| Revision as of 16:07, 6 December 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[user...← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 22:29, 10 January 2025 edit undoArthurfragoso (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Template editors4,591 edits dark mode fix | ||
| (105 intermediate revisions by 68 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 476997079 | ||
| | ImageFile = SodiumSalicylate.png | |||
| | ImageFile = Sodium salicylate2DCSD.svg | |||
| ⚫ | | ImageSize = | ||
| | ImageClass = skin-invert-image | |||
| | IUPACName = Sodium salicylate | |||
| ⚫ | | ImageSize = 100px | ||
| ⚫ | | OtherNames = Salsonin, Monosodium salicylate, Sodium o |
||
| | PIN = Sodium 2-hydroxybenzoate | |||
| | PubChem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=5900&ncount=51#Synonyms ...] | |||
| ⚫ | | OtherNames = Salsonin, Monosodium salicylate, Sodium ''o''-hydroxybenzoate, Salicylic acid sodium salt, Monosodium 2-hydroxybenzoate, Diuratin | ||
| | |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 5689 | | ChemSpiderID = 5689 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | CASNo = 54-21-7 | | CASNo = 54-21-7 | ||
| | |
| EINECS = 200-198-0 | ||
| | |
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEMBL = 447868 | | ChEMBL = 447868 | ||
| | PubChem = |
| PubChem = 16760658 | ||
| | |
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| | DrugBank = DB01398 | | DrugBank = DB01398 | ||
| | SMILES = .O=C()c1ccccc1O | | SMILES = .O=C()c1ccccc1O | ||
| | |
| InChI = 1/C7H6O3.Na/c8-6-4-2-1- 3-5(6)7(9)10;/h1-4,8H,(H,9,10); /q;+1/p-1/fC7H5O3.Na/q-1;m | ||
| | |
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| | KEGG = D00566 | | KEGG = D00566 | ||
| | |
| RTECS = VO5075000 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=7 | H=5 | Na=1 | O=3 | |||
| | Formula = C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>5</sub>NaO<sub>3</sub> | |||
| | |
| MolarMassUnit = g/mol | ||
| | |
| Appearance = White crystals | ||
| | |
| Density = | ||
| | |
| MeltingPtC = 200 | ||
| | |
| BoilingPt = | ||
| | Solubility = 25.08{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (-1.5{{nbsp}}°C)<br> 107.9{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (15{{nbsp}}°C)<br> 124.6{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (25{{nbsp}}°C)<br> 141.8{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (78.5{{nbsp}}°C)<br> 179{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (114{{nbsp}}°C)<ref name=chemister>{{cite web|url=http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=2993|title=sodium salicylate|website=chemister.ru|access-date=8 April 2018|archive-date=24 May 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140524024107/http://chemister.ru/Database/properties-en.php?dbid=1&id=2993|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | Solubility = ~ 660 g/l at 20 °C | |||
| | SolubleOther = Soluble in ], ], ]<ref name=chemister /> | |||
| | Solubility1 = 26.28{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (15{{nbsp}}°C)<br> 34.73{{nbsp}}g/100{{nnbsp}}g (67.2{{nbsp}}°C)<ref name=chemister /> | |||
| | Solvent1 = methanol | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section6={{Chembox Pharmacology | ||
| | ATCCode_prefix = N02 | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| ATCCode_suffix = BA04 | ||
| }} | |||
| | Autoignition = > 250 °C | |||
| |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | GHSPictograms = {{GHS07}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | GHS_ref = <ref name="sigma">], . Retrieved on 2014-05-26.</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | GHSSignalWord = Warning | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| HPhrases = {{H-phrases|314|331|400}} | ||
| | PPhrases = {{P-phrases|210|261|273|280|305+351+338|310}} | |||
| | SPhrases = {{S24/25}}, {{S26}}, {{S36/37/39}} | |||
| ⚫ | | MainHazards = Harmful | ||
| | EyeHazard = Irritant | |||
| | FlashPt = | |||
| | AutoignitionPtC = 250 | |||
| ⚫ | | NFPA-H = 1 | ||
| ⚫ | | NFPA-F = 1 | ||
| ⚫ | | NFPA-R = 0 | ||
| ⚫ | | NFPA-S = | ||
| | LD50 = 930 mg/kg (rats, oral)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/54-21-7|title=ChemIDplus - 54-21-7 - ABBQHOQBGMUPJH-UHFFFAOYSA-M - Sodium salicylate - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information.|first=Michael|last=Chambers|website=chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov|access-date=8 April 2018|archive-date=9 April 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180409171616/https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/54-21-7|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Sodium salicylate''' is a ] salt of ]. It can be prepared from ] and ] under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized |
'''Sodium salicylate''' is a ] salt of ]. It can be prepared from ] and ] under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized by refluxing ] (] oil) with an excess of ].<ref>Lehman, J.W., Operational Organich Chemistry, 4th ed., New Jersey, Prentice Hall, 2009</ref> | ||
| ==Properties== |
==Properties== | ||
| {{Expand section|date=July 2024}} | |||
| Sodium salicylate is of the ] family and this compound is known to trigger ] in children and adults, usually following a viral infection such as influenza or chicken pox. Products containing such salicylates should not be given to children under the age of 19.{{Citation needed|date=February 2011}} | |||
| Sodium salicylate is of the ] family. It is a shiny white powder with an aromatic taste.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Sodium salicylate {{!}} 54-21-7 |url=https://m.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB1255762.htm |access-date=2024-09-02 |website=ChemicalBook |language=en |archive-date=2024-09-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240902235509/https://m.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB1255762.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| It is used in medicine as an ] and ]. Sodium salicylate also acts as ] (NSAID), and induces ] in cancer cells <ref>{{cite journal | title = Sodium Salicylate Activates Caspases and Induces Apoptosis of Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines | journal = Blood | date = 1999-04-01 | first = Lidija | last = Klampfer | |
It is used in medicine as an ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Sodium salicylate {{!}} 54-21-7 |url=https://m.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB1255762.htm |access-date=2024-09-02 |website=ChemicalBook |language=en |archive-date=2024-09-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240902235509/https://m.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB1255762.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Sodium salicylate also acts as ] (NSAID), and induces ] in cancer cells <ref>{{cite journal | title = Sodium Salicylate Activates Caspases and Induces Apoptosis of Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines | journal = Blood | date = 1999-04-01 | first = Lidija | last = Klampfer |author2=Jörg Cammenga |author3=Hans-Georg Wisniewski |author4=Stephen D. Nimer | volume = 93 | issue = 7 | pages = 2386–94| doi = 10.1182/blood.V93.7.2386 | pmid=10090950}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | title = Elevated NF-κB responses and FLIP levels in leukemic but not normal lymphocytes: reduction by salicylate allows TNF-induced apoptosis | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA | date = 2007-07-31 | first = Colin | last = Rae |author2=Susana Langa |author3=Steven J. Tucker |author4=David J. MacEwan | volume = 104 | issue = 31 | pages = 12790–5| pmid=17646662 | pmc = 1937545 | doi=10.1073/pnas.0701437104| bibcode = 2007PNAS..10412790R | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | title = Aspirin activates the NF-κB signalling pathway and induces apoptosis in intestinal neoplasia in two in vivo models of human colorectal cancer | journal = Carcinogenesis | date = May 2007 | first = Lesley A. | last = Stark | volume = 28 | issue = 5 | pages = 968–76| pmid=17132819 | doi=10.1093/carcin/bgl220|display-authors=etal| doi-access = free }}</ref> and also ].<ref>{{cite journal | title = Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-induced p42/p44 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation by Sodium Salicylate | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | date = 1996-04-05 | first = Paul | last = Schwenger |author2=Edward Y. Skolnik |author3=Jan Vilcek | volume = 271 | issue = 14 | pages = 8089–94| pmid=8626494 | doi=10.1074/jbc.271.14.8089| doi-access = free }}</ref> It is also a potential replacement for ] for people sensitive to it. It may also be used as a phosphor for the detection of ] radiation and ].<ref>{{cite web|last=Samson|first=James|title=Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscopy|url=http://www.mcphersoninc.com/detectors/Sodium%20Salicylate.pdf|publisher=Pied Publications|access-date=July 26, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061016104429/http://www.mcphersoninc.com/detectors/Sodium%20Salicylate.pdf|archive-date=October 16, 2006}}</ref> | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 80: | ||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060523222443/http://physchem.ox.ac.uk/MSDS/SO/sodium_salicylate.html |date=2006-05-23 }} | ||
| * | * | ||
| {{Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products}} | {{Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic products}} | ||
| {{NSAIDs}} | |||
| {{Analgesics}} | {{Analgesics}} | ||
| {{Sodium compounds}} | {{Sodium compounds}} | ||
| {{Salicylates}} | {{Salicylates}} | ||
| {{Prostanoidergics}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Salicylate}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodium Salicylate}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:29, 10 January 2025
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Sodium 2-hydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names Salsonin, Monosodium salicylate, Sodium o-hydroxybenzoate, Salicylic acid sodium salt, Monosodium 2-hydroxybenzoate, Diuratin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.181 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H5NaO3 |
| Molar mass | 160.104 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Solubility in water | 25.08 g/100 g (-1.5 °C) 107.9 g/100 g (15 °C) 124.6 g/100 g (25 °C) 141.8 g/100 g (78.5 °C) 179 g/100 g (114 °C) |
| Solubility | Soluble in glycerol, 1,4-Dioxane, alcohol |
| Solubility in methanol | 26.28 g/100 g (15 °C) 34.73 g/100 g (67.2 °C) |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | N02BA04 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Harmful |
| Eye hazards | Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H314, H331, H400 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P261, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Autoignition temperature |
250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 930 mg/kg (rats, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
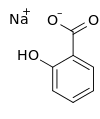
Sodium salicylate is a sodium salt of salicylic acid. It can be prepared from sodium phenolate and carbon dioxide under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized by refluxing methyl salicylate (wintergreen oil) with an excess of sodium hydroxide.
Properties
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2024) |
Sodium salicylate is of the salicylate family. It is a shiny white powder with an aromatic taste.
Uses
It is used in medicine as an analgesic and antipyretic. Sodium salicylate also acts as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), and induces apoptosis in cancer cells and also necrosis. It is also a potential replacement for aspirin for people sensitive to it. It may also be used as a phosphor for the detection of vacuum ultraviolet radiation and beta radiation.
References
- ^ "sodium salicylate". chemister.ru. Archived from the original on 24 May 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 54-21-7 - ABBQHOQBGMUPJH-UHFFFAOYSA-M - Sodium salicylate [USP:JAN] - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 9 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- Sigma-Aldrich Co., Sodium salicylate. Retrieved on 2014-05-26.
- Lehman, J.W., Operational Organich Chemistry, 4th ed., New Jersey, Prentice Hall, 2009
- "Sodium salicylate | 54-21-7". ChemicalBook. Archived from the original on 2024-09-02. Retrieved 2024-09-02.
- "Sodium salicylate | 54-21-7". ChemicalBook. Archived from the original on 2024-09-02. Retrieved 2024-09-02.
- Klampfer, Lidija; Jörg Cammenga; Hans-Georg Wisniewski; Stephen D. Nimer (1999-04-01). "Sodium Salicylate Activates Caspases and Induces Apoptosis of Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines". Blood. 93 (7): 2386–94. doi:10.1182/blood.V93.7.2386. PMID 10090950.
- Rae, Colin; Susana Langa; Steven J. Tucker; David J. MacEwan (2007-07-31). "Elevated NF-κB responses and FLIP levels in leukemic but not normal lymphocytes: reduction by salicylate allows TNF-induced apoptosis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 104 (31): 12790–5. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10412790R. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701437104. PMC 1937545. PMID 17646662.
- Stark, Lesley A.; et al. (May 2007). "Aspirin activates the NF-κB signalling pathway and induces apoptosis in intestinal neoplasia in two in vivo models of human colorectal cancer". Carcinogenesis. 28 (5): 968–76. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl220. PMID 17132819.
- Schwenger, Paul; Edward Y. Skolnik; Jan Vilcek (1996-04-05). "Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-induced p42/p44 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation by Sodium Salicylate". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (14): 8089–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.14.8089. PMID 8626494.
- Samson, James. "Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscopy" (PDF). Pied Publications. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2006. Retrieved July 26, 2012.
External links
- Chemicalland21
- vhc
- Some synonyms
- Safety data for sodium salicylate at Oxford University Archived 2006-05-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Sodium salicylate, definitions at National Cancer Institute
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (primarily M01A and M02A, also N02BA) | |
|---|---|
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams | |
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other | |
| NSAID combinations | |
| Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; WHO-Essential Medicines; withdrawn drugs; veterinary use. | |
| Sodium compounds | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic |
| ||||||||||||||
| Organic | |||||||||||||||
| Salicylates | |
|---|---|
|
| Prostanoid signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||