| Revision as of 02:16, 28 August 2013 edit99.119.130.219 (talk) Without reason summary. Undid revision 569355308 by Arthur Rubin (talk)← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:24, 28 August 2013 edit undoArthur Rubin (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers130,168 editsm Reverted 1 edit by 99.119.130.219 (talk) to last revision by Arthur Rubin. (TW)Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {| | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | |] ] | ||
| |} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| The '''Siberian Shelf''', one of the ] ] (such as ]), is the largest ] of the ], a part of the ]. It extends from the continent of ] in the general area of North ] (hence the name) into the ]. It stretches to {{convert|1500|km|mi|sp=us}} offshore. It is relatively shallow, with average depth of 100 m. A number of islands are within the shelf, including the ], ], and the ]. <ref></ref> | The '''Siberian Shelf''', one of the ] ] (such as ]), is the largest ] of the ], a part of the ]. It extends from the continent of ] in the general area of North ] (hence the name) into the ]. It stretches to {{convert|1500|km|mi|sp=us}} offshore. It is relatively shallow, with average depth of 100 m. A number of islands are within the shelf, including the ], ], and the ]. <ref></ref> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
| ==Flora and fauna== | ==Flora and fauna== | ||
| The Siberian Shelf is the habitat for numerous flora and fauna. Notably the ] is found through much of the shelf, including the ] and ]. | The Siberian Shelf is the habitat for numerous flora and fauna. Notably the ] is found through much of the shelf, including the ] and ]. | ||
| ==Gallery== | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| ⚫ | Arctic Ocean bathymetric features.png|Bathymetric/topographic map of the Arctic Ocean and the surrounds | ||
| Image:Kara Sea map.png | |||
| ⚫ | Image:East Siberian Sea map.png | ||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 28 August 2013
 
|
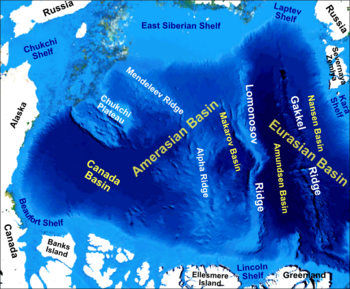
The Siberian Shelf, one of the Arctic Ocean coastal shelves (such as Milne Ice Shelf), is the largest continental shelf of the Earth, a part of the continental shelf of Russia. It extends from the continent of Eurasia in the general area of North Siberia (hence the name) into the Arctic Ocean. It stretches to 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) offshore. It is relatively shallow, with average depth of 100 m. A number of islands are within the shelf, including the Wrangel Island, Novaya Zemlya, and the New Siberian Islands.
It is encompassed by the Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, and East Siberian Sea, and respectively subdivided into the Kara Sea Shelf, Laptev Sea Shelf, and East Siberian Shelf.
Eastwards it merges into the Chukchi Shelf (of the Chukchi Sea) shared by Eurasia and Alaska (i.e., by Russia and the United States).
Westwards it merges into the Barents Shelf of the Barents Sea.
Also, the New Siberian Islands and the New Siberian Rift Basin define the New Siberian Shelf.
According to the split of the high Arctic by the Lomonosov mid-ocean ridge into the Eurasian Basin and Amerasian Basin, the Siberian Shelf is split between the Eurasian Shelf and the Amerasian Shelf.
Flora and fauna
The Siberian Shelf is the habitat for numerous flora and fauna. Notably the Polar bear is found through much of the shelf, including the Barents Sea and Chukchi Sea.
References
Categories: