| Revision as of 13:33, 16 October 2006 edit212.219.108.9 (talk) →Works← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:53, 28 November 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1);Tag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|5th century BC Athenian Greek tragedian}} | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| {{ |
{{About|the ancient Greek playwright}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2022}} | |||
| {{Infobox person | |||
| | name = Aeschylus | |||
| | image = Herma of Aeschylus, Klas08.jpg | |||
| | caption = Roman marble '']'' of Aeschylus dating to {{circa}} 30 BC, based on an earlier bronze Greek ''herma'', dating to around 340-320 BC | |||
| | native_name = {{nobold|Αἰσχύλος}} | |||
| | native_name_lang = Greek | |||
| | birth_date = {{circa|525}}/524 BC | |||
| | birth_place = ] | |||
| | death_date = {{circa|456 BC}} (aged approximately 67) | |||
| | death_place = ], ] | |||
| | occupation = Playwright and soldier | |||
| | children = {{bulleted list| ] | Euaeon}} | |||
| | parents = Euphorion (father) | |||
| | relatives = {{unbulleted list| ] (brother) | ] (brother) | Philopatho (sister) | ] (nephew)}} | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Aeschylus''' ({{IPAc-en|UK|ˈ|iː|s|k|ɪ|l|ə|s}},<ref>Jones, Daniel; Roach, Peter, James Hartman and Jane Setter, eds. ''Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary''. 17th edition. Cambridge UP, 2006.</ref> {{IPAc-en|US|ˈ|ɛ|s|k|ɪ|l|ə|s}};<ref>. '']''.</ref> {{langx|grc|]}} {{transliteration|grc|Aischýlos}}; {{circa|525}}/524 – {{circa|456}}/455 BC) was an ] ] often described as the father of ].<ref name="F243">{{harvnb|Freeman|1999|p=243}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Schlegel, August Wilhelm von |author-link=August Wilhelm von Schlegel |page=121 |url=https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/7148 |title=Lectures on Dramatic Art and Literature|date=December 2004 }}</ref> Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work,<ref>R. Lattimore, ''Aeschylus I: Oresteia'', 4</ref> and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is largely based on inferences made from reading his surviving plays.<ref>Martin Cropp, 'Lost Tragedies: A Survey'; ''A Companion to Greek Tragedy'', p. 273</ref> According to ], he expanded the number of characters in the theatre and allowed conflict among them. Formerly, characters interacted only with the ].<ref group="nb">The remnant of a commemorative inscription, dated to the 3rd century BC, lists four, possibly eight, dramatic poets (probably including Choerilus, Phrynichus, and Pratinas) who had won ] before Aeschylus had. ] was traditionally regarded the inventor of tragedy. According to another tradition, tragedy was established in Athens in the late 530s BC, but that may simply reflect an absence of records. Major innovations in dramatic form, credited to Aeschylus by Aristotle and the anonymous source ''The Life of Aeschylus'', may be exaggerations and should be viewed with caution (Martin Cropp (2006), "Lost Tragedies: A Survey" in ''A Companion to Greek Tragedy'', pp. 272–74)</ref> | |||
| Only seven of Aeschylus's estimated 70 to 90 plays have survived in complete form. There is a long-standing ], '']'', with some scholars arguing that it may be the work of his son ]. Fragments from other plays have survived in quotations, and more continue to be discovered on Egyptian ]. These fragments often give further insights into Aeschylus' work.<ref>P. Levi, ''Greek Drama'', 159</ref> He was likely the first dramatist to present plays as a ]. His '']'' is the only extant ancient example.<ref>S. Saïd, ''Aeschylean Tragedy'', 215</ref> At least one of his plays was influenced by the ] (480–479 BC). This work, '']'', is one of very few classical Greek tragedies concerned with contemporary events, and the only one extant.<ref>S. Saïd, ''Aeschylean Tragedy'', 221</ref> The significance of the war with Persia was so great to Aeschylus and the Greeks that his epitaph commemorates his participation in the Greek victory at ] while making no mention of his success as a playwright.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Pausanias, Description of Greece, *)attika/, chapter 14, section 5 |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0159:book=1:chapter=14:section=5 |access-date=2024-01-18 |website=www.perseus.tufts.edu}}</ref> | |||
| '''Aeschylus''' (]—]; ]: '''Α{{polytonic|ἰ}}σχύλος''') was a ] of ]. | |||
| Aeschylus was the earliest of the three greatest ], the others being ] and ]. | |||
| == |
==Life== | ||
| ], Aeschylus' hometown]] | |||
| Born at ] in western Attica, he wrote his first plays in ]. His earliest surviving ] is probably '']'', performed in ]. {{cn}} In ], he participated in the ], and in ] he fought at the ]. Salamis was the subject of '']''. Written eight years later; it is now generally accepted that '']'', was written in the last decade of his life, making ''The Persians'' his earliest ]. The Suppliants was once thought to be Aeschylus's earliest surviving tragedy. Also he is known for his very big nose. | |||
| Aeschylus was born around 525 BC in ], a small town about {{convert|27|km|mi}} northwest of ], in the fertile valleys of western ].{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} Some scholars argue that the date of Aeschylus's birth may be based on counting back 40 years from his first victory in the ].<ref>Grene, David, and Richmond Lattimore, eds. The Complete Greek Tragedies: Vol. 1, Aeschylus. University of Chicago Press, 1959.</ref> His family was wealthy and well established. His father, Euphorion, was said to be a member of the ], the ancient nobility of Attica,<ref name="Bates">{{harvnb |Bates |1906 |pp=53–59}}</ref><ref name=EB1911>{{harvnb |Sidgwick |1911 |p=272}}</ref> but this might be a fiction invented by the ancients to account for the grandeur of Aeschylus' plays.<ref>S. Saïd, ''Eschylean tragedy'', 217</ref> | |||
| As a youth, Aeschylus worked at a vineyard until, according to the 2nd-century AD geographer ], the god ] visited him in his sleep and commanded him to turn his attention to the nascent art of tragedy.<ref name=Bates/> As soon as he woke, he began to write a tragedy, and his first performance took place in 499 BC, when he was 26 years old.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}}<ref name=Bates/> He won his first victory at the Dionysia in 484 BC.<ref name=Bates/><ref name="F241">{{harvnb |Freeman |1999 |p=241}}</ref> | |||
| P.W. Buckham writes that Aeschylus was considered philosophically a ] and this was evidenced in some of his works.{{rf|1|Buckham1}} He also writes and quotes ] that Aeschylus was the inventor of tragedy. {{rf|2|Buckham2}} | |||
| In 510 BC, when Aeschylus was 15 years old, ] expelled the sons of ] from Athens, and ] came to power. Cleisthenes' reforms included a system of registration that emphasized the importance of the ] over family tradition. In the last decade of the 6th century, Aeschylus and his family were living in the deme of Eleusis.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472">Kopff 1997 pp. 1–472</ref> | |||
| Aeschylus frequently travelled to ], where the ] of ] was one of his patrons. In ] he travelled there for the last time; according to traditional legend, Aeschylus was killed in ] when an ] (or more likely a ]) dropped a live, and very savage ] on him, apparently because the bird mistook his ] head for a stone. Some accounts differ, claiming that the bird dropped a ''stone'' on his head, mistaking it for a large egg...a very shiny egg... | |||
| The ] played a large role in Aeschylus' life and career. In 490 BC, he and his brother ] fought to defend Athens against the invading army of ] at the ].{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} The Athenians emerged triumphant, and the victory was celebrated across the city-states of Greece.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} Cynegeirus was killed while trying to prevent a Persian ship retreating from the shore, for which his countrymen extolled him as a hero.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}}<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| The inscription on his gravestone may have been written by him, but makes no mention of his ] renown, commemorating only his military achievements. It read:<br/> | |||
| In 480 BC, Aeschylus was called into military service again, together with his younger brother ], against ]'s invading forces at the ]. Aeschylus also fought at the ] in 479 BC.<ref>{{Cite book | |||
| :''This tomb the dust of Aeschylus doth hide, <br/> | |||
| |url=https://topostext.org/work/229#4|access-date=2023-02-23 | |||
| :''Euphorion's son and fruitful Gela's pride <br/> | |||
| | title = Anonymous Life of Aeschylus | |||
| :''How tried his valor, Marathon may tell <br/> | |||
| | chapter= § 4 | |||
| :''And long-haired Medes, who knew it all too well | |||
| | translator = S. Burges Watson | |||
| | series = Living Poets | |||
| | publisher=Durham | |||
| | year =2014 | |||
| | quote = They say that he was noble and that he participated in the battle of '''Marathon''' together with his brother, '''Cynegirus''', and in the naval battle at '''Salamis''' with the youngest of his brothers, '''Ameinias''', and in the infantry battle at '''Plataea'''.}} (emphasis in original)</ref> ] was a witness for Aeschylus' war record and his contribution in Salamis.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472" /> Salamis holds a prominent place in ''The Persians'', his oldest surviving play, which was performed in 472 BC and won first prize at the Dionysia.<ref name="S34">{{harvnb |Sommerstein |2010 |p=34}}</ref> | |||
| Aeschylus was one of many Greeks who were initiated into the ], an ancient cult of ] based in his home town of Eleusis.<ref>{{harvnb |Martin |2000 |loc=§10.1}}</ref> According to ], Aeschylus was accused of ] (impiety) for revealing some of the cult's secrets on stage.<ref>'']'' 1111a8–10.</ref><ref>Filonik, J. (2013). Athenian impiety trials: a reappraisal. Dike-Rivista di Storia del Diritto Greco ed Ellenistico, 16, page 23.</ref><ref name=EB1911/> | |||
| In ]: <br/> | |||
| Other sources claim that an angry mob tried to kill Aeschylus on the spot but he fled the scene. ] asserts that the audience tried to stone Aeschylus. Aeschylus took refuge at the altar in the orchestra of the Theater of Dionysus. He pleaded ignorance at his trial. He was acquitted, with the jury sympathetic to the military service of him and his brothers during the Persian Wars. According to the 2nd-century AD author Aelian, Aeschylus' younger brother Ameinias helped to acquit Aeschylus by showing the jury the stump of the hand he had lost at Salamis, where he was voted bravest warrior. The truth is that the award for bravery at Salamis went not to Aeschylus' brother but to Ameinias of Pallene.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472" /> | |||
| {{polytonic|Αἰσχύλον Εὐφορίωνος Ἀθηναῖον τόδε κεύθει}}<br/> | |||
| :{{polytonic|μνῆμα καταφθίμενον πυροφόροιο Γέλας·}}<br/> | |||
| {{polytonic|ἀλκὴν δ’ εὐδόκιμον Μαραθώνιον ἄλσος ἂν εἴποι}}<br/> | |||
| :{{polytonic|καὶ βαρυχαιτήεις Μῆδος ἐπιστάμενος}}. | |||
| Aeschylus travelled to ] once or twice in the 470s BC, having been invited by ], tyrant of ], a major Greek city on the eastern side of the island. He produced ''The Women of Aetna'' during one of these trips (in honor of the city founded by Hieron), and restaged his ''Persians''.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} By 473 BC, after the death of ], one of his chief rivals, Aeschylus was the yearly favorite in the Dionysia, winning first prize in nearly every competition.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} In 472 BC, Aeschylus staged the production that included the ''Persians'', with ] serving as '']''.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| ==Personal life== | |||
| (''Anthologiae Graecae Appendix'', vol. 3, ''Epigramma sepulcrale'' 17) | |||
| Aeschylus married and had two sons, ] and Euaeon, both of whom became tragic poets. Euphorion won first prize in 431 BC in competition against both ] and ].<ref>{{cite book|title=The complete idiot's guide to classical mythology|author1=Osborn, K. |author2=Burges, D.|year=1998|publisher=Penguin|isbn=978-0-02-862385-6}}</ref> A nephew of Aeschylus, ] (his sister's son), was also a tragic poet, and won first prize in the competition against Sophocles' '']''.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/><ref name="Smith">{{harvnb |Smith |2005 |p=1}}</ref> Aeschylus had at least two brothers, ] and ]. | |||
| ==Death== | |||
| ]<ref>{{cite journal |title=Meditation in Solitude |author=Ursula Hoff |journal=Journal of the Warburg Institute |volume=1 |year=1938 |pages=292–294 |jstor=749994 |issue=44 |doi=10.2307/749994|s2cid=192234608 }}</ref>]] | |||
| In 458 BC, Aeschylus returned to Sicily for the last time, visiting the city of ], where he died in 456 or 455 BC. ] wrote that he was killed outside the city by a tortoise dropped by an eagle which had mistaken his head for a rock suitable for shattering the shell, and killed him.<ref name=CGC/> ], in his '']'', adds that Aeschylus had been staying outdoors to avoid a prophecy that he would be killed by a falling object,<ref name=CGC>{{citation |page=136 |quote=The unusual nature of Aeschylus' death ... |title=A Cabinet of Greek Curiosities: Strange Tales and Surprising Facts from the Cradle of Western Civilization |author =J. C. McKeown |publisher=] |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-19-998210-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author1=Pliny the Elder |title=The Natural History |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.02.0137%3Abook%3D10%3Achapter%3D3 |chapter=Book X, Chapter 3 |quote=This eagle has the instinct to break the shell of the tortoise by letting it fall from aloft, a circumstance which caused the death of the poet Æschylus. An oracle, it is said, had predicted his death on that day by the fall of a house, upon which he took the precaution of trusting himself only under the canopy of the heavens.}}</ref> but this story may be legendary and due to a misunderstanding of the iconography on Aeschylus' tomb.<ref>Critchley 2009</ref> Aeschylus' work was so respected by the Athenians that after his death his tragedies were the only ones allowed to be restaged in subsequent competitions.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} His sons ] and Euæon and his nephew Philocles also became playwrights.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}} | |||
| The inscription on Aeschylus' gravestone makes no mention of his theatrical renown, commemorating only his military achievements: | |||
| {{poemquote| | |||
| {{lang|grc|Αἰσχύλον Εὐφορίωνος Ἀθηναῖον τόδε κεύθει | |||
| μνῆμα καταφθίμενον πυροφόροιο Γέλας· | |||
| ἀλκὴν δ' εὐδόκιμον Μαραθώνιον ἄλσος ἂν εἴποι | |||
| καὶ βαθυχαιτήεις Μῆδος ἐπιστάμενος}} | |||
| Beneath this stone lies Aeschylus, son of Euphorion, the Athenian, | |||
| who perished in the wheat-bearing land of Gela; | |||
| of his noble prowess the grove of Marathon can speak, | |||
| and the long-haired Persian knows it well.|source={{cite book |title=Anthologiae Graecae Appendix, vol. 3, Epigramma sepulcrale |page=17}}}} | |||
| ==Works== | ==Works== | ||
| ] in Athens, where many of Aeschylus's plays were performed]] | |||
| Aeschylus' work has a strong moral and religious emphasis, concentrating on man's position in the cosmos in relation to the gods, divine law and divine punishment in the ] trilogy, which was quite a bit like the star wars trilogy, but with less jedi. Besides the literary merit of his work, Aeschylus' greatest contribution to the theater was the addition of a second actor to his scenes. Previously, the action took place between a single actor and the ]. This invention was attributed to him by Aristotle. | |||
| ] | |||
| The seeds of Greek drama were sown in religious festivals for the gods, chiefly ], the god of wine.<ref name=F241/> During Aeschylus' lifetime, dramatic competitions became part of the ], held in spring.<ref name=F241/> The festival opened with a procession which was followed by a competition of boys singing ]s, and all culminated in a pair of dramatic competitions.<ref name="F242">{{harvnb |Freeman |1999 |p=242}}</ref> The first competition Aeschylus would have participated in involved three playwrights each presenting three tragedies and one ].<ref name=F242/> A second competition involving five comedic playwrights followed, and the winners of both competitions were chosen by a panel of judges.<ref name=F242/> | |||
| Aeschylus entered many of these competitions, and various ancient sources attribute between seventy and ninety plays to him.<ref name="F243"/><ref name="P222"/> Only seven tragedies attributed to him have survived intact: '']'', '']'', '']'', the trilogy known as '']'' (the three tragedies '']'', '']'' and '']''), and '']'' (whose authorship is disputed). With the exception of this last play – the success of which is uncertain – all of Aeschylus's ] tragedies are known to have won first prize at the City Dionysia. | |||
| Aeschylus is known to have written about 76 plays, only 6 of which survive (its quite depressing really...): | |||
| *'']'' (]) (''Persai'') | |||
| *'']'' (]) (''Hepta epi Thebas'') | |||
| *'']'' (]?) (''Hiketides'') | |||
| *'']'' (]) | |||
| **'']'' | |||
| **'']'' (''Choephoroi'') | |||
| **'']'' | |||
| The Alexandrian ''Life of Aeschylus'' claims that he won the first prize at the City Dionysia thirteen times. This compares favorably with Sophocles' reported eighteen victories (with a substantially larger catalogue, an estimated 120 plays), and dwarfs the five victories of Euripides, who is thought to have written roughly 90 plays. | |||
| In addition, the existing canon of Aeschylus' plays includes a seventh, '']''. Attributed to Aeschylus in ], it is generally considered by modern scholars to be the work of an unknown playwright. One theory is that it was written by Euphorion, one of Aeschylus' sons, and produced as his father's work. Its language is much simpler than that which Aeschylus usually utilises, without nearly as much complex metaphor and imagery, and is closer to Sophocles' style (though it is not at all suggested that Sophocles is its author); its hostility to the figure of ] is completely at odds with the religious views of the other six plays. We know it must have been written before 429 BC, as ] makes reference to this play in his own ''The Wealth Gods''. | |||
| ===Trilogies=== | |||
| Lost and fragmentary plays include ''Phineas'', ''Glaukos Potnieus'' and ''Prometheus Pyrkaeus'', a ], belonging to the same tetralogy as ]; ''Laios'', ''Oedipus'' and ''Sphynx'', another satyr play, belonging to the same tetralogy as ]; ''Proteus'', the satyr play belonging to the Oresteia tetralogy; ''Eleusians'' and ''The Net-pullers''. | |||
| One hallmark of Aeschylean ] appears to have been his tendency to write connected trilogies in which each play serves as a chapter in a continuous dramatic narrative.<ref>{{harvnb |Sommerstein |2010}}</ref> The '']'' is the only extant example of this type of connected trilogy, but there is evidence that Aeschylus often wrote such trilogies. The satyr plays that followed his tragic trilogies also drew from myth. | |||
| --- in english--- | |||
| you f***ing nerds get a life | |||
| The satyr play ], which followed the ''Oresteia'', treated the story of Menelaus' detour in Egypt on his way home from the ]. It is assumed, based on the evidence provided by a catalogue of Aeschylean play titles, ], and play fragments recorded by later authors, that three other extant plays of his were components of connected trilogies: ''Seven Against Thebes'' was the final play in an Oedipus trilogy, and ''The Suppliants'' and ''Prometheus Bound'' were each the first play in a Danaid trilogy and Prometheus trilogy, respectively. Scholars have also suggested several completely lost trilogies, based on known play titles. A number of these treated myths about the Trojan War. One, collectively called the '']'', comprised ''Myrmidons'', ''Nereids'' and ''Phrygians'' (alternately, ''The Ransoming of Hector''). | |||
| Another trilogy apparently recounted the entrance of the Trojan ally ] into the war, and his death at the hands of Achilles (''Memnon'' and ''The Weighing of Souls'' being two components of the trilogy). ''The Award of the Arms'', ''The Phrygian Women'', and ''The Salaminian Women'' suggest a trilogy about the madness and subsequent suicide of the Greek hero ]. Aeschylus seems to have written about ]' return to Ithaca after the war (including his killing of his wife ]'s suitors and its consequences) in a trilogy consisting of ''The Soul-raisers'', ''Penelope'', and ''The Bone-gatherers''. Other suggested trilogies touched on the myth of Jason and the Argonauts (''Argô'', ''Lemnian Women'', ''Hypsipylê''), the life of Perseus (''The Net-draggers'', ''Polydektês'', ''Phorkides''), the birth and exploits of Dionysus (''Semele'', ''Bacchae'', ''Pentheus''), and the aftermath of the war portrayed in ''Seven Against Thebes'' (''Eleusinians'', ''Argives'' (or ''Argive Women''), ''Sons of the Seven'').{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010|p=34}} | |||
| ==Surviving plays== | |||
| ===''The Persians'' (472 BC)=== | |||
| {{Main|The Persians}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ''The Persians'' (''Persai'') is the earliest of Aeschylus' extant plays. It was performed in 472 BC. It was based on Aeschylus' own experiences, specifically the ].<ref name="F244">{{harvnb |Freeman |1999 |p=244}}</ref> It is unique among surviving Greek tragedies in that it describes a recent historical event.<ref name=F243/> ''The Persians'' focuses on the popular Greek theme of ] and blames Persia's loss on the pride of its king.<ref name=F244/> | |||
| It opens with the arrival of a messenger in ], the Persian capital, bearing news of the catastrophic Persian defeat at Salamis, to ], the mother of the Persian King ]. Atossa then travels to the tomb of Darius, her husband, where his ghost appears, to explain the cause of the defeat. It is, he says, the result of Xerxes' hubris in building a bridge across the ], an action which angered the gods. Xerxes appears at the end of the play, not realizing the cause of his defeat, and the play closes to lamentations by Xerxes and the chorus.<ref name="Vellacott">Vellacott: 7–19</ref> | |||
| ===''Seven Against Thebes'' (467 BC)=== | |||
| {{Main|Seven Against Thebes}} | |||
| ''Seven against Thebes'' (''Hepta epi Thebas'') was performed in 467 BC. It has the contrasting theme of the interference of the gods in human affairs.<ref name=F244/>{{clarify|reason=contrasting?|date=October 2020}} Another theme, with which Aeschylus' would continually involve himself, makes its first known appearance in this play, namely that the ] was a key development of human civilization.<ref name="F244246">{{harvnb |Freeman |1999 |pp=244–46}}</ref> | |||
| The play tells the story of ] and ], the sons of the shamed king of ], ]. Eteocles and Polynices agree to share and alternate the throne of the city. After the first year, Eteocles refuses to step down. Polynices therefore undertakes war. The pair kill each other in single combat, and the original ending of the play consisted of lamentations for the dead brothers.<ref name="Aeschylus pp.7–19">Aeschylus. "Prometheus Bound, The Suppliants, Seven Against Thebes, The Persians." Philip Vellacott's Introduction, pp. 7–19. Penguin Classics.</ref> But a new ending was added to the play some fifty years later: Antigone and Ismene mourn their dead brothers, a messenger enters announcing an edict prohibiting the burial of Polynices, and Antigone declares her intention to defy this edict.<ref name="Aeschylus pp.7–19"/> The play was the third in a connected Oedipus trilogy. The first two plays were ''Laius'' and ''Oedipus''. The concluding ] was ''The Sphinx''.<ref>Sommerstein 2002, 23.</ref> | |||
| ===''The Suppliants'' (463 BC)=== | |||
| {{Main|The Suppliants (Aeschylus)}} | |||
| ] showing the ] murdering their husbands]] | |||
| Aeschylus continued his emphasis on the polis with ''The Suppliants'' (''Hiketides'') in 463 BC. The play gives tribute to the democratic undercurrents which were running through Athens and preceding the establishment of a democratic government in 461. The ] (50 daughters of ], founder of ]) flee a forced marriage to their cousins in Egypt.{{clarify|date=October 2020}} They turn to King ] of Argos for protection, but Pelasgus refuses until the people of Argos weigh in on the decision (a distinctly democratic move on the part of the king). The people decide that the Danaids deserve protection and are allowed within the walls of Argos despite Egyptian protests.<ref name="F246">{{harvnb |Freeman |1999 |p=246}}</ref> | |||
| A Danaid trilogy had long been assumed because of ''The Suppliants''' cliffhanger ending. This was confirmed by the 1952 publication of Oxyrhynchus Papyrus 2256 fr. 3. The constituent plays are generally agreed to be ''The Suppliants'' and ''The Egyptians'' and ''The Danaids''. A plausible reconstruction of the trilogy's last two-thirds runs thus:<ref>See (e.g.) Sommerstein 1996, 141–51; Turner 2001, 36–39.</ref> In ''The Egyptians'', the Argive-Egyptian war threatened in the first play has transpired. King Pelasgus was killed during the war, and Danaus rules Argos. Danaus negotiates a settlement with Aegyptus, a condition of which requires his 50 daughters to marry the 50 sons of Aegyptus. Danaus secretly informs his daughters of an oracle which predicts that one of his sons-in-law would kill him. He orders the Danaids to murder their husbands therefore on their wedding night. His daughters agree. ''The Danaids'' would open the day after the wedding.<ref name="Sommerstein 2002, 89">Sommerstein 2002, 89.</ref> | |||
| It is revealed that 49 of the 50 Danaids killed their husbands. Hypermnestra did not kill her husband, Lynceus, and helped him escape. Danaus is angered by his daughter's disobedience and orders her imprisonment and possibly execution. In the trilogy's climax and dénouement, Lynceus reveals himself to Danaus and kills him, thus fulfilling the oracle. He and Hypermnestra will establish a ruling dynasty in Argos. The other 49 Danaids are absolved of their murders, and married off to unspecified Argive men. The satyr play following this trilogy was titled ''Amymone'', after one of the Danaids.<ref name="Sommerstein 2002, 89"/> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ===''The Oresteia'' (458 BC)=== | |||
| {{Main|Oresteia}} | |||
| Besides a few missing lines, the '']'' of 458 BC is the only complete trilogy of Greek plays by any playwright still extant (of '']'', the satyr play which followed, only fragments are known).<ref name=F244/> '']'' and '']'' (''Choephoroi'') and '']''<ref name=F244246/> together tell the violent story of the family of ], king of ]. | |||
| ====''Agamemnon''==== | |||
| ] (1817)]] | |||
| Aeschylus begins in Greece, describing the return of King ] from his victory in the ], from the perspective of the townspeople (the Chorus) and his wife, ]. Dark foreshadowings build to the death of the king at the hands of his wife, who was angry that their daughter ] was killed so that the gods would restore the winds and allow the Greek fleet to sail to Troy. Clytemnestra was also unhappy that Agamemnon kept the Trojan prophetess ] as his concubine. Cassandra foretells the murder of Agamemnon and of herself to the assembled townsfolk, who are horrified. She then enters the palace knowing that she cannot avoid her fate. The ending of the play includes a prediction of the return of ], son of Agamemnon, who will seek to avenge his father.<ref name=F244246/> | |||
| ====''The Libation Bearers''==== | |||
| ''The Libation Bearers'' opens with Orestes' arrival at Agamemnon's tomb, from exile in ]. Electra meets ] there. They plan revenge against Clytemnestra and her lover, ]. Clytemnestra's account of a nightmare in which she gives birth to a snake is recounted by the chorus. This leads her to order her daughter, ], to pour libations on Agamemnon's tomb (with the assistance of libation bearers) in hope of making amends. Orestes enters the palace pretending to bear news of his own death. Clytemnestra calls in Aegisthus to learn the news. Orestes kills them both. Orestes is then beset by the ], who avenge the murders of kin in Greek mythology.<ref name=F244246/> | |||
| ====''The Eumenides''==== | |||
| The third play addresses the question of Orestes' guilt.<ref name=F244246/> The Furies drive Orestes from Argos and into the wilderness. He makes his way to the temple of Apollo and begs Apollo to drive the Furies away. Apollo had encouraged Orestes to kill Clytemnestra, so he bears some of the guilt for the murder. Apollo sends Orestes to the temple of ] with ] as a guide.<ref name=F246/> | |||
| The Furies track him down, and Athena steps in and declares that a trial is necessary. Apollo argues Orestes' case, and after the judges (including Athena) deliver a tie vote, Athena announces that Orestes is acquitted. She renames the Furies ''The Eumenides'' (The Good-spirited, or Kindly Ones), and extols the importance of reason in the development of laws. As in ''The Suppliants'', the ideals of a democratic Athens are praised.<ref name=F246/> | |||
| ===''Prometheus Bound'' (date disputed)=== | |||
| {{Main|Prometheus Bound}} | |||
| ]'' by ] (1623)]] | |||
| ''Prometheus Bound'' is attributed to Aeschylus by ancient authorities. Since the late 19th century, however, scholars have increasingly doubted this ascription, largely on stylistic grounds. Its production date is also in dispute, with theories ranging from the 480s BC to as late as the 410s.{{sfn|Sommerstein|2010}}<ref>{{harvnb |Griffith |1983 |pp=32–34}}</ref> | |||
| The play consists mostly of static dialogue.{{clarify|date=October 2020}} The ] ] is bound to a rock throughout, which is his punishment from the ] ] for providing fire to humans. The god ] and the Titan ] and the ] of ] all express sympathy for Prometheus' plight. Prometheus is met by ], a fellow victim of Zeus' cruelty. He prophesies her future travels, revealing that one of her descendants will free Prometheus. The play closes with Zeus sending Prometheus into the abyss because Prometheus will not tell him of a potential marriage which could prove Zeus' downfall.<ref name=Vellacott/> | |||
| ''Prometheus Bound'' seems to have been the first play in a trilogy, the '']''. In the second play, '']'', Heracles frees Prometheus from his chains and kills the eagle that had been sent daily to eat Prometheus' perpetually regenerating liver, then believed the source of feeling.<ref>For example: ''Agamemnon'' 432 "Many things pierce the liver"; 791–2 "No sting of true sorrow reaches the liver"; ''Eumenides'' 135 "Sting your liver with merited reproaches".</ref> We learn that Zeus has released the other Titans which he imprisoned at the conclusion of the ], perhaps foreshadowing his eventual reconciliation with Prometheus.<ref name="ReferenceA">For a discussion of the trilogy's reconstruction, see (e.g.) Conacher 1980, 100–02.</ref> | |||
| In the trilogy's conclusion, '']'', it seems that the Titan finally warns Zeus not to sleep with the sea nymph ], for she is fated to beget a son greater than the father. Not wishing to be overthrown, Zeus marries Thetis off to the mortal Peleus. The product of that union is Achilles, Greek hero of the Trojan War. After reconciling with Prometheus, Zeus probably inaugurates a festival in his honor at Athens.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| ==Lost plays== | |||
| Of Aeschylus' other plays, only titles and assorted fragments are known. There are enough fragments (along with comments made by later authors and scholiasts) to produce rough synopses for some plays. | |||
| ===''Myrmidons''=== | |||
| This play was based on books 9 and 16 of the '']''. Achilles sits in silent indignation over his humiliation at Agamemnon's hands for most of the play.{{clarify|reason=which of these is for most of the play?|date=October 2020}} Envoys from the Greek army attempt to reconcile Achilles to ], but he yields only to ], who then battles the Trojans in Achilles' armour. The bravery and death of Patroclus are reported in a messenger's speech, which is followed by mourning.<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| ===''Nereids''=== | |||
| This play was based on books 18 and 19 and 22 of the ''Iliad''. It follows the Daughters of Nereus, the sea god, who lament Patroclus' death. A messenger tells how Achilles (perhaps reconciled to Agamemnon and the Greeks) slew ].<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| ===''Phrygians'', or ''Hector's Ransom''=== | |||
| After a brief discussion with ], Achilles sits in silent mourning over Patroclus. Hermes then brings in ], who wins over Achilles and ransoms his son's body in a spectacular ]. A scale is brought on stage and Hector's body is placed in one scale and gold in the other. The dynamic dancing of the chorus of Trojans when they enter with Priam is reported by ].<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| ===''Niobe''=== | |||
| The children of ], the heroine, have been slain by ] and ] because Niobe had gloated that she had more children than their mother, ]. Niobe sits in silent mourning on stage during most of the play. In the '']'', ] quotes the line "God plants a fault in mortals when he wills to destroy a house utterly."<ref name="Kopff 1997 pp.1-472"/> | |||
| These are the remaining 71 plays ascribed to Aeschylus which are known:{{Citation needed|date=October 2022}} | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=18em}} | |||
| *''Alcmene'' | |||
| *''Amymone'' | |||
| *''The Archer-Women'' | |||
| *''The Argivian Women'' | |||
| *''The Argo'', also titled ''The Rowers'' | |||
| *''Atalanta'' | |||
| *''Athamas'' | |||
| *''Attendants of the Bridal Chamber'' | |||
| *''Award of the Arms'' | |||
| *''The Bacchae'' | |||
| *''The Bassarae'' | |||
| *''The Bone-Gatherers'' | |||
| *''The Cabeiroi'' | |||
| *''Callisto'' | |||
| *''The Carians'', also titled ''Europa'' | |||
| *''Cercyon'' | |||
| *''Children of Hercules'' | |||
| *''Circe'' | |||
| *''The Cretan Women'' | |||
| *''Cycnus'' | |||
| *''The Danaids'' | |||
| *''Daughters of Helios'' | |||
| *''Daughters of Phorcys'' | |||
| *'']'' | |||
| *''The Edonians'' | |||
| *''The Egyptians'' | |||
| *''The Escorts'' | |||
| *''Glaucus of Pontus'' | |||
| *''Glaucus of Potniae'' | |||
| *''Hypsipyle'' | |||
| *''Iphigenia'' | |||
| *''Ixion'' | |||
| *''Laius'' | |||
| *''The Lemnian Women'' | |||
| *''The Lion'' | |||
| *''Lycurgus'' | |||
| *''Memnon'' | |||
| *''The Men of Eleusis'' | |||
| *''The Messengers'' | |||
| *''The Myrmidons'' | |||
| *''The Mysians'' | |||
| *''Nemea'' | |||
| *''The Net-Draggers'' | |||
| *''The Nurses of Dionysus'' | |||
| *''Orethyia'' | |||
| *''Palamedes'' | |||
| *''Penelope'' | |||
| *''Pentheus'' | |||
| *''Perrhaibides'' | |||
| *''Philoctetes'' | |||
| *''Phineus'' | |||
| *''The Phrygian Women'' | |||
| *''Polydectes'' | |||
| *''The Priestesses'' | |||
| *''Prometheus the Fire-Bearer'' | |||
| *''Prometheus the Fire-Kindler'' | |||
| *''Prometheus Unbound'' | |||
| *''Proteus'' | |||
| *''Semele'', also titled ''The Water-Bearers'' | |||
| *''Sisyphus the Runaway'' | |||
| *''Sisyphus the Stone-Roller'' | |||
| *''The Spectators'', also titled ''Athletes of the Isthmian Games'' | |||
| *''The Sphinx'' | |||
| *''The Spirit-Raisers'' | |||
| *''Telephus'' | |||
| *''The Thracian Women'' | |||
| *''Weighing of Souls'' | |||
| *''Women of Aetna'' (two versions) | |||
| *''Women of Salamis'' | |||
| *''Xantriae'' | |||
| *''The Youths'' | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==Influence== | |||
| ===Influence on Greek drama and culture=== | |||
| ], main character in Aeschylus's only surviving trilogy '']'']] | |||
| The theatre was just beginning to evolve when Aeschylus started writing for it. Earlier playwrights such as ] had already expanded the cast to include an actor who was able to interact with the ].<ref name="P222">{{harvnb|Pomeroy|1999|p=222}}</ref> Aeschylus added a second actor, allowing for greater dramatic variety, while the chorus played a less important role.<ref name=P222/> He is sometimes credited with introducing ''skenographia'', or scene-decoration,<ref>According to ]. See Summers 2007, 23.</ref> though Aristotle gives this distinction to Sophocles.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/830001324 |title=Performance in Greek and Roman theatre |date=2013 |publisher=Brill |others=George William Mallory Harrison, Vaios Liapēs |isbn=978-90-04-24545-7 |location=Leiden |pages=111 |oclc=830001324}}</ref> Aeschylus is also said to have made the costumes more elaborate and dramatic, and made his actors wear platform boots (''cothurni'') to make them more visible to the audience.<ref>{{cite web |last= |first= |title=Aeschylus |url=https://www.poemhunter.com/aeschylus/ |website=PoemHunter |access-date=23 September 2024}}</ref> According to a later account of Aeschylus' life, the chorus of Furies in the first performance of the ''Eumenides'' were so frightening when they entered that children fainted and patriarchs urinated and pregnant women went into labour.<ref>''Life of Aeschylus''.</ref> | |||
| Aeschylus wrote his plays in verse. No violence is performed onstage. The plays have a remoteness from daily life in Athens, relating stories about the gods, or being set, like ''The Persians'', far away.<ref name="P223">{{harvnb|Pomeroy|1999|p=223}}</ref> Aeschylus' work has a strong moral and religious emphasis.<ref name=P223/> The ''Oresteia'' trilogy concentrated on humans' position in the cosmos relative to the gods and divine law and divine punishment.<ref>{{harvnb|Pomeroy|1999|pp=224–25}}</ref> | |||
| Aeschylus' popularity is evident in the praise that the comic playwright ] gives him in '']'', produced some 50 years after Aeschylus' death. Aeschylus appears as a character in the play and claims, at line 1022, that his ''Seven against Thebes'' "made everyone watching it to love being warlike".<ref name="Scharffenberger 2007 229–249">{{Cite journal |last=Scharffenberger |first=Elizabeth W. |date=2007 |title="Deinon Eribremetas": The Sound and Sense of Aeschylus in Aristophanes' "Frogs" |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/25434023 |journal=The Classical World |volume=100 |issue=3 |pages=229–249 |jstor=25434023 |issn=0009-8418}}</ref> He claims, at lines 1026–7, that with ''The Persians'' he "taught the Athenians to desire always to defeat their enemies."<ref name="Scharffenberger 2007 229–249"/> Aeschylus goes on to say, at lines 1039ff., that his plays inspired the Athenians to be brave and virtuous. | |||
| ===Influence outside Greek culture=== | |||
| Aeschylus' works were influential beyond his own time. ] draws attention to ]'s reverence of Aeschylus. Michael Ewans argues in his ''Wagner and Aeschylus. The Ring and the Oresteia'' (London: Faber. 1982) that the influence was so great as to merit a direct character by character comparison between Wagner's ''Ring'' and Aeschylus's ''Oresteia''. But a critic of that book, while not denying that Wagner read and respected Aeschylus, has described the arguments as unreasonable and forced.<ref>{{cite journal |author = Furness, Raymond |title=Reviewed work: Wagner and Aeschylus. The 'Ring' and the 'Oresteia', Michael Ewans |journal=The Modern Language Review |volume=79 |issue=1 |date=January 1984 |pages= 239–40 |jstor=3730399 |doi=10.2307/3730399}}</ref> | |||
| ] argues in the second half of his ''Aeschylus and Sophocles: Their Work and Influence'' that Aeschylus and ] have played a major part in the formation of dramatic literature from the ] to the present, specifically in French and Elizabethan drama.{{clarify|date=October 2020}} He also claims that their influence went beyond just drama and applies to literature in general, citing Milton and the Romantics.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Aeschylus and Sophocles: their Work and Influence |journal=] |volume=47 |issue=2 |pages=265 |year=1927 |doi=10.2307/625177 |last=Sheppard |first=J. T. |author-link=J. T. Sheppard |jstor=625177 }}</ref> | |||
| ]'s '']'' (1931), a trilogy of three plays set in America after the Civil War, is modeled after the ''Oresteia''. Before writing his{{clarify|reason=this?|date=October 2020}} acclaimed trilogy, O'Neill had been developing a play about Aeschylus, and he noted that Aeschylus "so changed the system of the tragic stage that he has more claim than anyone else to be regarded as the founder (Father) of Tragedy."<ref>Floyd, Virginia, ed. ''Eugene O'Neill at Work''. New York: Frederick Ungar, 1981, p. 213. {{ISBN|0-8044-2205-2}}</ref> | |||
| During his presidential campaign in 1968, Senator ] quoted the ] translation of Aeschylus on the night of the assassination of ] Kennedy was notified of King's murder before a campaign stop in Indianapolis, Indiana, and was warned not to attend the event due to fears of rioting from the mostly African-American crowd. Kennedy insisted on attending and delivered an ] that delivered news of King's death.<ref name="flickr.com">{{cite web| url = https://www.flickr.com/photos/wallyg/3645184605/| title = Virginia – Arlington National Cemetery: Robert F. Kennedy Gravesite| date = 7 June 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Robert Kennedy: Delivering News of King's Death |url=https://www.npr.org/2008/04/04/89365887/robert-kennedy-delivering-news-of-kings-death |access-date=19 June 2022 |work=National Public Radio |date=April 4, 2008}}</ref> Acknowledging the audience's emotions, Kennedy referred to his own grief at the murder of Martin Luther King and, quoting a passage from the play ''Agamemnon'' (in translation), said: "My favorite poet was Aeschylus. And he once wrote: 'Even in our sleep, pain which cannot forget falls drop by drop upon the heart, until in our own despair, against our will, comes wisdom through the awful grace of God.' What we need in the United States is not division; what we need in the United States is not hatred; what we need in the United States is not violence and lawlessness; but is love and wisdom, and compassion toward one another, and a feeling of justice toward those who still suffer within our country, whether they be white or whether they be black ... Let us dedicate ourselves to what the Greeks wrote so many years ago: to tame the savageness of man and make gentle the life of this world."<ref>{{cite book | |||
| | last= Kennedy | first= Maxwell Taylor | title= Make Gentle the Life of This World: The Vision of Robert F. Kennedy | publisher= Harcourt Brace & Company | date= 1998 | location= New York | language= English | isbn= 0-15-100-356-4}}</ref> | |||
| <ref>{{cite web | url= https://www.jfklibrary.org/learn/about-jfk/the-kennedy-family/robert-f-kennedy/robert-f-kennedy-speeches/statement-on-assassination-of-martin-luther-king-jr-indianapolis-indiana-april-4-1968 | |||
| | title= Statement on Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr. | last= Kennedy | first= Robert F. | date= April 4, 1968 | website= The John F. Kennedy Presidential Library & Museum | publisher= Papers of Robert F. Kennedy. Senate Papers. Speeches and Press Releases, Box 4, "4/1/68 - 4/10/68." John F. Kennedy Presidential Library. | access-date= July 6, 2024}}</ref> The quotation from Aeschylus was later inscribed on a memorial at the gravesite of Robert Kennedy following his own assassination.<ref name="flickr.com"/> | |||
| ==Editions== | |||
| *], ''Aeschyli Tragoediae. Editio maior'', Berlin 1914. | |||
| *], ''Aeschyli Septem Quae Supersunt Tragoediae. Editio Altera'', Oxford 1955. | |||
| *], ''Aeschyli Septem Quae Supersunt Tragoediae'', Oxford 1972. | |||
| *], ''Aeschyli Tragoediae cum incerti poetae Prometheo'', 2nd ed., Stuttgart/Leipzig 1998. | |||
| *The first translation of the seven plays into English was by ] in 1779, using blank verse for the iambic trimeters and rhymed verse for the choruses, a convention adopted by most translators for the next century. | |||
| *] produced a verse translation in English of all seven surviving plays as ''The Dramas of Aeschylus'' in 1886 | |||
| *Stefan Radt (ed.), ''Tragicorum Graecorum Fragmenta. Vol. III: Aeschylus'' (Göttingen, Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 2009) (Tragicorum Graecorum Fragmenta, 3). | |||
| *Alan H. Sommerstein (ed.), ''Aeschylus, Volume II, Oresteia: Agamemnon. Libation-bearers. Eumenides. 146'' (Cambridge, Massachusetts/London: Loeb Classical Library, 2009); ''Volume III, Fragments. 505'' (Cambridge, Massachusetts/London: Loeb Classical Library, 2008). | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * ], an asteroid named for him | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * "]" | |||
| ==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| <references group="nb" /> | |||
| * {{ent|1|Buckham1}} P.W. Buckham, p.120, "''In philosophical sentiments Aeschylus is said to have been a Pythagorean''". cf. Cicero, ], ii.9, "''Veniat Aeschylus, non poeta solum, sed etiam Pythagoreus; sic eniam accepimus''" -- "Let us see what Aeschylus says, who was not only a poet but a Pythagorean philosopher also, for that is the account which you have received of him ..." Book II.10. | |||
| * {{ent|2|Buckham2}} P.W. Buckham, p.121., quoting from ''Lectures on Dramatic Art and Literature'' by ]. "''Aeschylus is to be considered as the creator of Tragedy: in full panoplyshe sprung from his head, like Pallas from the head of Jupiter. He clad her with dignity, and gave her an appropriate stage; he was the inventor of scenic pomp, and not only instructed the chorus in singing and dancing, but appeared himself as an actor. He was the first that expanded the dialogue, and set limits to the lyrical part of tragedy, which, however, still occupies too much space in his pieces.''" | |||
| ==Citations== | |||
| its all a bit gay really | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| *{{Cite book |last=Bates |first=Alfred |year=1906 |title=The Drama: Its History, Literature, and Influence on Civilization |volume=1 |location=London |publisher=Historical Publishing Company }} | |||
| <references /> | |||
| *Bierl, A. ''Die Orestie des Aischylos auf der modernen Bühne: Theoretische Konzeptionen und ihre szenische Realizierung'' (Stuttgart: Metzler, 1997) | |||
| <!--Can we convert these to <references />, yes lets start.--> | |||
| *Cairns, D., V. Liapis, ''Dionysalexandros: Essays on Aeschylus and His Fellow Tragedians in Honour of Alexander F. Garvie'' (Swansea: The Classical Press of Wales, 2006) | |||
| *Buckham, Philip Wentworth, ''Theatre of the Greeks'', 1827. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Critchley |first=Simon |year=2009 |title=The Book of Dead Philosophers |location=London |publisher=Granta Publications |isbn=978-1-84708079-0}} | |||
| *Cicero, ''Tusculanae Quaestiones'' (]). | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Cropp |first=Martin |editor-last=Gregory |editor-first=Justine |year=2006 |title=A Companion to Greek Tragedy |publisher=Blackwell Publishing |chapter=Lost Tragedies: A Survey}} | |||
| *Pickard-Cambridge, Sir Arthur Wallace | |||
| *Deforge, B. ''Une vie avec Eschyle. Vérité des mythes'' (Paris, Les Belles Lettres, 2010) | |||
| **''Dithyramb, Tragedy, and Comedy '', 1927. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Freeman |first=Charles |year=1999 |title=The Greek Achievement: The Foundation of the Western World |location=] |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-670-88515-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/greekachievement0000free }} | |||
| **''The Theatre of Dionysus in Athens'', 1946. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Goldhill |first=Simon |year=1992 |title=Aeschylus, The Oresteia |location=] |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-521-40293-4 |url=https://archive.org/details/aeschylusorestei00gold_0 }} | |||
| **''The Dramatic Festivals of Athens'', 1953. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Griffith |first=Mark |year=1983 |title=Aeschylus' Prometheus Bound |location=] |publisher=] |isbn= 978-0-521-27011-3 }} | |||
| *Schlegel, August Wilhelm, ''Lectures on Dramatic Art and Literature'', 1809. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Herington |first=C.J. |year=1986 |title=Aeschylus |location=New Haven, CT |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-03562-9 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/aeschylus0000heri }} | |||
| *Sommerstein, Alan H., ''Greek Drama and Dramatists'', Routledge, 2002 | |||
| *{{cite journal |doi=10.2307/627808 |last=Herington |first=C.J. |year=1967 |title=Aeschylus in Sicily |journal=The Journal of Hellenic Studies |volume=87 |pages=74–85|jstor=627808 |s2cid=162400889 }} | |||
| *Sourvinou-Inwood, Christiane, ''Tragedy and Athenian Religion'', Oxford University Press, 2003. | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Kopff |first=E. Christian |title=Ancient Greek Authors |publisher=] |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-8103-9939-6 |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientgreekauth00brig }} | |||
| *Wiles, David, ''The Masked Menander: Sign and Meaning in Greek and Roman Performance'', 1991. | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Lattimore |first=Richmond |year=1953 |title=Aeschylus I: Oresteia |publisher=University of Chicago Press}} | |||
| *] (1981). ''The Lives of the Greek Poets''. University of North Carolina Press | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Lesky |first=Albin |year=1979 |title=Greek Tragedy |location=London |publisher=Benn}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Lesky |first=Albin |year=1966 |title=A History of Greek Literature |location=New York |publisher=Crowell }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Levi |first=Peter |year=1986 |title=The Oxford History of the Classical World |publisher=Oxford University Press |chapter=Greek Drama}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Martin |first=Thomas |year=2000 |title=Ancient Greece: From Prehistoric to Hellenistic Times |publisher=] }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Murray |first=Gilbert |year=1978 |title=Aeschylus: The Creator of Tragedy |location=Oxford|publisher=Clarendon Press }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Podlecki |first=Anthony J. |year=1966 |title=The Political Background of Aeschylean Tragedy |location=Ann Arbor |publisher=University of Michigan Press }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Pomeroy |first=Sarah B. |author-link=Sarah B. Pomeroy |year=1999 |title=Ancient Greece: A Political, Social, and Cultural History |location=] |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-19-509743-6 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientgreecepol00sara }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Rosenmeyer |first=Thomas G. |year=1982 |title=The Art of Aeschylus |location=Berkeley |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-04440-1 |url=https://archive.org/details/artofaeschylus00rose }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Saïd |first=Suzanne |year=2006 |title=A Companion to Greek Tragedy |publisher=Blackwell Publishing |chapter=Aeschylean Tragedy }} | |||
| *{{Cite EB1911 |wstitle=Aeschylus |volume=1 |pp=272–276|first=Arthur |last=Sidgwick}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Smith |first=Helaine |year=2005 |title=Masterpieces of Classic Greek Drama |publisher=Greenwood |isbn=978-0-313-33268-5 }} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Smyth|first=Herbert Weir|year=1922 |title=Aeschylus |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts|publisher=Harvard University Press}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Sommerstein |first=Alan H. |year=2010 |title=Aeschylean Tragedy |location=London |publisher=Duckworth |edition=2nd |isbn=978-0-7156-3824-8 }} | |||
| *— (2002). ''Greek Drama and Dramatists''. London: Routledge Press. {{ISBN|0-415-26027-2}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last=Spatz|first=Lois|year=1982|title=Aeschylus|location=Boston|publisher=Twayne Publishers Press|isbn=978-0-8057-6522-9|url=https://archive.org/details/aeschylus00spat}} | |||
| *Summers, David (2007). ''Vision, Reflection, and Desire in Western Painting''. University of North Carolina Press | |||
| *] (1973) Aeschylus and Athens: A Study in the Social Origin of Drama. London: Lawrence and Wishart (4th edition) | |||
| *{{cite journal | last1 = Turner |first1 = Chad |year = 2001 |title = Perverted Supplication and Other Inversions in Aeschylus' Danaid Trilogy |journal = Classical Journal |volume = 97 |issue = 1|pages = 27–50 |jstor=3298432}} | |||
| *Vellacott, Philip, (1961). ''Prometheus Bound and Other Plays: Prometheus Bound, Seven Against Thebes, and The Persians''. New York: Penguin Classics. {{ISBN|0-14-044112-3}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Winnington-Ingram |first=R. P. |year=1985| title=The Cambridge History of Classical Literature: Greek Literature |publisher=Cambridge University Press|chapter=Aeschylus}} | |||
| *] (1982). ''Under the sign of the shield: semiotics and Aeschylus' Seven against Thebes''. Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books, 2nd ed. 2009 (Greek studies: interdisciplinary approaches) | |||
| *Zetlin, Froma (1996). "The dynamics of misogyny: myth and mythmaking in Aeschylus's ''Oresteia''<nowiki/>", in Froma Zeitlin, ''Playing the Other: Gender and Society in Classical Greek Literature''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 87–119. | |||
| *Zeitlin, Froma (1996). "The politics of Eros in the Danaid trilogy of Aeschylus", in Froma Zeitlin, ''Playing the Other: Gender and Society in Classical Greek Literature''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 123–171. | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Sister project links |s=Author:Aeschylus |v=no |n=no |b=History of Western Theatre: Greeks to Elizabethans/Playwrights}} | |||
| {{wikisource|el:Αισχύλος|Αισχύλος}} | |||
| {{Library resources box |by=yes |onlinebooks=yes |others=yes |about=yes |label=Aeschylus |viaf= |lccn= |lcheading= |wikititle= }} | |||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| *{{Gutenberg author|id=2825}} | |||
| {{Commonscat|Aeschylus}} | |||
| *{{StandardEbooks|Standard Ebooks URL=https://standardebooks.org/ebooks/aeschylus}} | |||
| *{{FadedPage |id=Aeschylus |name=Aeschylus (translated by George Gilbert Aimé)|author=yes}} | |||
| *{{Internet Archive author}} | |||
| *{{Librivox author |id=478}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| *{{gutenberg author|id=Aeschylus|name=Aeschylus}} | |||
| * | |||
| *Available by .pdf file at Textkit:<!-- do we need all of these? --> | |||
| * | |||
| ** | |||
| * | |||
| ** | |||
| *{{cite encyclopedia |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0004%3Aid%3Daeschylus-4 |title=Aeschylus (4) |last=Crane |first=Gregory |encyclopedia=Perseus Encyclopedia}} | |||
| ** | |||
| * | |||
| ** | |||
| * | |||
| ** | |||
| * | |||
| ** | |||
| * | |||
| {{Aeschylus}} | {{Aeschylus Plays}} | ||
| {{Ancient Greece topics}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ===Fragments=== | |||
| * | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Aeschylus}} | |||
| ===''Prometheus Bound''=== | |||
| ] | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:53, 28 November 2024
5th century BC Athenian Greek tragedian This article is about the ancient Greek playwright. For other uses, see Aeschylus (disambiguation).
| Aeschylus | |
|---|---|
| Αἰσχύλος | |
 Roman marble herma of Aeschylus dating to c. 30 BC, based on an earlier bronze Greek herma, dating to around 340-320 BC Roman marble herma of Aeschylus dating to c. 30 BC, based on an earlier bronze Greek herma, dating to around 340-320 BC | |
| Born | c. 525/524 BC Eleusis |
| Died | c. 456 BC (aged approximately 67) Gela, Sicily |
| Occupation(s) | Playwright and soldier |
| Children |
|
| Parent | Euphorion (father) |
| Relatives |
|
Aeschylus (UK: /ˈiːskɪləs/, US: /ˈɛskɪləs/; Ancient Greek: Αἰσχύλος Aischýlos; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is largely based on inferences made from reading his surviving plays. According to Aristotle, he expanded the number of characters in the theatre and allowed conflict among them. Formerly, characters interacted only with the chorus.
Only seven of Aeschylus's estimated 70 to 90 plays have survived in complete form. There is a long-standing debate regarding the authorship of one of them, Prometheus Bound, with some scholars arguing that it may be the work of his son Euphorion. Fragments from other plays have survived in quotations, and more continue to be discovered on Egyptian papyri. These fragments often give further insights into Aeschylus' work. He was likely the first dramatist to present plays as a trilogy. His Oresteia is the only extant ancient example. At least one of his plays was influenced by the Persians' second invasion of Greece (480–479 BC). This work, The Persians, is one of very few classical Greek tragedies concerned with contemporary events, and the only one extant. The significance of the war with Persia was so great to Aeschylus and the Greeks that his epitaph commemorates his participation in the Greek victory at Marathon while making no mention of his success as a playwright.
Life

Aeschylus was born around 525 BC in Eleusis, a small town about 27 kilometres (17 mi) northwest of Athens, in the fertile valleys of western Attica. Some scholars argue that the date of Aeschylus's birth may be based on counting back 40 years from his first victory in the Great Dionysia. His family was wealthy and well established. His father, Euphorion, was said to be a member of the Eupatridae, the ancient nobility of Attica, but this might be a fiction invented by the ancients to account for the grandeur of Aeschylus' plays.
As a youth, Aeschylus worked at a vineyard until, according to the 2nd-century AD geographer Pausanias, the god Dionysus visited him in his sleep and commanded him to turn his attention to the nascent art of tragedy. As soon as he woke, he began to write a tragedy, and his first performance took place in 499 BC, when he was 26 years old. He won his first victory at the Dionysia in 484 BC.
In 510 BC, when Aeschylus was 15 years old, Cleomenes I expelled the sons of Peisistratus from Athens, and Cleisthenes came to power. Cleisthenes' reforms included a system of registration that emphasized the importance of the deme over family tradition. In the last decade of the 6th century, Aeschylus and his family were living in the deme of Eleusis.
The Persian Wars played a large role in Aeschylus' life and career. In 490 BC, he and his brother Cynegeirus fought to defend Athens against the invading army of Darius I of Persia at the Battle of Marathon. The Athenians emerged triumphant, and the victory was celebrated across the city-states of Greece. Cynegeirus was killed while trying to prevent a Persian ship retreating from the shore, for which his countrymen extolled him as a hero.
In 480 BC, Aeschylus was called into military service again, together with his younger brother Ameinias, against Xerxes I's invading forces at the Battle of Salamis. Aeschylus also fought at the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. Ion of Chios was a witness for Aeschylus' war record and his contribution in Salamis. Salamis holds a prominent place in The Persians, his oldest surviving play, which was performed in 472 BC and won first prize at the Dionysia.
Aeschylus was one of many Greeks who were initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries, an ancient cult of Demeter based in his home town of Eleusis. According to Aristotle, Aeschylus was accused of asebeia (impiety) for revealing some of the cult's secrets on stage.
Other sources claim that an angry mob tried to kill Aeschylus on the spot but he fled the scene. Heracleides of Pontus asserts that the audience tried to stone Aeschylus. Aeschylus took refuge at the altar in the orchestra of the Theater of Dionysus. He pleaded ignorance at his trial. He was acquitted, with the jury sympathetic to the military service of him and his brothers during the Persian Wars. According to the 2nd-century AD author Aelian, Aeschylus' younger brother Ameinias helped to acquit Aeschylus by showing the jury the stump of the hand he had lost at Salamis, where he was voted bravest warrior. The truth is that the award for bravery at Salamis went not to Aeschylus' brother but to Ameinias of Pallene.
Aeschylus travelled to Sicily once or twice in the 470s BC, having been invited by Hiero I, tyrant of Syracuse, a major Greek city on the eastern side of the island. He produced The Women of Aetna during one of these trips (in honor of the city founded by Hieron), and restaged his Persians. By 473 BC, after the death of Phrynichus, one of his chief rivals, Aeschylus was the yearly favorite in the Dionysia, winning first prize in nearly every competition. In 472 BC, Aeschylus staged the production that included the Persians, with Pericles serving as choregos.
Personal life
Aeschylus married and had two sons, Euphorion and Euaeon, both of whom became tragic poets. Euphorion won first prize in 431 BC in competition against both Sophocles and Euripides. A nephew of Aeschylus, Philocles (his sister's son), was also a tragic poet, and won first prize in the competition against Sophocles' Oedipus Rex. Aeschylus had at least two brothers, Cynegeirus and Ameinias.
Death

In 458 BC, Aeschylus returned to Sicily for the last time, visiting the city of Gela, where he died in 456 or 455 BC. Valerius Maximus wrote that he was killed outside the city by a tortoise dropped by an eagle which had mistaken his head for a rock suitable for shattering the shell, and killed him. Pliny, in his Naturalis Historiæ, adds that Aeschylus had been staying outdoors to avoid a prophecy that he would be killed by a falling object, but this story may be legendary and due to a misunderstanding of the iconography on Aeschylus' tomb. Aeschylus' work was so respected by the Athenians that after his death his tragedies were the only ones allowed to be restaged in subsequent competitions. His sons Euphorion and Euæon and his nephew Philocles also became playwrights.
The inscription on Aeschylus' gravestone makes no mention of his theatrical renown, commemorating only his military achievements:
Αἰσχύλον Εὐφορίωνος Ἀθηναῖον τόδε κεύθει
— Anthologiae Graecae Appendix, vol. 3, Epigramma sepulcrale. p. 17.
μνῆμα καταφθίμενον πυροφόροιο Γέλας·
ἀλκὴν δ' εὐδόκιμον Μαραθώνιον ἄλσος ἂν εἴποι
καὶ βαθυχαιτήεις Μῆδος ἐπιστάμενος
Beneath this stone lies Aeschylus, son of Euphorion, the Athenian,
who perished in the wheat-bearing land of Gela;
of his noble prowess the grove of Marathon can speak,
and the long-haired Persian knows it well.
Works


The seeds of Greek drama were sown in religious festivals for the gods, chiefly Dionysus, the god of wine. During Aeschylus' lifetime, dramatic competitions became part of the City Dionysia, held in spring. The festival opened with a procession which was followed by a competition of boys singing dithyrambs, and all culminated in a pair of dramatic competitions. The first competition Aeschylus would have participated in involved three playwrights each presenting three tragedies and one satyr play. A second competition involving five comedic playwrights followed, and the winners of both competitions were chosen by a panel of judges.
Aeschylus entered many of these competitions, and various ancient sources attribute between seventy and ninety plays to him. Only seven tragedies attributed to him have survived intact: The Persians, Seven Against Thebes, The Suppliants, the trilogy known as The Oresteia (the three tragedies Agamemnon, The Libation Bearers and The Eumenides), and Prometheus Bound (whose authorship is disputed). With the exception of this last play – the success of which is uncertain – all of Aeschylus's extant tragedies are known to have won first prize at the City Dionysia.
The Alexandrian Life of Aeschylus claims that he won the first prize at the City Dionysia thirteen times. This compares favorably with Sophocles' reported eighteen victories (with a substantially larger catalogue, an estimated 120 plays), and dwarfs the five victories of Euripides, who is thought to have written roughly 90 plays.
Trilogies
One hallmark of Aeschylean dramaturgy appears to have been his tendency to write connected trilogies in which each play serves as a chapter in a continuous dramatic narrative. The Oresteia is the only extant example of this type of connected trilogy, but there is evidence that Aeschylus often wrote such trilogies. The satyr plays that followed his tragic trilogies also drew from myth.
The satyr play Proteus, which followed the Oresteia, treated the story of Menelaus' detour in Egypt on his way home from the Trojan War. It is assumed, based on the evidence provided by a catalogue of Aeschylean play titles, scholia, and play fragments recorded by later authors, that three other extant plays of his were components of connected trilogies: Seven Against Thebes was the final play in an Oedipus trilogy, and The Suppliants and Prometheus Bound were each the first play in a Danaid trilogy and Prometheus trilogy, respectively. Scholars have also suggested several completely lost trilogies, based on known play titles. A number of these treated myths about the Trojan War. One, collectively called the Achilleis, comprised Myrmidons, Nereids and Phrygians (alternately, The Ransoming of Hector).
Another trilogy apparently recounted the entrance of the Trojan ally Memnon into the war, and his death at the hands of Achilles (Memnon and The Weighing of Souls being two components of the trilogy). The Award of the Arms, The Phrygian Women, and The Salaminian Women suggest a trilogy about the madness and subsequent suicide of the Greek hero Ajax. Aeschylus seems to have written about Odysseus' return to Ithaca after the war (including his killing of his wife Penelope's suitors and its consequences) in a trilogy consisting of The Soul-raisers, Penelope, and The Bone-gatherers. Other suggested trilogies touched on the myth of Jason and the Argonauts (Argô, Lemnian Women, Hypsipylê), the life of Perseus (The Net-draggers, Polydektês, Phorkides), the birth and exploits of Dionysus (Semele, Bacchae, Pentheus), and the aftermath of the war portrayed in Seven Against Thebes (Eleusinians, Argives (or Argive Women), Sons of the Seven).
Surviving plays
The Persians (472 BC)
Main article: The Persians
The Persians (Persai) is the earliest of Aeschylus' extant plays. It was performed in 472 BC. It was based on Aeschylus' own experiences, specifically the Battle of Salamis. It is unique among surviving Greek tragedies in that it describes a recent historical event. The Persians focuses on the popular Greek theme of hubris and blames Persia's loss on the pride of its king.
It opens with the arrival of a messenger in Susa, the Persian capital, bearing news of the catastrophic Persian defeat at Salamis, to Atossa, the mother of the Persian King Xerxes. Atossa then travels to the tomb of Darius, her husband, where his ghost appears, to explain the cause of the defeat. It is, he says, the result of Xerxes' hubris in building a bridge across the Hellespont, an action which angered the gods. Xerxes appears at the end of the play, not realizing the cause of his defeat, and the play closes to lamentations by Xerxes and the chorus.
Seven Against Thebes (467 BC)
Main article: Seven Against ThebesSeven against Thebes (Hepta epi Thebas) was performed in 467 BC. It has the contrasting theme of the interference of the gods in human affairs. Another theme, with which Aeschylus' would continually involve himself, makes its first known appearance in this play, namely that the polis was a key development of human civilization.
The play tells the story of Eteocles and Polynices, the sons of the shamed king of Thebes, Oedipus. Eteocles and Polynices agree to share and alternate the throne of the city. After the first year, Eteocles refuses to step down. Polynices therefore undertakes war. The pair kill each other in single combat, and the original ending of the play consisted of lamentations for the dead brothers. But a new ending was added to the play some fifty years later: Antigone and Ismene mourn their dead brothers, a messenger enters announcing an edict prohibiting the burial of Polynices, and Antigone declares her intention to defy this edict. The play was the third in a connected Oedipus trilogy. The first two plays were Laius and Oedipus. The concluding satyr play was The Sphinx.
The Suppliants (463 BC)
Main article: The Suppliants (Aeschylus)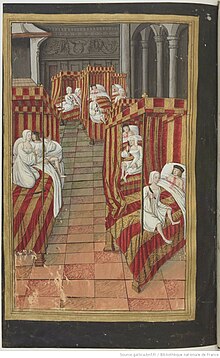
Aeschylus continued his emphasis on the polis with The Suppliants (Hiketides) in 463 BC. The play gives tribute to the democratic undercurrents which were running through Athens and preceding the establishment of a democratic government in 461. The Danaids (50 daughters of Danaus, founder of Argos) flee a forced marriage to their cousins in Egypt. They turn to King Pelasgus of Argos for protection, but Pelasgus refuses until the people of Argos weigh in on the decision (a distinctly democratic move on the part of the king). The people decide that the Danaids deserve protection and are allowed within the walls of Argos despite Egyptian protests.
A Danaid trilogy had long been assumed because of The Suppliants' cliffhanger ending. This was confirmed by the 1952 publication of Oxyrhynchus Papyrus 2256 fr. 3. The constituent plays are generally agreed to be The Suppliants and The Egyptians and The Danaids. A plausible reconstruction of the trilogy's last two-thirds runs thus: In The Egyptians, the Argive-Egyptian war threatened in the first play has transpired. King Pelasgus was killed during the war, and Danaus rules Argos. Danaus negotiates a settlement with Aegyptus, a condition of which requires his 50 daughters to marry the 50 sons of Aegyptus. Danaus secretly informs his daughters of an oracle which predicts that one of his sons-in-law would kill him. He orders the Danaids to murder their husbands therefore on their wedding night. His daughters agree. The Danaids would open the day after the wedding.
It is revealed that 49 of the 50 Danaids killed their husbands. Hypermnestra did not kill her husband, Lynceus, and helped him escape. Danaus is angered by his daughter's disobedience and orders her imprisonment and possibly execution. In the trilogy's climax and dénouement, Lynceus reveals himself to Danaus and kills him, thus fulfilling the oracle. He and Hypermnestra will establish a ruling dynasty in Argos. The other 49 Danaids are absolved of their murders, and married off to unspecified Argive men. The satyr play following this trilogy was titled Amymone, after one of the Danaids.
The Oresteia (458 BC)
Main article: OresteiaBesides a few missing lines, the Oresteia of 458 BC is the only complete trilogy of Greek plays by any playwright still extant (of Proteus, the satyr play which followed, only fragments are known). Agamemnon and The Libation Bearers (Choephoroi) and The Eumenides together tell the violent story of the family of Agamemnon, king of Argos.
Agamemnon

Aeschylus begins in Greece, describing the return of King Agamemnon from his victory in the Trojan War, from the perspective of the townspeople (the Chorus) and his wife, Clytemnestra. Dark foreshadowings build to the death of the king at the hands of his wife, who was angry that their daughter Iphigenia was killed so that the gods would restore the winds and allow the Greek fleet to sail to Troy. Clytemnestra was also unhappy that Agamemnon kept the Trojan prophetess Cassandra as his concubine. Cassandra foretells the murder of Agamemnon and of herself to the assembled townsfolk, who are horrified. She then enters the palace knowing that she cannot avoid her fate. The ending of the play includes a prediction of the return of Orestes, son of Agamemnon, who will seek to avenge his father.
The Libation Bearers
The Libation Bearers opens with Orestes' arrival at Agamemnon's tomb, from exile in Phocis. Electra meets Orestes there. They plan revenge against Clytemnestra and her lover, Aegisthus. Clytemnestra's account of a nightmare in which she gives birth to a snake is recounted by the chorus. This leads her to order her daughter, Electra, to pour libations on Agamemnon's tomb (with the assistance of libation bearers) in hope of making amends. Orestes enters the palace pretending to bear news of his own death. Clytemnestra calls in Aegisthus to learn the news. Orestes kills them both. Orestes is then beset by the Furies, who avenge the murders of kin in Greek mythology.
The Eumenides
The third play addresses the question of Orestes' guilt. The Furies drive Orestes from Argos and into the wilderness. He makes his way to the temple of Apollo and begs Apollo to drive the Furies away. Apollo had encouraged Orestes to kill Clytemnestra, so he bears some of the guilt for the murder. Apollo sends Orestes to the temple of Athena with Hermes as a guide.
The Furies track him down, and Athena steps in and declares that a trial is necessary. Apollo argues Orestes' case, and after the judges (including Athena) deliver a tie vote, Athena announces that Orestes is acquitted. She renames the Furies The Eumenides (The Good-spirited, or Kindly Ones), and extols the importance of reason in the development of laws. As in The Suppliants, the ideals of a democratic Athens are praised.
Prometheus Bound (date disputed)
Main article: Prometheus Bound
Prometheus Bound is attributed to Aeschylus by ancient authorities. Since the late 19th century, however, scholars have increasingly doubted this ascription, largely on stylistic grounds. Its production date is also in dispute, with theories ranging from the 480s BC to as late as the 410s.
The play consists mostly of static dialogue. The Titan Prometheus is bound to a rock throughout, which is his punishment from the Olympian Zeus for providing fire to humans. The god Hephaestus and the Titan Oceanus and the chorus of Oceanids all express sympathy for Prometheus' plight. Prometheus is met by Io, a fellow victim of Zeus' cruelty. He prophesies her future travels, revealing that one of her descendants will free Prometheus. The play closes with Zeus sending Prometheus into the abyss because Prometheus will not tell him of a potential marriage which could prove Zeus' downfall.
Prometheus Bound seems to have been the first play in a trilogy, the Prometheia. In the second play, Prometheus Unbound, Heracles frees Prometheus from his chains and kills the eagle that had been sent daily to eat Prometheus' perpetually regenerating liver, then believed the source of feeling. We learn that Zeus has released the other Titans which he imprisoned at the conclusion of the Titanomachy, perhaps foreshadowing his eventual reconciliation with Prometheus.
In the trilogy's conclusion, Prometheus the Fire-Bringer, it seems that the Titan finally warns Zeus not to sleep with the sea nymph Thetis, for she is fated to beget a son greater than the father. Not wishing to be overthrown, Zeus marries Thetis off to the mortal Peleus. The product of that union is Achilles, Greek hero of the Trojan War. After reconciling with Prometheus, Zeus probably inaugurates a festival in his honor at Athens.
Lost plays
Of Aeschylus' other plays, only titles and assorted fragments are known. There are enough fragments (along with comments made by later authors and scholiasts) to produce rough synopses for some plays.
Myrmidons
This play was based on books 9 and 16 of the Iliad. Achilles sits in silent indignation over his humiliation at Agamemnon's hands for most of the play. Envoys from the Greek army attempt to reconcile Achilles to Agamemnon, but he yields only to Patroclus, who then battles the Trojans in Achilles' armour. The bravery and death of Patroclus are reported in a messenger's speech, which is followed by mourning.
Nereids
This play was based on books 18 and 19 and 22 of the Iliad. It follows the Daughters of Nereus, the sea god, who lament Patroclus' death. A messenger tells how Achilles (perhaps reconciled to Agamemnon and the Greeks) slew Hector.
Phrygians, or Hector's Ransom
After a brief discussion with Hermes, Achilles sits in silent mourning over Patroclus. Hermes then brings in King Priam of Troy, who wins over Achilles and ransoms his son's body in a spectacular coup de théâtre. A scale is brought on stage and Hector's body is placed in one scale and gold in the other. The dynamic dancing of the chorus of Trojans when they enter with Priam is reported by Aristophanes.
Niobe
The children of Niobe, the heroine, have been slain by Apollo and Artemis because Niobe had gloated that she had more children than their mother, Leto. Niobe sits in silent mourning on stage during most of the play. In the Republic, Plato quotes the line "God plants a fault in mortals when he wills to destroy a house utterly."
These are the remaining 71 plays ascribed to Aeschylus which are known:
- Alcmene
- Amymone
- The Archer-Women
- The Argivian Women
- The Argo, also titled The Rowers
- Atalanta
- Athamas
- Attendants of the Bridal Chamber
- Award of the Arms
- The Bacchae
- The Bassarae
- The Bone-Gatherers
- The Cabeiroi
- Callisto
- The Carians, also titled Europa
- Cercyon
- Children of Hercules
- Circe
- The Cretan Women
- Cycnus
- The Danaids
- Daughters of Helios
- Daughters of Phorcys
- The Descendants
- The Edonians
- The Egyptians
- The Escorts
- Glaucus of Pontus
- Glaucus of Potniae
- Hypsipyle
- Iphigenia
- Ixion
- Laius
- The Lemnian Women
- The Lion
- Lycurgus
- Memnon
- The Men of Eleusis
- The Messengers
- The Myrmidons
- The Mysians
- Nemea
- The Net-Draggers
- The Nurses of Dionysus
- Orethyia
- Palamedes
- Penelope
- Pentheus
- Perrhaibides
- Philoctetes
- Phineus
- The Phrygian Women
- Polydectes
- The Priestesses
- Prometheus the Fire-Bearer
- Prometheus the Fire-Kindler
- Prometheus Unbound
- Proteus
- Semele, also titled The Water-Bearers
- Sisyphus the Runaway
- Sisyphus the Stone-Roller
- The Spectators, also titled Athletes of the Isthmian Games
- The Sphinx
- The Spirit-Raisers
- Telephus
- The Thracian Women
- Weighing of Souls
- Women of Aetna (two versions)
- Women of Salamis
- Xantriae
- The Youths
Influence
Influence on Greek drama and culture

The theatre was just beginning to evolve when Aeschylus started writing for it. Earlier playwrights such as Thespis had already expanded the cast to include an actor who was able to interact with the chorus. Aeschylus added a second actor, allowing for greater dramatic variety, while the chorus played a less important role. He is sometimes credited with introducing skenographia, or scene-decoration, though Aristotle gives this distinction to Sophocles. Aeschylus is also said to have made the costumes more elaborate and dramatic, and made his actors wear platform boots (cothurni) to make them more visible to the audience. According to a later account of Aeschylus' life, the chorus of Furies in the first performance of the Eumenides were so frightening when they entered that children fainted and patriarchs urinated and pregnant women went into labour.
Aeschylus wrote his plays in verse. No violence is performed onstage. The plays have a remoteness from daily life in Athens, relating stories about the gods, or being set, like The Persians, far away. Aeschylus' work has a strong moral and religious emphasis. The Oresteia trilogy concentrated on humans' position in the cosmos relative to the gods and divine law and divine punishment.
Aeschylus' popularity is evident in the praise that the comic playwright Aristophanes gives him in The Frogs, produced some 50 years after Aeschylus' death. Aeschylus appears as a character in the play and claims, at line 1022, that his Seven against Thebes "made everyone watching it to love being warlike". He claims, at lines 1026–7, that with The Persians he "taught the Athenians to desire always to defeat their enemies." Aeschylus goes on to say, at lines 1039ff., that his plays inspired the Athenians to be brave and virtuous.
Influence outside Greek culture
Aeschylus' works were influential beyond his own time. Hugh Lloyd-Jones draws attention to Richard Wagner's reverence of Aeschylus. Michael Ewans argues in his Wagner and Aeschylus. The Ring and the Oresteia (London: Faber. 1982) that the influence was so great as to merit a direct character by character comparison between Wagner's Ring and Aeschylus's Oresteia. But a critic of that book, while not denying that Wagner read and respected Aeschylus, has described the arguments as unreasonable and forced.
J.T. Sheppard argues in the second half of his Aeschylus and Sophocles: Their Work and Influence that Aeschylus and Sophocles have played a major part in the formation of dramatic literature from the Renaissance to the present, specifically in French and Elizabethan drama. He also claims that their influence went beyond just drama and applies to literature in general, citing Milton and the Romantics.
Eugene O'Neill's Mourning Becomes Electra (1931), a trilogy of three plays set in America after the Civil War, is modeled after the Oresteia. Before writing his acclaimed trilogy, O'Neill had been developing a play about Aeschylus, and he noted that Aeschylus "so changed the system of the tragic stage that he has more claim than anyone else to be regarded as the founder (Father) of Tragedy."
During his presidential campaign in 1968, Senator Robert F. Kennedy quoted the Edith Hamilton translation of Aeschylus on the night of the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. Kennedy was notified of King's murder before a campaign stop in Indianapolis, Indiana, and was warned not to attend the event due to fears of rioting from the mostly African-American crowd. Kennedy insisted on attending and delivered an impromptu speech that delivered news of King's death. Acknowledging the audience's emotions, Kennedy referred to his own grief at the murder of Martin Luther King and, quoting a passage from the play Agamemnon (in translation), said: "My favorite poet was Aeschylus. And he once wrote: 'Even in our sleep, pain which cannot forget falls drop by drop upon the heart, until in our own despair, against our will, comes wisdom through the awful grace of God.' What we need in the United States is not division; what we need in the United States is not hatred; what we need in the United States is not violence and lawlessness; but is love and wisdom, and compassion toward one another, and a feeling of justice toward those who still suffer within our country, whether they be white or whether they be black ... Let us dedicate ourselves to what the Greeks wrote so many years ago: to tame the savageness of man and make gentle the life of this world." The quotation from Aeschylus was later inscribed on a memorial at the gravesite of Robert Kennedy following his own assassination.
Editions
- Ulrich von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, Aeschyli Tragoediae. Editio maior, Berlin 1914.
- Gilbert Murray, Aeschyli Septem Quae Supersunt Tragoediae. Editio Altera, Oxford 1955.
- Denys Page, Aeschyli Septem Quae Supersunt Tragoediae, Oxford 1972.
- Martin L. West, Aeschyli Tragoediae cum incerti poetae Prometheo, 2nd ed., Stuttgart/Leipzig 1998.
- The first translation of the seven plays into English was by Robert Potter in 1779, using blank verse for the iambic trimeters and rhymed verse for the choruses, a convention adopted by most translators for the next century.
- Anna Swanwick produced a verse translation in English of all seven surviving plays as The Dramas of Aeschylus in 1886 full text
- Stefan Radt (ed.), Tragicorum Graecorum Fragmenta. Vol. III: Aeschylus (Göttingen, Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 2009) (Tragicorum Graecorum Fragmenta, 3).
- Alan H. Sommerstein (ed.), Aeschylus, Volume II, Oresteia: Agamemnon. Libation-bearers. Eumenides. 146 (Cambridge, Massachusetts/London: Loeb Classical Library, 2009); Volume III, Fragments. 505 (Cambridge, Massachusetts/London: Loeb Classical Library, 2008).
See also
- 2876 Aeschylus, an asteroid named for him
- Ancient Greek literature
- Ancient Greek mythology
- Ancient Greek religion
- Battle of Marathon
- Classical Greece
- Dionysia
- Music of ancient Greece
- Theatre of ancient Greece
- "Live by the sword, die by the sword"
Notes
- The remnant of a commemorative inscription, dated to the 3rd century BC, lists four, possibly eight, dramatic poets (probably including Choerilus, Phrynichus, and Pratinas) who had won tragic victories at the Dionysia before Aeschylus had. Thespis was traditionally regarded the inventor of tragedy. According to another tradition, tragedy was established in Athens in the late 530s BC, but that may simply reflect an absence of records. Major innovations in dramatic form, credited to Aeschylus by Aristotle and the anonymous source The Life of Aeschylus, may be exaggerations and should be viewed with caution (Martin Cropp (2006), "Lost Tragedies: A Survey" in A Companion to Greek Tragedy, pp. 272–74)
Citations
- Jones, Daniel; Roach, Peter, James Hartman and Jane Setter, eds. Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary. 17th edition. Cambridge UP, 2006.
- "Aeschylus". Webster's New World College Dictionary.
- ^ Freeman 1999, p. 243
- Schlegel, August Wilhelm von (December 2004). Lectures on Dramatic Art and Literature. p. 121.
- R. Lattimore, Aeschylus I: Oresteia, 4
- Martin Cropp, 'Lost Tragedies: A Survey'; A Companion to Greek Tragedy, p. 273
- P. Levi, Greek Drama, 159
- S. Saïd, Aeschylean Tragedy, 215
- S. Saïd, Aeschylean Tragedy, 221
- "Pausanias, Description of Greece, *)attika/, chapter 14, section 5". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 18 January 2024.
- ^ Sommerstein 2010.
- Grene, David, and Richmond Lattimore, eds. The Complete Greek Tragedies: Vol. 1, Aeschylus. University of Chicago Press, 1959.
- ^ Bates 1906, pp. 53–59
- ^ Sidgwick 1911, p. 272
- S. Saïd, Eschylean tragedy, 217
- ^ Freeman 1999, p. 241
- ^ Kopff 1997 pp. 1–472
- "§ 4". Anonymous Life of Aeschylus. Living Poets. Translated by S. Burges Watson. Durham. 2014. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
They say that he was noble and that he participated in the battle of Marathon together with his brother, Cynegirus, and in the naval battle at Salamis with the youngest of his brothers, Ameinias, and in the infantry battle at Plataea.
(emphasis in original) - Sommerstein 2010, p. 34
- Martin 2000, §10.1
- Nicomachean Ethics 1111a8–10.
- Filonik, J. (2013). Athenian impiety trials: a reappraisal. Dike-Rivista di Storia del Diritto Greco ed Ellenistico, 16, page 23.
- Osborn, K.; Burges, D. (1998). The complete idiot's guide to classical mythology. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-02-862385-6.
- Smith 2005, p. 1
- Ursula Hoff (1938). "Meditation in Solitude". Journal of the Warburg Institute. 1 (44): 292–294. doi:10.2307/749994. JSTOR 749994. S2CID 192234608.
- ^ J. C. McKeown (2013), A Cabinet of Greek Curiosities: Strange Tales and Surprising Facts from the Cradle of Western Civilization, Oxford University Press, p. 136, ISBN 978-0-19-998210-3,
The unusual nature of Aeschylus' death ...
- Pliny the Elder. "Book X, Chapter 3". The Natural History.
This eagle has the instinct to break the shell of the tortoise by letting it fall from aloft, a circumstance which caused the death of the poet Æschylus. An oracle, it is said, had predicted his death on that day by the fall of a house, upon which he took the precaution of trusting himself only under the canopy of the heavens.
- Critchley 2009
- ^ Freeman 1999, p. 242
- ^ Pomeroy 1999, p. 222
- Sommerstein 2010
- Sommerstein 2010, p. 34.
- ^ Freeman 1999, p. 244
- ^ Vellacott: 7–19
- ^ Freeman 1999, pp. 244–46
- ^ Aeschylus. "Prometheus Bound, The Suppliants, Seven Against Thebes, The Persians." Philip Vellacott's Introduction, pp. 7–19. Penguin Classics.
- Sommerstein 2002, 23.
- ^ Freeman 1999, p. 246
- See (e.g.) Sommerstein 1996, 141–51; Turner 2001, 36–39.
- ^ Sommerstein 2002, 89.
- Griffith 1983, pp. 32–34
- For example: Agamemnon 432 "Many things pierce the liver"; 791–2 "No sting of true sorrow reaches the liver"; Eumenides 135 "Sting your liver with merited reproaches".
- ^ For a discussion of the trilogy's reconstruction, see (e.g.) Conacher 1980, 100–02.
- According to Vitruvius. See Summers 2007, 23.
- Performance in Greek and Roman theatre. George William Mallory Harrison, Vaios Liapēs. Leiden: Brill. 2013. p. 111. ISBN 978-90-04-24545-7. OCLC 830001324.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - "Aeschylus". PoemHunter. Retrieved 23 September 2024.
- Life of Aeschylus.
- ^ Pomeroy 1999, p. 223
- Pomeroy 1999, pp. 224–25
- ^ Scharffenberger, Elizabeth W. (2007). ""Deinon Eribremetas": The Sound and Sense of Aeschylus in Aristophanes' "Frogs"". The Classical World. 100 (3): 229–249. ISSN 0009-8418. JSTOR 25434023.
- Furness, Raymond (January 1984). "Reviewed work: Wagner and Aeschylus. The 'Ring' and the 'Oresteia', Michael Ewans". The Modern Language Review. 79 (1): 239–40. doi:10.2307/3730399. JSTOR 3730399.
- Sheppard, J. T. (1927). "Aeschylus and Sophocles: their Work and Influence". The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 47 (2): 265. doi:10.2307/625177. JSTOR 625177.
- Floyd, Virginia, ed. Eugene O'Neill at Work. New York: Frederick Ungar, 1981, p. 213. ISBN 0-8044-2205-2
- ^ "Virginia – Arlington National Cemetery: Robert F. Kennedy Gravesite". 7 June 2009.
- "Robert Kennedy: Delivering News of King's Death". National Public Radio. 4 April 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2022.
- Kennedy, Maxwell Taylor (1998). Make Gentle the Life of This World: The Vision of Robert F. Kennedy. New York: Harcourt Brace & Company. ISBN 0-15-100-356-4.
- Kennedy, Robert F. (4 April 1968). "Statement on Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr". The John F. Kennedy Presidential Library & Museum. Papers of Robert F. Kennedy. Senate Papers. Speeches and Press Releases, Box 4, "4/1/68 - 4/10/68." John F. Kennedy Presidential Library. Retrieved 6 July 2024.
References
- Bates, Alfred (1906). The Drama: Its History, Literature, and Influence on Civilization. Vol. 1. London: Historical Publishing Company.
- Bierl, A. Die Orestie des Aischylos auf der modernen Bühne: Theoretische Konzeptionen und ihre szenische Realizierung (Stuttgart: Metzler, 1997)
- Cairns, D., V. Liapis, Dionysalexandros: Essays on Aeschylus and His Fellow Tragedians in Honour of Alexander F. Garvie (Swansea: The Classical Press of Wales, 2006)
- Critchley, Simon (2009). The Book of Dead Philosophers. London: Granta Publications. ISBN 978-1-84708079-0.
- Cropp, Martin (2006). "Lost Tragedies: A Survey". In Gregory, Justine (ed.). A Companion to Greek Tragedy. Blackwell Publishing.
- Deforge, B. Une vie avec Eschyle. Vérité des mythes (Paris, Les Belles Lettres, 2010)
- Freeman, Charles (1999). The Greek Achievement: The Foundation of the Western World. New York City: Viking Press. ISBN 978-0-670-88515-2.
- Goldhill, Simon (1992). Aeschylus, The Oresteia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-40293-4.
- Griffith, Mark (1983). Aeschylus' Prometheus Bound. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27011-3.
- Herington, C.J. (1986). Aeschylus. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-03562-9.
- Herington, C.J. (1967). "Aeschylus in Sicily". The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 87: 74–85. doi:10.2307/627808. JSTOR 627808. S2CID 162400889.
- Kopff, E. Christian (1997). Ancient Greek Authors. Gale. ISBN 978-0-8103-9939-6.
- Lattimore, Richmond (1953). Aeschylus I: Oresteia. University of Chicago Press.
- Lefkowitz, Mary (1981). The Lives of the Greek Poets. University of North Carolina Press
- Lesky, Albin (1979). Greek Tragedy. London: Benn.
- Lesky, Albin (1966). A History of Greek Literature. New York: Crowell.
- Levi, Peter (1986). "Greek Drama". The Oxford History of the Classical World. Oxford University Press.
- Martin, Thomas (2000). Ancient Greece: From Prehistoric to Hellenistic Times. Yale University Press.
- Murray, Gilbert (1978). Aeschylus: The Creator of Tragedy. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Podlecki, Anthony J. (1966). The Political Background of Aeschylean Tragedy. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
- Pomeroy, Sarah B. (1999). Ancient Greece: A Political, Social, and Cultural History. New York City: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509743-6.
- Rosenmeyer, Thomas G. (1982). The Art of Aeschylus. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04440-1.
- Saïd, Suzanne (2006). "Aeschylean Tragedy". A Companion to Greek Tragedy. Blackwell Publishing.
- Sidgwick, Arthur (1911). "Aeschylus" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 272–276.
- Smith, Helaine (2005). Masterpieces of Classic Greek Drama. Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-313-33268-5.
- Smyth, Herbert Weir (1922). Aeschylus. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Sommerstein, Alan H. (2010). Aeschylean Tragedy (2nd ed.). London: Duckworth. ISBN 978-0-7156-3824-8.
- — (2002). Greek Drama and Dramatists. London: Routledge Press. ISBN 0-415-26027-2
- Spatz, Lois (1982). Aeschylus. Boston: Twayne Publishers Press. ISBN 978-0-8057-6522-9.
- Summers, David (2007). Vision, Reflection, and Desire in Western Painting. University of North Carolina Press
- Thomson, George (1973) Aeschylus and Athens: A Study in the Social Origin of Drama. London: Lawrence and Wishart (4th edition)
- Turner, Chad (2001). "Perverted Supplication and Other Inversions in Aeschylus' Danaid Trilogy". Classical Journal. 97 (1): 27–50. JSTOR 3298432.
- Vellacott, Philip, (1961). Prometheus Bound and Other Plays: Prometheus Bound, Seven Against Thebes, and The Persians. New York: Penguin Classics. ISBN 0-14-044112-3
- Winnington-Ingram, R. P. (1985). "Aeschylus". The Cambridge History of Classical Literature: Greek Literature. Cambridge University Press.
- Zeitlin, Froma (1982). Under the sign of the shield: semiotics and Aeschylus' Seven against Thebes. Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books, 2nd ed. 2009 (Greek studies: interdisciplinary approaches)
- Zetlin, Froma (1996). "The dynamics of misogyny: myth and mythmaking in Aeschylus's Oresteia", in Froma Zeitlin, Playing the Other: Gender and Society in Classical Greek Literature. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 87–119.
- Zeitlin, Froma (1996). "The politics of Eros in the Danaid trilogy of Aeschylus", in Froma Zeitlin, Playing the Other: Gender and Society in Classical Greek Literature. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 123–171.
External links
Library resources aboutAeschylus
By Aeschylus
- Works by Aeschylus at Project Gutenberg
- Works by Aeschylus in eBook form at Standard Ebooks
- Works by Aeschylus (translated by George Gilbert Aimé) at Faded Page (Canada)
- Works by or about Aeschylus at the Internet Archive
- Works by Aeschylus at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Selected Poems of Aeschylus
- Aeschylus-related materials at the Perseus Digital Library
- Complete syntax diagrams at Alpheios
- Online English Translations of Aeschylus
- Photo of a fragment of The Net-pullers
- Crane, Gregory. "Aeschylus (4)". Perseus Encyclopedia.
- "Aeschylus, I: Persians" from the Loeb Classical Library, Harvard University Press
- "Aeschylus, II: The Oresteia" from the Loeb Classical Library, Harvard University Press
- "Aeschylus, III: Fragments" from the Loeb Classical Library, Harvard University Press
| Plays by Aeschylus | |
|---|---|
| Tetralogies |
|
| Extant plays |
|
| Fragmentary plays | |