| Revision as of 00:13, 19 December 2011 editJynto (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,197 edits Adding ball-and-stick model← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:04, 12 November 2023 edit undoBernanke's Crossbow (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,867 edits Move refs to references, mark DOI access as free, fix author fields | ||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 448773926 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageFileL1 = Oxepine.svg | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageSizeL1 = 110 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageAltL1 = Skeletal formula of oxepin | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageFileR1 = Oxepin-based-on-xtal-3D-bs-17.png | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageSizeR1 = 140 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ImageAltR1 = Ball-and-stick model of the oxepin molecule | ||
| ⚫ | |OtherNames=Oxacycloheptatriene |
||
| | ImageFile2 = Oxepin-based-on-xtal-3D-bs-17-side-view.png | |||
| ⚫ | |Section1= |
||
| | ImageSize2 = 140 | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PIN=Oxepine | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | OtherNames=Oxacycloheptatriene | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| ⚫ | | CASNo=291-70-3 | ||
| ⚫ | | PubChem=6451477 | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES=C1=CC=COC=C1 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| | UNII = CVP5X85XX5 | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 4953942 | |||
| | InChI = 1/C6H6O/c1-2-4-6-7-5-3-1/h1-6H | |||
| | InChIKey = ATYBXHSAIOKLMG-UHFFFAOYAS | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C6H6O/c1-2-4-6-7-5-3-1/h1-6H | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChIKey = ATYBXHSAIOKLMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2= |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=6 | H=6 | O=1 | |||
| | Formula=C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O | |||
| | Appearance= | |||
| | MolarMass=94.11 g/mol | |||
| | |
| Density= | ||
| | |
| MeltingPt= | ||
| | |
| BoilingPt= | ||
| | |
| Solubility= | ||
| | Solubility= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section3= |
|Section3={{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | |
| MainHazards= | ||
| | |
| FlashPt= | ||
| | AutoignitionPt = | |||
| | Autoignition= | |||
| }} | |||
| | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | |||
| | Related_ref = | |||
| | OtherFunction = | |||
| | OtherFunction_label = | |||
| | OtherCompounds = ]<br/>] | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
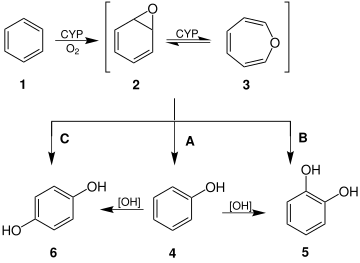
| '''Oxepin''' is an oxygen-containing ] consisting of a seven-membered ring with three ]. |
'''Oxepin''' is an ]-containing ] consisting of a seven-membered ] with three ]s. The parent C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O exists as an ] mixture with '''benzene oxide'''. | ||
| ] | |||
| The oxepin–benzene oxide equilibrium is affected by the ring ]s.<ref name=TautHist /> A related dimethyl derivative exists mainly as the oxepin isomer, an orange liquid.<ref name=Me2Synth /> | |||
| ]<br style="clear:left;"/> | |||
| Oxepin is an intermediate in the oxidation of ] by the ] (CYP).<ref name=Tox /> Other ]s are metabolites of the parent arene. | |||
| :] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| <references> | |||
| {{commonscat|Oxepins}} | |||
| <ref name=Me2Synth>{{cite journal|title=2,7-Dimethyloxepin|first1=Leo A.|last1=Paquette |author1-link= Leo Paquette |first2=J. H. |last2=Barrett|journal=Org. Synth.|year=1969|volume=49|page=62|doi=10.15227/orgsyn.049.0062}}</ref> | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| <ref name=Tox>{{cite journal |doi=10.1289/ehp.93100293 |journal=Environmental Health Perspectives |title=The Toxicology of Benzene |volume=100 |pages=293–306 |first1=R.|last1=Snyder |first2= G. |last2=Witz |first3= B. D. |last3=Goldstein |year=1993 |pmc=1519582 |pmid=8354177|jstor=3431535 |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=TautHist>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1002/anie.196703851 | journal = Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English | title=Benzene Oxide–Oxepin Valence Tautomerism| volume=6 |issue=5 |pages =385–401 |first1=E.|last1=Vogel |first2=H.|last2=Günther | year = 1967}}</ref> | |||
| </references> | |||
| {{Commons category|Oxepin}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:04, 12 November 2023
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Oxepine | |||
| Other names Oxacycloheptatriene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C6H6O | ||
| Molar mass | 94.113 g·mol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds | Cyclohexene oxide Oxonane | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Oxepin is an oxygen-containing heterocycle consisting of a seven-membered ring with three double bonds. The parent C6H6O exists as an equilibrium mixture with benzene oxide.
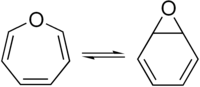
The oxepin–benzene oxide equilibrium is affected by the ring substituents. A related dimethyl derivative exists mainly as the oxepin isomer, an orange liquid.
Oxepin is an intermediate in the oxidation of benzene by the cytochrome P450 (CYP). Other arene oxides are metabolites of the parent arene.
References
- Vogel, E.; Günther, H. (1967). "Benzene Oxide–Oxepin Valence Tautomerism". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 6 (5): 385–401. doi:10.1002/anie.196703851.
- Paquette, Leo A.; Barrett, J. H. (1969). "2,7-Dimethyloxepin". Org. Synth. 49: 62. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.049.0062.
- Snyder, R.; Witz, G.; Goldstein, B. D. (1993). "The Toxicology of Benzene". Environmental Health Perspectives. 100: 293–306. doi:10.1289/ehp.93100293. JSTOR 3431535. PMC 1519582. PMID 8354177.