| '''Pyriprole''' is an ] used for topical treatment of fleas and ticks on domestic animals.<ref> | |||
| Schuele G, Barnett S, Bapst B, Cavaliero T, Luempert L, Strehlau G, Young DR, Moran C, Junquera P. The effect of water and shampooing on the efficacy of a pyriprole 12.5% topical solution against brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) and cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) infestations on dogs. ''Veterinary Parasitology''. 2008 Feb 14;151(2-4):300-11. PMID 18061355</ref><ref>Bouhsira E, Fysikopoulos A, Franc M. Efficacy of fipronil-(S)-methoprene, ] combined with amitraz, and pyriprole commercial spot-on products in preventing Culex pipiens pipiens from feeding on dogs. ''Veterinary Record''. 2009 Aug 1;165(5):135-7. PMID 19648637</ref> | |||
| Pyriprole is a ]] derivative similar to ].{{cn|date=December 2024}} Although introduced (in the 2000s) and under patent protection it is a "classic" insecticide.{{cn|date=December 2024}}{{clarify|date=October 2013}} It is only approved in the EU and a few other countries for use on dogs.{{cn|date=December 2024}} It is not approved for use on cats or livestock.{{cn|date=December 2024}} It has not been introduced as an agricultural or hygiene pesticide.{{cn|date=December 2024}} | |||
| Pyriprole applied as a spot-on is highly effective against fleas and several ticks species.{{cn|date=December 2024}} Efficacy against fleas is comparable to that of other modern insecticidal active ingredients such as fipronil, ] or ].{{cn|date=December 2024}} As most flea spot-ons it controls existing flea and tick infestations in about 1 to 2 days, and provides about 4 weeks protection against re-infestations.{{cn|date=December 2024}} | |||
| ==Mechanism of action== | |||
| {{unreferenced section|date=December 2024}} | |||
| Pyriprole is an insecticide and ]. It inhibits ] (GABA)-gated chloride channels (]s) resulting in uncontrolled hyperactivity of the central nervous system of fleas and ticks. | |||
| Parasites are killed through contact rather than by systemic exposure. Following topical administration pyriprole is rapidly distributed in the hair coat of dogs within one day after application. It can be found in the hair coat throughout the treatment interval. Insecticidal efficacy duration against new infestations with fleas persists for a minimum of four weeks. The substance can be used as part of a treatment strategy for the control of ] (FAD). | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| Line 39: | Line 90: | ||
| {{Insecticides}} | {{Insecticides}} | ||
| {{Portal bar | Medicine}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:39, 26 December 2024
Chemical compound| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Pyriprole" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Pharmaceutical compound
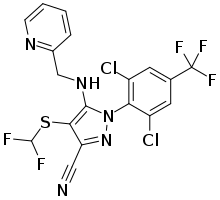 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Prac-tic |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| Drug class | Ectoparasiticide |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H10Cl2F5N5S |
| Molar mass | 494.27 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Pyriprole, sold under the brand name Prac-tic, is a veterinary medication used for dogs against external parasites such as fleas and ticks.
Pyriprole is a phenylpyrazole derivative similar to fipronil. Although introduced (in the 2000s) and under patent protection it is a "classic" insecticide. It is only approved in the EU and a few other countries for use on dogs. It is not approved for use on cats or livestock. It has not been introduced as an agricultural or hygiene pesticide.
Pyriprole applied as a spot-on is highly effective against fleas and several ticks species. Efficacy against fleas is comparable to that of other modern insecticidal active ingredients such as fipronil, imidacloprid or spinosad. As most flea spot-ons it controls existing flea and tick infestations in about 1 to 2 days, and provides about 4 weeks protection against re-infestations.
Mechanism of action
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Pyriprole is an insecticide and acaricide. It inhibits γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-gated chloride channels (GABAA receptors) resulting in uncontrolled hyperactivity of the central nervous system of fleas and ticks.
Parasites are killed through contact rather than by systemic exposure. Following topical administration pyriprole is rapidly distributed in the hair coat of dogs within one day after application. It can be found in the hair coat throughout the treatment interval. Insecticidal efficacy duration against new infestations with fleas persists for a minimum of four weeks. The substance can be used as part of a treatment strategy for the control of flea allergy dermatitis (FAD).
References
- "Prac-tic EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 18 December 2006. Retrieved 26 December 2024.
- "Prac-tic PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 20 December 2006. Retrieved 26 December 2024.
- Page SW (2008). "Antiparasitic Drugs". In Maddison JE, Page SW, Church DB (eds.). Small Animal Clinical Pharmacology (Second ed.). : Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 198–260 (229). doi:10.1016/B978-070202858-8.50012-9. ISBN 978-0-7020-2858-8.
- Londershausen M, Hansen O (2008). "Ectoparasiticides – Antagonists and Modulators of Chloride Channels". In Mehlhorn H (ed.). Encyclopedia of Parasitology (3rd ed.). Berlin: Springer Rechtswissenschaft. p. 431. ISBN 978-3-540-48994-8.