| Revision as of 07:43, 30 August 2011 editBogBot (talk | contribs)Bots53,132 edits populated new fields in {{drugbox}} and reordered per bot approval. Report errors and suggestions to User_talk:BogBot← Previous edit |
Latest revision as of 18:49, 12 January 2023 edit undoQuercus solaris (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users17,651 edits a trade name for the infobox (redirect from Tolinase) |
| (35 intermediate revisions by 23 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
|
|
{{short description|Chemical compound}} |
|
{{Drugbox |
|
{{Drugbox |
|
| verifiedrevid = 408966679 |
|
| verifiedrevid = 408966679 |
|
| IUPAC_name = ''N''--4-methylbenzenesulfonamide |
|
| IUPAC_name = ''N''--4-methylbenzenesulfonamide |
|
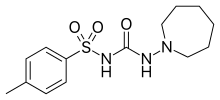
| image = Tolazamide.svg |
|
| image = Tolazamide.svg |
|
|
| image2 = Tolazamide ball-and-stick.png |
|
|
|
|
<!--Clinical data--> |
|
<!--Clinical data--> |
|
| tradename = |
|
| tradename = Tolinase |
|
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|tolazamide}} |
|
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|tolazamide}} |
|
| MedlinePlus = a682482 |
|
| MedlinePlus = a682482 |
| Line 13: |
Line 14: |
|
| legal_US = Rx-only |
|
| legal_US = Rx-only |
|
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
|
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
|
|
|
|
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|
| bioavailability = ? |
|
| bioavailability = ? |
|
| metabolism = ? |
|
| metabolism = metabolized in the liver to active metabolites |
|
| elimination_half-life = 7 hours |
|
| elimination_half-life = 7 hours |
|
| excretion = ] (85%) and fecal (7%) |
|
| excretion = ] (85%) and fecal (7%) |
|
|
|
|
<!--Identifiers--> |
|
<!--Identifiers--> |
|
|
| IUPHAR_ligand = 6847 |
|
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} |
|
|
| CAS_number = 1156-19-0 |
|
| CAS_number = 1156-19-0 |
|
| ATC_prefix = A10 |
|
| ATC_prefix = A10 |
|
| ATC_suffix = BB05 |
|
| ATC_suffix = BB05 |
|
| PubChem = 5503 |
|
| PubChem = 5503 |
|
|
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
|
| DrugBank = APRD01267 |
|
| DrugBank = DB00839 |
|
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|
| ChemSpiderID = 5302 |
|
| ChemSpiderID = 5302 |
| Line 33: |
Line 33: |
|
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
|
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
|
| KEGG = D00379 |
|
| KEGG = D00379 |
|
|
| ChEBI = 9613 |
|
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|
| ChEMBL = 817 |
|
| ChEMBL = 817 |
|
|
|
|
<!--Chemical data--> |
|
<!--Chemical data--> |
|
| C=14 | H=21 | N=3 | O=3 | S=1 |
|
| C=14 | H=21 | N=3 | O=3 | S=1 |
|
⚫ |
| SMILES = O=S(=O)(c1ccc(cc1)C)NC(=O)NN2CCCCCC2 |
|
| molecular_weight = 311.401 ]/] |
|
| ⚫ |
| smiles = O=S(=O)(c1ccc(cc1)C)NC(=O)NN2CCCCCC2 |
|
|
| InChI = 1/C14H21N3O3S/c1-12-6-8-13(9-7-12)21(19,20)16-14(18)15-17-10-4-2-3-5-11-17/h6-9H,2-5,10-11H2,1H3,(H2,15,16,18) |
|
|
| InChIKey = OUDSBRTVNLOZBN-UHFFFAOYAL |
|
|
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|
| StdInChI = 1S/C14H21N3O3S/c1-12-6-8-13(9-7-12)21(19,20)16-14(18)15-17-10-4-2-3-5-11-17/h6-9H,2-5,10-11H2,1H3,(H2,15,16,18) |
|
| StdInChI = 1S/C14H21N3O3S/c1-12-6-8-13(9-7-12)21(19,20)16-14(18)15-17-10-4-2-3-5-11-17/h6-9H,2-5,10-11H2,1H3,(H2,15,16,18) |
| Line 51: |
Line 48: |
|
|
|
|
|
==Synthesis== |
|
==Synthesis== |
|
|
] |
| ⚫ |
] is converted to its ] with ] in the presence of a base. Heating that intermediate with ] leads to the displacement of the ethoxy group and the formation of tolazemide:<ref>{{cite journal | author = Wright, J. B.; Willette, R. E. | journal = J. Med. Chem. | year = 1962 | volume = 5 | pages = 815–822 | doi = 10.1021/jm01239a016 | issue = 4}}</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
⚫ |
] is converted to its ] with ] in the presence of a base. Heating that intermediate with 1-amino-] leads to the displacement of the ethoxy group and the formation of tolazemide:<ref name = "Wright_1962" /> |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Azepane proper would lead to . |
| ⚫ |
==References== |
|
|
|
|
|
⚫ |
== References == |
|
{{reflist}} |
|
{{reflist}} |
|
|
|
|
|
==External links== |
|
== External links == |
|
* |
|
* {{cite web | title = Tolazamide | url = https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682482.html | work = Medline Plus | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine }} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
{{Oral hypoglycemics}} |
|
|
{{Ion channel modulators}} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
{{Oral_hypoglycemics}} |
|
|
|
|
| ⚫ |
] |
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
⚫ |
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
{{gastrointestinal-drug-stub}} |
|
{{gastrointestinal-drug-stub}} |
|
|
|
|
] |
|
|
] |
|
Azepane proper would lead to .