| Revision as of 16:38, 9 January 2021 view source83.227.81.54 (talk) →History← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:53, 12 January 2025 view source Orenburg1 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users166,367 editsm ce | ||
| (959 intermediate revisions by 93 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description| |
{{short description|European ethnic group}} | ||
| {{Other uses |
{{Other uses of|Rus}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2024}} | |||
| ] (1899)]] | |||
| ] trade routes: the ] (in red) and the ] (in purple). Sufficiently controlling strongholds, market places and portages along the routes was necessary for the Scandinavian raiders and traders.]] | |||
| {{undue|date=December 2020}} | |||
| The '''Rus{{'}} people''' (]: Рѹсь; Modern ], ], ], and ]: Русь, {{small|romanized:}} ''<nowiki>Rus'</nowiki>''; ]: '']''; ]: Ῥῶς, {{small|]:}} ''Rhos'') are generally understood in English-language scholarship as people of ]. Of the two main origin theories, the "Normanist" places them ancestrally as Northern people trading and raiding on ] from around the eighth to eleventh centuries AD, while the "anti-Normanist" theory places their origins in the Slavic region around the ]. | |||
| The '''Rus{{'}}''',{{efn|Also commonly spelled ''Rus'' without the apostrophe;<ref>{{cite book |last1=Rosenwein |first1=Barbara H. |title=A Short History of the Middle Ages, Volume I: From c.300 to c.1150, Fourth Edition |date=14 February 2014 |publisher=University of Toronto Press |isbn=978-1-4426-0616-6 |page=121 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mwZLBAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref> {{langx|orv|Роусь}}; ], ], ], and ]: Русь; ]: Ῥῶς, {{small|]:}} ''Rhos''}} also known as '''Russes''',<ref>{{cite book |last1=Dolukhanov |first1=Pavel |title=The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus |date=10 July 2014 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-317-89222-9 |page=182 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TIkABAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Magill |first1=Frank N. |title=The Middle Ages: Dictionary of World Biography, Volume 2 |date=12 November 2012 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-136-59313-0 |page=803 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aBHSc2hTfeUC |language=en}}</ref> were a people in ] Eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally ], mainly originating from present-day ], who settled and ruled along the ] between the ] and the ]s from around the 8th to 11th centuries AD. | |||
| According to the most prevalent theory, the name ''Rus''{{'}}, like the Proto-Finnic name for ] (''*Ruotsi''), is derived from an old Finnish term "{{lang|fi|ruskea}}", meaning light brown (which is related to the old Russian ''rusi'', "brown", hence the name Rus'). According to this theory, these ] basing themselves among ] and Volga people (i.e. ] and ] tribes) in the upper ] formed a diaspora of traders and raiders exchanging furs and slaves for silk, silver and other commodities available to the east and south. Around the 9th century, on the river routes to the ], they played an unclear but significant role in forming the principality of ], gradually assimilating with local ]. They also extended their operations much further east and south, among the ] and ], on the routes to the ]. By around the 11th century, the word ''Rus{{'}}'' was increasingly associated with the Principality of Kiev, and the term '']'' was becoming more common as a term for Scandinavians traveling the river-routes. | |||
| The two original centres of the Rus' were ] (''Aldeigja''), founded in the mid-8th century, and ] (''Holmr''), founded in the mid-9th century.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=60|loc=These two original centres of Rus were Staraja Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodishche}} The two settlements were situated at opposite ends of the ], between ] and ], and the Norsemen likely called this territory ''Gardar''.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=60}} From there, the name of the Rus' was transferred to the ], and the Rus' then moved eastward to where the ] tribes lived and southward to where the ] lived.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=60}} | |||
| Little, however, is certain about the Rus{{'}}. This is to a significant extent because, although Rus{{'}} people were active over a long period and vast distances, textual evidence for their activities is very sparse and almost never produced by contemporary Rus' people themselves. It is believed that writing was brought to the Rus by the Slavs for religious reasons, but this happened long after their early history. The word ''Rus{{'}}'' in the primary sources does not always denote the same thing as it does when used by modern scholars. Meanwhile, archaeological evidence and researchers' understanding of it is accumulating only gradually. As a trading diaspora, Rus' people intermingled extensively with Finnic, Slavic, and Turkic peoples and their customs and identity seem corresponding to have varied considerably over time and space. | |||
| The name '']'' was applied to the newly formed state of ],{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=1|loc=The state of the Eastern Slavs—''Russia'', or ''Rhosia'' according to the Byzantines of mid-tenth century—was called in the medieval Norse literature ''Gardariki'', or in the earlier, Viking-age sources just ''Gardar'', a term originally restricted to the non-Slav territory of Ladoga-Ilmen}} and the ruling Norsemen along with local Finnic tribes gradually assimilated into the ] population and came to speak ]. ] remained familiar to the elite until their complete assimilation by the second half of the 11th century,<ref name="mel"/> and in rural areas, vestiges of Norse culture persisted as late as the 14th and early 15th centuries, particularly in the north.<ref name="mel"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220215195340/https://history.wikireading.ru/hpnfDEhILm |date=15 February 2022 }}.</ref> | |||
| The other key reason for dispute about the origins of Rus' people is the likelihood that they had a role in ninth- to 10th-century state formation in eastern Europe (ultimately giving their name to ] and ]), making them relevant to what are today seen as the national histories of Russia, ], ], ], Belarus, ] and the ]. | |||
| The history of the Rus{{'}} is central to 9th through 10th-century state formation, and thus national origins, in Eastern Europe. They ultimately gave their name to ] and ], and they are relevant to the national histories of Russia, ] and Belarus. Because of this importance, there is a set of alternative so-called "]" views that are largely confined to a minor group of Eastern European scholars. | |||
| ==Key sources== | |||
| ===Etymology=== | |||
| {{Main|Rus' (name)}} | |||
| ] in the 9th century. ] is located along the coast of the northern tip of the pink area marked ''"Swedes and Goths"''.]] | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| The scholarly consensus <ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.historyextra.com/period/viking/the-vikings-at-home/|title=The Vikings at home|website=HistoryExtra|access-date=May 24, 2020}}</ref> is that the ] originated in what is currently coastal ] around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as ] in ] (with the older name being '']'').<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ancient.eu/Kievan_Rus/|title=Kievan Rus|website=Ancient History Encyclopedia|access-date=May 24, 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=The Vikings (780–1100) | |||
| {{Main|Names of Rusʹ, Russia and Ruthenia}} | |||
| |url=https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/vikg/hd_vikg.htm|website=www.metmuseum.org|access-date=2020-05-24}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.swedenhistorytours.se/|title=Viking Tours Stockholm, 20 Historical Cultural Transported Tours|website=Sweden History Tours|access-date=May 24, 2020}}</ref> According to the prevalent theory, the name ''Rus''{{'}}, like the Proto-Finnic name for ] (''*Ruotsi''), is derived from an old Finnish term "ruskea", meaning light brown (which is related to the old Russian ''rusi'', "brown", hence the name Rus'), and that it could be linked to the Swedish coastal area of ] (''Rus-law'') or '']'', at that time inhabited mainly by Baltish and Finnish-speaking tribes.<ref>. Eeva-Kristiina Harlin. "Archaeological finds suggest that the indigenous Sami people have lived in the Arctic region for thousands of years. From losing land to farmers and industries, to being subjugated to racial biology and having their religion, culture and language suppressed, the Sami culture and lifestyle has survived into modern society."</ref><ref> // European Kingdoms. | |||
| {{Old Norse language map}} | |||
| Northern Europe (article).</ref> The name ''Rus{{'}}'' would then have the same origin as the ] and ] names for Sweden: ''Ruotsi'' and ''Rootsi''.<ref name="auto">Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in '''', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7).</ref><ref name="etymonline.com">"Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069. Accessed 25 July 2018.</ref> | |||
| :Note: The þ (]) represents the ] /θ/ of ''th'' in English ''thing'', whereas the ð (]) represents the ] /ð/ of ''th'' in English ''the''. When þ appears in intervocalic position or before a voiced consonant, it is pronounced like ð, so the pronunciation difference between ''rōþer'' and ''róðr'' is minute. | |||
| ] in the 9th century. ] is located along the coast of the northern tip of the area marked ''"Swedes and Goths"''.]] | |||
| The name '']'' remains not only in names such as ''Russia'' and ''Belarus'', but it is also preserved in many place names in the ] and ], and it is the origin of the Greek ''Rōs''.<ref name="hell668">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''Ryssland''}}</ref> ''Rus{{'}}'' is generally considered to be a borrowing from ] '']'' ("Sweden").<ref name="hell668"/><ref name="auto" /><ref name="etymonline.com">{{cite web |title="Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press |access-date=12 January 2021 |url=http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069 |archive-date=26 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163729/https://www.oed.com/start;jsessionid=B3DE6DBBD31C4F6326E14523B4A92B99?authRejection=true&url=%2Fview%2FEntry%2F169069 |url-status=live }}</ref> There are two theories behind the origin of ''Rus{{'}}''/''Ruotsi'', which are not mutually exclusive. It is either derived more directly from ] '']'' (] ''róðr''<ref name="hell650f">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''Rodd''}}</ref>), which referred to rowing, the ], etc., or it is derived from this term through ''Rōþin'', an older name for the Swedish coastal region ].<ref name="hell668"/><ref name="auto">Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in '' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230414030955/https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ |date=14 April 2023 }}'', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7).</ref>{{sfnp|Blöndal|2007|p=1}}<ref name="vasmer"/> | |||
| The Finnish and Russian forms of the name have a final -s revealing an original compound where the first element was {{transliteration|ru|rōþ(r)s}}- (preceding a ] consonant, ''þ'' is pronounced like ''th'' in English ''thing'').<ref name="hell668"/> The prefix form ''rōþs-'' is found not only in ''Ruotsi'' and '']'', but also in ] ''róþsmenn'' and ''róþskarlar'', both meaning "rowers",<ref name="vasmer">{{Cite web |url=https://vasmer.slovaronline.com/11386-RUS |title=''Русь'' in "Vasmer's Etymological Dictionary" online |access-date=26 January 2021 |archive-date=2 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210702152720/https://vasmer.slovaronline.com/11386-RUS |url-status=live }}</ref> and in the modern Swedish name for the people of Roslagen – '']ar''<ref name="hell654">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''Roslagen''}}</ref> which derives from ON *''rōþsbyggiar'' ("inhabitants of Rōþin").<ref name="hell654f">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''Rospigg''}}</ref> The name ''Roslagen'' itself is formed with this element and the plural ] of the ] '']'', meaning "the teams", in reference to the teams of rowers in the Swedish kings' fleet levy.<ref name="hell654"/><ref name="hell339">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''2. lag''}}</ref> | |||
| There are at least two, probably three, instances of the root in Old Norse from two 11th c. runic inscriptions, fittingly located at two extremes of the ]. Two of them are '''roþ''' for ''rōþer ''/''róðr'', meaning "fleet levy", on the ], and as '''i ruþi''' (translated as "dominion") on the lost ], in the ] in the ],<ref name="BrinkPrice2008">{{cite book|author1=Stefan Brink|author2=Neil Price|title=The Viking World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA53|date=31 October 2008|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-31826-1|pages=53–54|access-date=22 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163640/https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA53|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>Joel Karlsson (2012) Stockholm university https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.123007.1360163562!/menu/standard/file/Karlsson_Joel_Ofria_omnamnda-pa_runstenar.pdf {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210122211000/https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.123007.1360163562!/menu/standard/file/Karlsson_Joel_Ofria_omnamnda-pa_runstenar.pdf |date=22 January 2021 }} page 4-5</ref> and the possible third one was identified by ] in the most widely accepted reading as '''{{transliteration|ru|italic=no|roþ(r)slanti}}''' on the ] originally located in ], where a runic inscription was most likely carved by Swedish mercenaries serving in the ].{{sfnp|Pritsak|1981|p=348}} Brate has reconstructed *''Rōþsland'', as an old name for Roslagen.<ref name="hell654"/> | |||
| Between the two compatible theories represented by ''róðr'' or ''Róðinn'', modern scholarship leans towards the former because at the time, the region covered by the latter term, Roslagen, remained sparsely populated and lacked the demographic strength necessary to stand out compared to the adjacent Swedish heartland of the Mälaren Valley. Consequently, an origin in word compounds such as ''róþs-menn'' and ''róþs-karlar'' is considered the most likely one. Moreover, the form ''róþs-'', from which ''Ruotsi'' and ''Rusʹ'' originate, is not derived directly from ON ''róðr'', but from its earlier ] form ''roðz''<ref>Can also be spelled ''roðʀ'', but ʀ and z are interchangeable.</ref> ({{lang|mis|rothz}}).<ref name="Larsson14f">Larsson, Mats G. (1997). ''Rusernas rike'' in ''Vikingar i österled''. Atlantis, Stockholm. {{ISBN|91-7486-411-4}}. pp. 14–15.</ref> | |||
| Other theories such as derivation from ''Rusa'', a name for the ], are rejected or ignored by mainstream scholarship.<ref name="hell668"/><ref name="vasmer"/> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{Anchor|Rus%27_people#History}} | |||
| {{Further|Norsemen|Vikings|Varangians}} | |||
| Having settled ] in the 750s, Scandinavian colonists played an important role in the early ethnogenesis of the Rus{{'}} people,{{sfn|Duczko|2004|pp=67–70}}<ref name="Peterson2016">{{cite book|author=Gary Dean Peterson|title=Vikings and Goths: A History of Ancient and Medieval Sweden|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=joawDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA203|date=21 June 2016|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-1-4766-2434-1|page=203|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163702/https://books.google.com/books?id=joawDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA203|url-status=live}}</ref> and in the formation of the ]. Ladoga, then known as ''Aldeigja'' by the Norsemen, was the earliest and most significant settlement of the Rus', while ], likely known as ''Holmr'', was founded over a century later.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=60|loc=Ladoga, or as it was then called Aldeigja, was the earliest and the most important place, while Gorodishche, probably with the Norse name ''Holmr'', was founded more than a century later}} It was from the Ladoga area, which formed the centre of the Rus', that the envoys went to ] in 838.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=61|loc=The Ladoga area was the core of the kaganate of Rus: it was from here the Rhos' envoys went to Constantinople in 838}} The ] are first mentioned in the '']'' as having exacted tribute from the Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859.<ref name="Jones2001">{{cite book|author=Gwyn Jones|title=A History of the Vikings|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lD74bDG3O5oC&pg=PA245|year=2001|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-280134-0|page=245|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163708/https://books.google.com/books?id=lD74bDG3O5oC&pg=PA245|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Jakobsson2020">{{cite book|author=Sverrir Jakobsson|title=The Varangians: In God's Holy Fire|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ji0DEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA64|year=2020|publisher=Springer Nature|isbn=978-3-030-53797-5|page=64|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163627/https://books.google.com/books?id=Ji0DEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA64|url-status=live}}</ref> It was the time of rapid expansion of the Vikings' presence in Northern Europe; England began to pay ] in 865,<ref name="ChartrandDurham2016">{{cite book|author1=René Chartrand|author2=Keith Durham|author3=Mark Harrison|author4=Ian Heath|title=The Vikings|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dLOhDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA7|date=22 September 2016|publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing|isbn=978-1-4728-1323-7|page=7|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163657/https://books.google.com/books?id=dLOhDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA7|url-status=live}}</ref> and the ] faced an invasion by the ] around the same time.<ref name="Mickevičius1997">{{cite journal |last1=Mickevičius |first1=Arturas |title=Curonian "Kings" and "Kingdoms" of the Viking Age |journal=Lithuanian Historical Studies |date=30 November 1997 |volume=2 |issue=1 |page=11 |doi=10.30965/25386565-00201001|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| The Varangians are mentioned in the ''Primary Chronicle'',{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=10}} which suggests that the term ''Rus{{'}}'' was used to denote Scandinavians until it became firmly associated with the now extensively Slavicised elite of Kievan Rus{{'}}.<ref name="Warner2002">{{cite book|author=Elizabeth Warner|title=Russian Myths|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_PoesCeU0iUC&pg=PA7|date=1 July 2002|publisher=University of Texas Press|isbn=978-0-292-79158-9|page=7|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163634/https://books.google.com/books?id=_PoesCeU0iUC&pg=PA7|url-status=live}}</ref>{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=210}} At that point, the new term ''Varangian'' was increasingly preferred to name the Scandinavians,<ref>Marika Mägi, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163644/https://books.google.com/books?id=CGdjDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA195 |date=26 April 2023 }}, The Northern World, Volume 84 (Leiden: Brill, 2018), p. 195, citing Alf Thulin, 'The Rus{{'}} of Nestor's Chronicle', ''Mediaeval Scandinavia'', 13 (2000)</ref> probably mostly from what is currently Sweden,<ref name=ForteOram2005>{{cite book|last1=Forte|first1=Angelo|first2=Richard|last2=Oram|first3=Frederik|last3=Pedersen|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_vEd859jvk0C&pg=PA13|title=Viking Empires|publisher=]|year=2005|isbn=0-521-82992-5|pages=13–14|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163636/https://books.google.com/books?id=_vEd859jvk0C&pg=PA13|url-status=live}}</ref> plying the river routes between the Baltic and the Black and Caspian Seas.<ref name="Kaplan1954">{{cite journal |last1=Kaplan |first1=Frederick I. |title=The Decline of the Khazars and the Rise of the Varangians |journal=American Slavic and East European Review |date=1954 |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=1–10 |doi=10.2307/2492161 |jstor=2492161 |issn=1049-7544}}</ref><ref name="Subtelny2000">{{cite book|author=Orest Subtelny|title=Ukraine: A History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=l5uiWHgRphQC&pg=PA26|date=1 January 2000|publisher=University of Toronto Press|isbn=978-0-8020-8390-6|page=26|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163654/https://books.google.com/books?id=l5uiWHgRphQC&pg=PA26|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="BjergLind2013">{{cite book|author1=Ole Crumlin-Pedersen|editor1=Line Bjerg|editor2=John H. Lind|editor3=Soren Michael Sindbaek|title=From Goths to Varangians: Communication and Cultural Exchange between the Baltic and the Black Sea|chapter=Vikling Warriors and the Byzantine Empire|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6ZufDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA297|date=31 December 2013|publisher=Aarhus University Press|isbn=978-87-7124-425-0|pages=297–|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163653/https://books.google.com/books?id=6ZufDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA297|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Magocsi201063">{{cite book|author=Paul R. Magocsi|title=A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TA1zVKTTsXUC&pg=PA63|date=1 January 2010|publisher=University of Toronto Press|isbn=978-1-4426-1021-7|pages=63–65|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163645/https://books.google.com/books?id=TA1zVKTTsXUC&pg=PA63|url-status=live}}</ref> Relatively few of the ] Varangians left in their native ] tell of their journeys abroad,<ref name="Sawyer2000">{{cite book |author=Birgit Sawyer |author-link=Birgit Sawyer |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MMFisCY78DYC&pg=PA116 |title=The Viking-age Rune-stones: Custom and Commemoration in Early Medieval Scandinavia |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-19-820643-9 |pages=116–119 |access-date=28 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163659/https://books.google.com/books?id=MMFisCY78DYC&pg=PA116 |archive-date=26 April 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> to such places as what is today Russia, Ukraine, Belarus,<ref name="ZaprudnikZaprudnik1993">{{cite book|author1=I︠A︡ Zaprudnik|author2=Jan Zaprudnik|author3=Ânka Zaprudnìk|title=Belarus: At A Crossroads In History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GfIiAQAAIAAJ&q=%22toward%20Kiev%20and%20Byzantium%22|date=16 August 1993|publisher=Avalon Publishing|isbn=978-0-8133-1339-9|page=5|access-date=3 February 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163655/https://books.google.com/books?id=GfIiAQAAIAAJ&q=%22toward%20Kiev%20and%20Byzantium%22|url-status=live}}</ref> Greece, and Italy.<ref name="Jesch2001">{{cite book|author=Judith Jesch|title=Ships and Men in the Late Viking Age: The Vocabulary of Runic Inscriptions and Skaldic Verse|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=p8ZK3v0hrk4C&pg=PA178|year=2001|publisher=Boydell & Brewer|isbn=978-0-85115-826-6|pages=86, 90, 178|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163648/https://books.google.com/books?id=p8ZK3v0hrk4C&pg=PA178|url-status=live}}</ref> Most of these rune stones can be seen today, and are a significant piece of historical evidence. The ] tell of many notable Varangian expeditions, and even recount the fates of individual warriors and travelers.{{sfnp|Blöndal|2007|pp=223–224}} | |||
| In Russian historiography, two cities are used to describe the beginnings of the country: Kiev and Novgorod.{{sfnp|Duczko|2004|page=60|loc=two towns used to symbolise the early history of Russia: Kiev and Novgorod}} In the first part of the 11th century the former was already a Slav metropolis, rich and powerful, a fast growing centre of civilisation adopted from Byzantium.<ref name="Meyendorff2010">{{cite book|author=John Meyendorff|title=Byzantium and the Rise of Russia: A Study of Byzantino-Russian Relations in the Fourteenth Century|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KKZdTvs1ySYC&pg=PA10|date=24 June 2010|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-13533-7|page=10|access-date=30 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163650/https://books.google.com/books?id=KKZdTvs1ySYC&pg=PA10|url-status=live}}</ref> The latter town, Novgorod, was another centre of the same culture but founded in different surroundings, where some old local traditions moulded this commercial city into the capital of a powerful oligarchic trading republic of a kind otherwise unknown in this part of Europe.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=60|loc=The latter town, Novgorod..., was another centre of the same culture but founded in different surroundings, where some old local traditions moulded this commercial city into a mighty oligarchic republic}} These towns have tended to overshadow the significance of other places that had existed long before Kiev and Novgorod were founded.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=60}} The two original centres of Rus{{'}} were Staraya Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodische, two points on the Volkhov, a river running for {{convert|200|km}} between ] in the south to ] in the north.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=60|loc=These two original centres of Rus were Staraja Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodishche}} This was the territory that most probably was originally called by the Norsemen ''Gardar'', a name that long after the Viking Age acquired a much broader meaning and became '']'', a denomination for the entire state.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=60}} The area between the lakes was the original Rus{{'}}, and it was from here that its name was transferred to the territories inhabited by the Slavs on the middle ], which eventually became the "land of Rus" (''Ruskaja zemlja'').{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=60|loc=The area between the lakes was the original Rus, and it was from here its name was transferred to the Slav territories on the middle Dnieper, which eventually became "Ruskaja zemlja"—the land of Rus}} The ''Primary Chronicle'' portrays the East Slavic tribe of ] as the most civilised of the East Slavs, and that they were therefore predisposed to host the Rus', but not give their name to the land.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=207}} From this area, the Rus' moved eastward to the lands inhabited by Finno-Ugric tribes in the Volga-Oka region, as well as south along the Dnieper.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|p=60|loc= It was from here the Rus moved eastward, to the Finno-Ugrian lands of the Volga-Oka region, and southward, to the Dnieper among the Slavs}} | |||
| The ] of the first territory of Rus{{'}} has been sought in the developments around the early-8th century, when Staraja Ladoga was founded as a manufacturing centre and to conduct trade, serving the operations of Scandinavian hunters and dealers in furs obtained in the north-eastern forest zone of Eastern Europe.<ref name="Basilevsky2016">{{cite book|author=Alexander Basilevsky|title=Early Ukraine: A Military and Social History to the Mid-19th Century|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3ED8CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA85|date=5 April 2016|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-1-4766-2022-0|page=85|quote=The main activity was the production of amber and glass beads for the fur trade where the pelts were bought from local hunters and sold to the Bulgars and Khazars for valuable silver dirhams. In fact, the Staraia Ladoga settlements were built initially as a manufacturing center and to conduct trade in the north and in the Baltic region. This is confirmed by silver dirham finds in some of the earliest log buildings constructed there |access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163651/https://books.google.com/books?id=3ED8CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA85|url-status=live}}</ref> In the early period (the second part of the 8th and first part of the 9th century), a Norse presence is only visible at Staraya Ladoga, and to a much lesser degree at a few other sites in the northern parts of Eastern Europe. The objects that represent Norse material culture of this period are rare outside Ladoga and mostly known as single finds. This rarity continues throughout the 9th century until the whole situation changes radically during the next century, when historians meet, at many places and in relatively large quantities, the material remains of a thriving Scandinavian culture.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=115}} For a short period of time, some areas of Eastern Europe became as much part of the Norse world as were Danish and Norwegian territories in the West. The culture of the Rus{{'}} contained Norse elements used as a manifestation of their Scandinavian background. These elements, which were current in 10th-century Scandinavia, appear at various places in the form of collections of many types of metal ornaments, mainly female but male also, such as weapons, decorated parts of horse bridles, and diverse objects embellished in contemporaneous Norse art styles.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=127}} | |||
| The Swedish king ] wanted to assist ], Grand prince of Kiev, in his campaigns against the Pechenegs. The so-called ], a Swedish Viking who wanted to conquer Georgia, also assisted Yaroslav with 3000 men in the war against the Pechenegs; however, he later continued on to Georgia.<ref>{{cite book |last=Larsson |first=G. |year=2013 |title=Ingvar the Fartraveller's Journey: Historical and Archaeological Sources |url=http://uu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1257116/FULLTEXT01.pdf |access-date=9 January 2021 |archive-date=10 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200610172202/http://uu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1257116/FULLTEXT01.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Yaroslav the Wise married the Swedish king's daughter, ], who became the Russian saint, Anna, while ], the Norwegian king who was a military commander of the Varangian guard, married ].{{sfnmp|Blöndal|2007|1pp=60–62|DeVries|1999|2pp=29–30}} The two first uncontroversially historical Swedish kings ] and ] both had Slavic wives. Danish kings and royals also frequently had Slavic wives. For example, ] married ]. Vikings also made up the bulk of the bodyguards of early Kievan Rus{{'}} rulers.{{sfnp|Pritsak|1981|p=386}} | |||
| Evidence for strong bloodline connections between the Kievan Rus{{'}} and Scandinavia existed and a strong alliance between Vikings and early Kievan rulers is indicated in early texts of Scandinavian and East Slavic history. Several thousand Swedish Vikings died for the defence of Kievan Rus{{'}} against the ]. | |||
| ===Scandinavian sources=== | |||
| ] from the 9th century.]] | |||
| In Scandinavian sources, the area is called ''Austr'' (the "East"), '']'' (the "realm of cities"), or simply ''Garðar'' (the "cities"), and ''Svíþjóð hin mikla'' ("Great Sweden"). The last name appears in the 12th century geographical work '']'' by the Icelandic abbot Nicolaus (d. 1161) and in '']'' by ], which indicates that the Icelanders considered Kievan Rus{{'}} to have been founded by the Swedes. The name "Great Sweden" is introduced as a non-Icelandic name with the phrase "which we call Garðaríki" (''sú er vér köllum Garðaríki''), and it is possible that it is a folk etymological interpretation of '']''. However, if this is the case, it can still be influenced by the tradition that Kievan Rus{{'}} was of Swedish origin, which recalls '']'' as a name for the Greek colonies in Italy.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://runeberg.org/ryskarik/0161.html |title=Vilhelm Thomsen. (1882). ''Ryska rikets grundläggning genom Skandinaverna'', p. 155 |year=1882 |access-date=29 January 2021 |archive-date=21 September 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210921082158/http://runeberg.org/ryskarik/0161.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| When the Norse sagas were put to text in the 13th century, the Norse colonisation of Eastern Europe, however, was a distant past, and little of historical value can be extracted. The oldest traditions were recorded in the '']s'' and there Garðaríki appears as a Norse kingdom where the rulers have Norse names, but where also dwelt the ] ] and ].<ref>E.g. ] and Rollaugr in '']'', ] in '']'' and Hreggviðr in '']''.</ref> There is, however, more reliable information from the 11th and the 12th centuries, but at that time most of the Scandinavian population had already assimilated, and the term ''Rus{{'}}'' referred to a largely Slavic-speaking population. Still, Eastern Europe is presented as the traditional Swedish sphere of interest.<ref>In e.g. '']''.</ref> The sagas preserve Old Norse names of several important Rus{{'}} settlements, including {{lang|non|Hólmgarðr}} (]), and {{lang|non|Kønugarðr}} (]); Fjodor Uspenskij argues that the use of the element {{lang|non|garðr}} in these names, as well as in the names {{lang|non|Garðar}} and {{lang|non|Miklagarðr}} (Constantinople), shows the influence of ] {{lang|orv|gorodǔ|italics=yes}} (city), as {{lang|non|garðr}} usually means farmstead in Old Norse. He further argues that the city names can be used to show that the Rus{{'}} were also competent in Old East Slavic.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Uspenskij |first=Fjodor |title=A NEW APPROACH TO THE ETYMOLOGY OF THE OLD NORSE NAME OF KIEV — KØNUGARÐR: (the thesis of Elsa Melin on the Name given to Kiev in the Icelandic Sagas, with an Excursus on Kind in Place-Names) |journal=Scrinum |volume=7–8 |issue=2 |year=2011 |url=https://brill.com/view/journals/scri/7-8/2/article-p326_15.xml |doi=10.1163/18177565-90000255 |pages=326–327 |doi-access=free |access-date=31 January 2021 |archive-date=11 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220311094154/https://brill.com/view/journals/scri/7-8/2/article-p326_15.xml |url-status=live }}</ref> At this time the Rus{{'}} borrowed some 15 Old East Slavic words,<ref name="tnl1043s">There were also about 14 other words borrowed from Old East Slavic: *''dyblitsa/dyfliza'' (*'']'', "dungeon"), *''Grikkiʀ'' ('']'', "Greek"), *''kassa/kaza'' ('']'', "gruel"), ''læðia'' (*''lodĭja'', "boat"), *''Læsiʀ'' (''l'äs'i'', "Poles"), *''poluta'' (''polota'', "palace"), *''polyði'' (*''pol'ud'je'', "Northmen's winter tour of East Slavic areas for lodging and provisions"), *''sabaló'' ('']'', "sable skin/fur"), *''stóll'' (''stolǔ'', "banquet table"), *''taparöks'' (''topor-'', "small war ax"), *''tulka'' (''tǔlkovati'', "to interpret"), *''tulkʀ'' (''tǔlkǔ'', "interpreter"), *''Waldimarr'' ('']'', "ruler of peace"), and *''warta'' (''vor(o)ta'', "gate"), in {{harvp|''The Nordic Languages''|2002|p=1043}}, citing Strumiński (1996, 246–54).</ref> such as the word for marketplace, '']'', as '']'', many of which spread to the other Old Norse-speaking regions as well.<ref name="tnl1043s"/><ref name="hell991">{{harvp|Hellquist|1922|loc=p. ''Torg''}}</ref> | |||
| The most contemporary sources are the ], but just like the sagas, the vast majority of them arrive relatively late. The earliest runestone that tells of eastwards voyages is the ] from the 9th century in ], but it does not specify where the expedition had gone. It was ]'s construction of the ] in the late 10th century that started the runestone fashion that resulted in the raising of thousands of runestones in Sweden during the 11th century; at that time the Swedes arrived as mercenaries and traders rather than settlers. In the 8th, 9th and 10th centuries runic memorials had consisted of runes on wooden poles that were erected in the ground, something which explains the lack of runic inscriptions from this period both in Scandinavia and in eastern Europe as wood is perishable. This tradition was described by ] who met Scandinavians on the shores of the ].<ref name="braun48">Braun, F. & Arne, T. J. (1914). "Den svenska runstenen från ön Berezanj utanför Dneprmynningen", in Ekhoff, E. (ed.) ''Fornvännen årgång 9'' pp. 44–48. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121104073916/http://fornvannen.se/1910talet/fornvannen_1914.html|date=4 November 2012}}, p. 48</ref>{{sfnp|Pritsak|1981|p=306}} | |||
| The ] gives a hint of the Old Norse spoken in Kievan Rus{{'}}, as ''folksgrimʀ'' may have been the title that the commander had in the ] of ] in ].{{sfnp|Pritsak|1981|p=366}} The suffix -{{lang|non|grimmr}} is a virtually unique word for "leader" which is otherwise only attested in the Swedish medieval poem '']'', but in the later form ''grim''. It is not attested as a noun in the sense "leader" in ] sources. In ], the basic meaning of the adjective {{lang|non|grimmr}} is "heartless, strict and wicked", and so {{lang|non|grimmr}} is comparable in semantics to Old Norse {{lang|non|gramr}} which meant both "wrath", "king" and "warrior".<ref name="birmingham"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220224110738/http://runicdictionary.nottingham.ac.uk/fullentry.php?elem=159 |date=24 February 2022 }} at the runic dictionary of the University of Nottingham.</ref> | |||
| Other runestones explicitly mentioning warriors serving the ruler of Kievan Rus{{'}} are ]s, the ] and most famously, the ] which immortalises the dead commander with a poem:<ref>{{cite book |last1=Aannestad |first1=Hanne Lovise |last2=Pedersen |first2=Unn |last3=Moen |first3=Marianne |last4=Naumann |first4=Elise |last5=Berg |first5=Heidi Lund |title=Vikings Across Boundaries: Viking-Age Transformations – Volume II |date=26 October 2020 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-000-20470-4 |page=185 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sg8HEAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| {| | |||
| | | |||
| :Brøðr vaʀu | |||
| :þæiʀ bæstra manna, | |||
| :a landi | |||
| :ok i liði uti, | |||
| :heldu sina huskarla ve. | |||
| :Hann fioll i orrustu | |||
| :austr i Garðum, | |||
| :liðs forungi, | |||
| :landmanna bæstr. | |||
| | | |||
| :These brothers were | |||
| :the best of men | |||
| :in the land | |||
| :and abroad in the retinue, | |||
| :held their ]s well. | |||
| :He fell in battle | |||
| :in the east in Garðar (Russia), | |||
| :commander of the retinue, | |||
| :the best of landholders. | |||
| | | |||
| |} | |||
| The ] is of note as it indicates that the riches that were acquired in Eastern Europe had led to the new procedure of legally buying ],<ref name="Jansson1">Jansson, Sven B. F. (1980). ''Runstenar''. STF, Stockholm. {{ISBN|91-7156-015-7}} p. 31</ref> and the Swedish chieftain Jarlabanke used his clan's acquired wealth to erect the monument ] after himself while alive and where he bragged that he owned the whole ].{{sfnp|Pritsak|1981|p=389}} | |||
| ===Slavic sources=== | ===Slavic sources=== | ||
| ] (1899)]] | |||
| The earliest Slavonic-language narrative account of Rus' history is the '']'', compiled and adapted from a wide range of sources in Kiev at the start of the 13th century. It has therefore been influential on modern history-writing, but it is also much later than the time it describes, and historians agree it primarily reflects the political and religious politics of the time of ]. | |||
| The earliest Slavonic-language narrative account of Rus{{'}} history is the '']'', compiled and adapted from a wide range of sources in Kiev at the start of the 13th century. It has therefore been influential in modern history-writing, but it was also compiled much later than the time it describes, and historians agree it primarily reflects the political and religious politics of the time of ]. | |||
| However, the chronicle does include the texts of a series of Rus'–Byzantine Treaties from ], ], and ]. |
However, the chronicle does include the texts of a series of Rus{{'}}–Byzantine Treaties from ], ], and ].{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014|pp=66–67}} The Rus{{'}}–Byzantine Treaties give a valuable insight into the names of the Rus{{'}}. Of the fourteen Rus{{'}} signatories to the ] in 907, all had Norse names. By the ] in 945, some signatories of the Rus{{'}} had Slavic names while the vast majority had Norse names.<ref name=Duczko>{{harvp|Duczko|2004|p=210}}</ref> | ||
| The Chronicle presents the following ] for the arrival of Rus' in the region of ]: the Rus' |
The Chronicle presents the following ] for the arrival of Rus{{'}} in the region of ]: the Rus{{'}}/] 'imposed tribute upon the ], the ], the ], the ], and the ]' (a variety of ] and ] peoples). | ||
| {{ |
{{blockquote|The tributaries of the Varangians drove them back beyond the sea and, refusing them further tribute, set out to govern themselves. There was no law among them, but tribe rose against tribe. Discord thus ensued among them, and they began to war one against the other. They said to themselves, "Let us seek a prince who may rule over us, and judge us according to the Law". They accordingly went overseas to the Varangian Russes: these particular Varangians were known as Russes, just as some are called ], and others ], ], and ], for they were thus named. The Chuds, the Slavs, the Krivichians and the Ves' then said to the people of Rus{{'}}, "Our land is great and rich, but there is no order in it. Come to rule and reign over us". Thus they selected three brothers, with their kinsfolk, who took with them all the Russes and migrated. The oldest, Rurik, located himself in Novgorod; the second, ], at ]; and the third, ], in ]. On account of these Varangians, the district of Novgorod became known as the land of Rus{{'}}. | ||
| <ref name="RPC">.</ref>}} | <ref name="RPC">, {{ISBN|0-910956-34-0}}, s.aa. 6368–6370 (860–862 CE) .</ref>}} | ||
| From among ]'s entourage it also introduces two Swedish merchants ] and Dir (in the chronicle they are called "]s", probably because of their noble class). The names Askold ({{langx|non|Haskuldr}}) and Dir ({{langx|non|Dyri}}) are Swedish;<ref>Kotlyar, M. ''''. Warhitory.ukrlife.org. 2002</ref> the chronicle says that these two merchants were not from the family of Rurik, but simply belonged to his retinue.<ref name="Plokhy2006">{{cite book|author=Serhii Plokhy|title=The Origins of the Slavic Nations: Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pCdUmCWxwJ8C&pg=PA30|date=7 September 2006|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-139-45892-4|page=30|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163652/https://books.google.com/books?id=pCdUmCWxwJ8C&pg=PA30|url-status=live}}</ref> Later, the ''Primary Chronicle'' claims, they conquered ] and created the state of ] (which may have been preceded by the ]).<ref name="NeumannWigen2018">{{cite book|author1=Iver B. Neumann|author2=Einar Wigen|title=The Steppe Tradition in International Relations: Russians, Turks and European State Building 4000 BCE–2017 CE|chapter=The Steppe in the Emergent Rusʹ Polity|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PgJiDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA170|date=19 July 2018|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-108-36891-9|pages=163, 170|quote=From the 860s onwards, then, but for all we know, even before that, there existed a Viking-led polity that was headed by a khagan and known as the Rusʹ Khaganate. Novoseltsev (1982) and Noonan (2001) make the case that the title 'khagan' was not only taken over from the Khazars (of which there is little doubt) but that it was specifically intended to ease the transfer of tribute-paying from one (Khazar) to another (Rusʹ) and generally to stake a claim first to equality and then to succession. As noted earlier, Noonan (2001) postulates a fully fledged ''translatio imperii''.}}</ref> | |||
| Later, the ''Primary Chronicle'' claims, they conquered ] and created the state of ] (which, most historians agree,{{citation needed|date=November 2013}} was preceded by the ]). | |||
| ===Arabic sources=== | ===Arabic sources=== | ||
| <!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before saving your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. See ] for details. (This text: ]) --> | <!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before saving your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. See ] for details. (This text: ]) --> | ||
| {{Further|Caspian expeditions of the |
{{Further|Caspian expeditions of the Rusʹ}} | ||
| ] of a ] chieftain as described by the ] traveler ] who visited north-eastern Europe in the 10th century.<br>] (1883)]] | ] of a ] chieftain as described by the ] traveler ] who visited north-eastern Europe in the 10th century.<br />] (1883)]] | ||
| ] | |||
| Arabic-language sources for Rus' people are relatively numerous, with over 30 relevant passages in roughly contemporaneous sources. |
Arabic-language sources for the Rus{{'}} people are relatively numerous, with over 30 relevant passages in roughly contemporaneous sources.{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014|p=68}} It can be difficult to be sure that when Arabic sources talk about ''Rus{{'}}'' they mean the same thing as modern scholars.<ref name="auto1">P.B. Golden, "Rūs", in ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'', Second Edition, Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs. Consulted online on 26 July 2018 {{doi|10.1163/1573-3912_islam_COM_0942}}.</ref><ref name="auto2">James E. Montgomery, ' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180716194634/https://www.journals.uio.no/index.php/JAIS/article/viewFile/4553/4006 |date=16 July 2018 }}', ''Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies'', 3 (2000), 1–25.</ref> Sometimes it seems to be a general term for Scandinavians: when ] recorded ''Rūs'' attacking Seville in 844, he was almost certainly talking about Vikings based in Frankia.<ref>Ann Christys, ''Vikings in the South'' (London: Bloomsbury, 2015), pp. 15–45 (esp. p. 31).</ref><ref>{{harvp|Brink|Price|2008|p=552}}</ref> At other times, it might denote people other than or alongside Scandinavians: thus the '']'' calls the Khazars and Rus{{'}} 'brothers'; later, ], ], and ] all identified the Rus{{'}} as a sub-group of the Turks.{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014|p=73}} These uncertainties have fed into debates about the origins of the Rus{{'}}. | ||
| Arabic sources for the Rus' had been collected, edited and translated for Western scholars by the mid-20th century.<ref>A. Seippel (ed.), ''Rerum normannicarum fonts arabici'', 2 vols (Oslo: Brøgger, 1896). This edition of Arabic sources for |
Arabic sources for the Rus{{'}} had been collected, edited and translated for Western scholars by the mid-20th century.<ref>A. Seippel (ed.), ''Rerum normannicarum fonts arabici'', 2 vols (Oslo: Brøgger, 1896). This edition of Arabic sources for references to Vikings was translated into Norwegian, and expanded, by H. Birkeland (ed. and trans.), ''Nordens historie: Middlealderen etter arabiske kilder'' (Oslo: Dyburad, 1954). It was translated into English by Alauddin I. Samarra'i (trans.), ''Arabic Sources on the Norse: English Translation and Notes Based on the Texts Edited by A. Seippel in 'Rerum Normannicarum fontes Arabici''' (unpublished doctoral thesis, University of Wisconsin–Madison, 1959).</ref> However, relatively little use was made of the Arabic sources in studies of the Rus{{'}} before the 21st century.<ref name="auto1"/><ref name="auto2"/><ref>James E. Montgomery, 'Ibn Rusta's Lack of "Eloquence", the Rus, and Samanid Cosmography', ''Edebiyat'', 12 (2001), 73–93.</ref><ref>James E. Montgomery, 'Arabic Sources on the Vikings', in ''The Viking World'', ed. by Stefan Brink (London: Routledge, 2008), pp. 550–61.</ref><ref>James E. Montgomery, 'Vikings and Rus in Arabic Sources', in ''Living Islamic History'', ed. by Yasir Suleiman (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2010), pp. 151–65.</ref>{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014}} This is partly because they mostly concern the region between the Black and the Caspian Seas, and from there north along the lower Volga and the Don. This made them less relevant than the Primary Chronicle to understanding European state formation further west. Imperialist ideologies, in Russia and more widely, discouraged research emphasising an ancient or distinctive history for Inner Eurasian peoples.{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014|pp=70–78}} Arabic sources portray Rus{{'}} people fairly clearly as a raiding and ], or as mercenaries, under the Volga Bulghars or the Khazars, rather than taking a role in state formation.<ref name="auto1"/>{{sfnp|Thorir Jonsson Hraundal|2014}} | ||
| The most extensive Arabic account of the Rus' is by the Muslim diplomat and traveller ], who visited ] in 922, described people under the label ''Rūs''/''Rūsiyyah'' at length, beginning thus: | The most extensive Arabic account of the Rus{{'}} is by the Muslim diplomat and traveller ], who visited ] in 922, and described people under the label ''Rūs''/''Rūsiyyah'' at length, beginning thus: | ||
| {{ |
{{Blockquote|I have seen the Rus as they came on their merchant journeys and encamped by the ]. I have never seen more perfect physical specimens, tall as ]s, blond and ruddy; they wear neither tunics nor caftans, but the men wear a garment which covers one side of the body and leaves a hand free. Each man has an axe, a sword, and a knife, and keeps each by him at all times. The swords are broad and grooved, of ] sort. Each woman wears on either breast a box of iron, silver, copper, or gold; the value of the box indicates the wealth of the husband. Each box has a ring from which depends a knife. The women wear neck-rings of gold and silver. Their most prized ornaments are green glass beads. They string them as necklaces for their women. | ||
| |Gwyn Jones|''A History of the Vikings''<ref>{{cite book|first= Gwyn|last= Jones|title= A History of the Vikings|publisher= ]|year= 2001|isbn= 0-19-280134-1|page= |url-access= registration|url= https://archive.org/details/historyofvikings00jone_0}}</ref>}} | |quoted in Gwyn Jones|''A History of the Vikings''<ref>{{cite book|first= Gwyn|last= Jones|title= A History of the Vikings|publisher= ]|year= 2001|isbn= 0-19-280134-1|page= |url-access= registration|url= https://archive.org/details/historyofvikings00jone_0}}</ref>}} | ||
| Apart from Ibn Fadlan's account, |
Apart from Ibn Fadlan's account, scholars draw heavily on the evidence of the ]n traveler ] who, it is postulated, visited ] (or ], according to ]) and described how the Rus{{'}} exploited the Slavs. | ||
| {{ |
{{Blockquote|As for the Rus, they live on an island ... that takes three days to walk round and is covered with thick undergrowth and forests; it is most unhealthy. ... They harry the Slavs, using ships to reach them; they carry them off as slaves and…sell them. They have no fields but simply live on what they get from the Slav's lands. ... When a son is born, the father will go up to the newborn baby, sword in hand; throwing it down, he says, "I shall not leave you with any property: You have only what you can provide with this weapon."|Ibn Rustah | ||
| <ref>Quoted from ], March 1985; | <ref>Quoted from ], March 1985; | ||
| Compare:{{cite book |last= Ferguson |first= Robert |title= The Hammer and the Cross: A New History of the Vikings |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=UOFe2pIwmGEC |publisher= Penguin UK |date= 2009 |isbn= |
Compare:{{cite book |last= Ferguson |first= Robert |title= The Hammer and the Cross: A New History of the Vikings |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=UOFe2pIwmGEC |publisher= Penguin UK |date= 2009 |isbn= 978-0-14-192387-1 |access-date= 2016-07-25 |quote= They have no fields but simply live on what they get from the Slavs' lands. |archive-date= 26 April 2023 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163701/https://books.google.com/books?id=UOFe2pIwmGEC |url-status= live }}</ref>}} | ||
| ===Byzantine sources=== | ===Byzantine sources=== | ||
| {{Further|Rusʹ–Byzantine War (disambiguation)|Rusʹ–Byzantine Treaty (disambiguation)}} | |||
| :''Further information: ] and ]''<!-- Further template not used due to disambig tags. Please restore this template once disambiguated {{Further|Rus'–Byzantine War|Rus'–Byzantine Treaty}}--> | |||
| ], which tells of two locations at the Dniepr cataracts, ''Eifor'' (one of the rapids) and ''Rufstein'' (''Rvanyj Kamin<nowiki>'</nowiki>'').]] | |||
| When the Varangians first appeared in ] (the ] in the 820s and the ] in 860), the Byzantines seem to have perceived the ''Rhos'' ({{ |
When the Varangians first appeared in ] (the ] in the 820s and the ] in 860), the Byzantines seem to have perceived these people, whom they called the ''Rhos'' ({{langx|el|Ῥώς}}),<ref name="Barraclough2016">{{cite book|author=Eleanor Rosamund Barraclough|title=Beyond the Northlands: Viking Voyages and the Old Norse Sagas|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xuUoDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA172|year=2016|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-870124-8|page=172|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163709/https://books.google.com/books?id=xuUoDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA172|url-status=live}}</ref> as a different people from the Slavs. At least no source says they are part of the Slavic race. Characteristically, ] and ] refer to the ''Rhos'' as ''dromitai'' (Δρομῖται), a word related to the Greek word meaning ''a run'', <!--Modern Greek speaker perceives the word Dromitai as meaning "someone walking from place to place without a permanent home"--> suggesting the ].<ref name="VoltPäll2005">{{cite book|last1=Volt|first1=Ivo|author2=Janika Päll|title=Byzantino-Nordica 2004: Papers Presented at the International Symposium of Byzantine Studies Held on 7–11 May 2004 in Tartu, Estonia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gItVKprpx7sC&pg=PA16|access-date=28 September 2016|year=2005|publisher=Morgenstern Society|isbn=978-9949-11-266-1|page=16|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163647/https://books.google.com/books?id=gItVKprpx7sC&pg=PA16|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| In his treatise '']'', ] describes the ''Rhos'' as the neighbours of ] who buy from the latter cows, horses, and sheep "because none of these animals may be found in ''Rhosia''"; his description represents the Rus{{'}} as a warlike northern tribe. Constantine also enumerates the names of the ] cataracts in both ''rhosisti'' ('ῥωσιστί', the language of the Rus{{'}}) and ''sklavisti'' ('σκλαβιστί', the language of the Slavs). The Rus{{'}} names are usually etymologised as ].<ref name="auto4">H. R. Ellis Davidson, ''The Viking Road to Byzantium'' (London: Allen & Unwin, 1976), p. 83.p. 83.</ref>{{sfnp|Blöndal|2007|p=9}} An argument used to support this view is that the name ''Aeifor'' in reference to the fourth cataract is also attested on the ] from the 10th c. on ].<ref name="BjergLind2013168">{{cite book|author1=Fedir Androshchuk|editor1=Line Bjerg|editor2=John H. Lind|editor3=Soren Michael Sindbaek|title=From Goths to Varangians: Communication and Cultural Exchange between the Baltic and the Black Sea|chapter=Byzantium and the Scandinavian world in the 9th–!0th century|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6ZufDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA168|date=31 December 2013|publisher=Aarhus University Press|isbn=978-87-7124-425-0|page=168|access-date=29 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163649/https://books.google.com/books?id=6ZufDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA168|url-status=live}}</ref> However, some researches indicate that at least several of the Rus{{'}} names can be Slavic and, as for the ] cataract ''Aeifar'' / ''Aeifor'', its name doesn't have an acceptable and convincing Scandinavian etymology.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Skli︠a︡renko |first1=V. H. |title=Rusʹ i vari︠a︡hy: istoryko-etymolohichne doslidz︠h︡enni︠a︡ |date=2006 |publisher=Dovira |location=Kyïv |isbn=966-507-205-6 |pages=75–89}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Brajchevskij |first1=M.Yu. |title="Russkie" nazvaniya porogov u Konstantina Bagryanorodnogo |journal=Zemli Yuzhnoj Rusi V IX–XIV Vv. |date=1985 |issue=Kyiv, Naukova dumka |page=26 |url=http://resource.history.org.ua/item/11103 |access-date=5 February 2022 |archive-date=5 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220205025139/http://resource.history.org.ua/item/11103 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus |last2=Moravcsik |first2=Gyula |last3=Jenkins |first3=Romilly J. H. |title=De administrando imperio |date=1967 |publisher=Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies |location=Washington, D.C. |isbn=978-0-88402-021-9 |pages=58–61 |edition=New, Revised}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus |last2=Meursius |first2=Johannes |title=De administrando imperio |date=1611 |publisher=Ioannes Balduini |location=Leiden |pages=16–18 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DYsuAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA16 |language=el |access-date=5 February 2022 |archive-date=5 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220205025138/https://books.google.com/books?id=DYsuAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA16 |url-status=live }}</ref> At the time, the Byzantines also recorded the existence of some of the lesser important Slavic tribes in the region, and the emperor only knew of ''Rhosia'', which referred to the Rus' who lived in Kiev, closer to Byzantium, and the Rus' who lived in the north, along the Volkhov River.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|page=207}} | |||
| In his treatise '']'', ] describes the Rhos as the neighbours of ] who buy from the latter cows, horses, and sheep "because none of these animals may be found in Rhosia". His description represents the Rus' as a warlike northern tribe. Constantine also enumerates the names of the ] cataracts in both rhosisti ('ῥωσιστί', the language of the Rus') and sklavisti ('σκλαβιοτί', the language of the Slavs). The Rus' names can most readily be etymologised as ], and have been argued to be older than the Slavic names:<ref name="auto4">H. R. Ellis Davidson, ''The Viking Road to Byzantium'' (London: Allen & Unwin, 1976), p. 83.</ref><ref>Sigfús Blöndal, <nowiki>''</nowiki>The Varangians of Byzantium: An Aspect of Byzantine Military History<nowiki>''</nowiki>, rev. and trans. by Benedikt S. Benedikz (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1978), pp. 9-12.</ref> | |||
| :{| class="wikitable" | :{| class="wikitable" | ||
| |+ | |+ | ||
| !Constantine's form | !Constantine's form for | ||
| the non-Slavonic names | |||
| !Latin transliteration | !Latin transliteration | ||
| !Constantine's interpretation | !Constantine's interpretation | ||
| of the Slavonic | of the Slavonic or both | ||
| !Proposed Old Norse etymons | !Proposed Old Norse etymons | ||
| for the non-Slavonic names | |||
| !Proposed Slavic etymons | |||
| for the non-Slavonic names | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Ἐσσουπῆ | |||
| |Ἐσσονπῆ | |||
| |Essoupi | |Essoupi | ||
| |" |
|"Do not sleep!" | ||
| |''nes uppi'' "upper promontory" | |''nes uppi'' "upper promontory" | ||
| ''súpandi'' "slurping" | ''súpandi'' "slurping" | ||
| |''не спи (ne spy)'' "do not sleep!" | |||
| (compare the Ukrainian ''не спи'' /ne spɪ/ "do not sleep!") | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Οὐλβορσί | |Οὐλβορσί | ||
| |Oulvorsi | |Oulvorsi | ||
| |" |
|"the Island of the Barrage" | ||
| |''Úlfarsey'' "Úlfar's island" | |''Úlfarsey'' "Úlfar's island" | ||
| ''hólm-foss'' "island rapid" | ''hólm-foss'' "island rapid" | ||
| |— | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Γελανδρί | |Γελανδρί | ||
| |Gelandri | |Gelandri | ||
| |" |
|"Noise of the Barrage" | ||
| |''gjallandi/gellandi'' "yelling, loudly ringing" | |''gjallandi/gellandi'' "yelling, loudly ringing" | ||
| |— | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Ἀειφόρ | |Ἀειφάρ, Ἀειφόρ | ||
| |Aeifor | |Aeifar, Aeifor | ||
| |''... because the pelicans nest in the stones of the barrage ...'' | |||
| |pelicans' nesting place | |||
| |''æ-fari''/''ey-færr'' "never passable" | |''æ-fari''/''ey-færr'' "never passable" | ||
| ''æ-for/ey-forr'' "ever fierce" | ''æ-for/ey-forr'' "ever fierce" | ||
| |— | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Βαρουφόρος | |||
| |Βαρονφόρος | |||
| |Varouforos | |Varouforos | ||
| |it forms a |
|''... because it forms a large lake ...'' | ||
| |''vara-foss'' "stony shore rapid" | |''vara-foss'' "stony shore rapid" | ||
| ''báru-foss'' "wave rapid" | ''báru-foss'' "wave rapid" | ||
| |— | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Λεάντι | |Λεάντι | ||
| |Leanti | |Leanti | ||
| |" |
|"the Boiling of the Water" | ||
| |''hlæjandi'' "laughing" | |''hlæjandi'' "laughing" | ||
| | ''lьjant'i'' (< Proto-Slavic ''*lьjǫtji'') "the one that pours" derived from ''lьjati'' (Proto-Slavic ''*lьjati'') "to pour" | |||
| (compare the Ukrainian ''лляти'' /ˈlʲːɑtɪ/ "to pour" | |||
| and the Polish ''lać'' /lat͡ɕ/ "to pour") | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Στρούκουν | |Στρούβουν, Στρούκουν | ||
| |Stroukoun | |Strouvoun, Stroukoun | ||
| |"Little Barrage" | |||
| |"the little fall" | |||
| |''strjúkandi'' "stroking, delicately touching" | |''strjúkandi'' "stroking, delicately touching" | ||
| ''strukum'', "rapid current" | ''strukum'', "rapid current" | ||
| |''стрибун (strybun)'' "the one that jumps" | |||
| from the Ukrainian ''стрибати'' /strɪˈbatɪ/ "to jump" | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| ===Western European sources=== | ===Western European sources=== | ||
| The first Western European source to mention the Rus{{'}} are the ] (Annales Bertiniani).<ref name="GoldenBen-Shammai2007">{{cite book|author1=Vladimir Petrukhin|editor1=Peter B. Golden|editor2=Haggai Ben-Shammai|editor3=András Róna-Tas|title=The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA245|year=2007|publisher=BRILL|isbn=978-90-04-16042-2|pages=245–246|chapter=Khazaria and Rus{{'}}: An examination of their historical relations|access-date=28 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163648/https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA245|url-status=live}}</ref> These relate that Emperor ]' court at ], in 839, was visited by a delegation from the ]. In this delegation there were men who called themselves ''Rhos'' (in the Latin text, ''... qui se, id est gentem suam, Rhos vocari dicebant, ...''; translated by ] as ''... who stated that they, i.e. their nation, were called Rhos, ...''). Once Louis enquired the reason of their arrival (in the Latin text, ''... Quorum adventus causam imperator diligentius investigans, ...''), he learnt that they were Swedes (''eos gentis esse Sueonum''; verbatim, ''their nation is Sveoni'').<ref name="dmgh">{{cite web |title=Annales Bertiniani |url=https://www.dmgh.de/mgh_ss_1/index.htm#page/434/mode/1up |website=Die Monumenta Germaniae Historica |access-date=3 February 2022 |archive-date=23 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220123154950/https://www.dmgh.de/mgh_ss_1/index.htm#page/434/mode/1up |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Nazarenko |first1=A. V. |last2=Dzhakson |first2=T. N. |last3=Konovalova |first3=I. G. |last4=Podosinov |first4=A. V. |title=Drevni︠a︡i︠a︡ Rusʹ v svete zarubezhnykh istochnikov: khrestomatii︠a︡. Vol. 4 |date=2010 |publisher=Russkiĭ fond sodeĭstvii︠a︡ obrazovanii︠u︡ i nauke |location=Moskva |isbn=978-5-91244-008-3 |page=20 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vHgyDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA20 |access-date=3 February 2022 |archive-date=11 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220311214914/https://books.google.com/books?id=vHgyDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA20 |url-status=live }}</ref> Fearing that they were spies, he detained them, before letting them proceed after receiving reassurances from Byzantium.{{sfn|Duczko|2004|pp=49–50}}<ref name="BrinkPrice2008497">{{cite book|author1=Jonathan Shepard|editor1=Stefan Brink|editor2=Neil Price|title=The Viking World|chapter=The Viking Rus and Byzantium|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA497|date=31 October 2008|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-31826-1|page=497|access-date=24 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163649/https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA497|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Martin2009">{{cite book|author=Janet Martin|editor=Abbott Gleason|title=A Companion to Russian History|chapter=The First East Slavic State|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JyN0hlKcfTcC|date=6 April 2009|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-4443-0842-6}}</ref> Subsequently, in the 10th and 11th centuries, Latin sources routinely confused the Rus{{'}} with the tribe of ]. ], for instance, was designated as queen of the Rugians (''reginae Rugorum'') in the Lotharingian Chronicle compiled by the anonymous ] of ].<ref name="GasparovRaevsky-Hughes2021">{{cite book|author1=Henrik Birnbaum|editor1=Boris Gasparov|editor2=Olga Raevsky-Hughes|title=California Slavic Studies, Volume XVI: Slavic Culture in the Middle Ages|chapter=Christianity Before Christianization |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=k7Z6d0ifWfEC&pg=PA53|volume=XVI|date=8 January 2021|publisher=Univ of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-30918-0|page=53}}</ref> At least after the 6th century, the name of the Rugii referred to Slavic speaking peoples including the Rus{{'}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Steinacher |first1=Roland |author-link1=:de:Roland Steinacher |year=2010 |chapter=The Herules: Fragments of a History |editor-last=Curta |editor-first=Florin |editor-link=Florin Curta |title=Neglected Barbarians |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6wXHSgAACAAJ |publisher=] |isbn=978-2-503-53125-0 |access-date=3 February 2022 |archive-date=26 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163659/https://books.google.com/books?id=6wXHSgAACAAJ |url-status=live }} pp.43-44.</ref> According to the Annals of St. Bertin, the Rus{{'}} leader had the title ''Khagan'' (''... quod rex illorum, Chacanus vocabulo, ...'').<ref name="dmgh" /><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Urbanczyk |first1=Przemyslaw |title=Who were the early Rusʹ? |url=https://www.academia.edu/11887801 |website=ACADEMIA |access-date=3 February 2022 |archive-date=12 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220312141925/https://www.academia.edu/11887801 |url-status=live |url-access=<!--WP:URLACCESS--> }}</ref> | |||
| The first Western European source to mention the Rus' are the ]. These relate that Emperor ]' court at ], in 839, was visited by a delegation from the ]. In this delegation there were two men who called themselves ''Rhos'' (''Rhos vocari dicebant''). Louis enquired about their origins and learnt that they were ] (''suoni''). Fearing that they were spies for their allies, the ], he incarcerated them, before letting them proceed after receiving reassurances from Byzantium.<ref name="auto5">Wladyslaw Duczko, ''Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe'' (Leiden: Brill, 2004), pp. 10-59.</ref><ref>Jonathan Shepard, 'The Viking Rus and Byzantium', ,in '''', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 496-516 (p. 497).</ref><ref name="auto6">Janet Martin, 'The First East Slavic State', in ''A Companion to Russian History'', ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 34-50 (p. 36).</ref> Subsequently, in the 10th and 11th centuries, Latin sources routinely confused the Rus' with the extinct East Germanic tribe of ]. ], for instance, was designated in one manuscript as a Rugian queen. | |||
| Another source comes from ], a 10th-century ] bishop |
Another source comes from ], a 10th-century ] bishop whose ''Antapodosis'', a report from ] to ], says that Constantinople 'stands in territory surrounded by warlike peoples. On the north it has the ... ''Rusii'' sometimes called by another name ''Nordmanni'', and the ''Bulgarii'' who live too close for harmony'.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Liudprand, Bishop of Cremona|url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015020219237&view=1up&seq=46&skin=2021&q1=Rusii|title=The works of Liudprand of Cremona ...|last2=Wright|first2=F. A.|date=1930|publisher=E.P. Dutton & company|location=New York|page=38|access-date=9 January 2022|archive-date=9 January 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220109155007/https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015020219237&view=1up&seq=46&skin=2021&q1=Rusii|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Thomsen|first1=Vilhelm|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DK0OAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA47|title=The Relations Between Ancient Russia and Scandinavia and the Origin of the Russian State: ...|date=1877|publisher=James Parker and Company|location=Oxford and London|page=47|language=en|access-date=18 January 2022|archive-date=12 March 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220312165710/https://books.google.com/books?id=DK0OAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA47|url-status=live}}</ref>{{sfnp|Blöndal|2007|p=40}} | ||
| == |
==Assimilation== | ||
| ] |
]]] | ||
| The Scandinavian influence in Kievan Rus{{'}} was most important during the late 9th c. and during the 10th c. In 976, ] (''Valdamarr gamli''<ref>'']'' ch. 21 (ed. ] 1902–8, p. 108).</ref>) fled from his brother ] to Sweden, ruled by ], where he gathered an invasion force that he used to conquer Kievan Rus{{'}}. Vladimir was initially a pagan who is reported by the ''Primary Chronicle'' to have worshiped ] and ], and this is probably a ] of the corresponding Norse gods ] and ],<ref>Chadwick, N. (1946). ''The Beginnings of Russian History''. Cambridge at the University Press. pp. 84–89.</ref> who beside ] were the two most important gods to the Swedes.<ref>In the 11 c., ] wrote about the ], where there were three statues of the main gods, Odin, Thor and Freyr. In Norse mythology, Freyr was seen as the progenitor of the Swedish royal house.</ref> However, in 988, he converted to the ], whereas the Norse in Scandinavia remained ] or converted to the ]. After this, the Norse influence decreased considerably both in character and in size, and in the 11th c. the Norse are mentioned as Varangian mercenaries and employees serving the princely family.<ref>Stefanovich, Petr S. (2016). Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas, 2016, Neue Folge, Bd. 64, H. 4, pp. 529–544.</ref> | |||
| The archaeological excavations of 19th century conducted by Count ] in the area of Upper Volga and Oka has shown no Slavic-type evidences. For his studies in 1873 Uvarov was awarded the Golden Constantine Medal by the Imperial ]. | |||
| ] at the ] notes that in Russian historiography, the assimilation of the Norse Rus{{'}} is presented as a very rapid affair, based on studies of material culture. However, material objects are not as strong an indicator of ethnic identity as the language spoken in a society. Usually, the only non-archaeological claim to rapid assimilation is the appearance of three Slavic names in the princely family, i.e. '']'', ''Predslava'', and ''Volodislav'', for the first time in the treaty with Byzantium of 944.<ref name="mel"/> Another reason for assuming a rapid assimilation is given by Yaroslav Shchapov, who writes that as a consequence of the Rus{{'}}adoption of Byzantine (Eastern) rather than Roman Christianity, as well as the assimilation of Byzantine culture, "writing, literature and law in the national language" spread much earlier than in Western countries.<ref name="Shchapov1992">{{cite book|author=Yaroslav Shchapov|editor=Yves Hamant|title=The Christianization of Ancient Russia: A Millennium, 988–1988|chapter-url=https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000084611|year=1992|publisher=Unesco|isbn=978-92-3-102642-3|pages=62–63|chapter=The assimilation by Kievan Rus{{'}} of the classical and Byzantine Heritage|access-date=31 January 2021|archive-date=24 September 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210924215834/https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000084611|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The quantity of archaeological evidence for the regions where Rus people were active grew steadily through the 20th century, and beyond, and the end of the ] made the full range of material increasingly accessible to researchers. Key excavations have included those at ], ], ], ], ], numerous settlements between the ] and the ] rivers. Twenty-first century research, therefore, is giving the synthesis of archaeological evidence an increasingly prominent place in understanding the Rus'.<ref name="auto7">Wladyslaw Duczko, ''Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe'' (Leiden: Brill, 2004).</ref><ref name="auto8">Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}}.</ref> The distribution of coinage, including the early 9th-century ], has provided important ways to trace the flow and quantity of trade in areas where Rus were active, and even, through graffiti on the coins, the languages spoken by traders.<ref name="auto1"/> | |||
| Melnikova comments that the disappearance of ] c. 1000, is better explained with ] and the introduction of Christian burial rites, a view described with some reservations by archaeologist ] of the Institute of Archeology and Ethnology at the ].<ref name="Urbanczyk2010">{{cite journal |last1=Urbanczyk |first1=Przemyslaw |title=Archaeological view of Christianization on two sides of the Baltic Sea |journal=Archeologia Polski |date=2010 |volume=55 |pages=89–91, 99 |url=http://rcin.org.pl/Content/49530/WA308_66151_P321_Archaeological-view_I.pdf |access-date=31 January 2021 |publisher=Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, Polish Academy of Sciences |language=English |quote=The written evidence gives us a view of the conversion of the peri-Baltic area through the eyes of the successful Christianizers who painted a process that was quick, historically necessary, and politically effective Therefore archaeologists have been convinced that discerning between 'pagan' and 'Christian' burials does not pose much of a problem and that a threshold of change exists. Today it is clear that the story of building a shared Christian identity was a much longer and difficult process on both sides of the Baltic Sea All this resulted in a long and difficult Christianization process and a vigorous resistance on the part of the indigenous population. This is archaeologically witnessed in syncretic practices and pagan burials which were still being observed on the peripheries in the High Middle Ages. |archive-date=11 September 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210911130420/http://rcin.org.pl/Content/49530/WA308_66151_P321_Archaeological-view_I.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> So the lack of Norse burials from c. 1000 is not a good indicator of assimilation into Slavic culture, and shows instead that the Rus{{'}} had turned Orthodox Christian. Also the use of material objects is more connected to change in fashion and to change of social status than it is to ethnical change. She also notes that no systematic studies of the various elements that manifest ethnic identity in relation to the Rus{{'}} has been done to support the theory of rapid assimilation, in spite of the fact that "he most important indications of ethno-cultural self-identification are language and literacy."<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{Anchor|Rus%27_people#History}} | |||
| {{Further|Norsemen|Vikings|Varangians}} | |||
| ] settlement (in red) and location of Slavic tribes (in grey), mid-9th century ] influence indicated with blue outline.]] | |||
| ===Urban=== | |||
| Having settled ] (Ladoga) in the 750s, Scandinavian colonists played an important role in the early ethnogenesis of the Rus' people and in the formation of the ]. The Varangians (''Varyags'', in ]) are first mentioned by the '']'' as having exacted tribute from the Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. It was the time of rapid expansion of the Vikings in Northern Europe; England began to pay ] in 859, and the ] of ] faced an invasion by the Swedes at about the same date. | |||
| ]. In ]'s time, the Norse elite mostly switched to ].<ref name="mel"/>]] | |||
| The Rus{{'}} elite became bilingual c. 950 but it was not until the end of the 11th century that ] can be shown to have become their native language. Until the mid-10th century all the attested Rus{{'}} names were Norse. In the ] there are 76 names among whom 12 belong to the ], 11 to emissaries, 27 to other agents, and 26 to merchants. In the princely family, there are three Slavic names ''Svjatoslav'', son of ] (Ingvar) and ''Volodislav'' and ''Predslava'' (of unknown relation). The other members of the family have Norse names, i.e. ] ('']''), Akun ('']''), Sfanda (''Svanhildr''), Uleb ('']''), Turd (''Þórðr''), Arfast (''Arnfastr''), and Sfir'ka ('']''). The emissaries also have Old Norse names except for three who have ] names. Olga has a representative by the Finnish name ''Iskusevi'', whereas Volodislav is represented by the Norse Uleb (''Óleifr''). Among the 27 agents there are some who have Finnish names, but none with Slavic, while among the 26 merchants there are three with Finnish names and two with Slavic.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| In the 980s, among Sviatoslav's grandchildren, the ''Primary Chronicle'' informs that ] had twelve sons and one daughter. Only one of them, a son, had a Norse name, ] (''Guðleifr''), whereas the other children had Slavic compound names mostly ending with -'']'' ("fame").<ref name="mel"/> After this generation, the ruling dynasty restricted itself to five Norse male names and one female name, of which the most popular ones would be Oleg, Igor and Gleb (was murdered in 1015 and canonised). The name Rurik (''Hrœrekr'') reappears in the mid-11th c. but stays restricted in use. Among female names, only Olga stays popular. The Norse names ''Hákon'', ''Óleifr'', and ''Ivarr'' remain in use among the East Slavic nobility, but Norse names become rarer at the end of the 10th c. which may point to increased assimilation of the Rus{{'}} into the Slavic population.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| It has been argued that the word ''Varangian'', in its many forms, does not appear in primary sources until the 11th century (though it does appear frequently in later sources describing earlier periods). This suggests that the term ''Rus{{'}}'' was used broadly to denote Scandinavians until it became too firmly associated with the now extensively Slavicised elite of Kievan Rus. At that point, the new term ''Varangian'' was increasingly preferred to name Scandinavians, probably mostly from what is currently Sweden,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Forte|first1=Angelo|first2=Richard|last2=Oram|first3=Frederik|last3=Pedersen|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_vEd859jvk0C |title=Viking Empires|publisher=]|year= 2005|isbn= 0-521-82992-5|pages=13–14}}</ref> plying the river-routes between the Baltic and the Black/Caspian Seas.<ref>Marika Mägi, ''In ''Austrvegr'': The Role of the Eastern Baltic in Viking Age Communication Across the Baltic Sea'', The Northern World, 84 (Leiden: Brill, 2018), p. 195, citing Alf Thulin, 'The Rus' of Nestor's Chronicle', ''Mediaeval Scandinavia'', 13 (2000), 70-96.</ref> | |||
| Among the Norse names that are not used in the ruling family, there is great variation in how they are spelled in the treaties. All names except for Oleg, Olga and Igor are spelled as closely to Old Norse as was possible in Old East Slavic. There were also variations in how the vowels were presented ''Óleifr'' was shown as ''Oleb'' or ''Uleb'', ''Hákon'' as ''Jakun'' and ''Akun'', ''Arnfastr'' as ''Arfast'' and ''Fastr'' as ''Fost''. The interdentals /þ/ and /ð/ are rendered as ''d'', but also rarely as ''z'' or ''t'' as in ''Turd'' from ''Þórðr'' and in ''Vuzlev'' from ''Guðleifr''. The ''Fr-'' in the beginning of names which was common in Old Norse but rare in Old East Slavic usually appeared as ''Pr-'' as in ''Prasten'' from ''Freysteinn''. There was no standard way of spelling ON names.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| Due largely to geographic considerations, it is often argued that most of the Varangians who traveled and settled in the lands of eastern Baltic, modern Russian Federation and lands to the south came from the area of modern ]. | |||
| While the ''Primary Chronicle'' uses the same Slavicised forms throughout, rendering ''Helgi'' as {{transliteration|ru|italic=no|Ol(e)g}}, ''Helga'' as Ol'ga, ''Ingvarr'' as Igor' and ''Guðleifr'' as Gleb, they are unlikely to represent the form the names had at the end of the 10th c. Foreign sources give forms closer to the Old Norse originals. Byzantine sources from the second half of the 10th c. preserve the nasalisation in ''Ingvarr'', and in the ] written in Hebrew, Helgi appears as HLGW, with initial H-. The adaptation of ''Guðleifr'' was still not complete by 1073, as shown in a manuscript where there is a vowel between G- and -l- in Gleb, showing that the name is still pronounced with an initial Gu-.<ref name="mel"/> Theses sources reflect authentic Old Norse pronunciation of these names, which shows that the adaptation of these names did not take place in the 10th c. but was finished a century later.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| The Varangians left a number of ] in their native ] that tell of their journeys to what is today Russia, Ukraine, Greece, and Belarus. Most of these rune stones can be seen today, and are a telling piece of historical evidence. The ] tell of many notable Varangian expeditions, and even account for the fates of individual warriors and travelers. | |||
| When the ''Primary Chronicle'' was written in 1113, the annalist used the already fully adapted Old East Slavic forms and he does not appear to have known that ''Gleb'' and ''Vuzlev'' both represented ''Guðleifr'', but instead kept them distinct. Later in the 12th c., in spite of the renown of the name Igor', the original Norse form ''Ingvar'' was borrowed again as a separate name, and it appears in the '']'' as the name of ] (d. 1212), and two princes of ]. One of the latter was named '']'', mentioned in 1207–1219, which shows that the two names were no longer connected. Consequently, Melnikova, considers that the 12th c. stands in stark contrast to the previous two centuries, showing that the Slavicisation of the Rus{{'}} elite would have been complete after the second half of the 11th c.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| In Russian history, two cities are used to describe the beginnings of the country: Kiev and Novgorod.<ref name="auto9">Duczko, Wladyslaw. Viking Rus : Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe. The Northern World. Leiden: Brill, 2004.</ref> In the first part of the 11th century the former was already a Slav metropolis, rich and powerful, a fast growing center of civilization adopted from Byzantium. The latter town, Novgorod, was another center of the same culture but founded in different surroundings, where some old local traditions molded this commercial city into a mighty oligarchic republic of a kind otherwise unknown in this part of Europe. These towns have tended to overshadow other places of a significance that they had acquired long before Kiev and Novgorod. The two original centers of Rus were Staraja Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodishche, two points on the ends the Volkhov, a river running for 200 km between ] in the south to ] in the north.<ref name="auto9"/> This was the territory that most probably was originally called by the Norsemen Gardar, a name that long after Viking Age was given much wider content and become Gardariki, denomination for whole Old Russian State. The area between the lakes was the original Rus, and it was from here its name was transferred to the Slav territories on the middle Dnieper, which eventually became ] (“Ruskaja zemlja”).<ref name="auto9"/> | |||
| (According to prominent Russian linguist Andrey Zaliznyak, Novgorod people did not call themselves Rus' up until the 14th century, calling Rus' only ], ] and ] principalities<ref>{{cite web |last1=Zaliznyak |first1=Andrey Anatolyevich |title=About Russian Language History |url=https://elementy.ru/nauchno-populyarnaya_biblioteka/431649/Ob_istorii_russkogo_yazyka |website=elementy.ru |publisher=Mumi-Trol School |access-date=21 May 2020}}</ref>) | |||
| The pre-history of the first territory of Rus has been sought in the developments around the mid-8th century, when Staraja Ladoga was founded as a trading place, serving the operations of Scandinavian hunters and dealers in furs obtained in the north-eastern forest zone of Eastern Europe. In the early period (the second part of the eighth and first part of the 9th century) Norse presence is only visible at Staraja Ladoga, and to a much lesser degree at a few other sites in the northern parts of Eastern Europe. The objects that represent Norse material culture of this period are rare outside Ladoga and mostly known as single finds. This rarity continues through the 9th century until the whole situation changes radically during the next century, when historians meet, at many places and in relatively large quantities, the material remains of a thriving Scandinavian culture.<ref name="auto9"/> For a short period of time, some areas of Eastern Europe became as much part of the Norse world as were Danish and Norwegian territories in the West. The culture of the Rus contained Norse elements used as a manifestation of their Scandinavian background. These elements, which were current in 10th-century Scandinavia, appear at various places in form of collections of many types of metal ornaments, mainly female but even male, such as weapons, decorated parts of horse bridle, and diverse objects embellished in current Norse art styles.<ref name="auto9"/> | |||
| On the other hand, the scholar ] considered that Old Norse must have been well known in Kiev and Novgorod, especially during the early decades of the 12th century.<ref name="Nyberg1985">{{cite book|author=Omeljan Pritsak|editor=Tore Nyberg|title=History and Heroic Tale: A Symposium|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=48fYAAAAMAAJ&q=%22especially%20during%20the%20first%20three%20decades%20of%20the%2012th%20century%22|chapter=On the Writing of History in Kievan Rus{{'}}|year=1985|publisher=Odense University Press|isbn=978-87-7492-534-7|page=154|access-date=1 February 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163703/https://books.google.com/books?id=48fYAAAAMAAJ&q=%22especially%20during%20the%20first%20three%20decades%20of%20the%2012th%20century%22|url-status=live}}</ref> The ] and ] ] held a contrasting opinion, writing that ], active at the court of ], and some of whose poetry may be preserved in the ] '']'', or ''Slovo'', in ], may have heard Scandinavian songs and conversations from visitors as late as 1110 (about the time his own work was done), and that even later, at the court of ] (''Haraldr''), there must have been many opportunities to hear them. He cautions, however, that it cannot be presumed that Old Norse was still habitually spoken in 12th-century princely courts. Further, he says that Bojan's own life and career did not necessarily coincide with the time of the men whose lives he commemorated, and that he may have written of princes of an earlier period known to him only by report. Scholarly consensus holds as well that the author of the ], ''Slovo'', writing in the late 12th century, was not composing in a milieu where there was still a flourishing school of poetry in the Old Norse language.<ref name="Jakobson2011">{{cite book|author=Roman Jakobson|title=Russian Epic Studies|url=https://archive.org/details/russianepicstudi42jako/page/106/mode/2up|year=2011|orig-date=1947|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|isbn=978-3-11-088958-1|pages=103–107|quote=The connections are present, then, and we may assume that Bojan himself, as late as 1110, may have heard Scandinavian songs and conversations from visitors; even later, at the court of that Mstislav who was also called ''Haraldr'', the opportunity must have presented itself often. But this is quite different from supposing that Old Norse was habitually still spoken in twelfth-century court circles, or even among traders, except in the presence of visitors.}}</ref> | |||
| The Swedish king Anund sent 3000 varangians to assist Yaroslav the Wise in his campaigns against the Pechnegs. The so-called ].When <ref> Larsson, G. (2013) Ingvar the Fartravellers Journey: Historical and Archaeological Sources http://uu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1257116/FULLTEXT01.pdf</ref>. | |||
| Yaroslav also married the Swedish kings daughter Anna. Harald Hardrada also were a part of the Varangian guard <ref> Blöndal & Benedikz (2007) pp. 60–62 </ref> <ref> DeVries (1999) pp. 29–30 </ref> The two first Swedish kings ] and ] had both 2 slavic wives.<ref> Also Queen consort of Norway. Danish kings also frequently had Slavic wives. For example ] married ]. Vikings also made up the bodyguards of early Kievan Rus rulers. <ref> Pritsak 1981:386 </ref> | |||
| ===Rural=== | |||
| Showing extensive ties between Kievan Rus and Scandinavia. | |||
| ] | |||
| There are remains of Old Norse culture as late as the 14th and early 15th centuries in the form of runic or rune-like inscriptions and as personal names. The c. 1000 ] from ] contain hundreds of names, most of them Slavic or Christian, and according to Melnikova there are seven letters with Old Norse names,<ref name="mel"/> but Sitzman identifies as many as 18, including Staraja Russa no. 36.<ref name="sitz">Sitzmann, A. 2007. "Die skandinavischen Personennamen in den Birkenrindeninschriften" Scando-Slavica 53; 25–31</ref> | |||
| The oldest of these letters (no. 526<ref name="sitz"/>) is from the 1080s, and refers to ''Asgut'' from a village in the vicinity of ] which was on the road between Novgorod and the central parts of Kievan Rus{{'}}. Another letter (no. 130<ref name="sitz"/>) is from the second half of the 14th century and was sent to Novgorod from another part of the ] and mentions the names Vigar' (Vigeirr or Végeirr), Sten (''steinn'') of Mikula, Jakun (''Hákon''), and the widow of a second Jakun. The most interesting of the letters (no. 2<ref name="sitz"/>) mentions a place called ''Gugmor-navolok'', which may derive from Guðmarr, and two people living in the vicinity called Vozemut (Guðmundr) and Vel'jut (Véljótr). Perhaps a Guðmarr once settled near a ] (''navolok'') on the route to ] and naming traditions were preserved in the settlement until the 14th century It is unlikely that he was a new settler because there are no traces of 14th century immigration, nor are there any Scandinavian remains. It is likely that his people adopted the local material culture but kept the family naming traditions.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| ==Debate on the origins of the Rus'== | |||
| The historiography of the origins of the Rus' is infamously contentious, due to its perceived importance for the legitimation of nation-building, imperialism, and independence movements within the Slavonic-speaking world, and for legitimating different political relationships between eastern and western European countries. The Rus' feature prominently in the history of the Baltic states, Scandinavia, Poland, and the Byzantine Empire.<ref name="auto1"/><ref>Roman Zakharii, '' (unpublished M.Phil. thesis, University of Oslo, 2002).</ref><ref>Wladyslaw Duczko, ''Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe'' (Leiden: Brill, 2004), pp. 3-9.</ref><ref>Serhii Plokhy, The Origins of the Slavic Nations Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), pp. 10-48.</ref><ref>Christian Raffensperger, '{{Dead link|date=December 2018|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}}', ''History Compass'', 12/11 (2014), 853–65 {{DOI|10.1111/hic3.12201}} (pp. 853-54).</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52.</ref><ref>{{Citation|last=History Time|title=Vikings Of The East: Igor & The Kievan Rus'|date=2017-08-01|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YvPSa8XoHDI|access-date=2019-02-20}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://onlineacademiccommunity.uvic.ca/byzantium/the-kievan-rus/treaties-between-the-rus-and-the-byzantine/|title=Treaties Between the Rus and the Byzantine – Eastwards to Miklagard|website=onlineacademiccommunity.uvic.ca|access-date=2019-02-20}}</ref> They are particularly important in the historiography and cultural history of Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Rus|title=Rus {{!}} people|website=Encyclopedia Britannica|language=en|access-date=2019-02-20}}</ref> but have also featured prominently for Poland.{{citation needed|date=February 2019}} Added to these ideological forces is a scarcity of contemporary evidence for the emergence of a Rus' polity, and the great ethnic diversity and complexity of the wide area where Rus' people were active.<ref>Janet Martin, 'The First East Slavic State', in ''A Companion to Russian History'', ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 34-50 (pp. 34-36).</ref> Notwithstanding the existence of a diverse range of historical debates, contention has crystallized around whether the development of Kievan Rus' was influenced by non-Slavic, Viking migrants (this idea is characterized as the 'Normanist theory'), or whether Rus' emerged from autochthonous Slavic political development (known as the 'anti-Normanist theory'). | |||
| Sten, the man from Mikula, could be a visitor from Sweden or Swedish-speaking Finland, but the other letters suggest people who had Norse names but were otherwise part of the local culture. They appear together with people of Slavic names and take part in the same activities, and they lived in scattered villages in the north-east periphery of the ]. The area was visited by Novgorod tribute collectors in the 11th century, and was integrated in the republic through colonisation during the 12th and 13th centuries. Since Varangians were part of the administration of Novgorod they likely ventured in the area and sometimes settled there. The use of their naming traditions in the 14th century show the conservatism of some of the Rus{{'}} traditions.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| ===Normanism {{Anchor|Normanist}}=== | |||
| ]: ] and his brothers ] and ] arrive to the lands of ].]] | |||
| The runic script survived for some time in remote parts of Kievan Rus{{'}}, as evidenced by two finds. One of them is a weaver's slate ] found in ] in the south-westerm part of Kievan Rus{{'}}. The whorl has the runic inscription '''si{X}riþ''', representing the Norse female name ''Sigrið'' on the flat top and two crosses and two ] (]) on the side.<ref name="frank113"/><ref name="mel"/><ref name="Rundata">UA Fridell2004;1 in {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210209131755/https://app.raa.se/open/runor/inscription?id=8cefe095-b620-412e-b556-d56b01384079 |date=9 February 2021 }}.</ref> The whorl is dated thanks to being found in a layer from the period 1115–1130, when the settlement grew and became a town. No other Scandinavian finds were made except for two other whorls with runic-like inscriptions from the same time. Another whorl with a runic-like inscription was found in the old Russian fort of Plesnesk not far from Zvenigorod. This was a strategically important location and there are several warrior burials dating to the late 10th c. These graves belonged to warriors of a rank similar to a Kievan grand prince and some of them could have been of Scandinavian descent.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| Whereas the term '']'' in English usually refers to the Scandinavian-descended ruling dynasty of ] in ] from the 10th century onwards, and their scions elsewhere in Western Europe, in the context of the Rus', 'Normanism' refers to the idea that the Rus' had their origins from the Normans (i.e. among ']').<ref>"Normanist, n. and adj." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/128286. Accessed 25 July 2018.</ref> However, the term is used to cover a diverse range of opinions, not all of which are held by all Normanists (some, indeed, may mostly exist as accusations about the views of Normanists by polemical anti-Normanists<ref name="auto10">Dmitry Nikolayevich Verkhoturov, 'Normanism: What's in a Name?', ''Valla'', 1.5 (2015), 57-65.</ref>). Nevertheless, an undeniable fact is the close connection of Russia with the Normans, which is confirmed by both Slavic-type settlements on the territory of modern Sweden, and a large number of Slavicisms in the Scandinavian languages.<ref>Simon Franklin and Jonathan Shepherd, The Emergence of Rus 750–1200 (Harlow, Essex: 1996), pp. 38–39.</ref> | |||
| The inscriptions could be from descendants of the Rus{{'}} who settled in the area as protection for the western border of Kievan Rus{{'}}. The inscription shows archaic features and the ] ('''X''') is from the ], which could be due to copying the inscription from generation to generation. In that case the name ''Sigriðr'' was inherited for generations in the family. However, the '''f''' runes show that this was not the case, because the rune and the cross have similar meaning, although in different religions. Only those who had adhered to ] and later converted to Christianity would understand their significance, which necessitates a survival of old Norse traditions. It is possible that this community of descendants of late 10th century Rus{{'}} who lived in a remote area of Kievan Rus{{'}} preserved family names, runic lore in archaic forms, ancestral beliefs and some of the Old Norse language, as evidenced by the runes.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| From the ], it is known that among ]'s entourage were two Swedish merchants ] and Dir (in the chronicle they are called "]s", probably because of their noble class). The names Askold ({{lang-on|Haskuldr}}) and Dir ({{lang-on|Dyri}}) are Swedish;<ref>Kotlyar, M. ''''. Warhitory.ukrlife.org. 2002</ref> the chronicle says that these two merchants were not from the family of Rurik, but simply belonged to his squad. | |||
| ] | |||
| There is another set of inscriptions that look like runes from an old fortification named ], on the river route of ]. It was on the ]n border and could control the river, although it was located several km away. The fort was used in the 12th and 13th century, and would later turn into a small castle. C. 110 bone fragments with graffiti have been found and they include inscriptions and pictures of warriors and weapons. The runic-like inscriptions are only three to six letters long and some can be interpreted. Some 30 of them are clearly Cyrillic, while 48 are runic.<ref name="mel"/><ref name="Duchits">Duchits, L. V. and Melnikova, E. A. "Nadpisi i znaki na kostiakh s gorodishscha Maskovichi (Severo-Zapadnaia Belorussiia) ''DGTSSSR'' 1980 god (1981), pp. 185–216</ref><ref name="frank113">Franklin, S. 2002 (2004). ''Writing, Society and Culture in Early Rus, c.950–1300''. Cambridge University Press. p. 113</ref> Some of the runic inscriptions are written with mirror-runes (]) and are illegible, but several can be read as personal names, words and individual runes. The reading of them is uncertain, but they were made by people who knew or remembered runes.<ref name="mel"/><ref name="Duchits"/> | |||
| Consequently, in Kievan Rus{{'}} there were descendants of the Rus{{'}} who preserved parts of their heritage during centuries, the countryside being more conservative than towns.<ref name="mel"/> | |||
| {{Verse translation | |||
| |1={{lang |non |Því at hánum fylgja | |||
| fimm ambáttir, | |||
| átta þjónar, | |||
| eðlum góðir, | |||
| fóstrman mitt | |||
| ok faðerni, | |||
| þat er Buðli gaf | |||
| barni sínu.}}<ref name="heimskringla">''''</ref> | |||
| |2=Bond-women five | |||
| shall follow him, | |||
| And eight of my thralls, | |||
| well-born are they, | |||
| Children with me, | |||
| and mine they were | |||
| As gifts that ] | |||
| his daughter gave.<ref name="Bellows">{{harvnb |Bellows |1936 |p=441}}.</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| In the Poetic Edda, the authors describe offerings of eight slave girls to the Valkyrie Brunhild and for the dead hero chieftain Sigurd to enjoy in Valhalla. Similar to those Ibn Fadlan described in his eye witness accounts of the Rus. <ref> http://www.vikinganswerlady.com/ibn_fdln.shtml </ref> | |||
| ] (1882)]] | |||
| In Sweden Ship, burials can be found, were several ship burials contain both a female and male person. <ref>http://www.diva-portal.se/smash/get/diva2:1281242/FULLTEXT01.pdf page 2</ref> | |||
| The Norse influence is considered to have left many traces on the Old East Slavic legal code, the '']'', and on literary works such as '']'', and even on the '']'', which are old heroic tales about the early Kievan Rus{{'}} (] and others),<ref>Forssman (1983) ''Skandinavische Spuren in der alt-russischen Sprache und Dichtung. En Beitrag zur Sprach- und Kulturgeschichte des ost- und nord-europäischen Raumes im Mittelalter'' (Ed. B. Forssman), 2nd ed. München. pp. 24–27, pp. 80–99</ref><ref name="tnl1041">{{harvp|''The Nordic Languages''|2002|p=1041}}</ref> where one of the words for "hero" is derived from ''Viking'', i.e. {{lang|ru-Latn|]}} ({{lang|ru|]}}).<ref name="tnl1042"/><ref name="Vasmer">{{Cite web |url=https://vasmer.slovaronline.com/1961-VITYAZ |title="витязь". "Vasmer's Etymological Dictionary" online |access-date=5 February 2021 |archive-date=3 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210803110815/https://vasmer.slovaronline.com/1961-VITYAZ |url-status=live }}</ref> Several scholars note that this is "of considerable importance generally, as far as social and cultural background of language is concerned".<ref name="tnl1041"/> Although, they also note that parallels may arise from general similarities between Germanic and Slavic societies, they state that these similarities remain a profitable field of comparative studies.<ref name="tnl1044">{{harvp|''The Nordic Languages''|2002|p=1044}}</ref> | |||
| Archaeologist found a ship grave was containing a horse and dog as a sacrifice in Sweden and with quality weapons. | |||
| <ref> https://arkeologerna.com/unika-batgravar-hittade-i-gamla-uppsala/ </ref> Swedish Archeologist believes that during the Viking age Scandinavian human sacrifice was still common and that there were more grave offerings for the deceased in the afterlife than earlier traditions that sacrificed human beings to the gods exclusively. <ref> https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.208758.1414677865!/menu/standard/file/Roos_Denise_Manniskor_deponerade_i_vatmark_och_grav.pdf page 23 </ref> | |||
| The inclusion of weapons, horses and slave girls also seem to have been in practice among the Rus.<ref> Shephard, pp. 122–3</ref> | |||
| Russian contains several layers of ] ]s that need to be separated from the ] words that entered Old East Slavic during the Viking Age.<ref>]: ''glaz'', ''duma'', ''knjaz{{'}}'', ''skot'', ''tyn'', ''chižin'', ''chlev'', ''cholm'', ''šolom''. ]: ''bljudo'', ''verbljud'', ''kotel'', ''kupit{{'}}'', -''kusit{{'}}'', ''lečit{{'}}'', ''lest{{'}}'', ''lichva'', ''osel'', ''polk'', ''stupa'', ''steklo'', ''chleb'', ''chudožnik'', ''car{{'}}'', ''čužoj''. "Balkan-Germanic": ''bukva'', ''vinograd'', ''smokva'', ''userjaz{{'}}/g'', ''skut''. ]: ''bondar{{'}}'', ''bočka'', ''bronja'', ''buk'', ''gradil{{'}}'', ''doska'', ''izba'', ''klej'', ''korol{{'}}'', ''krest'', ''luk'', ''myto'', ''petlja'', ''penjaz{{'}}'', ''pila'', ''plug'', ''pop'', ''post'', ''remen{{'}}'', ''truba''.</ref> Estimations of the number of loan words from Old Norse into Russian vary from author to author ranging from more than 100 words (Forssman)<ref name="tnl1042"/><ref>Forssman (1983) ''Skandinavische Spuren in der alt-russischen Sprache und Dichtung. En Beitrag zur Sprach- und Kulturgeschichte des ost- und nord-europäischen Raumes im Mittelalter'' (Ed. B. Forssman), 2nd ed. München. pp. 75–80</ref> down to as low as 34 (Kiparsky)<ref name="tnl1042"/><ref>Kiparsky, V. (1975). ''Russische historische Grammatik. Vol III: Entwicklung des Wortschatzes''. Heidelberg. pp. pp. 95–97.</ref> and 30 (Strumiński),<ref name="tnl1042"/><ref>Strumiński, Bohdan. (1996). ''Linguistic Interrelations in Early Rusʹ. Northmen, Finns and East Slavs. (Ninth to eleven centuries).'' Rome/Edmonton/Toronto. pp. 229–243.</ref> including personal names. According to the most critical and conservative analysis, commonly used ON words include '']'' ("]"), '']'' ("]"), '']'' ("silk"), and '']'' ("box"), whereas '']'' ("Varangian"), '']'' ("flag") and '']{{'}}'' ("hero", from '']'') mostly belong to historical novels. Many belong to a special field and ceased to be commonly used in the 13th c., such as '']'' (from ON *{{lang|non|birkisk}}, i.e. "]/] pound", referring to 164 kg), '']'', ''vitjaz{{'}}'', ] (from ''gulf'' meaning "box", "crate" or "shed"), '']{{'}}'', ''gridi'' (from ''griði'', ''grimaðr'' meaning a "king's bodyguard"), '']{{'}}'' (from *''lári'', ''lárr'' meaning "chest", "trunk"), '']'' (from ''pund'' referring to 16.38 kg), ''Rus{{'}}'' (see etymology section above), ''skala'' (''skál'', "scale"), ] (''thiónn'', "] official" in the 12th c.), '']'' (*''silki'', "silk"), and '']'' ('']'', "office").<ref name="tnl1042">{{harvp|''The Nordic Languages''|2002|p=1042}}</ref> | |||
| Norse settlers also left many toponyms across north-western Russia, where the names of settlements or nearby creeks reveal the name of the Norse settler, or where he came from. A man named Asviðr settled in a place today known as ''Ašvidovo'', Bófastr in '']'', Dýrbjǫrn in ''Djurbenevo'', Einarr in ''Inarevo'', Kynríkr in ''Kondrikovo'', Rødríkr in '']'', Ragnheiðr in '']'', Snæbjǫrn in '']'', Sveinn in '']'', Siófastr in ''Suchvostovo'', Steingrímr in '']'', and Thorbjǫrn in ''Turyborovo''. More common Norse names have left several toponyms, such as Ivarr in '']'' and ''Ivorovka'', Hákon in ''Jakunovo'' and ''Jakunicha'', Oléf in ''Ulebovo'', ''Olebino'' and ''Olibov'', and Bjǫrn, appears in '']'', '']'', ''Bemniški'', ''Bernavo'', and in ''Bernoviči''. There is also '']'' which is the same place name as '']'',<ref name="tnl1042"/> an old estate near Stockholm, in Sweden. Many place names also contain the word ''Varangian'', such as '']'', ''Varež(ka)'', ''Varyzki'', ''Varjaža'', ''Verjažino'', and ''Verjažka''. Other names recall the '']s'', such as ''Kolbežycze'', ''Kolbjagi'', and ''Kolbižicy'', and a group called "Burangians" (''Byringar''), in the names ''Burjaži'', ''Buregi'', ''Burigi'', ''Burezi'', ''Burjaki'', ''Burjaz{{'}}'', etc.<ref name="tnl1042"/> | |||
| ====Early proponents==== | |||
| The Normanist theory gained prominence in Russia (albeit not under that name) through the German historian ] (1705–1783), who was invited to work in the ] in 1725.<ref>Serhii Plokhy, ''Lost Kingdom: The Quest for Empire and the Making of the Russian Nation from 1740 to the Present'' (London: Allen Lane, 2017).</ref> Müller built on arguments made by his predecessor ] in the papers ''De Varagis'' ('on the Varangians', 1729) and ''Origines russicae'' ('Russian origins', 1736), and on the ], written in the 12th century, and covering the years 852 to 1110. At the beginning of an important speech in 1749, later published as ''Origines gentis et nominis Russorum'' ('The Origins of the People and the Name of the Russians'), Müller argued that Russia owed its name and early ruling dynasty to ethnically Scandinavian Varangians.<ref name="auto11">Serhii Plokhy, ''Ukraine and Russia: Representations of the Past'' (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2008), chapter 1.</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52 (p. 43).</ref> This statement caused anger in his Russian audience, and earned him much animosity during his professional career in Russia.<ref name="auto11"/><ref name="auto10"/> Scathing criticism from ], ], and other Russian historians led to Müller being forced to suspend his work on the issue until Lomonosov's death. It was even thought during the 20th century that much of his research was destroyed, but recent research suggests that this is not the case: Müller managed to rework it and had it reprinted as ''Origines Rossicae'' in 1768.<ref>Dmitry Nikolayevich Verkhoturov, 'Normanism: What's in a Name?', ''Valla'', 1.5 (2015), 57-65 (pp. 58-59).</ref> | |||
| As for other influences on the Russian language, they are less apparent, and could be due to coincidence. In Old Norse and the modern ] (except for the ] of Danish), the ] is used as an ] article after the noun. In Europe, this is otherwise only known from ] and from the ], in languages such as ] and ]. However, it also appears in ], too far away from Bulgarian to have been influenced by it. As standard Russian has no definite article at all, the appearance of a postpositioned definite article in Northern Russian dialects may be due to influence from Old Norse.<ref name="tnl1043">{{harvp|''The Nordic Languages''|2002|p=1043}}</ref> As for standard Russian, just like in Old Norse, and in the modern Scandinavian languages, there is a ] using an enclitic ], '']'' in North Germanic and '']'' in Russian. However, it is not known from written Russian before the 15th c. and a corresponding construction has appeared independently in modern ], e.g. ] '']''.<ref name="tnl1043"/> | |||
| Despite the negative reception in the mid-18th century, by the end of the century, Müller's views were the consensus in Russian historiography, and this remained largely the case through the 19th century and early twentieth centuries.<ref name="auto11"/><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52 (pp. 44-45).</ref> Russian historians who accepted this historical account included ] (1766–1826) and his disciple ] (1800–75), who gave credit to the claims of the ''Primary Chronicle'' that the Varangians were invited by East Slavs to rule over them and bring order.{{citation needed|date=July 2018}} | |||
| ==Archaeology== | |||
| The theory was not without political implications. For some, it fitted with embracing and celebrating the multiethnic character of the Russian Empire.<ref name="auto11"/> However, it was also consistent with the ] widespread at the time that Normans (and their descendants) were naturally suited to government, whereas Slavs were not.<ref>Christian Promitzer, 'Physical anthropology and ethnogenesis in Bulgaria, 1878–1944', ''Focaal—Journal of Global and Historical Anthropology'', 58 (2010), 47–62 {{DOI|10.3167/fcl.2010.580104}} (pp. 49-50).</ref><ref>Cf. Richard Mcmahon, 'Anthropological Race Psychology 1820–1945: A Common European System of Ethnic Identity Narratives', ''Nations and Nationalism'', 15 (2009), 575–96 (p. 579).</ref><ref>Cf. Matthew H. Hammond, '', ''The Scottish Historical Review'', vol. 85 (no. 219) (April 2006), 1-27, {{DOI|10.1353/shr.2006.0014}}.</ref> According to Karamzin the Norse migration formed the basis and justification for Russian autocracy (as opposed to anarchy of the pre-Rurikid period), and Pogodin used the theory to advance his view that Russia was immune to social upheavals and revolutions, because the Russian state originated from a voluntary treaty between the people of ] and ] rulers.{{citation needed|date=July 2018}} | |||
| ] in Gotland.]] | |||
| Numerous artefacts of Scandinavian affinity have been found in northern Russia (as well as artefacts of Slavic origin in Sweden). However, exchange between the northern and southern shores of the Baltic had occurred since the Iron Age (albeit limited to immediately coastal areas).{{sfnp|Franklin|Shepard|1996|p=9}} Northern Russia and adjacent Finnic lands had become a profitable meeting ground for peoples of diverse origins, especially for the trade of furs, and attracted by the presence of oriental silver from the mid-8th century AD.{{sfnp|Franklin|Shepard|1996|p=12}} There is an undeniable presence of goods and people of Scandinavian origin; however, the predominant people remained the local (Baltic and Finnic) peoples.{{sfnp|Franklin|Shepard|1996|pp=22–25}} | |||
| In the 21st century, analyses of the rapidly growing range of archaeological evidence further noted that high-status 9th- to 10th-century burials of both men and women in the vicinity of the Upper Volga exhibit material culture largely consistent with that of Scandinavia (though this is less the case away from the river, or further downstream). This has been seen as further demonstrating the Scandinavian character of elites in "Old Rusʹ".{{sfnp|Duczko|2004|pp=}}{{page needed|date=January 2023}}<ref name="auto8">Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 {{doi|10.1093/ehr/cew104}}.</ref> | |||
| ====Emergence of Western scholarly consensus==== | |||
| There is uncertainty as to how small the Scandinavian migration to Rus{{'}} was, but some recent archaeological work has argued for a substantial number of 'free peasants' settling in the upper Volga region.<ref>I. Jansson, 'Warfare, Trade or Colonisation? Some General Remarks on the Eastern Expansion of the Scandinavians in the Viking Period', in ''The Rural Viking in Russia and Sweden'', ed. by P. Hansson (Örebro, 1997), pp. 47–51.</ref><ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 (pp. 395–96) {{doi|10.1093/ehr/cew104}}.</ref> | |||
| During the historical debates of the 20th century, the key evidence for the Normanist view that Scandinavian migrants had an important role in the formation of Kievan Rus' emerged as the following: | |||
| * Notwithstanding other suggestions, the name ''Rus{{'}}'' can readily be interpreted as originating in ].<ref name="auto"/><ref name="etymonline.com"/> | |||
| * The personal names of the first few ] are etymologically Old Norse, from ] (from Old Norse '']'') down to ] (from Old Norse '']''). (From Olga's son ] onwards, Slavonic names take over.)<ref name="auto12">Omeljan Pritsak, "Rus'", in '''', ed. by Phillip Pulsiano (New York: Garland, 1993), pp. 555-56.</ref> | |||
| * The list of cataracts on the Dnieper listed by ] in his '']'' as belonging to the language of the ''Rhos'' can most readily be etymologised as ].<ref name="auto4"/><ref name="auto12"/> | |||
| * The ] account of the ''Rhos'' for 839 has them identify themselves as ''suoni'' (]).<ref name="auto5"/><ref>Jonathan Shepard, 'The Viking Rus and Byzantium', , in '''', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 496-516 (p. 497).</ref><ref name="auto6"/> | |||
| * 13th-century Icelandic historiography portrays close connections between the 11th-century rulers of Rus' and Scandinavian dynasties in England and Norway.<ref name="auto12"/> | |||
| The quantity of archaeological evidence for the regions where the Rus{{'}} people were active grew steadily through the 20th century, and beyond, and the end of the ] made the full range of material increasingly accessible to researchers. Key excavations have included those at ], ], ], ], ], numerous settlements between the Upper Volga and the Oka. Twenty-first century research, therefore, is giving the synthesis of archaeological evidence an increasingly prominent place in understanding the Rus{{'}}.{{sfnp|Duczko|2004|pp=}}{{page needed|date=January 2023}}<ref name="auto8"/> The distribution of coinage, including the early 9th-century ], has provided important ways to trace the flow and quantity of trade in areas where Rus{{'}} were active, and even, through graffiti on the coins, the languages spoken by traders.<ref name="auto1"/> | |||
| In the 21st century, analyses of the rapidly growing range of archaeological evidence further noted that high-status ninth- to 10th-century burials of both men and women in the vicinity of the Upper Volga exhibit material culture largely consistent with that of Scandinavia (though this is less the case away from the river, or further downstream). This has been seen as further demonstrating the Scandinavian character of elites in "Old Rus'".<ref name="auto7"/><ref name="auto8"/> | |||
| There is also a great number of ], on which voyages to the east (''Austr'') are mentioned.<ref name="Nowak1998">{{cite book|author=Sean Nowak|title=Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Runes and Runic Inscriptions in Göttingen, 4–9 August 1995|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KYqsisEVQHEC&pg=PA651|year=1998|publisher=Walter de Gruyter|isbn=978-3-11-015455-9|page=651|access-date=26 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163650/https://books.google.com/books?id=KYqsisEVQHEC&pg=PA651|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| It is also agreed, however, that ancestrally Scandinavian Rus' aristocrats, like Normans elsewhere, swiftly assimilated culturally to a Slavic identity: in the words of F. Donald Logan, "in 839, the Rus were ]; in 1043 the Rus were ]".<ref name="Logan.184">{{harvnb|Logan|2005|p=184}} "The controversies over the nature of the Rus and the origins of the Russian state have bedevilled Viking studies, and indeed Russian history, for well over a century. It is historically certain that the Rus were Swedes. The evidence is incontrovertible, and that a debate still lingers at some levels of historical writing is clear evidence of the holding power of received notions. The debate over this issue - futile, embittered, tendentious, doctrinaire - served to obscure the most serious and genuine historical problem which remains: the assimilation of these Viking Rus into the Slavic people among whom they lived. The principal historical question is not whether the Rus were Scandinavians or Slavs, but, rather, how quickly these Scandinavian Rus became absorbed into Slavic life and culture."</ref> This near absence of cultural traces (aside from several names, and perhaps the '']''-system of ], comparable to ] in Scandinavia),{{citation needed|date=July 2018}} is noteworthy, and the processes of cultural assimilation in Rus' are an important area of research.<ref name="Logan.184"/> | |||
| In the ] of the ], after her true love ] is killed, ] (Brynhildr in Old Norse) has eight slave girls and five serving maids killed and then stabs herself with her sword so that she can be with him in ], as told in The Short Lay of Sigurd, similarly to the sacrifices of slave girls that ] described in his eyewitness accounts of the Rus{{'}}.<ref name="Larrington2014">{{cite book|editor=Carolyne Larrington|title=The Poetic Edda|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=r2vrAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA176|year=2014|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-967534-0|page=176|chapter=A Short Poem about Sigurd|access-date=27 January 2021|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163657/https://books.google.com/books?id=r2vrAwAAQBAJ&pg=Pa176|url-status=live}}</ref> Swedish ]s sometimes contain both males and females. According to the website of ''Arkeologerna'' (The Archaeologists), part of the National Historical Museums in Sweden, archaeologists have also found in an area outside of ] a boat burial that contained the remains of a man, a horse and a dog, along with personal items including a sword, spear, shield, and an ornate comb.<ref name="Arkeologerna2019">{{cite web |author1=Ninna Bengtsson |title=Two rare Viking boat burials uncovered in Sweden |url=https://arkeologerna.com/two-rare-viking-boat-burials-uncovered-in-sweden/ |website=arkeologerna.com |access-date=27 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190706063312/https://arkeologerna.com/two-rare-viking-boat-burials-uncovered-in-sweden/ |archive-date=6 July 2019 |language=sv-SE}}</ref> Swedish archeologists believe that during the Viking age Scandinavian human sacrifice was still common and that there were more grave offerings for the deceased in the afterlife than in earlier traditions that sacrificed human beings to the gods exclusively.<ref>Denise Roos (2014) Människor deponerade i våtmark och grav En analys av äldre järnålderns och vikingatidens deponeringstraditioner. https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.208758.1414677865!/menu/standard/file/Roos_Denise_Manniskor_deponerade_i_vatmark_och_grav.pdf {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210205183554/https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.208758.1414677865!/menu/standard/file/Roos_Denise_Manniskor_deponerade_i_vatmark_och_grav.pdf |date=5 February 2021 }} page 23</ref> The inclusion of weapons, horses and slave girls in graves also seems to have been practiced by the Rus{{'}}.<ref>Shephard, pp. 122–3</ref> | |||
| There is uncertainty as to how small the Scandinavian migration to Rus' was, but some recent archaeological work has argued for a substantial number of 'free peasants' settling in the upper Volga region.<ref>I. Jansson, ‘Warfare, Trade or Colonisation? Some General Remarks on the Eastern Expansion of the Scandinavians in the Viking Period’, in ''The Rural Viking in Russia and Sweden'', ed. by P. Hansson (Örebro, 1997), pp. 47–51.</ref><ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 (pp. 395-96) {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}}.</ref> | |||
| ==Historiography== | |||
| It is important to note that a number of Anglophone scholars remain equivocal about whether the question of Rus' origins can really be solved, however, either because the evidence is not good enough or because the Rus' were never an ethnic group with a clear point of origin.<ref name="auto1"/><ref name="auto2"/><ref>Andrii Danylenko, '', ''Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas'', new series, 52 (2004), 1-32.</ref><ref>Marika Mägi, ''In ''Austrvegr'': The Role of the Eastern Baltic in Viking Age Communication Across the Baltic Sea'', The Northern World, 84 (Leiden: Brill, 2018), pp. 141-216.</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Anti-Normanism}} | |||
| Prior to the 18th century, it was the consensus of Russian historians that the Rus{{'}} arose out of the native Slavic populations of the region. This changed following a 1749 presentation by German historian ] before the ], built in part on earlier work by ] and based on primary sources, particularly the ]. He suggested that the founders of the Rus{{'}} were ethnically Scandinavian Varangians, what became known as the 'Normanist' view. Though Müller met with immediate nationalistic opprobrium,<ref>Pritsak, Omeljan, "The Origin of the Rusʹ", ''Russian Review'', vol. 36, No. 3 (Jul. 1977), pp. 249–273</ref> by the end of the century his views represented the consensus in Russian historiography.<ref name="auto11">Serhii Plokhy, ''Ukraine and Russia: Representations of the Past'' (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2008), chapter 1.</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (pp. 44–45).</ref> The attribution of a Slavic origin to the Rus{{'}} saw a politically motivated 'anti-Normanist' resurgence in the 20th century within the Soviet Union, and this revisionist view also received nationalistic support in the nation-building post-Soviet states, but the broad consensus of scholars is that the origin of the Rus{{'}} lies in Scandinavia.<ref name="auto12">Omeljan Pritsak, "Rus{{'}}", in '' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426163702/https://books.google.com/books?id=d-XiZO8V4qUC |date=26 April 2023 }}'', ed. by Phillip Pulsiano (New York: Garland, 1993), pp. 555–56.</ref>{{sfn|Duczko|2004|pp=3–9}}<ref>Abbott Gleason, 'Russian Historiography after the Fall', in ''A Companion to Russian History'', ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 1–14 (p. 5).</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (p. 42).</ref> | |||
| ==Genetics== | |||
| ====Use of Normanism in Nazi Germany==== | |||
| The ''cemetery of Ostriv'' is located in the region along the ]. By 2020, 67 inhumation graves had been excavated there and dated from the early 11th century. Most of the artefacts found there are uncommon in Ukraine, but typical for the East Baltic region. This suggests a complex multi-ethnic population, presumably consisting of Baltic region migrants and locals. The ancient DNA analysis shows that the tested individuals cluster with present-day ] and ]. They are on the edge of the variability of previously published Swedish Vikings and close to dated medieval individuals from Estonia.<ref>Roman Shiroukhov et al. (2022) Baltic Migrants in the Middle Dnipro Region: A Comparative Study of the Late Viking Age Archaeological Complex of Ostriv, Ukraine, Medieval Archaeology, 66:2, 221–265, DOI: 10.1080/00766097.2022.2118419</ref> | |||
| In the earlier 20th century, Nazi Germany promoted the idea that Russia owed its statehood to a Germanic, racially superior, elite.<ref name="auto13">Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}} (pp. 386-87).</ref> During the ], the German government promised the Fascist ] of Norway territory on the historic Austrvegr, reflecting Quisling's ambition to reenact his Normanist view of Viking history.<ref>Ole Kolsrud, “Kollaborasjon og imperialisme. Quisling-regjeringens 'Austrveg'-drøm 1941–1944”, ''Norsk historisk tidsskrift'', 67 (1988), 241–270.</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| Normanism was widely used in ] to prove the superiority of the Germans over the ]. ] in his work '']'' states that | |||
| {{Quote | |||
| |text=For the organization of a Russian State structure was not the result of Russian Slavdom's State-political capacity, but rather a wonderful example of the State-building activity of the German element in an inferior race.<ref>Adolf Hitler, ''Mein Kampf'' (Houghton Mifflin Company, 1941).</ref>}} | |||
| Later ] asserted that Russians are a ]: | |||
| {{Quote | |||
| |text=The Slav is never able to build anything himself. In the long run, he's not capable of it. I'll come back to this later. With the exception of a few phenomena produced by Asia every couple of centuries, through that mixture of two heredities which may be fortunate for Asia but is unfortunate for us Europeans — with the exception, therefore, of an Attilla, a Ghenghis Khan, a Tamerlaine, a Lenin, a Stalin — the mixed race of the Slavs is based on a sub-race with a few drops of blood of our blood, blood of a leading race; the Slav is unable to control himself and create order. He is able to argue, able to debate, able to disintegrate, able to offer resistance against every authority and to revolt. But these human shoddy goods are just as incapable of maintaining order today as they were 700 or 800 years ago, when they called in the Varangians, when they called in the Ruriks.<ref>Heinrich Himmler, The Posen speech to SS officers (6 October 1943).</ref>}} | |||
| ===Anti-Normanism {{Anchor|Anti-Normanist}}=== | |||
| {{POV|section|date=February 2020}} | |||
| <!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before saving your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. See ] for details. (This text: ]) --> | |||
| ] | |||
| Proponents of anti-normanism are of the opinion that the old Russian state existed even before the vocation of ].<ref name="auto12"/> Starting with ] (1711–1765), ] scholars have criticized the idea of Norse invaders. By the early 20th century, the traditional anti-Normanist doctrine (as articulated by ]{{citation needed|date=July 2018}}) seemed to have lost currency, but in ] Russia, the anti-Normanist arguments were revived and adopted in official Soviet historiography,<ref>Janet Martin, 'The First East Slavic State', in ''A Companion to Russian History'', ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 34-50 (pp. 37-42).</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52.</ref> partly in response to Nazi propaganda, which posited that Russia owed its existence to a Germanic ruling elite.<ref name="auto13"/> ] ranks among those who attempted to reconcile both theories by hypothesizing that the Kievan state united the southern Rus' (of Slavic stock) and the northern Rus' (of Germanic stock) into a single nation.<ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}} (p. 387).</ref> | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| |quote = In light of evidence, theories - most of them proposed by Soviet scholars with nationalistic agendas - of a Slav state in the Baltic region attacked by and ultimately absorbing Viking invaders are more likely the product of wishful thinking than of fact.<ref name="WM.668">{{harvnb|Waldman||Mason|2005|p=668}} "In light of evidence, theories - most of them proposed by Soviet scholars with nationalistic agendas - of a Slav state in the Baltic region attacked by and ultimately absorbing Viking invaders are more likely the product of wishful thinking than of fact."</ref> | |||
| |author = | |||
| |source = | |||
| |align = right | |||
| |width = 25% | |||
| }} | |||
| The staunchest advocate of the anti-Normanist views in the period following the Second World War was ], who argued that the cultural level of the Varangians could not have warranted an invitation from the culturally advanced Slavs. This conclusion leads Slavicists to deny the ''Primary Chronicle'', which writes that the Varangian Rus' were invited by the native Slavs. Rybakov assumed that ], putative author of the Chronicle, was biased against the pro-Greek party of ] and supported the pro-Scandinavian party of the ruling prince ]. He cites Nestor as a pro-Scandinavian manipulator and compares his account of Rurik's invitation with numerous similar stories found in folklore around the world.{{citation needed|date=July 2018}} | |||
| By the twenty-first century, most professional scholars, in both Anglophone and Slavonic-language scholarship, had reached a consensus that the origins of the Rus' people lay in Scandinavia and that this originally Scandinavian elite had a significant role in forming the polity of Kievan Rus'.<ref name="auto12"/><ref>Wladyslaw Duczko, ''Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe'' (Leiden: Brill, 2004), esp. pp. 3-9.</ref><ref>Abbott Gleason, 'Russian Historiography after the Fall', in ''A Companion to Russian History'', ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 1-14 (p. 5).</ref><ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52 (p. 42).</ref> Indeed, in 1995, the Russian archaeologist ] "gave a paper entitled ‘The End of the Discussion’, in the belief that anti-Normanism ‘was dead and buried’". However, Klejn soon had to revise this opinion as anti-Normanist ideas gained a new prominence in both public and academic discourse in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.<ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}} (p. 387), citing Leo S. Klejn, ''Soviet Archaeology: Trends, Schools, and History'', trans. by Rosh Ireland and Kevin Windle (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012), p. 119.</ref> Anglophone scholarship has identified the continued commitment to anti-Normanism in these countries since the collapse of the Soviet Union as being motivated by present-day ethno-nationalism and state-formation.<ref>Christian Raffensperger, '', ''History Compass'', 12/11 (2014), 853–65 {{DOI|10.1111/hic3.12201}} (esp. pp. 853-54, 858).</ref><ref>Dmitry Nikolayevich Verkhoturov, 'Normanism: What's in a Name?', ''Valla'', 1.5 (2015), 57-65 (esp. 63).</ref> One prominent Russian example occurred with an anti-Normanist conference in 2002, which was followed by publications on the same theme, and which appears to have been promoted by Russian government policy of the time.<ref>Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in ''Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions'', ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52, citing I. A. Nastenko (ed.), ''Sbornik Russkogo istoricheskogo obshchestva: Antinormanism'', vol 8. (no. 156) (Moskow: Russkaja Panorama, 2003) and V. V. Fomin, ''Varjagi i varjazhskaja Rus': Kitogam diskussii po varjazhskomu voprosu'' (Moscow: Russkaja Panorama, 2005).</ref> Accordingly, anti-Normanist accounts are prominent in some 21st century Russian school textbooks.<ref>Artem Istranin and Alexander Drono, '', in ''Mutual Images: Textbook Representations of Historical Neighbours in the East of Europe'', ed. by János M. Bak and Robert Maier, Eckert. Dossiers, 10 (: Georg Eckert Institute for International Textbook Research, 2017), 31-43 (pp. 35-36).</ref> Meanwhile, in Ukraine and to a lesser extent Belarus, post-Soviet nation-building opposed to a history of Russian imperialism has promoted anti-Normanist views in academia and, to a greater extent, popular culture.<ref>Serhii Plokhy, The Origins of the Slavic Nations Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), pp. 10-48 (esp. pp. 11-12).</ref> | |||
| ====Other anti-Normanist interpretations==== | |||
| ] (c. 958–1015), ] and ], who claimed descent from the Rus' Rurik.]] | |||
| There have been quite a few alternative, non-Normanist origins for the word ''Rus''', although none was endorsed in the Western academic mainstream: | |||
| * Three early emperors of the ] at ] from 8th to 6th century BC had their names ''Russa I'', ''Russa II'' and ''Russa III'', documented in ] monuments. | |||
| * The medieval legend of three brothers, one named ], had also its predecessor in very similar legend from ancient ]ns with almost the same classical name (studies by D.J. Marr). Furthermore, ] was founded centuries before the Rus' rule. | |||
| * The ancient ] tribe of the '']'' (from the ], ''ruhs'' 'light'; R ''русые волосы'' /rusyje volosy/ "light-brown hair"; cf. ]'s dictionary definition of ''Русь'' /rus/: ''Русь ж. в знач. мир, белсвет.'' Rus, fig. world, universe ). | |||
| * From the Old Slavic name that meant "river-people" (tribes of fishermen and ploughmen who settled near the rivers ], ], ] and ] and were known to navigate them). The ''rus'' root is preserved in the modern Slavic and Russian words "''ruslo''" (river-bed), "'']''" (]), etc. | |||
| * From one of two rivers in ] (near ] and ]), '']'' and ''Rusna'', whose names are derived from a postulated Slavic term for water, akin to ''rosa'' (dew) (related to the above theory). | |||
| * A Slavic word ''rusy'' (refers only to hair color — from dark ash-blond to light-brown), cognate with ''ryzhy'' (red-haired) and English ''red''. | |||
| * A postulated proto-Slavic word for ], cognate with Greek ''arctos'' and Latin ''ursus''. | |||
| ===New research: beyond the Normanist/anti-Normanist debate=== | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| |quote = The presence of Scandinavians on the territory of ancient Russia is indisputable, even as ordinary mercenaries, while the ruling elite of the ] were the Finno-Ugric peoples. It is already considered that the name of Russia has a Balto-Finnish (so-called Norman) origin, to them we owe the origin of the old Russian state.<ref>{{Cite book|language=ru | |||
| |title=Rurik, Varangians and the fate of Russian statehood|author=Andrey Sakharov | |||
| |date=2003|p=156|url=https://litresp.ru/chitat/ru/%D0%98/iljina-nataliya-nikolaevna/izgnanie-normannov-iz-russkoj-istorii-vipusk-1/6 }}. "The presence of Scandinavians on the territory of ancient Russia is indisputable, even as ordinary mercenaries, while the ruling elite of the ] were the Finno-Ugric peoples. It is already considered that the name of Russia has a Balto-Finnish (so-called Norman) origin, to them we owe the origin of the old Russian state."</ref> | |||
| |author = ] | |||
| |source = | |||
| |align = right | |||
| |width = 25% | |||
| }} | |||
| Scholars such as Omeljan Pritsak and Horace G. Lunt offer explanations that go beyond simplistic attempts to attribute 'ethnicity' on first glance interpretation of literary, philological, and archaeological evidence. They view the Rus' as disparate, and often mutually antagonistic, clans of charismatic warriors and traders who formed wide-ranging networks across the North and Baltic Seas.<ref name="Pritsak 1981 14">{{harvtxt|Pritsak|1981|p=14}}</ref><ref>{{harvtxt|Lunt|1975|p=271}}</ref> They were a "multi-ethnic, multilingual and non-territorial community of sea nomads and trading settlements" that contained numerous Norsemen—but equally Slavs, Balts, and Finns.<ref name="Pritsak 1981 14"/> | |||
| Evidence provided by the ''Primary Chronicle'', written some three centuries later, cannot be taken as an accurate ethnographic account; as tales of 'migration' from distant lands were common literary tropes used by rulers to legitimise their contemporary rule whilst at the same time differentiating themselves from their "Baltic" and "Slavic" subject tribes. Tolochko argues "the story of the royal clan's journey is a device with its own function within the narrative of the chronicle. ... Yet if we take it for what it actually is, if we accept that it is not a documentary ethnographic description of the 10th century, but a medieval ''origo gentis''{{efn|]}} masterfully constructed by a Christian cleric of the early 12th century, then we have to reconsider the established scholarly narrative of the earliest phase of East European history, which owes so much to the ''Primary Chronicle''.<ref>{{harvtxt|Tolochko|2008|p=184 & 188, resp}}</ref> | |||
| Archaeological research, synthesizing a wide range of 20th-century excavations, has begun to develop what Jonathan Shepard has called a 'bottom up' vision of the formation of the Rus' polity, in which, during the ninth and 10th century increasingly intensive trade networks criss-crossed linguistically and ethnically diverse groups around rivers like the Volga, the Don, the Dnieper. This may have produced 'an essentially voluntary convergence of groupings in common pursuit of primary produce exchangeable for artifacts from afar'.<ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}} (pp. 389-402, quoting p. 397).</ref> This fits well with the image of Rus' that dominates the Arabic sources, focusing further south and east, around the Black and Caspian Seas, the Caucasus and the Volga Bulghars.<ref>Thorir Jonsson Hraundal, 'New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources', ''Viking and Medieval Scandinavia'', 10 (2014), 65–69 {{DOI|10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213}} (pp. 70-71).</ref> Yet this narrative, though plausible, contends with the 'top-down' image of state development implied by the ''Primary Chronicle'', archaeological assemblages indicating Scandinavian-style weapon-bearing elites on the Upper Volga, and evidence for slave-trading and violent destruction of fortified settlements.<ref>Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', ''English Historical Review'', vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384-405 {{DOI|10.1093/ehr/cew104}} (pp. 389-402).</ref><ref>Thorir Jonsson Hraundal, 'New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources', ''Viking and Medieval Scandinavia'', 10 (2014), 65–69 {{DOI|10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213}} (p. 71).</ref> | |||
| Numerous artefacts of Scandinavian affinity have been found in northern Russia (as well as artifacts of Slavic origin in Sweden). However, exchange between the north and southern shores of the Baltic had occurred since the Iron Age (albeit limited to immediately coastal areas).<ref>{{harvtxt|Franklin|1996|p=9}}</ref> Northern Russia and adjacent Finnic lands had become a profitable meeting ground for peoples of diverse origins, especially for the trade of furs, and attracted by the presence of oriental silver from the mid-8th century AD.<ref>{{harvtxt|Franklin|1996|p=12}}</ref> There is an undeniable presence of goods and people of Scandinavian origin; however, the predominant people remained the local (Baltic and Finnic) peoples.<ref>{{harvtxt|Franklin|1996|pp=22–25}}</ref> | |||
| The increasing volume of trade and internal competition necessitated higher forms of organization. The Rus' appeared to emulate aspects of ] political organization—hence the mention of a Rus' '']'' in the ] court in 839 ('']''). Legitimization was sought by way of adopting a Christian and linguistically Slavic ''high culture'' that became the ''Kieven Rus<nowiki>'</nowiki>''.<ref>Pritsak, p. 31</ref> Moreover, there is doubt if the emerging Kievan Rus' were the same clan as the "Rus" who visited the Carolingians in 839 or who attacked Constantinople in 860 AD.<ref>Tolochko, p. 187</ref> | |||
| The rise of Kiev itself is mysterious. Devoid of any silver dirham finds in the 8th century AD, it was situated west of the profitable fur and silver trade networks that spanned from the Baltic to the Muslim lands, via the ]-] basins. At the prime hill in Kiev, fortifications and other symbols of consolidation and power appear from the 9th century, thus preceding the literary appearance of 'Rus' in the middle Dnieper region. By the 10th century, the lowlands around Kiev had extensive 'Slavic' styled settlements, and there is evidence of growing trade with the Byzantine lands. This might have attracted Rus' movements, and a shift in power, from the north to Kiev.<ref>{{harvtxt|Franklin|1996|pp=90–122}}</ref> Thus, Kiev does not appear to have evolved from the infrastructure of the Scandinavian trade networks, but rather it forcibly took them over, as evidenced by the destruction of numerous earlier trade settlements in the north, including the famous ].<ref>Tolochko p. 186</ref> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist |
{{reflist}} | ||
| ==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
| {{Main|Bibliography of the history of the Early Slavs and Rusʹ}} | |||
| * ''The Annals of Saint-Bertin'', transl. Janet L. Nelson, Ninth-Century Histories 1 (Manchester and New York, 1991). | |||
| <!-- B --> | |||
| * ]. '']''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1996. | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Blöndal|first=Sigfús|author-link=Sigfús Blöndal|editor-last=Benedikz|editor-first=Benedikt S.|year=2007|title=The Varangians of Byzantium|publisher=Cambridge University|isbn=978-0-521-21745-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vFRug14ui7gC}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bury |first1=John Bagnell |last2=Gwatkin |first2=Henry Melvill |date=1936 |title=The Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=H3bxAAAAMAAJ |publisher=] |isbn=0415327563 |author-link1=J. B. Bury |author-link2=Henry Melvill Gwatkin }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The Nordic Languages, An International Handbook of the History of the North Germanic Languages |volume=1 |editor-last1=Bandle |editor-first1=O. |others=Braunmüller, K.; Jahr, E. H.; Karker, A.; Naumann, H. P.; Teleman, U.; Consulting Editors: Elmevik, L.; Widmark, G. HSK 22.1. |publisher=Walter de Gruyter |location=Berlin, New York |year=2002 |ref={{sfnref|''The Nordic Languages''|2002}}}} | |||
| * Christian, David. ''A History of Russia, Mongolia, and Central Asia''. Blackwell, 1999. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Brink |first1=Stefan |last2=Price |first2=Price |title=The Viking World |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ |access-date=2 August 2014 |year=2008 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-134-31826-1 }} | |||
| * Danylenko, Andrii. "The name Rus': In search of a new dimension." Jahrbueher fuer Geschichte Osteuropas 52 (2004), 1–32. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bury |first1=John Bagnell |last2=Gwatkin |first2=Henry Melvill |date=1936 |title=The Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=H3bxAAAAMAAJ |publisher=] |isbn=0-415-32756-3 |author-link1=J. B. Bury |author-link2=Henry Melvill Gwatkin }} | |||
| * Davidson, H.R. Ellis, ''The Viking Road to Byzantium''. Allen & Unwin, 1976. | |||
| <!-- C --> | |||
| * Dolukhanov, Pavel M. ''The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus.'' New York: Longman, 1996. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Christian |first=David |title=A History of Russia, Mongolia, and Central Asia |publisher=Blackwell |year=1999}} | |||
| * Duczko, Wladyslaw. '' (The Northern World; 12)''. Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers, 2004 (hardcover, {{ISBN|90-04-13874-9}}). | |||
| <!-- D --> | |||
| * Goehrke, C. ''Frühzeit des Ostslaven.'' Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, 1992. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Danylenko |first=Andrii |title=The name Rus{{'}}: In search of a new dimension. |journal=Jahrbueher für Geschichte Osteuropas |volume=52 |year=2004 |pages=1–32}} | |||
| * ] ''A History of Ukraine.'' Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1996. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Davidson |first=H.R. Ellis |title=The Viking Road to Byzantium |publisher=Allen & Unwin |year=1976}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Origin of Rus{{'}}''. Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1991. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Davies |first=Norman |author-link=Norman Davies |title=] |location=New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1996}} | |||
| * Stang, Hakon. ''The Naming of Russia.'' Oslo: Middelelser, 1996. | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=DeVries|first=Kelly|author-link=Kelly DeVries|year=1999|title=The Norwegian Invasion of England in 1066|publisher=Boydell & Brewer Ltd|isbn=978-0-85115-763-4}} | |||
| * (]) | |||
| * {{cite book |last= |
* {{cite book |last=Dolukhanov |first=Pavel M. |title=The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus. |location=New York |publisher=Longman |year=1996}} | ||
| * {{cite book |last=Duczko |first=Wladyslaw |author-link=:pl:Władysław Duczko |title=Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hEawXSP4AVwC |access-date=5 May 2013 |year=2004 |publisher=] |isbn=90-04-13874-9 |series=The Northern World |volume=12}} | |||
| * ''On the language of old Rus: some questions and suggestions.'' Horace Gray Lunt. Harvard University, Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute, 1975 | |||
| <!-- E --> | |||
| * ''The Emergence of Rus: 750–1200.'' Simon Franklin, Jonathan Shephard. Longman Publishing Group, 1996 | |||
| <!-- F --> | |||
| * ''The Origin of Rus{{'}}''. Omeljan Pritsak. Harvard University Press, 1981 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Franklin |first1=Simon |last2=Shepard |first2=Jonathan |title=The Emergence of Rus: 750–1200 |year=1996 |publisher=Longman |isbn=978-0-582-49091-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4JnjSgAACAAJ |access-date=3 February 2021 |language=en}} | |||
| * The ''Primary Chronicle''{{'s}} 'Ethnography' Revisited: Slavs and Varangians in the Middle Dnieper Region and the Origin of the Rus' State. Olksiy P Tolochko; in ''Franks, Northmen and Slavs. Identities and State Formation in Early Medieval Europe''. Editors: Ildar H. Garipzanov, Patrick J. Geary, and Przemysław Urbańczyk. Brepols, 2008. | |||
| <!-- G --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Brink |first1=Stefan |last2=Price |first2=Price |title=The Viking World |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wuN-AgAAQBAJ |access-date=2 August 2014 |year=2008 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1134318261 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goehrke |first=C. |title=Frühzeit des Ostslaven. |location=Darmstadt |publisher=Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft |year=1992}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Duczko |first=Wladyslaw |author-link=:pl:Władysław Duczko |title=Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hEawXSP4AVwC |access-date=5 May 2013 |year=2004 |publisher=] |isbn=9004138749 }} | |||
| <!-- H --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Waldman |first1=Carl |last2=Mason |first2=Catherine |date=2005 |title=Encyclopedia of European Peoples |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kfv6HKXErqAC |publisher=] |isbn=1438129181 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hellquist |first=Elof |title=Svensk etymologisk ordbok |url=https://archive.org/details/svensketymologis00hell |trans-title=Swedish etymological dictionary |year=1922 |publisher=Gleerup |location=Lund |language=sv }} | |||
| <!-- I --> | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| <!-- J --> | |||
| <!-- K --> | |||
| <!-- L --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Logan |first=F. Donald |date=2005 |title=The Vikings in History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7K2ywwGox6IC |publisher=] |isbn=0-415-32756-3 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lunt |first=Horace Gray |title=On the language of old Rus: some questions and suggestions |publisher=Harvard University, Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute |year=1975}} | |||
| <!-- M --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Magocsi |first=Paul R. |title=A History of Ukraine. |location=Toronto |publisher=University of Toronto Press |year=1996}} | |||
| <!-- N --> | |||
| * {{cite book |translator-last=Nelson |translator-first=Janet L. |title=The Annals of Saint-Bertin |series=Ninth-Century Histories |volume=1 |location=Manchester and New York |year=1991}} | |||
| <!-- O --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pritsak |first=Omeljan |title=The Origin of Rus{{'}} |author-link=Omeljan Pritsak |publisher=Harvard University Press |location=Cambridge, Mass. |year=1981}} | |||
| <!-- P --> | |||
| <!-- Q --> | |||
| <!-- R --> | |||
| <!-- S --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stang |first=Hakon. |title=The Naming of Russia. |location=Oslo |publisher=Middelelser |year=1996}} | |||
| <!-- T --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |author1=Thorir Jonsson Hraundal |title=New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources |journal=Viking and Medieval Scandinavia |date=January 2014 |volume=10 |pages=65–97 |doi=10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213}} | |||
| * {{cite book |chapter=The ''Primary Chronicle''{{'s}} 'Ethnography' Revisited: Slavs and Varangians in the Middle Dnieper Region and the Origin of the Rus{{'}} State |first=Olksiy P |last=Tolochko |title=Franks, Northmen and Slavs. Identities and State Formation in Early Medieval Europe |editor-first1=Ildar H. |editor-last1=Garipzanov |editor-first2=Patrick J. |editor-last2=Geary |editor-first3=Przemysław |editor-last3=Urbańczyk |location=Brepols |year=2008}} | |||
| <!-- U --> | |||
| <!-- V --> | |||
| <!-- W --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Waldman |first1=Carl |last2=Mason |first2=Catherine |date=2005 |title=Encyclopedia of European Peoples |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kfv6HKXErqAC |publisher=] |isbn=1-4381-2918-1 }} | |||
| <!-- X --> | |||
| <!-- Y --> | |||
| <!-- Z --> | |||
| <!-- What even is this?!? --> | |||
| * (]) | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * {{Commons category-inline|Rus' people}} | * {{Commons category-inline|Rus' people}} | ||
| * James E. Montgomery, '', ''Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies'', 3 (2000), |
* James E. Montgomery, '', ''Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies'', 3 (2000), 1–25. Includes a translation of Ibn Fadlān's discussion of the ''Rūs''/''Rūsiyyah''. | ||
| {{Gardariki}} | |||
| {{Germanic peoples}} | |||
| {{Norse people footer}} | |||
| {{Middle Ages}} | |||
| {{Belarus topics}} | |||
| {{Russia topics}} | |||
| {{Ukraine topics}} | {{Ukraine topics}} | ||
| {{History of Europe}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2017}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Rus' people}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Rus' people}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 12 January 2025
European ethnic group For other uses of "Rus", see Rus (disambiguation).

The Rus', also known as Russes, were a people in early medieval Eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally Norsemen, mainly originating from present-day Sweden, who settled and ruled along the river-routes between the Baltic and the Black Seas from around the 8th to 11th centuries AD.
The two original centres of the Rus' were Ladoga (Aldeigja), founded in the mid-8th century, and Rurikovo Gorodische (Holmr), founded in the mid-9th century. The two settlements were situated at opposite ends of the Volkhov River, between Lake Ilmen and Lake Ladoga, and the Norsemen likely called this territory Gardar. From there, the name of the Rus' was transferred to the Middle Dnieper, and the Rus' then moved eastward to where the Finnic tribes lived and southward to where the Slavs lived.
The name Garðaríki was applied to the newly formed state of Kievan Rus', and the ruling Norsemen along with local Finnic tribes gradually assimilated into the East Slavic population and came to speak a common language. Old Norse remained familiar to the elite until their complete assimilation by the second half of the 11th century, and in rural areas, vestiges of Norse culture persisted as late as the 14th and early 15th centuries, particularly in the north.
The history of the Rus' is central to 9th through 10th-century state formation, and thus national origins, in Eastern Europe. They ultimately gave their name to Russia and Belarus, and they are relevant to the national histories of Russia, Ukraine and Belarus. Because of this importance, there is a set of alternative so-called "anti-Normanist" views that are largely confined to a minor group of Eastern European scholars.
Etymology
Main article: Names of Rusʹ, Russia and Ruthenia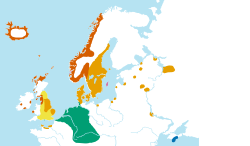
- Note: The þ (thorn letter) represents the voiceless dental fricative /θ/ of th in English thing, whereas the ð (eth letter) represents the voiced dental fricative /ð/ of th in English the. When þ appears in intervocalic position or before a voiced consonant, it is pronounced like ð, so the pronunciation difference between rōþer and róðr is minute.
The name Rusʹ remains not only in names such as Russia and Belarus, but it is also preserved in many place names in the Novgorod and Pskov districts, and it is the origin of the Greek Rōs. Rus' is generally considered to be a borrowing from Finnic Ruotsi ("Sweden"). There are two theories behind the origin of Rus'/Ruotsi, which are not mutually exclusive. It is either derived more directly from OEN rōþer (OWN róðr), which referred to rowing, the fleet levy, etc., or it is derived from this term through Rōþin, an older name for the Swedish coastal region Roslagen.
The Finnish and Russian forms of the name have a final -s revealing an original compound where the first element was rōþ(r)s- (preceding a voiceless consonant, þ is pronounced like th in English thing). The prefix form rōþs- is found not only in Ruotsi and Rusʹ, but also in Old Norse róþsmenn and róþskarlar, both meaning "rowers", and in the modern Swedish name for the people of Roslagen – rospiggar which derives from ON *rōþsbyggiar ("inhabitants of Rōþin"). The name Roslagen itself is formed with this element and the plural definite form of the neuter noun lag, meaning "the teams", in reference to the teams of rowers in the Swedish kings' fleet levy.
There are at least two, probably three, instances of the root in Old Norse from two 11th c. runic inscriptions, fittingly located at two extremes of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks. Two of them are roþ for rōþer /róðr, meaning "fleet levy", on the Håkan stone, and as i ruþi (translated as "dominion") on the lost Nibble stone, in the old Swedish heartland in the Mälaren Valley, and the possible third one was identified by Erik Brate in the most widely accepted reading as roþ(r)slanti on the Piraeus Lion originally located in Athens, where a runic inscription was most likely carved by Swedish mercenaries serving in the Varangian Guard. Brate has reconstructed *Rōþsland, as an old name for Roslagen.
Between the two compatible theories represented by róðr or Róðinn, modern scholarship leans towards the former because at the time, the region covered by the latter term, Roslagen, remained sparsely populated and lacked the demographic strength necessary to stand out compared to the adjacent Swedish heartland of the Mälaren Valley. Consequently, an origin in word compounds such as róþs-menn and róþs-karlar is considered the most likely one. Moreover, the form róþs-, from which Ruotsi and Rusʹ originate, is not derived directly from ON róðr, but from its earlier Proto-Norse form roðz (rothz).
Other theories such as derivation from Rusa, a name for the Volga, are rejected or ignored by mainstream scholarship.
History
Further information: Norsemen, Vikings, and Varangians
Having settled Ladoga in the 750s, Scandinavian colonists played an important role in the early ethnogenesis of the Rus' people, and in the formation of the Rus' Khaganate. Ladoga, then known as Aldeigja by the Norsemen, was the earliest and most significant settlement of the Rus', while Gorodische, likely known as Holmr, was founded over a century later. It was from the Ladoga area, which formed the centre of the Rus', that the envoys went to Constantinople in 838. The Varangians are first mentioned in the Primary Chronicle as having exacted tribute from the Slavic and Finnic tribes in 859. It was the time of rapid expansion of the Vikings' presence in Northern Europe; England began to pay Danegeld in 865, and the Curonians faced an invasion by the Swedes around the same time.
The Varangians are mentioned in the Primary Chronicle, which suggests that the term Rus' was used to denote Scandinavians until it became firmly associated with the now extensively Slavicised elite of Kievan Rus'. At that point, the new term Varangian was increasingly preferred to name the Scandinavians, probably mostly from what is currently Sweden, plying the river routes between the Baltic and the Black and Caspian Seas. Relatively few of the rune stones Varangians left in their native Sweden tell of their journeys abroad, to such places as what is today Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Greece, and Italy. Most of these rune stones can be seen today, and are a significant piece of historical evidence. The Varangian runestones tell of many notable Varangian expeditions, and even recount the fates of individual warriors and travelers.
In Russian historiography, two cities are used to describe the beginnings of the country: Kiev and Novgorod. In the first part of the 11th century the former was already a Slav metropolis, rich and powerful, a fast growing centre of civilisation adopted from Byzantium. The latter town, Novgorod, was another centre of the same culture but founded in different surroundings, where some old local traditions moulded this commercial city into the capital of a powerful oligarchic trading republic of a kind otherwise unknown in this part of Europe. These towns have tended to overshadow the significance of other places that had existed long before Kiev and Novgorod were founded. The two original centres of Rus' were Staraya Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodische, two points on the Volkhov, a river running for 200 kilometres (120 mi) between Lake Ilmen in the south to Lake Ladoga in the north. This was the territory that most probably was originally called by the Norsemen Gardar, a name that long after the Viking Age acquired a much broader meaning and became Garðaríki, a denomination for the entire state. The area between the lakes was the original Rus', and it was from here that its name was transferred to the territories inhabited by the Slavs on the middle Dnieper, which eventually became the "land of Rus" (Ruskaja zemlja). The Primary Chronicle portrays the East Slavic tribe of Polans as the most civilised of the East Slavs, and that they were therefore predisposed to host the Rus', but not give their name to the land. From this area, the Rus' moved eastward to the lands inhabited by Finno-Ugric tribes in the Volga-Oka region, as well as south along the Dnieper.
The prehistory of the first territory of Rus' has been sought in the developments around the early-8th century, when Staraja Ladoga was founded as a manufacturing centre and to conduct trade, serving the operations of Scandinavian hunters and dealers in furs obtained in the north-eastern forest zone of Eastern Europe. In the early period (the second part of the 8th and first part of the 9th century), a Norse presence is only visible at Staraya Ladoga, and to a much lesser degree at a few other sites in the northern parts of Eastern Europe. The objects that represent Norse material culture of this period are rare outside Ladoga and mostly known as single finds. This rarity continues throughout the 9th century until the whole situation changes radically during the next century, when historians meet, at many places and in relatively large quantities, the material remains of a thriving Scandinavian culture. For a short period of time, some areas of Eastern Europe became as much part of the Norse world as were Danish and Norwegian territories in the West. The culture of the Rus' contained Norse elements used as a manifestation of their Scandinavian background. These elements, which were current in 10th-century Scandinavia, appear at various places in the form of collections of many types of metal ornaments, mainly female but male also, such as weapons, decorated parts of horse bridles, and diverse objects embellished in contemporaneous Norse art styles.
The Swedish king Anund Jakob wanted to assist Yaroslav the Wise, Grand prince of Kiev, in his campaigns against the Pechenegs. The so-called Ingvar the Far-Travelled, a Swedish Viking who wanted to conquer Georgia, also assisted Yaroslav with 3000 men in the war against the Pechenegs; however, he later continued on to Georgia. Yaroslav the Wise married the Swedish king's daughter, Ingegerd Olofsdotter of Sweden, who became the Russian saint, Anna, while Harald Hardrada, the Norwegian king who was a military commander of the Varangian guard, married Elisiv of Kiev. The two first uncontroversially historical Swedish kings Eric the Victorious and Olof Skötkonung both had Slavic wives. Danish kings and royals also frequently had Slavic wives. For example, Harald Bluetooth married Tove of the Obotrites. Vikings also made up the bulk of the bodyguards of early Kievan Rus' rulers.
Evidence for strong bloodline connections between the Kievan Rus' and Scandinavia existed and a strong alliance between Vikings and early Kievan rulers is indicated in early texts of Scandinavian and East Slavic history. Several thousand Swedish Vikings died for the defence of Kievan Rus' against the Pechenegs.
Scandinavian sources

In Scandinavian sources, the area is called Austr (the "East"), Garðaríki (the "realm of cities"), or simply Garðar (the "cities"), and Svíþjóð hin mikla ("Great Sweden"). The last name appears in the 12th century geographical work Leiðarvísir ok Borgaskipan by the Icelandic abbot Nicolaus (d. 1161) and in Ynglinga saga by Snorri Sturluson, which indicates that the Icelanders considered Kievan Rus' to have been founded by the Swedes. The name "Great Sweden" is introduced as a non-Icelandic name with the phrase "which we call Garðaríki" (sú er vér köllum Garðaríki), and it is possible that it is a folk etymological interpretation of Scythia magna. However, if this is the case, it can still be influenced by the tradition that Kievan Rus' was of Swedish origin, which recalls Magna Graecia as a name for the Greek colonies in Italy.
When the Norse sagas were put to text in the 13th century, the Norse colonisation of Eastern Europe, however, was a distant past, and little of historical value can be extracted. The oldest traditions were recorded in the Legendary sagas and there Garðaríki appears as a Norse kingdom where the rulers have Norse names, but where also dwelt the Dwarves Dvalin and Durin. There is, however, more reliable information from the 11th and the 12th centuries, but at that time most of the Scandinavian population had already assimilated, and the term Rus' referred to a largely Slavic-speaking population. Still, Eastern Europe is presented as the traditional Swedish sphere of interest. The sagas preserve Old Norse names of several important Rus' settlements, including Hólmgarðr (Novgorod), and Kønugarðr (Kiev); Fjodor Uspenskij argues that the use of the element garðr in these names, as well as in the names Garðar and Miklagarðr (Constantinople), shows the influence of Old East Slavic gorodǔ (city), as garðr usually means farmstead in Old Norse. He further argues that the city names can be used to show that the Rus' were also competent in Old East Slavic. At this time the Rus' borrowed some 15 Old East Slavic words, such as the word for marketplace, tǔrgǔ, as torg, many of which spread to the other Old Norse-speaking regions as well.
The most contemporary sources are the Varangian runestones, but just like the sagas, the vast majority of them arrive relatively late. The earliest runestone that tells of eastwards voyages is the Kälvesten runestone from the 9th century in Östergötland, but it does not specify where the expedition had gone. It was Harald Bluetooth's construction of the Jelling stones in the late 10th century that started the runestone fashion that resulted in the raising of thousands of runestones in Sweden during the 11th century; at that time the Swedes arrived as mercenaries and traders rather than settlers. In the 8th, 9th and 10th centuries runic memorials had consisted of runes on wooden poles that were erected in the ground, something which explains the lack of runic inscriptions from this period both in Scandinavia and in eastern Europe as wood is perishable. This tradition was described by Ibn Fadlan who met Scandinavians on the shores of the Volga.
The Fagerlöt runestone gives a hint of the Old Norse spoken in Kievan Rus', as folksgrimʀ may have been the title that the commander had in the retinue of Yaroslav I the Wise in Novgorod. The suffix -grimmr is a virtually unique word for "leader" which is otherwise only attested in the Swedish medieval poem Stolt Herr Alf, but in the later form grim. It is not attested as a noun in the sense "leader" in West Norse sources. In Old Norse, the basic meaning of the adjective grimmr is "heartless, strict and wicked", and so grimmr is comparable in semantics to Old Norse gramr which meant both "wrath", "king" and "warrior".
Other runestones explicitly mentioning warriors serving the ruler of Kievan Rus' are one of the Skåäng runestones, the Smula runestone and most famously, the Turinge runestone which immortalises the dead commander with a poem:
|
|
The Veda runestone is of note as it indicates that the riches that were acquired in Eastern Europe had led to the new procedure of legally buying clan land, and the Swedish chieftain Jarlabanke used his clan's acquired wealth to erect the monument Jarlabanke Runestones after himself while alive and where he bragged that he owned the whole hundred.
Slavic sources

The earliest Slavonic-language narrative account of Rus' history is the Primary Chronicle, compiled and adapted from a wide range of sources in Kiev at the start of the 13th century. It has therefore been influential in modern history-writing, but it was also compiled much later than the time it describes, and historians agree it primarily reflects the political and religious politics of the time of Mstislav I of Kiev.
However, the chronicle does include the texts of a series of Rus'–Byzantine Treaties from 911, 945, and 971. The Rus'–Byzantine Treaties give a valuable insight into the names of the Rus'. Of the fourteen Rus' signatories to the Rus'–Byzantine Treaty in 907, all had Norse names. By the Rusʹ–Byzantine Treaty (945) in 945, some signatories of the Rus' had Slavic names while the vast majority had Norse names.
The Chronicle presents the following origin myth for the arrival of Rus' in the region of Novgorod: the Rus'/Varangians 'imposed tribute upon the Chuds, the Slavs, the Merians, the Ves', and the Krivichians' (a variety of Slavic and Finnic peoples).
The tributaries of the Varangians drove them back beyond the sea and, refusing them further tribute, set out to govern themselves. There was no law among them, but tribe rose against tribe. Discord thus ensued among them, and they began to war one against the other. They said to themselves, "Let us seek a prince who may rule over us, and judge us according to the Law". They accordingly went overseas to the Varangian Russes: these particular Varangians were known as Russes, just as some are called Swedes, and others Normans, English, and Gotlanders, for they were thus named. The Chuds, the Slavs, the Krivichians and the Ves' then said to the people of Rus', "Our land is great and rich, but there is no order in it. Come to rule and reign over us". Thus they selected three brothers, with their kinsfolk, who took with them all the Russes and migrated. The oldest, Rurik, located himself in Novgorod; the second, Sineus, at Beloozero; and the third, Truvor, in Izborsk. On account of these Varangians, the district of Novgorod became known as the land of Rus'.
From among Rurik's entourage it also introduces two Swedish merchants Askold and Dir (in the chronicle they are called "boyars", probably because of their noble class). The names Askold (Old Norse: Haskuldr) and Dir (Old Norse: Dyri) are Swedish; the chronicle says that these two merchants were not from the family of Rurik, but simply belonged to his retinue. Later, the Primary Chronicle claims, they conquered Kiev and created the state of Kievan Rusʹ (which may have been preceded by the Rusʹ Khaganate).
Arabic sources
Further information: Caspian expeditions of the Rusʹ
Henryk Siemiradzki (1883)

Arabic-language sources for the Rus' people are relatively numerous, with over 30 relevant passages in roughly contemporaneous sources. It can be difficult to be sure that when Arabic sources talk about Rus' they mean the same thing as modern scholars. Sometimes it seems to be a general term for Scandinavians: when Al-Yaqūbi recorded Rūs attacking Seville in 844, he was almost certainly talking about Vikings based in Frankia. At other times, it might denote people other than or alongside Scandinavians: thus the Mujmal al-Tawarikh calls the Khazars and Rus' 'brothers'; later, Muhammad al-Idrisi, Al-Qazwini, and Ibn Khaldun all identified the Rus' as a sub-group of the Turks. These uncertainties have fed into debates about the origins of the Rus'.
Arabic sources for the Rus' had been collected, edited and translated for Western scholars by the mid-20th century. However, relatively little use was made of the Arabic sources in studies of the Rus' before the 21st century. This is partly because they mostly concern the region between the Black and the Caspian Seas, and from there north along the lower Volga and the Don. This made them less relevant than the Primary Chronicle to understanding European state formation further west. Imperialist ideologies, in Russia and more widely, discouraged research emphasising an ancient or distinctive history for Inner Eurasian peoples. Arabic sources portray Rus' people fairly clearly as a raiding and trading diaspora, or as mercenaries, under the Volga Bulghars or the Khazars, rather than taking a role in state formation.
The most extensive Arabic account of the Rus' is by the Muslim diplomat and traveller Ahmad ibn Fadlan, who visited Volga Bulgaria in 922, and described people under the label Rūs/Rūsiyyah at length, beginning thus:
I have seen the Rus as they came on their merchant journeys and encamped by the Itil. I have never seen more perfect physical specimens, tall as date palms, blond and ruddy; they wear neither tunics nor caftans, but the men wear a garment which covers one side of the body and leaves a hand free. Each man has an axe, a sword, and a knife, and keeps each by him at all times. The swords are broad and grooved, of Frankish sort. Each woman wears on either breast a box of iron, silver, copper, or gold; the value of the box indicates the wealth of the husband. Each box has a ring from which depends a knife. The women wear neck-rings of gold and silver. Their most prized ornaments are green glass beads. They string them as necklaces for their women.
— quoted in Gwyn Jones, A History of the Vikings
Apart from Ibn Fadlan's account, scholars draw heavily on the evidence of the Persian traveler Ibn Rustah who, it is postulated, visited Novgorod (or Tmutarakan, according to George Vernadsky) and described how the Rus' exploited the Slavs.
As for the Rus, they live on an island ... that takes three days to walk round and is covered with thick undergrowth and forests; it is most unhealthy. ... They harry the Slavs, using ships to reach them; they carry them off as slaves and…sell them. They have no fields but simply live on what they get from the Slav's lands. ... When a son is born, the father will go up to the newborn baby, sword in hand; throwing it down, he says, "I shall not leave you with any property: You have only what you can provide with this weapon."
— Ibn Rustah
Byzantine sources
Further information: Rusʹ–Byzantine War (disambiguation) and Rusʹ–Byzantine Treaty (disambiguation)
When the Varangians first appeared in Constantinople (the Paphlagonian expedition of the Rusʹ in the 820s and the Siege of Constantinople in 860), the Byzantines seem to have perceived these people, whom they called the Rhos (Greek: Ῥώς), as a different people from the Slavs. At least no source says they are part of the Slavic race. Characteristically, Pseudo-Simeon and Theophanes Continuatus refer to the Rhos as dromitai (Δρομῖται), a word related to the Greek word meaning a run, suggesting the mobility of their movement by waterways.
In his treatise De Administrando Imperio, Constantine VII describes the Rhos as the neighbours of Pechenegs who buy from the latter cows, horses, and sheep "because none of these animals may be found in Rhosia"; his description represents the Rus' as a warlike northern tribe. Constantine also enumerates the names of the Dnieper cataracts in both rhosisti ('ῥωσιστί', the language of the Rus') and sklavisti ('σκλαβιστί', the language of the Slavs). The Rus' names are usually etymologised as Old Norse. An argument used to support this view is that the name Aeifor in reference to the fourth cataract is also attested on the Pilgårds runestone from the 10th c. on Gotland. However, some researches indicate that at least several of the Rus' names can be Slavic and, as for the Dnieper cataract Aeifar / Aeifor, its name doesn't have an acceptable and convincing Scandinavian etymology. At the time, the Byzantines also recorded the existence of some of the lesser important Slavic tribes in the region, and the emperor only knew of Rhosia, which referred to the Rus' who lived in Kiev, closer to Byzantium, and the Rus' who lived in the north, along the Volkhov River.
Constantine's form for the non-Slavonic names
Latin transliteration Constantine's interpretation of the Slavonic or both
Proposed Old Norse etymons for the non-Slavonic names
Proposed Slavic etymons for the non-Slavonic names
Ἐσσουπῆ Essoupi "Do not sleep!" nes uppi "upper promontory" súpandi "slurping"
не спи (ne spy) "do not sleep!" (compare the Ukrainian не спи /ne spɪ/ "do not sleep!")
Οὐλβορσί Oulvorsi "the Island of the Barrage" Úlfarsey "Úlfar's island" hólm-foss "island rapid"
— Γελανδρί Gelandri "Noise of the Barrage" gjallandi/gellandi "yelling, loudly ringing" — Ἀειφάρ, Ἀειφόρ Aeifar, Aeifor ... because the pelicans nest in the stones of the barrage ... æ-fari/ey-færr "never passable" æ-for/ey-forr "ever fierce"
— Βαρουφόρος Varouforos ... because it forms a large lake ... vara-foss "stony shore rapid" báru-foss "wave rapid"
— Λεάντι Leanti "the Boiling of the Water" hlæjandi "laughing" lьjant'i (< Proto-Slavic *lьjǫtji) "the one that pours" derived from lьjati (Proto-Slavic *lьjati) "to pour" (compare the Ukrainian лляти /ˈlʲːɑtɪ/ "to pour"
and the Polish lać /lat͡ɕ/ "to pour")
Στρούβουν, Στρούκουν Strouvoun, Stroukoun "Little Barrage" strjúkandi "stroking, delicately touching" strukum, "rapid current"
стрибун (strybun) "the one that jumps" from the Ukrainian стрибати /strɪˈbatɪ/ "to jump"
Western European sources
The first Western European source to mention the Rus' are the Annals of St. Bertin (Annales Bertiniani). These relate that Emperor Louis the Pious' court at Ingelheim, in 839, was visited by a delegation from the Byzantine emperor. In this delegation there were men who called themselves Rhos (in the Latin text, ... qui se, id est gentem suam, Rhos vocari dicebant, ...; translated by Aleksandr Nazarenko as ... who stated that they, i.e. their nation, were called Rhos, ...). Once Louis enquired the reason of their arrival (in the Latin text, ... Quorum adventus causam imperator diligentius investigans, ...), he learnt that they were Swedes (eos gentis esse Sueonum; verbatim, their nation is Sveoni). Fearing that they were spies, he detained them, before letting them proceed after receiving reassurances from Byzantium. Subsequently, in the 10th and 11th centuries, Latin sources routinely confused the Rus' with the tribe of Rugians. Olga of Kiev, for instance, was designated as queen of the Rugians (reginae Rugorum) in the Lotharingian Chronicle compiled by the anonymous continuator of Regino of Prüm. At least after the 6th century, the name of the Rugii referred to Slavic speaking peoples including the Rus'. According to the Annals of St. Bertin, the Rus' leader had the title Khagan (... quod rex illorum, Chacanus vocabulo, ...).
Another source comes from Liutprand of Cremona, a 10th-century Lombard bishop whose Antapodosis, a report from Constantinople to Holy Roman Emperor Otto I, says that Constantinople 'stands in territory surrounded by warlike peoples. On the north it has the ... Rusii sometimes called by another name Nordmanni, and the Bulgarii who live too close for harmony'.
Assimilation

The Scandinavian influence in Kievan Rus' was most important during the late 9th c. and during the 10th c. In 976, Vladimir the Great (Valdamarr gamli) fled from his brother Yaropolk to Sweden, ruled by Erik the Victorious, where he gathered an invasion force that he used to conquer Kievan Rus'. Vladimir was initially a pagan who is reported by the Primary Chronicle to have worshiped Perun and Veles, and this is probably a Slavic translation of the corresponding Norse gods Thor and Freyr, who beside Odin were the two most important gods to the Swedes. However, in 988, he converted to the Eastern Orthodox Church, whereas the Norse in Scandinavia remained Norse pagans or converted to the Catholic Church. After this, the Norse influence decreased considerably both in character and in size, and in the 11th c. the Norse are mentioned as Varangian mercenaries and employees serving the princely family.
Elena A. Melnikova at the Russian Academy of Sciences notes that in Russian historiography, the assimilation of the Norse Rus' is presented as a very rapid affair, based on studies of material culture. However, material objects are not as strong an indicator of ethnic identity as the language spoken in a society. Usually, the only non-archaeological claim to rapid assimilation is the appearance of three Slavic names in the princely family, i.e. Svjatoslav, Predslava, and Volodislav, for the first time in the treaty with Byzantium of 944. Another reason for assuming a rapid assimilation is given by Yaroslav Shchapov, who writes that as a consequence of the Rus'adoption of Byzantine (Eastern) rather than Roman Christianity, as well as the assimilation of Byzantine culture, "writing, literature and law in the national language" spread much earlier than in Western countries.
Melnikova comments that the disappearance of Norse funeral traditions c. 1000, is better explained with Christianisation and the introduction of Christian burial rites, a view described with some reservations by archaeologist Przemysław Urbańczyk of the Institute of Archeology and Ethnology at the Polish Academy of Sciences. So the lack of Norse burials from c. 1000 is not a good indicator of assimilation into Slavic culture, and shows instead that the Rus' had turned Orthodox Christian. Also the use of material objects is more connected to change in fashion and to change of social status than it is to ethnical change. She also notes that no systematic studies of the various elements that manifest ethnic identity in relation to the Rus' has been done to support the theory of rapid assimilation, in spite of the fact that "he most important indications of ethno-cultural self-identification are language and literacy."
Urban

The Rus' elite became bilingual c. 950 but it was not until the end of the 11th century that Old East Slavic can be shown to have become their native language. Until the mid-10th century all the attested Rus' names were Norse. In the Rus'–Byzantine Treaty of 944 or 945 there are 76 names among whom 12 belong to the ruling family, 11 to emissaries, 27 to other agents, and 26 to merchants. In the princely family, there are three Slavic names Svjatoslav, son of prince Igor' (Ingvar) and Volodislav and Predslava (of unknown relation). The other members of the family have Norse names, i.e. Olga (Helga), Akun (Hákon), Sfanda (Svanhildr), Uleb (Óleifr), Turd (Þórðr), Arfast (Arnfastr), and Sfir'ka (Sverkir). The emissaries also have Old Norse names except for three who have Finnish names. Olga has a representative by the Finnish name Iskusevi, whereas Volodislav is represented by the Norse Uleb (Óleifr). Among the 27 agents there are some who have Finnish names, but none with Slavic, while among the 26 merchants there are three with Finnish names and two with Slavic.
In the 980s, among Sviatoslav's grandchildren, the Primary Chronicle informs that Vladimir the Great had twelve sons and one daughter. Only one of them, a son, had a Norse name, Gleb (Guðleifr), whereas the other children had Slavic compound names mostly ending with -slav ("fame"). After this generation, the ruling dynasty restricted itself to five Norse male names and one female name, of which the most popular ones would be Oleg, Igor and Gleb (was murdered in 1015 and canonised). The name Rurik (Hrœrekr) reappears in the mid-11th c. but stays restricted in use. Among female names, only Olga stays popular. The Norse names Hákon, Óleifr, and Ivarr remain in use among the East Slavic nobility, but Norse names become rarer at the end of the 10th c. which may point to increased assimilation of the Rus' into the Slavic population.
Among the Norse names that are not used in the ruling family, there is great variation in how they are spelled in the treaties. All names except for Oleg, Olga and Igor are spelled as closely to Old Norse as was possible in Old East Slavic. There were also variations in how the vowels were presented Óleifr was shown as Oleb or Uleb, Hákon as Jakun and Akun, Arnfastr as Arfast and Fastr as Fost. The interdentals /þ/ and /ð/ are rendered as d, but also rarely as z or t as in Turd from Þórðr and in Vuzlev from Guðleifr. The Fr- in the beginning of names which was common in Old Norse but rare in Old East Slavic usually appeared as Pr- as in Prasten from Freysteinn. There was no standard way of spelling ON names.
While the Primary Chronicle uses the same Slavicised forms throughout, rendering Helgi as Ol(e)g, Helga as Ol'ga, Ingvarr as Igor' and Guðleifr as Gleb, they are unlikely to represent the form the names had at the end of the 10th c. Foreign sources give forms closer to the Old Norse originals. Byzantine sources from the second half of the 10th c. preserve the nasalisation in Ingvarr, and in the Cambridge document written in Hebrew, Helgi appears as HLGW, with initial H-. The adaptation of Guðleifr was still not complete by 1073, as shown in a manuscript where there is a vowel between G- and -l- in Gleb, showing that the name is still pronounced with an initial Gu-. Theses sources reflect authentic Old Norse pronunciation of these names, which shows that the adaptation of these names did not take place in the 10th c. but was finished a century later.
When the Primary Chronicle was written in 1113, the annalist used the already fully adapted Old East Slavic forms and he does not appear to have known that Gleb and Vuzlev both represented Guðleifr, but instead kept them distinct. Later in the 12th c., in spite of the renown of the name Igor', the original Norse form Ingvar was borrowed again as a separate name, and it appears in the Hypatian Codex as the name of Ingvar Yaroslavich (d. 1212), and two princes of Ryazan. One of the latter was named Ingvar Igorevich, mentioned in 1207–1219, which shows that the two names were no longer connected. Consequently, Melnikova, considers that the 12th c. stands in stark contrast to the previous two centuries, showing that the Slavicisation of the Rus' elite would have been complete after the second half of the 11th c.
On the other hand, the scholar Omeljan Pritsak considered that Old Norse must have been well known in Kiev and Novgorod, especially during the early decades of the 12th century. The linguist and literary theorist Roman Jakobson held a contrasting opinion, writing that Bojan, active at the court of Yaroslav the Wise, and some of whose poetry may be preserved in the epic poem The Tale of Igor's Campaign, or Slovo, in Old East Slavic, may have heard Scandinavian songs and conversations from visitors as late as 1110 (about the time his own work was done), and that even later, at the court of Mstislav (Haraldr), there must have been many opportunities to hear them. He cautions, however, that it cannot be presumed that Old Norse was still habitually spoken in 12th-century princely courts. Further, he says that Bojan's own life and career did not necessarily coincide with the time of the men whose lives he commemorated, and that he may have written of princes of an earlier period known to him only by report. Scholarly consensus holds as well that the author of the national epic, Slovo, writing in the late 12th century, was not composing in a milieu where there was still a flourishing school of poetry in the Old Norse language.
Rural

There are remains of Old Norse culture as late as the 14th and early 15th centuries in the form of runic or rune-like inscriptions and as personal names. The c. 1000 birch-bark letters from Novgorod contain hundreds of names, most of them Slavic or Christian, and according to Melnikova there are seven letters with Old Norse names, but Sitzman identifies as many as 18, including Staraja Russa no. 36.
The oldest of these letters (no. 526) is from the 1080s, and refers to Asgut from a village in the vicinity of Lake Seliger which was on the road between Novgorod and the central parts of Kievan Rus'. Another letter (no. 130) is from the second half of the 14th century and was sent to Novgorod from another part of the Novgorod Republic and mentions the names Vigar' (Vigeirr or Végeirr), Sten (steinn) of Mikula, Jakun (Hákon), and the widow of a second Jakun. The most interesting of the letters (no. 2) mentions a place called Gugmor-navolok, which may derive from Guðmarr, and two people living in the vicinity called Vozemut (Guðmundr) and Vel'jut (Véljótr). Perhaps a Guðmarr once settled near a portage (navolok) on the route to Lake Onega and naming traditions were preserved in the settlement until the 14th century It is unlikely that he was a new settler because there are no traces of 14th century immigration, nor are there any Scandinavian remains. It is likely that his people adopted the local material culture but kept the family naming traditions.
Sten, the man from Mikula, could be a visitor from Sweden or Swedish-speaking Finland, but the other letters suggest people who had Norse names but were otherwise part of the local culture. They appear together with people of Slavic names and take part in the same activities, and they lived in scattered villages in the north-east periphery of the Novgorod Republic. The area was visited by Novgorod tribute collectors in the 11th century, and was integrated in the republic through colonisation during the 12th and 13th centuries. Since Varangians were part of the administration of Novgorod they likely ventured in the area and sometimes settled there. The use of their naming traditions in the 14th century show the conservatism of some of the Rus' traditions.
The runic script survived for some time in remote parts of Kievan Rus', as evidenced by two finds. One of them is a weaver's slate spindle-whorl found in Zvenigorod in the south-westerm part of Kievan Rus'. The whorl has the runic inscription si{X}riþ, representing the Norse female name Sigrið on the flat top and two crosses and two f runes (![]() ) on the side. The whorl is dated thanks to being found in a layer from the period 1115–1130, when the settlement grew and became a town. No other Scandinavian finds were made except for two other whorls with runic-like inscriptions from the same time. Another whorl with a runic-like inscription was found in the old Russian fort of Plesnesk not far from Zvenigorod. This was a strategically important location and there are several warrior burials dating to the late 10th c. These graves belonged to warriors of a rank similar to a Kievan grand prince and some of them could have been of Scandinavian descent.
) on the side. The whorl is dated thanks to being found in a layer from the period 1115–1130, when the settlement grew and became a town. No other Scandinavian finds were made except for two other whorls with runic-like inscriptions from the same time. Another whorl with a runic-like inscription was found in the old Russian fort of Plesnesk not far from Zvenigorod. This was a strategically important location and there are several warrior burials dating to the late 10th c. These graves belonged to warriors of a rank similar to a Kievan grand prince and some of them could have been of Scandinavian descent.
The inscriptions could be from descendants of the Rus' who settled in the area as protection for the western border of Kievan Rus'. The inscription shows archaic features and the g rune (X) is from the Elder Futhark, which could be due to copying the inscription from generation to generation. In that case the name Sigriðr was inherited for generations in the family. However, the f runes show that this was not the case, because the rune and the cross have similar meaning, although in different religions. Only those who had adhered to Norse paganism and later converted to Christianity would understand their significance, which necessitates a survival of old Norse traditions. It is possible that this community of descendants of late 10th century Rus' who lived in a remote area of Kievan Rus' preserved family names, runic lore in archaic forms, ancestral beliefs and some of the Old Norse language, as evidenced by the runes.

There is another set of inscriptions that look like runes from an old fortification named Maskovichi, on the river route of Western Dvina. It was on the Latvian border and could control the river, although it was located several km away. The fort was used in the 12th and 13th century, and would later turn into a small castle. C. 110 bone fragments with graffiti have been found and they include inscriptions and pictures of warriors and weapons. The runic-like inscriptions are only three to six letters long and some can be interpreted. Some 30 of them are clearly Cyrillic, while 48 are runic. Some of the runic inscriptions are written with mirror-runes (right-to-left) and are illegible, but several can be read as personal names, words and individual runes. The reading of them is uncertain, but they were made by people who knew or remembered runes.
Consequently, in Kievan Rus' there were descendants of the Rus' who preserved parts of their heritage during centuries, the countryside being more conservative than towns.
Legacy

The Norse influence is considered to have left many traces on the Old East Slavic legal code, the Russkaja Pravda, and on literary works such as The Tale of Igor's Campaign, and even on the Byliny, which are old heroic tales about the early Kievan Rus' (Vladimir the Great and others), where one of the words for "hero" is derived from Viking, i.e. vitjaz' (витязь). Several scholars note that this is "of considerable importance generally, as far as social and cultural background of language is concerned". Although, they also note that parallels may arise from general similarities between Germanic and Slavic societies, they state that these similarities remain a profitable field of comparative studies.
Russian contains several layers of Germanic loanwords that need to be separated from the North Germanic words that entered Old East Slavic during the Viking Age. Estimations of the number of loan words from Old Norse into Russian vary from author to author ranging from more than 100 words (Forssman) down to as low as 34 (Kiparsky) and 30 (Strumiński), including personal names. According to the most critical and conservative analysis, commonly used ON words include knut ("knout"), seledka ("herring"), šelk ("silk"), and jaščik ("box"), whereas varjag ("Varangian"), stjag ("flag") and vitjaz' ("hero", from viking) mostly belong to historical novels. Many belong to a special field and ceased to be commonly used in the 13th c., such as berkovec (from ON *birkisk, i.e. "Birka/birk pound", referring to 164 kg), varjag, vitjaz', gol(u)bec (from gulf meaning "box", "crate" or "shed"), grid', gridi (from griði, grimaðr meaning a "king's bodyguard"), lar' (from *lári, lárr meaning "chest", "trunk"), pud (from pund referring to 16.38 kg), Rus' (see etymology section above), skala (skál, "scale"), ti(v)un (thiónn, "Novgorod official" in the 12th c.), šelk (*silki, "silk"), and jabeda (embætti, "office").
Norse settlers also left many toponyms across north-western Russia, where the names of settlements or nearby creeks reveal the name of the Norse settler, or where he came from. A man named Asviðr settled in a place today known as Ašvidovo, Bófastr in Buchvostovo, Dýrbjǫrn in Djurbenevo, Einarr in Inarevo, Kynríkr in Kondrikovo, Rødríkr in Redrikovo, Ragnheiðr in Rognedino, Snæbjǫrn in Sneberka, Sveinn in Sven', Siófastr in Suchvostovo, Steingrímr in Stegrimovo, and Thorbjǫrn in Turyborovo. More common Norse names have left several toponyms, such as Ivarr in Ivorovo and Ivorovka, Hákon in Jakunovo and Jakunicha, Oléf in Ulebovo, Olebino and Olibov, and Bjǫrn, appears in Bernovo, Bernjatino, Bemniški, Bernavo, and in Bernoviči. There is also Veliž which is the same place name as Vællinge, an old estate near Stockholm, in Sweden. Many place names also contain the word Varangian, such as Varegovo, Varež(ka), Varyzki, Varjaža, Verjažino, and Verjažka. Other names recall the Kolbangians, such as Kolbežycze, Kolbjagi, and Kolbižicy, and a group called "Burangians" (Byringar), in the names Burjaži, Buregi, Burigi, Burezi, Burjaki, Burjaz', etc.
As for other influences on the Russian language, they are less apparent, and could be due to coincidence. In Old Norse and the modern Scandinavian langues (except for the Jutish dialect of Danish), the definite article is used as an enclitic article after the noun. In Europe, this is otherwise only known from Basque and from the Balkan sprachbund, in languages such as Macedonian and Bulgarian. However, it also appears in dialects in Northern Russia, too far away from Bulgarian to have been influenced by it. As standard Russian has no definite article at all, the appearance of a postpositioned definite article in Northern Russian dialects may be due to influence from Old Norse. As for standard Russian, just like in Old Norse, and in the modern Scandinavian languages, there is a passive construction using an enclitic reflexive pronoun, -s in North Germanic and -s'(a) in Russian. However, it is not known from written Russian before the 15th c. and a corresponding construction has appeared independently in modern Romance languages, e.g. Italian vendesi.
Archaeology

Numerous artefacts of Scandinavian affinity have been found in northern Russia (as well as artefacts of Slavic origin in Sweden). However, exchange between the northern and southern shores of the Baltic had occurred since the Iron Age (albeit limited to immediately coastal areas). Northern Russia and adjacent Finnic lands had become a profitable meeting ground for peoples of diverse origins, especially for the trade of furs, and attracted by the presence of oriental silver from the mid-8th century AD. There is an undeniable presence of goods and people of Scandinavian origin; however, the predominant people remained the local (Baltic and Finnic) peoples.
In the 21st century, analyses of the rapidly growing range of archaeological evidence further noted that high-status 9th- to 10th-century burials of both men and women in the vicinity of the Upper Volga exhibit material culture largely consistent with that of Scandinavia (though this is less the case away from the river, or further downstream). This has been seen as further demonstrating the Scandinavian character of elites in "Old Rusʹ".
There is uncertainty as to how small the Scandinavian migration to Rus' was, but some recent archaeological work has argued for a substantial number of 'free peasants' settling in the upper Volga region.
The quantity of archaeological evidence for the regions where the Rus' people were active grew steadily through the 20th century, and beyond, and the end of the Cold War made the full range of material increasingly accessible to researchers. Key excavations have included those at Staraya Ladoga, Novgorod, Rurikovo Gorodische, Gnyozdovo, Shestovitsa, numerous settlements between the Upper Volga and the Oka. Twenty-first century research, therefore, is giving the synthesis of archaeological evidence an increasingly prominent place in understanding the Rus'. The distribution of coinage, including the early 9th-century Peterhof Hoard, has provided important ways to trace the flow and quantity of trade in areas where Rus' were active, and even, through graffiti on the coins, the languages spoken by traders.
There is also a great number of Varangian runestones, on which voyages to the east (Austr) are mentioned.
In the mythical lays of the Poetic Edda, after her true love Sigurd is killed, Brunhild (Brynhildr in Old Norse) has eight slave girls and five serving maids killed and then stabs herself with her sword so that she can be with him in Valhalla, as told in The Short Lay of Sigurd, similarly to the sacrifices of slave girls that Ibn Fadlan described in his eyewitness accounts of the Rus'. Swedish ship burials sometimes contain both males and females. According to the website of Arkeologerna (The Archaeologists), part of the National Historical Museums in Sweden, archaeologists have also found in an area outside of Uppsala a boat burial that contained the remains of a man, a horse and a dog, along with personal items including a sword, spear, shield, and an ornate comb. Swedish archeologists believe that during the Viking age Scandinavian human sacrifice was still common and that there were more grave offerings for the deceased in the afterlife than in earlier traditions that sacrificed human beings to the gods exclusively. The inclusion of weapons, horses and slave girls in graves also seems to have been practiced by the Rus'.
Historiography
Further information: Anti-NormanismPrior to the 18th century, it was the consensus of Russian historians that the Rus' arose out of the native Slavic populations of the region. This changed following a 1749 presentation by German historian Gerhardt Friedrich Müller before the Russian Academy of Sciences, built in part on earlier work by Gottlieb-Siegfried Bayer and based on primary sources, particularly the Russian Primary Chronicle. He suggested that the founders of the Rus' were ethnically Scandinavian Varangians, what became known as the 'Normanist' view. Though Müller met with immediate nationalistic opprobrium, by the end of the century his views represented the consensus in Russian historiography. The attribution of a Slavic origin to the Rus' saw a politically motivated 'anti-Normanist' resurgence in the 20th century within the Soviet Union, and this revisionist view also received nationalistic support in the nation-building post-Soviet states, but the broad consensus of scholars is that the origin of the Rus' lies in Scandinavia.
Genetics
The cemetery of Ostriv is located in the region along the Ros' River. By 2020, 67 inhumation graves had been excavated there and dated from the early 11th century. Most of the artefacts found there are uncommon in Ukraine, but typical for the East Baltic region. This suggests a complex multi-ethnic population, presumably consisting of Baltic region migrants and locals. The ancient DNA analysis shows that the tested individuals cluster with present-day Icelandic and East Baltic populations. They are on the edge of the variability of previously published Swedish Vikings and close to dated medieval individuals from Estonia.
Notes
- Also commonly spelled Rus without the apostrophe; Old East Slavic: Роусь; Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian: Русь; Greek: Ῥῶς, romanised: Rhos
References
- Rosenwein, Barbara H. (14 February 2014). A Short History of the Middle Ages, Volume I: From c.300 to c.1150, Fourth Edition. University of Toronto Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-4426-0616-6.
- Dolukhanov, Pavel (10 July 2014). The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus. Routledge. p. 182. ISBN 978-1-317-89222-9.
- Magill, Frank N. (12 November 2012). The Middle Ages: Dictionary of World Biography, Volume 2. Routledge. p. 803. ISBN 978-1-136-59313-0.
- ^ Duczko 2004, p. 60, These two original centres of Rus were Staraja Ladoga and Rurikovo Gorodishche.
- ^ Duczko 2004, p. 60.
- Duczko 2004, p. 1, The state of the Eastern Slavs—Russia, or Rhosia according to the Byzantines of mid-tenth century—was called in the medieval Norse literature Gardariki, or in the earlier, Viking-age sources just Gardar, a term originally restricted to the non-Slav territory of Ladoga-Ilmen.
- ^ Melnikova, E.A. (2003) The Cultural Assimilation of the Varangians in Eastern Europe from the Point of View of Language and Literacy in Runica – Germ. – Mediavalia (heiz./n.) Rga-e 37, pp. 454–465 Archived 15 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Hellquist (1922), p. 668 Ryssland
- ^ Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in The Viking World Archived 14 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7).
- ""Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press". Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- Hellquist (1922), p. 650f Rodd
- Blöndal (2007), p. 1.
- ^ "Русь in "Vasmer's Etymological Dictionary" online". Archived from the original on 2 July 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ^ Hellquist (1922), p. 654 Roslagen
- Hellquist (1922), p. 654f Rospigg
- Hellquist (1922), p. 339 2. lag
- Stefan Brink; Neil Price (31 October 2008). The Viking World. Routledge. pp. 53–54. ISBN 978-1-134-31826-1. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- Joel Karlsson (2012) Stockholm university https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.123007.1360163562!/menu/standard/file/Karlsson_Joel_Ofria_omnamnda-pa_runstenar.pdf Archived 22 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine page 4-5
- Pritsak (1981), p. 348.
- Can also be spelled roðʀ, but ʀ and z are interchangeable.
- Larsson, Mats G. (1997). Rusernas rike in Vikingar i österled. Atlantis, Stockholm. ISBN 91-7486-411-4. pp. 14–15.
- Duczko 2004, pp. 67–70.
- Gary Dean Peterson (21 June 2016). Vikings and Goths: A History of Ancient and Medieval Sweden. McFarland. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-4766-2434-1. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Duczko 2004, p. 60, Ladoga, or as it was then called Aldeigja, was the earliest and the most important place, while Gorodishche, probably with the Norse name Holmr, was founded more than a century later.
- Duczko 2004, p. 61, The Ladoga area was the core of the kaganate of Rus: it was from here the Rhos' envoys went to Constantinople in 838.
- Gwyn Jones (2001). A History of the Vikings. Oxford University Press. p. 245. ISBN 978-0-19-280134-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Sverrir Jakobsson (2020). The Varangians: In God's Holy Fire. Springer Nature. p. 64. ISBN 978-3-030-53797-5. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- René Chartrand; Keith Durham; Mark Harrison; Ian Heath (22 September 2016). The Vikings. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4728-1323-7. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Mickevičius, Arturas (30 November 1997). "Curonian "Kings" and "Kingdoms" of the Viking Age". Lithuanian Historical Studies. 2 (1): 11. doi:10.30965/25386565-00201001.
- Duczko 2004, p. 10.
- Elizabeth Warner (1 July 2002). Russian Myths. University of Texas Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-292-79158-9. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Duczko 2004, p. 210.
- Marika Mägi, In Austrvegr: The Role of the Eastern Baltic in Viking Age Communication Across the Baltic Sea Archived 26 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, The Northern World, Volume 84 (Leiden: Brill, 2018), p. 195, citing Alf Thulin, 'The Rus' of Nestor's Chronicle', Mediaeval Scandinavia, 13 (2000)
- Forte, Angelo; Oram, Richard; Pedersen, Frederik (2005). Viking Empires. Cambridge University Press. pp. 13–14. ISBN 0-521-82992-5. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Kaplan, Frederick I. (1954). "The Decline of the Khazars and the Rise of the Varangians". American Slavic and East European Review. 13 (1): 1–10. doi:10.2307/2492161. ISSN 1049-7544. JSTOR 2492161.
- Orest Subtelny (1 January 2000). Ukraine: A History. University of Toronto Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-8020-8390-6. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Ole Crumlin-Pedersen (31 December 2013). "Vikling Warriors and the Byzantine Empire". In Line Bjerg; John H. Lind; Soren Michael Sindbaek (eds.). From Goths to Varangians: Communication and Cultural Exchange between the Baltic and the Black Sea. Aarhus University Press. pp. 297–. ISBN 978-87-7124-425-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Paul R. Magocsi (1 January 2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples. University of Toronto Press. pp. 63–65. ISBN 978-1-4426-1021-7. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Birgit Sawyer (2000). The Viking-age Rune-stones: Custom and Commemoration in Early Medieval Scandinavia. Oxford University Press. pp. 116–119. ISBN 978-0-19-820643-9. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- I︠A︡ Zaprudnik; Jan Zaprudnik; Ânka Zaprudnìk (16 August 1993). Belarus: At A Crossroads In History. Avalon Publishing. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-8133-1339-9. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- Judith Jesch (2001). Ships and Men in the Late Viking Age: The Vocabulary of Runic Inscriptions and Skaldic Verse. Boydell & Brewer. pp. 86, 90, 178. ISBN 978-0-85115-826-6. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Blöndal (2007), pp. 223–224.
- Duczko (2004), p. 60, two towns used to symbolise the early history of Russia: Kiev and Novgorod.
- John Meyendorff (24 June 2010). Byzantium and the Rise of Russia: A Study of Byzantino-Russian Relations in the Fourteenth Century. Cambridge University Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-521-13533-7. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- Duczko 2004, p. 60, The latter town, Novgorod..., was another centre of the same culture but founded in different surroundings, where some old local traditions moulded this commercial city into a mighty oligarchic republic.
- Duczko 2004, p. 60, The area between the lakes was the original Rus, and it was from here its name was transferred to the Slav territories on the middle Dnieper, which eventually became "Ruskaja zemlja"—the land of Rus.
- ^ Duczko 2004, p. 207.
- Duczko 2004, p. 60, It was from here the Rus moved eastward, to the Finno-Ugrian lands of the Volga-Oka region, and southward, to the Dnieper among the Slavs.
- Alexander Basilevsky (5 April 2016). Early Ukraine: A Military and Social History to the Mid-19th Century. McFarland. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-4766-2022-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
The main activity was the production of amber and glass beads for the fur trade where the pelts were bought from local hunters and sold to the Bulgars and Khazars for valuable silver dirhams. In fact, the Staraia Ladoga settlements were built initially as a manufacturing center and to conduct trade in the north and in the Baltic region. This is confirmed by silver dirham finds in some of the earliest log buildings constructed there
- Duczko 2004, p. 115.
- Duczko 2004, p. 127.
- Larsson, G. (2013). Ingvar the Fartraveller's Journey: Historical and Archaeological Sources (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- Blöndal (2007), pp. 60–62; DeVries (1999), pp. 29–30.
- Pritsak (1981), p. 386.
- "Vilhelm Thomsen. (1882). Ryska rikets grundläggning genom Skandinaverna, p. 155". 1882. Archived from the original on 21 September 2021. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- E.g. Svafrlami and Rollaugr in Hervarar saga, Ráðbarðr in Sögubrot and Hreggviðr in Göngu-Hrólfs saga.
- In e.g. Óláfs saga helga.
- Uspenskij, Fjodor (2011). "A NEW APPROACH TO THE ETYMOLOGY OF THE OLD NORSE NAME OF KIEV — KØNUGARÐR: (the thesis of Elsa Melin on the Name given to Kiev in the Icelandic Sagas, with an Excursus on Kind in Place-Names)". Scrinum. 7–8 (2): 326–327. doi:10.1163/18177565-90000255. Archived from the original on 11 March 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ There were also about 14 other words borrowed from Old East Slavic: *dyblitsa/dyfliza (*tĭmĭnica, "dungeon"), *Grikkiʀ (Griky, "Greek"), *kassa/kaza (kaša, "gruel"), læðia (*lodĭja, "boat"), *Læsiʀ (l'äs'i, "Poles"), *poluta (polota, "palace"), *polyði (*pol'ud'je, "Northmen's winter tour of East Slavic areas for lodging and provisions"), *sabaló (soboljĭ, "sable skin/fur"), *stóll (stolǔ, "banquet table"), *taparöks (topor-, "small war ax"), *tulka (tǔlkovati, "to interpret"), *tulkʀ (tǔlkǔ, "interpreter"), *Waldimarr (Vol(o)dimēr, "ruler of peace"), and *warta (vor(o)ta, "gate"), in The Nordic Languages (2002), p. 1043, citing Strumiński (1996, 246–54).
- Hellquist (1922), p. 991 Torg
- Braun, F. & Arne, T. J. (1914). "Den svenska runstenen från ön Berezanj utanför Dneprmynningen", in Ekhoff, E. (ed.) Fornvännen årgång 9 pp. 44–48. Archived 4 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine, p. 48
- Pritsak (1981), p. 306.
- Pritsak (1981), p. 366.
- Runic Dictionary Entry for grimm Archived 24 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine at the runic dictionary of the University of Nottingham.
- Aannestad, Hanne Lovise; Pedersen, Unn; Moen, Marianne; Naumann, Elise; Berg, Heidi Lund (26 October 2020). Vikings Across Boundaries: Viking-Age Transformations – Volume II. Routledge. p. 185. ISBN 978-1-000-20470-4.
- Jansson, Sven B. F. (1980). Runstenar. STF, Stockholm. ISBN 91-7156-015-7 p. 31
- Pritsak (1981), p. 389.
- Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (2014), pp. 66–67.
- Duczko (2004), p. 210
- The Russian Primary Chronicle: Laurentian Text, ed. and trans. by Samuel Hazzard Cross and Olgerd P. Sherbowitz-Wetzor (Cambridge, MA: The Medieval Academy of America, 1953), ISBN 0-910956-34-0, s.aa. 6368–6370 (860–862 CE) .
- Kotlyar, M. Prinices of Kiev Kyi and Askold. Warhitory.ukrlife.org. 2002
- Serhii Plokhy (7 September 2006). The Origins of the Slavic Nations: Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-139-45892-4. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Iver B. Neumann; Einar Wigen (19 July 2018). "The Steppe in the Emergent Rusʹ Polity". The Steppe Tradition in International Relations: Russians, Turks and European State Building 4000 BCE–2017 CE. Cambridge University Press. pp. 163, 170. ISBN 978-1-108-36891-9.
From the 860s onwards, then, but for all we know, even before that, there existed a Viking-led polity that was headed by a khagan and known as the Rusʹ Khaganate. Novoseltsev (1982) and Noonan (2001) make the case that the title 'khagan' was not only taken over from the Khazars (of which there is little doubt) but that it was specifically intended to ease the transfer of tribute-paying from one (Khazar) to another (Rusʹ) and generally to stake a claim first to equality and then to succession. As noted earlier, Noonan (2001) postulates a fully fledged translatio imperii.
- Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (2014), p. 68.
- ^ P.B. Golden, "Rūs", in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs. Consulted online on 26 July 2018 doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_COM_0942.
- ^ James E. Montgomery, 'Ibn Faḍlān and the Rūsiyyah Archived 16 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine', Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies, 3 (2000), 1–25.
- Ann Christys, Vikings in the South (London: Bloomsbury, 2015), pp. 15–45 (esp. p. 31).
- Brink & Price (2008), p. 552
- Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (2014), p. 73.
- ' A. Seippel (ed.), Rerum normannicarum fonts arabici, 2 vols (Oslo: Brøgger, 1896). This edition of Arabic sources for references to Vikings was translated into Norwegian, and expanded, by H. Birkeland (ed. and trans.), Nordens historie: Middlealderen etter arabiske kilder (Oslo: Dyburad, 1954). It was translated into English by Alauddin I. Samarra'i (trans.), Arabic Sources on the Norse: English Translation and Notes Based on the Texts Edited by A. Seippel in 'Rerum Normannicarum fontes Arabici (unpublished doctoral thesis, University of Wisconsin–Madison, 1959).
- James E. Montgomery, 'Ibn Rusta's Lack of "Eloquence", the Rus, and Samanid Cosmography', Edebiyat, 12 (2001), 73–93.
- James E. Montgomery, 'Arabic Sources on the Vikings', in The Viking World, ed. by Stefan Brink (London: Routledge, 2008), pp. 550–61.
- James E. Montgomery, 'Vikings and Rus in Arabic Sources', in Living Islamic History, ed. by Yasir Suleiman (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2010), pp. 151–65.
- ^ Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (2014).
- Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (2014), pp. 70–78.
- Jones, Gwyn (2001). A History of the Vikings. Oxford University Press. p. 164. ISBN 0-19-280134-1.
- Quoted from National Geographic, March 1985;
Compare:Ferguson, Robert (2009). The Hammer and the Cross: A New History of the Vikings. Penguin UK. ISBN 978-0-14-192387-1. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
They have no fields but simply live on what they get from the Slavs' lands.
- Eleanor Rosamund Barraclough (2016). Beyond the Northlands: Viking Voyages and the Old Norse Sagas. Oxford University Press. p. 172. ISBN 978-0-19-870124-8. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- Volt, Ivo; Janika Päll (2005). Byzantino-Nordica 2004: Papers Presented at the International Symposium of Byzantine Studies Held on 7–11 May 2004 in Tartu, Estonia. Morgenstern Society. p. 16. ISBN 978-9949-11-266-1. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- H. R. Ellis Davidson, The Viking Road to Byzantium (London: Allen & Unwin, 1976), p. 83.p. 83.
- Blöndal (2007), p. 9.
- Fedir Androshchuk (31 December 2013). "Byzantium and the Scandinavian world in the 9th–!0th century". In Line Bjerg; John H. Lind; Soren Michael Sindbaek (eds.). From Goths to Varangians: Communication and Cultural Exchange between the Baltic and the Black Sea. Aarhus University Press. p. 168. ISBN 978-87-7124-425-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- Skli︠a︡renko, V. H. (2006). Rusʹ i vari︠a︡hy: istoryko-etymolohichne doslidz︠h︡enni︠a︡. Kyïv: Dovira. pp. 75–89. ISBN 966-507-205-6.
- Brajchevskij, M.Yu. (1985). ""Russkie" nazvaniya porogov u Konstantina Bagryanorodnogo". Zemli Yuzhnoj Rusi V IX–XIV Vv. (Kyiv, Naukova dumka): 26. Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus; Moravcsik, Gyula; Jenkins, Romilly J. H. (1967). De administrando imperio (New, Revised ed.). Washington, D.C.: Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies. pp. 58–61. ISBN 978-0-88402-021-9.
- Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus; Meursius, Johannes (1611). De administrando imperio (in Greek). Leiden: Ioannes Balduini. pp. 16–18. Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- Vladimir Petrukhin (2007). "Khazaria and Rus': An examination of their historical relations". In Peter B. Golden; Haggai Ben-Shammai; András Róna-Tas (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. BRILL. pp. 245–246. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- ^ "Annales Bertiniani". Die Monumenta Germaniae Historica. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- Nazarenko, A. V.; Dzhakson, T. N.; Konovalova, I. G.; Podosinov, A. V. (2010). Drevni︠a︡i︠a︡ Rusʹ v svete zarubezhnykh istochnikov: khrestomatii︠a︡. Vol. 4. Moskva: Russkiĭ fond sodeĭstvii︠a︡ obrazovanii︠u︡ i nauke. p. 20. ISBN 978-5-91244-008-3. Archived from the original on 11 March 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- Duczko 2004, pp. 49–50.
- Jonathan Shepard (31 October 2008). "The Viking Rus and Byzantium". In Stefan Brink; Neil Price (eds.). The Viking World. Routledge. p. 497. ISBN 978-1-134-31826-1. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- Janet Martin (6 April 2009). "The First East Slavic State". In Abbott Gleason (ed.). A Companion to Russian History. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-0842-6.
- Henrik Birnbaum (8 January 2021). "Christianity Before Christianization". In Boris Gasparov; Olga Raevsky-Hughes (eds.). California Slavic Studies, Volume XVI: Slavic Culture in the Middle Ages. Vol. XVI. Univ of California Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-520-30918-0.
- Steinacher, Roland (2010). "The Herules: Fragments of a History". In Curta, Florin (ed.). Neglected Barbarians. ISD. ISBN 978-2-503-53125-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2022. pp.43-44.
- Urbanczyk, Przemyslaw. "Who were the early Rusʹ?". ACADEMIA. Archived from the original on 12 March 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- Liudprand, Bishop of Cremona; Wright, F. A. (1930). The works of Liudprand of Cremona ... New York: E.P. Dutton & company. p. 38. Archived from the original on 9 January 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- Thomsen, Vilhelm (1877). The Relations Between Ancient Russia and Scandinavia and the Origin of the Russian State: ... Oxford and London: James Parker and Company. p. 47. Archived from the original on 12 March 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- Blöndal (2007), p. 40.
- Fagrskinna ch. 21 (ed. Finnur Jónsson 1902–8, p. 108).
- Chadwick, N. (1946). The Beginnings of Russian History. Cambridge at the University Press. pp. 84–89.
- In the 11 c., Adam of Bremen wrote about the Temple at Uppsala, where there were three statues of the main gods, Odin, Thor and Freyr. In Norse mythology, Freyr was seen as the progenitor of the Swedish royal house.
- Stefanovich, Petr S. (2016). Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas, 2016, Neue Folge, Bd. 64, H. 4, pp. 529–544.
- Yaroslav Shchapov (1992). "The assimilation by Kievan Rus' of the classical and Byzantine Heritage". In Yves Hamant (ed.). The Christianization of Ancient Russia: A Millennium, 988–1988. Unesco. pp. 62–63. ISBN 978-92-3-102642-3. Archived from the original on 24 September 2021. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- Urbanczyk, Przemyslaw (2010). "Archaeological view of Christianization on two sides of the Baltic Sea" (PDF). Archeologia Polski. 55. Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, Polish Academy of Sciences: 89–91, 99. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
The written evidence gives us a view of the conversion of the peri-Baltic area through the eyes of the successful Christianizers who painted a process that was quick, historically necessary, and politically effective Therefore archaeologists have been convinced that discerning between 'pagan' and 'Christian' burials does not pose much of a problem and that a threshold of change exists. Today it is clear that the story of building a shared Christian identity was a much longer and difficult process on both sides of the Baltic Sea All this resulted in a long and difficult Christianization process and a vigorous resistance on the part of the indigenous population. This is archaeologically witnessed in syncretic practices and pagan burials which were still being observed on the peripheries in the High Middle Ages.
- Omeljan Pritsak (1985). "On the Writing of History in Kievan Rus'". In Tore Nyberg (ed.). History and Heroic Tale: A Symposium. Odense University Press. p. 154. ISBN 978-87-7492-534-7. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- Roman Jakobson (2011) . Russian Epic Studies. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 103–107. ISBN 978-3-11-088958-1.
The connections are present, then, and we may assume that Bojan himself, as late as 1110, may have heard Scandinavian songs and conversations from visitors; even later, at the court of that Mstislav who was also called Haraldr, the opportunity must have presented itself often. But this is quite different from supposing that Old Norse was habitually still spoken in twelfth-century court circles, or even among traders, except in the presence of visitors.
- ^ Sitzmann, A. 2007. "Die skandinavischen Personennamen in den Birkenrindeninschriften" Scando-Slavica 53; 25–31
- ^ Franklin, S. 2002 (2004). Writing, Society and Culture in Early Rus, c.950–1300. Cambridge University Press. p. 113
- UA Fridell2004;1 in Runor Archived 9 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Duchits, L. V. and Melnikova, E. A. "Nadpisi i znaki na kostiakh s gorodishscha Maskovichi (Severo-Zapadnaia Belorussiia) DGTSSSR 1980 god (1981), pp. 185–216
- Forssman (1983) Skandinavische Spuren in der alt-russischen Sprache und Dichtung. En Beitrag zur Sprach- und Kulturgeschichte des ost- und nord-europäischen Raumes im Mittelalter (Ed. B. Forssman), 2nd ed. München. pp. 24–27, pp. 80–99
- ^ The Nordic Languages (2002), p. 1041
- ^ The Nordic Languages (2002), p. 1042
- ""витязь". "Vasmer's Etymological Dictionary" online". Archived from the original on 3 August 2021. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- The Nordic Languages (2002), p. 1044
- Proto-Germanic: glaz, duma, knjaz', skot, tyn, chižin, chlev, cholm, šolom. Gothic: bljudo, verbljud, kotel, kupit', -kusit', lečit', lest', lichva, osel, polk, stupa, steklo, chleb, chudožnik, car', čužoj. "Balkan-Germanic": bukva, vinograd, smokva, userjaz'/g, skut. West Germanic: bondar', bočka, bronja, buk, gradil', doska, izba, klej, korol', krest, luk, myto, petlja, penjaz', pila, plug, pop, post, remen', truba.
- Forssman (1983) Skandinavische Spuren in der alt-russischen Sprache und Dichtung. En Beitrag zur Sprach- und Kulturgeschichte des ost- und nord-europäischen Raumes im Mittelalter (Ed. B. Forssman), 2nd ed. München. pp. 75–80
- Kiparsky, V. (1975). Russische historische Grammatik. Vol III: Entwicklung des Wortschatzes. Heidelberg. pp. pp. 95–97.
- Strumiński, Bohdan. (1996). Linguistic Interrelations in Early Rusʹ. Northmen, Finns and East Slavs. (Ninth to eleven centuries). Rome/Edmonton/Toronto. pp. 229–243.
- ^ The Nordic Languages (2002), p. 1043
- Franklin & Shepard (1996), p. 9.
- Franklin & Shepard (1996), p. 12.
- Franklin & Shepard (1996), pp. 22–25.
- ^ Duczko (2004).
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104.
- I. Jansson, 'Warfare, Trade or Colonisation? Some General Remarks on the Eastern Expansion of the Scandinavians in the Viking Period', in The Rural Viking in Russia and Sweden, ed. by P. Hansson (Örebro, 1997), pp. 47–51.
- Jonathan Shepherd, 'Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics', English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 (pp. 395–96) doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104.
- Sean Nowak (1998). Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Runes and Runic Inscriptions in Göttingen, 4–9 August 1995. Walter de Gruyter. p. 651. ISBN 978-3-11-015455-9. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- Carolyne Larrington, ed. (2014). "A Short Poem about Sigurd". The Poetic Edda. Oxford University Press. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-19-967534-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- Ninna Bengtsson. "Two rare Viking boat burials uncovered in Sweden". arkeologerna.com (in Swedish). Archived from the original on 6 July 2019. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- Denise Roos (2014) Människor deponerade i våtmark och grav En analys av äldre järnålderns och vikingatidens deponeringstraditioner. https://www.archaeology.su.se/polopoly_fs/1.208758.1414677865!/menu/standard/file/Roos_Denise_Manniskor_deponerade_i_vatmark_och_grav.pdf Archived 5 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine page 23
- Shephard, pp. 122–3
- Pritsak, Omeljan, "The Origin of the Rusʹ", Russian Review, vol. 36, No. 3 (Jul. 1977), pp. 249–273
- Serhii Plokhy, Ukraine and Russia: Representations of the Past (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2008), chapter 1.
- Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (pp. 44–45).
- Omeljan Pritsak, "Rus'", in Medieval Scandinavia: An Encyclopedia Archived 26 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, ed. by Phillip Pulsiano (New York: Garland, 1993), pp. 555–56.
- Duczko 2004, pp. 3–9.
- Abbott Gleason, 'Russian Historiography after the Fall', in A Companion to Russian History, ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 1–14 (p. 5).
- Elena Melnikova, 'The "Varangian Problem": Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (p. 42).
- Roman Shiroukhov et al. (2022) Baltic Migrants in the Middle Dnipro Region: A Comparative Study of the Late Viking Age Archaeological Complex of Ostriv, Ukraine, Medieval Archaeology, 66:2, 221–265, DOI: 10.1080/00766097.2022.2118419
Bibliography
Main article: Bibliography of the history of the Early Slavs and Rusʹ- Blöndal, Sigfús (2007). Benedikz, Benedikt S. (ed.). The Varangians of Byzantium. Cambridge University. ISBN 978-0-521-21745-3.
- Bandle, O., ed. (2002). The Nordic Languages, An International Handbook of the History of the North Germanic Languages. Vol. 1. Braunmüller, K.; Jahr, E. H.; Karker, A.; Naumann, H. P.; Teleman, U.; Consulting Editors: Elmevik, L.; Widmark, G. HSK 22.1. Berlin, New York: Walter de Gruyter.
- Brink, Stefan; Price, Price (2008). The Viking World. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-31826-1. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- Bury, John Bagnell; Gwatkin, Henry Melvill (1936). The Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3. University Press. ISBN 0-415-32756-3.
- Christian, David (1999). A History of Russia, Mongolia, and Central Asia. Blackwell.
- Danylenko, Andrii (2004). "The name Rus': In search of a new dimension". Jahrbueher für Geschichte Osteuropas. 52: 1–32.
- Davidson, H.R. Ellis (1976). The Viking Road to Byzantium. Allen & Unwin.
- Davies, Norman (1996). Europe: A History. New York: Oxford University Press.
- DeVries, Kelly (1999). The Norwegian Invasion of England in 1066. Boydell & Brewer Ltd. ISBN 978-0-85115-763-4.
- Dolukhanov, Pavel M. (1996). The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus. New York: Longman.
- Duczko, Wladyslaw (2004). Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe. The Northern World. Vol. 12. Brill. ISBN 90-04-13874-9. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- Franklin, Simon; Shepard, Jonathan (1996). The Emergence of Rus: 750–1200. Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-49091-8. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- Goehrke, C. (1992). Frühzeit des Ostslaven. Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft.
- Hellquist, Elof (1922). Svensk etymologisk ordbok [Swedish etymological dictionary] (in Swedish). Lund: Gleerup.
- Logan, F. Donald (2005). The Vikings in History. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 0-415-32756-3.
- Lunt, Horace Gray (1975). On the language of old Rus: some questions and suggestions. Harvard University, Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute.
- Magocsi, Paul R. (1996). A History of Ukraine. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
- The Annals of Saint-Bertin. Ninth-Century Histories. Vol. 1. Translated by Nelson, Janet L. Manchester and New York. 1991.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Pritsak, Omeljan (1981). The Origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press.
- Stang, Hakon. (1996). The Naming of Russia. Oslo: Middelelser.
- Thorir Jonsson Hraundal (January 2014). "New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources". Viking and Medieval Scandinavia. 10: 65–97. doi:10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213.
- Tolochko, Olksiy P (2008). "The Primary Chronicle's 'Ethnography' Revisited: Slavs and Varangians in the Middle Dnieper Region and the Origin of the Rus' State". In Garipzanov, Ildar H.; Geary, Patrick J.; Urbańczyk, Przemysław (eds.). Franks, Northmen and Slavs. Identities and State Formation in Early Medieval Europe. Brepols.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2005). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 1-4381-2918-1.
- Gerard Miller as the author of the Normanist theory (Brockhaus and Efron)
External links
 Media related to Rus' people at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Rus' people at Wikimedia Commons- James E. Montgomery, 'Ibn Faḍlān and the Rūsiyyah', Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies, 3 (2000), 1–25. Archive.org. Includes a translation of Ibn Fadlān's discussion of the Rūs/Rūsiyyah.
| Garðaríki | ||
|---|---|---|
| Names in italics are settlements whose Norse names are not recorded | ||
| Volkhov-Volga trade route |  | |
| Dvina-Dnieper trade route | ||
| Other locations | ||
| Norse people | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| History | 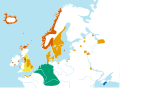 | ||
| Expansion |
| ||
| Paganism and mythology | |||
| Cosmology | |||
| Rituals and worship | |||
| Society | |||
| Events | |||
| Sources | |||
| Settlements | |||
| Belarus articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||
| Geography | |||||
| Politics | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Society |
| ||||
| Ukraine articles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||
| Geography | |||||||
| Politics | |||||||
| Economy | |||||||
| Society |
| ||||||
| History of Europe | |
|---|---|
| Prehistory | |
| Classical antiquity | |
| Middle Ages |
|
| Modern period |
|
| See also | |