| Revision as of 17:11, 7 January 2007 view sourceXyzzy n (talk | contribs)2,779 edits moving images to fix bunched up edit links← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:25, 2 January 2025 view source A1Cafel (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers10,764 edits →Morphology: poor quality | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Region of the torso of a primate that in females serves as a mammary gland}} | |||
| {{for|various cities in Europe pronounced in a similar way|Brest}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| ] woman’s breasts.]] | |||
| {{Pp|small=yes}} | |||
| The term '''breast''' refers to the upper ventral region of an animal’s ], particularly that of ]s, including ] beings. The breasts of a female mammal’s body contain the ], which secrete ] used to feed ]s. This article focuses on ] ] breasts, but ] humans also have breasts which are usually less prominent, but structurally identical and ] to the female, as they develop ] from the same tissues. In some situations male breast development does occur, a condition called ]. | |||
| {{Pp-move}} | |||
| {{wiktionarypar2|breasts|WikiSaurus:breasts}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=November 2024}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=November 2024}} | |||
| {{Infobox anatomy | |||
| | Name = Breast | |||
| | Latin = {{noitalic|{{wikt-lang|la|mamma}} ({{lang|la|mammalis}} 'of the breast')<ref> | |||
| {{cite web |url=http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/mammal |title=mammal |publisher=Dictionary.reference.com |access-date=31 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111114204020/http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/mammal |archive-date=14 November 2011 |url-status=live }}</ref>}} | |||
| | Image = Weibliche brust en.jpg | |||
| | Caption = ] of female human breasts, with the ], ], and ] | |||
| | Image2 = File:Male Thorax.jpg | |||
| | Caption2 = Male human breasts with defined ]s | |||
| | Precursor = | |||
| | System = | |||
| | Artery = ] | |||
| | Vein = ] | |||
| | Nerve = | |||
| | Lymph = | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''breasts''' are two prominences located on the upper ] region of the ] among humans and other ]s. Both sexes develop breasts from the same ] tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major ] between females and males. There is also considerable ] between individuals. Female humans are the only ]s which permanently develop breasts at ]; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy; at puberty, ], in conjunction with ], cause permanent ]. | |||
| In females, the breast serves as the ], which produces and secretes milk to feed ]s.<ref> | |||
| ==Anatomy== | |||
| {{cite web |url = http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/breast |title = Breast – Definition of breast |work = Merriam-Webster |access-date = 21 October 2015 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150906013636/http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/breast |archive-date = 6 September 2015 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> ] covers and envelops a network of ] that converge on the ], and these ] give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are ], or clusters of ], where milk is produced and stored in response to ].<ref name=SEER> | |||
| ] | |||
| {{cite web |title = SEER Training: Breast Anatomy |url = http://training.seer.cancer.gov/breast/anatomy/ |publisher = National Cancer Institute |access-date = 9 May 2012 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120502155537/http://training.seer.cancer.gov/breast/anatomy/ |archive-date = 2 May 2012 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }} | |||
| ] | |||
| </ref> During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including ]s, ], and ], that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of ] and ]. | |||
| The breasts are covered by ]. Each breast has one ] surrounded by the ]. The areola is colored from pink to dark brown and has several ]s. The larger ]s within the breast produce the milk. They are distributed throughout the breast, with two-thirds of the tissue found within 30 mm of the base of the nipple.<ref name="Ramsay">Anatomy of the lactating human breast redefined with ultrasound imaging, D.T. Ramsay et al., ''J. Anat.'' '''206''':525-534</ref> These are drained to the nipple by between 4 and 18 ''lactiferous ducts'', where each duct has its own opening. The network formed by these ducts is complex, like the tangled roots of a tree. It is not always arranged radially, and branches close to the nipple. The ducts near the nipple do not act as milk reservoirs. Ramsay '' et al.'' have shown that conventionally described ''lactiferous sinuses'' do not, in fact, exist. | |||
| Along with their major function in providing nutrition for infants, several cultures ascribe social and ] characteristics to female breasts, and may regard ] in ] as ] or ]. Breasts have been featured in ancient and modern sculpture, art, and photography. Breasts can represent ], ], or ]. They can figure prominently in the perception of a woman's body and ]. Breasts, especially the nipples, can be an ]. | |||
| The remainder of the breast is composed of ] (] and ]), ] (fat), and ]. The ratio of glands to adipose tissues rises from 1:1 in nonlactating women to 2:1 in lactating women.<ref name="Ramsay"/> | |||
| ==Etymology and terminology== | |||
| The breasts sit over the ] muscle and usually extend from the level of the 2nd rib to the level of the 6th rib ]. The ] quadrant of the breast extends diagonally upwards towards the axillae and is known as the ]. A thin layer of ] extends from the ] above to the seventh or eighth ribs below and from the midline to the edge of the ] ]. | |||
| The English word ''breast'' derives from the ] word {{lang|ang|brēost}} {{Gloss|breast, bosom}} from ] {{lang|gem-x-proto|breustam}} {{Gloss|breast}}, from the ] base {{lang|ine-x-proto|bhreus–}} {{Gloss|to swell, to sprout}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=Indo-European Lexicon |url=http://www.utexas.edu/cola/centers/lrc/ielex/PokornyMaster-X.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160420225029/http://www.utexas.edu/cola/centers/lrc/ielex/PokornyMaster-X.html |archive-date=20 April 2016 |website=The University of Texas at Austin }}</ref> The ''breast'' spelling conforms to the Scottish and North English dialectal pronunciations.<ref> | |||
| {{cite web |title=breast |url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=breast |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120202185418/http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=breast |archive-date=2 February 2012 |access-date=7 March 2011 |website=Online Etymology Dictionary }} | |||
| </ref> The ''Merriam-Webster Dictionary'' states that "] {{lang|enm|brest}}, from Old English {{lang|ang|brēost}}; akin to ] {{lang|goh|brust}}..., ] {{lang|sga|brú}} , Russian {{lang|ru-Latn|bryukho}}"; the first known usage of the term was before the 12th century.<ref> | |||
| {{cite web |title=Definition of breast |url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/breast |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161220084629/https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/breast |archive-date=20 December 2016 |access-date=10 December 2016 |website=Dictionary by Merriam-Webster }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| ''Breasts'' is often used to refer to female breasts in particular, though the stricter anatomical term refers to the same region on members of either sex. Male breasts are sometimes referred to in the singular to mean the collective upper chest area,{{efn|Such that one's hands might be folded "upon one's breast" or one's heart might be "within one's breast"}} whereas female breasts are referred to in the plural unless speaking of a specific left or right breast. | |||
| The ] ] ] to the breasts is derived from the ] (formerly called the ''internal mammary artery''), ], ], and posterior intercostal arteries. The ] drainage of the breast is mainly to the ], but there is some drainage to the ] and the intercostal veins. Both sexes have a large concentration of ]s and ]s in their ]s. | |||
| A large number of colloquial terms for female breasts are used in English, ranging from fairly polite terms to vulgar or slang.{{efn|See ]}} Some vulgar slang expressions may be considered to be derogatory or sexist to women.<ref>{{cite web |last=Groot |first=Sue de |date=18 September 2016 |title=Is there a respectful slang word for breasts? |url=https://www.timeslive.co.za/sunday-times/lifestyle/2016-09-18-is-there-a-respectful-slang-word-for-breasts/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161211114217/http://www.timeslive.co.za/sundaytimes/lifestyle/opinion/article1754258.ece |archive-date=11 December 2016 |access-date=11 December 2016 |website=Sunday Times }}</ref> | |||
| The breast is ] by the anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of the 4th through 6th intercostal ]s. The nipple is supplied by the T4 ]. | |||
| ==Evolutionary development== | |||
| The primary anatomical support for the breasts is thought to be provided by the ], with additional support from the ] covering the breasts themselves, and it is this support which determines the shape of the breasts. The external shape or size of the breast is not predictive of its internal anatomy nor of its lactation potential. In a small fraction of women, the frontal milk sinuses (ampulla) in the breasts are not flush with the surrounding breast tissue, which causes the sinus area to visibly bulge outward. | |||
| ] breastfeeding an infant]] | |||
| Humans are the only mammals whose breasts become permanently enlarged after ] (known in humans as ]). The reason for this evolutionary change is unknown.<ref name="DM">{{Cite web |last=Alex |first=Bridget |date=6 March 2019 |title=Scientists Still Stumped by the Evolution of Human Breasts |url=https://www.discovermagazine.com/planet-earth/scientists-still-stumped-by-the-evolution-of-human-breasts |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220204163722/https://www.discovermagazine.com/planet-earth/scientists-still-stumped-by-the-evolution-of-human-breasts |archive-date=4 February 2022 |access-date=4 February 2022 |website=]}}</ref> Several hypotheses have been put forward: | |||
| A link has been proposed to processes for synthesizing the ] ] precursor ] which takes place in fat rich regions of the body like the buttocks and breasts. These contributed to human brain development and played a part in increasing brain size. Breast enlargement may for this purpose have occurred as early as '']'' (1.7–1.4 ]).<ref name=":2" /> Other breast formation hypotheses may have then taken over as principal drivers.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=LeBlanc|first1=Steven A.|last2=Barnes|first2=Ethne|date=July 1974|title=On the Adaptive Significance of the Female Breast|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/282935|journal=The American Naturalist|volume=108|issue=962|pages=577–578|doi=10.1086/282935|bibcode=1974ANat..108..577L |s2cid=85243414|issn=0003-0147|access-date=24 November 2021|archive-date=4 March 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220304004849/https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/10.1086/282935|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite journal|last1=Howard|first1=Beatrice A.|last2=Veltmaat|first2=Jacqueline M.|date=18 May 2013|title=Embryonic Mammary Gland Development; a Domain of Fundamental Research with High Relevance for Breast Cancer Research|journal=Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia|volume=18|issue=2|pages=89–91|doi=10.1007/s10911-013-9296-2|pmid=23686554|s2cid=1657065|issn=1083-3021|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last1=Pawłowski|first1=Bogusław|last2=Żelaźniewicz|first2=Agnieszka|date=2021|title=The evolution of perennially enlarged breasts in women: a critical review and a novel hypothesis|url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/brv.12778|journal=Biological Reviews|language=en|volume=96|issue=6|pages=2794–2809|doi=10.1111/brv.12778|pmid=34254729|s2cid=235807642|issn=1469-185X|access-date=30 November 2021|archive-date=30 November 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211130190318/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/brv.12778|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| It has been suggested by zoologists Avishag and ] that the size of the human breasts can be explained by the ] of ]. This would see the explanation for larger breasts as them being an ] of the women's health and ability to grow and carry them in her life. Prospective mates can then evaluate the genes of a potential mate for their ability to sustain her health even with the additional energy demanding burden she is carrying.<ref>Geoffrey Miller: ''The Sexual Evolution. Choice of partner and the emergence of the mind.'' Spectrum Academic Publishing House, 2009, {{ISBN|978-3-8274-2508-9}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{cite journal |last1=Pawłowski |first1=Bogusław |last2=Żelaźniewicz |first2=Agnieszka |date=13 July 2021 |title=The evolution of perennially enlarged breasts in women: a critical review and a novel hypothesis |journal=Biological Reviews |volume=96 |issue=6 |pages=2794–2809 |doi=10.1111/brv.12778 |pmid=34254729 |s2cid=235807642| issn=0006-3231 }}</ref> | |||
| The zoologist ] describes a sociobiological approach in his science book '']''. He suggests, by making comparisons with the other primates, that breasts evolved to replace swelling buttocks as a sex signal of ovulation. He notes how humans have, relatively speaking, large penises as well as large breasts. Furthermore, early humans adopted bipedalism and face-to-face coitus. He therefore suggested enlarged sexual signals helped maintain the bond between a mated male and female even though they performed different duties and therefore were separated for lengths of time.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Dunbar |first1=Robin |last2=Saini |first2=Angela |last3=Garrod |first3=Ben |last4=Rutherford |first4=Adam |date=24 September 2017 |title=The Naked Ape at 50: 'Its central claim has surely stood the test of time ' |url=http://www.theguardian.com/science/2017/sep/24/the-naked-ape-at-50-desmond-morris-four-experts-assess-impact |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211116160057/https://www.theguardian.com/science/2017/sep/24/the-naked-ape-at-50-desmond-morris-four-experts-assess-impact |archive-date=16 November 2021 |access-date=24 November 2021 |website=The Guardian |language=en}}</ref><ref name=":0" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Binns |first=Corey |date=5 August 2010 |title=Why Do Women Have Breasts? |url=https://www.livescience.com/32745-why-do-women-have-breasts.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211124171609/https://www.livescience.com/32745-why-do-women-have-breasts.html |archive-date=24 November 2021 |access-date=24 November 2021 |website=Live Science |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| A 2001 study proposed that the rounded shape of a woman's breast evolved to prevent the sucking infant offspring from suffocating while feeding at the teat; that is, because of the human infant's small jaw, which did not project from the face to reach the nipple, they might block the ] against the mother's breast if it were of a flatter form (compare with the ]). Theoretically, as the human jaw receded into the face, the woman's body compensated with round breasts.<ref name="Bentley">{{cite journal |last = Bentley |first = Gillian R. |year = 2001 |title = The evolution of the human breast |journal = American Journal of Physical Anthropology |volume = 32 |issue = 38 |doi = 10.1002/ajpa.1033 |pages = 30–50 }}</ref> | |||
| ]e (1965) proposed that breasts came about as an adaptation for infant feeding for a different reason, as early human ancestors adopted bipedalism and the loss of body hair. Human upright stance meant infants must be carried at the hip or shoulder instead of on the back as in the apes. This gives the infant less opportunity to find the nipple or the purchase to cling on to the mother's body hair. The mobility of the nipple on a large breast in most human females gives the infant more ability to find it, grasp it and feed.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
| Other suggestions include simply that permanent breasts attracted mates, that "pendulous" breasts gave infants something to cling to, or that permanent breasts shared the function of a ], to store fat as an energy reserve.<ref name="DM"/> | |||
| == Structure == | |||
| ]. {{ordered list |] |]s |] |] |] |] |] |Skin}}]] | |||
| In women, the breasts overlie the ]s and extend on average from the level of the second rib to the level of the sixth rib in the front of the ]; thus, the breasts cover much of the chest area and the chest walls. At the front of the chest, the '''breast tissue''' can extend from the ] (collarbone) to the middle of the ] (breastbone). At the sides of the chest, the breast tissue can extend into the ] (armpit), and can reach as far to the back as the ], extending from the lower back to the ] bone (the bone of the upper arm). As a ], the breast is composed of differing layers of ], predominantly two types: ]; and ], which affects the lactation functions of the breasts.<ref name=GRAYS2005>{{cite book |last = Drake |first = Richard L. |title = Gray's anatomy for students |year = 2005 |publisher = Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone |location = Philadelphia |isbn = 978-0-8089-2306-0 |author2 = Vogl, Wayne |author3 = Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell |others = illustrations by Richard Richardson, Paul }}</ref>{{rp|115}} The natural ] of the human breast is about 2 ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Cameron |first1=John R. |last2=Skofronick |first2=James G. |last3=Grant |first3=Roderick M. |title=Physics of the Body |date=1999 |publisher=Medical Physics Publishing |location=Madison, Wis |isbn=978-0-944838-91-4 |pages=69–70 |edition=2nd |url=https://medicalphysics.org/SimpleCMS.php?content=bookpage.php&isbn=9781930524941}}</ref> | |||
| ], the breast is tear-shaped.<ref name="love_c1">{{cite book|last1=Love|first1=Susan M.|title=Dr. Susan Love's Breast Book|date=2015|publisher=Da Capo Press|location=U.S.|isbn=978-07382-1821-2|edition=6|chapter=1}}</ref> The superficial tissue layer (]) is separated from the skin by 0.5–2.5 cm of subcutaneous fat (adipose tissue). The ] are fibrous-tissue prolongations that radiate from the superficial fascia to the skin envelope. The female adult breast contains 14–18 irregular lactiferous lobes that converge at the nipple. The 2.0–4.5 mm milk ducts are immediately surrounded with dense connective tissue that support the glands. Milk exits the breast through the nipple, which is surrounded by a pigmented area of skin called the areola. The size of the areola can vary widely among women. The areola contains modified ] known as ]. These glands secrete oily fluid that lubricate and protect the nipple during breastfeeding.<ref name=stoppler>{{cite web |last1 = Stöppler |first1 = Melissa Conrad |title = Breast Anatomy |url = http://www.medicinenet.com/breast_anatomy/article.htm |access-date = 28 June 2015 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150627065040/http://www.medicinenet.com/breast_anatomy/article.htm |archive-date = 27 June 2015 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> Volatile compounds in these secretions may also serve as an olfactory stimulus for the newborn's appetite.<ref>{{cite journal |doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0007579 |title = The Secretion of Areolar (Montgomery's) Glands from Lactating Women Elicits Selective, Unconditional Responses in Neonates |year = 2009 |editor1-last = Hausberger |editor1-first = Martine |last1 = Doucet |first1 = Sébastien |last2 = Soussignan |first2 = Robert |last3 = Sagot |first3 = Paul |last4 = Schaal |first4 = Benoist |journal = PLOS ONE |volume = 4 |issue = 10 |pages = e7579 |pmid = 19851461 |pmc = 2761488 |bibcode = 2009PLoSO...4.7579D |doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ]s]] | |||
| The dimensions and weight of the breast vary widely among women. A small-to-medium-sized breast weighs 500 grams (1.1 pounds) or less, and a large breast can weigh approximately 750 to 1,000 grams (1.7 to 2.2 pounds) or more. In terms of composition, the breasts are about 80 to 90% ]l tissue (] and ]), while ] or ]ular tissue only accounts for about 10 to 20% of the volume of the breasts.<ref name="pmid16728564">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lorincz AM, Sukumar S |title=Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer |journal=Endocrine-Related Cancer |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=279–92 |year=2006 |pmid=16728564 |doi=10.1677/erc.1.00729 |quote=Adipocytes make up the bulk of the human breast, with epithelial cells accounting for only approximately 10% of human breast volume.|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="pmid11149569">{{cite journal |vauthors=Howard BA, Gusterson BA |title=Human breast development |journal=Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=119–37 |year=2000 |pmid=11149569 |doi= 10.1023/A:1026487120779|s2cid=10819224 |quote=In the stroma, there is an increase in the amount of fibrous and fatty tissue, with the adult nonlactating breast consisting of 80% or more of stroma.}}</ref><ref name="RosenfieldCookeRadovick2021">{{cite book | title = Sperling Pediatric Endocrinology | last1 = Rosenfield | first1 = Robert L. | last2 = Cooke | first2 = David W. | last3 = Radovick | first3 = Sally | chapter = Puberty in the Female and Its Disorders | date = 2021 | pages = 528–626 | publisher = Elsevier | doi = 10.1016/B978-0-323-62520-3.00016-6 | isbn = 9780323625203 | s2cid = 234131890 | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=8J7yDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA554 | quote = Estrogen stimulates the nipples to grow, mammary terminal duct branching to progress to the stage at which ductules are formed, and fatty stromal growth to increase until it constitutes about 85% of the mass of the breast. Lobulation appears around menarche, when multiple blind saccular buds form by branching of the terminal ducts. These effects are due to the presence of progesterone. Full alveolar development normally only occurs during pregnancy under the influence of additional progesterone and prolactin.}}</ref><ref name="pmid22206682">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hagisawa S, Shimura N, Arisaka O |title=Effect of excess estrogen on breast and external genitalia development in growth hormone deficiency |journal=Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology |volume=25 |issue=3 |pages=e61–3 |year=2012 |pmid=22206682 |doi=10.1016/j.jpag.2011.11.005 |quote=Estrogen stimulates growth of the nipples, progression of mammary duct branching to the stage at which ductiles are formed, and fatty stromal growth until it constitutes about 85% of the mass of the breast.}}</ref><ref name="pmid2942075">{{cite journal | vauthors = Drife JO | title = Breast development in puberty | journal = Ann N Y Acad Sci | volume = 464 | issue = 1| pages = 58–65 | date = 1986 | pmid = 2942075 | doi = 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15993.x | bibcode = 1986NYASA.464...58D | s2cid = 12735704 | url = | quote = Along with the glandular growth, there is an increase in the amount of fibrous and fatty tissue, and in fact these latter two constituents of the breast account for a far greater proportion of the morphologic growth than the proportion contributed by glandular tissue. In the nonlactating adult breast, glandular tissue accounts for no more than 20% of the breast volume, and often much less than this, and the morphologic changes at puberty are therefore mainly due to stromal expansion.}}</ref> The tissue composition ratios of the breast also vary among women. Some women's breasts have a higher proportion of glandular tissue than of adipose or ] tissues. The fat-to-connective-tissue ratio determines the density or firmness of the breast. During a woman's life, her breasts change size, shape, and weight due to hormonal changes during ], the ], ], breastfeeding, and ].<ref>Pamplona DC, de Abreu Alvim C. Breast Reconstruction with Expanders and Implants: a Numerical Analysis. Artificial Organs 8 (2004), pp. 353–356.</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1 = Grassley |first1 = JS |year = 2002 |title = Breast Reduction Surgery: What every Woman Needs to Know |journal = Lifelines |volume = 6 |issue = 3 |pages = 244–249 |doi = 10.1111/j.1552-6356.2002.tb00088.x |pmid = 12078570 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Glandular structure=== | |||
| {{Main articles|Mammary gland}} | |||
| ] of the breast.]] | |||
| The breast is an ] gland that produces the ] used to feed an infant. The ] of the breast is surrounded by the ] (nipple-areola complex). The areola has many sebaceous glands, and the skin color varies from pink to dark brown. The basic units of the breast are the terminal duct lobular units (TDLUs), which produce the fatty breast milk. They give the breast its offspring-feeding functions as a mammary gland. They are distributed throughout the body of the breast. Approximately two-thirds of the lactiferous tissue is within 30 mm of the base of the nipple. The terminal lactiferous ducts drain the milk from TDLUs into 4–18 lactiferous ducts, which drain to the nipple. The milk-glands-to-fat ratio is 2:1 in a lactating woman, and 1:1 in a non-lactating woman. In addition to the milk glands, the breast is also composed of connective tissues (], ]), white fat, and the suspensory Cooper's ligaments. Sensation in the breast is provided by the ] innervation by means of the front (anterior) and side (lateral) cutaneous branches of the fourth-, fifth-, and sixth ]. The T-4 nerve (]), which innervates the ], supplies sensation to the nipple-areola complex.<ref name=grabowski>{{cite book |first1 = Gerard J. |last1 = Tortora |first2 = Sandra Reynolds |last2 = Grabowski |title = Introduction to the Human Body: the Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology |date = 2001 |publisher = J. Wiley |location = New York; Toronto |isbn = 978-0-471-36777-2 |edition = Fifth. }}</ref> | |||
| ===Lymphatic drainage=== | ===Lymphatic drainage=== | ||
| Approximately 75% of the ] from the breast travels to the axillary ]s on the same side of the body, while 25% of the lymph travels to the parasternal nodes (beside the sternum bone).<ref name=GRAYS2005 />{{rp|116}} A small amount of remaining lymph travels to the other breast and to the abdominal lymph nodes. The subareolar region has a lymphatic plexus known as the "subareolar plexus of Sappey".<ref name="Pacifici">{{cite web |last1=Pacifici |first1=Stefano |title=Sappey plexus {{!}} Radiology Reference Article {{!}} Radiopaedia.org |url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sappey-plexus-1?lang=gb |website=Radiopaedia |date=11 October 2011 |access-date=25 August 2020 |archive-date=2 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210502224454/https://radiopaedia.org/articles/sappey-plexus-1?lang=gb |url-status=live }}</ref> The ]s include the pectoral (chest), subscapular (under the scapula), and humeral (humerus-bone area) lymph-node groups, which drain to the central ] and to the apical axillary lymph nodes. The lymphatic drainage of the breasts is especially relevant to ] because breast cancer is common to the mammary gland, and cancer cells can ] (break away) from a ] and be dispersed to other parts of the body by means of the lymphatic system. | |||
| == |
===Morphology=== | ||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| ===Breastfeeding and pregnancy=== | |||
| | image1 = Breasts of a woman.jpg | |||
| ].]] | |||
| | image2 = Breasts, young woman.png | |||
| The function of the ]s in female breasts is to nurture the young by producing ], which is secreted by the ]s during ]. While the ]s that produce milk are present in the male, they normally remain undeveloped. The orb-like shape of breasts may help limit heat loss, as a fairly high temperature is required for the production of milk. During lactation, the energy consumption of the breast exceeds that of the brain,<ref>See ''Hartmann''</ref> otherwise by far the body’s most energy-hungry organ. Alternatively, the human breast evolved in order to prevent infants from suffocating while feeding. Since human infants do not have a protruding ] like human evolutionary ancestors and other ]s, the infant’s ] might be blocked by a flat female chest while feeding. According to this theory, as the human jaw receded, the breasts became larger to compensate.<ref name="bentley">{{cite journal|last=Bentley|first=Gillian R.|year=2001|title=The Evolution of the Human Breast|journal=American Journal of Physical Anthropology|volume=32|issue=38}}</ref> | |||
| | footer = Breasts can vary significantly in both size and shape. | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | image3 = Small Breasts.jpg | |||
| | perrow = 2 / 2 | |||
| | total_width = 320 | |||
| | image4 = Breasts close-up (4).jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| The morphologic variations in the size, shape, volume, tissue density, pectoral locale, and spacing of the breasts determine their natural shape, appearance, and position on a woman's chest. ] and other characteristics do not predict the fat-to-milk-gland ratio or the potential for the woman to nurse an infant. The size and the shape of the breasts are influenced by normal-life hormonal changes (thelarche, menstruation, pregnancy, menopause) and medical conditions (e.g. ]).<ref name=wood>{{cite journal |vauthors = Wood K, Cameron M, Fitzgerald K |title = Breast Size, Bra Fit and Thoracic Pain in Young Women: A Correlational Study |journal = Chiropractic & Osteopathy |volume = 16 |page = 1 |year = 2008 |pmid = 18339205 |pmc = 2275741 |doi = 10.1186/1746-1340-16-1 |doi-access = free }}</ref> The shape of the breasts is naturally determined by the support of the suspensory Cooper's ligaments, the underlying muscle and bone structures of the chest, and by the skin envelope. The suspensory ligaments sustain the breast from the clavicle (collarbone) and the clavico-pectoral fascia (collarbone and chest) by traversing and encompassing the fat and milk-gland tissues. The breast is positioned, affixed to, and supported upon the chest wall, while its shape is established and maintained by the skin envelope.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Breast Anatomy – Breast360.org {{!}} The American Society of Breast Surgeons Foundation |url=https://breast360.org/topic/2017/01/01/breast-anatomy/ |access-date=2024-12-21 |website=breast360.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Breast Anatomy {{!}} SEER Training |url=https://training.seer.cancer.gov/breast/anatomy/ |access-date=2024-12-21 |website=training.seer.cancer.gov}}</ref> In most women, one breast is slightly larger than the other.<ref name=love_c1/> More obvious and persistent asymmetry in breast size occurs in up to 25% of women.<ref name=mgh2010>{{cite web |url = http://www.mgh.harvard.edu/children/adolescenthealth/articles/aa_breast_development.aspx |title = Breast Development |publisher = Massachusetts Hospital for Children |access-date = 2 June 2010 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20101225165742/http://www.mgh.harvard.edu/children/adolescenthealth/articles/aa_breast_development.aspx |archive-date = 25 December 2010 |url-status = dead |df = dmy }}</ref> | |||
| Milk production can also occur in both men and women as an ] of some medicinal ] (such as some ] medication), extreme physical stress or in endocrine disorders. Newborn babies are often capable of ] because they receive some amount of ] and ] (milk hormones) from their connection to the mother. | |||
| The base of each breast is attached to the chest by the deep fascia over the pectoralis major muscles. The base of the breast is semi-circular, however the shape and position of the breast above the surface is variable.<ref>{{Citation |last=Gould |first=Stanley F. |title=Anatomy of the Breast |date=1983 |work=Lactation: Physiology, Nutrition, and Breast-Feeding |pages=23–47 |editor-last=Neville |editor-first=Margaret C. |url=https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4613-3688-4_2 |access-date=2024-12-25 |place=Boston, MA |publisher=Springer US |language=en |doi=10.1007/978-1-4613-3688-4_2 |isbn=978-1-4613-3688-4 |editor2-last=Neifert |editor2-first=Marianne R.}}</ref> The space between the breast and the pectoralis major muscle, called ], gives mobility to the breast. The chest (]) progressively slopes outwards from the thoracic inlet (atop the ]) and above to the lowest ribs that support the breasts. The inframammary fold (IMF), where the lower portion of the breast meets the chest, is an anatomic feature created by the adherence of the breast skin and the underlying connective tissues of the chest; the IMF is the lower-most extent of the anatomic breast. Normal breast tissue has a texture that feels nodular or granular, with considerable variation from woman to woman.<ref name="love_c1" /> | |||
| ===Other suggested functions=== | |||
| ] point out that no female ] other than the human has breasts of comparable size when not lactating and that humans are the only ] that have permanently swollen breasts. This suggests that the external form of the breasts is connected to factors other than lactation alone. | |||
| Breasts have been categorized into four general morphological groups: "flat, spheric, protruded, and drooped", or "small/flat, large/inward, upward, and droopy".<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Suh |first1=Minyoung |last2=Park |first2=Jung Hyun |date=2022-01-01 |title=Breast Geometry Characterization of Young American Females Using 3D Image Analysis |journal=Applied Sciences |language=en |volume=12 |issue=17 |pages=8578 |doi=10.3390/app12178578 |doi-access=free |issn=2076-3417}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |title=Brassiere Pattern Development Based on 3D Measurements of Upper Body Types for Women in Their 30's |url=https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200827464608269.page |journal=The Research Journal of the Costume Culture|date=2008 |volume=16 |issue=3 |last1=Mi-Sook |first1=Cho }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Coltman |first1=Celeste E. |last2=Steele |first2=Julie R. |last3=McGhee |first3=Deirdre E. |date=2018-09-02 |title=Effects of age and body mass index on breast characteristics: a cluster analysis |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00140139.2018.1481229 |journal=Celeste E. Coltman |volume=61 |issue=9 |pages=1232–1245 |doi=10.1080/00140139.2018.1481229 |pmid=29792567 |issn=0014-0139}}</ref> | |||
| One theory is based around the fact that, unlike nearly all other primates, human females do not display clear, physical signs of ]. This could have plausibly resulted in human males evolving to respond to more subtle signs of ovulation. During ovulation, the increased ] present in the female body results in a slight swelling of the breasts, which then males could have evolved to find attractive. In response, there would be evolutionary pressures that would favor females with more swollen breasts who would, in a manner of speaking, appear to males to be the most likely to be ovulating. | |||
| ==== Support ==== | |||
| Some zoologists (notably ]) believe that the shape of female breasts evolved as a frontal counterpart to that of the ], the reason being that whilst other primates mate in the ] position, humans are more likely to successfully ] mating face on. A secondary sexual characteristic on a woman’s chest would have encouraged this in more primitive incarnations of the human race, and a face on encounter would have helped found a relationship between partners beyond merely a sexual one. | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | image1 = Pink underwire bra breasts close-up.jpg | |||
| | image2 = Young Woman Wearing Orange Sports Bra.jpg | |||
| | footer = Left: Underwire bra. Right: Sports bra | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | perrow = 2 / 2 | |||
| | total_width = 320 | |||
| }} | |||
| While it is a common belief that breastfeeding causes ],<ref name="lauersen">{{cite book |last = Lauersen |first = Niels H. |title = The Complete Book of Breast Care |year = 1998 |publisher = Fawcett Columbine/Ballantine |location = New York |isbn = 978-0-449-91241-6 |edition = 1st Trade Paperback |author2 = Stukane, Eileen |quote = ...there is no medical reason to wear a bra, so the decision is yours, based on your own personal comfort and aesthetics. Whether you have always worn a bra or always gone braless, age and breastfeeding will naturally cause your breasts to sag. |url = https://archive.org/details/completebookofbr00laue_0 }}</ref> researchers have found that a woman's breasts sag due to four key factors: cigarette smoking, ], ], and weight loss or gain.<ref name="thompson">{{cite journal |doi = 10.1016/j.asj.2008.07.004 |title = The Effect of Breastfeeding on Breast Aesthetics |year = 2008 |last1 = Rinker |first1 = B |last2 = Veneracion |first2 = M |last3 = Walsh |first3 = C |journal = Aesthetic Surgery Journal |volume = 28 |issue = 5 |pages = 534–7 |pmid = 19083576 |doi-access = free}} | |||
| ==Size and shape== | |||
| *{{cite news |author=Andrea Thompson |date=2 November 2007 |title=Breastfeeding Does Not Make Breasts Sag, Study Suggests |work=LiveScience |url = http://www.livescience.com/1998-breastfeeding-breasts-sag-study-suggests.html |access-date = 9 May 2015 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120703153917/http://www.livescience.com/1998-breastfeeding-breasts-sag-study-suggests.html |archive-date = 3 July 2012 |url-status = live}}</ref> Women sometimes wear bras because they mistakenly believe they prevent breasts from sagging as they get older.<ref name="burn" /> Physicians, lingerie retailers, teenagers, and adult women used to believe that bras were medically required to support breasts. In a 1952 article in ''Parents' Magazine'', Frank H. Crowell erroneously reported that it was important for teen girls to begin wearing bras early. According to Crowell, this would prevent sagging breasts, stretched blood vessels, and poor circulation later on.<ref name="brumberg">{{cite book |url=http://course1.winona.msus.edu/pjohnson/e111/e111f99/brumberg.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20020328155254/http://course1.winona.msus.edu/pjohnson/e111/e111f99/brumberg.htm |isbn=0-679-73529-1 |page=336|title=The Body Project: An Intimate History of American Girls|archive-date=28 March 2002|first=Joan Jacobs |last=Brumberg|year=1998 |publisher=Knopf Doubleday Publishing }}</ref> This belief was based on the false idea that breasts cannot anatomically support themselves.<ref name="burn">{{cite web |title=Don't burn your bra just yet |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/health-and-families/health-news/dont-burn-your-bra-just-yet-622008.html |website=The Independent |date=22 September 2011 |access-date=8 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180717232012/https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/health-and-families/health-news/dont-burn-your-bra-just-yet-622008.html |archive-date=17 July 2018 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="007b Breast">{{cite web |url=http://www.007b.com/why_wear_bras.php |title=Female Intelligence Agency: Why Do Women Wear Bras? |publisher=007b Breast |access-date=10 May 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110831044824/http://www.007b.com/why_wear_bras.php |archive-date=31 August 2011 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Shape and support=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ]s are sometimes used for cardiovascular exercise, sports bras are designed to secure the breasts closely to the body to prevent movement during high-motion activity such as running. Studies have indicated sports bras which are overly tight may restrict respiratory function.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ocran |first1=Francisca Margarita |last2=Ji |first2=Xiaofen |last3=Zhai |first3=Lina |date=January 2022 |title=A study to evaluate pressure distribution of different sports bras |journal=Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics |language=en |volume=17 |doi=10.1177/15589250221118643 |issn=1558-9250|doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Kipp |first1=Shalaya |last2=Leahy |first2=Michael G. |last3=Sheel |first3=A. William |date=2024-06-01 |title=Sports Bra Restriction on Respiratory Mechanics during Exercise |url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38350462/ |journal=Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise |volume=56 |issue=6 |pages=1168–1176 |doi=10.1249/MSS.0000000000003403 |issn=1530-0315 |pmid=38350462}}</ref> | |||
| Aside from size variations, there is naturally large variety in the ''shape'' of breasts. | |||
| As with all body parts, the shape of the breast is determined primarily by the differential rate of growth in different areas, and the direction of said growth. | |||
| Additionally, the shape of a woman’s breast is in large part dependent on their support, which primarily comes from the skin and the ligaments of the breasts themselves, and the underlying chest on which they rest. The breast is attached at its base to the chest wall by the deep fascia over the ]. On its upper surface it is suspended by the covering skin where it continues on to the upper chest wall. | |||
| ==Development== | |||
| In discussing the support of breasts, it is helpful to draw a distinction between breasts which extend below (the ''inframammary line'') to rest on the chest below, and those which do not. | |||
| {{Main|Breast development}} | |||
| Breasts which do not extend below the ] line at all form a rounded dome shape protruding almost horizontally from the chest wall. All breasts are like this in early stages of development, and such a shape is common in younger women and girls. This protruding or “high” breast is anchored to the chest at its base, and the weight is distributed evenly over the area of the base of the approximately ]-shaped breasts. | |||
| The breasts are principally composed of adipose, ], and ] tissues.<ref name="yen">{{citation |title = Yen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology |url = https://www.elsevier.com/books/yen-and-jaffes-reproductive-endocrinology/strauss/978-1-4160-4907-4 |author = Robert L. Barbieri |doi = 10.1016/B978-1-4160-4907-4.00010-3 |edition = 6th |publisher = Elsevier |date = 2009 |journal = Yen |pages = 235–248 |isbn = 978-1-4160-4907-4 |access-date = 6 March 2018 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20180306142739/https://www.elsevier.com/books/yen-and-jaffes-reproductive-endocrinology/strauss/978-1-4160-4907-4 |archive-date = 6 March 2018 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }} | |||
| In the “low” breast, a proportion of the breasts’ weight is actually supported by the chest against which the lower breast surface comes to rest, as well as the deep anchorage at the base. The weight is thus distributed over a larger area. This has the effect of reducing the strain. In both males and females, the ] slopes progressively outwards from the thoracic inlet (at the top of the ]) above to the lowest ribs which mark its lower boundary, allowing it to support the breasts. | |||
| </ref> Because these tissues have hormone receptors,<ref name="yen" /><ref name="gland activation">{{citation |title = Hormone Action in the Mammary Gland |author1 = Brisken |author2 = Malley |doi = 10.1101/cshperspect.a003178 |date = 2 December 2010 |pmid = 20739412 |pmc = 2982168 |volume = 2 |issue = 12 |journal = Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol |pages = a003178 }}</ref> their sizes and volumes fluctuate according to the hormonal changes particular to thelarche (sprouting of breasts), menstruation (egg production), pregnancy (reproduction), lactation (feeding of offspring), and menopause (end of menstruation). | |||
| ===Puberty=== | |||
| The ] (IMF) is an anatomic structure created by adherence between elements in the skin and underlying connective tissue<ref>Boutros S, Kattash M, Wienfeld A, Yuksel E, Baer S, Shenaq S. <u>The intradermal anatomy of the inframammary fold</u>. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998 Sep;102(4):1030-3. PMID 9734420</ref> and represents the inferior extent of breast anatomy. The relationship of the nipple positon to this IMF is described as '']''. Due to breast weight and relaxation of support structures, the NAC and breast tissue may eventually hang below the IMF, and in some cases the breasts may extend as far as, or even beyond, the ]. The length from the nipple to the sternal notch (central, upper border) in the youthful breast averages 21 cm and is a common anthropometric figure used to assess both breast symmetry and ptosis. Lengthening of both this measurement and the distance between the NAC and IMF are both characteristic of advancing grades of ptosis. Some teenagers may develop breasts whose skin comes into contact with the chest below the inframammary fold at an early age, and some women may never develop such breasts. Both situations are perfectly normal. | |||
| ] | |||
| The morphological structure of the human breast is identical in males and females until ]. For pubescent girls in thelarche (the breast-development stage), the female ]s (principally estrogens) in conjunction with ] promote the sprouting, growth, and development of the breasts. During this time, the mammary glands grow in size and volume and begin resting on the chest. These development stages of ]s (breasts, pubic hair, etc.) are illustrated in the five-stage ].<ref name="A.R.Greenbaum">{{cite journal |vauthors = Greenbaum AR, Heslop T, Morris J, Dunn KW |title = An Investigation of the Suitability of Bra fit in Women Referred for Reduction Mammaplasty |journal = British Journal of Plastic Surgery |volume = 56 |issue = 3 |pages = 230–6 |date = April 2003 |pmid = 12859918 |doi = 10.1016/S0007-1226(03)00122-X }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| During ], the developing breasts are sometimes of unequal size, and usually the left breast is slightly larger. This condition of asymmetry is transitory and statistically normal in female physical and sexual development.<ref name="asymmetry">{{cite journal |author = Loughry CW |title = Breast Volume Measurement of 598 Women using Biostereometric Analysis |journal = Annals of Plastic Surgery |year = 1989 |volume = 22 |issue = 5 |pages = 380–385 |doi = 10.1097/00000637-198905000-00002 |pmid = 2729845 |display-authors = 1 |last2 = Sheffer |first2 = Daniel B. |last3 = Price |first3 = Thomas E. |last4 = Einsporn |first4 = Richard L. |last5 = Bartfai |first5 = Ronald G. |last6 = Morek |first6 = Wayne M. |last7 = Meli |first7 = Nancy M. |s2cid = 8713713 }}</ref> Medical conditions can cause overdevelopment (e.g., virginal breast hypertrophy, ]) or underdevelopment (e.g., ], ]) in girls and women. | |||
| The end of the breast, which includes the nipple, may either be flat (a 180 degree angle) or angled (angles lower than 180 degrees). | |||
| Breast ends are rarely angled sharper than 60 degrees. | |||
| Angling of the end of the breast is caused in part by the ligaments that suspend it, such that the breast ends often have a more obtuse angle when a woman is lying on her back. | |||
| Breasts exist in a range of ratios between length and base diameter, usually ranging from 1/2 to 1. | |||
| Approximately two years after the onset of puberty (a girl's first ]), estrogen and growth hormone stimulate the development and growth of the glandular fat and suspensory tissues that compose the breast. This continues for approximately four years until the final shape of the breast (size, volume, density) is established at about the age of 21. ] (breast enlargement) in girls begins at puberty, unlike all other primates, in which breasts enlarge only during lactation.<ref name="stoppler" /> | |||
| ===Additional, external support=== | |||
| === Hormone replacement therapy === | |||
| Since the breasts are flexible, the shape of breasts may be strongly affected by clothing, and ] in particular. A ] may be worn to give additional support and to alter the shape of the breasts. There is some debate over whether such support is desirable. A long term clinical study showed that women with large breasts can suffer shoulder pain as a result of ],<ref>Ryan, EL, Pectoral girdle myalgia in women: a 5-year study in a clinical setting. Clin J Pain. 2000 Dec;16(4):298-303</ref> although a well fitting bra should support most of the breasts’ weight with proper sized cups and back band rather than on the shoulders. (See ].) | |||
| ] | |||
| ], including ], stimulates the growth of glandular and adipose tissue through estrogen supplementation.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=De |first1=Blok Christel |last2=Klaver |first2=Maartje |last3=Nota |first3=Nienke |last4=Dekker |first4=Marieke |last5=Den |first5=Heijer Martin |date=2016-05-13 |title=Breast development in male-to-female transgender patients after one year cross-sex hormonal treatment |url=https://www.endocrine-abstracts.org/ea/0041/ea0041gp146 |journal=Endocrine Abstracts |language=en |volume=41 |doi=10.1530/endoabs.41.GP146 |issn=1470-3947}}</ref> | |||
| In menopausal women, HRT helps restore breast volume and skin elasticity diminished by declining estrogen levels, typically using oral or transdermal estradiol.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement |date=2010 |pmc=6287288 |last1=Santen |first1=R. J. |last2=Allred |first2=D. C. |last3=Ardoin |first3=S. P. |last4=Archer |first4=D. F. |last5=Boyd |first5=N. |last6=Braunstein |first6=G. D. |last7=Burger |first7=H. G. |last8=Colditz |first8=G. A. |last9=Davis |first9=S. R. |last10=Gambacciani |first10=M. |last11=Gower |first11=B. A. |last12=Henderson |first12=V. W. |last13=Jarjour |first13=W. N. |last14=Karas |first14=R. H. |last15=Kleerekoper |first15=M. |last16=Lobo |first16=R. A. |last17=Manson |first17=J. E. |last18=Marsden |first18=J. |last19=Martin |first19=K. A. |last20=Martin |first20=L. |last21=Pinkerton |first21=J. V. |last22=Rubinow |first22=D. R. |last23=Teede |first23=H. |last24=Thiboutot |first24=D. M. |last25=Utian |first25=W. H. |author26=Endocrine Society |journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism |volume=95 |issue=7 Suppl 1 |pages=s1–s66 |doi=10.1210/jc.2009-2509 |pmid=20566620 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Changes in size and shape=== | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| In gender-affirming hormone therapy, breast development is induced through feminizing HRT, often combining estrogen with anti-androgens to suppress testosterone. Maximum growth is usually achieved after 2–3 years.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Information on Estrogen Hormone Therapy {{!}} Gender Affirming Health Program |url=https://transcare.ucsf.edu/article/information-estrogen-hormone-therapy |access-date=2024-12-02 |website=transcare.ucsf.edu}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Practical Guidelines for Transgender Hormone Treatment {{!}} Endocrinology, Diabetes, Nutrition & Weight Management |url=https://www.bumc.bu.edu/endo/clinics/transgender-medicine/guidelines/ |access-date=2024-12-02 |website=www.bumc.bu.edu}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Transgender and Gender Diverse Hormone Therapy |url=https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/-/media/center-for-transgender-health/documents/tgd-gaht-quick-guide.ashx |website=hopkinsmedicine.org}}</ref> | |||
| As breasts are mostly composed of adipose tissue, their size can change over time. This occurs for a number of reasons, for example if the woman gains or loses ]. Any rapid increase in size of the breasts, during puberty, weight gain or pregnancy, can result in the appearance of ] on the skin. | |||
| Factors such as age, genetics, and hormone dosage influence outcomes. | |||
| It is also typical for a number of changes to occur during ]: the breasts generally become larger and firmer, mainly due to ] of the mammary gland in response to the ] ]. The size of the nipples may increase noticeably and their pigmentation may become darker. These changes may continue during breastfeeding. The breasts generally revert to approximately their previous size after pregnancy, although there may be some increased sagging and ]. | |||
| ===Changes during the menstrual cycle=== | |||
| The size of a woman’s breasts usually also fluctuates during the ], particularly with ]. An increase in breast size is also a common ] of use of the ]. | |||
| During the menstrual cycle, the breasts are enlarged by ] and temporary growth as influenced by changing hormone levels.<ref name="mlpswelling">{{citation |title = Breast – premenstrual tenderness and swelling |url = https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003153.htm |publisher = A.D.A.M. |date = May 2012 |access-date = 21 March 2018 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160705060104/https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003153.htm |archive-date = 5 July 2016 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| ===Pregnancy and breastfeeding=== | |||
| {{Main articles|Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy|Breastfeeding}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The breasts reach full maturity only when a woman's first pregnancy occurs.{{sfn | Lawrence | 2016 | p=34}} Changes to the breasts are among the first signs of pregnancy. The breasts become larger, the nipple-areola complex becomes larger and darker, the ] enlarge, and veins sometimes become more visible. Breast tenderness during pregnancy is common, especially during the first trimester. By mid-pregnancy, the breast is physiologically capable of lactation and some women can express ], a form of breast milk.{{sfn | Lawrence | 2016 | p=58}} | |||
| Pregnancy causes elevated levels of the hormone ], which has a key role in the production of milk. However, milk production is blocked by the hormones ] and ] until after delivery, when progesterone and estrogen levels plummet.<ref name="NCBI Bookshelf 2008"/> | |||
| The breasts naturally sag through ], as the ] become elongated. This process may be accelerated by high impact ]s, and a ] may reduce this effect by providing external support, although the health benefits of wearing of a brassiere are not universally accepted. | |||
| ===Menopause=== | |||
| Some women undergo ] after ] for ], a result of the high value placed on ] of the human form in those cultures, and because women often identify their femininity and sense of self with their breasts. | |||
| ]]]{{Main article|Menopause}} | |||
| At menopause, breast atrophy occurs.<ref>{{Cite journal |title=Menopausal Transition, Body Mass Index, and Prevalence of Mammographic Dense Breasts in Middle-Aged Women |date=2020 |pmc=7465213 |last1=Kim |first1=E. Y. |last2=Chang |first2=Y. |last3=Ahn |first3=J. |last4=Yun |first4=J. S. |last5=Park |first5=Y. L. |last6=Park |first6=C. H. |last7=Shin |first7=H. |last8=Ryu |first8=S. |journal=Journal of Clinical Medicine |volume=9 |issue=8 |page=2434 |doi=10.3390/jcm9082434 |doi-access=free |pmid=32751482 }}</ref> The breasts can decrease in size when the levels of circulating estrogen decline. The adipose tissue and milk glands also begin to wither. The breasts can also become enlarged from ] of ]s. The size of the breasts can also increase and decrease in response to ] fluctuations.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Wanders |first1=Johanna Olga Pauline |last2=Bakker |first2=Marije Fokje |last3=Veldhuis |first3=Wouter Bernard |last4=Peeters |first4=Petra Huberdina Maria |last5=van Gils |first5=Carla Henrica |date=2015-05-30 |title=The effect of weight change on changes in breast density measures over menopause in a breast cancer screening cohort |journal=Breast Cancer Research |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=74 |doi=10.1186/s13058-015-0583-2 |doi-access=free |issn=1465-542X |pmc=4487974 |pmid=26025139}}</ref> | |||
| Physical changes to the breasts are often recorded in the ] of the skin envelope; they can serve as historical indicators of the increments and the decrements of the size and volume of a woman's breasts throughout the course of her life.{{Verification needed|date=December 2024|reason=This statement may not correspond to present sources}} | |||
| ==Plastic surgery== | |||
| Plastic surgical procedures of the breast include those for both cosmetic and reconstrucive surgery indications. After ] some women choose to have their breasts reconstructed, with either breast implants or autologous tissue transfer, using fat and tissues from the abdomen (TRAM flap) or back (latissiumus muscle flap). ] surgery is a common procedure which involves resecting excess breast tissue and skin with repositioning of the nipple-areolar complex (NAC). Cosmetic procedures include breast lifts (]), ] with implants, and procedures that combine both elements. Implants containing either ] gel or ] are available for augmentation or reconstructive surgeries. | |||
| Breast changes during menopause are sometimes treated with ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-02-07 |title=What You Should Know About Hormone Therapy and Menopause |url=https://www.cuimc.columbia.edu/news/what-you-should-know-about-hormone-therapy-and-menopause |access-date=2024-12-25 |website=Columbia University Irving Medical Center |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Any surgery of the breast carries with it the potential for interfering with future breast feeding. The risk of suffering from lactation insufficiency rises over threefold in post-surgical women.<ref name="Neifert">Neifert, MR et al. (1990) The influence of breast surgery, breast appearance and pregnancy-induced changes on lactation sufficiency as measured by infant weight gain. ''Birth'' '''17''':31-38</ref> Breast reduction surgery significantly shortens the median duration of exclusive breastfeeding (in one study dropping from an average of 3 months to 5 days<ref name="souto">Souto, GC et al. (2003) The impact of breast reduction surgery on breastfeeding. ''J Hum Lact''.'''19(1)''':43-49</ref>). Two thirds of breast augmentation surgery patients have been shown to have insufficient milk supply.<ref name="hurst">Hurst, N (1996) Lactation after augmentation mammoplasty. ''Obstet. Gynecol.'' '''87''':30-34</ref> Plastic surgery organizations have generally discouraged elective cosmetic breast surgery in teenagers as the volume of their breast tissue may continue to grow significantly as they mature and over concerns of understanding long-term risks and benefits of the procedure. | |||
| == |
===Cancer=== | ||
| {{Main|Breast cancer}} | |||
| Stages of development during puberty can be seen at . | |||
| Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue.<ref>{{cite web |title = Breast Cancer |url = http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/breast |website = NCI |access-date = 29 June 2014 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140625232947/http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/breast |archive-date = 25 June 2014 |date = January 1980 }}</ref> Signs of breast cancer may include a ] in the breast, a change in breast shape, ] of the skin, ], fluid coming from the ], a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin.<ref name=NCI2014Pt>{{cite web |title = Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) |url = http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/breast/Patient/page1/AllPages |website = NCI |date = 23 May 2014 |access-date = 29 June 2014 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140705110404/http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/breast/Patient/page1/AllPages |archive-date = 5 July 2014 }}</ref> In those with ], there may be ], swollen ]s, ], or ].<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Saunders C, Jassal S |title = Breast cancer |date = 2009 |publisher = Oxford University Press |location = Oxford |isbn = 978-0-19-955869-8 |page = Chapter 13 |edition = 1. |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=as46WowY_usC&pg=PT123 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20151025013217/https://books.google.com/books?id=as46WowY_usC&pg=PT123 |archive-date = 25 October 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| Risk factors for developing breast cancer include ], a ], alcohol consumption, ] during ], ], an early age at ], having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /><ref name="WCR2014">{{cite book |title = World Cancer Report 2014 |date = 2014 |publisher = World Health Organization |isbn = 978-92-832-0429-9 |pages = Chapter 5.2 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fakhri N, Chad MA, Lahkim M, Houari A, Dehbi H, Belmouden A, El Kadmiri N | title = Risk factors for breast cancer in women: an update review | journal = Medical Oncology | volume = 39 | issue = 12 | pages = 197 | date = September 2022 | pmid = 36071255 | doi = 10.1007/s12032-022-01804-x | s2cid = 252113509 }}</ref> About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition,<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> including ] among others.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of ] and the ] that supply these ducts with milk.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> Cancers developing from the ducts are known as ], while those developing from lobules are known as ]s.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> There are more than 18 other sub-types of breast cancer.<ref name=WCR2014 /> Some, such as ], develop from ].<ref name=WCR2014 /> The diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed by taking a ] of the concerning tissue.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> Once the diagnosis is made, further tests are carried out to determine if the cancer has spread beyond the breast and which treatments are most likely to be effective.<ref name=NCI2014Pt /> | |||
| ==Breastfeeding== | |||
| {{Main|Breastfeeding}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The primary function of the breasts, as mammary glands, is the nourishing of an infant with ]. Milk is produced in milk-secreting cells in the alveoli. When the breasts are stimulated by the suckling of her baby, the mother's brain secretes ]. High levels of oxytocin trigger the contraction of muscle cells surrounding the alveoli, causing milk to flow along the ducts that connect the alveoli to the nipple.<ref name="NCBI Bookshelf 2008">{{cite web | title=The physiological basis of breastfeeding | website=NCBI Bookshelf | date=5 November 2008 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK148970/ | access-date=13 February 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180119051121/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK148970/ | archive-date=19 January 2018 | url-status=live | df=dmy-all }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| Full-term newborns have an instinct and a need to suck on a nipple, and breastfed babies nurse for both nutrition and for comfort.{{sfn|Lawrence|2016|p=201}} Breast milk provides all necessary nutrients for the first six months of life, and then remains an important source of nutrition, alongside solid foods, until at least one or two years of age. | |||
| == Exercise == | |||
| Biomechanical studies have demonstrated that, depending on the activity and the size of a woman's breast, when she walks or runs braless, her breasts may move up and down by {{convert|4|to|18|cm}} or more, and also oscillate side to side.<ref name=nhsuk/> Researchers have also found that as women's breast size increased, they took part in less physical activity, especially vigorous exercise. Few very-large-breasted women jogged, for example. To avoid exercise-related discomfort and pain, medical experts suggest women wear a well-fitted ] during activity.<ref name=nhsuk>{{cite web |title=How a well-fitted sports bra can reduce breast pain |url=https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/exercise/right-sports-bra-can-reduce-breast-pain/ |website=nhs.uk |access-date=7 March 2019 |language=en |date=30 April 2018}}</ref> | |||
| ==Clinical significance== | |||
| {{Main|Breast disease}} | |||
| The breast is susceptible to numerous benign and malignant conditions. The most frequent benign conditions are ], ] and ]. | |||
| ] unrelated to pregnancy is known as ]. It can be caused by certain drugs (such as ] medications), extreme physical stress, or ] disorders. Lactation in newborns is caused by hormones from the mother that crossed into the baby's bloodstream during pregnancy. | |||
| ===Breast cancer=== | |||
| {{Main|Breast cancer}} | |||
| Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer death among women<ref> | |||
| {{cite web |author = World Health Organization |date = February 2006 |title = Fact sheet No. 297: Cancer |url =https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/index.html |access-date = 26 April 2007 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140213212322/http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/index.html |archive-date = 13 February 2014 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all |author-link = World Health Organization }}</ref> and it is one of the leading causes of death among women. Factors that appear to be implicated in decreasing the risk of breast cancer are regular breast examinations by health care professionals, regular ], ], healthy diet, exercise to decrease excess body fat,<ref> | |||
| {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100704055600/http://hms.harvard.edu/public/disease/breast_cancer/7things.html |date=4 July 2010 }} Harvard College. Last updated June 2008</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/26/5_Supplement/IA23|journal=Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention|title=Reducing cancer risk by enabling women to breastfeed|date=May 2017|volume=26|issue=5 Supplement|pages=IA23|doi=10.1158/1538-7755.CARISK16-IA23|access-date=23 September 2019|archive-date=23 September 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190923170533/https://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/26/5_Supplement/IA23|url-status=live|last1=Stuebe|first1=Alison M.}}</ref> | |||
| ===Male breasts=== | |||
| Both females and males develop breasts from the same ] tissues. Anatomically, male breasts do not normally contain lobules and acini that are present in females. In rare instances, it is possible for very few lobules to be present; this makes it possible for some men to develop lobular carcinoma of the breast.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Erhan |first1=Yamaç |last2=Zekioglu |first2=Osman |last3=Erhan |first3=Yildiz |date=October 2006 |title=Invasive lobular carcinoma of the male breast |journal=Canadian Journal of Surgery. Journal Canadien de Chirurgie |volume=49 |issue=5 |pages=365–366 |issn=0008-428X |pmc=3207588 |pmid=17152578}}</ref> Normally, males produce lower levels of estrogens and higher levels of ]s, namely ], which suppress the effects of estrogens in developing excessive breast tissue. In boys and men, abnormal breast development is manifested as ], the consequence of a biochemical imbalance between the normal levels of estrogen and testosterone in the male body.<ref>{{cite book |author = Olson, James Stuart |title = Bathsheba's Breast: Women, Cancer and History |publisher = The Johns Hopkins University Press |location = Baltimore |year = 2002 |page = |oclc = 186453370 |isbn = 978-0-8018-6936-5 |url = https://archive.org/details/bathshebasbreast00olso/page/109 }}</ref> Around 70% of boys temporarily develop breast tissue during adolescence.<ref name=mgh2010/> The condition usually resolves by itself within two years.<ref name=mgh2010/> When ] occurs, it is considered a symptom of a disorder of the ]. | |||
| ===Plastic surgery=== | |||
| ] myocutaneous flap reconstruction, prior to nipple reconstruction and tattooing ''(bottom)''.]] | |||
| Plastic surgery can be performed to ] or ] the size of breasts, or ] the breast in cases of deformative disease, such as breast cancer.<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.sexarchive.info/ATLAS_EN/html/secondary_characteristics.html |title = Secondary sex characteristics |publisher = .hu-berlin.de |access-date = 31 October 2011 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130622035035/http://www.sexarchive.info/ATLAS_EN/html/secondary_characteristics.html |archive-date = 22 June 2013 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }} | |||
| </ref> Breast augmentation and breast lift (]) procedures are done only for cosmetic reasons, whereas breast reduction is sometimes medically indicated.<ref name=love_c1/> In cases where a woman's breasts are severely asymmetrical, surgery can be performed to either enlarge the smaller breast, reduce the size of the larger breast, or both.<ref name=love_c1/> | |||
| Breast augmentation surgery generally does not interfere with future ability to breastfeed.{{sfn | Lawrence | 2016 | pp= 613–616}} Breast reduction surgery more frequently leads to decreased sensation in the nipple-areola complex, and to low milk supply in women who choose to breastfeed.{{sfn | Lawrence | 2016 | pp= 613–616}} Implants can interfere with ] (breast x-ray images). | |||
| ==Society and culture== | |||
| ===General=== | |||
| In ], some works of art depict women with their breasts in their hands or on a platter, signifying that they died as a martyr by having their breasts severed; one example of this is ].<ref>{{cite web |title = St Agatha |url = http://www.catholic.org/saints/saint.php?saint_id=14 |publisher = Catholic Online |access-date = 27 December 2015 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160304000129/http://www.catholic.org/saints/saint.php?saint_id=14 |archive-date = 4 March 2016 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| ] member participating in a protest]] | |||
| ] is a ] activist group which uses ]s as part of their campaigns against ]<ref name=FEMEN> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101207042451/http://www.kyivpost.com/news/politics/detail/65379 |date=7 December 2010 }}, '']'' (28 April 2010)</ref><ref name="movements1">{{cite web |url = http://www.movements.org/case-study/entry/ukraines-ladies-of-femen/ |title = Ukraine's Ladies of Femen |publisher = Movements.org |date = 16 August 2011 |access-date = 22 April 2013 |url-status = dead |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120414005441/http://www.movements.org/case-study/entry/ukraines-ladies-of-femen |archive-date = 14 April 2012 }}</ref> religious institutions,<ref name=BBCobservOct12> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180412230110/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-20028797 |date=12 April 2018 }}, ] (23 October 2012)</ref> ], and ].<ref>{{cite news |url = http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/04/24/topless-femen-protest-andre-jozef-leonard_n_3146609.html |title = Topless FEMEN Protesters Drench Belgian Archbishop André-Jozef Léonard, Protest Homophobia in Catholic Church (PHOTOS) |work = The Huffington Post |access-date = 23 March 2015 |date = 24 April 2013 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150416042913/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/04/24/topless-femen-protest-andre-jozef-leonard_n_3146609.html |archive-date = 16 April 2015 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> Femen activists have been regularly detained by police in response to their protests.<ref name=BBCTunis> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180827210121/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-22881163 |date=27 August 2018 }}, ] (12 June 2013)</ref> | |||
| There is a long history of female breasts being used by comedians as a subject for comedy fodder (e.g., British comic ] burlesque/slapstick routines).<ref name="thedailybeast.com" /> | |||
| ===Art history=== | |||
| In European pre-historic societies, sculptures of female figures with pronounced or highly exaggerated breasts were common. A typical example is the so-called ], one of many ] ] with ample hips and bosom. Artifacts such as bowls, rock carvings and sacred statues with breasts have been recorded from 15,000 BC up to late antiquity all across Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. | |||
| Many female deities representing love and fertility were associated with breasts and breast milk. Figures of the Phoenician goddess ] were represented as pillars studded with breasts. ], an Egyptian goddess who represented, among many other things, ideal motherhood, was often portrayed as suckling ], thereby confirming their divine status as rulers. Even certain male deities representing regeneration and fertility were occasionally depicted with breast-like appendices, such as the river god ] who was considered to be responsible for the annual overflowing of the ]. | |||
| ] from the ], {{circa|1600}} BC]] | |||
| Female breasts were also prominent in ] in the form of the famous ] statuettes, and a few other pieces, though most female breasts are covered. In ] there were several cults worshipping the "Kourotrophos", the suckling mother, represented by goddesses such as ], ] and ]. The worship of deities symbolized by the female breast in Greece became less common during the first millennium. The popular adoration of female goddesses decreased significantly during the rise of the Greek city states, a legacy which was passed on to the later ].<ref>Yalom (1998) pp. 9–16; see Eva Keuls (1993), ''Reign of the Phallus: Sexual Politics in Ancient Athens'' for a detailed study of male-dominant rule in ancient Greece.</ref> | |||
| During the middle of the first millennium BC, Greek culture experienced a gradual change in the perception of female breasts. Women in art were covered in clothing from the neck down, including female goddesses like ], the patron of Athens who represented heroic endeavor. There were exceptions: ], the goddess of love, was more frequently portrayed fully nude, though in postures that were intended to portray shyness or modesty, a portrayal that has been compared to modern ] by historian ].<ref>Yalom (1998), p. 18.</ref> Although nude men were depicted standing upright, most depictions of female nudity in Greek art occurred "usually with drapery near at hand and with a forward-bending, self-protecting posture".<ref>Hollander (1993), p. 6.</ref> A popular legend at the time was of the ], a tribe of fierce female warriors who socialized with men only for procreation and even removed one breast to become better warriors (the idea being that the right breast would interfere with the operation of a bow and arrow). The legend was a popular motif in art during Greek and Roman antiquity and served as an antithetical cautionary tale. | |||
| ===Body image=== | |||
| Many women regard their breasts as important to their ], as a sign of ] that is important to their ]. A woman with smaller breasts may regard her breasts as less attractive.<ref>Koff, E., Benavage, A. Breast Size Perception and Satisfaction, Body Image, and Psychological Functioning in Caucasian and Asian American College Women. Sex Roles 38, 655–673 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018802928210 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180604135059/https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1018802928210 |date=4 June 2018 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Clothing=== | |||
| {{See also|Bra|Cleavage (breasts)|Toplessness|Modesty|Naturism|Exhibitionism}} | |||
| ] woman of northern Namibia wears a traditional headdress and skirt]] | |||
| Because breasts are mostly fatty tissue, their shape can—within limits—be molded by clothing, such as ]s. ]s are commonly worn by about 90% of Western women,<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.1stbras.com/bra-cup-sizes.php |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160308210937/http://www.1stbras.com/bra-cup-sizes.php |url-status = dead |archive-date = 8 March 2016 |title = Bra Cup Sizes—getting fitted with the right size |publisher = 1stbras.com |access-date = 11 May 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.liv.com/right_bra.php |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090328083521/http://www.liv.com/right_bra.php |url-status = dead |archive-date = 28 March 2009 |title = The Right Bra |publisher = Liv.com |access-date = 11 May 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url = https://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/this-britain/breast-supporting-act-a-century-of-the-bra-5334510.html |title = Breast supporting act: a century of the bra |date = 15 August 2007 |publisher = The Independent UK |access-date = 11 May 2010 |location = London |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160305101134/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/this-britain/breast-supporting-act-a-century-of-the-bra-5334510.html |archive-date = 5 March 2016 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> and are often worn for support.<ref>{{cite journal |pmc = 2275741 |pmid = 18339205 |doi = 10.1186/1746-1340-16-1 |volume = 16 |title = Breast size, bra fit and thoracic pain in young women: a correlational study |year = 2008 |journal = Chiropr Osteopat |pages = 1 |last1 = Wood |first1 = K |last2 = Cameron |first2 = M |last3 = Fitzgerald |first3 = K |doi-access = free }}</ref> The ] in most ]s is to cover breasts in public, though the extent of coverage varies depending on the social context. Some religions ascribe a special status to the female breast, either in formal teachings or through symbolism.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Worshipping Breasts in the Maternal Landscape of India |journal=South Asian Studies |date=27 October 2015 |volume=31 |issue=2015 |doi=10.1080/02666030.2015.1094209 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02666030.2015.1094209 |access-date=30 September 2020 |last1=Bohidar |first1=Anannya |pages=247–253 |s2cid=194282633 |archive-date=2 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210102165529/https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02666030.2015.1094209 |url-status=live }}</ref> ] forbids free women from exposing their breasts in public. | |||
| Many cultures, including Western cultures in North America, associate breasts with sexuality and tend to regard bare breasts as ] or ]. In some cultures, like the ] in northern ], bare-breasted women are normal. In some African cultures, for example, the ] is regarded as highly sexualized and never exposed in public, but breast exposure is not taboo. In a few ] and regions female ] at a beach is acceptable, although it may not be acceptable in the town center.<ref name=":3">{{Cite web |date=2024-10-09 |title=Topless Beaches In Europe: Etiquette, Culture, And What To Expect |url=https://travelpander.com/are-all-beaches-in-europ-topless/ |access-date=2024-12-25 |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| The development of a woman’s breasts during ] is triggered by ]s, chiefly ]. This hormone has been demonstrated to cause the development of woman-like, enlarged breasts in men, a condition called ], and is sometimes used deliberately for this effect in ] ]. | |||
| Social attitudes and laws regarding ] vary widely. In many countries, breastfeeding in public is common, legally protected, and generally not regarded as an issue. However, even though the practice may be legal or socially accepted, some mothers may nevertheless be reluctant to expose a breast in public to breastfeed<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1186/1746-4358-3-11|title=Got milk? Not in public!|pmid=18680578|year=2008|last1=Wolf|first1=J.H.|volume=3|issue=1|page=11|pmc=2518137|journal=International Breastfeeding Journal |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name=Vance_2005>{{cite journal | last = Vance | first = Melissa R. | title = Breastfeeding Legislation in the United States: A General Overview and Implications for Helping Mothers | journal = LEAVEN | volume = 41 | issue = 3 | pages = 51–54 | date = June–July 2005 | url = http://www.llli.org/llleaderweb/LV/LVJunJul05p51.html | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070331220518/http://www.llli.org/llleaderweb/LV/LVJunJul05p51.html | archive-date = 31 March 2007}}</ref> due to actual or potential objections by other people, negative comments, or harassment.<ref name=Jordan_2002>{{cite book|editor-last=Jordan|editor-first=Tim|editor-last2=Pile|editor-first2=Steve|title=Social Change|page=|publisher=Blackwell|year=2002|isbn=9780631233114|url=https://archive.org/details/socialchange0000unse/page/233}}</ref> It is estimated that around 63% of mothers across the world have publicly breast-fed.<ref>{{Cite book|title = Breast Feeding With Confidence|last = Cox|first = Sue|publisher = Meadowbrook Press|year = 2002|isbn = 0684040050|location = United States|url-access = registration|url = https://archive.org/details/breastfeedingwit00suec}}</ref> Bare-breasted women are legal and culturally acceptable at public beaches in Australia and much of Europe.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Bennett |first=Theodore |title=Clothing Optional?: Nudity and the Law of the Australian Beach |url=https://doaj.org/article/3c5619e831254faca2c5e8cc6f9a617b |journal=Bond Law Review |language=en |issn=2202-4824}}</ref><ref name=":3" /> Filmmaker ] made a film entitled '']'', which is about "...laws against female toplessness or restrictions on images of female, but not male, nipples", which Esco states is an example of ] in society.<ref name="thedailybeast.com">{{cite news |url = http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2014/09/09/women-it-s-time-to-reclaim-our-breasts.html |title = Women, It's Time to Reclaim Our Breasts |first = Emily |last = Shire |date = 9 September 2014 |newspaper = The Daily Beast |access-date = 11 December 2016 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20161101085547/http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2014/09/09/women-it-s-time-to-reclaim-our-breasts.html |archive-date = 1 November 2016 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> | |||
| In most cases, the breasts do fold down over the chest wall during ], as shown in this .<ref>A.R. Greenbaum, T. Heslop, J. Morris and K.W. Dunn, An investigation of the suitability of bra fit in women referred for reduction mammaplasty, Br J Plast Surg 56 (2003) (3), pp. 230–236</ref> It is typical for a woman’s breasts to be unequal in size particularly while the breasts are developing during ]. Statistically it is slightly more common for the left breast to be the larger.<ref name="asymmetry">{{cite journal | |||
| | author=C.W. Loughry, ''et al'' | |||
| | title=Breast volume measurement of 598 women using biostereometric analysis | |||
| | journal=Annals of Plastic Surgery | |||
| | year=1989 | |||
| | volume=22 | |||
| | issue=5 | |||
| | pages=380 – 385 | |||
| }}</ref> In rare cases, the breasts may be significantly different in size, or one breast may fail to develop entirely. | |||
| ], also known as chest binding, is the flattening and hiding of breasts with constrictive materials such as cloth strips or purpose-built ]s. Binders may also be used as alternatives to ]s or for reasons of propriety. People who bind include women, ], ] people, and ] men with gynecomastia. | |||
| A vast number of medical conditions are known to cause abnormal development of the breasts during puberty. ] is a condition which involves excessive growth of the breasts during puberty, and in some cases the continued growth beyond the usual pubescent age. Breast ] is a condition where one or both breasts fail to develop during puberty. | |||
| ===Sexual characteristic=== | |||
| In ], some girls are subjected to ] to stunt breast growth in order to make them less sexually attractive and thus become less likely to become a victim of ]. | |||
| {{See also|Mammary intercourse|Breast fetishism|Stimulation of nipples}} | |||
| In some cultures, breasts play a role in ]. Breasts and especially the nipples are among the various human ]s. They are sensitive to the touch as they have many nerve endings; and it is common to press or ] them with hands or ] before or during sexual activity. During ], breast size increases, ] patterns across the breasts become more visible, and nipples harden.{{Citation needed|date=December 2024}} Compared to other primates, human breasts are proportionately large throughout adult females' lives. Some writers have suggested that they may have evolved as a visual signal of sexual maturity and fertility.<ref>{{cite journal |author = Anders Pape Møller |title = Breast asymmetry, sexual selection, and human reproductive success |journal = Ethology and Sociobiology |year = 1995 |volume = 16 |issue = 3 |pages = 207–219 |doi = 10.1016/0162-3095(95)00002-3 |display-authors = 1 |last2 = Soler |first2 = M |last3 = Thornhill |first3 = R }}</ref> In '']'', a 1951 analysis of 191 traditional cultures, the researchers noted that stimulation of the female breast by a male sexual partner "seemed absent in all subhuman forms, although it is common among the members of many different human societies."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach |url=http://archive.org/details/patternsofsexual0000clel_d2x3 |title=Patterns of Sexual Behaviour |date=1965 |others=Internet Archive |pages=70}}</ref> | |||
| ==Cultural status== | |||
| ], ''“Blonde Woman With Bare Breasts”'']] | |||
| Historically, breasts have been regarded as ] symbols, because they are the source of life-giving milk. Certain prehistoric female statuettes—so-called ]—often emphasised the breasts, as in the example of the ]. In historic times, goddesses such as ] were shown with many breasts, alluding to their role as goddesses of childbirth. | |||
| Many people regard bare female breasts to be aesthetically pleasing or ], and they can elicit heightened ]s in men in many cultures. In the ] work the '']'', light scratching of the breasts with nails and biting with teeth are considered erotic.<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.sacred-texts.com/sex/kama/index.htm |title = Sir Richard Burton's English translation of Kama Sutra |publisher = Sacred-texts.com |access-date = 31 October 2011 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100102051149/http://sacred-texts.com/sex/kama/index.htm |archive-date = 2 January 2010 |url-status = live |df = dmy }}</ref> Some people show a ] in female breasts distinct from that of the person, which may be regarded as a ].<ref>Hickey, Eric W. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Murder and Violent Crime. Sage Publications Inc. {{ISBN|978-0-7619-2437-1}}</ref> A number of Western fashions include clothing which accentuate the breasts, such as the use of ]s and ] (plunging neckline) gowns and blouses which show ]. While U.S. culture prefers breasts that are youthful and upright, some cultures venerate women with drooping breasts, indicating mothering and the wisdom of experience.<ref>{{cite book |last = Burns-Ardolino |first = Wendy |title = Jiggle: (Re)shaping American women |year = 2007 |publisher = Lexington Books |location = Lanham, MD |isbn = 978-0-7391-1299-1 |page = 31 }}</ref> | |||
| Breasts are secondary sex characteristics and sexually sensitive. Bare female breasts can elicit heightened sexual desires from men and women. Since they are associated with sex, in many cultures bare breasts are indecent, and they are not commonly displayed in public, in contrast to male chests. Other cultures view the baring of breasts as acceptable, and in some countries women have never been forbidden to bare their chests. Opinion on the exposure of breasts is often dependent on the place and context, and in some ] exposure of breasts on a beach may be acceptable, although in town centres, for example, it is usually indecent. In some areas, the prohibition against the display of a woman’s breasts generally only restricts exposure of the ]. | |||
| Research conducted at the ] showed that breasts are often the first thing men look at, and for a longer time than other body parts.<ref name=ASB>{{cite journal |last1 = Dixson |first1 = BJ |last2 = Grimshaw |first2 = GM |last3 = Linklater |first3 = WL |last4 = Dixson |first4 = AF |title = Eye-tracking of men's preferences for waist-to-hip ratio and breast size of women |journal = ] |volume = 40 |issue = 1 |pages = 43–50 |publisher = ] |date = February 2011 |doi = 10.1007/s10508-009-9523-5 |pmid = 19688590 |s2cid = 4997497 }}</ref> The writers of the study had initially speculated that the reason for this is due to ] with larger breasts indicating higher levels of estrogen and a sign of greater fertility,<ref name=ASB /><ref name=BBC>{{cite news |url = http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/3682657.stm |title = Hourglass figure fertility link |work = BBC News |date = 4 May 2004 |access-date = 31 October 2011 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20111011122830/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/3682657.stm |archive-date = 11 October 2011 |url-status = live |df = dmy-all }}</ref> but the researchers said that "Men may be looking more often at the breasts because they are simply aesthetically pleasing, regardless of the size."<ref name=ASB /> | |||
| When ], legal and social rules regarding indecent exposure and dress code, as well as inhibitions of the woman, tend to be relaxed. Numerous laws around the world have made public breastfeeding legal and disallow companies from prohibiting it in the workplace. Yet the public reaction at the sight of breastfeeding can make the situation uncomfortable for those involved. | |||
| Some women report achieving an ] from nipple stimulation, but this is rare.<ref name="Kinsey">{{cite book |author1 = Alfred C. Kinsey |author2 = Wardell B. Pomeroy |author3 = Clyde E. Martin |author4 = Paul H. Gebhard |title = Sexual Behavior in the Human Female |publisher = ] |isbn = 0-253-01924-9 |page = 587 |date = 1998 |access-date = 12 August 2017 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=JHWHCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA587 |quote = There are some females who appear to find no erotic satisfaction in having their breasts manipulated; perhaps half of them derive some distinct satisfaction, but not more than a very small percentage ever respond intensely enough to reach orgasm as a result of such stimulation (Chapter 5). Records of females reaching orgasm from breast stimulation alone are rare. }}</ref><ref name="Boston">{{cite book |author = Boston Women's Health Book Collective |title = The New Our Bodies, Ourselves: A Book by and for Women |publisher = ] |isbn = 0-684-82352-7 |page = 575 |date = 1996 |access-date = 12 August 2017 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=JFI4AQAAIAAJ |quote = A few women can even experience orgasm from breast stimulation alone. |archive-date = 24 December 2020 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20201224162656/https://books.google.com/books?id=JFI4AQAAIAAJ |url-status = live }}</ref> Research suggests that the orgasms are genital orgasms, and may also be directly linked to "the genital area of the brain". In these cases, it seems that sensation from the nipples travels to the same part of the brain as sensations from the vagina, clitoris and cervix. Nipple stimulation may trigger uterine contractions, which then produce a sensation in the genital area of the brain.<ref name="Smith">{{cite book |author = Merril D. Smith |title = Cultural Encyclopedia of the Breast |publisher = ] |isbn = 978-0-7591-2332-8 |page = 71 |date = 2014 |access-date = 12 August 2017 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=qrCCBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA71 }}</ref><ref name="Lehmiller">{{cite book |author = Justin J. Lehmiller |title = The Psychology of Human Sexuality |publisher = ] |isbn = 978-1-118-35132-1 |page = 120 |date = 2013 |access-date = 12 August 2017 |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=pQRgAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT120 |archive-date = 23 February 2019 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190223070048/https://books.google.com/books?id=pQRgAgAAQBAJ&pg=PT120 |url-status = live }}</ref><ref name="Komisaruk">{{Cite journal|author1-link=Barry Komisaruk|author1 = Komisaruk, B. R. |author2 = Wise, N. |author3 = Frangos, E. |author4 = Liu, W.C. |author5 = Allen, K. |author6 = Brody, S. |title = Women's Clitoris, Vagina, and Cervix Mapped on the Sensory Cortex: fMRI Evidence, Surprise finding in response to nipple stimulation |journal = ] |year = 2011 |doi = 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02388.x |volume = 8 |issue = 10 |pages = 2822–30 |pmid = 21797981 |pmc = 3186818}} | |||
| Women in some areas and cultures are approaching the issue of breast exposure as one of ], since men (and pre-pubescent children) may bare their ]s, but women and teenage girls are forbidden. In the ], the ] equality movement seeks to redress this imbalance. This movement won a decision in ] in the ] State Court of Appeals—“People v. Santorelli”, where the court ruled that the state’s indecent exposure laws do not ban women from being barebreasted. A similar movement succeeded in most parts of ] in the ]. In ] and much of ] it is acceptable for women and teenage girls to sunbathe topless on some public beaches and swimming pools, but these are generally the only public areas where exposing breasts is acceptable. | |||
| *{{cite news |author=Stephanie Pappas |date=5 August 2011 |title=Surprise finding in response to nipple stimulation |work=CBS News |url=http://www.cbsnews.com/news/surprise-finding-in-response-to-nipple-stimulation/ |access-date=12 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160701074316/http://www.cbsnews.com/news/surprise-finding-in-response-to-nipple-stimulation/ |archive-date=1 July 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Anthropomorphic geography=== | |||
| Some religions require that women always keep their breasts covered. For example, ] forbids public exposure of the female breasts.<ref>“They shall cover their chests” or “they should draw their khimar (veils) over their bosoms”, depending on the translation, ] (24:31)</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Breast-shaped hill}} | |||
| There are many mountains named after the breast because they resemble it in appearance and so are objects of religious and ancestral veneration as a fertility symbol and of well-being. In Asia, there was "Breast Mountain", which had a cave where the ] ] (Da Mo) spent much time in ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.usashaolintemple.org/chanbuddhism-history/ |title=The Story of Bodhidharma |publisher=Usashaolintemple.org |access-date=31 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111130054841/http://www.usashaolintemple.org/chanbuddhism-history/ |archive-date=30 November 2011 |url-status=live }}</ref> Other such breast mountains are ] on the ]–] border; {{lang|gd|]|italic=no}} and the ] in Scotland; the {{lang|tl|]|italic=no}} ('Maiden's breast mountains') in ], Philippines, the twin hills known as the ] ({{lang|ga|Dá Chích Anann}} or 'the breasts of ]'), near ] in Ireland; the 2,086 m high {{Lang|es|Tetica de Bacares|italic=no}} or {{lang|es|La Tetica|italic=no}} in the {{lang|es|]|italic=no}}, Spain; {{lang|th-Latn|]|italic=no}} in Thailand, {{lang|es|]|italic=no}} in ]; and the Breasts of Aphrodite in ], among many others. In the United States, the ] is named after the French word for 'nipple'.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/grte/grte_geology/sec1.htm |title=Creation of the Teton Landscape: The Geologic Story of Grand Teton National Park (The Story Begins) |publisher=] |date=19 January 2007 |access-date=23 September 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150419054617/http://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/grte/grte_geology/sec1.htm |archive-date=19 April 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In addition to the above references, see also ], ] and ]. | |||
| ==Measurement== | |||
| In some paintings women are shown with their breasts in their hands or on a platter, signifying that they died as a martyr by having their breasts severed. One example of this is ]. | |||
| {{Main|Breast measurement}} | |||
| The ] and ] of the breasts can be measured by a variety of different methods. These include ], ], ], ], the ], ], and ], among other measures. | |||
| ==Disorders== | |||
| ===Infections and inflammations=== | |||
| ] poster. ''Are you taking care of your breasts? Harden your nipples with daily washing in cold water.'']] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** bacterial mastitis | |||
| ** mastitis from milk engorgement | |||
| ** mastitis of mumps | |||
| ** subareolar mastitis | |||
| * Other infections | |||
| ** chronic intramammary abscess | |||
| ** chronic subareolar abscess | |||
| ** tuberculosis of the breast | |||
| ** syphilis of the breast | |||
| ** retromammary abscess | |||
| ** actinomycosis of the breast | |||
| * Inflammations | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** duct ectasia = periductal masbreastis | |||
| ** ] | |||
| == |
== See also == | ||
| {{Portal|Medicine|Human sexuality}} | |||
| * ]s | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ** ]/] (polymazia / polymastia)/duplicated nipples | |||
| * Aberrations of normal development and involution | |||
| ** cyclical nodularity | |||
| ** ]s | |||
| ** ] - benign tumor | |||
| * Duct ectasia/Periductal masbreastis | |||
| ** nipple discharge | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** mammary fistula | |||
| * Fibrocystic disease/Fibrocystic changes | |||
| ** cysts | |||
| ** epithelial hyperplasia | |||
| ** epithelial metaplasia | |||
| ** papillomas | |||
| ** adenosis | |||
| * ]-related | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** puerperal abscess | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| ===Malignant diseases=== | |||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| * ] (mammary carcinoma) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * Paget’s disease of the nipple, also known as ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <references /> | |||
| </div> | |||
| == |
=== Bibliography === | ||
| * {{cite book |last = Hollander |first = Anne |title = Seeing through clothes |publisher = University of California Press |location = Berkeley |year = 1993 |isbn = 978-0-520-08231-1 }} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] ''The Naked Ape: a zoologist's study of the human animal'' Bantam Books, Canada. 1967 | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{cite book |last = Yalom |first = Marilyn |title = A history of the breast |publisher = Pandora |location = London |year = 1998 |isbn = 978-0-86358-400-8 }} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{cite book |last = Venes |first = Donald |title = Taber's cyclopedic medical dictionary |publisher = F.A. Davis |location = Philadelphia |year = 2013 |isbn = 978-0-8036-2977-6 }} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{cite book | last=Lawrence | first=Ruth | title=Breastfeeding : a guide for the medical profession, 8th edition | publisher=Elsevier | location=Philadelphia, PA | year=2016 | isbn=978-0-323-35776-0 }} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Wiktionary|breast|breasts}} | |||
| {{commonscat|Breasts}} | |||
| {{Commons category|Breasts}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Wikibooks|Radiation Oncology/Breast}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Wikisource|1911 Encyclopædia Britannica/Breast}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite web |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20111202170751/http://www.nyu.edu/fas/ihpk/CultureMatters/Mascia-Lees.htm |title = Are Women Evolutionary Sex Objects?: Why Women Have Breasts |archive-date = 2 December 2011 |url = http://www.nyu.edu/fas/ihpk/CultureMatters/Mascia-Lees.htm }} | |||
| * | |||
| {{human anatomical features}} | |||
| {{Human regional anatomy}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Breast anatomy}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Disorders of the breast}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Sex}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 2 January 2025
Region of the torso of a primate that in females serves as a mammary gland For other uses, see Breast (disambiguation).
| Breast | |
|---|---|
 Morphology of female human breasts, with the areola, nipple, and inframammary fold Morphology of female human breasts, with the areola, nipple, and inframammary fold | |
 Male human breasts with defined pectoral muscles Male human breasts with defined pectoral muscles | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Internal thoracic artery |
| Vein | Internal thoracic vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | mamma (mammalis 'of the breast') |
| MeSH | D001940 |
| TA98 | A16.0.02.001 |
| TA2 | 7097 |
| FMA | 9601 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males. There is also considerable variation in size between individuals. Female humans are the only mammals which permanently develop breasts at puberty; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy; at puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth.
In females, the breast serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding.
Along with their major function in providing nutrition for infants, several cultures ascribe social and sexual characteristics to female breasts, and may regard bare breasts in public as immodest or indecent. Breasts have been featured in ancient and modern sculpture, art, and photography. Breasts can represent fertility, femininity, or abundance. They can figure prominently in the perception of a woman's body and sexual attractiveness. Breasts, especially the nipples, can be an erogenous zone.
Etymology and terminology
The English word breast derives from the Old English word brēost 'breast, bosom' from Proto-Germanic *breustam 'breast', from the Proto-Indo-European base *bhreus– 'to swell, to sprout'. The breast spelling conforms to the Scottish and North English dialectal pronunciations. The Merriam-Webster Dictionary states that "Middle English brest, from Old English brēost; akin to Old High German brust..., Old Irish brú , Russian bryukho"; the first known usage of the term was before the 12th century.
Breasts is often used to refer to female breasts in particular, though the stricter anatomical term refers to the same region on members of either sex. Male breasts are sometimes referred to in the singular to mean the collective upper chest area, whereas female breasts are referred to in the plural unless speaking of a specific left or right breast.
A large number of colloquial terms for female breasts are used in English, ranging from fairly polite terms to vulgar or slang. Some vulgar slang expressions may be considered to be derogatory or sexist to women.
Evolutionary development

Humans are the only mammals whose breasts become permanently enlarged after sexual maturity (known in humans as puberty). The reason for this evolutionary change is unknown. Several hypotheses have been put forward:
A link has been proposed to processes for synthesizing the endogenous steroid hormone precursor dehydroepiandrosterone which takes place in fat rich regions of the body like the buttocks and breasts. These contributed to human brain development and played a part in increasing brain size. Breast enlargement may for this purpose have occurred as early as Homo ergaster (1.7–1.4 MYA). Other breast formation hypotheses may have then taken over as principal drivers.
It has been suggested by zoologists Avishag and Amotz Zahavi that the size of the human breasts can be explained by the handicap theory of sexual dimorphism. This would see the explanation for larger breasts as them being an honest display of the women's health and ability to grow and carry them in her life. Prospective mates can then evaluate the genes of a potential mate for their ability to sustain her health even with the additional energy demanding burden she is carrying.
The zoologist Desmond Morris describes a sociobiological approach in his science book The Naked Ape. He suggests, by making comparisons with the other primates, that breasts evolved to replace swelling buttocks as a sex signal of ovulation. He notes how humans have, relatively speaking, large penises as well as large breasts. Furthermore, early humans adopted bipedalism and face-to-face coitus. He therefore suggested enlarged sexual signals helped maintain the bond between a mated male and female even though they performed different duties and therefore were separated for lengths of time.
A 2001 study proposed that the rounded shape of a woman's breast evolved to prevent the sucking infant offspring from suffocating while feeding at the teat; that is, because of the human infant's small jaw, which did not project from the face to reach the nipple, they might block the nostrils against the mother's breast if it were of a flatter form (compare with the common chimpanzee). Theoretically, as the human jaw receded into the face, the woman's body compensated with round breasts.
Ashley Montague (1965) proposed that breasts came about as an adaptation for infant feeding for a different reason, as early human ancestors adopted bipedalism and the loss of body hair. Human upright stance meant infants must be carried at the hip or shoulder instead of on the back as in the apes. This gives the infant less opportunity to find the nipple or the purchase to cling on to the mother's body hair. The mobility of the nipple on a large breast in most human females gives the infant more ability to find it, grasp it and feed.
Other suggestions include simply that permanent breasts attracted mates, that "pendulous" breasts gave infants something to cling to, or that permanent breasts shared the function of a camel's hump, to store fat as an energy reserve.
Structure

In women, the breasts overlie the pectoralis major muscles and extend on average from the level of the second rib to the level of the sixth rib in the front of the rib cage; thus, the breasts cover much of the chest area and the chest walls. At the front of the chest, the breast tissue can extend from the clavicle (collarbone) to the middle of the sternum (breastbone). At the sides of the chest, the breast tissue can extend into the axilla (armpit), and can reach as far to the back as the latissimus dorsi muscle, extending from the lower back to the humerus bone (the bone of the upper arm). As a mammary gland, the breast is composed of differing layers of tissue, predominantly two types: adipose tissue; and glandular tissue, which affects the lactation functions of the breasts. The natural resonant frequency of the human breast is about 2 hertz.
Morphologically, the breast is tear-shaped. The superficial tissue layer (superficial fascia) is separated from the skin by 0.5–2.5 cm of subcutaneous fat (adipose tissue). The suspensory Cooper's ligaments are fibrous-tissue prolongations that radiate from the superficial fascia to the skin envelope. The female adult breast contains 14–18 irregular lactiferous lobes that converge at the nipple. The 2.0–4.5 mm milk ducts are immediately surrounded with dense connective tissue that support the glands. Milk exits the breast through the nipple, which is surrounded by a pigmented area of skin called the areola. The size of the areola can vary widely among women. The areola contains modified sweat glands known as Montgomery's glands. These glands secrete oily fluid that lubricate and protect the nipple during breastfeeding. Volatile compounds in these secretions may also serve as an olfactory stimulus for the newborn's appetite.

The dimensions and weight of the breast vary widely among women. A small-to-medium-sized breast weighs 500 grams (1.1 pounds) or less, and a large breast can weigh approximately 750 to 1,000 grams (1.7 to 2.2 pounds) or more. In terms of composition, the breasts are about 80 to 90% stromal tissue (fat and connective tissue), while epithelial or glandular tissue only accounts for about 10 to 20% of the volume of the breasts. The tissue composition ratios of the breast also vary among women. Some women's breasts have a higher proportion of glandular tissue than of adipose or connective tissues. The fat-to-connective-tissue ratio determines the density or firmness of the breast. During a woman's life, her breasts change size, shape, and weight due to hormonal changes during puberty, the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause.
Glandular structure
Main article: Mammary gland
The breast is an apocrine gland that produces the milk used to feed an infant. The nipple of the breast is surrounded by the areola (nipple-areola complex). The areola has many sebaceous glands, and the skin color varies from pink to dark brown. The basic units of the breast are the terminal duct lobular units (TDLUs), which produce the fatty breast milk. They give the breast its offspring-feeding functions as a mammary gland. They are distributed throughout the body of the breast. Approximately two-thirds of the lactiferous tissue is within 30 mm of the base of the nipple. The terminal lactiferous ducts drain the milk from TDLUs into 4–18 lactiferous ducts, which drain to the nipple. The milk-glands-to-fat ratio is 2:1 in a lactating woman, and 1:1 in a non-lactating woman. In addition to the milk glands, the breast is also composed of connective tissues (collagen, elastin), white fat, and the suspensory Cooper's ligaments. Sensation in the breast is provided by the peripheral nervous system innervation by means of the front (anterior) and side (lateral) cutaneous branches of the fourth-, fifth-, and sixth intercostal nerves. The T-4 nerve (Thoracic spinal nerve 4), which innervates the dermatomic area, supplies sensation to the nipple-areola complex.
Lymphatic drainage
Approximately 75% of the lymph from the breast travels to the axillary lymph nodes on the same side of the body, while 25% of the lymph travels to the parasternal nodes (beside the sternum bone). A small amount of remaining lymph travels to the other breast and to the abdominal lymph nodes. The subareolar region has a lymphatic plexus known as the "subareolar plexus of Sappey". The axillary lymph nodes include the pectoral (chest), subscapular (under the scapula), and humeral (humerus-bone area) lymph-node groups, which drain to the central axillary lymph nodes and to the apical axillary lymph nodes. The lymphatic drainage of the breasts is especially relevant to oncology because breast cancer is common to the mammary gland, and cancer cells can metastasize (break away) from a tumor and be dispersed to other parts of the body by means of the lymphatic system.
Morphology



 Breasts can vary significantly in both size and shape.
Breasts can vary significantly in both size and shape.
The morphologic variations in the size, shape, volume, tissue density, pectoral locale, and spacing of the breasts determine their natural shape, appearance, and position on a woman's chest. Breast size and other characteristics do not predict the fat-to-milk-gland ratio or the potential for the woman to nurse an infant. The size and the shape of the breasts are influenced by normal-life hormonal changes (thelarche, menstruation, pregnancy, menopause) and medical conditions (e.g. virginal breast hypertrophy). The shape of the breasts is naturally determined by the support of the suspensory Cooper's ligaments, the underlying muscle and bone structures of the chest, and by the skin envelope. The suspensory ligaments sustain the breast from the clavicle (collarbone) and the clavico-pectoral fascia (collarbone and chest) by traversing and encompassing the fat and milk-gland tissues. The breast is positioned, affixed to, and supported upon the chest wall, while its shape is established and maintained by the skin envelope. In most women, one breast is slightly larger than the other. More obvious and persistent asymmetry in breast size occurs in up to 25% of women.
The base of each breast is attached to the chest by the deep fascia over the pectoralis major muscles. The base of the breast is semi-circular, however the shape and position of the breast above the surface is variable. The space between the breast and the pectoralis major muscle, called retromammary space, gives mobility to the breast. The chest (thoracic cavity) progressively slopes outwards from the thoracic inlet (atop the breastbone) and above to the lowest ribs that support the breasts. The inframammary fold (IMF), where the lower portion of the breast meets the chest, is an anatomic feature created by the adherence of the breast skin and the underlying connective tissues of the chest; the IMF is the lower-most extent of the anatomic breast. Normal breast tissue has a texture that feels nodular or granular, with considerable variation from woman to woman.
Breasts have been categorized into four general morphological groups: "flat, spheric, protruded, and drooped", or "small/flat, large/inward, upward, and droopy".
Support

 Left: Underwire bra. Right: Sports bra
Left: Underwire bra. Right: Sports bra
While it is a common belief that breastfeeding causes breasts to sag, researchers have found that a woman's breasts sag due to four key factors: cigarette smoking, number of pregnancies, gravity, and weight loss or gain. Women sometimes wear bras because they mistakenly believe they prevent breasts from sagging as they get older. Physicians, lingerie retailers, teenagers, and adult women used to believe that bras were medically required to support breasts. In a 1952 article in Parents' Magazine, Frank H. Crowell erroneously reported that it was important for teen girls to begin wearing bras early. According to Crowell, this would prevent sagging breasts, stretched blood vessels, and poor circulation later on. This belief was based on the false idea that breasts cannot anatomically support themselves.
Sports bras are sometimes used for cardiovascular exercise, sports bras are designed to secure the breasts closely to the body to prevent movement during high-motion activity such as running. Studies have indicated sports bras which are overly tight may restrict respiratory function.
Development
Main article: Breast developmentThe breasts are principally composed of adipose, glandular, and connective tissues. Because these tissues have hormone receptors, their sizes and volumes fluctuate according to the hormonal changes particular to thelarche (sprouting of breasts), menstruation (egg production), pregnancy (reproduction), lactation (feeding of offspring), and menopause (end of menstruation).
Puberty

The morphological structure of the human breast is identical in males and females until puberty. For pubescent girls in thelarche (the breast-development stage), the female sex hormones (principally estrogens) in conjunction with growth hormone promote the sprouting, growth, and development of the breasts. During this time, the mammary glands grow in size and volume and begin resting on the chest. These development stages of secondary sex characteristics (breasts, pubic hair, etc.) are illustrated in the five-stage Tanner scale.
During thelarche, the developing breasts are sometimes of unequal size, and usually the left breast is slightly larger. This condition of asymmetry is transitory and statistically normal in female physical and sexual development. Medical conditions can cause overdevelopment (e.g., virginal breast hypertrophy, macromastia) or underdevelopment (e.g., tuberous breast deformity, micromastia) in girls and women.
Approximately two years after the onset of puberty (a girl's first menstrual cycle), estrogen and growth hormone stimulate the development and growth of the glandular fat and suspensory tissues that compose the breast. This continues for approximately four years until the final shape of the breast (size, volume, density) is established at about the age of 21. Mammoplasia (breast enlargement) in girls begins at puberty, unlike all other primates, in which breasts enlarge only during lactation.
Hormone replacement therapy

Hormone replacement therapy, including gender-affirming hormone therapy, stimulates the growth of glandular and adipose tissue through estrogen supplementation.
In menopausal women, HRT helps restore breast volume and skin elasticity diminished by declining estrogen levels, typically using oral or transdermal estradiol.
In gender-affirming hormone therapy, breast development is induced through feminizing HRT, often combining estrogen with anti-androgens to suppress testosterone. Maximum growth is usually achieved after 2–3 years.
Factors such as age, genetics, and hormone dosage influence outcomes.
Changes during the menstrual cycle
During the menstrual cycle, the breasts are enlarged by premenstrual water retention and temporary growth as influenced by changing hormone levels.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Main articles: Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The breasts reach full maturity only when a woman's first pregnancy occurs. Changes to the breasts are among the first signs of pregnancy. The breasts become larger, the nipple-areola complex becomes larger and darker, the Montgomery's glands enlarge, and veins sometimes become more visible. Breast tenderness during pregnancy is common, especially during the first trimester. By mid-pregnancy, the breast is physiologically capable of lactation and some women can express colostrum, a form of breast milk.
Pregnancy causes elevated levels of the hormone prolactin, which has a key role in the production of milk. However, milk production is blocked by the hormones progesterone and estrogen until after delivery, when progesterone and estrogen levels plummet.
Menopause
At menopause, breast atrophy occurs. The breasts can decrease in size when the levels of circulating estrogen decline. The adipose tissue and milk glands also begin to wither. The breasts can also become enlarged from adverse side effects of combined oral contraceptive pills. The size of the breasts can also increase and decrease in response to weight fluctuations.
Physical changes to the breasts are often recorded in the stretch marks of the skin envelope; they can serve as historical indicators of the increments and the decrements of the size and volume of a woman's breasts throughout the course of her life.
Breast changes during menopause are sometimes treated with hormone replacement therapy.
Cancer
Main article: Breast cancerBreast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutations among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ducts with milk. Cancers developing from the ducts are known as ductal carcinomas, while those developing from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas. There are more than 18 other sub-types of breast cancer. Some, such as ductal carcinoma in situ, develop from pre-invasive lesions. The diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed by taking a biopsy of the concerning tissue. Once the diagnosis is made, further tests are carried out to determine if the cancer has spread beyond the breast and which treatments are most likely to be effective.
Breastfeeding
Main article: Breastfeeding
The primary function of the breasts, as mammary glands, is the nourishing of an infant with breast milk. Milk is produced in milk-secreting cells in the alveoli. When the breasts are stimulated by the suckling of her baby, the mother's brain secretes oxytocin. High levels of oxytocin trigger the contraction of muscle cells surrounding the alveoli, causing milk to flow along the ducts that connect the alveoli to the nipple.
Full-term newborns have an instinct and a need to suck on a nipple, and breastfed babies nurse for both nutrition and for comfort. Breast milk provides all necessary nutrients for the first six months of life, and then remains an important source of nutrition, alongside solid foods, until at least one or two years of age.
Exercise
Biomechanical studies have demonstrated that, depending on the activity and the size of a woman's breast, when she walks or runs braless, her breasts may move up and down by 4 to 18 centimetres (1.6 to 7.1 in) or more, and also oscillate side to side. Researchers have also found that as women's breast size increased, they took part in less physical activity, especially vigorous exercise. Few very-large-breasted women jogged, for example. To avoid exercise-related discomfort and pain, medical experts suggest women wear a well-fitted sports bra during activity.
Clinical significance
Main article: Breast diseaseThe breast is susceptible to numerous benign and malignant conditions. The most frequent benign conditions are puerperal mastitis, fibrocystic breast changes and mastalgia.
Lactation unrelated to pregnancy is known as galactorrhea. It can be caused by certain drugs (such as antipsychotic medications), extreme physical stress, or endocrine disorders. Lactation in newborns is caused by hormones from the mother that crossed into the baby's bloodstream during pregnancy.
Breast cancer
Main article: Breast cancerBreast cancer is the most common cause of cancer death among women and it is one of the leading causes of death among women. Factors that appear to be implicated in decreasing the risk of breast cancer are regular breast examinations by health care professionals, regular mammograms, self-examination of breasts, healthy diet, exercise to decrease excess body fat, and breastfeeding.
Male breasts
Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. Anatomically, male breasts do not normally contain lobules and acini that are present in females. In rare instances, it is possible for very few lobules to be present; this makes it possible for some men to develop lobular carcinoma of the breast. Normally, males produce lower levels of estrogens and higher levels of androgens, namely testosterone, which suppress the effects of estrogens in developing excessive breast tissue. In boys and men, abnormal breast development is manifested as gynecomastia, the consequence of a biochemical imbalance between the normal levels of estrogen and testosterone in the male body. Around 70% of boys temporarily develop breast tissue during adolescence. The condition usually resolves by itself within two years. When male lactation occurs, it is considered a symptom of a disorder of the pituitary gland.
Plastic surgery
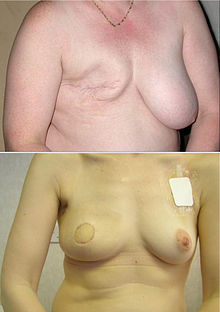
Plastic surgery can be performed to augment or reduce the size of breasts, or reconstruct the breast in cases of deformative disease, such as breast cancer. Breast augmentation and breast lift (mastopexy) procedures are done only for cosmetic reasons, whereas breast reduction is sometimes medically indicated. In cases where a woman's breasts are severely asymmetrical, surgery can be performed to either enlarge the smaller breast, reduce the size of the larger breast, or both.
Breast augmentation surgery generally does not interfere with future ability to breastfeed. Breast reduction surgery more frequently leads to decreased sensation in the nipple-areola complex, and to low milk supply in women who choose to breastfeed. Implants can interfere with mammography (breast x-ray images).
Society and culture
General
In Christian iconography, some works of art depict women with their breasts in their hands or on a platter, signifying that they died as a martyr by having their breasts severed; one example of this is Saint Agatha of Sicily.

Femen is a feminist activist group which uses topless protests as part of their campaigns against sex tourism religious institutions, sexism, and homophobia. Femen activists have been regularly detained by police in response to their protests.
There is a long history of female breasts being used by comedians as a subject for comedy fodder (e.g., British comic Benny Hill's burlesque/slapstick routines).
Art history
In European pre-historic societies, sculptures of female figures with pronounced or highly exaggerated breasts were common. A typical example is the so-called Venus of Willendorf, one of many Paleolithic Venus figurines with ample hips and bosom. Artifacts such as bowls, rock carvings and sacred statues with breasts have been recorded from 15,000 BC up to late antiquity all across Europe, North Africa and the Middle East.
Many female deities representing love and fertility were associated with breasts and breast milk. Figures of the Phoenician goddess Astarte were represented as pillars studded with breasts. Isis, an Egyptian goddess who represented, among many other things, ideal motherhood, was often portrayed as suckling pharaohs, thereby confirming their divine status as rulers. Even certain male deities representing regeneration and fertility were occasionally depicted with breast-like appendices, such as the river god Hapy who was considered to be responsible for the annual overflowing of the Nile.

Female breasts were also prominent in Minoan art in the form of the famous Snake Goddess statuettes, and a few other pieces, though most female breasts are covered. In Ancient Greece there were several cults worshipping the "Kourotrophos", the suckling mother, represented by goddesses such as Gaia, Hera and Artemis. The worship of deities symbolized by the female breast in Greece became less common during the first millennium. The popular adoration of female goddesses decreased significantly during the rise of the Greek city states, a legacy which was passed on to the later Roman Empire.
During the middle of the first millennium BC, Greek culture experienced a gradual change in the perception of female breasts. Women in art were covered in clothing from the neck down, including female goddesses like Athena, the patron of Athens who represented heroic endeavor. There were exceptions: Aphrodite, the goddess of love, was more frequently portrayed fully nude, though in postures that were intended to portray shyness or modesty, a portrayal that has been compared to modern pin ups by historian Marilyn Yalom. Although nude men were depicted standing upright, most depictions of female nudity in Greek art occurred "usually with drapery near at hand and with a forward-bending, self-protecting posture". A popular legend at the time was of the Amazons, a tribe of fierce female warriors who socialized with men only for procreation and even removed one breast to become better warriors (the idea being that the right breast would interfere with the operation of a bow and arrow). The legend was a popular motif in art during Greek and Roman antiquity and served as an antithetical cautionary tale.
Body image
Many women regard their breasts as important to their sexual attractiveness, as a sign of femininity that is important to their sense of self. A woman with smaller breasts may regard her breasts as less attractive.
Clothing
See also: Bra, Cleavage (breasts), Toplessness, Modesty, Naturism, and Exhibitionism
Because breasts are mostly fatty tissue, their shape can—within limits—be molded by clothing, such as foundation garments. Bras are commonly worn by about 90% of Western women, and are often worn for support. The social norm in most Western cultures is to cover breasts in public, though the extent of coverage varies depending on the social context. Some religions ascribe a special status to the female breast, either in formal teachings or through symbolism. Islam forbids free women from exposing their breasts in public.
Many cultures, including Western cultures in North America, associate breasts with sexuality and tend to regard bare breasts as immodest or indecent. In some cultures, like the Himba in northern Namibia, bare-breasted women are normal. In some African cultures, for example, the thigh is regarded as highly sexualized and never exposed in public, but breast exposure is not taboo. In a few Western countries and regions female toplessness at a beach is acceptable, although it may not be acceptable in the town center.
Social attitudes and laws regarding breastfeeding in public vary widely. In many countries, breastfeeding in public is common, legally protected, and generally not regarded as an issue. However, even though the practice may be legal or socially accepted, some mothers may nevertheless be reluctant to expose a breast in public to breastfeed due to actual or potential objections by other people, negative comments, or harassment. It is estimated that around 63% of mothers across the world have publicly breast-fed. Bare-breasted women are legal and culturally acceptable at public beaches in Australia and much of Europe. Filmmaker Lina Esco made a film entitled Free the Nipple, which is about "...laws against female toplessness or restrictions on images of female, but not male, nipples", which Esco states is an example of sexism in society.
Breast binding, also known as chest binding, is the flattening and hiding of breasts with constrictive materials such as cloth strips or purpose-built undergarments. Binders may also be used as alternatives to bras or for reasons of propriety. People who bind include women, trans men, non-binary people, and cisgender men with gynecomastia.
Sexual characteristic
See also: Mammary intercourse, Breast fetishism, and Stimulation of nipplesIn some cultures, breasts play a role in human sexual activity. Breasts and especially the nipples are among the various human erogenous zones. They are sensitive to the touch as they have many nerve endings; and it is common to press or massage them with hands or orally before or during sexual activity. During sexual arousal, breast size increases, venous patterns across the breasts become more visible, and nipples harden. Compared to other primates, human breasts are proportionately large throughout adult females' lives. Some writers have suggested that they may have evolved as a visual signal of sexual maturity and fertility. In Patterns of Sexual Behavior, a 1951 analysis of 191 traditional cultures, the researchers noted that stimulation of the female breast by a male sexual partner "seemed absent in all subhuman forms, although it is common among the members of many different human societies."
Many people regard bare female breasts to be aesthetically pleasing or erotic, and they can elicit heightened sexual desires in men in many cultures. In the ancient Indian work the Kama Sutra, light scratching of the breasts with nails and biting with teeth are considered erotic. Some people show a sexual interest in female breasts distinct from that of the person, which may be regarded as a breast fetish. A number of Western fashions include clothing which accentuate the breasts, such as the use of push-up bras and decollete (plunging neckline) gowns and blouses which show cleavage. While U.S. culture prefers breasts that are youthful and upright, some cultures venerate women with drooping breasts, indicating mothering and the wisdom of experience.
Research conducted at the Victoria University of Wellington showed that breasts are often the first thing men look at, and for a longer time than other body parts. The writers of the study had initially speculated that the reason for this is due to endocrinology with larger breasts indicating higher levels of estrogen and a sign of greater fertility, but the researchers said that "Men may be looking more often at the breasts because they are simply aesthetically pleasing, regardless of the size."
Some women report achieving an orgasm from nipple stimulation, but this is rare. Research suggests that the orgasms are genital orgasms, and may also be directly linked to "the genital area of the brain". In these cases, it seems that sensation from the nipples travels to the same part of the brain as sensations from the vagina, clitoris and cervix. Nipple stimulation may trigger uterine contractions, which then produce a sensation in the genital area of the brain.
Anthropomorphic geography
Main article: Breast-shaped hillThere are many mountains named after the breast because they resemble it in appearance and so are objects of religious and ancestral veneration as a fertility symbol and of well-being. In Asia, there was "Breast Mountain", which had a cave where the Buddhist monk Bodhidharma (Da Mo) spent much time in meditation. Other such breast mountains are Mount Elgon on the Uganda–Kenya border; Beinn Chìochan and the Maiden Paps in Scotland; the Bundok ng Susong Dalaga ('Maiden's breast mountains') in Talim Island, Philippines, the twin hills known as the Paps of Anu (Dá Chích Anann or 'the breasts of Anu'), near Killarney in Ireland; the 2,086 m high Tetica de Bacares or La Tetica in the Sierra de Los Filabres, Spain; Khao Nom Sao in Thailand, Cerro Las Tetas in Puerto Rico; and the Breasts of Aphrodite in Mykonos, among many others. In the United States, the Teton Range is named after the French word for 'nipple'.
Measurement
Main article: Breast measurementThe maturation and size of the breasts can be measured by a variety of different methods. These include Tanner staging, bra cup size, breast volume, breast–chest difference, the breast unit, breast hemicircumference, and breast circumference, among other measures.
See also
Notes
- Such that one's hands might be folded "upon one's breast" or one's heart might be "within one's breast"
- See Wiktionary:Thesaurus:breasts
References
- "mammal". Dictionary.reference.com. Archived from the original on 14 November 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- "Breast – Definition of breast". Merriam-Webster. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- "SEER Training: Breast Anatomy". National Cancer Institute. Archived from the original on 2 May 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2012.
- "Indo-European Lexicon". The University of Texas at Austin. Archived from the original on 20 April 2016.
- "breast". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on 2 February 2012. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- "Definition of breast". Dictionary by Merriam-Webster. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- Groot, Sue de (18 September 2016). "Is there a respectful slang word for breasts?". Sunday Times. Archived from the original on 11 December 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ^ Alex, Bridget (6 March 2019). "Scientists Still Stumped by the Evolution of Human Breasts". Discover. Archived from the original on 4 February 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ Pawłowski, Bogusław; Żelaźniewicz, Agnieszka (2021). "The evolution of perennially enlarged breasts in women: a critical review and a novel hypothesis". Biological Reviews. 96 (6): 2794–2809. doi:10.1111/brv.12778. ISSN 1469-185X. PMID 34254729. S2CID 235807642. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 30 November 2021.
- LeBlanc, Steven A.; Barnes, Ethne (July 1974). "On the Adaptive Significance of the Female Breast". The American Naturalist. 108 (962): 577–578. Bibcode:1974ANat..108..577L. doi:10.1086/282935. ISSN 0003-0147. S2CID 85243414. Archived from the original on 4 March 2022. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ Howard, Beatrice A.; Veltmaat, Jacqueline M. (18 May 2013). "Embryonic Mammary Gland Development; a Domain of Fundamental Research with High Relevance for Breast Cancer Research". Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia. 18 (2): 89–91. doi:10.1007/s10911-013-9296-2. ISSN 1083-3021. PMID 23686554. S2CID 1657065.
- Geoffrey Miller: The Sexual Evolution. Choice of partner and the emergence of the mind. Spectrum Academic Publishing House, 2009, ISBN 978-3-8274-2508-9
- ^ Pawłowski, Bogusław; Żelaźniewicz, Agnieszka (13 July 2021). "The evolution of perennially enlarged breasts in women: a critical review and a novel hypothesis". Biological Reviews. 96 (6): 2794–2809. doi:10.1111/brv.12778. ISSN 0006-3231. PMID 34254729. S2CID 235807642.
- Dunbar, Robin; Saini, Angela; Garrod, Ben; Rutherford, Adam (24 September 2017). "The Naked Ape at 50: 'Its central claim has surely stood the test of time '". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 November 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- Binns, Corey (5 August 2010). "Why Do Women Have Breasts?". Live Science. Archived from the original on 24 November 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- Bentley, Gillian R. (2001). "The evolution of the human breast". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 32 (38): 30–50. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1033.
- ^ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. illustrations by Richard Richardson, Paul. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- Cameron, John R.; Skofronick, James G.; Grant, Roderick M. (1999). Physics of the Body (2nd ed.). Madison, Wis: Medical Physics Publishing. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-0-944838-91-4.
- ^ Love, Susan M. (2015). "1". Dr. Susan Love's Breast Book (6 ed.). U.S.: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-07382-1821-2.
- ^ Stöppler, Melissa Conrad. "Breast Anatomy". Archived from the original on 27 June 2015. Retrieved 28 June 2015.
- Doucet, Sébastien; Soussignan, Robert; Sagot, Paul; Schaal, Benoist (2009). Hausberger, Martine (ed.). "The Secretion of Areolar (Montgomery's) Glands from Lactating Women Elicits Selective, Unconditional Responses in Neonates". PLOS ONE. 4 (10): e7579. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.7579D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007579. PMC 2761488. PMID 19851461.
- Lorincz AM, Sukumar S (2006). "Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 13 (2): 279–92. doi:10.1677/erc.1.00729. PMID 16728564.
Adipocytes make up the bulk of the human breast, with epithelial cells accounting for only approximately 10% of human breast volume.
- Howard BA, Gusterson BA (2000). "Human breast development". Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia. 5 (2): 119–37. doi:10.1023/A:1026487120779. PMID 11149569. S2CID 10819224.
In the stroma, there is an increase in the amount of fibrous and fatty tissue, with the adult nonlactating breast consisting of 80% or more of stroma.
- Rosenfield, Robert L.; Cooke, David W.; Radovick, Sally (2021). "Puberty in the Female and Its Disorders". Sperling Pediatric Endocrinology. Elsevier. pp. 528–626. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-62520-3.00016-6. ISBN 9780323625203. S2CID 234131890.
Estrogen stimulates the nipples to grow, mammary terminal duct branching to progress to the stage at which ductules are formed, and fatty stromal growth to increase until it constitutes about 85% of the mass of the breast. Lobulation appears around menarche, when multiple blind saccular buds form by branching of the terminal ducts. These effects are due to the presence of progesterone. Full alveolar development normally only occurs during pregnancy under the influence of additional progesterone and prolactin.
- Hagisawa S, Shimura N, Arisaka O (2012). "Effect of excess estrogen on breast and external genitalia development in growth hormone deficiency". Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. 25 (3): e61–3. doi:10.1016/j.jpag.2011.11.005. PMID 22206682.
Estrogen stimulates growth of the nipples, progression of mammary duct branching to the stage at which ductiles are formed, and fatty stromal growth until it constitutes about 85% of the mass of the breast.
- Drife JO (1986). "Breast development in puberty". Ann N Y Acad Sci. 464 (1): 58–65. Bibcode:1986NYASA.464...58D. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15993.x. PMID 2942075. S2CID 12735704.
Along with the glandular growth, there is an increase in the amount of fibrous and fatty tissue, and in fact these latter two constituents of the breast account for a far greater proportion of the morphologic growth than the proportion contributed by glandular tissue. In the nonlactating adult breast, glandular tissue accounts for no more than 20% of the breast volume, and often much less than this, and the morphologic changes at puberty are therefore mainly due to stromal expansion.
- Pamplona DC, de Abreu Alvim C. Breast Reconstruction with Expanders and Implants: a Numerical Analysis. Artificial Organs 8 (2004), pp. 353–356.
- Grassley, JS (2002). "Breast Reduction Surgery: What every Woman Needs to Know". Lifelines. 6 (3): 244–249. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6356.2002.tb00088.x. PMID 12078570.
- Tortora, Gerard J.; Grabowski, Sandra Reynolds (2001). Introduction to the Human Body: the Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology (Fifth. ed.). New York; Toronto: J. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-36777-2.
- Pacifici, Stefano (11 October 2011). "Sappey plexus | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 25 August 2020.
- Wood K, Cameron M, Fitzgerald K (2008). "Breast Size, Bra Fit and Thoracic Pain in Young Women: A Correlational Study". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 16: 1. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-16-1. PMC 2275741. PMID 18339205.
- "Breast Anatomy – Breast360.org | The American Society of Breast Surgeons Foundation". breast360.org. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- "Breast Anatomy | SEER Training". training.seer.cancer.gov. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "Breast Development". Massachusetts Hospital for Children. Archived from the original on 25 December 2010. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- Gould, Stanley F. (1983), Neville, Margaret C.; Neifert, Marianne R. (eds.), "Anatomy of the Breast", Lactation: Physiology, Nutrition, and Breast-Feeding, Boston, MA: Springer US, pp. 23–47, doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-3688-4_2, ISBN 978-1-4613-3688-4, retrieved 25 December 2024
- Suh, Minyoung; Park, Jung Hyun (1 January 2022). "Breast Geometry Characterization of Young American Females Using 3D Image Analysis". Applied Sciences. 12 (17): 8578. doi:10.3390/app12178578. ISSN 2076-3417.
- Mi-Sook, Cho (2008). "Brassiere Pattern Development Based on 3D Measurements of Upper Body Types for Women in Their 30's". The Research Journal of the Costume Culture. 16 (3).
- Coltman, Celeste E.; Steele, Julie R.; McGhee, Deirdre E. (2 September 2018). "Effects of age and body mass index on breast characteristics: a cluster analysis". Celeste E. Coltman. 61 (9): 1232–1245. doi:10.1080/00140139.2018.1481229. ISSN 0014-0139. PMID 29792567.
- Lauersen, Niels H.; Stukane, Eileen (1998). The Complete Book of Breast Care (1st Trade Paperback ed.). New York: Fawcett Columbine/Ballantine. ISBN 978-0-449-91241-6.
...there is no medical reason to wear a bra, so the decision is yours, based on your own personal comfort and aesthetics. Whether you have always worn a bra or always gone braless, age and breastfeeding will naturally cause your breasts to sag.
- Rinker, B; Veneracion, M; Walsh, C (2008). "The Effect of Breastfeeding on Breast Aesthetics". Aesthetic Surgery Journal. 28 (5): 534–7. doi:10.1016/j.asj.2008.07.004. PMID 19083576.
- Andrea Thompson (2 November 2007). "Breastfeeding Does Not Make Breasts Sag, Study Suggests". LiveScience. Archived from the original on 3 July 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ^ "Don't burn your bra just yet". The Independent. 22 September 2011. Archived from the original on 17 July 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- Brumberg, Joan Jacobs (1998). The Body Project: An Intimate History of American Girls. Knopf Doubleday Publishing. p. 336. ISBN 0-679-73529-1. Archived from the original on 28 March 2002.
- "Female Intelligence Agency: Why Do Women Wear Bras?". 007b Breast. Archived from the original on 31 August 2011. Retrieved 10 May 2011.
- Ocran, Francisca Margarita; Ji, Xiaofen; Zhai, Lina (January 2022). "A study to evaluate pressure distribution of different sports bras". Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics. 17. doi:10.1177/15589250221118643. ISSN 1558-9250.
- Kipp, Shalaya; Leahy, Michael G.; Sheel, A. William (1 June 2024). "Sports Bra Restriction on Respiratory Mechanics during Exercise". Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 56 (6): 1168–1176. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000003403. ISSN 1530-0315. PMID 38350462.
- ^ Robert L. Barbieri (2009), "Yen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology", Yen (6th ed.), Elsevier: 235–248, doi:10.1016/B978-1-4160-4907-4.00010-3, ISBN 978-1-4160-4907-4, archived from the original on 6 March 2018, retrieved 6 March 2018
- Brisken; Malley (2 December 2010), "Hormone Action in the Mammary Gland", Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2 (12): a003178, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a003178, PMC 2982168, PMID 20739412
- Greenbaum AR, Heslop T, Morris J, Dunn KW (April 2003). "An Investigation of the Suitability of Bra fit in Women Referred for Reduction Mammaplasty". British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 56 (3): 230–6. doi:10.1016/S0007-1226(03)00122-X. PMID 12859918.
- Loughry CW; et al. (1989). "Breast Volume Measurement of 598 Women using Biostereometric Analysis". Annals of Plastic Surgery. 22 (5): 380–385. doi:10.1097/00000637-198905000-00002. PMID 2729845. S2CID 8713713.
- De, Blok Christel; Klaver, Maartje; Nota, Nienke; Dekker, Marieke; Den, Heijer Martin (13 May 2016). "Breast development in male-to-female transgender patients after one year cross-sex hormonal treatment". Endocrine Abstracts. 41. doi:10.1530/endoabs.41.GP146. ISSN 1470-3947.
- Santen, R. J.; Allred, D. C.; Ardoin, S. P.; Archer, D. F.; Boyd, N.; Braunstein, G. D.; Burger, H. G.; Colditz, G. A.; Davis, S. R.; Gambacciani, M.; Gower, B. A.; Henderson, V. W.; Jarjour, W. N.; Karas, R. H.; Kleerekoper, M.; Lobo, R. A.; Manson, J. E.; Marsden, J.; Martin, K. A.; Martin, L.; Pinkerton, J. V.; Rubinow, D. R.; Teede, H.; Thiboutot, D. M.; Utian, W. H.; Endocrine Society (2010). "Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 95 (7 Suppl 1): s1 – s66. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2509. PMC 6287288. PMID 20566620.
- "Information on Estrogen Hormone Therapy | Gender Affirming Health Program". transcare.ucsf.edu. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Practical Guidelines for Transgender Hormone Treatment | Endocrinology, Diabetes, Nutrition & Weight Management". www.bumc.bu.edu. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Transgender and Gender Diverse Hormone Therapy". hopkinsmedicine.org.
- Breast – premenstrual tenderness and swelling, A.D.A.M., May 2012, archived from the original on 5 July 2016, retrieved 21 March 2018
- Lawrence 2016, p. 34.
- Lawrence 2016, p. 58.
- ^ "The physiological basis of breastfeeding". NCBI Bookshelf. 5 November 2008. Archived from the original on 19 January 2018. Retrieved 13 February 2018.
- Kim, E. Y.; Chang, Y.; Ahn, J.; Yun, J. S.; Park, Y. L.; Park, C. H.; Shin, H.; Ryu, S. (2020). "Menopausal Transition, Body Mass Index, and Prevalence of Mammographic Dense Breasts in Middle-Aged Women". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 9 (8): 2434. doi:10.3390/jcm9082434. PMC 7465213. PMID 32751482.
- Wanders, Johanna Olga Pauline; Bakker, Marije Fokje; Veldhuis, Wouter Bernard; Peeters, Petra Huberdina Maria; van Gils, Carla Henrica (30 May 2015). "The effect of weight change on changes in breast density measures over menopause in a breast cancer screening cohort". Breast Cancer Research. 17 (1): 74. doi:10.1186/s13058-015-0583-2. ISSN 1465-542X. PMC 4487974. PMID 26025139.
- "What You Should Know About Hormone Therapy and Menopause". Columbia University Irving Medical Center. 7 February 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2024.
- "Breast Cancer". NCI. January 1980. Archived from the original on 25 June 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- ^ "Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)". NCI. 23 May 2014. Archived from the original on 5 July 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- Saunders C, Jassal S (2009). Breast cancer (1. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. Chapter 13. ISBN 978-0-19-955869-8. Archived from the original on 25 October 2015.
- ^ World Cancer Report 2014. World Health Organization. 2014. pp. Chapter 5.2. ISBN 978-92-832-0429-9.
- Fakhri N, Chad MA, Lahkim M, Houari A, Dehbi H, Belmouden A, El Kadmiri N (September 2022). "Risk factors for breast cancer in women: an update review". Medical Oncology. 39 (12): 197. doi:10.1007/s12032-022-01804-x. PMID 36071255. S2CID 252113509.
- Lawrence 2016, p. 201.
- ^ "How a well-fitted sports bra can reduce breast pain". nhs.uk. 30 April 2018. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
- World Health Organization (February 2006). "Fact sheet No. 297: Cancer". Archived from the original on 13 February 2014. Retrieved 26 April 2007.
- Seven things you should know about breast cancer risk Archived 4 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine Harvard College. Last updated June 2008
- Stuebe, Alison M. (May 2017). "Reducing cancer risk by enabling women to breastfeed". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 26 (5 Supplement): IA23. doi:10.1158/1538-7755.CARISK16-IA23. Archived from the original on 23 September 2019. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- Erhan, Yamaç; Zekioglu, Osman; Erhan, Yildiz (October 2006). "Invasive lobular carcinoma of the male breast". Canadian Journal of Surgery. Journal Canadien de Chirurgie. 49 (5): 365–366. ISSN 0008-428X. PMC 3207588. PMID 17152578.
- Olson, James Stuart (2002). Bathsheba's Breast: Women, Cancer and History. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-8018-6936-5. OCLC 186453370.
- "Secondary sex characteristics". .hu-berlin.de. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Lawrence 2016, pp. 613–616.
- "St Agatha". Catholic Online. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- Femen wants to move from public exposure to political power Archived 7 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine, Kyiv Post (28 April 2010)
- "Ukraine's Ladies of Femen". Movements.org. 16 August 2011. Archived from the original on 14 April 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- Ukraine's Femen:Topless protests 'help feminist cause' Archived 12 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine, BBC News (23 October 2012)
- "Topless FEMEN Protesters Drench Belgian Archbishop André-Jozef Léonard, Protest Homophobia in Catholic Church (PHOTOS)". The Huffington Post. 24 April 2013. Archived from the original on 16 April 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
- Femen activists jailed in Tunisia for topless protest Archived 27 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine, BBC News (12 June 2013)
- ^ Shire, Emily (9 September 2014). "Women, It's Time to Reclaim Our Breasts". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on 1 November 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- Yalom (1998) pp. 9–16; see Eva Keuls (1993), Reign of the Phallus: Sexual Politics in Ancient Athens for a detailed study of male-dominant rule in ancient Greece.
- Yalom (1998), p. 18.
- Hollander (1993), p. 6.
- Koff, E., Benavage, A. Breast Size Perception and Satisfaction, Body Image, and Psychological Functioning in Caucasian and Asian American College Women. Sex Roles 38, 655–673 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018802928210 Archived 4 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- "Bra Cup Sizes—getting fitted with the right size". 1stbras.com. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- "The Right Bra". Liv.com. Archived from the original on 28 March 2009. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- "Breast supporting act: a century of the bra". London: The Independent UK. 15 August 2007. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- Wood, K; Cameron, M; Fitzgerald, K (2008). "Breast size, bra fit and thoracic pain in young women: a correlational study". Chiropr Osteopat. 16: 1. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-16-1. PMC 2275741. PMID 18339205.
- Bohidar, Anannya (27 October 2015). "Worshipping Breasts in the Maternal Landscape of India". South Asian Studies. 31 (2015): 247–253. doi:10.1080/02666030.2015.1094209. S2CID 194282633. Archived from the original on 2 January 2021. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- ^ "Topless Beaches In Europe: Etiquette, Culture, And What To Expect [Updated On 2024]". 9 October 2024. Retrieved 25 December 2024.
- Wolf, J.H. (2008). "Got milk? Not in public!". International Breastfeeding Journal. 3 (1): 11. doi:10.1186/1746-4358-3-11. PMC 2518137. PMID 18680578.
- Vance, Melissa R. (June–July 2005). "Breastfeeding Legislation in the United States: A General Overview and Implications for Helping Mothers". LEAVEN. 41 (3): 51–54. Archived from the original on 31 March 2007.
- Jordan, Tim; Pile, Steve, eds. (2002). Social Change. Blackwell. p. 233. ISBN 9780631233114.
- Cox, Sue (2002). Breast Feeding With Confidence. United States: Meadowbrook Press. ISBN 0684040050.
- Bennett, Theodore. "Clothing Optional?: Nudity and the Law of the Australian Beach". Bond Law Review. ISSN 2202-4824.
- Anders Pape Møller; et al. (1995). "Breast asymmetry, sexual selection, and human reproductive success". Ethology and Sociobiology. 16 (3): 207–219. doi:10.1016/0162-3095(95)00002-3.
- Clellan S. Ford and Frank A. Beach (1965). Patterns of Sexual Behaviour. Internet Archive. p. 70.
- "Sir Richard Burton's English translation of Kama Sutra". Sacred-texts.com. Archived from the original on 2 January 2010. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- Hickey, Eric W. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Murder and Violent Crime. Sage Publications Inc. ISBN 978-0-7619-2437-1
- Burns-Ardolino, Wendy (2007). Jiggle: (Re)shaping American women. Lanham, MD: Lexington Books. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-7391-1299-1.
- ^ Dixson, BJ; Grimshaw, GM; Linklater, WL; Dixson, AF (February 2011). "Eye-tracking of men's preferences for waist-to-hip ratio and breast size of women". Archives of Sexual Behavior. 40 (1). International Academy of Sex Research: 43–50. doi:10.1007/s10508-009-9523-5. PMID 19688590. S2CID 4997497.
- "Hourglass figure fertility link". BBC News. 4 May 2004. Archived from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- Alfred C. Kinsey; Wardell B. Pomeroy; Clyde E. Martin; Paul H. Gebhard (1998). Sexual Behavior in the Human Female. Indiana University Press. p. 587. ISBN 0-253-01924-9. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
There are some females who appear to find no erotic satisfaction in having their breasts manipulated; perhaps half of them derive some distinct satisfaction, but not more than a very small percentage ever respond intensely enough to reach orgasm as a result of such stimulation (Chapter 5). Records of females reaching orgasm from breast stimulation alone are rare.
- Boston Women's Health Book Collective (1996). The New Our Bodies, Ourselves: A Book by and for Women. Simon & Schuster. p. 575. ISBN 0-684-82352-7. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
A few women can even experience orgasm from breast stimulation alone.
- Merril D. Smith (2014). Cultural Encyclopedia of the Breast. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-7591-2332-8. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- Justin J. Lehmiller (2013). The Psychology of Human Sexuality. John Wiley & Sons. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-118-35132-1. Archived from the original on 23 February 2019. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- Komisaruk, B. R.; Wise, N.; Frangos, E.; Liu, W.C.; Allen, K.; Brody, S. (2011). "Women's Clitoris, Vagina, and Cervix Mapped on the Sensory Cortex: fMRI Evidence, Surprise finding in response to nipple stimulation". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 8 (10): 2822–30. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02388.x. PMC 3186818. PMID 21797981.
- Stephanie Pappas (5 August 2011). "Surprise finding in response to nipple stimulation". CBS News. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- "The Story of Bodhidharma". Usashaolintemple.org. Archived from the original on 30 November 2011. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- "Creation of the Teton Landscape: The Geologic Story of Grand Teton National Park (The Story Begins)". National Park Service. 19 January 2007. Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2011.
Bibliography
- Hollander, Anne (1993). Seeing through clothes. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-08231-1.
- Morris, Desmond The Naked Ape: a zoologist's study of the human animal Bantam Books, Canada. 1967
- Yalom, Marilyn (1998). A history of the breast. London: Pandora. ISBN 978-0-86358-400-8.
- Venes, Donald (2013). Taber's cyclopedic medical dictionary. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis. ISBN 978-0-8036-2977-6.
- Lawrence, Ruth (2016). Breastfeeding : a guide for the medical profession, 8th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-323-35776-0.
External links
- "Are Women Evolutionary Sex Objects?: Why Women Have Breasts". Archived from the original on 2 December 2011.
| Human regional anatomy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body | Skin | ||||
| Head | |||||
| Neck | |||||
| Torso (Trunk) | |||||
| Limbs |
| ||||
| Anatomy of the breast | |
|---|---|
| Structure | |
| Other | |
| Breast disease | |
|---|---|
| Inflammation | |
| Physiological changes and conditions | |
| Nipple | |
| Masses | |
| Other | |