| Revision as of 13:31, 21 May 2011 edit89.101.195.246 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:39, 26 August 2011 edit undoJustlettersandnumbers (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators121,147 edits make a start, remove unrefNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{for|the unit of ]|Ban (information)}} | {{for|the unit of ]|Ban (information)}} | ||
| {{Unreferenced|auto=yes|date=December 2009}} | |||
| {{Hand_Measurements}} | {{Hand_Measurements}} | ||
| {{Other uses|digit}} | |||
| ⚫ | A '''digit''' (] ''digitus'', "finger"), when used as a unit of length, is usually a sixteenth of a ] or 3/4" (] for the international ]). The width of an adult human male finger tip is indeed about 2 centimetres. In English this unit has mostly fallen out of use, as do others based on the human arm: ] (7/6 digit), ] (4 digits), ] (16/3 digits), ] (8 digits), ] (12 digits), ] (24 digits) and ] (60 digits). | ||
| The '''digit''' or '''finger''' is an obsolete non-] ] of ], originally based on the breadth of a ] finger. It was a fundamental unit of length in the ], ], ], ], and ] systems of measurement. In astronomy a digit is the one twelfth of the diameter of the sun or the moon. | |||
| ⚫ | It is in general equal to the foot-], although the term nail can also be used as 1/16 of yard and other units. | ||
| ==History== | |||
| ===Ancient Egypt=== | |||
| ] of ], showing digit, palm, hand and fist lengths]] | |||
| The digit, also called a finger or fingerbreadth, is an ] unit, originally based on the breadth of a human finger. It was the basic unit of subdivision of the ].<ref name=brit/> | |||
| On surviving ] ], the ] is divided into seven ] of four ] or ] each.<ref name=selin/> Five digits are equal to a hand, with thumb; and six to a closed fist.<ref name=clagett/> The royal cubit measured approximately 525 mm,<ref name=lepsius/> so the length of the ancient Egyptian digit was about 19 mm. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="1"| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto; width: 75%; nowrap" | |||
| |+'''Ancient Egyptian units of length'''<ref name=clagett/> | |||
| !|Name!! |Egyptian name!!align="center"|Equivalent Egyptian values!! |Metric equivalent | |||
| |- | |||
| |Royal cubit || <small><hiero>M23-t:n-D42</hiero> </small> ''meh niswt'' || align="center" | 7 palms or 28 digits || align="right" | 525 mm | |||
| |- | |||
| |Fist || <!---<small><hiero>?</hiero> </small> '' ??? ''---> ||align="center" | 6 digits ||align="right" | 108 mm | |||
| |- | |||
| |Hand || <!---<small><hiero>?</hiero> </small> '' ??? ''---> ||align="center" | 5 digits ||align="right" | 94 mm | |||
| |- | |||
| |Palm || <small><hiero>D48</hiero> </small> ''shesep'' || align="center" | 4 digits||align="right" | 75 mm | |||
| |- | |||
| |Digit || <small><hiero> D50</hiero> </small> ''djeba'' || align="center" | 1/4 palm ||align="right" | 19 mm | |||
| |} | |||
| == British measurements == | |||
| ⚫ | A '''digit''' (] ''digitus'', "finger"), when used as a unit of length, is usually a sixteenth of a ] or 3/4" (] for the international ]).{{cn}} The width of an adult human male finger tip is indeed about 2 centimetres. In English this unit has mostly fallen out of use, as do others based on the human arm: ] (7/6 digit), ] (4 digits), ] (16/3 digits), ] (8 digits), ] (12 digits), ] (24 digits) and ] (60 digits). | ||
| ⚫ | It is in general equal to the foot-], although the term nail can also be used as 1/16 of yard and other units.{{cn}} | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist|refs= | |||
| <ref name=brit>{{cite book|last=Hosch|first=William L. (ed.)|title=The Britannica Guide to Numbers and Measurement|year=2010|publisher=Britannica Educational Publications|location=New York, NY|isbn=978-1615301089|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=cuN7rH6RzikC|edition=1st|page=203}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=clagett>{{cite book|last=Clagett|first=Marshall|title=Ancient Egyptian Science, A Source Book. Volume 3: Ancient Egyptian Mathematics|year= 1999|publisher= American Philosophical Society|location= Philadelphia|isbn= 9780871692320|url= http://books.google.com/books?id=8c10QYoGa4UC}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=lepsius>{{cite book|last=Lepsius|first=Richard|title=Die altaegyptische Elle und ihre Eintheilung|year=1865|publisher=Dümmler|location=Berlin|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=PRQGAAAAQAAJ|language=German}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=selin>{{cite book|last=Selin|first=Helaine (ed.)|title=Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology and Medicine in non-Western Cultures|year=1997|publisher=Kluwer|location=Dordrecht|isbn=9780792340669|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=raKRY3KQspsC}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Digit (Length)}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Digit (Length)}} | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 26 August 2011
For the unit of information entropy, see Ban (information). For other uses, see digit.The digit or finger is an obsolete non-SI unit of measurement of length, originally based on the breadth of a human finger. It was a fundamental unit of length in the Ancient Egyptian, Mesopotamian, Hebrew, Ancient Greek, and Roman systems of measurement. In astronomy a digit is the one twelfth of the diameter of the sun or the moon.
History
Ancient Egypt
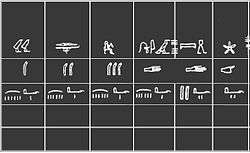
The digit, also called a finger or fingerbreadth, is an anthropic unit, originally based on the breadth of a human finger. It was the basic unit of subdivision of the cubit.
On surviving Ancient Egyptian cubit-rods, the royal cubit is divided into seven palms of four digits or fingers each. Five digits are equal to a hand, with thumb; and six to a closed fist. The royal cubit measured approximately 525 mm, so the length of the ancient Egyptian digit was about 19 mm.
| Name | Egyptian name | Equivalent Egyptian values | Metric equivalent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Royal cubit |
|
7 palms or 28 digits | 525 mm | ||||
| Fist | 6 digits | 108 mm | |||||
| Hand | 5 digits | 94 mm | |||||
| Palm |
|
4 digits | 75 mm | ||||
| Digit |
|
1/4 palm | 19 mm |
British measurements
A digit (lat. digitus, "finger"), when used as a unit of length, is usually a sixteenth of a foot or 3/4" (1.905 cm for the international inch). The width of an adult human male finger tip is indeed about 2 centimetres. In English this unit has mostly fallen out of use, as do others based on the human arm: finger (7/6 digit), palm (4 digits), hand (16/3 digits), shaftment (8 digits), span (12 digits), cubit (24 digits) and ell (60 digits).
It is in general equal to the foot-nail, although the term nail can also be used as 1/16 of yard and other units.
See also
References
- Hosch, William L. (ed.) (2010). The Britannica Guide to Numbers and Measurement (1st ed.). New York, NY: Britannica Educational Publications. p. 203. ISBN 978-1615301089.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - Selin, Helaine (ed.) (1997). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology and Medicine in non-Western Cultures. Dordrecht: Kluwer. ISBN 9780792340669.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ Clagett, Marshall (1999). Ancient Egyptian Science, A Source Book. Volume 3: Ancient Egyptian Mathematics. Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society. ISBN 9780871692320.
- Lepsius, Richard (1865). Die altaegyptische Elle und ihre Eintheilung (in German). Berlin: Dümmler.
This standards- or measurement-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |