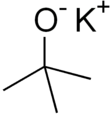| Revision as of 16:17, 30 January 2012 edit138.38.128.235 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:56, 25 November 2024 edit undoLaura240406 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users910 edits Link suggestions feature: 3 links added.Tags: Visual edit Newcomer task Suggested: add links | ||
| (120 intermediate revisions by 60 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{DISPLAYTITLE:Potassium ''tert''-butoxide}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Potassium ''tert''-butoxide}} | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 476994881 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| Name = Potassium ''tert''-butoxide | ||
| | ImageFileL1 = Potassium tert-butoxide.png | |||
| | ImageSizeL1 = 115px | |||
| | |
| ImageNameL1 = Skeletal formula of potassium tert-butoxide | ||
| | |
| ImageFileR1 = Potassium-tert-butoxide-cubane-tetramer-from-xtal-1991-3D-balls.png | ||
| | ImageNameR1 = Ball-and-stick model of the cubane tetramer that potassium tert-butoxide adopts in | |||
| | ImageSizeR1 = 125px | |||
| | |
| ImageFile2 = Potassium-tert-butoxide-3D-balls-ionic.png | ||
| | ImageSize2 = 180px | |||
| |IUPACName=potassium 2-methylpropan-2-olate | |||
| |OtherNames= | | OtherNames = KOt-Bu, potassium ''t''-butoxide. | ||
| ⚫ | | PIN = Potassium ''tert''-butoxide | ||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 63266 | | ChemSpiderID = 63266 | ||
| | InChI = 1/C4H9O.K/c1-4(2,3)5;/h1-3H3;/q-1;+1 | | InChI = 1/C4H9O.K/c1-4(2,3)5;/h1-3H3;/q-1;+1 | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
| | StdInChIKey = LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | StdInChIKey = LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | CASNo=865-47-4 |
| CASNo=865-47-4 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII = VR838VHE0V | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PubChem = 70077 | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = .C(C)(C)C | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| | |
| Formula=C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>9</sub>KO | ||
| | |
| MolarMass=112.21 g mol<sup>−1</sup> | ||
| | |
| Appearance= solid | ||
| ⚫ | | MeltingPtC=256 | ||
| | Density= | |||
| | BoilingPt_notes=sublimes at 220 °C (1 mmHg) or at 140 °C (0.01 hPa) | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | Solubility = Reacts with water | |||
| | BoilingPtC= | |||
| | Solvent1 = diethyl ether | |||
| | Solubility= | |||
| | Solubility1 = 4.34 g/100 g (25-26 °C)<ref name=EROS>{{cite encyclopedia | author = Caine D. | encyclopedia = e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis | title = Potassium tert-Butoxide | year = 2006| doi = 10.1002/047084289X.rp198.pub2 | chapter = Potassiumtert-Butoxide | isbn = 0471936235}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| | Solvent2 = Hexane | |||
| ⚫ | |Section3={{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | Solubility2 = 0.27 g/100 g (25-26 °C)<ref name=EROS/> | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | Solvent3 = Toluene | |||
| | EUClass = Harmful (Xn), Corrosive (C) | |||
| | Solubility3 = 2.27 g/100 g (25-26 °C)<ref name=EROS/> | |||
| | FlashPt= | |||
| | Solvent4 = THF | |||
| | Autoignition= | |||
| | Solubility4 = 25.00 g/100 g (25-26 °C)<ref name=EROS/> | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| ⚫ | | Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| ⚫ | | ExternalSDS = | ||
| | GHSPictograms = {{GHS02}} {{GHS05}} | |||
| | GHSSignalWord = danger | |||
| | HPhrases = {{HPhrases|H228|H252|H314}} | |||
| | EUPhrases = {{EUH-phrases|EUH014}} | |||
| | PPhrases = {{PPhrases|P405}} | |||
| | GHS_ref = <ref>{{GESTIS|ZVG=30280|Name=Potassium tert-butoxide|Date=2021-12-22}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Potassium ''tert''-butoxide''' is |
'''Potassium ''tert''-butoxide''' (or '''potassium ''t''-butoxide''') is a ] with the ] <sub>''n''</sub> (abbr. KOtBu). This colourless solid is a strong ] (pKa of conjugate acid around 17), which is useful in ]. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but its ionization depends on the solvent.<ref name=EROS/> | ||
| which is useful in ]. It exists as a tetrameric cubane-like ]. It is often seen written in chemical literature as potassium ''t''-butoxide. | |||
| ==Preparation== | ==Preparation== | ||
| Potassium ''t''-butoxide is commercially available as a solution and as a solid, but it is often generated ''in situ'' for laboratory use because samples are so sensitive and older samples are often of |
Potassium ''t''-butoxide is commercially available as a solution and as a solid, but it is often generated ''in situ'' for laboratory use because samples are so moisture-] and older samples are often of low purity. It is prepared by the reaction of dry ] with ] metal.<ref>{{OrgSynth | author = William S. Johnson and William P. Schneider | title = β-Carbethoxy-γ,γ-diphenylvinylacetic acid | collvol = 4 | collvolpages = 132 | prep = cv4p0132 | year = 1963}}</ref> The solid is obtained by evaporating these solutions followed by heating the solid. The solid can be purified by sublimation. | ||
| == |
==Structure== | ||
| It crystallizes as a tetrameric ]. It crystallises from ]/] at −20°C as <sub>∞</sub>, which consists of straight chains linked by ]ing. Sublimation of <sub>∞</sub> affords the tetramer <sub>4</sub>, which adopts a cubane-like structure. Mild ] solvents such as THF and ] do not break up the tetrameric structure, which persists in the solid, in solution and even in the gas phase.<ref>{{ cite journal | first1 = Malcolm H. | last1 = Chisholm | first2 = Simon R. | last2 = Drake | first3 = Ahmad A. | last3 = Naiini | first4 = William E. | last4 = Streib | title = Synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of the one-dimensional ribbon chains <sub>∞</sub> and the cubane species <sub>4</sub> (M = K and Rb) | journal = ] | volume = 10 | issue = 3 | year = 1991 | pages = 337–345 | doi = 10.1016/S0277-5387(00)80154-0}}</ref> | |||
| The ''tert''-butoxide species is itself useful as a strong, non-nucleophilic base in organic chemistry.<ref name=Craine>Drury Caine “Potassium t-Butoxide” in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2006. {{DOI| 10.1002/047084289X.rp198.pub2}}. Article Online Posting Date: September 15, 2006</ref> It is not as strong as amide bases, e.g. ], but stronger than potassium hydroxide. Its steric bulk inhibits the group from participating in nucleophilic addition, such as in a ] or an ] reaction. Substrates that are deprotonated by potassium ''t''-butoxide include terminal acetylenes and active methylene compounds. It is useful in ] reactions. It is a strong base | |||
| == |
==Reactions== | ||
| ===As a base=== | |||
| Many modifications have been reported that influence the reactivity of this reagent. The compound adopts a complex cluster structure (the picture |
Many modifications have been reported that influence the reactivity of this ]. The compound adopts a complex cluster structure (the adjacent picture is a simplified cartoon), and additives that modify the cluster affect the reactivity of the reagent. For example, ], ], ] (HMPA), and ] interact with the potassium center, yielding solvent separated ion pairs such as K(DMSO)<sub>x</sub><sup>+</sup> and ''tert''-BuO<sup>−</sup>. Whereas in benzene, on the other hand, the compound remains as a cluster structure, which is less basic.<ref name=EROS/> Even in polar solvents, it is not as strong as amide bases, e.g., ], but stronger than potassium hydroxide. Its steric bulk inhibits the group from participating in nucleophilic addition, such as in a ] or related ] reactions. {{Citation needed|date=April 2023}} | ||
| Substrates that are deprotonated by potassium ''t''-butoxide include terminal acetylenes and ]s. It is useful in ] reactions. Illustrating the latter behavior, potassium ''tert''-butoxide reacts with chloroform yielding ], which is useful for dichloro]s.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mTHQB7MkUFsC&dq=tert-butoxide+chloroform&pg=PA551|title=Organic Chemistry|last1=Brown|first1=William|last2=Foote|first2=Christopher|last3=Iverson|first3=Brent|last4=Anslyn|first4=Eric|date=2008-01-10|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=978-0495388579|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bLV55kunjA4C&dq=tert-butoxide+chloroform&pg=PA119|title=Hazardous Laboratory Chemicals Disposal Guide, Third Edition|author1=Margaret-Ann Armour|author-link=Margaret-Ann Armour|date=2016-04-19|publisher=CRC Press|isbn=9781420032383|language=en}}</ref> Potassium ''tert''-butoxide can abstract a beta-proton from alkylammonium cations, leading to the Hofmann product via an ]. | |||
| ===Other reactions=== | |||
| Potassium ''tert''-butoxide ] the reaction of ] and heterocyclic compounds to give the silyl derivatives, with release of H<sub>2</sub>.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Anton A. Toutov, Wen-Bo Liu, Kerry N. Betz, Alexey Fedorov, ], ] | journal = Nature | year = 2015 | volume = 518 | issue = 7537 | pages = 80–84 | doi = 10.1038/nature14126 | pmid = 25652999 | title = Silylation of C–H bonds in aromatic heterocycles by an Earth-abundant metal catalyst| bibcode = 2015Natur.518...80T | s2cid = 3117834 | url = https://authors.library.caltech.edu/51898/14/nature14126-s1.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| ==Safety== | |||
| Potassium ''tert''-butoxide is a very strong base that rapidly attacks living tissue. | |||
| Potassium ''tert''-butoxide forms explosive mixtures when treated with ].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4IPE8Pjhm8UC&dq=tert-butoxide+dichloromethane&pg=RA3-PT264|title=Hazardous Materials: Emergency Action Data|last1=Foden|first1=Charles R.|last2=Weddell|first2=Jack L.|date=1991-12-29|publisher=CRC Press|isbn=9780873715980|language=en}}</ref> <ref>{{Cite book|url=https://webwiser.nlm.nih.gov/substance?substanceId=48&identifier=Dichloromethane&identifierType=name&menuItemId=7&catId=64|title=Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards 4 ed.|last1=Bretherick|first1=L.|date=1990|publisher=Dichloromethane - Reactivities / Incompatibilities in NIH National Library of Medicine|isbn=9781483284668|page=475|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Related compounds== | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:56, 25 November 2024
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Potassium tert-butoxide | |||
| Other names KOt-Bu, potassium t-butoxide. | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.583 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C4H9KO | ||
| Molar mass | 112.21 g mol | ||
| Appearance | solid | ||
| Melting point | 256 °C (493 °F; 529 K) | ||
| Boiling point | sublimes at 220 °C (1 mmHg) or at 140 °C (0.01 hPa) | ||
| Solubility in water | Reacts with water | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 4.34 g/100 g (25-26 °C) | ||
| Solubility in Hexane | 0.27 g/100 g (25-26 °C) | ||
| Solubility in Toluene | 2.27 g/100 g (25-26 °C) | ||
| Solubility in THF | 25.00 g/100 g (25-26 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H228, H252, H314 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P405 | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Potassium tert-butoxide (or potassium t-butoxide) is a chemical compound with the formula n (abbr. KOtBu). This colourless solid is a strong base (pKa of conjugate acid around 17), which is useful in organic synthesis. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but its ionization depends on the solvent.
Preparation
Potassium t-butoxide is commercially available as a solution and as a solid, but it is often generated in situ for laboratory use because samples are so moisture-sensitive and older samples are often of low purity. It is prepared by the reaction of dry tert-butyl alcohol with potassium metal. The solid is obtained by evaporating these solutions followed by heating the solid. The solid can be purified by sublimation.
Structure
It crystallizes as a tetrameric cubane-type cluster. It crystallises from tetrahydrofuran/pentane at −20°C as ∞, which consists of straight chains linked by hydrogen bonding. Sublimation of ∞ affords the tetramer 4, which adopts a cubane-like structure. Mild Lewis basic solvents such as THF and diethyl ether do not break up the tetrameric structure, which persists in the solid, in solution and even in the gas phase.
Reactions
As a base
Many modifications have been reported that influence the reactivity of this reagent. The compound adopts a complex cluster structure (the adjacent picture is a simplified cartoon), and additives that modify the cluster affect the reactivity of the reagent. For example, DMF, DMSO, hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA), and 18-crown-6 interact with the potassium center, yielding solvent separated ion pairs such as K(DMSO)x and tert-BuO. Whereas in benzene, on the other hand, the compound remains as a cluster structure, which is less basic. Even in polar solvents, it is not as strong as amide bases, e.g., lithium diisopropylamide, but stronger than potassium hydroxide. Its steric bulk inhibits the group from participating in nucleophilic addition, such as in a Williamson ether synthesis or related SN2 reactions.
Substrates that are deprotonated by potassium t-butoxide include terminal acetylenes and active methylene compounds. It is useful in dehydrohalogenation reactions. Illustrating the latter behavior, potassium tert-butoxide reacts with chloroform yielding dichlorocarbene, which is useful for dichlorocyclopropanations. Potassium tert-butoxide can abstract a beta-proton from alkylammonium cations, leading to the Hofmann product via an elimination reaction.
Other reactions
Potassium tert-butoxide catalyzes the reaction of hydrosilanes and heterocyclic compounds to give the silyl derivatives, with release of H2.
Safety
Potassium tert-butoxide is a very strong base that rapidly attacks living tissue.
Potassium tert-butoxide forms explosive mixtures when treated with dichloromethane.
Related compounds
References
- ^ Caine D. (2006). "Potassiumtert-Butoxide". Potassium tert-Butoxide. e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp198.pub2. ISBN 0471936235.
- Record of Potassium tert-butoxide in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2021-12-22.
- William S. Johnson and William P. Schneider (1963). "β-Carbethoxy-γ,γ-diphenylvinylacetic acid". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 4, p. 132.
- Chisholm, Malcolm H.; Drake, Simon R.; Naiini, Ahmad A.; Streib, William E. (1991). "Synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of the one-dimensional ribbon chains ∞ and the cubane species 4 (M = K and Rb)". Polyhedron. 10 (3): 337–345. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00)80154-0.
- Brown, William; Foote, Christopher; Iverson, Brent; Anslyn, Eric (2008-01-10). Organic Chemistry. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0495388579.
- Margaret-Ann Armour (2016-04-19). Hazardous Laboratory Chemicals Disposal Guide, Third Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 9781420032383.
- Anton A. Toutov, Wen-Bo Liu, Kerry N. Betz, Alexey Fedorov, Brian Stoltz, Robert H. Grubbs (2015). "Silylation of C–H bonds in aromatic heterocycles by an Earth-abundant metal catalyst" (PDF). Nature. 518 (7537): 80–84. Bibcode:2015Natur.518...80T. doi:10.1038/nature14126. PMID 25652999. S2CID 3117834.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Foden, Charles R.; Weddell, Jack L. (1991-12-29). Hazardous Materials: Emergency Action Data. CRC Press. ISBN 9780873715980.
- Bretherick, L. (1990). Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards 4 ed. Dichloromethane - Reactivities / Incompatibilities in NIH National Library of Medicine. p. 475. ISBN 9781483284668.