| Revision as of 00:31, 30 March 2010 edit193.188.47.23 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:33, 30 March 2010 edit undo193.188.47.23 (talk) →PrehistoryNext edit → | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
| Pottery from the ] phase is similar to pottery found in ], Sicily. A culture of ] temple builders then either supplanted or arose from this early period. During 3500 BC, these people built some of the oldest existing, free-standing structures in the world in the form of the megalithic ] temples on ];<ref name=otsf>{{cite web|url=http://www.otsf.org/ |title=Old Temples Study Foundation |publisher=OTSF |date= |accessdate=31 March 2009}}</ref> other early temples include those at ] and ].<ref>{{cite book | last =Sheehan| first =Sean | title =Malta| publisher =Marshall Cavendish| url =http://books.google.com/books?id=LRGrRy7S750C&pg=PA87&dq=%C4%A6a%C4%A1ar+Qim+and+Mnajdra&sig=ACfU3U1ozj76aQDaWbOpgv4EsJxWGi8jgg| isbn=0761409939}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://users.aber.ac.uk/jpg/malta/arch.html |title=Aberystwyth, The University of Wales |publisher=Users.aber.ac.uk |date= |accessdate=31 March 2009}}</ref><ref>David Trump et al., ''Malta Before History'' (2004: Miranda Publishers)</ref> | Pottery from the ] phase is similar to pottery found in ], Sicily. A culture of ] temple builders then either supplanted or arose from this early period. During 3500 BC, these people built some of the oldest existing, free-standing structures in the world in the form of the megalithic ] temples on ];<ref name=otsf>{{cite web|url=http://www.otsf.org/ |title=Old Temples Study Foundation |publisher=OTSF |date= |accessdate=31 March 2009}}</ref> other early temples include those at ] and ].<ref>{{cite book | last =Sheehan| first =Sean | title =Malta| publisher =Marshall Cavendish| url =http://books.google.com/books?id=LRGrRy7S750C&pg=PA87&dq=%C4%A6a%C4%A1ar+Qim+and+Mnajdra&sig=ACfU3U1ozj76aQDaWbOpgv4EsJxWGi8jgg| isbn=0761409939}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://users.aber.ac.uk/jpg/malta/arch.html |title=Aberystwyth, The University of Wales |publisher=Users.aber.ac.uk |date= |accessdate=31 March 2009}}</ref><ref>David Trump et al., ''Malta Before History'' (2004: Miranda Publishers)</ref> | ||
| The temples have a distinctive architecture, typically a complex trefoil design, and were used from 4000–2500 BC. Animal bones and a knife found behind a removable altar stone suggest that temple rituals included ]. Tentative information suggests that the sacrifices were made to the goddess of fertility, whose statue is now in the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta.<ref>http://www.visitmalta.com/museum-of-archaeology</ref> The culture apparently disappeared from the Maltese Islands around 2500 BC. Archeologists speculate that the temple builders fell victim to famine or disease |
The temples have a distinctive architecture, typically a complex trefoil design, and were used from 4000–2500 BC. Animal bones and a knife found behind a removable altar stone suggest that temple rituals included ]. Tentative information suggests that the sacrifices were made to the goddess of fertility, whose statue is now in the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta.<ref>http://www.visitmalta.com/museum-of-archaeology</ref> The culture apparently disappeared from the Maltese Islands around 2500 BC. Archeologists speculate that the temple builders fell victim to famine or disease. Others have speculated on the links between this event and ]'s account of the disappearance of ]. | ||
| Another interesting archeological feature of the Maltese islands often attributed to these ancient builders, are equidistant uniform grooves dubbed "cart tracks" or "cart ruts" which can be found in several locations throughout the islands with the most prominent being those found in an area of Malta named "Clapham Junction". These may have been caused by wooden-wheeled carts eroding soft limestone.<ref></ref><ref>Mottershead, Derek; Alastair Pearson & Martin Schaefer "The cart ruts of Malta: an applied geomorphology approach" ''Antiquity'' Vol 82:318, 2008 pp 1065-1079 (pdf)</ref> | Another interesting archeological feature of the Maltese islands often attributed to these ancient builders, are equidistant uniform grooves dubbed "cart tracks" or "cart ruts" which can be found in several locations throughout the islands with the most prominent being those found in an area of Malta named "Clapham Junction". These may have been caused by wooden-wheeled carts eroding soft limestone.<ref></ref><ref>Mottershead, Derek; Alastair Pearson & Martin Schaefer "The cart ruts of Malta: an applied geomorphology approach" ''Antiquity'' Vol 82:318, 2008 pp 1065-1079 (pdf)</ref> | ||
Revision as of 00:33, 30 March 2010
This article is about the Mediterranean country. For other uses, see Malta (disambiguation).| Republic of MaltaRepubblika ta' Malta | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: L-Innu Malti ("The Maltese Hymn") | |
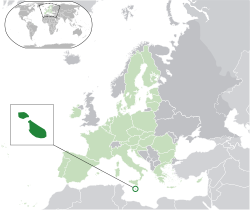 Location of Malta (dark green) Location of Malta (dark green)– in Europe (light green & dark gray) | |
| Capital | Valletta (de facto) |
| Largest city | Birkirkara |
| Official languages | Maltese, English |
| Ethnic groups | Maltese 95.3%, British 1.6%, other 3.1% |
| Religion | Roman Catholicism |
| Demonym(s) | Maltese |
| Government | Parliamentary Republic |
| • President | George Abela |
| • Prime Minister | Lawrence Gonzi |
| Independence | |
| • from the United Kingdom | 21 September 1964 |
| • Republic | 13 December 1974 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 316 km (122 sq mi) (200) |
| • Water (%) | 0.001 |
| Population | |
| • 2008 estimate | 413,609 (174th) |
| • 2005 census | 404,962 |
| • Density | 1,298/km (3,361.8/sq mi) (6th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $9.893 billion (142nd) |
| • Per capita | $23,971 (37th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $8.370 billion |
| • Per capita | $20,280 |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (38th) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Drives on | Left |
| Calling code | 356 |
| ISO 3166 code | MT |
| Internet TLD | .mt |
| Total population includes foreign residents. Maltese residents population estimate at end 2004 was 389,769. All official population data provided by the NSO. Before 2008: Maltese lira Also .eu, shared with other European Union member states. | |
Malta /ˈmɔːltə/, officially the Republic of Malta (Template:Lang-mt), is a developed southern European country and consists of an archipelago situated centrally in the Mediterranean, 93 km south of Sicily and 288 km north-east of Tunisia, with Gibraltar 1,826 km to the west and Alexandria 1,510 km to the east.
Malta covers just over 300 km² in land area, making it one of Europe's smallest and one of Europe's most densely populated countries. Its de facto capital is Valletta and the largest city is Birkirkara. Maltese is the national language and a co-official language, alongside English.
Throughout history, Malta's location has given it great strategic importance and a sequence of powers including the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Fatimids, Sicilians, Knights of St John, French and British have all ruled the islands. Malta gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1964 and became a Republic in 1974, whilst retaining membership in the Commonwealth of Nations. It is a member of the United Nations (since 1964) and a member of the European Union (since 2004). Malta is also party to the Schengen Agreement (since 2007) and member of the eurozone (since 2008).
Malta has a long Christian legacy and is an Apostolic See. According to the Acts of the Apostles, St. Paul was shipwrecked on Malta and ministered there. Catholicism continues to be the official and dominant religion in Malta. Malta is known for its world heritage sites, most prominently the Megalithic Temples which are the oldest free-standing structures in Europe.
Etymology
The origin of the term "Malta" is uncertain, and the modern-day variation derives from the Maltese language. The most common etymology derives from the Greek word μέλι (meli), 'honey'. The Greeks called the island Μελίτη (Melite) meaning "honey-sweet," possibly due to Malta's unique production of honey; an endemic species of bee lives on the island, giving it the popular nickname the "land of honey." The Romans went on to call the island Melita. Another etymology is the Phoenician word ���������� Maleth, the Phoenician name for the islands, meaning "a haven" in reference to Malta's many bays and coves.
History
Main articles: History of Malta and Timeline of Maltese historyPrehistory
See also: Megalithic Temples of Malta, Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni, Għar Dalam, and Heritage Malta
Pottery found by archeologists at Skorba resembles that found in Italy, and suggests that the Maltese islands were first settled in 5200 BC mainly by stone age hunters or farmers who had arrived from the larger island of Sicily, possibly the Sicani. The extinction of the dwarf hippos and dwarf elephants has been linked to the earliest arrival of humans on Malta. The most probable means by which people came to Malta was by using rafts. When they came to Malta they first settled in caves, such as Għar Dalam, and later built huts.
The Sicani were the only tribe known to have inhabited the island at this time and are generally regarded as related to the Iberians. The population on Malta grew cereals, raised domestic livestock and, in common with other ancient Mediterranean cultures, worshiped a fertility figure represented in Maltese prehistoric artifacts as exhibiting the large proportions seen in similar statuettes, including the Venus of Willendorf.


Pottery from the Għar Dalam phase is similar to pottery found in Agrigento, Sicily. A culture of megalithic temple builders then either supplanted or arose from this early period. During 3500 BC, these people built some of the oldest existing, free-standing structures in the world in the form of the megalithic Ġgantija temples on Gozo; other early temples include those at Ħaġar Qim and Mnajdra.
The temples have a distinctive architecture, typically a complex trefoil design, and were used from 4000–2500 BC. Animal bones and a knife found behind a removable altar stone suggest that temple rituals included animal sacrifice. Tentative information suggests that the sacrifices were made to the goddess of fertility, whose statue is now in the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta. The culture apparently disappeared from the Maltese Islands around 2500 BC. Archeologists speculate that the temple builders fell victim to famine or disease. Others have speculated on the links between this event and Plato's account of the disappearance of Atlantis.
Another interesting archeological feature of the Maltese islands often attributed to these ancient builders, are equidistant uniform grooves dubbed "cart tracks" or "cart ruts" which can be found in several locations throughout the islands with the most prominent being those found in an area of Malta named "Clapham Junction". These may have been caused by wooden-wheeled carts eroding soft limestone.
After 2500 BC, the Maltese Islands were depopulated for several decades until the arrival of a new influx of Bronze Age immigrants, a culture that cremated its dead and introduced smaller megalithic structures called dolmens to Malta.
Greeks, Phoenicians and Romans
See also: Magna Graecia, Phoenicia, Ancient Rome, Sicilia (Roman province), and Byzantine EmpireAround 700 BC, the Ancient Greeks settled on Malta, especially around the area where Valletta now stands. A century later, Phoenician traders, who used the islands as a stop on their trade routes from the eastern Mediterranean to Cornwall, joined the natives on the island. The Phoenicians inhabited the area now known as Mdina, and its surrounding town of Rabat, which they called Maleth. The Romans, who also lived in Mdina, referred to it (and the island) as Melita.

After the fall of Phoenicia, in 400 BC the area came under the control of Carthage, a former Phoenician colony. During this time the people on Malta mainly cultivated olives and carobs, and produced textiles.
During the First Punic War of 218 BC, tensions led the Maltese people to rebel against Carthage and turn control of their garrison over to the Roman Republic consul Sempronius. Malta remained loyal to Rome during the Second Punic War and the Romans rewarded it with the title Foederata Civitas, a designation that meant it was exempt from paying tribute or the rule of Roman law, although at this time it fell within the jurisdiction of Sicilia province.
By 117 AD, the Maltese Islands were a thriving part of the Roman Empire, being promoted to the status of Municipium under Hadrian. Catacombs in Rabat testify to an early Christian community on the islands, and the Acts of the Apostles recount the shipwreck of St Paul and his ministry on the island (see Religion).
When the Roman Empire split into Eastern and Western divisions in the 4th century, Malta fell under the control of the Greek speaking Byzantine Empire from 395 to 870, which ruled from Constantinople. Although Malta was under Byzantine rule for four centuries, not much is known from this period. There is evidence that Germanic tribes, including the Goths and Vandals, briefly took control of the islands before the Byzantines launched a counter attack and retook Malta.
Middle Ages
See also: Byzantine-Arab Wars, Emirate of Sicily, Kingdom of Sicily, and Crown of Aragon

Malta was involved in the Byzantine-Arab Wars, and the conquest of Malta is closely linked with that of Sicily due to admiral Euphemius' betrayal of his fellow Byzantines, requesting that the Aghlabid dynasty invade the area. As part of the Emirate of Sicily, rule switched to the Fatimids in 909. The Arabs introduced new irrigation, some fruits and cotton and the Siculo-Arabic language was adopted on the island from Sicily and Southern Italy: it would eventually evolve into the Maltese language.
The native Christians were allowed freedom of religion but had to pay jizya. The Normans, as part of their conquest of Sicily, took Malta in 1091. The local Christians warmly welcomed the arrival of Roger I and offered to fight for him; in response to this, Roger reportedly tore off a portion of his checkered red-and-white banner and presented it to the Maltese, forming the basis of the present-day Maltese flag.

The Norman period was productive; Malta became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Sicily which also covered the island of Sicily and the southern half of the Italian Peninsula. The Catholic Church was re-instated as the state religion with Malta under the See of Palermo and much Norman architecture sprung up around Malta especially in its ancient capital Mdina. Tancred of Sicily, the last Norman monarch, made Malta a feudal lordship or fief within the kingdom and a Count of Malta instated. As the islands were much desired due to their strategic importance, it was during this time the men of Malta were militarised to fend off capture attempts; the early counts were skilled Genoese corsairs.
The kingdom passed on to the House of Hohenstaufen from 1194 until 1266. Malta was part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation for 72 years. Malta was declared a county and a marquisate, but its trade was totally ruined. For a long time it remained solely a fortified garrison. It was in 1224 under Frederick II that all remaining Muslims were expelled from Malta or forced to convert and the entire Christian male population of Celano in Abruzzo was deported to Malta.

For a brief period the kingdom passed to the Capetian House of Anjou, however high taxes made the dynasty unpopular in Malta, due in part to Charles of Anjou's war against the Republic of Genoa and the island of Gozo was sacked in 1275. A large revolt on Sicily known as the Sicilian Vespers followed these attacks, that saw the Peninsula separating into the Kingdom of Naples; the Kingdom of Sicily, including Malta, then fell under the rule of the Aragonese.
Relatives of the kings of Aragon ruled the island until 1409, when it passed to the Crown of Aragon. Early on in the Aragonese reign the sons of the monarchy received the title, "Count of Malta". It was also during this time that much of the local nobility was created. However by 1397 the bearing of the title "Count of Malta" reverted to a feudal basis with two families fighting over the distinction, which caused much distress. This led the king to abolish the title. Dispute over the title returned when the title was reinstated a few years later and the Maltese, led by the local nobility, rose up against Count Gonsalvo Monroy. Although they opposed the Count, the Maltese voiced their loyalty to the Sicilian Crown, which so impressed Alfonso IV that he did not punish the people for their rebellion but promised never to grant the title to a third party, instead incorporating it back into the crown. The city of Mdina was given the title of Città Notabile as a result of this sequence of events.
Knights of Malta and Napoleon
See also: Knights Hospitaller and Great Siege of Malta
In 1530 Charles I of Spain gave the islands to the Order of Knights of the Hospital of St John of Jerusalem in perpetual lease. These knights, a military religious order now known as the Knights of Malta, had been driven out of Rhodes by the Ottoman Empire in 1522. In 1551, Barbary corsairs enslaved the entire population of the Maltese island Gozo, about 5,000, sending them to Libya. The knights withstood a full-blown siege by the Ottoman Turks in 1565, at the time the greatest naval power in the Mediterranean. The knights, fighting alongside the Maltese, were victorious and speaking of the battle Voltaire said, "Nothing is more well known than the siege of Malta".
After the siege they decided to increase Malta's fortifications, particularly in the inner-harbour area, where the new city of Valletta, named in honour of Grand Master Jean de la Valette, was built. They also established watchtowers along the coasts - the Wignacourt, Lascaris, and de Redin towers - named after the Grand Masters who ordered the work. The Knights' presence on the island saw the completion of many architectural and cultural projects, including the embellishment of Città Vittoriosa, the construction of new cities including Città Rohan and Città Hompesch and the introduction of new academic and social resources. Approximately 11,000 people out of a population of 70,000 died of plague in 1675.

The Knights' reign ended when Napoleon captured Malta on the way to Egypt during the French Revolutionary Wars in 1798. As a ruse, Napoleon asked for safe harbour to resupply his ships. Once safely inside Valletta's harbour he turned his guns against his hosts. Grand Master Ferdinand von Hompesch zu Bolheim capitulated and Napoleon stayed in Malta for a few days, during which time he systematically looted many movable assets of the island and established an administration controlled by his nominees. He then sailed for Egypt, leaving behind a substantial garrison.
The occupying French forces were deeply unpopular with the Maltese, due particularly to the French forces' hostility towards Catholicism. The French financial and religious policies angered the Maltese who rebelled, forcing the French to retreat within the city fortifications. Great Britain, along with the Kingdom of Naples and the Kingdom of Sicily, sent ammunition and aid to the Maltese and Britain also sent her navy, which blockaded the islands.
General Claude-Henri Belgrand de Vaubois surrendered his French forces in 1800. Maltese leaders presented the island to Sir Alexander Ball, asking that the island become a British Dominion. The Maltese people created a Declaration of Rights in which they agreed to come "under the protection and sovereignty of the King of the free people, His Majesty the King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland". The Declaration also stated that "his Majesty has no right to cede these Islands to any power...if he chooses to withdraw his protection, and abandon his sovereignty, the right of electing another sovereign, or of the governing of these Islands, belongs to us, the inhabitants and aborigines alone, and without control."
British Empire and World War II
Main article: Siege of Malta (World War II)
In 1814, as part of the Treaty of Paris, Malta officially became a part of the British Empire and was used as a shipping way-station and fleet headquarters. Malta's position half-way between Gibraltar and the Suez Canal proved to be its main asset during these years and it was considered an important stop on the way to India. In 1919 British troops fired on a rally protesting against new taxes, killing four Maltese men. This led to increased resistance and support for the pro-Italian parties that had challenged the British presence on the island. The event, known as Sette Giugno (Italian for 7 June), is commemorated every year.
In the early 1930s the British Mediterranean Fleet, which was at that time the main contributor to commerce on the island, moved to Alexandria as an economic measure.
During World War II, Malta played an important role owing to its proximity to Axis shipping lanes. The bravery of the Maltese people during the second Siege of Malta moved HM King George VI to award the George Cross to Malta on a collective basis on 15 April 1942 "to bear witness to a heroism and devotion that will long be famous in history". Some historians argue that the award caused Britain to incur disproportionate losses in defending Malta, as British credibility would have suffered if Malta surrendered, as Singapore had. A replica of the George Cross now appears in the upper hoist corner of the Flag of Malta. The collective award remained unique until April 1999, when the Royal Ulster Constabulary became the second– and, to date, the only other– recipient of a collective George Cross.
Independence and Republic
Malta achieved its independence on 21 September 1964 (Independence Day). Under its 1964 constitution, Malta initially retained Queen Elizabeth II as Queen of Malta and thus Head of State, with a Governor-General exercising executive authority on her behalf. On 13 December 1974 (Republic Day) Malta became a republic within the Commonwealth, with the President as head of state. A defence agreement signed soon after independence (and re-negotiated in 1972) expired on 31 March 1979 (Freedom Day), under the prime minister Dom Mintoff.
On that day British military forces departed and Admiral Sir John Hamilton GBE, Commander in Chief of the Eastern Mediterranean fleet, lowered the Union Jack for the last time. The Maltese then raised the Maltese flag over the Freedom Monument in Vittoriosa, to the sound of the first playing of Malta's national anthem. Malta adopted a policy of neutrality in 1980 and was a member of the Movement of Non-Aligned Countries until 2004. In 1989, Malta was the venue of a summit between US President George H.W. Bush and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, their first face-to-face encounter, which signaled the end of the Cold War.
Malta joined the European Union on 1 May 2004. Following the European Council of 21 June to 22 June 2007 it joined the Eurozone on 1 January 2008.
Government and politics

Malta is a republic, whose parliamentary system and public administration is closely modeled on the Westminster system. Malta had the second highest voter turnout in the world (and the highest for nations without mandatory voting), based on election turnout in national lower house elections from 1960 to 1995. The unicameral House of Representatives, (Maltese: Il-Kamra tad- Deputati), is elected by direct universal suffrage through single transferable vote every five years, unless the House is dissolved earlier by the President on advice of the Prime Minister.
The House of Representatives is made up of sixty-five Members of Parliament. However, where a party wins an absolute majority of votes, but does not have a majority of seats, that party is given additional seats to ensure a parliamentary majority. The Constitution of Malta provides that the President appoint as Prime Minister the member of the House who is best able to command a (governing) majority in the House.
The President of the Republic is elected every five years by the House of Representatives. The role of the president as head of state is largely ceremonial. The main political parties are the Nationalist Party, which is a Christian democratic party, and the Labour Party, with Dr. Joseph Muscat as its leader, which is a social democratic party. The Nationalist Party is currently at the helm of the government, the Prime Minister being Dr. Lawrence Gonzi. The Labour Party is in opposition. There are a number of smaller political parties in Malta that presently have no parliamentary representation.
Until World War II Maltese politics was dominated by the language question fought out by pro-Italian and pro-British parties. Post-War politics dealt with constitutional questions on the relations with Britain (first with integration then independence) and, eventually, relations with the European Union.
Local government
Main article: Local councils of MaltaSince 1993 Malta has been divided into 68 elected local councils, with each council responsible for the administration of cities or regions of varying sizes. Administrative responsibility is distributed between the local councils and the central government in Valletta. There are no intermediate levels between local government and national government and the levels of the six districts (five on the main island) and of the three regions (two on the main island) serve primarily statistical purposes.
The Local Councils Act, 1993 (Act XV of 1993) was published on 30 June 1993, subdividing Malta into 54 local councils in Malta and 14 in Gozo. The inhabitants who are registered elect the council every three years, as voters in the Local Councils' Electoral Register. Elections are held by means of the system of proportional representation using the single transferable vote. The mayor is the head of the local council and the representative of the Council for all effects under the Act.
The Executive Secretary, who is appointed by the council, is the executive, administrative, and financial head of the council. All decisions are taken collectively with the other members of the council. Local councils are responsible for the general upkeep and embellishment of the locality, allocation of local wardens and refuse collection; they also carry out general administrative duties for the central government such as collection of government rents and funds and answer government-related public inquiries.
Geography

Malta is an archipelago in the central Mediterranean Sea (in its eastern basin), some 93 km (58 mi) south of the Italian island of Sicily across the Malta Channel. Only the three largest islands — Malta Island (Malta), Gozo (Għawdex), and Comino (Kemmuna) — are inhabited. The smaller islands (see below) are uninhabited. The islands of the archipelago were formed from the high points of a land bridge between Sicily and North Africa that became isolated as sea levels rose after the last Ice Age. The archipelago lies on the edge of the African tectonic plate where it meets the Eurasian plate.

Numerous bays along the indented coastline of the islands provide good harbours. The landscape consists of low hills with terraced fields. The highest point is Ta' Dmejrek on Malta Island at 253 metres (830 ft) near Dingli. Although there are some small rivers at times of high rainfall, there are no permanent rivers or lakes on Malta. However, some watercourses have fresh water running all year round at Baħrija, l-Imtaħleb and San Martin, and at Lunzjata Valley in Gozo.
Phytogeographically, Malta belongs to the Liguro-Tyrrhenian province of the Mediterranean Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the WWF, the territory of Malta belongs to the ecoregion of "Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands and Scrub".
The south of Malta is not Europe's most southern point; that distinction belongs to the Greek island of Gavdos.
The Maltese archipelago
The minor islands that form part of the archipelago are uninhabited and include:
|
|
Climate
See also: Climate
The climate is Mediterranean (Köppen climate classification Csa) / Subtropical , with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers. There is no real thermal dormant season for plants, although plant growth can be checked briefly by abnormal cold in winter (patches of ground frost may occur in inland locales), and summer heat and aridity may cause vegetation to wilt. Effectively there are only two seasons, which makes the islands attractive for tourists, especially during the drier months. However, strong winds can make Malta feel cold during the springtime.

Water supply poses a problem on Malta, as the summer is both rainless and the time of greatest water use, and the winter rainfall often falls as heavy showers running off to the sea rather than soaking into the ground. Malta depends on underground reserves of fresh water, drawn through a system of water tunnels called the Ta' Kandja galleries, which average about 97 m below surface and extend like the spokes of a wheel. In the galleries in Malta's porous limestone, fresh water lies in a lens upon brine. More than half the potable water of Malta is produced by desalination, which creates further issues of fossil fuel use and pollution. Average water temperatures range from 16 °C (61 °F) in January to as high as 26 °C (79 °F) in August.
Average number of days above 21 °C (69.8 °F) is 189, average number of days above 32 °C (89.6 °F) is 15. Average morning relative humidity: 82%, average evening relative humidity: 64%
The lowest temperature ever recorded at Valletta was on 19 February 1895, with 1.2 °C (34.2 °F), and the highest temperature was 43.8 °C (110.8 °F) recorded in August 1999 at Luqa International Airport. An unofficial lowest temperature of −1.7 °C (28.9 °F) was recorded on 1 February 1962 in the Ta' Qali airfield with snow on the ground.
Snow is virtually unheard of, with very few and brief snow flurries recorded in February 1895, January 1905 and 31 January 1962. No accumulation has been reported on the coast at least since 1800, but on the last day of January 1962 snow briefly covered some parts of the interior of the main island. The following night the only frost in the history of Malta was recorded in the Ta' Qali airfield.
| Climate data for Malta | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization (UN) | |||||||||||||
Economy
Main article: Economy of MaltaUntil 1800 Malta depended on cotton, tobacco and its shipyards for exports. After the British arrived, they came to depend on the dockyard for support of the Royal Navy, especially during the Crimean War of 1854. The military base benefited craftsmen and all those who served the military.
In 1869 the opening of the Suez Canal gave Malta's economy a great boost, as there was a massive increase in the shipping which entered the port. Ships stopping at Malta's docks for refuelling helped the Entrepôt trade, which brought additional benefits to the island.
However, towards the end of the 19th century the economy began declining, and by the 1940s Malta's economy was in serious crisis. One factor was the longer range of newer merchant ships that required less frequent refuelling stops.

Presently, Malta’s major resources are limestone, a favourable geographic location and a productive labour force. Malta produces only about 20% of its food needs, has limited freshwater supplies and has no domestic energy sources. The economy is dependent on foreign trade (serving as a freight trans-shipment point), manufacturing (especially electronics and textiles) and tourism. Tourism infrastructure has increased dramatically over the years and a number of good-quality hotels are present on the island, although overdevelopment and the destruction of traditional housing is of growing concern. An increasing number of Maltese now travel abroad on holiday. Although they are still a net importer of tourism, the ratio of inbound tourists to outbound tourists is decreasing. The popular Mdina Glass enterprise was established on the island in 1968 by Michael Harris, a former tutor at the UK's RCA.
Film production is a growing contributor to the Maltese economy, with several big-budget foreign films shooting in Malta each year. The country has increased the exports of many other types of services such as banking and finance.
The government is investing heavily in education, including college.
Malta has recently privatised some state-controlled firms and liberalised markets in order to prepare for membership in the European Union, which it joined on 1 May 2004. For example, the government announced on 8 January 2007 that it is selling its 40% stake in Maltapost, in order to complete a privatisation process which has been ongoing for the past five years.
Malta and Tunisia are currently discussing the commercial exploitation of the continental shelf between their countries, particularly for petroleum exploration.
Malta does not have a property tax.
According to Eurostat data, Maltese PPS GDP per capita stood at 76 per cent of the EU average in 2008.
Malta's representative in Brussels, Joe Borg, has recently courted controversy by opposing a ban on the sale of bluefin tuna, an increasingly rare fish that sells in Japan for tens of thousands of pounds per fish. Malta's bluefin tuna industry, which employs 1,000 of the country's 400,000 citizens, is worth €100m (£87m) a year in revenue to the island.
Money and banking
The Central Bank of Malta (Bank Ċentrali ta' Malta), has two key areas of responsibility: the formulation and implementation of monetary policy and the promotion of a sound and efficient financial system. It was established by the Central Bank of Malta Act on 17 April 1968. The Maltese government entered ERM II on 4 May 2005, and adopted the euro as the country's currency on 1 January 2008.
Currency
Main articles: Maltese euro coins and Euro gold and silver commemorative coins (Malta)Maltese euro coins feature the Maltese Cross on €2 and €1 coins, the Maltese Coat of Arms on the €0.50, €0.20 and €0.10 coins, and the Mnajdra Temples on the €0.05, €0.02 and €0.01 coins.
Malta has already produced collectors' coins with face value ranging from 10 to 50 euro. These coins continue an existing national practice of minting of silver and gold commemorative coins. Unlike normal issues, these coins are not legal tender in all the eurozone. For instance, a €10 Maltese commemorative coin cannot be used in any other country.
From 1972 until introduction of the Euro in 2008, the currency was the Maltese Lira, which had replaced the Maltese pound. The pound replaced the Maltese scudo in 1798.
Banking
The two largest (and oldest) banks in the country are Bank of Valletta and HSBC Bank Malta, both of which can trace their origins back to the 19th Century. Malta is also home to an international financial center with several foreign offshore banks.
Healthcare
Malta has a long history of providing publicly funded health care. The first hospital recorded in the country was already functioning by 1372. Today, Malta has both a public healthcare system, known as the government healthcare service, where healthcare is free at the point of delivery, and a private healthcare system. Malta has a strong general practitioner-delivered primary care base and the public hospitals provide secondary and tertiary care. The Maltese Ministry of Health advises foreign residents to take out private medical insurance.
Malta was ranked number five in the World Health Organization's ranking of the world's health systems, compared to the United States (at 37), Australia (at 32), United Kingdom (at 18) and Canada (at 30). The healthcare system in Malta closely resembles the British system, as healthcare is free at the point of delivery.
Hospitals
Main article: List of hospitals in MaltaThe recently completed Mater Dei Hospital is Malta's primary hospital, and one of the largest medical buildings in Europe. Several other government hospitals in Malta are:
- Paul Boffa Hospital, an oncology hospital in Valletta.
- St Vincent De Paule Hospital, a geriatrics hospital.
- Gozo General Hospital, the only hospital found in Gozo.
In addition, Malta has three major private hospitals:
- St Philip's Hospital, with a capacity of 75 beds, is in Santa Venera.
- St James Capua Hospital (the former Capua Palace Hospital), with 80 beds, is in Sliema.
- St James Hospital has several sites, including a 13 bed unit in Zabbar, as well as a partner hospital in Libya.
St Mark's Clinic, in Msida, with a capacity of 5 beds, also offers some private hospital services.

The University of Malta has a medical school, and an Institute of Health Care. The latter offering diploma, (BSc)degree and postgraduate degree courses in a number of health care disciplines.
The Medical Association of Malta represents practitioners of the medical profession. MMSA is a separate body representing Maltese medical students, and is a member of EMSA and IFMSA. MIME, the Maltese Institute for Medical Education, is an institute set up recently to provide CME to doctors in Malta as well as medical students. The Foundation Program followed in the UK is to be introduced in Malta in order to stem the 'brain drain' of medical students to the British Isles. MADS, the Malta Association of Dental Students, is a student association set up to promote the rights of Dental Surgery Students studying within the faculty of Dental Surgery of the University of Malta. It is affiliated with IADS, the International Association of Dental Students.
Medical tourism
In recent years, Malta has advertised itself as a medical tourism destination, and a number of health tourism providers are developing the industry. However, no Maltese hospital has undergone independent international healthcare accreditation. Malta is popular with British medical tourists, pointing Maltese hospitals towards seeking UK-sourced accreditation, such as with the Trent Accreditation Scheme. Dual accreditation with the American-orientated Joint Commission is necessary if hospitals in Malta wish to compete with the Far East and Latin America for medical tourists from the United States.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of MaltaPopulation

A census of population and housing is held every ten years. The last census was held in November 2005, and managed to count an estimated 96% of the population. A preliminary report was issued in April 2006, and results were weighted to an estimate for 100% of the population.
Native Maltese people make up the majority of the island. However there are minorities, the largest of which are British people, many of whom retired to Malta. The resident population of Malta, which includes foreigners residing in Malta for at least a year, as of 27 November 2005 was estimated at 404,039 of whom 200,715 (49.7%) were male and 203,324 (50.3%) were female. Of these, 17.1 per cent were aged 14 and under, 68.2 per cent were within the 15–64 age bracket whilst the remaining 13.7 per cent were 65 years and over. Malta's population density of 1,282 per square kilometer (3,322/sq mi) is by far the highest in the EU, and one of the highest in the world. The only census year showing a fall in population was that of 1967, with a 1.7% total decrease, attributable to a substantial number of Maltese residents who emigrated.
The Maltese-resident population for 2004 was estimated to make up 97.0% of the total resident population. Through all the censuses since 1842 there was always a slightly higher female-to-male ratio. Closest to reaching equality were 1901 and 1911 censuses. The highest female-to-male ratio was reached in 1957 (1088:1000), and since the ratio has been constantly dropping. The 2005 census showed a 1013:1000 female-to-male ratio. Population growth has slowed down, from +9.5% between the 1985 and 1995 censuses, to +6.9% between the 1995 and 2005 censuses (a yearly average of +0.7%). The birth rate stood at 3860 (a decrease of 21.8% from the 1995 census) and the death rate stood at 3025. Thus, there was a natural population increase of 835 (compared to +888 for 2004, of which over a hundred were foreign residents).
The population's age composition is similar to the age structure prevalent in the EU. Since 1967 there was observed a trend indicating an aging population, and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio rose from 17.2% in 1995 to 19.8% in 2005, reasonably lower than the EU's 24.9% average. In fact, 31.5% of the Maltese population is aged under 25 (compared to the EU's 29.1%); but the 50-64 age group constitutes 20.3% of the population, significantly higher than the EU's 17.9%. In conclusion, Malta's old-age-dependency-ratio is expected to continue rising steadily in the coming years.
Maltese legislation recognizes both civil and canonical (ecclesiastical) marriages. Annulments by the Ecclesiastes and civil courts are unrelated and are not necessarily granted. There is no divorce legislation and abortion in Malta is illegal. A person must be 16 to marry. The number of brides aged under 25 decreased from 1471 in 1997 to 766 in 2005; while the number of grooms under 25 decreased from 823 to 311. There is a constant trend that females are more likely than males to marry young. In 2005 there were 51 brides aged between 16 and 19, compared to 8 grooms.
At the end of 2007, the population of the Maltese Islands stood at 410,290 and is expected to reach 424,028 by 2025. At the moment, females slightly outnumber males, making up 50.3 per cent of the population. The largest proportion of persons– 7.5 per cent– were aged 25–29, while there were 7.3 percent falling into each of the 45-49 and 55-59 age brackets.
Languages
Main article: Languages of Malta- See also: Languages in education section (below)
The Maltese language (Template:Lang-mt) is the constitutional national language of Malta. The Constitution also enshrines it as the country's official language, alongside English. Italian was the official language of Malta until 1934, when English and Maltese replaced it.
Maltese is a Semitic language descended from Siculo-Arabic (from southern Italy). The Maltese alphabet consists of 30 letters based on the Latin alphabet, including the diacritically altered letters ż, ċ and ġ, as well as the letters għ, ħ, and ie.
Maltese has substantial borrowing from Sicilian, Italian, a little French, and more recently, and increasingly, English. The language includes different dialects that can vary strongly from one town to another or from one island to the other.
The Eurobarometer states that 100% of the population speaks Maltese. Also, 88% of the population speaks English, 66% speaks Italian, and 17% speaks French. This widespread knowledge of second languages makes Malta one of the most multi-lingual countries in the European Union. A study collecting public opinion on what language was "preferred" discovered that 86% of the population express a preference for Maltese, 12% for English, and 2% for Italian. Still, Italian television channels from Italy-based broadcasters, such as Mediaset and RAI, reach Malta and remain popular.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Malta
The Constitution of Malta declares Roman Catholicism as the state religion although entrenched provisions for the freedom of religion are made. Freedom House and the World Factbook report that 98 percent of the population is Roman Catholic, making the nation one of the most Catholic countries in the world.
There are more than 360 churches in Malta, Gozo, and Comino, or one church for every 1,000 residents. The parish church (Maltese: "il-parroċċa", or "il-knisja parrokjali") is the architectural and geographic focal point of every Maltese town and village, and its main source of civic pride. This civic pride manifests itself in spectacular fashion during the local village festas, which mark the day of the patron saint of each parish with marching bands, religious processions, special Masses, fireworks (especially petards), and other festivities.

Malta is an Apostolic See; the Acts of the Apostles tells of how St. Paul, on his way from Crete to Rome to face trial, was shipwrecked on an island which some scholars have identified as Malta, an episode dated around AD 60. The Acts of the Apostles says St. Paul spent three months on the island, curing the sick including the father of Publius, the "chief man of the island". Various traditions are associated with this account. The shipwreck is said to have occurred in the place today known as St Paul's Bay. Saint Publius is said to have been made Malta's first bishop and a grotto in Rabat, now known as "St Paul's Grotto" (and in the vicinity of which evidence of Christian burials and rituals from 3rd century AD has been found), is amongst the earliest known places of Christian worship on the island.
Further evidence of Christian practices and beliefs during the period of Roman persecution appears in catacombs that lie beneath various sites around Malta, including St Paul’s Catacombs and St Agatha’s Catacombs in Rabat, just outside the walls of Mdina. The latter, in particular, were beautifully frescoed between 1200 and 1480, although marauding Turks defaced many of them in the 1550s. There are also a number of cave churches, including the grotto at Mellieħa, which is a Shrine of the Nativity of Our Lady where, according to legend, St. Luke painted a picture of the Madonna. It has been a place of pilgrimage since medieval times.
The Acts of the Council of Chalcedon record that in 451 AD, a certain Acacius was Bishop of Malta (Melitenus Episcopus). It is also known that in 501 AD, a certain Constantinus, Episcopus Melitenensis, was present at the Fifth General Council. In 588 AD, Pope Gregory I deposed Tucillus, Miletinae civitatis episcopus, and the clergy and people of Malta elected his successor Trajan in 599 AD. The last recorded Bishop of Malta before the invasion of the Islands was a Greek by the name of Manas, who was subsequently incarcerated at Palermo.
Maltese historian, Giovanni Francesco Abela, states that following their conversion to Christianity at the hand of St. Paul, the Maltese retained their Christian religion, despite the Fatimid invasion. Abela's writings describe Malta as a divinely ordained "bulwark of Christian, European civilization against the spread of Mediterranean Islam". The native Christian community that welcomed Roger I of Sicily was further bolstered by immigration to Malta from Italy, in the 12th and 13th centuries.

For centuries, the Church in Malta was subordinate to the Diocese of Palermo, except when it was under Charles of Anjou, who appointed bishops for Malta, as did - on rare occasions - the Spanish and later, the Knights. Since 1808 all bishops of Malta have been Maltese. As a result of the Norman and Spanish periods, and the rule of the Knights, Malta became the devout Catholic nation that it is today. It is worth noting that the Office of the Inquisitor of Malta had a very long tenure on the island following its establishment in 1530: the last Inquisitor departed from the Islands in 1798, after the Knights capitulated to the forces of Napoleon Bonaparte. During the period of the Republic of Venice, several Maltese families emigrated to Corfu. Their descendants account for about two-thirds of the community of some 4000 Catholics that now live on that island.
The patron saints of Malta are Saint Paul, Saint Publius, Saint Agatha and Saint George. Although not a patron saint, St George Preca (San Ġorġ Preca) is greatly revered as the first canonised Maltese saint. Pope Benedict XVI canonised him on 3 June 2007. Also, a number of Maltese individuals are recognised as Blessed, including Maria Adeodata Pisani and Nazju Falzon, with Pope John Paul II having beatified them in 2001.
Various Roman Catholic religious orders are present in Malta, including the Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominicans and Little Sisters of the Poor.
Most congregants of the local Protestant churches are not Maltese; their congregations draw on the many British retirees living in the country and vacationers from many other nations. There are approximately 500 Jehovah's Witnesses; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons), the Bible Baptist Church, and the Fellowship of Evangelical Churches have about 60 affiliates. There are also some churches of other denominations, such as St. Andrew's Scots Church in Valletta (a joint Presbyterian and Methodist congregation) and St Paul's Anglican Cathedral, as well as a Seventh-day Adventist church in Birkirkara.
The Jewish population of Malta reached its peak in the Middle Ages under Norman rule. In 1479, Malta and Sicily came under Aragonese rule and the Alhambra Decree of 1492 forced all Jews to leave the country, permitting them to take with them only a few of their belongings. Several dozen Maltese Jews may have converted to Christianity at the time in order to remain in the country. Today, there is one Jewish congregation.
Zen Buddhism and the Bahá'í Faith claim some 40 members. There is one Muslim mosque. A Muslim primary school recently opened; its existence remains a point of some controversy. Of the estimated 3,000 Muslims in Malta, approximately 2,250 are foreigners, approximately 600 are naturalized citizens, and approximately 150 are native-born Maltese.
Migration
EU nationals require neither a visa nor a passport (an ID card or an expired passport are enough) to enter the country. Citizens of a number of third world countries are not required to apply for a visa and require only a valid passport when residing in Malta for up to three months. Visas for other nationalities are valid for one month.
Immigrants, even those with EU citizenship, are required to apply for a work permit. This exception to EU law was agreed upon before accession to safeguard the Maltese labour market.
The estimated net inflow (using data for 2002 to 2004) was of 1,913 persons yearly. Over the last 10 years, Malta accepted back a yearly average of 425 returning emigrants.
During 2006, a total of 1,800 illegal immigrants reached Malta making the boat crossing from the North Africa coast. Most of them intended to reach mainland Europe and happened to come to Malta due to their sub-standard vessels breaking down, or being caught by Maltese and other EU officials. In the first half of 2006, 967 irregular immigrants arrived in Malta– almost double the 473 who arrived in the same period in 2005. Many immigrants have perished in the journey across the Mediterranean, with one notable incident being the May 2007 Malta migrant boat disaster.
Around 45% of immigrants landed in Malta have been granted refugee (5%) or protected humanitarian status (40%). A White Paper suggesting the grant of Maltese citizenship to refugees resident in Malta for over ten years was issued in 2005. Historically Malta gave refuge (and assisted in their resettlement) to eight hundred or so East African Asians who had been expelled from Uganda by Idi Amin and to just under a thousand Iraqis fleeing Saddam Hussein's regime.
Detention costs for the first half of 2006 alone cost € 746,385.
In 2005, Malta sought EU aid in relation to reception of irregular immigrants, repatriation of those denied refugee status, resettlement of refugees into EU countries, and maritime security. In December 2005, the European Council adopted The Global Approach to Migration: Priority Actions focusing on Africa and the Mediterranean; but the deployment of said actions has been limited to the western Mediterranean, thus putting further pressure on the central Mediterranean route for irregular immigration of which Malta forms a part.
|
Education
Main article: Education in Malta See also: List of schools in Malta
Primary schooling has been compulsory since 1946; secondary education up to the age of sixteen was made compulsory in 1971. The state provides education free of charge, and the Church and the private sector run a number of schools in Malta and Gozo, including De La Salle College in Cospicua, St. Aloysius' College in Birkirkara, San Anton School in the valley of L-Imselliet (near Mġarr) and Saint Monica Girls' School in Mosta. As of 2008, there are two international schools, Verdala International School and QSI Malta. The state pays a portion of the teachers' salary in Church schools.
Education in Malta is based on the British model. Primary school lasts six years. At the age of 11 pupils sit for an examination to enter a secondary school, either a church school (the Common Entrance Examination) or a state school. Pupils sit for SEC O-level examinations at the age of 16, with passes obligatory in certain subjects such as mathematics, English and Maltese. Pupils may opt to continue studying at a sixth form college such as Junior College, St Edward's College, St Aloysius' College or else at another post-secondary institution such as MCAST. The sixth form course lasts for two years, at the end of which students sit for the Matriculation examination. Subject to their performance, students may then apply for an undergraduate degree or diploma.
The University of Malta (U.o.M.) provides Tertiary education at diploma, undergraduate and postgraduate level. The adult literacy rate is 92.8%.
Languages in education
English and Maltese are both used to teach students at primary and secondary school level, and both languages are also compulsory subjects. Public schools tend to use both Maltese and English in a balanced manner. Private schools prefer to use English for teaching, as is also the case with most departments of the University of Malta; this has a limiting effect on the capacity and development of the Maltese language. Most university courses are in English.
Of the total number of students studying a first foreign language at secondary level, 51% take Italian whilst 38% take French. Other choices include German, Russian, Spanish, and Arabic.
Culture
Main article: Culture of MaltaThe culture of Malta reflects the various cultures that have come into contact with the Maltese Islands throughout the centuries, including neighbouring Mediterranean cultures, and the cultures of the nations that ruled Malta for long periods of time prior to its independence in 1964.
Music

While Maltese music today is largely western, traditional Maltese music includes what is known as għana. This consists of background folk guitar music, while a few people, generally men, take it in turns to argue a point in a singsong voice. The aim of the lyrics, which are improvised, are to create a friendly yet challenging atmosphere, and it takes a number of years of practice to be able to combine the required artistic qualities with the ability to debate effectively.
Literature
Documented Maltese literature is over 200 years old. However a recently unearthed love ballad testifies to literary activity in the local tongue from the Medieval period. Malta followed a Romantic literary tradition, culminating in the works of Dun Karm, Malta's National Poet. Subsequent writers like Ruzar Briffa and Karmenu Vassallo tried to estrange themselves from the rigidity of formal themes and versification.
It was late in the 1960s that Maltese literature experienced its most radical transformation amongst poets, prose writers and dramatists. Names of significant poets that stand out from the last quarter of the 20th century include Mario Azzopardi, Victor Fenech, Oliver Friggieri, Joe Friggieri, Charles Flores, Daniel Massa, Maria Ganado, Lillian Sciberras and Akille Mizzi. In prose, Frans Sammut, Paul P. Borg and Joe J. Camilleri led the avant-garde meanwhile among the prominent names in theatre are Francis Ebejer, Alfred Sant, Doreen Micallef, Oreste Calleja, Joe Friggieri and Martin Gauci.
The next generation of writers widened the tracks further, especially in prose. Guze' Stagno, Karl Schembri and Clare Azzopardi are young writers fast establishing themselves while in poetry, significant names include Adrian Grima, Immanuel Mifsud, Norbet Bugeja and Simone Inguanez.
In literary criticism, Peter Serracino Inglott, Oliver Friggieri and Charles Briffa introduced perceptive historical, philosophical and psycho-social themes into Maltese theory.
Other writers, born in Malta or of Maltese descent, have established careers abroad. These included the novelist Trezza Azzopardi, best-selling children's author Saviour Pirotta and comic-book artist/journalist Joe Sacco.
Art and architecture

Malta has a long history of architecture, influenced by many different Mediterranean cultures over its history, and most recently, British architecture. The first settlers on the island constructed Ġgantija, one of the oldest manmade freestanding structure in the world. Malta is currently undergoing large scale building projects that includes constructions such as SmartCity Malta, the M-Towers, and Pendergardens, while areas such as the Valletta Waterfront and Tigne Point are receiving renovation.
The Neolithic temple builders 3800-2500 BC endowed the numerous temples of Malta and Gozo with intricate bas relief designs, including spirals evocative of the tree of life and animal portraits, designs painted in red ochre, ceramics, and a vast collection of human form sculptures, particularly the Venus of Malta. These can be viewed at the temples themselves (most notably, the Hypogeum and Tarxien Temples), and at the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta.
The Roman period introduced highly decorative mosaic floors, marble colonnades and classical statuary, remnants of which are beautifully preserved and presented in the Roman Domus, a country villa just outside the walls of Mdina. The early Christian frescoes that decorate the catacombs beneath Malta reveal a propensity for eastern, Byzantine tastes. These tastes continued to inform the endeavours of medieval Maltese artists, but they were increasingly influenced by the Romanesque and Southern Gothic movements. Towards the end of the 15th century, Maltese artists, like their counterparts in neighbouring Sicily, came under the influence of the School of Antonello da Messina, which introduced Renaissance ideals and concepts to the decorative arts in Malta.
| Saint Jerome Writing | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Artist | Caravaggio |
| Year | c. 1607-1608 |
| Type | Oil on canvas |
| Location | St John's Co-Cathedral, Valletta |
The artistic heritage of Malta blossomed under the Knights of St. John, who brought Italian and Flemish Mannerist painters to decorate their palaces and the churches of these islands, most notably, Matteo Perez d'Aleccio, whose works appear in the Magisterial Palace and in the Conventual Church of St. John in Valetta, and Filippo Paladini, who was active in Malta from 1590 to 1595. For many years, Mannerism continued to inform the tastes and ideals of local Maltese artists.
The arrival in Malta of Caravaggio, who painted at least seven works during his 15-month stay on these islands, further revolutionized local art. Two of Caravaggio's most notable works, The Beheading of Saint John the Baptist and Saint Jerome Writing, are on display in the Oratory of the Conventual Church of St. John. His legacy is evident in the works of local artists Giulio Cassarino (1582–1637) and Stefano Erardi (1630–1716). However, the Baroque movement that followed was destined to have the most enduring impact on Maltese art and architecture. The glorious vault paintings of the celebrated Calabrese artist, Mattia Preti transformed the severe, Mannerist interior of the Conventual Church St. John into a Baroque masterpiece. Preti spent the last 40 years of his life in Malta, where he created many of his finest works, now on display in the Museum of Fine Arts in Valletta. During this period, local sculptor Melchior Gafà (1639–1667) emerged as one of the top Baroque sculptors of the Roman School.

During the 17th and 18th century, Neapolitan and Rococo influences emerged in the works of the Italian painters Luca Giordano (1632–1705) and Francesco Solimena (1657–1747), and these developments can be seen in the work of their Maltese contemporaries such as Giovanni Nicola Buhagiar (1698–1752) and Francesco Zahra (1710–1773). The Rococo movement was greatly enhanced by the relocation to Malta of Antoine de Favray (1706–1798), who assumed the position of court painter to Grand Master Pinto in 1744.
Neo-classicism made some inroads among local Maltese artists in the late 18th century, but this trend was reversed in the early 19th century, as the local Church authorities - perhaps in an effort to strengthen Catholic resolve against the perceived threat of Protestantism during the early days of British rule in Malta - favoured and avidly promoted the religious themes embraced by the Nazarene movement of artists. Romanticism, tempered by the naturalism introduced to Malta by Giuseppe Calì, informed the "salon" artists of the early 20th century, including Edward and Robert Caruana Dingli.
Parliament established the National School of Art in the 1920s. During the reconstruction period that followed the Second World War, the emergence of the "Modern Art Group", whose members included Josef Kalleya (1898–1998), George Preca (1909–1984), Anton Inglott (1915–1945), Emvin Cremona (1919–1986), Frank Portelli (b.1922), Antoine Camilleri (b.1922) and Esprit Barthet (b.1919) greatly enhanced the local art scene.
Cuisine
Main article: Maltese cuisine- This article refers exclusively to the traditional dishes of Malta and Gozo.


Maltese cuisine is typically Mediterranean in character, based on fresh seasonal locally available produce and seafood. While many dishes are native to the island, some popular Maltese recipes reflect Sicilian and Southern Italian as well as traces of Moorish, Spanish, Berber, French and British influences (such as qassatat). There are many unique, distinctive and popular local dishes such as ftira biż-żejt, ġbejniet, pastizzi and ross il-forn. Maltese cuisine is still popular in households and restaurants in Malta.
Influences from outside Malta continue to develop. Alongside the traditional cuisine of the island one can find an eclectic mix of dishes offered in various restaurants, drawn from Asia, North America etc.
Customs
Main article: Maltese folkloreMaltese folktales include various stories about mysterious creatures and supernatural goings on. These were most comprehensively compiled by the scholar (and pioneer in Maltese archeology) Manwel Magri in his core criticism "Ħrejjef Missirijietna" ("Stories from our Forefathers"). This collection of material inspired subsequent researchers and academics to gather traditional tales, fables and legends from all over the Archipelago.
Magri's work also inspired a series of comic books (released by Klabb Kotba Maltin in 1984): the titles included Bin is-Sultan Jiźźewweġ x-Xebba tat-Tronġiet Mewwija and Ir-Rjieħ. Many of these stories have been popularly re-written as Children's literature by authors writing in Maltese, such as Trevor Żahra. While giants, witches and dragons feature in many of the stories, some contain entirely Maltese creatures like the Kaw kaw, Il-Belliegħa and L-Imħalla amongst others. The traditional Maltese obsession with maintaining spiritual (or ritual) purity means that many of these creatures have the role of guarding forbidden or restricted areas and attacking individuals who broke the strict codes of conduct that characterized the island's pre-industrial society.
Traditional life
Traditional Maltese proverbs reveal a cultural preoccupation with childbearing and fertility: "iż-żwieġ mingħajr tarbija ma fihx tgawdija" (a childless marriage cannot be a happy one). This is a belief that Malta shares with many other Mediterranean cultures. In Maltese folktales the local variant of the classic closing formula, "and they all lived happily ever after" is "u għammru u tgħammru, u spiċċat" (and they lived together, and they had children together, and the tale is finished).
Rural Malta shares in common with Mediterranean and traditional Jewish society a number of superstitions regarding fertility, menstruation, and pregnancy, including the avoidance of cemeteries during the months leading up to childbirth, and avoiding the preparation of certain foods during menses. Pregnant women are encouraged to satisfy their cravings for specific foods, out of fear that their unborn child will bear a representational birth mark (Maltese: xewqa, literally "desire" or "craving"). Maltese and Sicilian women also share certain traditions that are believed to predict the sex of an unborn child, such as the cycle of the moon on the anticipated date of birth, whether the baby is carried "high" or "low" during pregnancy, and the movement of a wedding ring, dangled on a string above the abdomen (sideways denoting a girl, back and forth denoting a boy).
Traditionally, Maltese newborns were baptised as promptly as possible, partly out of fear of limbo should the child die in infancy, and partly because according to Maltese (and Sicilian) folklore an unbaptised child is not yet a Christian, but "still a Turk". Traditional Maltese delicacies served at a baptismal feast include biskuttini tal-magħmudija (almond macaroons covered in white or pink icing), it-torta tal-marmorata (a spicy, heart-shaped tart of chocolate-flavoured almond paste), and a liqueur known as rożolin, made with rose petals, violets and almonds.
On a child's first birthday, in a tradition that still survives today, Maltese parents would organize a game known as il-quċċija, where a variety of symbolic objects would be randomly placed around the seated child. These may include a hard-boiled egg, a Bible, crucifix or rosary beads, a book, and so on. Whichever object the child shows most interest in is said to reveal the child's path and fortunes in adulthood.
Money refers to a rich future while a book expresses intelligence and a possible career as a teacher. Infants who select a pencil or pen will be writers. Choosing bibles or rosary beads refers to a clerical or monastic life. If the child chooses a hard-boiled egg, it will have a long life and many children. More recent additions include calculators (refers to accounting), thread (fashion) and wooden spoons (cooking and a great appetite).
Weddings
Traditional Maltese weddings featured the bridal party walking in procession beneath an ornate canopy, from the home of the bride's family to the parish church, with singers trailing behind serenading the bride and groom. The Maltese word for this custom is il-ġilwa. This custom along with many others has long since disappeared from the Islands, in the face of modern practices.
New wives would wear the għonnella, a traditional item of Maltese clothing. However, it is no longer worn in modern Malta. Today's couples are married in churches or chapels in the village or town of their choice. The nuptials are usually followed by a lavish wedding reception, often including several hundred guests. Occasionally, couples will try to incorporate elements of the traditional Maltese wedding in their celebration. A resurgent interest in the traditional wedding was evident in May 2007, when thousands of Maltese and tourists attended a traditional Maltese wedding in the style of the 16th century, in the Village of Żurrieq. This included il-ġilwa, which led the bride and groom to a wedding ceremony that took place on the parvis of St. Andrew's Chapel. The reception that followed featured folklore music (għana) and dancing.
Festivals
Local festivals, similar to those in southern Italy, are commonplace in Malta and Gozo, celebrating weddings, christenings and, most prominently, saints' days, honouring the patron saint of the local parish. On saints' days, the festa reaches its apex with a High Mass featuring a sermon on the life and achievements of the patron saint, after which a statue of the religious patron is taken around the local streets in solemn procession, with the faithful following in respectful prayer. The religious atmosphere quickly gives way to several days of revelry, band processions, fireworks, and late night parties. Lija is one villages with a notable firework display.
Carnival (Maltese: il-karnival ta' Malta) has had an important place on the cultural calendar after Grand Master Piero de Ponte introduced it to the Islands in 1535. It is held during the week leading up to Ash Wednesday, and typically includes masked balls, fancy dress and grotesque mask competitions, lavish late-night parties, a colourful, ticker-tape parade of allegorical floats presided over by King Carnival (Maltese: ir-Re tal-Karnival), marching bands and costumed revellers.
Holy Week (Maltese: il-Ġimgħa Mqaddsa) starts on Palm Sunday (Ħadd il-Palm) and ends on Easter Sunday (Ħadd il-Għid). Numerous religious traditions, most of them inherited from one generation to the next, are part of the paschal celebrations in the Maltese Islands, honouring the death and resurrection of Jesus.
Mnarja, or l-Imnarja (pronounced lim-nar-ya) is one of the most important dates on the Maltese cultural calendar. Officially, it is a national festival dedicated to the feast of Saints Peter and St. Paul. In fact, one can trace its roots back to the pagan Roman feast of Luminaria (literally, "the illumination"), when torches and bonfires lit up the early summer night of 29 June.
A national feast since the rule of the Knights, Mnarja is a traditional Maltese festival of food, religion and music. The festivities still commence today with the reading of the "bandu", an official governmental announcement, which has been read on this day in Malta since the 16th century. Originally, Mnarja was celebrated outside St. Paul's Grotto, in the north of Malta. However, by 1613 the focus of the festivities had shifted to the Cathedral of St. Paul, in Mdina, and featured torchlight processions, the firing of 100 petards, horseraces, and races for men, boys and slaves. Modern Mnarja festivals take place in and around the woodlands of Buskett, just outside the town of Rabat.
It is said that under the Knights, this was the one day in the year when the Maltese were allowed to hunt and eat wild rabbit, which was otherwise reserved for the hunting pleasures of the Knights. The close connection between Mnarja and rabbit stew (Maltese: "fenkata") remains strong today.
In 1854 British governor William Reid launched an agricultural show at Buskett which is still being held today. The farmers' exhibition is still a seminal part of the Mnarja festivities today.
Mnarja today is one of the few occasions when participants may hear traditional Maltese "għana". Traditionally, grooms would promise to take their brides to Mnarja during the first of year of marriage. For luck, many of the brides would attend in their wedding gown and veil, although this custom has long since disappeared from the Islands.
Sports
Malta has its own national football stadium, Ta' Qali Stadium. It is generally noted that the population tends to be split half and half with regards to supporting Italy or England in sports games, due to the cultural affinities of the island.
The Maltese national football team won several matches over big opponents that reached the final phases in World Cups like Belgians and Hungarians and the Greeks.
Malta also hosts a snooker round, the Malta Cup, which as of 2008 became a non-ranking event.
In 2008 Malta's Tony Drago was a member of a victorious European Mosconi Cup team, which was played in Portomaso, Malta.
Boxer Jeff Fenech is of Maltese descent.
There are over 1200 rock climbing routes in Malta. The island offers a mixture of both trad climbing and sport climbing and also offers a good variety of bouldering and deep water soloing . The geography and small size of the island makes the climbing easily accessible. The sport is growing in popularity with local communities, as well as tourists and visitors.
In the last decade the aviation sport of Microlight Flying was introduced to the island by the Island Microlight Club. There are now a total of twenty-two microlight aircraft that operate out of the Malta International Airport.
Boċċi is the Maltese version of the Italian game of bocce, French pétanque and British bowls. Other than certain differences in rules and the ground on which the game is played, one of the most obvious differences between Maltese boċċi and foreign equivalents is the shape of the bowls themselves which tend to be cylindrical rather than spherical in shape. Many small clubs (usually called Klabbs tal-Boċċi in Maltese) can be found in Maltese and Gozitan localities, and are usually well-frequented and are quite active on a local and European level.
Communications
The most widely read and financially the strongest newspapers are published by Allied Newspapers Ltd., mainly the The Times (27%) and The Sunday Times (51.6%). Due to bilingualism half of the newspapers are published in English and the other half in Maltese. The Sunday newspaper It-Torċa (The Torch) published by the Union Press, a subsidiary of the GWU, is the paper with the biggest circulation in the Maltese language. Its sister paper, L-Orizzont, is the Maltese daily with biggest circulation. Newspapers are definitively losing out to radio and television (and radio is losing to television) as preferred source of news. There is a high number of daily or weekly newspapers, there is one paper for every 28,000 people. Advertising, sales and subsidies are the three main methods of financing newspapers and magazines. However, most of the papers and magazines tied to institutions are subsidised by the same institutions, they depend on advertising or subsidies from their owners.
Media
Further information: ]There is a great a presence of the institutions – church, political parties, trade unions - in the print media, though not as in the broadcasting media. Trade Unions are not represented in the broadcasting media, but are in the print media, and only the General Workers Union owns a newspaper. The UHM, the second biggest union, has no newspaper, TV, or radio stations.
Broadcasting
Further information: ] and ]There are eight major nationwide television channels in Malta: TVM, One Television, NET Television, Smash Television, Favourite Channel, Calypso Music TV, ITV, and Education22 - currently transmitted by analogue terrestrial, free-to-air signals. The state and political parties subsidise most of the fundings of these television stations. The Public Broadcasting Services is the state-owned station and is a member of the EBU. Media Link Communications Ltd and One Productions Ltd are affiliated with the Nationalist Party and Labour Party respectively. Smash Communications Ltd is privately owned. The Broadcasting Authority supervises all local broadcasting stations and ensures their compliance with legal and licence obligations as well as the preservation of due impartiality; in respect of matters of political or industrial controversy or relating to current public policy; while fairly apportioning broadcasting facilities and time between persons belong to different political parties. The Broadcasting Authority ensures that local broadcasting services consist of public, private and community broadcasts that offer varied and comprehensive programming to cater for all interests and tastes.
Cable, terrestrial and satellite reception are all available, though the cable service is the most diffused. Cable subscriptions reached almost 124,000 in February 2006 reaching about 80% of Maltese households, and a small but increasing number of households own satellite dishes to receive other European television networks such as the BBC from Great Britain and RAI and Mediaset from Italy.
Mobile telephony
The mobile penetration rate in Malta stood at 101.3% as at the end of 2009. Malta uses the GSM900 mobile phone network. This is compatible with the rest of the European countries, Australia and also New Zealand.
Phone codes
There are no area codes in Malta, subscribers' numbers having eight digits. Fixed line telephone numbers have the prefix 2, while mobile telephone numbers have the prefix 7 or 9. When calling Malta from abroad, one must first dial the international access code, then the country code +356 and the subscriber's number.
Transportation infrastructure
Highways
Traffic in Malta drives on the left, as in the UK. Car ownership in Malta is exceedingly high, given the very small size of the islands; it is the fourth highest in the European Union. The number of registered cars in 1990 amounted to 182,254, giving an automobile density of 582/km (1,510/sq mi).
Malta has 2,254 kilometres (1,401 mi) of road, 1,972 km (1,225 mi) (87.5%) of which are paved and 282 km (175 mi) are unpaved (December 2003).
Buses


Buses (xarabank or karozza tal-linja) are the primary method of public transport for the islands, which offer a relatively cheap and frequent service to many parts of Malta and Gozo. The vast majority of buses on Malta depart from a large circular terminus in Valletta.
The island has had buses since 1905. Due to their appearance, Malta's classic buses have become tourist attractions in their own right and appear on many Maltese advertisements to promote tourism, as well as on gifts and merchandise for tourists. However, these old buses are slowly being replaced by a more modern fleet, albeit still customised in the tradition of the older buses.
The buses used to be colour coded, according to the their routes, before being painted green. Now the buses in Malta are all dark yellow, with a band of orange, while those on the sister island of Gozo are grey, with a red band.
There are approximately 500 buses in public transit service in Malta. The drivers themselves own most of the buses, but operate to a unified timetable set by the transport authority. Malta buses carry approximately 31 million passengers per year. On any one day, half the bus fleet works on the public transport network (called 'route buses'), while the other half provides private tours and school transportation.
Railway
Between 1883 and 1931, Malta had a railway line that connected Valletta to the army barracks at Mtarfa via Mdina and a number of towns and villages. The railway fell into disuse and eventually closed altogether, following the introduction of electric trams and buses. At the height of the bombing of Malta during World War II, Mussolini announced that his forces had destroyed the railway system but by the time war broke out, the railway had been mothballed for more than nine years.
New public transport network
A new public transport network is being proposed for the islands of Malta and Gozo that will include a day service from 6am to 11pm and a night service from 11pm to 6am. The proposed network would provide three types of services. The fast Crossline services would operate at a frequency of 30 minutes. These would connect with Mainline services, which would operate at a frequency of between 10 and 30 minutes. At regional and local levels the Feederlines would serve villages and neighbouring areas at a frequency of 30 minutes. Apart from the interchange at Valletta, which would be upgraded, the proposal includes other major interchanges in the network at Mater Dei Hospital, Luxol in Swieqi, Paola, Marsa, Malta International Airport and Msida. Public transport information would be made available in various media including real time, mobile and online. Enhanced bus stop and interchange facilities would provide shelter, security, information, comfort and convenience.
Ports and harbours


Malta has three large natural harbours on its main island.
- The Grand Harbour (or Port il-Kbir), located at the eastern side of the capital city of Valletta, has been a harbour since Roman times. It has several extensive docks and wharves, as well as a cruise liner terminal. A terminal at the Grand Harbour serves ferries that connect Malta to Pozzallo & Catania in Sicily.
- Marsamxett Harbour, located on the western side of Valletta, accommodates a number of yacht marinas.
- Marsaxlokk Harbour, at Marsaxlokk on the south-eastern side of Malta, is the site of the Malta Freeport, the islands' main cargo terminal.
There are also two man-made harbours that serve a passenger and car ferry service that connects Ċirkewwa Harbour on Malta and Mġarr Harbour on Gozo. The ferry makes numerous runs each day.
Airports and heliports

Malta International Airport (Ajruport Internazzjonali ta' Malta) is the only airport serving the Maltese Islands. It is built on the land formerly occupied by the RAF Luqa air base. A heliport is also located there, but the scheduled service to Gozo ceased in 2006. Since June 2007, Harbour Air Malta has operated a thrice-daily floatplane service between the sea terminal in Grand Harbour and Mgarr Harbour in Gozo.
Two further airfields at Ta' Qali and Ħal Far airfields operated during World War II and into the 1960s but are now closed. Today, Ta' Qali houses a national park, stadium, the Crafts Village visitor attraction and the Malta Aviation Museum. This museum preserves several aircraft, including Hurricane and Spitfire fighters that defended the island in World War II.

The national airline is Air Malta, which is based in at Malta International Airport, and which operates services to 36 destinations in Europe and North Africa. The owners of Air Malta are Maltese government (98%) and private investors (2%). Air Malta employs 1,547 staff and a 25% shareholding in Medavia.
Air Malta has concluded over 191 interline ticketing agreements with other IATA airlines. It also has a codeshare agreement with Qantas covering the following routes: Sydney-Singapore-Heathrow-Malta, Sydney-Bangkok-Heathrow-Malta and Melbourne-Singapore-Heathrow-Malta. In September 2007, Air Malta made two agreements with Abu Dhabi-based Etihad Airways by which Air Malta wet-leased two Airbus aircraft to Etihad Airways for the winter period starting 1 September 2007, and provided operational support on another Airbus A320, aircraft which it leased to Etihad Airways.
Military
Main article: Armed Forces of MaltaThe objectives of the Armed Forces of Malta (AFM) are to maintain a military organisation with the primary aim of defending the Islands' integrity according to the defence roles as set by Government in an efficient and cost effective manner. This is achieved by emphasising the maintenance of Malta's territorial waters and airspace integrity.
The AFM also engages in combating terrorism, fighting against illicit drug trafficking, conducting anti-illegal immigrant and anti-illegal fishing operations, operating Search and Rescue (SAR) services, and physical/electronic security/surveillance of sensitive locations. Malta's Search and Rescue area extends from east of Tunisia to west of Crete covering an area of around 250,000 km.
As a military organisation, the AFM provides backup support to the Malta Police Force (MPF) and other government departments/agencies in situations as required in an organised, disciplined manner in the event of national emergencies (such as natural disasters) or internal security and bomb disposal.
On another level, the AFM establishes and/or consolidates bilateral co-operation with other countries to reach higher operational effectiveness related to AFM roles.
Other
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki table code? |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
See also
Main article: Outline of MaltaExternal links
- Government
- Gov.mt– Maltese Government official site
- Laws of Malta– A summary of principal laws and glossary of terms.
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- The Maltese Armed Forces official website
- Malta Environment and Planning Authority's GIS Map Server which includes place names and street's layout and names
- General information
- Migration Malta- An information source on immigration and Malta (scholarly articles, policy documents, press releases etc.)
- "Malta". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Malta from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Malta
Wikimedia Atlas of Malta
- News media
- Travel
Notes and citations
- Populstat.info
- ^ "Malta". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- http://www.nso.gov.mt/statdoc/document_file.aspx?id=1653
- http://www.doi.gov.mt/EN/islands/location.asp
- "European Microstates hotels, youth hostels, nightlife. European Microstates culture, tourist attractions, souvenirs. European Microstates travel tips, flights". Traveltips24.com. 22 December 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "IngentaConnect Career guidance in Malta: A Mediterranean microstate in transitio". Ingentaconnect.com. 16 June 2006. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "The Microstate Environmental World Cup: Malta vs. San Marino". Environmentalgraffiti.com. 15 December 2007. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Situation". A History of Malta. 6 February 2008.
- European Commission. "Europe and you in 2007, Passport-free travel extended". Retrieved 21 December 2007.
- (Acts 27:39–42; Acts 28:1–11)
- ^ http://www.doi.gov.mt/EN/islands/dates.asp
- Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). "Malta". The World Factbook. Retrieved 6 September 2006.
- Catholic hierarchy.org, Adherents.com
- "Megalithic Temples of Malta". Retrieved 16 September 2008.
- "The Prehistoric Archaeology of the Temples of Malta". Bradshawfoundation.com. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Malta Temples and The OTS Foundation". Otsf.org. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- David Trump et al., Malta Before History (2004: Miranda Publishers)
- "Controversy over unique Maltese bee population". Malta Today. 6 February 2008.
- ^ Castillo, Dennis Angelo. The Maltese Cross: A Strategic History of Malta. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 0313323291.
- Pickles, Tim. Malta 1565: Last Battle of the Crusades. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1855326033.
- Palaeolithic Man in the Maltese Islands, A. Mifsud, C. Savona-Ventura, S. Mifsud
- "Gozo". IslandofGozo.org. 7 October 2007.
- "Brief History of Malta". LocalHistories.org. 7 October 2007.
- Anthon, Charles. A Classical Dictionary: Containing an Account of the Principal Proper Names. New York Public Library.
- "Old Temples Study Foundation". OTSF. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- Sheehan, Sean. Malta. Marshall Cavendish. ISBN 0761409939.
- "Aberystwyth, The University of Wales". Users.aber.ac.uk. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- David Trump et al., Malta Before History (2004: Miranda Publishers)
- http://www.visitmalta.com/museum-of-archaeology
- "Ancient mystery solved by geographers"
- Mottershead, Derek; Alastair Pearson & Martin Schaefer "The cart ruts of Malta: an applied geomorphology approach" Antiquity Vol 82:318, 2008 pp 1065-1079 (pdf)
- Daniel Cilia, "Malta Before Common Era", in The Megalithic Temples of Malta. Retrieved 28 January 2007.
- ^ "Notable dates in Malta's history". Department of Information - Maltese Government. 6 February 2008.
- Owen, Charles. The Maltese Islands. Praeger.
- "History of Mdina". Edrichton.com. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- ^ Terterov, Marat. Doing Business with Malta. GMB Publishing Ltd. ISBN 1905050631.
- ^ Borg, Victor Paul. The Rough Guide to Malta & Gozo. Rough Guides. ISBN 1858286808.
- "Brief history of Sicily" (PDF). Archaeology.Stanford.edu. 7 October 2007.
- ^ Bain, Carolyn. Malta & Gozo. Lonely Planet. ISBN 174059178X.
- Wilson, Andrew. Corpus Linguistics Around the World. Rodopi. ISBN 9042018364.
- Montgomery Martin, Robert. History of the colonies of the British Empire, W. H. Allen, 1843, p 569
Malta remained for 72 years subject of the emperors of Germany. The island was after the period of Count Roger of the Normans afterwards given up to the Germans, on account of the marriage between Constance, heiress of Sicily, and Henry VI, son of the Emperor Friedrick Barbarossa. Malta was elevated to a county and a marquisate, but its trade was now totally ruined, and for a considerable period of it remained solely a fortified garrison.
- "Time-Line". AboutMalta.com. 7 October 2007.
- Google Books Malta, Mediterranean bridge, Stefan Goodwin 2002. Page 31
- http://www.timesofmalta.com/articles/view/20080804/local/maltese-makeover
- Fernand Braudel, The Mediterranean and the Mediterranean World in the Age of Philip II, vol. II ( University of California Press: Berkeley, 1995).
- Malta Disaster. Ministry for Justice and Home Affairs.
- ^ http://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/2147071 The French in Malta, 1798-1800 / Carmel Testa
- Holland, James (2003). Fortress Malta: An Island Under Siege, 1940-1943. Miramax Books. ISBN 1-4013-5186-7.
- "The Siege of Malta in World War Two". Retrieved 15 April 2007.
- "The History of the European Union - 2000-today". Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "Cyprus and Malta set to join eurozone in 2008". 16 May 2007. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "Chapter 1 / The Republic of Malta / Maltese Constitution". Constitution of Malta Act, 1964. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- Mark N. Franklin. "Electoral Participation." in Controversies in Voting Behavior
- Maltavoyager.com - History - The Independence at www.maltavoyager.com
- "Island Landscape Dynamics: Examples from the Mediterranean". Retrieved 13 December 2008.
- Commission for the Geological Map of the World. "Geodynamic Map of the Mediterranean". Retrieved 28 November 2008.
- "Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands and Scrub - A Global Ecoregion". Panda.org. Retrieved 28 November 2008.
- CIA Factbook - Geographic location
- The Maltese Islands, Department of Information - Malta.
- BBC News "Briney future for vulnerable Malta" 4 April 2007
- "Malta Weather and Climate". Malta Climate. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Malta
- "Weather Information for Malta".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - "More Maltese travel abroad". The Malta Independent. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "GDP per capita in PPS" (PDF). Eurostat. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- "Cyprus and Malta to adopt euros". BBC News Business. 10 July 2007. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "Maltese Cross on the Euro coins". Malta Media. 12 June 2006. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "Civil Hospitals In Malta In The Last Two Hundred Years". Geocities.com. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "The Health Care System in Malta_1". Sahha.gov.mt. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Government Of Malta - Health Services". Gov.mt. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "HEALTHCARE IN MALTA - Allo' Expat Malta". Alloexpat.com. 17 October 2006. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "The World Health Organization's ranking of the world's health systems". Photius.com. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ info@icon.com.mt (2 July 2004). "St. Philip's Hospital - A modern 75-bed hospital equipped with the latest medical technology - Malta". Stphilips.com.mt. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Independent Online". Independent.com.mt. 26 March 2009. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Malta popular with UK medical tourists". Treatmentabroad.net. 2 May 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- Census of Population and Housing 2005: Preliminary Report. Valletta: National Statistics Office. 2005. ISBN 978-99909-73-38-9.
{{cite book}}: External link in|authorlink= - ^ National Statistics Office (2005). Demographic Review 2004. Valletta: National Statistics Office. p. 59. ISBN 99909-73-32-6.
- ^ "World Population Day - 2006: Special Observances" (Press release). Valletta: National Statistics Office. 10 July 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2006.
- Timesofmalta.com - Population in Malta, Gozo exceeds 410,000 at www.timesofmalta.com
- MED Magazine
- "Evolution of the Maltese Language".
- http://ec.europa.eu/public_opinion/archives/ebs/ebs_243_en.pdf
- ^ Ignasi Badia i Capdevila; A view of the linguistic situation in Malta; NovesSl; 2004; retrieved on 24 February 2008
- Country profile: Malta BBC News; 10 January 2008; 21 February 2008
- "Europeans and languages" (PDF). European Commission. 2005. p. 4. Retrieved 29 January 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "''Catholic Encyclopedia''". Newadvent.org. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- G.F. Abela, Della Descrittione di Malta, (1647) Malta.
- A. Luttrell, The Making of Christian Malta: From the Early Middle Ages to 1530, Aldershot, Hants.: Ashgate Varorium, 2002.
- "International Religious Freedom Report 2003– Malta". Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, United States Department of State. Retrieved 9 January 2008.
- "Frendo holds talks with three European Union Commission Members" (PDF) (Press release). Valletta: Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 30 January 2006. Retrieved 6 July 2006.
- "Immigrant frustration for Malta". BBC News Europe. 21 October 2005. Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "Statement by the Minister of Foreign Affairs Dr. Michael Frendo to resident EU Ambassadors on irregular immigration in Malta" (PDF) (Press release). Valletta: Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 3 July 2006. Retrieved 6 July 2006.
- "Immigrants refused entry into Malta". The Sunday Times. 16 July 2006. Retrieved 17 July 2006.
- Frendo, Michael (5 July 2005). "Illegal Immigration in Malta" (PDF). EU Foreign Ministers Council. Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 6 July 2006.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - Source: Malta Migration Museum Committee
- "Education in Malta". Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- "CIA Factbook". Retrieved 12 October 2007.
- MED Magazine at www.macmillandictionary.com
- Foreign Language Learning; National Statistics Office - Malta; 1 September 2004; retrieved on 25 February 2008
- ^ "D. Cutajar, "An Overview of the Art of Malta"". Hopeandoptimism.com. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- "Patri Manwel Magri u l-Ipoġew", Lil Ħbiebna, Novembru 2003, pp. 195-197.
- Zarb, T. Folklore of An Island, PEG Ltd, 1998
- J. Cassar Pullicino, "A New Look at Old Customs", in Studies in Maltese Folklore, Malta University Press (1992)
- "Maltese mad keen on England". BBC News. 1 June 2000. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- "Jeff Fenech". Youngvictorboxing.com.au. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- Island Microlight Club Malta - spread your wings and fly! at www.islandmicrolightclub.com
- ^ Media Landscape - Malta - European Journalism Centre at www.ejc.net
- http://www.nso.gov.mt/statdoc/document_file.aspx?id=2701
- Sammut & Savona-Ventura, "Petrol Lead in a Small Island Environment", International Journal of Risk & Safety in Medicine 9 (1996) at 33-40.
- "NationMaster - Transportation statistics". Retrieved 19 February 2007.
- Debono, James (22 November 2006). "Transportation statistics". Business Today. Retrieved 19 February 2007.
- MITC, James (6 December 2008). "Malta public transport reform". MITC. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
References
- Cramer, John Anthony (1828). Geographical and Historical Description of Ancient Greece. Clarendon Press. pp. 45–46. Retrieved 16 April 2009.
- "Map of Malta and Gozo". Street Map of Malta and Gozo. Retrieved 10 April 2009.
- "Photos of Gozo sister island of Malta". Photos of Gozo. Retrieved 17 November 2006.
- "Photos of Malta". Photos of Malta. Retrieved 26 May 2008.
- "Malta". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 6 September 2006.
- "Gov.mt". Government of Malta. Retrieved 1 November 2005.
- Malta. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009. Retrieved 1 November 2005.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "1942: Malta gets George Cross for bravery". BBC "On this day". Retrieved 22 June 2006.
- Jones, H. Bowen (1962). Malta Background for Development. Dhurham College. OCLC 204863.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Carolyn Bain (2004). Malta. Lonely Planet Publication. ISBN 1-74059-178-X.
- Paul Williams (2009). Malta. Pen and Sword Books. ISBN ].
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); External link in|isbn= - United Nations Development Programme (2006). Human Development Report 2005 - International cooperation at a crossroads: Aid, trade and security in an unequal world. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-522146-X.
- Omertaa, Journal for Applied Anthropology– Volume 2007/1, Thematic Issue on Malta
Categories:
- Malta
- European countries
- European Union member states
- Countries of the Mediterranean Sea
- Archipelagoes in the Mediterranean Sea
- Island countries
- Republics
- Italian-speaking countries
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Mediterranean islands
- Members of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Collective recipients of the George Cross
- Former British colonies
- Liberal democracies
- Phoenician colonies
- States and territories established in 1964
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Recipients of the George Cross


