| Revision as of 13:38, 6 August 2004 editLord Emsworth (talk | contribs)28,672 edits →Development← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:24, 19 January 2025 edit undoRMCD bot (talk | contribs)Bots, Template editors1,006,496 edits Removing notice of move discussionTag: Manual revert | ||
| (949 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Representative of the Indian monarch}} | |||
| The '''Governor-General of India''' was the head of the British administration in ]. The office was created in ], with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over Fort William, but supervised other ] officials in India. Complete authority over all of British India was granted in ], and the official became known as the Governor-General of India. In ], India came under the direct control of the ], and the Governor-General acted as the Sovereign's representative. To reflect his role as Crown Representative, the term "Viceroy" was informally applied to him; the title was abandoned when India became independent in ]. The office of Governor-General continued to exist until India adopted a constitution in ]. | |||
| {{redirect|Viceroy of India|viceroys and governors of Portuguese India|List of governors of Portuguese India}} | |||
| {{For|a list of the office holders during the British Raj|List of governors-general of India}} | |||
| {{for multi|previous similar titles from 1680–1758|List of governors of Bengal Presidency}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2022}} | |||
| {{Use Indian English|date=July 2016}} | |||
| {{Infobox official post | |||
| | post = Viceroy and Governor-General | |||
| | body = India | |||
| | insignia = ] | |||
| | insigniacaption = Standard during the ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Flag of the Governor General of India |url=https://www.rmg.co.uk/collections/objects/rmgc-object-271 |archive-url=http://web.archive.org/web/20220724045920/https://www.rmg.co.uk/collections/objects/rmgc-object-271 |archive-date=July 24, 2022 |access-date=2024-09-07 |website=www.rmg.co.uk |publisher=] |place=]}}</ref> | |||
| | flag = ] | |||
| | flagcaption = Standard during the ]<ref>{{Cite book |last=Thapliyal |first=Uma Prasad |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gWnqZwEACAAJ |title=Military Flags of India: From the Earliest Times |date=2011 |publisher=B.R. Publishing Corporation |location=Delhi |isbn=978-81-7646-742-1 |pages=110 |language=en |quote=From 15 August 1947 to 26 January 1950, the flag of the Governor-General of India was dark blue with the Lion and Crown crest in the center and INDIA in golden letters below}}</ref> | |||
| | style = ] | |||
| | residence = {{plainlist| | |||
| *] (1858–1931) | |||
| *] (1931–1950) | |||
| *] (1888–1947)}} | |||
| | appointer = {{unbulleted list |{{nowrap|] (1774–1858)}} | |||
| |] (1858–1876) | |||
| |] (1876–1947) | |||
| |] (1947–1950)}} | |||
| | appointer_qualified = | |||
| | termlength = ] (''de jure'')<br>Five years{{clarify|text=, renewable|date=June 2024}} (''de facto'') | |||
| | superseded_by = {{plainlist| | |||
| *] (in territory that became ]) | |||
| *] ] (after ] became a ] by adopting ])}} | |||
| | formation = 20 October 1773 (])<br/>22 April 1834 (]) | |||
| | first = ] (])<br/>] (]) | |||
| | last = {{plainlist| | |||
| *] (21 February 1947 — 15 August 1947; as the ''Viceroy of India'') | |||
| *] (21 June 1948 — 26 January 1950; as the ''Governor-General of Dominion of India'')}} | |||
| | abolished = {{start date and years ago|1950|01|26|df=y|p=y}} | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''Governor-General of India''' (1833 to 1950, from 1858 to 1947 the '''Viceroy and Governor-General of India''', commonly shortened to '''Viceroy of India''') was the representative of the ] in their capacity as the ] and after ] in 1947, the representative of the ]. The office was created in 1773, with the title of ] of the ]. The officer had direct control only over his presidency but supervised other ] officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the governor-general of India. | |||
| Until 1858, the Governor-General was selected by the Court of Directors, to whom he was responsible. Thereafter, he was appointed by the Sovereign on the advice of the British government; the ], a member of the ], was responsible for instructing him on the exercise of his powers. After 1947, the Sovereign continued to appoint the Governor-General, but did so on the advice of the Indian government, rather than the British government. | |||
| In 1858, because of the ] the previous year, the territories and assets of the East India Company came under the direct control of the ]; as a consequence, ] was succeeded by the ]. The governor-general (now also the ]) headed the central government of India, which administered the provinces of ], including ], ], ], ], the ], and others.<ref>The term ] is mistakenly used to mean the same as the British Indian Empire, which included both the provinces and the ].</ref> However, much of India was not ruled directly by the British Government; outside the provinces of British India, there were hundreds of nominally independent ] or "native states", whose relationship was not with the British Government or the United Kingdom, but rather one of ] directly with the British monarch as sovereign successor to the ]. From 1858, to reflect the governor-general's new additional role as the monarch's representative in response to the fealty relationships vis the princely states, the additional title of viceroy was granted, such that the new office was entitled "Viceroy and Governor-General of India". This was usually shortened to "Viceroy of India". | |||
| Governors-General served five-year terms, but could be removed earlier. After the conclusion of a term, a provisional Governor-General was sometimes appointed until a new holder of the office could be chosen. Provisional Governors-General were often chosen from amongst the provincial Governors. | |||
| The title of viceroy was abandoned when British India was ] into the two independent ]s of ] and ], but the office of governor-general continued to exist in each country separately until they adopted republican constitutions in 1950 and 1956, respectively. | |||
| ==Development== | |||
| Much of India was originally governed by the East India Company, which nominally acted as the agent of the ]. In 1773, motivated by corruption in the Company, the British government assumed partial control over the governance of India with the passage of the Regulating Act. A Governor-General and Council were appointed to rule over the Presidency of Fort William in ]. The first Governor-General and Council were named in the Act; their successors were to be elected by the East India Company's Court of Directors. The Act provided for a five-year term for the Governor-General and Council, but the Sovereign had the power to remove any of them. | |||
| Until 1858, the governor-general was selected by the Court of Directors of the East India Company, to whom he was responsible. Thereafter, he was appointed by the sovereign on the advice of the British Government; the ], a member of the ], was responsible for instructing him on the exercise of their powers. After 1947, the sovereign continued to appoint the governor-general but thereafter did so on the advice of the government of the newly independent Dominion of India. | |||
| The Charter Act ] replaced the Governor-General and Council of Fort William with the Governor-General and Council of India. The power to elect the Governor-General was retained by the Court of Directors, but the choice became subject to the Sovereign's approval. | |||
| The governor-general served ], though the practice was to have them serve five-year terms. A governor-general could have their commission rescinded; and if one was removed, or left, a provisional governor-general was sometimes appointed until a new holder of the office could be chosen. The first governor-general in India (of Bengal) was ], the first official governor-general of British India was ], and the first governor-general of the Dominion of India was ]. | |||
| After the ], the East India Company was abolished, and India put under the direct control of the Sovereign. The Government of India Act 1858 vested the power to appoint the Governor-General in the Sovereign. The Governor-General, in turn, had the power to appoint all Lieutenant-Governors in India, subject to the Sovereign's approval. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| India and Pakistan acquired independence in 1947, but Governors-General continued to be appointed over each nation until permanent constitutions could be written. ] remained Governor-General of India for some time after independence, but the two nations were otherwise headed by native Governors-General. India became a republic in 1950; Pakistan became one in ]. | |||
| ], the first governor-general of ] from 1773 to 1785.]] | |||
| ==Role in government== | |||
| ], the first governor general of India from 1834 – 1835]] | |||
| The Governor-General originally had power only over the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal. The Regulating Act, however, granted them additional powers relating to foreign affairs and defence. The other Presidencies of the East India Company (], ] and ]) were neither allowed to declare war on nor make peace with an Indian prince without recieving the prior approval of the Governor-General and Council of Fort William. | |||
| Many parts of the ] were governed by the British ] (founded in 1600), which nominally acted as the agent of the ]. Early British administrators were ] of ]. In 1773, motivated by corruption in the company, the British government assumed partial control over the governance of India with the passage of the ]. A governor-general and ] were appointed to rule over the Presidency of ] in ]. The first governor-general and Council were named in the Act. | |||
| The ] replaced the governor-general and Council of Fort William with the governor-general and Council of India. The power to elect the governor-general was retained by the Court of Directors, but the choice became subject to the sovereign's approval via the ]. | |||
| The powers of the Governor-General in respect of foreign affairs were increased by the India Act 1784. The Act provided that the other Governors under the East India Company could not declare war, make peace or conclude a treaty with an Indian prince unless expressly directed to do so by the Governor-General, or by the Company's Court of Directors. | |||
| After the ], the British East India Company's territories in India were put under the direct control of the sovereign. The ] vested the power to appoint the governor-general in the sovereign. The governor-general, in turn, had the power to appoint all lieutenant governors in India, subject to the sovereign's approval. | |||
| While the Governor-General thus became the controller of foreign policy in India, he was not the explicit head of British India. This status only came with the Charter Act 1833, which granted him "superintendence, direction and control of the whole civil and military Government" of all of British India. The Act also granted legislative powers to the Governor-General and Council. | |||
| India and Pakistan acquired independence in 1947, but governors-general continued to be appointed over each nation until republican constitutions were written. ], remained governor-general of India for ten months after independence, but the two nations were otherwise headed by native governors-general. India became a secular republic in 1950; Pakistan became an Islamic one in 1956. | |||
| After 1858, the Governor-General functioned as the chief administrator of India and as the Sovereign's representative. India was divided into numerous provinces, each under the head of a Governor, Lieutenant-Governor or Chief Commissioner. Governors were appointed by the British government, to whom they were directly responsible; Lieutenant-Governors and Chief Commissioners, however, were appointed by and were subordinate to the Governor-General. The Governor-General also oversaw the most powerful ]: the Nizam of ], the Maharaja of ], the Maharaja of ] and the Maharaja Gaekwar of ]. The remaining princely rulers were overseen either by the ] Agency and Central India Agency (which were headed by representatives of the Governor-General), or by provincial authorities. | |||
| ==Functions== | |||
| Once India acquired independence, however, the Governor-General's role became entirely ceremonial, with actual power being held by elected Indian politicians. After the nation became a republic, the ] continued to perform the same ceremonial functions. | |||
| ] in his robes as viceroy of India, a post he held from 1899 to 1905.]] | |||
| ] addressing the ] as Crown Representative in the 1940s]] | |||
| The governor-general originally had power only over the ]. The Regulating Act, however, granted the governor-general additional powers relating to foreign affairs and defence. The other presidencies of the East India Company (], ] and ]) were not allowed to declare war on or make peace with an Indian prince without receiving the prior approval of the governor-general and Council of Fort William.{{Citation needed|date=April 2009}} | |||
| The powers of the governor-general, in respect of foreign affairs, were increased by the ]. The act provided that the other governors under the East India Company could not declare war, make peace or conclude a treaty with an Indian prince unless expressly directed to do so by the governor-general or by the company's Court of Directors. | |||
| While the governor-general thus became the controller of foreign policy in India, he was not the explicit head of British India. That status came only with the ], which granted him "superintendence, direction and control of the whole civil and military Government" of all of British India. The act also granted legislative powers to the governor-general and council. | |||
| In 1835, ] became the first governor general of India.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Lord William Bentinck {{!}} British government official |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Lord-William-Bentinck |access-date=2019-05-30 |website=Encyclopædia Britannica |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| After 1858, the governor-general (now usually known as the viceroy) functioned as the chief administrator of India and as the sovereign's representative. India was divided into numerous ], each under the head of a governor, lieutenant governor or chief commissioner or ]. Governors were appointed by the ], to whom they were directly responsible; lieutenant governors, chief commissioners, and administrators, however, were appointed by and were subordinate to the viceroy. The viceroy also oversaw the most powerful ]: the ], the ], the Maharaja (]) of ], the ] of ] and the ] (Gaekwar) Maharaja of ]. The remaining princely rulers were overseen either by the ] and ], which were headed by representatives of the viceroy or by provincial authorities. | |||
| The ] was an institution established in 1920 by a royal proclamation of King-Emperor ] to provide a forum in which the princely rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. The chamber usually met only once a year, with the viceroy presiding, but it appointed a standing committee, which met more often. | |||
| Upon independence in August 1947, the title of viceroy was abolished. The representative of ], King ], became known once again as the governor-general. In 1948, ] became the only Indian governor-general. The governor-general's role was almost entirely ceremonial, with power being exercised on a day-to-day basis by the Indian cabinet. After the nation became a republic in 1950, the ] continued to perform the same functions. | |||
| ==Council== | ==Council== | ||
| {{Main|Council of India|Viceroy's Executive Council}} | |||
| The Governor-General has always been advised by a Council on the exercise of his legislative and executive powers. The Governor-General, whilst exercising many of functions, was referred to as the "Governor-General in Council." | |||
| ] in ], built in 1888, was the summer residence of the viceroy of India]] | |||
| The governor-general was always advised by a Council on the exercise of his legislative and executive powers. The governor-general, while exercising many functions, was referred to as the "Governor-General in Council." | |||
| The ] provided for the election of four counsellors by the East India Company's Court of Directors. The governor-general was to be assisted by an executive council of four members and was given a casting vote but no veto. The decision of the council was binding on the governor-general. | |||
| In 1784, the council was reduced to three members; the governor-general continued to have both an ordinary vote and a casting vote. In 1786, the power of the governor-general was increased even further, as Council decisions ceased to be binding. | |||
| The Charter Act 1833 made further changes to the structure of the council. The Act was the first law to distinguish between the executive and legislative responsibilities of the governor-general. As provided under the Act, there were to be four members of the Council appointed by the Court of Directors. The first three members were permitted to participate on all occasions, but the fourth member was only allowed to sit and vote when legislation was being debated. | |||
| In 1858, the Court of Directors ceased to have the power to appoint members of the council. Instead, the one member who had a vote only on legislative questions came to be appointed by the sovereign, and the other three members by the ]. | |||
| The ] made several changes to the council's composition. Three members were to be appointed by the Secretary of State for India, and two by the Sovereign. The power to appoint all five members passed to the Crown in 1869. The viceroy was empowered to appoint an additional 'six to twelve' members (changed to 'ten to sixteen' in 1892, and to 'sixty' in 1909). The five individuals appointed by the sovereign or the Indian secretary headed the executive departments, while those appointed by the viceroy debated and voted on legislation. | |||
| In 1919, an Indian legislature, consisting of a Council of State and a Legislative Assembly, took over the legislative functions of the Viceroy's Council. The viceroy nonetheless retained significant power over legislation. He could authorise the expenditure of money without the Legislature's consent for "ecclesiastical, political defence" purposes, and for any purpose during "emergencies." He was permitted to veto, or even stop debate on, any bill. If he recommended the passage of a bill, but only one chamber cooperated, he could declare the bill passed over the objections of the other chamber. The legislature had no authority over foreign affairs and defence. The president of the Council of State was appointed by the viceroy; the Legislative Assembly elected its president, but the election required the viceroy's approval. | |||
| ==Style and title== | |||
| Until 1833, the title of the position was "governor-general of the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal". The ] converted the title into "governor-general of India", effective from 22 April 1834.<ref name=Keith>, Keith, Arthur Berriedale, ''Speeches & Documents on Indian Policy, 1750–1921'', see section 41 of the Act</ref> The title "viceroy and governor-general" was first used in the queen's proclamation appointing Viscount Canning in 1858.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://en.wikisource.org/Queen_Victoria%27s_Proclamation|title=Queen Victoria's Proclamation}}</ref> It was never conferred by an act of parliament but was used in ] and in the statutes of knightly orders. In usage, "viceroy" is employed where the governor-general's position as the monarch's representative is in view.<ref>H. Verney Lovett, "The Indian Governments, 1858–1918", ''The Cambridge History of the British Empire, Volume V: The Indian Empire, 1858–1918'' (Cambridge University Press, 1932), p. 226.</ref> The viceregal title was not used when the sovereign was present in India. It was meant to indicate new responsibilities, especially ritualistic ones, but it conferred no new statutory authority. The governor-general regularly used the title in communications with the ], but all legislation was made only in the name of the Governor-General-in-Council (or the Government of India).<ref>Arnold P. Kaminsky, ''The India Office, 1880–1910'' (Greenwood Press, 1986), p. 126.</ref> | |||
| The governor-general was styled ''Excellency'' and enjoyed precedence over all other government officials in India. He was referred to as 'His Excellency' and addressed as 'Your Excellency'. From 1858 to 1947, the governor-general was known as the viceroy of India (from the French ''roi'', meaning 'king'), and wives of Viceroys were known as Vicereines (from the French ''reine'', meaning 'queen'). The Vicereine was referred to as 'Her Excellency' and was also addressed as 'Your Excellency'. Neither title was employed while the Sovereign was in India. However, the only British sovereign to visit India during the period of British rule was ], who attended the ] in 1911 with his wife, ].{{Citation needed|date=October 2009}} | |||
| The Regulating Act 1773 provided for the election of four counsellors by the East India Company's Court of Directors. The Governor-General had a vote along with the counsellors, but he also had an additional vote to break ties. The decision of the Council was binding on the Governor-General. | |||
| When the ] was founded in 1861, the viceroy was made its grand master ''ex officio''. The viceroy was also made the ''ex officio'' grand master of the ] upon its foundation in 1877. | |||
| In 1784, the Council was reduced to three members; the Governor-General continued to have both an ordinary vote and a casting vote. In ], the power of the Governor-General was increased even further, as Council decisions ceased to be binding. | |||
| Most governors-general and viceroys were ]. Frequently, a viceroy who was already a peer would be granted a peerage of higher rank, as with the granting of a ] to ] and an ] and later a marquessate to ]. Of those viceroys who were not peers, ] was a ], and ] was entitled to the ] ']' because he was the son of a ]. Only the first and last governors-general{{spaced ndash}}] and ]{{spaced ndash}}as well as some provisional governors-general, had no honorific titles at all. | |||
| The Charter Act 1833 made further changes to the structure of the Council. The Act was the first law to distinguish between the executive and legislative responsibilities of the Governor-General. As provided under the Act, there were to be four members of the Council elected by the Court of Directors. The first three members were permitted to participate on all occasions, but the fourth member was only allowed to sit and vote when legislation was being debated. | |||
| ==Flag and insignia== | |||
| In 1858, the Court of Directors ceased to have the power to elect members of the Council. Instead, the one member who had a vote only on legislative questions came to be appointed by the Sovereign, and the other three members by the Secretary of State for India. | |||
| {{Main|Star of India (flag)}} | |||
| From around 1885, the viceroy of India was allowed to fly a ] augmented in the centre with the 'Star of India' surmounted by a crown. This flag was not the viceroy's personal flag; it was also used by governors, lieutenant governors, chief commissioners and other British officers in India. When at sea, only the viceroy flew the flag from the mainmast, while other officials flew it from the foremast. | |||
| The Indian Councils Act ] made several changes to the Council's composition. Three members were to be appointed by the Secretary of State for India, and two by the Sovereign. (The power to appoint all five members passed to the Crown in ].) The Governor-General was empowered to appoint an additional six to twelve members (changed to ten to sixteen in ], and to sixty in ]). The five individuals appointed by the Indian Secretary or Sovereign headed the executive departments, while those appointed by the Governor-General debated and voted on legislation. | |||
| From 1947 to 1950, the governor-general of India used a dark blue flag bearing the royal crest (a lion standing on the Crown), beneath which was the word 'India' in gold ]. The same design is still used by many other Commonwealth Realm governors-general. This last flag was the personal flag of the governor-general only. | |||
| In ], an Indian Legislature, consisting of a Council of State and a Legislative Assembly, took over the legislative functions of the Governor-General's Council. The Governor-General nonetheless retained significant power over legislation. He could authorise the expenditure of money without the Legislature's consent for "ecclesiastical, political defence" purposes, and for any purpose during "emergencies." He was permitted to veto, or even stop debate on, any bill. If he recommended the passage of a bill, but only one chamber co-operated, he could declare the bill passed over the objections of the other chamber. The Legislature had no authority over foreign affairs and defence. The President of the Council of State was appointed by the Governor-General; the Legislative Assembly elected its President, but the election required the Governor-General's approval. | |||
| <gallery class="center"> | |||
| ==Titles== | |||
| File:Badge of the Viceroy of India (1876-1904).svg|Badge of the viceroy of India (1876–1904) depicted with St. Edward's Crown | |||
| The Governor-General used the style ''Excellency'' and enjoyed precedence over all other government officials in India. From 1858 to 1947, Governors-General were colloquially known as "Viceroys" (from the ] ''roi'', meaning "king"). Wives of Viceroys were known as Vicereines (from the French ''reine'', meaning "queen"). Neither title was employed whilst the Sovereign was in India. These titles, though frequently applied, were never officially sanctioned by the British government. | |||
| File:Crest of the Viceroy of India.svg|Badge of the viceroy and governor-general (1904–1947) depicted with Tudor Crown | |||
| File:Flag of the Governor-General of India (1885–1947).svg|Standard of the viceroy and governor-general (1885–1947) | |||
| File:Flag of the Governor-General of India (1947-1950).svg|Standard of the governor-general (1947–50) | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Residence== | |||
| When the ] was founded in ], the Governor-General was made its Grand Master ''ex officio''. The Governor-General was also made the ''ex officio'' Grand Master of the ] upon its foundation in ]. | |||
| ] served as the Governor-General's residence during most of the nineteenth century.]] | |||
| Most Governors-General were ]. Of those that were not, ] was a ], ] were ]s, and ] was entitled to the ] "Lord" because he was the son of a ]. Only the first and last Governors-General—] and ]—as well as some Provisional Governors-General, had no special titles at all. | |||
| The governor-general of Fort William resided in ], ], until the early nineteenth century, when ] was constructed. In 1854, the lieutenant governor of Bengal took up residence there. Now, the Belvedere Estate houses the ]. | |||
| ], who is reputed to have said that 'India should be governed from a ], not from a ]', constructed a grand ], known as Government House in Calcutta, between 1799 and 1803. The mansion remained in use until the capital moved from Calcutta to ] in 1912. Thereafter, the lieutenant governor of Bengal, who had hitherto resided in Belvedere House, was upgraded to a full governor and transferred to Government House. Now, it serves as the residence of the ] of the Indian state of ], and is referred to by its ] name ]. | |||
| ==Flag== | |||
| ] | |||
| From around ], the Governor-General was allowed to fly a Union Flag defaced in the centre with the "Star of India" surmounted by a Crown. This flag was not the Governor-General's personal flag; it was also used by Governors, Lieutenant Governors, Chief Commissioners and other British officers in India. When at sea, only the Governor-General flew the flag from the mainmast, while other officials flew it from the foremast. | |||
| After the capital moved from Calcutta to Delhi, the viceroy occupied the newly built Viceroy's House, designed by Sir ]. Though construction began in 1912, it did not conclude until 1929; the palace was not formally inaugurated until 1931. The final cost exceeded £877,000 (over £35 million in modern terms)—more than twice the figure originally allocated. Today the residence, now known by the Hindi name of ']', is used by the ]. | |||
| From 1947 to 1950, the Governor-General of India used a dark blue flag bearing the royal crest (a lion standing on a crown), beneath which was the word "India" in gold majuscules. The same design was used by many other British Governors-General. This last flag was the personal flag of the Governor-General only. | |||
| Throughout the British administration, governors-general retreated to the ] ''(now Rashtrapati Niwas)'' at ] each summer to escape the heat, and the government of India moved with them. The Viceregal Lodge now houses the ]. The ] in Shimla was also used by several viceroys, although the original building was destroyed by fire in 1981. | |||
| ==Official residence== | |||
| ] | |||
| The Governor-General of Fort William resided in Belvedere House, ] until the early nineteenth century, when Government House was constructed. In ], the Lieutenant-Governor of Bengal took up residence there. Now, the Belvedere Estate houses the ]. | |||
| ==List== | |||
| ], who is reputed to have said that "India should be governed from a palace, not from a country house," constructed a grand mansion, known as Government House, between ] and ]. The mansion remained in use until the capital moved from Calcutta to ] in ]. Thereafter, the Lieutenant-Governor of Bengal, who had hitherto resided in Belvedere House, was upgraded to a full Governor and transferred to Government House. Now, it serves as the residence of the Governor of the Indian state of ], and is referred to by its ] name ("Raj Bhavan"). | |||
| {{main|List of governors-general of India}} | |||
| == See also == | |||
| After the capital moved from Calcutta to Delhi, the Viceroy occupied the Viceregal Lodge. Though construction began in 1912, it did not conclude until ]; the home was not formally inaugurated until ]. The final cost exceeded £877,000 (over £35,000,000 in modern terms)—more twice the figure originally allocated. The residence, now known by the Hindi name of "]," is used by the President of India. | |||
| {{Portal|India|Pakistan|United Kingdom|Politics}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | |||
| ==Governors-General== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| ===Governors-General of Fort William=== | |||
| * {{Dead link|date=December 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| * ], ], (editor) (1910) ''Selections from the State Papers of the Governors-General of India; Warren Hastings'' (2 vols), Oxford: ] | |||
| *''] (]–]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| * ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' ("British Empire" and "Viceroy"), London: ], 1911, 11th edition, | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| * James, Lawrence (1997) ''Raj: the Making and Unmaking of British India'' London: Little, Brown & Company {{ISBN|0-316-64072-7}} | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| * Keith, A. B. (editor) (1922) ''Speeches and Documents on Indian Policy, 1750–1921'', London: ] | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| * ( 2009-10-31) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| * | |||
| *] (]) | |||
| *''] (]–]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| ===Governors-General of India=== | |||
| {{Commons category|Governors-General of India}} | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *{{cite book|author=Arnold, Sir Edwin|title=The Marquis of Dalhousie's Administration of British India: Annexation of Pegu, Nagpor, and Oudh, and a general review of Lord Dalhousie's rule in India|publisher=Saunders, Otley, and Company|url=https://archive.org/details/marquisdalhousi04arnogoog|year=1865}} | |||
| *''] (]–]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| * Dodwell H. H., ed. ''The Cambridge History of India. Volume 6: The Indian Empire 1858–1918. With Chapters on the Development of Administration 1818–1858'' (1932) 660pp ; also published as vol 5 of the ''Cambridge History of the British Empire'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *]. ''The British Conquest and Dominion of India'' (2 vol. 1989) 1235pp; the fullest scholarly history of political and military events from a British top-down perspective; | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *Rudhra, A. B. (1940) ''The Viceroy and Governor-General of India''. London: H. Milford, Oxford University Press | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| * {{Citation| last1=Spear| first1=Percival| author-link= Percival Spear | year=1990| orig-year=First published 1965| title=A History of India |volume=2| publisher=New Delhi and London: Penguin Books. Pp. 298| isbn=978-0-14-013836-8}}. | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *''] (]–]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]–]) (Provisional)'' | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *''] (]) (During Lord Irwin's absence on leave) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| *] (]–]) | |||
| {{Governors-General of India}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Representatives of the monarch in Commonwealth realms and Dominions}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Governor-General of India}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| *"British Empire." (1911). ''Encyclopædia Britannica,'' 11th ed. London: Cambridge University Press. | |||
| ] | |||
| *James, L. (1997). ''Raj: The Making and Unmaking of British India.'' London: Little, Brown & Company. | |||
| *Keith, A. B. (Ed.). (1922). ''Speeches and Documents on Indian Policy, 1750-1921.'' London: Oxford University Press. | |||
| * | |||
| *"Viceroy." (1911). ''Encyclopædia Britannica,'' 11th ed. London: Cambridge University Press. | |||
Latest revision as of 05:24, 19 January 2025
Representative of the Indian monarch "Viceroy of India" redirects here. For viceroys and governors of Portuguese India, see List of governors of Portuguese India. For a list of the office holders during the British Raj, see List of governors-general of India. For previous similar titles from 1680–1758, see List of governors of Bengal Presidency.
| Viceroy and Governor-General of India | |
|---|---|
 Standard during the British Raj Standard during the British Raj | |
 Standard during the Dominion of India Standard during the Dominion of India | |
| Style | His Excellency |
| Residence |
|
| Appointer |
|
| Term length | At His Majesty's pleasure (de jure) Five years, renewable (de facto) |
| Formation | 20 October 1773 (Fort William) 22 April 1834 (India) |
| First holder | Warren Hastings (Fort William) Lord William Bentinck (India) |
| Final holder |
|
| Abolished | 26 January 1950 (74 years ago) (1950-01-26) |
| Superseded by |
|
The Governor-General of India (1833 to 1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom in their capacity as the emperor or empress of India and after Indian independence in 1947, the representative of the monarch of India. The office was created in 1773, with the title of governor-general of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over his presidency but supervised other East India Company officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the governor-general of India.
In 1858, because of the Indian Rebellion the previous year, the territories and assets of the East India Company came under the direct control of the British Crown; as a consequence, company rule in India was succeeded by the British Raj. The governor-general (now also the Viceroy) headed the central government of India, which administered the provinces of British India, including Bengal, Bombay, Madras, Punjab, the United Provinces, and others. However, much of India was not ruled directly by the British Government; outside the provinces of British India, there were hundreds of nominally independent princely states or "native states", whose relationship was not with the British Government or the United Kingdom, but rather one of homage directly with the British monarch as sovereign successor to the Mughal emperors. From 1858, to reflect the governor-general's new additional role as the monarch's representative in response to the fealty relationships vis the princely states, the additional title of viceroy was granted, such that the new office was entitled "Viceroy and Governor-General of India". This was usually shortened to "Viceroy of India".
The title of viceroy was abandoned when British India was partitioned into the two independent dominions of India and Pakistan, but the office of governor-general continued to exist in each country separately until they adopted republican constitutions in 1950 and 1956, respectively.
Until 1858, the governor-general was selected by the Court of Directors of the East India Company, to whom he was responsible. Thereafter, he was appointed by the sovereign on the advice of the British Government; the Secretary of State for India, a member of the British Cabinet, was responsible for instructing him on the exercise of their powers. After 1947, the sovereign continued to appoint the governor-general but thereafter did so on the advice of the government of the newly independent Dominion of India.
The governor-general served at the pleasure of the sovereign, though the practice was to have them serve five-year terms. A governor-general could have their commission rescinded; and if one was removed, or left, a provisional governor-general was sometimes appointed until a new holder of the office could be chosen. The first governor-general in India (of Bengal) was Warren Hastings, the first official governor-general of British India was Lord William Bentinck, and the first governor-general of the Dominion of India was Lord Mountbatten.
History


Many parts of the Indian subcontinent were governed by the British East India Company (founded in 1600), which nominally acted as the agent of the Mughal emperor. Early British administrators were presidents or governors of Bengal Presidency. In 1773, motivated by corruption in the company, the British government assumed partial control over the governance of India with the passage of the Regulating Act 1773. A governor-general and Supreme Council of Bengal were appointed to rule over the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal. The first governor-general and Council were named in the Act.
The Charter Act 1833 replaced the governor-general and Council of Fort William with the governor-general and Council of India. The power to elect the governor-general was retained by the Court of Directors, but the choice became subject to the sovereign's approval via the India Board.
After the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the British East India Company's territories in India were put under the direct control of the sovereign. The Government of India Act 1858 vested the power to appoint the governor-general in the sovereign. The governor-general, in turn, had the power to appoint all lieutenant governors in India, subject to the sovereign's approval.
India and Pakistan acquired independence in 1947, but governors-general continued to be appointed over each nation until republican constitutions were written. Louis Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma, remained governor-general of India for ten months after independence, but the two nations were otherwise headed by native governors-general. India became a secular republic in 1950; Pakistan became an Islamic one in 1956.
Functions


The governor-general originally had power only over the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal. The Regulating Act, however, granted the governor-general additional powers relating to foreign affairs and defence. The other presidencies of the East India Company (Madras, Bombay and Bencoolen) were not allowed to declare war on or make peace with an Indian prince without receiving the prior approval of the governor-general and Council of Fort William.
The powers of the governor-general, in respect of foreign affairs, were increased by the India Act 1784. The act provided that the other governors under the East India Company could not declare war, make peace or conclude a treaty with an Indian prince unless expressly directed to do so by the governor-general or by the company's Court of Directors.
While the governor-general thus became the controller of foreign policy in India, he was not the explicit head of British India. That status came only with the Charter Act 1833, which granted him "superintendence, direction and control of the whole civil and military Government" of all of British India. The act also granted legislative powers to the governor-general and council.
In 1835, Lord William Bentinck became the first governor general of India.
After 1858, the governor-general (now usually known as the viceroy) functioned as the chief administrator of India and as the sovereign's representative. India was divided into numerous provinces, each under the head of a governor, lieutenant governor or chief commissioner or administrator. Governors were appointed by the British government, to whom they were directly responsible; lieutenant governors, chief commissioners, and administrators, however, were appointed by and were subordinate to the viceroy. The viceroy also oversaw the most powerful princely rulers: the Nizam of Hyderabad, the Maharaja of Mysore, the Maharaja (Scindia) of Gwalior, the Maharaja of Jammu and Kashmir and the Gaekwad (Gaekwar) Maharaja of Baroda. The remaining princely rulers were overseen either by the Rajputana Agency and Central India Agency, which were headed by representatives of the viceroy or by provincial authorities.
The Chamber of Princes was an institution established in 1920 by a royal proclamation of King-Emperor George V to provide a forum in which the princely rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. The chamber usually met only once a year, with the viceroy presiding, but it appointed a standing committee, which met more often.
Upon independence in August 1947, the title of viceroy was abolished. The representative of India's sovereign, King George VI, became known once again as the governor-general. In 1948, C. Rajagopalachari became the only Indian governor-general. The governor-general's role was almost entirely ceremonial, with power being exercised on a day-to-day basis by the Indian cabinet. After the nation became a republic in 1950, the president of India continued to perform the same functions.
Council
Main articles: Council of India and Viceroy's Executive Council
The governor-general was always advised by a Council on the exercise of his legislative and executive powers. The governor-general, while exercising many functions, was referred to as the "Governor-General in Council."
The Regulating Act 1773 provided for the election of four counsellors by the East India Company's Court of Directors. The governor-general was to be assisted by an executive council of four members and was given a casting vote but no veto. The decision of the council was binding on the governor-general.
In 1784, the council was reduced to three members; the governor-general continued to have both an ordinary vote and a casting vote. In 1786, the power of the governor-general was increased even further, as Council decisions ceased to be binding.
The Charter Act 1833 made further changes to the structure of the council. The Act was the first law to distinguish between the executive and legislative responsibilities of the governor-general. As provided under the Act, there were to be four members of the Council appointed by the Court of Directors. The first three members were permitted to participate on all occasions, but the fourth member was only allowed to sit and vote when legislation was being debated.
In 1858, the Court of Directors ceased to have the power to appoint members of the council. Instead, the one member who had a vote only on legislative questions came to be appointed by the sovereign, and the other three members by the secretary of state for India.
The Indian Councils Act 1861 made several changes to the council's composition. Three members were to be appointed by the Secretary of State for India, and two by the Sovereign. The power to appoint all five members passed to the Crown in 1869. The viceroy was empowered to appoint an additional 'six to twelve' members (changed to 'ten to sixteen' in 1892, and to 'sixty' in 1909). The five individuals appointed by the sovereign or the Indian secretary headed the executive departments, while those appointed by the viceroy debated and voted on legislation.
In 1919, an Indian legislature, consisting of a Council of State and a Legislative Assembly, took over the legislative functions of the Viceroy's Council. The viceroy nonetheless retained significant power over legislation. He could authorise the expenditure of money without the Legislature's consent for "ecclesiastical, political defence" purposes, and for any purpose during "emergencies." He was permitted to veto, or even stop debate on, any bill. If he recommended the passage of a bill, but only one chamber cooperated, he could declare the bill passed over the objections of the other chamber. The legislature had no authority over foreign affairs and defence. The president of the Council of State was appointed by the viceroy; the Legislative Assembly elected its president, but the election required the viceroy's approval.
Style and title
Until 1833, the title of the position was "governor-general of the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal". The Government of India Act 1833 converted the title into "governor-general of India", effective from 22 April 1834. The title "viceroy and governor-general" was first used in the queen's proclamation appointing Viscount Canning in 1858. It was never conferred by an act of parliament but was used in warrants of precedence and in the statutes of knightly orders. In usage, "viceroy" is employed where the governor-general's position as the monarch's representative is in view. The viceregal title was not used when the sovereign was present in India. It was meant to indicate new responsibilities, especially ritualistic ones, but it conferred no new statutory authority. The governor-general regularly used the title in communications with the Imperial Legislative Council, but all legislation was made only in the name of the Governor-General-in-Council (or the Government of India).
The governor-general was styled Excellency and enjoyed precedence over all other government officials in India. He was referred to as 'His Excellency' and addressed as 'Your Excellency'. From 1858 to 1947, the governor-general was known as the viceroy of India (from the French roi, meaning 'king'), and wives of Viceroys were known as Vicereines (from the French reine, meaning 'queen'). The Vicereine was referred to as 'Her Excellency' and was also addressed as 'Your Excellency'. Neither title was employed while the Sovereign was in India. However, the only British sovereign to visit India during the period of British rule was George V, who attended the Delhi Durbar in 1911 with his wife, Mary.
When the Order of the Star of India was founded in 1861, the viceroy was made its grand master ex officio. The viceroy was also made the ex officio grand master of the Order of the Indian Empire upon its foundation in 1877.
Most governors-general and viceroys were peers. Frequently, a viceroy who was already a peer would be granted a peerage of higher rank, as with the granting of a marquessate to Lord Reading and an earldom and later a marquessate to Freeman Freeman-Thomas. Of those viceroys who were not peers, Sir John Shore was a baronet, and Lord William Bentinck was entitled to the courtesy title 'lord' because he was the son of a duke. Only the first and last governors-general – Warren Hastings and Chakravarti Rajagopalachari – as well as some provisional governors-general, had no honorific titles at all.
Flag and insignia
Main article: Star of India (flag)From around 1885, the viceroy of India was allowed to fly a Union Jack Flag augmented in the centre with the 'Star of India' surmounted by a crown. This flag was not the viceroy's personal flag; it was also used by governors, lieutenant governors, chief commissioners and other British officers in India. When at sea, only the viceroy flew the flag from the mainmast, while other officials flew it from the foremast.
From 1947 to 1950, the governor-general of India used a dark blue flag bearing the royal crest (a lion standing on the Crown), beneath which was the word 'India' in gold majuscules. The same design is still used by many other Commonwealth Realm governors-general. This last flag was the personal flag of the governor-general only.
-
 Badge of the viceroy of India (1876–1904) depicted with St. Edward's Crown
Badge of the viceroy of India (1876–1904) depicted with St. Edward's Crown
-
 Badge of the viceroy and governor-general (1904–1947) depicted with Tudor Crown
Badge of the viceroy and governor-general (1904–1947) depicted with Tudor Crown
-
 Standard of the viceroy and governor-general (1885–1947)
Standard of the viceroy and governor-general (1885–1947)
-
 Standard of the governor-general (1947–50)
Standard of the governor-general (1947–50)
Residence

The governor-general of Fort William resided in Belvedere House, Calcutta, until the early nineteenth century, when Government House was constructed. In 1854, the lieutenant governor of Bengal took up residence there. Now, the Belvedere Estate houses the National Library of India.
Lord Wellesley, who is reputed to have said that 'India should be governed from a palace, not from a country house', constructed a grand mansion, known as Government House in Calcutta, between 1799 and 1803. The mansion remained in use until the capital moved from Calcutta to Delhi in 1912. Thereafter, the lieutenant governor of Bengal, who had hitherto resided in Belvedere House, was upgraded to a full governor and transferred to Government House. Now, it serves as the residence of the governor of the Indian state of West Bengal, and is referred to by its Bengali name Raj Bhavan.
After the capital moved from Calcutta to Delhi, the viceroy occupied the newly built Viceroy's House, designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens. Though construction began in 1912, it did not conclude until 1929; the palace was not formally inaugurated until 1931. The final cost exceeded £877,000 (over £35 million in modern terms)—more than twice the figure originally allocated. Today the residence, now known by the Hindi name of 'Rashtrapati Bhavan', is used by the president of India.
Throughout the British administration, governors-general retreated to the Viceregal Lodge (now Rashtrapati Niwas) at Shimla each summer to escape the heat, and the government of India moved with them. The Viceregal Lodge now houses the Indian Institute of Advanced Study. The Peterhoff building in Shimla was also used by several viceroys, although the original building was destroyed by fire in 1981.
List
Main article: List of governors-general of IndiaSee also
- British Empire
- Commander-in-Chief, India
- Council of India
- Emperor of India
- History of Bangladesh
- History of India
- History of Pakistan
- India Office
- Indian Civil Service
- Indian independence movement
- List of governors-general of India
- Partition of India
References
- "Flag of the Governor General of India". www.rmg.co.uk. National Maritime Museum: Royal Museums Greenwich. Archived from the original on 24 July 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2024.
- Thapliyal, Uma Prasad (2011). Military Flags of India: From the Earliest Times. Delhi: B.R. Publishing Corporation. p. 110. ISBN 978-81-7646-742-1.
From 15 August 1947 to 26 January 1950, the flag of the Governor-General of India was dark blue with the Lion and Crown crest in the center and INDIA in golden letters below
- The term British India is mistakenly used to mean the same as the British Indian Empire, which included both the provinces and the princely states.
- "Lord William Bentinck | British government official". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- Government of India Act 1833, Keith, Arthur Berriedale, Speeches & Documents on Indian Policy, 1750–1921, see section 41 of the Act
- "Queen Victoria's Proclamation".
- H. Verney Lovett, "The Indian Governments, 1858–1918", The Cambridge History of the British Empire, Volume V: The Indian Empire, 1858–1918 (Cambridge University Press, 1932), p. 226.
- Arnold P. Kaminsky, The India Office, 1880–1910 (Greenwood Press, 1986), p. 126.
External links
- Association of Commonwealth Archivists and Record Managers (1999) "Government Buildings – India"
- Forrest, G. W., CIE, (editor) (1910) Selections from the State Papers of the Governors-General of India; Warren Hastings (2 vols), Oxford: Blackwell's
- Encyclopædia Britannica ("British Empire" and "Viceroy"), London: Cambridge University Press, 1911, 11th edition,
- James, Lawrence (1997) Raj: the Making and Unmaking of British India London: Little, Brown & Company ISBN 0-316-64072-7
- Keith, A. B. (editor) (1922) Speeches and Documents on Indian Policy, 1750–1921, London: Oxford University Press
- Oldenburg, P. (2004). "India." Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia. (Archived 2009-10-31)
- mountbattenofburma.com – Tribute & Memorial website to Louis, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma
Further reading
- Arnold, Sir Edwin (1865). The Marquis of Dalhousie's Administration of British India: Annexation of Pegu, Nagpor, and Oudh, and a general review of Lord Dalhousie's rule in India. Saunders, Otley, and Company.
- Dodwell H. H., ed. The Cambridge History of India. Volume 6: The Indian Empire 1858–1918. With Chapters on the Development of Administration 1818–1858 (1932) 660pp online edition; also published as vol 5 of the Cambridge History of the British Empire
- Moon, Penderel. The British Conquest and Dominion of India (2 vol. 1989) 1235pp; the fullest scholarly history of political and military events from a British top-down perspective;
- Rudhra, A. B. (1940) The Viceroy and Governor-General of India. London: H. Milford, Oxford University Press
- Spear, Percival (1990) , A History of India, vol. 2, New Delhi and London: Penguin Books. Pp. 298, ISBN 978-0-14-013836-8.
| Governors-general of India | ||
|---|---|---|
| Governors of the Presidency of Fort William (1774–1833) | 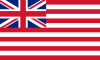   | |
| Governors-general of India (1833–1858) | ||
| Governors-general and viceroys of India (1858–1947) | ||
| Governors-general of the Union of India (1947–1950) | ||
| Representatives of the monarch in Commonwealth realms and dominions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | |||||||||||||
| Sub-national |
| ||||||||||||
| Former | |||||||||||||