| Revision as of 17:16, 3 June 2019 edit195.187.108.4 (talk) →Consonants← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:07, 28 October 2024 edit undoOhnoitsjamie (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Administrators261,297 editsm Reverted edit by 77.174.145.56 (talk) to last version by SkitashTag: Rollback | ||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Berber language of Morocco}} | |||
| {{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
| |name= Ghomara | |name= Ghomara | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
| |map=Ghomara Berber - Localisation.PNG | |map=Ghomara Berber - Localisation.PNG | ||
| |map2=Ghomara Berber - Details.PNG | |map2=Ghomara Berber - Details.PNG | ||
| |mapsize = 250px | |||
| |mapcaption2={{legend|#ffff66|Ghomara Berber}} | |mapcaption2={{legend|#ffff66|Ghomara Berber}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''Ghomara language''' is a ] language spoken in ]. It is the mother tongue of the ] ], who total around 10,000 people. Ghomara Berber is spoken on the western edge of the ], among the Beni Bu Zra and Beni Mansur tribes of the Ghomara confederacy. Despite being listed as endangered, it is still being passed on to children in these areas.<ref name="The Endangered Langauges Project">{{Cite web|url=http://www.endangeredlanguages.com/lang/8469|title=Did you know Ghomara is threatened?|website=Endangered Languages|language=en|access-date=2017-07-19}}</ref> |
The '''Ghomara language''' is a ] language spoken in ]. It is the mother tongue of the ] ], who total around 10,000 people. Ghomara Berber is spoken on the western edge of the ], among the Beni Bu Zra and Beni Mansur tribes of the Ghomara confederacy. Despite being listed as endangered, it is still being passed on to children in these areas.<ref name="The Endangered Langauges Project">{{Cite web|url=http://www.endangeredlanguages.com/lang/8469|title=Did you know Ghomara is threatened?|website=Endangered Languages|language=en|access-date=2017-07-19}}</ref> | ||
| Ghomara Berber is relatively similar to ] spoken around Ketama. However, it is difficult to understand for a speaker of ]. | Ghomara Berber is relatively similar to ] spoken around Ketama. However, it is difficult to understand for a speaker of ]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| ==Current status== | ==Current status== | ||
| Although elderly Ghomara teach children how to speak Ghomara Berber at home, the language is still considered threatened, with only 10,000 known speakers. A major reason can be attributed to the small geographical location where this language is used, as well as the more common usage of ] throughout Morocco. | Although elderly Ghomara teach children how to speak Ghomara Berber at home, the language is still considered threatened, with only 10,000 known speakers. A major reason can be attributed to the small geographical location where this language is used, as well as the more common usage of ] throughout Morocco. | ||
| ==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
| ===Vowels=== | ===Vowels=== | ||
| Like Arabic, Ghomara and the other Berber dialects have three vowels: a-, i-, u-.<ref name="J.Hannouche">{{Cite thesis|last=El Hannouche|first=Jamal|title=Ghomara Berber: A Brief Grammatical Survey|date= |
Like Arabic, Ghomara and the other Berber dialects have three vowels: a-, i-, u-.<ref name="J.Hannouche">{{Cite thesis |last=El Hannouche |first=Jamal |title=Ghomara Berber: A Brief Grammatical Survey |date=2008 |degree=Master |url=https://www.academia.edu/7963026}}</ref> | ||
| === Consonants === | === Consonants === | ||
| Ghomara has 44 consonants, and most consonants in Ghomara have geminated forms.<ref>{{ |
Ghomara has 44 consonants, and most consonants in Ghomara have geminated forms.<ref>{{harvnb|Mourigh|2015}}</ref> | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" | | ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" | | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | ! rowspan="2" |] | ||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | ! rowspan="2" |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !<small>plain</small> | !<small>plain</small> !! ] | ||
| !] | !<small>plain</small> !! ] | ||
| !<small>plain</small> | !<small>plain</small> !! ] | ||
| !] | !<small>plain</small> !! ] | ||
| !<small>plain</small> | |||
| !<small>]</small> | |||
| !<small>plain</small> | |||
| !] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! colspan="2" |] | ||
| |{{IPA link|m}} | |||
| !<small>voiceless</small> | |||
| |p | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|n}} | |||
| |t | |||
| |tˤ | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |k | |||
| |kʷ | |||
| |q | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |(ʔ) | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |b | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |d | |||
| |dˤ | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |g | |||
| |gʷ | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| Line 88: | Line 67: | ||
| | | | | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | ! rowspan="2" |]/<br>] | ||
| !<small>voiceless</small> | !<small>voiceless</small> | ||
| |{{IPA link|p}} | |||
| |ɸ | |||
| | |
| | ||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|t}} | |||
| |s | |||
| |{{IPA link|tˤ}} | |||
| |sˤ | |||
| |{{IPA link|t͡ʃ}} | |||
| |ʃ | |||
| |{{IPA link|k}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|kʷ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|q}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |x | |||
| |xʷ | |||
| |χ | |||
| |χʷ | |||
| |ħ | |||
| | | | | ||
| |({{IPA link|ʔ}}) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |{{IPA link|b}} | |||
| |β | |||
| |ð | |||
| |(ðˤ) | |||
| |z | |||
| |zˤ | |||
| |ʒ | |||
| | | | | ||
| |ɣ | |||
| |ɣʷ | |||
| |ʁ | |||
| |ʁʷ | |||
| |ʕ | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| !<small>voiceless</small> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |t͡ʃ | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|d}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|dˤ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|d͡ʒ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|g}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|gʷ}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| !<small>voiceless</small> | |||
| |{{IPA link|ɸ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|θ}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|s}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|sˤ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|ʃ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|x}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|xʷ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|χ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|χʷ}} | |||
| |{{IPA link|ħ}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |{{IPA link|β}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ð}} | |||
| | | |||
| |({{IPA link|ðˤ}}) | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|z}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|zˤ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ʒ}} | |||
| |d͡ʒ | |||
| |{{IPA link|ɣ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ɣʷ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ʁ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ʁʷ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPA link|ʕ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| |m | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |n | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |l | |||
| |(lˤ) | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|l}} | |||
| |j | |||
| |({{IPA link|lˤ}}) | |||
| |{{IPA link|j}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|w}} | |||
| |w | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |ʔ̞ | |{{IPA link|ʔ̞}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! colspan="2" |] | ! colspan="2" |] | ||
| Line 184: | Line 143: | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| |{{IPA link|r}} | |||
| |r | |||
| |rˤ | |{{IPA link|rˤ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| Line 198: | Line 156: | ||
| ==Grammar== | ==Grammar== | ||
| ===Nouns=== | ===Nouns=== | ||
| For ]s in Ghomara Berber, there are several common trends. The prefix a-, i-, or u- commonly identifies the masculine singular nouns in the language (i.e., ''arg'az'' “man”). For feminine singular nouns, there is both a prefix and a suffix such as ta- |
For ]s in Ghomara Berber, there are several common trends. The prefix a-, i-, or u- commonly identifies the masculine singular nouns in the language (i.e., ''arg'az'' “man”). For feminine singular nouns, there is both a prefix and a suffix such as ta-...-t (i.e., ''tarbat'' “girl”). This is the most common way to identify feminine singular nouns. Masculine plural nouns are characterized by i-...-en or i-...-an (i.e., ''irg'azen'' “men”). For feminine plural nouns, ti-...-an (i.e., ''tirbatan'' “girls”) is the most common circumfix.<ref name="J.Hannouche"/> | ||
| ===Pronouns=== | ===Pronouns=== | ||
| Line 209: | Line 167: | ||
| ===Verbs=== | ===Verbs=== | ||
| In Ghomara Berber verbs contain certain affixes that characterize singularity, plurality, and point of view (POV). The following is an example of the verb conjugations for the English word "to write" or ''ara'' in Ghomara Berber: | In Ghomara Berber verbs contain certain affixes that characterize singularity, plurality, and point of view (POV). The following is an example of the verb conjugations for the English word "to write" or ''ara'' in Ghomara Berber: | ||
| {{col-begin}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| {{col-break}} | |||
| |- | |||
| Singular: | |||
| ! colspan="2" | | |||
| *First POV: ara-x | |||
| ! singular | |||
| *Second POV: t-ara-t | |||
| ! plural | |||
| *Third Masculine POV: y-ara | |||
| |- | |||
| *Third Feminine POV: t-ara | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1st POV | |||
| {{col-break}} | |||
| | ara-x | |||
| Plural: | |||
| | n-ara | |||
| |- | |||
| *Second POV: t-ara-m | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2nd POV | |||
| *Third POV: ara-n* | |||
| | t-ara-t | |||
| {{col-break}} | |||
| | t-ara-m | |||
| {{col-end}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | 3rd POV | |||
| ! Masculine | |||
| | y-ara | |||
| | rowspan="2" | ara-n* | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Feminine | |||
| | t-ara | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Adjectives=== | ===Adjectives=== | ||
| Line 232: | Line 199: | ||
| ==Vocabulary== | ==Vocabulary== | ||
| An example of common English words in Ghomara Berber:<ref name="J.Hannouche"/> | An example of common English words in Ghomara Berber:<ref name="J.Hannouche" /> | ||
| *''targat'': “dream” | *''targat'': “dream” | ||
| *''ahlan'': “welcome, hello” | *''ahlan'': “welcome, hello” (borrowed from Arabic) | ||
| *''hemmam'': “bathroom” | *''hemmam'': “bathroom” (borrowed from Arabic) | ||
| *''tamuda'': “pig" | *''tamuda'': “pig" | ||
| *''lmakla'': “food” | *''lmakla'': “food” (borrowed from Arabic) | ||
| *''tanebdut'': “summer” | *''tanebdut'': “summer” | ||
| *''kama'': “bed” (borrowed from Spanish) | *''kama'': “bed” (borrowed from Spanish) | ||
| ==Numbers== | ==Numbers== | ||
| Ghomara Berber uses a numerical system similar to many other languages. ] ''yan'' (“one”, masculine) and ''yat'' (“one”, feminine) are the only Berber numerals in Ghomara, while all the other cardinal numbers are borrowed from Moroccan Arabic (''zuž'' (“two”), ''tlata'' (“three”), ''ɛišrin '' (“twenty”), ''tlatin'' (“thirty”), etc). | Ghomara Berber uses a numerical system similar to many other languages. ] ''yan'' (“one”, masculine) and ''yat'' (“one”, feminine) are the only Berber numerals in Ghomara, while all the other cardinal numbers are borrowed from Moroccan Arabic (''zuž'' (“two”), ''tlata'' (“three”), ''ɛišrin '' (“twenty”), ''tlatin'' (“thirty”), etc.). | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 248: | Line 215: | ||
| ==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
| * {{Cite thesis |last=Mourigh |first=Khalid |title=A grammar of Ghomara Berber |date=2015 |degree=PhD |publisher=Leiden University |hdl=1887/31685 |hdl-access=free }} | |||
| * Mourigh, K. (2015, February 18). A Grammar of Ghomara Berber. Retrieved February 12, 2016, from | |||
| * |
* {{Cite book |title=A Grammar of Ghomara Berber |last=Mourigh |first=Khalid |publisher=Rüdiger Köppe Verlag |year=2016 |location=Cologne}} | ||
| * Gabriel Camps and J. Vignet-Zunz. 1998. Ghomâra (Ghumara, Ghmara). In Gabriel Camps (ed.), Encyclopédie berbère: Gauda - Girrei, |
* Gabriel Camps and J. Vignet-Zunz. 1998. Ghomâra (Ghumara, Ghmara). In Gabriel Camps (ed.), Encyclopédie berbère: Gauda - Girrei, 3110–3119. Aix-en-Provence: Edisud. | ||
| * Colin, Georges S. 1929. Le parler berbère des Ġmāra. Hespéris: (pp. 43–58) archives berbères et bulletin de l'Institut des Hautes Etudes Marocaines. | * Colin, Georges S. 1929. Le parler berbère des Ġmāra. Hespéris: (pp. 43–58) archives berbères et bulletin de l'Institut des Hautes Etudes Marocaines. | ||
| * |
* {{Cite book |title=The Arabic influence on Northern Berber |last=Kossmann |first=Maarten G. |publisher=Brill |year=2013 |series=Studies in Semitic Languages and Linguistics 67 |location=Leiden}} (contains much discussion of Ghomara Berber based on Mourigh's materials). | ||
| {{Languages of Morocco}}{{Berber languages}} | {{Languages of Morocco}}{{Berber languages}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:07, 28 October 2024
Berber language of Morocco| Ghomara | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Morocco |
| Region | Chefchaouen Province |
| Ethnicity | Ghomara |
| Native speakers | 10,000 (2008) |
| Language family | Afro-Asiatic |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | gho |
| Glottolog | ghom1257 |
| ELP | Ghomara |
 | |
 Ghomara Berber Ghomara Berber | |
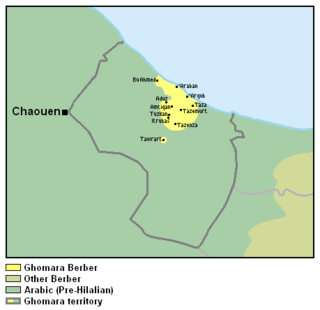
The Ghomara language is a Northern Berber language spoken in Morocco. It is the mother tongue of the Ghomara Berbers, who total around 10,000 people. Ghomara Berber is spoken on the western edge of the Rif, among the Beni Bu Zra and Beni Mansur tribes of the Ghomara confederacy. Despite being listed as endangered, it is still being passed on to children in these areas.
Ghomara Berber is relatively similar to Senhadja de Srair Berber spoken around Ketama. However, it is difficult to understand for a speaker of Rifian.
Some typical features that distinguish the Ghomara variety of Berber from Rifian Berber are the use of the preposition dar instead of the Rifian ghar, the feminine plural ending -an instead of -in, and the absence of spirantisation in word-initial position.
Current status
Although elderly Ghomara teach children how to speak Ghomara Berber at home, the language is still considered threatened, with only 10,000 known speakers. A major reason can be attributed to the small geographical location where this language is used, as well as the more common usage of Moroccan Arabic throughout Morocco.
Phonology
Vowels
Like Arabic, Ghomara and the other Berber dialects have three vowels: a-, i-, u-.
Consonants
Ghomara has 44 consonants, and most consonants in Ghomara have geminated forms.
| Bilabial | Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | phar. | plain | phar. | plain | lab. | plain | lab. | ||||||
| Nasal | m | n | |||||||||||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | tˤ | t͡ʃ | k | kʷ | q | (ʔ) | ||||
| voiced | b | d | dˤ | d͡ʒ | g | gʷ | |||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | ɸ | θ | s | sˤ | ʃ | x | xʷ | χ | χʷ | ħ | ||
| voiced | β | ð | (ðˤ) | z | zˤ | ʒ | ɣ | ɣʷ | ʁ | ʁʷ | ʕ | ||
| Approximant | l | (lˤ) | j | w | ʔ̞ | ||||||||
| Flap | r | rˤ | |||||||||||
Grammar
Nouns
For nouns in Ghomara Berber, there are several common trends. The prefix a-, i-, or u- commonly identifies the masculine singular nouns in the language (i.e., arg'az “man”). For feminine singular nouns, there is both a prefix and a suffix such as ta-...-t (i.e., tarbat “girl”). This is the most common way to identify feminine singular nouns. Masculine plural nouns are characterized by i-...-en or i-...-an (i.e., irg'azen “men”). For feminine plural nouns, ti-...-an (i.e., tirbatan “girls”) is the most common circumfix.
Pronouns
Ghomara Berber uses personal, singular, and plural pronouns.
The first person singular pronoun nekkin is equivalent to "I" in English. The second person singular male pronoun kedžin and female pronoun kemmin is equivalent to "you" in English. Similarly, in Ghomara Berber, the third person singular male pronoun netta and female pronoun nettaθa is equivalent to him or her in English respectively.
The first person plural pronoun nuçna is equivalent to "we" in English and the second person plural pronoun kunna is equivalent to "you all" in English. Lastly, niçma is the third person plural pronoun equivalent to "they" in English, and is not distinguished by gender.
Verbs
In Ghomara Berber verbs contain certain affixes that characterize singularity, plurality, and point of view (POV). The following is an example of the verb conjugations for the English word "to write" or ara in Ghomara Berber:
| singular | plural | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st POV | ara-x | n-ara | |
| 2nd POV | t-ara-t | t-ara-m | |
| 3rd POV | Masculine | y-ara | ara-n* |
| Feminine | t-ara | ||
Adjectives
Adjectives have either suffix -ø, which characterizes masculine singular nouns or -θ, which characterizes both feminine singular and all plural nouns. For example:
- Masculine singular: tayfur mellulø “the, a white table”
- Feminine singular: tamɣart mezziθ “the, a little woman”
- Masculine plural: irgazen muqqreθ “(the) big men”
- Feminine plural: timettutan muqqreθ “(the) big women”
Vocabulary
An example of common English words in Ghomara Berber:
- targat: “dream”
- ahlan: “welcome, hello” (borrowed from Arabic)
- hemmam: “bathroom” (borrowed from Arabic)
- tamuda: “pig"
- lmakla: “food” (borrowed from Arabic)
- tanebdut: “summer”
- kama: “bed” (borrowed from Spanish)
Numbers
Ghomara Berber uses a numerical system similar to many other languages. Cardinal numbers yan (“one”, masculine) and yat (“one”, feminine) are the only Berber numerals in Ghomara, while all the other cardinal numbers are borrowed from Moroccan Arabic (zuž (“two”), tlata (“three”), ɛišrin (“twenty”), tlatin (“thirty”), etc.).
References
- Jamal El Hannouche, Arabic influence in Ghomara Berber, 2010
- Maarten Kossmann, Berber subclassification (preliminary version), Leiden (2011)
- Sebastian Nordhoff et al., "Ghomara", in: Glottolog 2.2, Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (2013)
- "Did you know Ghomara is threatened?". Endangered Languages. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
- ^ El Hannouche, Jamal (2008). Ghomara Berber: A Brief Grammatical Survey (Master thesis).
- Mourigh 2015
Further reading
- Mourigh, Khalid (2015). A grammar of Ghomara Berber (PhD thesis). Leiden University. hdl:1887/31685.
- Mourigh, Khalid (2016). A Grammar of Ghomara Berber. Cologne: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag.
- Gabriel Camps and J. Vignet-Zunz. 1998. Ghomâra (Ghumara, Ghmara). In Gabriel Camps (ed.), Encyclopédie berbère: Gauda - Girrei, 3110–3119. Aix-en-Provence: Edisud.
- Colin, Georges S. 1929. Le parler berbère des Ġmāra. Hespéris: (pp. 43–58) archives berbères et bulletin de l'Institut des Hautes Etudes Marocaines.
- Kossmann, Maarten G. (2013). The Arabic influence on Northern Berber. Studies in Semitic Languages and Linguistics 67. Leiden: Brill. (contains much discussion of Ghomara Berber based on Mourigh's materials).
| Languages of Morocco | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Native vernaculars |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Main foreign languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Main liturgical languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Berber languages | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reconstructed | |||||||
| Eastern | |||||||
| Northern |
| ||||||
| Tuareg |
| ||||||
| Western | |||||||
| Others | |||||||
| Orthography | |||||||
| Institutions |
| ||||||
| Italics indicate extinct languages | |||||||