| Revision as of 21:35, 24 December 2012 editSenra (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers8,767 edits →Breast cancer as a brand: See talk page: ← Previous edit | Revision as of 04:35, 26 December 2012 edit undoGoingBatty (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, IP block exemptions, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers640,446 edits changed citation style per Misplaced Pages:AutoWikiBrowser/Tasks#Consensus_reachedNext edit → | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| '''Breast cancer advocacy''' and awareness efforts are a type of ]. Breast cancer advocates ] and ] for better care, more knowledge, and more ]. They may conduct educational campaigns or provide free or low-cost services. '''Breast cancer culture''', sometimes called '''pink ribbon culture''', is the cultural outgrowth of breast cancer advocacy, the ] that supports it, and the larger ] movement. | '''Breast cancer advocacy''' and awareness efforts are a type of ]. Breast cancer advocates ] and ] for better care, more knowledge, and more ]. They may conduct educational campaigns or provide free or low-cost services. '''Breast cancer culture''', sometimes called '''pink ribbon culture''', is the cultural outgrowth of breast cancer advocacy, the ] that supports it, and the larger ] movement. | ||
| The ] is the most prominent symbol of breast cancer awareness, and in most countries, the month of October is ]. Some national breast cancer organizations receive substantial financial support from ]s |
The ] is the most prominent symbol of breast cancer awareness, and in most countries, the month of October is ]. Some national breast cancer organizations receive substantial financial support from ]s.{{sfn|King|2006|p=2}} | ||
| ==Marketing approaches== | ==Marketing approaches== | ||
| The goal of breast cancer awareness campaigns is to raise the public's "]" for breast cancer, its detection, its treatment, and the need for a reliable, permanent cure. Increased awareness has increased the number of women receiving mammograms, the number of breast cancers detected, and the number of women receiving biopsies |
The goal of breast cancer awareness campaigns is to raise the public's "]" for breast cancer, its detection, its treatment, and the need for a reliable, permanent cure. Increased awareness has increased the number of women receiving mammograms, the number of breast cancers detected, and the number of women receiving biopsies.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=157–210}} Overall, as a result of awareness, breast cancers are being detected at an earlier, more treatable stage. Awareness efforts have successfully utilized marketing approaches to reduced the stigma associated with the disease. | ||
| Generally speaking, breast cancer awareness campaigns have been highly effective in getting attention for the disease. Breast cancer receives significantly more media coverage than other prevalent cancers, such as ] |
Generally speaking, breast cancer awareness campaigns have been highly effective in getting attention for the disease. Breast cancer receives significantly more media coverage than other prevalent cancers, such as ].{{sfn|Arnst|2007}} | ||
| ===Breast cancer as a brand=== | ===Breast cancer as a brand=== | ||
| ], |
], a universal symbol of breast cancer awareness.]] | ||
| Breast cancer advocacy uses the ] and the color ] as a ] to raise money and increase screening. The breast cancer brand is strong: people who support the "pink brand" are members of the ] ], who are in favor of improved lives for women, believe in positive thinking, trust biomedical science to be able to solve any problem if given enough money, and prefer curative treatments to prevention |
Breast cancer advocacy uses the ] and the color ] as a ] to raise money and increase screening. The breast cancer brand is strong: people who support the "pink brand" are members of the ] ], who are in favor of improved lives for women, believe in positive thinking, trust biomedical science to be able to solve any problem if given enough money, and prefer curative treatments to prevention.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=22}}{{sfn|King|2006|p=38}} | ||
| The brand ties together fear of cancer, hope for early identification and successful treatment, and the ] of women with breast cancer and anyone who visibly identifies themselves with breast cancer patients. This brand permits and even encourages people to substitute ] and individual ]s, like buying or wearing a pink ribbon, for concrete, practical results, such as ] aimed at discovering non-genetic causes of breast cancer |
The brand ties together fear of cancer, hope for early identification and successful treatment, and the ] of women with breast cancer and anyone who visibly identifies themselves with breast cancer patients. This brand permits and even encourages people to substitute ] and individual ]s, like buying or wearing a pink ribbon, for concrete, practical results, such as ] aimed at discovering non-genetic causes of breast cancer.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=133–146}} | ||
| The establishment of the brand and the entrenchment of the breast cancer movement has been uniquely successful, because no ] opposes the breast cancer movement or believes that breast cancer is desirable |
The establishment of the brand and the entrenchment of the breast cancer movement has been uniquely successful, because no ] opposes the breast cancer movement or believes that breast cancer is desirable.{{sfn|King|2006|p=111}} | ||
| ===Pink ribbon=== | ===Pink ribbon=== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| A ] is a symbol of breast cancer awareness. It may be worn to honor those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, or to identify products that a manufacturer would like to sell to consumers that are interested in breast cancer. Pink ribbons are sometimes sold as fundraisers, much like ]. | A ] is a symbol of breast cancer awareness. It may be worn to honor those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, or to identify products that a manufacturer would like to sell to consumers that are interested in breast cancer. Pink ribbons are sometimes sold as fundraisers, much like ]. | ||
| The pink ribbon is associated with individual generosity, faith in scientific progress, and an optimistic "can-do" attitude. It encourages individuals to focus on the emotionally appealing ultimate vision of a cure for breast cancer, rather than the reality that there is no certain cure for breast cancer, and no guarantee there will ever be such a cure |
The pink ribbon is associated with individual generosity, faith in scientific progress, and an optimistic "can-do" attitude. It encourages individuals to focus on the emotionally appealing ultimate vision of a cure for breast cancer, rather than the reality that there is no certain cure for breast cancer, and no guarantee there will ever be such a cure.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=359–361}} Despite these positive associations, the simple act of wearing a pink ribbon alone and promoting it as a symbol for breast cancer has not been credited with saving any lives. The practice of blindly wearing or displaying a pink ribbon without making other, more concrete efforts to cure breast cancer has been described as a kind of ] due to its lack of real effects,{{sfn|Landman|2008}} and has been compared to equally simple yet ineffective "awareness" practices like the drive for women to post the colors of their bras on ].{{sfn|Borrelli|2010}} Critics say that the feel-good nature of pink ribbons and "pink consumption" distracts society from the lack of progress in curing breast cancer.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=365–366}} It is also criticized for reinforcing gender stereotypes and ] women and their breasts.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=372–374}} | ||
| ===Events=== | ===Events=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| {{Main|National Breast Cancer Awareness Month}} | {{Main|National Breast Cancer Awareness Month}} | ||
| Each year, the month of October is recognized as ] by most governments, the media, and ]. The month-long campaign has been called ''Pinktober'' because of the increased production of pink goods for sale, and ''National Breast Cancer Industry Month'' by critics like ] |
Each year, the month of October is recognized as ] by most governments, the media, and ]. The month-long campaign has been called ''Pinktober'' because of the increased production of pink goods for sale, and ''National Breast Cancer Industry Month'' by critics like ].{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=48, 370}} NBCAM was begun in 1985 by the ] and pharmaceutical company ]. The organization that runs the official NBCAM aims to promote ] and other forms of early detection as the most effective means of saving lives.{{sfn|King|2006|p=xxi}} | ||
| Typical NCBAM events include fundraising-based ]s, ], and ] |
Typical NCBAM events include fundraising-based ]s, ], and ].{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} Participants solicit donations to a breast cancer-related charity in return for running, walking, or riding in the event. Through mass-participation events, breast cancer survivors form a single, united group that speaks and acts consistently and shares a coherent set of beliefs. There are little significant discrepancies among individuals.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=56}} They also reinforce the cultural connection between each individual's ] and ].{{sfn|King|2006|pp=46–49}} Typically, one-quarter to one-third of the money donated is spent on advertising and organizing the event itself.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} | ||
| Various ]s are illuminated in pink lights as a visible reminder of breast cancer, and public events, such as American football games, may use pink equipment or supplies. In 2010, all ] comic strips on one Sunday were printed in shades of red and pink, with a pink ribbon logo appearing prominently in one panel. | Various ]s are illuminated in pink lights as a visible reminder of breast cancer, and public events, such as American football games, may use pink equipment or supplies. In 2010, all ] comic strips on one Sunday were printed in shades of red and pink, with a pink ribbon logo appearing prominently in one panel. | ||
| Private companies may arrange a "pink day", in which employees wear pink clothes in support of breast cancer patients, or pay for the privilege of a relaxed ], such as ] |
Private companies may arrange a "pink day", in which employees wear pink clothes in support of breast cancer patients, or pay for the privilege of a relaxed ], such as ].{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} | ||
| Some events are directed at people in specific communities, such as the ], which was started in America to encourage appropriate medical care and reduce the stigma of breast cancer among Muslim women, and ''Male Breast Cancer Awareness Week'', which some organizations highlight during the third week of October. | Some events are directed at people in specific communities, such as the ], which was started in America to encourage appropriate medical care and reduce the stigma of breast cancer among Muslim women, and ''Male Breast Cancer Awareness Week'', which some organizations highlight during the third week of October. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| Most events are well-received, but some, like the unauthorized painting of the ] in ], are controversial. | Most events are well-received, but some, like the unauthorized painting of the ] in ], are controversial. | ||
| ] campaigns have encouraged users to use ] and ] in their status updates to remind readers about breast cancer. In 2009, a campaign asked women to post the color of their ], and in 2010, a campaign asked women to post where they keep their purses, resulting in status messages such as "I like it on the floor" |
] campaigns have encouraged users to use ] and ] in their status updates to remind readers about breast cancer. In 2009, a campaign asked women to post the color of their ], and in 2010, a campaign asked women to post where they keep their purses, resulting in status messages such as "I like it on the floor".{{sfn|Kingston|2010}} These campaigns have been criticized as ] the disease.{{sfn|Kingston|2010}} | ||
| Symbolism itself does not improve health, but it is an effective form of promoting the pink ribbon culture: fear of breast cancer, the hope for a scientific breakthrough, and the goodness of the people who support the cause. These supporters may feel socially compelled to participate, in a type of "obligatory voluntarism" critics say "can be exploitive" |
Symbolism itself does not improve health, but it is an effective form of promoting the pink ribbon culture: fear of breast cancer, the hope for a scientific breakthrough, and the goodness of the people who support the cause. These supporters may feel socially compelled to participate, in a type of "obligatory voluntarism" critics say "can be exploitive".{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=250, 308}} | ||
| ===Shopping for the cure=== | ===Shopping for the cure=== | ||
| ], including ], ink pens, candy, and ]s.]] | ], including ], ink pens, candy, and ]s.]] | ||
| Thousands of breast cancer-themed products are developed and sold each year |
Thousands of breast cancer-themed products are developed and sold each year.{{sfn|Ave|2006}} Some of these, like ] and ]s, have no purpose other than to display the wearer's interest in breast cancer. Others are everyday products that have been repackaged or repositioned to take advantage of ], such as teddy bears, clothing, jewelry, candles, and coffee mugs.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} These ] objects offer consumers an opportunity to simultaneously buy an object and make a donation to a breast cancer organization.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} Some of these products are produced and/or sold by breast cancer survivors or charities for fundraising purposes, while others are for profits in addition to fundraising. Manufacturers also produce products with pink labels or pink ribbon logos to donate a sum of money to support the cause.{{sfn|Levine|2005}} The donation is typically capped so that it is reached after a fixed level of sales, although in some cases the company is providing only free advertising for a selected charity. Although advertising costs are rarely disclosed, some companies have been found to spend far more money advertising "pink products" and tie-ins than they donate to charitable organizations supporting research or patients. For example, in 2005, ] spent US $500,000 advertising ] notes printed with a pink ribbon logo. Sales were nearly double what the company expected, but the campaign resulted in a $300,000 donation.{{sfn|Levine|2005}} | ||
| Advertisers and retail consultants have said that because of consumer cynicism, a company can benefit from marketing its support for a cause such as breast cancer awareness only when the company treats that support as "a commitment and not a marketing opportunity". Andrew Benett, an executive at ] said that because consumers "have become more mindful, more thoughtful, about how they consume, where they consume, why they consume", companies cannot succeed by "just slapping a pink ribbon on a product and people will buy more" |
Advertisers and retail consultants have said that because of consumer cynicism, a company can benefit from marketing its support for a cause such as breast cancer awareness only when the company treats that support as "a commitment and not a marketing opportunity". Andrew Benett, an executive at ] said that because consumers "have become more mindful, more thoughtful, about how they consume, where they consume, why they consume", companies cannot succeed by "just slapping a pink ribbon on a product and people will buy more".{{sfn|Elliott|2009}} Pink products have also been condemned as promoting ], ], and environmental degradation. Critics are also concerned that the ubiquity of pink products may mislead people into thinking that significant progress has been made, and that small, individual actions, like buying a breast cancer-themed product, are sufficient.{{sfn|Stukin|2006}} Responding to criticism, Komen CEO ] said that corporate promotions enabled the organization to reach new audiences and that "America is built on consumerism. To say we shouldn't use it to solve the social ills that confront us doesn't make sense to me."{{sfn|Singer|2011}} | ||
| The first breast cancer awareness stamp in the U.S., featuring a pink ribbon, was issued in 1996. As it did not sell well, a ] stamp without a pink ribbon, the ], was designed in 1998. Products like these emphasize the relationship between being a consumer and supporting women with breast cancer |
The first breast cancer awareness stamp in the U.S., featuring a pink ribbon, was issued in 1996. As it did not sell well, a ] stamp without a pink ribbon, the ], was designed in 1998. Products like these emphasize the relationship between being a consumer and supporting women with breast cancer.{{sfn|King|2006|pp=61–79}} In Canada, the Royal Canadian Mint produced 30 million 25-cent coins with pink ribbons during 2006 for normal circulation.{{sfn|Royal Canadian Mint|2006}} Designed by the mint's director of engraving, Cosme Saffioti (reverse), and Susanna Blunt (obverse), this colored coin is the second in history to be put into regular circulation.{{sfn|Royal Canadian Mint|2006}} | ||
| Business marketing campaigns, particularly sales promotions for products that increase pollution or have been linked to the development of breast cancer, such as alcohol, high-fat foods, some pesticides, or the ] and ] used by most cosmetic companies, have been condemned as ] (a ] of ''pink ribbon'' and ]) |
Business marketing campaigns, particularly sales promotions for products that increase pollution or have been linked to the development of breast cancer, such as alcohol, high-fat foods, some pesticides, or the ] and ] used by most cosmetic companies, have been condemned as ] (a ] of ''pink ribbon'' and ]).{{sfn|Mulholland|2010}} Such promotions generally result in a token donation to a breast cancer-related charity by taking advantage of the consumers' fear of cancer and grief for people who have died to drive sales.{{sfn|Landman|2008}} Critics say that these promotions, which net more than US $30 million each year just for fundraising powerhouse ], do little more than support the marketing machines that produce them.{{sfn|Stukin|2006}} Komen says that corporate sponsorships are necessary to pay for the organization's efforts: in the 2010 ] it spent $175 million on public health education and awareness campaigns, $75 million on medical research and about $67 million on treatment and screenings for patients.{{sfn|Singer|2011}} | ||
| Two significant campaigns against pink consumption are the ]'s "Not Just Ribbons" campaign, and ]'s "Think Before You Pink" campaign. NBCC's "Not Just Ribbons" campaign sought to focus awareness efforts onto substantive issues such as ], access to cancer treatment, ], and environmental breast cancer research |
Two significant campaigns against pink consumption are the ]'s "Not Just Ribbons" campaign, and ]'s "Think Before You Pink" campaign. NBCC's "Not Just Ribbons" campaign sought to focus awareness efforts onto substantive issues such as ], access to cancer treatment, ], and environmental breast cancer research.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=366–368}} "Think Before You Pink" encouraged consumers to ask questions about pink products (e.g., to find out how much of a donation was being made).{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=369–372}} | ||
| ===Advertisements=== | ===Advertisements=== | ||
| ] advertisement promotes ] company ] and breast cancer awareness. Because of the pink ribbon brand's strength, the advertisement is easily recognized as a promotion for breast cancer awareness, even among people who cannot read the Japanese text.]] | ] advertisement promotes ] company ] and breast cancer awareness. Because of the pink ribbon brand's strength, the advertisement is easily recognized as a promotion for breast cancer awareness, even among people who cannot read the Japanese text.]] | ||
| Many corporate and charitable organizations run advertisements related to breast cancer, especially during National Breast Cancer Awareness Month, in the hope of increasing sales by aligning themselves with a positive, helpful message |
Many corporate and charitable organizations run advertisements related to breast cancer, especially during National Breast Cancer Awareness Month, in the hope of increasing sales by aligning themselves with a positive, helpful message.{{sfn|King|2006}} In addition to selling pink products, corporate advertisements may promote the company's progressive policies, or may provide ] for a chosen charity. Medical institutions may run advertisements for ] or other breast-related services. Non-profit organizations often benefit from ]s, which are free advertisements provided by newspapers, radio and television stations, and other media. Some marketing blurs the line between advertisements and events, such as ]s as a form of ]. The typical participant in the breast cancer movement, and therefore the advertisers' ], is a white, middle-aged, middle-class, well-educated woman.{{sfn|King|2006|pp=110–111}} | ||
| Some corporate sponsors are criticized for having a ]. For example, some of the prominent sponsors of these advertisements include businesses that sell the expensive equipment needed to perform screening mammography; an increase in the number of women seeking mammograms means an increase in their sales. Their sponsorship is thus not a voluntary act of charity, but an effort to increase their sales |
Some corporate sponsors are criticized for having a ]. For example, some of the prominent sponsors of these advertisements include businesses that sell the expensive equipment needed to perform screening mammography; an increase in the number of women seeking mammograms means an increase in their sales. Their sponsorship is thus not a voluntary act of charity, but an effort to increase their sales.{{sfn|King|2006|p=37}} The regulated drug and medical device industry uses the color pink, positive images, and other themes of the pink ribbon culture in ] to associate their breast cancer products with the fear, hope, and wholesome goodness of the breast cancer movement. This is particularly evident in advertisements designed to sell screening mammograms.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=205–208}} | ||
| Women's magazines from the 1950-1960s recommended the use of ]s as a method for early detection |
Women's magazines from the 1950-1960s recommended the use of ]s as a method for early detection.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=115, 117}} More recently, breast self-examinations have been determined to be ineffective in low-risk and average-risk women. Some organizations' advertisements now advocate ], which is paying attention to any ] that may require medical attention. | ||
| ===Media=== | ===Media=== | ||
| Although more women die from ], breast cancer receives far more attention in ]s than any other cancer. Until the mid-1990s, nearly all of these stories were written from the perspective of the expert, who gave advice. Since then, the ], describing the personal experiences of individual patients, has become more prominent.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=133}}{{failed verification|date=December 2012}}. ], ] and frequent feature stories amount to free advertising for the brand and for the organizations that support it. | |||
| ==Social role of the woman with breast cancer== | ==Social role of the woman with breast cancer== | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
| ===The she-ro=== | ===The she-ro=== | ||
| The term "she-ro", derived from ], used in discussions of breast cancer to refer to women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, and sometimes to those who have survived breast cancer. The term describes an "idealized" patient who combines assertiveness, optimism, femininity and sexuality, despite the effects of treatment, and as a "paragon uses a diagnosis of breast cancer as a catalyst for a personal transformation" |
The term "she-ro", derived from ], used in discussions of breast cancer to refer to women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, and sometimes to those who have survived breast cancer. The term describes an "idealized" patient who combines assertiveness, optimism, femininity and sexuality, despite the effects of treatment, and as a "paragon uses a diagnosis of breast cancer as a catalyst for a personal transformation".{{sfn|Zuger|2010}} | ||
| ] Gayle Sulik analysis of the she-ro's social ] ascribes it qualities that include being an educated medical consumer with a brave, pleasant and ] public appearance and demeanor who aggressively fights breast cancer through compliance with screening guidelines and "disciplined practice of 'breast health'". In ] the she-ro is diagnosed early due to adherence to early ] recommendations, and, by definition, survives her diagnosis |
] Gayle Sulik analysis of the she-ro's social ] ascribes it qualities that include being an educated medical consumer with a brave, pleasant and ] public appearance and demeanor who aggressively fights breast cancer through compliance with screening guidelines and "disciplined practice of 'breast health'". In ] the she-ro is diagnosed early due to adherence to early ] recommendations, and, by definition, survives her diagnosis.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=158, 243}} The role emphasizes the ] and female ] of the she-ro, offsetting the ] characteristics of assertiveness, selfishness and "fighting" cancer by cultivating a feminine appearance and concern for others.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=78–89}} After treatment, the she-ro regains her femininity by using breast reconstruction, prosthetic devices, wigs, cosmetics, and clothing to present an aesthetically appealing, upper-class, heterosexual feminine appearance and by maintaining relationships in which she can nurture other people.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=42, 101–105, 374}} Ensuring the proper ] of the breast cancer culture is encouraged, including remaining optimistic of a full cure, rationalizing the selfishness of treatment as a temporary measure and feeling guilty that it forces her to put her needs momentarily above the needs of others or due to her perceived inadequacy in caring for her family or other women with cancer.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=225–272, 277}} Also included in the role is a form of have-it-all ], cultivating a normal appearance and activity level and minimizing the disruption that breast cancer causes to people around her.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=279–301}} | ||
| ====Consequences==== | ====Consequences==== | ||
| The effort of maintaining the role of a she-ro can be stressful. The role encourages women to care for others rather than themselves, which the patient may find comforting, but this may lead to the reluctance or inability to ask for help they need or want which can lead to bitterness that their friends and family did not offer these services unbidden |
The effort of maintaining the role of a she-ro can be stressful. The role encourages women to care for others rather than themselves, which the patient may find comforting, but this may lead to the reluctance or inability to ask for help they need or want which can lead to bitterness that their friends and family did not offer these services unbidden.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=279–301}} The success of the patient's normalization efforts may paradoxically increase their dissatisfaction, as their apparent ability to handle it all discourages people from offering help.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=283, 286}} While the she-ro model may reduce the ] of breast cancer overall, it also increases the stigma of being overwhelmed, depressed, anxious, abrasive, or unattractive while undergoing treatment.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=45}}{{failed verification|date=December 2012}} The breast cancer culture celebrates women who display the attitude deemed correct, which implies that their continued survival is due to this positive attitude and fighting spirit. While cheerfulness, hope, and good social support can be advantageous to health outcomes, it cannot determine survival rates.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=243–244}} Women who reject the she-ro model may find themselves socially isolated by the breast cancer ]s that are nominally supposed to help them. Support from "the sisterhood" favors the "passionately pink", and tends to overlook those whose response is incompatible with the pink ribbon culture because it is angry, unhappy, or afraid.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=274–277}} | ||
| The breast cancer culture is ill-equipped to deal with women who are dying or who have died |
The breast cancer culture is ill-equipped to deal with women who are dying or who have died{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=4}} and their experiences may not be memorialized, validated or represented as part of the movement, instead being ignored or shunned as failures and as hope-destroying examples of reality. Similarly, the culture is also ill-equipped to deal with the news that a previously hyped treatment or screening procedure has been determined to be ineffective, with women demanding acceptance and promotion of useless activities and harmful drugs.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=204–205}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=200–203}} | ||
| ===Breast cancer culture=== | ===Breast cancer culture=== | ||
| {{Undue-section|date=November 2012}} | {{Undue-section|date=November 2012}} | ||
| Breast cancer culture, or pink ribbon culture, is the set of activities, attitudes, and values that surround and shape breast cancer in public. The dominant values are selflessness, cheerfulness, unity, and optimism. It is pro-doctor, pro-medicine, and pro-mammogram. Health care professionals are sources of information, but the rightness of their advice is not to be seriously questioned by women with breast cancer. Patients are not encouraged to ask where research money is going or if the research industry is making progress in finding the "cure" |
Breast cancer culture, or pink ribbon culture, is the set of activities, attitudes, and values that surround and shape breast cancer in public. The dominant values are selflessness, cheerfulness, unity, and optimism. It is pro-doctor, pro-medicine, and pro-mammogram. Health care professionals are sources of information, but the rightness of their advice is not to be seriously questioned by women with breast cancer. Patients are not encouraged to ask where research money is going or if the research industry is making progress in finding the "cure".{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=365–366}} The emphasis on cheerfulness allows society to blame women for developing breast cancer and limits their responses to certain ]. The requirement of cheerful optimism arose from the theory that cancer had a ] origin and that people who were diagnosed with cancer had a "cancer personality" that was depressed, repressed, and self-loathing. ] was therefore considered an adjunct treatment used to produce a cheerful, self-affirming identity. This theory was predominant among psychiatrists through the 1970s, but has since been discredited.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=460–469}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=342}} The she-ro uses the emotional trauma of being diagnosed with breast cancer and the suffering of extended treatment to transform herself into a stronger, happier and more sensitive person who is grateful for the opportunity to become a better person. In particular, she sees breast cancer as an opportunity to give herself permission for necessary personal growth that she felt she was prohibited from or unable to make before.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=236}} Breast cancer thereby becomes a ] rather than a disease,{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=3}} with pink ribbon culture honoring the suffering of its she-roes by selecting them based on the amount of misery they have experienced{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=319}} and leading women whose treatment is less painful or debilitating to feel excluded and devalued. The suffering, particularly the extended suffering of months of chemotherapy and radiation treatment, forms a ]ical type of ] or ] that initiates women into the inner circle of breast cancer culture. ] describes it as: | ||
| <blockquote>Understood as a rite of passage, breast cancer resembles the initiation rites so exhaustively studied by Mircea Eliade: First there is the selection of the initiates -- by age in the tribal situation, by mammogram or palpation here. Then come the requisite ordeals -- scarification or circumcision within traditional cultures, surgery and chemotherapy for the cancer patient. Finally, the initiate emerges into a new and higher status -- an adult and a warrior -- or in the case of breast cancer, a "survivor." |
<blockquote>Understood as a rite of passage, breast cancer resembles the initiation rites so exhaustively studied by Mircea Eliade: First there is the selection of the initiates -- by age in the tribal situation, by mammogram or palpation here. Then come the requisite ordeals -- scarification or circumcision within traditional cultures, surgery and chemotherapy for the cancer patient. Finally, the initiate emerges into a new and higher status -- an adult and a warrior -- or in the case of breast cancer, a "survivor."{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}</blockquote> | ||
| Mainstream pink ribbon culture has aspects that are deemed trivializing, silencing, and infantilizing |
Mainstream pink ribbon culture has aspects that are deemed trivializing, silencing, and infantilizing.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=98}} Women with breast cancer are surrounded by pink teddy bears and crayons ("childish kitsch"), but there is no equivalent gift of toy cars for men diagnosed with ].{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=373}} Women who choose not to conform to the culture may feel excluded and isolated; those who cannot conform to the prescribed triumphant script report feeling unable to share their stories honestly. Anger, negativity and fatalism transgress the feeling rules, and women with breast cancer who express anger or negativity are corrected and disciplined by other women with breast cancer and members of the breast cancer support organizations. {{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=240–242}} Appearing unattractive—such as going out in public with a bare, bald head if treatment causes temporary hair loss—transgresses the approved, upper-class style of pink femininity and provokes shaming comments from strangers.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=35–45, 262}} Programs such as Reach to Recovery and Look Good, Feel Better inform breast cancer patients of this cultural standard and help them conform to it.{{sfn|Olson|2002|p=120}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=37–38, 42, 101-105, 374}} This standard is not universally adhered to, with "the question of wigs versus baldness one of the few real disagreements in breast-cancer culture," and some women have used the effects of their breast cancer treatments as an opportunity to engage in '']'' ]s: | ||
| <blockquote>One decorates her scalp with temporary tattoos of peace signs, panthers, and frogs; another expresses herself with a shocking purple wig; a third reports that unadorned baldness makes her feel 'sensual, powerful, able to recreate myself with every new day' using ]s, colored wigs or open baldness to reinvent their appearances according to radical, natural or cosmetically enhanced tastes |
<blockquote>One decorates her scalp with temporary tattoos of peace signs, panthers, and frogs; another expresses herself with a shocking purple wig; a third reports that unadorned baldness makes her feel 'sensual, powerful, able to recreate myself with every new day' using ]s, colored wigs or open baldness to reinvent their appearances according to radical, natural or cosmetically enhanced tastes.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}</blockquote> | ||
| Since the beginning of the 21st century, breast cancer culture has become more sexualized, and many awareness campaigns now reflect the old advertising truism that ]. The "booby campaigns", such as ] and the "I ♥ Boobies" gel bracelets, rely on a cultural obsession with breasts and a market that is already highly aware of breast cancer |
Since the beginning of the 21st century, breast cancer culture has become more sexualized, and many awareness campaigns now reflect the old advertising truism that ]. The "booby campaigns", such as ] and the "I ♥ Boobies" gel bracelets, rely on a cultural obsession with breasts and a market that is already highly aware of breast cancer.{{sfn|Kingston|2010}} This message trivializes women and reflects a belief that breast cancer is important because cancer and its treatment makes women feel less sexually desirable and interferes with men's sexual access to women's breasts.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=372}} These campaigns tend to attract a younger audience than traditional campaigns.{{sfn|Kingston|2010}} | ||
| At the same time, breast cancer culture tends to overlook ] and women who do not fit the white, middle-class archetype. ]s involved with breast cancer organizations often feel like their role is to be the ] |
At the same time, breast cancer culture tends to overlook ] and women who do not fit the white, middle-class archetype. ]s involved with breast cancer organizations often feel like their role is to be the ].{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=308–309}} | ||
| ===Feminism and the breast cancer wars=== | ===Feminism and the breast cancer wars=== | ||
| The '''breast cancer wars''' were a series of conflicts between advocates and others about the causes, treatments, and societal responses to breast cancer |
The '''breast cancer wars''' were a series of conflicts between advocates and others about the causes, treatments, and societal responses to breast cancer.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=192–220}} Women in the late 1980s and 1990s followed the successful approach used by ] and other ] groups, of staging media-friendly protests to increase political pressure. Prominent women who made the "wrong" choice were publicly excoriated, as when ] chose mastectomy over lumpectomy followed by six weeks of ]. The ] was formulated when an early study showed a connection between voluntary ]s and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women, which pitted breast cancer advocates against abortion rights advocates.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=192–220}} | ||
| ]. The ] was formulated when an early study showed a connection between voluntary ]s and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women, which pitted breast cancer advocates against abortion rights advocates (Olson 2002, pages 192–220). | |||
| Advocates for women's issues have said that breast cancer is special because of its status as a largely female disease, society's response to it is an ongoing indication of the status of women and the existence of ] |
Advocates for women's issues have said that breast cancer is special because of its status as a largely female disease, society's response to it is an ongoing indication of the status of women and the existence of ].{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=195–202}} Breast cancer activist Virginia Soffa stated that "s long as it is not a national priority, the breast cancer epidemic will remain a metaphor for how society treats women".{{sfn|Soffa|1994|p=208}} Before the feminist movement, women with breast cancer were often treated as passive, dependent ], incapable of making appropriate choices, whose role was to accept whatever treatment was decreed by the physicians, surgeons, or husbands, who held all of the power.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} Because of sexism in education, female surgeons were far outnumbered by their male counterparts, and until the 1990s, when ] of the ] Breast Center published ''Dr. Susan Love's Breast Book'', the physicians who provided breast cancer treatments were generally men. Love said that some male physicians tended to impose their own values on women, such as recommending mastectomy to older women because, being past the age of child bearing and breastfeeding, they no longer "needed" their breasts.{{sfn|Olson|2002|p=198}} The women's health movement promoted mutual aid, self-help, ], and an active, informed role in the patient's health care.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} Since the end of the breast cancer wars, feminists have again objected to the breast cancer culture's treatment of women with breast cancer as little girls who need to be obedient to authority figures, cooperative, pleasant and pretty.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} | ||
| ==Achievements of the breast cancer movement== | ==Achievements of the breast cancer movement== | ||
| Breast cancer has been known to educated women and caregivers throughout history, but modesty and horror at the consequences of a largely untreatable disease made it a ] subject. The breast cancer movement, which developed in the 1980s and 1990s out of 20th century ] and the women's health movement, has mostly remove those taboos through its modern advocacy and awareness campaigns |
Breast cancer has been known to educated women and caregivers throughout history, but modesty and horror at the consequences of a largely untreatable disease made it a ] subject. The breast cancer movement, which developed in the 1980s and 1990s out of 20th century ] and the women's health movement, has mostly remove those taboos through its modern advocacy and awareness campaigns.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=4}} | ||
| ===Educated, empowered patients=== | ===Educated, empowered patients=== | ||
| At the beginning and middle of the 20th century, breast cancer was usually discussed in hushed tones, as if it were shameful. Later, however, several celebrities publicly disclosed their own health challenges, and the resulting publicity reduced the stigma |
At the beginning and middle of the 20th century, breast cancer was usually discussed in hushed tones, as if it were shameful. Later, however, several celebrities publicly disclosed their own health challenges, and the resulting publicity reduced the stigma.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=124–144}} One of the first was ], the former child star, who announced her diagnosis in 1972. In October 1974, ], the wife of the then-President of the United States, openly discussed her breast cancer diagnosis and mastectomy. Two weeks later, the wife of the then-Vice President also had a mastectomy for breast cancer. The next year, journalist ] published her book, ''Breast Cancer: A Personal History and Investigative Report'', which she had written while recovering from a ]. The media reported these women's health and their treatment choices, and even invited some to appear on ]s to discuss breast cancer frankly.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=124–144}} | ||
| The breast cancer movement has resulted in widespread acceptance of ]s, the development of less invasive surgical procedures, the spread of ]s, and other advances in patient care |
The breast cancer movement has resulted in widespread acceptance of ]s, the development of less invasive surgical procedures, the spread of ]s, and other advances in patient care.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=121, 171–220}} The movement successfully separated ] from mastectomy surgery; before about 1980, it was common to perform the biopsy and, if a quick review of tissues indicated a probable need, a mastectomy in the same surgery.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}}{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=168–191}} The one-step surgery prevented women from seeking different opinions about their treatment, and sent them into the surgery without knowing whether their breasts would be removed that day. In response to women's concerns over ] after routine removal of ] during mastectomy, the more limited approach of ] was developed. Advocacy efforts also led to the formal recommendation against the routine use of the ] in favor of simple mastectomies and lumpectomies.{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=176, 185–186, 250}} | ||
| The breast cancer movement has supported practical, educational, emotional, and financial care for women with breast cancer. Support groups, individual counseling opportunities, and other resources are made available to patients. | The breast cancer movement has supported practical, educational, emotional, and financial care for women with breast cancer. Support groups, individual counseling opportunities, and other resources are made available to patients.{{Citation needed|date=November 2012}} | ||
| ===Increased resources for treatment and research=== | ===Increased resources for treatment and research=== | ||
| Supporting breast cancer was seen as a distinctively pro-woman stance for public officials to take, without any of the political risks associated with supporting other feminist goals, such as ] or ] |
Supporting breast cancer was seen as a distinctively pro-woman stance for public officials to take, without any of the political risks associated with supporting other feminist goals, such as ] or ].{{sfn|Olson|2002|p=202}} This has resulted in better access to care. For example, in much of the United States, low-income women with breast cancer may qualify for taxpayer-funded health care benefits, such as screening mammography, biopsies, or treatment, while women with the same income, but another form of cancer or a medical condition other than cancer, do not.<ref>As an example, the ] pays for breast cancer treatment in women whose of the ], but to be screened or treated for ], ], or ], the income .</ref> | ||
| Breast cancer advocates have successfully increased the amount of public money being spent on cancer research and shifted the research focus away from other diseases and towards breast cancer. Most breast cancer research is funded by government agencies |
Breast cancer advocates have successfully increased the amount of public money being spent on cancer research and shifted the research focus away from other diseases and towards breast cancer. Most breast cancer research is funded by government agencies.{{sfn|Mulholland|2010}} Breast cancer advocates also raise millions of dollars for research into cures each year, although most of the funds they raise is spent on screening programs, education and treatment.{{sfn|Ave|2006}} | ||
| The high level of awareness and organized political lobbying has resulted in a disproportionate level of funding and resources given to breast cancer research and care. Favoring breast cancer with disproportionate research may have the ] of costing lives elsewhere |
The high level of awareness and organized political lobbying has resulted in a disproportionate level of funding and resources given to breast cancer research and care. Favoring breast cancer with disproportionate research may have the ] of costing lives elsewhere.{{sfn|Browne|2001}} In 2001 UK MP ] said, "The treatment has been skewed by the lobbying, there is no doubt about that. Breast cancer sufferers get better treatment in terms of bed spaces, facilities and doctors and nurses".{{sfn|Browne|2001}} | ||
| ==Risks of too much awareness== | ==Risks of too much awareness== | ||
| Line 139: | Line 138: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Because breast cancer is a highly visible disease, most women significantly overestimate their personal risk of dying from it. Misleading statistics, such as the claim that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lives—a claim that depends on the patently unrealistic assumption that no woman will die of any other disease before the age of 95 |
Because breast cancer is a highly visible disease, most women significantly overestimate their personal risk of dying from it. Misleading statistics, such as the claim that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lives—a claim that depends on the patently unrealistic assumption that no woman will die of any other disease before the age of 95{{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=199–200}}—obscure the reality, which is that about ten times as many women will die from ] or ] than from breast cancer.{{sfn|Ave|2006}} | ||
| Awareness has also led to increased anxiety for women. Early detection efforts result in overdiagnosis of precancerous and cancerous tumors that would never risk the woman's life (about one-third of breast cancers), and result in her being subjected to invasive and sometimes dangerous radiological and surgical procedures |
Awareness has also led to increased anxiety for women. Early detection efforts result in overdiagnosis of precancerous and cancerous tumors that would never risk the woman's life (about one-third of breast cancers), and result in her being subjected to invasive and sometimes dangerous radiological and surgical procedures.{{sfn|Aschwanden|2009}} | ||
| The breast cancer culture has also promoted an expansive definition of breast cancer, which includes non-invasive, non-cancerous conditions like ] (LCIS) and pre-cancerous or "stage 0" conditions like ] (DCIS). Despite the now-regretted decision to use the word ''carcinoma'' in these relatively common conditions (almost a quarter of "breast cancer" diagnoses in the USA), they are not life-threatening ]s |
The breast cancer culture has also promoted an expansive definition of breast cancer, which includes non-invasive, non-cancerous conditions like ] (LCIS) and pre-cancerous or "stage 0" conditions like ] (DCIS). Despite the now-regretted decision to use the word ''carcinoma'' in these relatively common conditions (almost a quarter of "breast cancer" diagnoses in the USA), they are not life-threatening ]s.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=165–171}} Women with these conditions are promoted as breast cancer survivors due to the fear they experienced before they became educated about their condition, rather than in respect of any real threat to their lives. This effectively increases the ] for breast cancer organizations, medical establishments, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and the makers of mammography equipment.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=170–171}} | ||
| An emphasis on educating women about lifestyle changes that may have a small impact on preventing breast cancer often makes women feel guilty if they do develop breast cancer. Some women decide that their own cancer resulted from poor diet, lack of exercise, or other modifiable lifestyle factor, even though most cases of breast cancer are due to non-controllable factors, like genetics or naturally occurring background radiation. Adopting such a belief may increase their sense of being ] of their fate. Increased awareness inadvertently increases ] |
An emphasis on educating women about lifestyle changes that may have a small impact on preventing breast cancer often makes women feel guilty if they do develop breast cancer. Some women decide that their own cancer resulted from poor diet, lack of exercise, or other modifiable lifestyle factor, even though most cases of breast cancer are due to non-controllable factors, like genetics or naturally occurring background radiation. Adopting such a belief may increase their sense of being ] of their fate. Increased awareness inadvertently increases ]. {{sfn|Olson|2002|pp=240–242}}{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=74, 263}} Women who resist screening mammography or ]s are subjected to social pressure, scare tactics, guilt, and threats from some physicians to terminate the ].{{sfn|Welch|2010}} Similarly, the emphasis on early detection result in many women wrongly blaming themselves if their cancer is not detected at an early stage. | ||
| The promotion of research to make screening programs find ever more cancers is also criticized. One-third of diagnosed breast cancers might recede on their own |
The promotion of research to make screening programs find ever more cancers is also criticized. One-third of diagnosed breast cancers might recede on their own.{{sfn|Aschwanden|2009}} Screening mammography efficiently finds non-life-threatening, asymptomatic breast cancers and pre-cancers, even while overlooking serious cancers.<!-- Yes, the WHOLE PARAGRAPH is supported by the SAME SOURCE --> According to H. Gilbert Welch of the Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice, research on screening mammography has taken the "brain-dead approach that says the best test is the one that finds the most cancers" rather than the one that finds dangerous cancers.{{sfn|Aschwanden|2009}} | ||
| ==Independence of breast cancer organizations== | ==Independence of breast cancer organizations== | ||
| Some critics say that breast cancer awareness has transformed the disease into a market-driven industry of survivorship and corporate sales pitches |
Some critics say that breast cancer awareness has transformed the disease into a market-driven industry of survivorship and corporate sales pitches.{{sfn|Ave|2006}}{{sfn|King|2006}} Corporate marketing machines promote early detection of breast cancer, while also opposing public health efforts, such as stricter environmental legislation, that might decrease the incidence rate of breast cancer. These critics believe that some of the breast cancer organizations, particularly the highly visible Susan G. Komen for the Cure, have become ] that support and provide ] to the breast cancer industry, including ], mammography equipment manufacturers, and pollution-causing industries, as well as large corporations, creating or exacerbating other problems.{{sfn|Sulik|2000|pp=160–210}} | ||
| For example, ] ran a "Warriors in Pink" promotion on their ] sports car, which critics say was intended to sell cars and counter the bad publicity the company received by reducing its workforce by tens of thousands of people, causing many of them to lose their ], rather than to prevent or cure breast cancer |
For example, ] ran a "Warriors in Pink" promotion on their ] sports car, which critics say was intended to sell cars and counter the bad publicity the company received by reducing its workforce by tens of thousands of people, causing many of them to lose their ], rather than to prevent or cure breast cancer.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=130-135}} A Ford spokesperson acknowledged that the objective of the promotion was to "do good works throughout the community and derive some marketing exposure at the same time", but said that over the promotion's 15 years the company had donated $100 million and that the company continued the program during the ] because "It's part of our DNA now." Ford believes that the recipient of the funds, Susan G. Komen for the Cure, benefited because Ford helped it reach "people who might not have thought of this organization before or may be supporting other organizations."{{sfn|Elliott|2009}} | ||
| However, the primary sponsors are part of the breast cancer industry, particularly cancer drug makers like AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis. Because the national breast cancer organizations are dependent on ]s for survival, this situation may represent a ] that prevents these organizations from representing the needs of current and future people with breast cancer when those needs conflict with the profit-making motives of the corporate sponsors. |
However, the primary sponsors are part of the breast cancer industry, particularly cancer drug makers like AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis. Because the national breast cancer organizations are dependent on ]s for survival, this situation may represent a ] that prevents these organizations from representing the needs of current and future people with breast cancer when those needs conflict with the profit-making motives of the corporate sponsors..{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=209–210}} | ||
| The structure of the breast cancer movement may allow large organizations to claim to be the voice of women with breast cancer, while simultaneously ignoring their desires |
The structure of the breast cancer movement may allow large organizations to claim to be the voice of women with breast cancer, while simultaneously ignoring their desires.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=376}} | ||
| Some breast cancer organizations, such as ], refuse to accept funds from medical or other companies they disapprove of. | Some breast cancer organizations, such as ], refuse to accept funds from medical or other companies they disapprove of. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 161: | ||
| ==Environmental breast cancer movement== | ==Environmental breast cancer movement== | ||
| {{POV-section|date=December 2012}} | {{POV-section|date=December 2012}} | ||
| Most of the money raised by advocates is spent on advertising, increased awareness, ], and existing treatments |
Most of the money raised by advocates is spent on advertising, increased awareness, ], and existing treatments.{{sfn|Ave|2006}} Only a small fraction of the funds is spent on research, and most of that funding is spent on research to improve diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. To the dismay of advocates like ] and women's health issues scholar Samantha King, relatively little money or attention is devoted to identifying the non-genetic causes of breast cancer or taking steps to prevent breast cancer from occurring.{{sfn|Ave|2006}} The mainstream breast cancer culture is focused on a cure for existing breast cancer cases, rather than on preventing future cases.{{sfn|Ave|2006}}{{sfn|King|2006|p=38}} | ||
| As a result, screening mammography is promoted by the breast cancer industry as the sole possible approach to ] for breast cancer |
As a result, screening mammography is promoted by the breast cancer industry as the sole possible approach to ] for breast cancer.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=204}} Alternatives, such as pollution prevention, are largely ignored. | ||
| As the majority of women with breast cancer have no risk factors other than sex and age, the '''environmental breast cancer movement''' suspects pollution as a significant cause, possibly from pesticides, plastics, or petroleum products |
As the majority of women with breast cancer have no risk factors other than sex and age, the '''environmental breast cancer movement''' suspects pollution as a significant cause, possibly from pesticides, plastics, or petroleum products.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} The largest organizations, particularly Susan G. Komen for the Cure and the American Cancer Society, are not part of the environmental breast cancer movement.{{sfn|Ehrenreich|2001}} These organizations benefit the most from corporate sponsorships that critics deride as pinkwashing, e.g., polluting industries trying to buy public goodwill by publishing advertisements emblazoned with pink ribbons, rather than stopping their pollution under the ].{{sfn|King|2006|pp=1–2}}{{failed verification|date=December 2012}} | ||
| A 2011 ] carried out by the ] reported that the environmental factors that show "the most consistent evidence of a link with increased breast cancer risk included ], combination ], and greater postmenopausal weight....for many other factors, the evidence from human studies is more limited, contradictory, or absent" and called for additional research |
A 2011 ] carried out by the ] reported that the environmental factors that show "the most consistent evidence of a link with increased breast cancer risk included ], combination ], and greater postmenopausal weight....for many other factors, the evidence from human studies is more limited, contradictory, or absent" and called for additional research.{{sfn|Institute of Medicine|2011}} Conducting research into whether a chemical causes cancer is difficult, because "suspect chemicals cannot ethically be given to people to see if they cause cancer. People exposed in the past can be studied, but information about the dose and timing may be sketchy. Animal studies can provide useful information, but do not always apply to humans. And people are often exposed to mixtures of chemicals that may interact in complex ways, with effects that may also vary depending on an individual's genetic makeup".{{sfn|Grady|2011}} | ||
| Samantha King says that prevention research is minimized by the breast cancer industry because there is no way to make money off of cases of breast cancer that do not happen, whereas a mammography imaging system that finds more possible cancers, or a "magic bullet" that kills confirmed cancers, would be highly profitable |
Samantha King says that prevention research is minimized by the breast cancer industry because there is no way to make money off of cases of breast cancer that do not happen, whereas a mammography imaging system that finds more possible cancers, or a "magic bullet" that kills confirmed cancers, would be highly profitable.{{sfn|King|2006|p=38}} This paradigm applies equally to breast cancer organizations, because a reliable form of prevention would deplete their future supply of volunteers. | ||
| ==Dissent through art== | ==Dissent through art== | ||
| While the pink ribbon culture is dominant, there are alternatives. The environmental breast cancer movement is one type of dissent. Another is the rejection of compliant optimism, aesthetic normalization, and social pleasingness that the pink ribbon culture promotes |
While the pink ribbon culture is dominant, there are alternatives. The environmental breast cancer movement is one type of dissent. Another is the rejection of compliant optimism, aesthetic normalization, and social pleasingness that the pink ribbon culture promotes.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=229–377}} | ||
| In 1998, the Art.Rage.Us art collective published a book that collected some of the art work from their traveling collection. This included art that was shocking, painful and realistic rather than beautiful, such as several self-portraits that showed mastectomy scars |
In 1998, the Art.Rage.Us art collective published a book that collected some of the art work from their traveling collection. This included art that was shocking, painful and realistic rather than beautiful, such as several self-portraits that showed mastectomy scars.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=326–332}} | ||
| Another art form has a wider range: the ] has become a staple of breast cancer literature. This may take the form of a restitution or ] (the protagonist seeks a physical or spiritual return to a pre-diagnosis life), a ] (the protagonist must meet a goal before dying), or a ] (the situation inexorably goes from bad to worse). The cure and quest narratives fit neatly with the breast cancer culture. Chaos narratives, rarer with breast cancer, oppose it |
Another art form has a wider range: the ] has become a staple of breast cancer literature. This may take the form of a restitution or ] (the protagonist seeks a physical or spiritual return to a pre-diagnosis life), a ] (the protagonist must meet a goal before dying), or a ] (the situation inexorably goes from bad to worse). The cure and quest narratives fit neatly with the breast cancer culture. Chaos narratives, rarer with breast cancer, oppose it.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=321–326}} | ||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ], responsible for the ] that dramatically reduced death rates due to breast cancer, but later proved to be controversial in its own right.]] | ], responsible for the ] that dramatically reduced death rates due to breast cancer, but later proved to be controversial in its own right.]] | ||
| Breast cancer has been known and feared since ancient times. With no reliable treatments, and with surgical outcomes often fatal, women tended to conceal the possibility of breast cancer as long as possible. With the dramatic improvement in survival rates at the end of the 19th century—the radical mastectomy promoted by William Stewart Halsted raised long-term survival rates from 10% to 50%—efforts to educate women about the importance of early detection and prompt action were begun |
Breast cancer has been known and feared since ancient times. With no reliable treatments, and with surgical outcomes often fatal, women tended to conceal the possibility of breast cancer as long as possible. With the dramatic improvement in survival rates at the end of the 19th century—the radical mastectomy promoted by William Stewart Halsted raised long-term survival rates from 10% to 50%—efforts to educate women about the importance of early detection and prompt action were begun.{{sfn|Olson|2002|p=1}}{{sfn|King|2006|p=xix}} | ||
| Early campaigns included the "Women's Field Army", run by the American Society for the Control of Cancer (the forerunner of the ]) during the 1930s and 1940s. Explicitly using a military metaphor, they promoted early detection and prompt medical intervention as every woman's duty in the war on cancer. In 1952, the first peer-to-peer support group, called Reach to Recovery, was formed. Later taken over by the American Cancer Society, it provided post-mastectomy, in-hospital visits from women who had survived breast cancer, who shared their own experiences, practical advice, and emotional support, but never medical information. This was the first program designed to promote restoration of a feminine appearance, e.g., through providing ], as a goal |
Early campaigns included the "Women's Field Army", run by the American Society for the Control of Cancer (the forerunner of the ]) during the 1930s and 1940s. Explicitly using a military metaphor, they promoted early detection and prompt medical intervention as every woman's duty in the war on cancer. In 1952, the first peer-to-peer support group, called Reach to Recovery, was formed. Later taken over by the American Cancer Society, it provided post-mastectomy, in-hospital visits from women who had survived breast cancer, who shared their own experiences, practical advice, and emotional support, but never medical information. This was the first program designed to promote restoration of a feminine appearance, e.g., through providing ], as a goal.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|pp=37–38}} | ||
| ==Organizations== | ==Organizations== | ||
| Line 202: | Line 201: | ||
| * ]: Like Breast Cancer Action, they are a key player in the environmental breast cancer movement. | * ]: Like Breast Cancer Action, they are a key player in the environmental breast cancer movement. | ||
| While the large organizations dominate the media, most of the practical, day-to-day support for women with breast cancer is provided by small, local groups. While providing the bulk of unglamorous, practical assistance, like driving women to and from medical appointments, these organizations typically struggle for funding in the shadow of the large groups |
While the large organizations dominate the media, most of the practical, day-to-day support for women with breast cancer is provided by small, local groups. While providing the bulk of unglamorous, practical assistance, like driving women to and from medical appointments, these organizations typically struggle for funding in the shadow of the large groups.{{sfn|Sulik|2010|p=53}} | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 210: | Line 209: | ||
| ==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| {{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 220: | Line 219: | ||
| | journal = ] | | journal = ] | ||
| | issn = 0007-7135 | | issn = 0007-7135 | ||
| | url = http://www.businessweek.com/technology/content/jun2007/tc20070612_953676.htm |
| url = http://www.businessweek.com/technology/content/jun2007/tc20070612_953676.htm | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | title = The Trouble with Mammograms | | title = The Trouble with Mammograms | ||
| Line 228: | Line 228: | ||
| | newspaper = ] | | newspaper = ] | ||
| | issn = 0458-3035 | | issn = 0458-3035 | ||
| | url= http://articles.latimes.com/2009/aug/17/health/he-breast-overdiagnosis17 |
| url= http://articles.latimes.com/2009/aug/17/health/he-breast-overdiagnosis17 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Ave | | last = Ave | ||
| Line 236: | Line 237: | ||
| | date = 10 October 2006 | | date = 10 October 2006 | ||
| | issn = 1563-6291 | | issn = 1563-6291 | ||
| | url= http://www.sptimes.com/2006/10/06/Tampabay/All_may_not_be_in_the.shtml |
| url= http://www.sptimes.com/2006/10/06/Tampabay/All_may_not_be_in_the.shtml | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Borrelli | | last = Borrelli | ||
| Line 243: | Line 245: | ||
| | work = ] | | work = ] | ||
| | url = http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2010-06-01/entertainment/ct-live-0601-slacktivism-20100601_1_facebook-pages-conan-o-brien-slacktivism | | url = http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2010-06-01/entertainment/ct-live-0601-slacktivism-20100601_1_facebook-pages-conan-o-brien-slacktivism | ||
| | date = |
| date = 1 June 2010 | ||
| | ref= harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | url = http://www.guardian.co.uk/society/2001/oct/07/cancercare | | url = http://www.guardian.co.uk/society/2001/oct/07/cancercare | ||
| Line 252: | Line 255: | ||
| | title = Cancer Bias Puts Breasts First | | title = Cancer Bias Puts Breasts First | ||
| | issn = 0261-3077 | | issn = 0261-3077 | ||
| | date=7 October 2001 |
| date=7 October 2001 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Elliott | | last = Elliott | ||
| Line 260: | Line 264: | ||
| | date = 12 November 2009 | | date = 12 November 2009 | ||
| | page = F1 | | page = F1 | ||
| | url= http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C06E6DC163DF931A25752C1A96F9C8B63 |
| url= http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C06E6DC163DF931A25752C1A96F9C8B63 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{Cite news | * {{Cite news | ||
| | first = Barbara | | first = Barbara | ||
| Line 269: | Line 274: | ||
| | date = November 2001 | | date = November 2001 | ||
| | issn = 0017-789X | | issn = 0017-789X | ||
| | url = http://www.barbaraehrenreich.com/cancerland.htm |
| url = http://www.barbaraehrenreich.com/cancerland.htm | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Grady | | last = Grady | ||
| Line 277: | Line 283: | ||
| | date = 8 December 2011 | | date = 8 December 2011 | ||
| | page = A3 | | page = A3 | ||
| | url = http://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/08/health/scientific-panel-finds-few-clear-environmental-links-to-breast-cancer.html |
| url = http://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/08/health/scientific-panel-finds-few-clear-environmental-links-to-breast-cancer.html | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | author=Institute of Medicine | | author=Institute of Medicine | ||
| Line 286: | Line 293: | ||
| | isbn=0-309-22069-6 | | isbn=0-309-22069-6 | ||
| | oclc= | | oclc= | ||
| | doi= |
| doi= | ||
| | ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | last= King | | last= King | ||
| Line 295: | Line 303: | ||
| | location= Minneapolis | | location= Minneapolis | ||
| | year= 2006 | | year= 2006 | ||
| | isbn= 0-8166-4898-0 |
| isbn= 0-8166-4898-0 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Kingston | | last = Kingston | ||
| Line 305: | Line 314: | ||
| | volume = 123 | | volume = 123 | ||
| | number = 41 | | number = 41 | ||
| | page = 73 |
| page = 73 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{Cite web | * {{Cite web | ||
| | last = Landman | | last = Landman | ||
| Line 313: | Line 323: | ||
| | work = ] | | work = ] | ||
| | title = Pinkwashing: Can Shopping Cure Breast Cancer? | | title = Pinkwashing: Can Shopping Cure Breast Cancer? | ||
| | publisher = ] |
| publisher = ] | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{Cite news | * {{Cite news | ||
| | last = Levine | | last = Levine | ||
| Line 321: | Line 332: | ||
| | date = 30 September 2005 | | date = 30 September 2005 | ||
| | issn = 0890-0337 | | issn = 0890-0337 | ||
| | url = http://sanfrancisco.bizjournals.com/sanfrancisco/stories/2005/10/03/newscolumn5.html |
| url = http://sanfrancisco.bizjournals.com/sanfrancisco/stories/2005/10/03/newscolumn5.html | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | first = Carpenter | | first = Carpenter | ||
| | last = Mackenzie | | last = Mackenzie | ||
| | date = October 1 2006 | | date = October 1, 2006 | ||
| | url = http://www.post-gazette.com/stories/sectionfront/life/just-about-everything-turns-pink-for-cancer-in-october-452768/ | | url = http://www.post-gazette.com/stories/sectionfront/life/just-about-everything-turns-pink-for-cancer-in-october-452768/ | ||
| | title = Just about everything turns pink for cancer in October | | title = Just about everything turns pink for cancer in October | ||
| | work = ] |
| work = ] | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite web | * {{cite web | ||
| | url=http://www.mint.ca/store/mint/learn/breast-cancer-coin-2006-1600008 | | url=http://www.mint.ca/store/mint/learn/breast-cancer-coin-2006-1600008 | ||
| Line 334: | Line 347: | ||
| | publisher=] | | publisher=] | ||
| | year = 2006 | | year = 2006 | ||
| | accessdate=12 November 2010 |
| accessdate=12 November 2010 | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | title= Breast Cancer Month Overshadowed by 'Pinkwashing' | | title= Breast Cancer Month Overshadowed by 'Pinkwashing' | ||
| Line 341: | Line 355: | ||
| | first= Angela | | first= Angela | ||
| | publisher= CTV.ca News | | publisher= CTV.ca News | ||
| | url= http://ottawa.ctv.ca/servlet/an/local/CTVNews/20101008/pinkwashing-pink-ribbon-101009/20101009/?hub=OttawaHome |
| url= http://ottawa.ctv.ca/servlet/an/local/CTVNews/20101008/pinkwashing-pink-ribbon-101009/20101009/?hub=OttawaHome | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | last=Olson | | last=Olson | ||
| Line 351: | Line 366: | ||
| | year=2002 | | year=2002 | ||
| | oclc = 186453370 | | oclc = 186453370 | ||
| | isbn=0-8018-6936-6 |
| isbn=0-8018-6936-6 | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last=Singer | | last=Singer | ||
| Line 359: | Line 375: | ||
| | date=16 October 2011 | | date=16 October 2011 | ||
| | page=BU1 | | page=BU1 | ||
| | url=http://www.nytimes.com/2011/10/16/business/in-the-breast-cancer-fight-the-pinking-of-america.html?pagewanted=all |
| url=http://www.nytimes.com/2011/10/16/business/in-the-breast-cancer-fight-the-pinking-of-america.html?pagewanted=all | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | last=Soffa | | last=Soffa | ||
| Line 365: | Line 382: | ||
| | title=The Journey Beyond Breast Cancer: From the Personal to the Political | url = http://books.google.ca/books?id=C9XHrABMdwsC | | title=The Journey Beyond Breast Cancer: From the Personal to the Political | url = http://books.google.ca/books?id=C9XHrABMdwsC | ||
| | publisher=] | | publisher=] | ||
| | location=Rochester, |
| location=Rochester, VT | ||
| | year=1994 | | year=1994 | ||
| | oclc = 26217697 | | oclc = 26217697 | ||
| | isbn=0-89281-448-9 |
| isbn=0-89281-448-9 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last=Stukin | | last=Stukin | ||
| | first=Stacie | | first=Stacie | ||
| | title=Pink Ribbon Promises | | title=Pink Ribbon Promises | ||
| | journal=] | | journal=] | ||
| | date=8 October 2006 | | date=8 October 2006 | ||
| | issn = 0040-781X | | issn = 0040-781X | ||
| | url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1543947-1,00.html |
| url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1543947-1,00.html | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | last=Sulik | | last=Sulik | ||
| Line 386: | Line 405: | ||
| | year=2010 | | year=2010 | ||
| | oclc = 535493589 | | oclc = 535493589 | ||
| | isbn=0-19-974045-3 |
| isbn=0-19-974045-3 | ||
| | ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last=Welch | | last=Welch | ||
| Line 394: | Line 414: | ||
| | date=20 October 2010 | | date=20 October 2010 | ||
| | issn = 0458-3035 | | issn = 0458-3035 | ||
| | url=http://www.latimes.com/news/opinion/commentary/la-oe-welch-mammograms-20101020,0,2961910.story |
| url=http://www.latimes.com/news/opinion/commentary/la-oe-welch-mammograms-20101020,0,2961910.story | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite news | * {{cite news | ||
| | last = Zuger | | last = Zuger | ||
| Line 401: | Line 422: | ||
| | date = 25 October 2010 | | date = 25 October 2010 | ||
| | newspaper = The New York Times | | newspaper = The New York Times | ||
| | url = http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/26/health/26zuger.html?_r=0 |
| url = http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/26/health/26zuger.html?_r=0 | ||
| | ref = harv }} | |||
| ==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
| Line 412: | Line 434: | ||
| |year=2007 | |year=2007 | ||
| |isbn=0-521-82249-1 | |isbn=0-521-82249-1 | ||
| |oclc= |
|oclc= | ||
| |ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| |author=Kasper, Anne S.; Ferguson, Susan J. | |author=Kasper, Anne S.; Ferguson, Susan J. | ||
| Line 421: | Line 444: | ||
| |pages= | |pages= | ||
| |isbn=0-312-29451-4 | |isbn=0-312-29451-4 | ||
| |oclc= |
|oclc= | ||
| |ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| |author=Klawiter, Maren | |author=Klawiter, Maren | ||
| Line 430: | Line 454: | ||
| |pages= | |pages= | ||
| |isbn=0-8166-5108-6 | |isbn=0-8166-5108-6 | ||
| |oclc= |
|oclc= | ||
| |ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| |author=Leopold, Ellen | |author=Leopold, Ellen | ||
| Line 439: | Line 464: | ||
| |pages= | |pages= | ||
| |isbn=0-8070-6513-7 | |isbn=0-8070-6513-7 | ||
| |oclc= |
|oclc= | ||
| |ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| |author=Lerner, Barron H.; Barron H., Md Lerner | |author=Lerner, Barron H.; Barron H., Md Lerner | ||
| Line 448: | Line 474: | ||
| |pages= | |pages= | ||
| |isbn=0-19-516106-8 | |isbn=0-19-516106-8 | ||
| |oclc= |
|oclc= | ||
| |ref = harv}} | |||
| {{Breast cancer}} | {{Breast cancer}} | ||
| Line 454: | Line 481: | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2011}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2011}} | ||
| <!-- CATEGORIES --> | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 04:35, 26 December 2012
| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Breast cancer awareness is an effort to raise awareness and reduce the stigma of breast cancer through education on symptoms and treatment. Supporters hope that greater knowledge will lead to earlier detection of breast cancer, which is associated with higher long-term survival rates, and that money raised for breast cancer will produce a reliable, permanent cure.
Breast cancer advocacy and awareness efforts are a type of health advocacy. Breast cancer advocates raise funds and lobby for better care, more knowledge, and more patient empowerment. They may conduct educational campaigns or provide free or low-cost services. Breast cancer culture, sometimes called pink ribbon culture, is the cultural outgrowth of breast cancer advocacy, the social movement that supports it, and the larger women's health movement.
The pink ribbon is the most prominent symbol of breast cancer awareness, and in most countries, the month of October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month. Some national breast cancer organizations receive substantial financial support from corporate sponsorships.
Marketing approaches
The goal of breast cancer awareness campaigns is to raise the public's "brand awareness" for breast cancer, its detection, its treatment, and the need for a reliable, permanent cure. Increased awareness has increased the number of women receiving mammograms, the number of breast cancers detected, and the number of women receiving biopsies. Overall, as a result of awareness, breast cancers are being detected at an earlier, more treatable stage. Awareness efforts have successfully utilized marketing approaches to reduced the stigma associated with the disease.
Generally speaking, breast cancer awareness campaigns have been highly effective in getting attention for the disease. Breast cancer receives significantly more media coverage than other prevalent cancers, such as prostate cancer.
Breast cancer as a brand

Breast cancer advocacy uses the pink ribbon and the color pink as a concept brand to raise money and increase screening. The breast cancer brand is strong: people who support the "pink brand" are members of the socially aware niche market, who are in favor of improved lives for women, believe in positive thinking, trust biomedical science to be able to solve any problem if given enough money, and prefer curative treatments to prevention.
The brand ties together fear of cancer, hope for early identification and successful treatment, and the moral goodness of women with breast cancer and anyone who visibly identifies themselves with breast cancer patients. This brand permits and even encourages people to substitute conscientious consumption and individual symbolic actions, like buying or wearing a pink ribbon, for concrete, practical results, such as collective political action aimed at discovering non-genetic causes of breast cancer.
The establishment of the brand and the entrenchment of the breast cancer movement has been uniquely successful, because no countermovement opposes the breast cancer movement or believes that breast cancer is desirable.
Pink ribbon
Main article: Pink ribbonA pink ribbon is a symbol of breast cancer awareness. It may be worn to honor those who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, or to identify products that a manufacturer would like to sell to consumers that are interested in breast cancer. Pink ribbons are sometimes sold as fundraisers, much like poppies on Remembrance Day.
The pink ribbon is associated with individual generosity, faith in scientific progress, and an optimistic "can-do" attitude. It encourages individuals to focus on the emotionally appealing ultimate vision of a cure for breast cancer, rather than the reality that there is no certain cure for breast cancer, and no guarantee there will ever be such a cure. Despite these positive associations, the simple act of wearing a pink ribbon alone and promoting it as a symbol for breast cancer has not been credited with saving any lives. The practice of blindly wearing or displaying a pink ribbon without making other, more concrete efforts to cure breast cancer has been described as a kind of slacktivism due to its lack of real effects, and has been compared to equally simple yet ineffective "awareness" practices like the drive for women to post the colors of their bras on Facebook. Critics say that the feel-good nature of pink ribbons and "pink consumption" distracts society from the lack of progress in curing breast cancer. It is also criticized for reinforcing gender stereotypes and objectifying women and their breasts.
Events

Each year, the month of October is recognized as National Breast Cancer Awareness Month by most governments, the media, and cancer survivors. The month-long campaign has been called Pinktober because of the increased production of pink goods for sale, and National Breast Cancer Industry Month by critics like Breast Cancer Action. NBCAM was begun in 1985 by the American Cancer Society and pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca. The organization that runs the official NBCAM aims to promote mammography and other forms of early detection as the most effective means of saving lives.
Typical NCBAM events include fundraising-based foot races, walk-a-thons, and bicycle rides. Participants solicit donations to a breast cancer-related charity in return for running, walking, or riding in the event. Through mass-participation events, breast cancer survivors form a single, united group that speaks and acts consistently and shares a coherent set of beliefs. There are little significant discrepancies among individuals. They also reinforce the cultural connection between each individual's physical fitness and moral fitness. Typically, one-quarter to one-third of the money donated is spent on advertising and organizing the event itself.
Various landmarks are illuminated in pink lights as a visible reminder of breast cancer, and public events, such as American football games, may use pink equipment or supplies. In 2010, all King Features Syndicate comic strips on one Sunday were printed in shades of red and pink, with a pink ribbon logo appearing prominently in one panel.
Private companies may arrange a "pink day", in which employees wear pink clothes in support of breast cancer patients, or pay for the privilege of a relaxed dress code, such as Lee National Denim Day.
Some events are directed at people in specific communities, such as the Global Pink Hijab Day, which was started in America to encourage appropriate medical care and reduce the stigma of breast cancer among Muslim women, and Male Breast Cancer Awareness Week, which some organizations highlight during the third week of October.
Most events are well-received, but some, like the unauthorized painting of the Pink Bridge in Huntington, West Virginia, are controversial.
Facebook campaigns have encouraged users to use sexual innuendo and double entendres in their status updates to remind readers about breast cancer. In 2009, a campaign asked women to post the color of their brassieres, and in 2010, a campaign asked women to post where they keep their purses, resulting in status messages such as "I like it on the floor". These campaigns have been criticized as sexualizing the disease.
Symbolism itself does not improve health, but it is an effective form of promoting the pink ribbon culture: fear of breast cancer, the hope for a scientific breakthrough, and the goodness of the people who support the cause. These supporters may feel socially compelled to participate, in a type of "obligatory voluntarism" critics say "can be exploitive".
Shopping for the cure

Thousands of breast cancer-themed products are developed and sold each year. Some of these, like pink ribbons and awareness bracelets, have no purpose other than to display the wearer's interest in breast cancer. Others are everyday products that have been repackaged or repositioned to take advantage of cause-related marketing, such as teddy bears, clothing, jewelry, candles, and coffee mugs. These blended value objects offer consumers an opportunity to simultaneously buy an object and make a donation to a breast cancer organization. Some of these products are produced and/or sold by breast cancer survivors or charities for fundraising purposes, while others are for profits in addition to fundraising. Manufacturers also produce products with pink labels or pink ribbon logos to donate a sum of money to support the cause. The donation is typically capped so that it is reached after a fixed level of sales, although in some cases the company is providing only free advertising for a selected charity. Although advertising costs are rarely disclosed, some companies have been found to spend far more money advertising "pink products" and tie-ins than they donate to charitable organizations supporting research or patients. For example, in 2005, 3M spent US $500,000 advertising post-it notes printed with a pink ribbon logo. Sales were nearly double what the company expected, but the campaign resulted in a $300,000 donation.
Advertisers and retail consultants have said that because of consumer cynicism, a company can benefit from marketing its support for a cause such as breast cancer awareness only when the company treats that support as "a commitment and not a marketing opportunity". Andrew Benett, an executive at Euro RSCG said that because consumers "have become more mindful, more thoughtful, about how they consume, where they consume, why they consume", companies cannot succeed by "just slapping a pink ribbon on a product and people will buy more". Pink products have also been condemned as promoting consumerism, materialism, and environmental degradation. Critics are also concerned that the ubiquity of pink products may mislead people into thinking that significant progress has been made, and that small, individual actions, like buying a breast cancer-themed product, are sufficient. Responding to criticism, Komen CEO Nancy G. Brinker said that corporate promotions enabled the organization to reach new audiences and that "America is built on consumerism. To say we shouldn't use it to solve the social ills that confront us doesn't make sense to me."
The first breast cancer awareness stamp in the U.S., featuring a pink ribbon, was issued in 1996. As it did not sell well, a semi-postal stamp without a pink ribbon, the breast cancer research stamp, was designed in 1998. Products like these emphasize the relationship between being a consumer and supporting women with breast cancer. In Canada, the Royal Canadian Mint produced 30 million 25-cent coins with pink ribbons during 2006 for normal circulation. Designed by the mint's director of engraving, Cosme Saffioti (reverse), and Susanna Blunt (obverse), this colored coin is the second in history to be put into regular circulation.
Business marketing campaigns, particularly sales promotions for products that increase pollution or have been linked to the development of breast cancer, such as alcohol, high-fat foods, some pesticides, or the parabens and phthalates used by most cosmetic companies, have been condemned as pinkwashing (a portmanteau of pink ribbon and whitewash). Such promotions generally result in a token donation to a breast cancer-related charity by taking advantage of the consumers' fear of cancer and grief for people who have died to drive sales. Critics say that these promotions, which net more than US $30 million each year just for fundraising powerhouse Susan G. Komen for the Cure, do little more than support the marketing machines that produce them. Komen says that corporate sponsorships are necessary to pay for the organization's efforts: in the 2010 fiscal year it spent $175 million on public health education and awareness campaigns, $75 million on medical research and about $67 million on treatment and screenings for patients.
Two significant campaigns against pink consumption are the National Breast Cancer Coalition's "Not Just Ribbons" campaign, and Breast Cancer Action's "Think Before You Pink" campaign. NBCC's "Not Just Ribbons" campaign sought to focus awareness efforts onto substantive issues such as genetic discrimination, access to cancer treatment, patient rights, and environmental breast cancer research. "Think Before You Pink" encouraged consumers to ask questions about pink products (e.g., to find out how much of a donation was being made).
Advertisements

Many corporate and charitable organizations run advertisements related to breast cancer, especially during National Breast Cancer Awareness Month, in the hope of increasing sales by aligning themselves with a positive, helpful message. In addition to selling pink products, corporate advertisements may promote the company's progressive policies, or may provide free advertising for a chosen charity. Medical institutions may run advertisements for mammogram or other breast-related services. Non-profit organizations often benefit from public service announcements, which are free advertisements provided by newspapers, radio and television stations, and other media. Some marketing blurs the line between advertisements and events, such as flash mobs as a form of guerrilla marketing. The typical participant in the breast cancer movement, and therefore the advertisers' target audience, is a white, middle-aged, middle-class, well-educated woman.
Some corporate sponsors are criticized for having a conflict of interest. For example, some of the prominent sponsors of these advertisements include businesses that sell the expensive equipment needed to perform screening mammography; an increase in the number of women seeking mammograms means an increase in their sales. Their sponsorship is thus not a voluntary act of charity, but an effort to increase their sales. The regulated drug and medical device industry uses the color pink, positive images, and other themes of the pink ribbon culture in direct-to-consumer advertising to associate their breast cancer products with the fear, hope, and wholesome goodness of the breast cancer movement. This is particularly evident in advertisements designed to sell screening mammograms.
Women's magazines from the 1950-1960s recommended the use of breast self-examinations as a method for early detection. More recently, breast self-examinations have been determined to be ineffective in low-risk and average-risk women. Some organizations' advertisements now advocate breast awareness, which is paying attention to any changes in the breast that may require medical attention.
Media
Although more women die from lung cancer, breast cancer receives far more attention in women's magazines than any other cancer. Until the mid-1990s, nearly all of these stories were written from the perspective of the expert, who gave advice. Since then, the illness narrative, describing the personal experiences of individual patients, has become more prominent.. Embedded marketing, branded content and frequent feature stories amount to free advertising for the brand and for the organizations that support it.
Social role of the woman with breast cancer

The marketing of breast cancer awareness allows people to incorporate support for awareness into their personal identity or lifestyle. Socially aware, pro-woman individuals, businesses, politicians, and organizations use pink ribbons and other trappings of breast cancer awareness to signal their support for women, health, and mainstream medicine.
The she-ro
The term "she-ro", derived from hero, used in discussions of breast cancer to refer to women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, and sometimes to those who have survived breast cancer. The term describes an "idealized" patient who combines assertiveness, optimism, femininity and sexuality, despite the effects of treatment, and as a "paragon uses a diagnosis of breast cancer as a catalyst for a personal transformation".
Sociologist Gayle Sulik analysis of the she-ro's social role ascribes it qualities that include being an educated medical consumer with a brave, pleasant and optimistic public appearance and demeanor who aggressively fights breast cancer through compliance with screening guidelines and "disciplined practice of 'breast health'". In America the she-ro is diagnosed early due to adherence to early screening recommendations, and, by definition, survives her diagnosis. The role emphasizes the femininity and female gender role of the she-ro, offsetting the masculine characteristics of assertiveness, selfishness and "fighting" cancer by cultivating a feminine appearance and concern for others. After treatment, the she-ro regains her femininity by using breast reconstruction, prosthetic devices, wigs, cosmetics, and clothing to present an aesthetically appealing, upper-class, heterosexual feminine appearance and by maintaining relationships in which she can nurture other people. Ensuring the proper feeling rules of the breast cancer culture is encouraged, including remaining optimistic of a full cure, rationalizing the selfishness of treatment as a temporary measure and feeling guilty that it forces her to put her needs momentarily above the needs of others or due to her perceived inadequacy in caring for her family or other women with cancer. Also included in the role is a form of have-it-all superwoman, cultivating a normal appearance and activity level and minimizing the disruption that breast cancer causes to people around her.
Consequences
The effort of maintaining the role of a she-ro can be stressful. The role encourages women to care for others rather than themselves, which the patient may find comforting, but this may lead to the reluctance or inability to ask for help they need or want which can lead to bitterness that their friends and family did not offer these services unbidden. The success of the patient's normalization efforts may paradoxically increase their dissatisfaction, as their apparent ability to handle it all discourages people from offering help. While the she-ro model may reduce the social stigma of breast cancer overall, it also increases the stigma of being overwhelmed, depressed, anxious, abrasive, or unattractive while undergoing treatment. The breast cancer culture celebrates women who display the attitude deemed correct, which implies that their continued survival is due to this positive attitude and fighting spirit. While cheerfulness, hope, and good social support can be advantageous to health outcomes, it cannot determine survival rates. Women who reject the she-ro model may find themselves socially isolated by the breast cancer support groups that are nominally supposed to help them. Support from "the sisterhood" favors the "passionately pink", and tends to overlook those whose response is incompatible with the pink ribbon culture because it is angry, unhappy, or afraid.
The breast cancer culture is ill-equipped to deal with women who are dying or who have died and their experiences may not be memorialized, validated or represented as part of the movement, instead being ignored or shunned as failures and as hope-destroying examples of reality. Similarly, the culture is also ill-equipped to deal with the news that a previously hyped treatment or screening procedure has been determined to be ineffective, with women demanding acceptance and promotion of useless activities and harmful drugs.
Breast cancer culture
| This section may lend undue weight to certain ideas, incidents, or controversies. Please help to create a more balanced presentation. Discuss and resolve this issue before removing this message. (November 2012) |
Breast cancer culture, or pink ribbon culture, is the set of activities, attitudes, and values that surround and shape breast cancer in public. The dominant values are selflessness, cheerfulness, unity, and optimism. It is pro-doctor, pro-medicine, and pro-mammogram. Health care professionals are sources of information, but the rightness of their advice is not to be seriously questioned by women with breast cancer. Patients are not encouraged to ask where research money is going or if the research industry is making progress in finding the "cure". The emphasis on cheerfulness allows society to blame women for developing breast cancer and limits their responses to certain culturally determined scripts. The requirement of cheerful optimism arose from the theory that cancer had a psychosomatic origin and that people who were diagnosed with cancer had a "cancer personality" that was depressed, repressed, and self-loathing. Psychotherapy was therefore considered an adjunct treatment used to produce a cheerful, self-affirming identity. This theory was predominant among psychiatrists through the 1970s, but has since been discredited. The she-ro uses the emotional trauma of being diagnosed with breast cancer and the suffering of extended treatment to transform herself into a stronger, happier and more sensitive person who is grateful for the opportunity to become a better person. In particular, she sees breast cancer as an opportunity to give herself permission for necessary personal growth that she felt she was prohibited from or unable to make before. Breast cancer thereby becomes a rite of passage rather than a disease, with pink ribbon culture honoring the suffering of its she-roes by selecting them based on the amount of misery they have experienced and leading women whose treatment is less painful or debilitating to feel excluded and devalued. The suffering, particularly the extended suffering of months of chemotherapy and radiation treatment, forms a metaphorical type of ordeal or rite of passage that initiates women into the inner circle of breast cancer culture. Barbara Ehrenreich describes it as:
Understood as a rite of passage, breast cancer resembles the initiation rites so exhaustively studied by Mircea Eliade: First there is the selection of the initiates -- by age in the tribal situation, by mammogram or palpation here. Then come the requisite ordeals -- scarification or circumcision within traditional cultures, surgery and chemotherapy for the cancer patient. Finally, the initiate emerges into a new and higher status -- an adult and a warrior -- or in the case of breast cancer, a "survivor."
Mainstream pink ribbon culture has aspects that are deemed trivializing, silencing, and infantilizing. Women with breast cancer are surrounded by pink teddy bears and crayons ("childish kitsch"), but there is no equivalent gift of toy cars for men diagnosed with prostate cancer. Women who choose not to conform to the culture may feel excluded and isolated; those who cannot conform to the prescribed triumphant script report feeling unable to share their stories honestly. Anger, negativity and fatalism transgress the feeling rules, and women with breast cancer who express anger or negativity are corrected and disciplined by other women with breast cancer and members of the breast cancer support organizations. Appearing unattractive—such as going out in public with a bare, bald head if treatment causes temporary hair loss—transgresses the approved, upper-class style of pink femininity and provokes shaming comments from strangers. Programs such as Reach to Recovery and Look Good, Feel Better inform breast cancer patients of this cultural standard and help them conform to it. This standard is not universally adhered to, with "the question of wigs versus baldness one of the few real disagreements in breast-cancer culture," and some women have used the effects of their breast cancer treatments as an opportunity to engage in avant-garde makeovers:
One decorates her scalp with temporary tattoos of peace signs, panthers, and frogs; another expresses herself with a shocking purple wig; a third reports that unadorned baldness makes her feel 'sensual, powerful, able to recreate myself with every new day' using temporary tattoos, colored wigs or open baldness to reinvent their appearances according to radical, natural or cosmetically enhanced tastes.
Since the beginning of the 21st century, breast cancer culture has become more sexualized, and many awareness campaigns now reflect the old advertising truism that sex sells. The "booby campaigns", such as "Save the Tatas" and the "I ♥ Boobies" gel bracelets, rely on a cultural obsession with breasts and a market that is already highly aware of breast cancer. This message trivializes women and reflects a belief that breast cancer is important because cancer and its treatment makes women feel less sexually desirable and interferes with men's sexual access to women's breasts. These campaigns tend to attract a younger audience than traditional campaigns.
At the same time, breast cancer culture tends to overlook men with breast cancer and women who do not fit the white, middle-class archetype. African-Americans involved with breast cancer organizations often feel like their role is to be the token minority.
Feminism and the breast cancer wars
The breast cancer wars were a series of conflicts between advocates and others about the causes, treatments, and societal responses to breast cancer. Women in the late 1980s and 1990s followed the successful approach used by ACT-UP and other AIDS awareness groups, of staging media-friendly protests to increase political pressure. Prominent women who made the "wrong" choice were publicly excoriated, as when Nancy Reagan chose mastectomy over lumpectomy followed by six weeks of radiation therapy. The abortion–breast cancer hypothesis was formulated when an early study showed a connection between voluntary abortions and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women, which pitted breast cancer advocates against abortion rights advocates.
Advocates for women's issues have said that breast cancer is special because of its status as a largely female disease, society's response to it is an ongoing indication of the status of women and the existence of sexism. Breast cancer activist Virginia Soffa stated that "s long as it is not a national priority, the breast cancer epidemic will remain a metaphor for how society treats women". Before the feminist movement, women with breast cancer were often treated as passive, dependent objects, incapable of making appropriate choices, whose role was to accept whatever treatment was decreed by the physicians, surgeons, or husbands, who held all of the power. Because of sexism in education, female surgeons were far outnumbered by their male counterparts, and until the 1990s, when Susan Love of the University of California, Los Angeles Breast Center published Dr. Susan Love's Breast Book, the physicians who provided breast cancer treatments were generally men. Love said that some male physicians tended to impose their own values on women, such as recommending mastectomy to older women because, being past the age of child bearing and breastfeeding, they no longer "needed" their breasts. The women's health movement promoted mutual aid, self-help, networking, and an active, informed role in the patient's health care. Since the end of the breast cancer wars, feminists have again objected to the breast cancer culture's treatment of women with breast cancer as little girls who need to be obedient to authority figures, cooperative, pleasant and pretty.
Achievements of the breast cancer movement
Breast cancer has been known to educated women and caregivers throughout history, but modesty and horror at the consequences of a largely untreatable disease made it a taboo subject. The breast cancer movement, which developed in the 1980s and 1990s out of 20th century feminist movements and the women's health movement, has mostly remove those taboos through its modern advocacy and awareness campaigns.
Educated, empowered patients
At the beginning and middle of the 20th century, breast cancer was usually discussed in hushed tones, as if it were shameful. Later, however, several celebrities publicly disclosed their own health challenges, and the resulting publicity reduced the stigma. One of the first was Shirley Temple Black, the former child star, who announced her diagnosis in 1972. In October 1974, Betty Ford, the wife of the then-President of the United States, openly discussed her breast cancer diagnosis and mastectomy. Two weeks later, the wife of the then-Vice President also had a mastectomy for breast cancer. The next year, journalist Rose Kushner published her book, Breast Cancer: A Personal History and Investigative Report, which she had written while recovering from a modified radical mastectomy. The media reported these women's health and their treatment choices, and even invited some to appear on talk shows to discuss breast cancer frankly.
The breast cancer movement has resulted in widespread acceptance of second opinions, the development of less invasive surgical procedures, the spread of support groups, and other advances in patient care. The movement successfully separated diagnostic biopsy from mastectomy surgery; before about 1980, it was common to perform the biopsy and, if a quick review of tissues indicated a probable need, a mastectomy in the same surgery. The one-step surgery prevented women from seeking different opinions about their treatment, and sent them into the surgery without knowing whether their breasts would be removed that day. In response to women's concerns over lymphedema after routine removal of lymph nodes during mastectomy, the more limited approach of sentinel node biopsy was developed. Advocacy efforts also led to the formal recommendation against the routine use of the Halsted radical mastectomy in favor of simple mastectomies and lumpectomies.
The breast cancer movement has supported practical, educational, emotional, and financial care for women with breast cancer. Support groups, individual counseling opportunities, and other resources are made available to patients.
Increased resources for treatment and research
Supporting breast cancer was seen as a distinctively pro-woman stance for public officials to take, without any of the political risks associated with supporting other feminist goals, such as abortion rights or lesbian rights. This has resulted in better access to care. For example, in much of the United States, low-income women with breast cancer may qualify for taxpayer-funded health care benefits, such as screening mammography, biopsies, or treatment, while women with the same income, but another form of cancer or a medical condition other than cancer, do not.
Breast cancer advocates have successfully increased the amount of public money being spent on cancer research and shifted the research focus away from other diseases and towards breast cancer. Most breast cancer research is funded by government agencies. Breast cancer advocates also raise millions of dollars for research into cures each year, although most of the funds they raise is spent on screening programs, education and treatment.
The high level of awareness and organized political lobbying has resulted in a disproportionate level of funding and resources given to breast cancer research and care. Favoring breast cancer with disproportionate research may have the unintended consequence of costing lives elsewhere. In 2001 UK MP Ian Gibson said, "The treatment has been skewed by the lobbying, there is no doubt about that. Breast cancer sufferers get better treatment in terms of bed spaces, facilities and doctors and nurses".
Risks of too much awareness
Women are far more likely to die from heart disease or stroke than from breast cancer
Deaths from breast cancer (2%) Deaths from heart disease or stroke (32%) Deaths from other cancers (10%) Deaths from lung diseases (7%) Deaths from injuries (6%) Deaths from digestive diseases (3%) Deaths from neuropsychiatric disorders (5%) Other (35%)Because breast cancer is a highly visible disease, most women significantly overestimate their personal risk of dying from it. Misleading statistics, such as the claim that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lives—a claim that depends on the patently unrealistic assumption that no woman will die of any other disease before the age of 95—obscure the reality, which is that about ten times as many women will die from heart disease or stroke than from breast cancer.
Awareness has also led to increased anxiety for women. Early detection efforts result in overdiagnosis of precancerous and cancerous tumors that would never risk the woman's life (about one-third of breast cancers), and result in her being subjected to invasive and sometimes dangerous radiological and surgical procedures.
The breast cancer culture has also promoted an expansive definition of breast cancer, which includes non-invasive, non-cancerous conditions like lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) and pre-cancerous or "stage 0" conditions like ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Despite the now-regretted decision to use the word carcinoma in these relatively common conditions (almost a quarter of "breast cancer" diagnoses in the USA), they are not life-threatening cancers. Women with these conditions are promoted as breast cancer survivors due to the fear they experienced before they became educated about their condition, rather than in respect of any real threat to their lives. This effectively increases the market size for breast cancer organizations, medical establishments, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and the makers of mammography equipment.
An emphasis on educating women about lifestyle changes that may have a small impact on preventing breast cancer often makes women feel guilty if they do develop breast cancer. Some women decide that their own cancer resulted from poor diet, lack of exercise, or other modifiable lifestyle factor, even though most cases of breast cancer are due to non-controllable factors, like genetics or naturally occurring background radiation. Adopting such a belief may increase their sense of being in control of their fate. Increased awareness inadvertently increases victim blaming. Women who resist screening mammography or breast self-exams are subjected to social pressure, scare tactics, guilt, and threats from some physicians to terminate the relationship with the patient. Similarly, the emphasis on early detection result in many women wrongly blaming themselves if their cancer is not detected at an early stage.
The promotion of research to make screening programs find ever more cancers is also criticized. One-third of diagnosed breast cancers might recede on their own. Screening mammography efficiently finds non-life-threatening, asymptomatic breast cancers and pre-cancers, even while overlooking serious cancers. According to H. Gilbert Welch of the Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice, research on screening mammography has taken the "brain-dead approach that says the best test is the one that finds the most cancers" rather than the one that finds dangerous cancers.
Independence of breast cancer organizations
Some critics say that breast cancer awareness has transformed the disease into a market-driven industry of survivorship and corporate sales pitches. Corporate marketing machines promote early detection of breast cancer, while also opposing public health efforts, such as stricter environmental legislation, that might decrease the incidence rate of breast cancer. These critics believe that some of the breast cancer organizations, particularly the highly visible Susan G. Komen for the Cure, have become captive companies that support and provide social capital to the breast cancer industry, including big pharma, mammography equipment manufacturers, and pollution-causing industries, as well as large corporations, creating or exacerbating other problems.
For example, Ford Motor Company ran a "Warriors in Pink" promotion on their Ford Mustang sports car, which critics say was intended to sell cars and counter the bad publicity the company received by reducing its workforce by tens of thousands of people, causing many of them to lose their health insurance, rather than to prevent or cure breast cancer. A Ford spokesperson acknowledged that the objective of the promotion was to "do good works throughout the community and derive some marketing exposure at the same time", but said that over the promotion's 15 years the company had donated $100 million and that the company continued the program during the automotive industry crisis of 2008–2010 because "It's part of our DNA now." Ford believes that the recipient of the funds, Susan G. Komen for the Cure, benefited because Ford helped it reach "people who might not have thought of this organization before or may be supporting other organizations."
However, the primary sponsors are part of the breast cancer industry, particularly cancer drug makers like AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis. Because the national breast cancer organizations are dependent on corporate sponsorships for survival, this situation may represent a conflict of interest that prevents these organizations from representing the needs of current and future people with breast cancer when those needs conflict with the profit-making motives of the corporate sponsors..
The structure of the breast cancer movement may allow large organizations to claim to be the voice of women with breast cancer, while simultaneously ignoring their desires.
Some breast cancer organizations, such as Breast Cancer Action, refuse to accept funds from medical or other companies they disapprove of.
Environmental breast cancer movement
| The neutrality of this section is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Most of the money raised by advocates is spent on advertising, increased awareness, cancer screening, and existing treatments. Only a small fraction of the funds is spent on research, and most of that funding is spent on research to improve diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. To the dismay of advocates like Breast Cancer Action and women's health issues scholar Samantha King, relatively little money or attention is devoted to identifying the non-genetic causes of breast cancer or taking steps to prevent breast cancer from occurring. The mainstream breast cancer culture is focused on a cure for existing breast cancer cases, rather than on preventing future cases.
As a result, screening mammography is promoted by the breast cancer industry as the sole possible approach to public health for breast cancer. Alternatives, such as pollution prevention, are largely ignored.
As the majority of women with breast cancer have no risk factors other than sex and age, the environmental breast cancer movement suspects pollution as a significant cause, possibly from pesticides, plastics, or petroleum products. The largest organizations, particularly Susan G. Komen for the Cure and the American Cancer Society, are not part of the environmental breast cancer movement. These organizations benefit the most from corporate sponsorships that critics deride as pinkwashing, e.g., polluting industries trying to buy public goodwill by publishing advertisements emblazoned with pink ribbons, rather than stopping their pollution under the precautionary principle.
A 2011 literature review carried out by the Institute of Medicine reported that the environmental factors that show "the most consistent evidence of a link with increased breast cancer risk included ionizing radiation, combination estrogen–progestin hormone therapy, and greater postmenopausal weight....for many other factors, the evidence from human studies is more limited, contradictory, or absent" and called for additional research. Conducting research into whether a chemical causes cancer is difficult, because "suspect chemicals cannot ethically be given to people to see if they cause cancer. People exposed in the past can be studied, but information about the dose and timing may be sketchy. Animal studies can provide useful information, but do not always apply to humans. And people are often exposed to mixtures of chemicals that may interact in complex ways, with effects that may also vary depending on an individual's genetic makeup".
Samantha King says that prevention research is minimized by the breast cancer industry because there is no way to make money off of cases of breast cancer that do not happen, whereas a mammography imaging system that finds more possible cancers, or a "magic bullet" that kills confirmed cancers, would be highly profitable. This paradigm applies equally to breast cancer organizations, because a reliable form of prevention would deplete their future supply of volunteers.
Dissent through art
While the pink ribbon culture is dominant, there are alternatives. The environmental breast cancer movement is one type of dissent. Another is the rejection of compliant optimism, aesthetic normalization, and social pleasingness that the pink ribbon culture promotes.
In 1998, the Art.Rage.Us art collective published a book that collected some of the art work from their traveling collection. This included art that was shocking, painful and realistic rather than beautiful, such as several self-portraits that showed mastectomy scars.
Another art form has a wider range: the illness narrative has become a staple of breast cancer literature. This may take the form of a restitution or cure narrative (the protagonist seeks a physical or spiritual return to a pre-diagnosis life), a quest narrative (the protagonist must meet a goal before dying), or a chaos narrative (the situation inexorably goes from bad to worse). The cure and quest narratives fit neatly with the breast cancer culture. Chaos narratives, rarer with breast cancer, oppose it.
History
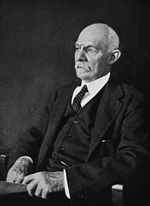
Breast cancer has been known and feared since ancient times. With no reliable treatments, and with surgical outcomes often fatal, women tended to conceal the possibility of breast cancer as long as possible. With the dramatic improvement in survival rates at the end of the 19th century—the radical mastectomy promoted by William Stewart Halsted raised long-term survival rates from 10% to 50%—efforts to educate women about the importance of early detection and prompt action were begun.
Early campaigns included the "Women's Field Army", run by the American Society for the Control of Cancer (the forerunner of the American Cancer Society) during the 1930s and 1940s. Explicitly using a military metaphor, they promoted early detection and prompt medical intervention as every woman's duty in the war on cancer. In 1952, the first peer-to-peer support group, called Reach to Recovery, was formed. Later taken over by the American Cancer Society, it provided post-mastectomy, in-hospital visits from women who had survived breast cancer, who shared their own experiences, practical advice, and emotional support, but never medical information. This was the first program designed to promote restoration of a feminine appearance, e.g., through providing breast prostheses, as a goal.
Organizations
A wide variety of charitable organizations are involved in breast cancer awareness and support. These organizations do everything from providing practical support, to educating the public, to dispensing millions of dollars for research and treatment. Thousands of small breast cancer organizations exist. The most largest and prominent are:
- Susan G. Komen for the Cure: Komen is the largest and best funded organization, with highly visible fundraisers. They represent the good, hopeful, happy, unified survivors who have embraced pink ribbon culture.
- National Breast Cancer Coalition: This large umbrella organization played key roles in several prominent pieces of American legislation, such as the creation of the United States Department of Defense's Breast Cancer Research Program, genetic non-discrimination laws, and the patients' bill of rights. They are committed to evidence-based medicine.
- Breast Cancer Action: Famous for its "Think Before You Pink" campaign against pinkwashing, BCA emphasizes the need for research into pollution as a cause of breast cancer. Like the National Women's Health Network, they refuse funding from any group that may have a conflict of interest, such as pharmaceutical companies, medical imaging companies, or pollution-causing industries.
- National Breast Cancer Organization: Closed in 2004. A dissenter to the notion of mandatory public unity, it provided case management and other services.
- New York State Breast Cancer Support and Education Network (US): An association of groups in New York that are not affiliated with Komen, they are committed to evidence-based medicine rather than conventional wisdom.
- Breast Cancer Fund: Like Breast Cancer Action, they are a key player in the environmental breast cancer movement.
While the large organizations dominate the media, most of the practical, day-to-day support for women with breast cancer is provided by small, local groups. While providing the bulk of unglamorous, practical assistance, like driving women to and from medical appointments, these organizations typically struggle for funding in the shadow of the large groups.
See also
Notes
- King 2006, p. 2.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 157–210.
- Arnst 2007.
- Sulik 2010, p. 22.
- ^ King 2006, p. 38.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 133–146.
- King 2006, p. 111.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 359–361.
- ^ Landman 2008.
- Borrelli 2010.
- ^ Sulik 2010, pp. 365–366.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 372–374.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 48, 370.
- King 2006, p. xxi.
- ^ Ehrenreich 2001.
- Sulik 2010, p. 56.
- King 2006, pp. 46–49.
- ^ Kingston 2010.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 250, 308.
- ^ Ave 2006.
- ^ Levine 2005.
- ^ Elliott 2009.
- ^ Stukin 2006.
- ^ Singer 2011.
- King 2006, pp. 61–79.
- ^ Royal Canadian Mint 2006. sfn error: no target: CITEREFRoyal_Canadian_Mint2006 (help)
- ^ Mulholland 2010.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 366–368.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 369–372.
- ^ King 2006.
- King 2006, pp. 110–111.
- King 2006, p. 37.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 205–208.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 115, 117.
- Sulik 2010, p. 133.
- Zuger 2010.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 158, 243.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 78–89.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 42, 101–105, 374.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 225–272, 277.
- ^ Sulik 2010, pp. 279–301.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 283, 286.
- Sulik 2010, p. 45.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 243–244.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 274–277.
- ^ Sulik 2010, p. 4.
- Olson 2002, pp. 204–205.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 200–203.
- Olson 2002, pp. 460–469.
- Sulik 2010, p. 342.
- Sulik 2010, p. 236.
- Sulik 2010, p. 3.
- Sulik 2010, p. 319.
- Sulik 2010, p. 98.
- Sulik 2010, p. 373.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 240–242.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 35–45, 262.
- Olson 2002, p. 120.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 37–38, 42, 101–105, 374.
- Sulik 2010, p. 372.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 308–309.
- ^ Olson 2002, pp. 192–220.
- Olson 2002, pp. 195–202.
- Soffa 1994, p. 208.
- Olson 2002, p. 198.
- ^ Olson 2002, pp. 124–144.
- Olson 2002, pp. 121, 171–220.
- Olson 2002, pp. 168–191.
- Olson 2002, pp. 176, 185–186, 250.
- Olson 2002, p. 202.
- As an example, the State of Texas pays for breast cancer treatment in women whose income is 200% of the Federal Poverty Income Guideline, but to be screened or treated for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or lung cancer, the income limit is 185% of FPIG.
- ^ Browne 2001.
- Olson 2002, pp. 199–200.
- ^ Aschwanden 2009.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 165–171.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 170–171.
- Olson 2002, pp. 240–242.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 74, 263.
- Welch 2010.
- Sulik 2000, pp. 160–210. sfn error: no target: CITEREFSulik2000 (help)
- Sulik 2010, pp. 130–135.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 209–210.
- Sulik 2010, p. 376.
- Sulik 2010, p. 204.
- King 2006, pp. 1–2.
- Institute of Medicine 2011. sfn error: no target: CITEREFInstitute_of_Medicine2011 (help)
- Grady 2011.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 229–377.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 326–332.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 321–326.
- Olson 2002, p. 1.
- King 2006, p. xix.
- Sulik 2010, pp. 37–38.
- Sulik 2010, p. 53.
References
- Arnst, Catherine (13 June 2007). "A Gender Gap in Cancer". Bloomberg Businessweek. ISSN 0007-7135.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Aschwanden, Christie (17 August 2009). "The Trouble with Mammograms". The Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Ave, Melanie (10 October 2006). "All May Not Be in the Pink". St. Petersburg Times. ISSN 1563-6291.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Borrelli, Christopher (1 June 2010). "Click. Support. Whatever. Social network campaigns build 'slacktivism' to new heights, but is there real impact behind these digital devotions?". Chicago Tribune.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Browne, Anthony (7 October 2001). "Cancer Bias Puts Breasts First". The Guardian. London. ISSN 0261-3077.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Elliott, Stuart (12 November 2009). "For Causes, It's a Tougher Sell". The New York Times. p. F1.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Ehrenreich, Barbara (November 2001). "Welcome to Cancerland". Harper's Magazine. ISSN 0017-789X.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Grady, Denise (8 December 2011). "Panel Finds Few Clear Environmental Links to Breast Cancer". The New York Times. p. A3.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Institute of Medicine (2012). Breast Cancer and the Environment: A Life Course Approach (Institute of Medicine). Washington, D.C: National Academies Press. ISBN 0-309-22069-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - King, Samantha (2006). Pink Ribbons, Inc.: Breast Cancer and the Politics of Philanthropy. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 0-8166-4898-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kingston, Anne (2010). "A Nice Rack of Slogans". Maclean's. Vol. 123, no. 41. p. 73. ISSN 0024-9262.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Landman, Anne (11 June 2008). "Pinkwashing: Can Shopping Cure Breast Cancer?". PR Watch. Center for Media and Democracy.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Levine, Daniel S. (30 September 2005). "Breast Cancer Group Questions Value of Pink Ribbon Campaigns". San Francisco Business Times. ISSN 0890-0337.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mackenzie, Carpenter (1 October 2006). "Just about everything turns pink for cancer in October". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "2006 Pink Ribbon Coin: Creating a Future Without Breast Cancer". Royal Canadian Mint. 2006. Retrieved 12 November 2010.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mulholland, Angela (9 October 2010). "Breast Cancer Month Overshadowed by 'Pinkwashing'". CTV.ca News.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Olson, James Stuart (2002). Bathsheba's Breast: Women, Cancer and History. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-6936-6. OCLC 186453370.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Singer, Natasha (16 October 2011). "Welcome, Fans, to the Pinking of America". The New York Times. p. BU1.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Soffa, Virginia M. (1994). The Journey Beyond Breast Cancer: From the Personal to the Political. Rochester, VT: Healing Arts Press. ISBN 0-89281-448-9. OCLC 26217697.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Stukin, Stacie (8 October 2006). "Pink Ribbon Promises". TIME. ISSN 0040-781X.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Sulik, Gayle (2010). Pink Ribbon Blues: How Breast Cancer Culture Undermines Women's Health. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-974045-3. OCLC 535493589.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Welch, H. Gilbert (20 October 2010). "The Risk of Being Too Aware". The Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Zuger, Abigail (25 October 2010). "Breast Cancer Tales: The Inspirational vs. the Actual". The New York Times.
{{cite news}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
Further reading
- Aronowitz, Robert A. (2007). Unnatural history: breast cancer and American society. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82249-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kasper, Anne S.; Ferguson, Susan J. (2002). Breast cancer: society shapes an epidemic. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0-312-29451-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Klawiter, Maren (2008). The biopolitics of breast cancer: changing cultures of disease and activism. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 0-8166-5108-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Leopold, Ellen (2000). A Darker Ribbon: A Twentieth-Century Story of Breast Cancer, Women, and Their Doctors. Beacon Press. ISBN 0-8070-6513-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lerner, Barron H.; Barron H., Md Lerner (2001). The breast cancer wars: hope, fear, and the pursuit of a cure in twentieth-century America. Oxford : Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-516106-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
| Breast cancer | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||
| Treatment | |||||||||
| Types |
| ||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
Categories: