| Revision as of 10:23, 28 October 2006 editAsh (talk | contribs)23,897 editsm Typo← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 01:51, 14 December 2024 edit undoShelfSkewed (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers292,674 edits (disambiguation) redirect for intentional link to dab page per WP:INTDABLINKTags: Undo Disambiguation links added | ||
| (526 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Roman system of power division among four rulers}} | |||
| {{otheruses4|the phase of Roman imperial government|other uses of this term and of "Tetrarch"|Tetrarch}} | |||
| {{About|the tetrarchy created by Diocletian|the tetrarchy formed from the kingdom of Herod|Herodian tetrarchy|other uses|Tetrarch (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{more footnotes needed|date=May 2012}} | |||
| {{infobox | |||
| | abovestyle = font-size:120%; color:#ffffff; background:#b80049;text-align:center; | |||
| | above = Roman imperial dynasties | |||
| | subheader = ] | |||
| | image = ] | |||
| | caption = '']'', two ] sculptures looted from the ] of Constantinople after 1204, now standing at the southwest corner of ], ] | |||
| | headerstyle = background:#E5E4E2; font-size: 110%; | |||
| | header1 = Chronology | |||
| | data2 = {{aligned table|fullwidth=y|leftright=y|cols=2 | |||
| | ''']''' as Augustus | |||
| | {{nowrap|284–286}} | |||
| | — with ] as Caesar | |||
| | 285–286 | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']'''<br/> as Augusti of the West and East | |||
| | 286–305 | |||
| | — with ] & ]<br/>as Caesares | |||
| | 293–305 | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']'''<br/>as Augusti of West and East | |||
| | 305–306 | |||
| | — with ] & ]<br/>as Caesares | |||
| | | |||
| | ''']''' and ''']''' as Augusti of West and East | |||
| | 306–307 | |||
| | — with ] and ] as Caesares | |||
| | | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']''' as usurpers in Italy and Africa | |||
| | 306–308 | |||
| | ''']''' as Augustus | |||
| | 307–308 | |||
| | — with ] as Caesar | |||
| | | |||
| | — with ] as<br/>self-proclaimed Augustus | |||
| | | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']'''<br/>as Augusti of West and East | |||
| | 308–311 | |||
| | — with ] and ] as Caesares | |||
| | | |||
| | ''']''' as usurper in Rome (and Asia Minor 311–312) | |||
| | 308–312 | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']'''<br/>as Augusti of West and East | |||
| | 311–313 | |||
| | — with ] as<br/>self-proclaimed Augustus | |||
| | | |||
| | ''']''' & ''']'''<br/>as Augusti of West and East | |||
| | 313–324 | |||
| | — with ], ] & ] as Caesares | |||
| | | |||
| | — with ''']''' as<br/>Augustus of the West | |||
| | 316–317 | |||
| | — with ''']''' as<br/>Augustus of the West | |||
| | 324 | |||
| }} | |||
| | header3 = Succession | |||
| | data4 = {{aligned table|leftright=y|fullwidth=y | |||
| |''Preceded by''<br/>] | |||
| |''Followed by''<br/>] | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Roman government}} | {{Roman government}} | ||
| The '''Tetrarchy''' was the system instituted by ] ] in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the '']'', and their junior colleagues and designated successors, the '']''. | |||
| ] sculpture sacked from a Byzantine palace in 1204, Treasury of St. Marks, ]]] | |||
| '''Tetrarchy''' (]: "leadership of four people") can be applied to any system of government where power is divided between four individuals but is rarely used. The most famous Tetrarchy is that instituted by ] ] in ] and lasted until ''c.'' ]. The establishment of the Tetrarchy usually marks the resolution of the ] and the recovery of the ]. | |||
| Initially Diocletian chose ] as his ''caesar'' in 285, raising him to co-''augustus'' the following year; Maximian was to govern the western provinces and Diocletian would administer the eastern ones. The role of the ''augustus'' was likened to ], while his ''caesar'' was akin to Jupiter's son ]. ] and ] were appointed ''caesares'' in March 293. Diocletian and Maximian retired on 1 May 305, raising Galerius and Constantius to the rank of ''augustus''. Their places as ''caesares'' were in turn taken by ] and ]. | |||
| ==Creation of the Tetrarchy== | |||
| The first phase (sometimes referred to as the ], 'the rule of two') involved the designation of the general ] as co-emperor - firstly as '']'' (junior emperor) in 285, followed by his promotion to '']'' in 286. Diocletian took care of matters in the Eastern regions of the Empire while Maximian similarly took charge of the Western regions. In 293, feeling more focus was needed on both civic and military problems, Diocletian (with Maximian's consent) expanded the imperial college by appointing two Caesars (one responsible to each ''Augustus'') - ] and ]. | |||
| The orderly system of two senior and two junior rulers endured until Constantius died in July 306, and his son ] was unilaterally acclaimed ''augustus'' and ''caesar'' by his father's army. Maximian's son ] contested Severus' title, styled himself ''princeps invictus'', and was appointed ''caesar'' by his retired father in 306. Severus surrendered to Maximian and Maxentius in 307. Maxentius and Constantine were both recognized as ''augusti'' by Maximian that same year. Galerius appointed ] ''augustus'' for the west in 308 and elevated Maximinus Daza to ''augustus'' in 310. | |||
| The senior emperors jointly abdicate and retire, allowing Constantius and Galerius to elevate in rank to '']''. They in turn appoint two new Caesars - ] in the west under Constantius, and ] in the east under Galerius. The first Tetrarchy was therefore created. | |||
| Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the ] in 312 left him in control of the western part of the empire, while Licinius was left in control of the east on the death of Maximinus Daza. Constantine and Licinius jointly recognized their sons – ], ], and ] – as ''caesares'' in March 317. Ultimately the tetrarchic system lasted until c. 324, when mutually destructive civil wars eliminated most of the claimants to power: ] resigned as ''augustus'' after losing the ], leaving Constantine in control of the entire empire. | |||
| ==Tetrarchic regions and capitals== | |||
| ], showing the dioceses and praetorian prefectures of Gaul, Italy, Illyricum and Oriens (East), roughly analogous to the four Tetrarchs' zones of influence. However, in 395, the western part of the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum (including Sirmium) was attached to the Praetorian prefecture of Italy.]] | |||
| The four Tetrarchs based themselves not at Rome but in other cities closer to the frontiers, mainly intended as headquarters for the defence of the empire against bordering rivals (notably ]) and ]s (mainly Germanic, and an endless procession from the eastern steppe; many nomadic or elsewhere chased tribes) at the Rhine and Danube. These centres are known as the 'Tetrarchic capitals'. Although Rome ceased to be an operational capital, the 'Eternal City' continued to be nominal capital of the entire empire, not reduced to the status of a province but under its own, unique Prefect of the City (], later copied in Constantinople). | |||
| The ]'s emperors retained some aspects of collegiate rule; Constantine appointed his son ] as another ''caesar'' in 324, followed by ] in 333 and his nephew ] in 335, and the three surviving sons of Constantine in 337 were declared joint ''augusti'' together, and the concept of the division of the empire under multiple joint emperors endured until the ]. In the ], ''augusti'' and ''caesares'' continued to be appointed sporadically. | |||
| The four Tetrarchic capitals were: | |||
| ==Terminology== | |||
| * ] in northwestern Asia Minor (modern ] in Turkey), a base for defence against invasion from the Balkans and Persia's Sassanids, not Constantinople (given that name at its later refounding), was the capital of Diocletian, the eastern (and most senior) ''Augustus''; in the final reorganisation by Constantine the Great, in 318AD, the equivalent of his domain, facing the most redoubtable foreign enemy, Persia, became the pretorian prefecture ''Oriens'' 'the East', the core of later Byzantium. | |||
| The term ''tetrarchy'' (from the {{langx|el|τετραρχία}}, ''tetrarchia'', "leadership of four "){{efn|Historian ] translates the term as "]". See idem., ''Constantine the Emperor'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013), 1.}} describes any form of government where power is divided among four individuals. | |||
| Although the term "tetrarch" was current in antiquity, it was never used in the imperial college (as it's often called) under Diocletian. Instead, the term was used to describe independent portions of a kingdom that were ruled under separate leaders. The ], established after the death of ], is the most famous example of the antique tetrarchy. The term was understood in the Latin world as well, where ] glossed it as follows: "each is the equivalent of a kingdom, and also part of one" (''regnorum instar singulae et in regna contribuuntur'').<ref>Qtd. and tr. Leadbetter, ''Galerius'', 3.</ref> | |||
| * ] (modern ]) in the ] region of modern ], and near ], on the ] border) was the capital of Galerius, the eastern ''Caesar''; this was to become the Balkans-Danube- prefecture ''Illyricum''. | |||
| As used by the ancients, the term describes not only different governments, but also a different system of government from the Diocletianic arrangements. The Judaean tetrarchy was a set of four independent and distinct states, where each tetrarch ruled a quarter of a kingdom as they saw fit; the Diocletianic tetrarchy was a ] led by a single supreme leader. When later authors described the period, this is what they emphasized: ] had Constantius II admonish ] for disobedience by appealing to the example in submission set by Diocletian's lesser colleagues; his successor Julian compared the Diocletianic tetrarchs to a chorus surrounding a leader, speaking in unison under his command.<ref>Amm. Marc. 14.11.10; Jul. ''Caes''. 315A-B.</ref> Only ], a contemporary of Diocletian and a deep ideological opponent of the Diocletianic state, referred to the tetrarchs as a simple multiplicity of rulers.<ref>Leadbetter, ''Galerius'', 3.</ref> | |||
| * ] (modern ], near the Alps), not Eternal Rome, was the capital of Maximian, the western ''Augustus''; his domain became "Italia et Africa", with only a short exterior border. | |||
| Much modern scholarship was written without the term. Although ] pioneered the description of the Diocletianic government as a "New Empire", he never used the term "tetrarchy"; neither did ]. It did not appear in the literature until used in 1887 by schoolmaster Hermann Schiller in a two-volume handbook on the Roman Empire (''Geschichte der Römischen Kaiserzeit''), to wit: "''die diokletianische Tetrarchie''". Even so, the term did not catch on in the literature until ] used it in 1897.<ref>Leadbetter, ''Galerius'', 3–4.</ref> | |||
| * ] (modern ], in Germany) was the excentric capital of Constantius Chlorus, the western ''Caesar'', near the strategic Rhine border, hence it had before been the capital of Gallic emperor ]; this quarter became the prefecture Galliae. | |||
| ]'' struck in ] under ], the tetrarchs offer sacrifice to celebrate a victory against the ].]] | |||
| ==Creation<!--Linked from 'Byzantine Empire'-->== | |||
| ], a port on the Adriatic coast, and ] (modern ], in northern England near the Celtic tribes of modern Scotland and Ireland), were also significant centres for Maximian and Constantius respectively. | |||
| The first phase, sometimes referred to as the ] ("rule of two"), involved the designation of the general ] as co-emperor—firstly as '']'' (heir apparent) in 285, followed by his promotion to ''augustus'' in 286. ] took care of matters in the eastern regions of the empire while Maximian similarly took charge of the western regions. In 293, Diocletian thought that more focus was needed on both civic and military problems, so with Maximian's consent, he expanded the imperial college by appointing two ''caesares'' (one responsible to each ''augustus'')—] and ].<ref>The chronology has been thoroughly established by Kolb, ''Diocletian'', and Kuhoff, ''Diokletian''.</ref> | |||
| In 305, the senior emperors jointly abdicated and retired, allowing Constantius and Galerius to be elevated in rank to ''augustus''. They in turn appointed two new ''caesares''—] in the west under Constantius, and ] in the east under Galerius—thereby creating the second Tetrarchy. | |||
| In terms of regional jurisdiction there was no precise division between the four Tetrarchs, and this period did not see the Roman state actually split up into four distinct sub-empires. Each emperor had his zone of influence within the Roman Empire, but little more, mainly high command in a 'war theatre', himself often in the field, while delegating most of the administration to the hierarchic bureaucracy headed by each Tetrarch's ], each supervising several ], the governors-general in charge of another, lasting new administrative level, the civilian ''diocese'', of which there were originally twelve, later several were split. | |||
| For a listing of the provinces, now known as ], within each quarter (known as a pretorian prefecture), see ]. | |||
| == Regions and capitals == | |||
| In the West, the ''Augustus'' Maximian controlled the provinces west of the Adriatic Sea and the Syrtis, and within that region his ''Caesar'', Constantius, controlled Gaul and Britain. In the East, the arrangements between the ''Augustus'' Diocletian and his ''Caesar'', Galerius, were much more flexible. | |||
| <!--Linked from ]--> | |||
| ] | |||
| The four tetrarchs based themselves not at Rome but in other cities closer to the frontiers, mainly intended as headquarters for the defence of the empire against bordering rivals (notably ]) and ]s (mainly Germanic, and an unending sequence of nomadic or displaced tribes from the eastern steppes) at the ] and ]. These centres are known as the tetrarchic capitals. Although Rome ceased to be an operational capital, Rome continued to be nominal capital of the entire Roman Empire, not reduced to the status of a province but under its own, unique Prefect of the city (], later copied in Constantinople). | |||
| However, it appears that some contemporary and later writers, such as the Christian author ], and ] (who wrote about fifty years later and from uncertain sources), misunderstood the Tetrarchic system in this respect, believing it to have involved a stricter division of territories between the four emperors. | |||
| The four tetrarchic capitals were: | |||
| *] in northwestern Asia Minor (modern ] in Turkey), a base for defence against invasion from the Balkans and Persia's Sassanids was the capital of Diocletian, the eastern (and most senior) ''augustus''; in the final reorganisation by Constantine the Great, in 318, the equivalent of his domain, facing the most redoubtable foreign enemy, ], became the praetorian prefecture Oriens, 'the East', the core of later Byzantium. | |||
| *] (modern ] in the ] region of modern ], and near ], on the ] border) was the capital of Galerius, the eastern ''caesar''; this was to become the Balkans-Danube prefecture Illyricum. | |||
| *] (modern ], near the Alps) was the capital of Maximian, the western ''augustus''; his domain became "Italia et Africa", with only a short exterior border. | |||
| *] (modern ], in Germany) was the capital of Constantius, the western ''caesar'', near the strategic Rhine border; it had been the capital of Gallic emperor ]. This quarter became the prefecture Galliae. | |||
| ], a port on the Adriatic coast, and ] (modern ], in northern England near the Celtic tribes of modern Scotland and Ireland), were also significant centres for Maximian and Constantius respectively. | |||
| In terms of regional jurisdiction there was no precise division among the four tetrarchs, and this period did not see the Roman state actually split up into four distinct sub-empires. Each emperor had his zone of influence within the Roman Empire, but little more, mainly high command in a 'war theater'. Each tetrarch was himself often in the field, while delegating most of the administration to the hierarchic bureaucracy headed by his respective ], each supervising several ], the governors-general in charge of another, lasting new administrative level, the civil ]. For a listing of the provinces, now known as ], within each quarter (known as a praetorian prefecture), see ]. | |||
| In the West, the ''augustus'' Maximian controlled the provinces west of the ] and the ], and within that region his ''caesar'', Constantius, controlled Gaul and Britain. In the East, the arrangements between the ''augustus'' Diocletian and his ''caesar'', Galerius, were much more flexible. | |||
| ==Public image== | ==Public image== | ||
| Although power was shared in the |
Although power was shared in the tetrarchic system, the public image of the four members of the imperial college was carefully managed to give the appearance of a united empire (''patrimonium indivisum''). This was especially important after ]. | ||
| The |
The tetrarchs appeared identical in all official portraits. Coinage dating from the tetrarchic period depicts every emperor with identical features—only the inscriptions on the coins indicate which one of the four emperors is being shown. The Byzantine sculpture '']'' shows the tetrarchs again with identical features and wearing the same military costume. | ||
| ==Military successes== | ==Military successes== | ||
| One of the greatest problems facing emperors in the Third Century Crisis was that they were only ever able to personally command troops on one front at any one time. While ] and ] were prepared to accompany their armies thousands of miles between war regions, this was not an ideal solution. Furthermore, it was risky for an emperor to delegate power in his absence to a subordinate general, who might win a victory and then be proclaimed as a rival emperor himself by his troops (which often happened). All members of the imperial college, on the other hand, were of essentially equal rank, despite two being senior emperors and two being junior; their functions and authorities were also equal. |
One of the greatest problems facing emperors in the Third Century Crisis was that they were only ever able to personally command troops on one front at any one time. While ] and ] were prepared to accompany their armies thousands of miles between war regions, this was not an ideal solution. Furthermore, it was risky for an emperor to delegate power in his absence to a subordinate general, who might win a victory and then be proclaimed as a rival emperor himself by his troops (which often happened). All members of the imperial college, on the other hand, were of essentially equal rank, despite two being senior emperors and two being junior; their functions and authorities were also equal. | ||
| Under the Tetrarchy a number of important military victories were secured. Both the |
Under the Tetrarchy a number of important military victories were secured. Both the dyarchic and the tetrarchic system ensured that an emperor was near to every crisis area to personally direct and remain in control of campaigns simultaneously on more than just one front. After suffering a defeat by the ] in 296, Galerius crushed ] in 298—reversing a series of Roman defeats throughout the century—capturing members of the imperial household and a substantial amount of booty and gaining a highly favourable peace treaty, which secured peace between the two powers for a generation. Similarly, Constantius defeated the British usurper ], Maximian pacified the Gauls, and Diocletian crushed the revolt of ] in ]. | ||
| ==Demise== | |||
| ==Fall of the Tetrarchy== | |||
| {{Main|Civil wars of the Tetrarchy}} | |||
| ]'', fresco by ], Vatican Rooms.]] | |||
| When in 305 the 20-year term of Diocletian and Maximian ended, both abdicated. Their ''caesares'', Galerius and Constantius Chlorus, were both raised to the rank of ''augustus'', and two new ''caesares'' were appointed: ] (''caesar'' to Galerius) and ] (''caesar'' to Constantius). These four formed the second tetrarchy. | |||
| However, the system broke down very quickly thereafter. When Constantius died in 306, ], Constantius' son, was proclaimed ''augustus'' by his father's troops; however, Galerius instead chose to promote Severus to ''augustus'' while granting Constantine the position of caesar to Severus. At the same time, ], the son of Maximian, resented being left out of the new arrangements, so he rebelled against and defeated Severus before forcing him to abdicate and then arranging his murder in 307. Maxentius and Maximian both then declared themselves ''augusti''. By 308 there were therefore no fewer than four claimants to the rank of ''augustus'' (Galerius, Constantine, Maximian and Maxentius), and only one to that of ''caesar'' (Maximinus Daza). | |||
| ===Confusion and collapse=== | |||
| When in 305 the 20-years reign term of Diocletian and Maximian ended, both abdicated. Their Caesares, Galerius and Constantius Chlorus, were both raised to the rank of Augustus, and two new Caesares were appointed: ] (Caesar to Galerius) and ] (Caesar to Constantius). These four formed the second Tetrarchy. | |||
| In 308 Galerius, together with the retired emperor Diocletian and the supposedly retired Maximian, called an imperial "conference" at ] on the River Danube. The council agreed that ] would become ''augustus'' in the West, with Constantine as his ''caesar''. In the East, Galerius remained ''augustus'' and Maximinus remained his ''caesar''. Maximian was to retire, and Maxentius was declared a usurper. This agreement proved disastrous: by 308 Maxentius had become ''de facto'' ruler of Italy and Africa even without any imperial status, and neither Constantine nor Maximinus—who had both been ''caesares'' since 306 and 305 respectively—were prepared to tolerate the promotion of the ''augustus'' Licinius as their superior. | |||
| However, the system broke down very quickly thereafter. When Constantius died in 306, Galerius promoted Severus to Augustus while ] was proclaimed Augustus to succeed his father Constantius, by his father's troops. At the same time, ], the son of Maximian, resented having been left out of the new arrangements, defeated Severus before forcing him to abdicate and then arranging his murder in 307. Maxentius and Maximian both then declared themselves Augusti. By 308 there were therefore no less than four claimants to the rank of Augustus (Galerius, Constantine, Maximian and Maxentius), and only one to that of Caesar (Maximinus). | |||
| After an abortive attempt to placate both Constantine and Maximinus with the meaningless title ''filius augusti'' ("son of the ''augustus''", essentially an alternative title for ''caesar''), they both had to be recognised as Augusti in 309. However, four full Augusti all at odds with each other did not bode well for the tetrarchic system. | |||
| In 308 Galerius, together with the retired emperor Diocletian and the supposedly-retired Maximian, called an imperial 'conference' at ] on the River Danube, which agreed that ] would become Augustus in the West, with Constantine as his Caesar. In the East, Galerius remained Augustus and Maximinus remained his Caesar. Maximian was to retire, and Maxentius was declared an usurper. This agreement proved disastrous: by 308 Maxentius had become ''de facto'' ruler of Italy and Africa anyway, even if he was deprived of imperial rank; neither Constantine nor Maximinus - who had both been Caesares since 305 - were prepared to tolerate the promotion of the Augustus Licinius as their superior. | |||
| Between 309 and 313 most of the claimants to the imperial office died or were killed in various civil wars. Constantine forced Maximian's suicide in 310. Galerius died naturally in 311. Maxentius was defeated by Constantine at the ] in 312 and subsequently killed. Maximinus committed suicide at ] in 313 after being defeated in battle by Licinius. | |||
| After an abortive attempt to placate both Constantine and Maximinus with the meaningless title ''filius Augusti'' ('son of the Augustus', which could have been an alternative title for Caesar, as either implied the right to succeed), they both had to be recognised as Augusti in 309. However, four full Augusti all at odds with each other did not bode well for the Tetrarchic system. | |||
| By 313, therefore, there remained only two rulers: Constantine in the West and Licinius in the East. The tetrarchic system was at an end, although it took until 324 for Constantine to finally defeat Licinius, reunite the two halves of the Roman Empire and declare himself sole ''augustus''.<ref>] (1776). "Chapter XIV". ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire''. Vol. II.</ref> | |||
| ===End of the Tetrarchy=== | |||
| Between 309 and 313 most of the claimants to the imperial office died or were killed in various internecine wars. Constantine arranged Maximian's death by strangulation in 310. Galerius died naturally in 311. Maxentius was defeated by Constantine at the ] in 312 and subsequently killed. Maximinus committed suicide at ] in 313 after being defeated in battle by Licinius. | |||
| == Emperors == | |||
| By 313, therefore, there remained only two emperors: Constantine in the West and Licinius in the East. The Tetrarchic system was at an end, although it took until 324 for Constantine to finally defeat Licinius, reunite the two halves of the Roman empire and declare himself sole Augustus. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ! Portrait | |||
| ! Name | |||
| ! Reign | |||
| ! Co-ruler(s) | |||
| ! Ref | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |]<br/><small>Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus</small> | |||
| ('''''Whole, then East''''') | |||
| |20 November 284 – 1 May 305<br/><small>(20 years, 5 months and 11 days)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''caesar'', 21 July 285; co-''augustus'', 1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 293)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 293)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Cooley|first=Alison E.|author-link=Alison E. Cooley |date=2012|chapter=Imperial titles, Augustus–Justinian (Appendix 2)|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/cambridge-manual-of-latin-epigraphy/imperial-titles-augustusjustinian/5EA1B4FCD0E56D0F6FC9DD3903C7A7FD|access-date=2020-06-26|title=The Cambridge Manual of Latin Epigraphy|pages=488–509|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VlghAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA488|doi=10.1017/cbo9781139020442.007|isbn=9780521840262}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |]<br/><small>Marcus Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus</small> | |||
| ('''''West''''') | |||
| |1 April 286 – 1 May 305<br/><small>(19 years and 1 month; retired)</small>pac | |||
| 28 October 306 – 11 November 308<br/><small>(2 years and 14 days)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''augustus'', 21 July 285; co-''augustus'', 1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 21 March 293)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 293)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(co-''augustus'', 306–308)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 25 July 306; co-''augustus'', 307)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |''']'''<br/><small>Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus</small> | |||
| ('''''East''''') | |||
| |1 May 305– 5 May 311<br/><small>(6 years and 4 days)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''augustus'', 21 March 293–1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''augustus'', 21 March 293–1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 293; co-''augustus'', 1 May 305–25 July 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305; co-''augustus'', August 306–April 307)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 28 October 306; junior co-''augustus'', April 307–May 311)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(designated ''augustus'' for the West, 11 November 308–311)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305; co-''augustus'', 1 May 310–early May 311)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |]<br/><small>Marcus Flavius Valerius Constantius</small> | |||
| ('''''West''''') | |||
| |1 May 305 – 25 July 306<br/><small>(1 year, 2 months and 24 days)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''augustus'', 1 March 293–1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''augustus'', 1 April 286–1 May 305)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 21 March 293; co-''augustus'', 1 May 305–25 July 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305 –July 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305–25 July 306)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| | align="center" |] | |||
| | align="center" |]<br/><small>Flavius Valerius Constantinus</small> | |||
| ('''''West''''') | |||
| |25 July 306 – 18 September 324<br /><small>(18 years, 1 month and 25 days;<br/>sole emperor 324–337)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 306–307; co-''augustus'', 307–308)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 306–307; co-''augustus''; 308)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 308–310; co-''augustus'', 310–316; rival, 316–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 317–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 317–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 324)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |''']'''<br/><small>Flavius Valerius Severus</small> | |||
| ('''''West''''') | |||
| |25 July 306 – April 307<br/><small>(8 months)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''augustus'', 25 July 306–April 307)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 28 October 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 306–307)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305–April 307)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |''']'''<br/><small>Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maxentius</small> | |||
| ('''''West''''') | |||
| |28 October 306 – 28 October 312<br/><small>(6 years)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(co-''augustus'', 306–308)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', August 306–April 307)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival-''augustus'', 11 November 308–28 October 312)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 25 July 306–28 October 312)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |''']'''<br/><small>Valerius Licinianus Licinius</small> | |||
| ('''''West, then East''''') | |||
| |11 November 308 – 19 September 324<br/><small>(15 years, 10 months and 8 days)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 308–310; co-''augustus'', 310–316; rival, 316–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(designated Western ''augustus'', October 316–February 317)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 317–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 317–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 March 317–324)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(designated Western ''augustus'', July–September 324)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | align="center" |]<br/><small>Galerius Valerius Maximinus</small> | |||
| ('''''East''''') | |||
| |310 – c. July 313<br/><small>(3 years)</small> | |||
| |] <small>(''augustus'', 1 May 305–25 July 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''augustus'', 1 May 305–25 July 311)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''caesar'', 1 May 305; ''augustus'' 25 July 306)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''augustus'', late 306–November 308)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 310–312)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(rival ''augustus'', 310–313)</small> | |||
| ] <small>(''augustus'', 308–313; rival ''augustus'', 313–313)</small> | |||
| |<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Family tree== | |||
| {{Simplified Tetrarchs family tree}} | |||
| ==Detailed timeline== | |||
| {| width=50% class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Diarchy</big><br />1 April 286 – 1 March 293 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ]<br/>{{small|in ] (286–293)}} | |||
| | colspan="2" |— | |||
| |} | |||
| Two ''caesares'' are appointed in 293, thus starting the Tetrarchy. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>First Tetrarchy</big><br />1 March 293 – 1 May 305 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] (286–293)}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] (297)}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] (293–296)}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] (297–298)}} | |||
| |} | |||
| After the retirement of the two a''ugusti'' both previous ''caesares'' succeeded them, and two new ''caesares'' were appointed. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Second Tetrarchy</big><br />1 May 305 – 25 July 306 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |} | |||
| After the sudden death of ] (who died of natural causes), the ''caesar'' ] succeeded him as ''augustus''. However, Constantius' troops immediately proclaimed Constantine, Constantius' son, as their new ''augustus''. Galerius accepted Constantine as part of the imperial college, but only as ''caesar''. On 28 October 306, Maximian's son ] proclaimed himself emperor in Rome. Maximian also proclaimed himself emperor, ruling jointly with his son. Despite being accepted by the ], they were not recognized by the other emperors.{{sfn|Barnes|1984|pp=30–33}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Third Tetrarchy</big><br />25 July 306 – September 307 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|(self-styled ''augustus'')}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in Italy and Africa<br/>(from 28 October 306)}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in Italy and Africa<br/>(from 28 October 306)}} | |||
| |} | |||
| Severus was taken hostage by Maximian in April 307, but Galerius still acknowledged him as the official emperor of the west. Constantine was denied the promotion to ''augustus'' even after Severus' death in September, as Galerius had decided to exclude him from the system altogether. Maximian acknowledge Constantine's status as ''augustus'', but this meant nothing given that he himself was declared an usurper. Galerius and Maximinus thus remained as the only "legimitate" members of the imperial college.{{sfn|Barnes|1984|pp=30–33}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Galerius as sole Augustus</big><br />September 307 – November 308 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="2" rowspan="2" |('''vacant''') | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in Italy and Africa}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in Italy and Africa}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] and ]}} | |||
| | colspan="2" | | |||
| |} | |||
| At the council of Carnutum, Diocletian decides that Licinius will be the new ''augustus'' of the west (although his western domains only consist of the ]). Constantine was given back the title of ''caesar'', which he continued to unacknowledge.{{sfn|Barnes|1984|pp=30–33}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Fourth Tetrarchy</big><br />11 November 308 – May 310 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|(self-styled ''augustus'')}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ]}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|in ] (308–310?)}} | |||
| |} | |||
| Maximinus was proclaimed ''augustus'' by his troops in about May 310. Galerius reluctantly agreed to recognize both Maximinus and Constantine as ''augusti'', thus breaking the Diocletian's tetrarchic system.{{sfn|Barnes|1984|pp=30–33}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Tetrarchy of Augusti</big><br />May 310 – May 311 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|In Italy and Africa}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|In Gaul, {{circa}} July 310}} | |||
| |} | |||
| After the death of Galerius' (who died of natural causes), Licinius acquires parts of his domains, thus ruling over territories both in the East and West. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>Tetrarchy of Augusti</big><br />May 311 – August 313 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ] | |||
| | colspan="2" |('''Licinius''') | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| |''']''' | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |Usurpers | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|In Italy and Africa<br/>(until 28 October 312)}} | |||
| | colspan="2" |— | |||
| |} | |||
| Licinius eventually fights and defeats Maximinus, gaining all eastern territories. He then makes peace with Constantine, who remains as the emperor of the West. This joint rule lasted until 316, when Licinius rejected Constantine's election of ] as ''caesar''. In the ensuing war, both ''augusti'' appointed their own sons as ''caesares'', restoring a dynastic system. Licinius appointed ] and ] as ''augustus'' in 316 and 324 respectively (literary sources refer to them as ''caesar'', but coins bear the title ''augustus''); almost nothing is known about them. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" width="50%" style="text-align:center" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="4" |<big>New Diarchy</big><br />August 313 – 18 September 324 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|from 317}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |''']'''<br />{{small|in 316}}{{efn|Nominal emperor of the West.}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|from 317}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |''']'''<br />{{small|in 324}}{{efn|Nominal emperor of the West.}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="2" |— | |||
| |] | |||
| |]<br />{{small|from 317}} | |||
| |} | |||
| == Chronological table == | |||
| {{Chronological scheme of the Tetrarchy}} | |||
| ==Legacy== | ==Legacy== | ||
| ]'', fresco by ], Vatican Rooms.]] | |||
| Although the Tetrarchic system as such only lasted until c. ], many aspects survived. The four-fold regional division of the empire continued in the form of ]s, each of which was overseen by a ] and subdivided into administrative ], and often reappeared in the title of the military supra-provincial command assigned to a ]. | |||
| Although the tetrarchic system as such only lasted until 313, many aspects of it survived. The fourfold regional division of the empire continued in the form of ]s, each of which was overseen by a ] and subdivided into administrative ], and often reappeared in the title of the military supra-provincial command assigned to a '']''. | |||
| The pre-existing notion of '']'', the sharing of imperial power, and |
The pre-existing notion of '']'', the sharing of imperial power, and the notion that an associate to the throne was the designated successor (possibly conflicting with the notion of hereditary claim by birth or adoption), was to reappear repeatedly. | ||
| The idea of the two halves, the |
The idea of the two halves, the east and the west, re-emerged and eventually resulted in the permanent de facto division into two separate Roman empires after the death of ]; though, importantly, the Empire was never formally divided. The emperors of the eastern and western halves legally ruled as one imperial college until the ] left Byzantium, the "second Rome", as the sole direct heir. | ||
| == |
==Other examples== | ||
| * |
*Tetrarchies in the ancient world existed in both ] (in northern Greece) and ] (in central ]; including ]) as well as among the British ]. | ||
| * |
*The constellation of Jewish principalities in the ] of ] was known as a tetrarchy; see ]. | ||
| *In the novel '']'', the ] siblings rule ] as a tetrarchy of two kings and two queens. | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *{{lang|la|]}}, a later document from the imperial chancery | |||
| {{Epochs of Roman Emperors}} | |||
| *{{annotated link|Problem of two emperors}} | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| ==Citations== | |||
| *], a later document from the imperial chancery | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| *], Realencyclopädie der Klassischen Altertumswissenschaft | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| <!-- Alphabetic order--> | |||
| (incomplete) | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Barnes |first=Timothy D. |author-link=Timothy Barnes (classicist) |url=https://archive.org/details/constantineeuseb0000barn |title=Constantine and Eusebius |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=1984 |isbn=0674165314}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Barnes |year=1982 |first=Timothy D. |title=The New Empire of Diocletian and Constantine |publisher=Harvard University Press |doi=10.4159/harvard.9780674280670 |place=Cambridge, MA |isbn=0-674-28066-0 |url=https://archive.org/details/barnes-new-empire}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Bowman |first=Alan |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.70256 |title=The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193–337 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1939 |isbn=9780521044943}} | |||
| *{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| | last = Corcoran | | last = Corcoran | ||
| | first = Simon |
| first = Simon | ||
| | author-link=Simon Corcoran | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | url= https://books.google.com/books?id=27XwuaqMmt0C | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = The Empire of the Tetrarchs, Imperial Pronouncements and Government AD |
| title = The Empire of the Tetrarchs, Imperial Pronouncements and Government AD 284–324 | ||
| | publisher = |
| publisher = Oxford University Press | ||
| | |
| year = 2000 | ||
| | |
| isbn =019815304X }} | ||
| * {{cite book |first=Frank |last=Kolb |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SVe6hD-MG9AC |location=Berlin |publisher=de Gruyter |language=de|title=Diocletian und die Erste Tetrarchie: Improvisation oder Experiment in der Organisation monarchischer Herrschaft? |isbn=978-3110846508 |year=2011 }} | |||
| | pages = | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kuhoff |first=Wolfgang |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gQnFQgAACAAJ |location=Frankfurt am Main |publisher=Lang |title=Diokletian und die Epoche der Tetrarchie: Das römische Reich zwischen Krisenbewältigung und Neuaufbau (284–313 n. Chr.) |isbn=978-3631367926 |year=2001 }} | |||
| | url = http://www.oup.com/uk/catalogue/?ci=9780198153047 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Leadbetter |first=William Lewis |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QBBjy7l-NWQC |location=London; New York |publisher=Routledge |title=Galerius and the Will of Diocletian |isbn=978-1135261320 |year=2009 }} | |||
| | doi = | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Rees|first=Roger|title=Diocletian and the Tetrarchy|year=2004|location=Edinburgh|publisher=Edinburgh University Press|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wV5oAAAAMAAJ|isbn=978-0748616602}} | |||
| | id = ISBN 019815304X }} | |||
| *{{cite book | |||
| | last = Barnes | |||
| | first = Timothy D. | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = Constantine and Eusebius | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | date = 1984 | |||
| | location = | |||
| | pages = | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | id = ISBN 0674165314 }} | |||
| *{{cite book | |||
| | last = Rees | |||
| | first = Roger | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = Diocletian and the Tetrarchy | |||
| | publisher = Edinburgh University Press | |||
| | date = 2004 | |||
| | location = | |||
| | pages = | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | id = ISBN 0748616616 }} | |||
| *{{cite book | |||
| | last = Bowman | |||
| | first = Alan | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193-337 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | date = 2005 | |||
| | location = | |||
| | pages = | |||
| | url = http://www.cambridge.org/catalogue/catalogue.asp?isbn=0521301998 | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | id = ISBN 0521301998 }} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons category|Tetrarchy}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Epochs of Roman Emperors}} | |||
| {{Ancient Rome topics}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:51, 14 December 2024
Roman system of power division among four rulers This article is about the tetrarchy created by Diocletian. For the tetrarchy formed from the kingdom of Herod, see Herodian tetrarchy. For other uses, see Tetrarch (disambiguation).| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Roman imperial dynasties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Tetrarchy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Portrait of the Four Tetrarchs, two porphyry sculptures looted from the Philadelphion of Constantinople after 1204, now standing at the southwest corner of St Mark's Basilica, Venice Portrait of the Four Tetrarchs, two porphyry sculptures looted from the Philadelphion of Constantinople after 1204, now standing at the southwest corner of St Mark's Basilica, Venice | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Succession | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Politics of ancient Rome |
|---|
 |
| Periods |
|
| Constitution |
| Political institutions |
| Assemblies |
| Ordinary magistrates |
| Extraordinary magistrates |
| Public law |
| Senatus consultum ultimum |
| Titles and honours |
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the augusti, and their junior colleagues and designated successors, the caesares.
Initially Diocletian chose Maximian as his caesar in 285, raising him to co-augustus the following year; Maximian was to govern the western provinces and Diocletian would administer the eastern ones. The role of the augustus was likened to Jupiter, while his caesar was akin to Jupiter's son Hercules. Galerius and Constantius were appointed caesares in March 293. Diocletian and Maximian retired on 1 May 305, raising Galerius and Constantius to the rank of augustus. Their places as caesares were in turn taken by Valerius Severus and Maximinus Daza.
The orderly system of two senior and two junior rulers endured until Constantius died in July 306, and his son Constantine was unilaterally acclaimed augustus and caesar by his father's army. Maximian's son Maxentius contested Severus' title, styled himself princeps invictus, and was appointed caesar by his retired father in 306. Severus surrendered to Maximian and Maxentius in 307. Maxentius and Constantine were both recognized as augusti by Maximian that same year. Galerius appointed Licinius augustus for the west in 308 and elevated Maximinus Daza to augustus in 310.
Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312 left him in control of the western part of the empire, while Licinius was left in control of the east on the death of Maximinus Daza. Constantine and Licinius jointly recognized their sons – Crispus, Constantine II, and Licinius II – as caesares in March 317. Ultimately the tetrarchic system lasted until c. 324, when mutually destructive civil wars eliminated most of the claimants to power: Licinius resigned as augustus after losing the Battle of Chrysopolis, leaving Constantine in control of the entire empire.
The Constantinian dynasty's emperors retained some aspects of collegiate rule; Constantine appointed his son Constantius II as another caesar in 324, followed by Constans in 333 and his nephew Dalmatius in 335, and the three surviving sons of Constantine in 337 were declared joint augusti together, and the concept of the division of the empire under multiple joint emperors endured until the Fall of the Western Roman Empire. In the Eastern Roman Empire, augusti and caesares continued to be appointed sporadically.
Terminology
The term tetrarchy (from the Greek: τετραρχία, tetrarchia, "leadership of four ") describes any form of government where power is divided among four individuals.
Although the term "tetrarch" was current in antiquity, it was never used in the imperial college (as it's often called) under Diocletian. Instead, the term was used to describe independent portions of a kingdom that were ruled under separate leaders. The tetrarchy of Judaea, established after the death of Herod the Great, is the most famous example of the antique tetrarchy. The term was understood in the Latin world as well, where Pliny the Elder glossed it as follows: "each is the equivalent of a kingdom, and also part of one" (regnorum instar singulae et in regna contribuuntur).
As used by the ancients, the term describes not only different governments, but also a different system of government from the Diocletianic arrangements. The Judaean tetrarchy was a set of four independent and distinct states, where each tetrarch ruled a quarter of a kingdom as they saw fit; the Diocletianic tetrarchy was a college led by a single supreme leader. When later authors described the period, this is what they emphasized: Ammianus had Constantius II admonish Gallus for disobedience by appealing to the example in submission set by Diocletian's lesser colleagues; his successor Julian compared the Diocletianic tetrarchs to a chorus surrounding a leader, speaking in unison under his command. Only Lactantius, a contemporary of Diocletian and a deep ideological opponent of the Diocletianic state, referred to the tetrarchs as a simple multiplicity of rulers.
Much modern scholarship was written without the term. Although Edward Gibbon pioneered the description of the Diocletianic government as a "New Empire", he never used the term "tetrarchy"; neither did Theodor Mommsen. It did not appear in the literature until used in 1887 by schoolmaster Hermann Schiller in a two-volume handbook on the Roman Empire (Geschichte der Römischen Kaiserzeit), to wit: "die diokletianische Tetrarchie". Even so, the term did not catch on in the literature until Otto Seeck used it in 1897.

Creation
The first phase, sometimes referred to as the diarchy ("rule of two"), involved the designation of the general Maximian as co-emperor—firstly as caesar (heir apparent) in 285, followed by his promotion to augustus in 286. Diocletian took care of matters in the eastern regions of the empire while Maximian similarly took charge of the western regions. In 293, Diocletian thought that more focus was needed on both civic and military problems, so with Maximian's consent, he expanded the imperial college by appointing two caesares (one responsible to each augustus)—Galerius and Constantius I.
In 305, the senior emperors jointly abdicated and retired, allowing Constantius and Galerius to be elevated in rank to augustus. They in turn appointed two new caesares—Severus II in the west under Constantius, and Maximinus in the east under Galerius—thereby creating the second Tetrarchy.
Regions and capitals
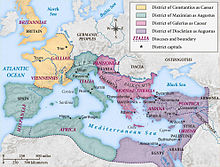
The four tetrarchs based themselves not at Rome but in other cities closer to the frontiers, mainly intended as headquarters for the defence of the empire against bordering rivals (notably Sassanian Persia) and barbarians (mainly Germanic, and an unending sequence of nomadic or displaced tribes from the eastern steppes) at the Rhine and Danube. These centres are known as the tetrarchic capitals. Although Rome ceased to be an operational capital, Rome continued to be nominal capital of the entire Roman Empire, not reduced to the status of a province but under its own, unique Prefect of the city (praefectus urbi, later copied in Constantinople).
The four tetrarchic capitals were:
- Nicomedia in northwestern Asia Minor (modern İzmit in Turkey), a base for defence against invasion from the Balkans and Persia's Sassanids was the capital of Diocletian, the eastern (and most senior) augustus; in the final reorganisation by Constantine the Great, in 318, the equivalent of his domain, facing the most redoubtable foreign enemy, Sassanid Persia, became the praetorian prefecture Oriens, 'the East', the core of later Byzantium.
- Sirmium (modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina region of modern Serbia, and near Belgrade, on the Danube border) was the capital of Galerius, the eastern caesar; this was to become the Balkans-Danube prefecture Illyricum.
- Mediolanum (modern Milan, near the Alps) was the capital of Maximian, the western augustus; his domain became "Italia et Africa", with only a short exterior border.
- Augusta Treverorum (modern Trier, in Germany) was the capital of Constantius, the western caesar, near the strategic Rhine border; it had been the capital of Gallic emperor Tetricus I. This quarter became the prefecture Galliae.
Aquileia, a port on the Adriatic coast, and Eboracum (modern York, in northern England near the Celtic tribes of modern Scotland and Ireland), were also significant centres for Maximian and Constantius respectively.
In terms of regional jurisdiction there was no precise division among the four tetrarchs, and this period did not see the Roman state actually split up into four distinct sub-empires. Each emperor had his zone of influence within the Roman Empire, but little more, mainly high command in a 'war theater'. Each tetrarch was himself often in the field, while delegating most of the administration to the hierarchic bureaucracy headed by his respective praetorian prefect, each supervising several vicarii, the governors-general in charge of another, lasting new administrative level, the civil diocese. For a listing of the provinces, now known as eparchy, within each quarter (known as a praetorian prefecture), see Roman province.
In the West, the augustus Maximian controlled the provinces west of the Adriatic Sea and the Syrtis, and within that region his caesar, Constantius, controlled Gaul and Britain. In the East, the arrangements between the augustus Diocletian and his caesar, Galerius, were much more flexible.
Public image
Although power was shared in the tetrarchic system, the public image of the four members of the imperial college was carefully managed to give the appearance of a united empire (patrimonium indivisum). This was especially important after the numerous civil wars of the 3rd century.
The tetrarchs appeared identical in all official portraits. Coinage dating from the tetrarchic period depicts every emperor with identical features—only the inscriptions on the coins indicate which one of the four emperors is being shown. The Byzantine sculpture Portrait of the Four Tetrarchs shows the tetrarchs again with identical features and wearing the same military costume.
Military successes
One of the greatest problems facing emperors in the Third Century Crisis was that they were only ever able to personally command troops on one front at any one time. While Aurelian and Probus were prepared to accompany their armies thousands of miles between war regions, this was not an ideal solution. Furthermore, it was risky for an emperor to delegate power in his absence to a subordinate general, who might win a victory and then be proclaimed as a rival emperor himself by his troops (which often happened). All members of the imperial college, on the other hand, were of essentially equal rank, despite two being senior emperors and two being junior; their functions and authorities were also equal.
Under the Tetrarchy a number of important military victories were secured. Both the dyarchic and the tetrarchic system ensured that an emperor was near to every crisis area to personally direct and remain in control of campaigns simultaneously on more than just one front. After suffering a defeat by the Persians in 296, Galerius crushed Narseh in 298—reversing a series of Roman defeats throughout the century—capturing members of the imperial household and a substantial amount of booty and gaining a highly favourable peace treaty, which secured peace between the two powers for a generation. Similarly, Constantius defeated the British usurper Allectus, Maximian pacified the Gauls, and Diocletian crushed the revolt of Domitianus in Egypt.
Demise
Main article: Civil wars of the TetrarchyWhen in 305 the 20-year term of Diocletian and Maximian ended, both abdicated. Their caesares, Galerius and Constantius Chlorus, were both raised to the rank of augustus, and two new caesares were appointed: Maximinus Daza (caesar to Galerius) and Valerius Severus (caesar to Constantius). These four formed the second tetrarchy.
However, the system broke down very quickly thereafter. When Constantius died in 306, Constantine, Constantius' son, was proclaimed augustus by his father's troops; however, Galerius instead chose to promote Severus to augustus while granting Constantine the position of caesar to Severus. At the same time, Maxentius, the son of Maximian, resented being left out of the new arrangements, so he rebelled against and defeated Severus before forcing him to abdicate and then arranging his murder in 307. Maxentius and Maximian both then declared themselves augusti. By 308 there were therefore no fewer than four claimants to the rank of augustus (Galerius, Constantine, Maximian and Maxentius), and only one to that of caesar (Maximinus Daza).
In 308 Galerius, together with the retired emperor Diocletian and the supposedly retired Maximian, called an imperial "conference" at Carnuntum on the River Danube. The council agreed that Licinius would become augustus in the West, with Constantine as his caesar. In the East, Galerius remained augustus and Maximinus remained his caesar. Maximian was to retire, and Maxentius was declared a usurper. This agreement proved disastrous: by 308 Maxentius had become de facto ruler of Italy and Africa even without any imperial status, and neither Constantine nor Maximinus—who had both been caesares since 306 and 305 respectively—were prepared to tolerate the promotion of the augustus Licinius as their superior.
After an abortive attempt to placate both Constantine and Maximinus with the meaningless title filius augusti ("son of the augustus", essentially an alternative title for caesar), they both had to be recognised as Augusti in 309. However, four full Augusti all at odds with each other did not bode well for the tetrarchic system.
Between 309 and 313 most of the claimants to the imperial office died or were killed in various civil wars. Constantine forced Maximian's suicide in 310. Galerius died naturally in 311. Maxentius was defeated by Constantine at the Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312 and subsequently killed. Maximinus committed suicide at Tarsus in 313 after being defeated in battle by Licinius.
By 313, therefore, there remained only two rulers: Constantine in the West and Licinius in the East. The tetrarchic system was at an end, although it took until 324 for Constantine to finally defeat Licinius, reunite the two halves of the Roman Empire and declare himself sole augustus.
Emperors
| Portrait | Name | Reign | Co-ruler(s) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Diocletian "Jovius" Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus (Whole, then East) |
20 November 284 – 1 May 305 (20 years, 5 months and 11 days) |
Maximian (caesar, 21 July 285; co-augustus, 1 May 305)
Galerius (caesar, 1 March 293) Constantius I (caesar, 1 March 293) |
|

|
Maximian "Herculius" Marcus Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus (West) |
1 April 286 – 1 May 305 (19 years and 1 month; retired)pac 28 October 306 – 11 November 308 |
Diocletian (augustus, 21 July 285; co-augustus, 1 May 305)
Galerius (caesar, 21 March 293) Constantius I (caesar, 1 March 293) Maxentius (co-augustus, 306–308) Constantine I (rival augustus, 25 July 306; co-augustus, 307) |
|

|
Galerius Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus (East) |
1 May 305– 5 May 311 (6 years and 4 days) |
Diocletian (augustus, 21 March 293–1 May 305)
Maximian (augustus, 21 March 293–1 May 305) Constantius I (caesar, 1 March 293; co-augustus, 1 May 305–25 July 306) Severus II (caesar, 1 May 305; co-augustus, August 306–April 307) Maxentius (caesar, 28 October 306; junior co-augustus, April 307–May 311) Licinius (designated augustus for the West, 11 November 308–311) Maximinus II (caesar, 1 May 305; co-augustus, 1 May 310–early May 311) |
|

|
Constantius I "Chlorus" Marcus Flavius Valerius Constantius (West) |
1 May 305 – 25 July 306 (1 year, 2 months and 24 days) |
Diocletian (augustus, 1 March 293–1 May 305)
Maximian (augustus, 1 April 286–1 May 305) Galerius (caesar, 21 March 293; co-augustus, 1 May 305–25 July 306) Severus II (caesar, 1 May 305 –July 306) Maximinus II (caesar, 1 May 305–25 July 306) |
|

|
Constantine I "the Great" Flavius Valerius Constantinus (West) |
25 July 306 – 18 September 324 (18 years, 1 month and 25 days; sole emperor 324–337) |
Maximian (rival augustus, 306–307; co-augustus, 307–308)
Maxentius (rival augustus, 306–307; co-augustus; 308) Licinius (rival augustus, 308–310; co-augustus, 310–316; rival, 316–324) Crispus (caesar, 1 March 317–324) Constantine II (caesar, 1 March 317–324) Martinian (rival augustus, 324) |
|

|
Severus II Flavius Valerius Severus (West) |
25 July 306 – April 307 (8 months) |
Galerius (augustus, 25 July 306–April 307)
Maxentius (rival augustus, 28 October 306) Constantine I (rival augustus, 306–307) Maximinus II (caesar, 1 May 305–April 307) |
|

|
Maxentius Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maxentius (West) |
28 October 306 – 28 October 312 (6 years) |
Maximian (co-augustus, 306–308)
Severus II (rival augustus, August 306–April 307) Licinius (rival-augustus, 11 November 308–28 October 312) Constantine I (rival augustus, 25 July 306–28 October 312) |
|

|
Licinius Valerius Licinianus Licinius (West, then East) |
11 November 308 – 19 September 324 (15 years, 10 months and 8 days) |
Constantine I (rival augustus, 308–310; co-augustus, 310–316; rival, 316–324)
Valens I (designated Western augustus, October 316–February 317) Licinius II (caesar, 1 March 317–324) Crispus (caesar, 1 March 317–324) Constantine II (caesar, 1 March 317–324) Martinian (designated Western augustus, July–September 324) |
|

|
Maximinus II "Daza" Galerius Valerius Maximinus (East) |
310 – c. July 313 (3 years) |
Constantius I (augustus, 1 May 305–25 July 306)
Galerius (augustus, 1 May 305–25 July 311) Severus II (caesar, 1 May 305; augustus 25 July 306) Maximian (augustus, late 306–November 308) Maxentius (rival augustus, 310–312) Constantine I (rival augustus, 310–313) Licinius (augustus, 308–313; rival augustus, 313–313) |
Family tree
| Simplified family tree of Tetrarchs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(See also: Chronological scheme of the Tetrarchy, 286–324)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Notes:
Bibliography:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Detailed timeline
| Diarchy 1 April 286 – 1 March 293 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Maximian Augustus | 
|
Diocletian Augustus |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Carausius in Britain (286–293) |
— | |
Two caesares are appointed in 293, thus starting the Tetrarchy.
| First Tetrarchy 1 March 293 – 1 May 305 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Maximian Augustus | 
|
Diocletian Augustus |

|
Constantius Caesar | 
|
Galerius Caesar |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Carausius in Britain (286–293) |

|
Domitian III in Egypt (297) |

|
Allectus in Britain (293–296) |
Achilleus in Egypt (297–298) | |
After the retirement of the two augusti both previous caesares succeeded them, and two new caesares were appointed.
| Second Tetrarchy 1 May 305 – 25 July 306 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Constantius Augustus | 
|
Galerius Augustus |

|
Severus Caesar | 
|
Maximinus Caesar |
After the sudden death of Constantius Chlorus (who died of natural causes), the caesar Flavius Severus succeeded him as augustus. However, Constantius' troops immediately proclaimed Constantine, Constantius' son, as their new augustus. Galerius accepted Constantine as part of the imperial college, but only as caesar. On 28 October 306, Maximian's son Maxentius proclaimed himself emperor in Rome. Maximian also proclaimed himself emperor, ruling jointly with his son. Despite being accepted by the Roman Senate, they were not recognized by the other emperors.
| Third Tetrarchy 25 July 306 – September 307 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Severus Augustus | 
|
Galerius Augustus |

|
Constantine Caesar (self-styled augustus) |

|
Maximinus Caesar |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Maxentius in Italy and Africa (from 28 October 306) |

|
Maximian in Italy and Africa (from 28 October 306) |
Severus was taken hostage by Maximian in April 307, but Galerius still acknowledged him as the official emperor of the west. Constantine was denied the promotion to augustus even after Severus' death in September, as Galerius had decided to exclude him from the system altogether. Maximian acknowledge Constantine's status as augustus, but this meant nothing given that he himself was declared an usurper. Galerius and Maximinus thus remained as the only "legimitate" members of the imperial college.
| Galerius as sole Augustus September 307 – November 308 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||
| (vacant) | 
|
Galerius Augustus | |

|
Maximinus Caesar | ||
| Usurpers | |||

|
Maxentius in Italy and Africa |

|
Maximian in Italy and Africa |

|
Constantine in Gaul and Hispania |
||
At the council of Carnutum, Diocletian decides that Licinius will be the new augustus of the west (although his western domains only consist of the Diocese of Pannonia). Constantine was given back the title of caesar, which he continued to unacknowledge.
| Fourth Tetrarchy 11 November 308 – May 310 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Licinius Augustus | 
|
Galerius Augustus |

|
Constantine Caesar (self-styled augustus) |

|
Maximinus Caesar |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Maxentius in Italy |

|
Domitius Alexander in Africa (308–310?) |
Maximinus was proclaimed augustus by his troops in about May 310. Galerius reluctantly agreed to recognize both Maximinus and Constantine as augusti, thus breaking the Diocletian's tetrarchic system.
| Tetrarchy of Augusti May 310 – May 311 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Licinius Augustus | 
|
Galerius Augustus |

|
Constantine Augustus | 
|
Maximinus Augustus |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Maxentius In Italy and Africa |

|
Maximian In Gaul, c. July 310 |
After the death of Galerius' (who died of natural causes), Licinius acquires parts of his domains, thus ruling over territories both in the East and West.
| Tetrarchy of Augusti May 311 – August 313 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Licinius Augustus | (Licinius) | |

|
Constantine Augustus | 
|
Maximinus Augustus |
| Usurpers | |||

|
Maxentius In Italy and Africa (until 28 October 312) |
— | |
Licinius eventually fights and defeats Maximinus, gaining all eastern territories. He then makes peace with Constantine, who remains as the emperor of the West. This joint rule lasted until 316, when Licinius rejected Constantine's election of Bassianus as caesar. In the ensuing war, both augusti appointed their own sons as caesares, restoring a dynastic system. Licinius appointed Valens and Martinian as augustus in 316 and 324 respectively (literary sources refer to them as caesar, but coins bear the title augustus); almost nothing is known about them.
| New Diarchy August 313 – 18 September 324 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Roman Empire | Eastern Roman Empire | ||

|
Constantine Augustus | 
|
Licinius Augustus |

|
Crispus Caesar from 317 |

|
Valens Augustus in 316 |

|
Constantine Caesar from 317 |

|
Martinian Augustus in 324 |
| — | 
|
Licinius Caesar from 317 | |
Chronological table
Legacy

Although the tetrarchic system as such only lasted until 313, many aspects of it survived. The fourfold regional division of the empire continued in the form of Praetorian prefectures, each of which was overseen by a praetorian prefect and subdivided into administrative dioceses, and often reappeared in the title of the military supra-provincial command assigned to a magister militum.
The pre-existing notion of consortium imperii, the sharing of imperial power, and the notion that an associate to the throne was the designated successor (possibly conflicting with the notion of hereditary claim by birth or adoption), was to reappear repeatedly.
The idea of the two halves, the east and the west, re-emerged and eventually resulted in the permanent de facto division into two separate Roman empires after the death of Theodosius I; though, importantly, the Empire was never formally divided. The emperors of the eastern and western halves legally ruled as one imperial college until the Fall of the Western Roman Empire left Byzantium, the "second Rome", as the sole direct heir.
Other examples
- Tetrarchies in the ancient world existed in both Thessaly (in northern Greece) and Galatia (in central Asia Minor; including Lycaonia) as well as among the British Cantiaci.
- The constellation of Jewish principalities in the Herodian kingdom of Judea was known as a tetrarchy; see Tetrarchy (Judea).
- In the novel The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe, the Pevensie siblings rule Narnia as a tetrarchy of two kings and two queens.
See also
- Notitia dignitatum, a later document from the imperial chancery
- Problem of two emperors – Problem arising when multiple people claim the title of emperor
Notes
- Historian David Potter translates the term as "gang of four". See idem., Constantine the Emperor (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013), 1.
- Nominal emperor of the West.
- Nominal emperor of the West.
Citations
- Qtd. and tr. Leadbetter, Galerius, 3.
- Amm. Marc. 14.11.10; Jul. Caes. 315A-B.
- Leadbetter, Galerius, 3.
- Leadbetter, Galerius, 3–4.
- The chronology has been thoroughly established by Kolb, Diocletian, and Kuhoff, Diokletian.
- Gibbon, Edward (1776). "Chapter XIV". The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire. Vol. II.
- ^ Cooley, Alison E. (2012). "Imperial titles, Augustus–Justinian (Appendix 2)". The Cambridge Manual of Latin Epigraphy. pp. 488–509. doi:10.1017/cbo9781139020442.007. ISBN 9780521840262. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- ^ Barnes 1984, pp. 30–33.
References
- Barnes, Timothy D. (1984). Constantine and Eusebius. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674165314.
- Barnes, Timothy D. (1982). The New Empire of Diocletian and Constantine. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. doi:10.4159/harvard.9780674280670. ISBN 0-674-28066-0.
- Bowman, Alan (1939). The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193–337. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521044943.
- Corcoran, Simon (2000). The Empire of the Tetrarchs, Imperial Pronouncements and Government AD 284–324. Oxford University Press. ISBN 019815304X.
- Kolb, Frank (2011). Diocletian und die Erste Tetrarchie: Improvisation oder Experiment in der Organisation monarchischer Herrschaft? (in German). Berlin: de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3110846508.
- Kuhoff, Wolfgang (2001). Diokletian und die Epoche der Tetrarchie: Das römische Reich zwischen Krisenbewältigung und Neuaufbau (284–313 n. Chr.). Frankfurt am Main: Lang. ISBN 978-3631367926.
- Leadbetter, William Lewis (2009). Galerius and the Will of Diocletian. London; New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1135261320.
- Rees, Roger (2004). Diocletian and the Tetrarchy. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0748616602.
External links
- A detailed chronology of the tetrarchy from Diocletian to Constantine
- A chart showing the tetrarchy from Diocletian to Constantine
| Roman emperors by time period | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Ancient Rome topics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||
| Constitution | |||||
| Law | |||||
| Government | |||||
| Magistrates |
| ||||
| Military | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Culture | |||||
| Society | |||||
| Technology | |||||
| Latin | |||||
| Writers |
| ||||
| Major cities | |||||
| Lists and other topics |
| ||||
- Tetrarchy
- 293 establishments
- 313 disestablishments
- 290s establishments in the Roman Empire
- 310s disestablishments in the Roman Empire
- 3rd century in the Roman Empire
- 4th century in the Roman Empire
- States and territories established in the 290s
- States and territories disestablished in the 4th century
- Constitutional state types
- Emperors
- Monarchy
- 290s in the Roman Empire
- Roman emperors
- Crisis of the Third Century