| Revision as of 09:04, 31 December 2014 editLagoset (talk | contribs)6,740 edits →Open ArchitectureTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 07:44, 22 October 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1);Tag: AWB | ||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Open source modular construction model}} | |||
| {{multiple issues| | {{multiple issues| | ||
| {{refimprove|date=December 2014}} | {{refimprove|date=December 2014}} | ||
| {{primary sources|date=December 2014}} | {{primary sources|date=December 2014}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | '''OpenStructures''' is an ] ] model based on a shared geometrical grid, called the OS grid. It was conceived by designer ], and first demonstrated at the ], a house for contemporary art.<ref name="dfe">{{cite web|work=openmaterials.org|access-date=31 December 2014|title=OpenStructures :: everyone designs for everyone|url=http://openmaterials.org/openstructures-everyone-designs-for-everyone/|date=2012}}</ref><ref>, Z33.be</ref> According to Lommee, the OpenStructures project explores the possibility of a modular system where "everyone designs for everyone." OpenStructures is developing a database where anyone can share designs which are in turn available for download by the public. Each component design in the OS system will feature previously designed OS parts that were used to create it. In addition, each part will feature component designs that can be made from it. | ||
| The OpenStructures model includes large and small scale manufacturers as well as craftsmen. They are invited to create their own designs according to the OS standard for sale on the market, which can in turn be fixed or disassembled at their end of life and made into new products.<ref>{{Cite web|title = Page > About. > show|url = http://openstructures.net/pages/2#vraag-1c|website = openstructures.net|access-date = 2016-01-13}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | '''OpenStructures''' |
||
| <!--needs expansion; http://openstructures.net/pages/2 --> | |||
| == Grid == | |||
| ] | |||
| The OpenStructures grid is built around a square of 4 x 4 cm and is scalable. The squares can be further subdivided or put together to form larger squares, without losing inter-compatibility. The image shows nine complete squares of each 4x4 cm put together. | |||
| Designers use the OS grid to determine dimensions, assembly points, and interconnecting diameters. This allows parts that were not originally from the same design to be used together in a new design. | |||
| == Scales== | == Scales== | ||
| OpenStructures works at several ], and analogies are made to ]s including (from smallest to biggest):<ref name="dfe"/> | |||
| * ''Parts'', like ]s. | |||
| ⚫ | * ''Components'', like ], formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. An example is a motor.<ref>{{cite web|work=openstructures.net|access-date=31 December 2014|volume=The Component Database|title=Search|url=http://openstructures.net/pages/11/components}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | * ''Structures'', like a group of related organs in an ]. Here, different components are composed with frames and joints, such as a bicycle.<ref>{{cite web|work=openstructures.net|access-date=31 December 2014|volume=The Structures Database|url=http://openstructures.net/pages/14/structures/35|title=Triangle bike}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|work=openstructures.net|access-date=31 December 2014|volume=The Structures Database|url=http://openstructures.net/pages/14/structures/3|title=OpenCargoBike}}</ref> | ||
| * ''Superstructures'', like ]s, can be understood as the whole hierarchical assembly of different structures that together function as a stable whole which has the capacity to grow and develop. Example are houses or ]s. | |||
| ⚫ | == Open architecture== | ||
| * Parts. | |||
| {{See also|Open-source architecture|Modular building}} | |||
| ⚫ | * Components |
||
| One of the research areas of OpenStructures is architecture. Architects of the ]<ref></ref> have worked on the subject.<ref>{{cite web|work=z33.be|access-date=31 December 2014|title=Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture|url=http://www.z33.be/en/projects/workshop-openstructures-open-architecture|date=December 2009}}</ref><ref>, The project Case Study n°1 is a master plan for a social centre and community in Katanga, Congo, developed in collaboration with ‘Intrastructures’, a Belgian design studio. This was developed according to the ‘OpenStructures’ principles.</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | * Structures, |
||
| ] ({{langx|vls|autarkytecture}}, {{ety|grc|auto|self||architecture}}) is based in OpenStructures and proposes flexible constructions that can adapt over time.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://m.z33.be/en/artworks/thomas-lommee-christiane-hoegner-autarkytecture|title=Thomas Lommée & Christiane Hoegner - Autarkytecture|work=z33.be|year=2013|access-date=1 January 2015|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141231104727/http://m.z33.be/en/artworks/thomas-lommee-christiane-hoegner-autarkytecture|archive-date=31 December 2014}}</ref> | |||
| == Open Architecture== | |||
| One of the research areas of OpenStructures is architecture. | |||
| Open ] elements and buildings can be based on OpenStructures. | |||
| Architects of the ] have worked on the subject. <ref>{{cite web|work=z33.be|accessdate=31 December 2014|title=Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture|url=http://www.z33.be/en/projects/workshop-openstructures-open-architecture|date=December 2009}}</ref> | |||
| == Other uses== | |||
| Autarkytect | |||
| ] Academy had been building several ]s making use of the OpenStructures system to make them more sustainable.<ref>, ]</ref> | |||
| == |
==See also== | ||
| *{{annotated link|3D printing}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| *{{annotated link|Contraptor}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| *{{annotated link|Modular building}} | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| *{{annotated link|Modular construction systems}} | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| *{{annotated link|Open architecture}} | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | *{{annotated link|Open source}} | ||
| *{{annotated link|Open-source architecture}} | |||
| ⚫ | *{{annotated link|Smart brick}} | ||
| *{{annotated link|WikiHouse}} | |||
| == References== | == References== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 50: | ||
| * {{URL|openstructures.net/|OpenStructures}} | * {{URL|openstructures.net/|OpenStructures}} | ||
| * {{URL|www.z33.be/en/projects/workshop-openstructures-open-architecture|Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture}} | * {{URL|www.z33.be/en/projects/workshop-openstructures-open-architecture|Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture}} | ||
| * {{URL|http://www.intrastructures.net/Intrastructures/About_-_what_we_are..htm|Instrastructures}} | |||
| * {{URL|enviu.org/our-work/open-source-house/|Open Source House}} | * {{URL|enviu.org/our-work/open-source-house/|Open Source House}} | ||
| * |
* at ] | ||
| * {{URL|vimeo.com/9641834|Brussels Cooperation (Case Study n°1: Congo) - Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture}} | * {{URL|vimeo.com/9641834|Brussels Cooperation (Case Study n°1: Congo) - Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture}} | ||
| * {{URL|www.contraptor.org/forum/t-273404/contraptor-openstructures|Contraptor + Openstructures ( 20mm metric version )}} | * {{URL|www.contraptor.org/forum/t-273404/contraptor-openstructures|Contraptor + Openstructures ( 20mm metric version )}} | ||
| * {{URL|p2pfoundation.net/Open_Structures_Project|Open Structures Project}} at the |
* {{URL|p2pfoundation.net/Open_Structures_Project|Open Structures Project}} at the P2P Foundation | ||
| * {{URL|urbantimes.co/2014/08/urbanization-design-concepts/|3 Design Concepts To Revolutionize Urbanization}} | * {{URL|urbantimes.co/2014/08/urbanization-design-concepts/|3 Design Concepts To Revolutionize Urbanization}} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:44, 22 October 2024
Open source modular construction modelThis article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
OpenStructures is an open source modular construction model based on a shared geometrical grid, called the OS grid. It was conceived by designer Thomas Lommée, and first demonstrated at the Z33, a house for contemporary art. According to Lommee, the OpenStructures project explores the possibility of a modular system where "everyone designs for everyone." OpenStructures is developing a database where anyone can share designs which are in turn available for download by the public. Each component design in the OS system will feature previously designed OS parts that were used to create it. In addition, each part will feature component designs that can be made from it.
The OpenStructures model includes large and small scale manufacturers as well as craftsmen. They are invited to create their own designs according to the OS standard for sale on the market, which can in turn be fixed or disassembled at their end of life and made into new products.
Grid
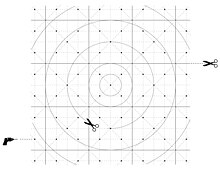
The OpenStructures grid is built around a square of 4 x 4 cm and is scalable. The squares can be further subdivided or put together to form larger squares, without losing inter-compatibility. The image shows nine complete squares of each 4x4 cm put together.
Designers use the OS grid to determine dimensions, assembly points, and interconnecting diameters. This allows parts that were not originally from the same design to be used together in a new design.
Scales
OpenStructures works at several scales, and analogies are made to biological systems including (from smallest to biggest):
- Parts, like body tissues.
- Components, like organs, formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. An example is a motor.
- Structures, like a group of related organs in an organ system. Here, different components are composed with frames and joints, such as a bicycle.
- Superstructures, like organisms, can be understood as the whole hierarchical assembly of different structures that together function as a stable whole which has the capacity to grow and develop. Example are houses or electric vehicles.
Open architecture
See also: Open-source architecture and Modular buildingOne of the research areas of OpenStructures is architecture. Architects of the Brussels Cooperation Collective have worked on the subject.
Autarchitecture (West Flemish: autarkytecture, from Ancient Greek auto 'self' and architecture) is based in OpenStructures and proposes flexible constructions that can adapt over time.
Open smart brick elements and buildings can be based on OpenStructures.
Other uses
Fab lab Academy had been building several beehives making use of the OpenStructures system to make them more sustainable.
See also
- 3D printing – Additive process used to make a three-dimensional object
- Contraptor
- Modular building – Prefabricated building or house that consists of repeated sections
- Modular construction systems – Construction techniquePages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Open architecture – Software design paradigm emphasizing ease of swapping out and modifying components
- Open source – Source code made freely available
- Open-source architecture – Emerging design paradigm emphasizing collaboration and ease of use
- Smart brick
- WikiHouse – Project for designing and building houses
References
- ^ "OpenStructures :: everyone designs for everyone". openmaterials.org. 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- About Z33, Z33.be
- "Page > About. > show". openstructures.net. Retrieved 2016-01-13.
- "Search". openstructures.net. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- "Triangle bike". openstructures.net. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- "OpenCargoBike". openstructures.net. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- Brussels Cooperation Collective
- "Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture". z33.be. December 2009. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- Short Description and Master Document Case Study n°1, The project Case Study n°1 is a master plan for a social centre and community in Katanga, Congo, developed in collaboration with ‘Intrastructures’, a Belgian design studio. This was developed according to the ‘OpenStructures’ principles.
- "Thomas Lommée & Christiane Hoegner - Autarkytecture". z33.be. 2013. Archived from the original on 31 December 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- Valldaura Bee Monitoring, OpenGreens
External links
- OpenStructures
- Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture
- Instrastructures
- Open Source House
- Open Structures: Thomas Lommee at TEDxEutropolis
- Brussels Cooperation (Case Study n°1: Congo) - Workshop OpenStructures / Open Architecture
- Contraptor + Openstructures ( 20mm metric version )
- Open Structures Project at the P2P Foundation
- 3 Design Concepts To Revolutionize Urbanization
This computer-aided design software article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |