| Revision as of 09:34, 24 April 2006 edit61.118.147.133 (talk) →Rube Goldberg machines on media← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:43, 5 January 2025 edit undo2603:8083:9940:26e:2e71:3aa7:26ed:37c1 (talk) →CareerTag: Manual revert | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|American cartoonist (1883–1970)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{for|the namesake contraption|Rube Goldberg machine}} | |||
| '''Reuben Lucius Goldberg''' (], ] � ], ]) was a cofounder and first ] of the ]. He is one of the most famous ]s in history. He earned lasting fame for his "Rube Goldberg machines" � devices that are exceedingly complex and perform very simple tasks in a very indirect and convoluted way. He was posthumously awarded the ] Gold Key Award in 1980. | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=May 2015}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=December 2022}} | |||
| {{Infobox person | |||
| | name = Rube Goldberg | |||
| | image = Rube Goldberg, 1929 (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image_size = | |||
| | caption = Goldberg in 1929 | |||
| | birth_name = Reuben Garrett Lucius Goldberg | |||
| | birth_date = {{Birth date|1883|7|4}} | |||
| | birth_place = ], U.S. | |||
| | death_date = {{Death date and age|1970|12|7|1883|7|4}} | |||
| | death_place = New York City, U.S. | |||
| | resting_place = Mount Pleasant Cemetery in ] | |||
| | known_for = ]s | |||
| | alma_mater = ] | |||
| | occupation = Engineer, sculptor, news reporter, cartoonist | |||
| | website = {{URL|rubegoldberg.org}} | |||
| | spouse = {{marriage|Irma Seeman|October 17, 1916}} | |||
| | children = 2, including ] | |||
| }} | |||
| ] | |||
| '''Reuben Garrett Lucius Goldberg''' (July 4, 1883 – December 7, 1970), better known as '''Rube Goldberg''' ({{IPAc-en|'|r|uː|b}}), was an American cartoonist, sculptor, author, engineer, and inventor. | |||
| Goldberg is best known for his popular cartoons depicting complicated gadgets performing simple tasks in indirect, convoluted ways. The cartoons led to the expression "]s" to describe similar gadgets and processes. Goldberg received many honors in his lifetime, including a ] for political cartooning in 1948, the ]'s Gold T-Square Award in 1955,<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|title=Rube Goldberg Awards Achieved, The Group, History and Significance of the awards.|url=http://www.rube-goldberg.com/t-square-award.html|access-date=2020-08-06|website=www.rube-goldberg.com}}</ref> and the Banshees' Silver Lady Award in 1959.<ref name=":0" /><ref name="ab">{{cite web | last = Goldberg | first = Reuben | title = Members / In Memoriam / Rube Goldberg | url = http://reuben.org/ncs/members/memorium/goldberg.jpg | format = JPEG | work = reuben.org | publisher = National Cartoonists Society | access-date = August 5, 2009 | archive-date = June 4, 2011 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110604003258/http://www.reuben.org/ncs/members/memorium/goldberg.jpg | url-status = dead }}</ref> He was a founding member and first president of the ],<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111223081551/http://www.reuben.org/history.html |date=December 23, 2011 }}. ''reuben.org''. National Cartoonists Society.</ref> which hosts the annual ], honoring the top cartoonist of the year and named after Goldberg, who won the award in 1967.<ref>{{cite web |title=NCS AWARDS The Reuben Award|url=https://www.nationalcartoonists.com/awards/ |website=National Cartoonists Society |access-date=21 January 2021}}</ref> He is the inspiration for international competitions known as ]s, which challenge participants to create a complicated machine to perform a simple task. | |||
| Goldberg earned a ] in ] from the ] in ]. Goldberg was hired by the city of ] as an ] out of college. However his fondness for drawing ]s prevailed, and after just a few months he left the city to employ for a job with the '']'' as a ] cartoonist. The following year he took a job with the '']'' where he remained until ], when he relocated to ]. | |||
| ==Early life and education== | |||
| He drew cartoons for several ]s, including the '']'' and the '']''. His work entered ] in ], beginning his nationwide popularity. A prolific ], Goldberg produced several cartoon series simultaneously; titles included '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. | |||
| Goldberg was born on July 4, 1883, in ], ], to ] parents Max and Hannah (] Cohn) Goldberg.<ref name="Cont448">{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kHREAAAAMAAJ&q=%22rube+goldberg%22+jewish+max+hannah |title=Contemporary Authors: First revision, Volumes 5–8 |publisher=Gale Research Company |year=1969 |page=448 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kHREAAAAMAAJ&q=%22rube+goldberg%22+francisco |title=Contemporary Authors: First revision |date=1969 |publisher=Gale Research Company |language=en}}</ref> He was the third of seven children, three of whom died as children; older brother Garrett, younger brother Walter, and younger sister Lillian also survived.<ref name="marzio">{{cite book |title=Rube Goldberg: His Life and Work |first=Peter C. |last=Marzio |publisher=Harper and Row |year=1973|isbn=978-0060128302 }}</ref> Goldberg began tracing illustrations when he was four years old, and he took his only drawing lessons with a local sign painter.<ref name="marzio"/> | |||
| ==Personal life== | |||
| In 1911, he built the R. L. Goldberg Building at 182–198 Gough Street, San Francisco, for his widowed father to live in, as well as to collect rental income.<ref>{{Cite web |title=San Francisco Landmark #268: Goldberg Building |url=https://noehill.com/sf/landmarks/sf268.asp |access-date=2022-11-05 |website=noehill.com}}</ref> | |||
| Goldberg married Irma Seeman on October 17, 1916.<ref name="Cont448"/> They lived at 98 Central Park West in New York City and had two sons: Thomas and ]. During ], as each of his sons headed off to college, Goldberg insisted that they change their surname because of antisemitic sentiment toward him stemming from the political nature of his cartoons.<ref>{{cite news |first=Alison J.|last=Peterson |title= George W. George, at 87; writer, producer of films and Broadway plays |url=http://www.boston.com/bostonglobe/obituaries/articles/2007/11/20/george_w_george_at_87_writer_producer_of_films_and_broadway_plays|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081205000343/http://www.boston.com/bostonglobe/obituaries/articles/2007/11/20/george_w_george_at_87_writer_producer_of_films_and_broadway_plays|url-status=dead|archive-date=2008-12-05|work= New York Times News Service |publisher=Boston Globe |date=November 20, 2007|access-date=May 24, 2024}}</ref> Thomas chose the surname George, and his brother, also named George, followed suit. In adopting the same surname, George wanted to keep a sense of family cohesiveness. | |||
| While all these series were quite popular, the one which led to his lasting fame involved a character named ]. In this series, Goldberg would draw labeled schematics of comical "]" which would later bear his name. In ], "Rube Goldberg's Inventions", depicting Professor Butts' Self-Operating Napkin, was one of 20 strips included in the ] series of commemorative ] ]. | |||
| ==Career== | |||
| He was awarded the ] for his political cartooning in ]. | |||
| ]'', 1916]] | |||
| Goldberg's father was a San Francisco ] and fire commissioner,<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kHREAAAAMAAJ&q=%22rube+goldberg%22+francisco |title=Contemporary Authors: First revision |date=1969 |publisher=Gale Research Company |language=en}}</ref> who encouraged the young Reuben to pursue a career in ]. Rube graduated from the ], in 1904 with a degree in Engineering<ref name="ab" /> and was hired by the ] as an engineer for the Water and Sewers Department.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kHREAAAAMAAJ&q=%22rube+goldberg%22+francisco |title=Contemporary Authors: First revision |date=1969 |publisher=Gale Research Company |language=en}}</ref> After six months he resigned his position with the city to join the '']'' where he became a sports ].<ref name="ab"/> The following year, he took a job with the ''San Francisco Bulletin'', where he remained until he moved to ] in 1907, finding employment as a sports cartoonist with the '']''.<ref name= marzio /> | |||
| Goldberg's first public hit was a ] called ''Foolish Questions'',<ref name="toonopediafoolishquestions" /> beginning in 1908. The invention cartoons began in 1912.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Sheets |first1=Hilarie M. |title=A Rube Goldberg Hand-Washing Contraption? The Race Is On |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/08/arts/design/rube-goldberg-bar-of-soap-challenge.html |access-date=1 January 2021 |agency=The New York Times |date=8 April 2020}}</ref> The ''New York Evening Mail'' was syndicated to the first newspaper ], the ], giving Goldberg's cartoons a wider distribution, and by 1915 he was earning $25,000 per year and being billed by the paper as America's most popular cartoonist.<ref name= marzio /> ] had offered Goldberg $2,600 <!-- $2,600 is not a typo. The Hearst chain offer was a highly prestigious position but at a low salary, and it was later raised to $50,000 --> per year in 1911 in an unsuccessful attempt to get him to move to ]'s newspaper chain, and in 1915 raised the offer to $50,000 per year. Rather than lose Goldberg to Hearst, the ''New York Evening Mail'' matched the salary offer and formed the Evening Mail Syndicate to syndicate Goldberg's cartoons nationally.<ref name= marzio /> | |||
| Later in his career Goldberg was employed by the '']'', remaining there until his retirement in ]. During his retirement he occupied himself with making ]s. Several one-man shows of his work were organized, the last one of his lifetime being in ] at the ] in ]. Shortly afterward, he died at the age of 87; he is buried at ] in ]. | |||
| In 1916, Goldberg created a series of seven short ] which focus on humorous aspects of everyday situations<ref>{{cite news | date=July 24, 2016 | title=Goldberg is Again Star of the Film: Artist-Humorist of The Times Seen in New Set of Animated Cartoons | work=The Washington Times | page=12 | url=https://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn84026749/1916-07-24/ed-1/seq-12/ | access-date=May 21, 2018}}</ref> in the form of an animated ].<ref>{{cite news | last=Photoplay Editor | date=May 5, 1916 | title=Pathé Boob Weekly News from Nowhere: Goldberg Does Some Clever Satiric Cartoons on News Pictures | page=10 | work=] | url=https://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn83045211/1916-05-05/ed-1/seq-10/ | access-date=May 21, 2018}}</ref> The seven films were released on these dates in 1916: May 8, ''The Boob Weekly''; May 22, ''Leap Year''; June 5, ''The Fatal Pie''; Jun 19, ''From Kitchen Mechanic to Movie Star''; July 3, ''Nutty News''; July 17, ''Home Sweet Home''; July 31, ''Losing Weight''.<ref>{{cite book | last=George | first=Jennifer | title=The Art of Rube Goldberg: (A) Inventive (B) Cartoon (C) Genius | date=November 12, 2013 | location=New York | publisher=] | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JpcxDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA60 | access-date=May 21, 2018 | isbn=978-1-419-70852-7}}</ref> | |||
| In addition to his Pulitzer Prize in 1948, he received the ] Gold T-Square Award in 1955, their ] for 1967, and was given their Gold Key Award (their Hall of Fame) posthumously in 1980. | |||
| Goldberg was syndicated by the ] from 1922 until 1934. | |||
| ==Rube Goldberg machines== | |||
| A '''Rube Goldberg''' machine or device is any exceedingly complex ] that performs a very simple task in a very indirect and convoluted way. Rube devised and drew several such ] devices. The best examples of his ]s have an anticipation factor. The fact that something so wacky is happening can only be topped by it happening in a suspenseful manner. A Rube Goldberg machine usually has at least ten steps. One story about Rube Goldberg is that while sleep-walking barefoot in a ] field, he screamed out an idea about a self-operating ]. | |||
| A prolific artist, it has been estimated that Goldberg created 50,000 cartoons during his lifetime.<ref>{{cite magazine |last=Wilson |first=Emily |date=May 1, 2018 |title=The Story Behind Rube Goldberg's Complicated Contraptions |url=https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/story-behind-rube-goldbergs-complicated-contraptions-180968928/ |magazine=Smithsonian Magazine |publisher=Joseph J. Bonsignore |access-date=January 10, 2021}}</ref> Some of these cartoons include '']'', '']'', ''Foolish Questions'',<ref name="toonopediafoolishquestions"> at ]. from the original on July 30, 2016.</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Foolish Questions hi|url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn85066387/1910-06-02/ed-1/seq-13 |newspaper=] |date=December 2, 1910 |page=13}}</ref> ''What Are You Kicking About'',<ref>{{cite news |title=What Are You Kicking About |url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn85066387/1910-06-01/ed-1/seq-13 |newspaper=] |date=June 1, 1910 |page=13}}</ref> ''Telephonies'',<ref>{{cite news |title=Telephonies |url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn85066387/1911-07-12/ed-1/seq-10 |newspaper=] |date=July 12, 1911 |page=10}}</ref> ''Lala Palooza'', ''The Weekly Meeting of the Tuesday Women's Club'', and the uncharacteristically serious ] strip, ''Doc Wright'', which ran for 10 months beginning January 29, 1933.<ref> at ]. {{webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20240527194002/https://www.webcitation.org/6gWihdn6h?url=http://toonopedia.com/docwri.htm |date=May 27, 2024 }} from the original on April 4, 2016.</ref> | |||
| The term also applies as a classification for generally over-complicated apparatus or ]. It first appeared in '']'' with the definition, "accomplishing by extremely complex roundabout means what actually or seemingly could be done simply." | |||
| The cartoon series that brought him lasting fame was ''The Inventions of Professor Lucifer Gorgonzola Butts, A.K.'', which ran in '']'' from January 26, 1929, to December 26, 1931. In that series, Goldberg drew labeled schematics in the form of patent applications of the comically intricate "inventions" that would later bear his name.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Tumey |first1=Paul C. |title=Screwball!: The Cartoonists Who Made the Funnies Funny |date=2019 |publisher=The Library of American Comics |isbn=978-1684051878 |page=135}}</ref> The character of Professor Butts was based on Rube's professor Frederick Slate at the College of Mining and Engineering at the ], where Rube attended from 1901 to 1903.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.brainstuffshow.com/podcasts/the-man-behind-rube-goldberg-machines.htm|title=The Man Behind Rube Goldberg Machines|date=2018-06-13|work=BrainStuff|access-date=2018-06-13|language=en}}</ref> Frederick Slate gave his engineering students the task of building a scale that could weigh the Earth. The scale was called the “Barodik". To Goldberg, this exemplified a comical combination of seriousness and ridiculousness that would come to serve as an inspiration in his work.<ref>{{cite magazine |last=Beschloss |first=Steven |title=19 July, 2013 |url=https://www.newyorker.com/tech/annals-of-technology/object-of-interest-rube-goldberg-machines |magazine=The New Yorker |location=New York, NY |access-date=January 18, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| In ], such a device would be called a ] contraption, after the ] cartoonist who also drew fantastic comic machinery, in his case tended by bespectacled men in overalls. See also ], who created many actual working machines of this type, such as the Breakfast Machine in the ] '']''. | |||
| From 1938 to 1941, Goldberg drew two weekly strips for the ]: ''Brad and Dad'' (1939–1941) and ''Side Show'' (1938–1941), a continuation of the invention drawings.<ref>, ''Who's Who of American Comic Book Artists, 1928–1999''. Accessed Jan. 5, 2018.</ref> | |||
| In ], they would be called ''Storm P maskiner'' after the Danish cartoonist ]. | |||
| Starting in 1938, Goldberg worked as the editorial cartoonist for the '']''.<ref name=sayej>{{cite news|title=Rube Goldberg: celebrating a remarkable life of cartoons and creations|work=The Guardian|author=Nadja Sayej|date=October 9, 2019|url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2019/oct/09/rube-goldberg-cartoons-pulitzer-queens-museum-new-york|access-date=2020-02-23}}</ref> He won the 1948 ] for a cartoon entitled "]".<ref name=sayej /> He moved to the '']'' in 1949 and worked there until his retirement in 1963.<ref>{{cite news|title=The Alphabet of Satire|work=City Journal|author=Stefan Kanfer|date=Winter 2015|url=https://www.city-journal.org/html/alphabet-satire-13707.html|access-date=2020-02-23}}</ref> In the 1960s, Goldberg began a ] career, primarily creating ].<ref>Rube Goldberg and Emily S. Nathan. Transcript of interview with Rube Goldberg, 1970. Emily Nathan papers, circa 1943-1985. Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution.</ref> | |||
| In ], they are called ?????? ('']''), which means ''] Machine''. | |||
| ==Cultural legacy== | |||
| In ] there is not a particular noun to mean such machines, but a reference akin to Goldberg's machines existed: ] cartoonist ] made up and drew many of those devices for a section in the ] ], allegedly designed by some Professor Franz from ]. | |||
| The popularity of Goldberg's cartoons was such that the term "Goldbergian" was in use in print by 1915,<ref>{{cite book|title=Oxford English Dictionary Online|publisher=Oxford University Press|quote=1915 ''Vanity Fair'' The Goldbergian answer would be ‘No, I paint my nose and eyes red every day to frighten the gypsy-moths away.'}}</ref> and "Rube Goldberg" by 1928.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Atkinson|first1=J. Brooks|title=THE PLAY; "Rain or Shine," Joe Cook|newspaper=The New York Times|date=10 February 1928|page=26|quote=He then introduces the Fuller Construction Orchestra, which is one of those Rube Goldberg crazy mechanical elaborations for passing a modest musical impulse from a buzz.}}</ref> "Rube Goldberg" appeared in the '']'' in 1966 meaning "having a fantastically complicated improvised appearance", or "deviously complex and impractical."<ref name="marzio"/>{{rp|118}} The 1915 usage of "Goldbergian" was in reference to Goldberg's early comic strip ''Foolish Questions'', which he drew from 1909 to 1934, while later use of the terms "Goldbergian", "Rube Goldberg" and "Rube Goldberg machine" refer to the crazy inventions for which he is now best known from his strip ''The Inventions of Professor Lucifer Gorgonzola Butts'', drawn from 1914 to 1964.<ref name="marzio"/>{{rp|305}} | |||
| The corresponding term in the UK was, and still is, "]", after the English illustrator with an equal devotion to odd machinery, also portraying sequential or ] elements. The Danish equivalent was the painter, author and cartoonist ], better known under his pen name Storm P. To this day, an overly complicated and/or useless object is known as a ''Storm P.-machine'' in Denmark. | |||
| The ] cartoonist and storyteller ] created a cartoon character named ] who constantly invented complex machinery. Though it was often built out of unlikely parts, it always performed very well. Felgen stars as the inventor of an extremely powerful but overly complex car ] in the ] animated puppet-film '']'' (]). | |||
| ] | |||
| Goldberg's work was commemorated posthumously in 1995 with the inclusion of ''Rube Goldberg's Inventions'', depicting his 1931 "Self-Operating Napkin" in the ] series of U.S. ]s.<ref>{{cite news| title = American Topics: 20 Classic Comic Strips Get (Postage) Stamp of Approval| url = https://www.nytimes.com/1995/05/08/news/08iht-amtopics_14.html| work = The New York Times | |||
| |date = May 8, 1995| access-date = August 5, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| The ] originated in 1949 as a competition at ] between two fraternities. It ran until 1956, and was revived in 1983 as a university-wide competition. In 1989 it became a national competition, with a high school division added in 1996. Devices must complete a simple task in a minimum of twenty steps and a maximum of seventy-five in the style of Goldberg. The contest is hosted nationwide by Rube Goldberg Inc., a not-for-profit 501(c)(3), founded by Rube's son ], and currently managed by Rube's granddaughter, Jennifer George.<ref name=oconner>{{cite journal |last=O'Connor |first=Brendan |date=2015-04-22 |journal=The Verge |title=A Simple Task: Inside the whimsical but surprisingly dark world of Rube Goldberg machines |url=https://www.theverge.com/2015/4/22/8381963/rube-goldberg-machine-contest-history-ideas |access-date=2015-04-23}}</ref> | |||
| Another related phenomenon is the ] of useful but unusable contraptions called ]. | |||
| In 1998, Justice Scalia remarked in a dissent in a habeas case that "Rube Goldberg would envy the scheme the Court has created."<ref>''Bousley v. United States'', 523 U.S. 614, 635 (1998).</ref> | |||
| ===Rube Goldberg machines on media=== | |||
| ===Film and television=== | |||
| In ]'s "]" series of shorts and features, Wallace's inventions are clearly Rube Goldberg-esque. A recurring joke throughout ''A Grand Day Out'', ''The Wrong Trousers'', ''A Close Shave'' and ''Curse of the Were-Rabbit'' are the absurd contraptions Wallace invents. Good examples are Wallace's "Knit-O-Matic machine" or the device that catapults a dollop of jam onto a piece of toast as it springs out of a pop-up toaster. However, it is more likely to be compared to the works of ], as Rube Golberg is comparatively little known in the UK. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Rube Goldberg wrote the first feature film for the pre-] version of ] called '']'', which was released in 1930 and starred ]. The film featured his machines and included cameos of Rube himself. | |||
| In the 1962 ] movie '']'', an invention to catch monkeys by character Pockets, played by ], is described as a "Rube Goldberg." | |||
| In the cartoon show '']'', the villain called "The Hooded Claw" used, in every episode, a Goldbergian machine in order to kill Penelope, the protagonist. Ironically, the needless complexity of the traps often gave the Ant Hill Mob enough time to save Penelope. | |||
| In the late 1960s and early '70s, educational shows like '']'', '']'' and '']'' routinely showed bits that involved Rube Goldberg devices, including the ''Rube Goldberg Alphabet Contraption'', and the ''What Happens Next Machine''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cog2a3YeDMM | archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211118/cog2a3YeDMM| archive-date=2021-11-18 | url-status=live|title=Sesame Street: What Happens Next Machine|publisher=YouTube |date=August 6, 2010 |access-date=December 8, 2013}}{{cbignore}}<!-- official, not copyvio--></ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B17OvPYM040 | archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211118/B17OvPYM040| archive-date=2021-11-18 | url-status=live|title=Rube Goldberg alphabet contraption, Sesame Street | date=October 10, 2006|publisher=YouTube |access-date=December 8, 2013}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| In the cartoon series '']'', ] often makes huge, complex machinery perform in an overstated and dramatic way to produce simple things such as a glow in the dark nose (it also translates Alien into even more incomprehensible Galactic). | |||
| Various other films and cartoons have included highly complicated machines that perform simple tasks. Among these are '']'', '']'', '']'',<ref></ref> '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', the ], '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', the ], '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']'' | |||
| Rube Goldberg devices frequently appear in the films of ], with or without partner ]. A recurring theme in '']'' is the character Aurore attempting to kill herself using such devices, which backfire and force her to live another day. In '']'', similar machines abound, including a famous set piece in which a little girl's teardrop triggers a chain of events that ultimately causes a shipwreck. The films '']'' and '']'' expand this theme further, moving from the physiological to the metaphysical. As noted by ]'s Sam Wood, fate itself operates as a Rube Goldberg device, "an endless chain of tricky coincidences whose final result is utterly beyond prediction." | |||
| In the '']'' film series the characters often die in Rube Goldberg-esque ways. In the film '']'', the villain Ratigan attempts to kill the film's heroes, Basil of Baker Street and David Q. Dawson, with a Rube Goldberg style device. | |||
| In the film ], as well as its sequels ] and ], the way "]" tracks down and kills its victims resemble deadly Rube Goldberg machines. | |||
| The classic video in this genre was done by the artist duo ] in 1987 with their 30-minute video ''Der Lauf der Dinge'' or ''The Way Things Go.'' | |||
| Honda produced a video in 2003 called "]" using many of the same principles that Fischli and Weiss had done in 1987. | |||
| ] television series makes use of a "ripple effect" Rube Goldberg plot element. | |||
| In 2005, the American alternative rock/indie band ] released a video for their debut single, "An Honest Mistake," which features the band performing the song in the middle of a Rube Goldberg machine. | |||
| ] also use a metaphorical Rube Goldberg machine to �correct� a problem in ]. | |||
| In 1999, an episode of '']'' was titled "]". The episode intertwined characters FBI agents Mulder and Scully, a simple apartment super, Henry Weems (Willie Garson) and an ailing young boy, Ritchie Lupone (]) in a real-life Goldberg device. | |||
| ] | |||
| The iCarly (2007) episode iDon’t Want to Fight, Spencer built a Rube Goldberg Machine to feed his fish. | |||
| In the 1999 book '']'' by ], the main character, a ] named ], uses a Rube Goldberg device involving a length of wire, an electric motor, a ] can, and the ] caused by a ] launch to kill a man with a ]. In a later book in the series, '']'', he uses another such device involving wire, ], two ]s, and a ] to burn someone to death. | |||
| The Suite Life on Deck episode A London Carol, Cody built a Rube Goldberg Machine to help Zack wake up at six a.m. | |||
| In the cartoon series '']'', ] uses a Rube Goldberg machine (one almost exactly like the breakfast machine in ]), that comically shoots Peter with a ] rather than make breakfast. | |||
| The 2010 music video "This Too Shall Pass – RGM Version" by the rock band ] features a machine that, after four minutes of kinetic activity, shoots the band members in the face with paint. "RGM" presumably stands for Rube Goldberg Machine.<ref name="yt">{{cite web | |||
| Rube Goldberg machines are often used by Tom in ]. | |||
| | title = OK Go – This Too Shall Pass – Rube Goldberg Machine version | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | date = March 1, 2010 | |||
| | url = https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qybUFnY7Y8w | |||
| | access-date = March 2, 2010}}<!-- official --></ref> | |||
| 2012 The CBS show '']'' features a machine in its opening sequence. | |||
| The ] short "Hook, Line, and Stinker" ended with the ] character attempting to use a Rube Goldberg machine to capture the ]. Many other ] and ] shorts employ such devices. | |||
| The 2012 Discovery Channel show '']'' pitted two teams against each other to create an elaborate Rube Goldberg machine. It was judged and executive-produced by ] and ], known for hosting the science entertainment series '']''. | |||
| The ] movie '']'' features a Wild West version of a Rube Goldberg device. One of the main characters, ] (]), is transported back in time to the year ], where he works as a blacksmith. When "rescued" by ] (]), he is working on an enormous steam-powered machine. The machine is easily 3 to 4 metres tall, with no immediate clue as to its function. When put into action, it shakes and groans and emits whistles and steam sounds (think of a loud ]) for about 20 seconds. When it falls silent, it produces two small irregularly-shaped bits of ice; it's an ]. Another such machine in the same movie is the Wakeup/ Breakfast Cooking Machine, which at the right time prepars toast and eggs for the Doc. There is another scene in the ] where there is another Rube Goldberg machine that Doc uses to feed his dog Einstein. | |||
| The 2014 web series ''Deadbeat'' on Hulu features an episode titled "The Ghost in the Machine," which features the protagonist Kevin helping the ghost of Rube Goldberg complete a contraption. It will bring his grandchildren together after they make a collection of random items into a machine that ends up systematically injuring two of his grandchildren so they end up in the same hospital and finally meet. | |||
| The ] film '']'' and its three sequels find the main character often employing the use of Goldberg-esque devices to trap and/or slow down the progress of burglars attempting to ransack his home. | |||
| ===Games=== | |||
| ] artists ] and ] produced a film in ] entitled '']'', which documents the motions of a large-scale Goldberg-style ] ]. This installation was then re-worked in the ] television commercial ], which featured a Rube Goldberg machine made from the parts of an ]. | |||
| Both board games and video games have been inspired by Goldberg's creations, such as the '60s board game '']'',<ref>{{cite magazine | last=Kiniry | first=Laura | date=November 13, 2013 | title=7 Unbelievable Rube Goldberg Machines We Love | magazine=] | url=https://www.popularmechanics.com/technology/g1348/7-unbelievable-rube-goldberg-machines-we-love/?slide=1 | access-date=April 10, 2018}}</ref> the 1990s series of '']'' games,<ref>{{cite magazine | last=Moore | first=Bo | date=May 13, 2013 | title=The Incredible Machine is Back, Spiritually | magazine=] | url=https://www.wired.com/2013/05/contraption-maker/ | access-date=April 10, 2018}}</ref> and '']''.<ref>{{cite web | last=Colayco | first=Bob | date=January 20, 2006 | title=Crazy Machines: The Wacky Contraptions Game Review | work=] | url=https://www.gamespot.com/reviews/crazy-machines-the-wacky-contraptions-game-review/1900-6142774/ | access-date=April 10, 2018}}</ref> The ] game '']'' involves searching for the missing pieces to a Rube Goldberg machine to complete the game. | |||
| In 1909 Goldberg invented the "Foolish Questions" game based on his successful cartoon by the same name. The game was published in many versions from 1909 to 1934.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Wolfe|first1=Maynard Frank|title=Rube Goldberg Inventions|date=2000|publisher=Simon & Schuster|isbn=978-0-684-86724-3|page=25}}</ref> | |||
| Tim Fort, a ] from Minnesota, creates chain-reaction gadgets that are reminiscent of both domino tumbling and classical Rube Goldberg gadgets. His gadgets are capable of doing simple tasks such as playing music with water-filled bottles or performing animation with a device resembling a ]. He is currently exploring the idea of making a working digital computer using nothing but kinetic-art techniques. | |||
| ''Rube Works: The Official Rube Goldberg Invention Game'', the first game authorized by The Heirs of Rube Goldberg, was published by Unity Games (the publishing arm of ]) in November 2013.<ref>{{cite web|title=Rube-Goldberg Puzzler "Rube Works" Now Available for iPad and iPhone|url=http://www.gamasutra.com/view/pressreleases/204689/RubeGoldberg_Puzzler_ldquoRube_Works_Now_Available_foriPad_and_iPhone.php|work=]|date= November 13, 2013|access-date=December 27, 2013}}</ref> | |||
| In the ] film '']'', Pee-wee uses a Rube Goldberg device to make his breakfast, and this same device was later featured in '']'' as the main character's science fair entry. Another ] film, '']'', also prominently featured several Rube Goldberg devices, both as performing practical applications (opening the front gate to let someone inside), and springing traps. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| A Rube Goldberg machine is featured in the ] ] '']''; it is used to close up Wilbur Turnblad's joke shop in ]. | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *], Swiss artist who created Rube Goldberg-like sculptures | |||
| *'']'' | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| The music video for ] by ] features a Rube Goldberg machine that fires a flaming arrow that ironically misses its target and leaves the band members in a confused state. | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| In the 7th season ] episode "]" Mulder and Scully meet a man who has a great amount of good luck that manifests as a sort of Rube Goldberg device, with improbable events combining to effect a certain outcome. | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| *{{cite book | last = Wolfe | first = Maynard Frank | title = Rube Goldberg: Inventions | publisher = Simon & Schuster | location = New York | year = 2000 | isbn = 978-0684867243 }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| In an episode of the cartoon series ] the Platypus brothers created a Rube Goldberg device, the final purpose of which was to alert one of the brothers to perform an action that the machine itself could easily have done. | |||
| {{Commons category|Rube Goldberg}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *{{IMDb name|0325298}} | |||
| * at ] | |||
| * by ], 1959 | |||
| * | |||
| {{PulitzerPrize EditorialCartooning 1922–1950}} | |||
| In a sketch of ], Andy creates a Rube Goldberg device to turn on his reading lamp (a meter away from him). The machine incorporated balloons, various toys, bowling balls, and his friend Larry. | |||
| {{Society of Illustrators' Hall of Fame}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| In an episode of ] Peter talks about his breakfast machine that he once bought, it quickly turns to a short clip of a Rube Goldberg device that eventually just shoots Peter in the arm. | |||
| In a short segment in an episode of Animaniacs, titled "Wakko's Gizmo", Wakko creates and sets off an elaborate Rube Goldberg machine in order to flatten a whoopie cushion. | |||
| A children's educational television show named ???????? ("]", or "Pythagorean Switch") features Rube Goldberg machines at the beginning and end of each episode, and at transition points within episodes. The show has been produced by ] since 2002. | |||
| The satirical ] features a comic strip entitled, "]", in which Cold War spies from opposing countries take turns trying to eliminate each other with improbably-designed traps. | |||
| The children's picturebook series ] by ] ] features the a boy who makes Goldberg like machines, with long and convolted steps. These include a pancake machine, dishwashing machine and firewood splitter among others. | |||
| ===Rube Goldberg machines in videogames=== | |||
| In ], ] released the computer game '']'', designed around the Rube Goldberg concept. Three more games were also released in the series, '']'', '']'', and '']''. None of these software titles are still sold: however, they are available via Gametap.com. | |||
| In Germany the video game company PepperGames is still producing and selling games that have the Rube Goldberg concept. Their names are "Crazy Machines" "Crazy Machines - Neue Herausforderungen" and "Crazy Machines - Neues aus dem Labor". | |||
| One popular function of ], A ] for the computer game ], enables you to manipulate objects and characters within a physics based environment. It is one contemporary example where Rube Goldberg machine principle is common. Elaborate traps or machines can be built by the player using a range of in-game objects. The resulting inventions are often recorded and are downloadable from gaming websites. | |||
| In ]'s acid pit scene, a Rube Goldberg style trap is featured. There was also a C64 game from the mid-80s called ''Creative Contraptions'', similar to The Incredible Machine, but much simpler, shorter and easier. | |||
| In 2005 a video game called Trapt used various Goldberg themed elements used to protect a homicidal princess, they usually all lead to a horribly gruesome death through uses of many little nonsensical things | |||
| ===Other references=== | |||
| The ] released a board game called '']'' in ] that was based on Rube Goldberg's ideas (this game is currently made by ]). | |||
| ] contains a working ], which can generally be found on the Pool Deck. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * and of Japanese Rube Golberg machines from Japanese ] children's educational television show produced by ]. | |||
| * commercial. | |||
| * | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Goldberg, Rube}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:43, 5 January 2025
American cartoonist (1883–1970) For the namesake contraption, see Rube Goldberg machine.
| Rube Goldberg | |
|---|---|
 Goldberg in 1929 Goldberg in 1929 | |
| Born | Reuben Garrett Lucius Goldberg (1883-07-04)July 4, 1883 San Francisco, California, U.S. |
| Died | December 7, 1970(1970-12-07) (aged 87) New York City, U.S. |
| Resting place | Mount Pleasant Cemetery in Hawthorne, New York |
| Alma mater | UC Berkeley |
| Occupation(s) | Engineer, sculptor, news reporter, cartoonist |
| Known for | Rube Goldberg machines |
| Spouse |
Irma Seeman (m. 1916) |
| Children | 2, including George W. George |
| Website | rubegoldberg |
Reuben Garrett Lucius Goldberg (July 4, 1883 – December 7, 1970), better known as Rube Goldberg (/ˈruːb/), was an American cartoonist, sculptor, author, engineer, and inventor.
Goldberg is best known for his popular cartoons depicting complicated gadgets performing simple tasks in indirect, convoluted ways. The cartoons led to the expression "Rube Goldberg machines" to describe similar gadgets and processes. Goldberg received many honors in his lifetime, including a Pulitzer Prize for political cartooning in 1948, the National Cartoonists Society's Gold T-Square Award in 1955, and the Banshees' Silver Lady Award in 1959. He was a founding member and first president of the National Cartoonists Society, which hosts the annual Reuben Award, honoring the top cartoonist of the year and named after Goldberg, who won the award in 1967. He is the inspiration for international competitions known as Rube Goldberg Machine Contests, which challenge participants to create a complicated machine to perform a simple task.
Early life and education
Goldberg was born on July 4, 1883, in San Francisco, California, to Jewish parents Max and Hannah (née Cohn) Goldberg. He was the third of seven children, three of whom died as children; older brother Garrett, younger brother Walter, and younger sister Lillian also survived. Goldberg began tracing illustrations when he was four years old, and he took his only drawing lessons with a local sign painter.
Personal life
In 1911, he built the R. L. Goldberg Building at 182–198 Gough Street, San Francisco, for his widowed father to live in, as well as to collect rental income.
Goldberg married Irma Seeman on October 17, 1916. They lived at 98 Central Park West in New York City and had two sons: Thomas and George. During World War II, as each of his sons headed off to college, Goldberg insisted that they change their surname because of antisemitic sentiment toward him stemming from the political nature of his cartoons. Thomas chose the surname George, and his brother, also named George, followed suit. In adopting the same surname, George wanted to keep a sense of family cohesiveness.
Career

Goldberg's father was a San Francisco police and fire commissioner, who encouraged the young Reuben to pursue a career in engineering. Rube graduated from the University of California, Berkeley, in 1904 with a degree in Engineering and was hired by the city of San Francisco as an engineer for the Water and Sewers Department. After six months he resigned his position with the city to join the San Francisco Chronicle where he became a sports cartoonist. The following year, he took a job with the San Francisco Bulletin, where he remained until he moved to New York City in 1907, finding employment as a sports cartoonist with the New York Evening Mail.
Goldberg's first public hit was a comic strip called Foolish Questions, beginning in 1908. The invention cartoons began in 1912. The New York Evening Mail was syndicated to the first newspaper syndicate, the McClure Newspaper Syndicate, giving Goldberg's cartoons a wider distribution, and by 1915 he was earning $25,000 per year and being billed by the paper as America's most popular cartoonist. Arthur Brisbane had offered Goldberg $2,600 per year in 1911 in an unsuccessful attempt to get him to move to William Randolph Hearst's newspaper chain, and in 1915 raised the offer to $50,000 per year. Rather than lose Goldberg to Hearst, the New York Evening Mail matched the salary offer and formed the Evening Mail Syndicate to syndicate Goldberg's cartoons nationally.
In 1916, Goldberg created a series of seven short animated films which focus on humorous aspects of everyday situations in the form of an animated newsreel. The seven films were released on these dates in 1916: May 8, The Boob Weekly; May 22, Leap Year; June 5, The Fatal Pie; Jun 19, From Kitchen Mechanic to Movie Star; July 3, Nutty News; July 17, Home Sweet Home; July 31, Losing Weight.
Goldberg was syndicated by the McNaught Syndicate from 1922 until 1934.
A prolific artist, it has been estimated that Goldberg created 50,000 cartoons during his lifetime. Some of these cartoons include Mike and Ike (They Look Alike), Boob McNutt, Foolish Questions, What Are You Kicking About, Telephonies, Lala Palooza, The Weekly Meeting of the Tuesday Women's Club, and the uncharacteristically serious soap-opera strip, Doc Wright, which ran for 10 months beginning January 29, 1933.
The cartoon series that brought him lasting fame was The Inventions of Professor Lucifer Gorgonzola Butts, A.K., which ran in Collier's Weekly from January 26, 1929, to December 26, 1931. In that series, Goldberg drew labeled schematics in the form of patent applications of the comically intricate "inventions" that would later bear his name. The character of Professor Butts was based on Rube's professor Frederick Slate at the College of Mining and Engineering at the University of California, where Rube attended from 1901 to 1903. Frederick Slate gave his engineering students the task of building a scale that could weigh the Earth. The scale was called the “Barodik". To Goldberg, this exemplified a comical combination of seriousness and ridiculousness that would come to serve as an inspiration in his work.
From 1938 to 1941, Goldberg drew two weekly strips for the Register and Tribune Syndicate: Brad and Dad (1939–1941) and Side Show (1938–1941), a continuation of the invention drawings.
Starting in 1938, Goldberg worked as the editorial cartoonist for the New York Sun. He won the 1948 Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning for a cartoon entitled "Peace Today". He moved to the New York Journal-American in 1949 and worked there until his retirement in 1963. In the 1960s, Goldberg began a sculpture career, primarily creating busts.
Cultural legacy
The popularity of Goldberg's cartoons was such that the term "Goldbergian" was in use in print by 1915, and "Rube Goldberg" by 1928. "Rube Goldberg" appeared in the Random House Dictionary of the English Language in 1966 meaning "having a fantastically complicated improvised appearance", or "deviously complex and impractical." The 1915 usage of "Goldbergian" was in reference to Goldberg's early comic strip Foolish Questions, which he drew from 1909 to 1934, while later use of the terms "Goldbergian", "Rube Goldberg" and "Rube Goldberg machine" refer to the crazy inventions for which he is now best known from his strip The Inventions of Professor Lucifer Gorgonzola Butts, drawn from 1914 to 1964.
The corresponding term in the UK was, and still is, "Heath Robinson", after the English illustrator with an equal devotion to odd machinery, also portraying sequential or chain reaction elements. The Danish equivalent was the painter, author and cartoonist Robert Storm Petersen, better known under his pen name Storm P. To this day, an overly complicated and/or useless object is known as a Storm P.-machine in Denmark.
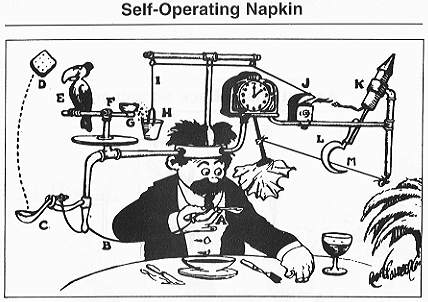
Goldberg's work was commemorated posthumously in 1995 with the inclusion of Rube Goldberg's Inventions, depicting his 1931 "Self-Operating Napkin" in the Comic Strip Classics series of U.S. postage stamps.
The Rube Goldberg Machine Contest originated in 1949 as a competition at Purdue University between two fraternities. It ran until 1956, and was revived in 1983 as a university-wide competition. In 1989 it became a national competition, with a high school division added in 1996. Devices must complete a simple task in a minimum of twenty steps and a maximum of seventy-five in the style of Goldberg. The contest is hosted nationwide by Rube Goldberg Inc., a not-for-profit 501(c)(3), founded by Rube's son George W. George, and currently managed by Rube's granddaughter, Jennifer George.
In 1998, Justice Scalia remarked in a dissent in a habeas case that "Rube Goldberg would envy the scheme the Court has created."
Film and television


Rube Goldberg wrote the first feature film for the pre-Curly Howard version of The Three Stooges called Soup to Nuts, which was released in 1930 and starred Ted Healy. The film featured his machines and included cameos of Rube himself.
In the 1962 John Wayne movie Hatari!, an invention to catch monkeys by character Pockets, played by Red Buttons, is described as a "Rube Goldberg."
In the late 1960s and early '70s, educational shows like Sesame Street, Vision On and The Electric Company routinely showed bits that involved Rube Goldberg devices, including the Rube Goldberg Alphabet Contraption, and the What Happens Next Machine.
Various other films and cartoons have included highly complicated machines that perform simple tasks. Among these are Flåklypa Grand Prix, Looney Tunes, Tom and Jerry, Wallace and Gromit, Pee-wee's Big Adventure, The Way Things Go, Edward Scissorhands, Back to the Future, Honey, I Shrunk the Kids, The Goonies, Gremlins, the Saw film series, Chitty Chitty Bang Bang, The Cat from Outer Space, Malcolm, Hotel for Dogs, the Home Alone film series, Family Guy, American Dad!, Casper, and Waiting...
In the Final Destination film series the characters often die in Rube Goldberg-esque ways. In the film The Great Mouse Detective, the villain Ratigan attempts to kill the film's heroes, Basil of Baker Street and David Q. Dawson, with a Rube Goldberg style device. The classic video in this genre was done by the artist duo Peter Fischli & David Weiss in 1987 with their 30-minute video Der Lauf der Dinge or The Way Things Go.
Honda produced a video in 2003 called "The Cog" using many of the same principles that Fischli and Weiss had done in 1987.
In 2005, the American alternative rock/indie band The Bravery released a video for their debut single, "An Honest Mistake," which features the band performing the song in the middle of a Rube Goldberg machine.
In 1999, an episode of The X-Files was titled "The Goldberg Variation". The episode intertwined characters FBI agents Mulder and Scully, a simple apartment super, Henry Weems (Willie Garson) and an ailing young boy, Ritchie Lupone (Shia LaBeouf) in a real-life Goldberg device.
The iCarly (2007) episode iDon’t Want to Fight, Spencer built a Rube Goldberg Machine to feed his fish.
The Suite Life on Deck episode A London Carol, Cody built a Rube Goldberg Machine to help Zack wake up at six a.m.
The 2010 music video "This Too Shall Pass – RGM Version" by the rock band OK Go features a machine that, after four minutes of kinetic activity, shoots the band members in the face with paint. "RGM" presumably stands for Rube Goldberg Machine.
2012 The CBS show Elementary features a machine in its opening sequence.
The 2012 Discovery Channel show Unchained Reaction pitted two teams against each other to create an elaborate Rube Goldberg machine. It was judged and executive-produced by Adam Savage and Jamie Hyneman, known for hosting the science entertainment series MythBusters.
The 2014 web series Deadbeat on Hulu features an episode titled "The Ghost in the Machine," which features the protagonist Kevin helping the ghost of Rube Goldberg complete a contraption. It will bring his grandchildren together after they make a collection of random items into a machine that ends up systematically injuring two of his grandchildren so they end up in the same hospital and finally meet.
Games
Both board games and video games have been inspired by Goldberg's creations, such as the '60s board game Mouse Trap, the 1990s series of The Incredible Machine games, and Crazy Machines. The Humongous Entertainment game Freddi Fish 2: The Case of the Haunted Schoolhouse involves searching for the missing pieces to a Rube Goldberg machine to complete the game.
In 1909 Goldberg invented the "Foolish Questions" game based on his successful cartoon by the same name. The game was published in many versions from 1909 to 1934.
Rube Works: The Official Rube Goldberg Invention Game, the first game authorized by The Heirs of Rube Goldberg, was published by Unity Games (the publishing arm of Unity Technologies) in November 2013.
See also
- Chindōgu
- Deathtrap (plot device)
- Domino effect
- Domino show
- Frederick Rowland Emett
- Jean Tinguely, Swiss artist who created Rube Goldberg-like sculptures
- Mickey One
- PythagoraSwitch
- W. Heath Robinson
References
- ^ "Rube Goldberg Awards Achieved, The Group, History and Significance of the awards". www.rube-goldberg.com. Retrieved August 6, 2020.
- ^ Goldberg, Reuben. "Members / In Memoriam / Rube Goldberg". reuben.org. National Cartoonists Society. Archived from the original (JPEG) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved August 5, 2009.
- "The History of the NCS" Archived December 23, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. reuben.org. National Cartoonists Society.
- "NCS AWARDS The Reuben Award". National Cartoonists Society. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- ^ Contemporary Authors: First revision, Volumes 5–8. Gale Research Company. 1969. p. 448.
- Contemporary Authors: First revision. Gale Research Company. 1969.
- ^ Marzio, Peter C. (1973). Rube Goldberg: His Life and Work. Harper and Row. ISBN 978-0060128302.
- "San Francisco Landmark #268: Goldberg Building". noehill.com. Retrieved November 5, 2022.
- Peterson, Alison J. (November 20, 2007). "George W. George, at 87; writer, producer of films and Broadway plays". New York Times News Service. Boston Globe. Archived from the original on December 5, 2008. Retrieved May 24, 2024.
- Contemporary Authors: First revision. Gale Research Company. 1969.
- Contemporary Authors: First revision. Gale Research Company. 1969.
- ^ at Don Markstein's Toonopedia. Archived from the original on July 30, 2016.
- Sheets, Hilarie M. (April 8, 2020). "A Rube Goldberg Hand-Washing Contraption? The Race Is On". The New York Times. The New York Times. Retrieved January 1, 2021.
- "Goldberg is Again Star of the Film: Artist-Humorist of The Times Seen in New Set of Animated Cartoons". The Washington Times. July 24, 2016. p. 12. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
- Photoplay Editor (May 5, 1916). "Pathé Boob Weekly News from Nowhere: Goldberg Does Some Clever Satiric Cartoons on News Pictures". Philadelphia Evening Ledger. p. 10. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
{{cite news}}:|last=has generic name (help) - George, Jennifer (November 12, 2013). The Art of Rube Goldberg: (A) Inventive (B) Cartoon (C) Genius. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 978-1-419-70852-7. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
- Wilson, Emily (May 1, 2018). "The Story Behind Rube Goldberg's Complicated Contraptions". Smithsonian Magazine. Joseph J. Bonsignore. Retrieved January 10, 2021.
- "Foolish Questions hi". The San Francisco Call. December 2, 1910. p. 13.
- "What Are You Kicking About". The San Francisco Call. June 1, 1910. p. 13.
- "Telephonies". The San Francisco Call. July 12, 1911. p. 10.
- Doc Wright at Don Markstein's Toonopedia. Archived May 27, 2024, at archive.today from the original on April 4, 2016.
- Tumey, Paul C. (2019). Screwball!: The Cartoonists Who Made the Funnies Funny. The Library of American Comics. p. 135. ISBN 978-1684051878.
- "The Man Behind Rube Goldberg Machines". BrainStuff. June 13, 2018. Retrieved June 13, 2018.
- Beschloss, Steven. "19 July, 2013". The New Yorker. New York, NY. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
- Goldberg profile, Who's Who of American Comic Book Artists, 1928–1999. Accessed Jan. 5, 2018.
- ^ Nadja Sayej (October 9, 2019). "Rube Goldberg: celebrating a remarkable life of cartoons and creations". The Guardian. Retrieved February 23, 2020.
- Stefan Kanfer (Winter 2015). "The Alphabet of Satire". City Journal. Retrieved February 23, 2020.
- Rube Goldberg and Emily S. Nathan. Transcript of interview with Rube Goldberg, 1970. Emily Nathan papers, circa 1943-1985. Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution.
- Oxford English Dictionary Online. Oxford University Press.
1915 Vanity Fair The Goldbergian answer would be 'No, I paint my nose and eyes red every day to frighten the gypsy-moths away.'
- Atkinson, J. Brooks (February 10, 1928). "THE PLAY; "Rain or Shine," Joe Cook". The New York Times. p. 26.
He then introduces the Fuller Construction Orchestra, which is one of those Rube Goldberg crazy mechanical elaborations for passing a modest musical impulse from a buzz.
- "American Topics: 20 Classic Comic Strips Get (Postage) Stamp of Approval". The New York Times. May 8, 1995. Retrieved August 5, 2009.
- O'Connor, Brendan (April 22, 2015). "A Simple Task: Inside the whimsical but surprisingly dark world of Rube Goldberg machines". The Verge. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- Bousley v. United States, 523 U.S. 614, 635 (1998).
- "Sesame Street: What Happens Next Machine". YouTube. August 6, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2021. Retrieved December 8, 2013.
- "Rube Goldberg alphabet contraption, Sesame Street". YouTube. October 10, 2006. Archived from the original on November 18, 2021. Retrieved December 8, 2013.
- "OK Go – This Too Shall Pass – Rube Goldberg Machine version". YouTube. March 1, 2010. Retrieved March 2, 2010.
- Kiniry, Laura (November 13, 2013). "7 Unbelievable Rube Goldberg Machines We Love". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- Moore, Bo (May 13, 2013). "The Incredible Machine is Back, Spiritually". Wired. Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- Colayco, Bob (January 20, 2006). "Crazy Machines: The Wacky Contraptions Game Review". GameSpot. Retrieved April 10, 2018.
- Wolfe, Maynard Frank (2000). Rube Goldberg Inventions. Simon & Schuster. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-684-86724-3.
- "Rube-Goldberg Puzzler "Rube Works" Now Available for iPad and iPhone". Gamasutra. November 13, 2013. Retrieved December 27, 2013.
- Wolfe, Maynard Frank (2000). Rube Goldberg: Inventions. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0684867243.
External links
- Official Rube Goldberg website
- Toonopedia entry
- Smithsonian's Archives of American Art: Oral History Interview with Rube Goldberg, 1970
- NCS Awards
- Rube Goldberg at IMDb
- Guide to the Rube Goldberg Papers at The Bancroft Library
- Rube Goldberg interviewed by Edward Murrow, 1959
- Rube Works: The Official Rube Goldberg Invention Game
| Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning (1922–1950) | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Society of Illustrators' Hall of Fame | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Rube Goldberg
- 1883 births
- 1970 deaths
- American editorial cartoonists
- Engineers from California
- UC Berkeley College of Engineering alumni
- American humorists
- American male journalists
- Journalists from California
- Artists from New York City
- Writers from San Francisco
- Pulitzer Prize for Editorial Cartooning winners
- Reuben Award winners
- Jewish caricaturists
- Jewish American illustrators
- 20th-century American illustrators
- Jewish American journalists
- Jewish engineers
- Jewish humorists
- Lowell High School (San Francisco) alumni
- Artists from San Francisco
- Engineers from New York (state)
- Members of The Lambs Club