| Revision as of 12:25, 27 June 2022 edit2001:818:dcba:3800:25f5:730b:8607:6150 (talk) →Distribution and habitat: added Portugal to the list, since it's one of the most common tree species that can be found there.← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:17, 28 June 2022 edit undoPeter coxhead (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors204,308 edits not native to Portugal according to Plants of the World Online.Next edit → | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| ==Distribution and habitat== | ==Distribution and habitat== | ||
| The range of ''Pinus halepensis'' extends from ], ], ], |
The native range of ''Pinus halepensis'' extends from ], ], ], and ] north to southern ], ], ], ], ], and ], and east to ]. It has been introduced into many parts of the world, including ]. There is an outlying population (from which it was first described) in ], ], southern ], ], ] and ]. | ||
| The species is generally found at low altitudes, mostly from sea level to {{convert|200|m|abbr=on}}, but can grow above {{convert|1000|m|abbr=on}} in southern and eastern Spain, well over {{convert|1200|m|abbr=on}} on ], and up to {{convert|1700|m|abbr=on}} in the south, in Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia.<ref name="farjon">Farjon, A. (2005). ''Pines. Drawings and Descriptions of the genus Pinus''. Brill, Leiden. {{ISBN|90-04-13916-8}}.</ref><ref name="rushforth">Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins {{ISBN|0-00-220013-9}}.</ref> | The species is generally found at low altitudes, mostly from sea level to {{convert|200|m|abbr=on}}, but can grow above {{convert|1000|m|abbr=on}} in southern and eastern Spain, well over {{convert|1200|m|abbr=on}} on ], and up to {{convert|1700|m|abbr=on}} in the south, in Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia.<ref name="farjon">Farjon, A. (2005). ''Pines. Drawings and Descriptions of the genus Pinus''. Brill, Leiden. {{ISBN|90-04-13916-8}}.</ref><ref name="rushforth">Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins {{ISBN|0-00-220013-9}}.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 28 June 2022
Species of conifer
| Pinus halepensis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Pinus halepensis in Sounion Natural Park, Greece | |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | P. subg. Pinus |
| Section: | P. sect. Pinus |
| Subsection: | Pinus subsect. Pinaster |
| Species: | P. halepensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus halepensis Mill. | |
| |
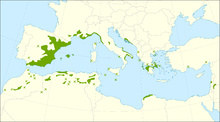
| Distribution map | |
Pinus halepensis, commonly known as the Aleppo pine, also known as the Jerusalem pine, is a pine native to the Mediterranean region.
Description
Pinus halepensis is a small to medium-sized tree, 15–25 metres (49–82 feet) tall, with a trunk diameter up to 60 centimetres (24 inches), exceptionally up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in). The bark is orange-red, thick, and deeply fissured at the base of the trunk, and thin and flaky in the upper crown. The leaves ('needles') are very slender, 6–12 cm (2+1⁄4–4+3⁄4 in) long, distinctly yellowish green, and produced in pairs (rarely a few in threes). The cones are narrow conic, 5–12 cm (2–4+3⁄4 in) long and 2–3 cm (3⁄4–1+1⁄4 in) broad at the base when closed, green at first, ripening glossy red-brown when 24 months old. They open slowly over the next few years, a process quickened if they are exposed to heat such as in forest fires. The cones open 5–8 cm (2–3+1⁄4 in) wide to allow the seeds to disperse. The seeds are 5–6 millimetres (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long, with a 20 mm (13⁄16 in) wing, and are wind-dispersed.
-
 Cones
Cones
-
 Foliage
Foliage
-
 Bark and trunk
Bark and trunk
-
 Plate from Lambert's Description of the Genus Pinus
Plate from Lambert's Description of the Genus Pinus
-
 Cone of pinus halepensis in Hebron
Cone of pinus halepensis in Hebron
-
Pinus halepensis forest
-
 A dead Aleppo pine in front of the Étang de Thau
A dead Aleppo pine in front of the Étang de Thau
-
 A grove of Aleppo pines in Pinet
A grove of Aleppo pines in Pinet
Related species
The Aleppo pine is closely related to the Turkish pine, Canary Island pine, and maritime pine, which all share many of its characteristics. Some authors include the Turkish pine as a subspecies of the Aleppo pine, as Pinus halepensis subsp. brutia (Ten.) Holmboe, but it is usually regarded as a distinct species. It is a relatively nonvariable species, in that its morphological characteristics stay constant over the entire range.
Distribution and habitat
The native range of Pinus halepensis extends from Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Spain north to southern France, Malta, Italy, Croatia, Montenegro, and Albania, and east to Greece. It has been introduced into many parts of the world, including Portugal. There is an outlying population (from which it was first described) in Syria, Lebanon, southern Turkey, Jordan, Israel and Palestine.
The species is generally found at low altitudes, mostly from sea level to 200 m (660 ft), but can grow above 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in southern and eastern Spain, well over 1,200 m (3,900 ft) on Crete, and up to 1,700 m (5,600 ft) in the south, in Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The tree is able to quickly colonize open and disturbed areas. It is classed as an invasive species in South Africa. It can grow on all substrates and almost in all bioclimates in the Mediterranean.
Pinus halepensis is a diagnostic species of the vegetation class Pinetea halepensis.
Uses
The resin of the Aleppo pine is used to flavor the Greek wine retsina.
From the pine nuts of the Aleppo pine is made a pudding called asidet zgougou in the Tunisian dialect; it is served in bowls, covered with cream, and topped with almonds and small candies.
The Maltese dessert prinjolata is also prepared using these pine nuts, both in its filling as well as a topping.
Aleppo pine are used for bonsai.
Forestry
In its native area, P. halepensis is widely planted for its fine timber, making it one of the most important forestry trees in Algeria and Morocco.
In Israel, natural patches of Aleppo pine forests can be found in the Carmel and Galilee regions. The Aleppo pine, along with Pinus brutia, has been planted extensively by the Jewish National Fund. It proved very successful in Yatir Forest in the northern Negev (on the edge of the desert), where foresters had not expected it to survive. Many Aleppo pine forests exist today in Israel and are used for recreational purposes. Although it is a local species, some argue that the historical replacement of natural oak maquis shrubland and garrigue with tall stands of pine has created "ecological deserts" and has significantly changed the species assemblage of these regions. The species produces timber which is valued for its hardness, density and unproblematic seasoning. Seasoned timber is inclined to tear out with planing, but this can be avoided by using sharp blades or adjusting the sharpening angle of tools.
The Aleppo pine is considered an invasive species though useful in South Africa; in South Australia, a control program is in place on Eyre Peninsula.
Landscape
Pinus halepensis is a popular ornamental tree, extensively planted in gardens, parks, and private and agency landscapes in hot dry areas such as Southern California and the Karoo in South Africa, where the Aleppo pine's considerable heat and drought tolerance, fast growth, and aesthetic qualities are highly valued.
In culture
Paul Cézanne had an Aleppo pine in his garden at Aix-en-Provence; this tree was the inspiration and model for his painting The Big Trees. As of 2005, the tree is still growing in Cézanne's garden.
References
- Farjon, A. (2013). "Pinus halepensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2013: e.T42366A2975569. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42366A2975569.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- Aisner, R.; Terkel, J. (1992-08-01). "Ontogeny of pine cone opening behaviour in the black rat, Rattus rattus". Animal Behaviour. 44: 327–336. doi:10.1016/0003-3472(92)90038-B. ISSN 0003-3472.
- ^ Farjon, A. (2005). Pines. Drawings and Descriptions of the genus Pinus. Brill, Leiden. ISBN 90-04-13916-8.
- ^ Rushforth, K. (1999). Trees of Britain and Europe. Collins ISBN 0-00-220013-9.
- ^ Nahal, I. (1962). Le Pin d'Alep (Pinus halepensis Miller). Étude taxonomique, phytogéographique, écologique et sylvicole. Annales de l'École National des Eaux et Forêts (Nancy) 19: 1–207.
- Christensen, K. I. (1997). Gymnospermae. Pp. 1–17 in Strid, A., & Tan, K., eds., Flora Hellenica 1. Königstein.
- Richardson, D. M., ed. (1998). Ecology and Biogeography of Pinus. Cambridge University Press ISBN 0-521-55176-5.
- "Aleppo pine – Invasive Species South Africa".
- Facy, B.; Semerci, H. & Vendramin, G.G. (2003). "Aleppo and Brutia pines - Pinus halepensis/Pinus brutia" (PDF). EUFORGEN Technical Guidelines for Genetic Conservation and Use.
- Bonari, Gianmaria; Fernández‐González, Federico; Çoban, Süleyman; Monteiro‐Henriques, Tiago; Bergmeier, Erwin; Didukh, Yakiv P.; Xystrakis, Fotios; Angiolini, Claudia; Chytrý, Kryštof; Acosta, Alicia T.R.; Agrillo, Emiliano (January 2021). Ewald, Jörg (ed.). "Classification of the Mediterranean lowland to submontane pine forest vegetation". Applied Vegetation Science. 24 (1). doi:10.1111/avsc.12544. hdl:10400.5/21923. ISSN 1402-2001. S2CID 228839165.
- Newman Information Center for Desert Research and Development, Aleppo pine
- F.T. Maestre, J. Cortina . "Are Pinus halepensis plantations useful as a restoration tool in semiarid Mediterranean areas?" Forest Ecology and Management, 2004 (Elsevier).
- Reducing Tear Out when Wood Planing
- Cézanne, P. "Visions". In Architectural Digest, December 2005: 117.
External links
- Gymnosperm Database: Pinus halepensis
- Pinus halepensis—distribution map, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN)
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Pinus halepensis |
|
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Drought-tolerant trees
- Flora of Lebanon and Syria
- Flora of Palestine (region)
- Garden plants of Africa
- Garden plants of Asia
- Least concern plants
- Ornamental trees
- Plants described in 1768
- Pinus
- Trees of Europe
- Trees of Mediterranean climate
- Trees of Morocco
- Taxa named by Philip Miller
- Flora of Malta