| Revision as of 15:25, 3 March 2017 edit174.205.17.76 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:11, 22 October 2024 edit undo2a02:a03f:faff:6b01:85f:65b6:8fd4:33bb (talk) Fixing vandalismTags: Manual revert Visual edit | ||
| (195 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|none}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see ] --> | |||
| {| border=1 align=right cellpadding=4 cellspacing=0 width=300 style="margin: 0.5em 0 1em 1em; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaaaaa solid; border-collapse: collapse; font-size: 95%;" | |||
| {{Infobox country geography | |||
| |+<big><big>'''Georgia'''</big></big> | |||
| | name = Georgia | |||
| |- | |||
| | map = Physical Map of Georgia (en).svg | |||
| | style="background:#efefef;" align="center" colspan="2" | | |||
| | map size = | |||
| {| border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" | |||
| | continent = ] and ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | region = ] | |||
| | align="center" width="140px" | ] | |||
| | coordinates = {{coord|42|00|N|43|30|E|type:country}} | |||
| |} | |||
| | area ranking = 119 | |||
| |- | |||
| | km area = 69,700 | |||
| | '''Continent''' || Europe / Eurasia | |||
| | percent water = {{#expr:(0/69700)*100 round 2}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | km coastline = 310 | |||
| | '''Subregion''' || ] | |||
| | exclusive economic zone = {{convert|21,946|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | borders = {{convert|1814|km|0|abbr=on}} <br> | |||
| | '''Geographic coordinates''' || {{coord|42|00|N|43|30|E|type:country}} | |||
| * ] (894 km) | |||
| |- | |||
| * ] (273 km) | |||
| | '''Area''' || {{convert|69,700|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} | |||
| * ] (219 km) | |||
| |- | |||
| * ] (428 km) | |||
| | highest point = ] {{convert|5201|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | lowest point = Between ] and ], (-1.5-2.3 m)<ref>Geography of Georgia - 9th grade book; G. Chanturia, D. Kereselidze; p. 43</ref> | |||
| | '''Land boundaries''' || 1,814 km | |||
| | longest river = ] {{convert|407|km|0|abbr=on}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | largest lake = ], {{convert|37.5|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} | |||
| | '''Countries bordered''' || Russia 894 km, Turkey 273 km, Armenia 219 km, Azerbaijan 428 km, | |||
| | climate = ] to ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | terrain = Mountainous with a coastal plain | |||
| | '''Maritime claims''' || {{convert|200|nmi|km mi|1|abbr=on|lk=in}} | |||
| | natural resources = timber, hydropower, ] deposits, ], ], minor ] and ] deposits; coastal climate and soils allow for important ] and ] growth | |||
| |- | |||
| | natural hazards = ]s | |||
| | '''Highest point''' || ], 5,201 m | |||
| | environmental issues = ] and ], ] from toxic chemicals | |||
| |- | |||
| }} | |||
| | '''Lowest point''' || ]s between ] and ], (-1.5-2.3 m)<ref>Geography of Georgia - 9th grade book; G. Chanturia, D. Kereselidze; p. 43</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| ] is a country in the ] region on the coast of the ]. Sometimes considered a ] country, it is located at the intersection of ] and ],<ref>{{Cite encyclopedia |title=Caucasus - region and mountains, Eurasia |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Caucasus |access-date=26 November 2018}} Quote: “One widely accepted scheme draws the dividing line along the crest of the Greater Caucasus range, putting the portion of the region north of the line in Europe...another scheme identifies the Aras River and the Turkish border as the line of continental demarcation, thereby locating...Georgia in Europe.”</ref> and is today generally regarded as part of Europe.<ref>International Geographic Encyclopaedia and Atlas. ]: p. 273</ref><ref>Encyclopedic World Atlas, George Philip & Son, ]: 2002, </ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Georgia - 46 States, one Europe |url=https://www.coe.int/en/web/portal/georgia |access-date=2023-08-12 |website=Council of Europe |language=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Europe - Georgia |url=https://www.who.int/georgia |access-date=2023-08-12 |website=World Health Organization |language=}}</ref> It is bordered to the north and northeast by ], to the south by ] and ], and to the southeast by ].<ref>], Andreas Dittmann, Lorenz King, Vazha Neidze (eds.): '']'', 138 pages, Steiner Verlag, 2018, {{ISBN|978-3-515-12057-9}}</ref> | |||
| | '''Longest river''' || ], 1,364 km | |||
| |- | |||
| == Location == | |||
| | '''Land Use'''<br> - Arable land<br> - Permanent<br> crops<br> - Other ||<br>5.76%<br><br>1.80%<br><br>92.44% (2012) | |||
| Georgia is largely surrounded by the ] and ] mountains, which form part of a natural boundary between Eastern Europe and West Asia. Because the ] is essentially a "historical and cultural construct",<ref>], :"The land boundary between Asia and Europe is a historical and cultural construct that has been defined variously" June 2021</ref> Georgia's continental placement has varied greatly. ] placed the boundary between Europe and Asia along the Phasis River (the modern ]), which effectively located northern parts of Georgia in Europe and the south in Asia, a convention also followed by ].<ref>'']'' 4.38. C.f. James Rennell, ''The geographical system of Herodotus examined and explained'', Volume 1, Rivington 1830, </ref> According to one 18th century definition, which set the ] as the continental boundary, Georgia and the entire Caucasus fell into Asia. However, yet another definition drew the line at ], effectively placing all of Georgia in Europe.<ref>]”, , June 2021: “another scheme identifies the Aras River and the Turkish border as the line of continental demarcation, thereby locating Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia in Europe.”</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''Climate''': || Ranging from ] to ], warm and pleasant, ]-like | |||
| Notwithstanding variations in geographic placement, Georgia's proximity to the bulk of Europe, combined with various historical, cultural and political forces, has led to its inclusion in Europe. The country has joined European organizations, such as the ] and ], and was deemed eligible to apply for membership of the ],<ref name="EU perspective">], , 17 July 2014: "...pursuant to Article 49 of the Treaty on European Union, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine – like any other European state – have a European perspective and may apply to become members of the Union…"</ref> which it did in 2022 and was ]. | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''Terrain''': || ]s, ]s, ]s | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''Natural resources''' || ], ], timber, ], ], ], ], ], and ] deposits | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''Natural hazards''' || ]s | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''Environmental issues''' || ] and ], ] from toxic chemicals | |||
| |} | |||
| ] is a country on the coast of the ]. Geographically, it has been variously classified as being entirely part of ],<ref name="Other Europes">Stephen White, Valentina Feklyunina. ''Identities and Foreign Policies in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus: The Other Europes.'' ], Oct 22, 2014 :"The Great Soviet Atlas put the entire Caucasus inside 'Europe', as far as the Turkish border with the USSR (Efremov, “Obsuzhdenie', p. 145); so did the Great Soviet Encyclopedia..."</ref><ref name="Geographic Encyclopaedia">''International Geographic Encyclopaedia and Atlas.'' ], 24 November 1979, p. 273</ref> or as having territory in both Europe and Asia.<ref name="Factbook">CIA World Factbook. , Retrieved: 23 May 2016, "land north of the Caucasus extending into Europe..."</ref> Georgia is bordered to the north and northeast by ], to the south by ] and ], and to the southeast by ]. It covers an area of {{convert|69,700|km2|sqmi}} and lies on roughly the same latitudes as ], ]; ], ]; and ], ]. | |||
| == Continental placement == | |||
| Georgia is tucked between the ] and ] mountain ranges, which form part of a natural boundary between ] and western parts of Asia. Because the Europe-Asia boundary is largely a historical and cultural concept,<ref>], :"The land boundary between Asia and Europe is a historical and cultural construct that has been defined variously" Retrieved: 23 May 2016</ref> Georgia's continental classification has varied. In modern geography, Georgia has been classified as being entirely part of Europe,<ref name="Other Europes"></ref><ref name="Geographic Encyclopaedia"></ref> as spanning both Europe and Asia,<ref name="Factbook"></ref> or various combinations thereof. | |||
| Regardless of which arbitrary continental boundary one chooses, due to historical, cultural, and political factors, Georgia is usually viewed as part of Europe and is eligible to ].<ref name="EU perspective">], , 17 July 2014: "...pursuant to Article 49 of the Treaty on European Union, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine – like any other European state – have a European perspective and may apply to become members of the Union..."</ref> Georgia is already a member of the ] and ], while also an official candidate for ] membership. By statute, all of these organizations require that a prospective member be recognized as a “European state”, a subjective concept that takes into account both geographic and socio-political factors. | |||
| ==Topography== | ==Topography== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| Despite its small area, Georgia has one of the most varied topographies of the former Soviet republics. Georgia lies mostly in the ], and its northern boundary is partly defined by the Greater Caucasus range. The Lesser Caucasus range, which runs parallel to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and the Surami and Imereti ranges, which connect the Greater Caucasus and the Lesser Caucasus, create natural barriers that are partly responsible for cultural and linguistic differences among regions. Because of their elevation and a poorly developed transportation infrastructure, many mountain villages are virtually isolated from the outside world during the winter. ]s and ]s in mountainous areas present a significant threat to life and property. Among the most recent natural disasters were massive rock- and mudslides in Ajaria in 1989 that displaced thousands in southwestern Georgia, and two earthquakes in 1991 that destroyed several villages in northcentral Georgia and South Ossetia. | |||
| Despite its small area, Georgia has one of the most varied topographies of the former Soviet republics.<ref name=":02">{{citation-attribution|1={{Cite book|last=Curtis|first=Glenn E.|url=https://www.loc.gov/item/94045459/|title=Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia : country studies|date=1995|publisher=]|isbn=0-8444-0848-4|edition=1st|location=Washington, D.C.|pages=175–177|oclc=31709972}}}}</ref> It is one of the most mountainous countries in Europe,<ref>Economic Commission for Europe. "Environmental Performance Reviews: Georgia", ]: 2016, p. 105</ref> lying mostly in the ], with its northern boundary partly defined by the Greater Caucasus range.<ref name=":02" /> The Lesser Caucasus range, which runs parallel to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and the ], which connects the Greater Caucasus and the Lesser Caucasus, create natural barriers that are partly responsible for cultural and linguistic differences among regions.<ref name=":02" /> Because of their elevation and a poorly developed transportation infrastructure, many mountain villages are virtually isolated from the outside world during the winter.<ref name=":02" /> ]s and ]s in mountainous areas present a significant threat to life and property.<ref name=":02" /> Among the most recent natural disasters were massive rock- and mudslides in Ajaria in 1989 that displaced thousands in southwestern Georgia, and two earthquakes in 1991 that destroyed several villages in ], upper ] and the ] (South Ossetia).<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| Georgia has about 25,000 rivers, many of which ] small ] stations. Drainage is into the ] to the west and through ] to the ] to the east. The largest river is the ], which flows 1,364 km from northeast Turkey across the plains of eastern Georgia, through the capital, Tbilisi, and into the Caspian Sea. The ], the largest river in western Georgia, rises in the Greater Caucasus and empties into the Black Sea at the port of ]. Soviet engineers turned the river lowlands along the Black Sea coast into prime subtropical agricultural land, embanked and straightened many stretches of river, and built an extensive system of canals. Deep mountain gorges form topographical belts within the Greater Caucasus. | |||
| Georgia has about 25,000 rivers, many of which power small ] stations.<ref name=":02" /> Drainage is into the Black Sea to the west and through Azerbaijan to the Caspian Sea to the east.<ref name=":02" /> The largest river is the ], which flows 1,364 km from northeast Turkey across the plains of eastern Georgia, through the capital, Tbilisi, and into the Caspian Sea.<ref name=":02" /> The ], the largest river in western Georgia, rises in the Greater Caucasus and empties into the Black Sea at the port of ].<ref name=":02" /> Soviet engineers turned the river lowlands along the Black Sea coast into prime subtropical agricultural land, embanked and straightened many stretches of river, and built an extensive system of canals.<ref name=":02" /> Deep mountain gorges form topographical belts within the Greater Caucasus.<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| ==Coastline== | ==Coastline== | ||
| ] | ] region, northwestern Georgia]] | ||
| ] coast of western Georgia, with the skyline of ] on the horizon.]] | ] coast of western Georgia, with the skyline of ] on the horizon.]] | ||
| The ] of Georgia about {{convert|315|km|mi}}:<ref name="NationsEncyclopedia">{{cite web |url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/economies/Europe/Georgia.html | title= Georgia |publisher= Encyclopedia of the Nations |access-date= 2 October 2012 |quote= The country has a coastline of {{convert|315|km|mi|abbr=off|sp=us}}.}}</ref> of the coastline, {{convert|57|km|mi}} is the coastline of ] (Ajara)<ref name="goBatumi">{{cite web |author= goBatumi.com |url= http://gobatumi.com/en/feelit/nature-geography |title= Geography |publisher= Website of the ] |access-date= 2 October 2012 |quote= The Ajara coastline is 57 km long. |archive-date= 9 April 2014 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20140409130828/http://gobatumi.com/en/feelit/nature-geography |url-status= dead }}</ref> and {{convert|200|km|mi}} is the coastline of ].<ref name="Proletarskaya Gazeta">{{cite web |author= Aleksey Danko |url= http://www.revolutionarydemocracy.org/rdv14n2/pgossetia.htm | title= The Class Roots and Sources of the Aggressive Actions of Georgia Against South Ossetia and Abkhazia and the Aggravation of the Situation in the Caucasus |publisher= Proletarskaya Gazeta #30 |date=November 2008 |access-date= 2 October 2012 |quote= Moreover, the Abkhazian coast stretches 200 kilometres, which has the potential to significantly increase the influence of either Russia or Georgia on the Black sea, including their military presence.}}</ref> Georgia has an ] of {{convert|21,946|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} in the ]. | |||
| The coastline of Georgia is 310 km long. Out of the Georgian coastline, 57 km is the coastline of ] (Ajara)<ref name="goBatumi">{{cite web |author= goBatumi.com |url= http://gobatumi.com/en/feelit/nature-geography | title= Geography |publisher= Website of the Department of Tourism and Resorts of Ajara Autonomous Republic |accessdate= 2 October 2012 |quote= The Ajara coastline is 57 km long.}}</ref>, and 200 km is the coastline of ]<ref name="Proletarskaya Gazeta">{{cite web |author= Aleksey Danko |url= http://www.revolutionarydemocracy.org/rdv14n2/pgossetia.htm | title= The Class Roots and Sources of the Aggressive Actions of Georgia Against South Ossetia and Abkhazia and the Aggravation of the Situation in the Caucasus |publisher= Proletarskaya Gazeta #30 |date=November 2008 |accessdate= 2 October 2012 |quote= Moreover, the Abkhazian coast stretches 200 kilometres, which has the potential to significantly increase the influence of either Russia or Georgia on the Black sea, including their military presence.}}</ref>. The ''Encyclopedia of the Nations'' lists the total length of the coastline as 315 km long.<ref name="NationsEncyclopedia">{{cite web |author= Group of editors |url=http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/economies/Europe/Georgia.html | title= Georgia |publisher= Encyclopedia of the Nations |accessdate= 2 October 2012 |quote= The country has a coastline of 315 kilometers (196 miles).}}</ref> | |||
| ==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
| ] | |||
| Georgia's climate is affected by ] influences from the west and ] influences from the east. The Greater Caucasus range moderates local climate by serving as a barrier against cold air from the north. Warm, moist air from the Black Sea moves easily into the coastal lowlands from the west. Climatic zones are determined by distance from the Black Sea and by altitude. Along the Black Sea coast, from ] to the Turkish border, and in the region known as the ] inland from the coast, the dominant subtropical climate features high humidity and heavy precipitation ({{convert|1000|to|2000|mm|in|1|abbr=on|disp=or}} per year; the Black Sea port of Batumi receives {{convert|2500|mm|in|1|abbr=on|disp=or}} per year). Several varieties of ] grow in these regions, where the midwinter average temperature is {{convert|5|°C|lk=on}} and the midsummer average is {{convert|22|°C|1}}. | |||
| Georgia's climate is affected by ] influences from the west and ] influences from the east.<ref name=":02" /> The Greater Caucasus range moderates local climate by serving as a barrier against cold air from the north.<ref name=":02" /> Warm, moist air from the Black Sea moves easily into the coastal lowlands from the west.<ref name=":02" /> Climatic zones are determined by distance from the Black Sea and by altitude.<ref name=":02" /> Along the Black Sea coast, from Abkhazia to the Turkish border, and in the region known as the ] inland from the coast, the dominant subtropical climate features high humidity and heavy precipitation ({{convert|1000|to|2000|mm|in|1|abbr=on|disp=or}} per year; the Black Sea port of Batumi receives {{convert|2500|mm|in|1|abbr=on|disp=or}} per year).<ref name=":02" /> Several varieties of ] and ] grow in these regions, where the midwinter average temperature is {{convert|5|°C|lk=on}} and the midsummer average is {{convert|22|°C|1}}.<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| The plains of eastern Georgia are shielded from the influence of the Black Sea by mountains that provide a more ]. Summer temperatures average {{convert|20|°C}} to {{convert|24|°C|1}}, winter temperatures {{convert|2|°C|1}} to {{convert|4|°C|1}}. Humidity is lower, and rainfall averages {{convert|500|to|800|mm|in|1|abbr=on}} per year. ] and ] regions in the east and west, as well as a ] region on the ] to the southeast, have distinct microclimates. | |||
| The plains of eastern Georgia are shielded from the influence of the Black Sea by mountains that provide a more ].<ref name=":02" /> Summer temperatures average {{convert|20|to|24|°C|1}}, winter temperatures {{convert|2|to|4|°C|1}}.<ref name=":02" /> Humidity is lower, and rainfall averages {{convert|500|to|800|mm|in|1|abbr=on}} per year.<ref name=":02" /> ] and ] regions in the east and west, as well as a ] region on the ] to the southeast, have distinct microclimates.<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| At higher elevations, precipitation is sometimes twice as heavy as in the eastern plains. In the west, the climate is subtropical to about {{convert|650|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}; above that altitude (and to the north and east) is a band of moist and moderately warm weather, then a band of cool and wet conditions. Alpine conditions begin at about {{convert|2100|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}, and above {{convert|3600|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} snow and ice are present year-round. | |||
| At higher elevations, precipitation is sometimes twice as heavy as in the eastern plains.<ref name=":02" /> In the west, the climate is subtropical to about {{convert|650|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}; above that altitude (and to the north and east) is a band of moist and moderately warm weather, then a band of cool and wet conditions.<ref name=":02" /> Alpine conditions begin at about {{convert|2100|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}, and above {{convert|3600|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} snow and ice are present year-round.<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| |location = Tbilisi (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1881–present) | |||
| |metric first = Yes | |||
| |single line = Yes | |||
| |width = auto | |||
| |collapsed = Yes | |||
| |Jan record high C = 19.5 | |||
| |Feb record high C = 22.4 | |||
| |Mar record high C = 28.9 | |||
| |Apr record high C = 34.4 | |||
| |May record high C = 35.1 | |||
| |Jun record high C = 40.2 | |||
| |Jul record high C = 42.0 | |||
| |Aug record high C = 40.4 | |||
| |Sep record high C = 37.9 | |||
| |Oct record high C = 33.3 | |||
| |Nov record high C = 27.2 | |||
| |Dec record high C = 22.8 | |||
| |year record high C = 42.0 | |||
| |Jan high C = 6.6 | |||
| |Feb high C = 7.7 | |||
| |Mar high C = 12.6 | |||
| |Apr high C = 18.9 | |||
| |May high C = 23.1 | |||
| |Jun high C = 28.1 | |||
| |Jul high C = 31.2 | |||
| |Aug high C = 30.9 | |||
| |Sep high C = 26.4 | |||
| |Oct high C = 19.8 | |||
| |Nov high C = 12.8 | |||
| |Dec high C = 8.4 | |||
| |year high C = 18.9 | |||
| |Jan mean C = 2.3 | |||
| |Feb mean C = 3.1 | |||
| |Mar mean C = 7.2 | |||
| |Apr mean C = 12.7 | |||
| |May mean C = 17.2 | |||
| |Jun mean C = 21.7 | |||
| |Jul mean C = 24.9 | |||
| |Aug mean C = 24.7 | |||
| |Sep mean C = 20.2 | |||
| |Oct mean C = 14.2 | |||
| |Nov mean C = 7.9 | |||
| |Dec mean C = 3.7 | |||
| |year mean C = 13.3 | |||
| |Jan low C = -0.8 | |||
| |Feb low C = 0.0 | |||
| |Mar low C = 3.2 | |||
| |Apr low C = 8.4 | |||
| |May low C = 12.4 | |||
| |Jun low C = 16.5 | |||
| |Jul low C = 19.8 | |||
| |Aug low C = 19.5 | |||
| |Sep low C = 15.4 | |||
| |Oct low C = 10.4 | |||
| |Nov low C = 4.9 | |||
| |Dec low C = 1.3 | |||
| |year low C = 9.3 | |||
| |Jan record low C = -24.4 | |||
| |Feb record low C = −14.8 | |||
| |Mar record low C = −12.8 | |||
| |Apr record low C = -3.8 | |||
| |May record low C = 1.0 | |||
| |Jun record low C = 6.3 | |||
| |Jul record low C = 9.3 | |||
| |Aug record low C = 8.9 | |||
| |Sep record low C = 0.8 | |||
| |Oct record low C = -6.4 | |||
| |Nov record low C = −7.1 | |||
| |Dec record low C = −20.5 | |||
| |year record low C = -24.4 | |||
| |precipitation colour = green | |||
| |Jan precipitation mm = 21 | |||
| |Feb precipitation mm = 23 | |||
| |Mar precipitation mm = 29 | |||
| |Apr precipitation mm = 51 | |||
| |May precipitation mm = 92 | |||
| |Jun precipitation mm = 85 | |||
| |Jul precipitation mm = 49 | |||
| |Aug precipitation mm = 37 | |||
| |Sep precipitation mm = 27 | |||
| |Oct precipitation mm = 41 | |||
| |Nov precipitation mm = 29 | |||
| |Dec precipitation mm = 23 | |||
| |year precipitation mm = 507 | |||
| |Jan humidity = 74 | |||
| |Feb humidity = 72 | |||
| |Mar humidity = 68 | |||
| |Apr humidity = 66 | |||
| |May humidity = 67 | |||
| |Jun humidity = 64 | |||
| |Jul humidity = 61 | |||
| |Aug humidity = 62 | |||
| |Sep humidity = 66 | |||
| |Oct humidity = 73 | |||
| |Nov humidity = 76 | |||
| |Dec humidity = 76 | |||
| |year humidity = 69 | |||
| |Jan rain days = 4 | |||
| |Feb rain days = 4 | |||
| |Mar rain days = 8 | |||
| |Apr rain days = 12 | |||
| |May rain days = 12 | |||
| |Jun rain days = 10 | |||
| |Jul rain days = 7 | |||
| |Aug rain days = 8 | |||
| |Sep rain days = 9 | |||
| |Oct rain days = 10 | |||
| |Nov rain days = 10 | |||
| |Dec rain days = 6 | |||
| |year rain days = 100 | |||
| |Jan snow days = 6 | |||
| |Feb snow days = 8 | |||
| |Mar snow days = 3 | |||
| |Apr snow days = 0.1 | |||
| |May snow days = 0 | |||
| |Jun snow days = 0 | |||
| |Jul snow days = 0 | |||
| |Aug snow days = 0 | |||
| |Sep snow days = 0 | |||
| |Oct snow days = 0.1 | |||
| |Nov snow days = 1 | |||
| |Dec snow days = 4 | |||
| |year snow days = 22 | |||
| |Jan sun = 99 | |||
| |Feb sun = 102 | |||
| |Mar sun = 142 | |||
| |Apr sun = 171 | |||
| |May sun = 213 | |||
| |Jun sun = 249 | |||
| |Jul sun = 256 | |||
| |Aug sun = 248 | |||
| |Sep sun = 206 | |||
| |Oct sun = 164 | |||
| |Nov sun = 103 | |||
| |Dec sun = 93 | |||
| |year sun = 2046 | |||
| |source 1 = Pogoda.ru.net<ref name=Tbilisipogoda>{{cite web | |||
| | url = http://www.pogodaiklimat.ru/climate2/37545.htm | |||
| | script-title = ru:Погода и Климат | |||
| | publisher = Pogodaiklimat.ru | |||
| | language = ru | |||
| | access-date = 19 October 2016 | |||
| | archive-date = 22 March 2021 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210322113406/http://www.pogodaiklimat.ru/climate2/37545.htm | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| |source 2 = NOAA (Sunshine hours 1961–1990)<ref name=NOAATbilisi >{{cite web | |||
| | url = ftp://ftp.atdd.noaa.gov/pub/GCOS/WMO-Normals/TABLES/REG_VI/GA/37549.TXT | |||
| | title = Tbilisi/Novoalexeye Climate Normals 1961–1990 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | access-date = 19 October 2016}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| |width= auto | |||
| |metric first= Yes | |||
| |single line= Yes | |||
| |location= Mta-Sabueti (1991-2020, extremes 1981-2020) {{coord|42|02|N|43|28|E}} | |||
| |collapsed = Yes | |||
| |precipitation colour=green | |||
| |Jan precipitation mm = 150.1 | |||
| |Feb precipitation mm = 124.8 | |||
| |Mar precipitation mm = 118.6 | |||
| |Apr precipitation mm = 78.6 | |||
| |May precipitation mm = 94.2 | |||
| |Jun precipitation mm = 79.6 | |||
| |Jul precipitation mm = 54.3 | |||
| |Aug precipitation mm = 54.1 | |||
| |Sep precipitation mm = 69.3 | |||
| |Oct precipitation mm = 89.4 | |||
| |Nov precipitation mm = 122.8 | |||
| |Dec precipitation mm = 128.1 | |||
| |Jan record high C = 13.3 | |||
| |Feb record high C = 16.4 | |||
| |Mar record high C = 19.4 | |||
| |Apr record high C = 27.8 | |||
| |May record high C = 26.5 | |||
| |Jun record high C = 30.0 | |||
| |Jul record high C = 31.1 | |||
| |Aug record high C = 34.4 | |||
| |Sep record high C = 31.4 | |||
| |Oct record high C = 26.1 | |||
| |Nov record high C = 23.6 | |||
| |Dec record high C = 15.9 | |||
| |year record high C = 34.4 | |||
| | Jan high C =0.3 | |||
| | Feb high C =1.0 | |||
| | Mar high C =5.1 | |||
| | Apr high C =11.2 | |||
| | May high C =16.0 | |||
| | Jun high C =19.5 | |||
| | Jul high C =22.1 | |||
| | Aug high C =23.1 | |||
| | Sep high C =18.8 | |||
| | Oct high C =13.4 | |||
| | Nov high C =6.7 | |||
| | Dec high C =2.0 | |||
| | year high C = | |||
| | Jan mean C =-2.5 | |||
| | Feb mean C =-2.3 | |||
| | Mar mean C =0.9 | |||
| | Apr mean C =5.9 | |||
| | May mean C =10.8 | |||
| | Jun mean C =14.4 | |||
| | Jul mean C =17.0 | |||
| | Aug mean C =17.7 | |||
| | Sep mean C =13.7 | |||
| | Oct mean C =8.9 | |||
| | Nov mean C =3.2 | |||
| | Dec mean C =-0.8 | |||
| | year mean C = | |||
| |Jan low C= -4.7 | |||
| |Feb low C= -4.8 | |||
| |Mar low C= -2.0 | |||
| |Apr low C= 2.3 | |||
| |May low C= 7.1 | |||
| |Jun low C= 10.7 | |||
| |Jul low C= 13.5 | |||
| |Aug low C= 13.9 | |||
| |Sep low C= 10.2 | |||
| |Oct low C= 5.9 | |||
| |Nov low C= 0.7 | |||
| |Dec low C= -3.0 | |||
| |Jan record low C = -18.3 | |||
| |Feb record low C = −18.2 | |||
| |Mar record low C = −14.6 | |||
| |Apr record low C = -11.8 | |||
| |May record low C = -2.2 | |||
| |Jun record low C = 0.1 | |||
| |Jul record low C = 3.1 | |||
| |Aug record low C = 5.0 | |||
| |Sep record low C = 1.6 | |||
| |Oct record low C = -5.2 | |||
| |Nov record low C = −8.6 | |||
| |Dec record low C = −13.4 | |||
| |year record low C = -18.3 | |||
| | unit precipitation days = 1.0 mm | |||
| | Jan precipitation days =14.2 | |||
| | Feb precipitation days =13.8 | |||
| | Mar precipitation days =14.9 | |||
| | Apr precipitation days =12.2 | |||
| | May precipitation days =13.4 | |||
| | Jun precipitation days =12.4 | |||
| | Jul precipitation days =10.3 | |||
| | Aug precipitation days =9.2 | |||
| | Sep precipitation days =9.5 | |||
| | Oct precipitation days =10.7 | |||
| | Nov precipitation days =11.3 | |||
| | Dec precipitation days =13.7 | |||
| | year precipitation days =145.6 | |||
| | humidity colour = | |||
| | time day = | |||
| | daily = | |||
| | Jan humidity =88.7 | |||
| | Feb humidity =88.7 | |||
| | Mar humidity =86.6 | |||
| | Apr humidity =82.3 | |||
| | May humidity =84.5 | |||
| | Jun humidity =86.6 | |||
| | Jul humidity =86.2 | |||
| | Aug humidity =83.7 | |||
| | Sep humidity =85.8 | |||
| | Oct humidity =87.9 | |||
| | Nov humidity =87 | |||
| | Dec humidity =88.2 | |||
| | year humidity = | |||
| |source = ]<ref name="ncei91">{{cite web |title=WMO Climate Normals for 1991-2020: Mta-Sabueti-37665 |url=https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/archive/arc0216/0253808/2.2/data/0-data/Region-6-WMO-Normals-9120/Georgia/CSV/MtaSabueti_37665.csv |website=ncei.noaa.gov |publisher=] |access-date=17 March 2024 |format=CSV}}</ref><ref name="Clino81">{{cite web |title=WMO Climate Normals for 1981-2010: Mta Sabueti |url=https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/pub/data/normals/WMO/1981-2010/RA-VI/Georgia/WMO_Normals_Georgia.xls |website=ncei.noaa.gov |publisher=] |access-date=17 March 2024 |page=6 |format=XLS}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ==Environmental issues== | ==Environmental issues== | ||
| {{main|Environmental issues in Georgia}} | |||
| {{update|section}} | |||
| Beginning in the 1980s, Black Sea pollution has greatly harmed Georgia's tourist industry. Inadequate sewage treatment is the main cause of that condition. In Batumi, for example, only 18 percent of wastewater |
Beginning in the 1980s, Black Sea pollution has greatly harmed Georgia's tourist industry.<ref name=":02" /> Inadequate sewage treatment is the main cause of that condition.<ref name=":02" /> In Batumi, for example, only 18 percent of wastewater was treated before release into the sea as of the early 1990s.<ref name=":02" /> As of the early 1990s, an estimated 70 percent of surface water contained health-endangering bacteria to which Georgia's high rate of intestinal disease was attributed.<ref name=":02" /> | ||
| The war in Abkhazia did substantial damage to the ecological habitats unique to that region. In other respects, experts considered Georgia's environmental problems less serious than those of more industrialized former Soviet republics. Solving Georgia's environmental problems was not a high priority of the national government in the post-Soviet years, however; in 1993 the minister for protection of the environment resigned to protest this inactivity. In January 1994, the Cabinet of Ministers announced a new, interdepartmental environmental monitoring system to centralize separate programs under the direction of the Ministry of Protection of the Environment. The system would include a central environmental and information and research agency. The ] used its small contingent in the parliament to press environmental issues in 1993. | The war in Abkhazia did substantial damage to the ecological habitats unique to that region.<ref name=":02" /> In other respects, experts considered Georgia's environmental problems less serious than those of more industrialized former Soviet republics.<ref name=":02" /> Solving Georgia's environmental problems was not a high priority of the national government in the post-Soviet years, however; in 1993 the minister for protection of the environment resigned to protest this inactivity.<ref name=":02" /> In January 1994, the Cabinet of Ministers announced a new, interdepartmental environmental monitoring system to centralize separate programs under the direction of the Ministry of Protection of the Environment.<ref name=":02" /> The system would include a central environmental and information and research agency.<ref name=":02" /> The ] used its small contingent in the parliament to press environmental issues in 1993.<ref name=":02" /> | ||
| Georgia participates in a number of international environmental agreements. It is a party to: ], ], ], Climate Change-], ], Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, ], Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, and Wetlands. | Georgia participates in a number of international environmental agreements. It is a party to: ], ], ], Climate Change-], ], Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, ], Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, and Wetlands. | ||
| == Extreme points == | |||
| * Northernmost point: (''de jure''): ] | |||
| * Northernmost point (''de facto''): ], ] | |||
| *Southernmost point: ], ] | |||
| * Westernmost point (''de jure''): Abkhazia | |||
| *Westernmost point (''de facto''): ] | |||
| * Easternmost point: Dedoplistsqaro Municipality, Kakheti (border with ]) | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| {{Georgia (country) topics}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * is a historical map from 1827 | |||
| {{Geography of Europe}} | {{Geography of Europe}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Geography of Asia}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Georgia (Country)}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:11, 22 October 2024
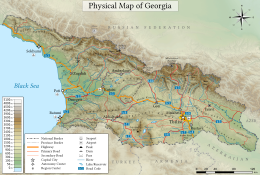 | |
| Continent | Europe and Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | Caucasus |
| Coordinates | 42°00′N 43°30′E / 42.000°N 43.500°E / 42.000; 43.500 |
| Area | Ranked 119 |
| • Total | 69,700 km (26,900 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 310 km (190 mi) |
| Borders | 1,814 km (1,127 mi)
|
| Highest point | Mount Shkhara 5,201 m (17,064 ft) |
| Lowest point | Between Poti and Kulevi, (-1.5-2.3 m) |
| Longest river | Alazani River 407 km (253 mi) |
| Largest lake | Paravani Lake, 37.5 km (14.5 sq mi) |
| Climate | Temperate to subtropical |
| Terrain | Mountainous with a coastal plain |
| Natural resources | timber, hydropower, manganese deposits, iron ore, copper, minor coal and petroleum deposits; coastal climate and soils allow for important tea and citrus growth |
| Natural hazards | earthquakes |
| Environmental issues | air and water pollution, soil pollution from toxic chemicals |
| Exclusive economic zone | 21,946 km (8,473 sq mi) |
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. Sometimes considered a transcontinental country, it is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan.
Location
Georgia is largely surrounded by the Greater Caucasus and Lesser Caucasus mountains, which form part of a natural boundary between Eastern Europe and West Asia. Because the Europe–Asia boundary is essentially a "historical and cultural construct", Georgia's continental placement has varied greatly. Anaximander placed the boundary between Europe and Asia along the Phasis River (the modern Rioni River), which effectively located northern parts of Georgia in Europe and the south in Asia, a convention also followed by Herodotus. According to one 18th century definition, which set the Kuma–Manych Depression as the continental boundary, Georgia and the entire Caucasus fell into Asia. However, yet another definition drew the line at Aras River, effectively placing all of Georgia in Europe.
Notwithstanding variations in geographic placement, Georgia's proximity to the bulk of Europe, combined with various historical, cultural and political forces, has led to its inclusion in Europe. The country has joined European organizations, such as the Council of Europe and Eurocontrol, and was deemed eligible to apply for membership of the European Union, which it did in 2022 and was recognized as a candidate member state.
Topography


Despite its small area, Georgia has one of the most varied topographies of the former Soviet republics. It is one of the most mountainous countries in Europe, lying mostly in the Caucasus Mountains, with its northern boundary partly defined by the Greater Caucasus range. The Lesser Caucasus range, which runs parallel to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and the Surami Range, which connects the Greater Caucasus and the Lesser Caucasus, create natural barriers that are partly responsible for cultural and linguistic differences among regions. Because of their elevation and a poorly developed transportation infrastructure, many mountain villages are virtually isolated from the outside world during the winter. Earthquakes and landslides in mountainous areas present a significant threat to life and property. Among the most recent natural disasters were massive rock- and mudslides in Ajaria in 1989 that displaced thousands in southwestern Georgia, and two earthquakes in 1991 that destroyed several villages in Racha, upper Imereti and the Tskhinvali Region (South Ossetia).
Georgia has about 25,000 rivers, many of which power small hydroelectric stations. Drainage is into the Black Sea to the west and through Azerbaijan to the Caspian Sea to the east. The largest river is the Kura River, which flows 1,364 km from northeast Turkey across the plains of eastern Georgia, through the capital, Tbilisi, and into the Caspian Sea. The Rioni River, the largest river in western Georgia, rises in the Greater Caucasus and empties into the Black Sea at the port of Poti. Soviet engineers turned the river lowlands along the Black Sea coast into prime subtropical agricultural land, embanked and straightened many stretches of river, and built an extensive system of canals. Deep mountain gorges form topographical belts within the Greater Caucasus.
Coastline


The coastline of Georgia about 315 kilometres (196 mi): of the coastline, 57 kilometres (35 mi) is the coastline of Ajaria (Ajara) and 200 kilometres (120 mi) is the coastline of Abkhazia. Georgia has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 21,946 km (8,473 sq mi) in the Black Sea.
Climate

Georgia's climate is affected by temperate humid influences from the west and continental influences from the east. The Greater Caucasus range moderates local climate by serving as a barrier against cold air from the north. Warm, moist air from the Black Sea moves easily into the coastal lowlands from the west. Climatic zones are determined by distance from the Black Sea and by altitude. Along the Black Sea coast, from Abkhazia to the Turkish border, and in the region known as the Colchis Lowland inland from the coast, the dominant subtropical climate features high humidity and heavy precipitation (1,000 to 2,000 mm or 39.4 to 78.7 in per year; the Black Sea port of Batumi receives 2,500 mm or 98.4 in per year). Several varieties of palm trees and citrus grow in these regions, where the midwinter average temperature is 5 °C (41 °F) and the midsummer average is 22 °C (71.6 °F).
The plains of eastern Georgia are shielded from the influence of the Black Sea by mountains that provide a more continental climate. Summer temperatures average 20 to 24 °C (68.0 to 75.2 °F), winter temperatures 2 to 4 °C (35.6 to 39.2 °F). Humidity is lower, and rainfall averages 500 to 800 mm (19.7 to 31.5 in) per year. Alpine and highland regions in the east and west, as well as a semi-arid region on the Iori Plateau to the southeast, have distinct microclimates.
At higher elevations, precipitation is sometimes twice as heavy as in the eastern plains. In the west, the climate is subtropical to about 650 m (2,133 ft); above that altitude (and to the north and east) is a band of moist and moderately warm weather, then a band of cool and wet conditions. Alpine conditions begin at about 2,100 m (6,890 ft), and above 3,600 m (11,811 ft) snow and ice are present year-round.
| Climate data for Tbilisi (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1881–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.5 (67.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
28.9 (84.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.1 (95.2) |
40.2 (104.4) |
42.0 (107.6) |
40.4 (104.7) |
37.9 (100.2) |
33.3 (91.9) |
27.2 (81.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.6 (43.9) |
7.7 (45.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.9 (87.6) |
26.4 (79.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
8.4 (47.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
12.7 (54.9) |
17.2 (63.0) |
21.7 (71.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.7 (76.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
14.2 (57.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
3.7 (38.7) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −0.8 (30.6) |
0.0 (32.0) |
3.2 (37.8) |
8.4 (47.1) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.5 (61.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.4 (50.7) |
4.9 (40.8) |
1.3 (34.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −24.4 (−11.9) |
−14.8 (5.4) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
1.0 (33.8) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
8.9 (48.0) |
0.8 (33.4) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−20.5 (−4.9) |
−24.4 (−11.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 21 (0.8) |
23 (0.9) |
29 (1.1) |
51 (2.0) |
92 (3.6) |
85 (3.3) |
49 (1.9) |
37 (1.5) |
27 (1.1) |
41 (1.6) |
29 (1.1) |
23 (0.9) |
507 (20.0) |
| Average rainy days | 4 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 100 |
| Average snowy days | 6 | 8 | 3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1 | 4 | 22 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 72 | 68 | 66 | 67 | 64 | 61 | 62 | 66 | 73 | 76 | 76 | 69 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 99 | 102 | 142 | 171 | 213 | 249 | 256 | 248 | 206 | 164 | 103 | 93 | 2,046 |
| Source 1: Pogoda.ru.net | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (Sunshine hours 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Mta-Sabueti (1991-2020, extremes 1981-2020) 42°02′N 43°28′E / 42.033°N 43.467°E / 42.033; 43.467 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
27.8 (82.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
23.6 (74.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 0.3 (32.5) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.2 (52.2) |
16.0 (60.8) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.1 (71.8) |
23.1 (73.6) |
18.8 (65.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
6.7 (44.1) |
2.0 (35.6) |
11.6 (52.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
0.9 (33.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.4 (57.9) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
13.7 (56.7) |
8.9 (48.0) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.7 (23.5) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
2.3 (36.1) |
7.1 (44.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
13.9 (57.0) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.9 (42.6) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
4.2 (39.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.3 (−0.9) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
1.6 (34.9) |
−5.2 (22.6) |
−8.6 (16.5) |
−13.4 (7.9) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 150.1 (5.91) |
124.8 (4.91) |
118.6 (4.67) |
78.6 (3.09) |
94.2 (3.71) |
79.6 (3.13) |
54.3 (2.14) |
54.1 (2.13) |
69.3 (2.73) |
89.4 (3.52) |
122.8 (4.83) |
128.1 (5.04) |
1,163.9 (45.81) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 14.2 | 13.8 | 14.9 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.4 | 10.3 | 9.2 | 9.5 | 10.7 | 11.3 | 13.7 | 145.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 88.7 | 88.7 | 86.6 | 82.3 | 84.5 | 86.6 | 86.2 | 83.7 | 85.8 | 87.9 | 87 | 88.2 | 86.4 |
| Source: NCEI | |||||||||||||
Environmental issues
Main article: Environmental issues in GeorgiaBeginning in the 1980s, Black Sea pollution has greatly harmed Georgia's tourist industry. Inadequate sewage treatment is the main cause of that condition. In Batumi, for example, only 18 percent of wastewater was treated before release into the sea as of the early 1990s. As of the early 1990s, an estimated 70 percent of surface water contained health-endangering bacteria to which Georgia's high rate of intestinal disease was attributed.
The war in Abkhazia did substantial damage to the ecological habitats unique to that region. In other respects, experts considered Georgia's environmental problems less serious than those of more industrialized former Soviet republics. Solving Georgia's environmental problems was not a high priority of the national government in the post-Soviet years, however; in 1993 the minister for protection of the environment resigned to protest this inactivity. In January 1994, the Cabinet of Ministers announced a new, interdepartmental environmental monitoring system to centralize separate programs under the direction of the Ministry of Protection of the Environment. The system would include a central environmental and information and research agency. The Green Party used its small contingent in the parliament to press environmental issues in 1993.
Georgia participates in a number of international environmental agreements. It is a party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, and Wetlands.
Extreme points
- Northernmost point: (de jure): Abkhazia
- Northernmost point (de facto): Mestia Municipality, Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti
- Southernmost point: Dedoplistsqaro Municipality, Kakheti
- Westernmost point (de jure): Abkhazia
- Westernmost point (de facto): Adjara
- Easternmost point: Dedoplistsqaro Municipality, Kakheti (border with Azerbaijan)
See also
References
- Geography of Georgia - 9th grade book; G. Chanturia, D. Kereselidze; p. 43
- "Caucasus - region and mountains, Eurasia". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 26 November 2018. Quote: “One widely accepted scheme draws the dividing line along the crest of the Greater Caucasus range, putting the portion of the region north of the line in Europe...another scheme identifies the Aras River and the Turkish border as the line of continental demarcation, thereby locating...Georgia in Europe.”
- International Geographic Encyclopaedia and Atlas. Springer: p. 273
- Encyclopedic World Atlas, George Philip & Son, Oxford University Press: 2002, p.104
- "Georgia - 46 States, one Europe". Council of Europe. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
- "Europe - Georgia". World Health Organization. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
- Nana Bolashvili, Andreas Dittmann, Lorenz King, Vazha Neidze (eds.): National Atlas of Georgia, 138 pages, Steiner Verlag, 2018, ISBN 978-3-515-12057-9
- Encyclopædia Britannica, Asia:"The land boundary between Asia and Europe is a historical and cultural construct that has been defined variously" June 2021
- Histories 4.38. C.f. James Rennell, The geographical system of Herodotus examined and explained, Volume 1, Rivington 1830, p. 244
- Encyclopedia Britannica”, Caucasus, June 2021: “another scheme identifies the Aras River and the Turkish border as the line of continental demarcation, thereby locating Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia in Europe.”
- European Parliament, European Parliament Resolution 2014/2717(RSP), 17 July 2014: "...pursuant to Article 49 of the Treaty on European Union, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine – like any other European state – have a European perspective and may apply to become members of the Union…"
- ^
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Curtis, Glenn E. (1995). Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia : country studies (1st ed.). Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division. pp. 175–177. ISBN 0-8444-0848-4. OCLC 31709972.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Curtis, Glenn E. (1995). Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia : country studies (1st ed.). Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division. pp. 175–177. ISBN 0-8444-0848-4. OCLC 31709972.
- Economic Commission for Europe. "Environmental Performance Reviews: Georgia", United Nations: 2016, p. 105
- "Georgia". Encyclopedia of the Nations. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
The country has a coastline of 315 kilometers (196 miles).
- goBatumi.com. "Geography". Website of the Department of Tourism and Resorts of Ajara Autonomous Republic. Archived from the original on 9 April 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
The Ajara coastline is 57 km long.
- Aleksey Danko (November 2008). "The Class Roots and Sources of the Aggressive Actions of Georgia Against South Ossetia and Abkhazia and the Aggravation of the Situation in the Caucasus". Proletarskaya Gazeta #30. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
Moreover, the Abkhazian coast stretches 200 kilometres, which has the potential to significantly increase the influence of either Russia or Georgia on the Black sea, including their military presence.
- Погода и Климат (in Russian). Pogodaiklimat.ru. Archived from the original on 22 March 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- "Tbilisi/Novoalexeye Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- "WMO Climate Normals for 1991-2020: Mta-Sabueti-37665" (CSV). ncei.noaa.gov. NOAA. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- "WMO Climate Normals for 1981-2010: Mta Sabueti" (XLS). ncei.noaa.gov. NOAA. p. 6. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
| Geography of Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |
| Geography of Asia | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other territories | |
