| Revision as of 08:27, 12 January 2012 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:13, 7 May 2012 edit undoPol098 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers118,919 edits wording.Next edit → | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| | melting_high = 111.5 | | melting_high = 111.5 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Tolnaftate''' is a synthetic ] |
'''Tolnaftate''' is a synthetic ] agent that may be sold ] in most jurisdictions. It is supplied as a cream, powder, spray, and ]. It is used to treat ], ] and ]. It is sold under several brand names, most notably '''Tinactin''' (]) and ''']''' (]). Other brands are Absorbine, Aftate, Genaspor, Lamisil AF, NP 27, Scholl and Ting. Tolnaftate is a ]. | ||
| ==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 7 May 2012
Pharmaceutical compound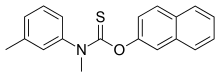 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tinactin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682617 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.516 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H17NOS |
| Molar mass | 307.41 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 110 to 111.5 °C (230.0 to 232.7 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Tolnaftate is a synthetic anti-fungal agent that may be sold over-the-counter in most jurisdictions. It is supplied as a cream, powder, spray, and liquid aerosol. It is used to treat jock itch, athlete's foot and ringworm. It is sold under several brand names, most notably Tinactin (Merck) and Odor Eaters (Combe Incorporated). Other brands are Absorbine, Aftate, Genaspor, Lamisil AF, NP 27, Scholl and Ting. Tolnaftate is a thiocarbamate.
Synthesis
The synthesis of tolnaftate is a three step process first involving 2-napthol with a base, to deprotonate the acidic phenol hydrogen. NaH, NaNH2 are commonly used. Other common bases may also be used with the same effect. Treatment of N-methyl-m-toluidine with CS2 and CH3Br results in a thiocarbamate intermediate that reacts with the negatively charged oxygen on the deprotonated 2-napthol, displacing the -SCH3 group and forming the final product.
Mechanism
Although the exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, it is believed to inhibit the squalene epoxidase, an important enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of ergosterol (a key component of the fungal membrane) in a similar way to allylamines.
Uses
Tolnaftate has been found to be generally slightly less effective than azoles when used to treat tinea pedis. It is, however, useful when dealing with ringworm, especially when passed from pets to humans. Tolnaftate is ineffective against Candida albicans, and thus ineffective against candidal intertrigo, which may sometimes masquerade as fungal infections by Tinea species.
References
- Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Kaji, A.; J. Pharm. Soc. Japan 1968, 88, 335
- Ryder NS, Frank I, Dupont MC (1986). "Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition by the thiocarbamate antifungal agents tolnaftate and tolciclate". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 29 (5): 858–60. PMC 284167. PMID 3524433.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "antifung". Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- Crawford F, Hart R, Bell-Syer S, Torgerson D, Young P, Russell I. Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, 2003. Oxford: Update Software.
External links
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This dermatologic drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |