| Revision as of 08:37, 27 August 2009 editNono64 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers96,246 editsm ExactMass template← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:14, 20 April 2011 edit undoCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | verifiedrevid = 310328256 | |||
| |ImageFile=Cladinose.png | |ImageFile=Cladinose.png | ||
| |ImageSize=150px | |ImageSize=150px | ||
Revision as of 12:14, 20 April 2011
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
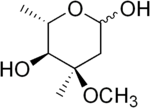
| IUPAC name (4R,5S,6S)-4-Methoxy-4,6-dimethyl-tetrahydropyran-2,5-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H16O4 |
| Molar mass | 176.21 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cladinose is a hexose deoxy sugar that in several antibiotics (such as erythromycin) is attached to the macrolide ring.
In ketolides, a relatively new class of antibiotics, the cladinose is replaced with a keto group.

External links
- Cladinose at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- PubChem
- Diagrams
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |