| Revision as of 17:20, 13 August 2006 view sourceMccready (talk | contribs)3,705 edits →Ireland Schools← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:31, 19 October 2024 view source PrimeBOT (talk | contribs)Bots2,066,063 editsm Task 24: elink template removal following a TFDTag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Form of alternative medicine}} | |||
| <!--INFOBOX -- SCROLL DOWN SEVERAL LINES FOR TEXT OF ARTICLE --> | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| <div style="float:right;width:200px;margin:0 0 1em 1em;"> | |||
| {{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} | |||
| <table border=1> | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=March 2020}} | |||
| <tr><td colspan="2" align="center" bgcolor="#ffcc99">'''Naturopathy'''</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td colspan="2" align="center">This article is part of the branches of CAM series.</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td colspan="2" align="center" bgcolor="#ffcc99">'''] Classifications'''</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td>]:</td><td>]</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td>]:</td><td>]</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td>]:</td><td>]</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td>]:</td><td>]</td></tr> | |||
| <tr><td colspan="2"> | |||
| {{msg:CamMenu}} | |||
| </table> | |||
| </div> | |||
| <!--//END OF INFOBOX--> | |||
| {{Infobox alternative medicine | |||
| '''Naturopathic medicine''' (also known as '''naturopathy''') is a school of ] philosophy and practice that seeks to improve ] and treat disease chiefly by assisting the body's innate capacity to recover from ] and ]. Naturopathic practice may include a broad array of different modalities, including ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and so on. Practitioners tend to emphasise an ] approach to patient care. Naturopathy has its origins in the ], but is today practised in many countries around the world in one form or another, where it is subject to different standards of regulation and levels of acceptance. | |||
| | name = Naturopathy | |||
| | image = Hepar.jpg | |||
| | image_size = 200 | |||
| | alt = Old homeopathic remedy, Hepar sulph. | |||
| | caption = A ] preparation of Hepar sulph – homeopathy can be offered as part of naturopathic treatment.<ref name=Gale_Frey/> | |||
| | claims = Diseases are cured through the body's "natural healing" ability which is primarily aided by practices labelled as "natural" (and not primarily by ]s, surgery, and other treatments within evidence-based medicine, not seen as "natural"), comprising widely ranging "nature cures" and any form of alternative medicine that may be labelled as "natural" | |||
| | topics = ] | |||
| | orig-date = early 20th century | |||
| | origprop = ]; ] | |||
| | laterprop = | |||
| | seealso = ], ], ] | |||
| | MeshID = D009324 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Alternative medical systems|fringe}} | |||
| '''Naturopathy''', or '''naturopathic medicine''', is a form of ].<ref name=Gale_Frey/> A wide array of practices branded as "natural", "non-invasive", or promoting "self-healing" are employed by its practitioners, who are known as '''naturopaths'''. Difficult to generalize, these treatments range from the ] and thoroughly discredited, like ], to the widely accepted, like certain forms of ].<ref name="Baran2014">{{cite book |doi=10.1007/978-1-4614-8541-4_2 |chapter=Science, Pseudoscience, and Not Science: How do They Differ? |title=Healthcare and Biomedical Technology in the 21st Century |year=2014 |last1=Baran |first1=George R. |last2=Kiani |first2=Mohammad F. |last3=Samuel |first3=Solomon Praveen |pages=19–57 |isbn=978-1-4614-8540-7 |quote=within the traditional medical community it is considered to be quackery }}</ref><ref name="oxcompus">{{cite book|author=Paul S. Boyer|url=https://archive.org/details/oxfordcompaniont00paul_0|title=The Oxford companion to United States history|year=2001|isbn=978-0-19-508209-8|page=|publisher=Oxford University Press |quote=After 1847, when regular doctors organized the American Medical Association (AMA), that body led the war on "quackery", especially targeting dissenting medical groups such as homeopaths, who prescribed infinitesimally small doses of medicine. Ironically, even as the AMA attacked all homeopathy as quackery, educated homeopathic physicians were expelling untrained quacks from their ranks.|access-date=January 15, 2013|url-access=registration}}</ref><ref>Psychotherapy can be evidence based, or pseudoscientific however, see: | |||
| Naturopathic practitioners do not use invasive ], or most synthetic ], preferring "natural" remedies, i.e. relatively unprocessed or whole medications, such as herbs and foods. Licensed physicians from accredited schools are trained to use diagnostic tests such as ] and ] before deciding upon the full course of treatment. | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Lilienfeld|first=Scott O.|author-link=Scott Lilienfeld|date=December 2015|title=Introduction to special section on pseudoscience in psychiatry|journal=]|volume=60|issue=12|pages=531–533|doi=10.1177/070674371506001202|pmc=4679160|pmid=26720820|quote=Although the boundaries separating pseudoscience from science are fuzzy, pseudosciences are characterized by several warning signs{{snd}}fallible but useful indicators that distinguish them from most scientific disciplines. ... In contrast to most accepted medical interventions, which are prescribed for a circumscribed number of conditions, many pseudoscientific techniques lack boundary conditions of application. For example, some proponents of ], an intervention that purports to correct imbalances in unobservable energy fields, using specified bodily tapping algorithms, maintain that it can be used to treat virtually any psychological condition, and that it is helpful not only for adults but also for children, dogs, and horses.}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Lee|first1=Catherine M.|last2=Hunsley|first2=John|date=December 2015|title=Evidence-based practice: separating science from pseudoscience|journal=]|volume=60|issue=12|pages=534–540|doi=10.1177/070674371506001203|pmc=4679161|pmid=26720821|quote=TFT, a treatment applied to mood, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders, is a prime example of practice founded on pseudoscience. TFT is based on the premise that bodily energy imbalances cause negative emotions. Treatment is purported to rectify imbalances by tapping on acupuncture meridians. Virtually no peer-reviewed research supports this treatment rationale. With only methodologically weak reports available in the literature, the so-called science cited to support TFT is primarily anecdotal and does not rule out placebo effects. Despite these criticisms, the TFT website continues to advance unsupported claims about TFT's ability to cure almost any emotional problem.}}</ref> The ideology and methods of naturopathy are based on ] and ] rather than ], although practitioners may use techniques supported by evidence.<ref name="Jagtenberg2006" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Tabish|first=Syed Amin|date=2008|title=Complementary and Alternative Healthcare: Is it Evidence-based?|journal=International Journal of Health Sciences|volume=2|issue=1|pages=v–ix |pmc=3068720|pmid=21475465}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Goldenberg |first1=Joshua Z. |last2=Burlingham |first2=Bonnie S. |last3=Guiltinan |first3=Jane |last4=Oberg |first4=Erica B. |title=Shifting attitudes towards research and evidence-based medicine within the naturopathic medical community |journal=Advances in Integrative Medicine |date=August 2017 |volume=4 |issue=2 |pages=49–55 |doi=10.1016/j.aimed.2017.08.003 }}</ref> The ethics of naturopathy have been called into question by medical professionals and its practice has been characterized as ].<ref name="atwood2003" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gorski DH | title = Integrative oncology: really the best of both worlds? | journal = Nature Reviews. Cancer | volume = 14 | issue = 10 | pages = 692–700 | date = October 2014 | pmid = 25230880 | doi = 10.1038/nrc3822 | ref = Gorski Nature | s2cid = 33539406 }}</ref><ref name="tot" /><ref name="ACS-2009">{{cite book |editor1-last=Russell |editor1-first=Jill |title=American Cancer Society complete guide to complementary & alternative cancer therapies |date=2009 |publisher=American Cancer Society |isbn=978-1-60443-054-7 |pages=116–119 |oclc=671655748 }}</ref><ref name="atwood2004" /> | |||
| Naturopathic practitioners commonly encourage alternative treatments that are rejected by conventional medicine, including resistance to ] or ] for some patients.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilson K, Busse JW, Gilchrist A, Vohra S, Boon H, Mills E | title = Characteristics of pediatric and adolescent patients attending a naturopathic college clinic in Canada | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 115 | issue = 3 | pages = e338-43 | date = March 2005 | pmid = 15741360 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2004-1901 | doi-access = }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Busse JW, Wilson K, Campbell JB | title = Attitudes towards vaccination among chiropractic and naturopathic students | journal = Vaccine | volume = 26 | issue = 49 | pages = 6237–6243 | date = November 2008 | pmid = 18674581 | doi = 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.020 }}</ref><ref name="wilson">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilson K, Mills E, Boon H, Tomlinson G, Ritvo P | title = A survey of attitudes towards paediatric vaccinations amongst Canadian naturopathic students | journal = Vaccine | volume = 22 | issue = 3–4 | pages = 329–334 | date = January 2004 | pmid = 14670313 | doi = 10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.08.014 | ref = naturopathi_students_low_vax }}</ref><ref name="Mielczarek2014">{{cite journal |last1=Engler |first1=Brian D. |last2=Mielczarek |first2=Eugenie V. |title=Selling Pseudoscience: A Rent in the Fabric of American Medicine |journal=Skeptical Inquirer |volume=38 |issue=3 |year=2014 |url=https://skepticalinquirer.org/2014/05/selling-pseudoscience-a-rent-in-the-fabric-of-american-medicine/ }}</ref> The diagnoses made by naturopaths often have no basis in science and are often not accepted by mainstream medicine.<ref name="atwood2003" /><ref name="AAFP">{{cite web|title=Family Physicians versus Naturopaths|url=http://www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/advocacy/workforce/gme/ES-FPvsNaturopaths-110810.pdf|website=aafp.org|publisher=American Academy of Family Physicians|access-date=20 July 2015|ref=aafp|archive-date=June 16, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150616081319/http://www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/advocacy/workforce/gme/ES-FPvsNaturopaths-110810.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The mainstream scientific community has found little evidence for the effectiveness of most naturopathic modalities, and the concept of ] itself is widely disputed. ] is often treated warily, as when a treatment is proven to be effective it is usually integrated into mainstream medicine. | |||
| Naturopaths frequently campaign for legal recognition in the United States. Naturopathy is prohibited in three ] (Florida, South Carolina, and Tennessee) and tightly regulated in many others. Some states, however, allow naturopaths to perform minor surgery or even prescribe drugs. While some schools exist for naturopaths, and some jurisdictions allow such practitioners to call themselves doctors, the lack of accreditation, scientific medical training, and quantifiable positive results means they lack the competency of true medical doctors. | |||
| ==History of naturopathic medicine== | |||
| The term naturopathy was coined before 1900, by John Scheel, and used by ]. Lust had been schooled in ] and other natural health practices in ] by Father ], who sent Lust to the ] to bring them Kneipp's methods. In 1905, Lust founded the ] in ], the first naturopathic college in the United States. Lust took great strides in promoting the profession, culminating in passage of licensing laws in several states prior to 1935, including ], ], ], ], ], and ] and the existence of several naturopathic colleges. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Naturopathic medicine went into decline, along with most other natural health professions, after the 1930s, with the discovery of penicillin and advent of synthetic drugs such as ] and ] in the post-war era, Lust's death, conflict between various schools of natural medicine (], ], ], ], naturopathy, etc.), the rise of medical technology, and consolidation of political power in conventional medicine were all contributing factors. In 1910, when the ] published the ] which criticized many aspects of medical education in various institutions (natural and conventional), it was mostly seen as an attack on low-quality natural medicine education. It caused many such programs to shut down and contributed to the popularity of conventional medicine. | |||
| The term "naturopathy" originates from "natura" (] root for birth) and "pathos" (the ] root for suffering) to suggest "natural healing".<ref name="NCAHF_np" /> Naturopaths claim the ancient Greek "Father of Medicine", ], as the first advocate of naturopathic medicine, before the term existed.<ref name="NCAHF_np">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncahf.org/articles/j-n/naturo.html |title=NCAHF Fact Sheet on Naturopathy |access-date=2009-04-17 |date=January 30, 2001 |orig-date=copyright 1997 |vauthors=Jarvis WT |publisher=] |archive-date=September 27, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927173337/http://www.ncahf.org/articles/j-n/naturo.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.naturopathy-uk.com/home/home-what-is-naturopathy/ |title=What is Naturopathy? |work=College of Naturopathic Medicine website |location=East Grinstead, England |access-date=16 September 2015 |author=<!-- no byline --> |archive-date=September 18, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100918040756/http://www.naturopathy-uk.com/home/home-what-is-naturopathy/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Naturopathy has its roots in the 19th-century ] of ].<ref name="pmid1139856">{{cite journal | vauthors = Brown PS | title = Nineteenth-century American health reformers and the early nature cure movement in Britain | journal = Medical History | volume = 32 | issue = 2 | pages = 174–194 | date = April 1988 | pmid = 3287059 | pmc = 1139856 | doi = 10.1017/S0025727300047980 }}</ref><ref name="N-UK-hist">{{Cite web | vauthors = Langley S |title=History of Naturopathy |work=College of Naturopathic Medicine website |publisher=<!-- College of Naturopathic Medicine redundant to website name--> |location=UK |url=http://www.naturopathy-uk.com/blog/2007/11/28/history-of-naturopathy/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120829125721/http://www.naturopathy-uk.com/blog/2007/11/28/history-of-naturopathy/ |archive-date=2012-08-29 }}</ref> In ], ] started advocating his "Hygienic Medicine" in the 1880s, promoting a natural diet and exercise with avoidance of tobacco and overwork.<ref>{{cite web |title= How it all began |url= http://www.allinsonflour.co.uk/history/ |author= <!-- no byline --> |work= ] website |publisher= Silver Spoon, ], ] |access-date= September 3, 2008 |archive-date= August 13, 2010 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20100813230535/http://www.allinsonflour.co.uk/history/ |url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |journal=] |series=Views & Reviews: Medical Classics |title=A system of hygienic medicine (1886) and The advantages of wholemeal bread (1889) | vauthors = Beard JA |issue=7651 |page=1023 |date=May 3, 2008 |doi=10.1136/bmj.39562.446528.59 |volume=336 |pmc=2364871 }}</ref> | |||
| The term ''naturopathy'' was coined in 1895 by John Scheel,<ref name="ama_1997" /> and purchased by ], whom naturopaths consider to be the "Father of U.S. Naturopathy".<ref name="Baer2001">{{cite journal | vauthors = Baer HA | title = The sociopolitical status of U.S. naturopathy at the dawn of the 21st century | journal = Medical Anthropology Quarterly | volume = 15 | issue = 3 | pages = 329–346 | date = September 2001 | pmid = 11693035 | doi = 10.1525/maq.2001.15.3.329 }}</ref> Lust had been schooled in ] and other natural health practices in Germany by Father ]; Kneipp sent Lust to the United States to spread his drugless methods.<ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy">{{cite web |url= http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/naturopathy.html |vauthors= Barrett S |title= A close look at naturopathy |work= ] |date= November 26, 2013 |access-date= 2015-03-21 |archive-date= April 6, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110406111422/http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/naturopathy.html |url-status= live }}</ref> Lust defined naturopathy as a broad discipline rather than a particular method, and included such techniques as hydrotherapy, ], and homeopathy, as well as eliminating overeating, tea, coffee, and alcohol.<ref name="Gale_Frey">{{cite book |vauthors=Boughton RJ, Frey B |chapter=Naturopathic Medicine |year=2005 |chapter-url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Naturopathic_Medicine.aspx |title=Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine |publisher=] |edition=2nd |access-date=March 21, 2015 |archive-date=June 24, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130624073748/http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Naturopathic_Medicine.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> He described the body in ] and vitalistic terms with "absolute reliance upon the cosmic forces of man's nature".<ref name="Whorton_2002">Lust, Benedict cited in: {{cite book| vauthors = Whorton JC |title=Nature Cures : The History of Alternative Medicine in America: The History of Alternative Medicine in America|url=https://archive.org/details/naturecureshisto00whor |url-access=registration|access-date=2013-09-03 |date=2002|publisher=] |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-534978-8 |page=}}</ref> According to the '']'', the first known use of "naturopathy" in print is from 1901.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/naturopath|title=Naturopathy - Definition of Naturopathy by Merriam-Webster|access-date=October 27, 2015|archive-date=November 19, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151119131441/http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/naturopath|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Naturopathic medicine never completely ceased to exist, however, as there were always a few states in which licensing laws existed—though at one point there were virtually no schools. One of the most visible steps towards the profession's modern renewal was the opening in 1956 of the ] in ]. This was the first of the modern naturopathic medical schools offering four-year naturopathic medical training with the intention of integrating mainstream science and naturopathic principles and practice. | |||
| From 1901, Lust founded the American School of Naturopathy in ]. In 1902, the original North American Kneipp Societies were discontinued and renamed "Naturopathic Societies". In September 1919, the Naturopathic Society of America was dissolved and Benedict Lust founded the American Naturopathic Association to supplant it.<ref name="Baer2001" /><ref name="Beyerstein_NW">{{cite web |title= Naturopathy: A Critical Analysis |vauthors= Beyerstein BL, Downie S |date= May 12, 2004 |access-date= 2009-03-21 |work= NaturoWatch |publisher= QuackWatch |url= http://www.naturowatch.org/general/beyerstein.html |archive-date= March 7, 2009 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090307135314/http://naturowatch.org/general/beyerstein.html |url-status= live }}</ref> Naturopaths became licensed under naturopathic or drugless practitioner laws in 25 states in the first three decades of the twentieth century.<ref name="Baer2001" /> Naturopathy was adopted by many ], and several schools offered both Doctor of Naturopathy (ND) and Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) degrees.<ref name="Baer2001" /> Estimates of the number of naturopathic schools active in the United States during this period vary from about one to two dozen.<ref name="ACS-2009" /><ref name="ama_1997">{{cite web |url= http://www.idt.mdh.se/kurser/ct3340/archives/ht03/assignment-2d-extra-articles/Alternative%20Medicine.pdf |title= Report 12 of the Council on Scientific Affairs (A-97) |year= 1997 |website=] |access-date= September 3, 2013 |archive-date= November 5, 2013 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131105123407/http://www.idt.mdh.se/kurser/ct3340/archives/ht03/assignment-2d-extra-articles/Alternative%20Medicine.pdf}}<!-- main link substituted with convenience copy --> | |||
| ===Naturopathy In India=== | |||
| *{{lay source |template=cite web |title=1997 Annual Meeting of the American Medical Association: Summaries and Recommendations of the Council on Scientific Affairs |website=American Medical Association |url=http://www.ama-assn.org/resources/doc/csaph/csaa-97.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140102190820/http://www.ama-assn.org/resources/doc/csaph/csaa-97.pdf |archive-date=2014-01-02 |date=1997}}</ref><ref name="Baer2001" /> | |||
| Naturopathy has another stream that started in India in the 1900s. It was popularized by Mahatma Gandhi. He adopted and popularized this system because it was cheap and adaptable to the Indian soil. The system grew in popularity towards the close of 1900s, and today there are two streams of Naturopaths in India. The first are graduates of All India Naturopathy Council and are awarded DNYS (Diploma in Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences) after 3 years of guided study and internship. The other are graduates of Universities who are awarded BNYS (Bachelor of Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences). The Indian stream of Naturopathy differs from the Western stream in many ways, particularly in their emphasis of strict vegetarianism and yoga. | |||
| After a period of rapid growth, naturopathy went into decline for several decades after the 1930s. In 1910, the ] published the ], which criticized many aspects of medical education, especially quality and lack of scientific rigour. The advent of ] and other "miracle drugs" and the consequent popularity of modern medicine also contributed to naturopathy's decline. In the 1940s and 1950s, a broadening in scope of practice laws led many chiropractic schools to drop their ND degrees, though many chiropractors continued to practice naturopathy. From 1940 to 1963, the ] campaigned against heterodox medical systems. By 1958, practice of naturopathy was licensed in only five states.<ref name="Baer2001" /> In 1968, the ] issued a report on naturopathy concluding that naturopathy was not grounded in medical science and that naturopathic education was inadequate to prepare graduates to make appropriate diagnosis and provide treatment; the report recommends against expanding ] coverage to include naturopathic treatments.<ref name="ACS-2009" /><ref name="HEW1968">{{cite web |title=HEW Report on Naturopathy (1968) |url=http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/hew.html |author=<!-- no byline --> |date=August 30, 1999 |work=QuackWatch |access-date=2013-09-03 |archive-date=August 14, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100814052625/http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/hew.html |url-status=live }} Citing: {{cite book | vauthors = Cohen WJ |title=Independent Practitioners Under Medicare: A Report to the Congress |publisher=] |year= 1969 |oclc= 3000280 }}</ref> In 1977 an Australian committee of inquiry reached similar conclusions; it did not recommend licensure for naturopaths.<ref name="Aust1977">{{cite web |title=Naturopathy: Report of the Australian Committee of Inquiry (1977) |url=http://www.naturowatch.org/hx/australia.html |author=<!-- no byline --> |work=NaturoWatch |publisher=QuackWatch |date=December 25, 2003 |access-date=2013-09-03 |archive-date=September 6, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100906221113/http://www.naturowatch.org/hx/australia.html |url-status=live }} Citing: {{cite book | vauthors = Webb EC |title=Report of the Committee of Inquiry into Chiropractic, Osteopathy, Homoeopathy and Naturopathy |publisher=Australian Government Publishing Service |location=Canberra |year=1977 |isbn= 978-0-642-92287-8 |display-authors=etal}}</ref> | |||
| ==Naturopathic physicians and traditional naturopaths== | |||
| There are two groups in the United States calling themselves "naturopaths" who have recently been engaged in legal battles. The term when originally coined by ], and popularized by Dr. ] (a German name pronounced "loost") was to apply to those receiving an education in the basic medical sciences with an emphasis on natural therapies: | |||
| *Naturopathic physicians | |||
| *"Traditional" naturopaths | |||
| Beginning in the 1970s, there was a revival of interest in the United States and Canada, in conjunction with the "holistic health" movement.<ref name="Baer2001" /><ref name="Gale_Frey" /> {{as of|2009}}, fifteen U.S. states, Puerto Rico, the US Virgin Islands and the District of Columbia licensed naturopathic doctors,<ref name="LicState">{{cite web |url=http://www.naturopathic.org/content.asp?contentid=57 |title=Licensed States & Licensing Authorities |work= American Association of Naturopathic Physicians website |author=<!-- no byline --> |publisher=<!-- redundant to website name --> |year=2009 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20091130234327/http://naturopathic.org/content.asp?contentid=57 |archive-date=November 30, 2009 }}</ref> and the State of Washington requires insurance companies to offer reimbursement for services provided by naturopathic physicians.<ref name="WAC 284-43-205">{{cite web |title= Washington Administrative Code: Title 284, Chapter 43, Section 205: Every category of health providers |url= http://apps.leg.wa.gov/WAC/default.aspx?cite=284-43-205 |publisher= Washington State Legislature |date= August 28, 1999 |access-date= November 19, 2010 |archive-date= October 11, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20111011211431/http://apps.leg.wa.gov/WAC/default.aspx?cite=284-43-205 |url-status= live }} (effective)</ref><ref name="PBS_WA">{{cite episode |title=Insuring Alternatives |series=NewsHour with Jim Lehrer |series-link= PBS NewsHour | vauthors = Minott R |transcript=Online NewsHour transcript |transcript-url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/health/july96/alt_medicines_7-3.html |date=July 3, 1996 |network=]}}</ref> On the other hand, some states such as South Carolina and Tennessee prohibit the practice of naturopathy.<ref name="SC Code" /><ref name="TN Code" /><ref name="AMA-SOP-ND" /> | |||
| ===Naturopathic physicians=== | |||
| Naturopathic physicians in the United States are independent providers with training in conventional medical sciences, diagnosis and treatment, and natural therapeutics with licenses or registration granted by an individual state Naturopathic Board of Medical Examiners. They graduate from four-year nationally accredited naturopathic medical ]s. Naturopathic physicians training with respect to ] is different, with a focus on ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. Some naturopathic physicians have additional training in the following: ], ], and ]. These subspecialties often involve additional years of study. Naturopathic physicians are required to attend continuing education yearly in order to maintain and renew their license. | |||
| In the United States, the ] began accepting naturopathic doctors in their clinics and practice in 2013, also making loan repayment available to ND's.<ref>"https://newsmaven.io/indiancountrytoday/archive/introducing-naturopathic-doctors-to-indian-health-service-clinics-Rn_RipOYh0Kgd9KR-5Ou_A/ {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191005024641/https://newsmaven.io/indiancountrytoday/archive/introducing-naturopathic-doctors-to-indian-health-service-clinics-Rn_RipOYh0Kgd9KR-5Ou_A/ |date=October 5, 2019 }}"</ref> | |||
| Naturopathic physicians are licensed to diagnose and treat disease in ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], US Territories: ] and ]. | |||
| In 2015, a former naturopathic doctor, ], began writing critically about her experience being trained in and practicing naturopathic medicine.<ref name="Senapathy2016" /><ref name="Thielking2016" /> Her blog garnered a large following among ] while enraging some proponents of alternative medicine.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Devlin |first1=Hannah |title=The naturopath whistleblower: 'It is surprisingly easy to sell snake oil' |url=https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2018/mar/27/naturopath-whistleblower-snake-oil-multi-billion-dollar |access-date=23 August 2021 |work=Guardian |date=27 March 2018}}</ref> | |||
| Naturopathic Physicians are working in cooperation with both conventional and alternative practitioners to provide patients with complete medical care. Naturopathic physicians can bridge disparate fields with their training in both conventional and non-conventional treatment. Naturopathic physicians are able to identify and prescribe appropriate treatment including referral to conventional ]. | |||
| <gallery widths="160" heights="200"> | |||
| For licensure as a naturopathic physician in one of those licensing U.S. states or Canadian provinces, candidates must have a ] (abbreviated as N.D. or less commonly D.N.M.) / ] (abbreviated as N.D.) from an accredited institution in the U.S. or Canada and pass certain examinations. The abbreviation N.D. can also denote the professional title and status ''Naturopathic Doctor'' that is conferred by the licensing body in the state or province. In contrast, the degree ] (abbreviated D.N.M.) does not qualify for licensure as a naturopathic physician. | |||
| File:Portrait of Sebastian Kneipp. Wellcome L0005598.jpg|] c. 1898, a Bavarian priest and forefather of naturopathy<ref name=Barrett-Naturopathy/> | |||
| File:BenedictLust.jpg|] c. 1902, the founder of naturopathy in the U.S.<ref name=Baer2001/> | |||
| File:QED 20161015 129.jpg|Britt Marie Hermes c. 2016, a former naturopathic doctor and major critic of naturopathic medicine<ref name="Thielking2016">{{cite news|vauthors=Thielking M|title='Essentially witchcraft:' A former naturopath takes on the field|url=https://www.statnews.com/2016/10/20/naturopath-critic-britt-hermes/|access-date=30 October 2016|work=]|date=20 October 2016|archive-date=October 25, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161025031403/https://www.statnews.com/2016/10/20/naturopath-critic-britt-hermes/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Practice == | |||
| ===Traditional Naturopaths=== | |||
| ] session]] | |||
| ''Vis medicatrix naturae'', or the healing power of nature, is the central tenet of Traditional Naturopathy. ] and ]es, which are always present, seldom cause problems in a healthy body. According to naturopathic practice, disease occurs when ]s that have accumulated internally – often due to incorrect lifestyle, a poor diet, and improper care of the body - weaken a person. While conventional medical treatments may rid the body of ]s, these treatments alone do not bring about true healing. Rather than trying to attack specific symptoms and diseases, Traditional Naturopathy offers a ] approach to the individual that supports the body in finding its way back to ]. | |||
| ], Chromax II]] | |||
| ] preparations are commonly used by naturopaths.<ref name="Boon HS" /><ref name="Caulfield2011" /> The practice is considered a ].<ref name="Smith2012">{{cite journal |vauthors=Smith K |title=Homeopathy is Unscientific and Unethical |journal=Bioethics |volume=26 |issue=9 |doi=10.1111/j.1467-8519.2011.01956.x |pages=508–512 |year=2012 |s2cid=143067523 |url=https://zenodo.org/record/1035885 |access-date=October 28, 2017 |archive-date=October 29, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171029012949/https://zenodo.org/record/1035885 |url-status=live }}</ref>]] | |||
| In 2003, a report<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Atwood |first=Kimball C. |date=2003-12-30 |title=Naturopathy: a critical appraisal |url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14745386/ |journal=MedGenMed: Medscape General Medicine |volume=5 |issue=4 |pages=39 |issn=1531-0132 |pmid=14745386}}</ref> was presented by ], an American medical doctor and researcher from ], best known as a critic of naturopathic medicine, stating among other criticisms that "The practice of naturopathy is based on a belief in the body's ability to heal itself through a special ] or force guiding bodily processes internally".<ref name="atwood2003" /> | |||
| Traditional Naturopathy is not a medical practice. While prescribing drugs and ]s, performing surgery, and other invasive procedures clearly have their place in the hands of properly trained medical doctors, these practices are outside the scope of Traditional Naturopathy and are at odds with its fundamental principles. Instead Traditional Naturopaths focus on ] clients to lead healthier lives and on the use of naturopathic ] such as ], ], ]s, ], and ] to ] and strengthen the body and support its natural healing process. | |||
| Diagnosis and treatment concern primarily ] and "natural" methods that naturopaths claim promote the body's natural ability to heal.<ref name="Gale_Frey" /><ref name="Skepdic_naturopathy">{{cite web |url= http://skepdic.com/natpathy.html |title= Naturopathy |access-date= March 21, 2015 |date= March 7, 2015 |vauthors= Carroll RT |work= ] |archive-date= September 1, 2010 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20100901033549/http://www.skepdic.com/natpathy.html |url-status= live }}</ref> Many naturopaths in India now use modern diagnostic techniques in their practice.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Nair |first1=Pradeep MK |last2=Nanda |first2=Awantika |title=Naturopathic medicine in India: Original Article |journal=Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies |date=September 2014 |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=140–147 |doi=10.1111/fct.12125 }}</ref> Naturopaths focus on a ] approach, avoiding the use of surgery and conventional medicines.<ref name="ACS-2009" /> Naturopaths aim to prevent illness through stress reduction and changes to diet and lifestyle, often rejecting the methods of evidence-based medicine.<ref name="Jagtenberg2006" /><ref name="ECHP">{{cite book |veditors= Clark CC, Gordon RJ |title= Encyclopedia of Complementary Health Practice |chapter-url= https://books.google.com/books?id=cwYnA1qunUwC&pg=PA57 |access-date= 2013-09-03 |year= 1999 |publisher= ] |isbn= 978-0-8261-1722-9 |pages= 57–59 |chapter= Naturopathy: Practice Issues |vauthors= Pizzorno JE |archive-date= April 13, 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20180413121208/https://books.google.com/books?id=cwYnA1qunUwC&pg=PA57 |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| Traditional Naturopaths receive training from correspondance schools or they receive their training from other practioners. None of the schools that award degrees to Traditional Naturopaths are accredited by the US Department of Education. | |||
| A consultation typically begins with a comprehensive patient interview assessing lifestyle, medical history, emotional tone, and physical features, as well as physical examination.<ref name="Gale_Frey" /> Many naturopaths present themselves as ], and some naturopathic physicians may prescribe ], perform minor surgery, and integrate other conventional medical approaches such as diet and lifestyle counselling with their naturopathic practice.<ref name="Gale_Frey" /><ref name="CNME-handbook">{{cite web |url= http://www.cnme.org/resources/2007_hoa.pdf |title= Handbook of Accreditation for Naturopathic Medicine Programs |year= 2007 |publisher= Council on Naturopathic Medical Education |access-date= 2010-11-20 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170209083708/http://www.cnme.org/resources/2007_hoa.pdf |archive-date= February 9, 2017 |url-status= dead }}</ref> Traditional naturopaths deal exclusively with lifestyle changes, not diagnosing or treating disease. Naturopaths do not generally recommend vaccines and ]s, based in part on the early views that shaped the profession, and they may provide alternative remedies even in cases where evidence-based medicine has been shown effective.<ref name="tot" /> | |||
| ==The Principles of Naturopathic Medicine== | |||
| Naturopathy is based on six tenets or principles : | |||
| #"The ] power of ]" | |||
| #"Identify and treat the ]" | |||
| #"First do no ]" | |||
| #"Treat the ]" | |||
| #"The ] as ]" | |||
| #"]" | |||
| === |
=== Methods === | ||
| Naturopaths are often opposed to mainstream medicine and take an ] stance.<ref name="tot">{{cite book |vauthors=Singh S, Ernst E |work=Trick or Treatment?: Alternative Medicine on Trial |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nWnR1JI7G6gC&pg=PT197 |year=2009 |publisher=Transworld |isbn=978-1-4090-8180-7 |pages=197– |title=Naturopathy |quote=many naturopaths are against mainstream medicine and advise their patients accordingly{{snd}}for instance many are not in favour of vaccination. |access-date=January 27, 2016 |archive-date=February 6, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160206135211/https://books.google.com/books?id=nWnR1JI7G6gC&pg=PT197 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The healing power of nature (''vis medicatrix naturae''), has two aspects: first that the ] has the ability to ] itself and it is the naturopathic doctor's role to facilitate this natural process, and second that ] heals. Following this principle includes getting enough ], ], feeding the body nutritional ] and, if needed, additional earth food, such as ]s, or ], which is a living ]. It is asserted, yet strongly refuted by critics, that plants can gently move the body into health without side effects posed by some synthetic chemicals in modern ]s. | |||
| The particular modalities used by a naturopath vary with training and scope of practice. These may include ], ],<ref name="Boon HS" /> ], nature cures, ], ],<ref name="PoaP" /> ],<ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /><ref name="Caulfield2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Caulfield T, Rachul C | title = Supported by science?: what canadian naturopaths advertise to the public | journal = Allergy, Asthma, and Clinical Immunology | volume = 7 | pages = 14 | date = September 2011 | issue = 1 | pmid = 21920039 | pmc = 3182944 | doi = 10.1186/1710-1492-7-14 | doi-access = free }}</ref> ],<ref name="atwood2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Atwood KC | title = Naturopathy, pseudoscience, and medicine: myths and fallacies vs truth | journal = MedGenMed | volume = 6 | issue = 1 | pages = 33 | date = March 2004 | pmid = 15208545 | pmc = 1140750 }}</ref> ],<ref name="PoaP">{{Cite book |url= http://www.pewscholars.com/pdf_files/Naturo2.pdf |title= Profile of a Profession: Naturopathic Practice | vauthors = Hough HJ, Dower C, O'Neil EH |publisher= Center for the Health Professions, ] |date=September 2001 |page= 54 |url-status= dead |archive-date= 2008-10-02 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20081002072928/http://www.pewscholars.com/pdf_files/Naturo2.pdf }}</ref> ], ], ],<ref name="PoaP" /> ], ],<ref name="ACS-2009" /> ], ] measures and ],<ref name="ECHP" /> ],<ref name="PoaP" /> ],<ref name="Beyerstein_NW" /> ], and ]. ''Nature cures'' include a range of therapies based on exposure to natural elements such as ], fresh air, or heat or cold, as well as ] advice such as following a ] and ] diet, ], or ] ] and ].<ref name="dummy">{{Cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/complementarymed0000youn |title=Complementary Medicine for Dummies |vauthors=Young J |publisher=Wiley |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-470-02625-0 |location=Chichester, England |chapter=Chapters 8 & 13 |oclc=174043853 |url-access=registration}}</ref> Physical medicine includes naturopathic, osseous, or soft tissue ], ], ], and ]. Psychological counseling includes ], ], and other methods of ].<ref name="dummy" /> | |||
| ==="Identify and treat the cause"=== | |||
| The underlying root causes of disease must be removed for complete healing to take place (''tolle causam''). These root causes can exist at many levels: ], ], ]al, and ]. It is the naturopathic doctor's ostensible role to identify this root cause, in addition to alleviate suffering by treating symptoms. | |||
| A 2004 survey determined the most commonly prescribed naturopathic therapeutics in ] and ] were botanical medicines, vitamins, minerals, homeopathy, and allergy treatments.<ref name="Boon HS">{{cite journal | vauthors = Boon HS, Cherkin DC, Erro J, Sherman KJ, Milliman B, Booker J, Cramer EH, Smith MJ, Deyo RA, Eisenberg DM | title = Practice patterns of naturopathic physicians: results from a random survey of licensed practitioners in two US States | journal = BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine | volume = 4 | pages = 14 | date = October 2004 | pmid = 15496231 | pmc = 529271 | doi = 10.1186/1472-6882-4-14 | doi-access = free }}</ref> An examination published in 2011 of naturopathic clinic websites in ] and ] found that the most commonly advertised therapies were homeopathy, botanical medicine, nutrition, acupuncture, lifestyle counseling, and detoxification.<ref name="Caulfield2011" /> | |||
| ==="First do no harm"=== | |||
| The process of healing includes the manifestations of ]s, so that any therapy that interferes with this natural healing process by masking symptoms is considered suppressive and should be avoided (''primum no nocere''). The natural ] of the individual should be supported to facilitate healing. | |||
| In 2020, a survey of methods used by naturopaths in fourteen countries reported that 27% of clients received acupuncture, 22% homeopathy, 16% "other energetic medicines", and 13.5% were given hydrotherapy. A mean of 4.0 "treatments" were provided to each customer. One-third (33%) of patients consulted with only the naturopath to manage their primary health concern.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Steel A, Foley H, Bradley R, Van De Venter C, Lloyd I, Schloss J, Wardle J, Reid R | title = Overview of international naturopathic practice and patient characteristics: results from a cross-sectional study in 14 countries | journal = BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 59 | date = February 2020 | pmid = 32070338 | pmc = 7076821 | doi = 10.1186/s12906-020-2851-7 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ==="Treat the whole person"=== | |||
| A core tenet of naturopathy is the belief that health must go beyond treatment of immediate ]s (as with ]), and instead treat the entire person's well being. That means treating the entire ], as well as the ]/] and ]. | |||
| === |
=== Evidence basis === | ||
| {{See also|Evidence-based medicine}} | |||
| It is the role of the naturopath to ] an individual in their practices and encourage that individual to "take responsibility for their own health" (''docere''). This cooperative relationship between doctor and patient is essential to healing. | |||
| ]s: a bag and a bucket, each holding a gallon. Enemas and ] are commonly used by naturopaths for a wide range of medical conditions,<ref name="Caulfield2011" /> for which there are no known health benefits.<ref name="Ernst1997">{{cite journal |last1=Ernst |first1=E. |title=Colonic Irrigation and the Theory of Autointoxication: A Triumph of Ignorance over Science |journal=Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology |date=June 1997 |volume=24 |issue=4 |pages=196–198 |doi=10.1097/00004836-199706000-00002 |pmid=9252839 |doi-access=free }}</ref>]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ], "Ozone is a toxic gas with no known useful medical application in specific, adjunctive, or preventive therapy."<ref name="FDAozone">{{cite web|title=Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Sec. 801.415 Maximum acceptable level of ozone|url=http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRsearch.cfm?fr=801.415|website=U.S. Food and Drug Administration|access-date=18 May 2016|date=1 April 2015|archive-date=March 4, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304035650/http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?FR=801.415|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| Naturopathy as a whole lacks an adequate scientific basis,<ref name="Jagtenberg2006">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jagtenberg T, Evans S, Grant A, Howden I, Lewis M, Singer J | title = Evidence-based medicine and naturopathy | journal = Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine | volume = 12 | issue = 3 | pages = 323–328 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16646733 | doi = 10.1089/acm.2006.12.323}}</ref> and it is rejected by the medical community.<ref name="Jagtenberg2006" /> Although it includes valid lifestyle advice from mainstream medicine (healthy sleep, balanced diet, regular exercise),<ref name="tot" /> it typically adds a range of pseudoscientific beliefs.<ref name="NCAHF_np" /> Some methods rely on immaterial "vital energy fields", the existence of which has not been proven, and there is concern that naturopathy as a field tends towards isolation from general scientific discourse.<ref name="NCAHF_np" /><ref name="Herbert1994">{{cite book | vauthors = Herbert V, Barrett S |title= The Vitamin Pushers: How the "Health Food" Industry is Selling America a Bill of Goods |publisher= Prometheus Books |location= Buffalo, NY |year= 1994 |isbn= 978-0-87975-909-4 |url= https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780879759094 }}</ref><ref name="isbn0-87975-761-2">{{cite book | vauthors = Barrett S, Raso J |title=Mystical Diets: Paranormal, Spiritual, and Occult Nutrition Practices |publisher=Prometheus Books |location=Buffalo, New York |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-87975-761-8 |url=https://archive.org/details/mysticaldietspar0000raso }}</ref> Naturopathy is criticized for its reliance on and its association with unproven, disproven, and other controversial alternative medical treatments, and for its vitalistic underpinnings.<ref name="tot" /><ref name="ACS-2009" /> Natural substances known as ]s show little promise in treating diseases, especially cancer, as laboratory experiments have shown limited therapeutic effect on ]s, while clinical trials demonstrate poor ].<ref name="neut">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ahmad A, Ginnebaugh KR, Li Y, Padhye SB, Sarkar FH | title = Molecular targets of naturopathy in cancer research: bridge to modern medicine | journal = Nutrients | volume = 7 | issue = 1 | pages = 321–334 | date = January 2015 | pmid = 25569626 | pmc = 4303842 | doi = 10.3390/nu7010321 | type = Review | doi-access = free }}</ref> According to the ], "scientific evidence does not support claims that naturopathic medicine can cure ] or any other disease".<ref name="ACS-2009" /> According to Britt Hermes, naturopath student programs are problematic because "As a naturopath , you are making justifications to make the rules and to fudge the standards of how to interpret research all along the way. Because if you don't, you're not left with anything, basically".<ref name="ESP50">{{cite web |title=Episode #050, feat. Britt Hermes |url=http://theesp.eu/podcast_archive/episode_050_britt_hermes.html |website=The European Skeptics Podcast |date=November 29, 2016 |access-date=15 September 2018 |archive-date=September 9, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180909000353/http://theesp.eu/podcast_archive/episode_050_britt_hermes.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==="Prevention"=== | |||
| The ultimate goal of the naturopathic physician is ]. The emphasis is on building ], not fighting illness. This is done by fostering healthy ]s, healthy ]s, and healthy ]s. | |||
| In 2015, the ] published the results of a review of alternative therapies that sought to determine if any were suitable for being covered by ]; Naturopathy was one of 17 therapies evaluated for which no clear evidence of effectiveness was found.<ref name="aus17">{{cite web |url=http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/content/0E9129B3574FCA53CA257BF0001ACD11/$File/Natural%20Therapies%20Overview%20Report%20Final%20with%20copyright%2011%20March.pdf |publisher=Australian Government – Department of Health |author=Baggoley C |title=Review of the Australian Government Rebate on Natural Therapies for Private Health Insurance |year=2015 |access-date=December 12, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160626024750/http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/content/0E9129B3574FCA53CA257BF0001ACD11/$File/Natural%20Therapies%20Overview%20Report%20Final%20with%20copyright%2011%20March.pdf |archive-date=June 26, 2016}} | |||
| ==Regulation== | |||
| *{{lay source |template=cite web |author=Gavura, S. |date=19 November 2015 |title=Australian review finds no benefit to 17 natural therapies |url=https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/australian-review-finds-no-benefit-to-17-natural-therapies |website=Science-Based Medicine}}</ref> | |||
| In some countries naturopathy is unregulated and the term "naturopath" is not clearly defined. This may lead to difficulty in ensuring that a practitioner is trained to a particular standard or has adequate liability insurance. | |||
| ] writes, in the journal ''Medscape General Medicine'',<ref name="atwood2003" />{{blockquote|Naturopathic physicians now claim to be primary care physicians proficient in the practice of both "conventional" and "natural" medicine. Their training, however, amounts to a small fraction of that of medical doctors who practice primary care. An examination of their literature, moreover, reveals that it is replete with pseudoscientific, ineffective, unethical, and potentially dangerous practices.|author=|title=|source=}} In another article, Atwood writes that "Physicians who consider naturopaths to be their colleagues thus find themselves in opposition to one of the fundamental ethical precepts of modern medicine. If naturopaths are not to be judged "nonscientific practitioners", the term has no useful meaning".<ref name="atwood2004" /> | |||
| ===Regulation in Australia=== | |||
| There is currently no state ] in ], rather the industry is self regulated. There is no protection of title, meaning that technically anyone can practise as a naturopath. The only way to obtain ] for professional ] or public ] is by joining a ], which can only be achieved having completed an ] course and gaining ]. | |||
| A former licensed naturopathic doctor, Britt Marie Hermes, states that "any product that is sold by a naturopath almost guarantees that there is no reliable scientific data to support whatever health claims are made,<ref name="Haglage">{{cite news|vauthors=Haglage A, Mak T|title=Trump Vitamins Were Fortified With B.S.|url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2016/05/25/inside-donald-trump-s-vitamin-scam.html|access-date=24 June 2016|work=The Daily Beast|date=25 May 2016|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003653/https://www.thedailybeast.com/trump-vitamins-were-fortified-with-bs|url-status=live}}</ref> and that while some naturopaths claim to only practice evidence based medicine, "the problem is, all naturopaths in an accredited naturopathic program are required to extensively study homeopathy, herbal medicine, energy healing, chiropractic techniques, water therapy" and other pseudoscientific practices.<ref name="ESP50" /> Hermes further notes that, while some naturopaths claim that their method can be effective treatments for psychological disorders, "no naturopathic treatment has been clinically proven to be safe and effective for bipolar disorder or any other condition."<ref name="DubiousclaimsHermesSI">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hermes B |title=Dubious claims in psychotherapy for youth |journal=Skeptical Inquirer |date=April 2020 |volume=44 |issue=2 |page=50 |url=https://skepticalinquirer.org/2020/01/dubious-claims-in-psychotherapy-for-youth/ }}</ref> | |||
| It is generally thought that with registration, a minimum four-year degree with a minimum 400 hours of supervised clinic practice will be required for practice. Currently only two institutions fulfil these requirements, the and ]. | |||
| According to ], the ''Textbook of Natural Medicine'' is inadequate as a teaching tool, as it omits to mention or treat in detail many common ailments, improperly emphasizes treatments "not likely to be effective" over those that are, and promotes unproven herbal remedies at the expense of pharmaceuticals. He concludes that "the risks to many sick patients seeking care from the average naturopathic practitioner would far outweigh any possible benefits".<ref name="Relman_text">{{cite web |url= http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/relman1.html |title= Textbook of Natural Medicine |access-date= 2009-04-17 |vauthors= Relman AS |author-link= Arnold S. Relman |orig-date= January 9, 2001 |date= April 10, 2002 |publisher= QuackWatch |archive-date= May 11, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110511175643/http://www.quackwatch.org/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/relman1.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| Professional naturopathic associations in Australia include: | |||
| *Australian Natural Therapists Association (ANTA) | |||
| *Australian Traditional-Medicine Society (ATMS), which has the largest membership base in the industry | |||
| *National Herbalists Association of Australia (NHAA) | |||
| *Australian Naturopathic Practitioners Association (ANPA) | |||
| There is currently debate in the industry over whether ] should be introduced for naturopaths, as with ], ] and ]. ATMS is opposed on the grounds that naturopathic treatment is potentially dangerous, and that registration would therefore instigate a significant rise in ]s. NHAA is pro-registration on the grounds that ] and naturopaths will never be taken seriously by the medical profession while unregistered. ANPA is also pro-registration, arguing that only registration of the profession will advance naturopathy as an integral part of healthcare in Australia. | |||
| The Massachusetts Medical Society states, "Naturopathic practices are unchanged by research and remain a large assortment of erroneous and potentially dangerous claims mixed with a sprinkling of non-controversial dietary and lifestyle advice."<ref name="MMStestimony2015" /> | |||
| ===Regulation in North America=== | |||
| Jurisdictions that currently regulate naturopathic medicine include: | |||
| *U.S. jurisdictions with full licensure: ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | |||
| *U.S. state with registration for naturopathic physicians: ] | |||
| *U.S. jurisdictions with two-tier licensure: ] | |||
| *U.S. states with legal basis for practice: ], ] | |||
| *U.S. states which specifically prohibit the practice of naturopathy: ], ] | |||
| *Canadian provinces with full licensure: ], ], ], ] | |||
| === Safety of natural treatments === | |||
| ===Regulation in the United Kingdom=== | |||
| Naturopaths often recommend exposure to naturally occurring substances, such as ], ] and certain foods, as well as activities they describe as natural, such as ], ] and ]. Naturopaths claim that these natural treatments help restore the body's innate ability to heal itself without the adverse effects of conventional medicine. However, "natural" methods and chemicals are not necessarily safer or more effective than "artificial" or "synthetic" ones, and any treatment capable of eliciting an effect may also have deleterious ]s.<ref name="ACS-2009" /><ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /><ref name="SkepDic_natural">{{cite web |url= http://skepdic.com/natural.html |title= Natural |access-date= 2013-09-08 |vauthors= Carroll R |work= The Skeptic's Dictionary |date= November 26, 2012 |archive-date= May 14, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110514011749/http://skepdic.com/natural.html |url-status= live }}</ref><ref name="NCAHF_herb">{{cite web |url= http://www.ncahf.org/pp/herbal.html |title= NCAHF Position Paper on Over the Counter Herbal Remedies (1995) |access-date= 2009-04-17 |year= 1995 |publisher= National Council Against Health Fraud |archive-date= July 7, 2011 |archive-url= http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20110707163329/http://www.ncahf.org/pp/herbal.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| In the ], naturopathy as a profession is very closely aligned with ]. There is no government sponsored regulation of the profession, the largest body, recognises three courses in the UK, two being taught at osteopathic schools: the ; The ; and one at the ] School of Integrated Health under the auspices of the B.Sc Health Science (Naturopathy) course. | |||
| Certain naturopathic treatments offered by naturopaths, such as ], ], and ], are widely considered ] or ].<ref name="NSBattitudes">{{cite web |title= Chapter 7 Science and Technology: Public Attitudes and Public Understanding, Section: Belief in Alternative Medicine |url= https://www.nsf.gov/statistics/seind02/c7/c7s5.htm#c7s5l2a |work= Science and Engineering Indicators - 2002 |date= January 15, 2002 |author= National Science Board |publisher= Division of Science Resources Statistics, ] |location= Arlington, VA |access-date= 2018-04-06 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160616181809/http://www.nsf.gov/statistics/seind02/c7/c7s5.htm#c7s5l2a |archive-date= 2016-06-16 |url-status= dead |author-link= National Science Board }}</ref><ref name="WahlbergQuack">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wahlberg A | title = A quackery with a difference-new medical pluralism and the problem of 'dangerous practitioners' in the United Kingdom | journal = Social Science & Medicine | volume = 65 | issue = 11 | pages = 2307–2316 | date = December 2007 | pmid = 17719708 | doi = 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.07.024 | url = https://curis.ku.dk/ws/files/49590510/Wahlberg.2007.Aquackerywithadifference.pdf | access-date = December 10, 2019 | archive-date = January 14, 2021 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003657/https://curis.ku.dk/ws/files/49590510/Wahlberg.2007.Aquackerywithadifference.pdf | url-status = live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title= Iridology is Nonsense |url= http://www.quackwatch.com/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/iridology.html |vauthors= Barrett S |date= March 28, 2008 |work= QuackWatch |access-date= 2013-09-08 |archive-date= April 6, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110406120005/http://www.quackwatch.com/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/iridology.html |url-status= live }}</ref> ] of ] and the ] has stated that naturopathy is "simplistic and that its practices are riddled with quackery".<ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /><ref>{{Cite web|title=Homeopathy|url=https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/homeopathy/|date=2017-10-18|website=nhs.uk|language=en|access-date=2020-05-21|archive-date=May 13, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200513190309/https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/homeopathy/|url-status=live}}</ref> "Non-scientific health care practitioners, including naturopaths, use unscientific methods and deception on a public who, lacking in-depth health care knowledge, must rely upon the assurance of providers. Quackery not only harms people, it undermines the ability to conduct scientific research and should be opposed by scientists", says ].<ref name="Jarvis WT">{{cite journal | vauthors = Jarvis WT | title = Quackery: a national scandal | journal = Clinical Chemistry | volume = 38 | issue = 8B Pt 2 | pages = 1574–1586 | date = August 1992 | pmid = 1643742 }}</ref> In the 2018 Australian case against Marlyin Bodnar, who advised a mother to treat her infant son's eczema with a raw food diet which nearly led to the child's starvation death, Judge Peter Berman said, "Well intentioned but seriously misguided advice is, as the facts of this case demonstrate, capable of causing great harm and even death to vulnerable children."<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = Sutton C |title=Naturopath jailed in starving baby case|url=http://www.news.com.au/national/nsw-act/courts-law/naturopath-faces-sentencing-in-starving-baby-case/news-story/bc594346e08341bfee402f19471b830d|website=news.com.au|access-date=24 April 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180424055207/http://www.news.com.au/national/nsw-act/courts-law/naturopath-faces-sentencing-in-starving-baby-case/news-story/bc594346e08341bfee402f19471b830d|archive-date=24 April 2018|language=en|date=5 April 2018}}</ref> Furthermore, Britt Hermes criticizes the "pervasive culture of ]" among naturopathic practitioners, where "when something doesn't work for the patient and the patient is not experiencing all of the positive effects and zero side-effects that are promised with the therapy, it's never because the therapy doesn't work, it's because the patient didn't do something right."<ref name="ESP50" /> | |||
| Members of this register will either have completed a three or four year full time ] level course or possibly be a ] (Medical Doctor, Osteopath, Chiropractor, Nurse) who has completed a two year post-graduate Naturopathic Diploma, the N.D. As the naturopathic profession has developed along different lines in the UK, naturopaths do not perform minor surgery or have prescribing rights. | |||
| === Vaccination === | |||
| ==Scope of practice== | |||
| {{See also|Vaccine hesitancy}} | |||
| In the United States both ] and ] use the degree designation of N.D. (doctor of naturopathic medicine), leading to considerable confusion about the ], education and training of a naturopathic practitioner (in the United Kingdom, N.D. stands for Diploma in Naturopathy). There is great contention between the two ], as their ]s are in opposition to each other: Naturopathic physicians, whose national professional organization is the American Association of Naturopathic Physicians, strive to recover ] in all 50 states, whereas traditional naturopaths, whose professional organization is the American Naturopathic Medical Association, oppose licensure and often block licensing attempts. ] is currently in progress between naturopathic physicians and traditional naturopaths to come to a resolution to this problem and agree to use different degree titles and designations, but so far this has not been a successful endeavour. | |||
| ] in 1963, with fewer than 25,000 cases reported in 1968. Outbreaks around 1971 and 1977 gave 75,000 and 57,000 cases, respectively. Cases were stable at a few thousand per year until an outbreak of 28,000 in 1990. Cases declined from a few hundred per year in the early 1990s to a few dozen in the 2000s. | thumb | ] cases reported in the United States fell dramatically after the introduction of the measles vaccine.]] | |||
| Many naturopathy practitioners voice their opposition to vaccination. The reasons for this opposition are based, in part, on the early views which shaped the foundation of this occupation.<ref name="Ernst-2001">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ernst E | title = Rise in popularity of complementary and alternative medicine: reasons and consequences for vaccination | journal = Vaccine | volume = 20 Suppl 1 | issue = Suppl. 1, 5th European Conference on Vaccinology: A Safe Future with Vaccination | pages = S90-3; discussion S89 | date = October 2001 | pmid = 11587822 | doi = 10.1016/S0264-410X(01)00290-0 | author-link = Edzard Ernst }}</ref> A naturopathy textbook, co-authored by Joseph Pizzorno, recalls anti-vaccine beliefs associated with the founding of naturopathy in the United States: "a return to nature in regulating the diet, breathing, exercising, bathing and the employment of various forces" ''in lieu'' of the ].<ref>{{cite book| vauthors = Pizzorno JE, Murray MT |title=Textbook of Natural Medicine e-edition: Text with Continually Updated Online Reference, 2-Volume Set|date=2011|publisher=Elsevier|isbn=978-1-4557-0527-6|edition=third|quote=To understand how revolting these products are, let us just refer to the vaccine matter which is supposed to be an efficient preventive of smallpox. The natural system for curing disease is based on a return to nature in regulating the diet, breathing, exercising, bathing and the employment of various forces to eliminate the poisonous products in the system, and so raise the vitality of the patient to a proper standard of health.|page=43}}</ref> | |||
| ==Science and naturopathy== | |||
| There is widespread support for the application of an ] framework to assess health outcomes and that systematic reviews with strict protocols are essential. Organisations such as the ] and ] publish such reviews. | |||
| In general, evidence about associations between naturopathy and pediatric vaccination is sparse, but "published reports suggest that only a minority of naturopathic physicians actively support full vaccination".<ref name="Downey">{{cite journal | vauthors = Downey L, Tyree PT, Huebner CE, Lafferty WE | title = Pediatric vaccination and vaccine-preventable disease acquisition: associations with care by complementary and alternative medicine providers | journal = Maternal and Child Health Journal | volume = 14 | issue = 6 | pages = 922–930 | date = November 2010 | pmid = 19760163 | pmc = 2924961 | doi = 10.1007/s10995-009-0519-5 }} Quote is taken from introduction to paper, not from results of research presented in this paper.</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Herzog R, Álvarez-Pasquin MJ, Díaz C, Del Barrio JL, Estrada JM, Gil Á | title = Are healthcare workers' intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review | journal = BMC Public Health | volume = 13 | pages = 154 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23421987 | pmc = 3602084 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2458-13-154 | doi-access = free }}</ref> In Washington state from 2000 to 2003, children were significantly less likely to receive immunizations if they had seen a naturopath.<ref name="Downey" /> A survey of naturopathic students published in 2004 found that students at the Canadian College of Naturopathic Medicine became less likely to recommend vaccinations to their patients and became more distrustful of public health and conventional medicine as they advanced in the program.<ref name="wilson" /> | |||
| There are reports of ] trials published for naturopathy. | |||
| The British Columbia Naturopathic Association lists several major concerns regarding the pediatric vaccine schedule and vaccines in general,<ref>{{cite web|title=BCNA Vaccination Position Paper|url=http://www.bcna.ca/files_3/articles-vaccination.php|publisher=British Columbia Naturopathic Association|access-date=15 July 2014|archive-date=July 19, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140719051132/http://www.bcna.ca/files_3/articles-vaccination.php|url-status=live}}</ref> and the group's policy is to not advocate for or against vaccines.<ref>{{cite journal|vauthors=Brown H|title=Influenza Virus, Vaccination and Naturopathic Practice|journal=Naturopathic Doctor News and Review|date=21 December 2007|url=http://ndnr.com/nature-cure/influenza-virus-vaccination-and-naturopathic-practice/|access-date=20 October 2016|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003701/https://ndnr.com/nature-cure/influenza-virus-vaccination-and-naturopathic-practice/|url-status=live}}</ref> The Oregon Association of Naturopathic Physicians reports that many naturopaths "customize" the pediatric vaccine schedule.<ref>{{cite web|title=Naturopathic Primary Care|url=http://www.thelundreport.org/sites/default/files/u967/ND%20Primary%20Care%20in%20Oregon%20White%20Paper%20-%20Final.pdf|publisher=Oregon Association of Naturopathic Physicians|access-date=15 July 2014|archive-date=June 14, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130614203253/http://www.thelundreport.org/sites/default/files/u967/ND%20Primary%20Care%20in%20Oregon%20White%20Paper%20-%20Final.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Some modalities used in naturopathy are widely regarded as ]. ]s often cite the large differences between naturopathic practitioners and the lack of scientific documentation of the safety and efficacy of their practices in order to justify limiting naturopathic scope. Advocates claim that naturopathic practitioners find it difficult to obtain financing for research due to the lack of prior research in many areas. Proponents state that this is slowly changing as naturopathic physicians develop research programs to help build up a foundation for evidence based treatment. | |||
| As of April 25, 2022, a British Columbia government report found that 69.2% of naturopaths reported having received at least two COVID vaccines or receiving a medical exemption. This was much lower than all the other regulated medical professions in the report. The number for two professions{{snd}}dieticians and physicians/surgeons{{snd}}was 98%.<ref name="cbc-covid-vaccines">{{cite news |title=Naturopaths, chiropractors least vaccinated of all B.C. health professionals, province says |last1=Larsen |first1=Karin |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/naturopaths-chiropractors-least-vaccinated-1.6439886 |access-date=11 May 2022 |agency=CBC |date=10 May 2022}}</ref><ref name="bc-gov-vaccines">{{cite news |title=Data published on vaccination status of regulated health professions |url=https://news.gov.bc.ca/releases/2022HLTH0138-000737 |access-date=11 May 2022 |work=news.gov.bc.ca |agency=BC Gov News |date=10 May 2022 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Conventional medicine is required to undergo rigorous testing; ]s often last for a decade. A criticism of ] is that they are not subject to detailed safety assessment. Restrospective analysis of various herbal agents have found many to be of little therapeutic value and others to be harmful. This can be tied to the fact that 'natural' does not necessarily correspond to being beneficial or even benign. Also of concern is the ambiguity of the word "natural" and poor agreement as to its meaning. | |||
| {{as of|2016}}, the American Association of Naturopathic Physicians, which is the largest professional organization for licensed naturopaths in the U.S., is "still discussing its stance on vaccinations".<ref name="Robins">{{cite news|vauthors=Robins R|title=Funded by vitamin makers, naturopaths push to expand in US|url=https://www.statnews.com/2016/05/17/naturopaths-go-mainstream/|access-date=18 May 2016|work=STAT|date=17 May 2016|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003710/https://www.statnews.com/2016/05/17/naturopaths-go-mainstream/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| While the above addresses a primary challenge to the validation process for "natural" remedies, perhaps of greater concern amongst critics is the lack of regulation of manufacturer claims in advertising. Common labeling practices suggest that herbal extracts are devoid of "drugs" or "chemicals". Claims of this type are patently false as every component of any plant extract is a chemical by definition. Likewise, claims as to the relative absence of ] in herbal extracts, when compared to conventional ] preparations, are tainted by incongruent regulations for reporting of side effects. The manufacturers of conventional pharmaceutical agents are legally bound to record and report any perceived negative experiences during large scale clinical trials, though there may be no actual link between the tested drug and the perceived side effect. To wit, it is often the case that drugs are labelled with side effects such as ], ], ], or sleep disturbance. These "side effects" are required to be listed even if they are found with no more regularity than they are in a placebo control group or within the general populace for that matter. Conversely, herbal manufacturers are not required to carry out such clinical studies nor to report any known adverse effects, even if said effects have been directly linked to injestion of the herbal preparation in question. While these advertising techniques do not negate the potential for some beneficial uses of various herbal agents, and they do not necessarily reflect upon the validity of naturopathic medicine as a field of study, critics suggest that they do serve to beguile the public through the employment of nothing more than legally permissible ] and selective reporting. | |||
| ==Practitioners== | |||
| Naturopathic modalities may be controversial (eg ]), or have proven effectiveness only for very specific conditions (eg ], ]) Some naturopaths may use these modalities as ] or to improve the patient's quality of life. | |||
| Naturopath practitioners can generally be categorized into three groups: 1) those with a government issued license; 2) those who practice outside of an official status ("traditional naturopaths"); 3) those who are primarily another kind of health professional who also practices naturopathy.<ref name="ACS-2009" /><ref name="NCCAM">{{Cite web | title =Naturopathy: An Introduction | publisher =], ], ] | orig-date =Created April 2007 | date =March 2012 | url =http://nccih.nih.gov/health/naturopathy/naturopathyintro.htm?nav=gsa | access-date =2013-03-16 | author =<!-- no byline --> | volume =NCCIH Pub. No. D372 | archive-date =February 23, 2015 | archive-url =https://web.archive.org/web/20150223110947/https://nccih.nih.gov/health/naturopathy/naturopathyintro.htm?nav=gsa | url-status =live }}</ref><ref name="IMB_policy">{{cite web |author= Iowa Board of Medicine |title= A Policy Statement on Naturopathy |url= http://medicalboard.iowa.gov/policies/naturopathy.html |publisher= <!-- Iowa Board of Medicine, redundant to author -->Iowa Department of Public Health, State of Iowa |date= February 7, 2002 |access-date= 2013-09-01 |archive-date= April 12, 2013 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130412204820/http://medicalboard.iowa.gov/policies/naturopathy.html |url-status= dead }}</ref><ref>The Platform of the American Naturopathic Association as drawn up by the Golden Jubilee Congress. July 27th – August 2nd, 1947</ref><ref name="MNNWG">{{cite web |url= http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/hpsc/hop/nawg/summary092308.pdf |title= Traditional Naturopathy Working Session Summary September 23 and October 1, 2008 |author= Naturopathy Work Group |publisher= Minnesota Department of Health |access-date= 2010-11-20 |url-status= dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110726104027/http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/hpsc/hop/nawg/summary092308.pdf |archive-date= July 26, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| In Switzerland, these divisions fall between those with a federal diploma, those recognized by health insurances, and those with neither federal diploma nor recognition by health insurances. Naturopaths with federal diploma can be divided into four categories: European traditional medicine, Chinese traditional medicine, ayurvedic medicine and homeopathy.<ref name="sbfi.admin.ch">{{cite web |url=http://www.sbfi.admin.ch/bvz/hbb/index.html?detail=1&typ=hfp&lang=fr&item=834&abfragen=Chercher |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904074545/http://www.sbfi.admin.ch/bvz/hbb/index.html?detail=1&typ=hfp&lang=fr&item=834&abfragen=Chercher |url-status=dead |archive-date=2015-09-04 |publisher=State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation |title=Naturopathe avec diplôme fédéral |location=CH }}</ref><ref name="apps.who.int">{{cite web |url=http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Jh2943e/7.19.html |publisher=World Health Organization |title=Legal Status of Traditional Medicine and Complementary/Alternative Medicine: A Worldwide Review |access-date=July 4, 2015 |archive-date=July 5, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150705180602/http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Jh2943e/7.19.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> The number of listed naturopaths (including traditional healers) in Switzerland rose from 223 in 1970 to 1835 in 2000.<ref name="bfs.admin.ch/">{{cite web |url=http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/14/03/04/key/01.html |title=Swiss Federal Statistical Office |location=Switzerland |access-date=2015-07-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708081400/http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/14/03/04/key/01.html |archive-date=2015-07-08 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] and ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| === Licensed naturopaths === | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| Licensed naturopaths may be referred to as "naturopathic doctors" or "naturopathic physicians" in 26 US states or territories and 5 Canadian provinces.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://aanmc.org/naturopathic-news/naturopathic-doctors-wisconsin-licensure/|title=Naturopathic Doctors are Now Licensed in Wisconsin|date=2022-02-17|access-date=2022-02-21|website=AANMC|quote=Wisconsin has just become the 26th U.S. state/territory to regulate naturopathic doctors.}}</ref> Licensed naturopaths present themselves as ].<ref name="Gale_Frey" /><ref name="CNME-handbook" /> Licensed naturopaths do not receive comparable training to medical doctors in terms of the quality of education or quantity of hours.<ref name="atwood2003" /><ref name="AAFP" /> | |||
| ===Advocacy=== | |||
| Naturopathic physicians: | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * by Gary Piscopo, ND, LAc and Eric Yarnell, ND, RH | |||
| * Link to research on naturopathy. | |||
| In ], legislation permits licensed naturopaths to use the title "doctor" or "physician".<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bclaws.ca/civix/document/id/complete/statreg/282_2008 |title=Health Professions Act: Naturopathic Physicians Regulation |at=B.C. Reg. 282/2008 M242/2008 |publisher=Queen's Printer |location=Victoria, British Columbia |date=October 2008 |access-date=18 August 2016 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003734/https://www.bclaws.gov.bc.ca/civix/document/id/complete/statreg/282_2008 |url-status=live }}</ref> However, section 102 of the bylaw of the College of Naturopathic Physicians of British Columbia (CNPBC), the terms "naturopathic" or "naturopathic medicine" must be included anytime the term doctor or physician is used by a member of the CNPBC.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cnpbc.bc.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019-12-27-CNPBC-Bylaws-Consolidation.pdf|title=Bylaws of the College of Naturopathic Physicians of British Columbia}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.straight.com/news/1360161/surrey-city-councillor-and-naturopath-allison-patton-fined-and-suspended-calling |title=Surrey city councillor and naturopath Allison Patton fined and suspended for calling herself a "physician" |date=February 13, 2020 |access-date=April 14, 2020 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003702/https://www.straight.com/news/1360161/surrey-city-councillor-and-naturopath-allison-patton-fined-and-suspended-calling |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.surreynowleader.com/news/surrey-councillor-fined-suspended-from-naturopathy-for-misusing-physician-title/ |title=Surrey councillor fined, suspended from naturopathy for misusing 'physician' title |date=February 12, 2020 |access-date=April 14, 2020 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003717/https://www.surreynowleader.com/news/surrey-councillor-fined-suspended-from-naturopathy-for-misusing-physician-title/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/complaint-filed-against-surrey-naturopath-turned-councillor-who-campaigned-as-physician-1.4907555 |title=Complaint filed against Surrey naturopath-turned-councillor who campaigned as 'physician' |access-date=April 14, 2020 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003716/https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/complaint-filed-against-surrey-naturopath-turned-councillor-who-campaigned-as-physician-1.4907555 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Traditional naturopaths: | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ==== Education ==== | |||
| Certifying Organizations: | |||
| ] trains students in naturopathic medicine who are eligible to become licensed in some jurisdictions in North America.]] | |||
| * | |||
| ], another naturopathic program whose graduates can become licensed naturopaths in some North American jurisdictions]] | |||
| * | |||
| Licensed naturopaths must pass the ] (NPLEX) administered by the North American Board of Naturopathic Examiners (NABNE)<ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.nabne.org/home/about/ |title= About Us |access-date= 3 September 2013 |publisher= North American Board of Naturopathic Examiners |author= <!-- no byline --> |date= <!-- no date in source --> |archive-date= October 5, 2013 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20131005181153/https://www.nabne.org/home/about/ |url-status= live }}</ref> after graduating from a program accredited by the Council on Naturopathic Medical Education (CNME).<ref name="CNME-handbook" /><ref>{{Cite web|title=Naturopathy|url=https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/naturopathy|website=NCCIH|language=en|access-date=2020-05-27|archive-date=March 31, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200331033317/https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/naturopathy|url-status=live}}</ref> Training in CNME-accredited programs includes basic medical diagnostics and procedures such as rudimentary physical exams and common ]s, in addition to pseudoscientific modalities, such as homeopathy, acupuncture, and energy modalities.<ref name="atwood2003">{{cite journal | vauthors = Atwood KC | title = Naturopathy: a critical appraisal | journal = MedGenMed | volume = 5 | issue = 4 | pages = 39 | date = December 2003 | pmid = 14745386 | url = http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/465994 | access-date = September 4, 2013 | archive-date = March 2, 2013 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130302030226/http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/465994 | url-status = live }}{{registration required}}</ref><ref name="atwood2004" /><ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /><ref name="Gale_Frey" /> | |||
| ===Criticism=== | |||
| These accredited programs have been criticized for misrepresenting their medical rigor and teaching subjects that are antithetical to the best understandings of science and medicine.<ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /><ref name="GorskiSBM" /><ref name="Hermes2015">{{cite web|vauthors=Hermes B|author-link1=Britt Marie Hermes|title=ND Confession, Part 1: Clinical training inside and out|url=https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/nd-confession-part-1-clinical-training-inside-and-out|website=]|access-date=23 July 2016|date=13 March 2015|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003703/https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/nd-confession-part-1-clinical-training-inside-and-out/|url-status=live}}</ref> The CNME as an accrediting authority has been characterized as unreliable and suffering from conflicts of interest.<ref name="Mangan1999">{{cite news|vauthors=Mangan KS|title=Report Recommends Stripping Naturopathy Council of Its Accrediting Authority|url=http://chronicle.com/article/Report-Recommends-Stripping/113719|access-date=23 July 2016|work=]|date=2 December 1999|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003742/https://www.chronicle.com/article/report-recommends-stripping-naturopathy-council-of-its-accrediting-authority/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Hermes2015b">{{cite web|vauthors=Hermes B|author-link1=Britt Marie Hermes|title=ND Confession, Part II: The Accreditation of Naturopathic "Medical" Education|url=https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/nd-confession-part-ii-the-accreditation-of-naturopathic-medical-education/|website=]|access-date=23 July 2016|date=29 August 2015|archive-date=July 10, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160710155040/https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/nd-confession-part-ii-the-accreditation-of-naturopathic-medical-education/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="sfsbmNDreport">{{Cite report |author=Society for Science-Based Medicine |date=2014 |title=Report to the Maryland Board of Physicians Naturopathic Advisory Committee: Recommendations for Naturopathic Regulation |url=http://sfsbm.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=486:naturopathic-board&catid=52:legislative&Itemid=435 |access-date=23 July 2016 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003654/http://sfsbm.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=486%3Anaturopathic-board&catid=52%3Alegislative&Itemid=435 |url-status=live }}</ref> The naturopathic licensing exam has been called a mystery by those outside the naturopathic profession<ref name="atwood2004" /><ref name="MMStestimony2015">{{cite web|title=MMS Testimony in Opposition to H. 1992 and S. 1205, An Act to Create a Board of Registration in Naturopathy|url=http://www.massmed.org/Advocacy/MMS-Testimony/MMS-Testimony-in-Opposition-to-H--1992-and-S--1205,-An-Act-to-Create-a-Board-of-Registration-in-Naturopathy/#.VtgJaZMrKrO|website=Massachusetts Medical Society|access-date=30 July 2016|archive-date=May 22, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522130005/http://www.massmed.org/Advocacy/MMS-Testimony/MMS-Testimony-in-Opposition-to-H--1992-and-S--1205,-An-Act-to-Create-a-Board-of-Registration-in-Naturopathy/#.VtgJaZMrKrO|url-status=live}}</ref> and criticized for testing on ] remedies,<ref name="GorskiSBM">{{cite web|vauthors=Gorski D|author-link1=David Gorski|title=Naturopathy and Science|url=https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/naturopathy-and-science/|publisher=ScienceBasedMedicine.org|access-date=3 March 2016|date=21 February 2011|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003753/https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/naturopathy-and-science/|url-status=live}}</ref> including for the use to treat ] emergencies.<ref name="Senapathy2016" /> | |||
| * – ] | |||
| * by Robert T. Carroll – The ] | |||
| * | |||
| * by Barry L. Beyerstein, PhD, and Susan Downie | |||
| Several schools in North America exist for the study of naturopathic medicine, some accredited by the CNME.<ref>{{cite web |title=Accredited Naturopathic Medical Schools |url=https://aanmc.org/naturopathic-schools/ |website=Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges }}</ref> The CNME and the Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges (AANMC) claim entrance requirements and curricula at accredited colleges are often similar or comparable to those required and offered at conventional medical schools.<ref>{{cite web |title=ND, MD/DO, NP: WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE? |url=https://aanmc.org/comparing-nd-md-curricula/ |website=Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges |access-date=15 November 2023}}</ref> However, the lack of accreditation by the ] may indicate insufficiency of scientific medical training and/or quantifiable positive results, and accordingly it remains disputed whether graduates of medical colleges accredited by the CNME have the competency of Medical Doctors and Doctors of Osteopathy.<ref name="AAFP"/><ref>{{cite web |title=ND Confession, Part II: The Accreditation of Naturopathic "Medical" Education |url=https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/nd-confession-part-ii-the-accreditation-of-naturopathic-medical-education/ |website=Science-Based Medicine |date=August 30, 2015 |access-date=15 November 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ===Support=== | |||
| "Profile of Profession: Naturopathic Practice" Center for the Health Professionals UCSF | |||
| *http://www.futurehealth.ucsf.edu/pdf_files/Naturo2.pdf | |||
| Naturopathic doctors are not eligible for ], which are available exclusively for medical doctors and doctors of osteopathic medicine. There are limited post-graduate "residency" positions available to naturopathic doctors offered through naturopathic schools and naturopathic clinics approved by the CNME.<ref name="CNME_residency">{{cite web|title=Handbook on CNME Postdoctoral Naturopathic Medical Education Sponsor Recognition Process and Standards (2005)|url=http://www.cnme.org/resources/residency_handbook.pdf|publisher=Council on Naturopathic Medical Education|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060615111625/https://cnme.org/resources/residency_handbook.pdf|archive-date=15 June 2006}}</ref> Most naturopathic doctors do not complete such a residency,<ref name="Boon HS" /> and naturopathic doctors are not mandated to complete one for licensure,<ref name="ACS-2009" /> except in the states of Utah and Connecticut.<ref name="UT license app">{{cite web |url=http://www.dopl.utah.gov/licensing/forms/applications/072_naturopathic_phys.pdf |title=Application for Licensure: Naturopathic Physician |website=Division of Occupational and Professional Licensing, Utah Department of Commerce |publisher=State of Utah |date=February 17, 2012 |page=1 |access-date=2013-09-08 |archive-date=June 29, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100629150914/http://dopl.utah.gov/licensing/forms/applications/072_naturopathic_phys.pdf}}</ref> ] in naturopathic modalities for health care professionals varies greatly.<ref name="PoaP" /> | |||
| ===North American Schools=== | |||
| * - Portland, Oregon | |||
| * - Seattle, Washington | |||
| * - Tempe, Arizona | |||
| * - Toronto, Ontario | |||
| * - Bridgeport, Connecticut | |||
| * - New Westminster, British Columbia | |||
| * - Association of the six above schools | |||
| ==== Political activity in the United States ==== | |||
| ===Australian Schools=== | |||
| Naturopathic practitioners affiliated with the CNME-accredited schools lobby state, provincial, and federal governments for medical licensure and participation in social health programs.<ref name="Robins" /><ref name="Weeks2016" /> The American Association of Naturopathic Physicians represents licensed naturopaths in the United States;<ref name="Robins" /> the Canadian Association of Naturopathic Doctors represents licensed naturopaths in Canada.<ref name="Weeks2016">{{cite news|vauthors=Carly W|title=Are we being served by the regulation of naturopaths? Not if patients are still being misled|url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/life/health-and-fitness/health/canadian-naturopaths-need-to-follow-the-rules-if-they-want-regulation/article29785140/|work=]|access-date=23 July 2016|date=29 April 2016|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003753/https://www.theglobeandmail.com/life/health-and-fitness/health/canadian-naturopaths-need-to-follow-the-rules-if-they-want-regulation/article29785140/|url-status=live}}</ref> Naturopathic lobbying efforts are funded by vitamin and supplement makers<ref name="Robins" /> and focus on portraying naturopathic education as comparable to ] received by ] and on having high professional standards.<ref name="Weeks2016" /><ref name="NDMDCA">{{cite news|title=ND vs MD -- Battle Lines Drawn in California|url=http://www.medpagetoday.com/publichealthpolicy/workforce/51917|access-date=24 July 2016|date=3 June 2015|archive-date=July 25, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160725123138/http://www.medpagetoday.com/publichealthpolicy/workforce/51917|url-status=live}}</ref> Medical societies and advocacy groups dispute these claims by citing evidence of licensed naturopathic practitioners using pseudoscientific methods without a sound evidence basis and lacking adequate clinical training to diagnose and treat disease competently according to the ].<ref name="Robins" /><ref name="NDMDCA" /><ref name="Frosch2011">{{cite news|vauthors=Frosch D|title=Licensing Naturopaths Incites Debate in Colorado|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/02/22/health/22license.html?_r=0|access-date=24 July 2016|work=The New York Times|date=21 February 2011|archive-date=February 2, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202003854/http://www.nytimes.com/2011/02/22/health/22license.html?_r=0|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Lambeck">{{cite news|vauthors=Lambeck L|title=New law could let Connecticut naturopathic physicians write prescriptions|url=http://www.ctpost.com/local/article/New-law-could-let-Connecticut-naturopathic-7942677.php|access-date=25 July 2016|work=Connecticut Post|date=24 May 2016|archive-date=August 28, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160828130127/http://www.ctpost.com/local/article/New-law-could-let-Connecticut-naturopathic-7942677.php|url-status=live}}</ref> Jann Bellamy has characterized the process by which naturopathic practitioners and other practitioners of pseudoscience convince lawmakers to provide them with medical licenses as "legislative alchemy".<ref name="Bellamy2014">{{cite web|vauthors=Bellamy J|title=Legislative Alchemy 2014 (so far)|url=https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/legislative-alchemy-2014-so-far/|website=]|access-date=21 July 2016|date=15 May 2014|archive-date=February 20, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160220135945/https://www.sciencebasedmedicine.org/legislative-alchemy-2014-so-far/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| * - Brisbane, Queensland and Melbourne, Victoria | |||
| * - Lismore, New South Wales | |||
| * (ACNT) ] | |||
| *, ] | |||
| *The ] offers a degree in naturopathy | |||
| Since 2005, the ] has opposed licensure based on concerns that NDs are not required to participate in residency and concerns that the practices of naturopaths included many "erroneous and potentially dangerous claims".<ref name="MassMed2005">{{cite web |first= <!-- contact not author Richard P. --> |last= <!-- contact not author Gulla --> |title= Massachusetts Medical Society Testifies in Opposition to Licensing Naturopaths |date= May 11, 2005 |publisher= ] |url= http://www.massmed.org/AM/PrinterTemplate.cfm?Section=Home&CONTENTID=12458&TEMPLATE=/CM/ContentDisplay.cfm |access-date= 2009-04-17 |archive-date= 2011-07-16 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110716132319/http://www.massmed.org/AM/PrinterTemplate.cfm?Section=Home&CONTENTID=12458&TEMPLATE=%2FCM%2FContentDisplay.cfm |url-status= dead }}</ref> The Massachusetts Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners rejected their concerns and recommended licensure.<ref name="MassCtte">{{cite web |title=Majority Report of the Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners: A Report to the Legislature |date=January 2002 |author=The Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners |publisher=Massachusetts: The Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners |url=http://www.quackwatch.com/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/majority.pdf |access-date=2010-11-10 |archive-date=January 21, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120121012802/http://www.quackwatch.com/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/Naturopathy/majority.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The Massachusetts Medical Society states:<ref name="MMStestimony2015" /> | |||
| ===UK Schools=== | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * London, Bristol, Brighton, Birmingham, Manchester, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Belfast | |||
| * | |||
| {{Blockquote|Naturopathic medical school is not a medical school in anything but the appropriation of the word medical. Naturopathy is not a branch of medicine. It is a hodge podge of nutritional advice, home remedies and discredited treatments ... Naturopathic colleges claim accreditation but follow a true "alternative" accreditation method that is virtually meaningless. They are not accredited by the same bodies that accredit real medical schools and while some courses have similar titles to the curricula of legitimate medical schools the content is completely different.|author=|title=|source=}} | |||
| ===Ireland Schools=== | |||
| * Dublin, Galway, Cork, Limerick | |||
| In 2015, a former naturopathic doctor, Britt Marie Hermes, who graduated from ] and practiced as a licensed ND in ] and ], began advocating against naturopathic medicine.<ref name="HermesSI2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hermes B |title=Beware the Naturopathic Cancer Quack |journal=Skeptical Inquirer |date=April 2020 |volume=44 |issue=2 |pages=38–44 |url=https://skepticalinquirer.org/2020/03/beware-the-naturopathic-cancer-quack/ }}</ref><ref name="Senapathy2016">{{cite news| vauthors = Senapathy K |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/kavinsenapathy/2016/05/31/why-is-big-naturopathy-afraid-of-this-lone-whistleblower|title=Why Is Big Naturopathy Afraid Of This Lone Whistleblower?|date=2016-05-31|work=Forbes|url-status=live|archive-url=https://archive.today/20200322212737/https://www.forbes.com/sites/kavinsenapathy/2016/05/31/why-is-big-naturopathy-afraid-of-this-lone-whistleblower/%233d54f5de7ee4|archive-date=March 22, 2020|location=US|access-date=September 5, 2017}}</ref><ref name="Belluz2015">{{cite news|vauthors=Belluz J|author-link=Julia Belluz|title=Why one naturopath quit after watching her peers treat cancer patients|url=https://www.vox.com/2015/9/2/9248713/britt-hermes|work=Vox|date=2 September 2015|access-date=June 13, 2017|archive-date=October 14, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171014084313/https://www.vox.com/2015/9/2/9248713/britt-hermes|url-status=live}}</ref> In addition to opposing further licensure, she believes that NDs should not be allowed to use the titles "doctor" or "physician",<ref name="Senapathy2016" /> and be barred from treating children.<ref name="Brown2016">{{cite news |publisher=] |author=Jim Brown |title=Former naturopathic doctor calls for an end to naturopathic pediatrics |work=The 180 |date=10 April 2016 |url=http://www.cbc.ca/radio/the180/a-former-naturopath-speaks-out-why-precarious-work-can-be-good-and-will-assisted-death-come-to-rural-canada-1.3525870/former-naturopathic-doctor-calls-for-an-end-to-naturopathic-pediatrics-1.3525946 |access-date=June 8, 2016 |archive-date=June 12, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160612215149/http://www.cbc.ca/radio/the180/a-former-naturopath-speaks-out-why-precarious-work-can-be-good-and-will-assisted-death-come-to-rural-canada-1.3525870/former-naturopathic-doctor-calls-for-an-end-to-naturopathic-pediatrics-1.3525946 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Kirkey2016">{{cite news| vauthors = Kirkey S |title=Should naturopaths be restricted from treating children after tragic death of Alberta toddler? |url=http://news.nationalpost.com/news/canada/should-naturopaths-be-restricted-from-treating-children-in-wake-of-death-of-alberta-toddler |access-date=8 June 2016 |work=] |date=4 April 2016 }}</ref> She states:<ref name="Hermes2016">{{cite web|vauthors=Britt H|author-link1=Britt Marie Hermes|title=How A Former Naturopath Can Help Unravel The Trickery Of Alternative Medicine|url=http://www.science20.com/britt_marie_hermes/how_a_former_naturopath_can_help_unravel_the_trickery_of_alternative_medicine-175036|website=Science 2.0|access-date=30 July 2016|date=21 June 2016|archive-date=January 14, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003748/https://www.science20.com/britt_marie_hermes/how_a_former_naturopath_can_help_unravel_the_trickery_of_alternative_medicine-175036|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Blockquote|Naturopaths aggressively lobby for laws to issue them medical licenses. I would characterize this political effort as a perverted redefinition of the words "physician", "doctor", "medical school", and "residency" in order to mask the inadequacy of the training provided in naturopathic programs. ND students do not realize that they are taking educational shortcuts and therefore do not possess any demonstrable competencies found in modern medicine.|author=|title=|source=}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| === Traditional naturopaths === | |||
| ] | |||
| ] in ], a pharmacy founded by ], a Scottish physician, in the mid-18th century. It is now a museum demonstrating 18th Century medical treatments.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Traditional naturopaths are represented in the United States by the American Naturopathic Association (ANA), representing about 1,800 practitioners<ref name="Swartout(Firm)2006">{{cite book|veditors=Swartout KA|title=Encyclopedia of Associations|edition=44|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Wf6PPHSMD4IC|access-date=2013-09-04|year=2006|publisher=Thomson Gale|isbn=978-0-7876-8286-6|pages=1777–1778|archive-date=December 3, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161203184157/https://books.google.com/books?id=Wf6PPHSMD4IC|url-status=live}}</ref> and the American Naturopathic Medical Association (ANMA).<ref name="Baer2001" /> | |||
| The level of naturopathic training varies among traditional naturopaths in the United States. Traditional naturopaths may complete non-degree certificate programs or undergraduate degree programs and generally refer to themselves as naturopathic consultants. These programs often offer online unaccredited degrees, but do not offer comprehensive biomedical education or clinical training. | |||
| Traditional naturopathic practitioners surveyed in Australia perceive evidence-based medicine to be an ideological assault on their beliefs in vitalistic and holistic principles.<ref name="Jagtenberg2006" /> They advocate for the integrity of natural medicine practice.<ref name="Jagtenberg2006" /> | |||
| Naturopaths graduating from accredited programs argued in 2002 that their training used evidence-based scientific principles unlike traditional naturopathic programs,<ref name="Smith MJ, Logan AC 2002 173–84">{{cite journal | vauthors = Smith MJ, Logan AC | title = Naturopathy | journal = The Medical Clinics of North America | volume = 86 | issue = 1 | pages = 173–184 | date = January 2002 | pmid = 11795088 | doi = 10.1016/S0025-7125(03)00079-8 }}</ref> but this claim remains inaccurate.<ref name="atwood2003" /><ref name="Barrett-Naturopathy" /> | |||
| == Regulation == | |||
| Naturopathy is practiced in many countries and is subject to different standards of regulation and levels of acceptance. The scope of practice varies widely between jurisdictions, with some covering naturopathy under medical regulation and allowing practitioners to prescribe drugs and perform minor surgery, while other jurisdictions outlaw naturopathy entirely.{{citation needed|date=November 2022}} | |||
| === Australia === | |||
| In 1977, a Commonwealth Government inquiry reviewed all colleges of naturopathy in Australia and found that despite having syllabuses appearing to cover the basic biomedical sciences, actual lectures had little connection to those syllabuses and no significant practical work was available. In addition, there did not appear to be significant or systematic coverage of techniques favoured by naturopaths, such as homeopathy, Bach's floral remedies, or mineral salts.<ref name=Aust1977/> | |||
| The position of the ] is that "evidence-based aspects of complementary medicine can be part of patient care by a medical practitioner", but it has concerns that there is "limited efficacy evidence regarding most complementary medicine. Unproven complementary medicines and therapies can pose a risk to patient health either directly through misuse or indirectly if a patient defers seeking medical advice." The AMA's position on regulation is that "there should be appropriate regulation of complementary medicine practitioners and their activities".<ref>{{cite web |url=https://ama.com.au/position-statement/complementary-medicine-2012 |title=AMA Position Statement: Complementary Medicine - 2012 |date=28 August 2012 |publisher=Australian Medical Association |access-date=21 March 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402150707/https://ama.com.au/position-statement/complementary-medicine-2012 |archive-date=April 2, 2015 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In 2015, the Australian government found no clear evidence of effectiveness for naturopathy.<ref name=aus17/> Accordingly, In 2017 the Australian government named naturopathy as a practice that would not qualify for insurance subsidies, saying this step would "ensure taxpayer funds are expended appropriately and not directed to therapies lacking evidence".<ref name=nosubsidy>{{cite journal |title=Homeopathy, naturopathy struck off private insurance list |author=Paola S |date=17 October 2017 |journal=Australian Journal of Pharmacy |url=https://ajp.com.au/news/homeopathy-naturopathy-struck-off-private-insurance-list/ |access-date=January 11, 2018 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003745/https://ajp.com.au/news/homeopathy-naturopathy-struck-off-private-insurance-list/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === India === | |||
| In India, naturopathy is overseen by the ] (AYUSH); there is a 5½-year degree in "Bachelor of Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences" (BNYS) degree that was offered by twelve colleges in India {{as of|2010|August|lc=y}}.<ref name=ayush1>Ministry of AYUSH. Page updated August 21, 2010 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150306043724/http://www.indianmedicine.nic.in/index2.asp?slid=34&sublinkid=22&lang=1 |date=2015-03-06 }}. Page accessed March 21, 2015</ref> The National Institute of Naturopathy in ] that operates under AYUSH, which was established on December 22, 1986, and encourages facilities for standardization and propagation of the existing knowledge and its application through research in naturopathy throughout India.<ref name=ayush2>Ministry of AYUSH. Page updated September 23, 2010 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150220002629/http://indianmedicine.nic.in/index3.asp?sslid=191&subsublinkid=84&lang=1 |date=2015-02-20 }}. Page accessed March 21, 2015</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://punenin.org/about.htm |title= About: National Institute of Naturopathy |access-date= March 21, 2015 |archive-date= March 6, 2015 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20150306211356/http://punenin.org/about.htm |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| {{anchor|Naturopathic Medical Doctor}} | |||
| === North America === | |||
| In five Canadian provinces, seventeen U.S. states, and the ], naturopathic doctors who are trained at an accredited school of naturopathic medicine in North America are entitled to use the designation ND or NMD. Elsewhere, the designations "naturopath", "naturopathic doctor", and "doctor of natural medicine" are generally unprotected or prohibited.<ref name="AMA-SOP-ND">{{Cite report |date=2009 |title=AMA Scope of Practice Data Series: Naturopaths |url=http://www.legis.state.ak.us/BASIS/get_documents.asp?session=26&docid=5692 |work=] |via=The Alaska State Legislature |access-date=30 July 2016 |archive-date=June 29, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160629235905/http://www.legis.state.ak.us/BASIS/get_documents.asp?session=26&docid=5692 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="IMB_policy" /> | |||
| In North America, each jurisdiction that regulates naturopathy defines a local scope of practice for naturopathic doctors that can vary considerably. Some regions permit minor surgery, access to prescription drugs, spinal manipulations, midwifery (natural childbirth), and gynecology; other regions exclude these from the naturopathic scope of practice or prohibit the practice of naturopathy entirely.<ref name="AMA-SOP-ND"/><ref name="Sunrise-2008">{{cite web|url=http://www.dora.state.co.us/OPR/archive/2008NaturopathicPhysiciansSunrise.pdf |archive-date= 2008-10-02 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20081002001141/http://www.dora.state.co.us/opr/archive/2008NaturopathicPhysiciansSunrise.pdf |date= January 4, 2008 |title=2008 Sunrise Review: Naturopathic Physicians |pages=18–19 |website=Department of Regulatory Agencies |publisher=State of Colorado}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Canada ==== | |||
| Five Canadian provinces license naturopathic doctors: ], ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.cand.ca/index.php?40 |title= Questions: Education and Regulation |access-date= 2013-09-06 |work= Canadian Association of Naturopathic Doctors website |publisher= <!-- redundant to website name --> |author= <!-- no byline --> |date= <!-- no date in source --> |archive-date= July 6, 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110706170455/http://www.cand.ca/index.php?40 |url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title = History of Naturopathic Medicine|url = http://www.cand.ca/index.php?51&L=0|website = www.cand.ca|access-date = 2016-02-17|archive-date = January 14, 2021|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210114003735/https://www.cand.ca/?51&L=0|url-status = live}}</ref> British Columbia has the largest scope of practice in Canada, allowing certified NDs to prescribe pharmaceuticals and perform minor surgeries.<ref>{{cite news |title= B.C. gives naturopaths right to prescribe drugs |url= https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/b-c-gives-naturopaths-right-to-prescribe-drugs-1.843524 |date= April 10, 2009 |author= <!-- no byline CBC News staff --> |work= ] |access-date= September 6, 2013 |archive-date= August 20, 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120820102601/http://www.cbc.ca/news/health/story/2009/04/10/bc-naturopaths.html |url-status= live }}</ref> Ontario also permits prescription from a modified formulary list, following separate examination.<ref name="FNMRAlaws">{{cite web |title=Naturopathic Regulatory Authority General Information Links |url=https://fnmra.org/ras |website=The Federation of Naturopathic Medicine Regulatory Authorities |access-date=15 November 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ====United States==== | |||
| * U.S. jurisdictions that currently regulate or license naturopathy include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oslpr.org/download/ES/1997/208s0783.pdf |title=Ley para Reglamentar el Ejercicio de la Medicina Naturopática en Puerto Rico |language=es |date=December 30, 1997 |url-status= dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20081002072926/http://www.oslpr.org/download/ES/1997/208s0783.pdf |archive-date= 2008-10-02}}</ref> ], ], ], and ].<ref name="FNMRAlaws"/><ref name="LicState"/> Additionally, ] licenses the practice of naturopathy under a ]. (This was previously also the case in Florida, though currently no practitioners remain active under the grandfather provisions).<ref name="AMA-SOP-ND"/><ref>{{cite web |title=AN ENDANGERED SPECIES NATUROPATHIC DOCTOR IS CLOSE TO EXTINCTION |url=https://www.orlandosentinel.com/1986/09/18/an-endangered-species-naturopathic-doctor-is-close-to-extinction/ |website=Orlando Sentinel |date=September 18, 1986 |access-date=17 November 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ** U.S. jurisdictions that permit access to prescription drugs: Arizona, California, District of Columbia, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Maine, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Vermont, and Washington.<ref name="FNMRAlaws"/> | |||
| ** U.S. jurisdictions that permit minor surgery: Arizona, District of Columbia, Kansas, Maine, Montana, Oregon, Utah, Vermont, and Washington. | |||
| * Three U.S. states specifically prohibit the practice of naturopathy: ],<ref name="ANCBlaws">{{cite web |title=Review of State Laws Regulating Naturopathy |url=https://ancb.net/legislative-action-and-advocacy/naturopathy-laws-state-by-state/ |website=American Naturopathic Certification Board |access-date=15 November 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Title XXXII REGULATION OF PROFESSIONS AND OCCUPATIONS Chapter 462 NATUROPATHY |url=http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=0400-0499/0462/0462.html |website=Online Sunshine |publisher=Florida Legislature |access-date=17 November 2023}}</ref> ]<ref name= "SC Code">{{cite web |url= http://www.scstatehouse.gov/code/t40c031.htm |work= South Carolina Code of Laws (Unannotated), Current through the end of the 2007 Regular Session |title= Title 40, Chapter 31, Sections 10 & 20 |url-status= dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090112214025/http://www.scstatehouse.gov/code/t40c031.htm |archive-date= January 12, 2009 |publisher= South Carolina Legislative Council}}</ref><ref name="AMA-SOP-ND"/> and ].<ref name= "TN Code">{{cite web |at=63.6.205 Practice of naturopathy |title=Title 63 Professions of the Healing Arts, Chapter 6 Medicine and Surgery, Part 2 General Provisions |work=Tennessee Code Annotated |author=State of Tennessee |publisher=Justia |url=http://law.justia.com/codes/tennessee/2010/title-63/chapter-6/part-2/63-6-205/ |year=2013 |access-date=September 7, 2013 |archive-date=October 7, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131007015741/http://law.justia.com/codes/tennessee/2010/title-63/chapter-6/part-2/63-6-205 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="AMA-SOP-ND"/> | |||
| === Switzerland === | |||
| The ] defines the Swiss Confederation and the ] within the scope of their powers to oversee complementary medicine.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.admin.ch/opc/en/classified-compilation/19995395/index.html#a118a/ |title= Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation |at= Art. 118a Complementary medicine |location= CH |access-date= July 4, 2015 |archive-date= June 21, 2016 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160621000507/https://www.admin.ch/opc/en/classified-compilation/19995395/index.html#a118a/ |url-status= live }} (English translation)</ref> In particular, the Federal authorities must set up diplomas for the practice of non-scientific medicine. The first of such diplomas has been validated in April 2015 for the practice of naturopathy.<ref name="sbfi.admin.ch"/> There is a long tradition of naturopathy and traditional medicine in Switzerland.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Swiss take an holistic approach|url=https://www.irishtimes.com/news/health/swiss-take-an-holistic-approach-1.771119|access-date=2021-11-29|newspaper=The Irish Times|language=en}}</ref> The ] make their own public health regulations. Although the law in certain cantons is typically monopolistic, the authorities are relatively tolerant with regard to alternative practitioners.<ref name="apps.who.int"/> | |||
| === United Kingdom === | |||
| Naturopathy is not regulated in the ]. In 2012, publicly funded universities in the United Kingdom dropped their alternative medicine programs, including naturopathy.<ref>{{cite news |vauthors= Bevanger L |title= UK universities drop alternative medicine degree programs |url= http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,,15673133,00.html |access-date= 2012-02-05 |newspaper= ] |date= January 18, 2012 |archive-date= January 25, 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120125180218/http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,,15673133,00.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{Portal|Medicine}} | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=22em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] and ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Naturopathy}} | |||
| {{Traditional Medicine}} | |||
| {{Pseudoscience}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:31, 19 October 2024
Form of alternative medicine
| Alternative medicine | |
|---|---|
 A homeopathic preparation of Hepar sulph – homeopathy can be offered as part of naturopathic treatment. A homeopathic preparation of Hepar sulph – homeopathy can be offered as part of naturopathic treatment. | |
| Claims | Diseases are cured through the body's "natural healing" ability which is primarily aided by practices labelled as "natural" (and not primarily by pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, and other treatments within evidence-based medicine, not seen as "natural"), comprising widely ranging "nature cures" and any form of alternative medicine that may be labelled as "natural" |
| Related fields | Alternative medicine |
| Original proponents | Benedict Lust; Sebastian Kneipp |
| MeSH | D009324 |
| See also | Humorism, heroic medicine, vitalism |
Naturopathy, or naturopathic medicine, is a form of alternative medicine. A wide array of practices branded as "natural", "non-invasive", or promoting "self-healing" are employed by its practitioners, who are known as naturopaths. Difficult to generalize, these treatments range from the pseudoscientific and thoroughly discredited, like homeopathy, to the widely accepted, like certain forms of psychotherapy. The ideology and methods of naturopathy are based on vitalism and folk medicine rather than evidence-based medicine, although practitioners may use techniques supported by evidence. The ethics of naturopathy have been called into question by medical professionals and its practice has been characterized as quackery.
Naturopathic practitioners commonly encourage alternative treatments that are rejected by conventional medicine, including resistance to surgery or vaccines for some patients. The diagnoses made by naturopaths often have no basis in science and are often not accepted by mainstream medicine.
Naturopaths frequently campaign for legal recognition in the United States. Naturopathy is prohibited in three U.S. states (Florida, South Carolina, and Tennessee) and tightly regulated in many others. Some states, however, allow naturopaths to perform minor surgery or even prescribe drugs. While some schools exist for naturopaths, and some jurisdictions allow such practitioners to call themselves doctors, the lack of accreditation, scientific medical training, and quantifiable positive results means they lack the competency of true medical doctors.
History
The term "naturopathy" originates from "natura" (Latin root for birth) and "pathos" (the Greek root for suffering) to suggest "natural healing". Naturopaths claim the ancient Greek "Father of Medicine", Hippocrates, as the first advocate of naturopathic medicine, before the term existed. Naturopathy has its roots in the 19th-century Natural Cure movement of Europe. In Scotland, Thomas Allinson started advocating his "Hygienic Medicine" in the 1880s, promoting a natural diet and exercise with avoidance of tobacco and overwork.
The term naturopathy was coined in 1895 by John Scheel, and purchased by Benedict Lust, whom naturopaths consider to be the "Father of U.S. Naturopathy". Lust had been schooled in hydrotherapy and other natural health practices in Germany by Father Sebastian Kneipp; Kneipp sent Lust to the United States to spread his drugless methods. Lust defined naturopathy as a broad discipline rather than a particular method, and included such techniques as hydrotherapy, herbal medicine, and homeopathy, as well as eliminating overeating, tea, coffee, and alcohol. He described the body in spiritual and vitalistic terms with "absolute reliance upon the cosmic forces of man's nature". According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, the first known use of "naturopathy" in print is from 1901.
From 1901, Lust founded the American School of Naturopathy in New York. In 1902, the original North American Kneipp Societies were discontinued and renamed "Naturopathic Societies". In September 1919, the Naturopathic Society of America was dissolved and Benedict Lust founded the American Naturopathic Association to supplant it. Naturopaths became licensed under naturopathic or drugless practitioner laws in 25 states in the first three decades of the twentieth century. Naturopathy was adopted by many chiropractors, and several schools offered both Doctor of Naturopathy (ND) and Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) degrees. Estimates of the number of naturopathic schools active in the United States during this period vary from about one to two dozen.
After a period of rapid growth, naturopathy went into decline for several decades after the 1930s. In 1910, the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching published the Flexner Report, which criticized many aspects of medical education, especially quality and lack of scientific rigour. The advent of penicillin and other "miracle drugs" and the consequent popularity of modern medicine also contributed to naturopathy's decline. In the 1940s and 1950s, a broadening in scope of practice laws led many chiropractic schools to drop their ND degrees, though many chiropractors continued to practice naturopathy. From 1940 to 1963, the American Medical Association campaigned against heterodox medical systems. By 1958, practice of naturopathy was licensed in only five states. In 1968, the United States Department of Health, Education, and Welfare issued a report on naturopathy concluding that naturopathy was not grounded in medical science and that naturopathic education was inadequate to prepare graduates to make appropriate diagnosis and provide treatment; the report recommends against expanding Medicare coverage to include naturopathic treatments. In 1977 an Australian committee of inquiry reached similar conclusions; it did not recommend licensure for naturopaths.
Beginning in the 1970s, there was a revival of interest in the United States and Canada, in conjunction with the "holistic health" movement. As of 2009, fifteen U.S. states, Puerto Rico, the US Virgin Islands and the District of Columbia licensed naturopathic doctors, and the State of Washington requires insurance companies to offer reimbursement for services provided by naturopathic physicians. On the other hand, some states such as South Carolina and Tennessee prohibit the practice of naturopathy.
In the United States, the Indian Health Service began accepting naturopathic doctors in their clinics and practice in 2013, also making loan repayment available to ND's.
In 2015, a former naturopathic doctor, Britt Marie Hermes, began writing critically about her experience being trained in and practicing naturopathic medicine. Her blog garnered a large following among skeptics while enraging some proponents of alternative medicine.
-
 Sebastian Kneipp c. 1898, a Bavarian priest and forefather of naturopathy
Sebastian Kneipp c. 1898, a Bavarian priest and forefather of naturopathy
-
 Benedict Lust c. 1902, the founder of naturopathy in the U.S.
Benedict Lust c. 1902, the founder of naturopathy in the U.S.
-
 Britt Marie Hermes c. 2016, a former naturopathic doctor and major critic of naturopathic medicine
Britt Marie Hermes c. 2016, a former naturopathic doctor and major critic of naturopathic medicine
Practice



In 2003, a report was presented by Kimball C. Atwood, an American medical doctor and researcher from Newton, Massachusetts, best known as a critic of naturopathic medicine, stating among other criticisms that "The practice of naturopathy is based on a belief in the body's ability to heal itself through a special vital energy or force guiding bodily processes internally".
Diagnosis and treatment concern primarily alternative therapies and "natural" methods that naturopaths claim promote the body's natural ability to heal. Many naturopaths in India now use modern diagnostic techniques in their practice. Naturopaths focus on a holistic approach, avoiding the use of surgery and conventional medicines. Naturopaths aim to prevent illness through stress reduction and changes to diet and lifestyle, often rejecting the methods of evidence-based medicine.
A consultation typically begins with a comprehensive patient interview assessing lifestyle, medical history, emotional tone, and physical features, as well as physical examination. Many naturopaths present themselves as primary care providers, and some naturopathic physicians may prescribe drugs, perform minor surgery, and integrate other conventional medical approaches such as diet and lifestyle counselling with their naturopathic practice. Traditional naturopaths deal exclusively with lifestyle changes, not diagnosing or treating disease. Naturopaths do not generally recommend vaccines and antibiotics, based in part on the early views that shaped the profession, and they may provide alternative remedies even in cases where evidence-based medicine has been shown effective.
Methods
Naturopaths are often opposed to mainstream medicine and take an antivaccinationist stance.
The particular modalities used by a naturopath vary with training and scope of practice. These may include herbalism, homeopathy, acupuncture, nature cures, physical medicine, applied kinesiology, colonic enemas, chelation therapy, color therapy, cranial osteopathy, hair analysis, iridology, live blood analysis, ozone therapy, psychotherapy, public health measures and hygiene, reflexology, rolfing, massage therapy, and traditional Chinese medicine. Nature cures include a range of therapies based on exposure to natural elements such as sunshine, fresh air, or heat or cold, as well as nutrition advice such as following a vegetarian and whole food diet, fasting, or abstention from alcohol and sugar. Physical medicine includes naturopathic, osseous, or soft tissue manipulative therapy, sports medicine, exercise, and hydrotherapy. Psychological counseling includes meditation, relaxation, and other methods of stress management.
A 2004 survey determined the most commonly prescribed naturopathic therapeutics in Washington state and Connecticut were botanical medicines, vitamins, minerals, homeopathy, and allergy treatments. An examination published in 2011 of naturopathic clinic websites in Alberta and British Columbia found that the most commonly advertised therapies were homeopathy, botanical medicine, nutrition, acupuncture, lifestyle counseling, and detoxification.
In 2020, a survey of methods used by naturopaths in fourteen countries reported that 27% of clients received acupuncture, 22% homeopathy, 16% "other energetic medicines", and 13.5% were given hydrotherapy. A mean of 4.0 "treatments" were provided to each customer. One-third (33%) of patients consulted with only the naturopath to manage their primary health concern.
Evidence basis
See also: Evidence-based medicine


Naturopathy as a whole lacks an adequate scientific basis, and it is rejected by the medical community. Although it includes valid lifestyle advice from mainstream medicine (healthy sleep, balanced diet, regular exercise), it typically adds a range of pseudoscientific beliefs. Some methods rely on immaterial "vital energy fields", the existence of which has not been proven, and there is concern that naturopathy as a field tends towards isolation from general scientific discourse. Naturopathy is criticized for its reliance on and its association with unproven, disproven, and other controversial alternative medical treatments, and for its vitalistic underpinnings. Natural substances known as nutraceuticals show little promise in treating diseases, especially cancer, as laboratory experiments have shown limited therapeutic effect on biochemical pathways, while clinical trials demonstrate poor bioavailability. According to the American Cancer Society, "scientific evidence does not support claims that naturopathic medicine can cure cancer or any other disease". According to Britt Hermes, naturopath student programs are problematic because "As a naturopath , you are making justifications to make the rules and to fudge the standards of how to interpret research all along the way. Because if you don't, you're not left with anything, basically".
In 2015, the Australian Government's Department of Health published the results of a review of alternative therapies that sought to determine if any were suitable for being covered by health insurance; Naturopathy was one of 17 therapies evaluated for which no clear evidence of effectiveness was found.
Kimball C. Atwood IV writes, in the journal Medscape General Medicine,
Naturopathic physicians now claim to be primary care physicians proficient in the practice of both "conventional" and "natural" medicine. Their training, however, amounts to a small fraction of that of medical doctors who practice primary care. An examination of their literature, moreover, reveals that it is replete with pseudoscientific, ineffective, unethical, and potentially dangerous practices.
In another article, Atwood writes that "Physicians who consider naturopaths to be their colleagues thus find themselves in opposition to one of the fundamental ethical precepts of modern medicine. If naturopaths are not to be judged "nonscientific practitioners", the term has no useful meaning".
A former licensed naturopathic doctor, Britt Marie Hermes, states that "any product that is sold by a naturopath almost guarantees that there is no reliable scientific data to support whatever health claims are made, and that while some naturopaths claim to only practice evidence based medicine, "the problem is, all naturopaths in an accredited naturopathic program are required to extensively study homeopathy, herbal medicine, energy healing, chiropractic techniques, water therapy" and other pseudoscientific practices. Hermes further notes that, while some naturopaths claim that their method can be effective treatments for psychological disorders, "no naturopathic treatment has been clinically proven to be safe and effective for bipolar disorder or any other condition."
According to Arnold S. Relman, the Textbook of Natural Medicine is inadequate as a teaching tool, as it omits to mention or treat in detail many common ailments, improperly emphasizes treatments "not likely to be effective" over those that are, and promotes unproven herbal remedies at the expense of pharmaceuticals. He concludes that "the risks to many sick patients seeking care from the average naturopathic practitioner would far outweigh any possible benefits".
The Massachusetts Medical Society states, "Naturopathic practices are unchanged by research and remain a large assortment of erroneous and potentially dangerous claims mixed with a sprinkling of non-controversial dietary and lifestyle advice."
Safety of natural treatments
Naturopaths often recommend exposure to naturally occurring substances, such as sunshine, herbs and certain foods, as well as activities they describe as natural, such as exercise, meditation and relaxation. Naturopaths claim that these natural treatments help restore the body's innate ability to heal itself without the adverse effects of conventional medicine. However, "natural" methods and chemicals are not necessarily safer or more effective than "artificial" or "synthetic" ones, and any treatment capable of eliciting an effect may also have deleterious side effects.
Certain naturopathic treatments offered by naturopaths, such as homeopathy, rolfing, and iridology, are widely considered pseudoscience or quackery. Stephen Barrett of QuackWatch and the National Council Against Health Fraud has stated that naturopathy is "simplistic and that its practices are riddled with quackery". "Non-scientific health care practitioners, including naturopaths, use unscientific methods and deception on a public who, lacking in-depth health care knowledge, must rely upon the assurance of providers. Quackery not only harms people, it undermines the ability to conduct scientific research and should be opposed by scientists", says William T. Jarvis. In the 2018 Australian case against Marlyin Bodnar, who advised a mother to treat her infant son's eczema with a raw food diet which nearly led to the child's starvation death, Judge Peter Berman said, "Well intentioned but seriously misguided advice is, as the facts of this case demonstrate, capable of causing great harm and even death to vulnerable children." Furthermore, Britt Hermes criticizes the "pervasive culture of patient blaming" among naturopathic practitioners, where "when something doesn't work for the patient and the patient is not experiencing all of the positive effects and zero side-effects that are promised with the therapy, it's never because the therapy doesn't work, it's because the patient didn't do something right."
Vaccination
See also: Vaccine hesitancy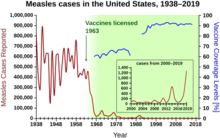
Many naturopathy practitioners voice their opposition to vaccination. The reasons for this opposition are based, in part, on the early views which shaped the foundation of this occupation. A naturopathy textbook, co-authored by Joseph Pizzorno, recalls anti-vaccine beliefs associated with the founding of naturopathy in the United States: "a return to nature in regulating the diet, breathing, exercising, bathing and the employment of various forces" in lieu of the smallpox vaccine.
In general, evidence about associations between naturopathy and pediatric vaccination is sparse, but "published reports suggest that only a minority of naturopathic physicians actively support full vaccination". In Washington state from 2000 to 2003, children were significantly less likely to receive immunizations if they had seen a naturopath. A survey of naturopathic students published in 2004 found that students at the Canadian College of Naturopathic Medicine became less likely to recommend vaccinations to their patients and became more distrustful of public health and conventional medicine as they advanced in the program.
The British Columbia Naturopathic Association lists several major concerns regarding the pediatric vaccine schedule and vaccines in general, and the group's policy is to not advocate for or against vaccines. The Oregon Association of Naturopathic Physicians reports that many naturopaths "customize" the pediatric vaccine schedule.
As of April 25, 2022, a British Columbia government report found that 69.2% of naturopaths reported having received at least two COVID vaccines or receiving a medical exemption. This was much lower than all the other regulated medical professions in the report. The number for two professions – dieticians and physicians/surgeons – was 98%.
As of 2016, the American Association of Naturopathic Physicians, which is the largest professional organization for licensed naturopaths in the U.S., is "still discussing its stance on vaccinations".
Practitioners
Naturopath practitioners can generally be categorized into three groups: 1) those with a government issued license; 2) those who practice outside of an official status ("traditional naturopaths"); 3) those who are primarily another kind of health professional who also practices naturopathy.
In Switzerland, these divisions fall between those with a federal diploma, those recognized by health insurances, and those with neither federal diploma nor recognition by health insurances. Naturopaths with federal diploma can be divided into four categories: European traditional medicine, Chinese traditional medicine, ayurvedic medicine and homeopathy. The number of listed naturopaths (including traditional healers) in Switzerland rose from 223 in 1970 to 1835 in 2000.
Licensed naturopaths
Licensed naturopaths may be referred to as "naturopathic doctors" or "naturopathic physicians" in 26 US states or territories and 5 Canadian provinces. Licensed naturopaths present themselves as primary care providers. Licensed naturopaths do not receive comparable training to medical doctors in terms of the quality of education or quantity of hours.
In British Columbia, legislation permits licensed naturopaths to use the title "doctor" or "physician". However, section 102 of the bylaw of the College of Naturopathic Physicians of British Columbia (CNPBC), the terms "naturopathic" or "naturopathic medicine" must be included anytime the term doctor or physician is used by a member of the CNPBC.
Education


Licensed naturopaths must pass the Naturopathic Physicians Licensing Examinations (NPLEX) administered by the North American Board of Naturopathic Examiners (NABNE) after graduating from a program accredited by the Council on Naturopathic Medical Education (CNME). Training in CNME-accredited programs includes basic medical diagnostics and procedures such as rudimentary physical exams and common blood tests, in addition to pseudoscientific modalities, such as homeopathy, acupuncture, and energy modalities. These accredited programs have been criticized for misrepresenting their medical rigor and teaching subjects that are antithetical to the best understandings of science and medicine. The CNME as an accrediting authority has been characterized as unreliable and suffering from conflicts of interest. The naturopathic licensing exam has been called a mystery by those outside the naturopathic profession and criticized for testing on homeopathic remedies, including for the use to treat pediatric emergencies.
Several schools in North America exist for the study of naturopathic medicine, some accredited by the CNME. The CNME and the Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges (AANMC) claim entrance requirements and curricula at accredited colleges are often similar or comparable to those required and offered at conventional medical schools. However, the lack of accreditation by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education may indicate insufficiency of scientific medical training and/or quantifiable positive results, and accordingly it remains disputed whether graduates of medical colleges accredited by the CNME have the competency of Medical Doctors and Doctors of Osteopathy.
Naturopathic doctors are not eligible for medical residencies, which are available exclusively for medical doctors and doctors of osteopathic medicine. There are limited post-graduate "residency" positions available to naturopathic doctors offered through naturopathic schools and naturopathic clinics approved by the CNME. Most naturopathic doctors do not complete such a residency, and naturopathic doctors are not mandated to complete one for licensure, except in the states of Utah and Connecticut. Continuing education in naturopathic modalities for health care professionals varies greatly.
Political activity in the United States
Naturopathic practitioners affiliated with the CNME-accredited schools lobby state, provincial, and federal governments for medical licensure and participation in social health programs. The American Association of Naturopathic Physicians represents licensed naturopaths in the United States; the Canadian Association of Naturopathic Doctors represents licensed naturopaths in Canada. Naturopathic lobbying efforts are funded by vitamin and supplement makers and focus on portraying naturopathic education as comparable to medical education received by physicians and on having high professional standards. Medical societies and advocacy groups dispute these claims by citing evidence of licensed naturopathic practitioners using pseudoscientific methods without a sound evidence basis and lacking adequate clinical training to diagnose and treat disease competently according to the standard of care. Jann Bellamy has characterized the process by which naturopathic practitioners and other practitioners of pseudoscience convince lawmakers to provide them with medical licenses as "legislative alchemy".
Since 2005, the Massachusetts Medical Society has opposed licensure based on concerns that NDs are not required to participate in residency and concerns that the practices of naturopaths included many "erroneous and potentially dangerous claims". The Massachusetts Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners rejected their concerns and recommended licensure. The Massachusetts Medical Society states:
Naturopathic medical school is not a medical school in anything but the appropriation of the word medical. Naturopathy is not a branch of medicine. It is a hodge podge of nutritional advice, home remedies and discredited treatments ... Naturopathic colleges claim accreditation but follow a true "alternative" accreditation method that is virtually meaningless. They are not accredited by the same bodies that accredit real medical schools and while some courses have similar titles to the curricula of legitimate medical schools the content is completely different.
In 2015, a former naturopathic doctor, Britt Marie Hermes, who graduated from Bastyr University and practiced as a licensed ND in Washington and Arizona, began advocating against naturopathic medicine. In addition to opposing further licensure, she believes that NDs should not be allowed to use the titles "doctor" or "physician", and be barred from treating children. She states:
Naturopaths aggressively lobby for laws to issue them medical licenses. I would characterize this political effort as a perverted redefinition of the words "physician", "doctor", "medical school", and "residency" in order to mask the inadequacy of the training provided in naturopathic programs. ND students do not realize that they are taking educational shortcuts and therefore do not possess any demonstrable competencies found in modern medicine.
Traditional naturopaths

Traditional naturopaths are represented in the United States by the American Naturopathic Association (ANA), representing about 1,800 practitioners and the American Naturopathic Medical Association (ANMA).
The level of naturopathic training varies among traditional naturopaths in the United States. Traditional naturopaths may complete non-degree certificate programs or undergraduate degree programs and generally refer to themselves as naturopathic consultants. These programs often offer online unaccredited degrees, but do not offer comprehensive biomedical education or clinical training.
Traditional naturopathic practitioners surveyed in Australia perceive evidence-based medicine to be an ideological assault on their beliefs in vitalistic and holistic principles. They advocate for the integrity of natural medicine practice.
Naturopaths graduating from accredited programs argued in 2002 that their training used evidence-based scientific principles unlike traditional naturopathic programs, but this claim remains inaccurate.
Regulation
Naturopathy is practiced in many countries and is subject to different standards of regulation and levels of acceptance. The scope of practice varies widely between jurisdictions, with some covering naturopathy under medical regulation and allowing practitioners to prescribe drugs and perform minor surgery, while other jurisdictions outlaw naturopathy entirely.
Australia
In 1977, a Commonwealth Government inquiry reviewed all colleges of naturopathy in Australia and found that despite having syllabuses appearing to cover the basic biomedical sciences, actual lectures had little connection to those syllabuses and no significant practical work was available. In addition, there did not appear to be significant or systematic coverage of techniques favoured by naturopaths, such as homeopathy, Bach's floral remedies, or mineral salts.
The position of the Australian Medical Association is that "evidence-based aspects of complementary medicine can be part of patient care by a medical practitioner", but it has concerns that there is "limited efficacy evidence regarding most complementary medicine. Unproven complementary medicines and therapies can pose a risk to patient health either directly through misuse or indirectly if a patient defers seeking medical advice." The AMA's position on regulation is that "there should be appropriate regulation of complementary medicine practitioners and their activities".
In 2015, the Australian government found no clear evidence of effectiveness for naturopathy. Accordingly, In 2017 the Australian government named naturopathy as a practice that would not qualify for insurance subsidies, saying this step would "ensure taxpayer funds are expended appropriately and not directed to therapies lacking evidence".
India
In India, naturopathy is overseen by the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy (AYUSH); there is a 5½-year degree in "Bachelor of Naturopathy and Yogic Sciences" (BNYS) degree that was offered by twelve colleges in India as of August 2010. The National Institute of Naturopathy in Pune that operates under AYUSH, which was established on December 22, 1986, and encourages facilities for standardization and propagation of the existing knowledge and its application through research in naturopathy throughout India.
North America
In five Canadian provinces, seventeen U.S. states, and the District of Columbia, naturopathic doctors who are trained at an accredited school of naturopathic medicine in North America are entitled to use the designation ND or NMD. Elsewhere, the designations "naturopath", "naturopathic doctor", and "doctor of natural medicine" are generally unprotected or prohibited.
In North America, each jurisdiction that regulates naturopathy defines a local scope of practice for naturopathic doctors that can vary considerably. Some regions permit minor surgery, access to prescription drugs, spinal manipulations, midwifery (natural childbirth), and gynecology; other regions exclude these from the naturopathic scope of practice or prohibit the practice of naturopathy entirely.
Canada
Five Canadian provinces license naturopathic doctors: Ontario, British Columbia, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta. British Columbia has the largest scope of practice in Canada, allowing certified NDs to prescribe pharmaceuticals and perform minor surgeries. Ontario also permits prescription from a modified formulary list, following separate examination.
United States
- U.S. jurisdictions that currently regulate or license naturopathy include Alaska, Arizona, California, Connecticut, Colorado, Delaware, District of Columbia, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Wisconsin, Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands, Utah, Vermont, and Washington. Additionally, Virginia licenses the practice of naturopathy under a grandfather clause. (This was previously also the case in Florida, though currently no practitioners remain active under the grandfather provisions).
- U.S. jurisdictions that permit access to prescription drugs: Arizona, California, District of Columbia, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Maine, Montana, New Hampshire, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Vermont, and Washington.
- U.S. jurisdictions that permit minor surgery: Arizona, District of Columbia, Kansas, Maine, Montana, Oregon, Utah, Vermont, and Washington.
- Three U.S. states specifically prohibit the practice of naturopathy: Florida, South Carolina and Tennessee.
Switzerland
The Swiss Federal Constitution defines the Swiss Confederation and the Cantons of Switzerland within the scope of their powers to oversee complementary medicine. In particular, the Federal authorities must set up diplomas for the practice of non-scientific medicine. The first of such diplomas has been validated in April 2015 for the practice of naturopathy. There is a long tradition of naturopathy and traditional medicine in Switzerland. The Cantons of Switzerland make their own public health regulations. Although the law in certain cantons is typically monopolistic, the authorities are relatively tolerant with regard to alternative practitioners.
United Kingdom
Naturopathy is not regulated in the United Kingdom. In 2012, publicly funded universities in the United Kingdom dropped their alternative medicine programs, including naturopathy.
See also
- Appeal to nature
- Arnold Ehret
- Essential nutrient
- Friedrich Eduard Bilz
- Barbara O'Neill
- Health freedom movement
- Heilpraktiker
- Kneipp facility
- List of ineffective cancer treatments
- List of topics characterized as pseudoscience
- Megavitamin therapy
- Orthomolecular medicine
- Osteopathy and osteopathic medicine
- Phytonutrient
- Therapeutic nihilism
References
- ^ Boughton RJ, Frey B (2005). "Naturopathic Medicine". Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine (2nd ed.). Gale. Archived from the original on June 24, 2013. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- Baran GR, Kiani MF, Samuel SP (2014). "Science, Pseudoscience, and Not Science: How do They Differ?". Healthcare and Biomedical Technology in the 21st Century. pp. 19–57. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8541-4_2. ISBN 978-1-4614-8540-7.
within the traditional medical community it is considered to be quackery
- Paul S. Boyer (2001). The Oxford companion to United States history. Oxford University Press. p. 630. ISBN 978-0-19-508209-8. Retrieved January 15, 2013.
After 1847, when regular doctors organized the American Medical Association (AMA), that body led the war on "quackery", especially targeting dissenting medical groups such as homeopaths, who prescribed infinitesimally small doses of medicine. Ironically, even as the AMA attacked all homeopathy as quackery, educated homeopathic physicians were expelling untrained quacks from their ranks.
- Psychotherapy can be evidence based, or pseudoscientific however, see:
- Lilienfeld SO (December 2015). "Introduction to special section on pseudoscience in psychiatry". The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 60 (12): 531–533. doi:10.1177/070674371506001202. PMC 4679160. PMID 26720820.
Although the boundaries separating pseudoscience from science are fuzzy, pseudosciences are characterized by several warning signs – fallible but useful indicators that distinguish them from most scientific disciplines. ... In contrast to most accepted medical interventions, which are prescribed for a circumscribed number of conditions, many pseudoscientific techniques lack boundary conditions of application. For example, some proponents of Thought Field Therapy, an intervention that purports to correct imbalances in unobservable energy fields, using specified bodily tapping algorithms, maintain that it can be used to treat virtually any psychological condition, and that it is helpful not only for adults but also for children, dogs, and horses.
- Lee CM, Hunsley J (December 2015). "Evidence-based practice: separating science from pseudoscience". The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 60 (12): 534–540. doi:10.1177/070674371506001203. PMC 4679161. PMID 26720821.
TFT, a treatment applied to mood, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders, is a prime example of practice founded on pseudoscience. TFT is based on the premise that bodily energy imbalances cause negative emotions. Treatment is purported to rectify imbalances by tapping on acupuncture meridians. Virtually no peer-reviewed research supports this treatment rationale. With only methodologically weak reports available in the literature, the so-called science cited to support TFT is primarily anecdotal and does not rule out placebo effects. Despite these criticisms, the TFT website continues to advance unsupported claims about TFT's ability to cure almost any emotional problem.
- Lilienfeld SO (December 2015). "Introduction to special section on pseudoscience in psychiatry". The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 60 (12): 531–533. doi:10.1177/070674371506001202. PMC 4679160. PMID 26720820.
- ^ Jagtenberg T, Evans S, Grant A, Howden I, Lewis M, Singer J (April 2006). "Evidence-based medicine and naturopathy". Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 12 (3): 323–328. doi:10.1089/acm.2006.12.323. PMID 16646733.
- Tabish SA (2008). "Complementary and Alternative Healthcare: Is it Evidence-based?". International Journal of Health Sciences. 2 (1): v–ix. PMC 3068720. PMID 21475465.
- Goldenberg JZ, Burlingham BS, Guiltinan J, Oberg EB (August 2017). "Shifting attitudes towards research and evidence-based medicine within the naturopathic medical community". Advances in Integrative Medicine. 4 (2): 49–55. doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2017.08.003.
- ^ Atwood KC (December 2003). "Naturopathy: a critical appraisal". MedGenMed. 5 (4): 39. PMID 14745386. Archived from the original on March 2, 2013. Retrieved September 4, 2013.(registration required)
- Gorski DH (October 2014). "Integrative oncology: really the best of both worlds?". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 14 (10): 692–700. doi:10.1038/nrc3822. PMID 25230880. S2CID 33539406.
- ^ Singh S, Ernst E (2009). Naturopathy. Transworld. pp. 197–. ISBN 978-1-4090-8180-7. Archived from the original on February 6, 2016. Retrieved January 27, 2016.
many naturopaths are against mainstream medicine and advise their patients accordingly – for instance many are not in favour of vaccination.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Russell J, ed. (2009). American Cancer Society complete guide to complementary & alternative cancer therapies. American Cancer Society. pp. 116–119. ISBN 978-1-60443-054-7. OCLC 671655748.
- ^ Atwood KC (March 2004). "Naturopathy, pseudoscience, and medicine: myths and fallacies vs truth". MedGenMed. 6 (1): 33. PMC 1140750. PMID 15208545.
- Wilson K, Busse JW, Gilchrist A, Vohra S, Boon H, Mills E (March 2005). "Characteristics of pediatric and adolescent patients attending a naturopathic college clinic in Canada". Pediatrics. 115 (3): e338-43. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1901. PMID 15741360.
- Busse JW, Wilson K, Campbell JB (November 2008). "Attitudes towards vaccination among chiropractic and naturopathic students". Vaccine. 26 (49): 6237–6243. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.020. PMID 18674581.
- ^ Wilson K, Mills E, Boon H, Tomlinson G, Ritvo P (January 2004). "A survey of attitudes towards paediatric vaccinations amongst Canadian naturopathic students". Vaccine. 22 (3–4): 329–334. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.08.014. PMID 14670313.
- Engler BD, Mielczarek EV (2014). "Selling Pseudoscience: A Rent in the Fabric of American Medicine". Skeptical Inquirer. 38 (3).
- ^ "Family Physicians versus Naturopaths" (PDF). aafp.org. American Academy of Family Physicians. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 16, 2015. Retrieved July 20, 2015.
- ^ Jarvis WT (January 30, 2001) . "NCAHF Fact Sheet on Naturopathy". National Council Against Health Fraud. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- "What is Naturopathy?". College of Naturopathic Medicine website. East Grinstead, England. Archived from the original on September 18, 2010. Retrieved September 16, 2015.
- Brown PS (April 1988). "Nineteenth-century American health reformers and the early nature cure movement in Britain". Medical History. 32 (2): 174–194. doi:10.1017/S0025727300047980. PMC 1139856. PMID 3287059.
- Langley S. "History of Naturopathy". College of Naturopathic Medicine website. UK. Archived from the original on August 29, 2012.
- "How it all began". Allinson Flour website. Silver Spoon, British Sugar, Associated British Foods. Archived from the original on August 13, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2008.
- Beard JA (May 3, 2008). "A system of hygienic medicine (1886) and The advantages of wholemeal bread (1889)". BMJ. Views & Reviews: Medical Classics. 336 (7651): 1023. doi:10.1136/bmj.39562.446528.59. PMC 2364871.
- ^ "Report 12 of the Council on Scientific Affairs (A-97)" (PDF). American Medical Association. 1997. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 5, 2013. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- Lay summary in: "1997 Annual Meeting of the American Medical Association: Summaries and Recommendations of the Council on Scientific Affairs" (PDF). American Medical Association. 1997. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 2, 2014.
- ^ Baer HA (September 2001). "The sociopolitical status of U.S. naturopathy at the dawn of the 21st century". Medical Anthropology Quarterly. 15 (3): 329–346. doi:10.1525/maq.2001.15.3.329. PMID 11693035.
- ^ Barrett S (November 26, 2013). "A close look at naturopathy". QuackWatch. Archived from the original on April 6, 2011. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- Lust, Benedict cited in: Whorton JC (2002). Nature Cures : The History of Alternative Medicine in America: The History of Alternative Medicine in America. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-19-534978-8. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- "Naturopathy - Definition of Naturopathy by Merriam-Webster". Archived from the original on November 19, 2015. Retrieved October 27, 2015.
- ^ Beyerstein BL, Downie S (May 12, 2004). "Naturopathy: A Critical Analysis". NaturoWatch. QuackWatch. Archived from the original on March 7, 2009. Retrieved March 21, 2009.
- "HEW Report on Naturopathy (1968)". QuackWatch. August 30, 1999. Archived from the original on August 14, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2013. Citing: Cohen WJ (1969). Independent Practitioners Under Medicare: A Report to the Congress. United States Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. OCLC 3000280.
- ^ "Naturopathy: Report of the Australian Committee of Inquiry (1977)". NaturoWatch. QuackWatch. December 25, 2003. Archived from the original on September 6, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2013. Citing: Webb EC, et al. (1977). Report of the Committee of Inquiry into Chiropractic, Osteopathy, Homoeopathy and Naturopathy. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 978-0-642-92287-8.
- ^ "Licensed States & Licensing Authorities". American Association of Naturopathic Physicians website. 2009. Archived from the original on November 30, 2009.
- "Washington Administrative Code: Title 284, Chapter 43, Section 205: Every category of health providers". Washington State Legislature. August 28, 1999. Archived from the original on October 11, 2011. Retrieved November 19, 2010. (effective)
- Minott R (July 3, 1996). "Insuring Alternatives". NewsHour with Jim Lehrer. PBS. Online NewsHour transcript.
- ^ "Title 40, Chapter 31, Sections 10 & 20". South Carolina Code of Laws (Unannotated), Current through the end of the 2007 Regular Session. South Carolina Legislative Council. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009.
- ^ State of Tennessee (2013). "Title 63 Professions of the Healing Arts, Chapter 6 Medicine and Surgery, Part 2 General Provisions". Tennessee Code Annotated. Justia. 63.6.205 Practice of naturopathy. Archived from the original on October 7, 2013. Retrieved September 7, 2013.
- ^ AMA Scope of Practice Data Series: Naturopaths. American Medical Association (Report). 2009. Archived from the original on June 29, 2016. Retrieved July 30, 2016 – via The Alaska State Legislature.
- "https://newsmaven.io/indiancountrytoday/archive/introducing-naturopathic-doctors-to-indian-health-service-clinics-Rn_RipOYh0Kgd9KR-5Ou_A/ Archived October 5, 2019, at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ Senapathy K (May 31, 2016). "Why Is Big Naturopathy Afraid Of This Lone Whistleblower?". Forbes. US. Archived from the original on March 22, 2020. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- ^ Thielking M (October 20, 2016). "'Essentially witchcraft:' A former naturopath takes on the field". STAT. Archived from the original on October 25, 2016. Retrieved October 30, 2016.
- Devlin H (March 27, 2018). "The naturopath whistleblower: 'It is surprisingly easy to sell snake oil'". Guardian. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ^ Boon HS, Cherkin DC, Erro J, Sherman KJ, Milliman B, Booker J, et al. (October 2004). "Practice patterns of naturopathic physicians: results from a random survey of licensed practitioners in two US States". BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 4: 14. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-4-14. PMC 529271. PMID 15496231.
- ^ Caulfield T, Rachul C (September 2011). "Supported by science?: what canadian naturopaths advertise to the public". Allergy, Asthma, and Clinical Immunology. 7 (1): 14. doi:10.1186/1710-1492-7-14. PMC 3182944. PMID 21920039.
- Smith K (2012). "Homeopathy is Unscientific and Unethical". Bioethics. 26 (9): 508–512. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8519.2011.01956.x. S2CID 143067523. Archived from the original on October 29, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2017.
- Atwood KC (December 30, 2003). "Naturopathy: a critical appraisal". MedGenMed: Medscape General Medicine. 5 (4): 39. ISSN 1531-0132. PMID 14745386.
- Carroll RT (March 7, 2015). "Naturopathy". The Skeptic's Dictionary. Archived from the original on September 1, 2010. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- Nair PM, Nanda A (September 2014). "Naturopathic medicine in India: Original Article". Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies. 19 (3): 140–147. doi:10.1111/fct.12125.
- ^ Pizzorno JE (1999). "Naturopathy: Practice Issues". In Clark CC, Gordon RJ (eds.). Encyclopedia of Complementary Health Practice. Springer Publishing. pp. 57–59. ISBN 978-0-8261-1722-9. Archived from the original on April 13, 2018. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- ^ "Handbook of Accreditation for Naturopathic Medicine Programs" (PDF). Council on Naturopathic Medical Education. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 9, 2017. Retrieved November 20, 2010.
- ^ Hough HJ, Dower C, O'Neil EH (September 2001). Profile of a Profession: Naturopathic Practice (PDF). Center for the Health Professions, University of California, San Francisco. p. 54. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2008.
- ^ Young J (2007). "Chapters 8 & 13". Complementary Medicine for Dummies. Chichester, England: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-02625-0. OCLC 174043853.
- Steel A, Foley H, Bradley R, Van De Venter C, Lloyd I, Schloss J, et al. (February 2020). "Overview of international naturopathic practice and patient characteristics: results from a cross-sectional study in 14 countries". BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies. 20 (1): 59. doi:10.1186/s12906-020-2851-7. PMC 7076821. PMID 32070338.
- Ernst E (June 1997). "Colonic Irrigation and the Theory of Autointoxication: A Triumph of Ignorance over Science". Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 24 (4): 196–198. doi:10.1097/00004836-199706000-00002. PMID 9252839.
- "Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Sec. 801.415 Maximum acceptable level of ozone". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. April 1, 2015. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- Herbert V, Barrett S (1994). The Vitamin Pushers: How the "Health Food" Industry is Selling America a Bill of Goods. Buffalo, NY: Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-0-87975-909-4.
- Barrett S, Raso J (1993). Mystical Diets: Paranormal, Spiritual, and Occult Nutrition Practices. Buffalo, New York: Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-0-87975-761-8.
- Ahmad A, Ginnebaugh KR, Li Y, Padhye SB, Sarkar FH (January 2015). "Molecular targets of naturopathy in cancer research: bridge to modern medicine". Nutrients (Review). 7 (1): 321–334. doi:10.3390/nu7010321. PMC 4303842. PMID 25569626.
- ^ "Episode #050, feat. Britt Hermes". The European Skeptics Podcast. November 29, 2016. Archived from the original on September 9, 2018. Retrieved September 15, 2018.
- ^ Baggoley C (2015). "Review of the Australian Government Rebate on Natural Therapies for Private Health Insurance" (PDF). Australian Government – Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 26, 2016. Retrieved December 12, 2015.
- Lay summary in: Gavura, S. (November 19, 2015). "Australian review finds no benefit to 17 natural therapies". Science-Based Medicine.
- Haglage A, Mak T (May 25, 2016). "Trump Vitamins Were Fortified With B.S." The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved June 24, 2016.
- Hermes B (April 2020). "Dubious claims in psychotherapy for youth". Skeptical Inquirer. 44 (2): 50.
- Relman AS (April 10, 2002) . "Textbook of Natural Medicine". QuackWatch. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- ^ "MMS Testimony in Opposition to H. 1992 and S. 1205, An Act to Create a Board of Registration in Naturopathy". Massachusetts Medical Society. Archived from the original on May 22, 2016. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- Carroll R (November 26, 2012). "Natural". The Skeptic's Dictionary. Archived from the original on May 14, 2011. Retrieved September 8, 2013.
- "NCAHF Position Paper on Over the Counter Herbal Remedies (1995)". National Council Against Health Fraud. 1995. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- National Science Board (January 15, 2002). "Chapter 7 Science and Technology: Public Attitudes and Public Understanding, Section: Belief in Alternative Medicine". Science and Engineering Indicators - 2002. Arlington, VA: Division of Science Resources Statistics, National Science Foundation. Archived from the original on June 16, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2018.
- Wahlberg A (December 2007). "A quackery with a difference-new medical pluralism and the problem of 'dangerous practitioners' in the United Kingdom" (PDF). Social Science & Medicine. 65 (11): 2307–2316. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.07.024. PMID 17719708. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved December 10, 2019.
- Barrett S (March 28, 2008). "Iridology is Nonsense". QuackWatch. Archived from the original on April 6, 2011. Retrieved September 8, 2013.
- "Homeopathy". nhs.uk. October 18, 2017. Archived from the original on May 13, 2020. Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- Jarvis WT (August 1992). "Quackery: a national scandal". Clinical Chemistry. 38 (8B Pt 2): 1574–1586. PMID 1643742.
- Sutton C (April 5, 2018). "Naturopath jailed in starving baby case". news.com.au. Archived from the original on April 24, 2018. Retrieved April 24, 2018.
- Ernst E (October 2001). "Rise in popularity of complementary and alternative medicine: reasons and consequences for vaccination". Vaccine. 20 Suppl 1 (Suppl. 1, 5th European Conference on Vaccinology: A Safe Future with Vaccination): S90-3, discussion S89. doi:10.1016/S0264-410X(01)00290-0. PMID 11587822.
- Pizzorno JE, Murray MT (2011). Textbook of Natural Medicine e-edition: Text with Continually Updated Online Reference, 2-Volume Set (third ed.). Elsevier. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-4557-0527-6.
To understand how revolting these products are, let us just refer to the vaccine matter which is supposed to be an efficient preventive of smallpox. The natural system for curing disease is based on a return to nature in regulating the diet, breathing, exercising, bathing and the employment of various forces to eliminate the poisonous products in the system, and so raise the vitality of the patient to a proper standard of health.
- ^ Downey L, Tyree PT, Huebner CE, Lafferty WE (November 2010). "Pediatric vaccination and vaccine-preventable disease acquisition: associations with care by complementary and alternative medicine providers". Maternal and Child Health Journal. 14 (6): 922–930. doi:10.1007/s10995-009-0519-5. PMC 2924961. PMID 19760163. Quote is taken from introduction to paper, not from results of research presented in this paper.
- Herzog R, Álvarez-Pasquin MJ, Díaz C, Del Barrio JL, Estrada JM, Gil Á (February 2013). "Are healthcare workers' intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review". BMC Public Health. 13: 154. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-154. PMC 3602084. PMID 23421987.
- "BCNA Vaccination Position Paper". British Columbia Naturopathic Association. Archived from the original on July 19, 2014. Retrieved July 15, 2014.
- Brown H (December 21, 2007). "Influenza Virus, Vaccination and Naturopathic Practice". Naturopathic Doctor News and Review. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- "Naturopathic Primary Care" (PDF). Oregon Association of Naturopathic Physicians. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 14, 2013. Retrieved July 15, 2014.
- Larsen K (May 10, 2022). "Naturopaths, chiropractors least vaccinated of all B.C. health professionals, province says". CBC. Retrieved May 11, 2022.
- "Data published on vaccination status of regulated health professions". news.gov.bc.ca. BC Gov News. May 10, 2022. Retrieved May 11, 2022.
- ^ Robins R (May 17, 2016). "Funded by vitamin makers, naturopaths push to expand in US". STAT. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- "Naturopathy: An Introduction". National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institutes of Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services. March 2012 . Archived from the original on February 23, 2015. Retrieved March 16, 2013.
- ^ Iowa Board of Medicine (February 7, 2002). "A Policy Statement on Naturopathy". Iowa Department of Public Health, State of Iowa. Archived from the original on April 12, 2013. Retrieved September 1, 2013.
- The Platform of the American Naturopathic Association as drawn up by the Golden Jubilee Congress. July 27th – August 2nd, 1947
- Naturopathy Work Group. "Traditional Naturopathy Working Session Summary September 23 and October 1, 2008" (PDF). Minnesota Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 26, 2011. Retrieved November 20, 2010.
- ^ "Naturopathe avec diplôme fédéral". CH: State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation. Archived from the original on September 4, 2015.
- ^ "Legal Status of Traditional Medicine and Complementary/Alternative Medicine: A Worldwide Review". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on July 5, 2015. Retrieved July 4, 2015.
- "Swiss Federal Statistical Office". Switzerland. Archived from the original on July 8, 2015. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- "Naturopathic Doctors are Now Licensed in Wisconsin". AANMC. February 17, 2022. Retrieved February 21, 2022.
Wisconsin has just become the 26th U.S. state/territory to regulate naturopathic doctors.
- "Health Professions Act: Naturopathic Physicians Regulation". Victoria, British Columbia: Queen's Printer. October 2008. B.C. Reg. 282/2008 M242/2008. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- "Bylaws of the College of Naturopathic Physicians of British Columbia" (PDF).
- "Surrey city councillor and naturopath Allison Patton fined and suspended for calling herself a "physician"". February 13, 2020. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Surrey councillor fined, suspended from naturopathy for misusing 'physician' title". February 12, 2020. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "Complaint filed against Surrey naturopath-turned-councillor who campaigned as 'physician'". Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- "About Us". North American Board of Naturopathic Examiners. Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- "Naturopathy". NCCIH. Archived from the original on March 31, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ Gorski D (February 21, 2011). "Naturopathy and Science". ScienceBasedMedicine.org. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved March 3, 2016.
- Hermes B (March 13, 2015). "ND Confession, Part 1: Clinical training inside and out". Science-Based Medicine. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- Mangan KS (December 2, 1999). "Report Recommends Stripping Naturopathy Council of Its Accrediting Authority". The Chronicle of Higher Education. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- Hermes B (August 29, 2015). "ND Confession, Part II: The Accreditation of Naturopathic "Medical" Education". Science-Based Medicine. Archived from the original on July 10, 2016. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- Society for Science-Based Medicine (2014). Report to the Maryland Board of Physicians Naturopathic Advisory Committee: Recommendations for Naturopathic Regulation (Report). Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- "Accredited Naturopathic Medical Schools". Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges.
- "ND, MD/DO, NP: WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE?". Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical Colleges. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- "ND Confession, Part II: The Accreditation of Naturopathic "Medical" Education". Science-Based Medicine. August 30, 2015. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- "Handbook on CNME Postdoctoral Naturopathic Medical Education Sponsor Recognition Process and Standards (2005)" (PDF). Council on Naturopathic Medical Education. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 15, 2006.
- "Application for Licensure: Naturopathic Physician" (PDF). Division of Occupational and Professional Licensing, Utah Department of Commerce. State of Utah. February 17, 2012. p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 29, 2010. Retrieved September 8, 2013.
- ^ Carly W (April 29, 2016). "Are we being served by the regulation of naturopaths? Not if patients are still being misled". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ "ND vs MD -- Battle Lines Drawn in California". June 3, 2015. Archived from the original on July 25, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- Frosch D (February 21, 2011). "Licensing Naturopaths Incites Debate in Colorado". The New York Times. Archived from the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- Lambeck L (May 24, 2016). "New law could let Connecticut naturopathic physicians write prescriptions". Connecticut Post. Archived from the original on August 28, 2016. Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- Bellamy J (May 15, 2014). "Legislative Alchemy 2014 (so far)". Science-Based Medicine. Archived from the original on February 20, 2016. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- "Massachusetts Medical Society Testifies in Opposition to Licensing Naturopaths". Massachusetts Medical Society. May 11, 2005. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- The Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners (January 2002). "Majority Report of the Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners: A Report to the Legislature" (PDF). Massachusetts: The Special Commission on Complementary and Alternative Medical Practitioners. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 21, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2010.
- Hermes B (April 2020). "Beware the Naturopathic Cancer Quack". Skeptical Inquirer. 44 (2): 38–44.
- Belluz J (September 2, 2015). "Why one naturopath quit after watching her peers treat cancer patients". Vox. Archived from the original on October 14, 2017. Retrieved June 13, 2017.
- Jim Brown (April 10, 2016). "Former naturopathic doctor calls for an end to naturopathic pediatrics". The 180. CBC. Archived from the original on June 12, 2016. Retrieved June 8, 2016.
- Kirkey S (April 4, 2016). "Should naturopaths be restricted from treating children after tragic death of Alberta toddler?". National Post. Retrieved June 8, 2016.
- Britt H (June 21, 2016). "How A Former Naturopath Can Help Unravel The Trickery Of Alternative Medicine". Science 2.0. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- Swartout KA, ed. (2006). Encyclopedia of Associations (44 ed.). Thomson Gale. pp. 1777–1778. ISBN 978-0-7876-8286-6. Archived from the original on December 3, 2016. Retrieved September 4, 2013.
- Smith MJ, Logan AC (January 2002). "Naturopathy". The Medical Clinics of North America. 86 (1): 173–184. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(03)00079-8. PMID 11795088.
- "AMA Position Statement: Complementary Medicine - 2012". Australian Medical Association. August 28, 2012. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- Paola S (October 17, 2017). "Homeopathy, naturopathy struck off private insurance list". Australian Journal of Pharmacy. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved January 11, 2018.
- Ministry of AYUSH. Page updated August 21, 2010 AYUSH: Naturopathy Archived 2015-03-06 at the Wayback Machine. Page accessed March 21, 2015
- Ministry of AYUSH. Page updated September 23, 2010 AYUSH: National Institute of Naturopathy, Pune Archived 2015-02-20 at the Wayback Machine. Page accessed March 21, 2015
- "About: National Institute of Naturopathy". Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- "2008 Sunrise Review: Naturopathic Physicians" (PDF). Department of Regulatory Agencies. State of Colorado. January 4, 2008. pp. 18–19. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2008.
- "Questions: Education and Regulation". Canadian Association of Naturopathic Doctors website. Archived from the original on July 6, 2011. Retrieved September 6, 2013.
- "History of Naturopathic Medicine". www.cand.ca. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved February 17, 2016.
- "B.C. gives naturopaths right to prescribe drugs". CBC News. April 10, 2009. Archived from the original on August 20, 2012. Retrieved September 6, 2013.
- ^ "Naturopathic Regulatory Authority General Information Links". The Federation of Naturopathic Medicine Regulatory Authorities. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- "Ley para Reglamentar el Ejercicio de la Medicina Naturopática en Puerto Rico [Law to Regulate the Practice of Naturopathic Medicine in Puerto Rico]" (PDF) (in Spanish). December 30, 1997. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2008.
- "AN ENDANGERED SPECIES NATUROPATHIC DOCTOR IS CLOSE TO EXTINCTION". Orlando Sentinel. September 18, 1986. Retrieved November 17, 2023.
- "Review of State Laws Regulating Naturopathy". American Naturopathic Certification Board. Retrieved November 15, 2023.
- "Title XXXII REGULATION OF PROFESSIONS AND OCCUPATIONS Chapter 462 NATUROPATHY". Online Sunshine. Florida Legislature. Retrieved November 17, 2023.
- "Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation". CH. Art. 118a Complementary medicine. Archived from the original on June 21, 2016. Retrieved July 4, 2015. (English translation)
- "Swiss take an holistic approach". The Irish Times. Retrieved November 29, 2021.
- Bevanger L (January 18, 2012). "UK universities drop alternative medicine degree programs". Deutsche Welle. Archived from the original on January 25, 2012. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
External links
- Council on Naturopathic Medical Education
- American Naturopathic Medical Association
- American Association of Naturopathic Physicians
- Canadian Association of Naturopathic Doctors

