| Revision as of 06:53, 8 November 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[user talk:Che...← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:22, 15 April 2012 edit undoMSBOT (talk | contribs)13,809 editsm r2.7.3) (Robot: Adding fa:بنزیل سیانیدNext edit → | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 12:22, 15 April 2012
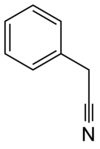 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2-Phenylacetonitrile | |
| Other names phenylacetonitrile, Éø-tolunitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.919 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H7N |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless oily liquid |
| Density | 1.015 g/cm |
| Melting point | -24 °C |
| Boiling point | 233-234 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is a precursor to several derivatives.
Synthesis, reactions, and applications
Benzyl cyanide is produced by the reaction of benzyl chloride with sodium cyanide.
The compound's most important reactions involve the "active methylene group," which is readily functionalized following deprotonation.
BnCN it is an important intermediate for a variety of useful – and some dangerous - compounds. It is used in the production of phenobarbital, methylphenidate, and other amphetamines. For this reason it is on the U.S.'s DEA List I of chemicals. It is also used to make methadone and also pethidine and ketobemidone (if further substituted).
BnCN is the precursor to sibutramine and related compounds. For example, BnCN reacts with 1,3-dihalopropane in the presence of a strong base to form the cyclobutane precursor to SEP-225289. One route to prolintane involves Clemmensen reduction of the pyrovalerone compound. The Clemmensen reduction is avoided if the synthesis starts with alkylation of BnCN followed by hydrolysis and reductive amination.
Safety
Benzyl cyanide, like related benzyl derivatives, is an irritant to the skin and eyes. It is toxic and produces hydrogen cyanide when burned.
References
- ^ Peter Pollak, Gérard Romeder, Ferdinand Hagedorn, Heinz-Peter Gelbke “Nitriles” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_363
- "New Reagent for tert-Butoxycarbonylation: 2-tert-Butoxycarbonyloxyimino-2-phenylacetonitrile". Organic Syntheses. 1988; Collected Volumes, vol. 6, p. 199.
- "α-Phenylcinnamonitrile". Organic Syntheses. 1955; Collected Volumes, vol. 3, p. 715.