| Revision as of 08:16, 7 August 2005 editCentauri (talk | contribs)2,355 edits NPOV← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:07, 7 August 2005 edit undoBollar (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,131 editsm correctionNext edit → | ||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | ||
| Bokak is one of the Pacific islands claimed on uncertain legal grounds, by the ], a ] linked to ]ulent banking activities. The Marshaellese government this claim. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 13:07, 7 August 2005
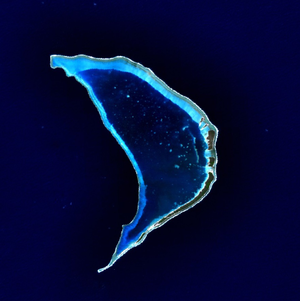
Bokak Atoll (also known as Taongi Atoll) is an uninhabited 3.2 square kilometer atoll located in the Pacific Ocean at 14°32′N 169°00′E / 14.533°N 169.000°E / 14.533; 169.000. It consists of eleven islands surrounding a 78 square kilometer lagoon. It is mentioned in the constitution of the Marshall Islands and is located in the Ratak Chain.
The first European to record discovering Bokak was Alonso de Salazar, a Spanish explorer, on August 21, 1526.
Bokak is one of the Pacific islands claimed on uncertain legal grounds, by the Dominion of Melchizedek, a micronation linked to fraudulent banking activities. The Marshaellese government rejects this claim.
Categories: