| Revision as of 17:00, 17 August 2004 view sourceFeloniousMonk (talk | contribs)18,409 editsm added link to nas science and creationism primer← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 09:44, 13 January 2025 view source Dave souza (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators48,760 edits →top: often pseudoscientific, but not always e.g evolutionary creationism and theistic evolution | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Belief that nature originated through supernatural acts}} | |||
| {{NPOV}} | |||
| {{hatnote|"Creationism" can also refer to ]s, or to an unrelated ].}} | |||
| {{for|the movement in Spanish literature|Creationism (literature movement)}} | |||
| {{pp-protect|small=yes}} | |||
| {{creationism2}} | |||
| {{Intelligent Design}} | |||
| '''Creationism''' is the ] that ], and aspects such as the ], ], ], and ]s, originated with ] acts of ], and is often ].<ref name="Gunn2004">], p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary'' says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'"</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=46aUBQAAQBAJ&q=Handbook+of+Evolutionary+Thinking+in+the+Sciences&pg=PA789|title=Handbook of Evolutionary Thinking in the Sciences|last1=Brosseau|first1=Olivier|last2=Silberstein|first2=Marc|publisher=Springer|year=2015|isbn=9789401790147|editor-last1=Heams|editor-first1=Thomas|place=Dordrecht|pages=881–96|contribution=Evolutionism(s) and Creationism(s)|editor-last2=Huneman|editor-first2=Philippe|editor-last3=Lecointre|editor-first3=Guillaume|editor-last4=Silberstein.|editor-first4=Marc}}</ref> In its broadest sense, creationism includes various religious views,<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=46aUBQAAQBAJ&q=Handbook+of+Evolutionary+Thinking+in+the+Sciences&pg=PA789|title=Handbook of Evolutionary Thinking in the Sciences|last1=Brosseau|first1=Olivier|last2=Silberstein|first2=Marc|publisher=Springer|year=2015|isbn=9789401790147|editor-last1=Heams|editor-first1=Thomas|place=Dordrecht|pages=881, 884|contribution=Evolutionism(s) and Creationism(s)|editor-last2=Huneman|editor-first2=Philippe|editor-last3=Lecointre|editor-first3=Guillaume|editor-last4=Silberstein.|editor-first4=Marc|quote=Creationism is not a single homogenous doctrine ... Evolution, as a process, is a tool God uses to continually create the world. Here we have arrived at another sub-category of creationism called 'evolutionist creationism' }}</ref><ref name="Stewart2009">], p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. ], as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'evolutionary creationists,' assert that the scientific theory of evolution and the religious beliefs of Christianity can both be true."</ref> which differ in their acceptance or rejection of ] such as ] that describe the origin and development of natural phenomena.<ref name="Scott quote" /><ref name="OD_creationism">{{cite web|url=http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/us/definition/american_english/creationism?q=creationism|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140303163316/http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/us/definition/american_english/creationism?q=creationism|url-status=dead|archive-date=March 3, 2014|title=creationism: definition of creationism in Oxford dictionary (American English) (US)|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|website=Oxford Dictionaries|publisher=]|location=Oxford|type=Definition|oclc=656668849|access-date=2014-03-05|quote=The belief that the universe and living organisms originate from specific acts of divine creation, as in the biblical account, rather than by natural processes such as evolution.}}</ref> | |||
| The term ''creationism'' most often refers to belief in ]: the claim that the universe and lifeforms were created as they exist today by divine action, and that the only true explanations are those which are compatible with a ] ] interpretation of the ] found in the ]'s ].<ref>{{harv|Scott|2009|pp=|quote=The term creationism to many people connotes the theological doctrine of special creationism: that God created the universe essentially as we see it today, and that this universe has not changed appreciably since that creation event. Special creationism includes the idea that God created living things in their present forms, and it reflects a literalist view of the Bible. It is most closely associated with the endeavour of "creation science," which includes the view that the universe is only 10,000 years old. But the most important aspect of special creation is the idea that things are created in their present forms.}}</ref> Since the 1970s, the most common form of this has been ] which posits special creation of the universe and lifeforms within the last 10,000 years on the basis of ], and promotes pseudoscientific ]. From the 18th century onward, ] accepted ] harmonized with Genesis through ] or ], while supporting ]. Modern old-Earth creationists support ] and continue to reject evolutionary explanations.<ref name="Scott1999">{{cite web |author=Eugenie Scott | title=The Creation/Evolution Continuum | website=] | date=13 February 2018 | url=https://ncse.com/library-resource/creationevolution-continuum | access-date=29 April 2019| author-link=Eugenie Scott }}</ref> Following ], creation science was reformulated as ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://ncse.com/creationism/general/what-is-intelligent-design-creationism|title=What is "Intelligent Design" Creationism?|date=2008-10-17|website=NCSE|access-date=2019-04-23}}</ref><ref name="Campbell_2006">{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2006/feb/21/religion.highereducation|title=Academics fight rise of creationism at universities|last=Campbell|first=Duncan|date=February 20, 2006|newspaper=]|access-date=2010-04-07|location=London}}</ref> | |||
| '''Creationism''' is the belief that the origin of the universe and everything in it is due to an event of ] brought about by the deliberate act of ]. | |||
| ]s and the ] reconcile modern science with their faith in Creation through forms of ] which hold that God purposefully created through the ], and accept evolution. Some groups call their belief ]ism.<ref name="Scott quote">{{cite web|url=https://ncse.com/library-resource/creationevolution-continuum|title=The Creation/Evolution Continuum|author=Eugenie Scott|date=13 February 2018|website=]|access-date=6 May 2019|quote=creationism comes in many forms, and not all of them reject evolution|author-link=Eugenie Scott}}</ref> Less prominently, there are also members of the ]<ref name="nytimes.com">{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/11/03/science/03islam.html?_r=0|title=Creationism, Without a Young Earth, Emerges in the Islamic World|last1=Chang|first1=Kenneth|date=November 2, 2009|work=The New York Times|language=en}}</ref><ref name="Huffpo">{{cite web|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/usaama-alazami/muslims-and-evolution-in-the-21st-century-a-galileo-moment_b_2688895.html|title=Muslims and Evolution in the 21st Century: A Galileo Moment?|last=al-Azami|first=Usaama|date=2013-02-14|work=Huffington Post Religion Blog|access-date=19 February 2013}}</ref> and ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/mom/groves.html|title=Creationism: The Hindu View|website=www.talkorigins.org|access-date=2019-04-23}}</ref> faiths who are creationists. Use of the term "creationist" in this context dates back to ]'s unpublished 1842 sketch draft for what became '']'',<ref name="CD usage">{{harvnb|Numbers|1998|p=}} "Since at least the early 1840s Darwin had occasionally referred to 'creationists' in his unpublished writings, but the epithet acquired little public currency." – – "if this had happened on an island, whence could the new forms have come,—here the geologist calls in creationists."</ref> and he used the term later in letters to colleagues.<ref name="Darwin_letters_1856_1863">{{cite web |url=http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/entry-1919 |title=Darwin, C. R. to Hooker, J. D. |last=Darwin |first=Charles |author-link=Charles Darwin |date=July 5, 1856 |website=] |publisher=] |location=Cambridge, UK |id=Letter 1919 |access-date=2010-08-11}} | |||
| This article focuses primarily on ] creationist arguments and beliefs, the role of Christian creationism in society, and the parts that prominent individual creationists play in the '''creation science''' movement. For a detailed discussion of beliefs concerning the origin of the universe in various religions and cultures, see ''']'''. For a discussion of creationism in the context of theology, see ''']'''. | |||
| *{{cite web |url=http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/entry-4196 |title=Darwin, C. R. to Gray, Asa |last=Darwin |first=Charles |date=May 31, 1863 |website=Darwin Correspondence Project |publisher=Cambridge University Library |location=Cambridge, UK |id=Letter 4196 |access-date=2010-08-11}}</ref> In 1873, ] published an article in '']'' saying a "special creationist" who held that species "were supernaturally originated just as they are, by the very terms of his doctrine places them out of the reach of scientific explanation."<ref name="Asa usage">{{harvnb|Numbers|1998|p=}} "In 1873 Asa Gray described a 'special creationist' (a phrase he placed in quotation marks) as one who maintained that species 'were supernaturally originated just as they are'," – {{cite book|title=The Nation|url=https://archive.org/details/nation04compgoog|date=October 16, 1873|publisher=J.H. Richards|page=}}</ref> | |||
| ==Biblical basis== | |||
| It is important to note that there is a ] many see as opposed to creationism known as biological ] that contends that no ] need occur in the creation of life. It does not actually disagree with creationism, rather it implies that a deity is not required. This debate is known as being highly controversial. | |||
| The basis for many creationists' beliefs is a ] or quasi-literal interpretation of the ]. The ]s (Genesis 1–2) describe how ] brings the Universe into being in a series of creative acts over six days and places the first man and woman (]) in the ]. This story is the basis of creationist cosmology and biology. The ] (Genesis 6–9) tells how God destroys the world and all life through a great flood, saving representatives of each form of life by means of ]. This forms the basis of creationist geology, better known as ]. | |||
| Recent decades have seen attempts to de-link creationism from the Bible and recast it as science; these include ] and ].<ref>Richard F. Carlson, Tremper Longman III, Science, Creation and the Bible: Reconciling Rival Theories of Origins, p.25</ref> | |||
| == Historical overview == | |||
| ==Types== | |||
| The creation beliefs of ], ] and ] (also known as the three ]ic religions) have their origins in classical Judaism and the Book of ]. In the West, until the late ], most Jews and Christians believed that all things originated by an act of God, with the single exception of God himself, who is said to have existed eternally. This ] viewpoint was predominant in ] during the ]. However, in the ] and ], scientific discoveries and new (along with the rediscovery of old) philosophical ideas led many to doubt the validity of these beliefs. | |||
| To counter the common misunderstanding that the ] was a simple ] of views, with "creationists" set against "evolutionists", ] of the ] produced a diagram and description of a ] of religious views as a spectrum ranging from extreme literal biblical creationism to materialist evolution, grouped under main headings. This was used in public presentations, then published in 1999 in ''Reports of the NCSE''.<ref name="Scott orig. continuum">{{cite journal|last=Scott|first=Eugenie C.|author-link=Eugenie Scott|date=7 December 2000|title=The Creation/Evolution Continuum|url=http://www.natcenscied.org/resources/articles/1593_the_creationevolution_continu_12_7_2000.asp|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080509170526/http://www.natcenscied.org/resources/articles/1593_the_creationevolution_continu_12_7_2000.asp|journal=Reports of the National Center for Science Education, July–August 1999|volume=19|issue=4|pages=16–17, 23–25|issn=2158-818X|archive-date=2008-05-09}} (original online version, with link to ''''</ref> Other versions of a ] of creationists were produced,<ref name="Wise-p30">{{cite journal |last=Wise |first=Donald U. |date=January 2001 |title=Creationism's Propaganda Assault on Deep Time and Evolution |url=http://nagt.org/nagt/jge/abstracts/jan01.html |journal=Journal of Geoscience Education |volume=49 |issue=1 |pages=30–35 |issn=1089-9995 |access-date=2014-03-09|bibcode=2001JGeEd..49...30W |doi=10.5408/1089-9995-49.1.30 |s2cid=152260926 }}</ref> and comparisons made between the different groupings.<ref name="nagt-pdf-Ross">{{cite journal |last=Ross |first=Marcus R. |author-link=Marcus R. Ross |date=May 2005 |title=Who Believes What? Clearing up Confusion over Intelligent Design and Young-Earth Creationism |url=http://nagt.org/files/nagt/jge/abstracts/Ross_v53n3p319.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://nagt.org/files/nagt/jge/abstracts/Ross_v53n3p319.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |journal=Journal of Geoscience Education |volume=53 |issue=3 |pages=319–323 |issn=1089-9995 |access-date=2014-03-09|bibcode=2005JGeEd..53..319R |doi=10.5408/1089-9995-53.3.319 |citeseerx=10.1.1.404.1340 |s2cid=14208021 }}</ref> In 2009 Scott produced a revised continuum taking account of these issues, emphasizing that intelligent design creationism overlaps other types, and each type is a grouping of various beliefs and positions. The revised diagram is labelled to shows a spectrum relating to positions on the ], and the part played by ] as against evolution. This was published in the book ''Evolution Vs. Creationism: An Introduction'',{{sfn|Scott|2009|pp=}} and the NCSE website rewritten on the basis of the book version.<ref name="Scott1999" /> | |||
| The main general types are listed below. | |||
| ]'s famous work, '']'' (]) introduced the theory of evolution by natural selection, a process which does not require supernatural acts to produce organisms well-adapted to their environment. Darwin's work was not intended to oppose religious accounts of creation, but rather ]'s theory of evolution by inheritance of ]. Darwin's subsequent book '']'' (]) applied his theory to the origin of humankind, and put forth the hypothesis that humans were descended from ape-like creatures by the mechanism of evolution by natural selection. A monumental controversy ensued in ] ], as this theory apparently contradicted the accounts of the creation of man given in the ], which had until then been the primary source on the matter. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| The modern creationist movement originated in the ] as part of ], which arose as a reaction to ] Biblical interpretation. One of the corollaries of the modernist approach was their belief that evolutionary theory could not be reconciled with any appropriate interpretation of the Bible, and that therefore the Bible was in error as to scientifically verifiable facts. Fundamentalist Christianity, reacting against modernism, codified its own belief in the plenary and ] inspiration of the Bible, including the creation stories of ]. | |||
| |+ Comparison of major creationist views | |||
| |- | |||
| ! | |||
| !Humanity | |||
| !Biological species | |||
| !Earth | |||
| !Age of Universe | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |rowspan="2"| Directly created by God. | |||
| |rowspan="2"| Directly created by God. ] does not occur. | |||
| |Less than 10,000 years old. Reshaped by global flood. | |||
| |Less than 10,000 years old, but some hold this view only for the Solar System. | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |Scientifically accepted age. Reshaped by global flood. | |||
| |rowspan="4"|Scientifically accepted age. | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |Directly created by God, based on ] anatomy. | |||
| |Direct creation + evolution. No single common ancestor. | |||
| |Scientifically accepted age. No global flood. | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |Proponents hold various beliefs. (For example, ] accepts evolution from primates.) | |||
| |] at some point in the past, as evidenced by what intelligent-design creationists call "]." Some adherents accept ], others do not. | |||
| |Some claim the existence of Earth is the result of divine intervention. | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] (]ism) | |||
| |Evolution from primates. | |||
| |Evolution from single common ancestor. | |||
| |Scientifically accepted age. No global flood. | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Young Earth creationism=== | |||
| While fundamentalists are credited as the originators of the movement, there are also creationists among ], ], ] and conservatives of mainline ] churches, such as the ]s, and some ], ]s and many ]. Consequently, "creationism" has developed into an umbrella term for any ] that requires the presence of ]. | |||
| {{Main|Young Earth creationism}} | |||
| ] is a young Earth creationism museum run by ] (AiG) in ], United States.]] | |||
| ] is a young Earth creationist museum run by ] (ICR) in Dallas, Texas, United States.]] | |||
| Young Earth creationists such as ] and ] believe that God created the Earth within the last ten thousand years, with a ] interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative, within the approximate time-frame of biblical genealogies. Most young Earth creationists believe that the universe has a similar age as the Earth. A few assign a much older age to the universe than to Earth. Young Earth creationism gives the universe an age consistent with the ] and other young Earth time frames. Other young Earth creationists believe that the Earth and the universe were ], so that the world appears to be much older than it is, and that this appearance is what gives the geological findings and other methods of dating the Earth and the universe their much longer ]s.{{cn|date=October 2021}} | |||
| The Christian organizations ] (AiG), ] (ICR) and the ] (CRS) promote young Earth creationism in the United States. ]'s ] in ], United States AiG's ] and ] in ], United States were opened to promote young Earth creationism. ] promotes young Earth views in Australia, Canada, South Africa, New Zealand, the United States, and the United Kingdom. | |||
| ==Types of creationist beliefs== | |||
| Among ], the ] for the Study of Creation promotes similar ideas. | |||
| Within the broader term ''creationist'', there is no single set of beliefs, but a few general categories do exist. One classification is based on beliefs about the age of the Earth. | |||
| ===Old Earth creationism=== | |||
| * ] believe that the Earth was created by ] around 6,000 years ago, usually in accord with the ]. | |||
| {{Main|Old Earth creationism}} | |||
| * ] believe that the Earth is millions or billions of years old. Old Earth Creationism comes in two flavours: | |||
| Old Earth creationism holds that the physical universe was created by God, but that the creation event described in the Book of Genesis is to be taken figuratively. This group generally believes that the ] and the age of the Earth are as described by ]s and ]s, but that details of ] are questionable.<ref name="Scott1999" /> | |||
| ** ] or ] — the view that life was immediately created on a pre-existing old Earth. This group generally translates Genesis 1:2 as "The earth ''became'' without form and void," indicating a destruction of the original creation by some unknown cataclysm. Some Gap Creationists identify this destruction with the fall of Lucifer. | |||
| **] — the view that the "six days" of ] are not ordinary twenty-four-hour days, but rather much longer periods (for instance, each "day" could be the equivalent of millions of years years of modern time). According to modern scholarship, however, the phrasing of the original ] text suggests that its author does mean an ordinary twenty-four-hour day. | |||
| Old Earth creationism itself comes in at least three types:<ref name="Scott1999" /> | |||
| Another classification is by how organisms are believed to be created or have been created. | |||
| ====Gap creationism==== | |||
| * ] states that new kinds of organisms are constantly being created to replace extinct ancient forms. | |||
| {{Main|Gap creationism}} | |||
| * ] states that life is too complex to have evolved without the intervention of an (unnamed) intelligent designer. The originator of this view is ] ]. | |||
| Gap creationism (also known as ''ruin-restoration creationism'', ''restoration creationism'', or ''the Gap Theory'') is a form of old Earth creationism that posits that the six-'']'' creation period, as described in the ], involved six literal 24-hour days, but that there was a gap of time between two distinct creations in the first and the second verses of Genesis, which the theory states explains many scientific observations, including the ]. Thus, the six days of creation (verse 3 onwards) start sometime after the Earth was "without form and void." This allows an indefinite gap of time to be inserted after the original creation of the universe, but prior to the ], (when present biological species and ]ity were created). Gap theorists can therefore agree with the ] regarding the age of the Earth and universe, while maintaining a literal interpretation of the biblical text.<ref>''Evolution vs. Creationism: An Introduction'', ], pp61-62</ref><ref>''The Scientific Case Against Scientific Creationism'', Jon P. Alston, p24</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/wic.html|title=What is Creationism?}}</ref> | |||
| * ], also called ], states that biological evolution happens, but that God controls the apparently random events or designed the fundamental physical laws that allow evolution. | |||
| * ] states that the ] was created by a God who then made no further intervention in its affairs. This is often expressed by the metaphor of the "Divine Watchmaker" who created a mechanism so perfect as to be self-regulating. Deists do not believe in ]s or ]s. | |||
| Some{{which|date=November 2013}} gap creationists expand the basic version of creationism by proposing a "primordial creation" of biological life within the "gap" of time. This is thought to be "the world that then was" mentioned in ] 3:3–6.<ref>{{Bibleref2|2 Peter|3:3-7|NRSV}}</ref> Discoveries of fossils and archaeological ruins older than 10,000 years are generally ascribed to this "world that then was," which may also be associated with ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Formless and Void: Gap Theory Creationism {{!}} National Center for Science Education|url=https://ncse.ngo/formless-and-void-gap-theory-creationism|access-date=2021-10-30|website=ncse.ngo|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Part of creationist expression is the ''creation science'' movement. Advocates of creation science attempt to offer scientific explanations for religious creation scenarios. Usually these theories disagree with mainstream scientific theories of ], ], the ], and the theory of ]. Not all Creationists accept creation science. | |||
| ====Day-age creationism==== | |||
| Many Christian creationists believe that a creator would logically attempt to communicate with intelligent members of his creation. ] and the ] are taken to be the creator's attempt at communication. However, there is strong disagreement in interpretation and in how literally the Bible is to be taken. | |||
| {{Main|Day-age creationism}} | |||
| Day-age creationism, a type of old Earth creationism, is a metaphorical ] of the creation accounts in ]. It holds that the six days referred to in the Genesis account of creation are not ordinary 24-hour days, but are much longer periods (from thousands to billions of years). The Genesis account is then reconciled with the ]. Proponents of the day-age theory can be found among both theistic evolutionists, who accept the ] on ], and ], who reject it. The theories are said to be built on the understanding that the Hebrew word '']'' is also used to refer to a time period, with a beginning and an end and not necessarily that of a 24-hour day. | |||
| The day-age theory attempts to reconcile the ] and modern science by asserting that the creation "days" were not ordinary 24-hour days, but actually lasted for long periods of time (as day-age implies, the "days" each lasted an age). According to this view, the sequence and duration of the creation "days" may be paralleled to the scientific consensus for the age of the ] and the ]. | |||
| Creationism is usually contrasted with ] via ] shaped by ]s, sometimes referred to as '']'' or '']''. | |||
| ====Progressive creationism==== | |||
| == Distribution of creationist views == | |||
| {{Main|Progressive creationism}} | |||
| Progressive creationism is the religious belief that ] created new forms of life gradually over a period of hundreds of millions of years. As a form of old Earth creationism, it accepts mainstream ] and ] estimates for the ], some tenets of ] such as ] as well as ] to make its case. In this view creation occurred in rapid bursts in which all "kinds" of plants and animals appear in stages lasting millions of years. The bursts are followed by periods of stasis or equilibrium to accommodate new arrivals. These bursts represent instances of ] creating new types of organisms by divine intervention. As viewed from the archaeological record, progressive creationism holds that "species do not gradually appear by the steady transformation of its ancestors; appear all at once and "fully formed."<ref>Gould, Stephen J. ''The Panda's Thumb'' (New York: W.W. Norton & CO., 1982), page 182.</ref> | |||
| The view rejects ], claiming it is biologically untenable and not supported by the ],<ref>Bocchino, Peter; Geisler, Norman "Unshakable Foundations" (Minneapolis: Bethany House., 2001). Pages 141–188</ref> as well as rejects the concept of ] from a ]. Thus the evidence for macroevolution is claimed to be false, but microevolution is accepted as a genetic parameter designed by the Creator into the fabric of genetics to allow for environmental adaptations and survival. Generally, it is viewed by proponents as a middle ground between literal creationism and evolution. Organizations such as ], founded by ], promote this version of creationism. | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| Progressive creationism can be held in conjunction with ] approaches to the Genesis creation narrative such as the ] or ]/metaphoric/poetic views. | |||
| In the ], creationism remains popular among non-scientists. According to several ]s over the last decade, 60-65% of Americans believe that "God created man pretty much in his present form at one time within the last 10,000 years." About 10% believe that the evolution of species occurred without any ]. The latter figure is higher among the upper class, Internet users and among college graduates, higher still among scientists (about 55% believe that evolution occurred without God over millions of years according to a 1997 Gallup poll ), and higher still among ]s and ]s. These data have remained relatively stable over time. | |||
| ===Philosophic and scientific creationism=== | |||
| In ], ] reported: "By one count there are some 700 scientists with respectable academic credentials (out of a total of 480,000 U.S. earth and life scientists) who give credence to creation science, the general theory that complex life forms did not evolve but appeared 'abruptly.'". A 2000 poll by ''People for the American Way'' examined the question of popular support for evolution and creationism in schools, and showed that a majority of 83% supported the teaching of the theory of evolution . | |||
| ====Creation science==== | |||
| ===The western world outside the US=== | |||
| {{Main|Creation science}} | |||
| Creation science, or initially scientific creationism, is a ]<ref>{{cite journal| pmc=2267227 | pmid=18059309 | doi=10.1038/sj.embor.7401131 | volume=8 | issue=12 | title=Taking on creationism. Which arguments and evidence counter pseudoscience? | date=December 2007 | journal=EMBO Rep. | pages=1107–9 | last1 = Greener | first1 = M | issn=1469-221X }}</ref><ref>], </ref><ref name=amicus>{{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/*/http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/edwards-v-aguillard/amicus1.html |date=* |title=Amicus Curiae Brief Of 72 Nobel Laureates, 17 State Academies Of Science, And 7 Other Scientific Organizations }}, '']''</ref><ref name=philofscience>{{cite book|author1=Sahotra Sarkar|author2=Jessica Pfeifer|title=The Philosophy of science: an encyclopedia. A-M|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=od68ge7aF6wC|year=2006|publisher=Psychology Press|isbn=978-0-415-93927-0|page=}}</ref><ref>], p. 127. Okasha's full statement is that "virtually all professional biologists regard creation science as a sham{{snd}}a dishonest and misguided attempt to promote religious beliefs under the guise of science, with extremely harmful educational consequences."</ref>{{Excessive citations inline|date=September 2021}} that emerged in the 1960s with proponents aiming to have young Earth creationist beliefs taught in school science classes as a counter to teaching of evolution. Common features of creation science argument include: creationist cosmologies which accommodate a universe on the order of thousands of years old, criticism of ] through a technical argument about ]s, explanations for the ] as a record of the ] (see ]), and explanations for the present diversity as a result of pre-designed genetic variability and partially due to the rapid degradation of the perfect ]s God placed in "]s" or "]" due to ]s. | |||
| ====Neo-creationism==== | |||
| The United States fundamentalist Christian community has no real parallels (in terms of numbers, prominence, and political influence) elsewhere in the Western world (aside from possibly ]), and because most vocal creationists are from the United States, it is generally assumed that creationist views are not as common elsewhere. Statistics are not clear on the issue. | |||
| {{Main|Neo-creationism}} | |||
| Neo-creationism is a ] movement which aims to restate creationism in terms more likely to be well received by the public, by policy makers, by educators and by the ]. It aims to ] the debate over the ] in non-religious terms and without appeals to scripture. This comes in response to the 1987 ruling by the ] in '']'' that creationism is an inherently religious concept and that advocating it as correct or accurate in public-school curricula violates the ] of the First Amendment.<ref name=morris_neo>{{cite web |url= http://www.icr.org/index.php?module=articles&action=view&ID=425 |title=Neocreationism |last=Morris |first=Henry M. |author-link=Henry M. Morris |website=icr.org |publisher=] |access-date=Sep 29, 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Safire |first =William |date=August 21, 2005 |title=On Language: Neo-Creo |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2005/08/21/magazine/21ONLANGUAGE.html?ref=onlanguage |journal= The New York Times |access-date=Sep 29, 2014}}</ref><ref name=Scott1996>{{cite conference | |||
| |author=Scott, Eugenie C. | |||
| |author-link=Eugenie Scott | |||
| |conference=The Flight from Science and Reason | |||
| |year=1996 | |||
| |title=Creationism, ideology, and science | |||
| |url= http://ncse.com/creationism/general/creationism-ideology-science | |||
| |access-date=2009-11-12 | |||
| |book-title=Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences | |||
| |volume=775 | |||
| |pages=505–22 | |||
| |doi= 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb23167.x | |||
| |bibcode=1995NYASA.775..505S | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| One of the principal claims of neo-creationism propounds that ostensibly ] orthodox science, with a foundation in ], is actually a dogmatically ] ].<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.darwinreconsidered.org/media/MaterialistMythology.pdf |title= Darwinism is Materialist Mythology, Not Science |last= Johnson |first= Phillip E. |date= October 2004 |website= DarwinReconsidered.org |access-date= Sep 29, 2014 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110725220342/http://www.darwinreconsidered.org/media/MaterialistMythology.pdf |archive-date= July 25, 2011 |url-status= dead |df= mdy-all }}</ref> Its proponents argue that the ] excludes certain explanations of phenomena, particularly where they point towards ] elements, thus effectively excluding religious insight from contributing to understanding the ]. This leads to an open and often hostile opposition to what neo-creationists term "]", which they generally mean to refer to ], but which they may extend to include such concepts as ], ] and the ] theory. | |||
| According to a ] documentary on evolution, Australian creationists claimed that "five percent of the Australian population now believe that Earth is thousands, rather than billions, of years old." The documentary further states that "Australia is a particular stronghold of the creationist movement". Taking these claims at face value, "young-earth" creationism is very much a minority position in Western countries other than the USA. | |||
| Unlike their philosophical forebears, neo-creationists largely do not believe in many of the traditional cornerstones of creationism such as a young Earth, or in a dogmatically ]. | |||
| In ], creationism is a less well defined phenomenon, and regular polls are not available; however, the option of teaching creationism in school has not yet been seriously considered in any Western European country. In ]-majority countries, ] acceptance of evolution as worthy of study has essentially ended debate on the matter for many people. Nevertheless, creationist groups such as the German ''Studiengemeinschaft Wort und Wissen'' are actively lobbying there as well. In the ] the ] (previously the Vardy Foundation), which owns two colleges in the north of England and plans to open several more, teaches that creationism and evolution are equally valid "faith positions". | |||
| === |
====Intelligent design==== | ||
| {{Main|Intelligent design}} | |||
| Intelligent design (ID) is the ] view<ref name="Boudry 2010">{{cite journal |last1=Boudry |first1=Maarten |author-link1=Maarten Boudry |last2=Blancke |first2=Stefaan |last3=Braeckman |first3=Johan |author-link3=Johan Braeckman |date=December 2010 |title=Irreducible Incoherence and Intelligent Design: A Look into the Conceptual Toolbox of a Pseudoscience |journal=] |volume=85 |issue=4 |pages=473–82 |doi=10.1086/656904 |pmid=21243965|url=https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/952482/file/6828579.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/952482/file/6828579.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |hdl=1854/LU-952482 |s2cid=27218269 |hdl-access=free }} Article available from </ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Pigliucci |first1=Massimo |author-link=Massimo Pigliucci |year=2010 |chapter=Science in the Courtroom: The Case against Intelligent Design |chapter-url=http://ncse.com/files/pub/evolution/Nonsenseonstilts.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://ncse.com/files/pub/evolution/Nonsenseonstilts.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=Nonsense on Stilts: How to Tell Science from Bunk |location=Chicago, Illinois |publisher=University of Chicago Press |isbn=978-0-226-66786-7 |lccn=2009049778 |oclc=457149439 |pages=160–86 |ref=Pigliucci 2010}}</ref> that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection."<ref name="DIposition">{{cite web |url=http://www.discovery.org/csc/topQuestions.php#questionsAboutIntelligentDesign |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |title=Top Questions: Questions About Intelligent Design: What is the theory of intelligent design? |website=] |publisher=] |location=Seattle, WA |access-date=2007-05-13}}</ref> All of its leading proponents are associated with the ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/dover/day6pm.html |title=Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District Trial transcript: Day 6 (October 5), PM Session, Part 1 |website=TalkOrigins Archive |publisher=The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. |location=Houston, TX |access-date=2014-03-13}}</ref> a think tank whose ] aims to replace the ] with "a science consonant with Christian and theistic convictions" which accepts supernatural explanations.<ref name="ForrestMay2007Paper">{{cite web|url=http://www.centerforinquiry.net/uploads/attachments/intelligent-design.pdf |title=Understanding the Intelligent Design Creationist Movement: Its True Nature and Goals |last=Forrest |first=Barbara |author-link=Barbara Forrest |date=May 2007 |website=] |publisher=Center for Inquiry |location=Washington, D.C. |type=A Position Paper from the Center for Inquiry, Office of Public Policy |access-date=2014-03-13 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110519124655/http://www.centerforinquiry.net/uploads/attachments/intelligent-design.pdf |archive-date=2011-05-19 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.antievolution.org/features/wedge.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070422235718/http://www.antievolution.org/features/wedge.pdf |archive-date=2007-04-22 |url-status=usurped |title=The Wedge |year=1999 |publisher=] |location=Seattle, WA |access-date=2014-03-13}}</ref> It is widely accepted in the scientific and academic communities that intelligent design is a form of creationism,<ref name="Wise-p30" /><ref name="nagt-pdf-Ross" /><ref>{{cite journal |last=Mu |first=David |date=Fall 2005 |title=Trojan Horse or Legitimate Science: Deconstructing the Debate over Intelligent Design |url=http://www.hcs.harvard.edu/~hsr/wp-content/themes/hsr/pdf/fall2005/mu.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.hcs.harvard.edu/~hsr/wp-content/themes/hsr/pdf/fall2005/mu.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |journal=Harvard Science Review |volume=19 |issue=1 |pages=22–25 |access-date=2014-03-13 |ref=Mu 2005 |quote=...for most members of the mainstream scientific community, ID is not a scientific theory, but a creationist pseudoscience.}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Klotzko |first=Arlene Judith |date=May 28, 2001 |title=Cynical Science and Stem Cells |url=http://www.the-scientist.com/?articles.view/articleNo/13410/title/Cynical-Science-and-Stem-Cells/ |journal=] |volume=15 |issue=11 |page=35 |issn=0890-3670 |quote=Creationists are repackaging their message as the pseudo-science of 'intelligent design theory.' |access-date=2014-03-13}} | |||
| * {{cite court |litigants=Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District |vol=04 |reporter=cv |opinion=2688 |date=December 20, 2005}}, ].</ref><ref name="Numbers 2006">]</ref>{{Excessive citations inline|date=September 2021}} and is sometimes referred to as "intelligent design creationism."<ref name="Scott1999" /><ref name="ForrestMay2007Paper" /><ref>]</ref><ref>], "Wizards of ID: Reply to Dembski," pp. 645–667, "Dembski chides me for never using the term 'intelligent design' without conjoining it to 'creationism'. He implies (though never explicitly asserts) that he and others in his movement are not creationists and that it is incorrect to discuss them in such terms, suggesting that doing so is merely a rhetorical ploy to 'rally the troops'. (2) Am I (and the many others who see Dembski's movement in the same way) misrepresenting their position? The basic notion of creationism is the rejection of biological evolution in favor of special creation, where the latter is understood to be supernatural. Beyond this there is considerable variability..." | |||
| * ]</ref><ref>]</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Young |first1=Matt |last2=Edis |first2=Taner | author-link2=Taner Edis |title=Why Intelligent Design Fails: A Scientific Critique of the New Creationism |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2006 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hYLKdtlVeQgC&q=Why+Intelligent+Design+Fails:+A+Scientific+Critique+of+the+New+Creationism|isbn=9780813538723 }}</ref>{{Excessive citations inline|date=September 2021}} | |||
| ID originated as a re-branding of creation science in an attempt to avoid a series of court decisions ruling out the teaching of creationism in American public schools, and the Discovery Institute has run ] to change school curricula.<ref name="Flank_April2006">{{cite web|url=http://www.talkreason.org/articles/HistoryID.cfm |title=Creationism/ID: A Short Legal History |last=Flank |first=Lenny |website=Talk Reason |date=April 24, 2006 |access-date=2014-03-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140823063247/http://www.talkreason.org/articles/HistoryID.cfm |archive-date=August 23, 2014 }}</ref> In Australia, where curricula are under the control of state governments rather than local school boards, there was a public outcry when the notion of ID being taught in science classes was raised by the Federal Education Minister ]; the minister quickly conceded that the correct forum for ID, if it were to be taught, is in religious or philosophy classes.<ref>{{cite news |last=Smith |first=Deborah |date=October 21, 2005 |title=Intelligent design not science: experts |url=http://www.smh.com.au/news/national/intelligent-design-not-science-experts/2005/10/20/1129775902661.html |newspaper=] |location=Sydney |publisher=] |access-date=2007-07-13}}</ref> | |||
| In the Islamic world the theory of evolution has generally been ignored or condemned with purely religious arguments. However, ], which are generally partial to secular scientific thought, tend to be more accepting of evolution. | |||
| In the US, teaching of intelligent design in public schools has been decisively ruled by a ] to be in violation of the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. In ], the court found that intelligent design is not science and "cannot uncouple itself from its creationist, and thus religious, antecedents,"<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District |vol=04 |reporter=cv |opinion=2688 |date=December 20, 2005}}, ].</ref> and hence cannot be taught as an alternative to evolution in public school science classrooms under the jurisdiction of that court. This sets a ], based on previous US ] decisions in ''Edwards v. Aguillard'' and '']'' (1968), and by the application of the ], that creates a legal hurdle to teaching intelligent design in public school districts in other federal court jurisdictions.<ref name="ForrestMay2007Paper" /><ref name="kitz">]</ref> | |||
| In recent years, however, the arguments of "Intelligent Design"-style creationism have fallen on fertile ground in parts of the Islamic world and among Muslim immigrants in the Western diaspora. | |||
| ===Geocentrism=== | |||
| The centre of the Islamic creationist movement is ]. Its main exponent is the writer ] (or. ], b. 1956) who uses the Internet for the propagation of his ideas. His BAV (Bilim Araştırma Vakfı/ Science Research Foundation) organizes conferences with leading American creationists. Another leading advocate of Islamic creationism is ] (b. 1941). | |||
| {{Main|Geocentric model}} | |||
| In ], the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system), is a description of the ] where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ]. As such, they assumed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and ] circled Earth, including the noteworthy systems of ] (see ]) and ]. | |||
| Articles arguing that geocentrism was the biblical perspective appeared in some early creation science newsletters associated with the Creation Research Society pointing to some passages in the Bible, which, when taken literally, indicate that the daily apparent motions of the Sun and the Moon are due to their actual motions around the Earth rather than due to the rotation of the Earth about its axis. For example, {{bibleverse|Joshua|10:12-13|HE}} where the Sun and Moon are said to stop in the sky, and {{bibleverse|Psalms|93:1|HE}} where the world is described as immobile.<ref name="Numbers1993">{{cite book |last=Numbers |first=Ronald L. |year=1993 |orig-year=Originally published 1992; New York: ] |title=The Creationists: The Evolution of Scientific Creationism |location=Berkeley, CA |publisher=] |page= |isbn=978-0-5200-8393-6 |lccn=93015804 |oclc=810488078 |url=https://archive.org/details/creationistsevol0000numb/page/237 }}</ref> Contemporary advocates for such ]s include ], co-author of the self-published ''Galileo Was Wrong: The Church Was Right'' (2006).<ref name="Sefton2006">{{cite news |first=Dru |last=Sefton |date=March 30, 2006 |title=In this world view, the sun revolves around the earth |url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?id=_1kaAAAAIBAJ&dq=robert-sungenis&pg=6714%2C4991566 |newspaper=] |location=Hendersonville, NC |publisher=Hendersonville Newspaper Corporation |agency=] |page=5A |access-date=2014-03-14}}</ref> These people subscribe to the view that a plain reading of the Bible contains an accurate account of the manner in which the universe was created and requires a geocentric worldview. | |||
| The movement seems to have a considerable following in ] and ] whereas interest seem to be low in the Arabic countries and Iran. As in the Western context, the theory of evolution is held responsible for a ] worldview that is the alleged base of all kinds of societal problems and negative political developments. | |||
| Most contemporary creationist organizations reject such perspectives.{{refn|group="note"|Donald B. DeYoung, for example, states that "Similar terminology is often used today when we speak of the sun's rising and setting, even though the earth, not the sun, is doing the moving. Bible writers used the 'language of appearance,' just as people always have. Without it, the intended message would be awkward at best and probably not understood clearly. When the Bible touches on scientific subjects, it is entirely accurate."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/1997/11/05/astronomy-bible |title=Astronomy and the Bible: Selected questions and answers excerpted from the book |last=DeYoung |first=Donald B. |date=November 5, 1997 |website=] |publisher=Answers in Genesis Ministries International |location=Hebron, KY |access-date=2013-12-01}}</ref>}} | |||
| === Omphalos hypothesis === | |||
| ==The creation stories of Genesis== | |||
| {{Main|Omphalos hypothesis}} | |||
| The Omphalos hypothesis is one attempt to reconcile the scientific evidence that the universe is billions of years old with a literal interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative, which implies that the Earth is only a few thousand years old.<ref name=":0">{{cite journal|url=http://www.roizen.com/ron/omph.htm|title=The rejection of Omphalos: a note on shifts in the intellectual hierarchy of mid-nineteenth century Britain|last=Roizen|first=Ron|journal=Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion|year=1982|volume=21|issue=4|pages=365–369|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070219011828/http://www.roizen.com/ron/omph.htm|archive-date=2007-02-19|doi=10.2307/1385525|jstor=1385525}}</ref> It is based on the religious belief that the universe was created by a divine being, within the past six to ten thousand years (in keeping with ]), and that the presence of objective, verifiable evidence that the universe is older than approximately ten millennia is due to the creator introducing false evidence that makes the universe appear significantly older. | |||
| The idea was named after the title of an 1857 book, '']'' by ], in which Gosse argued that in order for the world to be functional ] must have created the ] with mountains and canyons, trees with growth rings, Adam and Eve with fully grown hair, fingernails, and ]s<ref name="Gardner2000">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=z1NdAgAAQBAJ|title=Did Adam and Eve Have Navels?: Debunking Pseudoscience|last=Gardner|first=Martin|publisher=W. W. Norton & Company|year=2000|isbn=9780393322385|place=New York|pages=7–14}}</ref> (ὀμφαλός '']'' is ] for "navel"), and all living creatures with fully formed evolutionary features, etc..., and that, therefore, ''no'' ] about the ] or ] can be taken as reliable. | |||
| The Biblical story of creation occurs in the opening of Genesis. Many biblical scholars distinguish two separate creation stories: | |||
| Various supporters of Young Earth creationism have given different explanations for their belief that the universe is filled with false evidence of the universe's age, including a belief that some things needed to be created at a certain age for the ecosystems to function, or their belief that the creator was deliberately planting deceptive evidence. The idea has seen some revival in the 20th century by some modern creationists, who have extended the argument to address the ]. The idea has been criticised as ], and on the grounds that it requires a deliberately deceptive creator. | |||
| # The story of the creation in six days (Genesis 1:1 to 2:3) | |||
| # The story of the day of creation (Genesis 2:4-24) | |||
| ==Theistic evolution== | |||
| The two stories are not identical. There are arguments for and against their reconciliability. | |||
| {{Main|Theistic evolution}} | |||
| Theistic evolution, or evolutionary creation, is a belief that "the personal God of the Bible created the universe and life through evolutionary processes."<ref>], , "''Evolutionary Creation'' (or Theistic Evolution) asserts that the personal God of the Bible created the universe and life through evolutionary processes."</ref> According to the American Scientific Affiliation: | |||
| {{Blockquote|A theory of theistic evolution (TE){{snd}}also called evolutionary creation{{snd}}proposes that God's method of creation was to cleverly design a universe in which everything would naturally evolve. Usually the "evolution" in "theistic evolution" means Total Evolution{{snd}}astronomical evolution (to form galaxies, solar systems,...) and geological evolution (to form the earth's geology) plus chemical evolution (to form the first life) and biological evolution (for the development of life){{snd}}but it can refer only to biological evolution.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.asa3.org/ASA/education/origins/te2-cr.htm |title=Evolutionary Creation |last=Rusbult |first=Craig |year=1998 |publisher=American Scientific Affiliation |location=Ipswich, MA |access-date=2014-03-14 }}</ref>}} | |||
| ===The first story, Genesis 1:1-2:3=== | |||
| Through the 19th century the term ''creationism'' most commonly referred to ], in contrast to ]. Following the publication of '']'', there was interest in ideas of Creation by ]. In particular, the ] ] argued that this illustrated the Creator's power better than the idea of miraculous creation, which he thought ridiculous.<ref>], p. 139</ref> When ''On the Origin of Species'' was published, the cleric ] wrote of evolution as "just as noble a conception of Deity."<ref name="Darwinanddesign">{{cite web|url=http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/darwin-and-design-article |title=Darwin and design: historical essay |year=2007 |website=Darwin Correspondence Project |publisher=Cambridge University Library |location=Cambridge, UK |access-date=2012-04-18 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141021101910/http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/darwin-and-design-article |archive-date=2014-10-21 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/entry-2534 |title=Kingsley, Charles to Darwin, C. R. |last=Kingsley |first=Charles |author-link=Charles Kingsley |date=November 18, 1859 |website=Darwin Correspondence Project |publisher=Cambridge University Library |location=Cambridge, UK |id=Letter 2534 |access-date=2010-08-11}}</ref> Darwin's view at the time was of God creating life through the laws of nature,<ref name="James_Moore">{{cite interview |last=Moore |first=James |author-link=James Moore (biographer) |interviewer=] |title=Evolution and Wonder: Understanding Charles Darwin |url=http://www.onbeing.org/program/evolution-and-wonder-understanding-charles-darwin/transcript/899 |via=] |work=] |date=September 20, 2007 |publisher=] |access-date=2014-03-09 |archive-date=2015-11-18 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151118040338/http://www.onbeing.org/program/evolution-and-wonder-understanding-charles-darwin/transcript/899 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>], p. 119</ref> and the book makes several references to "creation," though he later regretted using the term rather than calling it an unknown process.<ref>], </ref> In America, ] argued that evolution is the secondary effect, or ''modus operandi'', of the first cause, design,<ref>], p. 27</ref> and published a pamphlet defending the book in theistic terms, ''Natural Selection not inconsistent with Natural Theology''.<ref name="Darwinanddesign" /><ref name="Miles_2001">{{cite journal |last=Miles |first=Sara Joan |date=September 2001 |title=Charles Darwin and Asa Gray Discuss Teleology and Design |url=http://www.asa3.org/ASA/PSCF/2001/PSCF9-01Miles.html |journal=Perspectives on Science and Christian Faith |volume=53 |pages=196–201 |access-date=2008-11-22}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Gray |first=Asa |author-link=Asa Gray |year=1860 |title=Natural Selection not inconsistent with Natural Theology |url=http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/content/view/84/69/ |journal=] |type=Reprint |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090220124011/http://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/content/view/84/69/ <!--Added by H3llBot--> |archive-date=2009-02-20 |access-date=2009-04-11}} "Atlantic Monthly for ''July'', ''August'', and ''October'', 1860, reprinted in 1861."</ref> Theistic evolution, also called, evolutionary creation, became a popular compromise, and ] was among those accepting evolution but attacking Darwin's naturalistic mechanism. Eventually it was realised that supernatural intervention could not be a scientific explanation, and naturalistic mechanisms such as ] were favoured as being more compatible with purpose than natural selection.<ref name="bowl202">], pp. 202–08</ref> | |||
| This story is an account of God (]) creating the universe in six days and resting on the seventh day. The order of creation is: | |||
| Some theists took the general view that, instead of faith being in opposition to biological evolution, some or all classical religious teachings about ] and creation are compatible with some or all of modern scientific theory, including specifically evolution; it is also known as "evolutionary creation." In ''Evolution versus Creationism'', ] and ] state that it is in fact a type of evolution.<ref>], pp. 62–63</ref> | |||
| *First day | |||
| **God creates the heavens and the Earth. (1:1) | |||
| **The Earth is dark and without form. (1:2) | |||
| **God creates light. (1:3-5) | |||
| *Second day | |||
| **God creates a "firmament" or a "dome", called "sky", to separate the heavens and Earth. (1:6-8) | |||
| *Third day | |||
| **God separates the seas and dry land. (1:9-10) | |||
| **God creates fruits and vegetation. (1:11-13) | |||
| *Fourth day | |||
| **God puts lights in the sky to separate day and night and to indicate the passing of the seasons. The sun, moon, and stars are created. (1:14-19) | |||
| *Fifth day | |||
| **God creates sea creatures and birds. (1:20-23) | |||
| *Sixth day | |||
| **God creates living creatures for the land: wild animals, cattle and creeping things. (1:24-25) | |||
| **God creates mankind, male and female, "in his own image". (1:26-31) | |||
| *Seventh day | |||
| **The Sabbath (2:1-3) | |||
| It generally views evolution as a tool used by God, who is both the ] and ] sustainer/upholder of the universe; it is therefore well accepted by people of strong ] (as opposed to ]) convictions. Theistic evolution can synthesize with the day-age creationist interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative; however most adherents consider that the first chapters of the Book of Genesis should not be interpreted as a "literal" description, but rather as a ] or allegory. | |||
| ===The second story, Genesis 2:4-2:25=== | |||
| From a theistic viewpoint, the underlying laws of nature were designed by God for a purpose, and are so self-sufficient that the complexity of the entire physical universe evolved from fundamental particles in processes such as ], life forms developed in biological evolution, and in the same way the ] has resulted from these laws.<ref name="The Origin of Life">{{cite web |url=http://www.talkorigins.org/faqs/abioprob/originoflife.html#intro |title=The Origin of Life |last=Moritz |first=Albrecht |date=October 31, 2006 |website=TalkOrigins Archive |publisher=The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. |location=Houston, TX |access-date=2008-11-22}}</ref> | |||
| This story is an account of the day the God (]) created the world. It begins on the day of the creation (2:4) before plants, rain, and men (2:5). | |||
| In one form or another, theistic evolution is the view of creation taught at the majority of mainline ] seminaries.<ref>]</ref> For Roman Catholics, human evolution is not a matter of religious teaching, and must stand or fall on its own scientific merits. ] are not in conflict. The ] comments positively on the theory of evolution, which is neither precluded nor required by the sources of faith, stating that scientific studies "have splendidly enriched our knowledge of the age and dimensions of the cosmos, the development of life-forms and the appearance of man."<ref>{{cite journal |last=Akin |first=Jimmy |date=January 2004 |title=Evolution and the Magisterium |url=http://www.catholic.com/thisrock/2004/0401bt.asp |journal=] |volume=15 |issue=1 |issn=1049-4561 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070804102139/http://www.catholic.com/thisrock/2004/0401bt.asp |archive-date=2007-08-04 |access-date=2014-03-14}}</ref> ] schools teach evolution without controversy on the basis that scientific knowledge does not extend beyond the physical, and scientific truth and religious truth cannot be in conflict.<ref>{{cite news |last=Guntzel |first=Jeff Severns |url=http://natcath.org/NCR_Online/archives2/2005a/032505/032505ssn.htm |date=March 25, 2005 |title=Catholic schools steer clear of anti-evolution bias |newspaper=] |location=Kansas City, MO |publisher=The National Catholic Reporter Publishing Company |issn=0027-8939 |access-date=2007-08-15}}</ref> Theistic evolution can be described as "creationism" in holding that ] brought about the origin of life or that divine laws govern formation of species, though many creationists (in the strict sense) would deny that the position is creationism at all. In the ], its proponents generally take the "evolutionist" side. This sentiment was expressed by Fr. ], (the ]'s chief astronomer between 1978 and 2006):<blockquote>...in America, creationism has come to mean some fundamentalistic, literal, scientific interpretation of Genesis. Judaic-Christian faith is radically creationist, but in a totally different sense. It is rooted in a belief that everything depends upon God, or better, all is a gift from God.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.catholic.org/national/national_story.php?id=18504 |title=Text of talk by Vatican Observatory director on 'Science Does Not Need God. Or Does It? A Catholic Scientist Looks at Evolution' |last=Coyne |first=George V. |author-link=George Coyne |date=January 30, 2006 |publisher=Catholic Online, LLC |access-date=2011-03-10 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606050849/http://www.catholic.org/national/national_story.php?id=18504 |archive-date=June 6, 2011 }}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| *The man is formed. (2:7) | |||
| *God plants the garden of Eden and places the man in it. (2:8) | |||
| *The trees grow in the Garden, including the tree of life and the tree of knowledge of good and evil. (2:9) | |||
| *Description of the rivers of Eden. (2:10-14) | |||
| *The man is put in garden to care for it. (2:15) | |||
| *The man is commanded not to eat from the tree of knowledge of good and evil. (2:16-17) | |||
| *God decides the man should not be alone. (2:18) | |||
| *God creates animals and birds and has Adam name them. (2:19-20) | |||
| *The creation of the first woman. (2:21-22) | |||
| *The man and the woman form the first family. (2:23-25) | |||
| While supporting the ] inherent in modern science, the proponents of theistic evolution reject the implication taken by some ] that this gives credence to ] ]. In fact, many modern philosophers of science,<ref>] | |||
| === Reconciling the two stories === | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://llanoestacado.org/freeinquiry/files/naturalism.html |title=Naturalism is an Essential Part of Science and Critical Inquiry |last=Schafersman |first=Steven D. |author-link=Steven Schafersman |date=May 1997 |website=Free Inquiry: The Humanist and Skeptic Website of Steven Schafersman |publisher=Steven Schafersman |access-date=2014-03-15}} | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://leiterreports.typepad.com/blog/2004/04/on_methodologic.html |title=On Methodological Naturalism and Intelligent Design (or Why Can't Lawrence VanDyke Leave Well Enough Alone?) |last=Leiter |first=Brian |author-link=Brian Leiter |date=April 6, 2004 |website=Leiter Reports: A Philosophy Blog |publisher=Brian Leiter |type=Blog |access-date=2014-03-15}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Burgeson |first=John W. |year=1997 |title=NTSE: An Intellectual Feast |url=http://www.arn.org/docs/odesign/od182/ntse182.htm |journal=Origins & Design |volume=18 |issue=2 |access-date=2014-03-15}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Pigliucci |first1=Massimo |author-link=Massimo Pigliucci |last2=Banta |first2=Joshua |last3=Bossu |first3=Christen |last4=Crouse |first4=Paula |last5=Dexter |first5=Troy |last6=Hansknecht |first6=Kerry |last7=Muth |first7=Norris |display-authors=1 |date=May–June 2004 |title=The Alleged Fallacies of Evolutionary Theory |url=http://philosophynow.org/issues/46/The_Alleged_Fallacies_of_Evolutionary_Theory |journal=] |issue=46 |issn=0961-5970 |access-date=2014-03-15}} | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://www.biology.uiowa.edu/ID.html |title=Statement on Intelligent Design |year=2005 |website=The Department of Biology |publisher=] |type=Petition |location=Iowa City, IA |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100901150357/http://www.biology.uiowa.edu/ID.html |archive-date=2010-09-01 |access-date=2014-03-15}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Pigliucci |first=Massimo |date=December 2005 |title=Science and fundamentalism |journal=EMBO Reports |volume=6 |issue=12 |doi=10.1038/sj.embor.7400589 |issn=1469-3178 |pmc=1369219 |pmid=16319954 |pages=1106–1109}} | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://infidels.org/library/modern/michael_martin/naturalism.html |title=Justifying Methodological Naturalism |last=Martin |first=Michael |author-link=Michael Martin (philosopher) |year=2002 |website=The Secular Web |publisher=] |location=Colorado Springs, CO |access-date=2014-03-15}}</ref> including atheists,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.butterfliesandwheels.org/2005/intelligent-design-or-natural-design/ |title=Intelligent Design or Natural Design |last=Bradley |first=Raymond |date=November 23, 2005 |website=Butterflies and Wheels |publisher=] |location=Seattle, WA |access-date=2014-03-16}}</ref> refer to the long-standing convention in the scientific method that ] events in nature should be explained by natural causes, with the distinction that it does not assume the actual existence or non-existence of the supernatural. <!---Among other things, it means that science does not deal with the question of the existence of a Creator, and argues neither for nor against it. | |||
| "while on the other hand many scientists support such faiths which allow a voice to their spiritual side." Don't know how to include this, it anyway should talk about scientific positions (and not faiths) and spiritual side---> | |||
| ==Religious views== | |||
| The order in which the events of creation take place in the two stories are significantly different in each version. However, within themselves the stories are consistent. Some interpretors claim that the second story is an expanded version of the first that explains what happened in detail to the creation described in the first story. Others state that some of the events are arranged out of their chronological order. | |||
| There are also non-Christian forms of creationism,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/christianity/beliefs/creationism_1.shtml |title=Creationism and intelligent design |date=2 June 2009 |access-date=2 October 2018 |work=]}}</ref> notably ]<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/11/03/science/03islam.html |title=Creationism, Minus a Young Earth, Emerges in the Islamic World |first=Kenneth |last=Chang |date=2 November 2009 |access-date=2 October 2018 |newspaper=] }}</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/belief/2009/nov/16/darwin-evolution-china-politics |title=Darwinism, through a Chinese lens |first=Riazat |last=Butt |date=16 November 2009 |access-date=2 October 2018 |newspaper=] |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Bahá'í Faith=== | |||
| Evolutionary creationists typically hold that the passages in Genesis are not to be interpreted literally, but are rather a symbolic or poetic account of the creation of the universe. Some believe that they are based on the prevailing knowledge of the physical world at the time that they were written. | |||
| {{main|Bahá'í Faith and science#Creation}} | |||
| In the creation myth taught by ], the ] founder, the universe has "neither beginning nor ending," and that the component elements of the material world have always existed and will always exist.<ref>], </ref> With regard to evolution and the origin of human beings, ] gave extensive comments on the subject when he addressed western audiences in the beginning of the 20th century. Transcripts of these comments can be found in '']'', '']'' and ''The Promulgation of Universal Peace''. 'Abdu'l-Bahá described the human species as having evolved from a primitive form to modern man, but that the capacity to form human intelligence was always in existence. | |||
| ===Buddhism=== | |||
| It is possible to view Genesis as an allegory for the process of humankind's development of ] and the emergence of human intelligence from a previous animal state. In this interpretation, the fruit of the ] is a key component as the Serpent claims it holds the power to impart understanding that would rival ]'s. The humans take a bite and get the ability to understand, but they do not eat the whole fruit, and so get only a partial understanding. Immediately they become ashamed of their nakedness, presumably because it belies their ]. God expels them from the ], which represents a contented animal existence, to toil in the world and face strife and conflict. | |||
| {{See also|Creator in Buddhism}} | |||
| ] denies a creator deity and posits that mundane deities such as ] are sometimes misperceived to be a creator.<ref>Harvey, Peter (2013). An Introduction to Buddhism: Teachings, History and Practices (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pg. 36-8</ref> While Buddhism includes belief in divine beings called ], it holds that they are mortal, limited in their power, and that none of them are creators of the universe.<ref name="Harvey, Peter 2019 p. 1">Harvey, Peter (2019). ''"Buddhism and Monotheism",'' p. 1. Cambridge University Press.</ref> In the ], the Buddha also states that the cycle of rebirths stretches back hundreds of thousands of eons, without discernible beginning.<ref>Keown, Damien (2013). ''"Encyclopedia of Buddhism."'' p. 162. Routledge.</ref> | |||
| Major Buddhist Indian philosophers such as ], ], ] and ], consistently critiqued Creator God views put forth by Hindu thinkers.<ref>Hsueh-Li Cheng. "Nāgārjuna's Approach to the Problem of the Existence of God" in Religious Studies, Vol. 12, No. 2 (Jun., 1976), pp. 207–216 (10 pages), Cambridge University Press.</ref><ref>Hayes, Richard P., "Principled Atheism in the Buddhist Scholastic Tradition", ''Journal of Indian Philosophy'', 16:1 (1988:Mar.).</ref><ref name="Harvey, Peter 2019 p. 1"/> | |||
| Some creationists do not believe that the two accounts of Genesis 1 and Genesis 2 are compatible. These take neither account as "history", but consider the creation of mankind to be the culmination of God's creating work. | |||
| ===Christianity=== | |||
| === Time in the creation stories === | |||
| {{Further|Genesis creation narrative|creation–evolution controversy}} | |||
| {{As of|2006}}, most ] around the world accepted evolution as the most likely explanation for the origins of species, and did not take a ] of the Genesis creation narrative. The United States is an exception where belief in religious ] is much more likely to affect attitudes towards evolution than it is for believers elsewhere. Political partisanship affecting religious belief may be a factor because political partisanship in the US is highly correlated with fundamentalist thinking, unlike in Europe.<ref name="Science survey">{{cite journal |last1=Miller |first1=Jon D. |last2=Scott |first2=Eugenie C. |author-link2=Eugenie Scott |last3=Okamoto |first3=Shinji |date=August 2006 |title=Public acceptance of evolution |journal=] |volume=313 |issue=5788 |pages=765–66 |doi=10.1126/science.1126746 |pmid=16902112 |s2cid=152990938 }}</ref> | |||
| Most contemporary Christian leaders and scholars from mainstream churches,<ref name="Denominational Views">{{cite web |url=http://ncse.com/religion/denominational-views |title=Denominational Views |date=October 17, 2008 |website=National Center for Science Education |location=Berkeley, CA |access-date=2010-05-17}}</ref> such as ]<ref name="Episcopal Church">{{cite web|url=http://ncse.com/media/voices/episcopal-church-general-convention-2006 |title=Episcopal Church, General Convention (2006) |website=National Center for Science Education |location=Berkeley, CA |access-date=2010-05-17|date=2008-09-09 }}</ref> and ],<ref name="Lutheran">{{cite encyclopedia |last=Schick |first=Edwin A. |editor-last=Bodensieck |editor-first=Julius |encyclopedia=The Encyclopedia of the Lutheran Church |url=http://ncse.com/media/voices/lutheran-world-federation |access-date=2010-05-17 |title=Evolution |year=1965 |publisher=] |volume=1 |location=Minneapolis, MN |lccn=64021500 |oclc=947120 }} Edited for the ]. | |||
| One difference between the two stories is that the first is about the ''six days'' of creation, while the second is about the ''day'' of creation. This apparent contradiction in two verses that are so close together has troubled many commentators (see ''A History of the Warfare of Science with Theology in Christendom'' by A.D. White, 1896, Dover Publications, 1960, page 5). The distinction is concealed by some translations, such as the ]. One explanation for this difference is given by the ]. | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Hollabaugh |first=Mark |date=October 2006 |title=God allows the universe to create itself and evolve |url=http://www.thelutheran.org/article/article.cfm?article_id=6093 |journal=] |issn=0024-743X |access-date=2014-03-16 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131231072935/http://www.thelutheran.org/article/article.cfm?article_id=6093 |archive-date=2013-12-31 }}</ref> consider that there is no conflict between the spiritual meaning of creation and the science of evolution. According to the former ], ], "for most of the history of Christianity, and I think this is fair enough, most of the history of the Christianity there's been an awareness that a belief that everything depends on the creative act of God, is quite compatible with a degree of uncertainty or latitude about how precisely that unfolds in creative time."<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=March 21, 2006 |title=Interview: Rowan Williams |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2006/mar/21/religion.uk |newspaper=The Guardian |type=Transcript |location=London |access-date=2014-03-16}}</ref> | |||
| Leaders of the Anglican<ref>{{cite news |last=Williams |first=Christopher |date=March 21, 2006 |title=Archbishop of Canterbury backs evolution |url=https://www.theregister.co.uk/2006/03/21/archbishop_backs_evolution/ |work=] |location=London |publisher=Situation Publishing Limited |access-date=2011-03-10}}</ref> and Roman Catholic<ref>{{cite journal |last=McDonell |first=Keelin |date=July 12, 2005 |title=What Catholics Think of Evolution |url=http://www.slate.com/id/2122506/ |journal=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050716003211/http://www.slate.com/id/2122506/ |archive-date=2005-07-16 |access-date=2014-03-16}}</ref>{{efn|See also the article ].}} churches have made statements in favor of evolutionary theory, as have scholars such as the physicist ], who argues that evolution is one of the principles through which God created living beings. Earlier supporters of evolutionary theory include ], Asa Gray and Charles Kingsley who were enthusiastic supporters of Darwin's theories upon their publication,<ref>], pp. 7–8</ref> and the French Jesuit priest and geologist ] saw evolution as confirmation of his Christian beliefs, despite condemnation from Church authorities for his more speculative theories. Another example is that of ], not providing any creation models, but instead focusing on the ]ism in beliefs of the time of authoring Genesis and the cultural environment. | |||
| There is a sharp distinction between ]s and ]s who hold contradictory views regarding the ]. Young Earth Creationism holds to the wording of the first story, where the Earth was created in six days. Young Earth Creationists usually date the Earth at somewhere around 6,000 years old using the genealogies and other details in the Bible; the ] of Bishop ] presents one famous interpretation of these details). Young Earth Creationists usually reject the ] theory of the origin of the universe. | |||
| Many Christians and Jews had been considering the idea of the creation history as an allegory (instead of historical) long before the development of Darwin's theory of evolution. For example, ], whose works were taken up by early Church writers, wrote that it would be a mistake to think that creation happened in six days, or in any set amount of time.<ref name="Philo_Chapter2">]</ref><ref name="www.earlychurch.org.uk">{{cite web |url=http://www.earlychurch.org.uk/philo.php |title=Philo of Alexandria (c. 20 BC{{snd}}c. AD 50) |last=Bradshaw |first=Rob |website=Early Church.org.uk |publisher=Steve Bradshaw |location=West Wickham, England |access-date=December 21, 2011}}</ref> Augustine of the late fourth century who was also a former neoplatonist argued that everything in the universe was created by God at the same moment in time (and not in six days as a literal reading of the Book of Genesis would seem to require);<ref name="Augustine">{{cite journal |last=Young |first=Davis A. |date=March 1988 |title=The Contemporary Relevance of Augustine's View of Creation |url=http://www.asa3.org/ASA/PSCF/1988/PSCF3-88Young.html |journal=] |volume=40 |issue=1 |pages=42–45 |issn=0892-2675 |access-date=2008-08-18}}</ref> It appears that both Philo and Augustine felt uncomfortable with the idea of a seven-day creation because it detracted from the notion of God's omnipotence. In 1950, ] stated limited support for the idea in his ] {{lang|la|]}}.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.vatican.va/holy_father/pius_xii/encyclicals/documents/hf_p-xii_enc_12081950_humani-generis_en.html |author=Pope Pius XII |author-link=Pope Pius XII |title=Humani Generis |website=Vatican: the Holy See |publisher=] |location=St. Peter's Basilica, Vatican City |type=] |date=August 12, 1950 |access-date=2011-11-08 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120419021937/https://www.vatican.va/holy_father/pius_xii/encyclicals/documents/hf_p-xii_enc_12081950_humani-generis_en.html |archive-date=April 19, 2012 }}</ref> In 1996, ] stated that "new knowledge has led to the recognition of the theory of evolution as more than a hypothesis," but, referring to previous papal writings, he concluded that "if the human body takes its origin from pre-existent living matter, the spiritual ] is immediately created by God."<ref>{{cite news |author=Pope John Paul II |author-link=Pope John Paul II |date=October 30, 1996 |title=Magisterium is concerned with question of evolution, for it involves conception of man |url=http://www.its.caltech.edu/~nmcenter/sci-cp/evolution.html |newspaper=] |type=Message to the ] |edition=Weekly English |location=Tipografia Vaticana, Vatican City |publisher=Holy See |number=44 |pages=3, 7 |access-date=2014-03-19 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160321064939/http://www.its.caltech.edu/%7Enmcenter/sci-cp/evolution.html |archive-date=March 21, 2016 |url-status=dead |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| Old Earth Creationists do not hold to the wording of either story and claim that the Earth is millions of years old. For example, ] holds that the six days referred to are not ordinary 24-hour days, but rather much longer periods (of thousands or millions of years); the Genesis account is then sometimes interpreted as an account of the process of evolution. Some believe that the six day period refers to the time spent by light traveling from the center of the ] at the time and point of creation. | |||
| In the US, Evangelical Christians have continued to believe in a literal Genesis. {{As of|2008}}, members of evangelical Protestant (70%), ] (76%) and ] (90%) denominations were the most likely to reject the evolutionary interpretation of the origins of life.<ref>{{cite report |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |year=2008 |title=U.S. Religious Landscape Survey |chapter-url=http://religions.pewforum.org/pdf/report2religious-landscape-study-chapter-2.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://religions.pewforum.org/pdf/report2religious-landscape-study-chapter-2.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |publisher=] |location=Washington, D.C. |chapter=Social and Political Views |page=95 |access-date=2014-03-19}} Report 2: Religious Beliefs & Practices, Chapter 2.</ref> | |||
| == The creationism versus evolution debate == | |||
| Jehovah's Witnesses assert that scientific evidence about the age of the universe is compatible with the Bible, but that the 'days' after Genesis 1:1 were each thousands of years in length. They view this belief as an alternative to Creationism rather than a variation of Creationism.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Chryssides|first1=George D.|title=Historical Dictionary of Jehovah's Witnesses|date=2008|publisher=Scarecrow Press|isbn=9780810862692|page=37|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xx6nUwZzeCsC&pg=PA37|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Most creationists reject the theory of ], viz. that ] gradually evolved over millions of years from simple to increasingly complex forms only by means of ] and ]. Evolutionary scientists hold that, on the contrary, there is abundant evidence in favour of evolution over time from sciences such as ], ] and ]. | |||
| The historic Christian literal interpretation of creation requires the harmonization of the two creation stories, Genesis 1:1–2:3<ref>{{bibleverse|Genesis|1–2:3}}</ref> and Genesis 2:4–25,<ref>{{bibleverse|Genesis|2:4–25}}</ref> for there to be a consistent interpretation.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.apologeticspress.org/articles/2194 |title=Are There Two Creation Accounts in Genesis? |last=Jackson |first=Wayne |website=Apologetics Press |date=31 December 1990 |location=Montgomery, Al |access-date=2007-05-23}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.rejectionofpascalswager.net/creationint.html |last=Tobin |first=Paul N. |year=2000 |title=The Creation Myths: Internal Difficulties |website=The Rejection of Pascal's Wager: A Skeptic's Guide to Christianity |publisher=Paul Tobin |location=Singapore |access-date=2014-03-19 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141008175621/http://www.rejectionofpascalswager.net/creationint.html |archive-date=2014-10-08 }}</ref> They sometimes seek to ensure that their belief is taught in science classes, mainly in American schools. Opponents reject the claim that the literalistic biblical view meets the criteria required to be considered scientific. Many religious groups teach that God created the Cosmos. From the days of the early Christian Church Fathers there were allegorical interpretations of the Book of Genesis as well as literal aspects.<ref name="rsf">]</ref> | |||
| The "creationism vs. evolution" debate began when evolution by natural selection was proposed by ] and ] in 1858. Darwin's (1859) '']'' became the focal point of creationist debate at a time when universities were still dominated by religious thought. Darwin was well aware of the likely implications of his work for people with strong religious beliefs (such as his own wife) and delayed its publication until he became aware that Wallace was about to publish similar views. Darwin's book sparked an immediate and furious controversy on both sides of the Atlantic, dividing not just secular and religious but also literal and non-literal theists. One of the most famous incidents in the debate was the Oxford Meeting of ], when ], Darwin's self-appointed "bulldog", publicly debated Darwin's theory with the Bishop of Oxford, ]. Darwin's ideas continued to arouse controversy in Europe for years afterwards, but by the ] it had become the accepted popular explanation for the modification of organisms over time. (see ]) | |||
| ], a system of thought and practice derived from the writings of ], interprets the Book of Genesis figuratively rather than literally. It holds that the material world is an illusion, and consequently not created by God: the only real creation is the spiritual realm, of which the material world is a distorted version. Christian Scientists regard the story of the creation in the Book of Genesis as having symbolic rather than literal meaning. According to Christian Science, both creationism and evolution are false from an absolute or "spiritual" point of view, as they both proceed from a (false) belief in the reality of a material universe. However, Christian Scientists do not oppose the teaching of evolution in schools, nor do they demand that alternative accounts be taught: they believe that both material science and literalist theology are concerned with the illusory, mortal and material, rather than the real, immortal and spiritual. With regard to material theories of creation, Eddy showed a preference for Darwin's theory of evolution over others.<ref name=S&Hp547>], p. 547</ref> | |||
| By contrast, the stronger presence of Christian fundamentalism in the ] meant that while academic opinion was generally in favour of Darwinism, public and legislative opinion, especially in the ] states of the South, was strongly pro-creationism. The clash between academia and legislatures came to a head in ], when the famous ] tested a law that forbade the teaching of evolution in ] public schools. The law was not repealed until 1968, when it was ruled unconstitutional by the ]. The debate has intensified in recent years with the growing involvement of the ] in U.S. politics, which has seen the creationism vs. evolution debate taking on increasingly partisan political overtones. | |||
| ===Hinduism=== | |||
| Creationism has shifted over the past century as the advance of scientific knowledge and growing judicial strictness in the interpretation of the U.S. Constitution have squeezed out the more overtly religious or unscientific creationist forays into the classroom. In recent times, Christian creationism has been a driving force of the ] (ID) movement. <!-- I don't find that ID proponents specify which theology is at the root of creation; rather they propose scientific concepts that they claim make sense of what is found in nature. --> Advocates of ID never explicitly name God as their intelligent designer. Opponents of ID criticise its theories as ] and accuse the movement of attempting to introduce a disguised version of creationism into the classroom. Although the ID movement is well-organised and well-funded by Christian conservatives, it has so far achieved relatively few endorsements. | |||
| {{Main|Hindu views on evolution}} | |||
| Hindu creationists claim that species of ] and ] are material forms adopted by pure consciousness which live an endless cycle of births and rebirths.<ref>], p. 140</ref> ] says that: "Hindu Creationists have insisted on the antiquity of humans, who they believe appeared fully formed as long, perhaps, as trillions of years ago."<ref>], p. 420</ref> Hindu creationism is a form of old Earth creationism, according to Hindu creationists the universe may even be older than billions of years. These views are based on the ], the creation myths of which depict an extreme antiquity of the universe and history of the Earth.<ref>], p. 167</ref><ref>], p. 10</ref> | |||
| In ], time cyclically repeats general events of creation and destruction, with many "first man", each known as ], the progenitor of mankind. Each Manu successively reigns over a 306.72 million year period known as a {{transliteration|sa|]}}, each ending with the destruction of mankind followed by a {{transliteration|sa|sandhya}} (period of non-activity) before the next {{transliteration|sa|manvantara}}. 120.53{{nbsp}}million years have elapsed in the current {{transliteration|sa|manvantara}} (current mankind) according to calculations on ].<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |editor-last1=Doniger |editor-first1=Wendy |editor-link1=Wendy Doniger |editor-last2=Hawley |editor-first2=John Stratton |year=1999 |title=Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780877790440 |url-access=registration |encyclopedia=] |publisher=] |page=691 (Manu) |isbn=0877790442 |quote=a day in the life of Brahma is divided into 14 periods called manvantaras ("Manu intervals"), each of which lasts for 306,720,000 years. In every second cycle the world is recreated, and a new Manu appears to become the father of the next human race. The present age is considered to be the seventh Manu cycle.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author-last=Krishnamurthy |author-first=V. |date=2019 |chapter=Ch. 20: The Cosmic Flow of Time as per Scriptures |title=Meet the Ancient Scriptures of Hinduism |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HF2NDwAAQBAJ&q=%227th+manvantara%22+%2228th%22&pg=PT407 |publisher=Notion Press |isbn=9781684669387 |quote=Each manvantara is preceded and followed by a period of 1,728,000 (= 4K) years when the entire earthly universe (bhu-loka) will submerge under water. The period of this deluge is known as manvantara-sandhya (sandhya meaning, twilight).{{nbsp}} According to the traditional time-keeping{{nbsp}} Thus in Brahma's calendar the present time may be coded as his 51st year – first month – first day – 7th manvantara – 28th maha-yuga – 4th yuga or kaliyuga.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author-last=Gupta |author-first=S. V. |year=2010 |chapter=Ch. 1.2.4 Time Measurements |editor-last1=Hull |editor-first1=Robert |editor-last2=Osgood |editor-first2=Richard M. Jr. |editor-link2=Richard M. Osgood Jr. |editor-last3=Parisi |editor-first3=Jurgen |editor-last4=Warlimont |editor-first4=Hans |title=Units of Measurement: Past, Present and Future. International System of Units |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pHiKycrLmEQC&pg=PA7 |series=Springer Series in Materials Science: 122 |publisher=] |pages=7 |isbn=9783642007378}}</ref> The universe is cyclically created at the start and destroyed at the end of a {{transliteration|sa|]}} (day of ]), lasting for 4.32{{nbsp}}billion years, which is followed by a {{transliteration|sa|]}} (period of dissolution) of equal length. 1.97{{nbsp}}billion years have elapsed in the current {{transliteration|sa|kalpa}} (current universe). The universal elements or building blocks (unmanifest matter) exists for a period known as a {{transliteration|sa|maha-kalpa}}, lasting for 311.04{{nbsp}}trillion years, which is followed by a {{transliteration|sa|maha-pralaya}} (period of great dissolution) of equal length. 155.52{{nbsp}}trillion years have elapsed in the current {{transliteration|sa|maha-kalpa}}.{{sfn|Gupta|2010|pages=7-8}}<ref>{{cite book |author-last=Penprase |author-first=Bryan E. |year=2017 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pQHNDgAAQBAJ |title=The Power of Stars |edition=2nd |publisher=] |page=182 |isbn=9783319525976}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Johnson|first=W.J.|title=A Dictionary of Hinduism|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=2009|isbn=978-0-19-861025-0|page=165}}</ref> | |||
| Creationism of any variety has also made little headway against mainstream scientific opinion; the vast majority of scientists accept the theory of evolution through mutations and natural selection. While many scientists believe in God, probably the reason for rejection of creationism or Intelligent Design is the need to have a God or an Intelligence to do the design, and to date no scientific experiments or observations support the hypothesis that such a being exists. However, perhaps as a result of resurgent Christian fundamentalism gaining converts among well-educated right-wing Americans, a small but vociferous number of academics have come out in favour of creationist ideas. | |||
| ===Islam=== | |||
| === Creationism and the origins of life === | |||
| {{Main|Islamic views on evolution|}} | |||
| {{See|Predestination in Islam}} | |||
| The creation myths in the Quran are more vague and allow for a wider range of interpretations similar to those in other Abrahamic religions.<ref name="nytimes.com"/> | |||
| Islam also has its own school of theistic evolutionism, which holds that mainstream scientific analysis of the origin of the universe is supported by the Quran. Some ] believe in evolutionary creation, especially among ].<ref name="Huffpo"/> | |||
| While the Bible makes no distinction between the ] and the ] — both are said to have been created by God — science does make this distinction. The question of the origins of life is known as ] and is treated by science as being quite distinct from the question of ]. The two subjects are also quite different in terms of scientific maturity and testability. Although scientists disagree about the fine details, the majority regard Darwin's principle of natural selection, combined with the discovery of genetic mutations, as the best explanation for the observable process of evolution. By contrast, there is no single widely accepted theory of abiogenesis and the process itself does not appear to be ongoing today, nor has anyone so far found a way of making it happen in the laboratory. This does not invalidate the concept of evolution, since it only addresses the way life develops, not how life originates. | |||
| Writing for '']'', Drake Bennett noted: "Without a Book of Genesis to account for{{nbsp}} Muslim creationists have little interest in proving that the age of the Earth is measured in the thousands rather than the billions of years, nor do they show much interest in the problem of the dinosaurs. And the idea that animals might evolve into other animals also tends to be less controversial, in part because there are passages of the Koran that seem to support it. But the issue of whether human beings are the product of evolution is just as fraught among Muslims."<ref name="Bennett 4">{{cite news |last=Bennett |first=Drake |date=October 25, 2009 |title=Islam's Darwin problem |url=http://www.boston.com/bostonglobe/ideas/articles/2009/10/25/in_the_muslim_world_creationism_is_on_the_rise/?page=full |newspaper=] |location=Boston, MA |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091030044754/http://www.boston.com/bostonglobe/ideas/articles/2009/10/25/in_the_muslim_world_creationism_is_on_the_rise/?page=full |archive-date=2009-10-30 |access-date=2014-03-21}}</ref> Khalid Anees, president of the ], states that Muslims do not agree that one species can develop from another.<ref name="PrizeforFossil">{{cite news |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/religion/3102103/Creationist-Adnan-Oktar-offers-trillion-pound-prize-for-fossil-proof-of-evolution.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/religion/3102103/Creationist-Adnan-Oktar-offers-trillion-pound-prize-for-fossil-proof-of-evolution.html |archive-date=2022-01-12 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |last=Irvine |first=Chris |date=September 29, 2008 |title=Creationist Adnan Oktar offers trillion-pound prize for fossil proof of evolution |newspaper=] |location=London |access-date=2014-03-21}}{{cbignore}}</ref><ref name=guardian0104>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=January 7, 2004 |url=http://education.guardian.co.uk/conferences/story/0,,1117752,00.html |title=Creationism: Science and Faith in Schools |newspaper=The Guardian |type=Conferences |location=London |access-date=2008-07-18}}</ref> | |||
| Creationists often answer both the question of evolution and of abiogenesis by arguing that because neither the origins of life nor the course of human evolution or the evolution of life can be reproduced experimentally, they fall outside the scope of empirical science and into ] or ] or ] (in turn, the concept of evolution is split into ] and ]). As such, they say, the full range of opinions — including creationism and related theories of divine intervention — should at least be discussed on an equal basis. Supporters of evolution reject this and claim that evolution can be observed experimentally in the laboratory, in the field, and in computer simulations. Although the actual creation of life has not yet been observed experimentally, much experimental work into the necessary conditions has been carried out (for instance, research into the formation of long proteins or into molecule formation in different atmospheres). By contrast, proposed explanations involving divine intervention are either impervious to scientific verification in principle, or have so far proven to be so. | |||
| Ottoman-Lebanese Sunni scholar Hussein al-Jisr, declared that there is no contradiction between evolution and the Islamic scriptures. He stated that "there is no evidence in the Quran to suggest whether all species, each of which exists by the grace of God, were created all at once or gradually", and referred to the aforementioned story of creation in Sūrat al-Anbiyā.<ref>{{cite web |last=Adra |first=Jawad |title=Political inheritance-Absent entirely within the Shia'a community, dwindling within the Maronite and Sunni communities and omnipresent within the Druze |url=https://monthlymagazine.com/article-desc_1812_ |access-date=20 July 2020 |website=Monthly Magazine |archive-date=20 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200720052715/https://monthlymagazine.com/article-desc_1812_ |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Iqbāl |first=Muẓaffar |title=Science and Islam |date=2007 |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-313-33576-1 |page=157}}</ref><ref>Majid, Abdul. "The Muslim responses to evolution." Science-Religion Dialogue (2002).</ref><ref>Varisco, Daniel. "Darwin and Dunya: Muslim Responses to Darwinian Evolution." Journal of International & Global Studies 9.2 (2018).</ref> In ], important scholars strove to accommodate the theory of evolution in Islamic scripture during the first decades of the Turkish Republic; their approach to the theory defended Islamic belief in the face of scientific theories of their times.<ref name="Vkaya">{{cite journal |last=Kaya |first=Veysel |date=April 2012 |title=Can the Quran Support Darwin? An Evolutionist Approach by Two Turkish Scholars after the Foundation of the Turkish Republic |journal=The Muslim World |volume=102 |issue=2 |page=357 |doi=10.1111/j.1478-1913.2011.01362.x}}</ref> | |||
| === Creation science === | |||
| The Saudi Arabian government, on the other hand, began funding and promoting denial of evolution in the 1970s in accordance to its ]-] interpretation of Islam.<ref name="BurtonIRNKSA2">{{cite journal |last=Burton |first=Elise K. |date=May–June 2010 |title=Teaching Evolution in Muslim States:Iran and Saudi Arabia Compared |url=http://xa.yimg.com/kq/groups/19234639/1613108208/name/Iran%20and%20Saudi%20Arabia%20Compared.pdf |url-status=dead |journal=Reports of the National Center for Science Education |volume=30 |issue=3 |pages=25–29 |issn=2158-818X |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180219014741/http://xa.yimg.com/kq/groups/19234639/1613108208/name/Iran%20and%20Saudi%20Arabia%20Compared.pdf |archive-date=2018-02-19 |access-date=2014-01-13}}</ref> This stance garnered criticism from the governments and academics of mainline Muslim countries such as Turkey,<ref>{{Cite web |date=1 March 2017 |title=Turkish academics tell ministry that evolution theory excluded from curriculum 'only in Saudi Arabia' |url=http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/turkish-academics-tell-ministry-that-evolution-theory-excluded-from-curriculum-only-in-saudi-arabia.aspx?PageID=238&NID=110307&NewsCatID=341 |access-date=24 April 2017 |website=Hürriyet Daily News}}</ref> Pakistan,<ref>{{cite web |author=IAP Member Academies |date=June 21, 2006 |title=IAP Statement on the Teaching of Evolution |url=http://www.interacademies.net/10878/13901.aspx |access-date=2014-06-20 |website=] |publisher=] |location=Trieste, Italy |archive-date=2011-07-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110717190031/http://www.interacademies.net/10878/13901.aspx |url-status=dead }}</ref> Lebanon,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Vlaardingerbroek |first1=Barend |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=grp_CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA161 |title=The Status of Evolutionary Theory in Undergraduate Biology |last2=Hachem-el-Masri |first2=Yasmine |date=23 October 2006 |journal=International Journal of Educational Reform |volume=15 |number=2 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |isbn=9781475816457 |pages=161–162}}</ref> and Iran,<ref name="BurtonIRNKSA2" /> where evolution was initially taught and promoted. Since the 1980s, Turkey has been a site of strong advocacy for creationism, supported by American adherents.<ref name="NCSE Edis">{{cite journal |last=Edis |first=Taner |date=November–December 1999 |title=Cloning Creationism in Turkey |url=http://ncse.com/rncse/19/6/cloning-creationism-turkey |journal=Reports of the National Center for Science Education |volume=19 |issue=6 |pages=30–35 |issn=2158-818X |access-date=2008-02-17}}</ref><ref name=WaPo2009>{{cite news |last=Kaufman |first=Marc |date=November 8, 2009 |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/11/07/AR2009110702233.html |title=In Turkey, fertile ground for creationism |newspaper=] |location=Washington, D.C. |access-date=2014-03-21}}</ref> | |||
| Some creationists posit that certain assumptions, procedures, theories, and findings of science, particularly the theory of evolution through natural selection, are scientifically incorrect. ''Creation science'' is a modern movement that attacks these ideas on ostensibly scientific grounds and proposes alternative theories that are more compatible with creationism. The term "creation science" covers a broad spectrum of beliefs. Some creation scientists do not seek to challenge mainstream science, while others go so far as to deny the applicability of the ] or ] to religiously-inspired beliefs about the physical world. | |||
| ===Judaism=== | |||
| Not all creationists are creation scientists. Some creationists view scientific truth as separate from spiritual truth and are unconcerned by apparent contradictions between the two. | |||
| {{Main|Jewish views on evolution}} | |||
| For ] who seek to reconcile discrepancies between science and the creation myths in the Bible, the notion that science and the Bible should even be reconciled through traditional scientific means is questioned. To these groups, science is as true as the ] and if there seems to be a problem, ] limits are to blame for apparently irreconcilable points. They point to discrepancies between what is expected and what actually is to demonstrate that things are not always as they appear.{{citation needed|date=November 2024}} They note that even the root word for 'world' in the ], {{langx|hbo|עולם|Olam|label=none}}, means 'hidden' ({{langx|hbo|נעלם|Neh-Eh-Lahm|label=none}}).{{citation needed|date=November 2024}} Just as they know from the Torah that God created man and trees and the light on its way from the stars in their observed state, so too can they know that the world was created in its over the six days of Creation that reflects progression to its currently-observed state, with the understanding that physical ways to verify this may eventually be identified.{{citation needed|date=November 2024}} This knowledge has been advanced by Rabbi ], former philosophy professor at ].{{Citation needed|date=August 2015}} | |||
| ] sources from well before the scientifically apparent age of the universe was first determined are also in close concord with modern scientific estimates of the age of the universe, according to Rabbi ], and based on Sefer Temunah, an early kabbalistic work attributed to the first-century ] ].{{Citation needed|date=November 2024}} Many kabbalists accepted the teachings of the ], including the medieval Jewish scholar ], his close student ], and ]. Other parallels are derived, among other sources, from Nahmanides, who expounds that there was a ]-like species with which Adam mated (he did this long before Neanderthals had even been discovered scientifically).<ref>]</ref><ref>]</ref><ref>]</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Tigay |first=Jeffrey H. |date=Winter 1987–1988 |title=Genesis, Science, and 'Scientific Creationism' |url=http://www.sas.upenn.edu/~jtigay/sci.htm |journal=] |volume=40 |issue=2 |pages=20–27 |issn=0010-6542 |access-date=2014-03-21}}</ref> ] does not take the Torah as a literal text, but rather as a symbolic or open-ended work. | |||
| Creation science has been criticized by many mainstream scientists for making fundamental scientific errors and misstatements in its assertions. For instance, some creation scientists claim that evolution violates the ], but mainstream scientists see no contradiction because such a claim assumes a system with no energy input, manifestly untrue of Earth which at a minimum receives energy from the Sun. Consequently most mainstream scientists regard creation science as, at best, a ]. | |||
| Some contemporary writers such as Rabbi Gedalyah Nadel have sought to reconcile the discrepancy between the account in the Torah, and scientific findings by arguing that each day referred to in the Bible was not 24 hours, but billions of years long.<ref name=slifkin>The Challenge of Creation: Judaism's Encounter with Science, Cosmology, and Evolution, Natan Slifkin, Zoo Torah, 2006</ref>{{rp|129}} Others claim that the Earth was created a few thousand years ago, but was deliberately made to look as if it was five billion years old, e.g. by being created with ready made fossils. The best known exponent of this approach being Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson.<ref name=slifkin/>{{rp|158}} Others state that although the world was physically created in six 24-hour days, the Torah accounts can be interpreted to mean that there was a period of billions of years before the six days of creation.<ref name=slifkin/>{{rp|169, 170}} | |||
| Many critics of creation science believe that all creation scientists attempt to falsely disguise the Biblical story of creation as science (Arthur, 1996). United States ]s, including the ], have been receptive to this argument, and have overturned various state laws seeking to give creation science equal time with the theory of evolution in public schools. See, for example, '']'', 482 U.S. 578 (1987) and '']'', 529 F.Supp. 1255 (1982); also '']'', 403 US 602 (1971). | |||
| ==Prevalence== | |||
| ==== Intelligent design ==== | |||
| {{Main|Level of support for evolution|Creationism by country}} | |||
| The above-mentioned ] movement allows for macroevolution but denies the theory of natural selection as a probable mechanism, arguing that God has guided the evolution. Most scientists argue that intelligent design is not scientific because it is ]. Another argument is that the possibility of an intelligent designer is real, but substantially more complex than alternative possibilities, such as a modified theory of evolution, or even the possibility of extraterrestrial origin. As such, the theory falls foul of the well-tested scientific principle of Occam's Razor. If God, or an unspecified "designer", guided the process, this raises further questions, such as: | |||
| ] |volume=198 |issue=2652 |page=31 |doi=10.1016/S0262-4079(08)60984-7 |issn=0262-4079 |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Hecht |first=Jeff |date=August 19, 2006 |title=Why doesn't America believe in evolution? |url=https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn9786-why-doesnt-america-believe-in-evolution.html |journal=New Scientist |volume=191 |issue=2565 |page=11 |doi=10.1016/S0262-4079(06)60136-X |issn=0262-4079 |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref>]] | |||
| Most vocal literalist creationists are from the US, and strict creationist views are much less common in other developed countries. According to a study published in '']'', a survey of the US, Turkey, ] and Europe showed that public acceptance of evolution is most prevalent in Iceland, Denmark and Sweden at 80% of the population.<ref name="Science survey" /> There seems to be no significant correlation between believing in evolution and understanding evolutionary science.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.culturalcognition.net/blog/2014/5/24/weekend-update-youd-have-to-be-science-illiterate-to-think-b.html |title=Weekend update: You'd have to be science illiterate to think 'belief in evolution' measures science literacy |last=Kahan |first=Dan |author-link=Dan Kahan |date=May 24, 2014 |website=] |publisher=] |location=New Haven, CT |type=Blog |access-date=2015-03-23 |archive-date=2021-02-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210217060100/http://www.culturalcognition.net/blog/2014/5/24/weekend-update-youd-have-to-be-science-illiterate-to-think-b.html |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Shtulman |first=Andrew |date=March 2006 |title=Qualitative differences between naïve and scientific theories of evolution |journal=Cognitive Psychology |volume=52 |issue=2 |pages=170–94 |doi=10.1016/j.cogpsych.2005.10.001 |pmid=16337619 |s2cid=20274446 |issn=0010-0285 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Australia=== | |||
| * What designed the Designer(s)? (see ]) | |||
| A 2009 ] poll showed that 23% of Australians believe "the biblical account of human origins," 42% believe in a "wholly scientific" explanation for the origins of life, while 32% believe in an evolutionary process "guided by God".<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.smh.com.au/national/faith-what-australians-believe-in-20091218-l5qy.html |title=Faith: What Australians believe in |last=Marr |first=David |date=December 19, 2009 |work=] |location=Melbourne, Australia |archive-url=https://archive.today/20181211051311/https://www.smh.com.au/national/faith-what-australians-believe-in-20091218-l5qy.html |archive-date=December 11, 2018 |url-status=live |access-date=December 11, 2018 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Maley |first=Jacqueline |date=December 19, 2009 |title=God is still tops but angels rate well |url=http://www.theage.com.au/national/god-is-still-tops-but-angels-rate-well-20091218-l5v9.html |work=] |location=Melbourne, Australia |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120913234134/http://www.theage.com.au/national/god-is-still-tops-but-angels-rate-well-20091218-l5v9.html |archive-date=September 13, 2012 |access-date=December 18, 2009 |url-status=live |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| * What is the Designers' motivation for guiding an evolutionary process? | |||
| * Who or what is the Designer(s)? | |||
| * What is the evidence for the existence of the Designer(s)? | |||
| * Which methods did the Designer(s) use to "guide" the process? | |||
| * What is the evidence for the use of such methods? | |||
| * Did or does the Designer also do this on other planets, or only on Earth? | |||
| * Why did the Designer(s) choose to use a process that requires further intervention? | |||
| A 2013 survey conducted by Auspoll and the ] found that 80% of Australians believe in evolution (70% believe it is currently occurring, 10% believe in evolution but do not think it is currently occurring), 12% were not sure and 9% stated they do not believe in evolution.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.science.org.au/files/userfiles/learning/documents/ScienceLiteracyReport2013.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.science.org.au/files/userfiles/learning/documents/ScienceLiteracyReport2013.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=Science literacy in Australia |date=2013 |work=] }}</ref> | |||
| A further problem is presented by the essential unprovability (or disprovability) of the Designer's methodology. Dr. Duane Gish, a prominent advocate of intelligent design, highlights this issue in his 1978 book ''Evolution? The Fossils Say No!'': "We do not know how the Creator created, what processes He used, ''for He used processes which are not now operating in the natural universe'' ... We cannot discover by scientific investigation anything about the creative processes used by the Creator." | |||
| ===Brazil=== | |||
| ===== Irreducible complexity ===== | |||
| A 2011 ] survey found that 47% of responders in ] identified themselves as "creationists and believe that human beings were in fact created by a spiritual force such as the God they believe in and do not believe that the origin of man came from evolving from other species such as apes".<ref name="Ipsos 2011">{{cite web |title=Ipsos Global @dvisory: Supreme Being(s), the Afterlife and Evolution |url=https://www.ipsos.com/en-us/news-polls/ipsos-global-dvisory-supreme-beings-afterlife-and-evolution |website=Ipsos |access-date=15 February 2020 |archive-date=17 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210817165805/https://www.ipsos.com/en-us/news-polls/ipsos-global-dvisory-supreme-beings-afterlife-and-evolution |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In 2004, ] conducted a poll in Brazil that asked questions about creationism and the teaching of creationism in schools. When asked if creationism should be taught in schools, 89% of people said that creationism should be taught in schools. When asked if the teaching of creationism should replace the teaching of evolution in schools, 75% of people said that the teaching of creationism should replace the teaching of evolution in schools.<ref>{{cite web |title=PESQUISA DE OPINIÃO PÚBLICA SOBRE O CRIACIONISMO |url=https://www.ibopeinteligencia.com/arquivos/Opp992-Revista%20Época.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.ibopeinteligencia.com/arquivos/Opp992-Revista%20Época.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |access-date=28 February 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Massarani |first1=Luisa |title=Few in Brazil accept scientific view of human evolution |url=https://www.scidev.net/global/news/few-in-brazil-accept-scientific-view-of-human-evol/ |access-date=28 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ] is the assertion that some structures, such as rotary ] and eyes, could not have developed gradually, because the necessary intermediate steps would be completely nonfunctional and maladaptive; therefore, such organs must be the work of an intelligent designer. This perspective has been extensively presented by biochemist Michael Behe in the book "Darwin's Black Box". | |||
| ===Canada=== | |||
| A common counterargument is that such organs do in fact have less-complex predecessors. Some see this as a ] argument in that the actual criteria that must be met is for all intermediate steps to be demonstrable as being both statistically explainable by genetic mutation, and individually functional and adaptive concurrent with this process. | |||
| ] in Big Valley, Alberta, Canada]] | |||
| A 2012 survey, by ] revealed that 61 percent of Canadians believe in evolution. The poll asked "Where did human beings come from{{snd}}did we start as singular cells millions of year ago and evolve into our present form, or did God create us in his image 10,000 years ago?"<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |title=Believe In Evolution: Canadians More Likely Than Americans To Endorse Evolution |url=http://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2012/09/06/believe-in-evolution_n_1861373.html |date=September 6, 2012 |work=] |publisher=] |access-date=2012-04-28 }} | |||
| * {{cite press release |last=Canseco |first=Mario |date=September 5, 2012 |title=Britons and Canadians More Likely to Endorse than Americans |url=http://www.angusreidglobal.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/2012.09.05_CreEvo.pdf |location=New York |publisher=] |access-date=2014-05-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140429224428/http://www.angusreidglobal.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/2012.09.05_CreEvo.pdf |archive-date=April 29, 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In 2019, a Research Co. poll asked people in Canada if creationism "should be part of the school curriculum in their province". 38% of Canadians said that creationism should be part of the school curriculum, 39% of Canadians said that it should not be part of the school curriculum, and 23% of Canadians were undecided.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Canseco |first1=Mario |title=Most Canadians Believe Human Beings on Earth Evolved |date=4 December 2019 |url=https://researchco.ca/2019/12/04/creationism-evolution-canada/ |access-date=28 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| The advent of computers has, to a limited extent, made claims of irreducible complexity testable through simple mathematical models. ], ''River out of Eden'' (1995) gives an example of a simulation where multiple independent organisms all showed a steady progression from a light-sensitive spot to a complex eye with a lens focus. | |||
| In 2023, a Research Co. poll found that 21% of Canadians "believe God created human beings in their present form within the last 10,000 years". The poll also found that "More than two-in-five Canadians (43%) think creationism should be part of the school curriculum in their province."<ref>{{cite web |last1=Canseco |first1=Mario |title=By a 3-to-1 Margin, Canadians Choose Evolution Over Creationism |url=https://researchco.ca/2023/04/14/evolution-2023/ |website=Research Co. |date=14 April 2023 |access-date=23 May 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Macroevolution vs. microevolution ==== | |||
| ===Europe=== | |||
| Creationists often make a distinction between ] — any evolutionary change at or above the level of kind—and ]—any evolutionary change below the level of a kind. They often cite Genesis 1:21,24-25 as evidence that each distinct type of creature is its own kind, and cannot be changed into another kind. For example, a man and a dog represent two different kinds, and so it is impossible to turn a man into a dog or vice versa. On the other hand, a ] and a ] are two breeds or ''varieties'' of the same kind, in this case the common ] ''Canis domesticus'', and it is clearly possible to effect change at the microevolutionary level by interbreeding them. | |||
| In Europe, literalist creationism is more widely rejected, though regular opinion polls are not available. Most people accept that evolution is the most widely accepted scientific theory as taught in most schools. In countries with a Roman Catholic majority, ] as worthy of study has essentially ended debate on the matter for many people. | |||
| In the UK, a 2006 poll on the "origin and development of life", asked participants to choose between three different perspectives on the origin of life: 22% chose creationism, 17% opted for intelligent design, 48% selected evolutionary theory, and the rest did not know.<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=January 26, 2006 |title=Britons unconvinced on evolution |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4648598.stm |work=BBC News |location=London |publisher=BBC |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ipsos-mori.com/researchpublications/researcharchive/poll.aspx?oItemId=262 |title=BBC Survey On The Origins Of Life |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=January 30, 2006 |website=] |publisher=Ipsos MORI |location=London |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref> A subsequent 2010 ] poll on the correct explanation for the origin of humans found that 9% opted for creationism, 12% intelligent design, 65% evolutionary theory and 13% didn't know.<ref name="YouGov">{{cite web |url=http://cdn.yougov.com/today_uk_import/YG-Archives-Pol-Prospect-Evolution-181110.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://cdn.yougov.com/today_uk_import/YG-Archives-Pol-Prospect-Evolution-181110.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=The origin of humans |date=November 20, 2010 |website=YouGov Global |publisher=] |location=London |type=Prospect Survey Results |access-date=2014-03-24}}</ref> The former Archbishop of Canterbury Rowan Williams, head of the worldwide ], views the idea of teaching creationism in schools as a mistake.<ref name="Archbishop_2006">{{cite news |last=Bates |first=Stephen |date=March 20, 2006 |title=Archbishop: stop teaching creationism |url=https://www.theguardian.com/uk/2006/mar/21/religion.topstories3 |newspaper=The Guardian |location=London |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref> In 2009, an Ipsos Mori survey in the United Kingdom found that 54% of Britons agreed with the view: "Evolutionary theories should be taught in science lessons in schools together with other possible perspectives, such as intelligent design and creationism."<ref>{{cite web |last1=Shepherd |first1=Jessica |title=Teach both evolution and creationism say 54% of Britons |website=] |date=25 October 2009 |url=https://www.theguardian.com/science/2009/oct/25/teach-evolution-creationism-britons |access-date=6 April 2020}}</ref> | |||
| With the rise of modern taxonomy, the scientific notion of species became distinct from the notion of a kind. However, they are often confused or conflated. To a creationist, a kind is an immutable attribute of every creature that propagates to its descendants; to a scientist, a species is a label that designates a creature as part of a larger group. For many creationists the very idea of macroevolution is a contradiction, because it is the change of an immutable attribute. | |||
| In Italy, Education Minister ] wanted to retire evolution from the secondary school level; after one week of massive protests, she reversed her opinion.<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=May 3, 2004 |title=Italy Keeps Darwin in its Classrooms |url=http://www.dw.de/italy-keeps-darwin-in-its-classrooms/a-1188423-1 |work=Deutsche Welle |location=Bonn, Germany |publisher=ARD |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Lorenzi |first=Rossella |date=April 28, 2004 |title=No evolution for Italian teens |url=http://www.the-scientist.com/?articles.view/articleNo/22817/title/No-evolution-for-Italian-teens/ |journal=] |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref> | |||
| Even as late as the ]s, this was also true of the scientific definition of species. Speciation was thought to be impossible, and ] expressed the conventional view when he opined that "there are as many species as the Creator produced forms in the beginning." But since the rise of evolutionary theory, almost all scientists have said that speciation is an ordinary event and that cases of speciation have been clearly documented. For scientists, this has turned macroevolution into a natural idea, since for them it's just a matter of calling different things by different names. | |||
| There continues to be scattered and possibly mounting efforts on the part of religious groups throughout Europe to introduce creationism into public education.<ref name="Economist_2007">{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=April 19, 2007 |title=In the beginning |url=http://www.economist.com/node/9036706 |newspaper=] |location=London |publisher=] |issn=0013-0613 |access-date=2007-04-25}} This article gives a worldwide overview of recent developments on the subject of the controversy.</ref> In response, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe has released a draft report titled ''The dangers of creationism in education'' on June 8, 2007,<ref name="Doc11297">{{cite web|url=http://www.assembly.coe.int/ASP/Doc/XrefViewHTML.asp?FileID=11678&Language=EN |title=The dangers of creationism in education |date=June 8, 2007 |work=Committee on Culture, Science and Education |publisher=Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe |type=Report |id=Doc. 11297 |access-date=2014-03-22 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130309011447/http://assembly.coe.int/ASP/Doc/XrefViewHTML.asp?FileID=11678&Language=EN |archive-date=March 9, 2013 }}</ref> reinforced by a further proposal of banning it in schools dated October 4, 2007.<ref name="R1580">{{cite web|url=http://assembly.coe.int/main.asp?link=/documents/adoptedtext/ta07/eres1580.htm |title=The dangers of creationism in education |date=October 4, 2007 |work=Committee on Culture, Science and Education |publisher=] |type=Resolution |id=Resolution 1580 |access-date=2014-03-22 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307163155/http://assembly.coe.int/Main.asp?link=%2FDocuments%2FAdoptedText%2Fta07%2FERES1580.htm |archive-date=March 7, 2014 }} Paras. 13, 18</ref> | |||
| Most creationists accept the observable evidence of microevolution in the light of examples such as ]es on the Galapagos islands evolving from one original base form into a variety of different forms adapted to the circumstances peculiar to their home islands. Similar examples are found in the fossil record and are commonly encountered in studies of organisms with a high rate of reproduction, particularly bacteria and insects. However, creationists treat macroevolution with considerably more skepticism and suggest that if it occurs at all—which some deny—it does not occur for the reasons proposed by evolutionary theory. | |||
| Serbia suspended the teaching of evolution for one week in September 2004, under education minister ], only allowing schools to reintroduce evolution into the curriculum if they also taught creationism.<ref name="Serbian_schools">{{cite news |last=de Quetteville |first=Harry |date=September 9, 2004 |title=Darwin is off the curriculum for Serbian schools |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/1471367/Darwin-is-off-the-curriculum-for-Serbian-schools.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/1471367/Darwin-is-off-the-curriculum-for-Serbian-schools.html |archive-date=2022-01-12 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |newspaper=The Daily Telegraph |location=London |access-date=January 24, 2012}}{{cbignore}}</ref> "After a deluge of protest from scientists, teachers and opposition parties" says the BBC report, Čolić's deputy made the statement, "I have come here to confirm Charles Darwin is still alive" and announced that the decision was reversed.<ref name="Serbia_Darwin">{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=September 9, 2004 |title=Serbia reverses Darwin suspension |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/3642460.stm |work=] |location=London |publisher=] |access-date=2014-03-21 }}</ref> Čolić resigned after the government said that she had caused "problems that had started to reflect on the work of the entire government."<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=September 16, 2004 |title='Anti-Darwin' Serb minister quits |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/3663196.stm |work=BBC News |location=London |publisher=BBC |access-date=2014-03-27}}</ref> | |||
| ===== Fossils and macroevolution ===== | |||
| Poland saw a major controversy over creationism in 2006, when the Deputy Education Minister, ], denounced evolution as "one of many lies" taught in Polish schools. His superior, Minister of Education ], has stated that the theory of evolution would continue to be taught in Polish schools, "as long as most scientists in our country say that it is the right theory." Giertych's father, ] ], has opposed the teaching of evolution and has claimed that ]s and humans co-existed.<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=December 18, 2006 |title=And finally... |url=http://www.wbj.pl/?command=article&id=35336&type=wbj |newspaper=] |location=Warsaw, Poland |publisher=Valkea Media |access-date=2014-03-27 |archive-date=2020-01-12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200112170259/https://wbj.pl/?command=article&id=35336&type=wbj |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| A June 2015 – July 2016 Pew poll of Eastern European countries, found that 56% of people from ] say that humans and other living things have "Existed in present state since the beginning of time". Armenia is followed by 52% from ], 42% from ], 37% from ], 34% from ] and ], 33% from ] and ], 31% from ], 29% from ] and ], 26% from ], 25% from ], 23% from ] and ], 21% from ] and ], and 16% from the ].<ref>{{cite news |title=6. Science and religion |newspaper=Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project |date=10 May 2017 |url=https://www.pewforum.org/2017/05/10/science-and-religion/ |access-date=27 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ===South Africa=== | |||
| A 2011 Ipsos survey found that 56% of responders in ] identified themselves as "creationists and believe that human beings were in fact created by a spiritual force such as the God they believe in and do not believe that the origin of man came from evolving from other species such as apes".<ref name="Ipsos 2011"/> | |||
| ===South Korea=== | |||
| In 2009, an ] survey in South Korea found that 63% of people believed that creation and evolution should both be taught in schools simultaneously.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Science, state, and spirituality: Stories of four creationists in South Korea |year=2018 |doi=10.1177/0073275317740268 |last1=Park |first1=Hyung Wook |last2=Cho |first2=Kyuhoon |journal=History of Science |volume=56 |issue=1 |pages=35–71 |pmid=29241363 |hdl=10220/44270 |s2cid=206433157 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| ] theme park in Williamstown, Kentucky, United States]] | |||
| ] in Glendive, Montana, United States]] | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| A 2017 poll by ] found that 62% of Americans believe humans have evolved over time and 34% of Americans believe humans and other living things have existed in their present form since the beginning of time.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Masci|first1=David|title=For Darwin Day, 6 facts about the evolution debate|url=http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/02/10/darwin-day/|work=Pew Research Center|date=10 February 2017}}</ref> A 2019 ] creationism survey found that 40% of adults in the United States inclined to the view that "God created humans in their present form at one time within the last 10,000 years" when asked for their views on the origin and development of human beings.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://news.gallup.com/poll/261680/americans-believe-creationism.aspx| date=July 26, 2019| title=40% of Americans Believe in Creationism}}</ref> | |||
| According to a 2014 Gallup poll,<ref name="Gallup2014">{{cite web |url=http://www.gallup.com/poll/170822/believe-creationist-view-human-origins.aspx |title=In U.S., 42% Believe Creationist View of Human Origins |last=Newport |first=Frank |date=November 19, 2004 |website=Gallup.com |publisher=Gallup, Inc. |location=Omaha, NE |access-date=2014-05-10}}</ref> about 42% of Americans believe that "God created human beings pretty much in their present form at one time within the last 10,000 years or so."<ref name="Gallup2014" /> Another 31% believe that "human beings have developed over millions of years from less advanced forms of life, but God guided this process,"and 19% believe that "human beings have developed over millions of years from less advanced forms of life, but God had no part in this process."<ref name="Gallup2014" /> | |||
| Creationists claim that though many varieties of ]s and ]s exist, there is no record of an animal capable of bridging the gap between them, and that "gaps in the fossil record" reveal "]s" between different species which refute the idea of gradual transitions. | |||
| Belief in creationism is inversely correlated to education; of those with ]s, 74% accept evolution.<ref>{{cite AV media |people=Newport, Frank (Host) |date=June 11, 2007 |title=Evolution Beliefs |url=http://www.gallup.com/video/27838/Evolution-Beliefs.aspx |series=The Gallup Poll Daily Briefing |access-date=2014-03-27 |location=Omaha, NE |publisher=Gallup, Inc. |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140427004950/http://www.gallup.com/video/27838/Evolution-Beliefs.aspx |archive-date=April 27, 2014 }}</ref><ref name="Robinson_BA">{{cite web |url=http://www.religioustolerance.org/ev_publi.htm |title=Beliefs of the U.S. public about evolution and creation |last=Robinson |first=Bruce A. |date=November 1995 |website=ReligiousTolerance.org |publisher=Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance |location=Kingston, Canada |access-date=2007-11-11}}</ref> In 1987, '']'' reported: "By one count there are some 700 scientists with respectable academic credentials (out of a total of 480,000 U.S. earth and life scientists) who give credence to creation-science, the general theory that complex life forms did not evolve but appeared 'abruptly.'"<ref name="Robinson_BA" /><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Martz |first1=Larry |last2=McDaniel |first2=Ann |date=June 29, 1987 |title=Keeping God Out of the Classroom |url=http://kgov.com/files/docs/Newsweek-1987-God-Classroom.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://kgov.com/files/docs/Newsweek-1987-God-Classroom.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |journal=] |pages=23–24 |issn=0028-9604 |access-date=2015-09-25}}</ref> | |||
| Fossil finds are generally restricted only to the extremely small amount of sedimentary rock that is exposed on the surface of the Earth at any one time. The vast majority of actual fossils remain concealed within the rock strata. Scientists contend that new fossils are constantly being found and that we have thousands of fossil examples for many species showing transition states from one form to another. Creationists suggest that this evidence only shows examples of microevolution. | |||
| A 2000 poll for ] found 70% of the US public felt that evolution was compatible with a belief in God.<ref name="pfaw">{{cite web |url=http://media.pfaw.org/pdf/creationism/creationism-poll.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://media.pfaw.org/pdf/creationism/creationism-poll.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=Evolution and Creationism In Public Education: An In-depth Reading Of Public Opinion |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=March 2000 |website=] |publisher=People For the American Way |location=Washington, D.C. |access-date=2014-03-28}}</ref> | |||
| In recent years, the theory of ] has suggested that there might be unevenness in the rate of evolution. It claims that rapid ] happens in small populations which are cut off from others of their species, and that evolution in these small groups may occur too quickly for any significant number of fossils to be deposited and survive to the present day. The fossil record would thus show an abrupt transition from one form to another. This view has gained significant support among scientists, but it is still somewhat controversial. Creationists counter that punctuated equilibrium is an attempt to dodge the question of gaps in the fossil record by moving the action of evolution into a timeframe when it is impossible to prove or disprove. | |||
| According to a study published in ''Science'', between 1985 and 2005 the number of adult ]ns who accept evolution declined from 45% to 40%, the number of adults who reject evolution declined from 48% to 39% and the number of people who were unsure increased from 7% to 21%. Besides the US the study also compared data from 32 European countries, Turkey, and Japan. The only country where acceptance of evolution was lower than in the US was Turkey (25%).<ref name="Science survey" /> | |||
| Some supporters of evolution say that creationists often query whether a claimed transitional fossil truly represents a transition. According to these supporters of evolution, when a fossil is found that appears to lie in between two existing fossils, instead of representing a transition between them, a creationist will say that this discovery creates two new gaps that need to be explained. But this effectively demands an unbroken family tree of fossils, and since fossilization of organisms is a rare and exceptional event, not the norm, most scientists consider this an unreasonable standard. As a reasonable standard, scientists point to the fossil record of animals such as the ], whose fossil record is so complete that it is generally agreed not to have any missing links. | |||
| According to a 2011 Fox News poll, 45% of Americans believe in creationism, down from 50% in a similar poll in 1999.<ref name="Fox Creationism Poll">{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=September 7, 2011 |title=Fox News Poll: Creationism |url=https://www.foxnews.com/us/fox-news-poll-creationism/ |work=] |publisher=] |access-date=2011-09-22}}</ref> 21% believe in 'the theory of evolution as outlined by Darwin and other scientists' (up from 15% in 1999), and 27% answered that both are true (up from 26% in 1999).<ref name="Fox Creationism Poll" /> | |||
| Some supporters of evolution also say that creationists misinterpret the classification of intermediate fossils. For example, no fossil has ever been classified as a "reptile-bird", and some creationists cite this as evidence that there have been no transitionary fossils between reptiles and birds. Evolutionists say that adding a separate "reptile-bird" class would only make classification more complex, and that instead fossils are classified according to the characteristics they display the most. Additionally, say the evolutionists, there is lively debate about how many of these intermediate fossils should be classified, and that classification is often difficult even for specialists—thus proving that some fossils are not clearly either reptile or bird, but are intermediate. | |||
| In September 2012, educator and television personality Bill Nye spoke with the ] and aired his fears about acceptance of creationism, believing that teaching children that creationism is the only true answer without letting them understand the way science works will prevent any future innovation in the world of science.<ref name="APNews-20120924">{{cite news |last=Luvan |first=Dylan |date=September 24, 2012 |title=Bill Nye Warns: Creation Views Threaten US Science |url=http://bigstory.ap.org/article/bill-nye-warns-creation-views-threaten-us-science |agency=] |access-date=2014-03-09 |archive-date=2013-10-14 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131014114115/http://bigstory.ap.org/article/bill-nye-warns-creation-views-threaten-us-science |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name="Youtube-20120823">{{cite web |last1=Fowler |first1=Jonathan |last2=Rodd |first2=Elizabeth |title=Bill Nye: Creationism Is Not Appropriate For Children |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gHbYJfwFgOU | archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211030/gHbYJfwFgOU| archive-date=2021-10-30|date=August 23, 2012 |website=] |publisher=] |location=New York |access-date=2012-09-24}}{{cbignore}}</ref><ref name="NYT-20141103-JD">{{cite news |last=Deiviscio |first=Jeffrey |title=A Fight for the Young Creationist Mind: In 'Undeniable,' Bill Nye Speaks Evolution Directly to Creationists |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2014/11/04/science/in-undeniable-bill-nye-speaks-evolution-directly-to-creationists.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/https://www.nytimes.com/2014/11/04/science/in-undeniable-bill-nye-speaks-evolution-directly-to-creationists.html |archive-date=2022-01-01 |url-access=limited |date=November 3, 2014 |work=] |access-date=November 4, 2014 }}{{cbignore}}</ref> In February 2014, Nye defended ] in a ] with creationist Ken Ham on the topic of whether creation is a viable model of origins in today's modern, ].<ref name="NBC-20140204">{{cite news |last=Boyle |first=Alan |author-link=Alan Boyle |date=February 5, 2014 |title=Bill Nye Wins Over the Science Crowd at Evolution Debate |url=http://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/bill-nye-wins-over-science-crowd-evolution-debate-n22836 |work=] |access-date=2014-02-06}}</ref><ref name="TG-20140204">{{cite news |last=Kopplin |first=Zack |author-link=Zack Kopplin |date=February 4, 2014 |title=Why Bill Nye the Science Guy is trying to reason with America's creationists |url=https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2014/feb/04/bill-nye-science-guy-evolution-debate-creationists |newspaper=The Guardian |location=London |access-date=2014-02-06}}</ref><ref name="Debate-20140204">{{Cite video |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z6kgvhG3AkI | archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211030/z6kgvhG3AkI| archive-date=2021-10-30|title=Bill Nye Debates Ken Ham |last=Foreman |first=Tom (Moderator) |author-link=Tom Foreman |date=February 4, 2014 |website=YouTube |publisher=Answers in Genesis |location=Hebron, KY |access-date=2014-02-05}}{{cbignore}} (program begins at 13:14).</ref> | |||
| ===== Differences in scale ===== | |||
| ====Education controversies==== | |||
| Most biologists consider the difference between microevolution and macroevolution to be relative. Creationists who reject Darwin's theory of ] through ] argue that the difference is absolute. They have proposed that microevolution always takes the form of destructive genetic mutations, which happen to confer an advantage to individuals in a specific environment. Because macroevolution requires many constructive genetic changes, they argue that microevolution cannot lead to macroevolution. One example of a destructive mutation that conferred a competitive advantage under a specific situation occurred in ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', some strains of which are resistant to ]. But this resistance requires the bacterium to expend extra resources that the nonresistant bacteria do not, and so it does not compete well with them in the absence of penicillin. Competitive advantage is the driving force behind natural selection, so the relevance is unclear to evolution advocates. | |||
| {{Main|Rejection of evolution by religious groups}} <!-- should the latter redirect be used? Or a policy against redirects: ] --> | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| In the US, creationism has become centered in the political controversy over ], and whether teaching creationism in science classes conflicts with the separation of church and state. Currently, the controversy comes in the form of whether advocates of the intelligent design movement who wish to "]" in science classes have conflated ].<ref name="kitz" /> | |||
| ] polled 1500 North Americans about the teaching of evolution and creationism in November and December 1999. They found that most North Americans were not familiar with creationism, and most North Americans had heard of evolution, but many did not fully understand the basics of the theory. The main findings were: | |||
| More specifically, the contention of creationists is that the observed and verified process of microevolution does not lead to increasingly complex species. When the mutations occur, they lead to the elimination of certain useless genetic traits, decreasing the genetic complexity and diversity of the affected species. Creationists claim proponents of ] accept that increases in genetic complexity are brought about solely through improbable major mutation. | |||
| {{bar box | |||
| |title= Americans believe that:<ref name="pfaw" /> | |||
| |barwidth=200px | |||
| |width=80% | |||
| |bars= | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * Public schools should teach evolution only|silver|60|20%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * '''Only evolution should be taught in science classes, religious explanations <br />can be discussed in another class'''|gray|51|17%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * Creationism can be discussed in science class as a 'belief,' not a scientific theory|silver|87|29%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * '''Creationism and evolution should be taught as 'scientific theories' in science class'''|gray|39|13%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * Only Creationism should be taught|silver|48|16%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * '''Teach both evolution and Creationism, but unsure how to do so'''|gray|12|4%}} | |||
| {{bar percent| | |||
| * No opinion|silver|3|1%}} | |||
| }} | |||
| In such political contexts, creationists argue that their particular religiously based origin belief is superior to those of other ]s, in particular those made through secular or scientific rationale. Political creationists are opposed by many individuals and organizations who have made detailed critiques and given testimony in various court cases that the ] are opposed by the ] of the scientific community.<ref name="aaas">{{cite web|url=http://www.aaas.org/news/releases/2006/pdf/0219boardstatement.pdf|title=Statement on the Teaching of Evolution|date=February 16, 2006|publisher=]|location=Washington, D.C.|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060221125539/http://www.aaas.org/news/releases/2006/pdf/0219boardstatement.pdf|archive-date=2006-02-21|access-date=2014-03-09}} | |||
| Supporters of evolution respond by saying that the mechanisms of mutation show no preference for simplification. Furthermore, if the mutation were disadvantageous, it would probably die out, leaving diversity unchanged, and if the mutation were neutral, it would coexist with the original form, increasing diversity. Lastly, a series of advantageous simplifying mutations could produce a new species. | |||
| * {{cite press release|title=AAAS Denounces Anti-Evolution Laws as Hundreds of K-12 Teachers Convene for 'Front Line' Event|date=February 19, 2006|publisher=American Association for the Advancement of Science|location=St. Louis, MO|url=http://www.aaas.org/news/releases/2006/0219boardstatement.shtml|last=Pinholster|first=Ginger|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060421193306/http://www.aaas.org/news/releases/2006/0219boardstatement.shtml|archive-date=2006-04-21|access-date=2014-08-05}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Delgado |first=Cynthia |date=July 28, 2006 |title=Finding the Evolution in Medicine |url=http://nihrecord.od.nih.gov/newsletters/2006/07_28_2006/story03.htm |journal=] |issn=1057-5871 |access-date=2014-03-31 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081122022815/http://nihrecord.od.nih.gov/newsletters/2006/07_28_2006/story03.htm |archive-date=November 22, 2008 }} "...While 99.9 percent of scientists accept evolution, 40 to 50 percent of college students do not accept evolution and believe it to be 'just' a theory."{{snd}}]</ref> | |||
| ==Criticism== | |||
| Creationists claim that although helpful mutations have been observed, mutations that increase genetic complexity have not. This claim does not, however, appear to be borne out by recent evidence from comparative ], since larger-scale genetic rearrangements other than mutation, such as ] and ] do lead to increased genetic complexity. | |||
| === |
===Christian criticism=== | ||
| Most Christians disagree with the teaching of creationism as an alternative to evolution in schools.<ref>{{cite book |title=Exploring and Proclaiming the Apostles' Creed |first1=Roger |last1=van Harn |first2=David F. |last2=Ford |first3=Colin E. |last3=Gunton |publisher=A&C Black |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-8192-8116-6 |page=44 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GCXUAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA44}} </ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Foundational Falsehoods of Creationism |first1=Aron |last1=Ra |publisher=Pitchstone Publishing |year=2016 |isbn=978-1-63431-079-6 |page=182 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F-rvDAAAQBAJ}} </ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Martin |first=Joel W. |date=September 2010 |title=Compatibility of Major U.S. Christian Denominations with Evolution |journal=Evolution: Education and Outreach |volume=3 |issue=3 |pages=420–431 |language=en |doi=10.1007/s12052-010-0221-5|s2cid=272665 |doi-access=free }}</ref> Several religious organizations, among them the ], hold that their faith does not conflict with the scientific consensus regarding evolution.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ncse.com/media/voices/religion |title=Statements from Religious Organizations |website=National Center for Science Education |location=Berkeley, CA |access-date=2011-03-10|date=2008-09-08 }}</ref> The ], which has collected more than 13,000 signatures, is an "endeavor designed to demonstrate that religion and science can be compatible." | |||
| In his 2002 article "Intelligent Design as a Theological Problem", George Murphy argues against the view that life on Earth, in all its forms, is direct evidence of God's act of creation (Murphy quotes ]'s claim that he is speaking "of a God who acted openly and left his fingerprints on all the evidence."). Murphy argues that this view of God is incompatible with the Christian understanding of God as "the one revealed in the cross and resurrection of Christ." The basis of this theology is ] 45:15, "Verily thou art a God that hidest thyself, O God of Israel, the Saviour." | |||
| Creationists who entirely reject macroevolution also reject '']'', the idea that all life on Earth is descended from a common ancestor. Amongst creationists who do accept the theory of evolution, there is debate over whether to accept or reject the theory of common descent, and in particular, the common descent of mankind and other species. Those who reject common descent argue that although other life on Earth evolved, ] were fashioned and given life directly by God, unique in the creation. Evolutionary creationists and many advocates of Intelligent Design accept common descent. ] is one, stating "I dispute the mechanism of natural selection, not common descent". | |||
| Murphy observes that the execution of a Jewish carpenter by ] authorities is in and of itself an ordinary event and did not require ]. On the contrary, for the crucifixion to occur, God had to limit or "empty" himself. It was for this reason that ] wrote, in ] 2:5-8: | |||
| ==== Further arguments ==== | |||
| <blockquote>Let this mind be in you, which was also in Christ Jesus: Who, being in the form of God, thought it not robbery to be equal with God: But made himself of no reputation, and took upon him the form of a servant, and was made in the likeness of men: And being found in fashion as a man, he humbled himself, and became obedient unto death, even the death of the cross.</blockquote> | |||
| Other arguments against materialistic evolution, together with common rebuttals, include: | |||
| Murphy concludes that,<blockquote>Just as the Son of God limited himself by taking human form and dying on a cross, God limits divine action in the world to be in accord with rational laws which God has chosen. This enables us to understand the world on its own terms, but it also means that natural processes hide God from scientific observation.</blockquote>For Murphy, a theology of the cross requires that Christians accept a ], meaning that one cannot invoke God to explain natural phenomena, while recognizing that such acceptance does not require one to accept a ], which proposes that nature is all that there is.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Murphy |first=George L. |year=2002 |title=Intelligent Design as a Theological Problem |url=http://puffin.creighton.edu/nrcse/IDTHG.html |journal=Covalence: The Bulletin of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America Alliance for Faith, Science and Technology |volume=IV |issue=2 |oclc=52753579 |access-date=2014-03-31 |archive-date=2016-04-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160411004103/http://puffin.creighton.edu/NRCSE/IDTHG.html |url-status=dead }} Reprinted with permission.</ref> | |||
| #Rock strata | |||
| #*Rock strata are apparently out of order in some places. Creationists say that this contradicts the idea that the depth of a stratum indicates the age of the rock. Geologists say they expect the strata to be out of order in places. They are sometimes visibly folded or overthrust, with adjacent layers remaining adjacent in all but the border zones. | |||
| #*Creationists suggest that the existence of strata and fossils mean they were laid down catastrophically. Paleontologists say that is highly improbable that fossils were laid out catastrophically, since fossils of different types occur only in specific strata, with almost no exceptions among billions of samples. | |||
| #Inaccuracy of ] | |||
| #*Creationists say that calculating the date of crystallization of a rock from the concentration of a decay product, such as argon, will be unreliable because some of the decay product may have been in the melt from which the rock crystallized. Chemists say that when rocks are heated to the melting point, any argon contained in them is released into the atmosphere. When the rock recrystallizes, it becomes impermeable to gases again. As the potassium K-40 in the rock decays into argon A-40, the gas is trapped in the rock and accumulates until the time the chemist measures its concentration. | |||
| #*Creationists say that radiocarbon dating makes assumptions about the conditions present in and around an object throughout history. Chemists say that the dating techniques have been confirmed extensively on artifacts from known times in history, and have shown a high degree of success. | |||
| #*Creationists claim that the speed of light may have changed over time, thus changing the speed of radioactive decay. While there is some recent, controversial evidence that the speed of light might have changed in the very early universe, physicists say that the possible change is too small to create the claimed effects. | |||
| #Relativity and time measurement | |||
| #*The ] implies that the passage of time on Earth may have been different from the passage of time in the wider universe. Creationists state that while a few thousand years elapsed on earth, millions of years may have elapsed in the wider universe. Physicists say that for time to be warped on Earth enough to cause such an effect would cause a gravitational distortion large enough to destroy the planet. | |||
| The Jesuit priest ] has stated that it is "unfortunate that, especially here in America, creationism has come to mean...some literal interpretation of Genesis." He argues that "...Judaic-Christian faith is radically creationist, but in a totally different sense. It is rooted in belief that everything depends on God, or better, all is a gift from God."<ref>{{cite book|last1=Purcell|first1=Brendan|title=From Big Bang to Big Mystery: Human Origins in the Light of Creation and Evolution|date=2012|publisher=New City Press of the Focolare|isbn=978-1565484337|pages=94}}</ref> | |||
| == Creationism and philosophical naturalism == | |||
| ===Teaching of creationism=== | |||
| Certain tenets of creationism are opposed to ] and ]: | |||
| Other Christians have expressed qualms about teaching creationism. In March 2006, then Archbishop of Canterbury Rowan Williams, the leader of the world's Anglicans, stated his discomfort about teaching creationism, saying that creationism was "a kind of ], as if the Bible were a theory like other theories." He also said: "My worry is creationism can end up reducing the doctrine of creation rather than enhancing it." The views of the ]{{snd}}a major American-based branch of the Anglican Communion{{snd}}on teaching creationism resemble those of Williams.<ref name="Archbishop_2006"/> | |||
| The National Science Teachers Association is opposed to teaching creationism as a science,<ref>{{cite web |title=NSTA Position Statement: The Teaching of Evolution |publisher=National Science Teachers Association | year=2013 |url=http://www.nsta.org/about/positions/evolution.aspx}}</ref> as is the Association for Science Teacher Education,<ref>{{cite web |title= ASTE Position Statement on Teaching Biological Evolution |year=2015 |publisher=Association for Science Teacher Education |url=https://theaste.org/about/aste-position-statement-on-teaching-biological-evolution/}}</ref> the National Association of Biology Teachers,<ref>{{cite web |title=NABT Position Statement on Teaching Evolution |publisher=National Association of Biology Teachers |year=2011 |url=http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/?p=92 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150916020337/http://www.nabt.org/websites/institution/?p=92 |archive-date=2015-09-16 }}</ref> the American Anthropological Association,<ref>{{cite web |title=Statement on Evolution and Creationism |publisher=American Anthropological Association |year=2000 |url=http://www.americananthro.org/ConnectWithAAA/Content.aspx?ItemNumber=2599}}</ref> the American Geosciences Institute,<ref>{{cite web |title=American Geological Institute Position on Teaching Evolution |publisher=American Geoscience Institute |year=2000 |url=http://www.agiweb.org/gapac/evolution_statement.html}}</ref> the Geological Society of America,<ref>{{cite web |year=2012 |title=Position Statement: Teaching Evolution |publisher=Geological Society of America |url=https://www.geosociety.org/positions/position1.htm |access-date=2019-08-29 |archive-date=2021-10-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211022084107/https://www.geosociety.org/positions/position1.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> the American Geophysical Union,<ref>{{cite web |title=AGU Position Statement on Teaching Creationism as Science |publisher=American Geophysical Institute |year=1998 |url=http://www.rbsp.info/rbs/CLONE/debate.html}}</ref> and numerous other professional teaching and scientific societies. | |||
| # There was an origin of the universe for which the direct intervention of God was required. | |||
| # The origin of life required the direct intervention of God. | |||
| # ], ], ], and the capacities for ] and ], are not reducible to physical processes alone, but were granted to living and intelligent creatures by the direct intervention of God. | |||
| # These capacities, and more basically life itself, are not possible to describe in terms of ] alone. | |||
| In April 2010, the ] issued ''Guidelines for Teaching About Religion in K‐12 Public Schools in the United States'', which included guidance that creation science or intelligent design should not be taught in science classes, as "Creation science and intelligent design represent worldviews that fall outside of the realm of science that is defined as (and limited to) a method of inquiry based on gathering observable and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning." However, they, as well as other "worldviews that focus on speculation regarding the origins of life represent another important and relevant form of human inquiry that is appropriately studied in literature or social sciences courses. Such study, however, must include a diversity of worldviews representing a variety of religious and philosophical perspectives and must avoid privileging one view as more legitimate than others."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ncse.com/news/2010/07/american-academy-religion-teaching-creationism-005712 |title=American Academy of Religion on teaching creationism |date=July 23, 2010 |website=National Center for Science Education |location=Berkeley, CA |access-date=2010-08-09}}</ref> | |||
| A general response to the modern creationism controversy has been articulated by creationist ], Professor of Law at the ], who argues that the entire issue of biological origins has been framed in terms of ], and that natural science per se is not identical with naturalism. According to him, the statement, "Science has nothing to say about whether or not there exists a supernatural realm," is true and based on the fact that rigorous physical science is naturalistic, but the statement, "Science holds that there is no supernatural realm," is false because it is beyond the scope of natural science to make such an assertion, but is instead a philosophical position. According to Johnson, this distinction opens the possibility of natural science and creationism being non-contradictory. However, such an assertion is problematic when trying to reconcile natural science with certain types of creationism that do make specific claims about the natural realm. | |||
| Randy Moore and Sehoya Cotner, from the biology program at the ], reflect on the relevance of teaching creationism in the article "The Creationist Down the Hall: Does It Matter When Teachers Teach Creationism?", in which they write: "Despite decades of science education reform, numerous legal decisions declaring the teaching of creationism in public-school science classes to be unconstitutional, overwhelming evidence supporting evolution, and the many denunciations of creationism as nonscientific by professional scientific societies, creationism remains popular throughout the United States."<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Moore |first1=Randy |last2=Cotner |first2=Sehoya |date=May 2009 |title=The Creationist Down the Hall: Does It Matter When Teachers Teach Creationism? |journal=] |volume=59 |issue=5 |pages=429–35 |doi=10.1525/bio.2009.59.5.10 |issn=0006-3568 |jstor=25502451 |s2cid=86428123 }}</ref> | |||
| == Creationism in public education == | |||
| ===Scientific criticism=== | |||
| In the United States, creationists and evolutionary scientists are engaged in a long-running battle over the primary and supplementary science ] of ]s. The high point of the controversy occurred in ], during the '']'', when a teacher defied a ] law forbidding the teaching of the theory of evolution. More recently, controversy has centered on attempts to either restrict the teaching of evolution or to provide "equal time" for creationism or creationist-inspired theories as well as evolutionary theories in science classes. The goal on both sides is to eliminate the other side's viewpoint from the public school curriculum; currently, evolutionary scientists seem to be winning. | |||
| {{Main|Rejection of evolution by religious groups}} | |||
| Science is a system of knowledge based on observation, empirical evidence, and the development of theories that yield testable explanations and predictions of natural phenomena. By contrast, creationism is often based on literal interpretations of the narratives of particular religious texts.<ref>], </ref> Creationist beliefs involve purported forces that lie outside of nature, such as supernatural intervention, and often do not allow predictions at all. Therefore, these can neither be confirmed nor disproved by scientists.<ref name="SEaC">], , "In science, explanations must be based on naturally occurring phenomena. Natural causes are, in principle, reproducible and therefore can be checked independently by others. If explanations are based on purported forces that are outside of nature, scientists have no way of either confirming or disproving those explanations."</ref> However, many creationist beliefs can be framed as testable predictions about phenomena such as the age of the Earth, its ] and the origins, ] and ] of living organisms found on it. ] incorporated elements of these beliefs, but as science developed these beliefs were gradually ] and were replaced with understandings based on accumulated and reproducible evidence that often allows the accurate prediction of future results.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.talkorigins.org/indexcc/index.html |title=An Index to Creationist Claims |editor-last=Isaak |editor-first=Mark |year=2006 |website=TalkOrigins Archive |publisher=The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. |location=Houston, TX |access-date=2012-12-09}}</ref><ref>]</ref> | |||
| Some scientists, such as ],<ref name="RoA">]</ref> consider science and religion to be two compatible and complementary fields, with authorities in distinct areas of human experience, so-called ].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Gould |first=Stephen Jay |date=March 1997 |title=Nonoverlapping Magisteria |url=http://www.stephenjaygould.org/library/gould_noma.html |journal=] |volume=106 |pages=16–22 |issue=3 |issn=0028-0712 |access-date=2014-03-31 |archive-date=2017-01-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170104061453/http://www.stephenjaygould.org/library/gould_noma.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> This view is also held by many theologians, who believe that ] and ] are addressed by religion, but favor verifiable scientific explanations of natural phenomena over those of creationist beliefs. Other scientists, such as ],<ref>], p. 5</ref> reject the non-overlapping magisteria and argue that, in disproving literal interpretations of creationists, the scientific method also undermines religious texts as a source of truth. Irrespective of this diversity in viewpoints, since creationist beliefs are not supported by empirical evidence, the scientific consensus is that any attempt to teach creationism as science should be rejected.<ref name="RoyalSociety_2006">{{cite web|url=http://royalsociety.org/news.asp?year=&id=4298|title=Royal Society statement on evolution, creationism and intelligent design|date=April 11, 2006|website=]|publisher=Royal Society|location=London|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080602213726/http://royalsociety.org/news.asp?year=&id=4298|archive-date=2008-06-02|access-date=2014-03-09}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://ncse.com/taking-action/ten-major-court-cases-evolution-creationism |title=Ten Major Court Cases about Evolution and Creationism |last1=Matsumura |first1=Molleen |last2=Mead |first2=Louise |date=February 14, 2001 |website=National Center for Science Education |location=Berkeley, CA |access-date=2008-11-04}} Updated 2007-07-31.</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://scienceblogs.com/pharyngula/2006/06/ann_coulter_no_evidence_for_ev.php |title=Ann Coulter: No evidence for evolution? |last=Myers |first=PZ |author-link=PZ Myers |date=June 18, 2006 |website=] |publisher=] |type=Blog |access-date=2007-09-12 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070809011055/http://scienceblogs.com/pharyngula/2006/06/ann_coulter_no_evidence_for_ev.php |archive-date=August 9, 2007 }}</ref> | |||
| The ] interprets the ] to the ] as prohibiting public schools from teaching religious beliefs as facts and has ruled that a government-funded science curriculum should not support the teaching of religious beliefs in science classes. It has specifically ruled in '']'' and '']'' that creationism, even when referred to as a science, is such a religious belief. | |||
| ==Organizations== | |||
| Creationists claim that this position does not consider the possibility that humankind and other living creatures were in fact created by God. They also claim that this viewpoint has been used to squelch classroom discussion by students who insist that their faith in creationism is relevant to the origins controversy. Supporters of evolution claim that the teaching of evolution is not necessarily incompatible with a belief that God is the ultimate creator of the universe, and therefore of all life. This is a position that is widely adopted by many, if not most, mainstream Christian denominations. | |||
| {| style="width:100%;" | |||
| |- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
| |width=47%| | |||
| ;Creationism (in general) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ;Young Earth creationism | |||
| Despite the Supreme Court rulings, Boards of Education and local communities continue to struggle with controversy when "creation science" is raised as an argument in opposition to the teaching of evolution. For example, supporters of ], who typically seek to differentiate intelligent design from faith-based creationism, argued in December 2002 for the inclusion of the hypothesis that life had an intelligent designer in the Ohio Board of Education standards for science education. | |||
| * ], a group promoting young Earth creationism | |||
| * ], an organisation promoting biblical creation | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ;Old Earth creationism | |||
| In the ], one of the few countries in which teaching religion in public schools is a legal requirement, there is an agreed syllabus for religious education with the right of parents to withdraw their children from these lessons. | |||
| * Old Earth Ministries (OEM), formerly Answers In Creation (AIC), led by Greg Neyman<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oldearth.org/about_aic.htm |title=About Old Earth Ministries? |website=Old Earth Ministries |location=Springfield, OH |access-date=2014-03-09}}</ref> | |||
| * ], led by ] | |||
| |width=6%| | |||
| |width=47%| | |||
| ;Intelligent design | |||
| The prescribed UK national curriculum for science includes the theory of evolution; one creationist teacher who insisted on teaching creationism instead of evolution was disciplined and eventually dismissed. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], a subsidiary of the ] | |||
| ;Evolutionary creationism | |||
| <!--Does anyone have any details on this? Name of teacher, school, date? --> | |||
| * ] | |||
| |} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Div col}} | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] and ]s for details on how creation is depicted. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] for more information on the role of creator in creationism. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] on Wiktionary | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==External links and references== | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| * — a list of sites, categorised by belief | |||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| * — Mark Isaak describes the varieties of Christian creationism, and additionally describes how the beliefs of other religions fit into the creationist spectrum. | |||
| {{Reflist|group="note"|refs= | |||
| * A site that documents the activities of Islamic creationists and their opponents | |||
| <!-- <ref name="myth" group="note">], . While the term '']'' is often used colloquially to refer to "a false story," this article uses the term in the academic meaning of "a sacred narrative explaining how the world and mankind came to be in their present form."</ref> -->}} | |||
| * by Eugenie C. Scott, for the National Center for Science Education | |||
| * | |||
| * from LiberalIslam.net | |||
| *Keane, Gerard: "Creation Rediscovered: Evolution & the Importance of the Origins Debate" | |||
| ==References== | |||
| === Young Earth Creationism === | |||
| ===Citations=== | |||
| * | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| === |
===Works cited=== | ||
| {{Refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |author=`Abdu'l-Bahá |author-link=`Abdu'l-Bahá |year=1982 |orig-year=Originally published 1922–1925 |title=The Promulgation of Universal Peace: Talks Delivered by 'Abdu'l-Bahá during His Visit to the United States and Canada in 1912 |others=Compiled by Howard MacNutt |edition=2nd |location=Wilmette, IL |publisher=Bahá'í Publishing Trust |isbn=978-0-8774-3172-5 |lccn=81021689 |oclc=853066452 |ref=`Abdu'l-Bahá 1982}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Aviezer |first=Nathan |author-link=Nathan Aviezer |year=1990 |title=In the Beginning—: Biblical Creation and Science |location=Hoboken, NJ |publisher=KTAV Publishing House |isbn=978-0-88125-328-3 |lccn=89049127 |oclc=20800545 |ref=Aviezer 1990}} | |||
| * (Harun Yahya site) | |||
| * {{cite journal |editor-last=Barlow |editor-first=Nora |editor-link=Nora Barlow |year=1963 |title=Darwin's Ornithological Notes |url=http://darwin-online.org.uk/content/frameset?pageseq=1&itemID=F1577&viewtype=side |journal=Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Historical Series |volume=2 |issue=7 |pages=201–278 |doi=10.5962/p.310422 |issn=0068-2306 |access-date=2009-06-10 |ref=Barlow 1963|doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bowler |first=Peter J. |year=2003 |title=Evolution: The History of an Idea |edition=3rd |location=Berkeley, CA |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-520-23693-6 |lccn=2002007569 |oclc=49824702 |ref=Bowler 2003 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/evolutionhistory0000bowl_n7y8 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bucaille |first=Maurice |author-link=Maurice Bucaille |year=1977 |orig-year=Original French edition published 1976 |title=The Bible, The Qur'an and Science: The Holy Scriptures Examined in the Light of Modern Knowledge |others=translated from the French by Alastair D. Pannell and the author |location=Paris |publisher=Seghers |lccn=76488005 |oclc=373529514 |ref=Bucaille 1977}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bucaille |first=Maurice |year=1976 |title=The Qur'an and Modern Science |url=http://www.sultan.org/articles/QScience.html |type=Booklet |location=Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia |publisher=Cooperative Offices for Call & Guidance at Al-Badiah & Industrial Area |oclc=52246825 |access-date=2014-03-21 |ref=Bucaille 1976}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Carmell |editor1-first=Aryeh |editor2-last=Domb |editor2-first=Cyril |year=1976 |title=Challenge: Torah Views on Science and its Problems |location=Jerusalem; New York |publisher=]; ] |isbn=978-0-87306-174-2 |lccn=77357516 |oclc=609518840 |ref=Carmell & Domb 1976}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Carper |editor1-first=James C. |editor2-last=Hunt |editor2-first=Thomas C. |year=2009 |title=The Praeger Handbook of Religion and Education in the United States |volume=1: A–L |location=Westport, CT |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-275-99228-6 |lccn=2008041156 |oclc=246888936 |ref=Carper & Hunt 2009}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Collins |first=Francis S. |author-link=Francis Collins |year=2006 |title=The Language of God: A Scientist Presents Evidence for Belief |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7432-8639-8 |lccn=2006045316 |oclc=65978711 |ref=Collins 2006|title-link=The Language of God: A Scientist Presents Evidence for Belief }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dasgupta |first=Surendranath |author-link=Surendranath Dasgupta |year=1922 |title=A History of Indian Philosophy |volume=1 |location=Cambridge, England |publisher=] |lccn=22018463 |oclc=4235820 |ref=Dasgupta 1922}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dawkins |first=Richard |author-link=Richard Dawkins |year=2006 |title=The God Delusion |location=London |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-5930-5548-9 |lccn=2006015506 |oclc=70671839 |ref=Dawkins 2006}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Desmond |first=Adrian |author-link=Adrian Desmond |year=1989 |title=The Politics of Evolution: Morphology, Medicine, and Reform in Radical London |url=https://archive.org/details/politicsofevolut00adri |url-access=registration |series=Science and its Conceptual Foundations |location=Chicago, Illinois |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-226-14346-0 |lccn=89005137 |oclc=828159401 |ref=Desmond 1989}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Desmond |first1=Adrian |last2=Moore |first2=James |author2-link=James Moore (biographer) |year=1991 |title=Darwin |location=London; New York |publisher=]; ] |isbn=978-0-7181-3430-3 |lccn=92196964 |oclc=26502431}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dewey |first=John |author-link=John Dewey |year=1994 |chapter=The Influence of Darwinism on Philosophy |editor=Martin Gardner |editor-link=Martin Gardner |title=Great Essays in Science |location=Buffalo, NY |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-87975-853-0 |lccn=93035453 |oclc=28846489 |ref=Dewey 1994}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Draper |first=Paul R. |author-link=Paul Draper (philosopher) |year=2005 |chapter=God, Science, and Naturalism |editor-last=Wainwright |editor-first=William J. |title=The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Religion |pages=272–303 |chapter-url=http://www.oxfordscholarship.com/view/10.1093/0195138090.001.0001/acprof-9780195138092-chapter-12 |location=Oxford; New York |publisher=] |doi=10.1093/0195138090.003.0012 |isbn=978-0-1951-3809-2 |lccn=2004043890 |oclc=54542845 |access-date=2014-03-15 |ref=Draper 2005}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dundes |first=Alan |author-link=Alan Dundes |year=1984 |chapter=Introduction |editor-last=Dundes |editor-first=Alan |title=Sacred Narrative: Readings in the Theory of Myth |location=Berkeley, CA |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-5200-5192-8 |lccn=83017921 |oclc=9944508 |ref=Dundes 1984 |chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/sacrednarrativer00dund |url=https://archive.org/details/sacrednarrativer00dund }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dundes |first=Alan |year=1996 |chapter=Madness in Method, Plus a Plea for Projective Inversion in Myth |editor1-last=Patton |editor1-first=Laurie L. |editor1-link=Laurie L. Patton |editor2-last=Doniger |editor2-first=Wendy |editor2-link=Wendy Doniger |title=Myth and Method |location=Charlottesville; London |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-8139-1657-6 |lccn=96014672 |oclc=34516050 |ref=Patton & Doniger 1996}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Eddy |first=Mary Baker |author-link=Mary Baker Eddy |year=1934 |orig-year=Originally published 1875 as ''Science and Health''; Christian Scientist Publishing Company: Boston, MA |title=Science and Health with Key to the Scriptures |edition=Sunday school |location=Boston, MA |publisher=] for the Trustees under the will of Mary Baker G. Eddy |lccn=42044682 |oclc=4579118 |ref=Eddy 1934|title-link=Science and Health with Key to the Scriptures }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Forrest |first1=Barbara |author-link1=Barbara Forrest |last2=Gross |first2=Paul R. |author-link2=Paul R. Gross |year=2004 |title=Creationism's Trojan Horse: The Wedge of Intelligent Design |location=Oxford; New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-515742-0 |oclc=50913078 |lccn=2002192677 |ref=Forrest & Gross 2004|title-link=Creationism's Trojan Horse: The Wedge of Intelligent Design }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Forster |first1=Roger |author-link1=Roger T. Forster |last2=Marston |first2=V. Paul |year=1999 |chapter=Genesis Through History |title=Reason, Science, and Faith |location=Crowborough, East Sussex |publisher=Monarch Books |isbn=978-1-85424-441-3 |lccn=99488551 |oclc=41159110 |ref=Forster & Marston 1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Futuyma |first=Douglas J. |author-link=Douglas J. Futuyma |year=2005 |chapter=Evolutionary Science, Creationism, and Society |title=Evolution |location=Sunderland, MA |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-87893-187-3 |lccn=2004029808 |oclc=57311264 |ref=Futuyma 2005 |chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/evolution0000futu |url=https://archive.org/details/evolution0000futu }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Giberson |first1=Karl W. |last2=Yerxa |first2=Donald A. |year=2002 |title=Species of Origins: America's Search for a Creation Story |location=Lanham, MD |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7425-0764-7 |lccn=2002002365 |oclc=49031109 |ref=Giberson & Yerxa 2002}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gosse |first=Philip Henry |author-link=Philip Henry Gosse |year=1857 |title=Omphalos: An Attempt to Untie the Geological Knot |location=London |publisher=] |lccn=11004351 |oclc=7631539 |ref=Gosse 1857|title-link=Omphalos (book) }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gould |first=Stephen Jay |author-link=Stephen Jay Gould |year=1999 |title=Rocks of Ages: Science and Religion in the Fullness of Life |series=Library of Contemporary Thought |edition=1st |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-345-43009-0 |lccn=98031335 |oclc=39886951 |ref=Gould 1999|title-link=Rocks of Ages }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Gunn |first=Angus M. |year=2004 |title=Evolution and Creationism in the Public Schools: A Handbook for Educators, Parents, and Community Leaders |location=Jefferson, NC |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7864-2002-5 |lccn=2004018788 |oclc=56319812 |ref=Gunn 2004 |url=https://archive.org/details/evolutioncreatio0000gunn }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hayward |first=James L. |year=1998 |title=The Creation/Evolution Controversy: An Annotated Bibliography |series=Magill Bibliographies |location=Lanham, MD; Pasadena, CA |publisher=Scarecrow Press; Salem Press |page= |isbn=978-0-8108-3386-9 |lccn=98003138 |oclc=38496519 |ref=Hayward 1998 |url=https://archive.org/details/creationevolutio0000hayw/page/253 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lamoureux |first=Denis O. |author-link=Denis Lamoureux |year=1999 |chapter=Evangelicals Inheriting the Wind: The Phillip E. Johnson Phenomenon |title=Darwinism Defeated?: The Johnson-Lamoureux Debate on Biological Origins |others=Foreword by ] |location=Vancouver, B.C. |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-57383-133-8 |oclc=40892139 |ref=Lamoureux 1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Masood |first=Steven |year=1994 |orig-year=Originally published 1986 |title=Jesus and the Indian Messiah |location=Oldham, England |publisher=Word of Life |isbn=978-1-898868-00-2 |lccn=94229476 |oclc=491161526 |ref=Masood 1994}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McComas |first=William F. |year=2002 |chapter=Science and Its Myths |editor-last=Shermer |editor-first=Michael |editor-link=Michael Shermer |title=The Skeptic Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience |volume=1 |location=Santa Barbara, CA |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-57607-653-8 |lccn=2002009653 |oclc=50155642 |ref=Shermer 2002|title-link=The Skeptic Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McGrath |first=Alister E. |author-link=Alister McGrath |year=2010 |title=Science and Religion: A New Introduction |edition=2nd |location=Malden, MA |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-4051-8790-9 |lccn=2009020180 |oclc=366494307 |ref=McGrath 2010}} | |||
| * {{cite book |author=National Academy of Sciences |author-link=National Academy of Sciences |year=1999 |title=Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences |url=https://archive.org/details/sciencecreationi0000unse |edition=2nd |location=Washington, D.C. |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-309-06406-4 |lccn=99006259 |oclc=43803228 |access-date=2014-11-22 |ref=NAS 1999 |url-access=registration }} | |||
| * {{cite book|author1=National Academy of Sciences |author2=Institute of Medicine |author-link2=Institute of Medicine |year=2008 |title=Science, Evolution, and Creationism |journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=105 |issue=1 |pages= |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780309105866/page/3 |location=Washington, D.C. |publisher=National Academy Press |isbn=978-0-309-10586-6 |lccn=2007015904 |oclc=123539346 |access-date=2014-11-22 |ref=NAS 2008 |bibcode=2008PNAS..105....3A |doi=10.1073/pnas.0711608105 |pmid=18178613 |pmc=2224205 |doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Numbers |first=Ronald L. |author-link=Ronald Numbers |year=1998 |title=Darwinism Comes to America |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-674-19312-3 |lccn=98016212 |oclc=38747194|url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/darwinismcomesto0000numb }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Numbers |first=Ronald L. |year=2006 |orig-year=Originally published 1992 as ''The Creationists: The Evolution of Scientific Creationism''; New York: ] |title=The Creationists: From Scientific Creationism to Intelligent Design |edition=Expanded ed., 1st Harvard University Press pbk. |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-674-02339-0 |lccn=2006043675 |oclc=69734583 |ref=Numbers 2006|title-link=The Creationists }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Okasha |first=Samir |year=2002 |title=Philosophy of Science: A Very Short Introduction |series=Very Short Introductions |volume=67 |location=Oxford; New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-280283-5 |lccn=2002510456 |oclc=48932644 |ref=Okasha 2002}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Pennock |first=Robert T. |author-link=Robert T. Pennock |year=1999 |title=Tower of Babel: The Evidence Against the New Creationism |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-262-16180-0 |lccn=98027286 |oclc=44966044 |ref=Pennock 1999 |url=https://archive.org/details/towerofbabelevid00penn }} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Pennock |editor-first=Robert T |editor-link=Robert T. Pennock |year=2001 |title=Intelligent Design Creationism and Its Critics: Philosophical, Theological, and Scientific Perspectives |url=https://archive.org/details/intelligentdesig00robe |url-access=registration |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-262-66124-9 |lccn=2001031276 |oclc=46729201 |ref=Pennock 2001}}<!--|access-date=2014-01-10 --> | |||
| * {{cite book |author=Philo, of Alexandria |author-link=Philo |year=1854–55 |chapter=The First Book of the Treatise on The Allegories of the Sacred Laws, after the Work of the Six Days of Creation |chapter-url=http://www.earlychristianwritings.com/yonge/book2.html |title=The Works of Philo Judaeus |url=https://archive.org/details/worksofphilojuda01yonguoft |series=Bohn's Classical Library |others=Translated from the Greek, by ] |location=London |publisher=] |lccn=20007801 |oclc=1429769 |access-date=2014-03-09 |ref=Philo}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Plimer |first=Ian |author-link=Ian Plimer |year=1994 |title=Telling Lies for God: Reason vs Creationism |location=Milsons Point, NSW |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-09-182852-3 |lccn=94237744 |oclc=32608689 |ref=Plimer 1994}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Polkinghorne |first=John |author-link=John Polkinghorne |year=1998 |title=Science and Theology: An Introduction |location=Minneapolis, MN |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-8006-3153-6 |lccn=98229115 |oclc=40117376 |ref=Polkinghorne 1998}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Quammen |first=David |author-link=David Quammen |year=2006 |title=The Reluctant Mr. Darwin: An Intimate Portrait of Charles Darwin and the Making of His Theory of Evolution |series=Great Discoveries |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-393-05981-6 |lccn=2006009864 |oclc=65400177 |ref=Quammen 2006 |url=https://archive.org/details/reluctantmrdarwi00quam }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Rainey |first=David |title=Faith Reads: A Selective Guide to Christian Nonfiction |year=2008 |location=Westport, CT |publisher=Libraries Unlimited |isbn=978-1-59158-602-9 |lccn=2008010352 |oclc=213599217 |ref=Rainey 2012 |url=https://archive.org/details/faithreadsselect0000rain }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Schroeder |first=Gerald L. |author-link=Gerald Schroeder |year=1998 |orig-year=Originally published 1997; New York: ] |title=The Science of God: The Convergence of Scientific and Biblical Wisdom |edition=1st Broadway Books trade paperback |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7679-0303-5 |lccn=97014978 |oclc=39162332 |ref=Schroeder 1998}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Scott |first=Eugenie C. |author-link=Eugenie Scott |year=1999 |chapter=Science, Religion, and Evolution |editor1-last=Springer |editor1-first=Dale A. |editor2-last=Scotchmoor |editor2-first=Judy |title=Evolution: Investigating the Evidence |chapter-url=http://www.ncseweb.org/resources/articles/528_science_religion_and_evoluti_6_19_2001.asp |type=Reprint |series=The Paleontological Society Special Publications |volume=9 |location=Pittsburgh, PA |publisher=] |lccn=00274093 |oclc=42725350 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030628210954/http://www.ncseweb.org/resources/articles/528_science_religion_and_evoluti_6_19_2001.asp |archive-date=2003-06-28 |ref=Scott 1999}} "Presented as a Paleontological Society short course at the annual meeting of the Geological Society of America, Denver, Colorado, October 24, 1999." | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Scott |first=Eugenie C. |author-link=Eugenie Scott |year=2005 |orig-year=Originally published 2004; Westport, CT: ] |title=Evolution vs. Creationism: An Introduction |others=Foreword by ] |edition=1st paperback |location=Berkeley, CA |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-24650-8 |lccn=2005048649 |oclc=60420899 |ref=Scott 2005 |url=https://archive.org/details/evolutionvscreat00scot }} | |||
| * {{cite book|first=Eugenie C. |last=Scott|title=Evolution Vs. Creationism: An Introduction|edition=2nd|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FAAlDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA1|date=3 August 2009|publisher=Univ of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-26187-7|pages=i–331}} | |||
| * {{cite book|author-link=James A. Secord |last=Secord |first=James A. |title=Victorian Sensation: The Extraordinary Publication, Reception, and Secret Authorship of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation |location=Chicago, Illinois |publisher=University of Chicago Press |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-226-74410-0 |lccn=00009124 |oclc=43864195 |ref=Secord 2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Stewart |editor-first=Melville Y. |editor-link=Melville Y. Stewart |year=2010 |title=Science and Religion in Dialogue |location=Malden, MA |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=978-1-4051-8921-7 |lccn=2009032180 |oclc=430678957 |ref=Stewart 2010}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Sweet |editor1-first=William |editor1-link=William Sweet |editor2-last=Feist |editor2-first=Richard |year=2007 |title=Religion and the Challenges of Science |location=Aldershot, England; Burlington, VT |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7546-5715-6 |lccn=2006030598 |oclc=71778930 |ref=Sweet & Feist 2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wilder-Smith |first=A. E. |author-link=A. E. Wilder-Smith |year=1978 |title=Die Naturwissenschaften kennen keine Evolution: Empirische und theoretische Einwände gegen die Evolutionstheorie |trans-title=The Natural Sciences Know Nothing of Evolution |location=Basel, Switzerland |publisher=Schwabe Verlag |isbn=978-3-7965-0691-8 |lccn=80067425 |oclc=245955034 |ref=Wilder-Smith 1978}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Young |first=Davis A. |year=1995 |title=The Biblical Flood: A Case Study of the Church's Response to Extrabiblical Evidence |location=Grand Rapids, MI |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-8028-0719-9 |lccn=95001899 |oclc=246813515 |ref=Young 1995}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| === Intelligent Design === | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Anderson |first=Bernard W. |author-link=Bernhard Anderson |year=1967 |title=Creation versus Chaos: The Reinterpretation of Mythical Symbolism in the Bible |location=New York |publisher=Association Press |lccn=67014578 |oclc=671184 |ref=Anderson 1967}} | |||
| * Kenneth Einar Himma, "Design Arguments for the Existence of God", ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy''; at http://www.iep.utm.edu/d/design.htm | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Anderson |editor-first=Bernhard W. |year=1984 |title=Creation in the Old Testament |series=Issues in Religion and Theology |volume=6 |others=Introduction by Bernhard W. Anderson |location=Philadelphia; London |publisher=Fortress Press; ] |isbn=978-0-8006-1768-4 |lccn=83048910 |oclc=10374840 |ref=Anderson 1984 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/creationinoldtes00unse }} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Barbour |first=Ian G. |author-link=Ian Barbour |year=1997 |title=Religion and Science: Historical and Contemporary Issues |edition=1st HarperCollins revised |location=San Francisco, CA |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-06-060938-2 |lccn=97006294 |oclc=36417827 |ref=Barbour 1997}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Barbour |first=Ian G. |year=2000 |title=When Science Meets Religion |edition=1st |location=San Francisco, CA |publisher=HarperSanFrancisco |isbn=978-0-06-060381-6 |lccn=99055579 |oclc=42752713 |ref=Barbour 2000 |url=https://archive.org/details/whensciencemeets00barb }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Clark |first=Kelly James |year=2014 |title=Religion and the Sciences of Origins: Historical and Contemporary Discussions |edition=1st |location=Basingstoke, UK |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-137-41483-0 |lccn=2014466739 |oclc=889777438 |ref=Clark 2014}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Darwin |first=Charles |author-link=Charles Darwin |year=1958 |editor-last=Barlow |editor-first=Nora |title=The Autobiography of Charles Darwin, 1809-1882: With original omissions restored; Edited and with Appendix and Notes by his grand-daughter, Nora Barlow |url=http://darwin-online.org.uk/content/frameset?itemID=F1497&viewtype=side&pageseq=1 |location=London |publisher=Collins |lccn=93017940 |oclc=869541868 |access-date=2009-01-09 |ref=Darwin 1958}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kaplan |first=Aryeh |author-link=Aryeh Kaplan |year=1993 |title=Immortality, Resurrection, and the Age of the Universe: A Kabbalistic View |others=With an appendix Derush Or ha-Hayyim by Israel Lipschitz; translated and annotated by Yaakov Elman |location=Hoboken, NJ |publisher=KTAV Publishing House in association with the ] |isbn=978-0-88125-345-0 |lccn=92036917 |oclc=26800167 |ref=Kaplan 1993}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Kauffman |first=Stuart A. |author-link=Stuart Kauffman |year=2008 |title=Reinventing the Sacred: A New View of Science, Reason and Religion |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-465-00300-6 |lccn=2007052263 |oclc=191023778 |ref=Kauffman 2008 |url=https://archive.org/details/reinventingsacre00kauf_0 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last1=Leeming |first1=David Adams |last2=Leeming |first2=Margaret |year=1995 |title=A Dictionary of Creation Myths |location=New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-510275-8 |lccn=95039961 |oclc=33160980 |ref=Leeming & Leeming 1995 |url=https://archive.org/details/dictionaryofcrea00leem }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Primack |first1=Joel R. |author-link1=Joel Primack |last2=Abrams |first2=Nancy Ellen |date=Jan–Feb 1995 |title=In a Beginning...: Quantum Cosmology and Kabbalah |url=http://physics.ucsc.edu/cosmo/primack_abrams/InABeginningTikkun1995.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://physics.ucsc.edu/cosmo/primack_abrams/InABeginningTikkun1995.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |journal=] |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=66–73 |issn=0887-9982 |access-date=2014-04-24}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Roberts |first=Michael |year=2008 |title=Evangelicals and Science |series=Greenwood Guides to Science and Religion |location=Westport, CT |publisher=Greenwood Press |isbn=978-0-313-33113-8 |lccn=2007041059 |oclc=174138819 |ref=Roberts 2008}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == |
==External links== | ||
| <!--======================== {{No more links}} ============================ | |||
| * | |||
| | PLEASE BE CAUTIOUS IN ADDING MORE LINKS TO THIS ARTICLE. Misplaced Pages | | |||
| * — anti-creationism site, links | |||
| | is not a collection of links nor should it be used for advertising. | | |||
| * | |||
| | | | |||
| * Critical discussion of ]'s methods. Published in the ''Skeptic'', magazine of the Skeptic Society, Vol. 4, No. 4, 1996, pp. 88-93. | |||
| | Excessive or inappropriate links WILL BE DELETED. | | |||
| * — see ] | |||
| | See ] & ] for details. | | |||
| * | |||
| | | | |||
| * | |||
| | If there are already plentiful links, please propose additions or | | |||
| * | |||
| | replacements on this article's discussion page, or submit your link | | |||
| | to the relevant category at the Open Directory Project (dmoz.org) | | |||
| | and link back to that category using the {{dmoz}} template. | | |||
| ======================= {{No more links}} =============================--> | |||
| {{Commons}}{{Wikiquote}} | |||
| <!-- overviews of creationism, i.e. all these links are similar because they describe the variety of viewpoints that have been described as creationist. --> | |||
| * at the ] by ] | |||
| * at ] by Julia Layton | |||
| * {{snd}}Focuses on major historical and recent events in the scientific and political debate | |||
| * {{cite web|url= http://images.derstandard.at/20051012/Evolution-and-Creationism.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://images.derstandard.at/20051012/Evolution-and-Creationism.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=Evolution and Creationism: A Guide for Museum Docents }} {{small|(204 KB)}} by Warren D. Allmon, Director of the ] | |||
| * at ] by Mark Isaak | |||
| * by ] | |||
| * by ], editor in chief of '']'' magazine | |||
| * "" by Allison Hopper, '']'' (July 5, 2021). | |||
| * {{snd}}], ] (August 2016) | |||
| {{Creationism topics}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Philosophy of religion}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Genesis 1}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Portal bar|Evolutionary biology|Science}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:44, 13 January 2025
Belief that nature originated through supernatural acts "Creationism" can also refer to creation myths, or to an unrelated concept about the origin of the soul. For the movement in Spanish literature, see Creationism (literature movement).
| Part of a series on | ||||
| Creationism | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| History | ||||
| Types | ||||
| Biblical cosmology | ||||
| Creation science | ||||
| Rejection of evolution by religious groups | ||||
| Religious views | ||||
|
||||
| Part of a series on |
| Intelligent design |
|---|
 Watchmaker analogy Watchmaker analogy |
| Concepts |
| Movement |
| Campaigns |
| Authors |
| Organisations |
| Reactions |
| Creationism |
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation, and is often pseudoscientific. In its broadest sense, creationism includes various religious views, which differ in their acceptance or rejection of modern scientific concepts such as evolution that describe the origin and development of natural phenomena.
The term creationism most often refers to belief in special creation: the claim that the universe and lifeforms were created as they exist today by divine action, and that the only true explanations are those which are compatible with a Christian fundamentalist literal interpretation of the creation myth found in the Bible's Genesis creation narrative. Since the 1970s, the most common form of this has been Young Earth creationism which posits special creation of the universe and lifeforms within the last 10,000 years on the basis of flood geology, and promotes pseudoscientific creation science. From the 18th century onward, Old Earth creationism accepted geological time harmonized with Genesis through gap or day-age theory, while supporting anti-evolution. Modern old-Earth creationists support progressive creationism and continue to reject evolutionary explanations. Following political controversy, creation science was reformulated as intelligent design and neo-creationism.
Mainline Protestants and the Catholic Church reconcile modern science with their faith in Creation through forms of theistic evolution which hold that God purposefully created through the laws of nature, and accept evolution. Some groups call their belief evolutionary creationism. Less prominently, there are also members of the Islamic and Hindu faiths who are creationists. Use of the term "creationist" in this context dates back to Charles Darwin's unpublished 1842 sketch draft for what became On the Origin of Species, and he used the term later in letters to colleagues. In 1873, Asa Gray published an article in The Nation saying a "special creationist" who held that species "were supernaturally originated just as they are, by the very terms of his doctrine places them out of the reach of scientific explanation."
Biblical basis
The basis for many creationists' beliefs is a literal or quasi-literal interpretation of the Book of Genesis. The Genesis creation narratives (Genesis 1–2) describe how God brings the Universe into being in a series of creative acts over six days and places the first man and woman (Adam and Eve) in the Garden of Eden. This story is the basis of creationist cosmology and biology. The Genesis flood narrative (Genesis 6–9) tells how God destroys the world and all life through a great flood, saving representatives of each form of life by means of Noah's Ark. This forms the basis of creationist geology, better known as flood geology.
Recent decades have seen attempts to de-link creationism from the Bible and recast it as science; these include creation science and intelligent design.
Types
To counter the common misunderstanding that the creation–evolution controversy was a simple dichotomy of views, with "creationists" set against "evolutionists", Eugenie Scott of the National Center for Science Education produced a diagram and description of a continuum of religious views as a spectrum ranging from extreme literal biblical creationism to materialist evolution, grouped under main headings. This was used in public presentations, then published in 1999 in Reports of the NCSE. Other versions of a taxonomy of creationists were produced, and comparisons made between the different groupings. In 2009 Scott produced a revised continuum taking account of these issues, emphasizing that intelligent design creationism overlaps other types, and each type is a grouping of various beliefs and positions. The revised diagram is labelled to shows a spectrum relating to positions on the age of the Earth, and the part played by special creation as against evolution. This was published in the book Evolution Vs. Creationism: An Introduction, and the NCSE website rewritten on the basis of the book version.
The main general types are listed below.
| Humanity | Biological species | Earth | Age of Universe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young Earth creationism | Directly created by God. | Directly created by God. Macroevolution does not occur. | Less than 10,000 years old. Reshaped by global flood. | Less than 10,000 years old, but some hold this view only for the Solar System. |
| Gap creationism | Scientifically accepted age. Reshaped by global flood. | Scientifically accepted age. | ||
| Progressive creationism | Directly created by God, based on primate anatomy. | Direct creation + evolution. No single common ancestor. | Scientifically accepted age. No global flood. | |
| Intelligent design | Proponents hold various beliefs. (For example, Michael Behe accepts evolution from primates.) | Divine intervention at some point in the past, as evidenced by what intelligent-design creationists call "irreducible complexity." Some adherents accept common descent, others do not. | Some claim the existence of Earth is the result of divine intervention. | |
| Theistic evolution (evolutionary creationism) | Evolution from primates. | Evolution from single common ancestor. | Scientifically accepted age. No global flood. |
Young Earth creationism
Main article: Young Earth creationism

Young Earth creationists such as Ken Ham and Doug Phillips believe that God created the Earth within the last ten thousand years, with a literalist interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative, within the approximate time-frame of biblical genealogies. Most young Earth creationists believe that the universe has a similar age as the Earth. A few assign a much older age to the universe than to Earth. Young Earth creationism gives the universe an age consistent with the Ussher chronology and other young Earth time frames. Other young Earth creationists believe that the Earth and the universe were created with the appearance of age, so that the world appears to be much older than it is, and that this appearance is what gives the geological findings and other methods of dating the Earth and the universe their much longer timelines.
The Christian organizations Answers in Genesis (AiG), Institute for Creation Research (ICR) and the Creation Research Society (CRS) promote young Earth creationism in the United States. Carl Baugh's Creation Evidence Museum in Texas, United States AiG's Creation Museum and Ark Encounter in Kentucky, United States were opened to promote young Earth creationism. Creation Ministries International promotes young Earth views in Australia, Canada, South Africa, New Zealand, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
Among Roman Catholics, the Kolbe Center for the Study of Creation promotes similar ideas.
Old Earth creationism
Main article: Old Earth creationismOld Earth creationism holds that the physical universe was created by God, but that the creation event described in the Book of Genesis is to be taken figuratively. This group generally believes that the age of the universe and the age of the Earth are as described by astronomers and geologists, but that details of modern evolutionary theory are questionable.
Old Earth creationism itself comes in at least three types:
Gap creationism
Main article: Gap creationismGap creationism (also known as ruin-restoration creationism, restoration creationism, or the Gap Theory) is a form of old Earth creationism that posits that the six-yom creation period, as described in the Book of Genesis, involved six literal 24-hour days, but that there was a gap of time between two distinct creations in the first and the second verses of Genesis, which the theory states explains many scientific observations, including the age of the Earth. Thus, the six days of creation (verse 3 onwards) start sometime after the Earth was "without form and void." This allows an indefinite gap of time to be inserted after the original creation of the universe, but prior to the Genesis creation narrative, (when present biological species and humanity were created). Gap theorists can therefore agree with the scientific consensus regarding the age of the Earth and universe, while maintaining a literal interpretation of the biblical text.
Some gap creationists expand the basic version of creationism by proposing a "primordial creation" of biological life within the "gap" of time. This is thought to be "the world that then was" mentioned in 2 Peter 3:3–6. Discoveries of fossils and archaeological ruins older than 10,000 years are generally ascribed to this "world that then was," which may also be associated with Lucifer's rebellion.
Day-age creationism
Main article: Day-age creationismDay-age creationism, a type of old Earth creationism, is a metaphorical interpretation of the creation accounts in Genesis. It holds that the six days referred to in the Genesis account of creation are not ordinary 24-hour days, but are much longer periods (from thousands to billions of years). The Genesis account is then reconciled with the age of the Earth. Proponents of the day-age theory can be found among both theistic evolutionists, who accept the scientific consensus on evolution, and progressive creationists, who reject it. The theories are said to be built on the understanding that the Hebrew word yom is also used to refer to a time period, with a beginning and an end and not necessarily that of a 24-hour day.
The day-age theory attempts to reconcile the Genesis creation narrative and modern science by asserting that the creation "days" were not ordinary 24-hour days, but actually lasted for long periods of time (as day-age implies, the "days" each lasted an age). According to this view, the sequence and duration of the creation "days" may be paralleled to the scientific consensus for the age of the earth and the universe.
Progressive creationism
Main article: Progressive creationismProgressive creationism is the religious belief that God created new forms of life gradually over a period of hundreds of millions of years. As a form of old Earth creationism, it accepts mainstream geological and cosmological estimates for the age of the Earth, some tenets of biology such as microevolution as well as archaeology to make its case. In this view creation occurred in rapid bursts in which all "kinds" of plants and animals appear in stages lasting millions of years. The bursts are followed by periods of stasis or equilibrium to accommodate new arrivals. These bursts represent instances of God creating new types of organisms by divine intervention. As viewed from the archaeological record, progressive creationism holds that "species do not gradually appear by the steady transformation of its ancestors; appear all at once and "fully formed."
The view rejects macroevolution, claiming it is biologically untenable and not supported by the fossil record, as well as rejects the concept of common descent from a last universal common ancestor. Thus the evidence for macroevolution is claimed to be false, but microevolution is accepted as a genetic parameter designed by the Creator into the fabric of genetics to allow for environmental adaptations and survival. Generally, it is viewed by proponents as a middle ground between literal creationism and evolution. Organizations such as Reasons To Believe, founded by Hugh Ross, promote this version of creationism.
Progressive creationism can be held in conjunction with hermeneutic approaches to the Genesis creation narrative such as the day-age creationism or framework/metaphoric/poetic views.
Philosophic and scientific creationism
Creation science
Main article: Creation scienceCreation science, or initially scientific creationism, is a pseudoscience that emerged in the 1960s with proponents aiming to have young Earth creationist beliefs taught in school science classes as a counter to teaching of evolution. Common features of creation science argument include: creationist cosmologies which accommodate a universe on the order of thousands of years old, criticism of radiometric dating through a technical argument about radiohalos, explanations for the fossil record as a record of the Genesis flood narrative (see flood geology), and explanations for the present diversity as a result of pre-designed genetic variability and partially due to the rapid degradation of the perfect genomes God placed in "created kinds" or "baramins" due to mutations.
Neo-creationism
Main article: Neo-creationismNeo-creationism is a pseudoscientific movement which aims to restate creationism in terms more likely to be well received by the public, by policy makers, by educators and by the scientific community. It aims to re-frame the debate over the origins of life in non-religious terms and without appeals to scripture. This comes in response to the 1987 ruling by the United States Supreme Court in Edwards v. Aguillard that creationism is an inherently religious concept and that advocating it as correct or accurate in public-school curricula violates the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment.
One of the principal claims of neo-creationism propounds that ostensibly objective orthodox science, with a foundation in naturalism, is actually a dogmatically atheistic religion. Its proponents argue that the scientific method excludes certain explanations of phenomena, particularly where they point towards supernatural elements, thus effectively excluding religious insight from contributing to understanding the universe. This leads to an open and often hostile opposition to what neo-creationists term "Darwinism", which they generally mean to refer to evolution, but which they may extend to include such concepts as abiogenesis, stellar evolution and the Big Bang theory.
Unlike their philosophical forebears, neo-creationists largely do not believe in many of the traditional cornerstones of creationism such as a young Earth, or in a dogmatically literal interpretation of the Bible.
Intelligent design
Main article: Intelligent designIntelligent design (ID) is the pseudoscientific view that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." All of its leading proponents are associated with the Discovery Institute, a think tank whose wedge strategy aims to replace the scientific method with "a science consonant with Christian and theistic convictions" which accepts supernatural explanations. It is widely accepted in the scientific and academic communities that intelligent design is a form of creationism, and is sometimes referred to as "intelligent design creationism."
ID originated as a re-branding of creation science in an attempt to avoid a series of court decisions ruling out the teaching of creationism in American public schools, and the Discovery Institute has run a series of campaigns to change school curricula. In Australia, where curricula are under the control of state governments rather than local school boards, there was a public outcry when the notion of ID being taught in science classes was raised by the Federal Education Minister Brendan Nelson; the minister quickly conceded that the correct forum for ID, if it were to be taught, is in religious or philosophy classes.
In the US, teaching of intelligent design in public schools has been decisively ruled by a federal district court to be in violation of the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. In Kitzmiller v. Dover, the court found that intelligent design is not science and "cannot uncouple itself from its creationist, and thus religious, antecedents," and hence cannot be taught as an alternative to evolution in public school science classrooms under the jurisdiction of that court. This sets a persuasive precedent, based on previous US Supreme Court decisions in Edwards v. Aguillard and Epperson v. Arkansas (1968), and by the application of the Lemon test, that creates a legal hurdle to teaching intelligent design in public school districts in other federal court jurisdictions.
Geocentrism
Main article: Geocentric modelIn astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system), is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece. As such, they assumed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth, including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy.
Articles arguing that geocentrism was the biblical perspective appeared in some early creation science newsletters associated with the Creation Research Society pointing to some passages in the Bible, which, when taken literally, indicate that the daily apparent motions of the Sun and the Moon are due to their actual motions around the Earth rather than due to the rotation of the Earth about its axis. For example, Joshua 10:12–13 where the Sun and Moon are said to stop in the sky, and Psalms 93:1 where the world is described as immobile. Contemporary advocates for such religious beliefs include Robert Sungenis, co-author of the self-published Galileo Was Wrong: The Church Was Right (2006). These people subscribe to the view that a plain reading of the Bible contains an accurate account of the manner in which the universe was created and requires a geocentric worldview. Most contemporary creationist organizations reject such perspectives.
Omphalos hypothesis
Main article: Omphalos hypothesisThe Omphalos hypothesis is one attempt to reconcile the scientific evidence that the universe is billions of years old with a literal interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative, which implies that the Earth is only a few thousand years old. It is based on the religious belief that the universe was created by a divine being, within the past six to ten thousand years (in keeping with flood geology), and that the presence of objective, verifiable evidence that the universe is older than approximately ten millennia is due to the creator introducing false evidence that makes the universe appear significantly older.
The idea was named after the title of an 1857 book, Omphalos by Philip Henry Gosse, in which Gosse argued that in order for the world to be functional God must have created the Earth with mountains and canyons, trees with growth rings, Adam and Eve with fully grown hair, fingernails, and navels (ὀμφαλός omphalos is Greek for "navel"), and all living creatures with fully formed evolutionary features, etc..., and that, therefore, no empirical evidence about the age of the Earth or universe can be taken as reliable.
Various supporters of Young Earth creationism have given different explanations for their belief that the universe is filled with false evidence of the universe's age, including a belief that some things needed to be created at a certain age for the ecosystems to function, or their belief that the creator was deliberately planting deceptive evidence. The idea has seen some revival in the 20th century by some modern creationists, who have extended the argument to address the "starlight problem". The idea has been criticised as Last Thursdayism, and on the grounds that it requires a deliberately deceptive creator.
Theistic evolution
Main article: Theistic evolutionTheistic evolution, or evolutionary creation, is a belief that "the personal God of the Bible created the universe and life through evolutionary processes." According to the American Scientific Affiliation:
A theory of theistic evolution (TE) – also called evolutionary creation – proposes that God's method of creation was to cleverly design a universe in which everything would naturally evolve. Usually the "evolution" in "theistic evolution" means Total Evolution – astronomical evolution (to form galaxies, solar systems,...) and geological evolution (to form the earth's geology) plus chemical evolution (to form the first life) and biological evolution (for the development of life) – but it can refer only to biological evolution.
Through the 19th century the term creationism most commonly referred to direct creation of individual souls, in contrast to traducianism. Following the publication of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation, there was interest in ideas of Creation by divine law. In particular, the liberal theologian Baden Powell argued that this illustrated the Creator's power better than the idea of miraculous creation, which he thought ridiculous. When On the Origin of Species was published, the cleric Charles Kingsley wrote of evolution as "just as noble a conception of Deity." Darwin's view at the time was of God creating life through the laws of nature, and the book makes several references to "creation," though he later regretted using the term rather than calling it an unknown process. In America, Asa Gray argued that evolution is the secondary effect, or modus operandi, of the first cause, design, and published a pamphlet defending the book in theistic terms, Natural Selection not inconsistent with Natural Theology. Theistic evolution, also called, evolutionary creation, became a popular compromise, and St. George Jackson Mivart was among those accepting evolution but attacking Darwin's naturalistic mechanism. Eventually it was realised that supernatural intervention could not be a scientific explanation, and naturalistic mechanisms such as neo-Lamarckism were favoured as being more compatible with purpose than natural selection.
Some theists took the general view that, instead of faith being in opposition to biological evolution, some or all classical religious teachings about Christian God and creation are compatible with some or all of modern scientific theory, including specifically evolution; it is also known as "evolutionary creation." In Evolution versus Creationism, Eugenie Scott and Niles Eldredge state that it is in fact a type of evolution.
It generally views evolution as a tool used by God, who is both the first cause and immanent sustainer/upholder of the universe; it is therefore well accepted by people of strong theistic (as opposed to deistic) convictions. Theistic evolution can synthesize with the day-age creationist interpretation of the Genesis creation narrative; however most adherents consider that the first chapters of the Book of Genesis should not be interpreted as a "literal" description, but rather as a literary framework or allegory.
From a theistic viewpoint, the underlying laws of nature were designed by God for a purpose, and are so self-sufficient that the complexity of the entire physical universe evolved from fundamental particles in processes such as stellar evolution, life forms developed in biological evolution, and in the same way the origin of life by natural causes has resulted from these laws.
In one form or another, theistic evolution is the view of creation taught at the majority of mainline Protestant seminaries. For Roman Catholics, human evolution is not a matter of religious teaching, and must stand or fall on its own scientific merits. Evolution and the Roman Catholic Church are not in conflict. The Catechism of the Catholic Church comments positively on the theory of evolution, which is neither precluded nor required by the sources of faith, stating that scientific studies "have splendidly enriched our knowledge of the age and dimensions of the cosmos, the development of life-forms and the appearance of man." Roman Catholic schools teach evolution without controversy on the basis that scientific knowledge does not extend beyond the physical, and scientific truth and religious truth cannot be in conflict. Theistic evolution can be described as "creationism" in holding that divine intervention brought about the origin of life or that divine laws govern formation of species, though many creationists (in the strict sense) would deny that the position is creationism at all. In the creation–evolution controversy, its proponents generally take the "evolutionist" side. This sentiment was expressed by Fr. George Coyne, (the Vatican's chief astronomer between 1978 and 2006):
...in America, creationism has come to mean some fundamentalistic, literal, scientific interpretation of Genesis. Judaic-Christian faith is radically creationist, but in a totally different sense. It is rooted in a belief that everything depends upon God, or better, all is a gift from God.
While supporting the methodological naturalism inherent in modern science, the proponents of theistic evolution reject the implication taken by some atheists that this gives credence to ontological materialism. In fact, many modern philosophers of science, including atheists, refer to the long-standing convention in the scientific method that observable events in nature should be explained by natural causes, with the distinction that it does not assume the actual existence or non-existence of the supernatural.
Religious views
There are also non-Christian forms of creationism, notably Islamic creationism and Hindu creationism.
Bahá'í Faith
Main article: Bahá'í Faith and science § CreationIn the creation myth taught by Bahá'u'lláh, the Bahá'í Faith founder, the universe has "neither beginning nor ending," and that the component elements of the material world have always existed and will always exist. With regard to evolution and the origin of human beings, 'Abdu'l-Bahá gave extensive comments on the subject when he addressed western audiences in the beginning of the 20th century. Transcripts of these comments can be found in Some Answered Questions, Paris Talks and The Promulgation of Universal Peace. 'Abdu'l-Bahá described the human species as having evolved from a primitive form to modern man, but that the capacity to form human intelligence was always in existence.
Buddhism
See also: Creator in BuddhismBuddhism denies a creator deity and posits that mundane deities such as Mahabrahma are sometimes misperceived to be a creator. While Buddhism includes belief in divine beings called devas, it holds that they are mortal, limited in their power, and that none of them are creators of the universe. In the Saṃyutta Nikāya, the Buddha also states that the cycle of rebirths stretches back hundreds of thousands of eons, without discernible beginning.
Major Buddhist Indian philosophers such as Nagarjuna, Vasubandhu, Dharmakirti and Buddhaghosa, consistently critiqued Creator God views put forth by Hindu thinkers.
Christianity
Further information: Genesis creation narrative and creation–evolution controversyAs of 2006, most Christians around the world accepted evolution as the most likely explanation for the origins of species, and did not take a literal view of the Genesis creation narrative. The United States is an exception where belief in religious fundamentalism is much more likely to affect attitudes towards evolution than it is for believers elsewhere. Political partisanship affecting religious belief may be a factor because political partisanship in the US is highly correlated with fundamentalist thinking, unlike in Europe.
Most contemporary Christian leaders and scholars from mainstream churches, such as Anglicans and Lutherans, consider that there is no conflict between the spiritual meaning of creation and the science of evolution. According to the former archbishop of Canterbury, Rowan Williams, "for most of the history of Christianity, and I think this is fair enough, most of the history of the Christianity there's been an awareness that a belief that everything depends on the creative act of God, is quite compatible with a degree of uncertainty or latitude about how precisely that unfolds in creative time."
Leaders of the Anglican and Roman Catholic churches have made statements in favor of evolutionary theory, as have scholars such as the physicist John Polkinghorne, who argues that evolution is one of the principles through which God created living beings. Earlier supporters of evolutionary theory include Frederick Temple, Asa Gray and Charles Kingsley who were enthusiastic supporters of Darwin's theories upon their publication, and the French Jesuit priest and geologist Pierre Teilhard de Chardin saw evolution as confirmation of his Christian beliefs, despite condemnation from Church authorities for his more speculative theories. Another example is that of Liberal theology, not providing any creation models, but instead focusing on the symbolism in beliefs of the time of authoring Genesis and the cultural environment.
Many Christians and Jews had been considering the idea of the creation history as an allegory (instead of historical) long before the development of Darwin's theory of evolution. For example, Philo, whose works were taken up by early Church writers, wrote that it would be a mistake to think that creation happened in six days, or in any set amount of time. Augustine of the late fourth century who was also a former neoplatonist argued that everything in the universe was created by God at the same moment in time (and not in six days as a literal reading of the Book of Genesis would seem to require); It appears that both Philo and Augustine felt uncomfortable with the idea of a seven-day creation because it detracted from the notion of God's omnipotence. In 1950, Pope Pius XII stated limited support for the idea in his encyclical Humani generis. In 1996, Pope John Paul II stated that "new knowledge has led to the recognition of the theory of evolution as more than a hypothesis," but, referring to previous papal writings, he concluded that "if the human body takes its origin from pre-existent living matter, the spiritual soul is immediately created by God."
In the US, Evangelical Christians have continued to believe in a literal Genesis. As of 2008, members of evangelical Protestant (70%), Mormon (76%) and Jehovah's Witnesses (90%) denominations were the most likely to reject the evolutionary interpretation of the origins of life.
Jehovah's Witnesses assert that scientific evidence about the age of the universe is compatible with the Bible, but that the 'days' after Genesis 1:1 were each thousands of years in length. They view this belief as an alternative to Creationism rather than a variation of Creationism.
The historic Christian literal interpretation of creation requires the harmonization of the two creation stories, Genesis 1:1–2:3 and Genesis 2:4–25, for there to be a consistent interpretation. They sometimes seek to ensure that their belief is taught in science classes, mainly in American schools. Opponents reject the claim that the literalistic biblical view meets the criteria required to be considered scientific. Many religious groups teach that God created the Cosmos. From the days of the early Christian Church Fathers there were allegorical interpretations of the Book of Genesis as well as literal aspects.
Christian Science, a system of thought and practice derived from the writings of Mary Baker Eddy, interprets the Book of Genesis figuratively rather than literally. It holds that the material world is an illusion, and consequently not created by God: the only real creation is the spiritual realm, of which the material world is a distorted version. Christian Scientists regard the story of the creation in the Book of Genesis as having symbolic rather than literal meaning. According to Christian Science, both creationism and evolution are false from an absolute or "spiritual" point of view, as they both proceed from a (false) belief in the reality of a material universe. However, Christian Scientists do not oppose the teaching of evolution in schools, nor do they demand that alternative accounts be taught: they believe that both material science and literalist theology are concerned with the illusory, mortal and material, rather than the real, immortal and spiritual. With regard to material theories of creation, Eddy showed a preference for Darwin's theory of evolution over others.
Hinduism
Main article: Hindu views on evolutionHindu creationists claim that species of plants and animals are material forms adopted by pure consciousness which live an endless cycle of births and rebirths. Ronald Numbers says that: "Hindu Creationists have insisted on the antiquity of humans, who they believe appeared fully formed as long, perhaps, as trillions of years ago." Hindu creationism is a form of old Earth creationism, according to Hindu creationists the universe may even be older than billions of years. These views are based on the Vedas, the creation myths of which depict an extreme antiquity of the universe and history of the Earth.
In Hindu cosmology, time cyclically repeats general events of creation and destruction, with many "first man", each known as Manu, the progenitor of mankind. Each Manu successively reigns over a 306.72 million year period known as a manvantara, each ending with the destruction of mankind followed by a sandhya (period of non-activity) before the next manvantara. 120.53 million years have elapsed in the current manvantara (current mankind) according to calculations on Hindu units of time. The universe is cyclically created at the start and destroyed at the end of a kalpa (day of Brahma), lasting for 4.32 billion years, which is followed by a pralaya (period of dissolution) of equal length. 1.97 billion years have elapsed in the current kalpa (current universe). The universal elements or building blocks (unmanifest matter) exists for a period known as a maha-kalpa, lasting for 311.04 trillion years, which is followed by a maha-pralaya (period of great dissolution) of equal length. 155.52 trillion years have elapsed in the current maha-kalpa.
Islam
Main article: Islamic views on evolution Further information: Predestination in IslamThe creation myths in the Quran are more vague and allow for a wider range of interpretations similar to those in other Abrahamic religions.
Islam also has its own school of theistic evolutionism, which holds that mainstream scientific analysis of the origin of the universe is supported by the Quran. Some Muslims believe in evolutionary creation, especially among liberal movements within Islam.
Writing for The Boston Globe, Drake Bennett noted: "Without a Book of Genesis to account for Muslim creationists have little interest in proving that the age of the Earth is measured in the thousands rather than the billions of years, nor do they show much interest in the problem of the dinosaurs. And the idea that animals might evolve into other animals also tends to be less controversial, in part because there are passages of the Koran that seem to support it. But the issue of whether human beings are the product of evolution is just as fraught among Muslims." Khalid Anees, president of the Islamic Society of Britain, states that Muslims do not agree that one species can develop from another.
Ottoman-Lebanese Sunni scholar Hussein al-Jisr, declared that there is no contradiction between evolution and the Islamic scriptures. He stated that "there is no evidence in the Quran to suggest whether all species, each of which exists by the grace of God, were created all at once or gradually", and referred to the aforementioned story of creation in Sūrat al-Anbiyā. In Kemalist Turkey, important scholars strove to accommodate the theory of evolution in Islamic scripture during the first decades of the Turkish Republic; their approach to the theory defended Islamic belief in the face of scientific theories of their times.
The Saudi Arabian government, on the other hand, began funding and promoting denial of evolution in the 1970s in accordance to its Salafi-Wahhabi interpretation of Islam. This stance garnered criticism from the governments and academics of mainline Muslim countries such as Turkey, Pakistan, Lebanon, and Iran, where evolution was initially taught and promoted. Since the 1980s, Turkey has been a site of strong advocacy for creationism, supported by American adherents.
Judaism
Main article: Jewish views on evolutionFor Orthodox Jews who seek to reconcile discrepancies between science and the creation myths in the Bible, the notion that science and the Bible should even be reconciled through traditional scientific means is questioned. To these groups, science is as true as the Torah and if there seems to be a problem, epistemological limits are to blame for apparently irreconcilable points. They point to discrepancies between what is expected and what actually is to demonstrate that things are not always as they appear. They note that even the root word for 'world' in the Hebrew language, עולם, Olam, means 'hidden' (נעלם, Neh-Eh-Lahm). Just as they know from the Torah that God created man and trees and the light on its way from the stars in their observed state, so too can they know that the world was created in its over the six days of Creation that reflects progression to its currently-observed state, with the understanding that physical ways to verify this may eventually be identified. This knowledge has been advanced by Rabbi Dovid Gottlieb, former philosophy professor at Johns Hopkins University.
Kabbalistic sources from well before the scientifically apparent age of the universe was first determined are also in close concord with modern scientific estimates of the age of the universe, according to Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan, and based on Sefer Temunah, an early kabbalistic work attributed to the first-century Tanna Nehunya ben HaKanah. Many kabbalists accepted the teachings of the Sefer HaTemunah, including the medieval Jewish scholar Nahmanides, his close student Isaac ben Samuel of Acre, and David ben Solomon ibn Abi Zimra. Other parallels are derived, among other sources, from Nahmanides, who expounds that there was a Neanderthal-like species with which Adam mated (he did this long before Neanderthals had even been discovered scientifically). Reform Judaism does not take the Torah as a literal text, but rather as a symbolic or open-ended work.
Some contemporary writers such as Rabbi Gedalyah Nadel have sought to reconcile the discrepancy between the account in the Torah, and scientific findings by arguing that each day referred to in the Bible was not 24 hours, but billions of years long. Others claim that the Earth was created a few thousand years ago, but was deliberately made to look as if it was five billion years old, e.g. by being created with ready made fossils. The best known exponent of this approach being Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson. Others state that although the world was physically created in six 24-hour days, the Torah accounts can be interpreted to mean that there was a period of billions of years before the six days of creation.
Prevalence
Main articles: Level of support for evolution and Creationism by country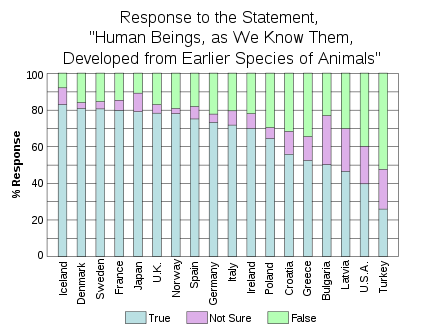
Most vocal literalist creationists are from the US, and strict creationist views are much less common in other developed countries. According to a study published in Science, a survey of the US, Turkey, Japan and Europe showed that public acceptance of evolution is most prevalent in Iceland, Denmark and Sweden at 80% of the population. There seems to be no significant correlation between believing in evolution and understanding evolutionary science.
Australia
A 2009 Nielsen poll showed that 23% of Australians believe "the biblical account of human origins," 42% believe in a "wholly scientific" explanation for the origins of life, while 32% believe in an evolutionary process "guided by God".
A 2013 survey conducted by Auspoll and the Australian Academy of Science found that 80% of Australians believe in evolution (70% believe it is currently occurring, 10% believe in evolution but do not think it is currently occurring), 12% were not sure and 9% stated they do not believe in evolution.
Brazil
A 2011 Ipsos survey found that 47% of responders in Brazil identified themselves as "creationists and believe that human beings were in fact created by a spiritual force such as the God they believe in and do not believe that the origin of man came from evolving from other species such as apes".
In 2004, IBOPE conducted a poll in Brazil that asked questions about creationism and the teaching of creationism in schools. When asked if creationism should be taught in schools, 89% of people said that creationism should be taught in schools. When asked if the teaching of creationism should replace the teaching of evolution in schools, 75% of people said that the teaching of creationism should replace the teaching of evolution in schools.
Canada

A 2012 survey, by Angus Reid Public Opinion revealed that 61 percent of Canadians believe in evolution. The poll asked "Where did human beings come from – did we start as singular cells millions of year ago and evolve into our present form, or did God create us in his image 10,000 years ago?"
In 2019, a Research Co. poll asked people in Canada if creationism "should be part of the school curriculum in their province". 38% of Canadians said that creationism should be part of the school curriculum, 39% of Canadians said that it should not be part of the school curriculum, and 23% of Canadians were undecided.
In 2023, a Research Co. poll found that 21% of Canadians "believe God created human beings in their present form within the last 10,000 years". The poll also found that "More than two-in-five Canadians (43%) think creationism should be part of the school curriculum in their province."
Europe
In Europe, literalist creationism is more widely rejected, though regular opinion polls are not available. Most people accept that evolution is the most widely accepted scientific theory as taught in most schools. In countries with a Roman Catholic majority, papal acceptance of evolutionary creationism as worthy of study has essentially ended debate on the matter for many people.
In the UK, a 2006 poll on the "origin and development of life", asked participants to choose between three different perspectives on the origin of life: 22% chose creationism, 17% opted for intelligent design, 48% selected evolutionary theory, and the rest did not know. A subsequent 2010 YouGov poll on the correct explanation for the origin of humans found that 9% opted for creationism, 12% intelligent design, 65% evolutionary theory and 13% didn't know. The former Archbishop of Canterbury Rowan Williams, head of the worldwide Anglican Communion, views the idea of teaching creationism in schools as a mistake. In 2009, an Ipsos Mori survey in the United Kingdom found that 54% of Britons agreed with the view: "Evolutionary theories should be taught in science lessons in schools together with other possible perspectives, such as intelligent design and creationism."
In Italy, Education Minister Letizia Moratti wanted to retire evolution from the secondary school level; after one week of massive protests, she reversed her opinion.
There continues to be scattered and possibly mounting efforts on the part of religious groups throughout Europe to introduce creationism into public education. In response, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe has released a draft report titled The dangers of creationism in education on June 8, 2007, reinforced by a further proposal of banning it in schools dated October 4, 2007.
Serbia suspended the teaching of evolution for one week in September 2004, under education minister Ljiljana Čolić, only allowing schools to reintroduce evolution into the curriculum if they also taught creationism. "After a deluge of protest from scientists, teachers and opposition parties" says the BBC report, Čolić's deputy made the statement, "I have come here to confirm Charles Darwin is still alive" and announced that the decision was reversed. Čolić resigned after the government said that she had caused "problems that had started to reflect on the work of the entire government."
Poland saw a major controversy over creationism in 2006, when the Deputy Education Minister, Mirosław Orzechowski, denounced evolution as "one of many lies" taught in Polish schools. His superior, Minister of Education Roman Giertych, has stated that the theory of evolution would continue to be taught in Polish schools, "as long as most scientists in our country say that it is the right theory." Giertych's father, Member of the European Parliament Maciej Giertych, has opposed the teaching of evolution and has claimed that dinosaurs and humans co-existed.
A June 2015 – July 2016 Pew poll of Eastern European countries, found that 56% of people from Armenia say that humans and other living things have "Existed in present state since the beginning of time". Armenia is followed by 52% from Bosnia, 42% from Moldova, 37% from Lithuania, 34% from Georgia and Ukraine, 33% from Croatia and Romania, 31% from Bulgaria, 29% from Greece and Serbia, 26% from Russia, 25% from Latvia, 23% from Belarus and Poland, 21% from Estonia and Hungary, and 16% from the Czech Republic.
South Africa
A 2011 Ipsos survey found that 56% of responders in South Africa identified themselves as "creationists and believe that human beings were in fact created by a spiritual force such as the God they believe in and do not believe that the origin of man came from evolving from other species such as apes".
South Korea
In 2009, an EBS survey in South Korea found that 63% of people believed that creation and evolution should both be taught in schools simultaneously.
United States



A 2017 poll by Pew Research found that 62% of Americans believe humans have evolved over time and 34% of Americans believe humans and other living things have existed in their present form since the beginning of time. A 2019 Gallup creationism survey found that 40% of adults in the United States inclined to the view that "God created humans in their present form at one time within the last 10,000 years" when asked for their views on the origin and development of human beings.
According to a 2014 Gallup poll, about 42% of Americans believe that "God created human beings pretty much in their present form at one time within the last 10,000 years or so." Another 31% believe that "human beings have developed over millions of years from less advanced forms of life, but God guided this process,"and 19% believe that "human beings have developed over millions of years from less advanced forms of life, but God had no part in this process."
Belief in creationism is inversely correlated to education; of those with postgraduate degrees, 74% accept evolution. In 1987, Newsweek reported: "By one count there are some 700 scientists with respectable academic credentials (out of a total of 480,000 U.S. earth and life scientists) who give credence to creation-science, the general theory that complex life forms did not evolve but appeared 'abruptly.'"
A 2000 poll for People for the American Way found 70% of the US public felt that evolution was compatible with a belief in God.
According to a study published in Science, between 1985 and 2005 the number of adult North Americans who accept evolution declined from 45% to 40%, the number of adults who reject evolution declined from 48% to 39% and the number of people who were unsure increased from 7% to 21%. Besides the US the study also compared data from 32 European countries, Turkey, and Japan. The only country where acceptance of evolution was lower than in the US was Turkey (25%).
According to a 2011 Fox News poll, 45% of Americans believe in creationism, down from 50% in a similar poll in 1999. 21% believe in 'the theory of evolution as outlined by Darwin and other scientists' (up from 15% in 1999), and 27% answered that both are true (up from 26% in 1999).
In September 2012, educator and television personality Bill Nye spoke with the Associated Press and aired his fears about acceptance of creationism, believing that teaching children that creationism is the only true answer without letting them understand the way science works will prevent any future innovation in the world of science. In February 2014, Nye defended evolution in the classroom in a debate with creationist Ken Ham on the topic of whether creation is a viable model of origins in today's modern, scientific era.
Education controversies
Main article: Rejection of evolution by religious groups
In the US, creationism has become centered in the political controversy over creation and evolution in public education, and whether teaching creationism in science classes conflicts with the separation of church and state. Currently, the controversy comes in the form of whether advocates of the intelligent design movement who wish to "Teach the Controversy" in science classes have conflated science with religion.
People for the American Way polled 1500 North Americans about the teaching of evolution and creationism in November and December 1999. They found that most North Americans were not familiar with creationism, and most North Americans had heard of evolution, but many did not fully understand the basics of the theory. The main findings were:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In such political contexts, creationists argue that their particular religiously based origin belief is superior to those of other belief systems, in particular those made through secular or scientific rationale. Political creationists are opposed by many individuals and organizations who have made detailed critiques and given testimony in various court cases that the alternatives to scientific reasoning offered by creationists are opposed by the consensus of the scientific community.
Criticism
Christian criticism
Most Christians disagree with the teaching of creationism as an alternative to evolution in schools. Several religious organizations, among them the Catholic Church, hold that their faith does not conflict with the scientific consensus regarding evolution. The Clergy Letter Project, which has collected more than 13,000 signatures, is an "endeavor designed to demonstrate that religion and science can be compatible."
In his 2002 article "Intelligent Design as a Theological Problem", George Murphy argues against the view that life on Earth, in all its forms, is direct evidence of God's act of creation (Murphy quotes Phillip E. Johnson's claim that he is speaking "of a God who acted openly and left his fingerprints on all the evidence."). Murphy argues that this view of God is incompatible with the Christian understanding of God as "the one revealed in the cross and resurrection of Christ." The basis of this theology is Isaiah 45:15, "Verily thou art a God that hidest thyself, O God of Israel, the Saviour."
Murphy observes that the execution of a Jewish carpenter by Roman authorities is in and of itself an ordinary event and did not require divine action. On the contrary, for the crucifixion to occur, God had to limit or "empty" himself. It was for this reason that Paul the Apostle wrote, in Philippians 2:5-8:
Let this mind be in you, which was also in Christ Jesus: Who, being in the form of God, thought it not robbery to be equal with God: But made himself of no reputation, and took upon him the form of a servant, and was made in the likeness of men: And being found in fashion as a man, he humbled himself, and became obedient unto death, even the death of the cross.
Murphy concludes that,
Just as the Son of God limited himself by taking human form and dying on a cross, God limits divine action in the world to be in accord with rational laws which God has chosen. This enables us to understand the world on its own terms, but it also means that natural processes hide God from scientific observation.
For Murphy, a theology of the cross requires that Christians accept a methodological naturalism, meaning that one cannot invoke God to explain natural phenomena, while recognizing that such acceptance does not require one to accept a metaphysical naturalism, which proposes that nature is all that there is.
The Jesuit priest George Coyne has stated that it is "unfortunate that, especially here in America, creationism has come to mean...some literal interpretation of Genesis." He argues that "...Judaic-Christian faith is radically creationist, but in a totally different sense. It is rooted in belief that everything depends on God, or better, all is a gift from God."
Teaching of creationism
Other Christians have expressed qualms about teaching creationism. In March 2006, then Archbishop of Canterbury Rowan Williams, the leader of the world's Anglicans, stated his discomfort about teaching creationism, saying that creationism was "a kind of category mistake, as if the Bible were a theory like other theories." He also said: "My worry is creationism can end up reducing the doctrine of creation rather than enhancing it." The views of the Episcopal Church – a major American-based branch of the Anglican Communion – on teaching creationism resemble those of Williams.
The National Science Teachers Association is opposed to teaching creationism as a science, as is the Association for Science Teacher Education, the National Association of Biology Teachers, the American Anthropological Association, the American Geosciences Institute, the Geological Society of America, the American Geophysical Union, and numerous other professional teaching and scientific societies.
In April 2010, the American Academy of Religion issued Guidelines for Teaching About Religion in K‐12 Public Schools in the United States, which included guidance that creation science or intelligent design should not be taught in science classes, as "Creation science and intelligent design represent worldviews that fall outside of the realm of science that is defined as (and limited to) a method of inquiry based on gathering observable and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning." However, they, as well as other "worldviews that focus on speculation regarding the origins of life represent another important and relevant form of human inquiry that is appropriately studied in literature or social sciences courses. Such study, however, must include a diversity of worldviews representing a variety of religious and philosophical perspectives and must avoid privileging one view as more legitimate than others."
Randy Moore and Sehoya Cotner, from the biology program at the University of Minnesota, reflect on the relevance of teaching creationism in the article "The Creationist Down the Hall: Does It Matter When Teachers Teach Creationism?", in which they write: "Despite decades of science education reform, numerous legal decisions declaring the teaching of creationism in public-school science classes to be unconstitutional, overwhelming evidence supporting evolution, and the many denunciations of creationism as nonscientific by professional scientific societies, creationism remains popular throughout the United States."
Scientific criticism
Main article: Rejection of evolution by religious groupsScience is a system of knowledge based on observation, empirical evidence, and the development of theories that yield testable explanations and predictions of natural phenomena. By contrast, creationism is often based on literal interpretations of the narratives of particular religious texts. Creationist beliefs involve purported forces that lie outside of nature, such as supernatural intervention, and often do not allow predictions at all. Therefore, these can neither be confirmed nor disproved by scientists. However, many creationist beliefs can be framed as testable predictions about phenomena such as the age of the Earth, its geological history and the origins, distributions and relationships of living organisms found on it. Early science incorporated elements of these beliefs, but as science developed these beliefs were gradually falsified and were replaced with understandings based on accumulated and reproducible evidence that often allows the accurate prediction of future results.
Some scientists, such as Stephen Jay Gould, consider science and religion to be two compatible and complementary fields, with authorities in distinct areas of human experience, so-called non-overlapping magisteria. This view is also held by many theologians, who believe that ultimate origins and meaning are addressed by religion, but favor verifiable scientific explanations of natural phenomena over those of creationist beliefs. Other scientists, such as Richard Dawkins, reject the non-overlapping magisteria and argue that, in disproving literal interpretations of creationists, the scientific method also undermines religious texts as a source of truth. Irrespective of this diversity in viewpoints, since creationist beliefs are not supported by empirical evidence, the scientific consensus is that any attempt to teach creationism as science should be rejected.
Organizations
|
|
See also
- Biblical inerrancy
- Biogenesis
- Dangers of creationism in education
- Evolution of complexity
- Flying Spaghetti Monster
- History of creationism
- Religious cosmology
Notes
- See also the article Catholic Church and evolution.
- Donald B. DeYoung, for example, states that "Similar terminology is often used today when we speak of the sun's rising and setting, even though the earth, not the sun, is doing the moving. Bible writers used the 'language of appearance,' just as people always have. Without it, the intended message would be awkward at best and probably not understood clearly. When the Bible touches on scientific subjects, it is entirely accurate."
References
Citations
- Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The Concise Oxford Dictionary says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'"
- Brosseau, Olivier; Silberstein, Marc (2015). "Evolutionism(s) and Creationism(s)". In Heams, Thomas; Huneman, Philippe; Lecointre, Guillaume; Silberstein., Marc (eds.). Handbook of Evolutionary Thinking in the Sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 881–96. ISBN 9789401790147.
- Brosseau, Olivier; Silberstein, Marc (2015). "Evolutionism(s) and Creationism(s)". In Heams, Thomas; Huneman, Philippe; Lecointre, Guillaume; Silberstein., Marc (eds.). Handbook of Evolutionary Thinking in the Sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 881, 884. ISBN 9789401790147.
Creationism is not a single homogenous doctrine ... Evolution, as a process, is a tool God uses to continually create the world. Here we have arrived at another sub-category of creationism called 'evolutionist creationism'
- Haarsma 2010, p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. Intelligent design, as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'evolutionary creationists,' assert that the scientific theory of evolution and the religious beliefs of Christianity can both be true."
- ^ Eugenie Scott (13 February 2018). "The Creation/Evolution Continuum". NCSE. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
creationism comes in many forms, and not all of them reject evolution
- "creationism: definition of creationism in Oxford dictionary (American English) (US)". Oxford Dictionaries (Definition). Oxford: Oxford University Press. OCLC 656668849. Archived from the original on March 3, 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-05.
The belief that the universe and living organisms originate from specific acts of divine creation, as in the biblical account, rather than by natural processes such as evolution.
- (Scott 2009, pp. 57, 97–98)
- ^ Eugenie Scott (13 February 2018). "The Creation/Evolution Continuum". NCSE. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- "What is "Intelligent Design" Creationism?". NCSE. 2008-10-17. Retrieved 2019-04-23.
- Campbell, Duncan (February 20, 2006). "Academics fight rise of creationism at universities". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-04-07.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (November 2, 2009). "Creationism, Without a Young Earth, Emerges in the Islamic World". The New York Times.
- ^ al-Azami, Usaama (2013-02-14). "Muslims and Evolution in the 21st Century: A Galileo Moment?". Huffington Post Religion Blog. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- "Creationism: The Hindu View". www.talkorigins.org. Retrieved 2019-04-23.
- Numbers 1998, p. 50 "Since at least the early 1840s Darwin had occasionally referred to 'creationists' in his unpublished writings, but the epithet acquired little public currency." – sketch written in 1842 – "if this had happened on an island, whence could the new forms have come,—here the geologist calls in creationists."
- Darwin, Charles (July 5, 1856). "Darwin, C. R. to Hooker, J. D." Darwin Correspondence Project. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Library. Letter 1919. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- Darwin, Charles (May 31, 1863). "Darwin, C. R. to Gray, Asa". Darwin Correspondence Project. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Library. Letter 4196. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- Numbers 1998, p. 50 "In 1873 Asa Gray described a 'special creationist' (a phrase he placed in quotation marks) as one who maintained that species 'were supernaturally originated just as they are'," – The Nation. J.H. Richards. October 16, 1873. p. 260.
- Richard F. Carlson, Tremper Longman III, Science, Creation and the Bible: Reconciling Rival Theories of Origins, p.25
- Scott, Eugenie C. (7 December 2000). "The Creation/Evolution Continuum". Reports of the National Center for Science Education, July–August 1999. 19 (4): 16–17, 23–25. ISSN 2158-818X. Archived from the original on 2008-05-09. (original online version, with link to the Creation/Evolution Continuum graphic
- ^ Wise, Donald U. (January 2001). "Creationism's Propaganda Assault on Deep Time and Evolution". Journal of Geoscience Education. 49 (1): 30–35. Bibcode:2001JGeEd..49...30W. doi:10.5408/1089-9995-49.1.30. ISSN 1089-9995. S2CID 152260926. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- ^ Ross, Marcus R. (May 2005). "Who Believes What? Clearing up Confusion over Intelligent Design and Young-Earth Creationism" (PDF). Journal of Geoscience Education. 53 (3): 319–323. Bibcode:2005JGeEd..53..319R. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.404.1340. doi:10.5408/1089-9995-53.3.319. ISSN 1089-9995. S2CID 14208021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Scott 2009, pp. 63–75.
- Evolution vs. Creationism: An Introduction, Eugenie Scott, pp61-62
- The Scientific Case Against Scientific Creationism, Jon P. Alston, p24
- "What is Creationism?".
- 2 Peter 3:3–7
- "Formless and Void: Gap Theory Creationism | National Center for Science Education". ncse.ngo. Retrieved 2021-10-30.
- Gould, Stephen J. The Panda's Thumb (New York: W.W. Norton & CO., 1982), page 182.
- Bocchino, Peter; Geisler, Norman "Unshakable Foundations" (Minneapolis: Bethany House., 2001). Pages 141–188
- Greener, M (December 2007). "Taking on creationism. Which arguments and evidence counter pseudoscience?". EMBO Rep. 8 (12): 1107–9. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7401131. ISSN 1469-221X. PMC 2267227. PMID 18059309.
- NAS 1999, p. R9
- Amicus Curiae Brief Of 72 Nobel Laureates, 17 State Academies Of Science, And 7 Other Scientific Organizations at the Wayback Machine (archive index), Edwards v. Aguillard
- Sahotra Sarkar; Jessica Pfeifer (2006). The Philosophy of science: an encyclopedia. A-M. Psychology Press. p. 194. ISBN 978-0-415-93927-0.
- Okasha 2002, p. 127. Okasha's full statement is that "virtually all professional biologists regard creation science as a sham – a dishonest and misguided attempt to promote religious beliefs under the guise of science, with extremely harmful educational consequences."
- Morris, Henry M. "Neocreationism". icr.org. Institute for Creation Research. Retrieved Sep 29, 2014.
- Safire, William (August 21, 2005). "On Language: Neo-Creo". The New York Times. Retrieved Sep 29, 2014.
- Scott, Eugenie C. (1996). "Creationism, ideology, and science". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. The Flight from Science and Reason. Vol. 775. pp. 505–22. Bibcode:1995NYASA.775..505S. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb23167.x. Retrieved 2009-11-12.
- Johnson, Phillip E. (October 2004). "Darwinism is Materialist Mythology, Not Science" (PDF). DarwinReconsidered.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 25, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2014.
- Boudry, Maarten; Blancke, Stefaan; Braeckman, Johan (December 2010). "Irreducible Incoherence and Intelligent Design: A Look into the Conceptual Toolbox of a Pseudoscience" (PDF). The Quarterly Review of Biology. 85 (4): 473–82. doi:10.1086/656904. hdl:1854/LU-952482. PMID 21243965. S2CID 27218269. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Article available from Universiteit Gent
- Pigliucci, Massimo (2010). "Science in the Courtroom: The Case against Intelligent Design" (PDF). Nonsense on Stilts: How to Tell Science from Bunk. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. pp. 160–86. ISBN 978-0-226-66786-7. LCCN 2009049778. OCLC 457149439. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- "Top Questions: Questions About Intelligent Design: What is the theory of intelligent design?". Center for Science and Culture. Seattle, WA: Discovery Institute. Retrieved 2007-05-13.
- "Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District Trial transcript: Day 6 (October 5), PM Session, Part 1". TalkOrigins Archive. Houston, TX: The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- ^ Forrest, Barbara (May 2007). "Understanding the Intelligent Design Creationist Movement: Its True Nature and Goals" (PDF). Center for Inquiry (A Position Paper from the Center for Inquiry, Office of Public Policy). Washington, D.C.: Center for Inquiry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-19. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- "The Wedge" (PDF). Seattle, WA: Center for the Renewal of Science and Culture. 1999. Archived from the original on 2007-04-22. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- Mu, David (Fall 2005). "Trojan Horse or Legitimate Science: Deconstructing the Debate over Intelligent Design" (PDF). Harvard Science Review. 19 (1): 22–25. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
...for most members of the mainstream scientific community, ID is not a scientific theory, but a creationist pseudoscience.
- Klotzko, Arlene Judith (May 28, 2001). "Cynical Science and Stem Cells". The Scientist. 15 (11): 35. ISSN 0890-3670. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
Creationists are repackaging their message as the pseudo-science of 'intelligent design theory.'
- Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District, 04 cv 2688 (December 20, 2005)., Curriculum, Conclusion, p. 136.
- Klotzko, Arlene Judith (May 28, 2001). "Cynical Science and Stem Cells". The Scientist. 15 (11): 35. ISSN 0890-3670. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- Numbers 2006
- Forrest & Gross 2004
- Pennock 2001, "Wizards of ID: Reply to Dembski," pp. 645–667, "Dembski chides me for never using the term 'intelligent design' without conjoining it to 'creationism'. He implies (though never explicitly asserts) that he and others in his movement are not creationists and that it is incorrect to discuss them in such terms, suggesting that doing so is merely a rhetorical ploy to 'rally the troops'. (2) Am I (and the many others who see Dembski's movement in the same way) misrepresenting their position? The basic notion of creationism is the rejection of biological evolution in favor of special creation, where the latter is understood to be supernatural. Beyond this there is considerable variability..."
- Scott 2005
- Young, Matt; Edis, Taner (2006). Why Intelligent Design Fails: A Scientific Critique of the New Creationism. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813538723.
- Flank, Lenny (April 24, 2006). "Creationism/ID: A Short Legal History". Talk Reason. Archived from the original on August 23, 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Smith, Deborah (October 21, 2005). "Intelligent design not science: experts". The Sydney Morning Herald. Sydney: Fairfax Media. Retrieved 2007-07-13.
- Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District, 04 cv 2688 (December 20, 2005)., Curriculum, Conclusion, p. 136.
- ^ Full text of U.S. District Judge John E. Jones III's ruling in Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District, dated December 20, 2005.
- Numbers, Ronald L. (1993) . The Creationists: The Evolution of Scientific Creationism. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-5200-8393-6. LCCN 93015804. OCLC 810488078.
- Sefton, Dru (March 30, 2006). "In this world view, the sun revolves around the earth". Times-News. Hendersonville, NC: Hendersonville Newspaper Corporation. Religion News Service. p. 5A. Retrieved 2014-03-14.
- DeYoung, Donald B. (November 5, 1997). "Astronomy and the Bible: Selected questions and answers excerpted from the book". Answers in Genesis. Hebron, KY: Answers in Genesis Ministries International. Retrieved 2013-12-01.
- Roizen, Ron (1982). "The rejection of Omphalos: a note on shifts in the intellectual hierarchy of mid-nineteenth century Britain". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 21 (4): 365–369. doi:10.2307/1385525. JSTOR 1385525. Archived from the original on 2007-02-19.
- Gardner, Martin (2000). Did Adam and Eve Have Navels?: Debunking Pseudoscience. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 7–14. ISBN 9780393322385.
- Sweet & Feist 2007, p. 48, "Evolutionary Creation (or Theistic Evolution) asserts that the personal God of the Bible created the universe and life through evolutionary processes."
- Rusbult, Craig (1998). "Evolutionary Creation". Ipswich, MA: American Scientific Affiliation. Retrieved 2014-03-14.
- Bowler 2003, p. 139
- ^ "Darwin and design: historical essay". Darwin Correspondence Project. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Library. 2007. Archived from the original on 2014-10-21. Retrieved 2012-04-18.
- Kingsley, Charles (November 18, 1859). "Kingsley, Charles to Darwin, C. R." Darwin Correspondence Project. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Library. Letter 2534. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- Moore, James (September 20, 2007). "Evolution and Wonder: Understanding Charles Darwin". Speaking of Faith with Krista Tippett (Interview). Interviewed by Krista Tippett. American Public Media. Archived from the original on 2015-11-18. Retrieved 2014-03-09 – via NPR.
- Quammen 2006, p. 119
- Barlow 1963, p. 207
- Dewey 1994, p. 27
- Miles, Sara Joan (September 2001). "Charles Darwin and Asa Gray Discuss Teleology and Design". Perspectives on Science and Christian Faith. 53: 196–201. Retrieved 2008-11-22.
- Gray, Asa (1860). "Natural Selection not inconsistent with Natural Theology". The Atlantic Monthly (Reprint). Archived from the original on 2009-02-20. Retrieved 2009-04-11. "Atlantic Monthly for July, August, and October, 1860, reprinted in 1861."
- Bowler 2003, pp. 202–08
- Scott 2005, pp. 62–63
- Moritz, Albrecht (October 31, 2006). "The Origin of Life". TalkOrigins Archive. Houston, TX: The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. Retrieved 2008-11-22.
- Scott 1999
- Akin, Jimmy (January 2004). "Evolution and the Magisterium". This Rock. 15 (1). ISSN 1049-4561. Archived from the original on 2007-08-04. Retrieved 2014-03-14.
- Guntzel, Jeff Severns (March 25, 2005). "Catholic schools steer clear of anti-evolution bias". National Catholic Reporter. Kansas City, MO: The National Catholic Reporter Publishing Company. ISSN 0027-8939. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
- Coyne, George V. (January 30, 2006). "Text of talk by Vatican Observatory director on 'Science Does Not Need God. Or Does It? A Catholic Scientist Looks at Evolution'". Catholic Online, LLC. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-10.
- Pennock 1999
- Schafersman, Steven D. (May 1997). "Naturalism is an Essential Part of Science and Critical Inquiry". Free Inquiry: The Humanist and Skeptic Website of Steven Schafersman. Steven Schafersman. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Leiter, Brian (April 6, 2004). "On Methodological Naturalism and Intelligent Design (or Why Can't Lawrence VanDyke Leave Well Enough Alone?)". Leiter Reports: A Philosophy Blog (Blog). Brian Leiter. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Burgeson, John W. (1997). "NTSE: An Intellectual Feast". Origins & Design. 18 (2). Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Draper 2005
- Pigliucci, Massimo; et al. (May–June 2004). "The Alleged Fallacies of Evolutionary Theory". Philosophy Now (46). ISSN 0961-5970. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- "Statement on Intelligent Design". The Department of Biology (Petition). Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa. 2005. Archived from the original on 2010-09-01. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Pigliucci, Massimo (December 2005). "Science and fundamentalism". EMBO Reports. 6 (12): 1106–1109. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400589. ISSN 1469-3178. PMC 1369219. PMID 16319954.
- Martin, Michael (2002). "Justifying Methodological Naturalism". The Secular Web. Colorado Springs, CO: Internet Infidels, Inc. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Bradley, Raymond (November 23, 2005). "Intelligent Design or Natural Design". Butterflies and Wheels. Seattle, WA: Ophelia Benson. Retrieved 2014-03-16.
- "Creationism and intelligent design". BBC. 2 June 2009. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- Chang, Kenneth (2 November 2009). "Creationism, Minus a Young Earth, Emerges in the Islamic World". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- Butt, Riazat (16 November 2009). "Darwinism, through a Chinese lens". The Guardian. Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- `Abdu'l-Bahá 1982, p. 220
- Harvey, Peter (2013). An Introduction to Buddhism: Teachings, History and Practices (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pg. 36-8
- ^ Harvey, Peter (2019). "Buddhism and Monotheism", p. 1. Cambridge University Press.
- Keown, Damien (2013). "Encyclopedia of Buddhism." p. 162. Routledge.
- Hsueh-Li Cheng. "Nāgārjuna's Approach to the Problem of the Existence of God" in Religious Studies, Vol. 12, No. 2 (Jun., 1976), pp. 207–216 (10 pages), Cambridge University Press.
- Hayes, Richard P., "Principled Atheism in the Buddhist Scholastic Tradition", Journal of Indian Philosophy, 16:1 (1988:Mar.).
- ^ Miller, Jon D.; Scott, Eugenie C.; Okamoto, Shinji (August 2006). "Public acceptance of evolution". Science. 313 (5788): 765–66. doi:10.1126/science.1126746. PMID 16902112. S2CID 152990938.
- "Denominational Views". National Center for Science Education. Berkeley, CA. October 17, 2008. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- "Episcopal Church, General Convention (2006)". National Center for Science Education. Berkeley, CA. 2008-09-09. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- Schick, Edwin A. (1965). "Evolution". In Bodensieck, Julius (ed.). The Encyclopedia of the Lutheran Church. Vol. 1. Minneapolis, MN: Augsburg Publishing House. LCCN 64021500. OCLC 947120. Retrieved 2010-05-17. Edited for the Lutheran World Federation.
- Hollabaugh, Mark (October 2006). "God allows the universe to create itself and evolve". The Lutheran. ISSN 0024-743X. Archived from the original on 2013-12-31. Retrieved 2014-03-16.
- "Interview: Rowan Williams". The Guardian (Transcript). London. March 21, 2006. Retrieved 2014-03-16.
- Williams, Christopher (March 21, 2006). "Archbishop of Canterbury backs evolution". The Register. London: Situation Publishing Limited. Retrieved 2011-03-10.
- McDonell, Keelin (July 12, 2005). "What Catholics Think of Evolution". Slate. Archived from the original on 2005-07-16. Retrieved 2014-03-16.
- Polkinghorne 1998, pp. 7–8
- Philo
- Bradshaw, Rob. "Philo of Alexandria (c. 20 BC – c. AD 50)". Early Church.org.uk. West Wickham, England: Steve Bradshaw. Retrieved December 21, 2011.
- Young, Davis A. (March 1988). "The Contemporary Relevance of Augustine's View of Creation". Perspectives on Science and Christian Faith. 40 (1): 42–45. ISSN 0892-2675. Retrieved 2008-08-18.
- Pope Pius XII (August 12, 1950). "Humani Generis". Vatican: the Holy See (Papal encyclical). St. Peter's Basilica, Vatican City: Holy See. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved 2011-11-08.
- Pope John Paul II (October 30, 1996). "Magisterium is concerned with question of evolution, for it involves conception of man". L'Osservatore Romano (Message to the Pontifical Academy of Sciences). No. 44 (Weekly English ed.). Tipografia Vaticana, Vatican City: Holy See. pp. 3, 7. Archived from the original on March 21, 2016. Retrieved March 19, 2014.
- "Social and Political Views" (PDF). U.S. Religious Landscape Survey (Report). Washington, D.C.: Pew Research Center. 2008. p. 95. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-03-19. Report 2: Religious Beliefs & Practices, Chapter 2.
- Chryssides, George D. (2008). Historical Dictionary of Jehovah's Witnesses. Scarecrow Press. p. 37. ISBN 9780810862692.
- Genesis 1–2:3
- Genesis 2:4–25
- Jackson, Wayne (31 December 1990). "Are There Two Creation Accounts in Genesis?". Apologetics Press. Montgomery, Al. Retrieved 2007-05-23.
- Tobin, Paul N. (2000). "The Creation Myths: Internal Difficulties". The Rejection of Pascal's Wager: A Skeptic's Guide to Christianity. Singapore: Paul Tobin. Archived from the original on 2014-10-08. Retrieved 2014-03-19.
- Forster & Marston 1999
- Eddy 1934, p. 547
- McGrath 2010, p. 140
- Numbers 2006, p. 420
- Carper & Hunt 2009, p. 167
- Dasgupta 1922, p. 10
- Doniger, Wendy; Hawley, John Stratton, eds. (1999). "Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions". Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster, Incorporated. p. 691 (Manu). ISBN 0877790442.
a day in the life of Brahma is divided into 14 periods called manvantaras ("Manu intervals"), each of which lasts for 306,720,000 years. In every second cycle the world is recreated, and a new Manu appears to become the father of the next human race. The present age is considered to be the seventh Manu cycle.
- Krishnamurthy, V. (2019). "Ch. 20: The Cosmic Flow of Time as per Scriptures". Meet the Ancient Scriptures of Hinduism. Notion Press. ISBN 9781684669387.
Each manvantara is preceded and followed by a period of 1,728,000 (= 4K) years when the entire earthly universe (bhu-loka) will submerge under water. The period of this deluge is known as manvantara-sandhya (sandhya meaning, twilight). According to the traditional time-keeping Thus in Brahma's calendar the present time may be coded as his 51st year – first month – first day – 7th manvantara – 28th maha-yuga – 4th yuga or kaliyuga.
- Gupta, S. V. (2010). "Ch. 1.2.4 Time Measurements". In Hull, Robert; Osgood, Richard M. Jr.; Parisi, Jurgen; Warlimont, Hans (eds.). Units of Measurement: Past, Present and Future. International System of Units. Springer Series in Materials Science: 122. Springer. p. 7. ISBN 9783642007378.
- Gupta 2010, pp. 7–8.
- Penprase, Bryan E. (2017). The Power of Stars (2nd ed.). Springer. p. 182. ISBN 9783319525976.
- Johnson, W.J. (2009). A Dictionary of Hinduism. Oxford University Press. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-19-861025-0.
- Bennett, Drake (October 25, 2009). "Islam's Darwin problem". The Boston Globe. Boston, MA. Archived from the original on 2009-10-30. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- Irvine, Chris (September 29, 2008). "Creationist Adnan Oktar offers trillion-pound prize for fossil proof of evolution". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 2022-01-12. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- "Creationism: Science and Faith in Schools". The Guardian (Conferences). London. January 7, 2004. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- Adra, Jawad. "Political inheritance-Absent entirely within the Shia'a community, dwindling within the Maronite and Sunni communities and omnipresent within the Druze". Monthly Magazine. Archived from the original on 20 July 2020. Retrieved 20 July 2020.
- Iqbāl, Muẓaffar (2007). Science and Islam. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 157. ISBN 978-0-313-33576-1.
- Majid, Abdul. "The Muslim responses to evolution." Science-Religion Dialogue (2002).
- Varisco, Daniel. "Darwin and Dunya: Muslim Responses to Darwinian Evolution." Journal of International & Global Studies 9.2 (2018).
- Kaya, Veysel (April 2012). "Can the Quran Support Darwin? An Evolutionist Approach by Two Turkish Scholars after the Foundation of the Turkish Republic". The Muslim World. 102 (2): 357. doi:10.1111/j.1478-1913.2011.01362.x.
- ^ Burton, Elise K. (May–June 2010). "Teaching Evolution in Muslim States:Iran and Saudi Arabia Compared" (PDF). Reports of the National Center for Science Education. 30 (3): 25–29. ISSN 2158-818X. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-02-19. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Turkish academics tell ministry that evolution theory excluded from curriculum 'only in Saudi Arabia'". Hürriyet Daily News. 1 March 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- IAP Member Academies (June 21, 2006). "IAP Statement on the Teaching of Evolution". IAP. Trieste, Italy: The World Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2014-06-20.
- Vlaardingerbroek, Barend; Hachem-el-Masri, Yasmine (23 October 2006). "The Status of Evolutionary Theory in Undergraduate Biology". International Journal of Educational Reform. 15 (2). Rowman & Littlefield: 161–162. ISBN 9781475816457.
- Edis, Taner (November–December 1999). "Cloning Creationism in Turkey". Reports of the National Center for Science Education. 19 (6): 30–35. ISSN 2158-818X. Retrieved 2008-02-17.
- Kaufman, Marc (November 8, 2009). "In Turkey, fertile ground for creationism". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- Aviezer 1990
- Carmell & Domb 1976
- Schroeder 1998
- Tigay, Jeffrey H. (Winter 1987–1988). "Genesis, Science, and 'Scientific Creationism'". Conservative Judaism. 40 (2): 20–27. ISSN 0010-6542. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- ^ The Challenge of Creation: Judaism's Encounter with Science, Cosmology, and Evolution, Natan Slifkin, Zoo Torah, 2006
- Le Page, Michael (April 19, 2008). "Evolution myths: It doesn't matter if people don't grasp evolution". New Scientist. 198 (2652): 31. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(08)60984-7. ISSN 0262-4079. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- Hecht, Jeff (August 19, 2006). "Why doesn't America believe in evolution?". New Scientist. 191 (2565): 11. doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(06)60136-X. ISSN 0262-4079. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- Kahan, Dan (May 24, 2014). "Weekend update: You'd have to be science illiterate to think 'belief in evolution' measures science literacy". Cultural Cognition Project (Blog). New Haven, CT: Yale Law School. Archived from the original on 2021-02-17. Retrieved 2015-03-23.
- Shtulman, Andrew (March 2006). "Qualitative differences between naïve and scientific theories of evolution". Cognitive Psychology. 52 (2): 170–94. doi:10.1016/j.cogpsych.2005.10.001. ISSN 0010-0285. PMID 16337619. S2CID 20274446.
- Marr, David (December 19, 2009). "Faith: What Australians believe in". The Age. Melbourne, Australia. Archived from the original on December 11, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2018.
- Maley, Jacqueline (December 19, 2009). "God is still tops but angels rate well". The Age. Melbourne, Australia. Archived from the original on September 13, 2012. Retrieved December 18, 2009.
- "Science literacy in Australia" (PDF). Australian Academy of Science. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ "Ipsos Global @dvisory: Supreme Being(s), the Afterlife and Evolution". Ipsos. Archived from the original on 17 August 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- "PESQUISA DE OPINIÃO PÚBLICA SOBRE O CRIACIONISMO" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- Massarani, Luisa. "Few in Brazil accept scientific view of human evolution". Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- "Believe In Evolution: Canadians More Likely Than Americans To Endorse Evolution". HuffPost Canada. AOL. September 6, 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-28.
- Canseco, Mario (September 5, 2012). "Britons and Canadians More Likely to Endorse than Americans" (PDF) (Press release). New York: Angus Reid Public Opinion. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 29, 2014. Retrieved 2014-05-11.
- Canseco, Mario (4 December 2019). "Most Canadians Believe Human Beings on Earth Evolved". Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- Canseco, Mario (14 April 2023). "By a 3-to-1 Margin, Canadians Choose Evolution Over Creationism". Research Co. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- "Britons unconvinced on evolution". BBC News. London: BBC. January 26, 2006. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- "BBC Survey On The Origins Of Life". Ipsos MORI. London: Ipsos MORI. January 30, 2006. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- "The origin of humans" (PDF). YouGov Global (Prospect Survey Results). London: YouGov Plc. November 20, 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-03-24.
- ^ Bates, Stephen (March 20, 2006). "Archbishop: stop teaching creationism". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- Shepherd, Jessica (25 October 2009). "Teach both evolution and creationism say 54% of Britons". TheGuardian.com. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- "Italy Keeps Darwin in its Classrooms". Deutsche Welle. Bonn, Germany: ARD. May 3, 2004. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- Lorenzi, Rossella (April 28, 2004). "No evolution for Italian teens". The Scientist. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- "In the beginning". The Economist. London: Economist Group. April 19, 2007. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2007-04-25. This article gives a worldwide overview of recent developments on the subject of the controversy.
- "The dangers of creationism in education". Committee on Culture, Science and Education (Report). Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe. June 8, 2007. Doc. 11297. Archived from the original on March 9, 2013. Retrieved 2014-03-22.
- "The dangers of creationism in education". Committee on Culture, Science and Education (Resolution). Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe. October 4, 2007. Resolution 1580. Archived from the original on March 7, 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-22. Paras. 13, 18
- de Quetteville, Harry (September 9, 2004). "Darwin is off the curriculum for Serbian schools". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 2022-01-12. Retrieved January 24, 2012.
- "Serbia reverses Darwin suspension". BBC News. London: BBC. September 9, 2004. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- "'Anti-Darwin' Serb minister quits". BBC News. London: BBC. September 16, 2004. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- "And finally..." Warsaw Business Journal. Warsaw, Poland: Valkea Media. December 18, 2006. Archived from the original on 2020-01-12. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- "6. Science and religion". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 10 May 2017. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- Park, Hyung Wook; Cho, Kyuhoon (2018). "Science, state, and spirituality: Stories of four creationists in South Korea". History of Science. 56 (1): 35–71. doi:10.1177/0073275317740268. hdl:10220/44270. PMID 29241363. S2CID 206433157.
- Masci, David (10 February 2017). "For Darwin Day, 6 facts about the evolution debate". Pew Research Center.
- "40% of Americans Believe in Creationism". July 26, 2019.
- ^ Newport, Frank (November 19, 2004). "In U.S., 42% Believe Creationist View of Human Origins". Gallup.com. Omaha, NE: Gallup, Inc. Retrieved 2014-05-10.
- Newport, Frank (Host) (June 11, 2007). Evolution Beliefs. The Gallup Poll Daily Briefing. Omaha, NE: Gallup, Inc. Archived from the original on April 27, 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ^ Robinson, Bruce A. (November 1995). "Beliefs of the U.S. public about evolution and creation". ReligiousTolerance.org. Kingston, Canada: Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance. Retrieved 2007-11-11.
- Martz, Larry; McDaniel, Ann (June 29, 1987). "Keeping God Out of the Classroom" (PDF). Newsweek: 23–24. ISSN 0028-9604. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2015-09-25.
- ^ "Evolution and Creationism In Public Education: An In-depth Reading Of Public Opinion" (PDF). People For the American Way. Washington, D.C.: People For the American Way. March 2000. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-03-28.
- ^ "Fox News Poll: Creationism". Fox News. News Corporation. September 7, 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-22.
- Luvan, Dylan (September 24, 2012). "Bill Nye Warns: Creation Views Threaten US Science". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2013-10-14. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Fowler, Jonathan; Rodd, Elizabeth (August 23, 2012). "Bill Nye: Creationism Is Not Appropriate For Children". YouTube. New York: Big Think. Archived from the original on 2021-10-30. Retrieved 2012-09-24.
- Deiviscio, Jeffrey (November 3, 2014). "A Fight for the Young Creationist Mind: In 'Undeniable,' Bill Nye Speaks Evolution Directly to Creationists". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2022-01-01. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- Boyle, Alan (February 5, 2014). "Bill Nye Wins Over the Science Crowd at Evolution Debate". NBCNews.com. Retrieved 2014-02-06.
- Kopplin, Zack (February 4, 2014). "Why Bill Nye the Science Guy is trying to reason with America's creationists". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2014-02-06.
- Foreman, Tom (Moderator) (February 4, 2014). Bill Nye Debates Ken Ham. YouTube. Hebron, KY: Answers in Genesis. Archived from the original on 2021-10-30. Retrieved 2014-02-05. (program begins at 13:14).
- "Statement on the Teaching of Evolution" (PDF). Washington, D.C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science. February 16, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-02-21. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Pinholster, Ginger (February 19, 2006). "AAAS Denounces Anti-Evolution Laws as Hundreds of K-12 Teachers Convene for 'Front Line' Event" (Press release). St. Louis, MO: American Association for the Advancement of Science. Archived from the original on 2006-04-21. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
- Delgado, Cynthia (July 28, 2006). "Finding the Evolution in Medicine". NIH Record. ISSN 1057-5871. Archived from the original on November 22, 2008. Retrieved 2014-03-31. "...While 99.9 percent of scientists accept evolution, 40 to 50 percent of college students do not accept evolution and believe it to be 'just' a theory." – Brian Alters
- van Harn, Roger; Ford, David F.; Gunton, Colin E. (2004). Exploring and Proclaiming the Apostles' Creed. A&C Black. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-8192-8116-6. Extract of page 44
- Ra, Aron (2016). Foundational Falsehoods of Creationism. Pitchstone Publishing. p. 182. ISBN 978-1-63431-079-6. Extract of page 182
- Martin, Joel W. (September 2010). "Compatibility of Major U.S. Christian Denominations with Evolution". Evolution: Education and Outreach. 3 (3): 420–431. doi:10.1007/s12052-010-0221-5. S2CID 272665.
- "Statements from Religious Organizations". National Center for Science Education. Berkeley, CA. 2008-09-08. Retrieved 2011-03-10.
- Murphy, George L. (2002). "Intelligent Design as a Theological Problem". Covalence: The Bulletin of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America Alliance for Faith, Science and Technology. IV (2). OCLC 52753579. Archived from the original on 2016-04-11. Retrieved 2014-03-31. Reprinted with permission.
- Purcell, Brendan (2012). From Big Bang to Big Mystery: Human Origins in the Light of Creation and Evolution. New City Press of the Focolare. p. 94. ISBN 978-1565484337.
- "NSTA Position Statement: The Teaching of Evolution". National Science Teachers Association. 2013.
- "ASTE Position Statement on Teaching Biological Evolution". Association for Science Teacher Education. 2015.
- "NABT Position Statement on Teaching Evolution". National Association of Biology Teachers. 2011. Archived from the original on 2015-09-16.
- "Statement on Evolution and Creationism". American Anthropological Association. 2000.
- "American Geological Institute Position on Teaching Evolution". American Geoscience Institute. 2000.
- "Position Statement: Teaching Evolution". Geological Society of America. 2012. Archived from the original on 2021-10-22. Retrieved 2019-08-29.
- "AGU Position Statement on Teaching Creationism as Science". American Geophysical Institute. 1998.
- "American Academy of Religion on teaching creationism". National Center for Science Education. Berkeley, CA. July 23, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
- Moore, Randy; Cotner, Sehoya (May 2009). "The Creationist Down the Hall: Does It Matter When Teachers Teach Creationism?". BioScience. 59 (5): 429–35. doi:10.1525/bio.2009.59.5.10. ISSN 0006-3568. JSTOR 25502451. S2CID 86428123.
- NAS 2008, p. 12
- NAS 2008, p. 10, "In science, explanations must be based on naturally occurring phenomena. Natural causes are, in principle, reproducible and therefore can be checked independently by others. If explanations are based on purported forces that are outside of nature, scientists have no way of either confirming or disproving those explanations."
- Isaak, Mark, ed. (2006). "An Index to Creationist Claims". TalkOrigins Archive. Houston, TX: The TalkOrigins Foundation, Inc. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- Futuyma 2005
- Gould 1999
- Gould, Stephen Jay (March 1997). "Nonoverlapping Magisteria". Natural History. 106 (3): 16–22. ISSN 0028-0712. Archived from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2014-03-31.
- Dawkins 2006, p. 5
- "Royal Society statement on evolution, creationism and intelligent design". Royal Society. London: Royal Society. April 11, 2006. Archived from the original on 2008-06-02. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Matsumura, Molleen; Mead, Louise (February 14, 2001). "Ten Major Court Cases about Evolution and Creationism". National Center for Science Education. Berkeley, CA. Retrieved 2008-11-04. Updated 2007-07-31.
- Myers, PZ (June 18, 2006). "Ann Coulter: No evidence for evolution?". Pharyngula (Blog). ScienceBlogs LLC. Archived from the original on August 9, 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-12.
- "About Old Earth Ministries?". Old Earth Ministries. Springfield, OH. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
Works cited
- `Abdu'l-Bahá (1982) . The Promulgation of Universal Peace: Talks Delivered by 'Abdu'l-Bahá during His Visit to the United States and Canada in 1912. Compiled by Howard MacNutt (2nd ed.). Wilmette, IL: Bahá'í Publishing Trust. ISBN 978-0-8774-3172-5. LCCN 81021689. OCLC 853066452.
- Aviezer, Nathan (1990). In the Beginning—: Biblical Creation and Science. Hoboken, NJ: KTAV Publishing House. ISBN 978-0-88125-328-3. LCCN 89049127. OCLC 20800545.
- Barlow, Nora, ed. (1963). "Darwin's Ornithological Notes". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Historical Series. 2 (7): 201–278. doi:10.5962/p.310422. ISSN 0068-2306. Retrieved 2009-06-10.
- Bowler, Peter J. (2003). Evolution: The History of an Idea (3rd ed.). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23693-6. LCCN 2002007569. OCLC 49824702.
- Bucaille, Maurice (1977) . The Bible, The Qur'an and Science: The Holy Scriptures Examined in the Light of Modern Knowledge. translated from the French by Alastair D. Pannell and the author. Paris: Seghers. LCCN 76488005. OCLC 373529514.
- Bucaille, Maurice (1976). The Qur'an and Modern Science (Booklet). Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Cooperative Offices for Call & Guidance at Al-Badiah & Industrial Area. OCLC 52246825. Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- Carmell, Aryeh; Domb, Cyril, eds. (1976). Challenge: Torah Views on Science and its Problems. Jerusalem; New York: Association of Orthodox Jewish Scientists; Feldheim Publishers. ISBN 978-0-87306-174-2. LCCN 77357516. OCLC 609518840.
- Carper, James C.; Hunt, Thomas C., eds. (2009). The Praeger Handbook of Religion and Education in the United States. Vol. 1: A–L. Westport, CT: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 978-0-275-99228-6. LCCN 2008041156. OCLC 246888936.
- Collins, Francis S. (2006). The Language of God: A Scientist Presents Evidence for Belief. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-7432-8639-8. LCCN 2006045316. OCLC 65978711.
- Dasgupta, Surendranath (1922). A History of Indian Philosophy. Vol. 1. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. LCCN 22018463. OCLC 4235820.
- Dawkins, Richard (2006). The God Delusion. London: Bantam Press. ISBN 978-0-5930-5548-9. LCCN 2006015506. OCLC 70671839.
- Desmond, Adrian (1989). The Politics of Evolution: Morphology, Medicine, and Reform in Radical London. Science and its Conceptual Foundations. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-14346-0. LCCN 89005137. OCLC 828159401.
- Desmond, Adrian; Moore, James (1991). Darwin. London; New York: Michael Joseph; Viking Penguin. ISBN 978-0-7181-3430-3. LCCN 92196964. OCLC 26502431.
- Dewey, John (1994). "The Influence of Darwinism on Philosophy". In Martin Gardner (ed.). Great Essays in Science. Buffalo, NY: Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-0-87975-853-0. LCCN 93035453. OCLC 28846489.
- Draper, Paul R. (2005). "God, Science, and Naturalism". In Wainwright, William J. (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Religion. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 272–303. doi:10.1093/0195138090.003.0012. ISBN 978-0-1951-3809-2. LCCN 2004043890. OCLC 54542845. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Dundes, Alan (1984). "Introduction". In Dundes, Alan (ed.). Sacred Narrative: Readings in the Theory of Myth. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-5200-5192-8. LCCN 83017921. OCLC 9944508.
- Dundes, Alan (1996). "Madness in Method, Plus a Plea for Projective Inversion in Myth". In Patton, Laurie L.; Doniger, Wendy (eds.). Myth and Method. Charlottesville; London: University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-1657-6. LCCN 96014672. OCLC 34516050.
- Eddy, Mary Baker (1934) . Science and Health with Key to the Scriptures (Sunday school ed.). Boston, MA: Christian Science Publishing Society for the Trustees under the will of Mary Baker G. Eddy. LCCN 42044682. OCLC 4579118.
- Forrest, Barbara; Gross, Paul R. (2004). Creationism's Trojan Horse: The Wedge of Intelligent Design. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515742-0. LCCN 2002192677. OCLC 50913078.
- Forster, Roger; Marston, V. Paul (1999). "Genesis Through History". Reason, Science, and Faith. Crowborough, East Sussex: Monarch Books. ISBN 978-1-85424-441-3. LCCN 99488551. OCLC 41159110.
- Futuyma, Douglas J. (2005). "Evolutionary Science, Creationism, and Society". Evolution. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 978-0-87893-187-3. LCCN 2004029808. OCLC 57311264.
- Giberson, Karl W.; Yerxa, Donald A. (2002). Species of Origins: America's Search for a Creation Story. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7425-0764-7. LCCN 2002002365. OCLC 49031109.
- Gosse, Philip Henry (1857). Omphalos: An Attempt to Untie the Geological Knot. London: J. Van Voorst. LCCN 11004351. OCLC 7631539.
- Gould, Stephen Jay (1999). Rocks of Ages: Science and Religion in the Fullness of Life. Library of Contemporary Thought (1st ed.). New York: Ballantine Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-345-43009-0. LCCN 98031335. OCLC 39886951.
- Gunn, Angus M. (2004). Evolution and Creationism in the Public Schools: A Handbook for Educators, Parents, and Community Leaders. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company. ISBN 978-0-7864-2002-5. LCCN 2004018788. OCLC 56319812.
- Hayward, James L. (1998). The Creation/Evolution Controversy: An Annotated Bibliography. Magill Bibliographies. Lanham, MD; Pasadena, CA: Scarecrow Press; Salem Press. p. 253. ISBN 978-0-8108-3386-9. LCCN 98003138. OCLC 38496519.
- Lamoureux, Denis O. (1999). "Evangelicals Inheriting the Wind: The Phillip E. Johnson Phenomenon". Darwinism Defeated?: The Johnson-Lamoureux Debate on Biological Origins. Foreword by J. I. Packer. Vancouver, B.C.: Regent College Publishing. ISBN 978-1-57383-133-8. OCLC 40892139.
- Masood, Steven (1994) . Jesus and the Indian Messiah. Oldham, England: Word of Life. ISBN 978-1-898868-00-2. LCCN 94229476. OCLC 491161526.
- McComas, William F. (2002). "Science and Its Myths". In Shermer, Michael (ed.). The Skeptic Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience. Vol. 1. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-653-8. LCCN 2002009653. OCLC 50155642.
- McGrath, Alister E. (2010). Science and Religion: A New Introduction (2nd ed.). Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-8790-9. LCCN 2009020180. OCLC 366494307.
- National Academy of Sciences (1999). Science and Creationism: A View from the National Academy of Sciences (2nd ed.). Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. ISBN 978-0-309-06406-4. LCCN 99006259. OCLC 43803228. Retrieved 2014-11-22.
- National Academy of Sciences; Institute of Medicine (2008). Science, Evolution, and Creationism. Vol. 105. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. pp. 3–4. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105....3A. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711608105. ISBN 978-0-309-10586-6. LCCN 2007015904. OCLC 123539346. PMC 2224205. PMID 18178613. Retrieved 2014-11-22.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Numbers, Ronald L. (1998). Darwinism Comes to America. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-19312-3. LCCN 98016212. OCLC 38747194.
- Numbers, Ronald L. (2006) . The Creationists: From Scientific Creationism to Intelligent Design (Expanded ed., 1st Harvard University Press pbk. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-02339-0. LCCN 2006043675. OCLC 69734583.
- Okasha, Samir (2002). Philosophy of Science: A Very Short Introduction. Very Short Introductions. Vol. 67. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280283-5. LCCN 2002510456. OCLC 48932644.
- Pennock, Robert T. (1999). Tower of Babel: The Evidence Against the New Creationism. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-16180-0. LCCN 98027286. OCLC 44966044.
- Pennock, Robert T, ed. (2001). Intelligent Design Creationism and Its Critics: Philosophical, Theological, and Scientific Perspectives. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-66124-9. LCCN 2001031276. OCLC 46729201.
- Philo, of Alexandria (1854–55). "The First Book of the Treatise on The Allegories of the Sacred Laws, after the Work of the Six Days of Creation". The Works of Philo Judaeus. Bohn's Classical Library. Translated from the Greek, by C. D. Yonge. London: H.G. Bohn. LCCN 20007801. OCLC 1429769. Retrieved 2014-03-09.
- Plimer, Ian (1994). Telling Lies for God: Reason vs Creationism. Milsons Point, NSW: Random House Australia. ISBN 978-0-09-182852-3. LCCN 94237744. OCLC 32608689.
- Polkinghorne, John (1998). Science and Theology: An Introduction. Minneapolis, MN: Fortress Press. ISBN 978-0-8006-3153-6. LCCN 98229115. OCLC 40117376.
- Quammen, David (2006). The Reluctant Mr. Darwin: An Intimate Portrait of Charles Darwin and the Making of His Theory of Evolution. Great Discoveries. New York: Atlas Books/W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-05981-6. LCCN 2006009864. OCLC 65400177.
- Rainey, David (2008). Faith Reads: A Selective Guide to Christian Nonfiction. Westport, CT: Libraries Unlimited. ISBN 978-1-59158-602-9. LCCN 2008010352. OCLC 213599217.
- Schroeder, Gerald L. (1998) . The Science of God: The Convergence of Scientific and Biblical Wisdom (1st Broadway Books trade paperback ed.). New York: Broadway Books. ISBN 978-0-7679-0303-5. LCCN 97014978. OCLC 39162332.
- Scott, Eugenie C. (1999). "Science, Religion, and Evolution". In Springer, Dale A.; Scotchmoor, Judy (eds.). Evolution: Investigating the Evidence (Reprint). The Paleontological Society Special Publications. Vol. 9. Pittsburgh, PA: Paleontological Society. LCCN 00274093. OCLC 42725350. Archived from the original on 2003-06-28. "Presented as a Paleontological Society short course at the annual meeting of the Geological Society of America, Denver, Colorado, October 24, 1999."
- Scott, Eugenie C. (2005) . Evolution vs. Creationism: An Introduction. Foreword by Niles Eldredge (1st paperback ed.). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24650-8. LCCN 2005048649. OCLC 60420899.
- Scott, Eugenie C. (3 August 2009). Evolution Vs. Creationism: An Introduction (2nd ed.). Univ of California Press. pp. i–331. ISBN 978-0-520-26187-7.
- Secord, James A. (2000). Victorian Sensation: The Extraordinary Publication, Reception, and Secret Authorship of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-74410-0. LCCN 00009124. OCLC 43864195.
- Stewart, Melville Y., ed. (2010). Science and Religion in Dialogue. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-8921-7. LCCN 2009032180. OCLC 430678957.
- Sweet, William; Feist, Richard, eds. (2007). Religion and the Challenges of Science. Aldershot, England; Burlington, VT: Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-5715-6. LCCN 2006030598. OCLC 71778930.
- Wilder-Smith, A. E. (1978). Die Naturwissenschaften kennen keine Evolution: Empirische und theoretische Einwände gegen die Evolutionstheorie [The Natural Sciences Know Nothing of Evolution]. Basel, Switzerland: Schwabe Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7965-0691-8. LCCN 80067425. OCLC 245955034.
- Young, Davis A. (1995). The Biblical Flood: A Case Study of the Church's Response to Extrabiblical Evidence. Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans. ISBN 978-0-8028-0719-9. LCCN 95001899. OCLC 246813515.
Further reading
- Anderson, Bernard W. (1967). Creation versus Chaos: The Reinterpretation of Mythical Symbolism in the Bible. New York: Association Press. LCCN 67014578. OCLC 671184.
- Anderson, Bernhard W., ed. (1984). Creation in the Old Testament. Issues in Religion and Theology. Vol. 6. Introduction by Bernhard W. Anderson. Philadelphia; London: Fortress Press; Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. ISBN 978-0-8006-1768-4. LCCN 83048910. OCLC 10374840.
- Barbour, Ian G. (1997). Religion and Science: Historical and Contemporary Issues (1st HarperCollins revised ed.). San Francisco, CA: HarperSanFrancisco. ISBN 978-0-06-060938-2. LCCN 97006294. OCLC 36417827.
- Barbour, Ian G. (2000). When Science Meets Religion (1st ed.). San Francisco, CA: HarperSanFrancisco. ISBN 978-0-06-060381-6. LCCN 99055579. OCLC 42752713.
- Clark, Kelly James (2014). Religion and the Sciences of Origins: Historical and Contemporary Discussions (1st ed.). Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-137-41483-0. LCCN 2014466739. OCLC 889777438.
- Darwin, Charles (1958). Barlow, Nora (ed.). The Autobiography of Charles Darwin, 1809-1882: With original omissions restored; Edited and with Appendix and Notes by his grand-daughter, Nora Barlow. London: Collins. LCCN 93017940. OCLC 869541868. Retrieved 2009-01-09.
- Kaplan, Aryeh (1993). Immortality, Resurrection, and the Age of the Universe: A Kabbalistic View. With an appendix Derush Or ha-Hayyim by Israel Lipschitz; translated and annotated by Yaakov Elman. Hoboken, NJ: KTAV Publishing House in association with the Association of Orthodox Jewish Scientists. ISBN 978-0-88125-345-0. LCCN 92036917. OCLC 26800167.
- Kauffman, Stuart A. (2008). Reinventing the Sacred: A New View of Science, Reason and Religion. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-00300-6. LCCN 2007052263. OCLC 191023778.
- Leeming, David Adams; Leeming, Margaret (1995). A Dictionary of Creation Myths. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-510275-8. LCCN 95039961. OCLC 33160980.
- Primack, Joel R.; Abrams, Nancy Ellen (Jan–Feb 1995). "In a Beginning...: Quantum Cosmology and Kabbalah" (PDF). Tikkun. 10 (1): 66–73. ISSN 0887-9982. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2014-04-24.
- Roberts, Michael (2008). Evangelicals and Science. Greenwood Guides to Science and Religion. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-33113-8. LCCN 2007041059. OCLC 174138819.
External links
- "Creationism" at the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy by Michael Ruse
- "How Creationism Works" at HowStuffWorks by Julia Layton
- "TIMELINE: Evolution, Creationism and Intelligent Design" – Focuses on major historical and recent events in the scientific and political debate
- "Evolution and Creationism: A Guide for Museum Docents" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. (204 KB) by Warren D. Allmon, Director of the Museum of the Earth
- "What is creationism?" at talk.origins by Mark Isaak
- "The Creation/Evolution Continuum" by Eugenie Scott
- "15 Answers to Creationist Nonsense" by John Rennie, editor in chief of Scientific American magazine
- "Race, Evolution and the Science of Human Origins" by Allison Hopper, Scientific American (July 5, 2021).
- Human Timeline (Interactive) – Smithsonian, National Museum of Natural History (August 2016)
| Creationism | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Book of Genesis | |
| Types | |
| Controversies | |
| Related | |
| Philosophy of religion | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concepts in religion | |||||||||||||
| Conceptions of God |
| ||||||||||||
| Existence of God |
| ||||||||||||
| Theology |
| ||||||||||||
| Religious language | |||||||||||||
| Problem of evil | |||||||||||||
| Philosophers of religion (by date active) |
| ||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||
| Genesis 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Noted verses |
| ||
| Divine figures | |||
| Creation |
| ||
| Phrases |
| ||
| Characters | |||
| Related | |||