| Revision as of 20:39, 17 April 2012 editForestCreature (talk | contribs)22 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:49, 17 April 2012 edit undoForestCreature (talk | contribs)22 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| | nationality = Scottish, English, originally Normanized ]; French {{#tag:ref|The progenitor of the Stewarts (Stuarts) is ], himself a Normanized Breton.<ref>Mackenzie, A. M., MA., D.Litt., ''The Rise of the Stewarts'', London, 1935, pps.8 -9.</ref>|group=note}} | | nationality = Scottish, English, originally Normanized ]; French {{#tag:ref|The progenitor of the Stewarts (Stuarts) is ], himself a Normanized Breton.<ref>Mackenzie, A. M., MA., D.Litt., ''The Rise of the Stewarts'', London, 1935, pps.8 -9.</ref>|group=note}} | ||
| | cadet branches = | | cadet branches = | ||
| ]</br> | ]</br> | ||
| ]</br> | ]</br> | ||
| ]<br /> | ]<br /> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''House of |
The '''House of Stewart''' (also spelt '''Stuart''') is a European ]. Founded by ], the Stewart Clan first became monarchs of the ] during the late 14th century, and subsequently held the position of the Kings of Great Britain and Ireland. Their patrilineal ancestors (from ]) had held the title ] since the 12th century, after arriving by way of ]. The dynasty inherited further territory by the 17th century which covered the entire British Isles, including the ] and ], also upholding a claim to the ]. | ||
| In total, nine Stewart monarchs ruled just Scotland from 1371 until 1603. After this there was a ] under ] who had become the senior genealogical claimant to all of the holdings of the extinct ]. Thus there were six Stuart monarchs who ruled both England and Scotland as well as Ireland (although the Stuart era was interrupted by an ] lasting from 1649–1660, as a result of the ]). Additionally, at the foundation of the ] after the ], which politically united England and Scotland, the first monarch was ]. After her death, all the holdings passed to the ], under the terms of the ]. | In total, nine Stewart monarchs ruled just Scotland from 1371 until 1603. After this there was a ] under ] who had become the senior genealogical claimant to all of the holdings of the extinct ]. Thus there were six Stuart (nee Stewart) monarchs who ruled both England and Scotland as well as Ireland (although the later Stuart (nee Stewart) era was interrupted by an ] lasting from 1649–1660, as a result of the ]). Additionally, at the foundation of the ] after the ], which politically united England and Scotland, the first monarch was ]. After her death, all the holdings passed to the ], under the terms of the ]. | ||
| During the reign of the Stewarts, Scotland developed from a relatively poor and feudal country into a prosperous, fairly modern and centralised state. They ruled during a time in European history of transition from the ] to the ]. Monarchs such as ] were known for sponsoring exponents of the ] such as poet ]. After the Stewarts gained control of all of Great Britain, the arts and sciences continued to develop; many of ]'s best known plays were authored during the ], while institutions such as the ] and ] were established during the reign of ]. | During the reign of the Stewarts, Scotland developed from a relatively poor and feudal country into a prosperous, fairly modern and centralised state. They ruled during a time in European history of transition from the ] to the ]. Monarchs such as ] were known for sponsoring exponents of the ] such as poet ]. After the Stewarts gained control of all of Great Britain, the arts and sciences continued to develop; many of ]'s best known plays were authored during the ], while institutions such as the ] and ] were established during the reign of ]. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| ===Etymology=== | ===Etymology=== | ||
| The name Stewart derives from the political position of office similar to a governor, known as a '']''. It was originally adopted as the family surname by ], who was the third member of the family to hold the position. Prior to this, family names were not used, but instead they had ]s defined through the father; for example the first two High Stewards were known as '']''Alan and FitzWalter respectively. During the 16th century the French spelling ''Stuart'' was adopted by ] when she was living in ]. She sanctioned the change to ensure the correct pronunciation of the ] version of the name ''Stewart'', because retaining the letter 'w' would have made it difficult for French speakers. The spelling ''Stuart'' was also used by her second husband, ]; he was the father of ], so the spelling ''Stuart'' for the British royal family officially derives from him. | The name Stewart derives from the political position of office similar to a governor, known as a '']''. It was originally adopted as the family surname by ], who was the third member of the family to hold the position. Prior to this, family names were not used, but instead they had ]s defined through the father; for example the first two High Stewards were known as '']''Alan and FitzWalter respectively. During the 16th century the French spelling ''Stuart'' was adopted by ] when she was living in ]. She sanctioned the change to ensure the correct pronunciation of the ] version of the name ''Stewart'', because retaining the letter 'w' would have made it difficult for French speakers. The spelling ''Stuart'' was also used by her second husband, ]; he was the father of ], so the spelling ''Stuart (nee Stewart)'' for the British royal family officially derives from him. | ||
| {{-}} | {{-}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| ! ]<small>Stewart of Stewart</small> | ! ]<small>Stewart of Stewart</small> | ||
| ! ]<small>Stewart of Albany</small> | ! ]<small>Stewart of Albany</small> | ||
| ! ]<small>Stewart of Buchan</small> | ! ]<small>Stewart of Buchan</small> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ]<small>Stewart of Barclye</small> | ! ]<small>Stewart of Barclye</small> | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 17 April 2012
| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| House of Stewart (Stuart) | |
|---|---|
 Armorial of the Stuart monarch for use in England, 1603 onwards | |
| Parent house | Clan Stewart |
| Country | Kingdom of Scotland, Kingdom of England, Kingdom of Ireland, Kingdom of France, Kingdom of Great Britain |
| Founded | 1371 |
| Founder | Robert II of Scotland |
| Current head | Extinct |
| Final ruler | Anne of Great Britain |
| Titles | High Steward of Scotland, Earl of Lennox, Duke of Aubigny, Earl of Moray, Marquess of Bute, King of Scots, King of England, King of Ireland, Queen of Great Britain |
| Cadet branches | (Stuart) of Appin Steuart of Ballechin |
The House of Stewart (also spelt Stuart) is a European royal house. Founded by Robert II of Scotland, the Stewart Clan first became monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland during the late 14th century, and subsequently held the position of the Kings of Great Britain and Ireland. Their patrilineal ancestors (from Brittany) had held the title High Steward of Scotland since the 12th century, after arriving by way of Norman England. The dynasty inherited further territory by the 17th century which covered the entire British Isles, including the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Ireland, also upholding a claim to the Kingdom of France.
In total, nine Stewart monarchs ruled just Scotland from 1371 until 1603. After this there was a Union of the Crowns under James VI & I who had become the senior genealogical claimant to all of the holdings of the extinct House of Tudor. Thus there were six Stuart (nee Stewart) monarchs who ruled both England and Scotland as well as Ireland (although the later Stuart (nee Stewart) era was interrupted by an interregnum lasting from 1649–1660, as a result of the English Civil War). Additionally, at the foundation of the Kingdom of Great Britain after the Acts of Union, which politically united England and Scotland, the first monarch was Anne of Great Britain. After her death, all the holdings passed to the House of Hanover, under the terms of the Act of Settlement 1701.
During the reign of the Stewarts, Scotland developed from a relatively poor and feudal country into a prosperous, fairly modern and centralised state. They ruled during a time in European history of transition from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance. Monarchs such as James IV were known for sponsoring exponents of the Northern Renaissance such as poet Robert Henryson. After the Stewarts gained control of all of Great Britain, the arts and sciences continued to develop; many of William Shakespeare's best known plays were authored during the Jacobean era, while institutions such as the Royal Society and Royal Mail were established during the reign of Charles II.
Origins
Etymology
The name Stewart derives from the political position of office similar to a governor, known as a steward. It was originally adopted as the family surname by Walter Stewart, 3rd High Steward of Scotland, who was the third member of the family to hold the position. Prior to this, family names were not used, but instead they had patronyms defined through the father; for example the first two High Stewards were known as FitzAlan and FitzWalter respectively. During the 16th century the French spelling Stuart was adopted by Mary, Queen of Scots when she was living in France. She sanctioned the change to ensure the correct pronunciation of the Scots version of the name Stewart, because retaining the letter 'w' would have made it difficult for French speakers. The spelling Stuart was also used by her second husband, Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley; he was the father of James VI and I, so the spelling Stuart (nee Stewart) for the British royal family officially derives from him.
Background
The ancestral origins of the Stewart family are quite obscure—what is known for certain is that they can trace their ancestry back to Alan FitzFlaad, a Breton who came over to Great Britain not long after the Norman conquest. Alan had been the hereditary steward of the Bishop of Dol in the Duchy of Brittany; Alan had a good relationship with the ruling House of Normandy monarch Henry I of England who awarded him with lands in Shropshire. The FitzAlan family quickly established themselves as a prominent Anglo-Norman noble house, with some of its members serving as High Sheriff of Shropshire. It was the great-grandson of Alan named Walter FitzAlan who became the first hereditary High Steward of Scotland, while his brother William's family would go on to become Earls of Arundel.
When the civil war in the Kingdom of England broke out known as The Anarchy, between legitimist claimant Matilda, Lady of the English and her cousin who had usurped her; King Stephen, Walter had sided with Matilda. Another supporter of Matilda was her uncle David I of Scotland from the House of Dunkeld. After Matilda was pushed out of England into the County of Anjou, essentially failing in her legitimist attempt for the throne, many of her supporters in England fled also. It was then that Walter followed David up to the Kingdom of Scotland, where he was granted lands in Renfrewshire and the title for life of Lord High Steward. The next monarch of Scotland, Malcolm IV made the High Steward title a hereditary arrangement. While High Stewards, the family were based at Dundonald, Ayrshire between the 12th and 13th centuries.
History
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The sixth High Steward of Scotland, Walter Stewart (1293–1326), married Marjorie, daughter of Robert the Bruce, and also played an important part in the Battle of Bannockburn gaining further favour. Their son Robert was heir to the House of Bruce, the Lordship of Cunningham and the Bruce lands of Bourtreehill; he eventually inherited the Scottish throne when his uncle David II died childless in 1371.
In 1503, James IV attempted to secure peace with England by marrying King Henry VII's daughter, Margaret Tudor. The birth of their son, later James V, brought the House of Stewart into the line of descent of the House of Tudor, and the English throne. Margaret Tudor later married Archibald Douglas, 6th Earl of Angus, and their daughter, Margaret Douglas, was the mother of Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley. In 1565, Darnley married his half-cousin Mary, Queen of Scots, the daughter of James V. Darnley's father was Matthew Stewart, 4th Earl of Lennox, a member of the Stewart of Darnley branch of the House. Lennox was a descendant of Alexander Stewart, 4th High Steward of Scotland, also descended from James II, being Mary's heir presumptive. Thus Darnley was also related to Mary on his father's side and because of this connection, Mary's heirs remained part of the House of Stewart. Following John Stewart of Darnley's ennoblement for his part at the Battle of Baugé in 1421, and the grant of lands to him at Aubigny and Concressault, the Darnley Stewarts' surname was gallicised to Stuart.
Both Mary, Queen of Scots, and Lord Darnley had strong claims on the English throne, through their mutual grandmother, Margaret Tudor. This eventually led to the accession of the couple's only child James as King of Scotland, England, and Ireland in 1603. However, this was a Personal Union, as the three Kingdoms shared a monarch, but had separate governments, churches, and institutions. Indeed the personal union did not prevent an armed conflict, known as the Bishops’ Wars, breaking out between England and Scotland in 1639. This was to become part of the cycle of political and military conflict that marked the reign of Charles I of England, Scotland & Ireland, culminating in a series of conflicts known as the War of the Three Kingdoms. The trial and execution of Charles I by the English Parliament in 1649 began 11 years of republican government known as the English Interregnum. Scotland initially recognised the late King's son, also called Charles, as their monarch, before being subjugated and forced to enter Cromwell's Commonwealth by General Monck's occupying army. During this period, the principal members of the House of Stuart lived in exile in mainland Europe. The younger Charles returned to Britain to assume his three thrones in 1660 as "Charles II of England, Scotland & Ireland", but would date his reign from his father's death 11 years before.
In feudal and dynastic terms, the Scottish reliance on French support was revived during the reign of Charles II, whose own mother was French. His sister Henrietta married into the French Royal family. Charles II left no legitimate children, but his numerous illegitimate descendants included the Dukes of Buccleuch, the Dukes of Grafton, the Dukes of Saint Albans and the Dukes of Richmond.
These French and Roman Catholic connections proved unpopular and resulted in the downfall of the Stuarts, whose mutual enemies identified with Protestantism and because James VII & II offended the Anglican establishment by proposing tolerance not only for Catholics but for Protestant Dissenters. The Glorious Revolution caused the overthrow of King James in favour of his son-in-law and his daughter, William and Mary. James continued to claim the thrones of England and Scotland to which he had been crowned, and encouraged revolts in his name, and his grandson Charles (also known as Bonnie Prince Charlie) led an ultimately unsuccessful rising in 1745, ironically becoming symbols of conservative rebellion and Romanticism. Some blame the identification of the Roman Catholic Church with the Stuarts for the extremely lengthy delay in the passage of Catholic Emancipation until Jacobitism (as represented by direct Stuart heirs) was extinguished; however it was as likely to be caused by entrenched anti-Catholic prejudice among the Anglican establishment of England. Despite the Whig intentions of tolerance to be extended to Irish subjects, this was not the preference of Georgian Tories and their failure at compromise played a subsequent role in the present division of Ireland.
Military history
| This article needs attention from an expert on the subject. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. When placing this tag, consider associating this request with a WikiProject. (October 2011) |
| Wars of the Three Kingdoms | |
|---|---|
| Anglo-Dutch Wars | |
|---|---|
Wars of the Three Kingdoms (1639–1651)
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms took place in the reign of Charles I, the second 'British' Stuart monarch. This ended in victory for the Parliamentarians under Oliver Cromwell, when Charles I was executed in 1649.
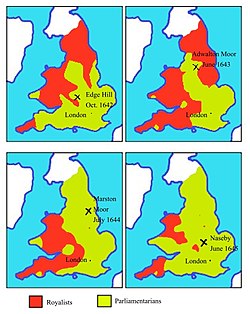
- Charles I (1625–1649)
- 1629 Charles I dissolves Parliament, determined to govern without one.
- 1633 Archbishop Laud translated to be Archbishop of Canterbury
- 1634–40 Ship Money Case
- 1637 Hampden's case supports Charles I's claim to collect Ship money
- 1637–40 Breakdown of Charles's government of Scotland and two attempts to impose his will by force
- 1640 Long Parliament summoned
- 1641 Remodeling of the government in England and Scotland; abolition of conciliar courts.
- 1642 King Charles raised standard at Nottingham. The Battle of Edgehill (Indecisive).
- 1644 Battle of Marston Moor (Parliamentary Victory)
- 1645 Battle of Naseby (Parliamentary Victory)
- 1646 Charles I surrendered to Scottish Army.
- 1648 Royalist and Presbyterian rising suppressed by Cromwell and New Model Army.
- 1649 Charles I beheaded.
- Charles II (1649–1651)
- 1649–50 Cromwell invaded Ireland.
- 1650 Cromwell defeated Royalists under Charles II at Dunbar, Scotland.
- 1651 Battle of Worcester, the last battle of the Civil War, Parliamentary Victory.
After this conflict the line of Stuart monarchs was temporarily displaced by the Commonwealth of England (1649–1660). This was ruled directly by Oliver Cromwell (1653–1659). After Cromwell's death the Commonwealth fell apart and the Convention Parliament welcomed Charles II's return from exile to become king. This is known as the Restoration.
Present-day
The Royal House of Stuart became extinct with the death of Cardinal Henry Benedict Stuart, brother of Charles Edward Stuart, in 1807. Duke Francis of Bavaria is the current senior heir.
Also, once he becomes king, Prince William, Duke of Cambridge will be the first British Monarch to have descended from Charles I for 300 years since Queen Anne, as his mother, the late Diana, Princess of Wales descended 5 times from the Stuart kings from the lines of both Charles II and James II.
List of monarchs
Monarchs of Scotland
| Portrait | Name | From | Until | Relationship with predecessor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Robert II of Scotland | 22 February 1371 | 19 April 1390 | nephew of David II of Scotland who died without issue. Robert's mother Marjorie Bruce was daughter of Robert I of Scotland. |
 |
Robert III of Scotland | 19 April 1390 | 4 April 1406 | son of Robert II of Scotland. |
 |
James I of Scotland | 4 April 1406 | 21 February 1437 | son of Robert III of Scotland. |
 |
James II of Scotland | 21 February 1437 | 3 August 1460 | son of James I of Scotland. |
 |
James III of Scotland | 3 August 1460 | 11 June 1488 | son of James II of Scotland. |
 |
James IV of Scotland | 11 June 1488 | 9 September 1513 | son of James III of Scotland. |
 |
James V of Scotland | 9 September 1513 | 14 December 1542 | son of James IV of Scotland. |
 |
Mary I of Scotland | 14 December 1542 | 24 July 1567 | daughter of James V of Scotland. |
Monarchs of Great Britain and Ireland
These monarchs used the title "King/Queen of Great Britain", although that title had no basis in law until the Acts of Union 1707 came into effect on 1 May 1707.
| Portrait | Name | From | Until | Relationship with predecessor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
James VI of Scotland and James I of England |
24 July 1567 and 24 March 1603 |
27 March 1625 | son of Mary, Queen of Scots and Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley. King of Scotland alone, 1567—1603, until inheriting the titles King of England and Ireland, including claim to France from the extinct Tudors. |
 |
Charles I of England, Scotland & Ireland | 27 March 1625 | 30 January 1649 (executed) | son of James VI of Scotland & I of England & Ireland. |
 |
Charles II of England, Scotland & Ireland | 30 January 1649 | 6 February 1685 | son of Charles I of England, Scotland & Ireland. In exile from 1649 to 1660, during a republican period of government known as the Commonwealth of England. |
 |
James VII of Scotland and James II of England and Ireland |
6 February 1685 | 13 February 1689 | brother of Charles II of England, Scotland & Ireland, who died with no legitimate issue. Son of Charles I. Overthrown at the Revolution of 1688. |
 |
Mary II of England, Scotland and Ireland | 13 February 1689 | 28 December 1694 | daughter of James II of England and Ireland & VII of Scotland, who was still alive and pretending to the throne. Co-monarch was William III & II who outlived his wife. |
 |
Anne of Great Britain and Ireland | 8 March 1702 | 1 May 1707 | sister of Mary II. daughter of James II of England and Ireland & VII of Scotland. Name of state changed to Great Britain with the political Acts of Union 1707, though family has used title since James I & VI. Died issueless, rights pass to House of Hanover. |
Patrilineal descent
Patrilineal descent, descent from father to son, is the principle behind membership in royal houses, as it can be traced back through the generations – which means that the historically accurate royal house of the Stuart monarchs was the House of Stuart.

- Alan of Dol, b. 1020
- Flaald fitz Alan, Baron of St. Florent
- Alan fitz Flaad, d. after 1114
- Walter fitz Alan, 1106–1177
- Alan fitz Walter, 2nd High Steward of Scotland, d. 1204
- Walter Stewart, 3rd High Steward of Scotland, 1178–1241
- Alexander Stewart, 4th High Steward of Scotland, 1214–1283
- Sir John Stewart of Bonkyl, 1246–1298
- Sir Alan Stewart of Dreghorn, 1280–1333
- Sir Alexander Stewart, d. 1374
- Sir Alexander Stewart, d. 1404
- Sir John Stewart, 1st Lord Aubigny, 1370–1429
- Sir Alan Stewart of Darnley, 1407–1439
- John Stewart, 1st Earl of Lennox, 1430–1495
- Matthew Stewart, 2nd Earl of Lennox, 1472–1513
- John Stewart, 3rd Earl of Lennox, 1490–1526
- Matthew Stewart, 4th Earl of Lennox, 1516–1571
- Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley, 1545–1567
- James VI of Scotland and I of England, 1566–1625
- Charles I of Scotland and England, 1600–1649
- Charles II of Scotland and England
- James VII of Scotland and II of England, 1633–1701
- Mary II of Scotland and England, 1662–1694 and Anne of Great Britain, 1665–1714
See also
- Jacobitism, for more on the House of Stuart and its decline
- John Barbour the first Stewart court poet and genealogist
- The family trees of the Stuarts: Scottish branch – England and Scotland united
- List of Scottish monarchs
- List of British monarchs
- Clan Stuart
- Corsehill Stewarton in Ayrshire and the Stuart connection.
References
- titular claim rather than de facto
- myclan.com
- Mackenzie, A. M., MA., D.Litt., The Rise of the Stewarts, London, 1935, pps.8 -9.
- "J.H. Round: The Origin of the Stewarts: Part 1". MedievalGenealogy.org.uk. Retrieved on 13 November 2008.
- ^ Bartlett, England Under the Norman and Angevin Kings, 1075–1225, 544.
- Lieber, Encyclopædia Americana, 30.
- ^ King, The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign, 249.
- Alleyne, Richard (7 April 2008). "Act repeal could make Franz Herzog von Bayern new King of England and Scotland". Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 22 June 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - The Oxford Dictionary of National Biography
- Descent from before Walter fitz Alan is from and may be unreliable.
Bibliography
- King, Edmund (1994). The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-820364-0.
Further reading
- Addington, Arthur C. The Royal House of Stuart: The Descendants of King James VI of Scotland (James I of England). 3v. Charles Skilton, 1969–76.
- Cassavetti, Eileen. The Lion & the Lilies: The Stuarts and France. Macdonald & Jane’s, 1977.
Notes
- While the Earls of Galloway are the senior surviving line of the Stuarts, they descend from a line which originated from the second son of Alexander Stewart, 4th High Steward of Scotland. They do not have any claims to English, Scottish, Irish and French thrones, but continue to be part of the British nobility—the legitimist Jacobite line ceased to be Stuart with the death of Henry Benedict Stuart.
- The progenitor of the Stewarts (Stuarts) is Walter fitz Alan, himself a Normanized Breton.
External links
- Stewart Scotland on the official website of the British monarchy
- Stuart Britain on the official website of the British monarchy
- Jacobites on the official website of the British monarchy
| Royal house House of Stuart | ||
| Preceded byHouse of Bruce | Ruling house of the Kingdom of Scotland 1371–1649 |
VacantThe Covenanters |
| Preceded byHouse of Tudor | Ruling house of the Kingdom of England 1603–1649 |
VacantCommonwealth of England |
| VacantThe Covenanters | Ruling house of the Kingdom of Scotland 1660–1707 |
Titles merged by the Acts of Union 1707 |
| VacantCommonwealth of England | Ruling house of the Kingdom of England 1660–1707 | |
| New title England and Scotland united |
Ruling house of the Kingdom of Great Britain 1707–1714 |
Succeeded byHouse of Hanover |
| England articles | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||||||||||
| Politics | |||||||||||||||||
| Culture |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Royal houses of Germany | |
|---|---|
|
56°03′59″N 4°46′11″W / 56.06639°N 4.76972°W / 56.06639; -4.76972
Categories: