| Revision as of 16:16, 24 October 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 13:28, 29 May 2024 edit undoSmokefoot (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers75,037 edits rm "recently" | ||
| (109 intermediate revisions by 56 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Chemical compound}} | |||
| {{Drugbox | {{Drugbox | ||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 462252883 | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| | IUPAC_name = 1,4-dihydroxy-5,8-bis-anthracene-9,10-dione | | IUPAC_name = 1,4-dihydroxy-5,8-bis-anthracene-9,10-dione | ||
| | image = Mitoxantrone skeletal.svg | | image = Mitoxantrone skeletal.svg | ||
| | image2 = Mitoxantrone ball-and-stick.png | |||
| <!--Clinical data--> | <!--Clinical data--> | ||
| | tradename = Novantrone | | tradename = Novantrone | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| | pregnancy_US = D | | pregnancy_US = D | ||
| | legal_status = Rx-only | | legal_status = Rx-only | ||
| | routes_of_administration = |
| routes_of_administration = Mainly ] | ||
| <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| | bioavailability = n/a | | bioavailability = n/a | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
| | elimination_half-life = 75 hours | | elimination_half-life = 75 hours | ||
| | excretion = ] | | excretion = ] | ||
| <!--Identifiers--> | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| | IUPHAR_ligand = 7242 | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| | CAS_number = 65271-80-9 | | CAS_number = 65271-80-9 | ||
| Line 28: | Line 26: | ||
| | PubChem = 4212 | | PubChem = 4212 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| | DrugBank = |
| DrugBank = DB01204 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 4067 | | ChemSpiderID = 4067 | ||
| Line 35: | Line 33: | ||
| | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| | KEGG = D08224 | | KEGG = D08224 | ||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite| |
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEBI = 50729 | | ChEBI = 50729 | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEMBL = 58 | | ChEMBL = 58 | ||
| | PDB_ligand = MIX | |||
| <!--Chemical data--> | <!--Chemical data--> | ||
| | C=22 | H=28 | N=4 | O=6 |
| C=22 | H=28 | N=4 | O=6 | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = O=C2c1c(c(NCCNCCO)ccc1NCCNCCO)C(=O)c3c2c(O)ccc3O | ||
| | molecular_weight = 444.481 ]/] | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | InChI = 1/C22H28N4O6/c27-11-9-23-5-7-25-13-1-2-14(26-8-6-24-10-12-28)18-17(13)21(31)19-15(29)3-4-16(30)20(19)22(18)32/h1-4,23-30H,5-12H2 | |||
| | InChIKey = KKZJGLLVHKMTCM-UHFFFAOYAS | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C22H28N4O6/c27-11-9-23-5-7-25-13-1-2-14(26-8-6-24-10-12-28)18-17(13)21(31)19-15(29)3-4-16(30)20(19)22(18)32/h1-4,23-30H,5-12H2 | | StdInChI = 1S/C22H28N4O6/c27-11-9-23-5-7-25-13-1-2-14(26-8-6-24-10-12-28)18-17(13)21(31)19-15(29)3-4-16(30)20(19)22(18)32/h1-4,23-30H,5-12H2 | ||
| Line 51: | Line 46: | ||
| | StdInChIKey = KKZJGLLVHKMTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | StdInChIKey = KKZJGLLVHKMTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Mitoxantrone''' |
'''Mitoxantrone''' (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as '''Mitozantrone''' in Australia; trade name '''Novantrone''') is an ] ] agent. | ||
| ==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly ]. It improves the survival rate of children suffering from ] relapse.<ref name="Parker">{{cite journal | vauthors = Parker C, Waters R, Leighton C, Hancock J, Sutton R, Moorman AV, Ancliff P, Morgan M, Masurekar A, Goulden N, Green N, Révész T, Darbyshire P, Love S, Saha V | display-authors = 6 | title = Effect of mitoxantrone on outcome of children with first relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL R3): an open-label randomised trial | journal = Lancet | volume = 376 | issue = 9757 | pages = 2009–2017 | date = December 2010 | pmid = 21131038 | pmc = 3010035 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62002-8 }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | The combination of mitoxantrone and ] is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory ]. This combination |
||
| ⚫ | The combination of mitoxantrone and ] is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory ]. This combination was once the first line of treatment; however, a combination of ] and prednisone improves survival rates and lengthens the disease-free period.<ref>{{cite book |chapter=Cancer Chemotherapy | vauthors = Katzung BG |title=Basic and clinical pharmacology |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division |location=New York |year=2006 |isbn=0-07-145153-6 |edition=10th |oclc=157011367}}</ref> | ||
| Mitoxantrone is also used to treat ] (MS), most notably the subset known as secondary |
Mitoxantrone is also used to treat ] (MS), most notably the ] known as secondary-progressive MS. In the absence of a cure, mitoxantrone is effective in slowing the progression of secondary-progressive MS and extending the time between relapses in both relapsing-remitting MS and progressive-relapsing MS.<ref name="Fox">{{cite journal | vauthors = Fox EJ | title = Management of worsening multiple sclerosis with mitoxantrone: a review | journal = Clinical Therapeutics | volume = 28 | issue = 4 | pages = 461–474 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16750460 | doi = 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.04.013 }}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | ==Mechanism of action== | ||
| Mitoxantrone is a ] ]; it disrupts ] and ] in both healthy cells and cancer cells. | |||
| It also engages in ].<ref name="pmid">{{cite journal |author=Mazerski J, Martelli S, Borowski E |title=The geometry of intercalation complex of antitumor mitoxantrone and ametantrone with DNA: molecular dynamics simulations |journal=Acta Biochim. Pol. |volume=45 |issue=1 |pages=1–11 |year=1998 |pmid= 9701490|doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| ==Side effects== | ==Side effects== | ||
| Mitoxantrone, as with other drugs in its class, may cause ] of varying severity, including ], ], ], heart damage and ], possibly with delayed onset. ] is a particularly concerning effect as it is irreversible; thus regular monitoring with ]s or ]s is recommended for patients. | |||
| Because of the risk of cardiomyopathy, mitoxantrone carries a limit on the cumulative lifetime dose (based on body surface area) in MS patients.<ref name="FDA Postmarket Drug Safety">{{cite web|title=Mitoxantrone Hydrochloride (marketed as Novantrone and generics) – Healthcare Professional Sheet text version|url=https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm126445.htm|publisher=U.S. Food and Drug Administration|access-date=19 September 2014|ref=fdapostmarket}}</ref> | |||
| The medication carries a total lifetime dose based on body surface area.<ref name="Fox"/> | |||
| ⚫ | ==Mechanism of action== | ||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
| Mitoxantrone is a ] ]; it disrupts ] and ] in both healthy cells and cancer cells by ]<ref name="pmid">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mazerski J, Martelli S, Borowski E | title = The geometry of intercalation complex of antitumor mitoxantrone and ametantrone with DNA: molecular dynamics simulations | journal = Acta Biochimica Polonica | volume = 45 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–11 | year = 1998 | pmid = 9701490 | doi = 10.18388/abp.1998_4280 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kapuscinski J, Darzynkiewicz Z | title = Interactions of antitumor agents Ametantrone and Mitoxantrone (Novatrone) with double-stranded DNA | journal = Biochemical Pharmacology | volume = 34 | issue = 24 | pages = 4203–4213 | date = December 1985 | pmid = 4074383 | doi = 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90275-8 }}</ref> between DNA bases. It is also classified as an antibiotic.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://livertox.nlm.nih.gov/Mitoxantrone.htm | title=Mitoxantrone}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Cite journal|doi=10.1021/jm00195a002|title=Antitumor agents. 1. 1,4-Bis-9,10-anthracenediones|pmid=490545|year=1979|last1=Murdock|first1=K. C.|last2=Child|first2=R. G.|last3=Fabio|first3=P. F.|last4=Angier|first4=Robert D.|last5=Wallace|first5=Roslyn E.|last6=Durr|first6=Frederick E.|last7=Citarella|first7=R. V.|journal=Journal of Medicinal Chemistry|volume=22|issue=9|pages=1024}} | |||
| ==See also== | == See also == | ||
| *], a mitoxantrone ] under development | * ], a mitoxantrone ] under development | ||
| * ] | |||
| * Naphtoquinoxalinediones, potential antitumorals, obtained from diamino-1,2 anthraquinones using a regioselective synthesis.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Baron M, Giorgi-Renault S, Renault J, ''et al.'' |title=Heterocycles with a quinone function.5.An abnormal reaction of butanedione with 1,2-diaminoanthraquinone - Crystalline structure obtained from naphto(2,3-f) quinoxaline-7,12 dione |journal=Can. J. Chem. |volume=62 |issue=3 |pages=526–530 |year=1984 |doi=10.1139/v84-087 |url=http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/doi/abs/10.1139/v84-087 |language=French}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | == References == | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| == External links == | |||
| * {{cite web | url = https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/mitoxantrone | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine | work = Drug Information Portal | title = Mitoxantrone }} | |||
| {{Demyelinating diseases of CNS}} | |||
| {{Merck Serono|state=autocollapse}} | |||
| {{Chemotherapeutic agents}} | {{Chemotherapeutic agents}} | ||
| {{Portal bar | Medicine}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:28, 29 May 2024
Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Novantrone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608019 |
| Routes of administration | Mainly intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | 78% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2E1) |
| Elimination half-life | 75 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H28N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 444.488 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent.
Uses
Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the survival rate of children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse.
The combination of mitoxantrone and prednisone is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. This combination was once the first line of treatment; however, a combination of docetaxel and prednisone improves survival rates and lengthens the disease-free period.
Mitoxantrone is also used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), most notably the subset of the disease known as secondary-progressive MS. In the absence of a cure, mitoxantrone is effective in slowing the progression of secondary-progressive MS and extending the time between relapses in both relapsing-remitting MS and progressive-relapsing MS.
Side effects
Mitoxantrone, as with other drugs in its class, may cause adverse reactions of varying severity, including nausea, vomiting, hair loss, heart damage and immunosuppression, possibly with delayed onset. Cardiomyopathy is a particularly concerning effect as it is irreversible; thus regular monitoring with echocardiograms or MUGA scans is recommended for patients.
Because of the risk of cardiomyopathy, mitoxantrone carries a limit on the cumulative lifetime dose (based on body surface area) in MS patients.
Mechanism of action
Mitoxantrone is a type II topoisomerase inhibitor; it disrupts DNA synthesis and DNA repair in both healthy cells and cancer cells by intercalation between DNA bases. It is also classified as an antibiotic.
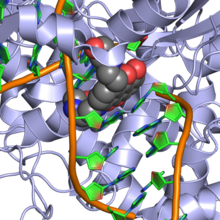
See also
- Pixantrone, a mitoxantrone analogue under development
- Losoxantrone
References
- "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- Parker C, Waters R, Leighton C, Hancock J, Sutton R, Moorman AV, et al. (December 2010). "Effect of mitoxantrone on outcome of children with first relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL R3): an open-label randomised trial". Lancet. 376 (9757): 2009–2017. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62002-8. PMC 3010035. PMID 21131038.
- Katzung BG (2006). "Cancer Chemotherapy". Basic and clinical pharmacology (10th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division. ISBN 0-07-145153-6. OCLC 157011367.
- Fox EJ (April 2006). "Management of worsening multiple sclerosis with mitoxantrone: a review". Clinical Therapeutics. 28 (4): 461–474. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.04.013. PMID 16750460.
- "Mitoxantrone Hydrochloride (marketed as Novantrone and generics) – Healthcare Professional Sheet text version". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- Mazerski J, Martelli S, Borowski E (1998). "The geometry of intercalation complex of antitumor mitoxantrone and ametantrone with DNA: molecular dynamics simulations". Acta Biochimica Polonica. 45 (1): 1–11. doi:10.18388/abp.1998_4280. PMID 9701490.
- Kapuscinski J, Darzynkiewicz Z (December 1985). "Interactions of antitumor agents Ametantrone and Mitoxantrone (Novatrone) with double-stranded DNA". Biochemical Pharmacology. 34 (24): 4203–4213. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90275-8. PMID 4074383.
- "Mitoxantrone".
- Wu CC, Li YC, Wang YR, Li TK, Chan NL (December 2013). "On the structural basis and design guidelines for type II topoisomerase-targeting anticancer drugs". Nucleic Acids Research. 41 (22): 10630–10640. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt828. PMC 3905874. PMID 24038465.
External links
- "Mitoxantrone". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signs and symptoms | |||||||||
| Investigations and diagnosis |
| ||||||||
| Approved treatment | |||||||||
| Other treatments | |||||||||
| Demyelinating diseases |
| ||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Merck Serono | |
|---|---|
| Products | |
| Related | |