| Revision as of 07:50, 19 December 2006 view sourceAAA765 (talk | contribs)22,145 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:52, 7 January 2025 view source Bobfrombrockley (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users29,587 edits →1970s: early debates: LinksTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| '''New antisemitism''' is the concept of an international resurgence of attacks on Jewish symbols, as well as the acceptance of ] beliefs and their expression in public discourse, coming from three political directions: the political ], ], and ]. <ref>Sources for the first sentence are: | |||
| {{Short description|none}} | |||
| *]. , Ha'aretz, September 6, 2002. | |||
| {{Antisemitism |expanded=Manifestations}} | |||
| *]. ''The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It'', Jossey-Bass, 2003, pp. 158-159, 181. | |||
| *]. , accessed March 5, 2006. | |||
| *Doward, Jamie. , '']'', August 8, 2004. | |||
| *]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005, pp. 65-79. | |||
| *]. {{PDFlink}}, 2003, retrieved April 22, 2006. | |||
| *]. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004, p 272.</ref> | |||
| '''New antisemitism''' is the concept that a new form of ] developed in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, typically manifesting itself as ].<ref name="Fastenbauer 2020">{{cite book |author-last=Fastenbauer |author-first=Raimund |year=2020 |editor1-last=Lange |editor1-first=Armin |editor2-last=Mayerhofer |editor2-first=Kerstin |editor3-last=Porat |editor3-first=Dina |editor4-last=Schiffman |editor4-first=Lawrence H. |title=An End to Antisemitism! – Volume 2: Confronting Antisemitism from the Perspectives of Christianity, Islam, and Judaism |chapter=Islamic Antisemitism: Jews in the Qur’an, Reflections of European Antisemitism, Political Anti-Zionism: Common Codes and Differences |location=] and ] |publisher=] |pages=279–300 |doi=10.1515/9783110671773-018 |doi-access=free |isbn=9783110671773}}</ref>{{rp|296–297}} The concept is included in some definitions of antisemitism, such as the ] and the ]. The concept dates to the early 1970s.<ref>{{cite book |last=Berkman |first=Matthew |url=https://www.academia.edu/89802558 |title=Routledge Companion to the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=2022 |isbn=978-0-429-64861-8 |editor=A. Siniver |page=522 |chapter= The Conflict on Campus|quote=Attempts to rearticulate antisemitism to encompass opposition to Israel's "right to exist" or its character as a Jewish state date back to the 1970s, when the Anti-Defamation League first popularized a discourse on "the new antisemitism" (see Forster and Epstein 1974; on the subsequent development of that discourse see Judaken 2008). The identification of anti-Zionism with antisemitism has long been de rigueur in Jewish communal and broader pro-Israel circles, but only in the last two decades have Israel advocacy groups endeavoured to establish it as a principle of United States anti-discrimination law. The earliest step in this direction was taken in 2004, when Kenneth L. Marcus, the Assistant Secretary of Education for the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) under President George W. Bush, issued a game-changing policy guidance letter empowering OCR staff, for the first time, to investigate complaints under Title VI of the Civil Rights Act alleging pervasive antisemitism on college campuses. |access-date=2023-05-21}}</ref> | |||
| The term has entered common usage to refer to what some writers describe as a wave of antisemitism that escalated, particularly in ], after the ] in 2000, the failure of the ], and the ]. <ref name=Taguieff>Taguieff, Pierre-André. ''Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004. </ref><ref name=Rosenbaum>Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004.</ref> The concept is used to distinguish this wave from classical antisemitism, which was largely associated with the ]. <ref name=Endelman69>]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005, p. 69.</ref> According to others, however the term has emerged as a result of recent gradual re-definitions of anti-semitism to cover anything that opposes the policies and interests of the state of Israel. <ref> Allan Brownfeld, ''Anti-Semitism: Its Changing Meaning'', Journal of Palestine Studies , Vol. 16, No. 3 ] link: </ref> | |||
| Proponents of the concept generally posit that in the late 20th and early 21st centuries much of what is purported to be ] is in fact tantamount to ], and that together with evidence of a resurgence of antisemitic attacks on ],<ref name="USCIRF 2020">{{cite web |url=https://www.uscirf.gov/sites/default/files/USCIRF%202020%20Annual%20Report_42720_new_0.pdf |title=USCIRF 2020 Annual Report: "Rising Anti-Semitism in Europe and Elsewhere" |author=<!--Not stated--> |date=April 2020 |website=Uscirf.gov |location=] |publisher=] |pages=87–88 |access-date=30 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200428174043/https://www.uscirf.gov/sites/default/files/USCIRF%202020%20Annual%20Report_42720_new_0.pdf |archive-date=28 April 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> desecration of ] and ],<ref name="USCIRF 2020" /> ],<ref name="USCIRF 2020" /> and an increased acceptance of antisemitic beliefs in public discourse and ],<ref name="USCIRF 2020" /> such demonization represents an evolution in the appearance of antisemitic beliefs.<ref>Manfred Gerstenfeld, . ''Jewish Political Studies Review'' 17:1–2 Spring 2005</ref> Proponents argue that anti-Zionism and demonization of ], or ]s applied to its conduct (some also include ], ], and ]) may be linked to antisemitism, or constitute disguised antisemitism, particularly when emanating simultaneously from the ], ], and the ].<ref name="Fastenbauer 2020"/>{{rp|296–297}}<ref name=Taguieff>Taguieff, Pierre-André. ''Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004.</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=o846LgEACAAJ&q=The+New+Anti-Semitism|title=The New Anti-Semitism Israel Model: Empirical Tests|last=Cohen|first=Florette|date=September 2011|publisher=BiblioBazaar|isbn=978-1-243-56139-8}}</ref> | |||
| ] in San Francisco on ], ], this placard mixes ], ], ] and ] imagery with some classic ] motifs. Photograph taken by zombie of . <ref>Zombie. , ''zombietime.com''. | |||
| *Jaffe, Ben-Zion. , ''] Blog Central'', December 11, 2005. | |||
| *, '']'', December 8, 2003. | |||
| *Moormeister, Robyn. , '']'', May 2, 2003. | |||
| *, ''Watch'', retrieved August 27, 2006. | |||
| *, ''BackSpin Weblog of ]'', December 4, 2003.</ref>]] | |||
| Critics of the concept argue that it is used in practice to ] in order to silence political debate and ] regarding the ongoing ], by conflating political anti-Zionism and criticism of the Israeli government with racism, condoning violence against Jews or ]. Such arguments have in turn been criticized as antisemitic and rhetorically irrelevant to the contested reality of new antisemitism.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Hirsh |first=David |date=January 2010 |title=Accusations of malicious intent in debates about the Palestine-Israel conflict and about antisemitism: The Livingstone Formulation, 'playing the antisemitism card' and contesting the boundaries of antiracist discourse |url=https://research.gold.ac.uk/id/eprint/7144/1/hirsh_transversal_2010.pdf |journal=Transversal |pages=47–77}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Citation |last=Klaff |first=Lesley |title=Holocaust inversion in British politics : the case of David Ward |date=2016-12-01 |url=http://www.nebraskapress.unl.edu/product/Anti-Judaism-Antisemitism-and-Delegitimizing-Isr,677309.aspx |pages=185–196 |editor-last=Wistrich |editor-first=Robert S. |access-date=2024-01-09 |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |language=en |isbn=978-0-8032-9671-8}}</ref> Further critical arguments include that the concept defines legitimate criticism of Israel too narrowly and demonization too broadly, and that it trivializes the meaning of antisemitism.<ref>]. . '']'', posted January 15, 2004 (February 2, 2004 issue), accessed January 9, 2006; and ]. , posted February 5, 2007, accessed February 6, 2007.</ref><ref>Steven Beller, ], Vol. 41, No. 2, 2007 pp.215-238, 223:' The idea that there has been an explosion of antisemitic sentiment in Europe has more to do with American, Israeli and Zionist discomfort with strong European criticism of Israeli policy than it has with actual antisemitism.'</ref><ref>Scott Ury, ], October 2018, vol. 123, 4 pp. 1151-1171, p.1552: 'One of the biggest problems facing the study of anti-Semitism today: its ongoing, seemingly inescapable connection to public affairs and the extent to which contemporary political concerns, in particular those regarding Zionism and the State of Israel, influence and shape the way that many scholars frame, interpret, and research anti-Semitism.'</ref> | |||
| Proponents of the concept argue that ], ], ], ], and opposition to the existence of the ] as a Jewish homeland are coupled with antisemitism, or constitute disguised antisemitism. <ref name=Taguieff/><ref name=Rosenbaum/> Critics of the concept argue that it serves to equate legitimate criticism of ] with antisemitism, and that it is used to silence debate. <ref name=Klug>Klug, Brian. . '']'', posted January 15, 2004 (February 2, 2004 issue), accessed January 9, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ==History== | == History of the concept == | ||
| An early use of the concept in close to its modern form was in the late 1940s, when the ] was accused of pursuing a "new anti-Semitism" against Jews, of the sort manifested in the so-called ], a supposed conspiracy by Jewish doctors to poison the Soviet leadership. <ref>Schwarz, Solomon M. "The New Anti-Semitism of the Soviet Union," ''Commentary'', June 1949.</ref> ] opposition to "]s" – a euphemism for Jews – was rooted in the belief, as expressed by ], that "treason and espionage infiltrate the ranks of the Communist Party. This channel is ]." <ref>''Pravda'', November 21, 1952.</ref> | |||
| ] cartoon circa 1938 depicts the Jews as an octopus encircling the globe; see article ] <ref> as part of the Zichronam l'Vracha site. Accessed 24 September 2006.</ref> ]] | |||
| ]'' by ]. <ref> on intelligence.org.il, site of the Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center | |||
| at the Center for Special Studies (C.S.S), Israel. Accessed 24 September 2006.</ref> ]] | |||
| === 1960s: origins === | |||
| French philosopher ] writes that the first wave of the new antisemitism emerged in the Arab-Muslim world and the Soviet sphere following the 1967 ], citing papers by Jacques Givet (1968) and historian ] (1969) in which the idea of a new anti-Semitism rooted in anti-Zionism was discussed. <ref>] cites the following early works on the new antisemitism: Jacques Givet, ''La Gauche contre Israel? Essai sur le néo-antisémitisme, Paris 1968; idem, "Contre une certain gauche," ''Les Nouveaux Cahiers'', No. 13-14, Spring-Summer 1968, pp. 116-119; Léon Poliakov, ''De l'antisionisme a l'antisémitisme, Paris 1969; Shmuel Ettinger, "Le caractère de l'antisémitisme contemporain," ''Dispersion et Unité'', No. 14, 1975, pp. 141-157; and Michael Curtis, ed., ''Antisemitism in the Modern World, Boulder, 1986. All cited in ]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 159-160, footnote 1.</ref> He argues that anti-Jewish themes centered on the demonical figures of Israel and what he calls "fantasy-world Zionism": that Jews plot together, seek to conquer the world, and are imperialistic and bloodthirsty, which gave rise to the reactivation of stories about ritual murder and the poisoning of food and water supplies. The Israeli victory of 1967, the Israeli invasion of Lebanon in 1982, and the Palestinian deaths during the ] all served to reinforce the caricature. <ref name=Taguieff>]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 62. </ref> | |||
| French philosopher ] argues that the first wave of "''la nouvelle judéophobie''" emerged in the Arab-Muslim world and the ] following the 1967 ]. He cites papers by Jacques Givet (1968) and historian ] (1969) discussing the idea of a new antisemitism rooted in anti-Zionism.<ref>] cites the following early works on the new antisemitism: Jacques Givet, ''La Gauche contre Israel? Essai sur le néo-antisémitisme, Paris 1968; idem, "Contre une certain gauche," ''Les Nouveaux Cahiers'', No. 13-14, Spring-Summer 1968, pp. 116–119; Léon Poliakov, ''De l'antisionisme a l'antisémitisme, Paris 1969; Shmuel Ettinger, "Le caractère de l'antisémitisme contemporain," ''Dispersion et Unité'', No. 14, 1975, pp. 141–157; and Michael Curtis, ed., ''Antisemitism in the Modern World, Boulder, 1986. All cited in ]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 159-160, footnote 1.</ref> He argues that anti-Jewish themes centered on the demonical figures of Israel and what he calls "fantasy-world Zionism": that ], seek to conquer the world, and are imperialistic and bloodthirsty, which gave rise to the reactivation of stories about ritual murder and the poisoning of food and water supplies.<ref name=Taguieff62>]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 62.</ref> | |||
| === 1970s: early debates === | |||
| In 1974, Forster and Epstein, officials of the ], published ''The New anti-Semitism'', which appears to be the first book-length treatment of the subject. They expressed concern about manifestations of antisemitism and opposition to Israel, drawing attention to what they called "Arab propaganda" and "the oil weapon" in international affairs. <ref name=Forster165>Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974, p.165.</ref> Part of their criticism is directed towards left-wing American organizations of the period, such as the ], ], and the ]. <ref name=Forster9>Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974, p.9.</ref> | |||
| Writing in the ]' '']'' in 1973, the ] ] identified ] as "the new anti-Semitism", saying:<ref>''Congress Bi-weekly'', American Jewish Congress, Vol. 40, Issues 2-14, 1973, p. xxv</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>ecently we have witnessed the rise of the new left which identifies Israel with the establishment, with acquisition, with smug satisfaction, with, in fact, all the basic enemies ... Let there be no mistake: the new left is the author and the progenitor of the new anti-Semitism. One of the chief tasks of any dialogue with the Gentile world is to prove that the distinction between anti-Semitism and anti-Zionism is not a distinction at all. Anti-Zionism is merely the new anti-Semitism. The old classic anti-Semitism declared that equal rights belong to all individuals within the society, except the Jews. The new anti-Semitism says that the right to establish and maintain an independent national sovereign state is the prerogative of all nations, so long as they happen not to be Jewish. And when this right is exercised not by the Maldive Islands, not by the state of Gabon, not by Barbados ... but by the oldest and most authentic of all nationhoods, then this is said to be exclusivism, particularism, and a flight of the Jewish people from its universal mission.</blockquote> | |||
| In 1974, ] and ] of the ] published the book ''The New anti-Semitism''. They expressed concern about what they described as new manifestations of antisemitism coming from radical left, radical right, and pro-Arab figures in the U.S.<ref>Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974, p.165. See for instance chapters entitled "]'s Road" (19–48), "The Radical Right" (285–296), "Arabs and Pro-Arabs" (155–174), "The Radical Left" (125–154)</ref> Forster and Epstein argued that it took the form of indifference to the fears of the Jewish people, apathy in dealing with anti-Jewish bias, and an inability to understand the importance of Israel to Jewish survival.<ref name=ForsterEpstein324>Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974, p. 324.</ref> | |||
| In the 1980s, radical left-wing movements voiced increasing opposition to Israel, controversially claiming that Zionism was a racist and ] movement. In 1984, historian ] delivered a lecture in the home of ], the ], in which he spoke of a "new anti-Semitic anti-Zionism," the characteristic mode of which was the equation of Zionism with ]. He stated that "in recent years these grotesque Soviet blood-libels have been taken up by a part of the radical Left — especially the ]s — in Western Europe and America". <ref name=Wistrich1984>]. , lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the ], December 10, 1984.</ref> | |||
| ], on January 10, 2009 ]] | |||
| In the mid-1980s, the Israeli foreign minister ] argued that "the New Left is the author and progenitor of the new anti-Semitism."<ref>Rubin, Daniel. (ed.) ''Anti-Semitism and Zionism: Selected Marxist Writings''. International Publishers, 1987, p. 35.</ref> Other commentators stated that the tendency to criticize Israel actions more vehemently than those of other nations was a form of antisemitic prejudice. Monsignor ] said in 1983: "Nobody says anything against the Egyptian authorities for oppressing the Coptic Christians. No one protested vehemently against the forced closing of St. Joseph's College years ago in Iraq, nor against the laws in Jordan prior to 1967 which prohibited Christians from acquiring new property. If Israel did any of these things, everyone would cry bloody murder... This is prejudice." <ref>James C. O'Neill, ''Our Sunday Visitor'', July 10, 1983</ref> | |||
| Reviewing Forster and Epstein's work in '']'', ], founding director of the Nathan Perlmutter Institute for Jewish Advocacy at ], argued that a "new anti-Semitism" was indeed emerging in America, in the form of opposition to the collective rights of the Jewish people, but he criticized Forster and Epstein for conflating it with anti-Israel bias.<ref>Raab, Earl. "Is there a New Anti-Semitism?", ''Commentary'', May 1974, pp. 53–54.</ref> ] wrote in the '']'' that Forster and Epstein's new definition of antisemitism trivialized the concept by turning it into "a form of political blackmail" and "a weapon with which to silence any criticism of either Israel or U.S. policy in the Middle East,"<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |title = Anti-Semitism: Its Changing Meaning | |||
| |last = Brownfeld | |||
| |first = Allan | |||
| |journal = ] | |||
| |publisher = ] | |||
| |issn = 1533-8614 | |||
| |volume = 16 | |||
| |issue = 3 | |||
| |year = 1987 | |||
| |pages = 53–67 | |||
| |doi = 10.2307/2536789 | |||
| |jstor = 2536789 | |||
| }}</ref> while ], in ''A Time for Healing: American Jewry Since World War II'', has written that "Forster and Epstein implied that the new anti-Semitism was the inability of Gentiles to love Jews and Israel enough."<ref>Edward S. Shapiro. ''A Time for Healing: American Jewry Since World War II''. Johns Hopkins University Press. 1992. {{ISBN|0-8018-4347-2}}. Page 47.</ref> | |||
| === 1980s–present day: continued debate === | |||
| ] of ], an American research group that tracks the far right, writes that, during the early 1980s, isolationists on the far right made overtures to anti-war activists on the left to join forces against government policies in areas where they shared concerns,<ref name=berletzog>]. , ''New Internationalist'', October 2004.</ref> mainly civil liberties, opposition to U.S. military intervention overseas, and opposition to U.S. support for Israel.<ref name=berletwoos>Berlet, Chip. , ''Publiceye.org'', December 20, 1990; revised February 22, 1994, revised again 1999.</ref> <ref>Berlet reports that the right-wing use of ] as a cover for anti-Semitism can be seen in a 1981 issue of ''Spotlight'', published by the neo-Nazi ]: "A brazen attempt by influential "Israel-firsters" in the policy echelons of the Reagan administration to extend their control to the day-to-day espionage and covert-action operations of the CIA was the hidden source of the controversy and scandals that shook the U.S. intelligence establishment this summer. The dual loyalists ... have long wanted to grab a hand in the on-the-spot "field control" of the CIA's worldwide clandestine services. They want this control, not just for themselves, but on behalf of the ], Israel's terrorist secret police. (''Spotlight, August 24, 1981, cited in Berlet, Chip. , ''Publiceye.org'', December 20, 1990; revised February 22, 1994, revised again 1999.)</ref> | |||
| ], 2003]] | |||
| Historian ] addressed the issue in a 1984 lecture delivered in the home of ] ], in which he argued that a "new anti-Semitic anti-Zionism" was emerging, distinguishing features of which were the equation of Zionism with ] and the belief that Zionists had actively collaborated with Nazis during ]. He argued that such claims were prevalent in the Soviet Union, but added that similar rhetoric had been taken up by a part of the radical Left, particularly ] groups in Western Europe and America.<ref name=Wistrich1984>]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170512173240/http://sicsa.huji.ac.il/Antizionism.htm |date=2017-05-12 }}, lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the ], December 10, 1984.</ref> | |||
| When asked in 2014 if "anti-Zionism is the new anti-Semitism", ] stated:<ref>{{cite web|last1=Chomsky|first1=Noam|title=TRANSCRIPT of Amy Goodman interview of Noam Chomsky|website=]|url=http://www.democracynow.org/2014/11/27/noam_chomsky_at_united_nations_it|access-date=19 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| As they interacted, some of the classic right-wing anti-Semitic ] conspiracy theories began to seep into progressive circles, <ref name=berletwoos/> including stories about how a "]", also called the "Shadow Government" or "The Octopus," <ref name=berletzog/> was manipulating world governments. Berlet writes that antisemitic conspiracism <ref>Berlet does not himself use the expression "new antisemitism"; nor does he comment on whether he believes the current wave of antisemitism should be regarded as a new phenomenon or not.</ref> was "peddled aggressively" by right-wing groups, and that the left adopted the rhetoric, which Berlet argues was made possible by the left's lack of knowledge of the history of ] and its use of "scapegoating, ] and simplistic solutions, ], and a conspiracy theory of history." <ref name=berletwoos/> | |||
| <blockquote>Actually, the locus classicus, the best formulation of this, was by an ambassador to the United Nations, ], ... He advised the American Jewish community that they had two tasks to perform. One task was to show that criticism of the policy, what he called anti-Zionism{{spaced ndash}} that means actually criticisms of the policy of the state of Israel{{spaced ndash}} were anti-Semitism. That's the first task. Second task, if the criticism was made by Jews, their task was to show that it's neurotic self-hatred, needs psychiatric treatment. Then he gave two examples of the latter category. One was ]. The other was me. So, we have to be treated for our psychiatric disorders, and non-Jews have to be condemned for anti-Semitism, if they're critical of the state of Israel. That's understandable why Israeli propaganda would take this position. I don't particularly blame Abba Eban for doing what ambassadors are sometimes supposed to do. But we ought to understand that there is no sensible charge. No sensible charge. There's nothing to respond to. It's not a form of anti-Semitism. It's simply criticism of the criminal actions of a state, period. | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| == Definitions and arguments for and against the concept == | |||
| Toward the end of 1990, as the movement against the ] began to build, Berlet writes that a number of far-right and antisemitic groups sought out alliances with left-wing anti-war coalitions, who began to speak openly about a "Jewish lobby" that was encouraging the United States to invade the Middle East. This idea morphed into conspiracy theories about a "]" (ZOG), which Berlet writes is the modern incarnation of the antisemitic hoax, '']''. <ref name=berletzog/> Berlet adds: "It is important to recognize that as a whole the antiwar movement overwhelmingly rejected these overtures by the political right, while recognizing that the attempt reflected a larger ongoing problem." He cites the example of ] anti-war activist Alan Ruff, who appeared on a panel in ] to discuss the Gulf War. Also on the panel on the anti-war side was another local activist, Emmanuel Branch. "Suddenly I heard Branch saying the war was the result of a Zionist banking conspiracy," said Ruff. "I found myself squeezed between pro-war hawks and this anti-Jewish nut, it destroyed the ability of those of us who opposed the war to make our point." <ref name=berletwoos/> | |||
| === A new phenomenon === | |||
| ==Arguments for and against the concept== | |||
| ], Professor of Law at ] and a scholar of human rights, has identified nine aspects of what he considers to constitute the "new anti-Semitism":<ref>] cited ]. ''The Case For Israel''. ], 2003, p. 210-211.</ref> | |||
| ===A new phenomenon=== | |||
| * Genocidal antisemitism: ] and/or the Jewish people. | |||
| ], chair of history at ], writes that the new anti-Semitism is a new phenomenon stemming from what he calls an "unprecedented coalition" of enemies: "leftists, vociferously opposed to the policies of Israel, and right-wing antisemites, committed to the destruction of Israel, were joined by millions of ]s, including ], who immigrated to Europe ... and who brought with them their hatred of Israel in particular and of Jews in general." It is this new political alignment, he argues, that makes new antisemitism unique. <ref name=Fischel>Fischel, Jack R. , ''The Virginia Quarterly Review'', Summer 2005, pp. 225-234.</ref> ] of '']'' links it to ], describing it as "the medieval image of the 'Christ-killing' Jew resurrected on the editorial pages of cosmopolitan European newspapers. It is the ] refusing to put the ] on their ambulances ... It is ] donning checkered Palestinian ]s and Palestinians lining up to buy copies of '']''." <ref name=strauss272>Strauss, Mark. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004, p 272.</ref> | |||
| * Political antisemitism: denial of the Jewish people's right to ], ] as a state, attributions to Israel of all the world's evils. | |||
| * Ideological antisemitism: "Nazifying" Israel by comparing ] and racism. | |||
| * Theological antisemitism: convergence of ] and Christian ], drawing on the classical hatred of Jews. | |||
| * Cultural antisemitism: the emergence of anti-Israel attitudes, sentiments, and discourse in "fashionable" salon intellectuals.{{vague|date=January 2014}} | |||
| * Economic antisemitism: ] and the ] application of ] against countries trading with Israel. | |||
| * Holocaust denial. | |||
| * Anti-Jewish racist terrorism. | |||
| * International legal discrimination ("Denial to Israel of equality before the law in the international arena"). | |||
| Cotler defines "classical or traditional anti-Semitism" as "the discrimination against, denial of or assault upon the rights of Jews to live as equal members of whatever host society they inhabit" and "new anti-Semitism" as "discrimination against the right of the Jewish people to live as an equal member of the family of nations{{spaced ndash}}the denial of and assault upon the Jewish people's right even to live{{spaced ndash}}with Israel as the "collective Jew among the nations."<ref name="Judenstaatrein">Irwin Cotler, {{dead link|date=February 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}, '']'', February 22, 2009.</ref> | |||
| {{rquote|right|'''''It is the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement refusing to put the Star of David on their ambulances ... It is neo-Nazis donning checkered Palestinian ]s and Palestinians lining up to buy copies of '']'''''. — ] <ref name=strauss272>Strauss, Mark. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004, p 272.</ref>}} | |||
| The French philosopher ] argues that ''Judenhass'' based on ] and ] has been replaced by a new form based on anti-racism and anti-nationalism. He identifies some of its main features as the use of anti-racism for anti-Jewish purposes, identifying Zionism as racism; the use of material related to ] becomes an ordinary feature of discourse e.g. doubts about the number of victims, allegations of a Holocaust industry; discourse is borrowed from ], ], ], ], and ]; there is widespread dissemination of what he calls the "myth" of the "intrinsically good Palestinian — the innocent victim ''par excellence''. <ref name=Taguieff67>]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 67-68.</ref> | |||
| Cotler elaborated on this position in a June 2011 interview for Israeli television. He re-iterated his view that the world is "witnessing a new and escalating ... and even lethal anti-Semitism" focused on hatred of Israel, but cautioned that this type of antisemitism should not be defined in a way that precludes "free speech" and "rigorous debate" about Israel's activities. Cotler said that it is "too simplistic to say that anti-Zionism, ''per se'', is anti-Semitic" and argued that ], while in his view "distasteful", is "still within the boundaries of argument" and not inherently antisemitic. He continued: "It's you say, because it's an apartheid state, it has to be dismantled{{spaced ndash}}then crossed the line into a racist argument, or an anti-Jewish argument."<ref>], , ''Haaretz'', 1 July 2011. Accessed 7 July 2011.</ref> | |||
| In part because the concept of new antisemitism is a recent one, and because of the nature of it, there are no indices of measurement, according to ], Professor of Law at ], and Canada's former ]. <ref name=Cotler>]. , ''FrontPageMagazine.com'', ], ].</ref> Cotler defines classical antisemitism as "the ] against, or denial of, the right of Jews to live as equal members of a free society," the focus of which is discrimination against Jews as individuals. He argues that the new antisemitism, by contrast, "involves the discrimination against the right of the Jewish people to live as an equal member of the family of nations"; that is, discrimination against Jews as a people. He argues that antisemitism has expanded from hatred of Jews (classical antisemitism) to hatred of Jewish national aspirations (new antisemitism). <ref name=Cotler/> The latter is hard to measure because the usual indices used by governments to detect discrimination — standard of living, housing, health, and employment — are useful only in measuring discrimination against individuals. Because it is difficult to measure, it is difficult to show convincingly that the concept is a valid one. | |||
| ], former chair of history at ], writes that new antisemitism is a new phenomenon stemming from a coalition of "leftists, vociferously opposed to the policies of Israel, and right-wing antisemites, committed to the destruction of Israel, were joined by millions of Muslims, including Arabs, who immigrated to Europe... and who brought with them their hatred of Israel in particular and of Jews in general." It is this new political alignment, he argues, that makes new antisemitism unique.<ref name="Fischel">Fischel, Jack R. , ''The Virginia Quarterly Review'', Summer 2005, pp. 225–234.</ref> ] of '']'' links new antisemitism to ], describing it as "the medieval image of the "Christ-killing" Jew resurrected on the editorial pages of cosmopolitan European newspapers."<ref name="Strauss2009">{{Cite web |last=Strauss |first=Mark |date=2009-11-02 |title=Anti-globalism's Jewish Problem |url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2009/11/02/anti-globalisms-jewish-problem/ |access-date=2023-09-26 |website=Foreign Policy |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| ===A new phenomenon, but not antisemitism=== | |||
| ] argues that the new prejudice is not antisemitism, new or old; not a mutation of an existing virus, but "a brand new 'bug'." <ref name=KlugCatalyst>]. , ], March 17, 2006.</ref>]] | |||
| That there has been a resurgence of antisemitic attacks and attitudes is accepted by most opponents of the concept of new antisemitism. <ref>] argues that there has been no significant rise in antisemitism: "What does the evidence show? There has been good investigation done, serious investigation. All the evidence shows there's no — there's no evidence at all for a rise of a new anti-Semitism, whether in Europe or in North America. The evidence is zero. And, in fact, there's a new book put out by an Israel stalwart. His name is Walter Laqueur, a very prominent scholar. It's called ''The Changing Face of Anti-Semitism''. It just came out, 2006, from ]. He looks at the evidence, and he says no. There's some in Europe among the Muslim community, there's some anti-Semitism, but the notion that in the heart of European society or North American society there's anti-Semitism is preposterous. And in fact — or no, a significant rise in anti-Semitism is preposterous." | |||
| (, Interview of Norman Finkelstein by Amy Goodman, August 29, 2006.) | |||
| Rajesh Krishnamachari, researcher with the South Asia Analysis Group, analyzed antisemitism in Iran, Turkey, Palestine, Pakistan, Malaysia, Bangladesh and Saudi Arabia and posited that the recent surge in antisemitism across the Muslim world should be attributed to political expediency of the local elite in these countries rather than to any theological imperative.<ref name="rajeshPaper">Tembarai Krishnamachari, Rajesh. {{usurped|1=}} in South Asia Analysis Group, Paper 5907, April 2015.</ref> | |||
| In his another 2006 book, Laqueur writes: "... behind the cover of "anti-Zionism" lurks a variety of motives that ought to be called by their true name. When, in the 1950s under Stalin, the Jews of the Soviet Union came under severe attack and scores were executed, it was under the banner of anti-Zionism rather than anti-Semitism, which had been given a bad name by Adolf Hitler. When in later years the policy of Israeli governments was attacked as racist or colonialist in various parts of the world, the basis of the criticism was quite often the belief that Israel had no right to exist in the first place, not opposition to specific policies of the Israeli government. | |||
| Traditional anti-Semitism has gone out of fashion in the West except on the extreme right. But something we might call post-anti-Semitism has taken its place. It is less violent in its aims, but still very real. By and large it has not been too difficult to differentiate between genuine and bogus anti-Zionism. The test is twofold. It is almost always clear whether the attacks are directed against a specific policy carried out by an Israeli government (for instance, as an occupying power) or against the existence of Israel. Secondly, there is the test of selectivity. If from all the evils besetting the world, the misdeeds, real or imaginary, of Zionism are singled out and given constant and relentless publicity, it can be taken for granted that the true motive is not anti-Zionism but something different and more sweeping." (]: ''"Dying for Jerusalem: The Past, Present and Future of the Holiest City"'' (Sourcebooks, Inc., 2006) ISBN 1-4022-0632-1. p. 55)</ref> What is not accepted is that this constitutes a different kind of antisemitism. | |||
| {{rquote|left|It is the ]. ... It is ] donning checkered Palestinian ]s and Palestinians lining up to buy copies of '']''. | |||
| ], senior research fellow in philosophy at ] — who gave expert testimony in February 2006 to a British parliamentary inquiry into antisemitism in the UK, and in November 2004 to the Hearing on Anti-Semitism at the German ] — argues against the idea that there is a "single, unified phenomenon" that could be called "new" antisemitism. He accepts that there is reason for the Jewish community to be concerned, citing the ], an arson attack on an ] school in Paris, the reappearance of anti-Semitic slogans during demonstrations opposing the ], and the increase in ]. He writes that some researchers report a 60 percent increase worldwide of assaults on Jews in 2002 compared to the previous year. <ref name=Klug1>]. . '']'', February 2, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006, p.1.</ref> | |||
| —]<ref name="Strauss2009" />}} | |||
| The French philosopher ] argues that antisemitism based on racism and ] has been replaced by a new form based on ] and ]. He identifies some of its main features as the identification of Zionism with racism; the use of material related to ] (such as doubts about the number of victims and allegations that there is a "]"); a discourse borrowed from ], ], ], ] and ]; and the dissemination of what he calls the "myth" of the "intrinsically good Palestinian{{spaced ndash}}the innocent victim ''par excellence''."<ref name=Taguieff67>Taguieff, Pierre-André. ''Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, pp. 67–68.</ref> | |||
| Klug argues that the antisemitism involved in such incidents is not a new phenomenon but "classical" antisemitism, and that "it is closer to the truth to say that anti-Zionism today takes the form of anti-Semitism rather than the other way round." Proponents of the new antisemitism concept, he writes, see an "organizing principle" that allows them to formulate a new concept, but it is only in terms of this concept that many of the examples cited in evidence of it count as examples in the first place. <ref name=Klug1/> That is, the creation of the concept may be based on a circular argument or ]. He argues that it is an unhelpful concept, because it devalues the term "anti-Semitism," leading to widespread cynicism about the use of it, which undermines the credibility of those who fight it. People of goodwill who support the Palestinians resent being falsely accused of being anti-Semites. <ref name=KlugCatalyst>]. , ], March 17, 2006.</ref> | |||
| In early 2009, 125 parliamentarians from various countries gathered in ] for the founding conference of a group called the "Interparliamentary Coalition for Combating Anti-Semitism" (ICCA). They suggest that while classical antisemitism "overlaps" modern antisemitism, it is a different phenomenon and a more dangerous one for Jews.<ref name="Judenstaatrein" /> | |||
| Klug defines classical antisemitism as "an ingrained European fantasy about Jews as Jews," arguing that whether Jews are seen as a ], ], or ], and whether antisemitism comes from the right or the left, the antisemite's image of the Jew is always as "a people set apart, not merely by their customs but by their collective character. They are arrogant, secretive, cunning, always looking to turn a profit. Loyal only to their own, wherever they go they form a state within a state, preying upon the societies in whose midst they dwell. Mysteriously powerful, their hidden hand controls the banks and the media. They will even drag governments into war if this suits their purposes. Such is the figure of 'the Jew,' transmitted from generation to generation." <ref name=KlugRedPepper>]. , ''Red Pepper'', November 24, 2005.</ref> | |||
| === A new phenomenon, but not antisemitism === | |||
| He argues that, although it is true that the new antisemitism incorporates the idea that anti-Semitism is hostility to Jews as Jews, the source of the hostility has changed; therefore, to continue using the same expression for it — antisemitism — causes confusion. Today's hostility to Jews as Jews is based on the ], not on ancient European fantasies. Israel proclaims itself as the state of the Jewish people, and many Jews align themselves with Israel for that very reason. It is out of this alignment that the hostility to Jews as Jews arises, rather than hostility to Israelis or to Zionists. Klug agrees that it is a prejudice, because it is a generalization about individuals; nevertheless, he argues, it is "not rooted in the ideology of 'the Jew'," and is therefore a different phenomenon from antisemitism. <ref name=KlugCatalyst/> | |||
| ] argues that the new prejudice is not antisemitism, new or old, nor a mutation of an existing virus, but "a brand new 'bug{{'"}}.<ref name="KlugCatalyst">]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927143329/http://www.catalystmagazine.org.uk/Default.aspx.LocID-0hgnew0bv.RefLocID-0hg01b00100600f009.Lang-EN.htm|date=2007-09-27}}, ], March 17, 2006.</ref>]] | |||
| ], senior research fellow in philosophy at ]{{spaced ndash}}who gave expert testimony in February 2006 to a British parliamentary inquiry into antisemitism in the UK, and in November 2004 to the Hearing on Anti-Semitism at the German ]{{spaced ndash}}argues against the idea that there is a "single, unified phenomenon" that could be called "new" antisemitism. He accepts that there is reason for the Jewish community to be concerned, but argues that any increase in antisemitic incidents is attributable to classical antisemitism. Proponents of the new antisemitism concept, he writes, see an organizing principle that allows them to formulate a new concept, but it is only in terms of this concept that many of the examples cited in evidence of it count as examples in the first place.<ref name=Klug>]. {{Webarchive|url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20090701082702/http://www.thenation.com/doc.mhtml?i=20040202&s=klug |date=2009-07-01 }}. '']'', February 2, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006</ref> That is, the creation of the concept may be based on a circular argument or ]. He argues that it is an unhelpful concept, because it devalues the term "antisemitism," leading to widespread cynicism about the use of it. People of goodwill who support the Palestinians resent being falsely accused of antisemitism.<ref name="KlugCatalyst" /> | |||
| Klug defines classical antisemitism as "an ingrained European fantasy about Jews as Jews," arguing that whether Jews are seen as a race, religion, or ethnicity, and whether antisemitism comes from the right or the left, the antisemite's image of the Jew is always as "a people set apart, not merely by their customs but by their collective character. They are arrogant, secretive, cunning, always looking to turn a profit. Loyal only to their own, wherever they go they form a state within a state, preying upon the societies in whose midst they dwell. Mysteriously powerful, their hidden hand controls the banks and the media. They will even drag governments into war if this suits their purposes. Such is the figure of 'the Jew,' transmitted from generation to generation."<ref name=KlugRedPepper>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061023055516/http://www.jfjfp.org/BackgroundJ/klug_redpepper_2006.htm |date=2006-10-23 }}, ''Red Pepper'', November 24, 2005.</ref> | |||
| The problem with calling this new prejudice "new antisemitism" is that it gives the impression of an ideological continuum from religious to racial to "new" antisemitism. Klug writes that religious antisemitism mutated into racial antisemitism, and that the latter was clearly a variation on a pre-existing theme. Not so with the new phenomenon, he argues, which has entirely different origins and content. It is not a mutation of an existing virus, but "a brand new 'bug'." <ref name=KlugCatalyst/> | |||
| {{rquote|left|hen anti-Semitism is everywhere, it is nowhere. And when every anti-Zionist is an anti-Semite, we no longer know how to recognize the real thing—the concept of anti-Semitism loses its significance. | |||
| —]<ref name=Klug />}} | |||
| He argues that although it is true that the new antisemitism incorporates the idea that antisemitism is hostility to Jews as Jews, the source of the hostility has changed; therefore, to continue using the same expression for it{{spaced ndash}}antisemitism{{spaced ndash}}causes confusion. Today's hostility to Jews as Jews is based on the ], not on ancient European fantasies. Israel proclaims itself as the state of the Jewish people, and many Jews align themselves with Israel for that very reason. It is out of this alignment that the hostility to Jews as Jews arises, rather than hostility to Israelis or to Zionists. Klug agrees that it is a prejudice, because it is a generalization about individuals; nevertheless, he argues, it is "not rooted in the ideology of 'the Jew'," and is therefore a different phenomenon from antisemitism.<ref name=KlugCatalyst /> | |||
| That is, Klug argues that there are three distinct components of what some scholars are calling "new antisemitism": | |||
| In 2006, ] argued that there has been no significant rise in antisemitism: "What does the evidence show? There has been good investigation done, serious investigation. All the evidence shows there's no evidence at all for a rise of a new anti-Semitism, whether in Europe or in North America. The evidence is zero. And, in fact, there's a new book put out by an Israel stalwart. His name is ], a very prominent scholar. It's called ''The Changing Face of Anti-Semitism''. It just came out, 2006, from ]. He looks at the evidence, and he says no. There's some in Europe among the Muslim community, there's some anti-Semitism, but the notion that in the heart of European society or North American society there's anti-Semitism is preposterous. And in fact{{spaced ndash}}or no, a significant rise in anti-Semitism is preposterous."<ref>Goodman, Amy. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061115192616/http://www.normanfinkelstein.com/article.php?pg=11&ar=479 |date=2006-11-15 }}, interview with Norman Finkelstein, August 29, 2006.</ref> | |||
| *Antisemitism, a prejudice that is based on the stereotypical construction of 'the Jew'; | |||
| *] and antagonism to Israel, based on a political cause or moral code, and not anti-Jewish ''per se''; | |||
| *Prejudice against all Jews that is derived from the latter. <ref name=KlugCatalyst/> | |||
| In 2023, according to the ], antisemitic hate crimes in the United States surged 63 percent to 1,832 recorded incidents, the highest on record.<ref name="g393">{{cite web |date=2024-09-23 |title=FBI Releases 2023 Crime in the Nation Statistics |url=https://www.fbi.gov/news/press-releases/fbi-releases-2023-crime-in-the-nation-statistics |access-date=2024-11-16 |website=Federal Bureau of Investigation}}</ref> Antisemitic incidents represented 15% of all hate crimes and 68% of all religion-based hate crimes, though Jews only make up about 2% of the population.<ref name="r933">{{cite web |last=Kirsh |first=Elana |last2=Fabian |first2=Emanuel |last3=Lehmann |first3=Noam |date=2024-09-23 |title=Antisemitic hate crimes in US surged 63% in 2023, to all-time high of 1,832 – FBI |url=https://www.timesofisrael.com/antisemitic-hate-crimes-in-us-surged-63-in-2023-to-all-time-high-of-1832-fbi/ |access-date=2024-11-16 |website=The Times of Israel}}</ref> In 2024, reports of bomb threats to synagogues, antisemitic harassment, vandalism and assault reached record-high numbers in four of the past six years in the United States.<ref name="NYT 2024">{{cite web |last=Diaz |first=Johnny |date=2024-10-06 |title=Antisemitic Incidents Reach New High in the U.S., Report Finds |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2024/10/06/us/antisemitic-incidents-us-adl-report.html |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=The New York Times}}</ref><ref name="q917">{{cite web |last=Barber |first=Rachel |date=2024-04-16 |title=Record number of antisemitic incidents hit US amid Israel-Hamas war |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/politics/2024/04/16/record-number-antisemitic-incidents-2023/73332503007/ |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=USA TODAY}}</ref> | |||
| {{rquote|right|'''''People of goodwill who support the Palestinians resent being falsely accused of being anti-Semites.''''' — ] <ref name=KlugCatalyst/>}} | |||
| The discourse of the new antisemitism conflates these, he argues, leading not only to the branding as anti-Semitic of legitimate political views about Israel, but to inflated estimates of the scale of antisemitic incidents. The line between "fair and foul" criticism of Israel tends to be drawn in such a way that it rules out criticism "that goes much beyond a gentle rap across the government's knuckles or finger-wagging at the laws of the land." If most anti-Zionist arguments do cross the line, and if crossing the line is antisemitic, it follows that most attacks on Israel are antisemitic, as is any attack on a Jewish target that is inspired by the line that has been crossed. This is compelling logic, writes Klug, but the effect of it is "to produce, at a stroke, a quantum leap in the amount of antisemitism worldwide, if not a veritable 'war against the Jews'," given how much controversy Israel currently inspires. <ref name=Klug2>Klug, Brian. . ''The Nation'', February 2, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006, p.2.</ref> He argues that crossing the line from fair to foul is | |||
| a normal part of political debate. Pro-Israelis aren't necessarily racists when they do it; pro-Palestinians are not necessarily anti-Semites when they do. Jumping to conclusions about people's prejudices is itself a form of prejudice. <ref name=KlugCatalyst/> | |||
| === Criticism of Israel is not always antisemitism === | |||
| Klug writes that contemporary antisemitism can be identified by looking for the use of the antisemitic figure of 'the Jew'. Whenever a text or image projects this figure (a) onto Israel because Israel is a Jewish state; (b) onto Zionism because Zionism is a Jewish movement; or (c) onto Jews as individuals or a group in association with Israel or Zionism, then it is antisemitic. <ref name=KlugCatalyst/> | |||
| The ] is a set of criteria put forth by ] to distinguish legitimate criticism of Israel from antisemitism. The three Ds stand for ], Demonization of Israel, and subjecting Israel to Double standards, each of which, according to the test, indicates antisemitism.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://umdrive.memphis.edu/jjudaken/public/publications/PoP%20New%20Antisemitism.pdf?uniq=-5aa3|title=So What's New? Rethinking the 'New Antisemitism' in a Global Age|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130327165258/https://umdrive.memphis.edu/jjudaken/public/publications/PoP%20New%20Antisemitism.pdf?uniq=-5aa3|archive-date=2013-03-27|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/rm/2011/178448.htm|title=Remarks at the 2011 B'nai B'rith International Policy Conference|date=2012-12-02|access-date=2018-06-11}}</ref> The test is intended to draw the line between legitimate criticism towards the State of ], its actions and policies, and non-legitimate criticism that becomes antisemitic.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=o846LgEACAAJ&q=The+New+Anti-Semitism|title=The New Anti-Semitism Israel Model: Empirical Tests|last=Cohen|first=Florette|date=September 2011|publisher=BiblioBazaar|isbn=978-1-243-56139-8}}</ref> | |||
| ] writes that "here is a new surge of antisemitism in the world, and much prejudice against Israel is driven by such antisemitism," but argues that charges of antisemitism based on anti-Israel opinions generally lack credibility. He writes that "a grave educational misdirection is imbedded in formulations suggesting that if we somehow get rid of antisemitism, we will get rid of anti-Israelism. This reduces the problems of prejudice against Israel to cartoon proportions." Raab describes prejudice against Israel as a "serious breach of morality and good sense," and argues that it is often a bridge to antisemitism, but distinguishes it from antisemitism as such.<ref>Raab, Earl. , ''Judaism'', Fall 2002.</ref> | |||
| ====The Klug/Wistrich correspondence==== | |||
| In correspondence with Klug, ], Neuburger Professor of European and Jewish history at the ] and director of its International Center for the Study of Antisemitism — who also testified in February 2006 to the British parliamentary inquiry — responds that his own ] of when criticism of Israel becomes antisemitism is when the critic wishes to dismantle the ] without calling for the dismantling of other states; ] Israel; brands it "Nazi" or "racist"; or relies on classic antisemitic stereotypes: for example, the "Jewish Lobby." He notes that Britain's Association of University Teachers voted to boycott Israeli universities, but not Russian academics for the Chechen atrocities, China for its occupation of Tibet, Saudi Arabian universities for "]," or Palestinian universities for "glorifying ]i terrorism." These decisions are "inexplicable without taking anti-Semitism into account," he writes. Wistrich also takes issue with the notion that Israelis are European interlopers in the Middle East; they are an "] people returning to their historic homeland and source of national identity." He argues that half the Israeli population is not European anyway, but was "uprooted from the Arab Middle East by exclusivist pan-Arabism, Islamic fanaticism, and the pressures of decolonization." <ref name=Klug/Wistrich>] & ] , International Center for the Study of Anti-Semitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, retrieved September 8, 2006.</ref> He writes: | |||
| Steven Zipperstein, professor of Jewish Culture and History at ], argues that a belief in the State of Israel's responsibility for the Arab-Israeli conflict is considered "part of what a reasonably informed, progressive, decent person thinks." He argues that Jews have a tendency to see the State of Israel as a victim because they were very recently themselves "the quintessential victims".<ref name=zipperstein61>Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in Derek J. Penslar et al., ed., ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005, p. 61.</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>ixty years ago, there were more than a million Jews in Arab lands. Their exodus says it all. Israel integrated them, providing a haven, pride, dignity and freedom as it did for the Jewish survivors of ]. Palestinian refugees, on the other hand, were left to rot in UN ]s by their Arab brethren, fed with ] delusions about their inalienable "]" to Israel. If the Middle East tragedy is to be resolved, it is these camps – the seedbed of ] and an entire culture of hatred – which have to be dismantled and not the thriving Jewish state. <ref name=Klug/Wistrich/></blockquote> | |||
| === Accusations of misuse of the term to stifle criticism of Israel === | |||
| Klug agrees that it is "simplistic" to regard Israel as an interloper in the Middle East, but that nevertheless it is how the Jewish state has "looked through Arab eyes." The view that Jews are "an aboriginal people returning to their historic homeland" is equally one-sided, he argues, and is just one version of the Zionist point of view. Both sides must grasp what he calls this "clash of perspectives" and stop relying on one-sided accounts. Klug sums up his own view of when criticism of Israel becomes antisemitism: | |||
| {{main|Weaponization of antisemitism}} | |||
| ] argues that organizations such as the ] have brought forward charges of new antisemitism at various intervals since the 1970s, "not to fight antisemitism but rather to exploit the historical suffering of Jews in order to immunize Israel against criticism".<ref name=Finkelstein21>Finkelstein, Norman. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp. 21–22.</ref> He writes that most evidence purporting to show a new antisemitism has been taken from organizations that are linked in some way to Israel, or that have "a material stake in inflating the findings of anti-Semitism," and that some antisemitic incidents reported in recent years either did not occur or were misidentified.<ref name="Finkelstein66/68">Finkelstein, Norman. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 66–71.</ref> As an example of the misuse of the term "antisemitism," he cites the ]'s 2003 report, which included displays of the ], support for the ], and the ] in its list of antisemitic activities and beliefs.<ref name=Finkelstein37>Finkelstein, Norman. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 37.</ref> | |||
| ] writes that anger at what he calls "Israel's brutal occupation has undoubtedly slipped over to an animus against Jews generally", which he describes as "lamentable" but "hardly cause for wonder".<ref name=Finkelstein81>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 81.</ref>]] | |||
| <blockquote>Seen through the eyes of an anti-semite, Jews are essentially alien, powerful, cohesive, cunning, parasitic, and so on. Opposition to Israel or its government is anti-Semitic when it employs some variation or other of this fantasy – just as criticism of Arabs is racist when it is based on the stock figure of the Arab as cunning, lying and degenerate, or as a hateful terrorist who attaches no value to human life. <ref name=Klug/Wistrich/></blockquote> | |||
| He writes that what is called the new antisemitism consists of three components: (i) "exaggeration and fabrication"; (ii) "mislabeling legitimate criticism of Israeli policy"; and (iii) "the unjustified yet predictable spillover from criticism of Israel to Jews generally."<ref name=Finkelstein66>Finkelstein, Norman. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 66.</ref> He argues that Israel's apologists have denied a causal relationship between Israeli policies and hostility toward Jews, since "if Israeli policies, and widespread Jewish support for them, evoke hostility toward Jews, it means that Israel and its Jewish supporters might themselves be causing anti-Semitism; and it might be doing so because Israel and its Jewish supporters are ''in the wrong''".<ref name=Finkelstein78>Finkelstein, Norman. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp. 78–79.</ref> | |||
| ], a British-Pakistani historian and political activist, argues that the concept of new antisemitism amounts to an attempt to subvert the language in the interests of the State of Israel. He writes that the campaign against "the supposed new 'anti-semitism{{'"}} in modern Europe is a "cynical ploy on the part of the Israeli Government to seal off the Zionist state from any criticism of its regular and consistent brutality against the Palestinians.... Criticism of Israel can not and should not be equated with anti-semitism." He argues that most pro-Palestinian, anti-Zionist groups that emerged after the ] were careful to observe the distinction between anti-Zionism and antisemitism.<ref>{{cite book|first1=Tariq|last1=Ali|title=Street Fighting Years: An Autobiography of the Sixties|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xZsoDwAAQBAJ|publisher=Verso Books|date=1 May 2018|isbn=978-1-78663-602-7|via=Google Books|page=43}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first1=Anthony|last1=Julius|title=Trials of the Diaspora: A History of Anti-Semitism in England|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sHAVDAAAQBAJ|publisher=Oxford University Press|date=9 February 2012|isbn=978-0-19-960072-4|via=Google Books|page=525}}</ref>{{undue weight inline|reason=not an authority on this topic in any way - this is just a passing comment in his autobiography|date=January 2022}} | |||
| Wistrich argues there is a "continuum of prejudice" against Jews that can lead from social discrimination to ]ization and worse, and that Klug "radically underestimates" the effects of the liberal-left delegitimization of Zionism. "What we have seen in recent years is indeed a new form of anti-Semitism operating under a humanist façade which (falsely) pillories Israel and Jews as being inherently 'racist'." Wistrich writes that anti-Semitism is now driven by "] who set the tone" by demonizing America, Israel, and the Jews, while "the media, the academic, artistic, religious and political elites in the ] meekly follow suit." <ref name=Klug/Wistrich/> | |||
| === A third wave === | |||
| Klug agrees that the "continuum of prejudice" exists, but argues that it is part of European history, not Middle Eastern; and that Zionism was the response to it, the empowerment of the powerless. He writes that the Zionist movement succeeded, and Israel is now a major power. For that very reason, he argues, when people object to the way it exercises its power, it should not be regarded as antisemitism. <ref name=Klug/Wistrich/> | |||
| ] argues that the new antisemitism{{spaced ndash}}what he calls "ideological antisemitism"{{spaced ndash}}has mutated out of religious and racial antisemitism.]] | |||
| Historian ] argues that the new antisemitism represents the third, or ideological, wave of antisemitism, the first two waves being ] and racial antisemitism.<ref name=LewisBrandeis>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110908010822/http://hnn.us/blogs/entries/21832.html |date=2011-09-08 }}, ''The American Scholar'', Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25–36 The paper is based on a lecture delivered at ] on March 24, 2004.</ref> | |||
| Lewis defines antisemitism as a special case of prejudice, hatred, or persecution directed against people who are in some way different from the rest. According to Lewis, antisemitism is marked by two distinct features: Jews are judged according to a standard different from that applied to others, and they are accused of cosmic evil. He writes that what he calls the first wave of antisemitism arose with the advent of ] because of the Jews' rejection of ] as ]. The second wave, racial antisemitism, emerged in Spain when large numbers of Jews were forcibly ], and doubts about the sincerity of the converts led to ideas about the importance of "''la limpieza de sangre''", purity of blood.<ref name=LewisBrandeis /> | |||
| ===Criticism of Israel is not necessarily antisemitism=== | |||
| Earl Raab, founding director of the Nathan Perlmutter Institute for Jewish Advocacy at ] writes that "here is a new surge of antisemitism in the world, and much prejudice against Israel is driven by such antisemitism," but argues that "charges of antisemitism based on anti-Israel remarks alone have proven to lack credibility in most circles". He adds that "a grave educational misdirection is imbedded in formulations suggesting that if we somehow get rid of antisemitism, we will get rid of anti-Israelism. This reduces the problems of prejudice against Israel to cartoon proportions." Raab describes prejudice against Israel as a "serious breach of morality and good sense," and argues that it is often a bridge to antisemitism, but distinguishes it from antisemitism as such. <ref>, ''Judaism'', Fall 2002.</ref> | |||
| He associates the third wave with the ] and writes that it arose only in part because of the establishment of the State of Israel. Until the 19th century, ]s had regarded Jews with what Lewis calls "amused, tolerant superiority{{spaced ndash}}they were seen as physically weak, cowardly and unmilitary{{spaced ndash}}and although Jews living in Muslim countries were not treated as equals, they were shown a certain amount of respect. The Western form of antisemitism{{spaced ndash}}what Lewis calls "the cosmic, ]ic version of Jew hatred{{spaced ndash}}arrived in the Middle East in several stages, beginning with ] in the 19th century and continued to grow slowly into the 20th century up to the establishment of the ]. He writes that it increased because of the humiliation of the Israeli military victories of ] and ].<ref name=LewisBrandeis /> | |||
| Steven Zipperstein, professor of Jewish Culture and History at ], argues that a belief in the ]'s responsibility for the ] is considered "part of what a reasonably informed, progressive, decent person thinks," <ref name=zipperstein53>Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', p. 53.</ref> and a disproportionate criticism of Israel is not the result of new anti-Semitism, or even classical anti-Semitism, but is simply a "by-product of the wildly disproportionate responses that mark the post-September 11 world." <ref name=zipperstein60>Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', p. 60.</ref> Zipperstein writes that "anti-Israelism" is shaped by "a much distorted, simplistic, but this-worldly political analysis devoid of anti-Jewish bias." <ref name=zipperstein61/> | |||
| {{rquote|right|''''' are prone to see a Jewish state as ... more vulnerable, less powerful, less culpable, as victim and not as an actor, at least partly because — so very recently in our own history — we were the quintessential victims.''''' — Steven Zipperstein <ref name=zipperstein61>Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. in Derek J. Penslar et al, ed., ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005, pp. 61-62.</ref>}} | |||
| Into this mix entered the ]. Lewis argues that the international public response and the United Nations' handling of the 1948 refugee situation convinced the Arab world that discrimination against Jews was acceptable. When the ancient Jewish community in ] was ], they were offered no help. Similarly, when Jewish refugees ], no help was offered, but elaborate arrangements were made for Arabs who fled or were driven out of the area that became Israel. All the Arab governments involved in the conflict announced that they would not admit Israelis of any religion into their territories, and that they would not give visas to Jews, no matter which country they were citizens of. Lewis argues that the failure of the United Nations to protest sent a clear message to the Arab world.<ref name=LewisBrandeis /> | |||
| He argues that Jews have a tendency to see the ] as "more vulnerable, less powerful, and less culpable, as victim and not as an actor" because they were very recently themselves "the quintessential victims." <ref name=zipperstein61/> He writes that: "We were mostly undefended and overwhelmingly friendless, and this trauma continues to haunt and perhaps at times to distort our sense of the world around us now. When we encounter antagonism — especially outsized, disproportionate antagonism — the memories of horrible times, whether personally experienced or imbibed secondhand, elicit reactions that are often sincere, acute, and disorienting." <ref name=zipperstein62>Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', p. 62.</ref> | |||
| He writes that this third wave of antisemitism has in common with the first wave that Jews are able to be part of it. With religious antisemitism, Jews were able to distance themselves from Judaism, and Lewis writes that some even reached high rank within the church and the ]. With racial antisemitism, this was not possible, but with the new, ideological, antisemitism, Jews are once again able to join the critics. The new antisemitism also allows non-Jews, he argues, to criticize or attack Jews without feeling overshadowed by the crimes of the Nazis.<ref name=LewisBrandeis /> | |||
| ===The third wave=== | |||
| ] argues that the new anti-Semitism — what he calls "ideological anti-Semitism" — has mutated out of religious and racial anti-Semitism.]] | |||
| ], Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Studies at ], argues that the new antisemitism represents the third or "ideological" wave of antisemitism, the first two waves being ] and racial antisemitism, respectively. <ref name=LewisBrandeis1>]. , ''The American Scholar'', Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25-36. The paper is based on a lecture delivered at ] on ], ].</ref> | |||
| === Antisemitism, but not a new phenomenon === | |||
| Lewis defines antisemitism as a special case of prejudice, hatred, or persecution directed against people who are in some way different from the rest. According to Lewis, antisemitism is marked by two distinct features: Jews are judged according to a standard different from that applied to others, and they are accused of "cosmic evil." Thus, "it is perfectly possible to hate and even to persecute Jews without necessarily being anti-Semitic" unless this hatred or persecution displays one of the two features specific to antisemitism. <ref name=LewisBrandeis1/> | |||
| ] argues that "new" antisemitism is not actually new.]] | |||
| ], professor of ] at the ], considers the concept "new antisemitism" false, describing the phenomenon as old, latent antisemitism that recurs when triggered. In his view, the current trigger is the Israeli situation, and if a compromise were achieved there antisemitism would decline but not disappear.<ref name="HatesRevival">{{cite journal | |||
| |url=http://www.aijac.org.au/news/article/hate-s-revival | |||
| |journal=Australia/Israel Review | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |date=May 2007 | |||
| |title=Hate's Revival | |||
| |author=Tzvi Fleischer | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| Dina Porat, professor at ] says that, while in principle there is no new antisemitism, we can speak of antisemitism in a new envelope. Otherwise Porat speaks of a new and violent form of antisemitism in Western Europe starting after the ].<ref name="HatesRevival" /> | |||
| He writes that what he calls the first wave of antisemitism arose with the advent of ] because of the Jews' rejection of ] as ]. The second wave, racial anti-Semitism, emerged in Spain when large numbers of Jews were forcibly ], and doubts about the sincerity of the converts led to ideas about the importance of "''la limpieza de sangre''", purity of blood. <ref name=LewisBrandeis>]. , ''The American Scholar'', Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25-36.</ref> | |||
| ], a British novelist and journalist, calls this phenomenon "Jew-hating pure and simple, the Jew-hating which many of us have always suspected was the only explanation for the disgust that contorts and disfigures faces when the mere word Israel crops up in conversation."<ref>{{cite web| last = Fulford| first = Robert| title = When criticizing Israel becomes ritual| publisher = nationalpost.com| date = 2009-08-15| url = https://nationalpost.com/opinion/columnists/story.html?id=686c1928-3518-472c-b2d6-60e15f81e140| archive-url = https://archive.today/20120912182353/http://www.nationalpost.com/opinion/columnists/story.html?id=686c1928-3518-472c-b2d6-60e15f81e140| url-status = dead| archive-date = 2012-09-12| access-date = 2009-08-15}}</ref> | |||
| Lewis associates the third wave with the ]s, and writes that it arose only in part because of the establishment of the ]. Until the 19th century, ]s had regarded Jews with what Lewis calls "amused, tolerant superiority" — they were seen as physically weak, cowardly, and unmilitary — and although Jews living in Muslim countries were not treated as equals, they were shown a certain amount of respect. The Western form of anti-Semitism — what Lewis calls "the cosmic, ] version of Jew hatred" — arrived in the Middle East in several stages, beginning with ] in the 19th century, and continued to grow slowly into the 20th century, up to the establishment of the ]. He writes that it increased because of the humiliation of the Israeli military victories of 1948 and 1967. ''(See ] and ].)'' <ref name=LewisBrandeis/> | |||
| === An inappropriate redefinition === | |||
| Into this mix entered the ]. Lewis argues that the United Nations' handling of the 1948 refugee situation convinced the Arab world that discrimination against Jews was acceptable. When the ancient Jewish community in ] was evicted and its monuments desecrated or destroyed, they were offered no help. Similarly, when Jewish refugees fled or were driven out of Arab countries, no help was offered, but elaborate arrangements were made for Arabs who fled or were driven out of the area that became Israel. All the Arab governments involved in the conflict announced that they would not admit Israelis of any religion into their territories, but the United Nations did not protest; and furthermore announced that they would not give visas to Jews, no matter which country they were citizens of. Again, the United Nations did not protest. All of this has sent what Lewis calls a "clear message" to the Arab world. Lewis writes that this third wave of antisemitism has in common with the first wave that Jews are able to be part of it. With religious antisemitism, Jews were able to distance themselves from Judaism and convert, and Lewis writes that some even reached high rank within the church and the ]. With racial antisemitism, this was not possible, but with the new, ideological antisemitism, Jews are once again able to join the critics. The new antisemitism also allows non-Jews, he argues, to criticize or attack Jews without feeling overshadowed by the crimes of the Nazis. <ref name=LewisBrandeis/> | |||
| ], writing in the Israeli newspaper '']'' in September 2008, argues that the concept of a "new antisemitism" has brought about "a revolutionary change in the discourse about anti-Semitism". He writes that most contemporary discussions concerning antisemitism have become focused on issues concerning Israel and Zionism, and that the equation of anti-Zionism with antisemitism has become for many a "new orthodoxy". He adds that this redefinition has often resulted in "Jews attacking other Jews for their alleged anti-Semitic anti-Zionism". While Lerman accepts that exposing alleged Jewish antisemitism is "legitimate in principle", he adds that the growing literature in this field "exceeds all reason"; the attacks are often vitriolic, and encompass views that are not inherently anti-Zionist. | |||
| Lerman argues that this redefinition has had unfortunate repercussions. He writes that serious scholarly research into contemporary antisemitism has become "virtually non-existent", and that the subject is now most frequently studied and analyzed by "people lacking any serious expertise in the subject, whose principal aim is to excoriate Jewish critics of Israel and to promote the "anti-Zionism = anti-Semitism" equation. Lerman concludes that this redefinition has ultimately served to stifle legitimate discussion, and that it cannot create a basis on which to fight antisemitism.<ref>, ''Ha'aretz'', 12 September 2008, accessed 13 September 2008.</ref> | |||
| ===The fourth wave since 1945=== | |||
| ] writes that the new anti-Semitism is the fourth wave of anti-Semitism to spread across the West since 1945.]] | |||
| Peter Beaumont, writing in '']'', agrees that proponents of the concept of "new antisemitism" have attempted to co-opt anti-Jewish sentiment and attacks by some European Muslims as a way to silence opposition to the policies of the Israeli government. "riticise Israel," he writes, "and you are an anti-Semite just as surely as if you were throwing paint at a ] in ]."<ref name=beaumont>Beaumont, Peter. , ''The Observer'', February 17, 2002.</ref> | |||
| ], Professor of Holocaust Studies at the ], writes that there have been three waves of anti-Semitism since 1945 — 1958-60; 1968-1972; and 1987-1992 — and that we are now experiencing the fourth, which he estimates started in 1999 or 2000. <ref name=Bauer2>Bauer, Yehuda. {{PDFlink|}}, 2003, p 2.</ref> Each wave has had different causes, some of them to do with economic downturns. The common ground, however, has been "an underlying latency of anti-Semitism that waits to explode when aroused by some outside crisis." <ref name=Bauer4>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 4.</ref> He describes the fourth wave as an upper-middle class, intellectual phenomenon, "widespread in the media, in universities, and in well-manicured circles. | |||
| === Antisemitic anti-Zionism === | |||
| Bauer notes that the two crises that led to the post-1945 waves of antisemitism are the ] and the establishment of the ]. The Holocaust created an unease about Jews, he writes, especially in Europe, where people "have to live with six million ghosts, created by a deadly mutation of European culture." <ref name=Bauer4/> Although a feeling of relief accompanied the creation of Israel, because Europeans no longer had to deal with the Jews, at the same time, he argues, it turned the Jews from victims into perpetrators. He argues that the Arab-Israeli conflict "provide ample material for an antisemitism that sees itself as anti-Zionist." Anti-Zionism need not be antisemitic, "but only if one says that all national movements are evil, and all national states should be abolished. But if one says that the ] have the right to independence, and so do the ] or the ]ns, but the Jews have no such right, then one is anti-Jewish, and as one singles out the Jews for nationalistic reasons, one is anti-Semitic, with an attendant strong suspicion of being racist." Citing ], Bauer writes that "the status of the collective Jew, that is Israel, is akin to the status of the individual Jew in the ]." <ref name=Bauer5>Bauer, Yehuda. {{PDFlink|}}, 2003, p 5.</ref> | |||
| Scholars including ], ], ], ] and ] have described a distinctively 21st century form of antisemitic anti-Zionism characterized by left-wing hostility to Jews.<ref name="Bergmann">{{cite book|last1=Pelinka|first1=Anton|title=Handbook of Prejudice. Chapter on Anti-Semitism by Werner Bergmann|date=2009|publisher=Cambria Press|isbn=978-1-60497-627-4|page=56|display-authors=etal}}</ref><ref name="Schama">{{cite news|last1=Schama|first1=Simon|title=The left's problem with Jews has a long and miserable history|url=http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/d6a75c3c-d6f3-11e5-829b-8564e7528e54.html#axzz41CoraTzu|archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221211141210/https://www.ft.com/content/d6a75c3c-d6f3-11e5-829b-8564e7528e54#axzz41CoraTzu|archive-date=11 December 2022|url-access=subscription|access-date=26 February 2016|work=]|date=19 February 2016|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="HirshEmbracingPrejudice">{{cite news|last1=Hirsh|first1=David|title=Openly Embraing Prejudice|url=https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2006/nov/30/anewmenacingcurrentisappe|access-date=6 March 2016|work=]|date=30 November 2006}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Julius|first1=Anthony| author-link = Anthony Julius |title=Trials of the Diaspora: A History of Anti-Semitism in England|title-link=Trials of the Diaspora: A History of Anti-Semitism in England|date=2010|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-929705-4|page=476}}</ref><ref name="Johnson">{{cite news|last1=Johnson|first1=Alan|author-link1=Alan Johnson (political theorist)|title=The Left and the Jews: Time for a Rethink|url=http://fathomjournal.org/the-left-and-the-jews-time-for-a-rethink/|access-date=26 February 2016|work=Fathom|date=Fall 2015}}</ref> According to historian ], opposition to Zionism (being against a Jewish state) can be legitimately described as racist in essence.<ref>{{cite news|last=Alderman|first=Geoffrey|author-link=Geoffrey Alderman|url=http://www.thejc.com/comment-and-debate/columnists/90023/why-anti-zionists-are-racists|title=Why anti-Zionists are racists|work=]|date=November 8, 2012|access-date=June 8, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160705045947/http://www.thejc.com/comment-and-debate/columnists/90023/why-anti-zionists-are-racists|archive-date=July 5, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.jewishjournal.com/opinion/article/formula_could_combat_campus_racism_20050610 |title=Formula Could Combat Campus Racism |work=Jewish Weekly |date=June 5, 2005 |access-date=June 8, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160829030800/http://www.jewishjournal.com/opinion/article/formula_could_combat_campus_racism_20050610 |archive-date=August 29, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] describes the ] movement as failing all of ]'s 3D's, since the movement delegitimizes Israel, demonizes Israel, and applies double standards for criticizing Israel out of proportion to other nations, ignoring other countries' misdeeds.<ref name="Saying no to Hate">{{cite book |last=Finkelstein |first=Norman H. |title=Saying No to Hate |date=2024 |publisher=U of Nebraska Press |isbn=978-0-8276-1523-6 |page=199}}</ref> | |||
| Although the Arab-Israeli conflict has produced real tragedy for Palestinians, Bauer suggests that Western latent antisemitism has fastened onto that tragedy in order to brand the Jews as mass murderers and Nazis as a way of solving the West's own psychological problems caused by the Holocaust. "Facts do not matter there," he writes, arguing that the number of Palestinians killed between the beginning of the ] in 2000 and 2003 (when he was writing) was around 2,000, which is one sixth of the daily number of Jews shipped to ] in the spring of 1944. Bearing these figures in mind, "ny kind of simplistic comparison becomes totally ridiculous," he argues. <ref name=Bauer6>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 6.</ref> | |||
| {{rquote|right|'''''A charming TV personality asked little Basmallah, a 3½ year old girl, 'Do you know who the Jews are?' "Yes." 'Do you like them?' "No." 'Why?' "Because they are monkeys and swine ..."''''' <br>— ] <ref name=Bauer8>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 8.</ref>}} | |||
| In 2024, over 1000 entertainers, authors and artists signed an open letter, released by the non-profit Creative Community for Peace (CCFP), opposing boycotts of Israeli and Jewish authors and literary institutions. The letter decried efforts to "demonize and ostracize Jewish authors across the globe".<ref name="y441">{{cite web |last=Kaloi |first=Stephanie |date=2024-10-31 |title=David Mamet, Diane Warren and Debra Messing Among 1000+ Entertainers and Artists to Oppose Israel Boycotts in Open Letter |url=https://www.thewrap.com/david-mamet-diane-warren-and-debra-messing-among-oppose-israel-boycotts-in-open-letter/ |access-date=2024-11-14 |website=TheWrap}}</ref> | |||
| Bauer regards this wave of antisemitism as dangerous because of ]. He identifies Islamism as one of three major ideologies to have emerged during the 20th century, alongside Soviet ] and ], <ref name=Bauer13>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 13.</ref> and argues that all three saw or see the Jews as a main enemy. <ref name=Bauer14>Bauer, Yehuda. {{PDFlink|}}, 2003, p 14.</ref> The language used about Jews by the Muslim media is, he says, "clearly and unmistakably genocidal," the ideology of ] "in a different dress."<ref name=Bauer15>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 15.</ref> He cites a television program broadcast on ], ] on the ]ian television station IQRAA, during which a three-year-old girl was asked whether she knew who the Jews were and whether she liked them. She replied that she did not like them, because "they are monkeys and swine ... and also because they tried to poison the wife of our ]." <ref name=Bauer8/> Bauer writes that 1.2 billion Muslims are being exposed to these teachings, making this fourth wave of antisemitism a "genocidal threat to the Jewish people." <ref name=Bauer17>Bauer, Yehuda. (pdf), 2003, p 17.</ref> | |||
| In fall 2024, campus protests using chants such as "Divest!" and "Ceasefire now!" reportedly evolved in a direction more explicitly endorsing Hamas, Hezbollah, and Houthis.<ref name="v962">{{cite web |last=Otterman |first=Sharon |date=2024-10-09 |title=Pro-Palestinian Group at Columbia Now Backs ‘Armed Resistance’ by Hamas |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2024/10/09/nyregion/columbia-pro-palestinian-group-hamas.html |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=The New York Times}}</ref> Some protesters used slogans such as "Glory to the resistance!", called the October 7 attacks "Al-Aqsa flood", celebrated ], and used the Hamas inverted red triangle.<ref name="b616">{{cite web |last=Meckler |first=Laura |last2=Svrluga |first2=Susan |date=2024-11-10 |title=Pro-Hamas messages intensify on college campuses |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2024/11/10/pro-hamas-protesters-college-campuses/ |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=Washington Post}}</ref> Jewish students were called "baby killers" and "terrorists", according to a Baruch College student.<ref name="b616" /> | |||
| ===A contradictory political ploy=== | |||
| ], a political scientist at ], has criticized the concept of new antisemitism. He argues that organizations such as the ] have brought forward charges of "new antisemitism" at varied intervals since the 1970s, "not to fight antisemitism but rather to exploit the historical suffering of Jews in order to immunize Israel against criticism". <ref name=Finkelstein21>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp. 21-22.</ref> He has criticized much of the recent literature on the subject, including works by ], ] and ]. <ref name=Finkelstein34>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp. 34, 38-39 , 39-40 , 41-45].</ref> | |||
| In November 2024, hundreds of posters depicting Jewish faculty members as "wanted" were spread across the ] campus. The posters accused Jewish faculty members of ethnic cleansing, racism, hate speech, and intimidation. University President Sarah Mangelsdorf called the incident an act of antisemitism.<ref name="k874">{{cite web |last=Marbury |first=Justice |last2=Nguyen |first2=Thao |date=2024-11-14 |title='Wanted' posters target Jewish faculty at University of Rochester |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2024/11/13/posters-university-of-rochester-jewish-faculty/76268943007/ |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=USA TODAY}}</ref> | |||
| Finkelstein writes that what is currently called the new antisemitism consists of three components: (i) "exaggeration and fabrication", (ii) "mislabeling legitimate criticism of Israeli policy," and (iii) "the unjustified yet predictable spillover from criticism of Israel to Jews generally". <ref name=Finkelstein66>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 66.</ref> Finkelstein argues that most evidence purporting to show a new anti-Semitism has been taken from "organizations directly or indirectly linked to Israel or having a material stake in inflating the findings of anti-Semitism" and that some anti-Semitic incidents reported in recent years either did not occur or were misidentified. <ref name=Finkelstein66/68>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 66, 68-71.</ref> He draws attention to the European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia's 2003 report on antisemitism, which included displays of the ], support for the ], and ] in its list of antisemitic activities and beliefs. <ref name=Finkelstein37>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 37.</ref> | |||
| == International perspectives == | |||
| Finkelstein argues that much recent hostility toward Israel and its "vocal Jewish supporters abroad" has been misinterpreted as resulting from "an irrational, inexplicable, and ineluctable" hatred of Jews, rather than from opposition to Israel's actions against the ]. He writes that "Israel's apologists" have denied a causal relationship between Israeli policies and hostility toward Jews, since "if Israeli policies, and widespread Jewish support for them, evoke hostility toward Jews, it means that Israel and its Jewish supporters might themselves be causing anti-Semitism; and it might be doing so because Israel and its Jewish supporters are ''in the wrong''". <ref name=Finkelstein78>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp. 78-79.</ref> Finkelstein notes that Jewish figures such as ] and ], who have argued that such a causal relationship exists, have been criticized by groups such as the ADL and the ]. <ref name=Finkelstein78/> | |||
| {{Globalize|date=November 2012}} | |||
| {{rquote|right|'''f Israeli policies, and widespread Jewish support for them, evoke hostility toward Jews, it means that Israel and its Jewish supporters might themselves be causing anti-Semitism; and it might be doing so because Israel and its Jewish supporters are ''in the wrong''.''' — ]. <ref name=Finkelstein78/>}} | |||
| === Europe === | |||
| Finkelstein acknowledges that "n some quarters anger at Israel's brutal occupation has undoubtedly slipped over to an animus against Jews generally", a phenomenon that he describes as "lamentable" but "hardly cause for wonder." <ref name=Finkelstein81>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 81.</ref> The wars in Vietnam and Iraq contributed to ], and the aggression of ] gave rise to anti-] sentiment. Why does it surprise us, he asks, that an occupation by a self-declared Jewish state should cause antipathy towards Jews? The only surprise, he argues, is that the antipathy does not run deeper, given that mainstream Jewish organizations offer uncritical support to Israel, that Israel defines itself juridically as the sovereign state of the Jewish people, and that Jews themselves sometimes argue that to distinguish between Israel and world Jewry is itself an example of antisemitism.<ref name=Finkelstein81/2>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, pp 81-82.</ref> | |||
| The European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia (EUMC) (superseded in 2007 by the ]) noted an upswing in antisemitic incidents in France, Germany, Austria, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Belgium, and The Netherlands between July 2003 and December 2004.<ref name=State>"(U.S.) State Department report on Anti-Semitism: Europe and Eurasia" excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 – December 15, 2004.</ref> In September 2004, the European Commission against Racism and Intolerance, a part of the ], called on its member nations to ensure that anti-racist criminal law covers antisemitism, and in 2005, the EUMC offered a discussion paper on a ] in an attempt to enable a standard definition to be used for data collection:<ref>Whine, Michael. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220226131202/https://www.jcpa.org/phas/phas-041-whine.htm |date=2022-02-26 }}, ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, February 1, 2006.</ref> It defined antisemitism as "a certain perception of Jews, which may be expressed as hatred towards Jews. Rhetorical and physical manifestations of antisemitism are directed towards Jews and non-Jewish individuals and/or their property, towards Jewish community institutions and religious facilities." The paper's “Examples of the ways in which anti-Semitism manifests itself with regard to the state of Israel taking into account the overall context could include": | |||
| * Denying the Jewish people the right to self-determination, e.g. by claiming that the existence of a state of Israel is a racist endeavor; | |||
| * Applying double standards by requiring of Israel a behavior not expected or demanded of any other democratic nation; | |||
| * Using the symbols and images associated with classic antisemitism (e.g. claims of Jews killing Jesus or blood libel) to characterize Israel or Israelis; | |||
| * Drawing comparisons of contemporary Israeli policy to that of the Nazis. | |||
| * Holding Jews collectively responsible for actions of the State of Israel.<ref name=workingdef> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110125001633/http://fra.europa.eu/fraWebsite/material/pub/AS/AS-WorkingDefinition-draft.pdf |date=2011-01-25 }}, EUMC.</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Working Definition of Antisemitism |url=http://fra.europa.eu/fraWebsite/material/pub/AS/AS-WorkingDefinition-draft.pdf |publisher=European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights |access-date=23 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110304162430/http://www.fra.europa.eu/fraWebsite/material/pub/AS/AS-WorkingDefinition-draft.pdf |archive-date=4 March 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The EUMC added that criticism of Israel cannot be regarded as antisemitism so long as it is "similar to that leveled against any other country."<ref name=workingdef /> | |||
| Finkelstein identifies several proponents of the concept of new antisemitism who appear to contradict themselves or each other on the issue of whether to identify Jews with Israel. ] argues, on the one hand, that "anyone who does not distinguish between Jews and the Jewish state is an anti-Semite," but on the other that "Israel is our heart and soul ... we ''are'' family." <ref>]. ''The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It'', Jossey-Bass, 2003, pp. 192, 209-11, 245 cited in ]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 82.</ref> Gabriel Schoenfeld, the editor of '']'' magazine, writes that "Iranian anti-Semitic propagandists make a point of erasing all distinctions among Israel, Zionism and the Jews," <ref>Schoenfeld, Gabriel. ''The Return of Anti-Semitism'', Encounter Books, 2004, p. 11, cited in ]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 82.</ref> while ] argues that "Israel is the state of the Jews ... To defame Israel is to defame the Jews,"<ref>]. "The Return of Anti-Semitism," ''Commentary'', February 2002, cited in ]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 82.</ref> and Italian journalist Fiamma Nirenstein that "Jews everywhere should consider their being identified with Israel a virtue and honor." <ref>Nirenstein, Fiamma. "How I became an unconscious fascist," in Rosenbaum, Ron. (ed) ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004, p. 302, cited in ]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 82.</ref> It would seem to be anti-Semitic, Finkelstein concludes, "both to identify and not to identify Israel with Jews." <ref name=Finkelstein82>]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', University of California Press, 2005, p. 82.</ref> | |||
| The discussion paper was never adopted by the EU as a working definition, although it was posted on the EUMC website until 2013 when it was removed during a clear-out of non-official documents.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.wiesenthal.com/site/apps/nlnet/content.aspx?c=lsKWLbPJLnF&b=8776547&ct=13381863 |title=SWC to EU Baroness Ashton: "Return Anti-Semitism Definition Document to EU Fundamental Rights Agency Website" | Simon Wiesenthal Center |website=Wiesenthal.com |date=2013-11-06 |access-date=2016-02-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160301080434/http://www.wiesenthal.com/site/apps/nlnet/content.aspx?c=lsKWLbPJLnF&b=8776547&ct=13381863 |archive-date=2016-03-01 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name=ToI>{{cite news|title=EU drops its 'working definition' of anti-Semitism|url=http://www.timesofisrael.com/eu-drops-its-working-definition-of-anti-semitism/|access-date=2014-01-24|newspaper=Times of Israel}}</ref> | |||
| ==Political directions== | |||
| ===The far right and Islamism=== | |||
| ]n edition of the '']'' repeats the ] that Jews use the blood of gentile children to bake ]s on ]." <ref> on intelligence.org.il, site of the Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center at the Center for Special Studies (C.S.S), Israel. Accessed 24 September 2006.</ref>]] | |||
| ==== France ==== | |||
| The September 2006 British "All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism" heard evidence from '']'', the ] magazine, that: "the far right have started to use 'Zionists' as a euphemism for 'Jews,' to disguise their anti-Semitism, a phenomenon that also occurs on the left and among Islamist extremists." <ref name=APP25>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.25.</ref> The ]'s ''Voice of Freedom'' wrote of the war in Iraq that "Tony Blair swapped British blood for donations from a clique of filthy-rich Zionist businessmen." <ref name=APP25/> The ] (MPACUK) has cited the ] as a "Zionist holy book," <ref name=APP29>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.29.</ref> and describes Zionism as an "octopus that now penetrates every western nation and pushes it to start world war three against Muslims," <ref name=APP29/> an anti-Semitic ] used by the Nazis. | |||
| {{Main|Antisemitism in 21st-century France}} | |||
| In France, Interior Minister ] commissioned a report on racism and antisemitism from ], president of ] and former vice-president of ], in which Rufin challenges the perception that the new antisemitism in France comes exclusively from ]n immigrant communities and the ].<ref name=BBCnas>, BBC News, October 2004.</ref><ref name=statefrance>, U.S. Department of State.</ref> | |||
| The report describes a "symbiotic relationship" between Islamists and the far right,<ref name=APP29/> united in their hatred of Jews, Zionism, and Israel. <ref name=APP30>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.30.</ref> The inquiry saw evidence of the shared use of materials, such as the same newspaper articles appearing on the MPACUK and ] websites. MPACUK published a photograph of George Bush standing next to the Israeli flag, adding the caption: "Some say Lobbying the Government doesn't make a difference. We humbly disagree," while the ] used the same photograph, with the caption: "There is no Zionist conspiracy." Islamist and far right groups also share ] literature, and the organizations' websites publish each other's authors. <ref name=APP30/> | |||
| Reporting in October 2004, Rufin writes that "he new anti-Semitism appears more heterogeneous," and identifies what he calls a new and "subtle" form of antisemitism in "radical anti-Zionism" as expressed by far-left and anti-globalization groups, in which criticism of Jews and Israel is used as a pretext to "legitimize the armed Palestinian conflict."<ref name=Rufin>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090327180811/http://lesrapports.ladocumentationfrancaise.fr/BRP/044000500/0000.pdf |date=2009-03-27 }}, presented to the French Ministry of the Interior, October 19, 2004.</ref><ref name=bryant>Bryant, Elizabeth. "," United Press International, October 20, 2004.</ref> | |||
| ], the late Palestinian-American literary theorist, warned of a "nasty, creeping wave of anti-Semitism" insinuating itself into Palestinian politics, writing that the "notion that the Jews never suffered and that the Holocaust is an obfuscatory confection ... is one that is acquiring too much, far too much, currency". <ref name=said518>]. "A Desolation and They Called It Peace," in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004, p. 518.</ref> ], the majority party of the ], has called the Holocaust "an alleged and invented story with no basis." <ref>Paz, Reuven. , ''Washington Institute Peace Watch, NO. 255, April 21, 2000.</ref> Political scientist ] writes that the statements by Iranian president ] that the Holocaust is a "myth" and that Israel should be "wiped off the map" were met with public approval from Hamas, the Egyptian ], American ] ], and the ], a leading Holocaust-denial group. <ref name=Michael309>]. ''The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right''. University Press of Kansas, 2006, p.309.</ref> | |||
| ==== United Kingdom ==== | |||
| Michael cites as an example of the new Islamist/far right alliance the March 2001 conference in ], ] on "Revisionism and Zionism," organized by the Institute for Historical Review, where there was a plan to present lectures in English, French, and Arabic. The Lebanese government cancelled the conference after protests from Jewish groups and the American government, but a smaller meeting was held in May 2001 in ], ]. <ref name=Michael156>]. ''The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right''. University Press of Kansas, 2006, p.156.</ref> | |||
| In June 2011, Chief Rabbi of the United Kingdom, ] (Lord Sacks), said that the basis for the new antisemitism was the 2001 ]. Rabbi Sacks also said that the new antisemitism "unites radical Islamists with human-rights NGOs{{spaced ndash}}the right wing and the left wing{{spaced ndash}}against a common enemy, the State of Israel."<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.jewishjournal.com/at_home_abroad/item/uk_chief_rabbi_jonathan_sacks_the_new_anti-semitism_is_a_virus_20110622/|title=UK Chief Rabbi Jonathan Sacks: "The New Anti-Semitism is a Virus"}}</ref> | |||
| ], former leader of a ] faction, on ]n television in November 2005. He told viewers that "] makes the ] state look very, very moderate." <ref>, interview with ] on Syrian television, the Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI), November 25, 2005. The clip can be viewed .</ref>]] | |||
| In September 2006, the ] of the ] published the Report of the All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Antisemitism, the result of an investigation into whether the belief that the "prevailing opinion both within the Jewish community and beyond" that antisemitism had "receded to the point that it existed only on the margins of society." was correct. It concluded that "the evidence we received indicates that there has been a reversal of this progress since the year 2000". In defining antisemitism, the Group wrote that it took into account the view of racism expressed by the MacPherson report, which was published after the murder of ], that, for the purpose of investigating and recording complaints of crime by the police, an act must be recorded by the police as racist if it is defined as such by its victim. It formed the view that, broadly, "any remark, insult or act the purpose or effect of which is to violate a Jewish person's dignity or create an intimidating, hostile, degrading, humiliating or offensive environment for him is antisemitic" and concluded that, given that, "it is the Jewish community itself that is best qualified to determine what does and does not constitute antisemitism."<ref name=APP1> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130822190807/http://www.antisemitism.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/All-Party-Parliamentary-Inquiry-into-Antisemitism-REPORT.pdf |date=2013-08-22 }}, September 2006, p. 1.</ref> | |||
| Michael writes that Duke, a former ] leader, has been at the forefront of efforts to foster cooperation between the far right and the Islamic world, in what Michael calls a "cross-fertilization of rhetoric" against Zionism, Jews, and Israel. <ref name=Michael309/> Duke presented two lectures in ] in 2002 entitled "The Global Struggle against Zionism," and "Israeli Involvement in September 11," after being invited by the Discover Islam Center, an Islamist group who admired the anti-Semitic rhetoric on Duke's website. Duke told Michael: "The ADL issued a protest to Bahrain 'How can they have a white supremacist in Bahrain?' But the people in Bahrain understand very well that I am not a white supremacist and that I am a European American who wants to preserve my heritage ... but the real danger to all heritages is Jewish supremacism ..." <ref name=Michael162>]. ''The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right''. University Press of Kansas, 2006, p.162.</ref> | |||
| The report states that some left-wing activists and Muslim extremists are using criticism of Israel as a "pretext" for antisemitism,<ref name=Temko>Temko, Ned. , ''The Observer'', February 3, 2006.</ref> and that the "most worrying discovery" is that antisemitism appears to be entering the mainstream.<ref name=BBCreport>, BBC News, September 6, 2006.</ref> It argues that anti-Zionism may become antisemitic when it adopts a view of Zionism as a "global force of unlimited power and malevolence throughout history," a definition that "bears no relation to the understanding that most Jews have of the concept: that is, a movement of Jewish national liberation ..." Having re-defined Zionism, the report states, traditional antisemitic motifs of Jewish "conspiratorial power, manipulation and subversion" are often transferred from Jews onto Zionism. The report notes that this is "at the core of the 'New Antisemitism', on which so much has been written," adding that many of those who gave evidence called anti-Zionism "the '']'' of antisemitic movements."<ref name=APP22> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130822190807/http://www.antisemitism.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/All-Party-Parliamentary-Inquiry-into-Antisemitism-REPORT.pdf |date=2013-08-22 }}, September 2006, p. 22.</ref> | |||
| In November 2005, Duke addressed a rally in ], saying "It saddens my heart to tell you that part of my country is occupied by Zionists, just as part of your country, the ], is occupied by Zionists. occupy most of the American media and now control much of the American government ... It is not just the ] of Palestine, it is not just the Golan Heights that are occupied by the Zionists, but Washington D.C. and New York and London and many other capitals of the world. Your fight for freedom is the same as our fight for freedom." <ref name=halevi>HaLevi, Ezra. , ''Arutz Sheva'', November 29, 2005. The clip can be viewed . </ref> In an interview with Syrian television, Duke said that "Jewish supremacists" are in control of the U.S. government and that "Israel makes the Nazi state look very, very moderate." <ref>, interview with ] on Syrian television, the Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI), November 25, 2005. The clip can be viewed .</ref> | |||
| === |
=== Israel === | ||
| In November 2001 according to the Israeli Ministry of Diaspora Affairs, in response to an Abu-Dhabi television broadcast depicting ] drinking the blood of Palestinian children, the ] set up the "Coordinating Forum for Countering Antisemitism", headed by Deputy Foreign Minister Rabbi ]. According to Melchior, "in each and every generation antisemitism tries to hide its ugly face behind various disguises{{spaced ndash}}and hatred of the State of Israel is its current disguise." He added that, "hate against Israel has crossed the red line, having gone from criticism to unbridled antisemitic venom, which is a precise translation of classical antisemitism whose past results are all too familiar to the entire world."<ref>, November 18, 2001.</ref> | |||
| ], Eve Garrard, ], Shalom Lappin, and ] at the launch of the ] in 2006. They wrote that anti-Zionism has "developed to a point where supposed organizations of the Left are willing to entertain openly anti-Semitic speakers and to form alliances with anti-Semitic groups."<ref name=euston>, March 29, 2006.</ref>]] | |||
| Those who argue in favor of the centrality of the left to the new anti-Semitism say that anti-Zionism may function as a ] for anti-Semitism, allowing a socially acceptable opposition to the Israeli state to be espoused, rather than a socially unacceptable ] or ]. At the same time, genuine grievances against Israel stemming from the Arab-Israeli conflict may become anti-Semitic in character and may manifest themselves as hostility toward Jews in general. <ref>Daniel Lazare wrote, in a paraphrase of ], that: "Anti-Semitism is the anti-Zionism of fools ...," an allusion to Bebel's famous remark, "Anti-Semitism is the socialism of fools." (Lazare, Daniel. , '']'', December 19, 2005, p.36, accessed January 8, 2005.)</ref><ref>] of the ] (ADL) has said: "The harsh but un-deniable truth is this: what some like to call anti-Zionism is, in reality, anti-Semitism — always, everywhere, and for all time ... Therefore, anti-Zionism is not a politically legitimate point of view but rather an expression of ] and hatred." (]. . '']'', February 2, 2004) Foxman argues that it is anti-Semitic to criticize the occupation by the Jews of the West Bank if one does not also criticize the "Indian Hindus and their occupation of Muslim ]." (] . Speech given before the ] Executive Committee, Palm Beach, Florida, February 8, 2002, accessed January 3, 2006)</ref> | |||
| === United Nations === | |||
| Historian ] argues that "left-leaning Judeophobes ... never call themselves 'anti-Semitic.' Indeed, they are usually indignant at the very suggestion that they have anything against Jews. Such denials notwithstanding, they are usually obsessed with stigmatizing Israel ..." <ref name=Wistrich1112>Wistrich, Robert S. {{PDFlink|}}, American Jewish Committee, 2005, pp 11-12.</ref> Wistrich adds that not all criticism of Israel is anti-Semitic — his checklist to identify the "anti-Semitic wolf in anti-Israeli sheep's clothing" includes the singling-out by writers of the "Jewish lobby" or the "Jewish vote"; complaining about Jewish solidarity with Israel; gratuitous emphasis on Jewish wealth or alleged Jewish control of the media; calls for economic boycotts directed exclusively against Israeli products and academic institutions; and the assertion that Jews reject all criticism as anti-Semitic. <ref name=Wistrich1112/> | |||
| {{See also|Israel and the United Nations}} | |||
| A number of commentators argue that the ] has condoned antisemitism. ], then-president of ], wrote that the UN's World Conference on Racism failed to condemn human rights abuses in China, Rwanda, or anywhere in the Arab world, while raising Israel's alleged ethnic cleansing and crimes against humanity.<ref>] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041010174207/http://president.harvard.edu/speeches/2002/morningprayers.html |date=2004-10-10 }}, September 17, 2002. On the site of ], accessed January 9, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ], senior counsel to ] Canada, has written that the UN is a forum for antisemitism, citing the example of the Palestinian representative to the UN ] who claimed in 1997 that Israeli doctors had injected Palestinian children with the ] virus.<ref name=Matas>Matas, David. ''Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism''. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005, pp. 129–144.</ref> Congressman ] told the U.S. ] in 2005 that the commission took "several months to correct in its record a statement by the ]n ambassador that Jews allegedly had killed non-Jewish children to make ] for ].<ref>, June 17, 2005. Accessed March 6, 2006.</ref> | |||
| The 2006 British All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism (See ] for more details.) <ref name=APP>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006.</ref> heard evidence that "contemporary antisemitism in Britain is now more commonly found on the left of the political spectrum than on the right." <ref name=APP32>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.32.</ref> The chairman, former Europe Minister ], referred in a radio interview to what he called "a 'witch's brew' of anti-semitism including the far left and 'ultra-Islamist' extremists", who use criticism of Israel as a "pretext" for "spreading hatred against British Jews." <ref name=Temko>Temko, Ned. , ''The Observer'', February 3, 2006.</ref> The report notes that "lliances between extremist and fundamentalist groups have created links between groups on the far left and radical Islamists." <ref name=APP33>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.33.</ref> Professor ] of ] gave evidence that anti-Semitism "no longer has any resemblance to classical Nazi-style Jew hatred, because it is masked by or blended inadvertently into anti-Zionism, and because it is often articulated in the language of human rights. <ref name=APP32/> The report states that ignorance of the history of anti-Semitism means that some may not even realize that the language and imagery they use are part of the tradition of anti-Semitic discourse. <ref name=APP33/> | |||
| ], a Canadian legal scholar who addressed the UN about its treatment of Israel, argues that the UN hijacks the language of human rights to discriminate and demonize Jews. She writes that over one quarter of the resolutions condemning a state's human rights violations have been directed at Israel. "But there has never been a single resolution about the decades-long repression of the civil and political rights of 1.3 billion people in ], or the million female migrant workers in ] kept as virtual slaves, or the virulent racism which has brought 600,000 people to the brink of starvation in ]."<ref>]. , '']'' ], June 21, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ], publisher of the anti-fascist '']'', agrees that "a lot of anti-semitism is driven by the left. There are elements who take up a position on Israel and Palestine which in reality puts them in league with anti-Semites."<ref name=Gable>, '']'', August 8, 2004.</ref> '']'' reported in August 2006 that "omen pushing their children in buggies bearing the familiar symbol of the ] marched last weekend alongside banners proclaiming 'We are all ] now' and Muslim extremists chanting 'Oh Jew, the army of Muhammad will return'." <ref>Baxter, Sarah. , ''The Sunday Times'', August 13, 2006.</ref> | |||
| In a 2008 report on antisemitism from the ] to the US Congress,<ref>{{cite web| last = Rickman| first = Gregg J.| title = Contemporary global anti-semitism| publisher = USDOS| year = 2008| url = https://2009-2017.state.gov/documents/organization/102301.pdf| access-date = 2008-03-27}}</ref> | |||
| Radu Ioanid, director of the Meed Registry of Jewish Holocaust Survivors at the ], writes in his foreword to ''Rising from the Muck'', ]'s book about the new anti-Semitism in Europe, that during the student uprising in France in 1968, protesters could be heard shouting: "''Nous sommes tous des Juifs Allemands''" ("We are all German Jews") in support of Daniel Cohn-Bendit, one of their expelled leaders. In 2002, in contrast, the slogans heard at rallies in Paris were "Death to the Jews" and "Jews to the ovens." <ref name=Ioanidxi>Ioanid, Radu. Foreword ]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. xi.</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>Motives for criticizing Israel in the UN may stem from legitimate concerns over policy or from illegitimate prejudices. ... However, regardless of the intent, disproportionate criticism of Israel as barbaric and unprincipled, and corresponding discriminatory measures adopted in the UN against Israel, have the effect of causing audiences to associate negative attributes with Jews in general, thus fueling anti-Semitism.</blockquote> | |||
| ] argues that the "supposed new 'anti-Semitism'" is a "cynical ploy." <ref name=ali>]. , ''Counterpunch'', March 4, 2004, first published in ''il manifesto'', February 26, 2004.</ref>]] | |||
| === United States === | |||
| A group of left-wing British academics, journalists, and activists founded the ] in April 2006, a new declaration of principles for the democratic left. It declares that: "'Anti-Zionism' has now developed to a point where supposed organizations of the Left are willing to entertain openly anti-Semitic speakers and to form alliances with anti-Semitic groups. Amongst educated and affluent people are to be found individuals unembarrassed to claim that the ] was fought on behalf of Jewish interests, or to make other 'polite' and subtle allusions to the harmful effect of Jewish influence in international or national politics — remarks of a kind that for more than fifty years after ] no one would have been able to make without publicly disgracing themselves." <ref name=euston/> | |||
| ] | |||
| In September 2006, ] announced that it had established ],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://isgap.org/|title=ISGAP|website=isgap.org}}</ref> the first university-based institute in North America dedicated to the study of antisemitism. Charles Small, head of the institute, said in a press release that antisemitism has "reemerged internationally in a manner that many leading scholars and policy makers take seriously ... Increasingly, Jewish communities around the world feel under threat. It's almost like going back into the lab. I think we need to understand the current manifestation of this disease."<ref>, ''Associated Press'', September 19, 2006; also see ] & ] "Anti-Israel sentiment predicts anti-Semitism in Europe," ''Journal of Conflict Resolution'', Vol 50, No. 4, 548–561, August 2006.</ref> | |||
| The association of anti-Zionism with new anti-Semitism has been controversial. British writer ] has argued that the campaign against "the supposed new 'anti-semitism'" in modern Europe is in effect a "cynical ploy on the part of the Israeli Government to seal off the Zionist state from any criticism of its regular and consistent brutality against the Palestinians."<ref name=ali/> Ali argues that the new anti-Semitism is, in fact, "Zionist blackmail," and that Israel, far from being a victim, is "the strongest state in the region. It possesses real, not imaginary, weapons of mass destruction. It possesses more tanks and bomber jets and pilots than the rest of the Arab world put together. To say that the Zionist state is threatened by any Arab country is pure demagogy." <ref name=ali/><ref name=beaumont>Beaumont, Peter. , ''The Observer'', February 17, 2002.</ref> | |||
| YIISA has presented several seminars and working papers on the topic, for instance "The Academic and Public Debate Over the Meaning of the 'New Antisemitism{{'"}}.<ref>.</ref> | |||
| ] argues that traditional anti-Semitism is ignored while criticism of Israel is vilified. <ref name=Chomsky92>]. , letter. March 31, 1992. Accessed January 9l, 2006.</ref>]] | |||
| In July 2006, the ] issued a Campus Antisemitism report that declared that "Anti-Semitic bigotry is no less morally deplorable when camouflaged as anti-Israelism or anti-Zionism."<ref>U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, Campus Anti-Semitism (2006) at 72.</ref> At the time, the commission also announced that antisemitism is a "serious problem" on many campuses throughout the United States.<ref>''Id.''</ref> | |||
| Although proponents of the concept of the new anti-Semitism agree that it appeared to start, or gain ], around the beginning of the ], they refuse to accept that anti-Israel or anti-Zionist feeling may be a justifiably critical response to Israel's handling of the uprising, according to Peter Beaumont, writing in '']''. He argues that "Israel's brutal response to the often equally reprehensible anti-Israeli Palestinian violence of the intifada has produced one of the most vigorous media critiques of Israel's policies in the European media in a generation. The reply to this criticism, say those most vocal in reporting the existence of the new anti-Semitism, particularly in the Israeli press, is devastating in its simplicity: criticise Israel, and you are an anti-Semite just as surely as if you were throwing paint at a ] in ]." Israel cannot be declared out of bounds, writes Beaumont, for fear of invoking Europe's "last great taboo — the fear of being declared an anti-Semite." <ref name=beaumont/> | |||
| The U.S. State Department's 2004 ''Report on Global Anti-Semitism'' identified four sources of rising antisemitism, particularly in Europe: | |||
| ], professor of linguistics at ], maintains that Jewish groups see criticism of Israeli policies as examples of new anti-Semitism while turning a blind eye to traditional anti-Semitism. He cites the allegations in 1988 that several known anti-Semites occupied senior positions in the ]. <ref name=Chomsky92/><ref name=Berke>Berke, Richard L. "Bush Panelist Out After Reports of Anti-Jewish Ties," ''New York Times,'' September 9, 1988, p. A15 (reporting that Jerome Brentar, a ] travel agent, was dismissed from a Republican Party advisory panel after it was brought to public attention that Brentar had raised funds and made public speeches to defend ], a fellow-Cleveland resident and former Cleveland autoworker, against the unfair death sentence that the Israeli court had imposed after finding that Demjanjuk had "committed atrocities as a guard at the Treblinka camp in Nazi-occupied Poland.") In prefacing the announcement of the dismissal of Brentar from the advisory panel, ], the ] campaign chairman had said, "there is absolutely no room for anti-Semitism or bigotry of any sort in our campaign." ''Id.'' ''See also,'' Rosenthal, Andrew. "Campaign Tactics Provoke New Charges," ''New York Times,'' October 31, 1988, p. B6 (comparing political attack fliers published by rival state party officials). The Maryland state Republican Party had published a flier that "showed a picture of ] and ], a murderer who escaped while on furlough from a Massachusetts prison and later raped a Maryland woman and stabbed her fiancé;" the flier asked, "'Is this your pro-family team for 1988,' ... referring repeatedly to the 'Dukakis/Horton team.'" In response to complaints about this flier, James A. Baker responded by attacking the similar untruthfulness in the flier by California Democratic party affiliates that claimed that "'anti-Semitic and pro-Nazi activists' were infiltrating the Bush campaign." ''Id.'' </ref> '']'' argued that the discovery of "seven aging ]an fascists in the Republican apparatus" wasn't the threat it was made out to be; the greater threat lay in the anti-Semitism of the left, which had a salient agenda: "the delegitimization of the Jewish national movement". | |||
| * "Traditional anti-Jewish prejudice... This includes ultra-nationalists and others who assert that the Jewish community controls governments, the media, international business, and the financial world." | |||
| * "Strong anti-Israel sentiment that crosses the line between objective criticism of Israeli policies and anti-Semitism." | |||
| * "Anti-Jewish sentiment expressed by some in Europe's growing Muslim population, based on longstanding antipathy toward both Israel and Jews, as well as Muslim opposition to developments in Israel and the occupied territories, and more recently in Iraq." | |||
| * "Criticism of both the United States and globalization that spills over to Israel, and to Jews in general who are identified with both."<ref name=State /> | |||
| == Anti-globalization movement == | |||
| ==Responses== | |||
| The anti-globalization movement of the late 1990s and early 2000s was accused by writers and researchers such as ], ], and ] of displaying elements of new antisemitism. Critics of the Laqueur–Berman–Strauss view argue that the allegation is either unfounded or exaggerated, intended to discredit legitimate ] and of ] economic policies.{{citation needed|date=July 2021}} | |||
| ===European Union=== | |||
| Groups monitoring ] and violence in the ] have noted an upswing in attacks on Jewish people and Jewish institutions in many European countries. <ref name=State-1>, excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 – December 15, 2004. Accessed 6 Jan 2005.</ref> | |||
| === Mark Strauss's allegations === | |||
| In ], the ] released a report detailing a new wave of antisemitic incidents in most of Western Europe in the wake of the ], in contrast to neutral or pro-Israel sentiment in the former Eastern bloc as well as ].<ref>{{cite news | |||
| ] of '']'' argues that globalization has stirred anxieties about "outside forces", and that with "familiar anxieties come familiar scapegoats."<ref name=Strauss>{{cite news |last1=Strauss |first1=Mark |author-link1=Mark Strauss (journalist) |title=Antiglobalism's Jewish Problem |url=https://yaleglobal.yale.edu/content/antiglobalisms-jewish-problem |work=Foreign Policy |date=November 12, 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130312085916/http://yaleglobal.yale.edu/content/antiglobalisms-jewish-problem |archive-date=March 12, 2013 |url-status=dead}}</ref> He writes that what he calls the "backlash against globalization" has united a variety of political elements, from the left to the far-right, via a common cause, and that in so doing it has "foster a common enemy." He quotes the French Jewish leader Roger Cukierman who identifies the ] as "an anti-Semitic ]", which includes ultra-nationalists, Islamists, and communists.<ref name=Strauss /> | |||
| | first = Spritzer | |||
| | last = Dinah | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | author = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = Study: European anti-Semitism up since war | |||
| | url = | |||
| | format = | |||
| | work = | |||
| | publisher = Connecticut Jewish Ledger | |||
| | pages = 8-9 | |||
| | page = | |||
| | date = 2006-11-17 | |||
| | accessdate = 2006-11-17 | |||
| | language = English | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| The report cited | |||
| *the first instances of antisemitism in ] since the change of regime in ] | |||
| *83 instances of antisemitism in ] from April through August 2006, compared to 50 in the same period of 2005 | |||
| *61 instances of antisemitism in ] from April through August 2006, compared to 34 in the same period of 2005 | |||
| *a doubling of the rate of antisemitic incidents in Great Britain, compared to the previous year | |||
| *normalization of antisemitic political and media rhetoric in ] after the conflict | |||
| Strauss cites ] of the far-right ] and ] of France's ] as examples of the far right exploiting their electorate's concerns about globalization. The fringe ] in ] identifies globalization as an "instrument in the hands of international Zionism" according to Strauss, while in Eastern Europe ultranationalists and communists have united against foreign investors and multinationals, identifying Jews as a common enemy.<ref name=Strauss /> | |||
| In September 2004, the European Commission against Racism and Intolerance, a part of the ], called on its member nations to ensure that anti-racist criminal law covers anti-Semitism. In 2005, the ] (EUMC) offered a definition of new or contemporary anti-Semitism, one that the British government was urged to adopt by a 2006 all-party parliamentary inquiry. | |||
| ], an American ] of the ], stated of the ] that they were "incredibly successful from the point of view of the rioters as well as our Church. They helped shut down talks of the Jew World Order WTO and helped make a mockery of the Jewish Occupational Government around the world. Bravo."<ref name=Strauss /> Strauss also cites the ], a ] party which set up a website called the ''Anti-Globalism Action Network'' in order to "broaden ... the anti-globalism movement to include divergent and marginalized voices."<ref name=Strauss /> | |||
| :* Denying the Jewish people the right to self-determination, e.g. by claiming that the existence of a state of Israel is a racist endeavor; | |||
| :* Applying double standards by requiring of Israel a behavior not expected or demanded of any other democratic nation; | |||
| :* Using the symbols and images associated with classic anti-Semitism (e.g. claims of Jews killing Jesus or blood libel) to characterize Israel or Israelis; | |||
| :* Drawing comparisons of contemporary Israeli policy to that of the Nazis; | |||
| :* Holding Jews collectively responsible for actions of the State of Israel. <ref name=eu>{{PDFlink|}}, ], May 2006.</ref> | |||
| Strauss writes that, as a result of far-right involvement, a "bizarre ideological turf war has broken out", whereby anti-globalization activists are fighting a "two-front battle," one against the ], ], and ], the other against the extremists who turn up at their rallies.<ref name=Strauss /> He points to an anti-globalization march in ], Brazil, at which he says some marchers displayed ]s and that Jewish peace activists were assaulted. He wrote: | |||
| ===France=== | |||
| <blockquote>"Held two months prior to the U.S.-led attack on Iraq, this year's conference{{spaced ndash}} an annual grassroots riposte to the well-heeled World Economic Forum in Davos{{spaced ndash}} had the theme, 'Another World is Possible.' But the more appropriate theme might have been 'Yesterday's World is Back.' Marchers among the 20,000 activists from 120 countries carried signs reading 'Nazis, Yankees, and Jews: No More Chosen Peoples!' Some wore T-shirts with the ] twisted into Nazi swastikas. Members of a Palestinian organization pilloried Jews as the 'true fundamentalists who control United States capitalism.' Jewish delegates carrying banners declaring 'Two peoples – Two states: Peace in the Middle East' were assaulted.<ref name=Strauss /></blockquote> | |||
| In France, Interior Minister ] commissioned a report on racism and anti-Semitism from ], president of ] and former vice-president of ], in which Rufin challenges the perception that the new anti-Semitism in France comes exclusively from ]n immigrant communities and the ]. <ref name=BBCnas>, BBC News, October 2004.</ref><ref name=statefrance>, U.S. Department of State.</ref> Reporting in October 2004, Rufin writes that "he new anti-Semitism appears more heterogeneous," and identifies what he calls a new and "subtle" form of anti-Semitism in "radical anti-Zionism" as expressed by far-left and anti-globalization groups, in which criticism of Jews and Israel is used as a pretext to "legitimize the armed Palestinian conflict." <ref name=Rufin>Rufin, Jean-Christophe. {{PDFlink|}}, presented October 19, 2004.</ref><ref name=bryant>Bryant, Elizabeth. "," United Press International, October 20, 2004.</ref> | |||
| Rufin recommended that French law be changed to "make it possible to punish those who would make unfounded charges of racism against groups, institutions or States, or would make unjustified comparisons with apartheid or Nazism about them."<ref name=Rufin/><ref>Exact quote (with context) in French: ''"C’est pourquoi nous invitons à réfléchir sur l’opportunité et l’applicabilité d’un texte de loi qui complèterait les dispositions de la loi du 1 juillet 1972 et celles de la loi du 13 juillet 1990 (dite loi Gayssot). Ce texte permettrait de punir ceux qui porteraient sans fondement à l’encontre de groupes, d’institutions ou d’Etats des accusations de racisme et utiliseraient à leur propos des comparaisons injustifiées avec l’apartheid ou le nazisme."'' page 30.</ref><ref>, AFP, March 22, 2006.</ref> ] described Rufin's recommendation as "truly terrifying", the "stigmatizing of dissent as a disease that must be wiped out by the state."<ref>Norman G. Finkelstein, ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History'', Berkley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2005, p. 49.</ref> | |||
| Strauss argues that the anti-globalization movement is not itself antisemitic but that it "helps enable anti-Semitism by peddling conspiracy theories."<ref name=Strauss /> Strauss's arguments have been met with strong criticism from many in the anti-globalization movement. Oded Grajew, one of the founders of the ], has written that the WSF "is not anti-Semitic, anti-American, or even anti-socially-responsible capitalism". He claims that some fringe parties have attempted to infiltrate the WSF's demonstrations and promote demonstrations of their own, but adds that "he success of the WSF ... is a threat to political extremist groups that resort to violence and hatred". Grajew has also written that, to his knowledge, Strauss's claim of Nazi symbols being displayed at an anti-globalization demonstration in Porto Alegre, Brazil is false.<ref>Oded Grajew, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , ''Foreign Policy'', 1 March 2004, p. 4.</ref> | |||
| ===Israel=== | |||
| In November 2001, in response to an Abu-Dhabi television broadcast showing ] drinking blood of Palestinian children, the ] set up the "Coordinating Forum for Countering Antisemitism," headed by Deputy Foreign Minister Rabbi ]. According to Melchior, "in each and every generation antisemitism tries to hide its ugly face behind various disguises - and hatred of the State of Israel is its current disguise." He also noted that "... hate against Israel has crossed the red line, having gone from criticism to unbridled antisemitic venom, which is a precise translation of classical antisemitism whose past results are all too familiar to the entire world." <ref> (antisemitism.org.il)</ref> The multilingual forum regularly issues reports, articles and press releases. <ref> </ref> | |||
| === |
=== Response to Strauss === | ||
| ], national chairperson of the ], argues that Strauss has "inflamed, not enlightened" the debate over globalization by making "no distinction between the far right's critique of globalization and that of the global social justice movement", which is premised on "respect for human rights and cultural diversity". She notes that the Council of Canadians has condemned antisemitism, and that it expelled some individuals who tried to organize a ] tour under its auspices.<ref>Maude Barlow, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , ''Foreign Policy'', 1 March 2004, p. 4.</ref> John Cavanagh of the International Policy Centre has also criticized Strauss for using unproven allegations of antisemitism to criticize the entire anti-globalization movement, and for failing to research the movement's core beliefs.<ref>John Cavanagh, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , ''Foreign Policy'', 1 March 2004, p. 4.</ref> | |||
| }}, September 7, 2006, Summary. </ref>]] | |||
| In response to these criticisms, Strauss has written that antisemitic views "might not reflect the core values of the ] or its leading figures, yet they are facts of life in an amorphous, grassroots movement where any number of individuals or organizations express their opinions or seek to set the agenda". He has also reiterated his concern that "anti-capitalist rhetoric provides intellectual fodder for far right groups".<ref>Mark Strauss, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , ''Foreign Policy'', 1 March 2004, p. 4.</ref> | |||
| The British All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism in the UK published its report in September 2006. <ref name=inquiry> The panel consisted of Chair: Rt Hon Dr ] (Lab); Rt Hon ] MP (Lab); ] MP (Con); Rt Hon ] MP (Con); Rt Hon ] MP (Con); ] MP (Con); Rt Hon ] MP (Lab); Lady ] MP (UUP); ] MP (Lib Dem); ] MP (Con); ] MP (Lab); ] MP (Lab); Rt Hon ] MP (Lab), and ] MP (Con).</ref> Those who gave evidence included then-Home Secretary ]; the Attorney General ]; chief Rabbi ]; chairman of the ], ]; the former head of the ], Sir ]; Prof ] of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem; Brian Klug of St Benet's Hall, Oxford; and Prof Gert Weisskirchen of the German ]. <ref name=inquiry/> | |||
| === Other views === | |||
| The inquiry adopted the view of racism expressed by the MacPherson report after the murder of ], namely that a racist act is defined by its victim, and that it is the Jewish community that is in the best position to determine what is anti-Semitic. <ref name=APP1>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.1.</ref> The report states that left-wing activists and Muslim extremists are using criticism of Israel as a "pretext" for anti-Semitism, <ref name=Temko/> and that the "most worrying discovery" is that anti-Semitism appears to be entering the mainstream. <ref name=BBCreport>, BBC News, September 6, 2006.</ref> The inquiry calls for the adoption of a clearer definition of anti-Semitism that reflects its "complex and multi-faceted" nature. <ref name=BBCreport/> It argues that anti-Zionism may become anti-Semitic when it adopts a view of Zionism as a "global force of unlimited power and malevolence throughout history," a definition that "bears no relation to the understanding that most Jews have of the concept: that is, a movement of Jewish national liberation ..." Having re-defined Zionism, traditional anti-Semitic ]s of Jewish "conspiratorial power, manipulation and subversion" are transferred from Jews onto Zionism. This is "at the core of the 'New Anti-Semitism'," the report concludes, adding that many of those who gave evidence called anti-Zionism "the '']'' of antisemitic movements." <ref name=APP22>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.22.</ref> | |||
| ] describes this phenomenon:<ref>] (2006): ''The Changing Face of Anti-Semitism: From Ancient Times to the Present Day''. Oxford University Press, 2006 {{ISBN|0-19-530429-2}} p.186</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>Although traditional Trotskyite ideology is in no way close to radical Islamic teachings and the shariah, since the radical Islamists also subscribed to anticapitalism, antiglobalism, and anti-Americanism, there seemed to be sufficient common ground for an alliance. Thus, the militants of the far left began to march side by side with the radical Islamists in demonstrations, denouncing American aggression and Israeli crimes. ... And it was only natural that in protest demonstrations militants from the far right would join in, antisemitic banners would be displayed, anti-Jewish literature such as the '']'' would be sold. </blockquote> | |||
| ], then president of Harvard University, also stated that "erious and thoughtful people are advocating and taking actions that are anti-Semitic in their effect if not their intent. For example ... t the same rallies where protesters, many of them university students, condemn the IMF and global capitalism and raise questions about globalization, it is becoming increasingly common to also lash out at Israel. Indeed, at the anti-IMF rallies last spring, chants were heard equating ] and ]."<ref name=Summers>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110812001233/http://president.harvard.edu/speeches/summers_2002/morningprayers.php |date=2011-08-12 }}, Office of the President, Harvard University, September 17, 2002.</ref> | |||
| ] gave evidence regarding anti-Semitic remarks made to him in Parliament. After the arrest of ], for example, another peer approached him and said: "We've got rid of Saddam Hussein now. Your lot are next." When asked what she meant by "your lot," she replied: "Yes, you cannot go on killing Palestinians forever, you know." <ref name=APP17>{{PDFlink|}}, September 2006, p.17.</ref> ], former MP for Bethnal Green and Bow, gave evidence that many of her former constituents told her they could not vote for her because she was funded by the ].<ref name=APP17/> | |||
| A March 2003 report on antisemitism in the ] by ] and ] of the ] identifies anti-globalization rallies as one of the sources of antisemitism on the left.<ref>Bergmann, Werner & Wetzel, Juliane. ])}}, Center for Research on Antisemitism, Technische Universitaet Berlin, March 2003.</ref> | |||
| ===United Nations === | |||
| <blockquote>In the extreme left-wing scene, anti-Semitic remarks were to be found mainly in the context of pro-Palestinian and anti-globalisation rallies and in newspaper articles using anti-Semitic stereotypes in their criticism of Israel. Often this generated a combination of anti-Zionist and anti-American views that formed an important element in the emergence of an anti-Semitic mood in Europe.<ref name=Bergmann /> | |||
| {{Antisemitism}} | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| General-Secretary ] told a June 2004 seminar on anti-Semitism that "t is hard to believe that 60 years after the tragedy of the Holocaust, anti-Semitism is once again rearing its head. But it is clear that we are witnessing an alarming resurgence of these phenomena in new forms and manifestations." <ref name=Annan>]. , ''The UN Chronicle'', accessed March 6, 2006.</ref> He has called the 1975 General Assembly resolution equating Zionism with racism, repealed in 1991, "lamentable," saying that "its negative resonance even today is difficult to overestimate," <ref name=Matas>Matas, David. ''Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism''. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005, pp. 129-144.</ref> | |||
| ], then U.S. Acting Assistant Secretary for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor, told reporters in 2005 that people within the anti-globalization movement have conflated their legitimate concerns "with this idea that Jews run the world and globalization is the fault of Jews."<ref name=Kozak>, U.S. Department of State, January 5, 2005.</ref> He said:<ref name="Kozak" /> | |||
| A number of commentators argue that the ] has condoned anti-Semitism.<ref>, UN Watch, February 1998 (originally published December 1997), accessed March 6, 2005.</ref> ], then-president of ], wrote that the UN's World Conference on Racism failed to condemn human rights abuses in China, Rwanda, or anywhere in the Arab world, while raising Israel's alleged "ethnic cleansing" and "crimes against humanity." <ref>] , September 17, 2002. On the site of ], accessed January 9, 2006.</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>I think one of the disturbing things is that you're starting to see this in some{{spaced ndash}} you know, it's not just sort of right-wing ultranationalist skinhead types. It's now you're getting some fairly otherwise respectable intellectuals that are left of center who are anti-globalization who are starting to let this stuff creep into their rhetoric.</blockquote> | |||
| <blockquote>And that's disturbing because it starts to{{spaced ndash}} it starts to take what is a legitimate issue for debate, anti-globalization or the war in Iraq or any other issue, and when you start turning that into an excuse for saying therefore we should hate Jews, that's where you cross the line, in my view. It's not that you're not entitled to question all those other issues. Of course, those are fair game. But it's the same as saying, you know, you start hating all Muslims because of some policy you don't like by one Muslim country or something.</blockquote> | |||
| === Conflation of globalization, Jews and Israel === | |||
| David Matas, senior counsel to ], has written that the UN is a forum for anti-Semitism. <ref name=Matas/> He argues that statements are made within the UN that would not be tolerated within any democratic parliament, citing the example of the Palestinian representative to the UN ] who, in an echo of the traditional ], claimed in 1997 that Israeli doctors had injected Palestinian children with the ] virus. <ref name=Matas/> Congressman ] told the U.S. ] in 2005 that the commission took "several months to correct in its record a statement by the ]n ambassador that Jews allegedly had killed non-Jewish children to make ] for ]. <ref>, June 17, 2005. Accessed March 6, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ], Professor of European and Jewish History at the ], told ] that globalization has given rise to an ] left that is "viscerally anti-American, anti-capitalist, and hostile to world Jewry."<ref name=Wistrich>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111128132255/http://www.jcpa.org/JCPA/Templates/ShowPage.asp?DRIT=3&DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=111&FID=624&PID=0&IID=636&TTL= |date=2011-11-28 }}, ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', at the ], October 1, 2004.</ref> He argues that the decade that preceded the current increase in antisemitism was one that saw accelerated globalization of the world economy, a process in which the losers included the Arab and Muslim worlds, and who are now the "major consumers of anti-Jewish poison and conspiracy theories that blame everyone except themselves. Israel is only one piece on this chessboard, but it has assumed such inflated importance because it serves a classic anti-Semitic function of being an ']'."<ref name=Wistrich /> | |||
| <!-- Image with inadequate rationale removed: ]'' depicting image of the "]" on cover]] --> | |||
| As an example of the alleged ] of globalization, the U.S. and Israel, ], editor and publisher of '']'' and adjunct professor at ], cited ], a French anti-globalization activist and leader of the ''Confédération Paysanne''.<ref name=RothFrance> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121119110757/http://www.tau.ac.il/Anti-Semitism/asw2002-3/france.htm |date=2012-11-19 }}, The Stephen Roth Institute for the Study of Antisemitism and Racism, Tel Aviv University, 2003.</ref> Bové led what Joffe calls a "deconstructionist mob" against ] to protest against its effects on French cuisine, later turning up in ] to denounce Israel and announce his support for ]. "Arafat's cause was Bové's cause ... here was a spokesman for the anti-globalization movement who was conflating globalization with ] and extending his loathing of both to Israel."<ref name=Joffe9>]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060909045833/http://sicsa.huji.ac.il/ppjoffe.pdf |date=2006-09-09 }}, Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2004, p.9.</ref> Joffe argues that ''Kapitalismuskritik'' is a "mainstay of the antisemitic faith, a charge that has passed smoothly from Jews to America. Like Jews, Americans are money-grubbers who know only the value of money, and the worth of nothing. Like Jews, they seek to reduce all relationships to exchange and money. Like them, Americans are motivated only by profit, and so they respect no tradition."<ref name=Joffe12>]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060909045833/http://sicsa.huji.ac.il/ppjoffe.pdf |date=2006-09-09 }}, Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2004, p.12.</ref> | |||
| ], writing in '']'', argues against this that "instances of anti-capitalism spilling into 'rich Jew' bigotry are ... well documented" but "stand out precisely because they conflict so sharply with the Left's universalism and its opposition to ethnic discrimination".<ref name=Clark>]. , ''The Guardian'', March 6, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ], a Canadian legal scholar who addressed the UN about its treatment of Israel, argues that the UN hijacks the language of human rights to discriminate and demonize Jews. She writes that over one quarter of the resolutions condemning a state's human rights violations have been directed at Israel. "But there has never been a single resolution about the decades-long repression of the civil and political rights of 1.3 billion people in ], or the million female migrant workers in ] kept as virtual slaves, or the virulent racism which has brought 600,000 people to the brink of starvation in ]." <ref>]. , '']'', June 21, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006.</ref> In the early years of its existence, she writes, the Human Rights Commission focused only on themes. When it shifted its focus to countries, it targeted only ] and Israel, and for six years, from 1969 until 1975, those two countries were the only two the Commission would consider. For the last 40 years, almost 30 percent of country-specific resolutions and 15 percent of the Commission's time has been directed against Israel. <ref>]. "The UN and the Jews", ''Commentary Magazine'', February 2004 </ref> During its annual six-week session in 2002, the Commission spent half its time on Israel, more than it spent on all the other countries in the world combined. <ref name=Matas/> | |||
| In early 2004, ], author of "Culture Jam" and founder of '']'', two influential and widely read anti-globalization texts, generated controversy when he wrote an editorial entitled "Why won't anyone say they are Jewish?".<ref name=Lasn>]. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090614072646/http://canadiancoalition.com/adbusters01/ |date=2009-06-14 }} ] Magazine, March/April 2004</ref> In it he stated "Drawing attention to the Jewishness of the neocons is a tricky game. Anyone who does so can count on automatically being smeared as an anti-Semite. But the point is not that Jews (who make up less than 2 percent of the American population) have a monolithic perspective. Indeed, American Jews overwhelmingly vote Democrat and many of them disagree strongly with Ariel Sharon's policies and Bush's aggression in Iraq. The point is simply that the neocons seem to have a special affinity for Israel that influences their political thinking and consequently American foreign policy in the Middle East."<ref name=Lasn /> The editorial suggested that Jews represent a disproportionately high percentage of the ] who control American foreign policy, and that this may affect policy with respect to Israel.<ref name="Raynes=Goldie">Raynes-Goldie, Kate. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071018003106/http://nowtoronto.com/issues/2004-03-18/news_story6.php |date=2007-10-18 }}, ''Nowtoronto.com'', March 18, 2004 – March 24, 2004.</ref> Lasn included a list of influential neo-conservatives, with dots next to the names of those who were Jewish.<ref name=Lasn /> | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| The U.S. ]'s 2004 '']'' identified four sources of rising anti-Semitism, particularly in Europe: | |||
| * "Traditional anti-Jewish prejudice ... This includes ultra-nationalists and others who assert that the Jewish community controls governments, the media, international business, and the financial world." | |||
| * "Strong anti-Israel sentiment that crosses the line between objective criticism of Israeli policies and anti-Semitism." | |||
| * "Anti-Jewish sentiment expressed by some in Europe's growing Muslim population, based on longstanding antipathy toward both Israel and Jews, as well as Muslim opposition to developments in Israel and the occupied territories, and more recently in Iraq." | |||
| * "Criticism of both the United States and globalization that spills over to Israel, and to Jews in general who are identified with both." <ref name="State-1"/> | |||
| Lasn was criticized by a number of anti-globalization activists. Klaus Jahn, professor of the philosophy of history at the ] condemned Lasn's article stating "Whether listing physicians who perform abortions in ] tracts, gays and lesbians in office memos, Communists in government and the entertainment industry ], Jews in Central Europe under Nazism and so on, such list-making has always produced pernicious consequences."<ref name=RaynesGoldie>Raynes-Goldie, Kate, " {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071018003106/http://nowtoronto.com/issues/2004-03-18/news_story6.php |date=2007-10-18 }}", '']'', March 18024, 2004</ref> | |||
| ====Yale University==== | |||
| ] and ] of ] conducted a study based on a survey of 5,000 people: 500 citizens in each of 10 European countries. Their report, published in August 2006, concluded that anti-Israel sentiment reliably predicted the probability that an individual was an anti-Semite, with the likelihood of measured anti-Semitism increasing with the extent of anti-Israel sentiment observed. The authors write that, based on their analysis, "when an individual's criticism of Israel becomes sufficiently severe, it does become reasonable to ask whether such criticism is a mask for underlying anti-Semitism." <ref name=KaplanSmall>] & ] {{PDFlink|}}, ''Journal of Conflict Resolution'', Vol 50, No. 4, 548-561, August 2006.</ref> | |||
| Meredith Warren, a Montreal anti-globalization activist responded to the article by saying "The U.S. government has only an economic interest in having control over that region. It wants oil and stability – it has nothing to do with Jews or Judaism. Pointing out the various religious stances of those in power totally misses the point of the U.S. government's interest in Israel."<ref name=RaynesGoldie /> | |||
| The study found that 56 percent of those who voiced strong anti-Israel opinions held anti-Semitic views. Those who believed the ] "intentionally targets Palestinian civilians" and that Palestinian suicide bombers who target Israeli civilians are "justified" also believed that "Jews don't care what happens to anyone but their own kind," "Jews have a lot of irritating faults" and "Jews are more willing than others to use shady practices to get what they want." <ref name=CongerYale>] & ] {{PDFlink|}}, ''Journal of Conflict Resolution'', Vol 50, No. 4, 548-561, August 2006, cited in Conger, George. , ''The Jerusalem Post'', September 5, 2006.</ref> Of those who were the most negative about Israel, "some 60% also believed that Jews engaged in shady financial practices, and more than 70% thought that Jews had too much business power." <ref name=opinionjournal>], , Opinion Journal from the ].</ref> | |||
| === Controversy over alleged antisemitism within the French movement === | |||
| The percentage of those expressing anti-Semitic views increased with age and decreased with income level; men were more likely to be anti-Semitic than women; the degree of social interaction with Jews had no significant impact; individuals who were less tolerant of illegal immigrants were more likely to express anti-Semitic views; and Muslims were disproportionately more likely to hold anti-Semitic views than Christians, Jews, or those with no religious beliefs. <ref name=CongerYale/> | |||
| {{See also|Red–green–brown alliance}} | |||
| According to a report by the ], a major event for the anti-globalization movement in France was the European Social Forum (ESF) in Paris in November 2003. The organizers allegedly included a number of Islamic groups, such as ''Présence Musulmane'', ''Secours Islamique'', and ''Collectif des Musulmans de France''. ], the grandson of ], the Egyptian founder of the ], also attended meetings. A few weeks earlier, Ramadan had published a controversial article on a website{{spaced ndash}} after ''Le Monde'' and ''Le Figaro'' refused to publish it{{spaced ndash}} criticizing several French intellectuals, who according to the institute, were either Jewish or "others he mistakenly thought were Jewish," for having "supposedly betrayed their universalist beliefs in favor of unconditional support for Zionism and Israel."<ref name=RothFrance /> | |||
| ], one of the intellectuals who was criticized, called on the French anti-globalization movement to distance itself from Ramadan. In an interview with ''Le Monde'', Lévy said: "Mr. Ramadan, dear anti-globalizationist friends, is not and cannot be one of yours. ... I call you on you quickly to distance yourselves from this character who, in crediting the idea of an elitist conspiracy under the control of Zionism, is only inflaming people's thoughts and opening the way to the worst."<ref name=Monnot>Monnot, Caroline & Ternisien, Xavier. Caroline Monnot and Xavier Ternisien. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081005200850/http://watch.windsofchange.net/themes_67.htm |date=2008-10-05 }}, ''Le Monde'', October 10, 2003.</ref> | |||
| In September 2006, Yale announced that it had established the Yale Initiative for Interdisciplinary Study of Antisemitism, <ref></ref> the first university-based institute in North America dedicated to the study of anti-Semitism. Charles Small, who will head the institute, said in a press release that anti-Semitism has "reemerged internationally in a manner that many leading scholars and policy makers take seriously ... Increasingly, Jewish communities around the world feel under threat. It's almost like going back into the lab. I think we need to understand the current manifestation of this disease." <ref>, ''Associated Press'', September 19, 2006.</ref> | |||
| ''Le Monde'' reported that many members of the anti-globalization movement in France agreed that Ramadan's article "has no place on a European Social Forum mailing list."<ref name=Monnot /> | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | |||
| <references/> | |||
| </div> | |||
| Other activists defended Ramadan. One activist told the newspaper that "ne of the characteristics of the European Social Forum is the stark rise in immigrant and Muslim organizations. It is an important phenomenon and a positive one in many ways."<ref name=Monnot /> Another activist, Peter Khalfa, said: "Ramadan's essay is not anti-Semitic. It is dangerous to wave the red flag of anti-Semitism at any moment. However, it is a text marked partly by Ramadan's communitarian thought and which communicates his view of the world to others."<ref name=Monnot /> One of the leaders of the anti-globalization movement in France, José Bové of the ''Confédération Paysanne'', told ''Le Monde'': "The anti-globalization movement defends universalist points of view which are therefore necessarily secular in their political expression. That there should be people of different cultures and religions is only natural. The whole effort is to escape such determinisms."<ref name=Monnot /> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Jew}} | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| *]. , ''Counterpunch'', March 4, 2004. | |||
| *Asserson, Trevor & Williams, Cassie. , BBC Watch, retrieved August 20, 2006. | |||
| *Barkun, Michael. ''A Culture of Conspiracy'', University of California Press, 2003; this edition 2006 | |||
| *]. {{PDFlink|}}, 2003, retrieved April 22, 2006. | |||
| *Baxter, Sarah. , ''The Sunday Times'', August 13, 2006. | |||
| *]. "One Small Step," ''Wall Street Journal'', June 21, 2004. | |||
| *]. "The UN and the Jews", ''Commentary Magazine'', February 2004. | |||
| *Beaumont, Peter. , '"The Observer, February 17, 2002. | |||
| *Berger, Luciana. , ''The Guardian'' , April 15, 2005 | |||
| *]. , ''New Internationalist'', October 2004. | |||
| *]. , ''Publiceye.org'', December 20, 1990; revised February 22, 1994, revised again 1999. | |||
| *Berlin, Howard. , NewsJournal, March 8, 2004. | |||
| *Booth, Jenny. , ''The Times'', May 11, 2005. | |||
| *Bryant, Elizabeth. "France stung by new report on anti-Semitism," United Press International, October 20, 2004. | |||
| *] ''The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It'', Jossey-Bass, 2003. ISBN 0-7879-7803-5 | |||
| *]. , accessed January 9, 2006. | |||
| *Cooper, Abraham. ]' and Conjures Up 'Blood Libel' Canard"], January 30, 2003. | |||
| *Conger, George. , ''The Jerusalem Post'', September 5, 2006. | |||
| *]. , ''FrontPageMagazine.com'', February 16, 2004. | |||
| *Curtis, Polly. , '']'', April 12, 2005. | |||
| *]. ''The Case For Israel'', John Wiley & Sons, 2003, paperback 2004. ISBN 0-471-67952-6 | |||
| *Doward, Jamie. , ''The Guardian'', August 8, 2004. | |||
| *Dickter, Adam. , ''World Jewish Review'', July 2002. | |||
| *]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005. | |||
| *]. "The View from Ground Zero," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| *]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History''. Berkley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2005. | |||
| *]. , ''The Virginia Quarterly Review'', Summer 2005, pp. 225-234. | |||
| *]. ''Antisemitism resurfaces'', ''Midstream'', February 1, 2004. | |||
| *]. , ''The Forward'', March 29, 2002. | |||
| *Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974. ISBN 0-07-021615-0 | |||
| *]. ''Never Again? The Threat of the New Anti-Semitism''. Harper, 2003. | |||
| *]. , ''Jewish Political Studies Review'' 15:3-4 (Fall 2003). | |||
| *]. "Anti-Semitic Motifs in Anti-Israelism," ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', no. 2, 1 November 2002. | |||
| *]. "The Rough Beast Returns" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| *Goldenberg, Suzanne. , ''The Guardian'', July 8, 2002. | |||
| *Gross, Tom. "Jeningrad: What the British Media Said," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| *HaLevi, Ezra. , ''Arutz Sheva'', November 29, 2005. | |||
| *] & ] "Anti-Israel sentiment predicts anti-Semitism in Europe," ''Journal of Conflict Resolution'', Vol 50, No. 4, 548-561, August 2006. | |||
| *]. , accessed March 5, 2006. | |||
| *]. . '']'', posted January 15, 2004; February 2, 2004 issue. | |||
| *]. , ''Red Pepper'', November 24, 2005. | |||
| *] & ] , International Center for the Study of Anti-Semitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, retrieved September 8, 2006. | |||
| *]. , ], March 17, 2006. | |||
| *]. "A boycott all the way", ''Ha'aretz'', May 17, 2005. | |||
| *Lazare, Daniel. , ''The Nation'', December 19, 2005. | |||
| *]. , ''The American Scholar'', Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25-36. The paper is based on a lecture delivered at ] on ], ]. | |||
| *]. , ''The Guardian'', July 17, 2002. | |||
| *]. ''Denying the Holocaust: The Growing Assault on Truth and Memory''. Penguin 1994. | |||
| *Matas, David. Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005, pp. 129-144. ISBN 1-55002-553-8 | |||
| *] & ]. ''Why the Jews? The Reasons for Antisemitism''. Simon & Schuster, 2003. | |||
| *]. ''The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right''. University Press of Kansas, 2006. ISBN 0-7006-1444-3 | |||
| *Morse, Jane A. , September 14, 2001. | |||
| *Paz, Reuven. , Washington Institute Peace Watch, No. 255, April 21, 2000. | |||
| *Reeves, Phil. "Amid the ruins, the grisly evidence of a war crime," ''The Independent'', April 16, 2002. | |||
| *] & Simmonds, Florence. ''Orpheus: A General History of Religions'', G. P. Putnam & Sons, 1909, p. 210. | |||
| *Rosenbaum, Ron. (ed) ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004. ISBN 0-8129-7203-1 | |||
| *Rubin, Daniel. (ed.) ''Anti-Semitism and Zionism: Selected Marxist Writings''. International Publishers, 1987, p. 35. | |||
| *]. ''Chantier sur la lutte contre le racisms et l'antisemitisme'', Ministry of the Interior, France. October 19, 2004. | |||
| *]. , Ha'aretz, September 6, 2002. | |||
| *]. "A Desolation and They Called It Peace," in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| *Schoenfeld, Gabriel. ''The Return of Anti-Semitism''. Encounter Books, 2004. | |||
| *]. , ''Jerusalem Post'', February 23, 2004. | |||
| *Schwarz, Solomon M. "The New Anti-Semitism of the Soviet Union," ''Commentary'', June 1949.*]. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| *] , Harvard University, September 17, 2002. | |||
| *]. ''Rising From the Muck : The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2002. ISBN 1-56663-571-3 (published in France as ''La nouvelle judéophobie''. Editions mille et une nuits. ISBN 2-84205-650-7). | |||
| *Temko, Ned. , ''The Observer'', February 3, 2006. | |||
| *Wiener, Jon. , ''The Nation'', July 11, 2005. | |||
| *]. , lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the ], December 10, 1984. | |||
| *] ''Antisemitism: The Longest Hatred''. Pantheon Books, 1992. | |||
| *] {{PDFlink|}}, '']'', Number 72, Summer 2003. | |||
| *] {{PDFlink|}}, American Jewish Committee, 2005. | |||
| *Wurmbrand, Max & ]. ''The Jewish People: 4000 Years of Survival'', p.403 and ''passim''. Massadah-P. E. C. Press, 1966. | |||
| *Zipperstein, Steven J. "Historical Reflections on Contemporary Antisemitism", in Derek J. Penslar et al, ed., ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World'', Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005. | |||
| *Zoloth, Laurie. "Fear and Loathing at San Francisco State" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| *Zwartz, Barney & Morton, Adam. , ''The Age'', September 4, 2006. | |||
| *{{PDFlink|}}, European Union, 2004. | |||
| *2004 ] Antisemitic Incidents Report. | |||
| *, BBC News, December 14, 2004. | |||
| *, posted April 29, 2004. U.S. Department of State. | |||
| *, London, March 29, 2006. | |||
| *, interview with ] on Syrian television, the Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI), November 25, 2005. Clip of the interview and of Duke's speech to a Syrian rally can be viewed . | |||
| *"The Architecture of Bigotry," ''Policy Dispatch'', no. 80, Institute of the World Jewish Congress, June 2002. | |||
| *, CAMERA, July 26, 2004. | |||
| *, ''World Net Daily'', December 3, 2002. | |||
| *, retrieved September 6, 2006. | |||
| *{{PDFlink|}}, September 7, 2006. | |||
| </div> | |||
| === Concern within the political left === | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| ], a Jewish Canadian writer and activist in the anti-globalization movement, expressed concern in 2002 at finding antisemitic rhetoric on some activist websites that she had visited: "I couldn't help thinking about all the recent events I've been to where ] violence was rightly condemned, but no mention was made of attacks on Jewish synagogues, cemeteries, and community centers."<ref name=Klein>{{cite news |last1=Klein |first1=Naomi |title=Sharon's Best Weapon: The left must confront anti-Semitism head-on |url=http://www.inthesetimes.com/issue/26/13/feature2.shtml |date=April 26, 2002 |work=In These Times |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060822075533/https://inthesetimes.com/issue/26/13/feature2.shtml |archive-date=August 22, 2006}}</ref> Klein urged activists to confront antisemitism as part of their work for social justice. She also suggested that allegations of antisemitism can be often politically motivated, and that activists should avoid political simplifications that could be perceived as antisemitic:<ref name="Klein" /> | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <blockquote>The globalization movement isn't anti-Semitic, it just hasn't fully confronted the implications of diving into the ] conflict. Most people on the left are simply choosing sides. In the Middle East, where one side is under occupation and the other has the U.S. military behind it, the choice seems clear. But it is possible to criticize Israel while forcefully condemning the rise of anti-Semitism. And it is equally possible to be pro-Palestinian independence without adopting a simplistic pro-Palestinian/anti-Israel dichotomy, a mirror image of the ] equations so beloved by President ]. | |||
| *]. , ''The Observer'', June 22, 2003. | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| *Abram, Morris B. | |||
| *Arenson, David & Grynberg, Simon. . | |||
| In October 2004, the '']'' magazine published a special issue covering the insertion of antisemitic rhetoric into some progressive debates.<ref name=internationalist>, ''New Internationalist'', October 2004.</ref> Adam Ma'anit wrote:<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Ma'anit |first=Adam |title=A human balance |url=http://newint.org/features/2004/10/01/keynote/ |date=October 2004 |magazine=New Internationalist |issue=372 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150502022403/http://newint.org/features/2004/10/01/keynote/ |archive-date=May 2, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| *]. , ''Gush Shalom''. | |||
| <blockquote>Take ''Adbusters'' magazine's founder Kalle Lasn's recent editorial rant against Jewish neoconservatives.{{nbsp}}... The article includes a self-selected 'well-researched list' of 50 of the supposedly most influential 'neocons' with little black dots next to all those who are Jewish.{{nbsp}}... If it's not the neocons then it's the all-powerful 'Jewish lobby' which holds governments to ransom all over the world (because Jews control the global economy of course) to do their bidding. Meanwhile, rightwing Judeophobes often talk of a leftist Jewish conspiracy to promote equality and human rights through a new internationalism embodied in the UN in order to control governments and suppress national sovereignty. They call it the 'New World Order' or the 'Jew World Order'. They make similar lists to Lasn's of prominent Jews in the global justice movement (Noam Chomsky, Naomi Klein, etc.) to argue their case.</blockquote> | |||
| *Bergmann, Werner & Wetzel, Julie. {{PDFlink|}}, Berlin Research Centre on Anti-Semitism, Berlin Technical University. | |||
| *Bourne, Jenny. , ''Race and Class'', Vol. 46, 2004. | |||
| The issue observes, however, that "While antisemitism is rife in the Arab World, the Israeli Government often uses it as moral justification for its policies."<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Agbarieh |first=Asma |title=Spreading the Stain |url=http://newint.org/features/2004/10/01/arab-antisemitism/ |date=October 2004 |magazine=] |issue=372 }}</ref> | |||
| *]. , ''The Guardian'', December 6, 2003. | |||
| *Chittenden, Maurice. , ''The Sunday Times'', April 17, 2005 | |||
| '''<big>Antisemitism during the Israel-Hamas War</big>''' | |||
| *]. ''New Statesman'', October 10, 2005. | |||
| *]. , ''The Observer'', April 17, 2005 | |||
| ] increased significantly around the world.<ref name="i380">{{cite web |last=Farivar |first=Masood |date=2023-10-11 |title=Antisemitism Surges Around World as Israel, Hamas Clash |url=https://www.voanews.com/a/antisemitism-surges-around-world-as-israel-hamas-clash/7306956.html |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=Voice of America}}</ref><ref name="i731">{{cite web |date=2023-10-15 |title=Israel-Hamas war unleashes wave of antisemitism in Europe |url=https://www.ft.com/content/ed744535-d04f-4519-ac27-2be077cac912 |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=Financial Times}}</ref><ref name="h429">{{cite web |last=Chrisafis |first=Angelique |last2=Kassam |first2=Ashifa |last3=Connolly |first3=Kate |last4=Giuffrida |first4=Angela |date=2023-10-20 |title=‘A lot of pain’: Europe’s Jews fear rising antisemitism after Hamas attack |url=https://www.theguardian.com/news/2023/oct/20/a-lot-of-pain-europes-jews-fear-rising-antisemitism-after-hamas-attack |access-date=2024-11-17 |website=the Guardian}}</ref> | |||
| *]. , ], September 25, 2006. | |||
| *]. , Jewish People Policy Planning Institute, November 2002. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| *Curthoys, Ned. "A new anti-Semitism: American discourse since September 11 has seen a reinvention of the eternal anti-semitism thesis applied to critics of Israel," ''Arena Magazine'', April 1, 2004. | |||
| *Dinnerstein, Leonard. "Is There a New Anti-Semitism in the United States?" ''Society'', 41 (January/February 2004), 53-58. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *]. , an interview with ], ], October 1, 2004. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *]. , ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', No. 21, ], June 1, 2004. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *]. ''Europe’s Crumbling Myths: The Post-Holocaust Origins of Today’s Anti-Semitism'', ]/]/], 2003. ISBN 965-218-045-9 | |||
| * ] | |||
| *Gordon, Neve. "Seeing through the 'new anti-Semitism': Norman Finkelstein critiques Israel's human rights record and Alan Dershowitz's defense of it," ''National Catholic Reporter'', October 14, 2005. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *Grant, Linda. , ''The Guardian'', December 18, 2001. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *Greenspan, Miriam. (Nov-Dec 2003). "The New Anti-Semitism". '']'' '''18''':6. p. 33. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *]. , ''Ha'aretz'', April 4, 2004. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *Glazov, Jamie. , ''FrontPageMagazine.com'', September 19, 2003 | |||
| *Horowitz, Craig. , ''New York Magazine''. | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| *Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) ''New European Extremism: Hating America, Israel and the Jews''. Profile Books Limited, 2006. ISBN 1-86197-792-1 | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| *Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) ''A New Antisemitism? Debating Judeophobia in 21st Century Britain'', Profile Books Limited, 2003. ISBN 1-86197-651-8 | |||
| *]. , ''National Post'', October 27, 2003. | |||
| == References == | |||
| *]. , Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, 2004. | |||
| {{refbegin|2}} | |||
| *Kite, Melissa. , ''The Telegraph'', April 17, 2005. | |||
| * Asserson, Trevor & Williams, Cassie. , BBC Watch, retrieved August 20, 2006. | |||
| *]. , May 2, 2002. | |||
| * Barkun, Michael. ''A Culture of Conspiracy'', University of California Press, 2003; this edition 2006 | |||
| *]. "The collective Jew: Israel and the new antisemitism," used as a resource by the EUMC in their report ''Manifestations of Antisemitism in the EU 2002-2003'', Vienna, March 2004. See especially pp. 12-13, 225-241. | |||
| * ]. {{Cite web |url=http://humanities.ucsc.edu/JewishStudies/docs/YBauerLecture.pdf |title=Problems of Contemporary Anti-Semitism |access-date=January 11, 2008 |archive-date=July 5, 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030705131522/http://humanities.ucsc.edu/JewishStudies/docs/YBauerLecture.pdf |url-status=dead }}, lecture to the Jewish Studies Dept of the ], 2003, retrieved April 22, 2006. | |||
| *]. "Muslim Anti-Semitism" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past'', Random House, 2003. pp. 549-62. | |||
| * Baxter, Sarah. {{dead link|date=September 2024|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}, ''The Sunday Times'', August 13, 2006, retrieved January 13, 2008. | |||
| *Lopez, Kathryn Jean. , ''National Review Online'', November 25, 2003. | |||
| *]. , '' |
* ]. , '']'', June 21, 2004, retrieved January 9, 2006. | ||
| * |
* Beaumont, Peter. , '"The Observer, February 17, 2002, retrieved January 13, 2008. | ||
| * ]. , ''New Internationalist'', October 2004. | |||
| *Minerbi, Sergio I. , Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, Fall 2003. | |||
| * ]. , ''Publiceye.org'', December 20, 1990; revised February 22, 1994, revised again 1999. | |||
| *Nirenstein, Fiamma. ''Terror: The New Anti-Semitism And The War Against The West'', 2005. ISBN 1-57525-377-1 | |||
| * Booth, Jenny. , ''The Times'', May 11, 2005. | |||
| *Pfeifer, Karl. , ]. | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| *]. . | |||
| |title = Anti-Semitism: Its Changing Meaning | |||
| *Rosenblum, April. . | |||
| |last = Brownfeld | |||
| *Rosenthal, John. , ''Policy Review Online'', retrieved August 29, 2006. | |||
| |first = Allan | |||
| *]. , June 2002. | |||
| |journal = ] | |||
| *]. . | |||
| |publisher = ] | |||
| *]. , '']'', November 2003. | |||
| |issn = 1533-8614 | |||
| *]. , January 1, 2002. | |||
| |volume = 16 | |||
| *Smith, Lewis. , ''The Times'', April 18, 2005 | |||
| |issue = 3 | |||
| *Yemini, Ben Dror. . | |||
| |year = 1987 | |||
| *] , ''US News and World Report'', March 11, 2003. | |||
| |pages = 53–67 | |||
| *, "Make your point", Haaretz, July 18, 2004. | |||
| |doi = 10.2307/2536789 | |||
| *, American Jewish Committee. | |||
| |jstor = 2536789 | |||
| *, Christian Action for Israel. | |||
| }} | |||
| *, CTV News, March 6, 2003. | |||
| * Bryant, Elizabeth. "France stung by new report on anti-Semitism," United Press International, October 20, 2004. | |||
| *, BeitShalom.org | |||
| * Chanes, Jerome. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111128080506/http://www.jcpa.org/JCPA/Templates/ShowPage.asp?DRIT=5&DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=111&FID=624&PID=0&IID=1094&TTL=Review_Essay%3A_What%27s_ |date=2011-11-28 }}, ''Jewish Political Studies Review'' 16:1–2 (Spring 2004). | |||
| *, ], retrieved September 7, 2006. | |||
| * ] ''The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It'', Jossey-Bass, 2003. {{ISBN|0-7879-7803-5}} | |||
| * | |||
| * Conger, George. {{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}, ''The Jerusalem Post'', September 5, 2006. | |||
| *, Department for Jewish Zionist Education, The Jewish Agency for Israel. | |||
| * Curtis, Polly. , '']'', April 12, 2005. | |||
| * ]. ''The Case For Israel'', John Wiley & Sons, 2003, paperback 2004. {{ISBN|0-471-67952-6}} | |||
| * Doward, Jamie. , ''The Guardian'', August 8, 2004. | |||
| * Dickter, Adam. , ''World Jewish Review'', July 2002. | |||
| * ]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005. | |||
| * ]. ''Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History''. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2005. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Virginia Quarterly Review'', Summer 2005, pp. 225–234. | |||
| * ]. ''Antisemitism resurfaces'', ''Midstream'', February 1, 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Forward'', March 29, 2002. | |||
| * Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974. {{ISBN|0-07-021615-0}} | |||
| * ] ''Never Again? The Threat of the New Anti-Semitism''. New York: HarperSanFrancisco (an imprint of ]), 2003. {{ISBN|0-06-054246-2}} (10); {{ISBN|978-0-06-054246-7}} (13). | |||
| * Goodman, Amy. , interview with Norman Finkelstein, August 29, 2006. | |||
| * Harrison, Bernard. ''The Resurgence of Anti-Semitism: Jews, Israel, and Liberal Opinion''. Rowman & Littlefield, 2006. 0742552276 | |||
| * HaLevi, Ezra. , ''Arutz Sheva'', November 29, 2005; see clip of . | |||
| * ]. "The Return of Anti-Semitism," ''Commentary'', February 2002 | |||
| * Hodgson, Jessica. , ''The Guardian'', February 7, 2002. | |||
| * Ioanid, Radu. Foreword in ]. ''Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004. | |||
| * Jaffe, Ben-Zion. , ''] Blog Central'', December 11, 2005. | |||
| * ] & ] "Anti-Israel sentiment predicts anti-Semitism in Europe," ''Journal of Conflict Resolution'', Vol 50, No. 4, 548–561, August 2006. | |||
| * ]. , retrieved March 5, 2006. | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20090701082702/http://www.thenation.com/doc.mhtml?i=20040202&s=klug |date=2009-07-01 }}. '']'', posted January 15, 2004; February 2, 2004 issue. | |||
| * ]. , ''Red Pepper'', November 24, 2005. | |||
| * ]. , ], March 17, 2006. | |||
| * ]. , Augean Stables, February 5, 2007. | |||
| * Lazare, Daniel. , ''The Nation'', December 19, 2005. | |||
| * Lerman, Tony. , ''The Guardian: Comment is Free'', February 6, 2007, retrieved August 11, 2007. | |||
| * ]. , posted February 5, 2007, retrieved February 6, 2007. | |||
| * ]. , ''The American Scholar'', Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25–36. The paper is based on a lecture delivered at ] on March 24, 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Guardian'', July 17, 2002. | |||
| * ]. ''Denying the Holocaust: The Growing Assault on Truth and Memory''. Penguin 1994. | |||
| * ], ''Jurisprudence of the New Anti-Semitism,'' Wake Forest Law Review, Vol. 44, 2009. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1376592 | |||
| * Matas, David. ''Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism''. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005. {{ISBN|1-55002-553-8}} | |||
| * ] & ]. ''Why the Jews? The Reasons for Antisemitism''. Simon & Schuster, 2003. | |||
| * ]. ''The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right''. University Press of Kansas, 2006. {{ISBN|0-7006-1444-3}} | |||
| * Moormeister, Robyn. , '']'', May 2, 2003. | |||
| * Morse, Jane A. , September 14, 2001. | |||
| * Paz, Reuven. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071209053826/http://ict.org.il/articles/hamas_holocaust.htm |date=2007-12-09 }}, Washington Institute Peace Watch, No. 255, April 21, 2000. | |||
| * Raab, Earl. "Is there a New Anti-Semitism?", ''Commentary'', May 1974, pp. 53–54. | |||
| * Raab, Earl. , ''Judaism'', Fall 2002. | |||
| * Radler, Melissa. "Anti-Semitic riot at San Francisco State University," ''The Jerusalem Post'', May 16, 2002. | |||
| * Reeves, Phil. "Amid the ruins, the grisly evidence of a war crime," ''The Independent'', April 16, 2002. | |||
| * ] & Simmonds, Florence. ''Orpheus: A General History of Religions'', G. P. Putnam & Sons, 1909. | |||
| * Rosenbaum, Ron. (ed) ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004. {{ISBN|0-8129-7203-1}} | |||
| * Rubin, Daniel. (ed.) ''Anti-Semitism and Zionism: Selected Marxist Writings''. International Publishers, 1987, p. 35. | |||
| * ]. ''Chantier sur la lutte contre le racisms et l'antisemitisme'', Ministry of the Interior, France. October 19, 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''Ha'aretz'', September 6, 2002. | |||
| * ]. "A Desolation and They Called It Peace," in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| * Schoenfeld, Gabriel. ''The Return of Anti-Semitism''. Encounter Books, 2004. | |||
| * Sewell, Dennis. , ''New Statesman'', January 14, 2002. | |||
| * ]. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| * Stillwell, Cinnamon. , ''San Francisco Chronicle'', December 14, 2004, retrieved January 12, 2008. | |||
| * Strauss, Mark. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| * ] , September 17, 2002, retrieved January 9, 2006. | |||
| * ]. ''Rising From the Muck : The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2002. {{ISBN|1-56663-571-3}} (published in France as ''La nouvelle judéophobie''. Editions mille et une nuits. {{ISBN|2-84205-650-7}}). | |||
| * Temko, Ned. , ''The Observer'', February 3, 2006. | |||
| * Whine, Michael. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220226131202/https://www.jcpa.org/phas/phas-041-whine.htm |date=2022-02-26 }}, ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, February 1, 2006. | |||
| * Wiener, Jon. , ''The Nation'', July 11, 2005. | |||
| * Wilby, Peter. ''The New Statesman.'' February 11, 2002, retrieved February 8, 2008. | |||
| * ]. , lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the ], December 10, 1984. | |||
| * Wurmbrand, Max & ]. ''The Jewish People: 4000 Years of Survival'', p. 403 and ''passim''. Massadah-P. E. C. Press, 1966. | |||
| * Zipperstein, Steven J. "Historical Reflections on Contemporary Antisemitism", in Derek J. Penslar et al., ed., ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005. | |||
| * Zoloth, Laurie. "Fear and Loathing at San Francisco State" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| * Zuckerman, Mortimer B. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220523084726/https://www.jewishworldreview.com/mort/zuckerman_new_anti_sem.php3 |date=2022-05-23 }}, ''U.S. News & World Report''. March 11, 2003, retrieved January 12, 2008. | |||
| * Zwartz, Barney & Morton, Adam. , ''The Age'', September 4, 2006. | |||
| * , European Union, 2004. | |||
| * 2004 ] Antisemitic Incidents Report. | |||
| * , BBC News, December 14, 2004. | |||
| * , posted April 29, 2004. U.S. Department of State. | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080420164234/http://eustonmanifesto.org/joomla/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=12&Itemid=41 |date=2008-04-20 }}, London, March 29, 2006. | |||
| * , interview with ] on Syrian television, the Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI), November 25, 2005. Clip of the interview and of Duke's speech to a Syrian rally can be viewed here . | |||
| * "The Architecture of Bigotry," ''Policy Dispatch'', no. 80, Institute of the World Jewish Congress, June 2002. | |||
| * , CAMERA, July 26, 2004. | |||
| * {{usurped|1=}}, September 7, 2006. | |||
| * , ''Watch'', retrieved August 27, 2006. | |||
| * , ''BackSpin Weblog of ]'', December 4, 2003. | |||
| * , November 10, 1975, retrieved January 13, 2008. | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080420164234/http://eustonmanifesto.org/joomla/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=12&Itemid=41 |date=2008-04-20 }}, March 29, 2006. | |||
| * "(U.S.) State Department report on Anti-Semitism: Europe and Eurasia," December 15, 2004; see Global Anti-Semitism Review Act of 2004. | |||
| * , BBC News, October 2004. | |||
| * , BBC News, September 6, 2006. | |||
| * , June 17, 2005, retrieved March 6, 2006. | |||
| * , EUMC. | |||
| * , ], May 2006. | |||
| * , ''Associated Press'', September 19, 2006. | |||
| * Arnold Forster & Benjamin Epstein, ''The New Anti-Semitism''. McGraw-Hill 1974, p. 165. See for instance chapters entitled "]'s Road" (19–48), "The Radical Right" (285–296), "Arabs and Pro-Arabs" (155–174), "The Radical Left" (125–154). | |||
| * ]. , lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the ], December 10, 1984. | |||
| * ]. ''The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It'', Jossey-Bass, 2003, pp. 158–159, 181. | |||
| * Doward, Jamie. , '']'', August 8, 2004. | |||
| * ]. , accessed March 5, 2006. | |||
| * ]. , Ha'aretz, September 6, 2002, retrieved on January 10, 2007. | |||
| * ]. in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004, p 272. | |||
| * ]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005, pp. 65–79. | |||
| * Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| * Taguieff, Pierre-André. ''Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe''. Ivan R. Dee, 2004. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| {{refbegin|2}} | |||
| * ]. , ''The Observer'', June 22, 2003. | |||
| * Abram, Morris B. | |||
| * Arenson, David & Grynberg, Simon. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040726081359/http://www.aish.com/jewishissues/middleeast/Anti-Globalization_The_New_Anti-Semitism.asp |date=2004-07-26 }}. | |||
| * ]. , ''Gush Shalom''. | |||
| * ]. "The UN and the Jews", ''Commentary Magazine'', February 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Guardian'', April 15, 2005 | |||
| * Bergmann, Werner & Wetzel, Julie. {{cite web |url=http://eumc.eu.int/eumc/material/pub/FT/Draft_anti-Semitism_report-web.pdf |title=Manifestations of Anti-Semitism in the European Union |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050415100309/http://eumc.eu.int/eumc/material/pub/FT/Draft_anti-Semitism_report-web.pdf |archive-date=2005-04-15 }} {{small|(751 KB)}}, Berlin Research Centre on Anti-Semitism, Technische Universität Berlin. | |||
| * Bourne, Jenny. , ''Race and Class'', Vol. 46, 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Guardian'', December 6, 2003. | |||
| * Chittenden, Maurice. , ''The Sunday Times'', April 17, 2005 | |||
| * ]. {{Cite web |url=http://www.zmag.org/chomsky/ni/ni-contents.html |title=''Necessary Illusions'' |access-date=January 9, 2006 |archive-date=September 13, 2002 |archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20020913220833/http://www.zmag.org/chomsky/ni/ni-contents.html |url-status=bot: unknown }}, accessed January 9, 2006. | |||
| * ]. ''Jewish Political Studies Review'' 16:3–4 via the ], Fall 2004. | |||
| * ]. ''New Statesman'', October 10, 2005. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Observer'', April 17, 2005. | |||
| * Cooper, Abraham. , January 30, 2003. | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060825093810/http://www.aish.com/jewishissues/jewishsociety/Identifying_the_New_Anti-Semitism.asp |date=2006-08-25 }}, Jewish People Policy Planning Institute, November 2002. | |||
| * ]. | |||
| * Curthoys, Ned. "A new anti-Semitism: American discourse since September 11 has seen a reinvention of the eternal anti-semitism thesis applied to critics of Israel," ''Arena Magazine'', April 1, 2004. | |||
| * ]. "Is There a New Anti-Semitism in the United States?" ''Society'', 41 (January/February 2004), 53–58. | |||
| * ]. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in ''Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World''. University of Toronto Press, 2005. | |||
| * ]. "The View from Ground Zero," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| * ]. , ''Ha'aretz'', April 4, 2004. | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070929091738/http://www.jcpa.org/JCPA/Templates/ShowPage.asp?DRIT=3&DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=111&FID=388&PID=1666&IID=1673&TTL=Anti-Israelism_and_Anti-Semitism:_Common_Characteristics_and_Motifs |date=2007-09-29 }}''Jewish Political Studies Review 19:1–2'' ], March 1, 2007. | |||
| * ]. , an interview with ], October 1, 2004. | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070929090309/http://www.jcpa.org/JCPA/Templates/ShowPage.asp?DRIT=3&DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=111&FID=253&PID=0&IID=644&TTL=Major_Anti-Semitic_Motifs_in_Arab_Cartoons |date=2007-09-29 }}, ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', No. 21, ], June 1, 2004. | |||
| * ]. ''Europe’s Crumbling Myths: The Post-Holocaust Origins of Today’s Anti-Semitism'', ]/]/], 2003. {{ISBN|965-218-045-9}}. | |||
| * ]. , ''Jewish Political Studies Review'' 15:3–4 (Fall 2003). | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070926214829/http://www.jcpa.org/JCPA/Templates/ShowPage.asp?DRIT=3&DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=111&FID=253&PID=0&IID=648&TTL=Anti-Semitic_Motifs_in_Anti-Israelism |date=2007-09-26 }} ''Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism'', no. 2, 1 November 2002. | |||
| * ]. "The Rough Beast Returns" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past''. Random House, 2004. | |||
| * Goldberg, Sol & Ury, Scott & Weiser, Kalman, eds., Palgrave-Macmillan, 2021. {{ISBN|978-3-030-51658-1}} | |||
| * Goldenberg, Suzanne. , ''The Guardian'', July 8, 2002. | |||
| * Gordon, Neve. "Seeing through the 'new anti-Semitism': Norman Finkelstein critiques Israel's human rights record and Alan Dershowitz's defense of it," ''National Catholic Reporter'', October 14, 2005. | |||
| * Grant, Linda. , ''The Guardian'', December 18, 2001. | |||
| * Greenspan, Miriam. (Nov–Dec 2003). "The New Anti-Semitism". '']'' '''18''':6. p. 33. | |||
| * Gross, Tom. "Jeningrad: What the British Media Said," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). ''Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism'', Random House 2004. | |||
| * Harris, Ben. , JTA, January 23, 2006. | |||
| * Horowitz, Craig. , ''New York Magazine''. | |||
| * | |||
| * Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) ''New European Extremism: Hating America, Israel and the Jews''. Profile Books Limited, 2006. {{ISBN|1-86197-792-1}} | |||
| * Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) ''A New Antisemitism? Debating Judeophobia in 21st Century Britain'', Profile Books Limited, 2003. {{ISBN|1-86197-651-8}} | |||
| * ]. , ''National Post'', October 27, 2003. | |||
| * ]. , Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, 2004. | |||
| * Kaye/Kantrowitz, Melanie. , '']'', March 2007. | |||
| * Kite, Melissa. , ''The Telegraph'', April 17, 2005. | |||
| * ]. "The collective Jew: Israel and the new antisemitism," used as a resource by the EUMC in their report ''Manifestations of Antisemitism in the EU 2002–2003'', Vienna, March 2004. See especially pp. 12–13, 225–241. | |||
| * ] & ] , International Center for the Study of Anti-Semitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, retrieved September 8, 2006. | |||
| * ]. "Muslim Anti-Semitism" in Rosenbaum, Ron. ''Those who forget the past'', Random House, 2003. pp. 549–62. | |||
| * Kuruvila, Matthai Chakko. , ''San Francisco Chronicle'', January 27, 2007. | |||
| * Lappin, Shalom. '''The New Antisemitism''': The Resurgence of an Ancient Hatred in the Modern World, Cambridge : Polity Press, 2024, ISBN 9781509558568. | |||
| * Lopez, Kathryn Jean. , ''National Review Online'', November 25, 2003. | |||
| * ]. , ''The Guardian'', September 7, 2006. | |||
| * McGeal, Chris. , ''The Guardian'', November 25, 2003 | |||
| * Minerbi, Sergio I. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060614043720/http://www.jcpa.org/phas/phas-minerbi-f03.htm |date=2006-06-14 }}, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, Fall 2003. | |||
| * Nirenstein, Fiamma. ''Terror: The New Anti-Semitism And The War Against The West'', 2005. {{ISBN|1-57525-377-1}} | |||
| * ]. , '']'', March 15, 2009. | |||
| * Pfeifer, Karl. , Scholars for Peace in the Middle East. | |||
| * ]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040603172154/http://www.freeman.org/m_online/jan98/pipes.htm |date=2004-06-03 }}. | |||
| * ] '']'' | |||
| * Rosenblum, April. . | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Rosenfeld |editor-first=Alvin H. |editor-link=Alvin Hirsch Rosenfeld |title=Deciphering the New Antisemitism |date=2015 |publisher=] |location=Bloomington, Indianapolis |isbn=9780253018694 |oclc=928716737}} {{Project MUSE|43135}} | |||
| * Rosenthal, John. , ''Policy Review Online'', retrieved August 29, 2006. | |||
| * ]. , June 2002. | |||
| * ]. . | |||
| * ]. , '']'', November 2003. | |||
| * ]. , January 1, 2002. | |||
| * Smith, Lewis. , ''The Times'', April 18, 2005 | |||
| * Ury, Scott. | |||
| * Whine, Michael. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080407072742/http://www.thecst.org.uk/docs/RUSI%20Homeland%20Security.doc |date=2008-04-07 }} (DOC file), Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies. | |||
| * {{Interlanguage link|Guillaume Weill-Raynal|fr|3=Guillaume Weill-Raynal|lt=Weill-Raynal, Guillaume|vertical-align=sup}}, ''Une haine imaginaire : contre-enquête sur le nouvel antisémitisme'' (An imaginary hatred: investigation about the new antisemitism), Paris, Armand Colin, 2005, {{ISBN|2-200-26912-9}}. | |||
| * ] ''Antisemitism: The Longest Hatred''. Pantheon Books, 1992. | |||
| * ] , '']'', Number 72, Summer 2003. | |||
| * ] , American Jewish Committee, 2005. | |||
| * ] "From Ambivalence to Betrayal: The Left, the Jews, and Israel (Studies in Antisemitism)". University of Nebraska Press, 2012 | |||
| * ] , ''U.S. News & World Report'', March 11, 2003. | |||
| * , "Make your point", Haaretz, July 18, 2004. | |||
| * , American Jewish Committee. | |||
| * , Christian Action for Israel. | |||
| * , CTV News, March 6, 2003. | |||
| * , BeitShalom.org | |||
| * , ], retrieved September 7, 2006. | |||
| * | |||
| * , Department for Jewish Zionist Education, The Jewish Agency for Israel. | |||
| '''Reports''' | '''Reports''' | ||
| * From government and inter-governmental sources | * From government and inter-governmental sources | ||
| ** , excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 |
** , excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 – December 15, 2004]. | ||
| ** |
** {{cite web |url=http://eumc.eu.int/eumc/material/pub/FT/Draft_anti-Semitism_report-web.pdf |title=Manifestations of Anti-Semitism in the European Union |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050415100309/http://eumc.eu.int/eumc/material/pub/FT/Draft_anti-Semitism_report-web.pdf |archive-date=2005-04-15 }} {{small|(751 KB)}} Unpublished EU report from 2003 | ||
| ** | ** {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060512013120/http://lesrapports.ladocumentationfrancaise.fr/BRP/054000193/0000.pdf |date=2006-05-12 }} | ||
| * From the ] | * From the ] | ||
| ** , Anti-Defamation League, July 11, 2002 | |||
| **, Anti-Defamation League | |||
| ** based on a . | |||
| **, Anti-Defamation League, July 11, 2002 | |||
| ** . | |||
| ** based on a . | |||
| ** , ], August 22, 2006. | |||
| **. | |||
| *, ], |
** , ], January 28, 2003. | ||
| * From the ] | |||
| *, ], January 28, 2003. | |||
| ** December 21, 2003 | |||
| ** , December 2006 | |||
| * From Zionism on the Web | |||
| ** , June 2006 | |||
| ** The at | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ** | |||
| ** | |||
| == External links == | |||
| '''Organizations that fight anti-Semitism''' | |||
| * an online lecture by Professor David Bankier of ] | |||
| * | |||
| * from the | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Internet Archive film clip|id=openmind_ep399|description="The Open Mind – Anti-Semitism, Part I (1981)"}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Internet Archive film clip|id=openmind_ep400|description="The Open Mind – Anti-Semitism, Part II (1981)"}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Antisemitism topics}} | |||
| {{World topic| prefix= Fascism in |title= ]|noredlinks=yes}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 7 January 2025
New antisemitism is the concept that a new form of antisemitism developed in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, typically manifesting itself as anti-Zionism. The concept is included in some definitions of antisemitism, such as the working definition of antisemitism and the 3D test of antisemitism. The concept dates to the early 1970s.
Proponents of the concept generally posit that in the late 20th and early 21st centuries much of what is purported to be criticism of Israel is in fact tantamount to demonization, and that together with evidence of a resurgence of antisemitic attacks on Jews, desecration of Jewish symbols and Judaism, Holocaust denial, and an increased acceptance of antisemitic beliefs in public discourse and online hate speech, such demonization represents an evolution in the appearance of antisemitic beliefs. Proponents argue that anti-Zionism and demonization of Israel, or double standards applied to its conduct (some also include anti-Americanism, anti-globalization, and Third-Worldism) may be linked to antisemitism, or constitute disguised antisemitism, particularly when emanating simultaneously from the far-left, Islamism, and the far-right.
Critics of the concept argue that it is used in practice to weaponize antisemitism in order to silence political debate and freedom of speech regarding the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict, by conflating political anti-Zionism and criticism of the Israeli government with racism, condoning violence against Jews or likening the Israeli government's actions to the Holocaust. Such arguments have in turn been criticized as antisemitic and rhetorically irrelevant to the contested reality of new antisemitism. Further critical arguments include that the concept defines legitimate criticism of Israel too narrowly and demonization too broadly, and that it trivializes the meaning of antisemitism.
History of the concept
1960s: origins
French philosopher Pierre-André Taguieff argues that the first wave of "la nouvelle judéophobie" emerged in the Arab-Muslim world and the Soviet sphere following the 1967 Six-Day War. He cites papers by Jacques Givet (1968) and historian Léon Poliakov (1969) discussing the idea of a new antisemitism rooted in anti-Zionism. He argues that anti-Jewish themes centered on the demonical figures of Israel and what he calls "fantasy-world Zionism": that Jews plot together, seek to conquer the world, and are imperialistic and bloodthirsty, which gave rise to the reactivation of stories about ritual murder and the poisoning of food and water supplies.
1970s: early debates
Writing in the American Jewish Congress' Congress Bi-Weekly in 1973, the Foreign Minister of Israel Abba Eban identified anti-Zionism as "the new anti-Semitism", saying:
ecently we have witnessed the rise of the new left which identifies Israel with the establishment, with acquisition, with smug satisfaction, with, in fact, all the basic enemies ... Let there be no mistake: the new left is the author and the progenitor of the new anti-Semitism. One of the chief tasks of any dialogue with the Gentile world is to prove that the distinction between anti-Semitism and anti-Zionism is not a distinction at all. Anti-Zionism is merely the new anti-Semitism. The old classic anti-Semitism declared that equal rights belong to all individuals within the society, except the Jews. The new anti-Semitism says that the right to establish and maintain an independent national sovereign state is the prerogative of all nations, so long as they happen not to be Jewish. And when this right is exercised not by the Maldive Islands, not by the state of Gabon, not by Barbados ... but by the oldest and most authentic of all nationhoods, then this is said to be exclusivism, particularism, and a flight of the Jewish people from its universal mission.
In 1974, Arnold Forster and Benjamin Epstein of the Anti-Defamation League published the book The New anti-Semitism. They expressed concern about what they described as new manifestations of antisemitism coming from radical left, radical right, and pro-Arab figures in the U.S. Forster and Epstein argued that it took the form of indifference to the fears of the Jewish people, apathy in dealing with anti-Jewish bias, and an inability to understand the importance of Israel to Jewish survival.
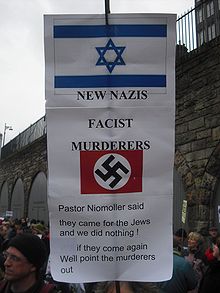
Reviewing Forster and Epstein's work in Commentary, Earl Raab, founding director of the Nathan Perlmutter Institute for Jewish Advocacy at Brandeis University, argued that a "new anti-Semitism" was indeed emerging in America, in the form of opposition to the collective rights of the Jewish people, but he criticized Forster and Epstein for conflating it with anti-Israel bias. Allan Brownfeld wrote in the Journal of Palestine Studies that Forster and Epstein's new definition of antisemitism trivialized the concept by turning it into "a form of political blackmail" and "a weapon with which to silence any criticism of either Israel or U.S. policy in the Middle East," while Edward S. Shapiro, in A Time for Healing: American Jewry Since World War II, has written that "Forster and Epstein implied that the new anti-Semitism was the inability of Gentiles to love Jews and Israel enough."
1980s–present day: continued debate

Historian Robert Wistrich addressed the issue in a 1984 lecture delivered in the home of Israeli President Chaim Herzog, in which he argued that a "new anti-Semitic anti-Zionism" was emerging, distinguishing features of which were the equation of Zionism with Nazism and the belief that Zionists had actively collaborated with Nazis during World War II. He argued that such claims were prevalent in the Soviet Union, but added that similar rhetoric had been taken up by a part of the radical Left, particularly Trotskyist groups in Western Europe and America.
When asked in 2014 if "anti-Zionism is the new anti-Semitism", Noam Chomsky stated:
Actually, the locus classicus, the best formulation of this, was by an ambassador to the United Nations, Abba Eban, ... He advised the American Jewish community that they had two tasks to perform. One task was to show that criticism of the policy, what he called anti-Zionism – that means actually criticisms of the policy of the state of Israel – were anti-Semitism. That's the first task. Second task, if the criticism was made by Jews, their task was to show that it's neurotic self-hatred, needs psychiatric treatment. Then he gave two examples of the latter category. One was I.F. Stone. The other was me. So, we have to be treated for our psychiatric disorders, and non-Jews have to be condemned for anti-Semitism, if they're critical of the state of Israel. That's understandable why Israeli propaganda would take this position. I don't particularly blame Abba Eban for doing what ambassadors are sometimes supposed to do. But we ought to understand that there is no sensible charge. No sensible charge. There's nothing to respond to. It's not a form of anti-Semitism. It's simply criticism of the criminal actions of a state, period.
Definitions and arguments for and against the concept
A new phenomenon
Irwin Cotler, Professor of Law at McGill University and a scholar of human rights, has identified nine aspects of what he considers to constitute the "new anti-Semitism":
- Genocidal antisemitism: calling for the destruction of Israel and/or the Jewish people.
- Political antisemitism: denial of the Jewish people's right to self-determination, de-legitimization of Israel as a state, attributions to Israel of all the world's evils.
- Ideological antisemitism: "Nazifying" Israel by comparing Zionism and racism.
- Theological antisemitism: convergence of Islamic antisemitism and Christian "replacement" theology, drawing on the classical hatred of Jews.
- Cultural antisemitism: the emergence of anti-Israel attitudes, sentiments, and discourse in "fashionable" salon intellectuals.
- Economic antisemitism: BDS movements and the extraterritorial application of restrictive covenants against countries trading with Israel.
- Holocaust denial.
- Anti-Jewish racist terrorism.
- International legal discrimination ("Denial to Israel of equality before the law in the international arena").
Cotler defines "classical or traditional anti-Semitism" as "the discrimination against, denial of or assault upon the rights of Jews to live as equal members of whatever host society they inhabit" and "new anti-Semitism" as "discrimination against the right of the Jewish people to live as an equal member of the family of nations – the denial of and assault upon the Jewish people's right even to live – with Israel as the "collective Jew among the nations."
Cotler elaborated on this position in a June 2011 interview for Israeli television. He re-iterated his view that the world is "witnessing a new and escalating ... and even lethal anti-Semitism" focused on hatred of Israel, but cautioned that this type of antisemitism should not be defined in a way that precludes "free speech" and "rigorous debate" about Israel's activities. Cotler said that it is "too simplistic to say that anti-Zionism, per se, is anti-Semitic" and argued that labelling Israel as an apartheid state, while in his view "distasteful", is "still within the boundaries of argument" and not inherently antisemitic. He continued: "It's you say, because it's an apartheid state, it has to be dismantled – then crossed the line into a racist argument, or an anti-Jewish argument."
Jack Fischel, former chair of history at Millersville University of Pennsylvania, writes that new antisemitism is a new phenomenon stemming from a coalition of "leftists, vociferously opposed to the policies of Israel, and right-wing antisemites, committed to the destruction of Israel, were joined by millions of Muslims, including Arabs, who immigrated to Europe... and who brought with them their hatred of Israel in particular and of Jews in general." It is this new political alignment, he argues, that makes new antisemitism unique. Mark Strauss of Foreign Policy links new antisemitism to anti-globalism, describing it as "the medieval image of the "Christ-killing" Jew resurrected on the editorial pages of cosmopolitan European newspapers."
Rajesh Krishnamachari, researcher with the South Asia Analysis Group, analyzed antisemitism in Iran, Turkey, Palestine, Pakistan, Malaysia, Bangladesh and Saudi Arabia and posited that the recent surge in antisemitism across the Muslim world should be attributed to political expediency of the local elite in these countries rather than to any theological imperative.
It is the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement refusing to put the Star of David on their ambulances. ... It is neo-Nazis donning checkered Palestinian kaffiyehs and Palestinians lining up to buy copies of Mein Kampf. —Mark Strauss
The French philosopher Pierre-André Taguieff argues that antisemitism based on racism and nationalism has been replaced by a new form based on anti-racism and anti-nationalism. He identifies some of its main features as the identification of Zionism with racism; the use of material related to Holocaust denial (such as doubts about the number of victims and allegations that there is a "Holocaust industry"); a discourse borrowed from third worldism, anti-imperialism, anti-colonialism, anti-Americanism and anti-globalization; and the dissemination of what he calls the "myth" of the "intrinsically good Palestinian – the innocent victim par excellence."
In early 2009, 125 parliamentarians from various countries gathered in London for the founding conference of a group called the "Interparliamentary Coalition for Combating Anti-Semitism" (ICCA). They suggest that while classical antisemitism "overlaps" modern antisemitism, it is a different phenomenon and a more dangerous one for Jews.
A new phenomenon, but not antisemitism

Brian Klug, senior research fellow in philosophy at St Benet's Hall, Oxford – who gave expert testimony in February 2006 to a British parliamentary inquiry into antisemitism in the UK, and in November 2004 to the Hearing on Anti-Semitism at the German Bundestag – argues against the idea that there is a "single, unified phenomenon" that could be called "new" antisemitism. He accepts that there is reason for the Jewish community to be concerned, but argues that any increase in antisemitic incidents is attributable to classical antisemitism. Proponents of the new antisemitism concept, he writes, see an organizing principle that allows them to formulate a new concept, but it is only in terms of this concept that many of the examples cited in evidence of it count as examples in the first place. That is, the creation of the concept may be based on a circular argument or tautology. He argues that it is an unhelpful concept, because it devalues the term "antisemitism," leading to widespread cynicism about the use of it. People of goodwill who support the Palestinians resent being falsely accused of antisemitism.
Klug defines classical antisemitism as "an ingrained European fantasy about Jews as Jews," arguing that whether Jews are seen as a race, religion, or ethnicity, and whether antisemitism comes from the right or the left, the antisemite's image of the Jew is always as "a people set apart, not merely by their customs but by their collective character. They are arrogant, secretive, cunning, always looking to turn a profit. Loyal only to their own, wherever they go they form a state within a state, preying upon the societies in whose midst they dwell. Mysteriously powerful, their hidden hand controls the banks and the media. They will even drag governments into war if this suits their purposes. Such is the figure of 'the Jew,' transmitted from generation to generation."
hen anti-Semitism is everywhere, it is nowhere. And when every anti-Zionist is an anti-Semite, we no longer know how to recognize the real thing—the concept of anti-Semitism loses its significance. —Brian Klug
He argues that although it is true that the new antisemitism incorporates the idea that antisemitism is hostility to Jews as Jews, the source of the hostility has changed; therefore, to continue using the same expression for it – antisemitism – causes confusion. Today's hostility to Jews as Jews is based on the Arab–Israeli conflict, not on ancient European fantasies. Israel proclaims itself as the state of the Jewish people, and many Jews align themselves with Israel for that very reason. It is out of this alignment that the hostility to Jews as Jews arises, rather than hostility to Israelis or to Zionists. Klug agrees that it is a prejudice, because it is a generalization about individuals; nevertheless, he argues, it is "not rooted in the ideology of 'the Jew'," and is therefore a different phenomenon from antisemitism.
In 2006, Norman Finkelstein argued that there has been no significant rise in antisemitism: "What does the evidence show? There has been good investigation done, serious investigation. All the evidence shows there's no evidence at all for a rise of a new anti-Semitism, whether in Europe or in North America. The evidence is zero. And, in fact, there's a new book put out by an Israel stalwart. His name is Walter Laqueur, a very prominent scholar. It's called The Changing Face of Anti-Semitism. It just came out, 2006, from Oxford University Press. He looks at the evidence, and he says no. There's some in Europe among the Muslim community, there's some anti-Semitism, but the notion that in the heart of European society or North American society there's anti-Semitism is preposterous. And in fact – or no, a significant rise in anti-Semitism is preposterous."
In 2023, according to the FBI, antisemitic hate crimes in the United States surged 63 percent to 1,832 recorded incidents, the highest on record. Antisemitic incidents represented 15% of all hate crimes and 68% of all religion-based hate crimes, though Jews only make up about 2% of the population. In 2024, reports of bomb threats to synagogues, antisemitic harassment, vandalism and assault reached record-high numbers in four of the past six years in the United States.
Criticism of Israel is not always antisemitism
The 3D Test of Antisemitism is a set of criteria put forth by Natan Sharansky to distinguish legitimate criticism of Israel from antisemitism. The three Ds stand for Delegitimization of Israel, Demonization of Israel, and subjecting Israel to Double standards, each of which, according to the test, indicates antisemitism. The test is intended to draw the line between legitimate criticism towards the State of Israel, its actions and policies, and non-legitimate criticism that becomes antisemitic.
Earl Raab writes that "here is a new surge of antisemitism in the world, and much prejudice against Israel is driven by such antisemitism," but argues that charges of antisemitism based on anti-Israel opinions generally lack credibility. He writes that "a grave educational misdirection is imbedded in formulations suggesting that if we somehow get rid of antisemitism, we will get rid of anti-Israelism. This reduces the problems of prejudice against Israel to cartoon proportions." Raab describes prejudice against Israel as a "serious breach of morality and good sense," and argues that it is often a bridge to antisemitism, but distinguishes it from antisemitism as such.
Steven Zipperstein, professor of Jewish Culture and History at Stanford University, argues that a belief in the State of Israel's responsibility for the Arab-Israeli conflict is considered "part of what a reasonably informed, progressive, decent person thinks." He argues that Jews have a tendency to see the State of Israel as a victim because they were very recently themselves "the quintessential victims".
Accusations of misuse of the term to stifle criticism of Israel
Main article: Weaponization of antisemitismNorman Finkelstein argues that organizations such as the Anti-Defamation League have brought forward charges of new antisemitism at various intervals since the 1970s, "not to fight antisemitism but rather to exploit the historical suffering of Jews in order to immunize Israel against criticism". He writes that most evidence purporting to show a new antisemitism has been taken from organizations that are linked in some way to Israel, or that have "a material stake in inflating the findings of anti-Semitism," and that some antisemitic incidents reported in recent years either did not occur or were misidentified. As an example of the misuse of the term "antisemitism," he cites the European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia's 2003 report, which included displays of the Palestinian flag, support for the PLO, and the comparisons between Israel and apartheid-era South Africa in its list of antisemitic activities and beliefs.

He writes that what is called the new antisemitism consists of three components: (i) "exaggeration and fabrication"; (ii) "mislabeling legitimate criticism of Israeli policy"; and (iii) "the unjustified yet predictable spillover from criticism of Israel to Jews generally." He argues that Israel's apologists have denied a causal relationship between Israeli policies and hostility toward Jews, since "if Israeli policies, and widespread Jewish support for them, evoke hostility toward Jews, it means that Israel and its Jewish supporters might themselves be causing anti-Semitism; and it might be doing so because Israel and its Jewish supporters are in the wrong".
Tariq Ali, a British-Pakistani historian and political activist, argues that the concept of new antisemitism amounts to an attempt to subvert the language in the interests of the State of Israel. He writes that the campaign against "the supposed new 'anti-semitism'" in modern Europe is a "cynical ploy on the part of the Israeli Government to seal off the Zionist state from any criticism of its regular and consistent brutality against the Palestinians.... Criticism of Israel can not and should not be equated with anti-semitism." He argues that most pro-Palestinian, anti-Zionist groups that emerged after the Six-Day War were careful to observe the distinction between anti-Zionism and antisemitism.
A third wave

Historian Bernard Lewis argues that the new antisemitism represents the third, or ideological, wave of antisemitism, the first two waves being religious and racial antisemitism.
Lewis defines antisemitism as a special case of prejudice, hatred, or persecution directed against people who are in some way different from the rest. According to Lewis, antisemitism is marked by two distinct features: Jews are judged according to a standard different from that applied to others, and they are accused of cosmic evil. He writes that what he calls the first wave of antisemitism arose with the advent of Christianity because of the Jews' rejection of Jesus as Messiah. The second wave, racial antisemitism, emerged in Spain when large numbers of Jews were forcibly converted, and doubts about the sincerity of the converts led to ideas about the importance of "la limpieza de sangre", purity of blood.
He associates the third wave with the Arabs and writes that it arose only in part because of the establishment of the State of Israel. Until the 19th century, Muslims had regarded Jews with what Lewis calls "amused, tolerant superiority – they were seen as physically weak, cowardly and unmilitary – and although Jews living in Muslim countries were not treated as equals, they were shown a certain amount of respect. The Western form of antisemitism – what Lewis calls "the cosmic, satanic version of Jew hatred – arrived in the Middle East in several stages, beginning with Christian missionaries in the 19th century and continued to grow slowly into the 20th century up to the establishment of the Third Reich. He writes that it increased because of the humiliation of the Israeli military victories of 1948 and 1967.
Into this mix entered the United Nations. Lewis argues that the international public response and the United Nations' handling of the 1948 refugee situation convinced the Arab world that discrimination against Jews was acceptable. When the ancient Jewish community in East Jerusalem was evicted and its monuments desecrated or destroyed, they were offered no help. Similarly, when Jewish refugees fled or were driven out of Arab countries, no help was offered, but elaborate arrangements were made for Arabs who fled or were driven out of the area that became Israel. All the Arab governments involved in the conflict announced that they would not admit Israelis of any religion into their territories, and that they would not give visas to Jews, no matter which country they were citizens of. Lewis argues that the failure of the United Nations to protest sent a clear message to the Arab world.
He writes that this third wave of antisemitism has in common with the first wave that Jews are able to be part of it. With religious antisemitism, Jews were able to distance themselves from Judaism, and Lewis writes that some even reached high rank within the church and the Inquisition. With racial antisemitism, this was not possible, but with the new, ideological, antisemitism, Jews are once again able to join the critics. The new antisemitism also allows non-Jews, he argues, to criticize or attack Jews without feeling overshadowed by the crimes of the Nazis.
Antisemitism, but not a new phenomenon

Yehuda Bauer, professor of Holocaust studies at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, considers the concept "new antisemitism" false, describing the phenomenon as old, latent antisemitism that recurs when triggered. In his view, the current trigger is the Israeli situation, and if a compromise were achieved there antisemitism would decline but not disappear.
Dina Porat, professor at Tel Aviv University says that, while in principle there is no new antisemitism, we can speak of antisemitism in a new envelope. Otherwise Porat speaks of a new and violent form of antisemitism in Western Europe starting after the Second Intifada.
Howard Jacobson, a British novelist and journalist, calls this phenomenon "Jew-hating pure and simple, the Jew-hating which many of us have always suspected was the only explanation for the disgust that contorts and disfigures faces when the mere word Israel crops up in conversation."
An inappropriate redefinition
Antony Lerman, writing in the Israeli newspaper Ha'aretz in September 2008, argues that the concept of a "new antisemitism" has brought about "a revolutionary change in the discourse about anti-Semitism". He writes that most contemporary discussions concerning antisemitism have become focused on issues concerning Israel and Zionism, and that the equation of anti-Zionism with antisemitism has become for many a "new orthodoxy". He adds that this redefinition has often resulted in "Jews attacking other Jews for their alleged anti-Semitic anti-Zionism". While Lerman accepts that exposing alleged Jewish antisemitism is "legitimate in principle", he adds that the growing literature in this field "exceeds all reason"; the attacks are often vitriolic, and encompass views that are not inherently anti-Zionist.
Lerman argues that this redefinition has had unfortunate repercussions. He writes that serious scholarly research into contemporary antisemitism has become "virtually non-existent", and that the subject is now most frequently studied and analyzed by "people lacking any serious expertise in the subject, whose principal aim is to excoriate Jewish critics of Israel and to promote the "anti-Zionism = anti-Semitism" equation. Lerman concludes that this redefinition has ultimately served to stifle legitimate discussion, and that it cannot create a basis on which to fight antisemitism.
Peter Beaumont, writing in The Observer, agrees that proponents of the concept of "new antisemitism" have attempted to co-opt anti-Jewish sentiment and attacks by some European Muslims as a way to silence opposition to the policies of the Israeli government. "riticise Israel," he writes, "and you are an anti-Semite just as surely as if you were throwing paint at a synagogue in Paris."
Antisemitic anti-Zionism
Scholars including Werner Bergmann, Simon Schama, Alan Johnson, David Hirsh and Anthony Julius have described a distinctively 21st century form of antisemitic anti-Zionism characterized by left-wing hostility to Jews. According to historian Geoffrey Alderman, opposition to Zionism (being against a Jewish state) can be legitimately described as racist in essence.
Norman H. Finkelstein describes the BDS movement as failing all of Natan Sharansky's 3D's, since the movement delegitimizes Israel, demonizes Israel, and applies double standards for criticizing Israel out of proportion to other nations, ignoring other countries' misdeeds.
In 2024, over 1000 entertainers, authors and artists signed an open letter, released by the non-profit Creative Community for Peace (CCFP), opposing boycotts of Israeli and Jewish authors and literary institutions. The letter decried efforts to "demonize and ostracize Jewish authors across the globe".
In fall 2024, campus protests using chants such as "Divest!" and "Ceasefire now!" reportedly evolved in a direction more explicitly endorsing Hamas, Hezbollah, and Houthis. Some protesters used slogans such as "Glory to the resistance!", called the October 7 attacks "Al-Aqsa flood", celebrated Yahya Sinwar, and used the Hamas inverted red triangle. Jewish students were called "baby killers" and "terrorists", according to a Baruch College student.
In November 2024, hundreds of posters depicting Jewish faculty members as "wanted" were spread across the University of Rochester campus. The posters accused Jewish faculty members of ethnic cleansing, racism, hate speech, and intimidation. University President Sarah Mangelsdorf called the incident an act of antisemitism.
International perspectives
| The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (November 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Europe
The European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia (EUMC) (superseded in 2007 by the Fundamental Rights Agency) noted an upswing in antisemitic incidents in France, Germany, Austria, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Belgium, and The Netherlands between July 2003 and December 2004. In September 2004, the European Commission against Racism and Intolerance, a part of the Council of Europe, called on its member nations to ensure that anti-racist criminal law covers antisemitism, and in 2005, the EUMC offered a discussion paper on a working definition of antisemitism in an attempt to enable a standard definition to be used for data collection: It defined antisemitism as "a certain perception of Jews, which may be expressed as hatred towards Jews. Rhetorical and physical manifestations of antisemitism are directed towards Jews and non-Jewish individuals and/or their property, towards Jewish community institutions and religious facilities." The paper's “Examples of the ways in which anti-Semitism manifests itself with regard to the state of Israel taking into account the overall context could include":
- Denying the Jewish people the right to self-determination, e.g. by claiming that the existence of a state of Israel is a racist endeavor;
- Applying double standards by requiring of Israel a behavior not expected or demanded of any other democratic nation;
- Using the symbols and images associated with classic antisemitism (e.g. claims of Jews killing Jesus or blood libel) to characterize Israel or Israelis;
- Drawing comparisons of contemporary Israeli policy to that of the Nazis.
- Holding Jews collectively responsible for actions of the State of Israel.
The EUMC added that criticism of Israel cannot be regarded as antisemitism so long as it is "similar to that leveled against any other country."
The discussion paper was never adopted by the EU as a working definition, although it was posted on the EUMC website until 2013 when it was removed during a clear-out of non-official documents.
France
Main article: Antisemitism in 21st-century FranceIn France, Interior Minister Dominique de Villepin commissioned a report on racism and antisemitism from Jean-Christophe Rufin, president of Action Against Hunger and former vice-president of Médecins Sans Frontières, in which Rufin challenges the perception that the new antisemitism in France comes exclusively from North African immigrant communities and the far right.
Reporting in October 2004, Rufin writes that "he new anti-Semitism appears more heterogeneous," and identifies what he calls a new and "subtle" form of antisemitism in "radical anti-Zionism" as expressed by far-left and anti-globalization groups, in which criticism of Jews and Israel is used as a pretext to "legitimize the armed Palestinian conflict."
United Kingdom
In June 2011, Chief Rabbi of the United Kingdom, Jonathan Sacks (Lord Sacks), said that the basis for the new antisemitism was the 2001 Durban Conference. Rabbi Sacks also said that the new antisemitism "unites radical Islamists with human-rights NGOs – the right wing and the left wing – against a common enemy, the State of Israel."
In September 2006, the All-Party Parliamentary Group against Anti-Semitism of the British parliament published the Report of the All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Antisemitism, the result of an investigation into whether the belief that the "prevailing opinion both within the Jewish community and beyond" that antisemitism had "receded to the point that it existed only on the margins of society." was correct. It concluded that "the evidence we received indicates that there has been a reversal of this progress since the year 2000". In defining antisemitism, the Group wrote that it took into account the view of racism expressed by the MacPherson report, which was published after the murder of Stephen Lawrence, that, for the purpose of investigating and recording complaints of crime by the police, an act must be recorded by the police as racist if it is defined as such by its victim. It formed the view that, broadly, "any remark, insult or act the purpose or effect of which is to violate a Jewish person's dignity or create an intimidating, hostile, degrading, humiliating or offensive environment for him is antisemitic" and concluded that, given that, "it is the Jewish community itself that is best qualified to determine what does and does not constitute antisemitism."
The report states that some left-wing activists and Muslim extremists are using criticism of Israel as a "pretext" for antisemitism, and that the "most worrying discovery" is that antisemitism appears to be entering the mainstream. It argues that anti-Zionism may become antisemitic when it adopts a view of Zionism as a "global force of unlimited power and malevolence throughout history," a definition that "bears no relation to the understanding that most Jews have of the concept: that is, a movement of Jewish national liberation ..." Having re-defined Zionism, the report states, traditional antisemitic motifs of Jewish "conspiratorial power, manipulation and subversion" are often transferred from Jews onto Zionism. The report notes that this is "at the core of the 'New Antisemitism', on which so much has been written," adding that many of those who gave evidence called anti-Zionism "the lingua franca of antisemitic movements."
Israel
In November 2001 according to the Israeli Ministry of Diaspora Affairs, in response to an Abu-Dhabi television broadcast depicting Ariel Sharon drinking the blood of Palestinian children, the Israeli government set up the "Coordinating Forum for Countering Antisemitism", headed by Deputy Foreign Minister Rabbi Michael Melchior. According to Melchior, "in each and every generation antisemitism tries to hide its ugly face behind various disguises – and hatred of the State of Israel is its current disguise." He added that, "hate against Israel has crossed the red line, having gone from criticism to unbridled antisemitic venom, which is a precise translation of classical antisemitism whose past results are all too familiar to the entire world."
United Nations
See also: Israel and the United NationsA number of commentators argue that the United Nations has condoned antisemitism. Lawrence Summers, then-president of Harvard University, wrote that the UN's World Conference on Racism failed to condemn human rights abuses in China, Rwanda, or anywhere in the Arab world, while raising Israel's alleged ethnic cleansing and crimes against humanity.
David Matas, senior counsel to B'nai B'rith Canada, has written that the UN is a forum for antisemitism, citing the example of the Palestinian representative to the UN Human Rights Commission who claimed in 1997 that Israeli doctors had injected Palestinian children with the AIDS virus. Congressman Steve Chabot told the U.S. House of Representatives in 2005 that the commission took "several months to correct in its record a statement by the Syrian ambassador that Jews allegedly had killed non-Jewish children to make unleavened bread for Passover.
Anne Bayefsky, a Canadian legal scholar who addressed the UN about its treatment of Israel, argues that the UN hijacks the language of human rights to discriminate and demonize Jews. She writes that over one quarter of the resolutions condemning a state's human rights violations have been directed at Israel. "But there has never been a single resolution about the decades-long repression of the civil and political rights of 1.3 billion people in China, or the million female migrant workers in Saudi Arabia kept as virtual slaves, or the virulent racism which has brought 600,000 people to the brink of starvation in Zimbabwe."
In a 2008 report on antisemitism from the United States Department of State to the US Congress,
Motives for criticizing Israel in the UN may stem from legitimate concerns over policy or from illegitimate prejudices. ... However, regardless of the intent, disproportionate criticism of Israel as barbaric and unprincipled, and corresponding discriminatory measures adopted in the UN against Israel, have the effect of causing audiences to associate negative attributes with Jews in general, thus fueling anti-Semitism.
United States

In September 2006, Yale University announced that it had established the Yale Initiative for the Interdisciplinary Study of Anti-Semitism, the first university-based institute in North America dedicated to the study of antisemitism. Charles Small, head of the institute, said in a press release that antisemitism has "reemerged internationally in a manner that many leading scholars and policy makers take seriously ... Increasingly, Jewish communities around the world feel under threat. It's almost like going back into the lab. I think we need to understand the current manifestation of this disease." YIISA has presented several seminars and working papers on the topic, for instance "The Academic and Public Debate Over the Meaning of the 'New Antisemitism'".
In July 2006, the U.S. Commission on Civil Rights issued a Campus Antisemitism report that declared that "Anti-Semitic bigotry is no less morally deplorable when camouflaged as anti-Israelism or anti-Zionism." At the time, the commission also announced that antisemitism is a "serious problem" on many campuses throughout the United States.
The U.S. State Department's 2004 Report on Global Anti-Semitism identified four sources of rising antisemitism, particularly in Europe:
- "Traditional anti-Jewish prejudice... This includes ultra-nationalists and others who assert that the Jewish community controls governments, the media, international business, and the financial world."
- "Strong anti-Israel sentiment that crosses the line between objective criticism of Israeli policies and anti-Semitism."
- "Anti-Jewish sentiment expressed by some in Europe's growing Muslim population, based on longstanding antipathy toward both Israel and Jews, as well as Muslim opposition to developments in Israel and the occupied territories, and more recently in Iraq."
- "Criticism of both the United States and globalization that spills over to Israel, and to Jews in general who are identified with both."
Anti-globalization movement
The anti-globalization movement of the late 1990s and early 2000s was accused by writers and researchers such as Walter Laqueur, Paul Berman, and Mark Strauss of displaying elements of new antisemitism. Critics of the Laqueur–Berman–Strauss view argue that the allegation is either unfounded or exaggerated, intended to discredit legitimate criticism of globalization and of free trade economic policies.
Mark Strauss's allegations
Mark Strauss of Foreign Policy argues that globalization has stirred anxieties about "outside forces", and that with "familiar anxieties come familiar scapegoats." He writes that what he calls the "backlash against globalization" has united a variety of political elements, from the left to the far-right, via a common cause, and that in so doing it has "foster a common enemy." He quotes the French Jewish leader Roger Cukierman who identifies the anti-globalization movement as "an anti-Semitic brown-green-red alliance", which includes ultra-nationalists, Islamists, and communists.
Strauss cites Jörg Haider of the far-right Freedom Party of Austria and Jean-Marie Le Pen of France's National Front as examples of the far right exploiting their electorate's concerns about globalization. The fringe Fascism and Freedom Movement in Italy identifies globalization as an "instrument in the hands of international Zionism" according to Strauss, while in Eastern Europe ultranationalists and communists have united against foreign investors and multinationals, identifying Jews as a common enemy.
Matthew F. Hale, an American white nationalist of the World Church of the Creator, stated of the 1999 protests in Seattle that they were "incredibly successful from the point of view of the rioters as well as our Church. They helped shut down talks of the Jew World Order WTO and helped make a mockery of the Jewish Occupational Government around the world. Bravo." Strauss also cites the National Alliance, a neo-Nazi party which set up a website called the Anti-Globalism Action Network in order to "broaden ... the anti-globalism movement to include divergent and marginalized voices."
Strauss writes that, as a result of far-right involvement, a "bizarre ideological turf war has broken out", whereby anti-globalization activists are fighting a "two-front battle," one against the World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund, and World Bank, the other against the extremists who turn up at their rallies. He points to an anti-globalization march in Porto Alegre, Brazil, at which he says some marchers displayed swastikas and that Jewish peace activists were assaulted. He wrote:
"Held two months prior to the U.S.-led attack on Iraq, this year's conference – an annual grassroots riposte to the well-heeled World Economic Forum in Davos – had the theme, 'Another World is Possible.' But the more appropriate theme might have been 'Yesterday's World is Back.' Marchers among the 20,000 activists from 120 countries carried signs reading 'Nazis, Yankees, and Jews: No More Chosen Peoples!' Some wore T-shirts with the Star of David twisted into Nazi swastikas. Members of a Palestinian organization pilloried Jews as the 'true fundamentalists who control United States capitalism.' Jewish delegates carrying banners declaring 'Two peoples – Two states: Peace in the Middle East' were assaulted.
Strauss argues that the anti-globalization movement is not itself antisemitic but that it "helps enable anti-Semitism by peddling conspiracy theories." Strauss's arguments have been met with strong criticism from many in the anti-globalization movement. Oded Grajew, one of the founders of the World Social Forum, has written that the WSF "is not anti-Semitic, anti-American, or even anti-socially-responsible capitalism". He claims that some fringe parties have attempted to infiltrate the WSF's demonstrations and promote demonstrations of their own, but adds that "he success of the WSF ... is a threat to political extremist groups that resort to violence and hatred". Grajew has also written that, to his knowledge, Strauss's claim of Nazi symbols being displayed at an anti-globalization demonstration in Porto Alegre, Brazil is false.
Response to Strauss
Maude Barlow, national chairperson of the Council of Canadians, argues that Strauss has "inflamed, not enlightened" the debate over globalization by making "no distinction between the far right's critique of globalization and that of the global social justice movement", which is premised on "respect for human rights and cultural diversity". She notes that the Council of Canadians has condemned antisemitism, and that it expelled some individuals who tried to organize a David Icke tour under its auspices. John Cavanagh of the International Policy Centre has also criticized Strauss for using unproven allegations of antisemitism to criticize the entire anti-globalization movement, and for failing to research the movement's core beliefs.
In response to these criticisms, Strauss has written that antisemitic views "might not reflect the core values of the Global Justice Movement or its leading figures, yet they are facts of life in an amorphous, grassroots movement where any number of individuals or organizations express their opinions or seek to set the agenda". He has also reiterated his concern that "anti-capitalist rhetoric provides intellectual fodder for far right groups".
Other views
Walter Laqueur describes this phenomenon:
Although traditional Trotskyite ideology is in no way close to radical Islamic teachings and the shariah, since the radical Islamists also subscribed to anticapitalism, antiglobalism, and anti-Americanism, there seemed to be sufficient common ground for an alliance. Thus, the militants of the far left began to march side by side with the radical Islamists in demonstrations, denouncing American aggression and Israeli crimes. ... And it was only natural that in protest demonstrations militants from the far right would join in, antisemitic banners would be displayed, anti-Jewish literature such as the Protocols would be sold.
Lawrence Summers, then president of Harvard University, also stated that "erious and thoughtful people are advocating and taking actions that are anti-Semitic in their effect if not their intent. For example ... t the same rallies where protesters, many of them university students, condemn the IMF and global capitalism and raise questions about globalization, it is becoming increasingly common to also lash out at Israel. Indeed, at the anti-IMF rallies last spring, chants were heard equating Hitler and Sharon."
A March 2003 report on antisemitism in the European Union by Werner Bergmann and Juliane Wetzel of the Berlin Research Centre on Anti-Semitism identifies anti-globalization rallies as one of the sources of antisemitism on the left.
In the extreme left-wing scene, anti-Semitic remarks were to be found mainly in the context of pro-Palestinian and anti-globalisation rallies and in newspaper articles using anti-Semitic stereotypes in their criticism of Israel. Often this generated a combination of anti-Zionist and anti-American views that formed an important element in the emergence of an anti-Semitic mood in Europe.
Michael Kozak, then U.S. Acting Assistant Secretary for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor, told reporters in 2005 that people within the anti-globalization movement have conflated their legitimate concerns "with this idea that Jews run the world and globalization is the fault of Jews." He said:
I think one of the disturbing things is that you're starting to see this in some – you know, it's not just sort of right-wing ultranationalist skinhead types. It's now you're getting some fairly otherwise respectable intellectuals that are left of center who are anti-globalization who are starting to let this stuff creep into their rhetoric.
And that's disturbing because it starts to – it starts to take what is a legitimate issue for debate, anti-globalization or the war in Iraq or any other issue, and when you start turning that into an excuse for saying therefore we should hate Jews, that's where you cross the line, in my view. It's not that you're not entitled to question all those other issues. Of course, those are fair game. But it's the same as saying, you know, you start hating all Muslims because of some policy you don't like by one Muslim country or something.
Conflation of globalization, Jews and Israel

Robert Wistrich, Professor of European and Jewish History at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, told Manfred Gerstenfeld that globalization has given rise to an anti-globalist left that is "viscerally anti-American, anti-capitalist, and hostile to world Jewry." He argues that the decade that preceded the current increase in antisemitism was one that saw accelerated globalization of the world economy, a process in which the losers included the Arab and Muslim worlds, and who are now the "major consumers of anti-Jewish poison and conspiracy theories that blame everyone except themselves. Israel is only one piece on this chessboard, but it has assumed such inflated importance because it serves a classic anti-Semitic function of being an 'opium for the masses'." As an example of the alleged conflation of globalization, the U.S. and Israel, Josef Joffe, editor and publisher of Die Zeit and adjunct professor at Stanford University, cited José Bové, a French anti-globalization activist and leader of the Confédération Paysanne. Bové led what Joffe calls a "deconstructionist mob" against McDonald's to protest against its effects on French cuisine, later turning up in Ramallah to denounce Israel and announce his support for Yasser Arafat. "Arafat's cause was Bové's cause ... here was a spokesman for the anti-globalization movement who was conflating globalization with Americanization and extending his loathing of both to Israel." Joffe argues that Kapitalismuskritik is a "mainstay of the antisemitic faith, a charge that has passed smoothly from Jews to America. Like Jews, Americans are money-grubbers who know only the value of money, and the worth of nothing. Like Jews, they seek to reduce all relationships to exchange and money. Like them, Americans are motivated only by profit, and so they respect no tradition."
David Clark, writing in The Guardian, argues against this that "instances of anti-capitalism spilling into 'rich Jew' bigotry are ... well documented" but "stand out precisely because they conflict so sharply with the Left's universalism and its opposition to ethnic discrimination".
In early 2004, Kalle Lasn, author of "Culture Jam" and founder of Adbusters, two influential and widely read anti-globalization texts, generated controversy when he wrote an editorial entitled "Why won't anyone say they are Jewish?". In it he stated "Drawing attention to the Jewishness of the neocons is a tricky game. Anyone who does so can count on automatically being smeared as an anti-Semite. But the point is not that Jews (who make up less than 2 percent of the American population) have a monolithic perspective. Indeed, American Jews overwhelmingly vote Democrat and many of them disagree strongly with Ariel Sharon's policies and Bush's aggression in Iraq. The point is simply that the neocons seem to have a special affinity for Israel that influences their political thinking and consequently American foreign policy in the Middle East." The editorial suggested that Jews represent a disproportionately high percentage of the neo-conservatives who control American foreign policy, and that this may affect policy with respect to Israel. Lasn included a list of influential neo-conservatives, with dots next to the names of those who were Jewish.
Lasn was criticized by a number of anti-globalization activists. Klaus Jahn, professor of the philosophy of history at the University of Toronto condemned Lasn's article stating "Whether listing physicians who perform abortions in anti-abortion tracts, gays and lesbians in office memos, Communists in government and the entertainment industry under McCarthy, Jews in Central Europe under Nazism and so on, such list-making has always produced pernicious consequences."
Meredith Warren, a Montreal anti-globalization activist responded to the article by saying "The U.S. government has only an economic interest in having control over that region. It wants oil and stability – it has nothing to do with Jews or Judaism. Pointing out the various religious stances of those in power totally misses the point of the U.S. government's interest in Israel."
Controversy over alleged antisemitism within the French movement
See also: Red–green–brown allianceAccording to a report by the Stephen Roth Institute for the Study of Antisemitism, a major event for the anti-globalization movement in France was the European Social Forum (ESF) in Paris in November 2003. The organizers allegedly included a number of Islamic groups, such as Présence Musulmane, Secours Islamique, and Collectif des Musulmans de France. Tariq Ramadan, the grandson of Hassan al-Banna, the Egyptian founder of the Muslim Brotherhood, also attended meetings. A few weeks earlier, Ramadan had published a controversial article on a website – after Le Monde and Le Figaro refused to publish it – criticizing several French intellectuals, who according to the institute, were either Jewish or "others he mistakenly thought were Jewish," for having "supposedly betrayed their universalist beliefs in favor of unconditional support for Zionism and Israel."
Bernard-Henri Lévy, one of the intellectuals who was criticized, called on the French anti-globalization movement to distance itself from Ramadan. In an interview with Le Monde, Lévy said: "Mr. Ramadan, dear anti-globalizationist friends, is not and cannot be one of yours. ... I call you on you quickly to distance yourselves from this character who, in crediting the idea of an elitist conspiracy under the control of Zionism, is only inflaming people's thoughts and opening the way to the worst."
Le Monde reported that many members of the anti-globalization movement in France agreed that Ramadan's article "has no place on a European Social Forum mailing list."
Other activists defended Ramadan. One activist told the newspaper that "ne of the characteristics of the European Social Forum is the stark rise in immigrant and Muslim organizations. It is an important phenomenon and a positive one in many ways." Another activist, Peter Khalfa, said: "Ramadan's essay is not anti-Semitic. It is dangerous to wave the red flag of anti-Semitism at any moment. However, it is a text marked partly by Ramadan's communitarian thought and which communicates his view of the world to others." One of the leaders of the anti-globalization movement in France, José Bové of the Confédération Paysanne, told Le Monde: "The anti-globalization movement defends universalist points of view which are therefore necessarily secular in their political expression. That there should be people of different cultures and religions is only natural. The whole effort is to escape such determinisms."
Concern within the political left
Naomi Klein, a Jewish Canadian writer and activist in the anti-globalization movement, expressed concern in 2002 at finding antisemitic rhetoric on some activist websites that she had visited: "I couldn't help thinking about all the recent events I've been to where anti-Muslim violence was rightly condemned, but no mention was made of attacks on Jewish synagogues, cemeteries, and community centers." Klein urged activists to confront antisemitism as part of their work for social justice. She also suggested that allegations of antisemitism can be often politically motivated, and that activists should avoid political simplifications that could be perceived as antisemitic:
The globalization movement isn't anti-Semitic, it just hasn't fully confronted the implications of diving into the Middle East conflict. Most people on the left are simply choosing sides. In the Middle East, where one side is under occupation and the other has the U.S. military behind it, the choice seems clear. But it is possible to criticize Israel while forcefully condemning the rise of anti-Semitism. And it is equally possible to be pro-Palestinian independence without adopting a simplistic pro-Palestinian/anti-Israel dichotomy, a mirror image of the good versus evil equations so beloved by President George W. Bush.
In October 2004, the New Internationalist magazine published a special issue covering the insertion of antisemitic rhetoric into some progressive debates. Adam Ma'anit wrote:
Take Adbusters magazine's founder Kalle Lasn's recent editorial rant against Jewish neoconservatives. ... The article includes a self-selected 'well-researched list' of 50 of the supposedly most influential 'neocons' with little black dots next to all those who are Jewish. ... If it's not the neocons then it's the all-powerful 'Jewish lobby' which holds governments to ransom all over the world (because Jews control the global economy of course) to do their bidding. Meanwhile, rightwing Judeophobes often talk of a leftist Jewish conspiracy to promote equality and human rights through a new internationalism embodied in the UN in order to control governments and suppress national sovereignty. They call it the 'New World Order' or the 'Jew World Order'. They make similar lists to Lasn's of prominent Jews in the global justice movement (Noam Chomsky, Naomi Klein, etc.) to argue their case.
The issue observes, however, that "While antisemitism is rife in the Arab World, the Israeli Government often uses it as moral justification for its policies."
Antisemitism during the Israel-Hamas War
Antisemitism during the Israel-Hamas war increased significantly around the world.
See also
- Antisemitism during the Israel-Hamas war
- Antisemitism
- Antisemitism by country
- Antisemitism in the United Kingdom
- Antisemitism in Islam
- Antisemitism in the Arab world
- Antisemitism in the United States
- Antisemitism in Europe
Notes
- ^ Fastenbauer, Raimund (2020). "Islamic Antisemitism: Jews in the Qur'an, Reflections of European Antisemitism, Political Anti-Zionism: Common Codes and Differences". In Lange, Armin; Mayerhofer, Kerstin; Porat, Dina; Schiffman, Lawrence H. (eds.). An End to Antisemitism! – Volume 2: Confronting Antisemitism from the Perspectives of Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter. pp. 279–300. doi:10.1515/9783110671773-018. ISBN 9783110671773.
- Berkman, Matthew (2022). "The Conflict on Campus". In A. Siniver (ed.). Routledge Companion to the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict. Taylor & Francis. p. 522. ISBN 978-0-429-64861-8. Retrieved 2023-05-21.
Attempts to rearticulate antisemitism to encompass opposition to Israel's "right to exist" or its character as a Jewish state date back to the 1970s, when the Anti-Defamation League first popularized a discourse on "the new antisemitism" (see Forster and Epstein 1974; on the subsequent development of that discourse see Judaken 2008). The identification of anti-Zionism with antisemitism has long been de rigueur in Jewish communal and broader pro-Israel circles, but only in the last two decades have Israel advocacy groups endeavoured to establish it as a principle of United States anti-discrimination law. The earliest step in this direction was taken in 2004, when Kenneth L. Marcus, the Assistant Secretary of Education for the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) under President George W. Bush, issued a game-changing policy guidance letter empowering OCR staff, for the first time, to investigate complaints under Title VI of the Civil Rights Act alleging pervasive antisemitism on college campuses.
- ^ "USCIRF 2020 Annual Report: "Rising Anti-Semitism in Europe and Elsewhere"" (PDF). Uscirf.gov. Washington, D.C.: United States Commission on International Religious Freedom. April 2020. pp. 87–88. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 April 2020. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- Manfred Gerstenfeld, The Deep Roots of Anti-Semitism in European Society. Jewish Political Studies Review 17:1–2 Spring 2005
- Taguieff, Pierre-André. Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004.
- Cohen, Florette (September 2011). The New Anti-Semitism Israel Model: Empirical Tests. BiblioBazaar. ISBN 978-1-243-56139-8.
- Hirsh, David (January 2010). "Accusations of malicious intent in debates about the Palestine-Israel conflict and about antisemitism: The Livingstone Formulation, 'playing the antisemitism card' and contesting the boundaries of antiracist discourse" (PDF). Transversal: 47–77.
- Klaff, Lesley (2016-12-01), Wistrich, Robert S. (ed.), Holocaust inversion in British politics : the case of David Ward, University of Nebraska Press, pp. 185–196, ISBN 978-0-8032-9671-8, retrieved 2024-01-09
- Klug, Brian. The Myth of the New Anti-Semitism. The Nation, posted January 15, 2004 (February 2, 2004 issue), accessed January 9, 2006; and Lerner, Michael. There Is No New Anti-Semitism, posted February 5, 2007, accessed February 6, 2007.
- Steven Beller, 'In Zion’s hall of mirrors: a comment on Neuer Antisemitismus?,' Patterns of Prejudice, Vol. 41, No. 2, 2007 pp.215-238, 223:' The idea that there has been an explosion of antisemitic sentiment in Europe has more to do with American, Israeli and Zionist discomfort with strong European criticism of Israeli policy than it has with actual antisemitism.'
- Scott Ury, 'Strange Bedfellows? Anti-Semitism, Zionism, and the Fate of “the Jews”,' American Historical Review, October 2018, vol. 123, 4 pp. 1151-1171, p.1552: 'One of the biggest problems facing the study of anti-Semitism today: its ongoing, seemingly inescapable connection to public affairs and the extent to which contemporary political concerns, in particular those regarding Zionism and the State of Israel, influence and shape the way that many scholars frame, interpret, and research anti-Semitism.'
- Pierre-André Taguieff cites the following early works on the new antisemitism: Jacques Givet, La Gauche contre Israel? Essai sur le néo-antisémitisme, Paris 1968; idem, "Contre une certain gauche," Les Nouveaux Cahiers, No. 13-14, Spring-Summer 1968, pp. 116–119; Léon Poliakov, De l'antisionisme a l'antisémitisme, Paris 1969; Shmuel Ettinger, "Le caractère de l'antisémitisme contemporain," Dispersion et Unité, No. 14, 1975, pp. 141–157; and Michael Curtis, ed., Antisemitism in the Modern World, Boulder, 1986. All cited in Pierre-André Taguieff. Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 159-160, footnote 1.
- Taguieff, Pierre André. Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, p. 62.
- Congress Bi-weekly, American Jewish Congress, Vol. 40, Issues 2-14, 1973, p. xxv
- Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, The New Anti-Semitism. McGraw-Hill 1974, p.165. See for instance chapters entitled "Gerald Smith's Road" (19–48), "The Radical Right" (285–296), "Arabs and Pro-Arabs" (155–174), "The Radical Left" (125–154)
- Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, The New Anti-Semitism. McGraw-Hill 1974, p. 324.
- Raab, Earl. "Is there a New Anti-Semitism?", Commentary, May 1974, pp. 53–54.
- Brownfeld, Allan (1987). "Anti-Semitism: Its Changing Meaning". Journal of Palestine Studies. 16 (3). Institute for Palestine Studies: 53–67. doi:10.2307/2536789. ISSN 1533-8614. JSTOR 2536789.
- Edward S. Shapiro. A Time for Healing: American Jewry Since World War II. Johns Hopkins University Press. 1992. ISBN 0-8018-4347-2. Page 47.
- Wistrich, Robert. "Anti-zionism as an Expression of Anti-Semitism in Recent Years" Archived 2017-05-12 at the Wayback Machine, lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the President of Israel, December 10, 1984.
- Chomsky, Noam. "TRANSCRIPT of Amy Goodman interview of Noam Chomsky". Democracy Now!. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- Irwin Cotler cited Dershowitz, Alan. The Case For Israel. John Wiley and Sons, 2003, p. 210-211.
- ^ Irwin Cotler, Making the world 'Judenstaatrein', The Jerusalem Post, February 22, 2009.
- David Sheen, "Canadian MP Cotler: Calling Israel an apartheid state can be legitimate free speech", Haaretz, 1 July 2011. Accessed 7 July 2011.
- Fischel, Jack R. "The New Anti-Semitism", The Virginia Quarterly Review, Summer 2005, pp. 225–234.
- ^ Strauss, Mark (2009-11-02). "Anti-globalism's Jewish Problem". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- Tembarai Krishnamachari, Rajesh. "Localized motivations for antisemitism within the Ummah" in South Asia Analysis Group, Paper 5907, April 2015.
- Taguieff, Pierre-André. Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004, pp. 67–68.
- ^ Klug, Brian. "In search of clarity" Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine, Catalyst, March 17, 2006.
- ^ Klug, Brian. The Myth of the New Anti-Semitism Archived 2009-07-01 at the Portuguese Web Archive. The Nation, February 2, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006
- Klug, Brian. Israel, Antisemitism and the left Archived 2006-10-23 at the Wayback Machine, Red Pepper, November 24, 2005.
- Goodman, Amy. "Finkelstein on DN! No New Antisemitism" Archived 2006-11-15 at the Wayback Machine, interview with Norman Finkelstein, August 29, 2006.
- "FBI Releases 2023 Crime in the Nation Statistics". Federal Bureau of Investigation. 2024-09-23. Retrieved 2024-11-16.
- Kirsh, Elana; Fabian, Emanuel; Lehmann, Noam (2024-09-23). "Antisemitic hate crimes in US surged 63% in 2023, to all-time high of 1,832 – FBI". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 2024-11-16.
- Diaz, Johnny (2024-10-06). "Antisemitic Incidents Reach New High in the U.S., Report Finds". The New York Times. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- Barber, Rachel (2024-04-16). "Record number of antisemitic incidents hit US amid Israel-Hamas war". USA TODAY. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- "So What's New? Rethinking the 'New Antisemitism' in a Global Age" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-27.
- "Remarks at the 2011 B'nai B'rith International Policy Conference". 2012-12-02. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- Cohen, Florette (September 2011). The New Anti-Semitism Israel Model: Empirical Tests. BiblioBazaar. ISBN 978-1-243-56139-8.
- Raab, Earl. "Antisemitism, anti-Israelism, anti-Americanism", Judaism, Fall 2002.
- Zipperstein, Steven. "Historical Reflections of Contemporary Antisemitism" in Derek J. Penslar et al., ed., Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World, Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005, p. 61.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, pp. 21–22.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, p. 66–71.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, p. 37.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, p. 81.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, p. 66.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History, University of California Press, 2005, pp. 78–79.
- Ali, Tariq (1 May 2018). Street Fighting Years: An Autobiography of the Sixties. Verso Books. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-78663-602-7 – via Google Books.
- Julius, Anthony (9 February 2012). Trials of the Diaspora: A History of Anti-Semitism in England. Oxford University Press. p. 525. ISBN 978-0-19-960072-4 – via Google Books.
- ^ Lewis, Bernard. "The New Anti-Semitism" Archived 2011-09-08 at the Wayback Machine, The American Scholar, Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25–36 The paper is based on a lecture delivered at Brandeis University on March 24, 2004.
- ^ Tzvi Fleischer (May 2007). "Hate's Revival". Australia/Israel Review. AIJAC.
- Fulford, Robert (2009-08-15). "When criticizing Israel becomes ritual". nationalpost.com. Archived from the original on 2012-09-12. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- Antony Lerman, "Jews attacking Jews", Ha'aretz, 12 September 2008, accessed 13 September 2008.
- Beaumont, Peter. "The new anti-semitism?", The Observer, February 17, 2002.
- ^ Pelinka, Anton; et al. (2009). Handbook of Prejudice. Chapter on Anti-Semitism by Werner Bergmann. Cambria Press. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-60497-627-4.
- Schama, Simon (19 February 2016). "The left's problem with Jews has a long and miserable history". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 11 December 2022. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- Hirsh, David (30 November 2006). "Openly Embraing Prejudice". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- Julius, Anthony (2010). Trials of the Diaspora: A History of Anti-Semitism in England. Oxford University Press. p. 476. ISBN 978-0-19-929705-4.
- Johnson, Alan (Fall 2015). "The Left and the Jews: Time for a Rethink". Fathom. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- Alderman, Geoffrey (November 8, 2012). "Why anti-Zionists are racists". The Jewish Chronicle. Archived from the original on July 5, 2016. Retrieved June 8, 2016.
- "Formula Could Combat Campus Racism". Jewish Weekly. June 5, 2005. Archived from the original on August 29, 2016. Retrieved June 8, 2016.
- Finkelstein, Norman H. (2024). Saying No to Hate. U of Nebraska Press. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-8276-1523-6.
- Kaloi, Stephanie (2024-10-31). "David Mamet, Diane Warren and Debra Messing Among 1000+ Entertainers and Artists to Oppose Israel Boycotts in Open Letter". TheWrap. Retrieved 2024-11-14.
- Otterman, Sharon (2024-10-09). "Pro-Palestinian Group at Columbia Now Backs 'Armed Resistance' by Hamas". The New York Times. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- ^ Meckler, Laura; Svrluga, Susan (2024-11-10). "Pro-Hamas messages intensify on college campuses". Washington Post. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- Marbury, Justice; Nguyen, Thao (2024-11-14). "'Wanted' posters target Jewish faculty at University of Rochester". USA TODAY. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- ^ "(U.S.) State Department report on Anti-Semitism: Europe and Eurasia" excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 – December 15, 2004.
- Whine, Michael. "Progress in the Struggle Against Anti-Semitism in Europe: The Berlin Declaration and the European Union Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia's Working Definition of Anti-Semitism" Archived 2022-02-26 at the Wayback Machine, Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, February 1, 2006.
- ^ tp://eumc.eu.int/eumc/material/pub/AS/AS-WorkingDefinition-draft.pdf "Working definition of antisemitism" Archived 2011-01-25 at the Wayback Machine, EUMC.
- "Working Definition of Antisemitism" (PDF). European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "SWC to EU Baroness Ashton: "Return Anti-Semitism Definition Document to EU Fundamental Rights Agency Website" | Simon Wiesenthal Center". Wiesenthal.com. 2013-11-06. Archived from the original on 2016-03-01. Retrieved 2016-02-17.
- "EU drops its 'working definition' of anti-Semitism". Times of Israel. Retrieved 2014-01-24.
- "French concern about race attacks", BBC News, October 2004.
- "France: International Religious Freedom Report 2005", U.S. Department of State.
- Rufin, Jean-Christophe. "Chantier sur la lutte contre le racisme et l'antisémitisme" Archived 2009-03-27 at the Wayback Machine, presented to the French Ministry of the Interior, October 19, 2004.
- Bryant, Elizabeth. "France stung by new report on anti-Semitism," United Press International, October 20, 2004.
- "UK Chief Rabbi Jonathan Sacks: "The New Anti-Semitism is a Virus"".
- "Report of the All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism" Archived 2013-08-22 at the Wayback Machine, September 2006, p. 1.
- Temko, Ned. "Critics of Israel 'fuelling hatred of British Jews'", The Observer, February 3, 2006.
- MPs deliver anti-Semitism report, BBC News, September 6, 2006.
- "Report of the All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism" Archived 2013-08-22 at the Wayback Machine, September 2006, p. 22.
- Announcement by the Forum, November 18, 2001.
- Summers, Lawrence H. Address at morning prayers Archived 2004-10-10 at the Wayback Machine, September 17, 2002. On the site of Harvard University, accessed January 9, 2006.
- Matas, David. Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005, pp. 129–144.
- House Passes Chabot’s Bipartisan United Nations Reform Amendment, June 17, 2005. Accessed March 6, 2006.
- Bayefsky, Anne. One Small Step, Wall Street Journal opinion article, June 21, 2004, accessed January 9, 2006.
- Rickman, Gregg J. (2008). "Contemporary global anti-semitism" (PDF). USDOS. Retrieved 2008-03-27.
- "ISGAP". isgap.org.
- "Yale Creates Center to Study Antisemitism", Associated Press, September 19, 2006; also see Kaplan, Edward H. & Small, Charles A. "Anti-Israel sentiment predicts anti-Semitism in Europe," Journal of Conflict Resolution, Vol 50, No. 4, 548–561, August 2006.
- "The Academic and Public Debate Over the Meaning of the 'New Antisemitism'".
- U.S. Commission on Civil Rights, Campus Anti-Semitism (2006) at 72.
- Id.
- ^ Strauss, Mark (November 12, 2003). "Antiglobalism's Jewish Problem". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on March 12, 2013.
- Oded Grajew, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , Foreign Policy, 1 March 2004, p. 4.
- Maude Barlow, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , Foreign Policy, 1 March 2004, p. 4.
- John Cavanagh, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , Foreign Policy, 1 March 2004, p. 4.
- Mark Strauss, "Debating Anti-Semitism" , Foreign Policy, 1 March 2004, p. 4.
- Walter Laqueur (2006): The Changing Face of Anti-Semitism: From Ancient Times to the Present Day. Oxford University Press, 2006 ISBN 0-19-530429-2 p.186
- Summers, Lawrence. "Address at morning prayers" Archived 2011-08-12 at the Wayback Machine, Office of the President, Harvard University, September 17, 2002.
- Bergmann, Werner & Wetzel, Juliane. ["Manifestations of anti-Semitism in the European Union" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-04-15. (751 KiB), Center for Research on Antisemitism, Technische Universitaet Berlin, March 2003.
- ^ "Global Anti-Semitism Report", U.S. Department of State, January 5, 2005.
- ^ Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "Something is Rotten in the State of Europe": Anti-Semitism as a Civilizational Pathology. An Interview with Robert Wistrich" Archived 2011-11-28 at the Wayback Machine, Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism, Institute for Global Jewish Affairs at the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, October 1, 2004.
- ^ "France" Archived 2012-11-19 at the Wayback Machine, The Stephen Roth Institute for the Study of Antisemitism and Racism, Tel Aviv University, 2003.
- Joffe, Josef. "Nations we love to hate: Israel, America and the New Anti-Semitism" Archived 2006-09-09 at the Wayback Machine, Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2004, p.9.
- Joffe, Josef. "Nations we love to hate: Israel, America and the New Anti-Semitism" Archived 2006-09-09 at the Wayback Machine, Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 2004, p.12.
- Clark, David. "Accusations of anti-semitic chic are poisonous intellectual thuggery", The Guardian, March 6, 2006.
- ^ Lasn, Kalle. "Why Won't Anyone Say They are Jewish?" Archived 2009-06-14 at the Wayback Machine Adbusters Magazine, March/April 2004
- Raynes-Goldie, Kate. "Race Baiting: Adbusters' listing of Jewish neo-cons the latest wacko twist in left mag's remake" Archived 2007-10-18 at the Wayback Machine, Nowtoronto.com, March 18, 2004 – March 24, 2004.
- ^ Raynes-Goldie, Kate, "Race baiting Archived 2007-10-18 at the Wayback Machine", Now Magazine, March 18024, 2004
- ^ Monnot, Caroline & Ternisien, Xavier. Caroline Monnot and Xavier Ternisien. "Tariq Ramadan accusé d'antisémitisme" Archived 2008-10-05 at the Wayback Machine, Le Monde, October 10, 2003.
- ^ Klein, Naomi (April 26, 2002). "Sharon's Best Weapon: The left must confront anti-Semitism head-on". In These Times. Archived from the original on August 22, 2006.
- "Judeophobia", New Internationalist, October 2004.
- Ma'anit, Adam (October 2004). "A human balance". New Internationalist. No. 372. Archived from the original on May 2, 2015.
- Agbarieh, Asma (October 2004). "Spreading the Stain". New Internationalist. No. 372.
- Farivar, Masood (2023-10-11). "Antisemitism Surges Around World as Israel, Hamas Clash". Voice of America. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- "Israel-Hamas war unleashes wave of antisemitism in Europe". Financial Times. 2023-10-15. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- Chrisafis, Angelique; Kassam, Ashifa; Connolly, Kate; Giuffrida, Angela (2023-10-20). "'A lot of pain': Europe's Jews fear rising antisemitism after Hamas attack". the Guardian. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
References
- Asserson, Trevor & Williams, Cassie. "The BBC and the Middle East", BBC Watch, retrieved August 20, 2006.
- Barkun, Michael. A Culture of Conspiracy, University of California Press, 2003; this edition 2006
- Bauer, Yehuda. "Problems of Contemporary Anti-Semitism" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 5, 2003. Retrieved January 11, 2008., lecture to the Jewish Studies Dept of the University of California, Santa Cruz, 2003, retrieved April 22, 2006.
- Baxter, Sarah. "Wimmin at War", The Sunday Times, August 13, 2006, retrieved January 13, 2008.
- Bayefsky, Anne. One Small Step, Wall Street Journal, June 21, 2004, retrieved January 9, 2006.
- Beaumont, Peter. "The new anti-semitism?", '"The Observer, February 17, 2002, retrieved January 13, 2008.
- Berlet, Chip. "ZOG Ate My Brains", New Internationalist, October 2004.
- Berlet, Chip. "Right woos Left", Publiceye.org, December 20, 1990; revised February 22, 1994, revised again 1999.
- Booth, Jenny. "Oona King reveals 'yid' taunts during election", The Times, May 11, 2005.
- Brownfeld, Allan (1987). "Anti-Semitism: Its Changing Meaning". Journal of Palestine Studies. 16 (3). Institute for Palestine Studies: 53–67. doi:10.2307/2536789. ISSN 1533-8614. JSTOR 2536789.
- Bryant, Elizabeth. "France stung by new report on anti-Semitism," United Press International, October 20, 2004.
- Chanes, Jerome. "Review Essay: What's "New" – and what's not – about the New Antisemitism?" Archived 2011-11-28 at the Wayback Machine, Jewish Political Studies Review 16:1–2 (Spring 2004).
- Chesler, Phyllis The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It, Jossey-Bass, 2003. ISBN 0-7879-7803-5
- Conger, George. "UK MPs find leap in anti-Semitism", The Jerusalem Post, September 5, 2006.
- Curtis, Polly. "Jewish NUS officials resign over anti-semitism row", The Guardian, April 12, 2005.
- Dershowitz, Alan. The Case For Israel, John Wiley & Sons, 2003, paperback 2004. ISBN 0-471-67952-6
- Doward, Jamie. Jews predict record level of hate attacks", The Guardian, August 8, 2004.
- Dickter, Adam. Fear over European kosher bans, World Jewish Review, July 2002.
- Endelman, Todd M. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World. University of Toronto Press, 2005.
- Finkelstein, Norman. Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2005.
- Fischel, Jack. "The New Anti-Semitism", The Virginia Quarterly Review, Summer 2005, pp. 225–234.
- Fischel, Jack. Antisemitism resurfaces, Midstream, February 1, 2004.
- Fischel, Jack. "Conspiracy Theories as Comfort Food", The Forward, March 29, 2002.
- Forster, Arnold & Epstein, Benjamin, The New Anti-Semitism. McGraw-Hill 1974. ISBN 0-07-021615-0
- Foxman, Abraham H. Never Again? The Threat of the New Anti-Semitism. New York: HarperSanFrancisco (an imprint of HarperCollins), 2003. ISBN 0-06-054246-2 (10); ISBN 978-0-06-054246-7 (13).
- Goodman, Amy. "Finkelstein on DN! No New Antisemitism", interview with Norman Finkelstein, August 29, 2006.
- Harrison, Bernard. The Resurgence of Anti-Semitism: Jews, Israel, and Liberal Opinion. Rowman & Littlefield, 2006. 0742552276
- HaLevi, Ezra. "David Duke in Syria: Zionists Occupy Washington, NY and London", Arutz Sheva, November 29, 2005; see clip of David Duke's interview in Syria.
- Halkin, Hillel. "The Return of Anti-Semitism," Commentary, February 2002
- Hodgson, Jessica. "Editor apologises for 'Kosher Conspiracy' furore", The Guardian, February 7, 2002.
- Ioanid, Radu. Foreword in Taguieff, Pierre André. Rising from the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004.
- Jaffe, Ben-Zion. "Big Jew on Campus: The Jewish obsession", Jerusalem Post Blog Central, December 11, 2005.
- Kaplan, Edward H. & Small, Charles A. "Anti-Israel sentiment predicts anti-Semitism in Europe," Journal of Conflict Resolution, Vol 50, No. 4, 548–561, August 2006.
- Kinsella, Warren. The New anti-Semitism, retrieved March 5, 2006.
- Klug, Brian. The Myth of the New Anti-Semitism Archived 2009-07-01 at the Portuguese Web Archive. The Nation, posted January 15, 2004; February 2, 2004 issue.
- Klug, Brian. Israeli, Antisemitism and the left, Red Pepper, November 24, 2005.
- Klug, Brian. "In search of clarity", Catalyst, March 17, 2006.
- Landes, Richard. "Michael Lerner Weighs in, Disturbingly", Augean Stables, February 5, 2007.
- Lazare, Daniel. "The Chosen People", The Nation, December 19, 2005.
- Lerman, Tony. "Reflecting the reality of Jewish diversity", The Guardian: Comment is Free, February 6, 2007, retrieved August 11, 2007.
- Lerner, Michael. There Is No New Anti-Semitism, posted February 5, 2007, retrieved February 6, 2007.
- Lewis, Bernard. "The New Anti-Semitism", The American Scholar, Volume 75 No. 1, Winter 2006, pp. 25–36. The paper is based on a lecture delivered at Brandeis University on March 24, 2004.
- Liddle, Rod. "Just how many islands does Spain want?", The Guardian, July 17, 2002.
- Lipstadt, Deborah. Denying the Holocaust: The Growing Assault on Truth and Memory. Penguin 1994.
- Kenneth L. Marcus, Jurisprudence of the New Anti-Semitism, Wake Forest Law Review, Vol. 44, 2009. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1376592
- Matas, David. Anti-Zionism and Anti-Semitism. Dundurn Press, Toronto, 2005. ISBN 1-55002-553-8
- Prager, Dennis & Telushkin, Joseph. Why the Jews? The Reasons for Antisemitism. Simon & Schuster, 2003.
- Michael, George. The Enemy of my Enemy: The Alarming Convergence of Militant Islam and the Extreme Right. University Press of Kansas, 2006. ISBN 0-7006-1444-3
- Moormeister, Robyn. "Holocaust survivor organizes UCSC conference on anti-semitism", Santa Cruz Sentinel, May 2, 2003.
- Morse, Jane A. "World Trade Center Tragedy Hits All Nationalities", September 14, 2001.
- Paz, Reuven. "Palestinian Holocaust Denial" Archived 2007-12-09 at the Wayback Machine, Washington Institute Peace Watch, No. 255, April 21, 2000.
- Raab, Earl. "Is there a New Anti-Semitism?", Commentary, May 1974, pp. 53–54.
- Raab, Earl. "Antisemitism, anti-Israelism, anti-Americanism", Judaism, Fall 2002.
- Radler, Melissa. "Anti-Semitic riot at San Francisco State University," The Jerusalem Post, May 16, 2002.
- Reeves, Phil. "Amid the ruins, the grisly evidence of a war crime," The Independent, April 16, 2002.
- Reinach, Salomon & Simmonds, Florence. Orpheus: A General History of Religions, G. P. Putnam & Sons, 1909.
- Rosenbaum, Ron. (ed) Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism. Random House, 2004. ISBN 0-8129-7203-1
- Rubin, Daniel. (ed.) Anti-Semitism and Zionism: Selected Marxist Writings. International Publishers, 1987, p. 35.
- Rufin, Jean-Christophe. Chantier sur la lutte contre le racisms et l'antisemitisme, Ministry of the Interior, France. October 19, 2004.
- Sacks, Jonathan. "The New Antisemitism", Ha'aretz, September 6, 2002.
- Said, Edward. "A Desolation and They Called It Peace," in Rosenbaum, Ron. Those Who Forget the Past: The Question of Anti-Semitism. Random House, 2004.
- Schoenfeld, Gabriel. The Return of Anti-Semitism. Encounter Books, 2004.
- Sewell, Dennis. "A kosher conspiracy?", New Statesman, January 14, 2002.
- Strauss, Mark. "Antiglobalism's Jewish Problem" in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism, Random House 2004.
- Stillwell, Cinnamon. "SFSU's Legacy Of Intolerance", San Francisco Chronicle, December 14, 2004, retrieved January 12, 2008.
- Strauss, Mark. "Antiglobalism's Jewish Problem" in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism, Random House 2004.
- Summers, Lawrence H. "Address at morning prayers", September 17, 2002, retrieved January 9, 2006.
- Taguieff, Pierre-André. Rising From the Muck : The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2002. ISBN 1-56663-571-3 (published in France as La nouvelle judéophobie. Editions mille et une nuits. ISBN 2-84205-650-7).
- Temko, Ned. "Critics of Israel 'fuelling hatred of British Jews'", The Observer, February 3, 2006.
- Whine, Michael. "Progress in the Struggle Against Anti-Semitism in Europe: The Berlin Declaration and the European Union Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia's Working Definition of Anti-Semitism" Archived 2022-02-26 at the Wayback Machine, Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, February 1, 2006.
- Wiener, Jon. "Giving Chutzpah New Meaning", The Nation, July 11, 2005.
- Wilby, Peter. The New Statesman and anti-Semitism. The New Statesman. February 11, 2002, retrieved February 8, 2008.
- Wistrich, Robert. "Anti-zionism as an Expression of Anti-Semitism in Recent Years", lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the President of Israel, December 10, 1984.
- Wurmbrand, Max & Roth, Cecil. The Jewish People: 4000 Years of Survival, p. 403 and passim. Massadah-P. E. C. Press, 1966.
- Zipperstein, Steven J. "Historical Reflections on Contemporary Antisemitism", in Derek J. Penslar et al., ed., Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005.
- Zoloth, Laurie. "Fear and Loathing at San Francisco State" in Rosenbaum, Ron. Those who forget the past. Random House, 2004.
- Zuckerman, Mortimer B. "Graffiti on History's Walls" Archived 2022-05-23 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. News & World Report. March 11, 2003, retrieved January 12, 2008.
- Zwartz, Barney & Morton, Adam. "An unholy alliance", The Age, September 4, 2006.
- 2004 Annual Report on the activities of the parliamentary commissioner for the rights of national and ethnic minorities, European Union, 2004.
- 2004 Community Security Trust Antisemitic Incidents Report.
- "France pulls plug on Arab network", BBC News, December 14, 2004.
- "'Anti-Semitism Shall Have No Place Among Us,' Powell Says", posted April 29, 2004. U.S. Department of State.
- "The Euston Manifesto" Archived 2008-04-20 at the Wayback Machine, London, March 29, 2006.
- "American White Supremacist David Duke: Israel Makes the Nazi State Look Very Moderate", interview with David Duke on Syrian television, the Middle East Media Research Institute (MEMRI), November 25, 2005. Clip of the interview and of Duke's speech to a Syrian rally can be viewed here .
- "The Architecture of Bigotry," Policy Dispatch, no. 80, Institute of the World Jewish Congress, June 2002.
- CAMERA, "Can the BBC Change?", CAMERA, July 26, 2004.
- "Report of the All-Party Parliamentary Inquiry into Anti-Semitism", September 7, 2006.
- "December 8, 2003", Watch, retrieved August 27, 2006.
- "Scene from a 'peace rally'", BackSpin Weblog of Honest Reporting, December 4, 2003.
- United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, November 10, 1975, retrieved January 13, 2008.
- "The Euston Manifesto" Archived 2008-04-20 at the Wayback Machine, March 29, 2006.
- "(U.S.) State Department report on Anti-Semitism: Europe and Eurasia," December 15, 2004; see Global Anti-Semitism Review Act of 2004.
- "French concern about race attacks", BBC News, October 2004.
- "MPs deliver anti-Semitism report", BBC News, September 6, 2006.
- House Passes Chabot’s Bipartisan United Nations Reform Amendment, June 17, 2005, retrieved March 6, 2006.
- "Working definition of antisemitism", EUMC.
- "Antisemitism: Summary overview of the situation in the European Union, 2001–2005 (working paper)", European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia, May 2006.
- "Yale Creates Center to Study Antisemitism", Associated Press, September 19, 2006.
- Arnold Forster & Benjamin Epstein, The New Anti-Semitism. McGraw-Hill 1974, p. 165. See for instance chapters entitled "Gerald Smith's Road" (19–48), "The Radical Right" (285–296), "Arabs and Pro-Arabs" (155–174), "The Radical Left" (125–154).
- Wistrich, Robert. "Anti-zionism as an Expression of Anti-Semitism in Recent Years", lecture delivered to the Study Circle on World Jewry in the home of the President of Israel, December 10, 1984.
- Chesler, Phyllis. The New Anti-Semitism: The Current Crisis and What We Must Do About It, Jossey-Bass, 2003, pp. 158–159, 181.
- Doward, Jamie. Jews predict record level of hate attacks: Militant Islamic media accused of stirring up new wave of anti-semitism, The Guardian, August 8, 2004.
- Kinsella, Warren. The New anti-Semitism, accessed March 5, 2006.
- Sacks, Jonathan. "The New Antisemitism", Ha'aretz, September 6, 2002, retrieved on January 10, 2007.
- Strauss, Mark. "Antiglobalism's Jewish Problem" in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism, Random House 2004, p 272.
- Endelman, Todd M. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World. University of Toronto Press, 2005, pp. 65–79.
- Rosenbaum, Ron. Those who forget the past. Random House, 2004.
- Taguieff, Pierre-André. Rising From the Muck: The New Anti-Semitism in Europe. Ivan R. Dee, 2004.
Further reading
- Aaronovitch, David. "The New Anti-Semitism", The Observer, June 22, 2003.
- Abram, Morris B. Anti-Semitism in the United Nations
- Arenson, David & Grynberg, Simon. Anti-Globalization and the New Anti-Semitism Archived 2004-07-26 at the Wayback Machine.
- Avneri, Uri. Anti-Semitism: A Practical Manual, Gush Shalom.
- Bayefsky, Anne. "The UN and the Jews", Commentary Magazine, February 2004.
- Berger, Luciana. "Why I had to resign", The Guardian, April 15, 2005
- Bergmann, Werner & Wetzel, Julie. "Manifestations of Anti-Semitism in the European Union" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-04-15. (751 KB), Berlin Research Centre on Anti-Semitism, Technische Universität Berlin.
- Bourne, Jenny. "Anti-Semitism or Anti-Criticism?", Race and Class, Vol. 46, 2004.
- Burchill, Julie. "The hate that shames us", The Guardian, December 6, 2003.
- Chittenden, Maurice. "Dons' boycott raises Jewish student fear", The Sunday Times, April 17, 2005
- Chomsky, Noam. "Necessary Illusions". Archived from the original on September 13, 2002. Retrieved January 9, 2006.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link), accessed January 9, 2006. - Cohen, Ben. "The Persistence of Anti-Semitism on the British Left" Jewish Political Studies Review 16:3–4 via the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, Fall 2004.
- Cohen, Nick. "One woman's war: anti-Semitism," New Statesman, October 10, 2005.
- Cohen, Nick. "Following Mosley's East End footsteps", The Observer, April 17, 2005.
- Cooper, Abraham. SWC: "The Independent's Sharon Cartoon in Tradition of 'Der Stürmer' and Conjures Up 'Blood Libel' Canard", January 30, 2003.
- Cotler, Irwin. "Identifying the New Anti-Semitism" Archived 2006-08-25 at the Wayback Machine, Jewish People Policy Planning Institute, November 2002.
- Cotler, Irwin. Human Rights and the New Anti-Jewishness: Sounding the Alarm
- Curthoys, Ned. "A new anti-Semitism: American discourse since September 11 has seen a reinvention of the eternal anti-semitism thesis applied to critics of Israel," Arena Magazine, April 1, 2004.
- Dinnerstein, Leonard. "Is There a New Anti-Semitism in the United States?" Society, 41 (January/February 2004), 53–58.
- Endelman, Todd M. "Antisemitism in Western Europe Today" in Contemporary Antisemitism: Canada and the World. University of Toronto Press, 2005.
- Evans, Harold. "The View from Ground Zero," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism, Random House 2004.
- Foxman, Abraham H. Blurring the Line, Ha'aretz, April 4, 2004.
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "Anti-Israelism and Anti-Semitism: Common Characteristics and Motifs" Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback MachineJewish Political Studies Review 19:1–2 Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, March 1, 2007.
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "Something is rotten in the State of Europe: Anti-Semitism as a Civilizational Pathology", an interview with Robert S. Wistrich, October 1, 2004.
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "Major Anti-Semitic Motifs in Arab Cartoons: An Interview with Joël Kotek" Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine, Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism, No. 21, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, June 1, 2004.
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. Europe’s Crumbling Myths: The Post-Holocaust Origins of Today’s Anti-Semitism, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs/Yad Vashem/World Jewish Congress, 2003. ISBN 965-218-045-9.
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "The Academic Boycott Against Israel", Jewish Political Studies Review 15:3–4 (Fall 2003).
- Gerstenfeld, Manfred. "Anti-Semitic Motifs in Anti-Israelism," Archived 2007-09-26 at the Wayback Machine Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism, no. 2, 1 November 2002.
- Gitlin, Todd. "The Rough Beast Returns" in Rosenbaum, Ron. Those who forget the past. Random House, 2004.
- Goldberg, Sol & Ury, Scott & Weiser, Kalman, eds., Key Concepts in the Study of Antisemitism Palgrave-Macmillan, 2021. ISBN 978-3-030-51658-1
- Goldenberg, Suzanne. "Israeli boycott divides academics", The Guardian, July 8, 2002.
- Gordon, Neve. "Seeing through the 'new anti-Semitism': Norman Finkelstein critiques Israel's human rights record and Alan Dershowitz's defense of it," National Catholic Reporter, October 14, 2005.
- Grant, Linda. "The hate that will not die", The Guardian, December 18, 2001.
- Greenspan, Miriam. (Nov–Dec 2003). "The New Anti-Semitism". Tikkun 18:6. p. 33.
- Gross, Tom. "Jeningrad: What the British Media Said," in Rosenbaum, Ron (ed). Those who forget the past: The Question of Anti-Semitism, Random House 2004.
- Harris, Ben. "'Progressive' anti-Semitism? S.F. meet considers phenomenon", JTA, January 23, 2006.
- Horowitz, Craig. "The Return of Anti-Semitism", New York Magazine.
- David Hirsh, writing on contemporary antisemitism on the guardian's Comment Is Free website
- Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) New European Extremism: Hating America, Israel and the Jews. Profile Books Limited, 2006. ISBN 1-86197-792-1
- Iganski, Paul & Kosmin, Barry. (eds) A New Antisemitism? Debating Judeophobia in 21st Century Britain, Profile Books Limited, 2003. ISBN 1-86197-651-8
- Jonas, George. "Pragmatic anti-Semites", National Post, October 27, 2003.
- Joffe, Josef. "Nations we love to hate: Israel, America and the New Anti-Semitism", Posen Papers in Contemporary Antisemitism, No.1, Vidal Sassoon Center for the Study of Antisemitism, 2004.
- Kaye/Kantrowitz, Melanie. "Some Notes on Anti-Semitism from a Progressive Jewish Perspective", Jewish Currents, March 2007.
- Kite, Melissa. "Labour should have fought back on immigration, says Euan Blair's girlfriend", The Telegraph, April 17, 2005.
- Klug, Brian. "The collective Jew: Israel and the new antisemitism," used as a resource by the EUMC in their report Manifestations of Antisemitism in the EU 2002–2003, Vienna, March 2004. See especially pp. 12–13, 225–241.
- Klug, Brian & Wistrich, Robert S. "Correspondence between Prof. Robert Wistrich and Brian Klug: When Is Opposition to Israel and Its Policies Anti-Semitic?", International Center for the Study of Anti-Semitism, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, retrieved September 8, 2006.
- Lewis, Bernard. "Muslim Anti-Semitism" in Rosenbaum, Ron. Those who forget the past, Random House, 2003. pp. 549–62.
- Kuruvila, Matthai Chakko. "Bay Area debate flares over 'new anti-Semitism'", San Francisco Chronicle, January 27, 2007.
- Lappin, Shalom. The New Antisemitism: The Resurgence of an Ancient Hatred in the Modern World, Cambridge : Polity Press, 2024, ISBN 9781509558568.
- Lopez, Kathryn Jean. "Liberal & Pro-Israel, Feminist Phyllis Chesler on 'The New Anti-Semitism'", National Review Online, November 25, 2003.
- MacShane, Denis. "Anti-semitism is back", The Guardian, September 7, 2006.
- McGeal, Chris. "The 'new' anti-semitism: is Europe in grip of worst bout of hatred since the Holocaust?", The Guardian, November 25, 2003
- Minerbi, Sergio I. "Neo Anti-Semitism in Today's Italy" Archived 2006-06-14 at the Wayback Machine, Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, Fall 2003.
- Nirenstein, Fiamma. Terror: The New Anti-Semitism And The War Against The West, 2005. ISBN 1-57525-377-1
- Pearl, Judea. Is anti-Zionism hate?, Los Angeles Times, March 15, 2009.
- Pfeifer, Karl. "Antisemitism unites left and right extremists", Scholars for Peace in the Middle East.
- Pipes, Daniel. The New Anti-Semitism Archived 2004-06-03 at the Wayback Machine.
- Rich, Dave The Left's Jewish Problem
- Rosenblum, April. "If Not Together, How?".
- Rosenfeld, Alvin H., ed. (2015). Deciphering the New Antisemitism. Bloomington, Indianapolis: Indiana University Press. ISBN 9780253018694. OCLC 928716737. Project MUSE 43135
- Rosenthal, John. "Leftist myths and leftist responsibility", Policy Review Online, retrieved August 29, 2006.
- Sacks, Jonathan. A New Antisemitism?, June 2002.
- Samuels, Shimon. Applying the Lessons of the Holocaust: from Particularism to Universalism and Back.
- Sharansky, Natan. On Hating the Jews, Commentary, November 2003.
- Sharansky, Natan. The New Antisemitism, January 1, 2002.
- Smith, Lewis. "Jews criticise lecturer boycott", The Times, April 18, 2005
- Ury, Scott. "Strange Bedfellows? Anti-Semitism, Zionism, and the Fate of 'the Jews'” American Historical Review 123, 4 (Oct. 2018) 1151-1171.
- Whine, Michael. "Islamist recruitment and antisemitism on British campuses" Archived 2008-04-07 at the Wayback Machine (DOC file), Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies.
- Weill-Raynal, Guillaume, Une haine imaginaire : contre-enquête sur le nouvel antisémitisme (An imaginary hatred: investigation about the new antisemitism), Paris, Armand Colin, 2005, ISBN 2-200-26912-9.
- Wistrich, Robert S. Antisemitism: The Longest Hatred. Pantheon Books, 1992.
- Wistrich, Robert S. "The Old-New Anti-Semitism", The National Interest, Number 72, Summer 2003.
- Wistrich, Robert S. "European Anti-Semitism Reinvents Itself", American Jewish Committee, 2005.
- Wistrich, Robert S. "From Ambivalence to Betrayal: The Left, the Jews, and Israel (Studies in Antisemitism)". University of Nebraska Press, 2012
- Zuckerman, Mortimer B. "Graffiti On History's Walls", U.S. News & World Report, March 11, 2003.
- " Drawing the line: the 'new anti-Semitism' versus legitimate criticism of Israel", "Make your point", Haaretz, July 18, 2004.
- "The New Anti-Semitism in Western Europe", American Jewish Committee.
- "The New Anti-Semitism", Christian Action for Israel.
- "Audit finds anti-Semitism rising across Canada", CTV News, March 6, 2003.
- "Anti-Semitism in the Church?", BeitShalom.org
- "Post-Holocaust and Anti-Semitism", Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs, retrieved September 7, 2006.
- Large collection of quotes by Hindu philosophers and writers against Anti-Semitism
- "The New Face of Antisemitism", Department for Jewish Zionist Education, The Jewish Agency for Israel.
Reports
- From government and inter-governmental sources
- (U.S.) State Department report on Anti-Semitism: Europe and Eurasia, excerpted from a longer piece, and covering the period of July 1, 2003 – December 15, 2004].
- "Manifestations of Anti-Semitism in the European Union" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-04-15. (751 KB) Unpublished EU report from 2003
- Annual Report on Racism and Antisemitism published by French National Consultative Commission of Human Rights 2004 Archived 2006-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- From the Anti-Defamation League
- "Deceptive Web Site Attempts to Lure Anti-Globalization Activists to Neo-Nazi Movement", Anti-Defamation League, July 11, 2002
- Map of Attitudes Toward Jews in 12 European Countries based on a 2005 ADL Survey.
- The New Anti-Semitism in Europe and The Middle East: Threat is "Potent and Very Real" ADL Leader Says in Major Address.
- "ANSWER, Antiwar Rallies and Support for Terror Organizations", Anti-Defamation League, August 22, 2006.
- "Anti-Semitism on Display", Anti-Defamation League, January 28, 2003.
- From the American Jewish Committee
- Anti-Zionism in Great Britain and Beyond: A "Respectable" Anti-Semitism? December 21, 2003
- Progressive Jewish Thought and the New Antisemitism, December 2006
- Antisemitism Made in Iran: Against Al Quds Day, June 2006
External links
- The Nature of Modern Antisemitism an online lecture by Professor David Bankier of Yad Vashem
- “Voices on Antisemitism” Interview with Alain Finkielkraut from the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- Rosner's Domain: Robert Wistrich on the meaning of "new" anti-Semitism
- A film clip "The Open Mind – Anti-Semitism, Part I (1981)" is available for viewing at the Internet Archive
- A film clip "The Open Mind – Anti-Semitism, Part II (1981)" is available for viewing at the Internet Archive
