| Revision as of 00:32, 25 June 2005 edit60.236.190.205 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:42, 25 June 2005 edit undoFred J (talk | contribs)16,207 edits structureNext edit → | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| The main city on Gotland is ], an old ] city, sporting a largely intact city wall, as well as many historical buildings. | The main city on Gotland is ], an old ] city, sporting a largely intact city wall, as well as many historical buildings. | ||
| Gotland is the main island of: | |||
| ⚫ | *], or ''Gotland'' - an historical ] | ||
| ⚫ | *], or ''Gotlands län'' - a current ] | ||
| ⚫ | *], or ''Gotlands kommun'' - a current ] | ||
| After World War II at Gotland several new methods of electric power transmission were tested. So between Sweden and Gotland the first operational ]-system in the Western hemisphere was installed, the ]. | After World War II at Gotland several new methods of electric power transmission were tested. So between Sweden and Gotland the first operational ]-system in the Western hemisphere was installed, the ]. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 13: | ||
| Gotland has its own language branch called ]. | Gotland has its own language branch called ]. | ||
| For more information see: | |||
| ⚫ | *''']''', or ''Gotland'' - an historical ] | ||
| ⚫ | *''']''', or ''Gotlands län'' - a current ] | ||
| ⚫ | *''']''', or ''Gotlands kommun'' - a current ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 25 June 2005
For other uses, see Gotland (disambiguation).Gotland is the largest island in the Baltic Sea. At 2,994 km² it is also the largest island belonging to Sweden, ahead of Öland. Inhabitants of the island number 57,381 (2002 figure) and the primary income sources are tourism and agriculture.
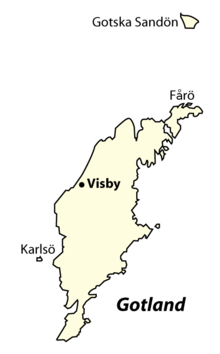

The main city on Gotland is Visby, an old Hanseatic city, sporting a largely intact city wall, as well as many historical buildings.
After World War II at Gotland several new methods of electric power transmission were tested. So between Sweden and Gotland the first operational HVDC-system in the Western hemisphere was installed, the HVDC Gotland. In 1999 for the first time a windpark was connected by an HVDC-system (HVDC Visby-Nas).
Gotland has its own language branch called Gutniska.
For more information see:
- Gotlandia, or Gotland - an historical Province of Sweden
- Gotland County, or Gotlands län - a current County of Sweden
- Gotland Municipality, or Gotlands kommun - a current Municipality of Sweden