| Revision as of 00:21, 11 August 2018 edit49.199.26.185 (talk) Added Cultural component of East asian Culture.Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 07:46, 4 January 2025 edit undo5.123.129.233 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Subregion of the Asian continent}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | {{Other uses}} | ||
| {{pp-move |
{{pp-move}} | ||
| {{Infobox continent | |||
| |title = East Asia | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | |||
| |image = East Asia (orthographic projection).svg | |||
| <!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> | |||
| |area = {{convert|11840000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} (]) | |||
| | name = East Asia | |||
| |population = 1.6 billion (2023; ]) | |||
| | native_name = {{nobold|{{lang|zh-hans|东亚}} <small>{{zh-hans icon}}</small><br />{{lang|zh-hant|東亞}} <small>{{zh-hant icon}}</small><br />{{lang|ja|東アジア }} <small>{{ja icon}}</small><br />{{lang|ko|동아시아}} <small>{{ko icon}}</small>}} | |||
| |density = {{convert|141.9|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} | |||
| | settlement_type = ] of ] | |||
| |GDP_nominal = $25.7 trillion (2024)<ref name="IMF"/> | |||
| | image_skyline = | |||
| |GDP_PPP = $47.6 trillion (2024)<ref name="IMF"/> | |||
| | image_alt = | |||
| |GDP_per_capita = $16,000 (nominal)<ref name="IMF"/> | |||
| | image_caption = | |||
| |demonym = ] | |||
| | image_map = East Asia (orthographic projection).svg | |||
| |countries = {{collapsible list | |||
| | map_alt = | |||
| | list_style = text-align:left; | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = ] and other ] | |||
| | title = ]<ref name="Kort 2005 7" /><ref name="RAND"/><ref name="NO">{{cite web |title=Countries of Asia |url=https://www.nationsonline.org/oneworld/asia.htm#East-Asia |website=nationsonline.org |publisher=Nations Online |access-date=12 August 2021 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010701135048/http://www.nationsonline.org:80/oneworld/asia.htm |archive-date=2001-07-01 }}</ref> | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = {{plainlist| | |||
| | 1 = {{flag|China}} | |||
| | 2 = {{flag|Japan}} | |||
| ** ] ] | |||
| | 3 = {{flag|Mongolia}} | |||
| ** ] ] | |||
| | 4 = {{flag|North Korea}} | |||
| * {{JPN}} | |||
| | 5 = {{flag|South Korea}} | |||
| * {{MNG}} | |||
| | 6 = {{flag|Taiwan}} | |||
| * {{KOR}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |dependencies = {{collapsible list | |||
| | subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| | list_style = text-align:left; | |||
| | subdivision_name2 = {{plainlist| | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| * China | |||
| | 1 = {{HKG}} | |||
| ** ] ] | |||
| | 2 = {{MAC}} | |||
| *** {{MAC}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |languages = | |||
| | subdivision_type3 = Major cities | |||
| {{Plainlist| | |||
| | subdivision_name3 = {{plainlist| | |||
| * China | |||
| ** ] ] | |||
| *** ''']''' | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** {{HKG}} | |||
| *** {{MAC}} | |||
| ** ] ] | |||
| *** ''']''' | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| * {{JPN}} | |||
| ** ''']''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * {{KOR}} | |||
| ** ''']''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * {{PRK}} | |||
| ** ''']''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * {{MNG}} | |||
| ** ''']''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| }} | |||
| | unit_pref = Metric | |||
| | area_footnotes = <ref group="note">The area figure is based on the combined areas of ], ], ], ] and ] as listed at ].</ref> | |||
| | area_total_km2 = 11839074 | |||
| | area_land_km2 = | |||
| | area_water_km2 = | |||
| | area_water_percent = <!-- square kilometers --> | |||
| | area_note = | |||
| | dimensions_footnotes = | |||
| | length_km = | |||
| | width_km = | |||
| | population_total = {{UN_Population|Eastern Asia}} | |||
| | population_as_of = {{UN_Population|Year}} | |||
| | population_footnotes = <ref group=note>The population figure is the combined populations of ], ], ], ] and ] as listed at {{UN_Population|source}}.</ref> | |||
| | population_rank = ] | |||
| | population_density_km2 = auto | |||
| | utc_offset1 = | |||
| | timezone1 = {{Plainlist| | |||
| * ] (]) | |||
| * ] (], ], ], ], ]) | |||
| * ] (], ], ]) | |||
| }} | |||
| | timezone1_DST = | |||
| | utc_offset1_DST = | |||
| | blank_name_sec1 = Languages and language families | |||
| | blank_info_sec1 = {{Flatlist| | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 108: | Line 35: | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] (]) | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| }} | |||
| |time = ], ] & ] | |||
| |cities = ]:<br>{{hlist|] |]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|] |]|] |] |]}} | |||
| |m49 = <code>030</code> – Eastern Asia<br /><code>142</code> – ]<br /><code>001</code> – ] | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Infobox Chinese | |||
| | t = 東亞/東亞細亞 | |||
| | s = 东亚/东亚细亚 | |||
| | order = st | |||
| | p = Dōngyǎ/Dōngyà ''or'' Dōng Yǎxìyǎ/Dōng Yàxìyà | |||
| | w = Tung1-ya3 | |||
| | j = dung1 aa3 | |||
| | poj = Tang-a | |||
| | gan = Tung1 nga3 | |||
| | wuu = ton<sup>平</sup> ia<sup>去</sup> | |||
| | h = dung<sup>24</sup> a<sup>31</sup> | |||
| | tib = ཨེ་ཤ་ཡ་ཤར་མ་ | |||
| | mon = Зүүн Ази <br />{{MongolUnicode|ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠠᠽᠢ}} | |||
| | monr = Dzuun Azi | |||
| | uig = شەرقىي ئاسىي | |||
| | kana = ひがしアジア/とうあ | |||
| | shinjitai = 東亜細亜(東アジア)/東亜 | |||
| | kyujitai = 東亞細亞/東亞 | |||
| | revhep = Higashi Ajia/Tō-A | |||
| | kunrei = Higasi Azia/Tou-A | |||
| | hanja = 東아시아/東亞細亞/東亞 | |||
| | hangul = 동아시아/동아세아/동아 | |||
| | rr = Dong Asia/Dong Asea/Dong A | |||
| | uly = sherqiy asiy | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''East Asia''' is a geographical and cultural region of ] including ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="Kort 2005 7">{{Cite book |last=Kort |first=Michael |url=https://archive.org/details/handbookofeastas0000kort/page/7 |title=The Handbook Of East Asia |publisher=Lerner |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-761-32672-4 |page=}}</ref><ref name="RAND">{{cite web |title=East Asia |url=https://www.rand.org/topics/east-asia.html |website=rand.org |publisher=] |access-date=12 August 2021 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110102093024/http://www.rand.org:80/topics/east-asia.html |archive-date=2011-01-02 }}</ref> Additionally, ] and ] are the two ]. The economies of ], ], ], and ] are among the world's largest and most prosperous. East Asia borders ] to the north, ] to the south, ] to the southwest, and ] to the west. To its east is the ]. | |||
| {{Chinese | |||
| |t = 東亞/東亞細亞 | |||
| |s = 东亚/东亚细亚 | |||
| |order = st | |||
| |p = Dōngyà ''or'' Dōng Yàxìyà | |||
| |w = Tung<sup>1</sup>-ya<sup>3</sup> | |||
| |j = dung1 aa3 | |||
| |poj = Tang-a | |||
| |gan = Tung1 nga3 | |||
| |wuu = ton<sup>平</sup> ia<sup>去</sup> | |||
| |h = dung<sup>24</sup> a<sup>31</sup> | |||
| |tib = ཨེ་ཤ་ཡ་ཤར་མ་ | |||
| |mon = Зүүн Ази <br />{{MongolUnicode|ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠠᠽᠢ}} | |||
| |monr = Dzuun Azi | |||
| |uig = شەرقىي ئاسىي | |||
| |kana = ひがしアジア/とうあ | |||
| |shinjitai = 東亜細亜(東アジア)/東亜 | |||
| |kyujitai = 東亞細亞/東亞 | |||
| |revhep = Higashi Ajia/Tō-A | |||
| |kunrei = Higasi Azia/Tou-A | |||
| |hanja = 東아시아/東亞細亞/東亞 | |||
| |hangul = 동아시아/동아세아/동아 | |||
| |chuhan = 東亞 | |||
| |qn = Đông Á | |||
| |rr = Dong Asia/Dong Asea/Dong A | |||
| |rus = Восточная Азия | |||
| |rusr = Vostochnaja Azija | |||
| }} | |||
| East Asia, especially ], is regarded as one of the earliest ]. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the ], ], and ] civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past but have since been absorbed into neighbouring civilizations in the present day, such as ], ], and ] (Okinawa), among many others. Taiwan has a relatively young ] in the region after the ]; originally, it was a major site of ] civilisation prior to colonisation by European colonial powers and China from the 17th century onward. For thousands of years, China was the leading civilization in the region, exerting influence on its neighbours.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Zaharna |first1=R. S. |title=Relational, Networked and Collaborative Approaches to Public Diplomacy: The Connective Mindshift |last2=Arsenault |first2=Amelia |last3=Fisher |first3=Ali |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-415-63607-0 |page=93}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Holcombe |first=Charles |title=A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-107-54489-5 |page=13}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Szonyi |first=Michael |title=A Companion to Chinese History |publisher=Wiley–Blackwell |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-118-62460-9 |page=90}}</ref> Historically, societies in East Asia have fallen within the ], and East Asian vocabularies and scripts are often derived from ] and ]. The ] serves as the root from which many other East Asian calendars are derived. | |||
| '''East Asia''' is the eastern ] of the Asian continent, which can be defined in either ]<ref name=encarta-east-asia>{{cite web | |||
| |url = http://encarta.msn.com/dictionary_1861672714/East_Asia.html | |||
| |title = East Asia | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-01-12 | |||
| |work = ] | |||
| |publisher = Microsoft | |||
| |quote = the countries and regions of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Mongolia, South Korea, North Korea and Japan. | |||
| |archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5kwbU9Hqq?url=http://encarta.msn.com/dictionary_1861672714/East_Asia.html | |||
| |archivedate=2009-10-31 | |||
| |deadurl=yes | |||
| |df= | |||
| }}</ref> or ]<ref name=easia-columbia> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080227154316/http://afe.easia.columbia.edu/webcourse/key_points/kp_5.htm |date=2008-02-27 }} "The East Asian cultural sphere evolves when Japan, Korea, and what is today Vietnam all share adapted elements of Chinese civilization of this period (that of the Tang dynasty), in particular Buddhism, Confucian social and political values, and literary Chinese and its writing system."</ref> terms.<ref name="Prescott 2015">{{Cite book |title = East Asia in the World: An Introduction |last=Prescott |first= Anne |publisher=Routledge |year=2015 |isbn=978-0765643223 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Modern East Asia: An Introductory History |last=Miller |first=David Y. |publisher=Routledge |year=2007 |isbn=978-0765618221 |pages=xxi–xxiv }}</ref> Geographically and geopolitically, the region constitutes China, ], ], ] and ].<ref name="Prescott 2015" /><ref name="Kort 2005 7">{{cite book |title=The Handbook Of East Asia |last = Kort |first=Michael |publisher=Lerner Publishing Group |year=2005 |isbn=978-0761326724 |page=7 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www1.essex.ac.uk/armedcon/world/asia/east_asia/default.htm |title=Country Profiles: East Asia |website=Children and Armed Conflict Unit at the University of Essex }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |title=East Asia |url = https://link.springer.com/journal/12140 |publisher=Springer Netherlands }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.dictionary.com/browse/east-asia |title=East Asia |website=Dictionary.com }}</ref><ref name="encarta-east-asia"/><ref>{{cite web |url = https://asiasociety.org/china-korea-and-japan-forgiveness-and-mourning |title=China, Korea and Japan: Forgiveness and Mourning |last=Seybolt |first= Peter J. |website=Center for Asian Studies |publisher=Center for Asian Studies }}</ref><ref name="Asian History Module Learning">{{cite book |title=Asian History Module Learning |publisher=Rex Bookstore Inc. |year= 2002 |isbn=978-9712331244 |page=186 }}</ref><ref name="Salkind 2008 56">{{cite book |title=Encyclopedia of Educational Psychology |last=Salkind |first=Neil J. |publisher=Sage Publications |year=2008 |isbn = 978-1412916882 |page=56 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century |last=Holcombe |first= Charles |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2010 |isbn=978-0521731645 |page = 3 }}</ref> | |||
| Major ] include ] (mostly ]),<ref>{{Cite book |last=Selin |first=Helaine |title=Nature Across Cultures: Views of Nature and the Environment in Non-Western Cultures |publisher=Springer |year=2010 |isbn=978-9-048-16271-0 |page=350}}</ref> ] and ], ],<ref name=":2">{{Cite book |last1=Laozi |author-link=Laozi |title=Tao Te Ching: The Classic Book of Integrity and the Way |last2=Mair |first2=Victor H. |author-link2=Victor H. Mair |publisher=] |year=1998 |isbn=978-0-965-06475-0 |location=New York |pages=x}}</ref> ], and ] in Mainland China, ], ] and ], ] in Japan, and ] and ] in Korea.<ref name="Salkind 2008 56">{{Cite book |last=Salkind |first=Neil J. |url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaeduc00salk |title=Encyclopedia of Educational Psychology |publisher=Sage Publications |year=2008 |isbn=978-1-412-91688-2 |page= |url-access=limited}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Kim |first=Chongho |title=Korean Shamanism: The Cultural Paradox |publisher=Ashgate |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-754-63185-9}}</ref><ref>Andreas Anangguru Yewangoe, "Theologia crucis in Asia", 1987 Rodopi</ref> ] and ] are prevalent among ] and ] while other religions such as ] are widespread among the indigenous populations of northeastern China such as the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Heissig |first=Walther |title=The Religions of Mongolia |publisher=Kegan Paul International |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-710-30685-2 |page=46 |translator-last=Samuel |translator-first=Geoffrey}}</ref> The major ] include ], ], and ]. The major ] include the ] in China and Taiwan, ] in Japan, ] in North and South Korea, and ]s in Mongolia. There are 76 officially-recognized ] or ] ethnic groups in East Asia; ] (including ], Manchus, ], Tibetans, ], and ] in the ]), 16 native to the ] (collectively known as ]), one native to the ] of ] (the ]) and four native to ] (]). The ] are an unrecognized ethnic group indigenous to the ] in southern Japan, which stretch from ] to Taiwan. There are also several unrecognized indigenous ethnic groups in mainland China and Taiwan. | |||
| Culturally, ], ], ] and ] are commonly seen as being encompassed by '''cultural East Asia''' (]). | |||
| East Asians comprise around {{#expr:{{replace|{{UN_Population|Eastern Asia}}|,||}}/1e9 round 1}} billion people, making up about 33% of the population in Continental Asia and 20% of the global population.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Wang |first1=Yuchen |last2=Lu |first2=Dongsheng |last3=Chung |first3=Yeun-Jun |last4=Xu |first4=Shuhua |year=2018 |title=Genetic structure, divergence and admixture of Han Chinese, Japanese and Korean populations |journal=Hereditas |volume=155 |page=19 |doi=10.1186/s41065-018-0057-5 |pmc=5889524 |pmid=29636655 |doi-access=free}}</ref>{{Update inline|date=August 2023}} The region is home to major world metropolises such as ]–], ]–]–]–], ], ], ]–]–], ], ], ], ], and ]. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in ] and ], both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the ]. The overall population density of the region is {{convert|133|PD/km2}}, about three times the world average of {{convert|45|/km2|abbr=on}}.{{When|date=May 2020}}{{Citation needed|date=May 2020}} | |||
| The region was the cradle of various ancient civilizations such as ], ], ], and the ].<ref>{{cite book |title = Towards a Sustainable Asia: The Cultural Perspectives |author = Association of Academies of Sciences in Asia |publisher=Springer |year=2012 |isbn= 978-3642166686 |page=17 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title = Ethnic Groups of North, East, and Central Asia: An Encyclopedia |last= Minahan |first= James B. |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2014 |isbn=978-1610690171 |pages = xx–xxvi }}</ref> East Asia was one of the cradles of world civilization, with ]. For thousands of years, China largely influenced East Asia as it was principally the leading civilization in the region exerting its enormous prestige and influence on its neighbors.<ref>{{Cite book |title = Relational, Networked and Collaborative Approaches to Public Diplomacy: The Connective Mindshift |last= Zaharna |first= R.S. |last2=Arsenault |first2= Amelia |last3=Fisher |first3= Ali |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-0415636070 |edition=1st |publication-date = 2013-05-01 |page=93 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title = A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century |last= Holcombe |first=Charles |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2017 |isbn=978-1107544895 |page=13 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=A Companion to Chinese History |last=Szonyi |first=Michael |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |year=2017 |isbn=978-1118624609 |page = 90 }}</ref> Historically, societies in East Asia have been part of the ], and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from ] and ]. The ] preserves traditional East Asian culture and serves as the root to which many other East Asian calendars are derived from. Major ] include ] (mostly ]<ref group="note">includes ] traditionally prevailing in Tibetan and Mongolian areas</ref>), ] and ], ], ], and ] in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, ] and ] in Japan, and ], ] and ] in Korea.<ref name="Salkind 2008 56" /> ] is also prevalent among ] and other indigenous populations of northern East Asia such as the ]s.<ref>Chongho Kim, "Korean Shamanism", 2003 Ashgate Publishing</ref><ref>Andreas Anangguru Yewangoe, "Theologia crucis in Asia", 1987 Rodopi</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] comprise around {{#expr:{{replace|{{UN_Population|Eastern Asia}}|,||}}/1e9 round 1}} billion people, making up about 38% of the population in Continental Asia and 22% of the global population. The region is home to major world metropolises such as ], ], ], ], ], and ]. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in ] and ], both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the ]. The overall ] of the region is {{convert|133|PD/km2}}, about three times the world average of {{convert|45|/km2|abbr=on}}. | |||
| == History == | |||
| {{Main|History of East Asia}} | {{Main|History of East Asia}} | ||
| === Ancient era === | |||
| In comparison with the profound influence of the Ancient Greeks and Romans on Europe and the Western World, China would already possess an advanced civilization nearly half a millennia before Japan and Korea.<ref name="Ellington 2009 21">{{cite book |title=Japan (Nations in Focus) |last=Ellington |first=Lucien |year=2009 |page=21 }}</ref> As Chinese civilization existed for about 1500 years before other East Asian civilizations emerged into history, Imperial China would exert much of its cultural, economic, technological, and political muscle onto its neighbors.<ref>{{cite book |title=East Asia: A New History |last=Walker |first=Hugh Dyson |publisher=AuthorHouse |year=2012 |page=119 }}</ref><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121">{{cite book |title=The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America |publisher=Penguin Press HC |author1=Amy Chua |author2 = Jed Rubenfeld |year=2014 |page=121 |isbn=978-1594205460 }}</ref><ref name="Kang 2012 33–34" /> Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically and militarily for over two millennia.<ref name="Kang 2012 33–34">{{Cite book |title=East Asia Before the West: Five Centuries of Trade and Tribute |last=Kang |first=David C. |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=2012 |isbn=978-0231153195 |pages=33–34}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=World History: Journeys from Past to Present |last=Goucher |first=Candice |last2=Walton |first2=Linda |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn=978-0415670029 |publication-date=September 11, 2012 |page=232 }}</ref> Imperial China's cultural preeminence not only led the country to become East Asia's first literate nation in the entire region, it also supplied Japan, Vietnam and Korea with Chinese loanwords and linguistic influences rooted in their writing systems.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Chinese |last=Norman |first=Jerry |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1988 |isbn=978-0521296533 |page=17 }}</ref> In addition, the Chinese ] hosted the largest unified population in East Asia, the most literate and urbanized as well as being the most technologically and culturally advanced civilization in the region.<ref>{{cite book |title=Day of Empire: How Hyperpowers Rise to Global Dominance--and Why They Fall |last=Chua |first= Amy |publisher=Anchor |year=2009 |isbn=978-1400077410 |page=62 }}</ref> Cultural and religious interaction between the Chinese and other regional East Asian dynasties and kingdoms occurred. China's impact and influence on Korea began with the Han dynasty's ] in 108 BC when the Han Chinese conquered the northern part of the Korean peninsula and established a province called ]. Chinese influence would soon take root in Korea through the inclusion of the Chinese writing system, monetary system, rice culture, and Confucian political institutions.<ref>{{cite book |title=Maritime Taiwan: Historical Encounters with the East and the West |last= Tsai |first= Henry |date = 2009-02-15 |publisher= Routledge |isbn = 978-0765623287 |page = 3 }}</ref> Jomon society in ancient Japan incorporated wet-rice cultivation and metallurgy through its contact with Korea. Vietnamese society was greatly impacted by Chinese influence, the northern part of Vietnam was occupied by Chinese empires and states for almost all of the period from 111 BC to 938 AD. In addition to administration, and making Chinese the language of administration, the long period of Chinese domination introduced Chinese techniques of dike construction, rice cultivation, and animal husbandry. Chinese culture, having been established among the elite mandarin class, remained the dominant current among that elite for most of the next 1,000 years (939-1870s) until the loss of independence under French Indochina. This cultural affiliation to China remained true even when militarily defending Vietnam against attempted invasion, such as against the Mongol Kublai Khan. The only significant exceptions to this were the 7 years of the strongly anti-Chinese Hồ dynasty which banned the use of Chinese (among other actions triggering the fourth Chinese invasion), but then after the expulsion of the Ming the rise in vernacular chữ nôm literature. Although 1,000 years of Chinese rule left many traces, the collective memory of the period reinforced Vietnam's cultural and later political independence. As full-fledged medieval East Asian states were established, Korea by the fourth century AD and Japan by the seventh century AD, Korea, Japan and Vietnam actively began to incorporate Chinese influences such as ], the use of ], ], state institutions, political philosophies, religion, urban planning, and various scientific and technological methods into their culture and society through direct contacts with succeeding Chinese dynasties.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Oxford Companion to Archaeology |last=Fagan |first=Brian M. |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0195076189 |page=362 }}</ref> For many centuries, most notably from the 7th to the 14th centuries, China stood as East Asia's most advanced civilization, commanding influence across the region up until the early modern period.<ref>{{cite book |title = China, Japan, Korea: Culture and Customs |last= Brown |first=John |publisher=Createspace Independent |year=2006 |isbn=978-1419648939 |page = 33 }}</ref> The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.<ref>{{cite book |title=Daily Lives of Civilians in Wartime Asia: From the Taiping Rebellion to the Vietnam War |last= Lone |first= Stewart |publisher=Greenwood |year=2007 |isbn=978-0313336843 |page = 3 }}</ref><ref name="Warren I. Cohen 2000">Warren I. Cohen. ''East Asia at the Center : Four Thousand Years of Engagement with the World.'' (New York: Columbia University Press, 2000. {{ISBN|0231101082}}</ref><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121"/> The transmission of advanced Chinese cultural practices and ways of thinking greatly shaped the region up until the 19th century.<ref name="Ellington 2009 21"/> | |||
| China was the first region settled in East Asia and was undoubtedly the core of East Asian civilization from where other parts of East Asia were formed. The various other regions in East Asia were selective in the Chinese influences they adopted into their local customs. Historian ] referred to China as the cradle of Eastern civilization, in parallel with the ] along the ] encompassing ] and ]<ref>{{Cite book |last=Holcombe |first=Charles |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kYKlDQAAQBAJ&q=east+asia+history&pg=PA12 |title=A History of East Asia |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-107-11873-7}}</ref> as well as the ] encompassing ]. | |||
| Chinese civilization emerged early, and prefigured other East Asian civilisations. Throughout history, imperial China would exert cultural, economic, technological, and political influence on its neighbours.<ref name="Ball 2005 104">{{Cite book |last=Ball |first=Desmond |title=The Transformation of Security in the Asia/Pacific Region |publisher=Routledge |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-714-64661-9 |page=104}}</ref><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121">{{Cite book |last1=Chua |first1=Amy |title=The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America |last2=Rubenfeld |first2=Jed |publisher=Penguin |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-594-20546-0 |page=121}}</ref><ref name="Kang 2012 33–34" /> Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically and militarily for over two millennia.<ref name="Kang 2012 33–34">{{Cite book |last=Kang |first=David C. |title=East Asia Before the West: Five Centuries of Trade and Tribute |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-2-311-5319-5 |pages=33–34}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Goucher |first1=Candice |title=World History: Journeys from Past to Present |last2=Walton |first2=Linda |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-415-67002-9 |page=232}}</ref><ref name="2000years">{{Cite book |last=Smolnikov |first=Sergey |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3LJZDwAAQBAJ&q=pax+sinica+han+dynasty&pg=PA112 |title=Great Power Conduct and Credibility in World Politics |publisher=Springer |year=2018 |isbn=978-3-319-71885-9}}</ref> The ] shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Lone |first=Stewart |url=https://archive.org/details/dailylivescivili00lone |title=Daily Lives of Civilians in Wartime Asia: From the Taiping Rebellion to the Vietnam War |publisher=Greenwood |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-313-33684-3 |page= |url-access=limited}}</ref><ref name="Warren I. Cohen 2000">{{Cite book |last=Cohen |first=Warren I. |author-link=Warren I. Cohen |title=East Asia at the Center: Four Thousand Years of Engagement with the World |publisher=Columbia University Press |year=2000 |isbn=0-231-10108-2 |location=New York}}</ref><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121" /> Imperial China's cultural preeminence not only led the country to become East Asia's first literate nation in the entire region, it also supplied Japan and Korea with Chinese loanwords and linguistic influences rooted in their writing systems.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Chinese |last=Norman |first=Jerry |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1988 |isbn=978-0-521-29653-3 |page=17}}</ref> | |||
| Under ], the ] made China the regional powerhouse in East Asia, projecting much of its imperial influence onto its neighbours.<ref name="Kang 2012 33–34" />{{sfn|Cohen|2000|page=60}} Han China hosted the largest unified population in East Asia, the most literate and urbanised as well as being the most economically developed, as well as the most technologically and culturally advanced civilization in the region at the time.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Chua |first=Amy |title=Day of Empire: How Hyperpowers Rise to Global Dominance—and Why They Fall |publisher=Anchor |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-400-07741-0 |page=62}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Leibo |first=Steve |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9781610488853/page/19 |title=East and Southeast Asia 2012 |publisher=Stryker-Post |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-610-48885-3 |page=}}</ref> Cultural and religious interaction between the Chinese and other regional East Asian dynasties and kingdoms occurred. China's impact and influence on Korea began with the Han dynasty's ] in 108 BC when the Han Chinese conquered the northern part of the Korean peninsula and established a province called ]. Chinese influences were transmitted and soon took root in Korea through the inclusion of the Chinese writing system, monetary system, rice culture, philosophical schools of thought, and Confucian political institutions.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Tsai |first=Henry |title=Maritime Taiwan: Historical Encounters with the East and the West |publisher=Routledge |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-765-62328-7 |page=3}}</ref> Jomon society in ancient Japan incorporated wet-rice cultivation and metallurgy through its contact with Korea. Starting in the fourth century AD, Japan adopted ], which remain integral to the ]. Utilizing the Chinese writing system allowed the Japanese to conduct their daily activities, maintain historical records and give form to various ideas, thoughts, and philosophies. | |||
| === Medieval era === | |||
| ] compared to today's ]]]During the ], China exerted its greatest influence on East Asia as various aspects of Chinese culture spread to ] and ].<ref name="lockard1999p2-3">{{Cite journal |last=Lockard |first=Craig |year=1999 |title=Tang Civilization and the Chinese Centuries |url=http://www.columbia.edu/itc/ealac/moerman/fall2000/edit/pdfs/wk5/tangci.pdf |journal=Encarta Historical Essays |pages=2–3, 7}}</ref> The establishment of the medieval Tang dynasty rekindled the impetus of Chinese expansionism across the geopolitical confines of East Asia. Similar to its ] predecessor, Tang China reasserted itself as the center of East Asian geopolitical influence during the early medieval period which spearheaded and marked another ]. During the Tang dynasty, China exerted its greatest influence on East Asia as various aspects of Chinese culture spread to Japan and Korea.<ref name="lockard1999p2-3" /><ref name="lockard1999p7">{{harvnb|Lockard|1999|p=7}}</ref> In addition, Tang China also managed to maintain control over northern Vietnam and ].<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Injae |first1=Lee |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=46OTBQAAQBAJ&q=goguryeo+tang+war&pg=PA29 |title=Korean History in Maps |last2=Miller |first2=Owen |last3=Jinhoon |first3=Park |last4=Hyun-Hae |first4=Yi |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-107-09846-6 |via=Google Books}}</ref> | |||
| As full-fledged medieval East Asian states were established, Korea by the fourth century AD and Japan by the seventh century AD, Japan and Korea actively began to incorporate Chinese influences such as ], the use of ], ], state institutions, ], religion, urban planning, and various ] methods into their culture and society through direct contacts with Tang China and succeeding Chinese dynasties.<ref name="lockard1999p2-3" /><ref name="lockard1999p7" /><ref>{{Cite book |last=Fagan |first=Brian M. |title=The Oxford Companion to Archaeology |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-195-07618-9 |page=362}}</ref> Drawing inspiration from the Tang political system, Prince ] launched the ] in 645 AD where he radically transformed Japan's political bureaucracy into a more centralised bureaucratic empire.<ref name="lockard1999p8">{{harvnb|Lockard|1999|p=8}}</ref> The Japanese also adopted Mahayana Buddhism, Chinese style architecture, and the imperial court's rituals and ceremonies, including the orchestral music and state dances had Tang influences. Written Chinese gained prestige and aspects of Tang culture such as ], ], and ] became widespread.<ref name="lockard1999p8" /> During the ], Japan began to aggressively import Chinese culture and styles of government which included Confucian protocol that served as a foundation for Japanese culture as well as political and social philosophy.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Lockard |first=Craig A. |title=Societies Networks And Transitions: Volume B From 600 To 1750 |publisher=Wadsworth |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-439-08540-0 |pages=290–291}}</ref><ref name="Tang6">{{Cite book |last1=Embree |first1=Ainslie |url=https://archive.org/details/asiainwesternwor00ains |title=Asia in Western and World History: A Guide for Teaching |last2=Gluck |first2=Carol |publisher=M. E. Sharpe |year=1997 |isbn=978-1-563-24265-6 |page= |url-access=registration}}</ref> The Japanese also created laws adopted from the Chinese legal system that was used to govern in addition to the ], which was inspired from Chinese '']'' during the eighth century. | |||
| === Modern era === | |||
| ] and expansion of the empire|left]] | |||
| For many centuries, most notably from the 7th to the 14th centuries, China stood as East Asia's most advanced civilization and foremost military and economic power, exerting its influence as the transmission of advanced Chinese cultural practices and ways of thinking greatly shaped the region up until the nineteenth century.<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Lind |first=Jennifer |date=February 13, 2018 |title=Life in China's Asia: What Regional Hegemony Would Look Like |url=https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/china/2018-02-13/life-chinas-asia |magazine=Foreign Affairs |volume=97 |issue=March/April 2018}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Lockard|1999}}</ref><ref name="Ellington 2009 21">{{Cite book |last=Ellington |first=Lucien |title=Japan |publisher=Bloomsbury |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-598-84163-3 |series=Nations in Focus |page=21}}</ref> From third century through the eighteenth century, diplomatic and trade relations between China and other East Asian countries and the steppe kingdoms was governed through a tributary system.<ref name=":02" />{{Rp|pages=13-14}} Under this system, the Chinese emperor received tribute from other rulers and in return received political benefits (like recognition or non-aggression agreements) or physical gifts, like porcelain and silks.<ref name=":02" />{{Rp|page=14}} Through this system, the Chinese emperor conferred legitimacy on other rulers.<ref name=":02" />{{Rp|page=14}} | |||
| As East Asia's connections with Europe and the Western world strengthened during the late nineteenth century, China's power began to decline.<ref name="Ball 2005 104" /><ref>{{Cite book |last=Roberts |first=John M. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3QZXvUhGwhAC |title=A Short History of the World |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1997 |isbn=0-195-11504-X |page=272}}</ref> By the mid-nineteenth century, the weakening ] became fraught with political corruption, obstacles and stagnation that was incapable of rejuvenating itself as a world power in contrast to the industrializing Imperial European colonial powers and a rapidly modernizing Japan.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hayes |first=Louis D. |title=Political Systems of East Asia: China, Korea, and Japan |publisher=Greenlight |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-765-61786-6 |page=xi}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Hayes|2009|p=15}}</ref> The United States Commodore ] would ], and the country would expand in earnest after the 1860s.<ref name="Tindall 2009 926">{{Cite book |last1=Tindall |first1=George Brown |title=America: A Narrative History |last2=Shi |first2=David E. |publisher=W. W. Norton |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-393-934083 |page=926}}</ref><ref name="April 2007 163">{{Cite book |last1=April |first1=K. |url=https://archive.org/details/diversitynewreal00apri |title=Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World |last2=Shockley |first2=M. |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-230-00133-6 |pages= |url-access=limited}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Cohen|2000|p=3}}</ref> Around the same time, the ] in Japan sparked rapid societal transformation from an isolated feudal state into East Asia's first industrialised nation.<ref name="Batty 2005">{{Cite AV media |title=Japan's War in Colour |date=2005-01-17 |last=Batty |first=David |type=documentary |publisher=TWI}}</ref><ref name="April 2007 163" /> The modern and militarily powerful Japan would galvanise its position in the Orient as East Asia's greatest power with a global mission poised to advance to lead the entire world.<ref name="Batty 2005" /><ref name="Goldman 2000 3">{{Cite book |title=Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World |last1= Goldman |first1= Merie |last2=Gordon |first2=Andrew |publisher=Harvard University Press |year= 2000 |isbn=978-0-674-00097-1 |page=3}}</ref> By the early 1900s, the ] succeeded in asserting itself as East Asia's most dominant geopolitical force.<ref name="Goldman 2000 3" /> | |||
| ] and ] in East Asia and Oceania, circa 1914]] | |||
| With its newly found international status, Japan would begin to challenge the European colonial powers and inextricably took on a more active role within the East Asian geopolitical order and world affairs at large.{{sfn|Cohen|2000|p=273}} Flexing its nascent political and military might, Japan soundly defeated the stagnant Qing dynasty during the ] as well as defeating Russia in the ] in 1905; the first major military victory in the modern era of an East Asian power over a European one.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Hua |first1=Shiping |title=East Asian Development Model: Twenty-first century perspectives |last2=Hu |first2=Amelia |publisher=Routledge |year=2014 |isbn=978-0-415-73727-2 |pages=78–79}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Lee |first1=Yong Wook |title=China's Rise and Regional Integration in East Asia: Hegemony or community? |last2=Key |first2=Young Son |publisher=Routledge |year=2014 |isbn=978-0-313-35082-5 |page=45}}</ref><ref>{{Cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/546176/Sino-Japanese-War|title=Sino-Japanese War (1894–95)|encyclopedia=]|access-date=12 November 2012}}</ref><ref name="Tindall 2009 926" /> Its hegemony was the heart of an empire that would include ] and ].<ref name="Batty 2005" /> During World War II, Japanese expansionism with its imperialist aspirations through the ] would incorporate Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China and Manchuria, Hong Kong, and Southeast Asia under its control establishing itself as a maritime colonial power in East Asia.<ref>{{harvnb|Tindall|Shi|2009|p=1147}}</ref> | |||
| === Contemporary era === | |||
| {{See also|Pacific Century}} | |||
| After a century of exploitation by the European and Japanese colonialists, post-colonial East Asia saw the ] and ] by the victorious Allies. The end of World War II did not result in east Asian countries obtaining independence or national unification.<ref name=":02">{{Cite book |last=Li |first=Xiaobing |title=The Cold War in East Asia |date=2018 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-138-65179-1 |location=Abingdon, Oxon}}</ref>{{Rp|page=4}} Independence and national unification were primary concerns for the first generation of east Asian post-World War II leaders.<ref name=":02" />{{Rp|page=4}} | |||
| The ] resumed after the defeat of the Japanese, with the Communists defeating the Nationalist Republic of China government. The ] and the ] on 1 October 1949. | |||
| Post-war, the ], leading to the development of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (]) and the Republic of Korea (]). The ] (1950-1953) increased regional and international tensions.<ref name=":12222">{{Cite book |last=Liff |first=Adam P. |title=The Taiwan Question in Xi Jinping's Era: Beijing's Evolving Taiwan Policy and Taiwan's Internal and External Dynamics |last2=Lee |first2=Chaewon |publisher=] |year=2024 |isbn=9781032861661 |editor-last=Zhao |editor-first=Suisheng |editor-link=Suisheng Zhao |location=London and New York |pages= |chapter=Korea-Taiwan "Unofficial" Relations after 30 Years (1992-2022): Reassessing Seoul's "One China" Policy |doi=}}</ref>{{Rp|page=163}} The northeast part of east Asia hardened along communist and anti-communist lines.<ref name=":12222" />{{Rp|page=163}} South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States increased their ties.<ref name=":12222" />{{Rp|page=163}} | |||
| During the latter half of the twentieth century, the region would see the ], which ushered in three decades of unprecedented growth, only to experience an ], but nonetheless Japan continues to remain a global economic power. East Asia would also see the ], ], and ], in addition to the respective handovers of ] and ] near the end of the twentieth century. | |||
| As East Asia's connections with Europe and the Western world strengthened during the late 19th century, China's power began to decline. U.S. Commodore ] would ], and the country would expand in earnest after the 1860s.<ref name="Tindall 2009 926">{{Cite book |title=America: A Narrative History |last= Tindall |first=George Brown |last2=Shi |first2= David E. |publisher= W. W. Norton & Company |year=2009 |isbn=978-0393934083 |edition=1st |publication-date=November 16, 2009 |page=926 }}</ref><ref name="April 2007 163">{{cite book |title = Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World |last= April |first= K. |last2=Shockley |first2=M. |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year= 2007 |isbn=978-0230001336 |publication-date=February 6, 2007 |page=163 }}</ref> Around the same time, Japan with its ] transformed itself from an isolated feudal samurai state into East Asia's first industrialized nation.<ref name="Batty 2005">{{cite video |title=Japan's War in Colour |date = 2005-01-17 |last=Batty |first=David |type=documentary |publisher=TWI |year=2005 }}</ref><ref name="Asian History Module Learning"/><ref name="April 2007 163" /> The modern and powerful Japan would galvanize its position in the Orient as East Asia's greatest power with a global mission poised to advance to lead the entire world.<ref name="Batty 2005"/> By the early 1900s, the ] succeeded in asserting itself as East Asia's first modern power. With its newly found international status, Japan would begin to inextricably take a more active position in East Asia and leading role in world affairs at large. Flexing its nascent political and military might, Japan soundly defeated the stagnant ] during the ] as well as vanquishing imperial rival ] in 1905; the first major military victory in the modern era of an East Asian power over a European one.<ref>{{cite web |url = https://www.nakasendoway.com/the-japanese-economy/ |title = The Japanese Economy |website = Walk Japan }}</ref><ref name="Tindall 2009 926"/> Its hegemony was the heart of an ] that would include ] and ].<ref name="Batty 2005" /> During World War II, Japanese expansionism with its imperialist aspirations through the ] would incorporate Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China and Manchuria, Hong Kong, Vietnam and Southeast Asia under its control establishing itself as a maritime colonial power in East Asia.<ref>{{Cite book |title=America: A Narrative History |last= Tindall |first=George Brown |last2=Shi |first2= David E. |publisher= W. W. Norton & Company |year=2009 |isbn=978-0393934083 |edition=1st |publication-date=November 16, 2009 |page=1147 }}</ref> After a century of exploitation by the European and Japanese colonialists, post-colonial East Asia saw the ] and ] by the victorious Allies as well as the division of China and ] during the ]. The Korean peninsula became independent but then it was divided into ], while Taiwan became the main territory of de facto state ] after the latter lost Mainland China to the ] in the ]. During the latter half of the twentieth century, the region would see the ], the economic rise of ] and ], and the integration of ] through its entry in the ] while enhancing its emerging international status as a ].<ref name="Kort 2005 7"/><ref>{{Cite book |title=Encyclopedia of World Trade: From Ancient Times to the Present |last= Northrup |first= Cynthia Clark |last2=Bentley |first2= Jerry H. |last3= Eckes Jr. |first3= Alfred E. |publisher= Routledge |year=2004 |isbn= 978-0765680587 |page=297 }}</ref> | |||
| The onset of the 21st-century in East Asia led to the integration of ] through its entry in the ] while also enhancing its ] as a potential world power reinforced with its aim of restoring its historical established significance and enduring international prominence in the world economy.<ref name="Kort 2005 7" /><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Northrup |first1=Cynthia Clark |url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofwo0000unse_d8h7/page/297 |title=Encyclopedia of World Trade: From Ancient Times to the Present |last2=Bentley |first2=Jerry H. |last3=Eckes |first3=Alfred E. Jr. |publisher=Routledge |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-765-68058-7 |page=}}</ref><ref name="Paul 2012 114">{{Cite book |last=Paul |first=Erik |title=Neoliberal Australia and US Imperialism in East Asia |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2012 |isbn=978-1-137-27277-5 |page=114}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Maddison |first=Angus |author-link=Angus Maddison |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=a-JGGp2suQUC&q=angus+maddison |title=Contours of the World Economy 1–2030 AD: Essays in Macro-Economic History |publisher=] |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-191-64758-1 |page=379}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last1=Dahlman |first1=Carl J |last2=Aubert |first2=Jean-Eric |title=China and the Knowledge Economy: Seizing the 21st Century. WBI Development Studies |url=http://www.eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/custom/portlets/recordDetails/detailmini.jsp?_nfpb=true&_&ERICExtSearch_SearchValue_0=ED460052&ERICExtSearch_SearchType_0=no&accno=ED460052 |access-date=26 July 2014 |publisher=Institute of Education Sciences}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Angus Maddison. Chinese Economic Performance in the Long Run. Development Centre Studies. |url=http://piketty.pse.ens.fr/files/Maddison98.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://piketty.pse.ens.fr/files/Maddison98.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |access-date=15 September 2017 |page=29}}</ref><ref>. WBI Development Studies. ] publications. Accessed January 30, 2008.</ref><ref>]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141015212817/http://browse.oecdbookshop.org/oecd/pdfs/product/4107091e.pdf |date=2014-10-15 }}. Development Centre Studies. Accessed 2007. p.29 See the "Table 1.3. Levels of Chinese and European GDP Per Capita, 1–1700 AD" in page 29, Chinese GDP Per Capita was 450 and European GDP Per Capital was 422 in 960AD. Chinese GDP Per Capita was 600 while European was 576. During this time, Chinese per capita income rose by about a third.</ref> | |||
| As of at least 2022, the region is more peaceful, integrated, wealthy, and stable than any time in the previous 150 years.<ref name=":Ma&Kang">{{Cite book |last=Ma |first=Xinru |title=Beyond Power Transitions: The Lessons of East Asian History and the Future of U.S.-China Relations |last2=Kang |first2=David C. |date=2024 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-231-55597-5 |series=Columbia Studies in International Order and Politics |location=New York}}</ref>{{Rp|page=183}} | |||
| ==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
| ] region that overlap with conceptions of East Asia<!--DO NOT REMOVE There is an overlap between the concepts of East Asia and Central Asia that needs to be illustrated here.-->]] | |||
| In common usage, the term East Asia typically refers to a region including ], ], ] and ].<ref>Gilbet Rozman (2004), ''Northeast asia's stunted regionalism: bilateral distrust in the shadow of globalization''. Cambridge University Press, pp. 3-4.</ref><ref>"." Retrieved on August 8, 2001.</ref><ref>"." Retrieved on August 8, 2011.</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Wastewater Sludge |last= Spinosa |first=Ludovico |publisher= Iwa Publishing |year= 2007 |isbn= 978-1843391425 |page=57}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Solution-Focused Brief Therapy: A Multicultural Approach |last=Kim |first=Johnny S. |publisher=Sage Publications |year=2013 |isbn=978-1452256672 |page=55 }}</ref> | |||
| In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including ], ], ] and ].<ref name="Paul 2012 114" /><ref>{{Cite web |date=September 10, 2016 |title=Introducing East Asian Peoples |url=https://www.imb.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Introducing_EAP_Booklet_09_2016_10.pdf |website=International Mission Board}}</ref><ref>Gilbet Rozman (2004), ''Northeast Asia's stunted regionalism: bilateral distrust in the shadow of globalization''. Cambridge University Press, pp. 3-4</ref><ref>"." Retrieved on August 8, 2001.</ref><ref>"."{{dead link|date=August 2024}} Retrieved on August 8, 2011.</ref>{{sfn|Hua|Hu|2014|p=3}}<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Ness |first1=Immanuel |title=The Global Prehistory of Human Migration |last2=Bellwood |first2=Peter |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-118-97059-1 |page=217}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Kort|2005|pages=7–9}}</ref> | |||
| ], ], and ] represent the three core countries and civilizations of traditional East Asia - as they once shared a common written language, culture, as well as sharing Confucian philosophical tenets and the Confucian societal value system once instituted by Imperial China.<ref>{{cite book |title=Economic Development in Twentieth-Century East Asia: The International Context |last=Ikeo |first=Aiko |publisher= Routledge |year=1996 |isbn=978-0415149006 |page=1 }}</ref><ref name="Yoshimatsu 2014 1">{{cite book |title=Comparing Institution-Building in East Asia: Power Politics, Governance, and Critical Junctures |last=Yoshimatsu |first=H. |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2014 |isbn=978-1137370549 |page=1 }}</ref><ref name="Yoshimatsu 2014 1" /><ref>{{cite book |title=Routledge Handbook of Memory and Reconciliation in East Asia |last= Kim |first= Mikyoung |publisher= Routledge |year=2015 |isbn= 978-0415835138 }}</ref><ref name="Hazen 2005 1">{{cite book |title=Building Area Studies Collections |last= Hazen |first= Dan |last2=Spohrer |first2=James H. |publisher=Otto Harrassowitz |year=2005 |isbn=978-3447055123 |publication-date = 2005-12-31 |page=1 }}</ref> Other usages define Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, South Korea, North Korea and Taiwan as countries that constitute East Asia based on their geographic proximity as well as historical and modern cultural and economic ties, particularly with Japan and Korea having strong cultural influences that originated from China.<ref name="Hazen 2005 1" /><ref>{{cite book |title=Economic Development: A Regional, Institutional, and Historical Approach |last=Grabowski |first=Richard |last2=Self |first2=Sharmistha |last3=Shields |first3=William |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn= 978-0765633538 |edition=2nd |publication-date=September 25, 2012 |page=59 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url = https://www.bluebackglobal.com/east-asia-market-overview/ |title=East Asia is the World’s Largest Economy at $29.6 Trillion USD, Including 4 of the Top 25 Countries Globally |last= Ng |first=Arden |website=Blueback }}</ref><ref name="Prescott 2015"/><ref>{{Cite book |title=Through the Eyes of the Pack |last=Currie |first=Lorenzo |publisher=Xlibris Corp |year= 2013 |isbn=978-1493145171 |page = 163 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Handbook for Asian Studies Specialists: A Guide to Research Materials and Collection Building Tools |last= Asato |first= Noriko |publisher= Libraries Unlimited |year=2013 |isbn=978-1598848427 |page=1 }}</ref> Some scholars include ] as part of East Asia as it has been considered part of the greater ] of Chinese influence. Though Confucianism continues to play an important role in Vietnamese culture, Chinese characters are no longer used in its written language and many scholarly organizations classify Vietnam as a Southeast Asian country.<ref name="Prescott 2015"/><ref name="Miller 2007 xi">{{cite book |title=Modern East Asia: An Introductory History |last=Miller |first=David Y. |publisher=Routledge |year=2007 |isbn=978-0765618221 |page=xi }}</ref> Mongolia is geographically north of Mainland China yet Confucianism and the Chinese writing system and culture had no impact in Mongolian society. Thus, Mongolia is sometimes grouped with Central Asian countries such as Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan.<ref name="Prescott 2015" /><ref name="Miller 2007 xi" /> | |||
| ], ], and ] represent the three core countries and civilizations of traditional East Asia, as they once had a shared written language, a shared culture, and a shared Confucian societal value system (involving shared Confucian philosophical tenets) once instituted by Imperial China.<ref name="Prescott 2015 3">{{Cite book |title = East Asia in the World: An Introduction |last=Prescott |first= Anne |publisher=Routledge |year=2015 |isbn=978-0765643223 |pages =3 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Ikeo |first=Aiko |title=Economic Development in Twentieth-Century East Asia: The International Context |publisher=Routledge |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-415-14900-6 |page=1}}</ref><ref name="Yoshimatsu 2014 1">{{Cite book |last=Yoshimatsu |first=H. |title=Comparing Institution-Building in East Asia: Power Politics, Governance, and Critical Junctures |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-137-37054-9 |page=1}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Kim |first=Mikyoung |title=Routledge Handbook of Memory and Reconciliation in East Asia |publisher=Routledge |year=2015 |isbn=978-0-415-83513-8}}</ref><ref name="Hazen 2005 1">{{Cite book |last1=Hazen |first1=Dan |title=Building Area Studies Collections |last2=Spohrer |first2=James H. |publisher=Otto Harrassowitz |year=2005 |isbn=978-3-447-05512-3 |page=130}}</ref> Other usages define China, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan as countries that constitute East Asia based on their geographic proximity as well as historical and modern cultural and economic ties, particularly with ] and ] in having retained strong cultural influences that originated from China.<ref name="Prescott 2015 3"/><ref name="Hazen 2005 1" /><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Grabowski |first1=Richard |title=Economic Development: A Regional, Institutional, and Historical Approach |last2=Self |first2=Sharmistha |last3=Shields |first3=William |publisher=Routledge |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-765-63353-8 |edition=2nd |publication-date=September 25, 2012 |page=59}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Currie |first=Lorenzo |title=Through the Eyes of the Pack |publisher=Xlibris Corp |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-493-14517-1 |page=163}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Asato |first=Noriko |title=Handbook for Asian Studies Specialists: A Guide to Research Materials and Collection Building Tools |publisher=Libraries Unlimited |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-598-84842-7 |page=1}}</ref> Some scholars include ] as part of East Asia as it has been considered part of the greater ]. Though Confucianism continues to play an important role in Vietnamese culture, Chinese characters are no longer used in its written language and many scholarly organizations classify Vietnam as a Southeast Asian country.<ref name="Prescott 2015 6">{{harvnb|Prescott|2015|p=6}}</ref><ref name="Miller 2007 xi">{{Cite book |last=Miller |first=David Y. |title=Modern East Asia: An Introductory History |publisher=Routledge |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-765-61822-1 |page=xi}}</ref><ref name="afe.easia.columbia.edu">{{Cite web|url=http://afe.easia.columbia.edu/main_pop/kpct/ct_china.htm|title=Central Themes for a Unit on China r Educators |publisher=Columbia University|website=afe.easia.columbia.edu|access-date=2018-12-01}} "Within the Pacific region, China is potentially a major economic and political force. Its relations with Japan, Korea, and its Southeast Asian neighbours, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and the Philippines, will be determined by how they perceive this power will be used."</ref> Mongolia is geographically north of Mainland China yet Confucianism and the Chinese writing system and culture had limited impact on Mongolian society. Thus, Mongolia is sometimes grouped with Central Asian countries such as Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan.<ref name="Prescott 2015 6" /><ref name="Miller 2007 xi" /> ] and ] are sometimes seen as part of Central Asia (see also ]).<ref>{{Cite book |last=Cummings |first=Sally N. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SRafuiRUJaMC&q=humboldt+central+asia+definition&pg=PT28 |title=Understanding Central Asia: Politics and Contested Transformations |publisher=Routledge |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-134-43319-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Saez |first1=Lawrence |title=The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): An emerging collaboration architecture |date=2012 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-136-67108-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yTzKWI42uR4C&q=humboldt+central+asia+Afghanistan&pg=PA35}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Cornell |first=Svante E. |url=http://silkroadstudies.org/resources/1811CA-Regional.pdf |title=Modernization and Regional Cooperation in Central Asia: A New Spring? |publisher=Central Asia-Caucasus Institute and the Silk Road Studies}}</ref> | |||
| Broader and looser definitions by international organizations such as the ] refer to the "three major Northeast Asian economies, i.e. ], ], and ]", as well as ], ], the ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Integration of Markets vs. Integration by Agreements|first=Nathalie|last=Aminian|first2=K.C.|last2=Fung|first3=Francis|last3=Ng|work=Policy Research Working Paper|number=4546|publisher=] |url = http://www-wds.worldbank.org/servlet/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2008/03/04/000158349_20080304084358/Rendered/PDF/wps4546.pdf }}</ref> The ] includes the Russia Far East, ], and ].<ref name="Northeast Asia"/> The World Bank also acknowledges the roles of sub-national or ], such as ], ], and ]. The Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia defines the region as "China, Japan, ]s, Nepal, Mongolia, and eastern regions of the ]".<ref>{{cite book|title=Japan and Russia in Northeast Asia: Partners in the 21st Century|author=Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|year=1999|page=248}}</ref> | |||
| Broader and looser definitions by international agencies and organisations such as the ] refer to East Asia as the "three major Northeast Asian economies, i.e. ], Japan, and ]", as well as Mongolia, ], the ], and ].<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Aminian |first1=Nathalie |last2=Fung |first2=K. C. |last3=Ng |first3=Francis |title=Integration of Markets vs. Integration by Agreements |url=http://www-wds.worldbank.org/servlet/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2008/03/04/000158349_20080304084358/Rendered/PDF/wps4546.pdf |website=Policy Research Working Paper |publisher=] |number=4546}}</ref> The ] includes the Russia Far East, Mongolia, and ].<ref name="Northeast Asia">{{cite web|url=http://www.cfr.org/region/478/northeast_asia.html|title=Northeast Asia|publisher=]|access-date=August 10, 2009}}</ref> The World Bank also acknowledges the roles of Chinese special administrative regions ] and ], as well as ], a country with limited recognition. The Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia defines the region as "China, Japan, the ]s, Nepal, Mongolia, and eastern regions of the ]".<ref>{{Cite book |last=Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia |title=Japan and Russia in Northeast Asia: Partners in the 21st Century |publisher=Greenwood |year=1999 |page=248}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] geoscheme for Asia based on statistic convenience rather than implying any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories:<ref name="auto">{{cite web |url = http://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm |title=United Nations Statistics Division – Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49) |publisher=] |accessdate=2010-07-24 |date = 2015-05-06 }}</ref> | |||
| ] (UNSD) ] for Asia works with subregions defined in terms of UN ] statistics.<ref name=m49>{{Cite web |title=UNSD — Methodology |website= unstats.un.org |url= https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/ |access-date= 2023-12-10}}</ref> The UNSD geoscheme is based on statistic convenience rather than implying any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories:<ref name="auto">{{Cite web |date=2015-05-06 |title=United Nations Statistics Division – Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49) |url=http://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm |access-date=2010-07-24 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{legend|#0000E0|]}} | {{legend|#0000E0|]}} | ||
| {{legend|#E000E0|]}} | {{legend|#E000E0|]}} | ||
| Line 182: | Line 132: | ||
| {{legend|#FFFF20|'''East Asia'''}} | {{legend|#FFFF20|'''East Asia'''}} | ||
| {{legend|#FFC000|]}}]] | {{legend|#FFC000|]}}]] | ||
| The ] definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience,<ref name="auto" /> but others commonly use the same definition of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan, and Japan.<ref name="encarta-east-asia">{{cite web |url = http://encarta.msn.com/dictionary_1861672714/East_Asia.html |title = East Asia |access-date = 2008-01-12 |work = ] |publisher = Microsoft |quote = the countries and regions of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Mongolia, South Korea, North Korea and Japan. |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20091109184354/http://encarta.msn.com/dictionary_1861672714/East_Asia.html |archive-date=2009-11-09 |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="UN regions">{{Cite web |date=11 February 2013 |title=Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings |url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm |access-date=28 May 2013 |publisher=United Nations Statistics Division}}</ref> | |||
| Certain Japanese islands are associated with Oceania due to non-continental geology, distance from mainland Asia or biogeographical similarities with ].<ref name="realm">{{Cite book |last=Todd |first=Ian |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gcEJAQAAIAAJ&q=%22French+language+cultures%22+1974+pacific |title=Island Realm: A Pacific Panorama |publisher=Angus & Robertson |year=1974 |isbn=978-0-207-127618- |page=190}}</ref><ref name="class">{{cite web |last1=Udvardy |first1=Miklos D. F. |title=A Classification of the Biogeographical Provinces of the World |url=https://fnad.org/Documentos/A%20Classification%20of%20the%20Biogeographical%20Provinces%20of%20the%20World%20Miklos%20D.F.%20Udvardy.pdf |publisher=UNESCO |access-date=7 March 2022 |archive-date=18 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220218131430/http://www.fnad.org/Documentos/A%20Classification%20of%20the%20Biogeographical%20Provinces%20of%20the%20World%20Miklos%20D.F.%20Udvardy.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> Some groups, such as the ], categorize China, Japan and Korea with Australia and the rest of Oceania. The World Health Organization label this region the "Western Pacific", with East Asia not being used in their concept of major world regions. Their definition of this region further includes Mongolia and the adjacent area of ], as well as the countries of the South East Asia Archipelago (excluding ] and ]).<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Countries-and-areas-in-WHOs-Western-Pacific-Region_fig1_256404088 |title=IMAGE: Countries and areas in WHO's Western Pacific Region |via=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Alternative definitions=== | |||
| {{See also|Pacific Asia}} | |||
| In the context of business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to the geographical area covering ten ]n countries in ], ], Japan, and Korea. However, in this context, the term "]" is used by the Europeans to cover ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. On rare occasions, the term is also sometimes taken to include ] and other South Asian countries that are not situated within the bounds of the Asia-Pacific, although the term ] is more commonly used for such a definition.<ref>{{Cite web |date=15 September 2021 |title=Forget Asia-Pacific, it's Indo-Pacific now. Where is that? |url=https://www.smh.com.au/national/forget-asia-pacific-it-s-the-indo-pacific-we-live-in-now-where-is-that-exactly-20210810-p58hku.html}}</ref> | |||
| Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term ] to refer to China, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with the region of ] covering the ten ] countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia".<ref>{{cite book|first=Christopher M. |last=Dent|year=2008|title=East Asian regionalism|url=https://archive.org/details/eastasianregiona00dent|url-access=limited|publisher=Routledge|pages=–8}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Harvie |first1=Charles |title=New East Asian regionalism |last2=Fukunari |first2=Kimura |last3=Lee |first3=Hyun-Hoon |publisher=Edward Elgar |year=2005 |pages=3–6}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Katzenstein |first1=Peter J. |title=Beyond Japan: the dynamics of East Asian regionalism |last2=Takashi |first2=Shiraishi |publisher=Cornell University Press |year=2006 |location=Ithaca |pages=1–33}}</ref> The ] of the United States defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.<ref name="Northeast Asia"/> | |||
| ==Climate== | |||
| The ] definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience,<ref name="auto" /> but also other common definitions of East Asia contain the Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan and Japan.<ref name=encarta-east-asia/><ref name="UN regions">{{cite web |title = Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings |publisher = United Nations Statistics Division |date = 11 February 2013 |url = http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm |accessdate = 28 May 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| ].]] | |||
| East Asia is home to many climatic zones. It also has unique weather patterns such as the ] and the ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=An |first=Z |date=April 2000 |title=Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon |journal=Quaternary Science Reviews |volume=19 |issue=8 |pages=743–762 |bibcode=2000QSRv...19..743A |doi=10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00031-1}}</ref> | |||
| Culturally, ], ], ] and ] are commonly seen as being encompassed by '''cultural East Asia''' (]).<ref name=easia-columbia/><ref>R. Keith Schopper's ''''</ref><ref>Joshua A. Fogel (UC Santa Barbara/University of Indiana) ''''</ref><ref>United Nations Environment Programme (mentions sinosphere countries) ''Approaches to Solution of Eutrophication'' </ref> | |||
| ===Climate change=== | |||
| === Alternative definitions === | |||
| {{Main|Climate change in Asia}} | |||
| There are mixed debates around the world whether these countries or regions should be considered in East Asia or not. | |||
| ] over at the ], which is particularly vulnerable as widespread ] results in very moist air. There is a risk that agricultural labourers will be physically unable to work outdoors on hot summer days at the end of the century, particularly under the scenario of greatest emissions and warming.<ref name="Kang2018">{{Cite journal |last1=Kang |first1=Suchul |last2=Eltahir |first2=Elfatih A. B. |date=31 July 2018 |title=North China Plain threatened by deadly heatwaves due to climate change and irrigation |journal=Nature Communications |volume=9 |issue=1 |page=3528 |doi=10.1038/s41467-023-38906-7 |doi-access=free |pmid=37402712 |pmc=10319847 |bibcode=2023NatCo..14.3528K }}</ref>]] | |||
| * ] (officially part of ] geographically, although culturally it is a part of the ], politically, it is related to both ] and East Asia) | |||
| * ] in ] (often described as ] due to its location, although this part of Russia is often seen as more closely related to its East Asian neighbours) | |||
| * Sovereignty issues exist over some ]. | |||
| Like the rest of the world, East Asia has been getting warmer due to climate change, and there had been a measurable increase in the frequency and severity of ]s.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" />{{rp|1464}} The region is also expected to see the intensification of its monsoon, leading to more flooding.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10">Shaw, R., Y. Luo, T. S. Cheong, S. Abdul Halim, S. Chaturvedi, M. Hashizume, G. E. Insarov, Y. Ishikawa, M. Jafari, A. Kitoh, J. Pulhin, C. Singh, K. Vasant, and Z. Zhang, 2022: . In . Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, New York, US, pp. 1457–1579 |doi=10.1017/9781009325844.012.</ref>{{rp|1459}} China has notably embarked on the ] program, where cities are designed to increase the area of ]s and ]s in order to help deal with ]s caused by greater precipitation extremes.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" />{{rp|1504}} Under high-warming scenarios, "critical health thresholds" for heat stress during the 21st century will be at times breached,<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" />{{rp|1465}} in areas like the ].<ref name="Kang2018" /> | |||
| In business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to a wide geographical area covering ten ]n countries in ], ], Japan and Korea. However, in this context, the term "Far East" is used by the Europeans to cover ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. However, being a Eurocentric term, ] describes the region's geographical position in relation to Europe rather than its location within Asia. Alternatively, the term "]" is often used in describing East Asia, Southeast Asia as well as ]. | |||
| China, Japan and the Republic of Korea are expected to see some of the largest economic losses caused by sea level rise.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" /> The city of ] is projected to experience the single largest ''annual'' economic losses from sea level rise in the world, potentially reaching US$254 million by 2050. Under the highest climate change scenario and in the absence of adaptation, cumulative economic losses caused by sea level rise in Guangzhou would exceed US$1 trillion by 2100.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" /> ] is also expected to experience annual losses of around 1% of the local GDP in the absence of adaptation.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" /> The ] basin is a sensitive and biodiverse ecosystem, yet around 20% of its species may be lost throughout the century under {{convert|2|C-change|F-change}} and ~43% under {{convert|4.5|C-change|F-change}}.<ref name="AR6_WGII_Chapter10" />{{rp|1476}} | |||
| Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term ] to refer to the greater China area, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with ] covering the ten ] countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia".<ref>{{cite book|author=Christopher M. Dent|year=2008|title=East Asian regionalism|publisher=London: Routledge|pages=1–8}}</ref><ref>Charles Harvie, Fukunari Kimura, and Hyun-Hoon Lee (2005), ''New East Asian regionalism''. Cheltenham and Northamton: Edward Elgar, pp. 3–6.</ref><ref>Peter J. Katzenstein and Takashi Shiraishi (2006), ''Beyond Japan: the dynamics of East Asian regionalism''. Ithaca: Cornell University Press, pp. 1–33</ref> The ] defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.<ref name="Northeast Asia">"." '']''. Retrieved on August 10, 2009.</ref> | |||
| == |
==Economy== | ||
| {{Main|Economy of East Asia}} | {{Main|Economy of East Asia}} | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| !class="unsortable" | |
!class="unsortable" | ] | ||
| ! data-sort-type="number"|]<br />billions of USD ( |
! data-sort-type="number" | ]<br />billions of USD (2024)<ref name="IMF">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/April/weo-report?c=111,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2027&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: April 2024|publisher=]|website=imf.org}}</ref> | ||
| ! data-sort-type="number"|]<br />USD ( |
! data-sort-type="number" | ]<br />USD (2024)<ref name="IMF"/> | ||
| ! data-sort-type="number"|]<br />billions of USD ( |
! data-sort-type="number" | ]<br />billions of USD (2024)<ref name="IMF"/> | ||
| ! data-sort-type="number"|]<br />USD ( |
! data-sort-type="number" | ]<br />USD (2024)<ref name="IMF"/> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{ |
| {{PRC}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 18,532,633 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 13,136 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 35,291,015 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 25,015 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{HKG}} |
| {{HKG}}{{efn|Listed as "Hong Kong SAR" by IMF}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 406,775 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 53,606 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 570,082 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 75,128 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{MAC}} |
| {{MAC}}{{efn|Listed as "Macao SAR" by IMF}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 54,677 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 78,962 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 92,885 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 125,510 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{JPN}} | | {{JPN}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 4,110,452 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 33,138 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 6,720,962 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 54,184 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{ |
| {{MNG}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 21,943 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 6,182 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 58,580 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 16,504 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{ |
| {{PRK}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | N/A | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | N/A | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | N/A | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | N/A | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{ |
| {{KOR}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,760,947 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 34,165 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 3,057,995 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 59,330 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{TWN}} |
| {{TWN}}{{efn|Listed as "]" by IMF}} | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 802,958 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 34,432 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,792,349 | ||
| |style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 76,858 | ||
| |- | |||
| ! East Asia | |||
| ! $25,690,385 | |||
| ! $15,612 | |||
| ! $47,583,868 | |||
| ! $28,916 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| == |
==Territorial and regional data== | ||
| China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state because of severe ongoing ] in the region, specifically the ] and the ]. | |||
| ===Etymology=== | ===Etymology=== | ||
| {| class=wikitable | {| class=wikitable | ||
| !rowspan=2|Flag!!colspan=2|Common Name!!colspan=2|Official |
! rowspan=2 | Flag !! colspan=2 | Common Name !! colspan=2 | Official name !! colspan=4 | ISO 3166 Country Codes<ref name=":0">{{cite web |url = https://www.iso.org/iso-3166-country-codes.html |title=Country codes |website=iso.org}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !]!!]!!]!!]!!ISO Short Name!!Alpha-2 Code!!Alpha-3 Code!!Numeric | ! ] !! ] !! ] !! ] !! ISO Short Name !! Alpha-2 Code !! Alpha-3 Code !! Numeric | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|CHN}}||]||align=center|{{lang|zh-cn|]}}|| |
| {{flagdeco|CHN}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|zh-cn|]}} || People's Republic of China || {{lang|zh-cn|中华人民共和国}} || China || CN || CHN || 156 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|HKG}}||]||align=center|{{lang|zh|]}}||Hong Kong Special Administrative Region<br>of the |
| {{flagdeco|HKG}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|zh|]}} || Hong Kong Special Administrative Region<br />of the People's Republic of China || {{lang|zh-hk|中華人民共和國香港特別行政區}} || Hong Kong || HK || HKG || 344 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|MAC}}||]||align=center|{{lang|zh-hk|]}}||Macao Special Administrative Region<br>of the |
| {{flagdeco|MAC}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|zh-hk|]}} || Macao Special Administrative Region<br />of the People's Republic of China || {{lang|zh-hk|中華人民共和國澳門特別行政區}} || Macao || MO || MAC || 446 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|JPN}}||]||align=center|{{lang|ja|]}}|| |
| {{flagdeco|JPN}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|ja|]}} || Japan || {{lang|ja|日本国}} || Japan || JP || JPN || 392 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|MNG}}||]||align=center|{{lang|mn|]}}||Mongolia||{{lang|mn|Монгол Улс}} |
| {{flagdeco|MNG}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|mn|] / {{MongolUnicode|ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ<br />ᠤᠯᠤᠰ}}}} || Mongolia || {{lang|mn|Монгол Улс}} ({{MongolUnicode|ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ<br />ᠤᠯᠤᠰ}})|| Mongolia || MN || MNG || 496 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|PRK}}||]||align=center|{{lang|ko|]}}||Democratic |
| {{flagdeco|PRK}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|ko|]}} || Democratic People's Republic of Korea || {{lang|ko|조선민주주의인민공화국}} || Korea (the Democratic People's Republic of) || KP || PRK || 408 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|KOR}}||]||align=center|{{lang|ko|]}}||Republic of Korea||{{lang|ko|대한민국 |
| {{flagdeco|KOR}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|ko|]}} || Republic of Korea || {{lang|ko|대한민국}} || Korea (the Republic of) || KR || KOR || 410 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |{{flagdeco|TWN}}||] |
| {{flagdeco|TWN}} || ] || align=center | {{lang|zh-tw|] / ]}} || Republic of China || {{lang|zh-tw|中華民國}} || Taiwan (Province of China)<ref name=":0" />|| TW || TWN || 158 | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| == Demographics == | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | State/Territory | ! class="unsortable" | State/Territory | ||
| ! ] km<sup>2</sup> | ! ] km<sup>2</sup> | ||
| ! ] |
! ] in | ||
| thousands (2023){{UN_Population|ref}} | |||
| ! ]<br />per km<sup>2</sup> | |||
| !% of East Asia | |||
| ! ] | |||
| !% of World | |||
| ! class="unsortable" | ] | |||
| ! ] <br /> per km<sup>2</sup> | |||
| ! ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hdr.undp.org/en/2018-update|title= Human Development Reports|website=www.hdr.undp.org|date=January 2018 |language=en|access-date=2018-10-14}}</ref> | |||
| ! class="unsortable" | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{flag|PRC|name=China}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{flag|PRC|name=China}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 9,640,011{{efn|Includes all area which under PRC's government control {{citation needed span|(excluding "]" and disputed islands).|date=November 2021}}}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,425,671{{efn|name=un-twn|A note by the United Nations: "For statistical purposes, the data for China do not include Hong Kong and Macao, Special Administrative Regions (SAR) of China, and ]."{{UN_Population|ref}} | ||
| }} | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 138 | |||
| |85.76% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.738 | |||
| |17.72% | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 138 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.788 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | | style="text-align:left;" | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{HKG}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{HKG}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,104 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 7,492 | ||
| |0.45% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 6,390 | |||
| |0.093% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.917 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 6,390 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.956 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | | style="text-align:left;" | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{MAC}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{MAC}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 30 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 704 | ||
| |0.042% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 18,662 | |||
| |0.0087% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.905 | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 18,662 | ||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.925 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{JPN}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{JPN}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 377,930 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 123,295 | ||
| |7.42% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 337 | |||
| |1.53% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.903 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 337 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.920 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | | style="text-align:left;" | ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{MNG}} | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 1,564,100 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 3,447 | |||
| |0.2% | |||
| |0.042% | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 2 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.741 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{PRK}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{PRK}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 120,538 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 26,161 | ||
| |1.57% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 198 | |||
| |0.33% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.733 | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 198 | ||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.733{{Citation needed|reason=Please cite the relevant source to the data acquired.|date=February 2023}} | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{KOR}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{KOR}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 100,210 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 51,784 | ||
| |3.11% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 500 | |||
| |0.64% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.901 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 500 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.929 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | | style="text-align:left;" | ] | ||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{MNG}} | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 1,564,100 | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | {{UN_Population|Mongolia}} | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 2 | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.735 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | style="text-align:left;" | {{TWN}} | | style="text-align:left;" | {{TWN}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 36,197 | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 23,923 | ||
| |1.44% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 639 | |||
| |0.297% | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 0.885 | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 639 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ]<ref>Taipei is the ROC's seat of government by regulation. Constitutionally, there is no official capital appointed for the ROC.</ref> | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 0.926 | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| !East Asia | |||
| !11,840,000 | |||
| !1,662,477 | |||
| !'''100%''' | |||
| !'''20.66%''' | |||
| !141 | |||
| ! | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| === |
===Ethnic groups=== | ||
| {{Main|East Asians|Ethnic groups of East Asia}} | {{Main|East Asians|Ethnic groups of East Asia}} | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Ethnicity | ! class="unsortable" | Ethnicity | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Native name | ! class="unsortable" | Native name | ||
| !Population | ! Population | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Language(s) | ! class="unsortable" | Language(s) | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Writing system(s) | ! class="unsortable" | Writing system(s) | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Major states/territories* | ! class="unsortable" | Major states/territories* | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | |
! class="unsortable" | Traditional attire | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |]/] | | ]/] | ||
| | |
| {{lang|zh-hant|漢族}} or {{lang|zh-hans|汉族}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,313,345,856<ref name="ciastat">{{Cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html |title=CIA Factbook |access-date=2018-03-17 |archive-date=2016-10-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161013030611/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| |] |
| ] (], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], etc.) | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}}({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |]/] | | ]/] | ||
| | |
| {{lang|ja|大和民族}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 125,117,000<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.stat.go.jp/data/jinsui/pdf/201612.pdf | script-title =ja:人口推計 – 平成 28年 12月 報 | work = stat.go.jp}}</ref> | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |Han characters (]), Katakana, Hiragana | | Han characters (]), Katakana, Hiragana | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|JPN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| ] | ||
| |{{lang|ko- |
| {{lang|ko-kp|조선민족 (朝鮮民族)}} <br /> {{lang|ko-kr|한민족 (韓民族)}} | ||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 84,790,105<ref></ref><ref>{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Korea North|access-date=8 April 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|accessdate=1 February 2022|date=2021|location=South Korea|publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade|script-title=ko:재외동포현황|trans-title=Total number of overseas Koreans|url=http://www.mofa.go.kr/www/wpge/m_21509/contents.do}}</ref> | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 79,432,225{{cn|date=July 2018}} | |||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |Hangul, Han characters (]) | | ], Han characters (]) | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|ROK}} {{flagicon|PRK}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh|白族}} | | {{lang|zh|白族}} | ||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 2,091,543<ref name=":1">{{cite web |title=China Statistical Yearbook 2021 |url=http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2021/indexee.htm}}</ref> | |||
| | style="text-align:Right;" | 1,858,063 | |||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| | |
| Simplified characters, Latin script | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh|回族 |
| {{lang|zh|回族}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 11,377,914<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| |], other Chinese Dialects, ], etc. | | ], other Chinese Dialects, ], etc. | ||
| | |
| Simplified characters | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |]s | | ]s | ||
| |Монголчууд |
| {{lang|mn|Монголчууд}} {{MongolUnicode|ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯᠴᠤᠳ}} <br />Монгол/{{MongolUnicode|ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 8,942,528 | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MGL}} {{flagicon|RUS}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hans|壮族}}/{{lang|za|Bouxcuengh}} | | {{lang|zh-hans|壮族}}/{{lang|za|Bouxcuengh}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 19,568,546<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| |], ], etc. | | ], ], etc. | ||
| |Simplified Han characters, ] | | Simplified Han characters, ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] |
| ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh |
| {{lang|zh|维吾尔族}}/ئۇيغۇر | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;"| 11,774,538<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | |
| ] | ||
| | |
| ], ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]s | |||
| |]/] | |||
| | {{lang|zh-hans|满族}}/{{ManchuSibeUnicode|ᠮᠠᠨᠵᡠ}} | |||
| |Ghaob Xongb/Hmub/Mongb | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 10,423,303<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | |
| ], ] | ||
| | |
| Simplified Han characters, Mongol script | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}}{{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]/] | |||
| |] | |||
| | {{lang|zh|苗族}}/Ghaob Xongb/Hmub/Mongb | |||
| |{{bo-textonly|བོད་པ་}} | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 11,067,929<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | ], ] | |||
| |Tibetan, Rgyal Rong, Rgu, etc. | |||
| | Latin script, Simplified Han characters | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang| |
| {{lang|zh|藏族}}/{{bo-textonly|བོད་པ་}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 7,060,731<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | Tibetan, Rgyal Rong, Rgu, etc. | |||
| |Various ], Southwestern Mandarin | |||
| |] |
| ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh| |
| {{lang|zh|彝族}}/{{lang|ii|ꆈꌠ}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 9,830,327<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | Various ], Southwestern Mandarin | |||
| |Northern Tujia, Southern Tujia | |||
| |Simplified Han characters | | ], Simplified Han characters | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| | {{lang|zh|土家族}} | |||
| |Gaeml | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 9,587,732<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| | ], Southern Tujia | |||
| |Gaeml | |||
| |Simplified Han characters |
| Simplified Han characters | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh| |
| {{lang|zh|侗族}}/Gaeml | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 3,495,993<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| |] |
| ] | ||
| |Simplified Han characters | | Simplified Han characters, Latin script | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh |
| {{lang|zh|土族}}/Monguor | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 289,565 | ||
| |], |
| ], Northwestern Mandarin | ||
| | |
| Simplified Han characters | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | {{lang|zh-hans|达斡尔族}}/{{MongolUnicode|ᠳᠠᠭᠤᠷ}} | |||
| |Pangcah, etc. | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 131,992 | ||
| | |
| ], Northeastern Mandarin | ||
| | |
| Mongol script, Simplified Han characters | ||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MGL}} | |||
| |{{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | {{lang|zh|臺灣原住民}}/ {{lang|zh-cn|高山族}}/ {{lang|ami|Yincomin}}/ {{lang|pwn|Kasetaivang}}/ {{lang|pyu|Inanuwayan}} | |||
| |{{lang|ja|(琉球民族(りゅうきゅうみんぞく)}}<br />{{lang|ja|沖縄人 (おきなわじん)}} | |||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 533,600 | ||
| |] |
| ] (], ]), etc. | ||
| | Latin script, Traditional Han characters | |||
| |Han characters (]), Katakana, Hiragana | |||
| | {{flagicon |
| {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| | | |||
| |] | |||
| ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang |
| {{lang|ryu|琉球民族}} | ||
| | style="text-align: |
| style="text-align:right;" | 1,900,000 | ||
| | ]<br />] | |||
| |]<br>]<ref>{{cite book |editor-last=Gordon |editor-first=Raymond G. Jr. |year=2005 |title=Ethnologue: Languages of the World |edition=15th |location=Dallas |publisher=SIL International |isbn=1-55671-159-X |oclc=224749653}}</ref> | |||
| |Han characters (]), Katakana, Hiragana | | Han characters (]), Katakana, Hiragana | ||
| | {{flagicon| |
| {{flagicon|JPN}} | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| | {{lang|ain|アイヌ}}/ {{lang|ain|Aynu}}/ {{lang|ain|Айну}} | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | 200,000 | |||
| | ] <br /> ]<ref>{{cite book |editor-last=Gordon |editor-first=Raymond G. Jr. |year=2005 |title=Ethnologue: Languages of the World |edition=15th |location=Dallas |publisher=SIL International |isbn=978-1-55671-159-6 |oclc=224749653}}</ref> | |||
| | Ainu uses both the ] and ] scripts<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.omniglot.com/writing/ainu.htm | title=Ainu language and alphabet }}</ref> | |||
| | {{flagicon|JPN}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| '''*Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.''' | |||
| * Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only. | |||
| == Culture == | |||
| {{Main|Culture of East Asia}} | |||
| {{Main category|East Asian culture}} | |||
| == |
==Culture== | ||
| {{Main category|Culture of East Asia}} | |||
| The culture of East Asia has largely been ]d by ], as it was the civilization that had the most dominant influence in the region throughout the ages that ultimately laid the foundation for East Asian civilization.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Asia Civilizations: Ancient to 1800 AD |last= Lim |first= SK |publisher=ASIAPAC |isbn=978-9812295941 |page=56}}</ref> The vast knowledge and ingenuity of Chinese civilization and the classics of Chinese literature and culture were seen as the foundations for a civilized life in East Asia. ] served as a vehicle through which the adoption of Confucian ethical philosophy, Chinese calendar system, political and legal systems, architectural style, diet, terminology, institutions, religious beliefs, ]s that emphasized a knowledge of Chinese classics, political philosophy and cultural value systems, as well as historically sharing a common ] reflected in the histories of ] and ].<ref name="Goscha 2016">{{Cite book |title=The Penguin History of Modern Vietnam: A History |last= Goscha |first= Christopher |publisher= Allen Lane |year=2016 |isbn= 978-1846143106 }}</ref><ref name="Kang 2012 33–34" /><ref>{{cite book | title=The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America | publisher=Penguin Press HC |author1 = Amy Chua |author2 = Jed Rubenfeld | year=2014 |page=122 |isbn=978-1594205460 }}</ref><ref name="Walker 2012 2">{{cite book |title=East Asia: A New History |last=Walker |first=Hugh Dyson |publisher=AuthorHouse |year=2012 |page=2}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=China's Cosmopolitan Empire: The Tang Dynasty |last=Lewis |first=Mark Edward |publisher=Belknap Press |year=2012 |isbn= 978-0674064010 |publication-date=April 9, 2012 |page=156 }}</ref><ref name="Reischauer">Edwin O. Reischauer, "The Sinic World in Perspective," ''Foreign Affairs ''52.2 (January 1974): 341—348. </ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Asia Civilizations: Ancient to 1800 AD |last= Lim |first= SK |publisher=ASIAPAC |isbn=978-9812295941 |page=89 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Redesigning Asian Business: In the Aftermath of Crisis |last= Richter |first=Frank-Jurgen |publisher=Quorum Books |year=2002 |isbn=978-1567205251 |page=15 }}</ref><ref name="Hazen 2005 1" /> The Imperial Chinese tributary system was the bedrock of network of trade and foreign relations between China and its East Asian tributaries, which helped to shape much of East Asian affairs during the ancient and medieval eras. Through the tributary system, the various dynasties of Imperial China facilitated frequent economic and cultural exchange that influenced the cultures of Japan and Korea and drew them into a ].<ref>{{harvnb|Vohra|1999|p=22}}</ref><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122">{{cite book | title=The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America |publisher=Penguin Press HC |author1 = Amy Chua |author2 = Jed Rubenfeld |year=2014 |pages=121–122 |isbn=978-1594205460 }}</ref> The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's foreign policy and trade for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural dominance over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.<ref name="Warren I. Cohen 2000" /><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122"/> The relationship between China and its cultural influence on East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of ] on Europe and the ].<ref name="Reischauer" /><ref name="Walker 2012 2" /><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122" /><ref name="Goscha 2016" /> | |||
| ===Overview=== | |||
| The culture of East Asia has been ], as it was the civilization that had the most dominant influence in the region throughout the ages that ultimately laid the foundation for East Asian civilization. The vast knowledge and ingenuity of Chinese civilization and the classics of Chinese literature and culture were seen as the foundations for a civilized life in East Asia. ] served as a vehicle through which the adoption of Confucian ethical philosophy, Chinese calendar system, political and legal systems, architectural style, diet, terminology, institutions, religious beliefs, ]s that emphasised a knowledge of Chinese classics, political philosophy and cultural value systems, as well as historically sharing a common writing system reflected in the histories of ] and ].<ref name="Goscha 2016">{{Cite book |last=Goscha |first=Christopher |title=The Penguin History of Modern Vietnam: A History |publisher=Allen Lane |year=2016 |isbn=978-1-846-143106}}</ref><ref name="Kang 2012 33–34" /><ref>{{harvnb|Chua|Rubenfeld|2014|p=122}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=China's Cosmopolitan Empire: The Tang Dynasty |last=Lewis |first=Mark Edward |publisher=Belknap |year=2012 |isbn= 978-0-674-06401-0 |page=156}}</ref><ref name="Reischauer">{{Cite journal |last=Reischauer |first=Edwin O. |year=1974 |title=The Sinic World in Perspective |journal=Foreign Affairs |volume=52 |issue=2 |pages=341–348 |doi=10.2307/20038053 |jstor=20038053}}</ref><ref name="Hazen 2005 1" /> | |||
| The Imperial Chinese tributary system was the bedrock of network of trade and foreign relations between China and its East Asian tributaries, which helped to shape much of East Asian affairs during the ancient and medieval eras. Through the tributary system, the various dynasties of Imperial China facilitated frequent economic and cultural exchange that influenced the cultures of Japan and Korea and drew them into a Chinese international order.<ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122">{{harvnb|Chua|Rubenfeld|2014|p=121–122}}</ref> The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's foreign policy and trade for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural dominance over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.<ref name="Warren I. Cohen 2000" /><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122" /> The relationship between China and its cultural influence on East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of ] on classical Western civilisation.<ref name="Reischauer" /><ref name="Amy Chua, Jed Rubenfeld 2014 121–122" /><ref name="Goscha 2016" /> | |||
| === Religions === | |||
| Since the late 19th century, the initially unequal encounter with ] has also shaped East Asia.<ref>{{Citation |last=Seo |first=Yongseok |title=Chapter 22. East Asian Response to the Globalization of Culture: Perceptional Change and Cultural Policy |date=2006-04-30 |work=Fairness, Globalization, and Public Institutions: East Asia and Beyond |pages=319–336 |editor-last=Dator |editor-first=Jim |url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9780824841966-023/html?lang=en&srsltid=AfmBOorLR_G6ZoXN9Cj4ZXOg8OdMPytPhkz2ql0wQCO_9yvF8Y---dBx |access-date=2024-12-21 |publisher=University of Hawaii Press |language=en |doi=10.1515/9780824841966-023/html?lang=en&srsltid=afmboorlr_g6zoxn9cj4zxog8odmpytphkz2ql0wqco_9yvf8y---dbx |isbn=978-0-8248-4196-6 |editor2-last=Pratt |editor2-first=Richard C. |editor3-last=Seo |editor3-first=Yongseok}}</ref> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{Main|East Asian religions}} | {{Main|East Asian religions}} | ||
| {{Pie chart | |||
| |thumb = right | |||
| |caption = Religion in East Asia (2020)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projection-table/2020/percent/all/|title=Religious Composition by Country, 2010-2050|website=Pew|date=2 April 2015|access-date=2020-10-18|archive-date=2019-12-21|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191221014350/https://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projection-table/2020/percent/all/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| |label1 = ] | |||
| |value1 = 52.10 | |||
| |color1 = Gold | |||
| |label2 = Buddhism | |||
| |value2 = 19.65 | |||
| |color2 = Red | |||
| |label3 = ] | |||
| |value3 = 19.62 | |||
| |color3 = Grey | |||
| |label4 = ] | |||
| |value4 = 5.56 | |||
| |color4 = DodgerBlue | |||
| |label5 = ] | |||
| |value5 = 1.57 | |||
| |color5 = Green | |||
| |label7 = Other | |||
| |value7 = 1.44 | |||
| |color7 = Chartreuse | |||
| }} | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Religion | ! class="unsortable" | Religion | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Native name | ! class="unsortable" | Native name | ||
| !Creator/Current Leader | |||
| ! class="unsortable" | Denomination | |||
| !Founded Time | |||
| ! class="unsortable" | Main Denomination | |||
| ! class="unsortable" | Major book | ! class="unsortable" | Major book | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Type | ! class="unsortable" | Type | ||
| !Est. Followers | ! Est. Followers | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | Ethnic groups | ! class="unsortable" | Ethnic groups | ||
| ! class="unsortable" | States/territories | ! class="unsortable" | States/territories | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| | |
| {{lang|zh-hant|中國民間信仰}} or {{lang|zh-hant|中国民间信仰}} | ||
| |Spontaneous formation | |||
| |Taoism, Confucianism, ], ], ] | |||
| |Prehistoric period | |||
| |], ], ], etc. | |||
| |], ], ] | |||
| |Pantheism/polytheism | |||
| | ], ], ], etc. | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | ~900,000,000<ref>{{cite article |last=Wenzel-Teuber |first=Katharina |year=2012 |title=People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011 |journal=Religions & Christianity in Today's China |volume=II |number=3 |pages=29–54 |url=http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2012-3/RCTC_2012-3.29-54_Wenzel-Teuber_Statistical_Overview_2011.pdf |issn=2192-9289 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170427151725/http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2012-3/RCTC_2012-3.29-54_Wenzel-Teuber_Statistical_Overview_2011.pdf |archive-date=21 April 2017}}</ref><ref name=CZ20172>{{cite article |last=Wenzel-Teuber |first=Katharina |year=2017 |title=Statistics on Religions and Churches in the People's Republic of China – Update for the Year 2016 |journal=Religions & Christianity in Today's China |volume=VII |number=2 |pages=26–53 |url=http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2017-2/RCTC_2017-2.26-53_Wenzel-Teuber__Statistics_on_Religions_and_Churches_in_the_PRC_%E2%80%93_Update_for_the_Year_2016.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170722112103/http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2017-2/RCTC_2017-2.26-53_Wenzel-Teuber__Statistics_on_Religions_and_Churches_in_the_PRC_%E2%80%93_Update_for_the_Year_2016.pdf |archive-date=22 July 2017}}</ref> | |||
| | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | |||
| |Han, ], ], Tujia (worship of the same ancestor-gods) | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | ~900,000,000<ref>{{cite journal |last=Wenzel-Teuber |first=Katharina |year=2012 |title=People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011 |journal=Religions & Christianity in Today's China |volume=II |number=3 |pages=29–54 |url=http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2012-3/RCTC_2012-3.29-54_Wenzel-Teuber_Statistical_Overview_2011.pdf |issn=2192-9289 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170427151725/http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2012-3/RCTC_2012-3.29-54_Wenzel-Teuber_Statistical_Overview_2011.pdf |archive-date=27 April 2017}}</ref><ref name=CZ20172>{{cite journal |last=Wenzel-Teuber |first=Katharina |year=2017 |title=Statistics on Religions and Churches in the People's Republic of China – Update for the Year 2016 |journal=Religions & Christianity in Today's China |volume=VII |number=2 |pages=26–53 |url=http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2017-2/RCTC_2017-2.26-53_Wenzel-Teuber__Statistics_on_Religions_and_Churches_in_the_PRC_%E2%80%93_Update_for_the_Year_2016.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170722112103/http://www.china-zentrum.de/fileadmin/downloads/rctc/2017-2/RCTC_2017-2.26-53_Wenzel-Teuber__Statistics_on_Religions_and_Churches_in_the_PRC_%E2%80%93_Update_for_the_Year_2016.pdf |archive-date=22 July 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}} {{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| | Han, ], ], Tujia (worship of the same ancestor-gods) | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh|道教}} | | {{lang|zh|道教}} | ||
| | ], ] (]) | |||
| |Zhengyi, Quanzhen | |||
| |125 AD ]{{citation needed|date=November 2020}} | |||
| |] | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |Pantheism/polytheism | |||
| | ] | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | ~20,000,000<ref name="CZ20172" /> | |||
| | Pantheism, polytheism | |||
| |Han, Zhuang, Hmong, Yao, Qiang, Tujia | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | ~20,000,000<ref name="CZ20172"/> | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}} {{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| | Han, Zhuang, Hmong, Yao, Qiang, Tujia | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]/] | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{lang|zh| |
| {{lang|zh-hant|漢傳佛教}} or {{lang|zh-hans|汉传佛教}} | ||
| | ] (introduced to China), ] (introduced to ]), ] (introduced to Japan) | |||
| |Cheng-Zhu, Lu-Wang | |||
| |67 AD ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | Mahayana | |||
| |]/pantheism | |||
| | ] | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | N/A | |||
| | Non-God, Dualism. | |||
| |Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | ~300,000,000 | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}} {{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|JPN}} {{Flagicon|KOR}} {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| | Han, Koreans, Yamato | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant| |
| {{lang|zh-hant|藏傳佛教}} or {{lang|zh-hans|藏传佛教}}/{{bo-textonly|བོད་བརྒྱུད་ནང་བསྟན།}} | ||
| |] | |||
| |Mahayana | |||
| |1800 years ago | |||
| |] | |||
| | Mahayana, ] | |||
| |Non-God | |||
| | ] | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | ~300,000,000 | |||
| | Non-God | |||
| |Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | ~10,000,000 | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}} {{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|JPN}} {{Flagicon|KOR}} {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| | Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| | {{lang|zh-hant|薩滿教}} or {{lang|mn|Бөө мөргөл}} | |||
| |{{bo-textonly|བོད་བརྒྱུད་ནང་བསྟན།}} | |||
| |Spontaneous formation | |||
| |Mahayana | |||
| |Prehistoric period | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |Non-God | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | ~10,000,000 | |||
| | Prehistoric, polytheism, and pantheism | |||
| |Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | N/A | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} {{Flagicon|MNG}} | |||
| | Manchus, Mongols, Oroqens | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |]<ref group="note">almost ], ]</ref> and ], etc. | |||
| | {{lang|zh|神道}} | |||
| |{{lang|mn|Бөө мөргөл}}, {{bo-textonly|བོན }} | |||
| |Spontaneous formation | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |]<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hardacre |first=Helen |title=Shinto: a history |year=2017 |isbn=978-0-190-62171-1 |location=New York |pages=18 |publisher=Oxford University Press }}</ref> | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | ] | |||
| |Polytheism/pantheism | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | N/A | |||
| | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | |||
| |Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols, Oroqen | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | N/A | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} {{Flagicon|MNG}} | |||
| | Yamato | |||
| | {{flagicon|JPN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{lang| |
| {{lang|ko|신도}} or {{lang|ko|무교}} | ||
| |Spontaneous formation | |||
| |] | |||
| |900 years ago{{Citation needed|date=September 2022}} | |||
| |], ] | |||
| | Musok sects | |||
| |Polytheism/pantheism | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | N/A | |||
| | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | |||
| |Yamato | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | N/A | |||
| |{{Flagicon|JPN}} | |||
| | Koreans | |||
| | {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{lang| |
| {{lang|ja|琉球神道}} or {{lang|ja|ニライカナイ信仰}} | ||
| |Spontaneous formation | |||
| |Sindo sects | |||
| |N/A | |N/A | ||
| | N/A | |||
| |Polytheism/pantheism | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | N/A | |||
| | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | |||
| |Joseon | |||
| | style="text-align:right;" | N/A | |||
| |{{Flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| | Ryukyuans | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{flagicon|JPN}} ({{flagicon|Okinawa}}) | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{lang|ja|琉球神道}} or {{lang|ja|ニライカナイ信仰}} | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |Polytheism/pantheism | |||
| |style="text-align:Right;" | N/A | |||
| |Ryukyuan | |||
| |{{Flagicon|JPN}} ({{Flagicon|Okinawa}}) | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| === |
===Festivals=== | ||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=November 2020}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| !Festival | ! Festival | ||
| !Native Name | ! Native Name | ||
| !Other name | ! Other name | ||
| !Calendar | ! Calendar | ||
| !Date | ! Date | ||
| !] date | ! ] date | ||
| !Activity | ! Activity | ||
| !Religious practices | ! Religious practices | ||
| !Food | ! Food | ||
| !Major ethnicities | ! Major ethnicities | ||
| !Major states/territories | ! Major states/territories | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant| |
| {{lang|zh-hant|農曆新年}}/{{lang|zh-hans|农历新年}} or {{lang|zh-hant|春節}}/{{lang|zh-hans|春节}} | ||
| |Spring Festival | | Spring Festival | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |Month 1 Day 1 | | Month 1 Day 1 | ||
| |21 Jan–20 Feb | | 21 Jan–20 Feb | ||
| |Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | ||
| |Worship the King of Gods | | Worship the King of Gods | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| | |
| Han, Manchus etc. | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|MNG}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang| |
| {{lang|ko|설날}} or {{lang|ko|설}} | ||
| | Seollal | |||
| |Yuan Dan | |||
| | ] | |||
| |Gregorian | |||
| | Month 1 Day 1 | |||
| |1 Jan | |||
| | 21 Jan–20 Feb | |||
| |1 Jan | |||
| | Ancestors Worship, Family Reunion, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| |Fireworks | |||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| | ] | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | Koreans | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}}{{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|JPN}} {{Flagicon|PRK}} {{Flagicon|KOR}} {{Flagicon|MNG}} {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] or ] | | ] or ] | ||
| |{{bo-textonly|ལོ་གསར་}} or {{lang|mn|Цагаан сар}} | | {{lang|zh|藏历新年}}/{{bo-textonly|ལོ་གསར་}} or {{lang|zh|查干萨日}}/{{lang|mn|Цагаан сар}} | ||
| |White Moon | | White Moon | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |Month 1 Day 1 | | Month 1 Day 1 | ||
| |25 |
| 25 Jan – 2 Mar | ||
| |Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |] or ] | | ] or ] | ||
| |Tibetans, Mongols, ] etc. | | Tibetans, Mongols, ] etc. | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} | ||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{lang|zh|元旦}} | |||
| | Yuan Dan | |||
| | Gregorian | |||
| | 1 Jan | |||
| | 1 Jan | |||
| | Fireworks | |||
| | N/A | |||
| | N/A | |||
| | N/A | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{lang|zh-hant|元宵節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|元宵节}} | |||
| | Upper Yuan Festival ({{lang|zh-hans|上元节}}) | |||
| | Chinese | |||
| | Month 1 Day 15 | |||
| | 4 Feb – 6 Mar | |||
| | Lanterns Expo, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| | Birthdate of the God of Sky-officer | |||
| | Yuanxiao | |||
| | Han | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{lang|ko|대보름}} or {{lang|ko|정월 대보름}} | |||
| | Great Full Moon | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Month 1 Day 15 | |||
| | 4 Feb – 6 Mar | |||
| | Greeting of the moon, kite-flying, ], eating ] (]) | |||
| | Bonfires (daljip taeugi) | |||
| | ], ], nuts | |||
| | Korean | |||
| | {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant| |
|{{lang|zh-hant|寒食節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|寒食节}} | ||
| | Cold Food Festival | |||
| |Upper Yuan Festival ({{lang|zh-hans|上元节}}) | |||
| | ] | |||
| |Chinese | |||
| | Traditionally, on the 105th day after the ]. Revised to 1 day before the Qingming Festival by ] (Chinese: {{zhi|c=汤若望}}) during the ]. | |||
| |Month 1 Day 15 | |||
| | April 3–5 | |||
| |4 Feb–6 Mar | |||
| | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, No cooking hot meal/setting fire, Cold food only. ], etc. (People used to mix this one with the Qingming Festival due to their close dates) | |||
| |Lanterns Expo, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| | In Memory of a loyal Ancient named ] (Chinese: {{zhi|c=介子推}}), ordered by the Monarch of the ], ] (Chinese: {{zhi|c=重耳}}) | |||
| |Birthdate of the God of Sky-officer | |||
| | Cold Food, e.g. ] | |||
| |Yuanxiao | |||
| |Han, |
| Han, Koreans, Mongols | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant|清明節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|清明节}} | |{{lang|zh-hant|清明節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|清明节}} or Ханш нээх | ||
| |Tomb Sweeping Day | |Tomb Sweeping Day | ||
| |Solar | |] | ||
| |15th day |
|15th day after the ]. Just 1 day after the Hanshi Festival, but in much higher repute. | ||
| |April 4-6th | |||
| |4 Apr–6 April | |||
| |Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, ], Planting trees, Flying kites, ], ], etc. (Almost the same with the Hanshi Festival's, due to their close dates) | |||
| |Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| |Burning ] | |Burning ] for deceased family members. Planting willow branches to keep ghosts away from houses. | ||
| |Boiled eggs | |||
| |Cold Food | |||
| |Han, |
|Han, Koreans, Mongols | ||
| |{{ |
|{{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|MNG}} {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant|端午節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|端午节}} | | {{lang|zh-hant|端午節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|端午节}} or {{lang|ko|단오}} | ||
| |Duanwu Festival | | Duanwu Festival / ] | ||
| | ] / ] | |||
| |Chinese | |||
| |Month 5 Day 5 | | Month 5 Day 5 | ||
| | | | | ||
| |Driving poisons & plague away |
| Driving poisons & plague away. (China: Dragon Boat Race, Wearing coloured lines, Hanging felon herb on the front door.) / (Korea: Washing hair with iris water, ]) | ||
| |Worship various Gods | | Worship various Gods | ||
| |] | | ] / Surichwitteok (rice cake with herbs) | ||
| |Han, |
| Han, Koreans, Yamato | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant|中元節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|中元节}} | | {{lang|zh-hant|中元節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|中元节}} or {{lang|ko|백중}} | ||
| |Mid Yuan Festival | | Mid Yuan Festival | ||
| |Chinese | | Chinese | ||
| |Month 7 Day 15 | | Month 7 Day 15 | ||
| | | | | ||
| |Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | ||
| |Birthdate of the God of Earth-officer | | Birthdate of the God of Earth-officer | ||
| | | | | ||
| |Han, |
| Han, Koreans, Yamato | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant|中秋節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|中秋节}} | | {{lang|zh-hant|中秋節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|中秋节}} | ||
| |{{lang|zh|中秋祭}} | | {{lang|zh|中秋祭}} | ||
| |Chinese | | Chinese | ||
| |Month 8 Day 15 | | Month 8 Day 15 | ||
| | | | | ||
| |Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | ||
| |Worship the Moon Goddess | | Worship the Moon Goddess | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| | Han | |||
| |Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |Double Ninth Festival | |||
| |{{lang| |
| {{lang|ko|추석}} or {{lang|ko|한가위}} | ||
| | Hangawi | |||
| |Double Positive Festival | |||
| | ] | |||
| |Chinese | |||
| |Month |
| Month 8 Day 15 | ||
| | | | | ||
| | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Enjoying Moon view | |||
| |Climbing Mountain, Taking care of elderly, Wearing Cornus. | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |Worship various Gods | |||
| | ], Torantang (Taro soup) | |||
| | Koreans | |||
| | {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{lang|ja|月見}} or {{lang|ja|お月見}} | |||
| | Tsukimi or Otsukimi | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Month 8 Day 15 | |||
| | | | | ||
| | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | |||
| |Han, Joseon, Yamato | |||
| | Worship the Moon | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}} {{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|PRK}} {{Flagicon|KOR}} {{Flagicon|JPN}} {{Flagicon|TWN}}<sup>*</sup> | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| | Yamato | |||
| | {{flagicon|JPN}} <sup>*</sup> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
| Double Ninth Festival | ||
| |{{lang|zh-hant| |
| {{lang|zh-hant|重陽節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|重阳节}} | ||
| | Double Positive Festival | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |Chinese | | Chinese | ||
| |Month |
| Month 9 Day 09 | ||
| | | |||
| | Climbing Mountain, Taking care of elderly, Wearing Cornus. | |||
| | Worship various Gods | |||
| | | | | ||
| | Han, Korean, Yamato | |||
| |Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|TWN}}<sup>*</sup> | |||
| |Birthdate of the God of Water-officer | |||
| |Ciba | |||
| |Han, Joseon | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}}{{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|PRK}} {{Flagicon|KOR}} {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | Lower Yuan Festival | |||
| |Small New Year | |||
| |{{lang|zh| |
| {{lang|zh-hant|下元節}} or {{lang|zh-hans|下元节}} | ||
| | N/A | |||
| |Jizao ({{lang|zh|祭灶}}) | |||
| |Chinese | | Chinese | ||
| |Month |
| Month 10 Day 15 | ||
| | | | | ||
| | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | |||
| |Cleaning Houses | |||
| | |
| Birthdate of the God of Water-officer | ||
| | Ciba | |||
| |] | |||
| | Han | |||
| |Han, Mongols | |||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | Dongzhi Festival | |||
| |International Labor Day | |||
| | {{lang|zh|冬至}} or {{lang|ko|동지}} or {{lang|ja|冬至}} | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |Gregorian | | Gregorian | ||
| | Between Dec 21 and Dec 23 | |||
| |1 May | |||
| | Between Dec 21 and Dec 23 | |||
| |1 May | |||
| | Ancestors Worship, Rites to dispel bad spirits | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| | ], ], ], ] | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | Han, Koreans, Yamato | |||
| |N/A | |||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|PRK}} {{flagicon|KOR}} {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | Small New Year | |||
| |International Women's Day | |||
| | {{lang|zh|小年}} | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | Jizao ({{lang|zh|祭灶}}) | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | Chinese | |||
| |Gregorian | |||
| | Month 12 Day 23 | |||
| |8 Mar | |||
| | | |||
| |8 Mar | |||
| | Cleaning Houses | |||
| |Taking care of women | |||
| | Worship the God of Hearth | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | ] | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | Han, Mongols | |||
| |N/A | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} ({{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}}) {{flagicon|MNG}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |All | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| <nowiki>*</nowiki>Japan switched the date to the ] after the Meiji Restoration. | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Japan switched the date to the ] after the Meiji Restoration. | ||
| <br> | |||
| <nowiki>*</nowiki>Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4. | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4. | ||
| == |
=== Entertainment === | ||
| East Asian popular culture, such as anime and manga from Japan and ] and ] from South Korea, have become highly popular worldwide in the 21st century.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Hollingsworth |first=Julia |date=2019-12-29 |title=Why the past decade saw the rise and rise of East Asian pop culture |url=https://www.cnn.com/2019/12/28/entertainment/east-asia-pop-culture-rise-intl-hnk/index.html |access-date=2024-11-18 |website=CNN |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === |
=== Sports === | ||
| ]]] | |||
| ], formerly the ], is a ] organised by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since ] among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the ] (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of ], which is a member of the ]. | |||
| ] is one of the main sports in East Asia, having been introduced through mid-19th century American contact and further spread by the Japanese Empire.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Cho |first=Younghan |date=2016 |title=Double binding of Japanese colonialism: trajectories of baseball in Japan, Taiwan, and Korea |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09502386.2015.1094498 |journal=Cultural Studies |language=en |volume=30 |issue=6 |pages=926–948 |doi=10.1080/09502386.2015.1094498 |issn=0950-2386}}</ref> The game has gained ] since the 2010s.<ref>{{Cite web |last=杜娟 |title=MLB's China operation knocking it out the ball park |url=https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202108/20/WS611f1093a310efa1bd66a009.html |access-date=2024-10-22 |website=www.chinadaily.com.cn}}</ref> | |||
| ==== East Asian Youth Games ==== | |||
| The East Asian Games is 1 of 5 Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the East Asian Games, the ], the ], the ] (SEA Games), and the ]. | |||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=November 2020}} | |||
| {{Main|East Asian Youth Games}}Formerly the ], it is a ] organized by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since ] among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the ] (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of ], which is a member of the ]. | |||
| It is one of five Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the ], the ] (SEA Games), the ] and the ]. | |||
| === Free trade agreements === | |||
| == Collaboration == | |||
| ===Free trade agreements=== | |||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=November 2020}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| !Name of agreement | ! Name of agreement | ||
| !Parties | ! Parties | ||
| !Leaders at the time | ! Leaders at the time | ||
| !Negotiation begins | ! Negotiation begins | ||
| !Signing date | ! Signing date | ||
| !Starting time | ! Starting time | ||
| !Current status | ! Current status | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |China–South Korea FTA | | China–South Korea FTA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |May, 2012 | | May, 2012 | ||
| |Jun 01, 2015 | | Jun 01, 2015 | ||
| |Dec 30, 2015 | | Dec 30, 2015 | ||
| |Enforced | | Enforced | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |China–Japan–South Korea FTA | | China–Japan–South Korea FTA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | ||
| |], ], ] | | ], ], ] | ||
| |Mar 26, 2013 | | Mar 26, 2013 | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |10 round negotiation | | 10 round negotiation | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Japan-Mongolia EPA | | Japan-Mongolia EPA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|JPN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Feb 10, 2015 | | Feb 10, 2015 | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Enforced | | Enforced | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |China-Mongolia FTA | | China-Mongolia FTA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MNG}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |Officially proposed | | Officially proposed | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |China-HK CEPA | | China-HK CEPA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|HKG}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Jun 29, 2003 | | Jun 29, 2003 | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Enforced | | Enforced | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |China-Macau CEPA | | China-Macau CEPA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|MAC}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Oct 18, 2003 | | Oct 18, 2003 | ||
| |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | | <nowiki>-</nowiki> | ||
| |Enforced | | Enforced | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Hong Kong-Macau CEPA | | Hong Kong-Macau CEPA | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|HKG}} {{flagicon|MAC}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |Oct 09, 2015 | | Oct 09, 2015 | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |Negotiating | | Negotiating | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | | ] | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |Jan 26, 2010 | | Jan 26, 2010 | ||
| |Jun 29, 2010 | | Jun 29, 2010 | ||
| |Aug 17, 2010 | | Aug 17, 2010 | ||
| |Enforced | | Enforced | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |CSSTA (Based on ECFA) | | CSSTA (Based on ECFA) | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |Mar, 2011 | | Mar, 2011 | ||
| |Jun 21, 2013 | | Jun 21, 2013 | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |Abolished | | Abolished | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |CSGTA (Based on ECFA) | | CSGTA (Based on ECFA) | ||
| |{{ |
| {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|TWN}} | ||
| |], ] | | ], ] | ||
| |Feb 22, 2011 | | Feb 22, 2011 | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |N/A | | N/A | ||
| |Suspended | | Suspended | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| === |
===Military alliances=== | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| !Name | ! Name | ||
| ! Parties within the region | |||
| !Abbr. | |||
| !Parties within the region | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | {{flagicon|CHN}} {{flagicon|PRK}} | |||
| |SCO | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}}{{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|RUS}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |General Security of Military Information Agreement | |||
| | {{flagicon|USA}} {{flagicon|JPN}} | |||
| |GSOMIA | |||
| |{{Flagicon|JPN}}{{Flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| | {{flagicon|USA}} {{flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| | - | |||
| |{{Flagicon|CHN}} ({{Flagicon|HKG}}{{Flagicon|MAC}}) {{Flagicon|PRK}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | - | |||
| |{{Flagicon|USA}} ({{Flagicon|GUM}} {{Flagicon|MNP}}) {{Flagicon|JPN}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| | - | |||
| |{{Flagicon|USA}} ({{Flagicon|GUM}}{{Flagicon|MNP}}) {{Flagicon|KOR}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] (] before 1980) | |||
| |TRA (SAMDT) | |||
| |{{Flagicon|USA}} ({{Flagicon|GUM}} {{Flagicon|MNP}}) {{Flagicon|TWN}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |] (] of ]) | |||
| | - | |||
| |{{Flagicon|NATO}}{{Flagicon|USA}}({{Flagicon|GUM}}{{Flagicon|MNP}}){{Flagicon|AUS}}{{Flagicon|JPN}}{{Flagicon|KOR}}{{Flagicon|TWN}}<ref name="Kan2009">{{cite book|author=Shirley Kan|title=Taiwan: Major U.S. Arms Sales Since 1990|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fJSHhOZo_j8C&pg=PA52|date=December 2009|publisher=DIANE Publishing|isbn=978-1-4379-2041-3|page=52}}</ref> | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| ==Major cities== | |||
| == Cities and towns == | |||
| {{Main|Cities of East Asia}} | {{Main|Cities of East Asia}} | ||
| {{Largest population centres | |||
| | name = Largest urban areas of East Asia | |||
| <gallery widths="660" heights="220" perrow="1"> | |||
| | country = East Asia | |||
| File:The Forbidden City - View from Coal Hill.jpg|] is the capital of the People's Republic of China and the largest metropolis in northern China. | |||
| | stat_ref = <ref name="UN-World-Cities-2016">{{cite web|url=https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/urbanization/the_worlds_cities_in_2016_data_booklet.pdf|title=The World's Cities in 2016|last=United Nations|date=March 12, 2017|website=United Nations}}</ref><ref name="korea1">{{cite web|url=http://rcps.egov.go.kr:8081/jsp/stat/ppl_stat_jf.jsp|script-title=ko:통계표명 : 주민등록 인구통계|publisher=Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs|language=ko|access-date=4 April 2015|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110303195830/http://rcps.egov.go.kr:8081/jsp/stat/ppl_stat_jf.jsp|archive-date=3 March 2011}}</ref> | |||
| File:Shanghai skyline at night, panoramic. China, East Asia-2.jpg|] is the largest city in China and one of the largest in the world, and is a global financial centre and transport hub with the ]. | |||
| | list_by_pop = <!-- link to the list of cities in the given country, if possible sorted by population --> | |||
| File:Guangzhou dusk panorama.jpg|] is one of the most important cities in southern China. It has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road and continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub today. | |||
| | div_name = Country | |||
| File:XiAn qujiang.jpg|] or ] is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties. It has a significant cultural influence in East Asia. | |||
| | div_link = <!-- the template will automatically create a link for "div_name of country" (e.g. Provinces of Chile), if this doesn't work you can use this field --> | |||
| File:Hong Kong Night Skyline2.jpg|] is one of the world's leading ] and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis. | |||
| | city_1 = Tokyo| div_1 = Japan| pop_1 = 38,140,000| img_1 = Tokyo Skyline20210123.jpg | |||
| File:ChiangKai-shek memorial2009 amk.jpg|] is the capital of the Republic of China and anchors a major high-tech industrial area in Taiwan. | |||
| | city_2 = Seoul| div_2 = South Korea| pop_2 = 25,520,000| img_2 = Seoul (South Korea).jpg | |||
| File:Skyscrapers of Shinjuku 2009 January.jpg|] is the capital of Japan and one of the largest cities in the world, both in ] and ]. | |||
| | city_3 = Shanghai| div_3 = China| pop_3 = 24,484,000| img_3 = | |||
| File:Ufoto-wiki-01 Osaka-Skyline May2014.jpg|] is the second largest metropolitan area in Japan | |||
| | city_4 = Beijing| div_4 = China| pop_4 = 21,240,000| img_4 = Beijing Sunset2.jpg | |||
| File:四条京阪前(バス), Kyoto, Japan (Unsplash).jpg|] was the Imperial capital of Japan for more than one thousand years. | |||
| | city_5 = Osaka| div_5 = Japan| pop_5 = 20,337,000 | |||
| File:Gangam-001.jpg|] is the capital of South Korea, one of the largest cities in the world and a leading global technology hub. | |||
| | city_6 = Chongqing| div_6 = China| pop_6 = 13,744,000 | |||
| File:Pyonyang from Yanggakdo.jpg|] is the capital of North Korea, and is a significant metropolis on the ]. | |||
| | city_7 = Guangzhou| div_7 = China| pop_7 = 13,070,000 | |||
| File:Gandan Monastery 24.JPG|] is the capital of Mongolia with a population of 1 million as of 2008. | |||
| | city_8 = Tianjin| div_8 = China| pop_8 = 11,558,000 | |||
| | city_9 = Shenzhen| div_9 = China| pop_9 = 10,828,000 | |||
| | city_10 = Chengdu| div_10 = China| pop_10 = 10,104,000 | |||
| }} | |||
| <gallery mode="packed" style="text-align: center;" heights="110" perrow="3"> | |||
| File:Shinjuku skyline, Tokyo - Sony A7R (11831328835).jpg|] is the capital of Japan and the world's largest city, both in ] and ]. | |||
| File:Beijing Guomao CBD.jpg|] is the capital of China. It has a history of over 3300 years. | |||
| File:Namdaemun-ro, Seoul.jpg|] is the capital of South Korea. | |||
| File:Osaka Umeda Sky Building Panoramablick 05.jpg|] is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan. | |||
| File:Guangzhou Night.jpg|] is one of the most important economic centers in southern China. | |||
| File:Nagoya Night View.jpg|] is the third-largest metropolitan area in Japan. Nagoya is a major port city and the location of ] headquarters. | |||
| File:Kyoto, Japan (Unsplash UIN-pFfJ7c).jpg|] was the imperial capital of Japan for eleven centuries. | |||
| File:UB downtown.jpg|] is the capital of Mongolia, with a population of 1.6 million as of 2021. | |||
| File:Taipei Skyline 2022.06.29.jpg|] is the capital of Taiwan, with a population of 2.6 million. | |||
| File:Hong Kong Harbour Night 2019-06-11.jpg|] is one of the ] and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis. | |||
| File:Gwangandaegyo_Bridge_in_Busan,_South_Korea_(iau2207b).jpg|] is second largest city in ] and financial centre along with Seoul | |||
| File:Pyongyang City - Ryugyong Hotel in Background (13913572409).jpg|] is the capital of North Korea, and a major city on the ]. | |||
| File:Xi'an Gulou.jpg|] or ] is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. | |||
| File:Pass over Eastern Asia to Philippine Sea and Guam.ogv|Pass of the ISS over Mongolia, looking out west towards the Pacific Ocean, China, and Japan. As the video progresses, major cities along the Chinese coast and the Japanese islands on the ] are visible. The island of ] can be seen further down the pass into the Philippine Sea, and the pass ends just to the east of New Zealand. | |||
| </gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| ]. The island of ] can be seen further down the pass into the Philippine Sea, and the pass ends just to the east of New Zealand. A lightning storm can be seen as light pulses near the end of the video.]] | |||
| == |
==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Geography |
{{Portal|Geography|Asia|China|Hong Kong|Japan|North Korea|South Korea|Taiwan | ||
| }} | |||
| <!-- {{main|Outline of East Asia|Index of East Asia-related articles}} --> | <!-- {{main|Outline of East Asia|Index of East Asia-related articles}} --> | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == |
==Notes== | ||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| {{Reflist|group="note"}} | |||
| == |
==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * Church, Peter. ''A short history of South-East Asia'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2017). | |||
| {{Commons category|East Asia}} | |||
| * Chung, Eunbin. ''Pride, Not Prejudice: National Identity as a Pacifying Force in East Asia'' (University of Michigan Press, 2022) | |||
| * Clyde, Paul H., and Burton F. Beers. ''The Far East: A History of Western Impacts and Eastern Responses, 1830–1975'' (1975) | |||
| * Crofts, Alfred. ''A history of the Far East'' (1958) | |||
| * Dennett, Tyler. ''Americans in Eastern Asia'' (1922) | |||
| * Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, and Anne Walthall. ''East Asia: A cultural, social, and political history'' (Cengage Learning, 2013). | |||
| * Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988) | |||
| ** ; ; ; | |||
| * Fairbank, John K., Edwin Reischauer, and Albert M. Craig. ''East Asia: The great tradition'' and ''East Asia: The modern transformation'' (1960) , famous textbook. | |||
| * Flynn, Matthew J. ''China Contested: Western Powers in East Asia'' (2006), for secondary schools | |||
| * Gelber, Harry. ''The dragon and the foreign devils: China and the world, 1100 BC to the present'' (2011). | |||
| * Green, Michael J. ''By more than providence: grand strategy and American power in the Asia Pacific since 1783'' (2017) a major scholarly survey | |||
| * Hall, D.G.E. ''History of South East Asia'' (Macmillan International Higher Education, 1981). | |||
| * Holcombe, Charles. ''A History of East Asia'' (2d ed. Cambridge UP, 2017). | |||
| * Iriye, Akira. ''After Imperialism; The Search for a New Order in the Far East 1921–1931.'' (1965). | |||
| * Jensen, Richard, Jon Davidann, and Yoneyuki Sugita, eds. ''Trans-Pacific Relations: America, Europe, and Asia in the Twentieth Century'' (Praeger, 2003), 304 pp | |||
| * Keay, John. ''Empire's End: A History of the Far East from High Colonialism to Hong Kong'' (Scribner, 1997). | |||
| * Levinson, David, and Karen Christensen, eds. ''Encyclopedia of Modern Asia''. (6 vol. Charles Scribner's Sons, 2002). | |||
| * Mackerras, Colin. ''Eastern Asia: an introductory history'' (Melbourne: Longman Cheshire, 1992). | |||
| * Macnair, Harley F. & Donald Lach. ''Modern Far Eastern International Relations.'' (2nd ed 1955) , 780pp; focus on 1900–1950. | |||
| * Miller, David Y. ''Modern East Asia: An Introductory History'' (Routledge, 2007) | |||
| * Murphey, Rhoads. ''East Asia: A New History'' (1996) | |||
| * Norman, Henry. ''The Peoples and Politics of the Far East: Travels and studies in the British, French, Spanish and Portuguese colonies, Siberia, China, Japan, Korea, Siam and Malaya'' (1904) | |||
| * Paine, S. C. M. ''The Wars for Asia, 1911–1949'' (2014) | |||
| * Prescott, Anne. ''East Asia in the World: An Introduction'' (Routledge, 2015) | |||
| * Ring, George C. ''Religions of the Far East: Their History to the Present Day'' (Kessinger Publishing, 2006). | |||
| * Szpilman, Christopher W. A., Sven Saaler. "Japan and Asia" in ''Routledge Handbook of Modern Japanese History'' (2017) | |||
| * Steiger, G. Nye. ''A history of the Far East'' (1936). | |||
| * Vinacke, Harold M. ''A History of the Far East in Modern Times'' (1964) | |||
| * Vogel, Ezra. ''China and Japan: Facing History'' (2019) | |||
| * Woodcock, George. ''The British in the Far East'' (1969) | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{commons category|East Asia}} | |||
| {{Wiktionary}} | {{Wiktionary}} | ||
| {{Wikivoyage|East Asia}} | |||
| <!-- {{Misplaced Pages-Books}} --> | |||
| * | |||
| {{-}} | |||
| {{Asia topics}} | {{Asia topics}} | ||
| {{East Asian topics |state = expanded |
{{East Asian topics |state = expanded}} | ||
| {{Geographic location | {{Geographic location | ||
| |Centre |
| Centre = East Asia | ||
| |North |
| North = ] | ||
| |Northeast = ]<br />] | | Northeast = ]<br />] | ||
| |East |
| East = ] | ||
| |Southeast = ] | | Southeast = ] | ||
| |South = ]<br />] | | South = ]<br />] | ||
| |Southwest = ] | | Southwest = ] | ||
| |West = ] | | West = ] | ||
| |Northwest = ]<br />] | | Northwest = ]<br />] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:46, 4 January 2025
Subregion of the Asian continent For other uses, see East Asia (disambiguation).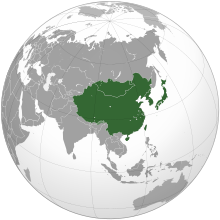 | |
| Area | 11,840,000 km (4,570,000 sq mi) (3rd) |
|---|---|
| Population | 1.6 billion (2023; 2nd) |
| Population density | 141.9 km (54.8 sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | $47.6 trillion (2024) |
| GDP (nominal) | $25.7 trillion (2024) |
| GDP per capita | $16,000 (nominal) |
| Demonym | East Asian |
| Countries | 6 countries |
| Dependencies | Two special administrative regions of China |
| Languages | |
| Time zones | UTC+7, UTC+8 & UTC+9 |
| Largest cities | List of urban areas: |
| UN M49 code | 030 – Eastern Asia142 – Asia001 – World |
| East Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 东亚/东亚细亚 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 東亞/東亞細亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan | ཨེ་ཤ་ཡ་ཤར་མ་ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hangul | 동아시아/동아세아/동아 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanja | 東아시아/東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Зүүн Ази ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠠᠽᠢ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kana | ひがしアジア/とうあ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shinjitai | 東亜細亜(東アジア)/東亜 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur | شەرقىي ئاسىي | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
East Asia is a geographical and cultural region of Asia including China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. Additionally, Hong Kong and Macau are the two special administrative regions of China. The economies of China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan are among the world's largest and most prosperous. East Asia borders North Asia to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To its east is the Pacific Ocean.
East Asia, especially Chinese civilization, is regarded as one of the earliest cradles of civilization. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the Japanese, Korean, and Mongolian civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past but have since been absorbed into neighbouring civilizations in the present day, such as Tibet, Manchuria, and Ryukyu (Okinawa), among many others. Taiwan has a relatively young history in the region after the prehistoric era; originally, it was a major site of Austronesian civilisation prior to colonisation by European colonial powers and China from the 17th century onward. For thousands of years, China was the leading civilization in the region, exerting influence on its neighbours. Historically, societies in East Asia have fallen within the Chinese sphere of influence, and East Asian vocabularies and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. The Chinese calendar serves as the root from which many other East Asian calendars are derived.
Major religions in East Asia include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana), Confucianism and Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, ancestral worship, and Chinese folk religion in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, Shinto in Japan, and Christianity and Musok in Korea. Tengerism and Tibetan Buddhism are prevalent among Mongols and Tibetans while other religions such as Shamanism are widespread among the indigenous populations of northeastern China such as the Manchus. The major languages in East Asia include Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, and Korean. The major ethnic groups of East Asia include the Han in China and Taiwan, Yamato in Japan, Koreans in North and South Korea, and Mongols in Mongolia. There are 76 officially-recognized minority or indigenous ethnic groups in East Asia; 55 native to mainland China (including Hui, Manchus, Chinese Mongols, Tibetans, Uyghurs, and Zhuang in the frontier regions), 16 native to the island of Taiwan (collectively known as Taiwanese indigenous peoples), one native to the major Japanese island of Hokkaido (the Ainu) and four native to Mongolia (Turkic peoples). The Ryukyuan people are an unrecognized ethnic group indigenous to the Ryukyu Islands in southern Japan, which stretch from Kyushu to Taiwan. There are also several unrecognized indigenous ethnic groups in mainland China and Taiwan.
East Asians comprise around 1.7 billion people, making up about 33% of the population in Continental Asia and 20% of the global population. The region is home to major world metropolises such as Beijing–Tianjin, Busan–Daegu–Ulsan–Changwon, Guangzhou, Hong Kong, Osaka–Kyoto–Kobe, Seoul, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Taipei, and Tokyo. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in Mongolia and Western China, both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the lowest population density of a sovereign state. The overall population density of the region is 133 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi), about three times the world average of 45/km (120/sq mi).
History
Main article: History of East AsiaAncient era
China was the first region settled in East Asia and was undoubtedly the core of East Asian civilization from where other parts of East Asia were formed. The various other regions in East Asia were selective in the Chinese influences they adopted into their local customs. Historian Ping-ti Ho referred to China as the cradle of Eastern civilization, in parallel with the cradle of Middle Eastern civilization along the Fertile Crescent encompassing Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt as well as the cradle of Western civilization encompassing Ancient Greece.
Chinese civilization emerged early, and prefigured other East Asian civilisations. Throughout history, imperial China would exert cultural, economic, technological, and political influence on its neighbours. Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically and militarily for over two millennia. The tributary system of China shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular. Imperial China's cultural preeminence not only led the country to become East Asia's first literate nation in the entire region, it also supplied Japan and Korea with Chinese loanwords and linguistic influences rooted in their writing systems.
Under Emperor Wu of Han, the Han dynasty made China the regional powerhouse in East Asia, projecting much of its imperial influence onto its neighbours. Han China hosted the largest unified population in East Asia, the most literate and urbanised as well as being the most economically developed, as well as the most technologically and culturally advanced civilization in the region at the time. Cultural and religious interaction between the Chinese and other regional East Asian dynasties and kingdoms occurred. China's impact and influence on Korea began with the Han dynasty's northeastern expansion in 108 BC when the Han Chinese conquered the northern part of the Korean peninsula and established a province called Lelang. Chinese influences were transmitted and soon took root in Korea through the inclusion of the Chinese writing system, monetary system, rice culture, philosophical schools of thought, and Confucian political institutions. Jomon society in ancient Japan incorporated wet-rice cultivation and metallurgy through its contact with Korea. Starting in the fourth century AD, Japan adopted Chinese characters, which remain integral to the Japanese writing system. Utilizing the Chinese writing system allowed the Japanese to conduct their daily activities, maintain historical records and give form to various ideas, thoughts, and philosophies.
Medieval era

During the Tang dynasty, China exerted its greatest influence on East Asia as various aspects of Chinese culture spread to Japan and Korea. The establishment of the medieval Tang dynasty rekindled the impetus of Chinese expansionism across the geopolitical confines of East Asia. Similar to its Han predecessor, Tang China reasserted itself as the center of East Asian geopolitical influence during the early medieval period which spearheaded and marked another golden age in Chinese history. During the Tang dynasty, China exerted its greatest influence on East Asia as various aspects of Chinese culture spread to Japan and Korea. In addition, Tang China also managed to maintain control over northern Vietnam and northern Korea.
As full-fledged medieval East Asian states were established, Korea by the fourth century AD and Japan by the seventh century AD, Japan and Korea actively began to incorporate Chinese influences such as Confucianism, the use of Chinese characters, architecture, state institutions, political philosophies, religion, urban planning, and various scientific and technological methods into their culture and society through direct contacts with Tang China and succeeding Chinese dynasties. Drawing inspiration from the Tang political system, Prince Naka no oe launched the Taika Reform in 645 AD where he radically transformed Japan's political bureaucracy into a more centralised bureaucratic empire. The Japanese also adopted Mahayana Buddhism, Chinese style architecture, and the imperial court's rituals and ceremonies, including the orchestral music and state dances had Tang influences. Written Chinese gained prestige and aspects of Tang culture such as poetry, calligraphy, and landscape painting became widespread. During the Nara period, Japan began to aggressively import Chinese culture and styles of government which included Confucian protocol that served as a foundation for Japanese culture as well as political and social philosophy. The Japanese also created laws adopted from the Chinese legal system that was used to govern in addition to the kimono, which was inspired from Chinese hanfu during the eighth century.
Modern era

For many centuries, most notably from the 7th to the 14th centuries, China stood as East Asia's most advanced civilization and foremost military and economic power, exerting its influence as the transmission of advanced Chinese cultural practices and ways of thinking greatly shaped the region up until the nineteenth century. From third century through the eighteenth century, diplomatic and trade relations between China and other East Asian countries and the steppe kingdoms was governed through a tributary system. Under this system, the Chinese emperor received tribute from other rulers and in return received political benefits (like recognition or non-aggression agreements) or physical gifts, like porcelain and silks. Through this system, the Chinese emperor conferred legitimacy on other rulers.
As East Asia's connections with Europe and the Western world strengthened during the late nineteenth century, China's power began to decline. By the mid-nineteenth century, the weakening Qing dynasty became fraught with political corruption, obstacles and stagnation that was incapable of rejuvenating itself as a world power in contrast to the industrializing Imperial European colonial powers and a rapidly modernizing Japan. The United States Commodore Matthew C. Perry would open Japan to Western influence, and the country would expand in earnest after the 1860s. Around the same time, the Meiji Restoration in Japan sparked rapid societal transformation from an isolated feudal state into East Asia's first industrialised nation. The modern and militarily powerful Japan would galvanise its position in the Orient as East Asia's greatest power with a global mission poised to advance to lead the entire world. By the early 1900s, the Empire of Japan succeeded in asserting itself as East Asia's most dominant geopolitical force.

With its newly found international status, Japan would begin to challenge the European colonial powers and inextricably took on a more active role within the East Asian geopolitical order and world affairs at large. Flexing its nascent political and military might, Japan soundly defeated the stagnant Qing dynasty during the First Sino-Japanese War as well as defeating Russia in the Russo-Japanese War in 1905; the first major military victory in the modern era of an East Asian power over a European one. Its hegemony was the heart of an empire that would include Taiwan and Korea. During World War II, Japanese expansionism with its imperialist aspirations through the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere would incorporate Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China and Manchuria, Hong Kong, and Southeast Asia under its control establishing itself as a maritime colonial power in East Asia.
Contemporary era
See also: Pacific CenturyAfter a century of exploitation by the European and Japanese colonialists, post-colonial East Asia saw the defeat and occupation of Japan by the victorious Allies. The end of World War II did not result in east Asian countries obtaining independence or national unification. Independence and national unification were primary concerns for the first generation of east Asian post-World War II leaders.
The Chinese Civil War resumed after the defeat of the Japanese, with the Communists defeating the Nationalist Republic of China government. The government of the Republic of China retreated to Taiwan and the People's Republic of China was proclaimed on 1 October 1949.
Post-war, the Korean peninsula was partitioned, leading to the development of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea). The Korean War (1950-1953) increased regional and international tensions. The northeast part of east Asia hardened along communist and anti-communist lines. South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States increased their ties.
During the latter half of the twentieth century, the region would see the post war economic miracle of Japan, which ushered in three decades of unprecedented growth, only to experience an economic slowdown during the 1990s, but nonetheless Japan continues to remain a global economic power. East Asia would also see the economic rise of Hong Kong, South Korea, and Taiwan, in addition to the respective handovers of Hong Kong and Macau near the end of the twentieth century.
The onset of the 21st-century in East Asia led to the integration of Mainland China into the global economy through its entry in the World Trade Organization while also enhancing its emerging international status as a potential world power reinforced with its aim of restoring its historical established significance and enduring international prominence in the world economy.
As of at least 2022, the region is more peaceful, integrated, wealthy, and stable than any time in the previous 150 years.
Definitions
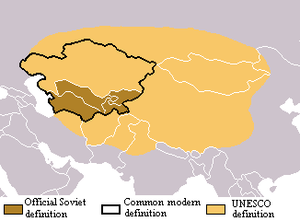
In common usage, the term "East Asia" typically refers to a region including Greater China, Japan, Korea and Mongolia.
China, Japan, and Korea represent the three core countries and civilizations of traditional East Asia, as they once had a shared written language, a shared culture, and a shared Confucian societal value system (involving shared Confucian philosophical tenets) once instituted by Imperial China. Other usages define China, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan as countries that constitute East Asia based on their geographic proximity as well as historical and modern cultural and economic ties, particularly with Japan and Korea in having retained strong cultural influences that originated from China. Some scholars include Vietnam as part of East Asia as it has been considered part of the greater Chinese cultural sphere. Though Confucianism continues to play an important role in Vietnamese culture, Chinese characters are no longer used in its written language and many scholarly organizations classify Vietnam as a Southeast Asian country. Mongolia is geographically north of Mainland China yet Confucianism and the Chinese writing system and culture had limited impact on Mongolian society. Thus, Mongolia is sometimes grouped with Central Asian countries such as Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan. Xinjiang and Tibet are sometimes seen as part of Central Asia (see also Greater Central Asia).
Broader and looser definitions by international agencies and organisations such as the World Bank refer to East Asia as the "three major Northeast Asian economies, i.e. mainland China, Japan, and South Korea", as well as Mongolia, North Korea, the Russian Far East, and Siberia. The Council on Foreign Relations includes the Russia Far East, Mongolia, and Nepal. The World Bank also acknowledges the roles of Chinese special administrative regions Hong Kong and Macau, as well as Taiwan, a country with limited recognition. The Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia defines the region as "China, Japan, the Koreas, Nepal, Mongolia, and eastern regions of the Russian Federation".


The UNSD definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience, but others commonly use the same definition of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan, and Japan.
Certain Japanese islands are associated with Oceania due to non-continental geology, distance from mainland Asia or biogeographical similarities with Micronesia. Some groups, such as the World Health Organization, categorize China, Japan and Korea with Australia and the rest of Oceania. The World Health Organization label this region the "Western Pacific", with East Asia not being used in their concept of major world regions. Their definition of this region further includes Mongolia and the adjacent area of Cambodia, as well as the countries of the South East Asia Archipelago (excluding East Timor and Indonesia).
Alternative definitions
See also: Pacific AsiaIn the context of business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to the geographical area covering ten Southeast Asian countries in ASEAN, Greater China, Japan, and Korea. However, in this context, the term "Far East" is used by the Europeans to cover ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. On rare occasions, the term is also sometimes taken to include India and other South Asian countries that are not situated within the bounds of the Asia-Pacific, although the term Indo-Pacific is more commonly used for such a definition.
Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term Northeast Asia to refer to China, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with the region of Southeast Asia covering the ten ASEAN countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia". The Council on Foreign Relations of the United States defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.
Climate
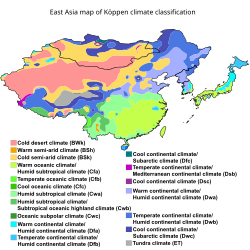
East Asia is home to many climatic zones. It also has unique weather patterns such as the East Asian rainy season and the East Asian Monsoon.
Climate change
Main article: Climate change in Asia
Like the rest of the world, East Asia has been getting warmer due to climate change, and there had been a measurable increase in the frequency and severity of heatwaves. The region is also expected to see the intensification of its monsoon, leading to more flooding. China has notably embarked on the sponge cities program, where cities are designed to increase the area of urban green spaces and permeable pavings in order to help deal with flash floods caused by greater precipitation extremes. Under high-warming scenarios, "critical health thresholds" for heat stress during the 21st century will be at times breached, in areas like the North China Plain.
China, Japan and the Republic of Korea are expected to see some of the largest economic losses caused by sea level rise. The city of Guangzhou is projected to experience the single largest annual economic losses from sea level rise in the world, potentially reaching US$254 million by 2050. Under the highest climate change scenario and in the absence of adaptation, cumulative economic losses caused by sea level rise in Guangzhou would exceed US$1 trillion by 2100. Shanghai is also expected to experience annual losses of around 1% of the local GDP in the absence of adaptation. The Yangtze River basin is a sensitive and biodiverse ecosystem, yet around 20% of its species may be lost throughout the century under 2 °C (3.6 °F) and ~43% under 4.5 °C (8.1 °F).
Economy
Main article: Economy of East Asia| Customs territory | GDP nominal billions of USD (2024) |
GDP nominal per capita USD (2024) |
GDP PPP billions of USD (2024) |
GDP PPP per capita USD (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18,532,633 | 13,136 | 35,291,015 | 25,015 | |
| 406,775 | 53,606 | 570,082 | 75,128 | |
| 54,677 | 78,962 | 92,885 | 125,510 | |
| 4,110,452 | 33,138 | 6,720,962 | 54,184 | |
| 21,943 | 6,182 | 58,580 | 16,504 | |
| N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 1,760,947 | 34,165 | 3,057,995 | 59,330 | |
| 802,958 | 34,432 | 1,792,349 | 76,858 | |
| East Asia | $25,690,385 | $15,612 | $47,583,868 | $28,916 |
Territorial and regional data
China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state because of severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan.
Etymology
| Flag | Common Name | Official name | ISO 3166 Country Codes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exonym | Endonym | Exonym | Endonym | ISO Short Name | Alpha-2 Code | Alpha-3 Code | Numeric | |
| China | 中国 | People's Republic of China | 中华人民共和国 | China | CN | CHN | 156 | |
| Hong Kong | 香港 | Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China |
中華人民共和國香港特別行政區 | Hong Kong | HK | HKG | 344 | |
| Macau | 澳門 | Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China |
中華人民共和國澳門特別行政區 | Macao | MO | MAC | 446 | |
| Japan | 日本 | Japan | 日本国 | Japan | JP | JPN | 392 | |
| Mongolia | Монгол улс / ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ |
Mongolia | Монгол Улс (ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ) |
Mongolia | MN | MNG | 496 | |
| North Korea | 조선 | Democratic People's Republic of Korea | 조선민주주의인민공화국 | Korea (the Democratic People's Republic of) | KP | PRK | 408 | |
| South Korea | 한국 | Republic of Korea | 대한민국 | Korea (the Republic of) | KR | KOR | 410 | |
| Taiwan | 臺灣 / 台灣 | Republic of China | 中華民國 | Taiwan (Province of China) | TW | TWN | 158 | |
Demographics

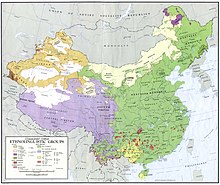
| State/Territory | Area km | Population in
thousands (2023) |
% of East Asia | % of World | Population density per km |
HDI | Capital/Administrative Centre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9,640,011 | 1,425,671 | 85.76% | 17.72% | 138 | 0.788 | Beijing | |
| 1,104 | 7,492 | 0.45% | 0.093% | 6,390 | 0.956 | Hong Kong | |
| 30 | 704 | 0.042% | 0.0087% | 18,662 | 0.925 | Macao | |
| 377,930 | 123,295 | 7.42% | 1.53% | 337 | 0.920 | Tokyo | |
| 1,564,100 | 3,447 | 0.2% | 0.042% | 2 | 0.741 | Ulaanbaatar | |
| 120,538 | 26,161 | 1.57% | 0.33% | 198 | 0.733 | Pyongyang | |
| 100,210 | 51,784 | 3.11% | 0.64% | 500 | 0.929 | Seoul | |
| 36,197 | 23,923 | 1.44% | 0.297% | 639 | 0.926 | Taipei | |
| East Asia | 11,840,000 | 1,662,477 | 100% | 20.66% | 141 |
Ethnic groups
Main articles: East Asians and Ethnic groups of East Asia| Ethnicity | Native name | Population | Language(s) | Writing system(s) | Major states/territories* | Traditional attire |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Han/Chinese | 漢族 or 汉族 | 1,313,345,856 | Chinese (Mandarin, Min, Wu, Yue, Jin, Gan, Hakka, Xiang, Huizhou, Pinghua, etc.) | Simplified Han characters, Traditional Han characters | 
| |
| Yamato/Japanese | 大和民族 | 125,117,000 | Japanese | Han characters (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana | 
| |
| Korean | 조선민족 (朝鮮民族) 한민족 (韓民族) |
84,790,105 | Korean | Hangul, Han characters (Hanja) | 
| |
| Bai | 白族 | 2,091,543 | Bai, Southwestern Mandarin | Simplified characters, Latin script | 
| |
| Hui | 回族 | 11,377,914 | Northwestern Mandarin, other Chinese Dialects, Huihui language, etc. | Simplified characters | 
| |
| Mongols | Монголчууд ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯᠴᠤᠳ Монгол/ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ |
8,942,528 | Mongolian | Mongol script, Cyrillic script | 
| |
| Zhuang | 壮族/Bouxcuengh | 19,568,546 | Zhuang, Southwestern Mandarin, etc. | Simplified Han characters, Latin script | 
| |
| Uyghurs | 维吾尔族/ئۇيغۇر | 11,774,538 | Uyghur | Arabic alphabet, Latin script | 
| |
| Manchus | 满族/ᠮᠠᠨᠵᡠ | 10,423,303 | Northeastern Mandarin, Manchu language | Simplified Han characters, Mongol script | 
| |
| Hmong/Miao | 苗族/Ghaob Xongb/Hmub/Mongb | 11,067,929 | Hmong/Miao, Southwestern Mandarin | Latin script, Simplified Han characters | 
| |
| Tibetans | 藏族/བོད་པ་ | 7,060,731 | Tibetan, Rgyal Rong, Rgu, etc. | Tibetan script | 
| |
| Yi | 彝族/ꆈꌠ | 9,830,327 | Various Loloish, Southwestern Mandarin | Yi script, Simplified Han characters | 
| |
| Tujia | 土家族 | 9,587,732 | Northern Tujia, Southern Tujia | Simplified Han characters | 
| |
| Kam | 侗族/Gaeml | 3,495,993 | Gaeml | Simplified Han characters, Latin script | 
| |
| Tu | 土族/Monguor | 289,565 | Tu, Northwestern Mandarin | Simplified Han characters | 
| |
| Daur | 达斡尔族/ᠳᠠᠭᠤᠷ | 131,992 | Daur, Northeastern Mandarin | Mongol script, Simplified Han characters | 
| |
| Indigenous Taiwanese | 臺灣原住民/ 高山族/ Yincomin/ Kasetaivang/ Inanuwayan | 533,600 | Austronesian languages (Amis, Yami), etc. | Latin script, Traditional Han characters | ||
| Ryukyuan | 琉球民族 | 1,900,000 | Japanese Ryukyuan |
Han characters (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana | 
| |
| Ainu | アイヌ/ Aynu/ Айну | 200,000 | Japanese Ainu |
Ainu uses both the Katakana and Latin scripts | 
|
- Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.
Culture
Main category: Culture of East AsiaOverview
The culture of East Asia has been deeply influenced by China, as it was the civilization that had the most dominant influence in the region throughout the ages that ultimately laid the foundation for East Asian civilization. The vast knowledge and ingenuity of Chinese civilization and the classics of Chinese literature and culture were seen as the foundations for a civilized life in East Asia. Imperial China served as a vehicle through which the adoption of Confucian ethical philosophy, Chinese calendar system, political and legal systems, architectural style, diet, terminology, institutions, religious beliefs, imperial examinations that emphasised a knowledge of Chinese classics, political philosophy and cultural value systems, as well as historically sharing a common writing system reflected in the histories of Japan and Korea.
The Imperial Chinese tributary system was the bedrock of network of trade and foreign relations between China and its East Asian tributaries, which helped to shape much of East Asian affairs during the ancient and medieval eras. Through the tributary system, the various dynasties of Imperial China facilitated frequent economic and cultural exchange that influenced the cultures of Japan and Korea and drew them into a Chinese international order. The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's foreign policy and trade for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural dominance over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular. The relationship between China and its cultural influence on East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of Greco-Roman civilization on classical Western civilisation.
Since the late 19th century, the initially unequal encounter with Western influences has also shaped East Asia.
Religion
Main article: East Asian religions <div style="border:solid transparent;background-color:initial;position:absolute;width:100px;line-height:0;Religion in East Asia (2020)
Chinese Folk Religion (52.10%) Buddhism (19.65%) No Religion (19.62%) Christianity (5.56%) Islam (1.57%) Other (1.44%)| Religion | Native name | Creator/Current Leader | Founded Time | Main Denomination | Major book | Type | Est. Followers | Ethnic groups | States/territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese folk religion | 中國民間信仰 or 中国民间信仰 | Spontaneous formation | Prehistoric period | Salvationist, Wuism, Nuo | Chinese classics, Huangdi Sijing, precious scrolls, etc. | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | ~900,000,000 | Han, Hmong, Qiang, Tujia (worship of the same ancestor-gods) | |
| Taoism | 道教 | Zhang Daoling, Wang Chongyang (Quanzhen School) | 125 AD Eastern Han dynasty | Zhengyi, Quanzhen | Tao Te Ching | Pantheism, polytheism | ~20,000,000 | Han, Zhuang, Hmong, Yao, Qiang, Tujia | |
| East Asian Buddhism/Chinese Buddhism | 漢傳佛教 or 汉传佛教 | Emperor Ming of Han (introduced to China), Mālānanda (introduced to Baekje), King Seong of Baekje (introduced to Japan) | 67 AD Eastern Han dynasty | Mahayana | Diamond Sutra | Non-God, Dualism. | ~300,000,000 | Han, Koreans, Yamato | |
| Tibetan Buddhism | 藏傳佛教 or 藏传佛教/བོད་བརྒྱུད་ནང་བསྟན། | Tonpa Shenrab Miwoche | 1800 years ago | Mahayana, Bon | Anuttarayoga Tantra | Non-God | ~10,000,000 | Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols | |
| Shamanism | 薩滿教 or Бөө мөргөл | Spontaneous formation | Prehistoric period | N/A | Prehistoric, polytheism, and pantheism | N/A | Manchus, Mongols, Oroqens | ||
| Shinto | 神道 | Spontaneous formation | Yayoi period | Shinto sects | Kojiki, Nihon Shoki | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | N/A | Yamato | |
| Musok/Muism | 신도 or 무교 | Spontaneous formation | 900 years ago | Musok sects | N/A | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | N/A | Koreans | |
| Ryukyuan religion | 琉球神道 or ニライカナイ信仰 | Spontaneous formation | N/A | N/A | N/A | Prehistoric, pantheism, and polytheism | N/A | Ryukyuans |
Festivals
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (November 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Festival | Native Name | Other name | Calendar | Date | Gregorian date | Activity | Religious practices | Food | Major ethnicities | Major states/territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese New Year | 農曆新年/农历新年 or 春節/春节 | Spring Festival | Chinese | Month 1 Day 1 | 21 Jan–20 Feb | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | Worship the King of Gods | Nian gao | Han, Manchus etc. | |
| Korean New Year | 설날 or 설 | Seollal | Korean | Month 1 Day 1 | 21 Jan–20 Feb | Ancestors Worship, Family Reunion, Tomb Sweeping | N/A | Tteokguk | Koreans | |
| Losar or Tsagaan Sar | 藏历新年/ལོ་གསར་ or 查干萨日/Цагаан сар | White Moon | Tibetan, Mongolian | Month 1 Day 1 | 25 Jan – 2 Mar | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | N/A | Chhaang or Buuz | Tibetans, Mongols, Tu etc. | |
| New Year | 元旦 | Yuan Dan | Gregorian | 1 Jan | 1 Jan | Fireworks | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Lantern Festival | 元宵節 or 元宵节 | Upper Yuan Festival (上元节) | Chinese | Month 1 Day 15 | 4 Feb – 6 Mar | Lanterns Expo, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Sky-officer | Yuanxiao | Han | |
| Daeboreum | 대보름 or 정월 대보름 | Great Full Moon | Korean | Month 1 Day 15 | 4 Feb – 6 Mar | Greeting of the moon, kite-flying, Jwibulnori, eating nuts (Bureom) | Bonfires (daljip taeugi) | Ogok-bap, namul, nuts | Korean | |
| Hanshi Festival | 寒食節 or 寒食节 | Cold Food Festival | Solar term | Traditionally, on the 105th day after the Winter solstice. Revised to 1 day before the Qingming Festival by Johann Adam Schall von Bell (Chinese: 汤若望) during the Qing dynasty. | April 3–5 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, No cooking hot meal/setting fire, Cold food only. Cuju, etc. (People used to mix this one with the Qingming Festival due to their close dates) | In Memory of a loyal Ancient named Jie Zhitui (Chinese: 介子推), ordered by the Monarch of the Jin (Chinese state), Duke Wen of Jin (Chinese: 重耳) | Cold Food, e.g. Qingtuan | Han, Koreans, Mongols | |
| Qingming Festival | 清明節 or 清明节 or Ханш нээх | Tomb Sweeping Day | Solar term | 15th day after the Vernal Equinox. Just 1 day after the Hanshi Festival, but in much higher repute. | April 4-6th | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Excursion, Planting trees, Flying kites, Tug of war, Cuju, etc. (Almost the same with the Hanshi Festival's, due to their close dates) | Burning Hell money for deceased family members. Planting willow branches to keep ghosts away from houses. | Boiled eggs | Han, Koreans, Mongols | |
| Dragon Boat Festival | 端午節 or 端午节 or 단오 | Duanwu Festival / Dano (Surit-nal) | Chinese / Korean | Month 5 Day 5 | Driving poisons & plague away. (China: Dragon Boat Race, Wearing coloured lines, Hanging felon herb on the front door.) / (Korea: Washing hair with iris water, ssireum) | Worship various Gods | Zongzi / Surichwitteok (rice cake with herbs) | Han, Koreans, Yamato | ||
| Ghost Festival | 中元節 or 中元节 or 백중 | Mid Yuan Festival | Chinese | Month 7 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Earth-officer | Han, Koreans, Yamato | |||
| Mid-Autumn Festival | 中秋節 or 中秋节 | 中秋祭 | Chinese | Month 8 Day 15 | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | Worship the Moon Goddess | Mooncake | Han | ||
| Chuseok | 추석 or 한가위 | Hangawi | Korean | Month 8 Day 15 | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Enjoying Moon view | N/A | Songpyeon, Torantang (Taro soup) | Koreans | ||
| Tsukimi | 月見 or お月見 | Tsukimi or Otsukimi | Gregorian | Month 8 Day 15 | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | Worship the Moon | Tsukimi Dango, Sweet Potato | Yamato | ||
| Double Ninth Festival | 重陽節 or 重阳节 | Double Positive Festival | Chinese | Month 9 Day 09 | Climbing Mountain, Taking care of elderly, Wearing Cornus. | Worship various Gods | Han, Korean, Yamato | |||
| Lower Yuan Festival | 下元節 or 下元节 | N/A | Chinese | Month 10 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Water-officer | Ciba | Han | ||
| Dongzhi Festival | 冬至 or 동지 or 冬至 | N/A | Gregorian | Between Dec 21 and Dec 23 | Between Dec 21 and Dec 23 | Ancestors Worship, Rites to dispel bad spirits | N/A | Tangyuan, Patjuk, Zenzai, Kabocha | Han, Koreans, Yamato | |
| Small New Year | 小年 | Jizao (祭灶) | Chinese | Month 12 Day 23 | Cleaning Houses | Worship the God of Hearth | tanggua | Han, Mongols |
*Japan switched the date to the Gregorian calendar after the Meiji Restoration.
*Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4.
Entertainment
East Asian popular culture, such as anime and manga from Japan and K-pop and K-dramas from South Korea, have become highly popular worldwide in the 21st century.
Sports

Baseball is one of the main sports in East Asia, having been introduced through mid-19th century American contact and further spread by the Japanese Empire. The game has gained millions of fans in China since the 2010s.
East Asian Youth Games
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (November 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Formerly the East Asian Games, it is a multi-sport event organized by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since 2019 among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of Guam, which is a member of the Oceania National Olympic Committees.
It is one of five Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the Central Asian Games, the Southeast Asian Games (SEA Games), the South Asian Games and the West Asian Games.
Collaboration
Free trade agreements
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (November 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Name of agreement | Parties | Leaders at the time | Negotiation begins | Signing date | Starting time | Current status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Park Geun-hye | May, 2012 | Jun 01, 2015 | Dec 30, 2015 | Enforced | |
| China–Japan–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Shinzō Abe, Park Geun-hye | Mar 26, 2013 | N/A | N/A | 10 round negotiation | |
| Japan-Mongolia EPA | Shinzō Abe, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | - | Feb 10, 2015 | - | Enforced | |
| China-Mongolia FTA | Xi Jinping, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | N/A | N/A | N/A | Officially proposed | |
| China-HK CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Tung Chee-hwa | - | Jun 29, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| China-Macau CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Edmund Ho Hau-wah | - | Oct 18, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| Hong Kong-Macau CEPA | Carrie Lam, Fernando Chui | Oct 09, 2015 | N/A | N/A | Negotiating | |
| ECFA | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Jan 26, 2010 | Jun 29, 2010 | Aug 17, 2010 | Enforced | |
| CSSTA (Based on ECFA) | Xi Jinping, Ma Ying-jeou | Mar, 2011 | Jun 21, 2013 | N/A | Abolished | |
| CSGTA (Based on ECFA) | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Feb 22, 2011 | N/A | N/A | Suspended |
Military alliances
Major cities
Main article: Cities of East Asia| Largest population centres of East Asia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City name | Country | Pop.
| ||||||
 Tokyo |
1 | Tokyo | Japan | 38,140,000 | |||||
| 2 | Seoul | South Korea | 25,520,000 | ||||||
| 3 | Shanghai | China | 24,484,000 | ||||||
| 4 | Beijing | China | 21,240,000 | ||||||
| 5 | Osaka | Japan | 20,337,000 | ||||||
| 6 | Chongqing | China | 13,744,000 | ||||||
| 7 | Guangzhou | China | 13,070,000 | ||||||
| 8 | Tianjin | China | 11,558,000 | ||||||
| 9 | Shenzhen | China | 10,828,000 | ||||||
| 10 | Chengdu | China | 10,104,000 | ||||||
-
 Tokyo is the capital of Japan and the world's largest city, both in metropolitan population and economy.
Tokyo is the capital of Japan and the world's largest city, both in metropolitan population and economy.
-
 Beijing is the capital of China. It has a history of over 3300 years.
Beijing is the capital of China. It has a history of over 3300 years.
-
 Seoul is the capital of South Korea.
Seoul is the capital of South Korea.
-
 Osaka is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan.
Osaka is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan.
-
 Guangzhou is one of the most important economic centers in southern China.
Guangzhou is one of the most important economic centers in southern China.
-
 Nagoya is the third-largest metropolitan area in Japan. Nagoya is a major port city and the location of Lexus headquarters.
Nagoya is the third-largest metropolitan area in Japan. Nagoya is a major port city and the location of Lexus headquarters.
-
 Kyoto was the imperial capital of Japan for eleven centuries.
Kyoto was the imperial capital of Japan for eleven centuries.
-
 Ulaanbaatar is the capital of Mongolia, with a population of 1.6 million as of 2021.
Ulaanbaatar is the capital of Mongolia, with a population of 1.6 million as of 2021.
-
 Taipei City is the capital of Taiwan, with a population of 2.6 million.
Taipei City is the capital of Taiwan, with a population of 2.6 million.
-
 Hong Kong is one of the global financial centres and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis.
Hong Kong is one of the global financial centres and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis.
-
 Busan is second largest city in South Korea and financial centre along with Seoul
Busan is second largest city in South Korea and financial centre along with Seoul
-
 Pyongyang is the capital of North Korea, and a major city on the Korean Peninsula.
Pyongyang is the capital of North Korea, and a major city on the Korean Peninsula.
-
 Xi'an or Chang'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China.
Xi'an or Chang'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China.
- Pass of the ISS over Mongolia, looking out west towards the Pacific Ocean, China, and Japan. As the video progresses, major cities along the Chinese coast and the Japanese islands on the Philippine Sea are visible. The island of Guam can be seen further down the pass into the Philippine Sea, and the pass ends just to the east of New Zealand.
See also
- East Asia–United States relations
- East Asian Community
- China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit
- East Asia Summit
- East Asian studies
Notes
- Listed as "Hong Kong SAR" by IMF
- Listed as "Macao SAR" by IMF
- Listed as "Taiwan, Province of China" by IMF
- Includes all area which under PRC's government control (excluding "South Tibet" and disputed islands).
- A note by the United Nations: "For statistical purposes, the data for China do not include Hong Kong and Macao, Special Administrative Regions (SAR) of China, and Taiwan Province of China."
References
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: April 2024". imf.org. International Monetary Fund.
- ^ Kort, Michael (2005). The Handbook Of East Asia. Lerner. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-761-32672-4.
- ^ "East Asia". rand.org. RAND Corporation. Archived from the original on 2011-01-02. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- "Countries of Asia". nationsonline.org. Nations Online. Archived from the original on 2001-07-01. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- Zaharna, R. S.; Arsenault, Amelia; Fisher, Ali (2013). Relational, Networked and Collaborative Approaches to Public Diplomacy: The Connective Mindshift. Routledge. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-415-63607-0.
- Holcombe, Charles (2017). A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-107-54489-5.
- Szonyi, Michael (2017). A Companion to Chinese History. Wiley–Blackwell. p. 90. ISBN 978-1-118-62460-9.
- Selin, Helaine (2010). Nature Across Cultures: Views of Nature and the Environment in Non-Western Cultures. Springer. p. 350. ISBN 978-9-048-16271-0.
- Laozi; Mair, Victor H. (1998). Tao Te Ching: The Classic Book of Integrity and the Way. New York: Quality Paperback Book Club. pp. x. ISBN 978-0-965-06475-0.
- Salkind, Neil J. (2008). Encyclopedia of Educational Psychology. Sage Publications. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-412-91688-2.
- Kim, Chongho (2003). Korean Shamanism: The Cultural Paradox. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-754-63185-9.
- Andreas Anangguru Yewangoe, "Theologia crucis in Asia", 1987 Rodopi
- Heissig, Walther (2000). The Religions of Mongolia. Translated by Samuel, Geoffrey. Kegan Paul International. p. 46. ISBN 978-0-710-30685-2.
- Wang, Yuchen; Lu, Dongsheng; Chung, Yeun-Jun; Xu, Shuhua (2018). "Genetic structure, divergence and admixture of Han Chinese, Japanese and Korean populations". Hereditas. 155: 19. doi:10.1186/s41065-018-0057-5. PMC 5889524. PMID 29636655.
- Holcombe, Charles (2017). A History of East Asia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-11873-7.
- ^ Ball, Desmond (2005). The Transformation of Security in the Asia/Pacific Region. Routledge. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-714-64661-9.
- ^ Chua, Amy; Rubenfeld, Jed (2014). The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America. Penguin. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-594-20546-0.
- ^ Kang, David C. (2012). East Asia Before the West: Five Centuries of Trade and Tribute. Columbia University Press. pp. 33–34. ISBN 978-0-2-311-5319-5.
- Goucher, Candice; Walton, Linda (2012). World History: Journeys from Past to Present. Routledge. p. 232. ISBN 978-0-415-67002-9.
- Smolnikov, Sergey (2018). Great Power Conduct and Credibility in World Politics. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-71885-9.
- Lone, Stewart (2007). Daily Lives of Civilians in Wartime Asia: From the Taiping Rebellion to the Vietnam War. Greenwood. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-313-33684-3.
- ^ Cohen, Warren I. (2000). East Asia at the Center: Four Thousand Years of Engagement with the World. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-10108-2.
- Norman, Jerry (1988). Chinese. Cambridge University Press. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-521-29653-3.
- Cohen 2000, p. 60.
- Chua, Amy (2009). Day of Empire: How Hyperpowers Rise to Global Dominance—and Why They Fall. Anchor. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-400-07741-0.
- Leibo, Steve (2012). East and Southeast Asia 2012. Stryker-Post. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-610-48885-3.
- Tsai, Henry (2009). Maritime Taiwan: Historical Encounters with the East and the West. Routledge. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-765-62328-7.
- ^ Lockard, Craig (1999). "Tang Civilization and the Chinese Centuries" (PDF). Encarta Historical Essays: 2–3, 7.
- ^ Lockard 1999, p. 7
- Injae, Lee; Miller, Owen; Jinhoon, Park; Hyun-Hae, Yi (2014). Korean History in Maps. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-09846-6 – via Google Books.
- Fagan, Brian M. (1999). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. Oxford University Press. p. 362. ISBN 978-0-195-07618-9.
- ^ Lockard 1999, p. 8
- Lockard, Craig A. (2009). Societies Networks And Transitions: Volume B From 600 To 1750. Wadsworth. pp. 290–291. ISBN 978-1-439-08540-0.
- Embree, Ainslie; Gluck, Carol (1997). Asia in Western and World History: A Guide for Teaching. M. E. Sharpe. p. 352. ISBN 978-1-563-24265-6.
- Lind, Jennifer (February 13, 2018). "Life in China's Asia: What Regional Hegemony Would Look Like". Foreign Affairs. Vol. 97, no. March/April 2018.
- Lockard 1999
- Ellington, Lucien (2009). Japan. Nations in Focus. Bloomsbury. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-598-84163-3.
- ^ Li, Xiaobing (2018). The Cold War in East Asia. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-138-65179-1.
- Roberts, John M. (1997). A Short History of the World. Oxford University Press. p. 272. ISBN 0-195-11504-X.
- Hayes, Louis D. (2009). Political Systems of East Asia: China, Korea, and Japan. Greenlight. p. xi. ISBN 978-0-765-61786-6.
- Hayes 2009, p. 15
- ^ Tindall, George Brown; Shi, David E. (2009). America: A Narrative History. W. W. Norton. p. 926. ISBN 978-0-393-934083.
- ^ April, K.; Shockley, M. (2007). Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 163. ISBN 978-0-230-00133-6.
- Cohen 2000, p. 3
- ^ Batty, David (2005-01-17). Japan's War in Colour (documentary). TWI.
- ^ Goldman, Merie; Gordon, Andrew (2000). Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World. Harvard University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-674-00097-1.
- Cohen 2000, p. 273.
- Hua, Shiping; Hu, Amelia (2014). East Asian Development Model: Twenty-first century perspectives. Routledge. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-415-73727-2.
- Lee, Yong Wook; Key, Young Son (2014). China's Rise and Regional Integration in East Asia: Hegemony or community?. Routledge. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-313-35082-5.
- "Sino-Japanese War (1894–95)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- Tindall & Shi 2009, p. 1147
- ^ Liff, Adam P.; Lee, Chaewon (2024). "Korea-Taiwan "Unofficial" Relations after 30 Years (1992-2022): Reassessing Seoul's "One China" Policy". In Zhao, Suisheng (ed.). The Taiwan Question in Xi Jinping's Era: Beijing's Evolving Taiwan Policy and Taiwan's Internal and External Dynamics. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 9781032861661.
- Northrup, Cynthia Clark; Bentley, Jerry H.; Eckes, Alfred E. Jr. (2004). Encyclopedia of World Trade: From Ancient Times to the Present. Routledge. p. 297. ISBN 978-0-765-68058-7.
- ^ Paul, Erik (2012). Neoliberal Australia and US Imperialism in East Asia. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 114. ISBN 978-1-137-27277-5.
- Maddison, Angus (2007). Contours of the World Economy 1–2030 AD: Essays in Macro-Economic History. Oxford University Press. p. 379. ISBN 978-0-191-64758-1.
- Dahlman, Carl J; Aubert, Jean-Eric. "China and the Knowledge Economy: Seizing the 21st Century. WBI Development Studies". Institute of Education Sciences. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- "Angus Maddison. Chinese Economic Performance in the Long Run. Development Centre Studies" (PDF). p. 29. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 15 September 2017.
- Dahlman, Carl J; Aubert, Jean-Eric. China and the Knowledge Economy: Seizing the 21st Century. WBI Development Studies. World Bank publications. Accessed January 30, 2008.
- Angus Maddison. Chinese Economic Performance in the Long Run Archived 2014-10-15 at the Wayback Machine. Development Centre Studies. Accessed 2007. p.29 See the "Table 1.3. Levels of Chinese and European GDP Per Capita, 1–1700 AD" in page 29, Chinese GDP Per Capita was 450 and European GDP Per Capital was 422 in 960AD. Chinese GDP Per Capita was 600 while European was 576. During this time, Chinese per capita income rose by about a third.
- Ma, Xinru; Kang, David C. (2024). Beyond Power Transitions: The Lessons of East Asian History and the Future of U.S.-China Relations. Columbia Studies in International Order and Politics. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-55597-5.
- "Introducing East Asian Peoples" (PDF). International Mission Board. September 10, 2016.
- Gilbet Rozman (2004), Northeast Asia's stunted regionalism: bilateral distrust in the shadow of globalization. Cambridge University Press, pp. 3-4
- "Northeast Asia dominates patent filing growth." Retrieved on August 8, 2001.
- "Paper: Economic Integration in Northeast Asia." Retrieved on August 8, 2011.
- Hua & Hu 2014, p. 3.
- Ness, Immanuel; Bellwood, Peter (2014). The Global Prehistory of Human Migration. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 217. ISBN 978-1-118-97059-1.
- Kort 2005, pp. 7–9
- ^ Prescott, Anne (2015). East Asia in the World: An Introduction. Routledge. p. 3. ISBN 978-0765643223.
- Ikeo, Aiko (1996). Economic Development in Twentieth-Century East Asia: The International Context. Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-415-14900-6.
- Yoshimatsu, H. (2014). Comparing Institution-Building in East Asia: Power Politics, Governance, and Critical Junctures. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-137-37054-9.
- Kim, Mikyoung (2015). Routledge Handbook of Memory and Reconciliation in East Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-83513-8.
- ^ Hazen, Dan; Spohrer, James H. (2005). Building Area Studies Collections. Otto Harrassowitz. p. 130. ISBN 978-3-447-05512-3.
- Grabowski, Richard; Self, Sharmistha; Shields, William (2012). Economic Development: A Regional, Institutional, and Historical Approach (2nd ed.). Routledge (published September 25, 2012). p. 59. ISBN 978-0-765-63353-8.
- Currie, Lorenzo (2013). Through the Eyes of the Pack. Xlibris Corp. p. 163. ISBN 978-1-493-14517-1.
- Asato, Noriko (2013). Handbook for Asian Studies Specialists: A Guide to Research Materials and Collection Building Tools. Libraries Unlimited. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-598-84842-7.
- ^ Prescott 2015, p. 6
- ^ Miller, David Y. (2007). Modern East Asia: An Introductory History. Routledge. p. xi. ISBN 978-0-765-61822-1.
- "Central Themes for a Unit on China r Educators". afe.easia.columbia.edu. Columbia University. Retrieved 2018-12-01. "Within the Pacific region, China is potentially a major economic and political force. Its relations with Japan, Korea, and its Southeast Asian neighbours, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and the Philippines, will be determined by how they perceive this power will be used."
- Cummings, Sally N. (2013). Understanding Central Asia: Politics and Contested Transformations. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-43319-3.
- Saez, Lawrence (2012). The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): An emerging collaboration architecture. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-67108-1.
- Cornell, Svante E. Modernization and Regional Cooperation in Central Asia: A New Spring? (PDF). Central Asia-Caucasus Institute and the Silk Road Studies.
- Aminian, Nathalie; Fung, K. C.; Ng, Francis. "Integration of Markets vs. Integration by Agreements" (PDF). Policy Research Working Paper. World Bank.
- ^ "Northeast Asia". Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved August 10, 2009.
- Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia (1999). Japan and Russia in Northeast Asia: Partners in the 21st Century. Greenwood. p. 248.
- "UNSD — Methodology". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 2023-12-10.
- ^ "United Nations Statistics Division – Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". United Nations Statistics Division. 2015-05-06. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
- "East Asia". Encarta. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2009-11-09. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
the countries and regions of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Mongolia, South Korea, North Korea and Japan.
- "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings". United Nations Statistics Division. 11 February 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- Todd, Ian (1974). Island Realm: A Pacific Panorama. Angus & Robertson. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-207-127618-.
- Udvardy, Miklos D. F. "A Classification of the Biogeographical Provinces of the World" (PDF). UNESCO. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2022. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- "IMAGE: Countries and areas in WHO's Western Pacific Region" – via ResearchGate.
- "Forget Asia-Pacific, it's Indo-Pacific now. Where is that?". 15 September 2021.
- Dent, Christopher M. (2008). East Asian regionalism. Routledge. pp. 1–8.
- Harvie, Charles; Fukunari, Kimura; Lee, Hyun-Hoon (2005). New East Asian regionalism. Edward Elgar. pp. 3–6.
- Katzenstein, Peter J.; Takashi, Shiraishi (2006). Beyond Japan: the dynamics of East Asian regionalism. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. pp. 1–33.
- An, Z (April 2000). "Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon". Quaternary Science Reviews. 19 (8): 743–762. Bibcode:2000QSRv...19..743A. doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00031-1.
- ^ Kang, Suchul; Eltahir, Elfatih A. B. (31 July 2018). "North China Plain threatened by deadly heatwaves due to climate change and irrigation". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 3528. Bibcode:2023NatCo..14.3528K. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-38906-7. PMC 10319847. PMID 37402712.
- ^ Shaw, R., Y. Luo, T. S. Cheong, S. Abdul Halim, S. Chaturvedi, M. Hashizume, G. E. Insarov, Y. Ishikawa, M. Jafari, A. Kitoh, J. Pulhin, C. Singh, K. Vasant, and Z. Zhang, 2022: Chapter 10: Asia. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability . Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, New York, US, pp. 1457–1579 |doi=10.1017/9781009325844.012.
- ^ "Country codes". iso.org.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- "Human Development Reports". www.hdr.undp.org. January 2018. Retrieved 2018-10-14.
- "CIA Factbook". Archived from the original on 2016-10-13. Retrieved 2018-03-17.
- 人口推計 – 平成 28年 12月 報 (PDF). stat.go.jp.
- 주민등록 인구통계
- "Korea North". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 8 April 2023. (Archived 2023 edition.)
- 재외동포현황 [Total number of overseas Koreans]. South Korea: Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "China Statistical Yearbook 2021".
- Gordon, Raymond G. Jr., ed. (2005). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (15th ed.). Dallas: SIL International. ISBN 978-1-55671-159-6. OCLC 224749653.
- "Ainu language and alphabet".
- ^ Goscha, Christopher (2016). The Penguin History of Modern Vietnam: A History. Allen Lane. ISBN 978-1-846-143106.
- Chua & Rubenfeld 2014, p. 122
- Lewis, Mark Edward (2012). China's Cosmopolitan Empire: The Tang Dynasty. Belknap. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-674-06401-0.
- ^ Reischauer, Edwin O. (1974). "The Sinic World in Perspective". Foreign Affairs. 52 (2): 341–348. doi:10.2307/20038053. JSTOR 20038053.
- ^ Chua & Rubenfeld 2014, p. 121–122
- Seo, Yongseok (2006-04-30), Dator, Jim; Pratt, Richard C.; Seo, Yongseok (eds.), "Chapter 22. East Asian Response to the Globalization of Culture: Perceptional Change and Cultural Policy", Fairness, Globalization, and Public Institutions: East Asia and Beyond, University of Hawaii Press, pp. 319–336, doi:10.1515/9780824841966-023/html?lang=en&srsltid=afmboorlr_g6zoxn9cj4zxog8odmpytphkz2ql0wqco_9yvf8y---dbx, ISBN 978-0-8248-4196-6, retrieved 2024-12-21
- "Religious Composition by Country, 2010-2050". Pew. 2 April 2015. Archived from the original on 2019-12-21. Retrieved 2020-10-18.
- Wenzel-Teuber, Katharina (2012). "People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011" (PDF). Religions & Christianity in Today's China. II (3): 29–54. ISSN 2192-9289. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2017.
- ^ Wenzel-Teuber, Katharina (2017). "Statistics on Religions and Churches in the People's Republic of China – Update for the Year 2016" (PDF). Religions & Christianity in Today's China. VII (2): 26–53. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2017.
- Hardacre, Helen (2017). Shinto: a history. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-190-62171-1.
- Hollingsworth, Julia (2019-12-29). "Why the past decade saw the rise and rise of East Asian pop culture". CNN. Retrieved 2024-11-18.
- Cho, Younghan (2016). "Double binding of Japanese colonialism: trajectories of baseball in Japan, Taiwan, and Korea". Cultural Studies. 30 (6): 926–948. doi:10.1080/09502386.2015.1094498. ISSN 0950-2386.
- 杜娟. "MLB's China operation knocking it out the ball park". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2024-10-22.
- United Nations (March 12, 2017). "The World's Cities in 2016" (PDF). United Nations.
- 통계표명 : 주민등록 인구통계 (in Korean). Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs. Archived from the original on 3 March 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
Further reading
- Church, Peter. A short history of South-East Asia (John Wiley & Sons, 2017).
- Chung, Eunbin. Pride, Not Prejudice: National Identity as a Pacifying Force in East Asia (University of Michigan Press, 2022) online reviews by six scholars
- Clyde, Paul H., and Burton F. Beers. The Far East: A History of Western Impacts and Eastern Responses, 1830–1975 (1975) online 3rd edition 1958
- Crofts, Alfred. A history of the Far East (1958) online free to borrow
- Dennett, Tyler. Americans in Eastern Asia (1922) online free
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, and Anne Walthall. East Asia: A cultural, social, and political history (Cengage Learning, 2013).
- Embree, Ainslie T., ed. Encyclopedia of Asian history (1988)
- Fairbank, John K., Edwin Reischauer, and Albert M. Craig. East Asia: The great tradition and East Asia: The modern transformation (1960) online free to borrow, famous textbook.
- Flynn, Matthew J. China Contested: Western Powers in East Asia (2006), for secondary schools
- Gelber, Harry. The dragon and the foreign devils: China and the world, 1100 BC to the present (2011).
- Green, Michael J. By more than providence: grand strategy and American power in the Asia Pacific since 1783 (2017) a major scholarly survey excerpt
- Hall, D.G.E. History of South East Asia (Macmillan International Higher Education, 1981).
- Holcombe, Charles. A History of East Asia (2d ed. Cambridge UP, 2017). excerpt
- Iriye, Akira. After Imperialism; The Search for a New Order in the Far East 1921–1931. (1965).
- Jensen, Richard, Jon Davidann, and Yoneyuki Sugita, eds. Trans-Pacific Relations: America, Europe, and Asia in the Twentieth Century (Praeger, 2003), 304 pp online review
- Keay, John. Empire's End: A History of the Far East from High Colonialism to Hong Kong (Scribner, 1997). online free to borrow
- Levinson, David, and Karen Christensen, eds. Encyclopedia of Modern Asia. (6 vol. Charles Scribner's Sons, 2002).
- Mackerras, Colin. Eastern Asia: an introductory history (Melbourne: Longman Cheshire, 1992).
- Macnair, Harley F. & Donald Lach. Modern Far Eastern International Relations. (2nd ed 1955) 1950 edition online free, 780pp; focus on 1900–1950.
- Miller, David Y. Modern East Asia: An Introductory History (Routledge, 2007)
- Murphey, Rhoads. East Asia: A New History (1996)
- Norman, Henry. The Peoples and Politics of the Far East: Travels and studies in the British, French, Spanish and Portuguese colonies, Siberia, China, Japan, Korea, Siam and Malaya (1904) online
- Paine, S. C. M. The Wars for Asia, 1911–1949 (2014) excerpt
- Prescott, Anne. East Asia in the World: An Introduction (Routledge, 2015)
- Ring, George C. Religions of the Far East: Their History to the Present Day (Kessinger Publishing, 2006).
- Szpilman, Christopher W. A., Sven Saaler. "Japan and Asia" in Routledge Handbook of Modern Japanese History (2017) online
- Steiger, G. Nye. A history of the Far East (1936).
- Vinacke, Harold M. A History of the Far East in Modern Times (1964) online free
- Vogel, Ezra. China and Japan: Facing History (2019) excerpt
- Woodcock, George. The British in the Far East (1969) online
External links
| East Asia | ||
|---|---|---|
| Countries and regions |  | |
| Ethnic groups | ||
| Culture |
| |
| Environment | ||
| Economy and Politics | ||
| History | ||
| Sports | ||
| Education | ||
| Military | ||
| Science and technology | ||
| Places adjacent to East Asia | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||

